Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Promote cell death" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
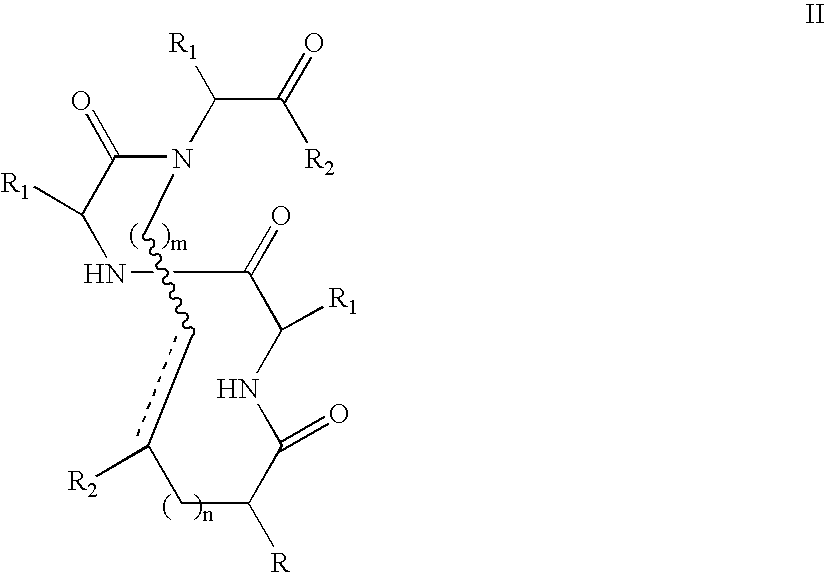
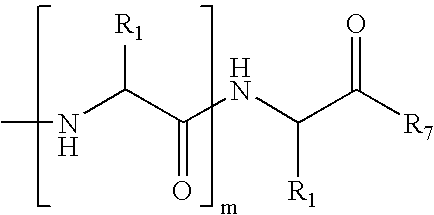
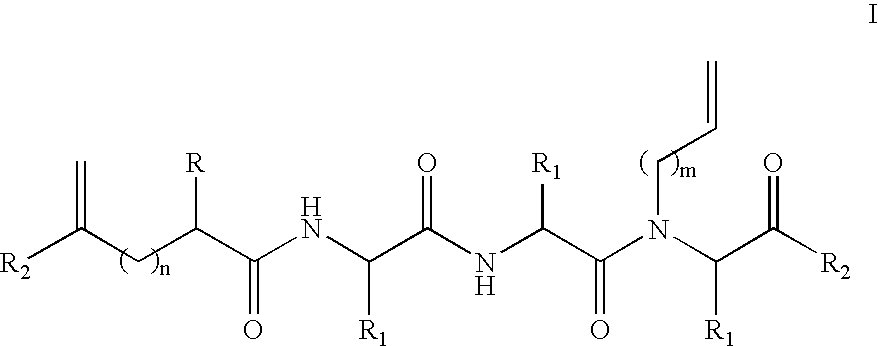
Methods for preparing internally constrained peptides and peptidomimetics
ActiveUS20060014675A1Promote cell deathAvoid interactionPeptide preparation methodsImmunoglobulinsGreek letter betaBeta sheet
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a peptide having a stable, internally constrained alpha-helical, beta-sheet / beta-turn, 310-helical, or pi-helical region and a method of stabilizing an alpha-helical, beta-sheet / beta-turn, 310-helical, or pi-helical region within a peptide structure. The resulting peptides and methods of using them are also disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
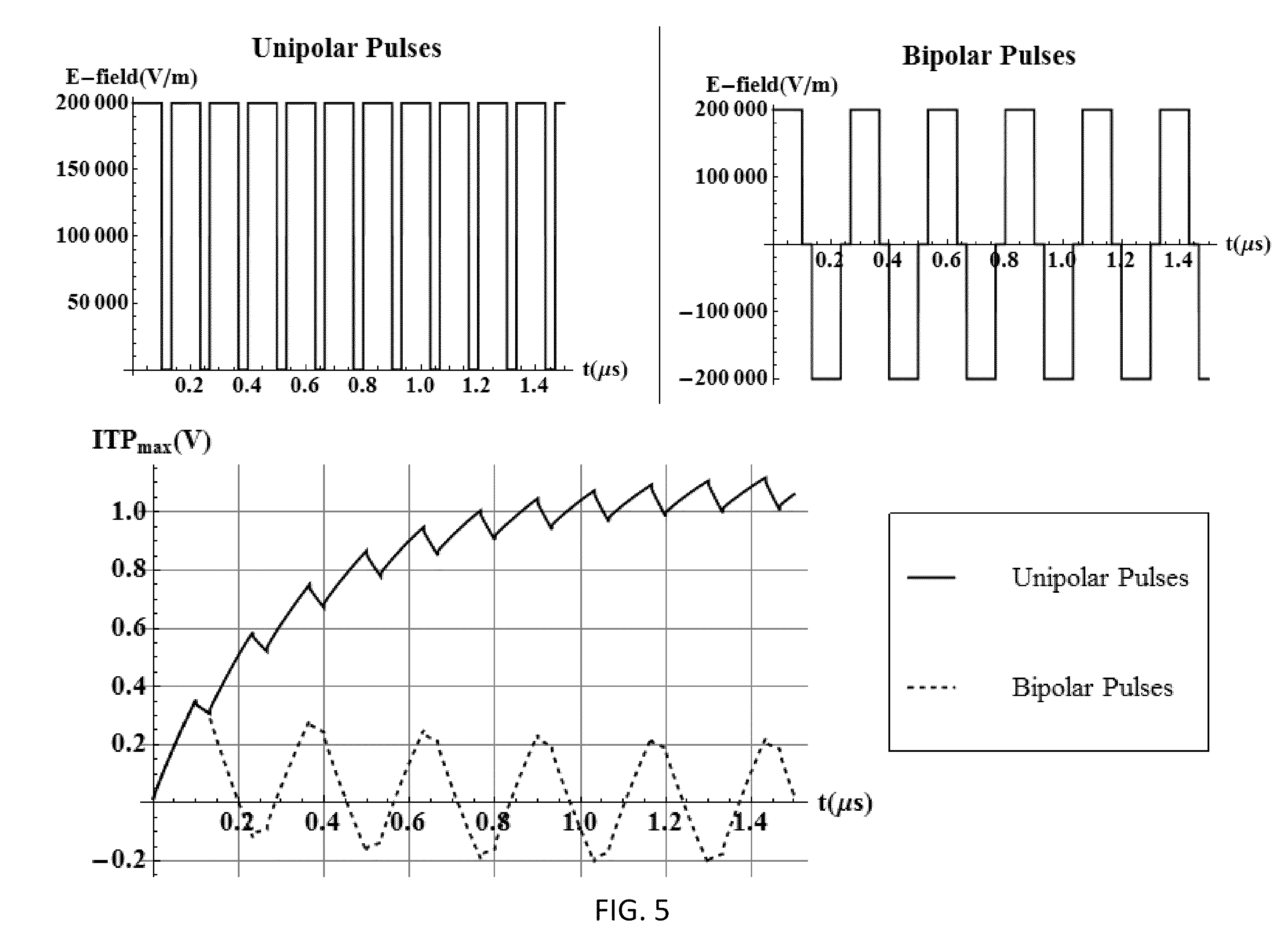
Integration of very short electric pulses for minimally to noninvasive electroporation
ActiveUS8926606B2Reduce the amount requiredHigh energyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesBrain tumorIrreversible electroporation
The present invention provides methods, devices, and systems for in vivo treatment of cell proliferative disorders. The invention can be used to treat solid tumors, such as brain tumors. The methods rely on non-thermal irreversible electroporation (IRE) or supra-poration to cause cell death in treated tumors. In embodiments, the methods comprise the integration of ultra-short electric pulses, both temporally and spatially, to achieve the desired modality of cell death.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
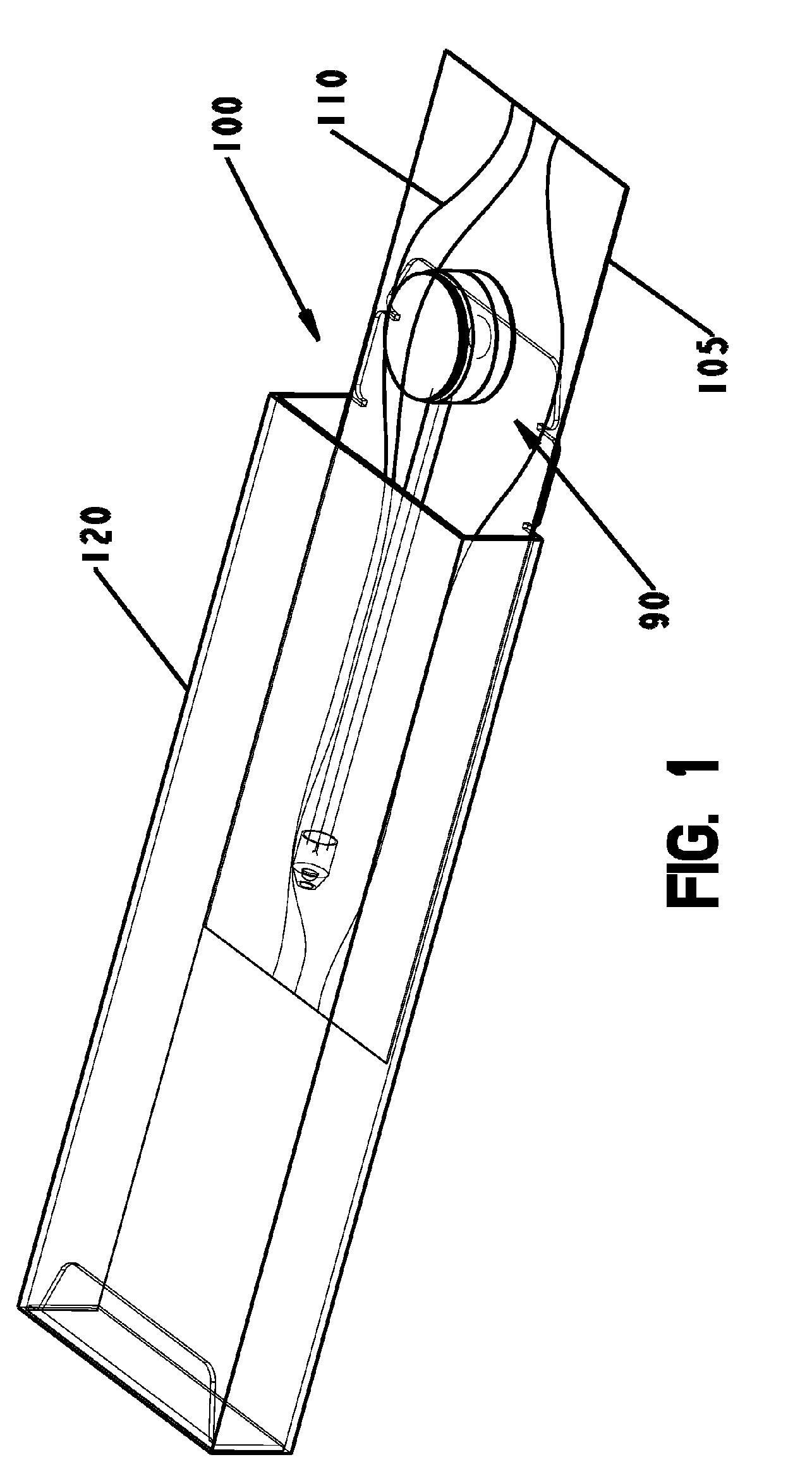
Medical Illumination Device with a Base
InactiveUS20070081358A1Selectively mountablePrecise positioningPoint-like light sourceLighting elementsUltimate tensile strengthBiomedical engineering
Owner:SHEA TODD +1
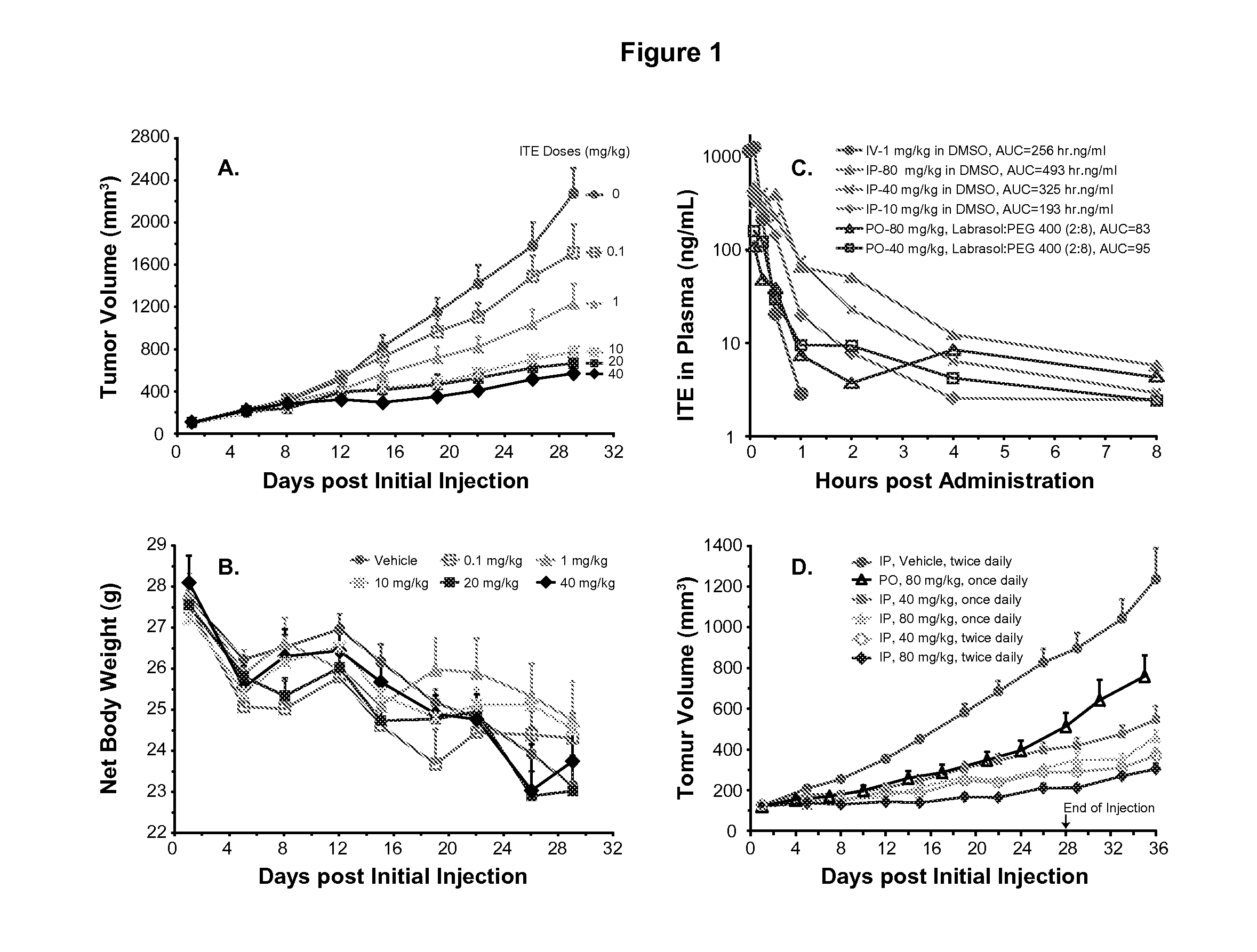
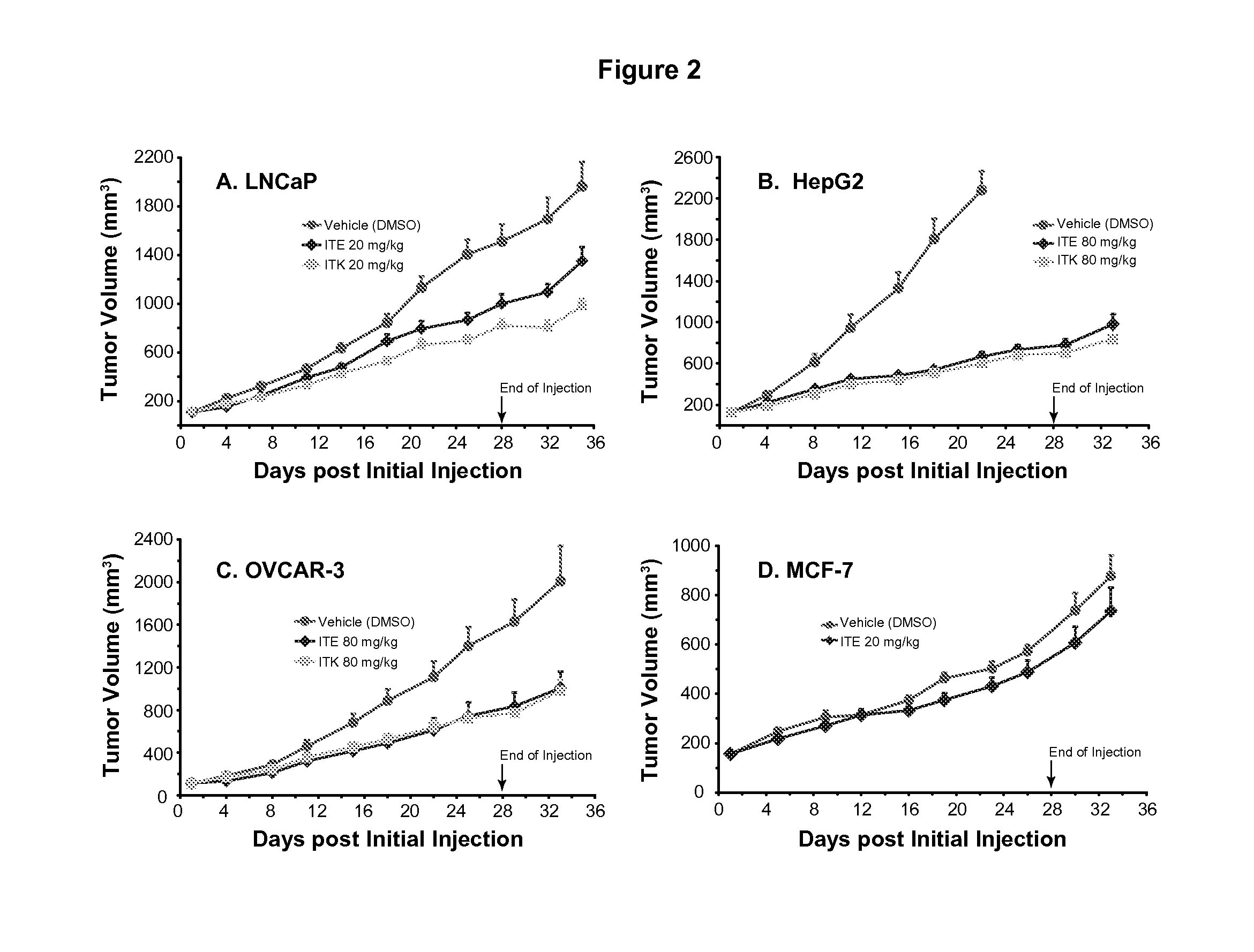
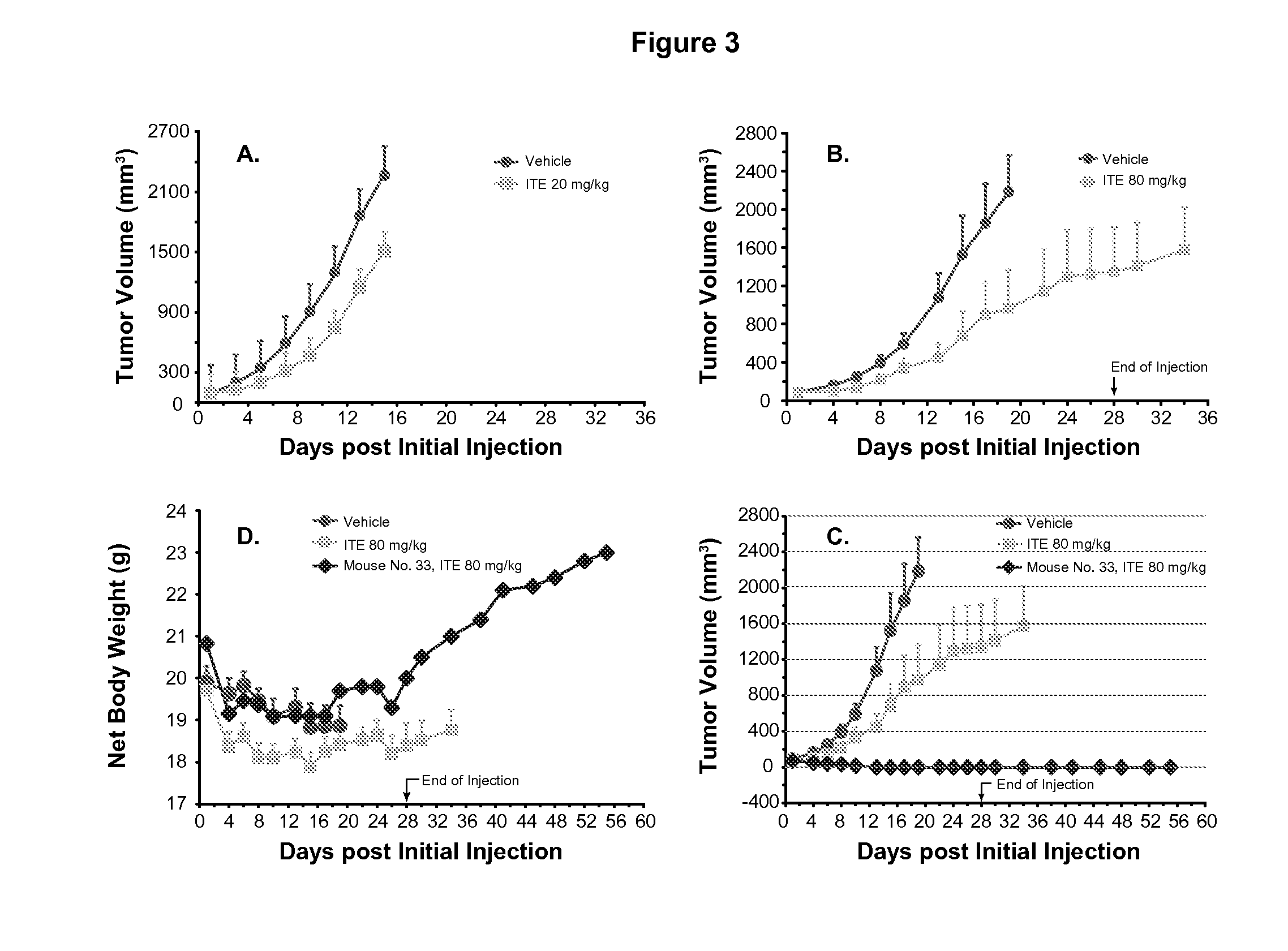
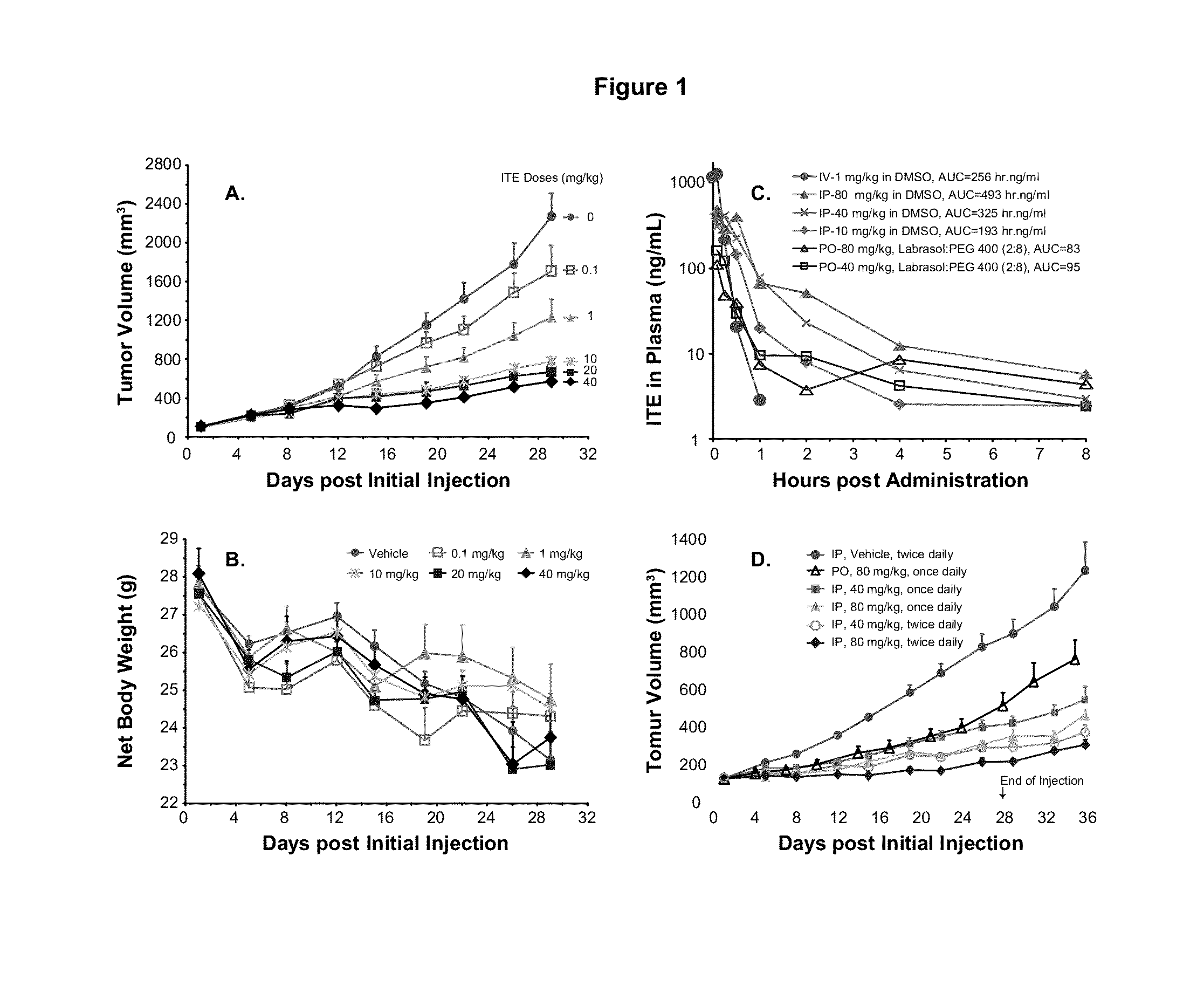
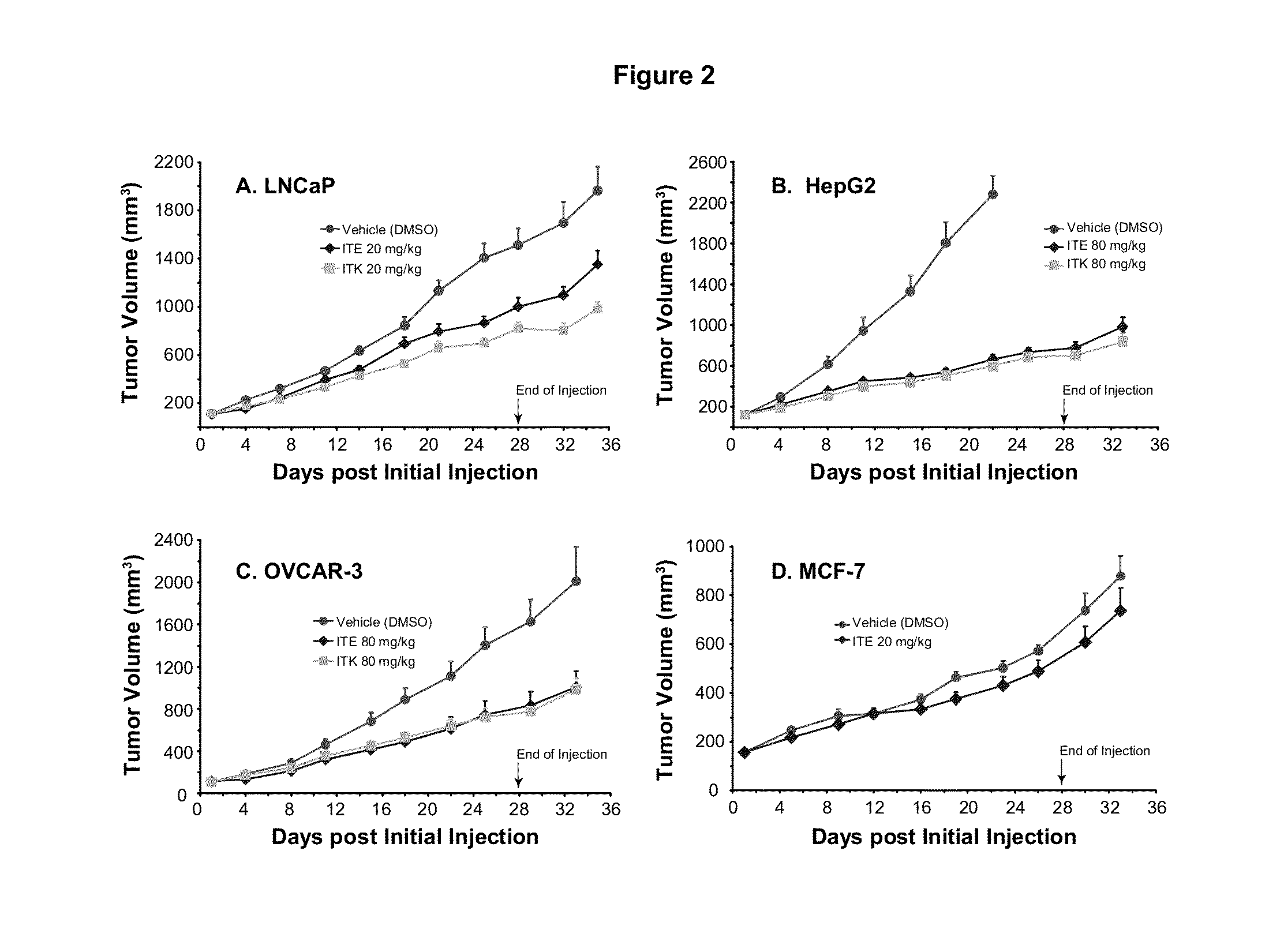
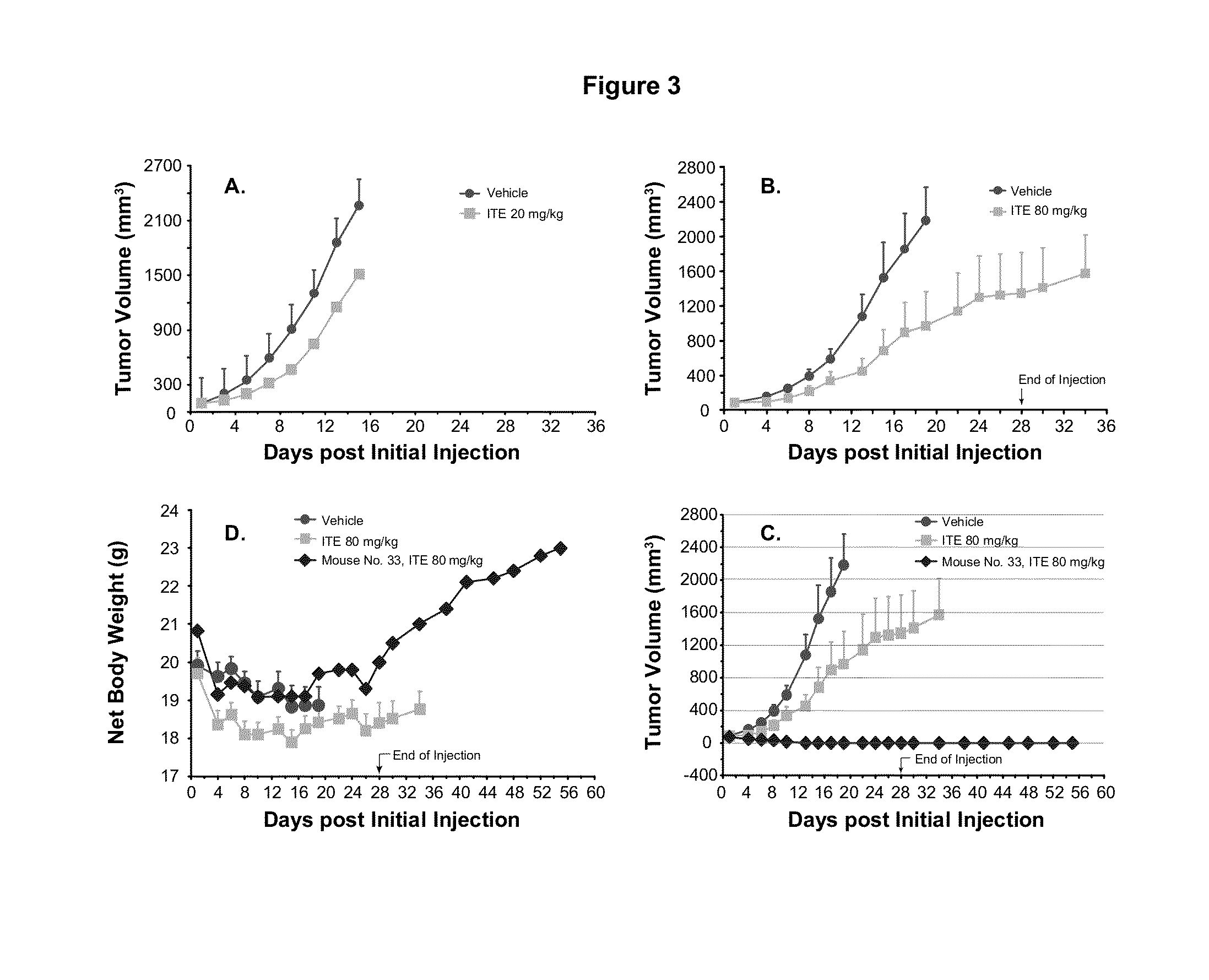
ITE for Cancer Intervention and Eradication
ActiveUS20120214853A1Inhibit angiogenesisInduce cell differentiationPhotovoltaic supportsBiocideCancer InterventionProstate cancer
A method of cancer intervention or eradication by administering an effective amount of an endogenous ligand for the aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor (AhR) named ITE or one of its analogs (the active ingredient) to a subject with cancer is disclosed. An effective dose and dosing frequency of the active ingredient are determined by measuring its blood levels of the subject after dosing. The active ingredient formulated with a carrier system is applied topically, enterally, or parenterally to the subject. The formulated drug can also be administered together with one or more of other cancer therapeutic agents. A maintenance dosing is provided after the subject is free of cancer to insure the cancer eradication. Subjects with cancers of prostate, liver, lung, ovarian, and breast are preferably accepted for treatment.
Owner:ARIAGEN INC
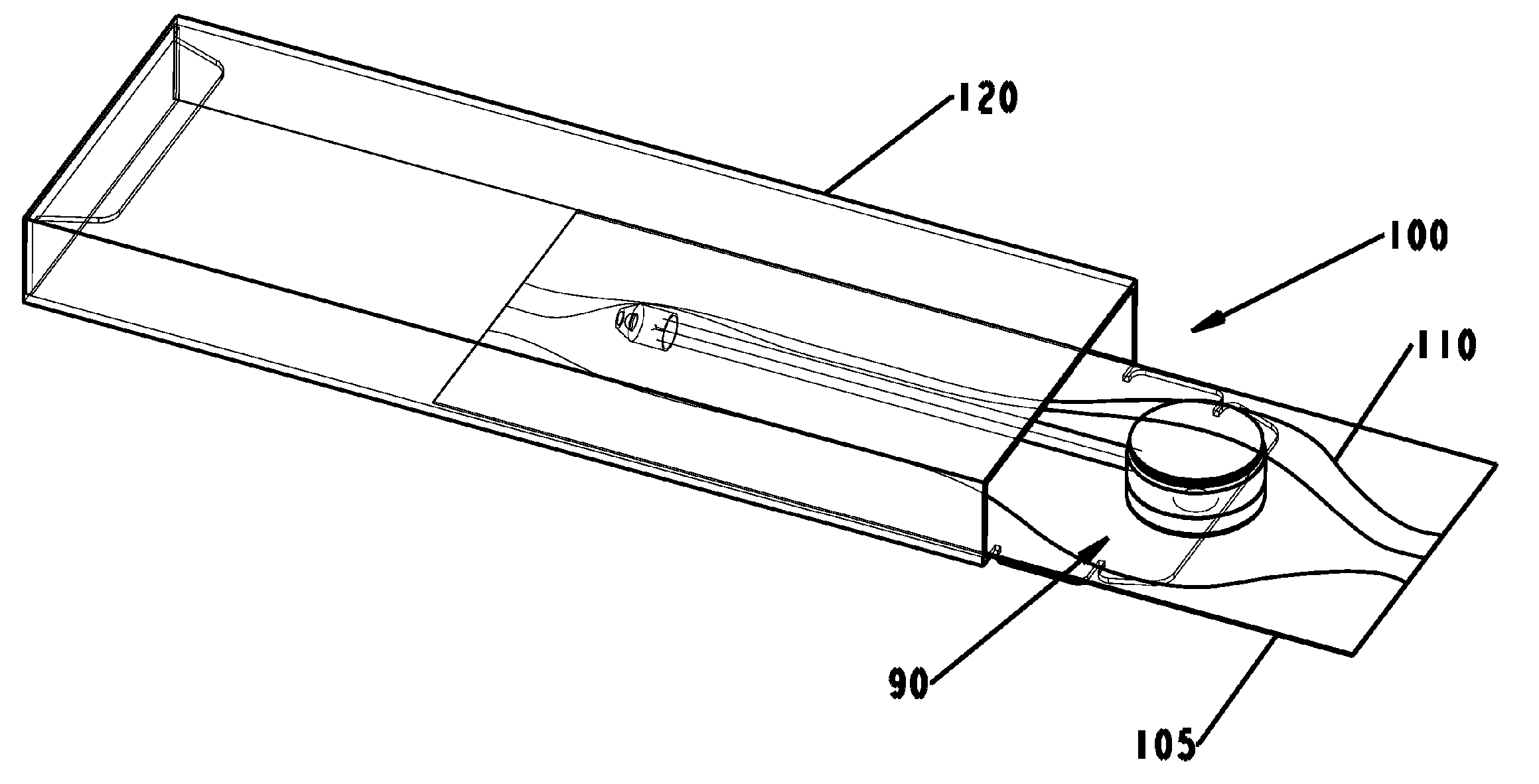
Medical Illumination Device with Sterile Packaging
InactiveUS20070081348A1Selectively mountablePrecise positioningDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiomedical engineeringMedical treatment
A medical illumination device including a sterile package, a base, a light housing, and a flexible body. An attachment component of the base may include an adhesive exposable upon removal of the component from the package. The base may have sufficient surface area, sufficient base weight, and sufficient holding strength to effectively provide stability for repositioning. The base may be 50% of the device weight and have a surface area of 1.0 square inch. A second portion of the attachment component may be repositionable without detaching the first portion. Portions may be separately removable from the sterile package. The device may include a second flexible body attaching a second light source to the base. The device may provide a base containing a power means, a lighting means, and a flexible body means. The device may also include a sterile packaging means and repositioning means.
Owner:SHEA TODD +1
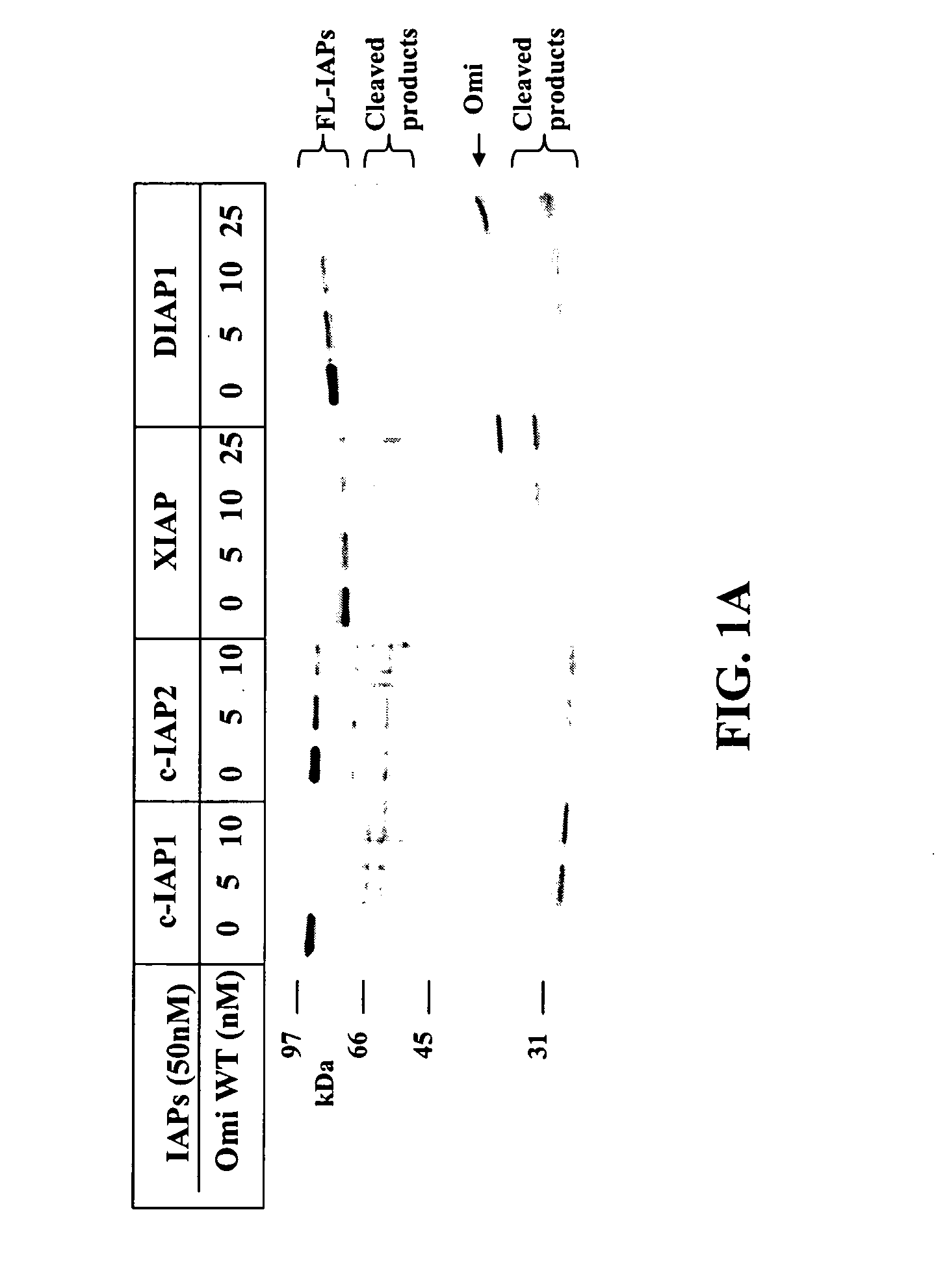
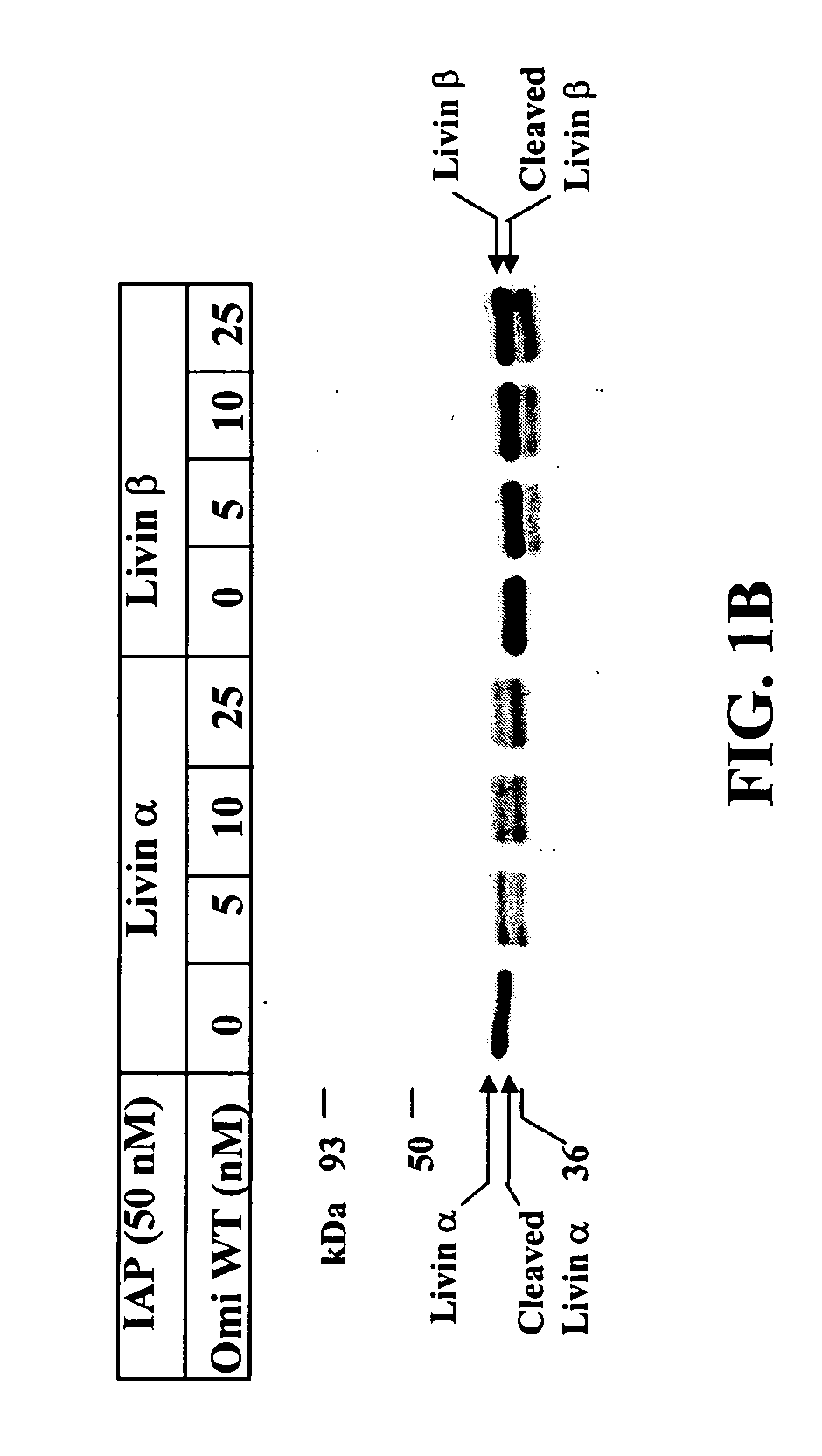
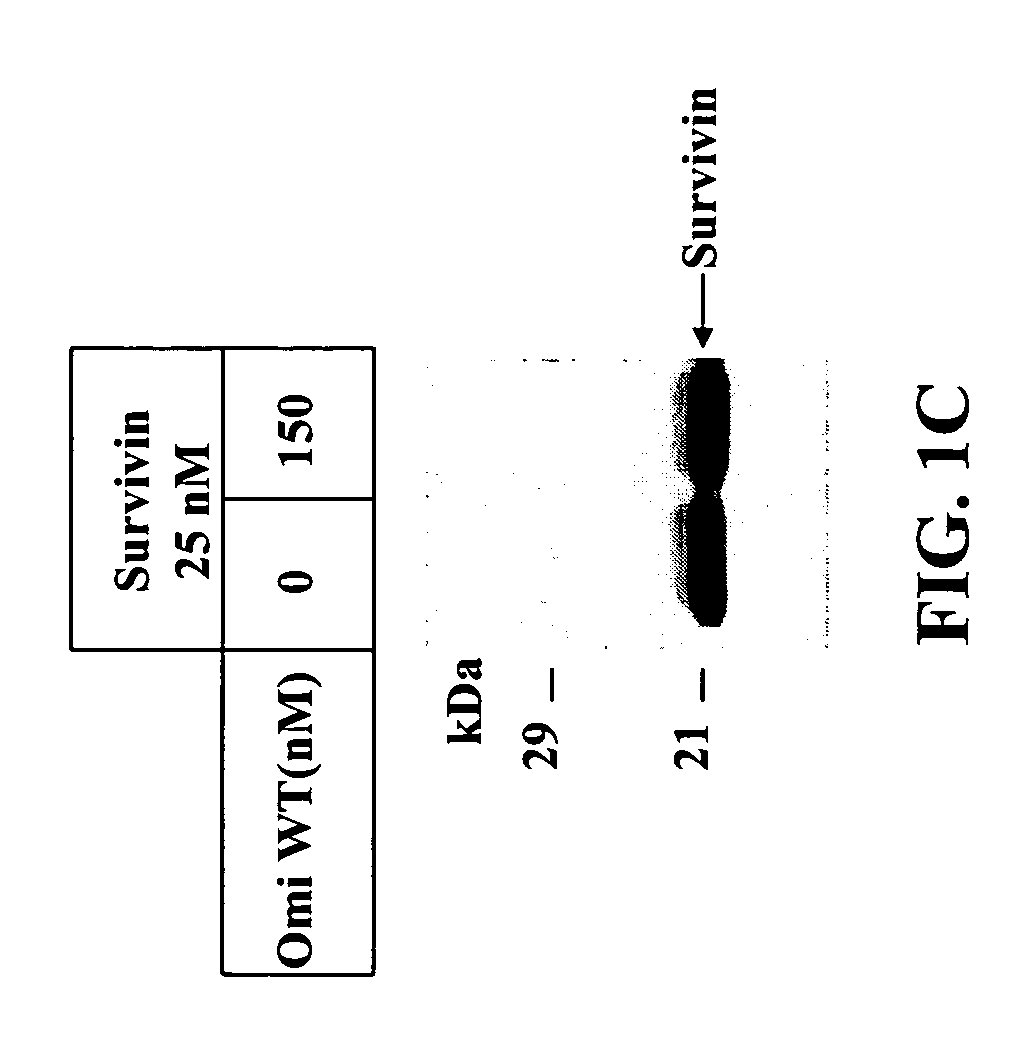
Compositions and methods for cleaving IAP
InactiveUS20040171105A1Efficient infectionPreventing IAP ubiquitinationHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideGenetics
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for making and using Omi-related and IAP-cleaving nucleotide sequences, mutant nucleotide sequences, and polypeptide sequences expressed therefrom, including both biologically active and inactive molecules. The present invention relates to cleaving IAP using an Omi polypeptide.
Owner:STOWERS INST FOR MEDICAL RES
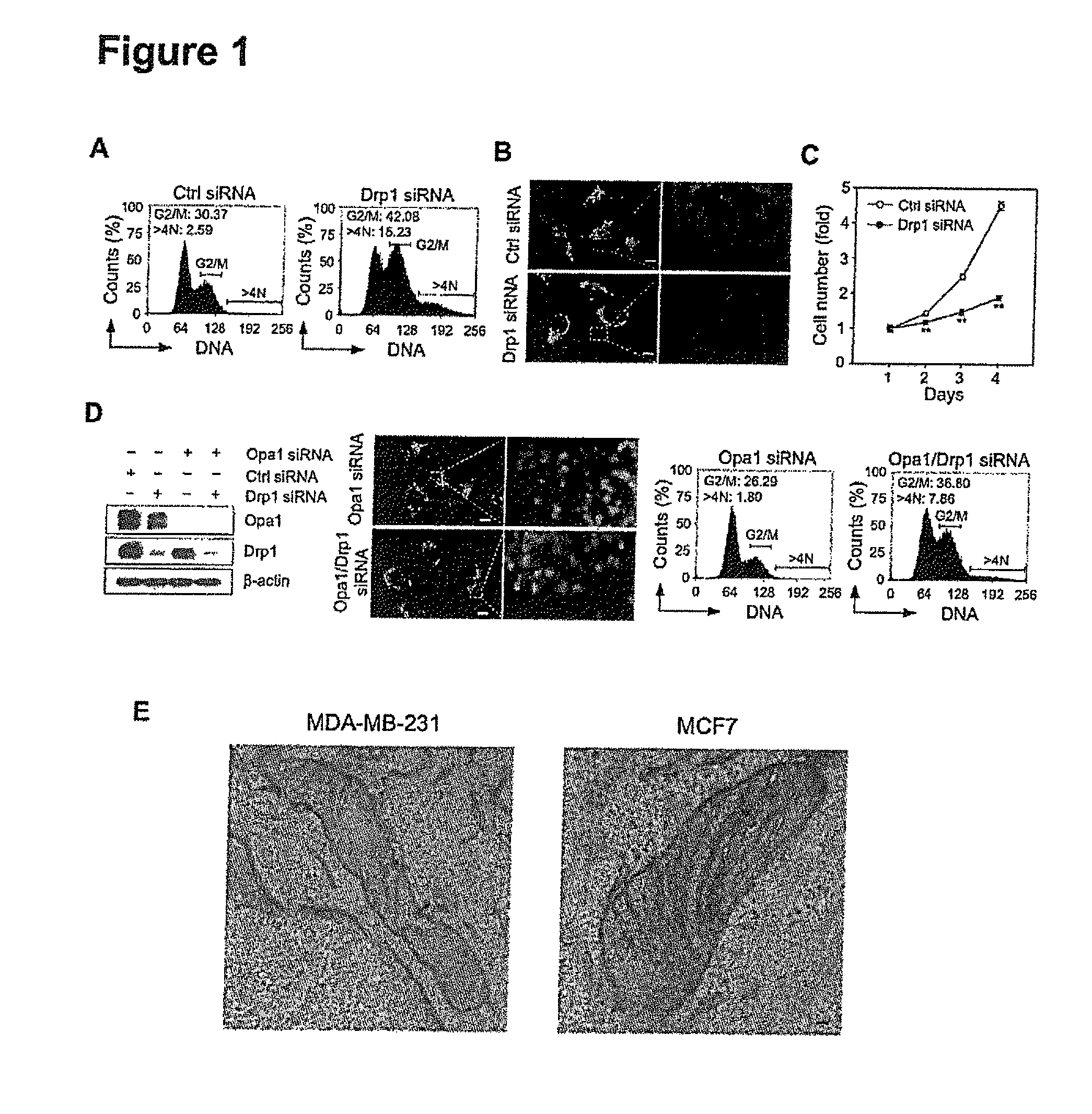
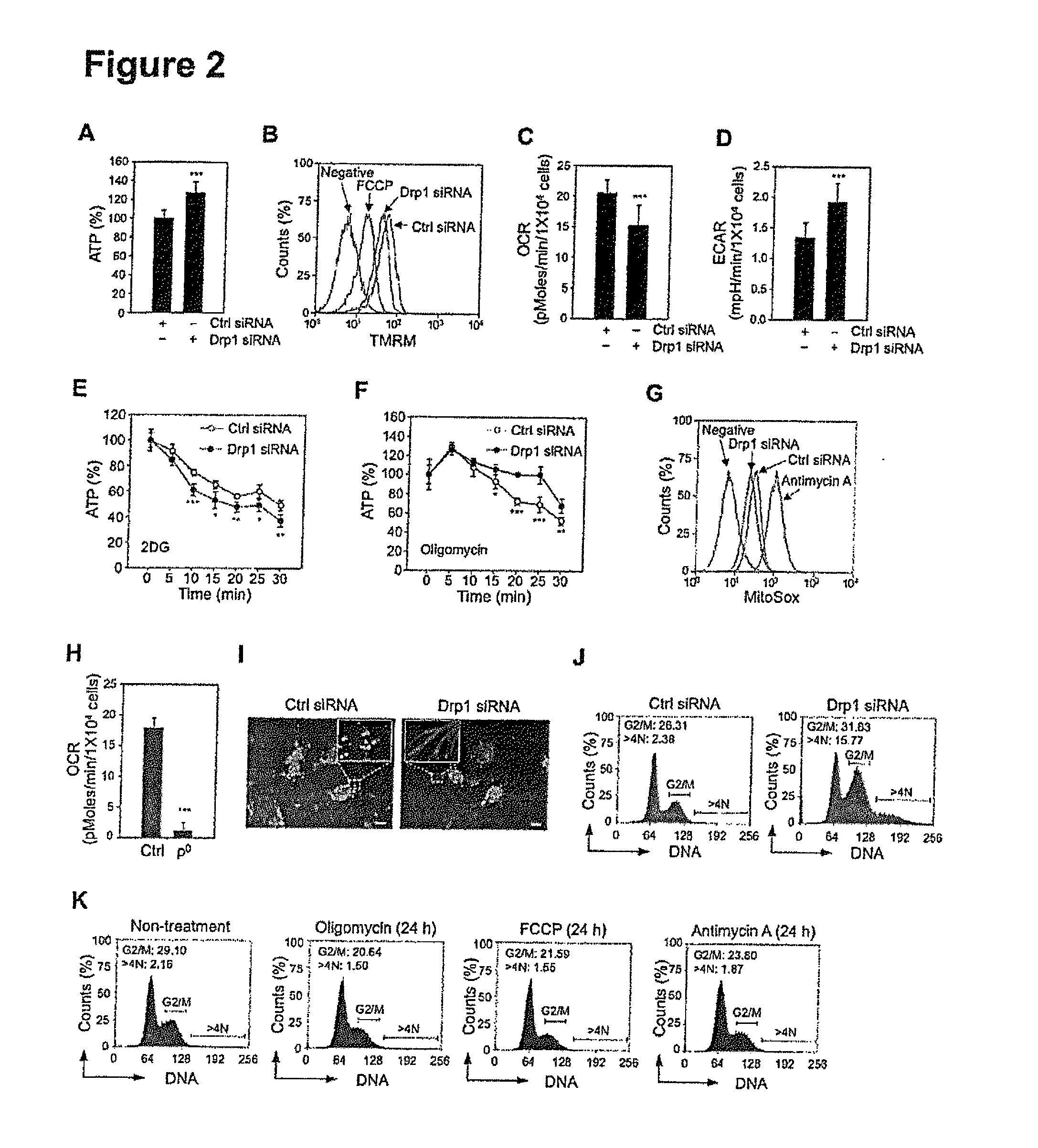
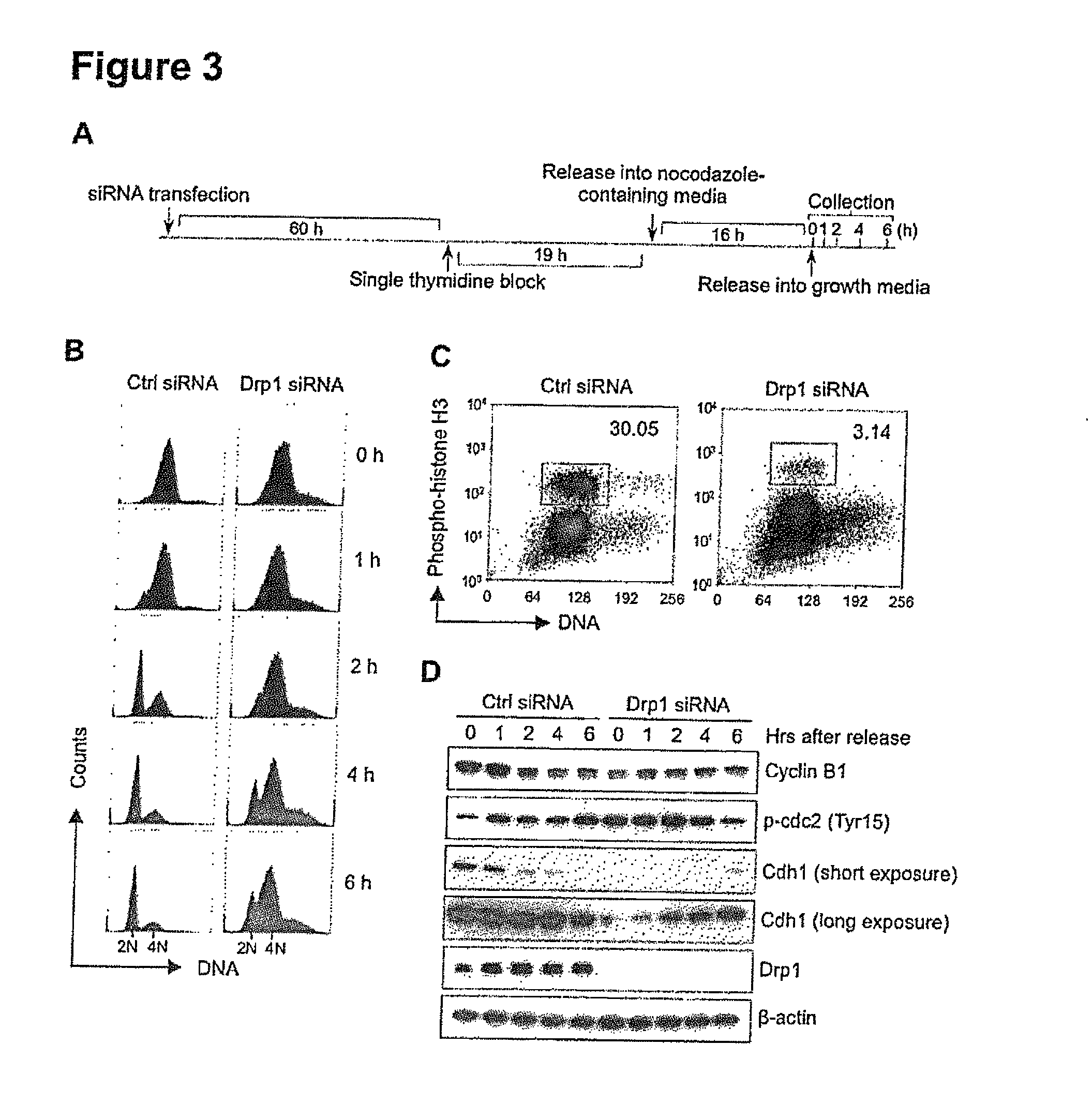
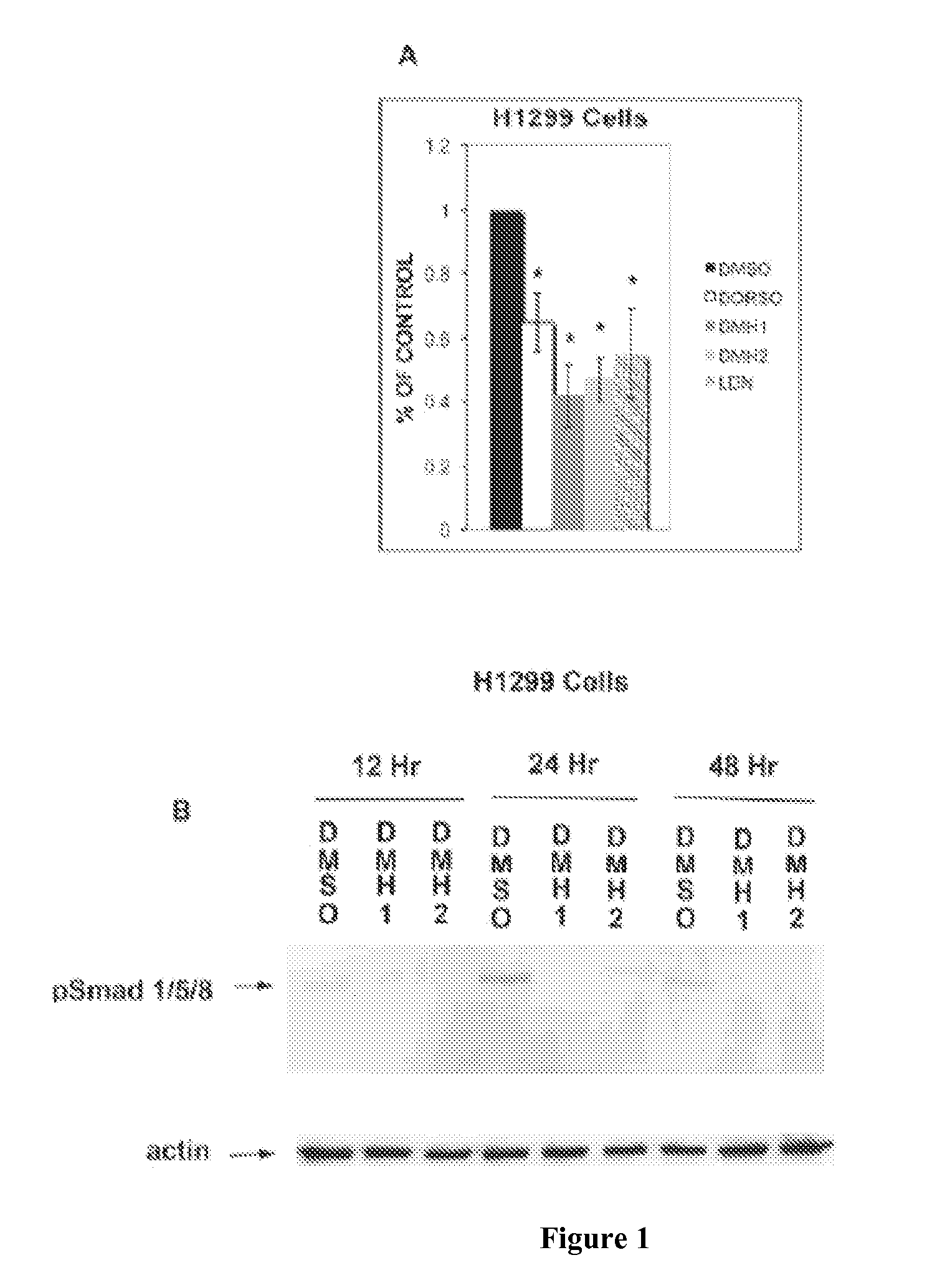
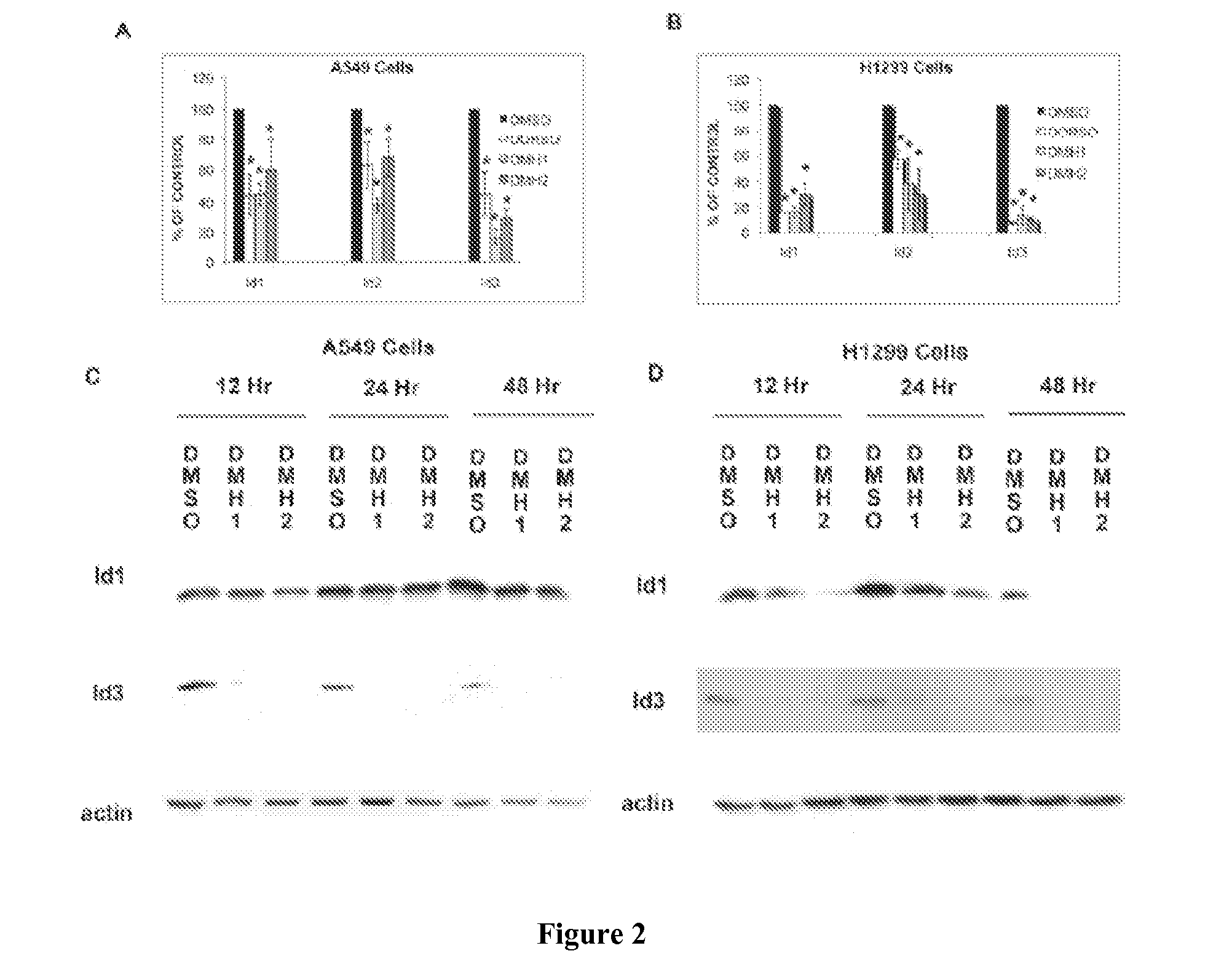
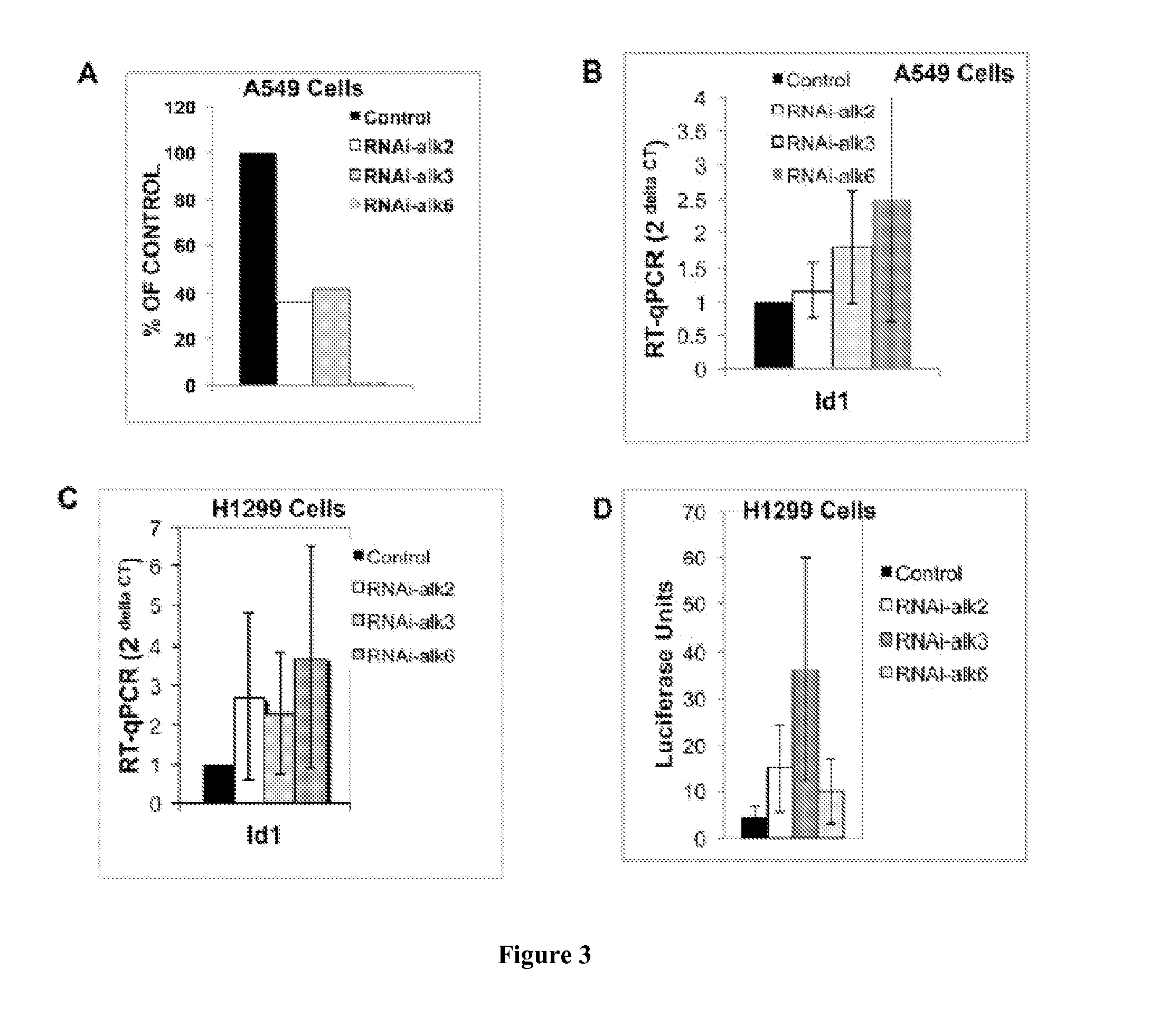
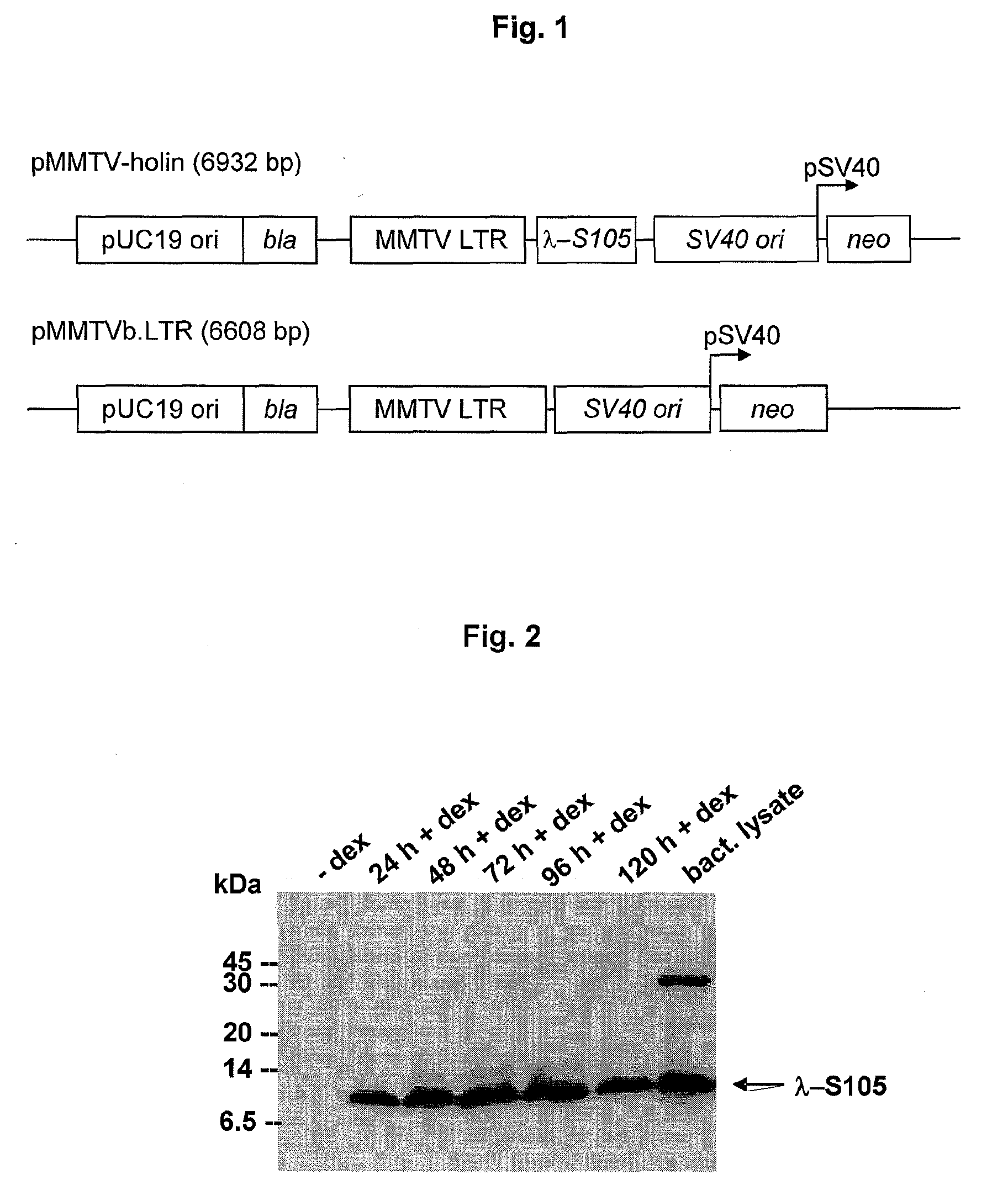
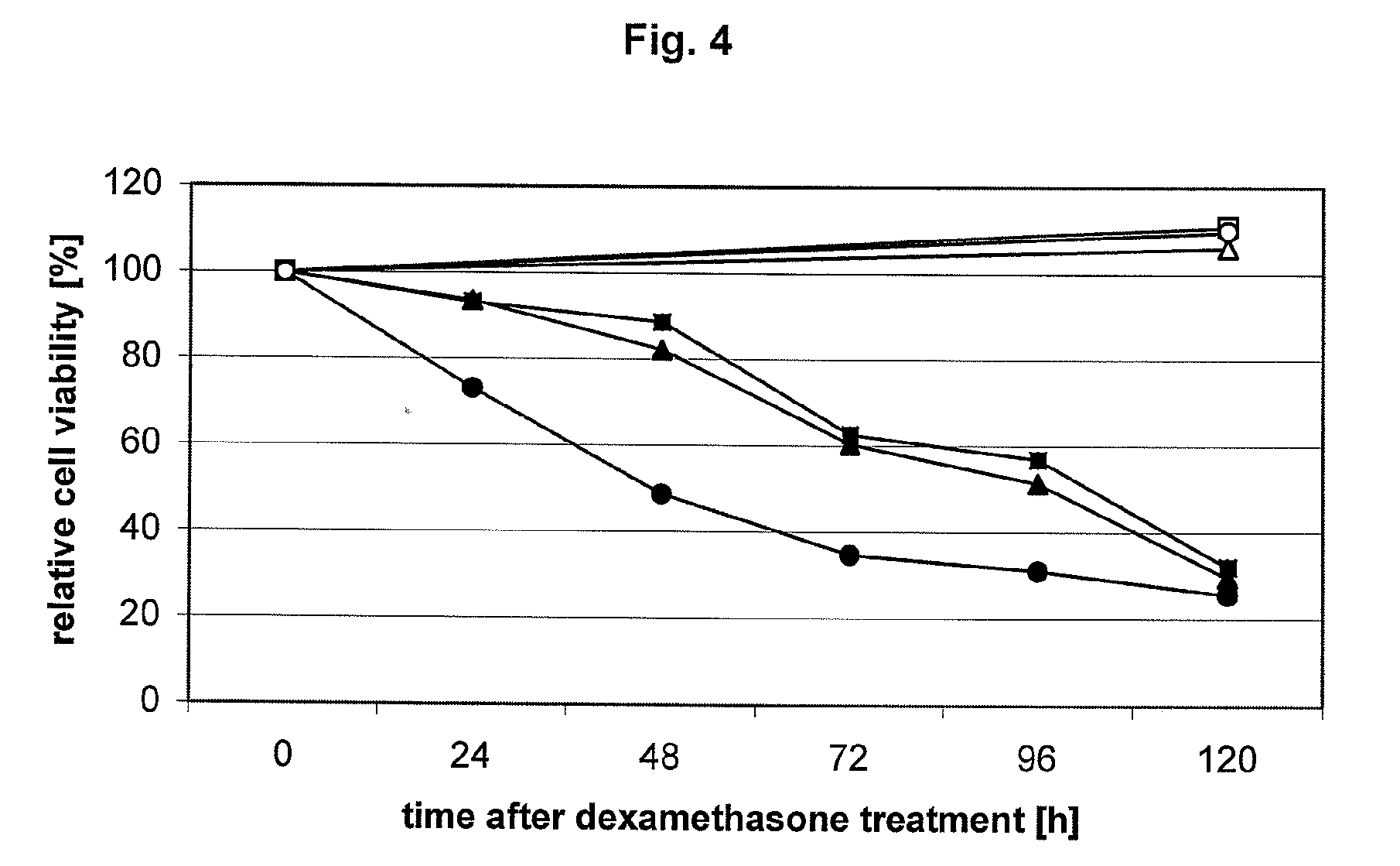
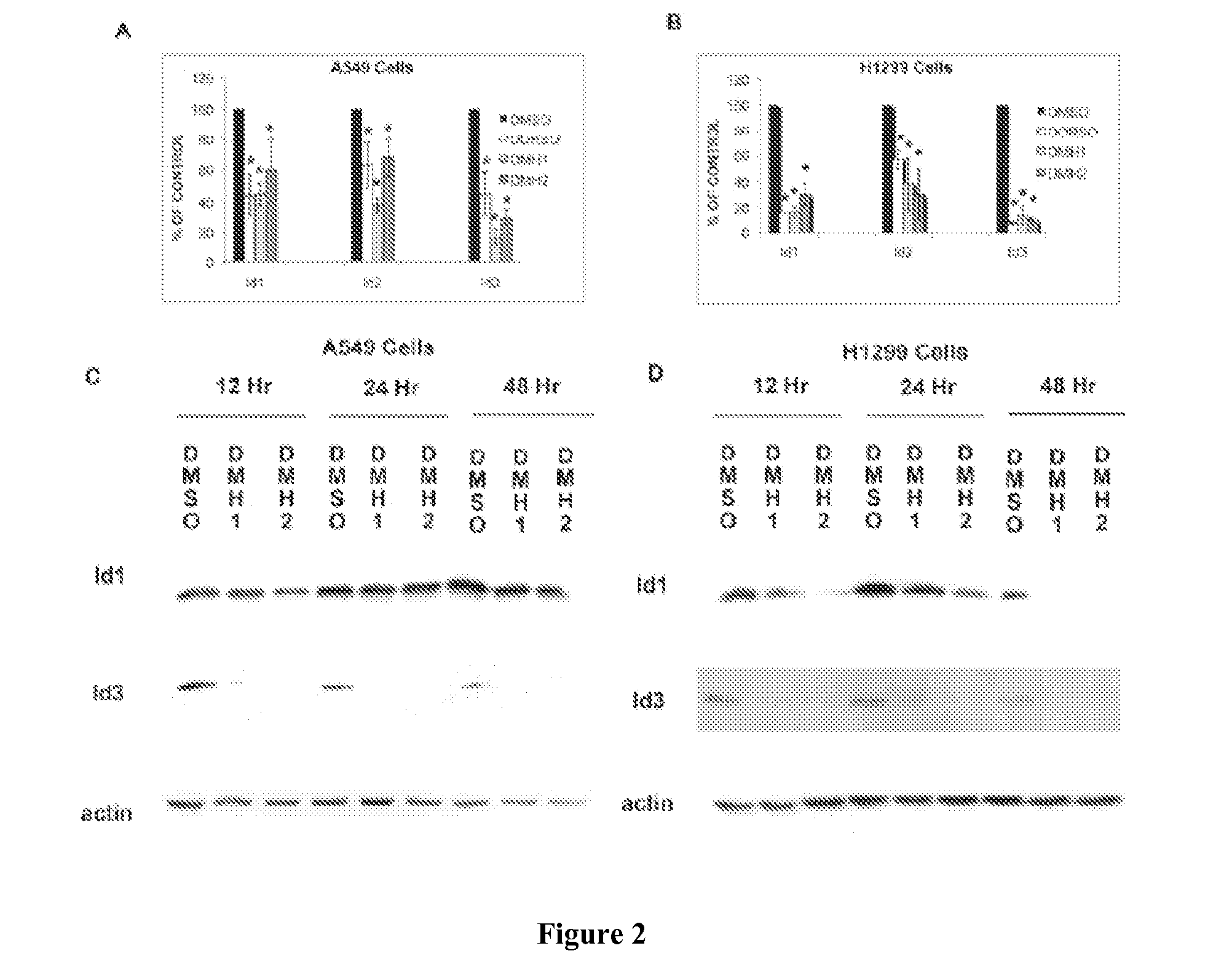
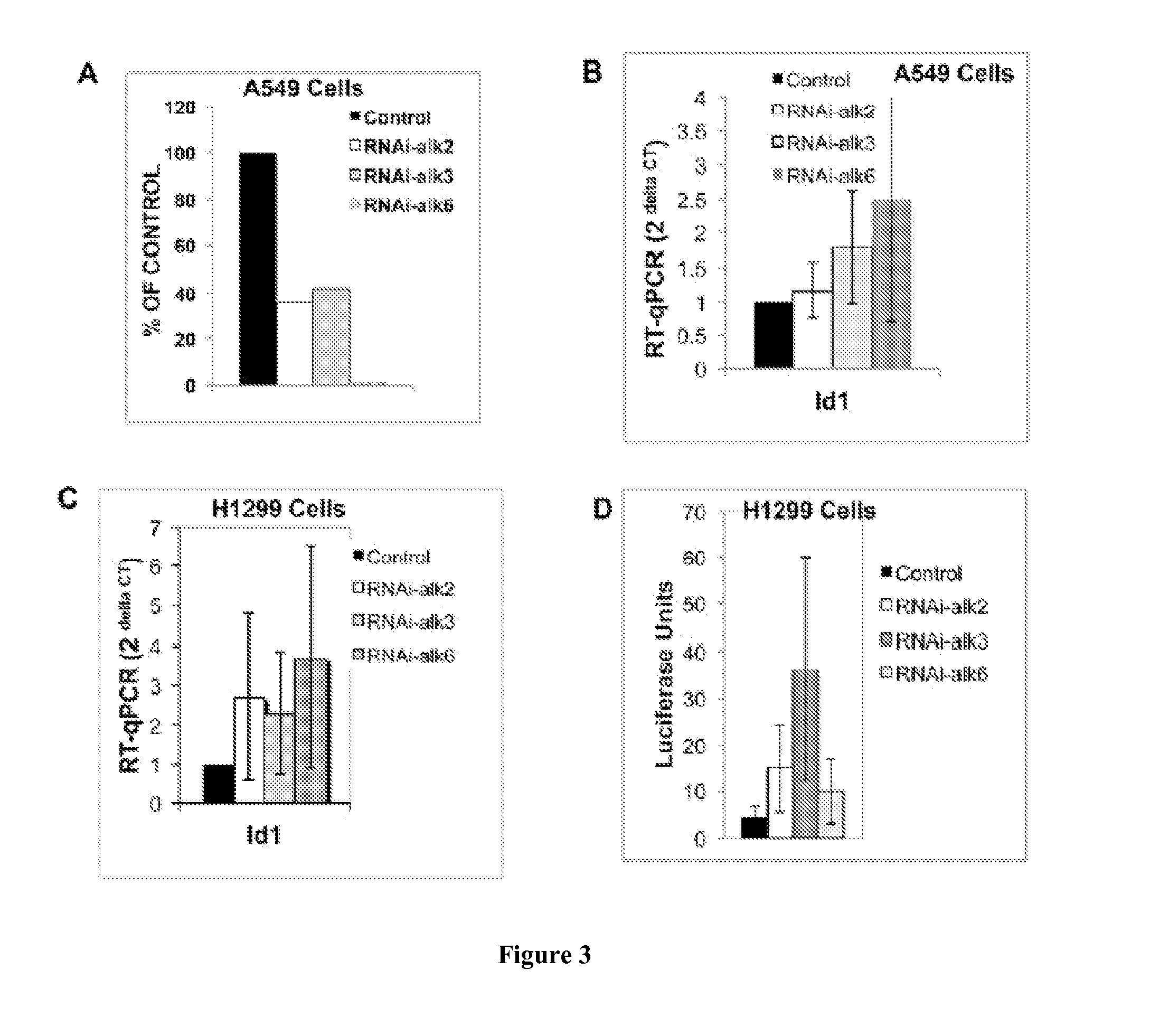
Inhibition of dynamin related protein 1 to promote cell death
ActiveUS20150017262A1Reduce cell proliferationPromote cell deathHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDNA injuryCancer research
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for reducing cell proliferation and / or promoting cell death by inhibiting Drp1. It is based, at least in part, on the discoveries that (i) Drp1 disruption-induced mitochondrial hyperfusion is functionally linked to the cell cycle regulation apparatus, so that Drp1 inhibition results in a disruption of the cell cycle and DNA aberrancies; (ii) inhibition of both Drp1 and ATR are synthetic lethal causing increased DNA damage and apoptotic cell death; and (iii) even in resistant cell lines, Drp1 inhibitor (e.g., mdivi-1) together with a second antiproliferative agent (e.g., cisplatin or carboplatin) act synergistically to promote apoptosis. Accordingly, the present invention provides for novel anticancer strategies.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
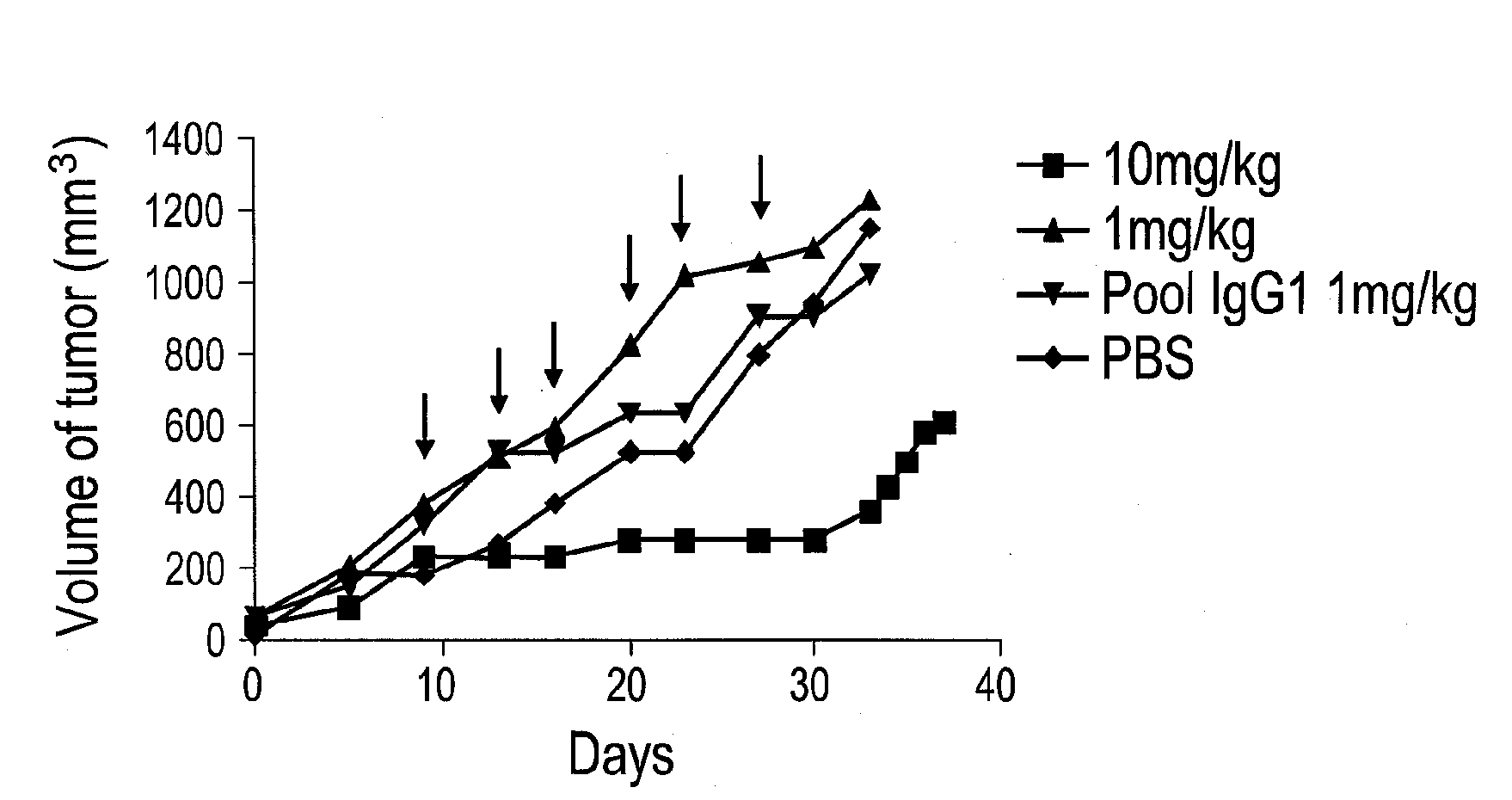
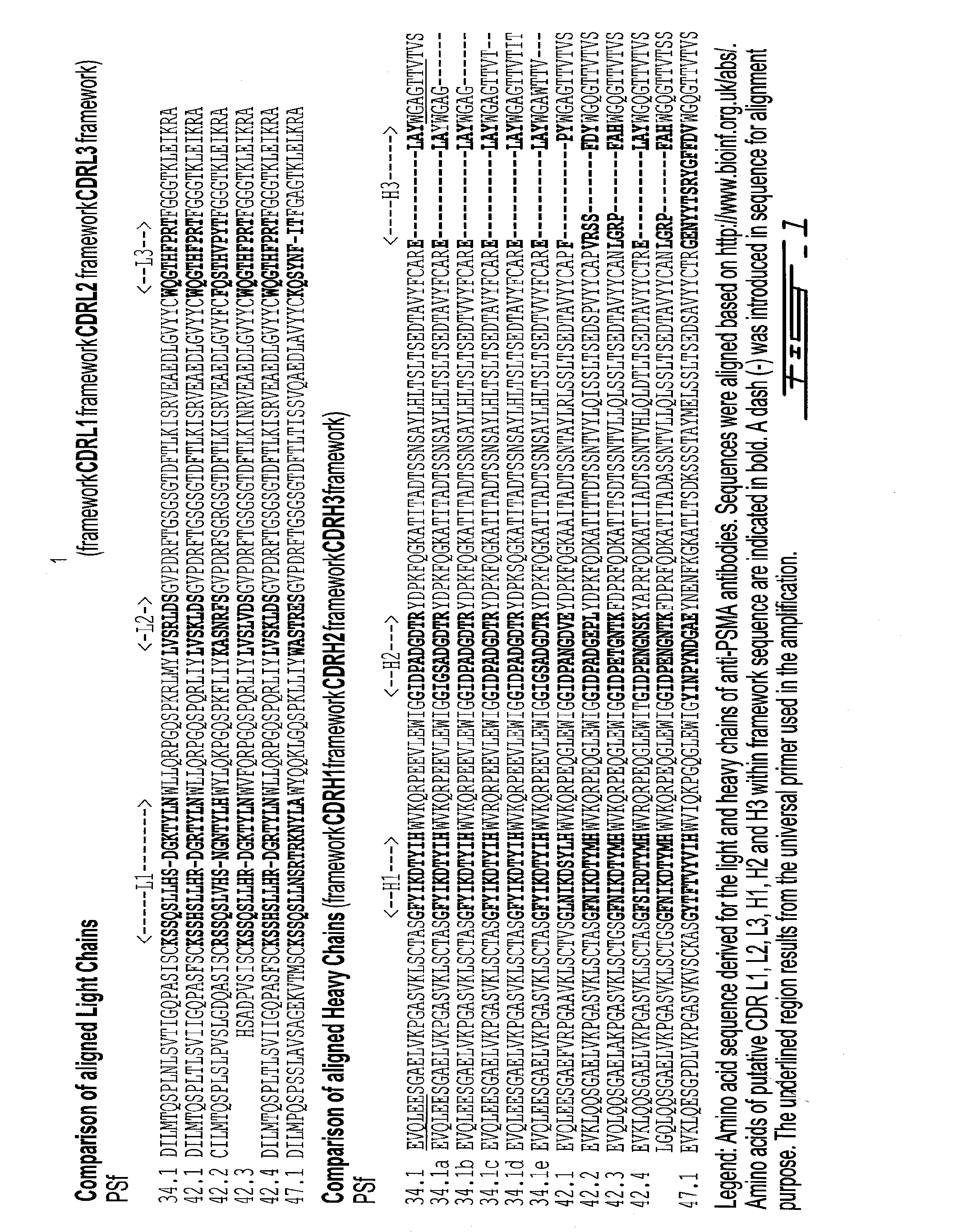
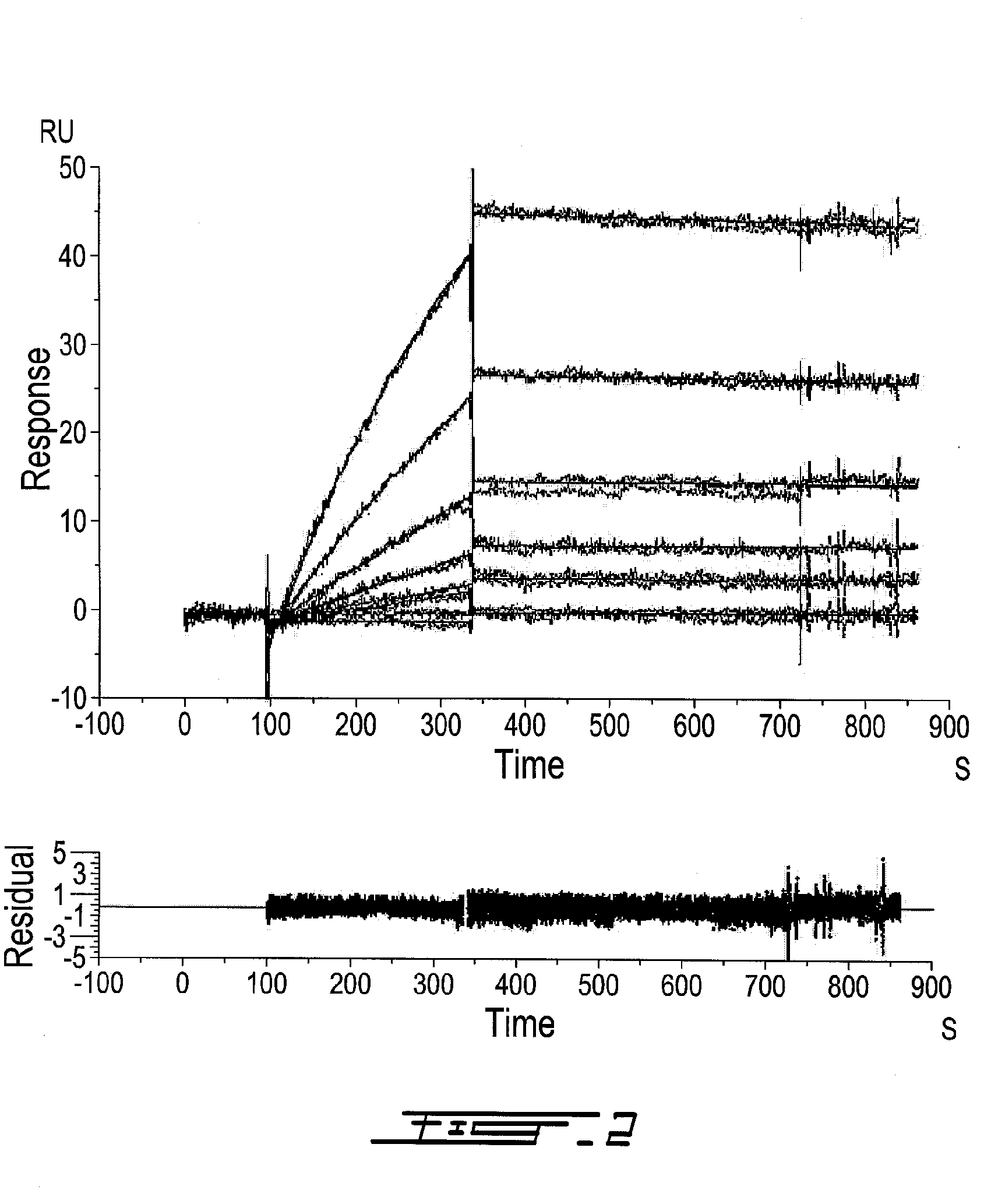
Prostate specific membrane antigen antibodies and antigen binding fragments
InactiveUS20110189093A1Reduce the overall heightPromote cell deathImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsProstate specific membraneAntigen Binding Fragment
Polypeptides, antibodies or antigen-binding fragments capable of binding to prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) are provided. These polypeptides, antibodies or antigen-binding fragments may be used for diagnostic and / or therapeutic purposes.
Owner:PROSCAN RX PHARMA
Cancer treatment using bmp inhibitor
ActiveUS20140256720A1Promoting death of cancer cellReduce signalingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCancer cellCell growth
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
Nk cell receptor conjugates for treating malignancies
InactiveUS20060165592A1Reducing and inhibiting growth of tumorPromoting internalizationVirusesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsNK Cell Receptors
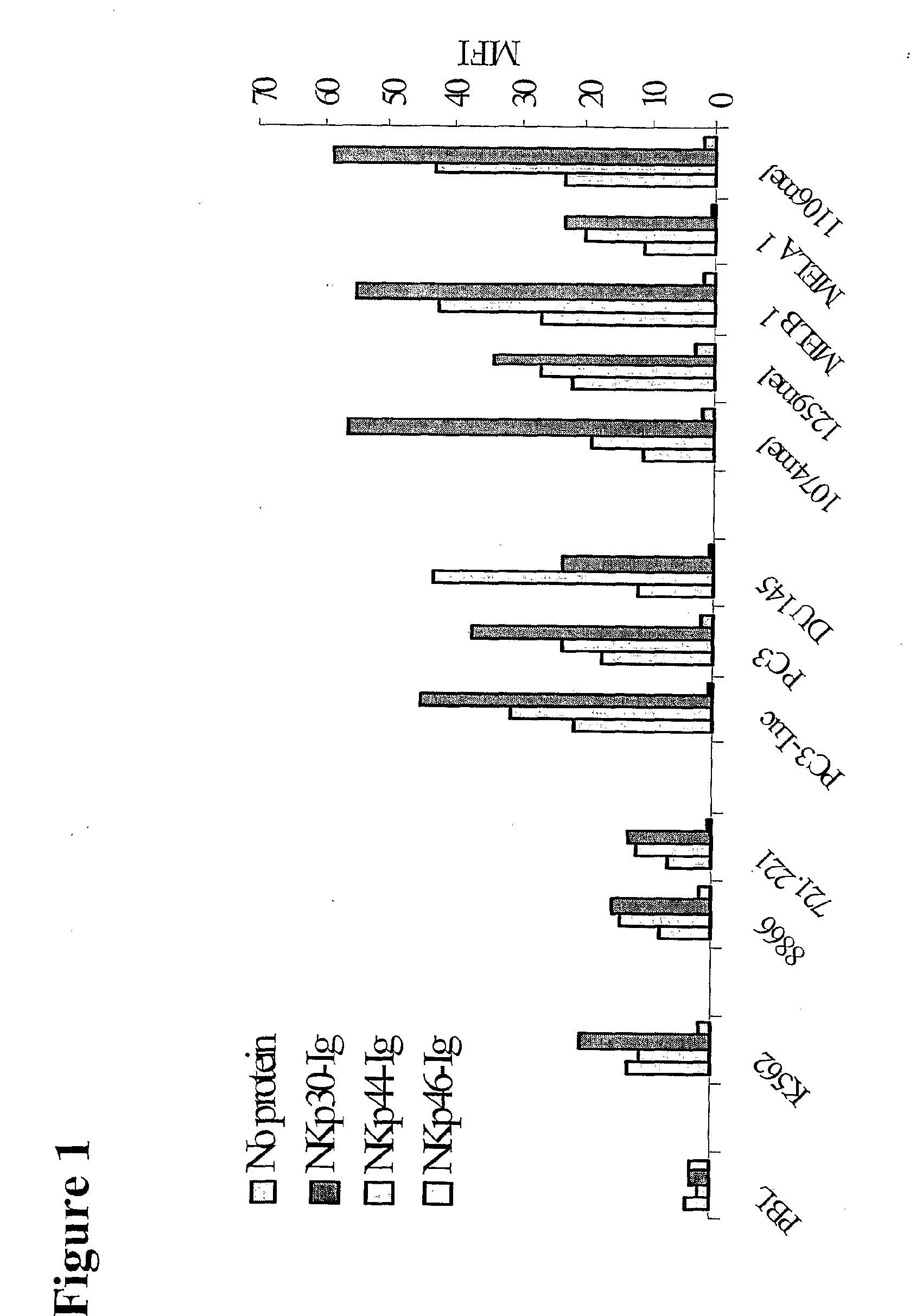
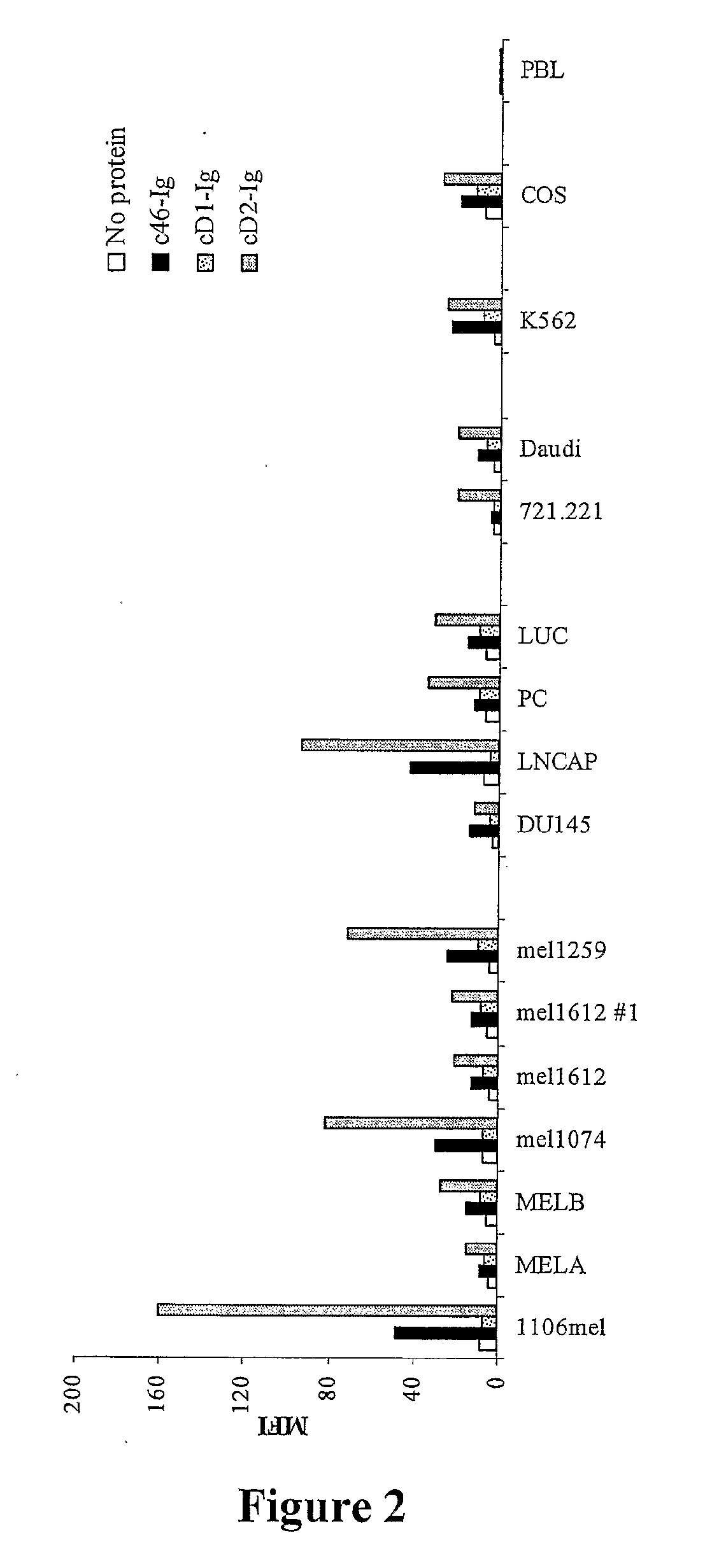
The present invention relates generally to compositions useful in therapies involving the selective destruction of tumor cells in vivo. In particular, this invention relates to a conjugate which comprises a target recognition segment and an active cytotoxic segment. The target recognition segment comprises a receptor specific to NK cells, wherein the receptor binds to a cellular ligand expressed on the surface of a tumor cell, and the active segment comprises an agent capable of exerting a cytotoxic effect on the tumor cell. The target recognition segment derived form the natural killer receptor NKp3O has been found to be particularly effective in vivo.
Owner:NATSPEARS
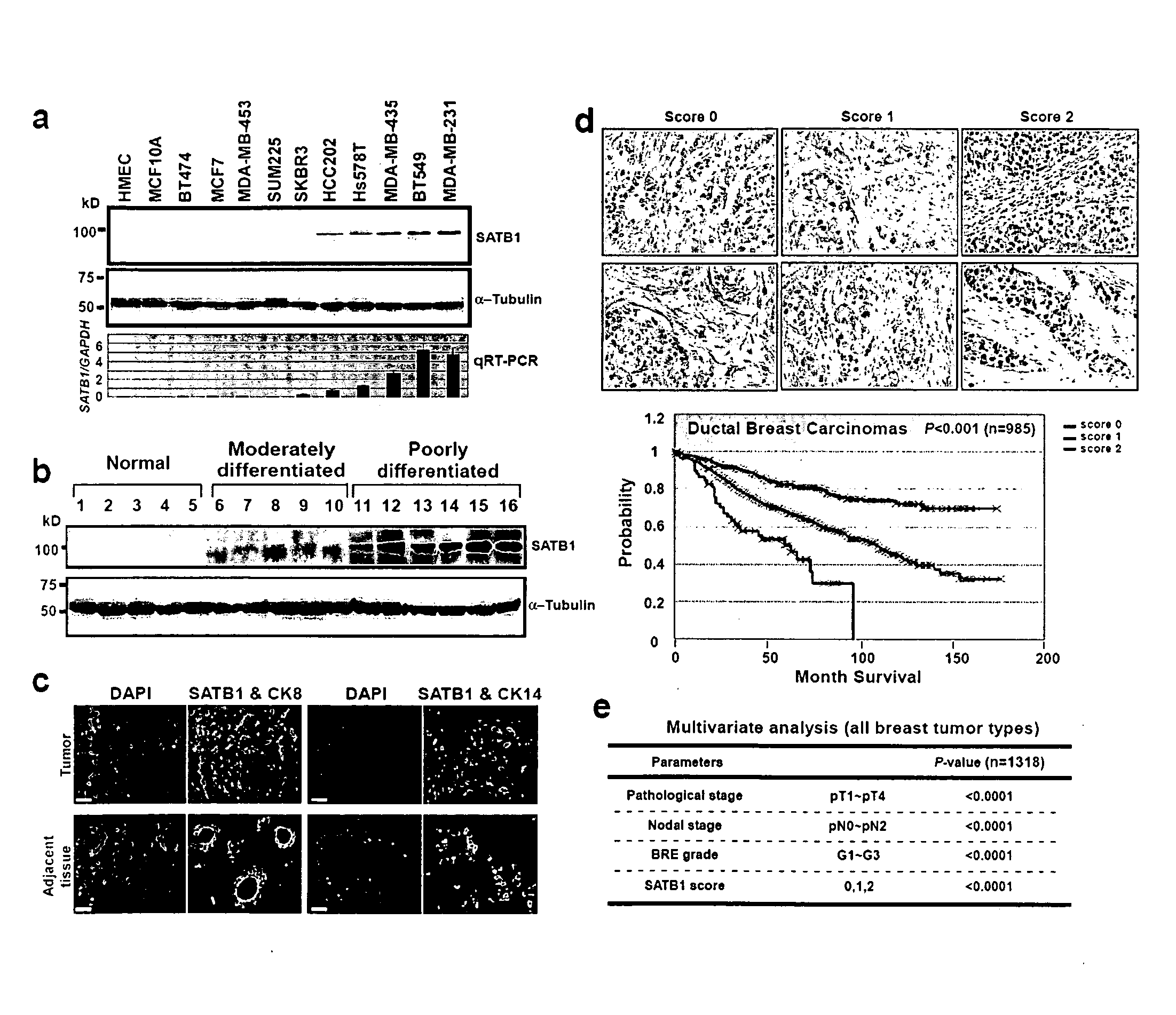
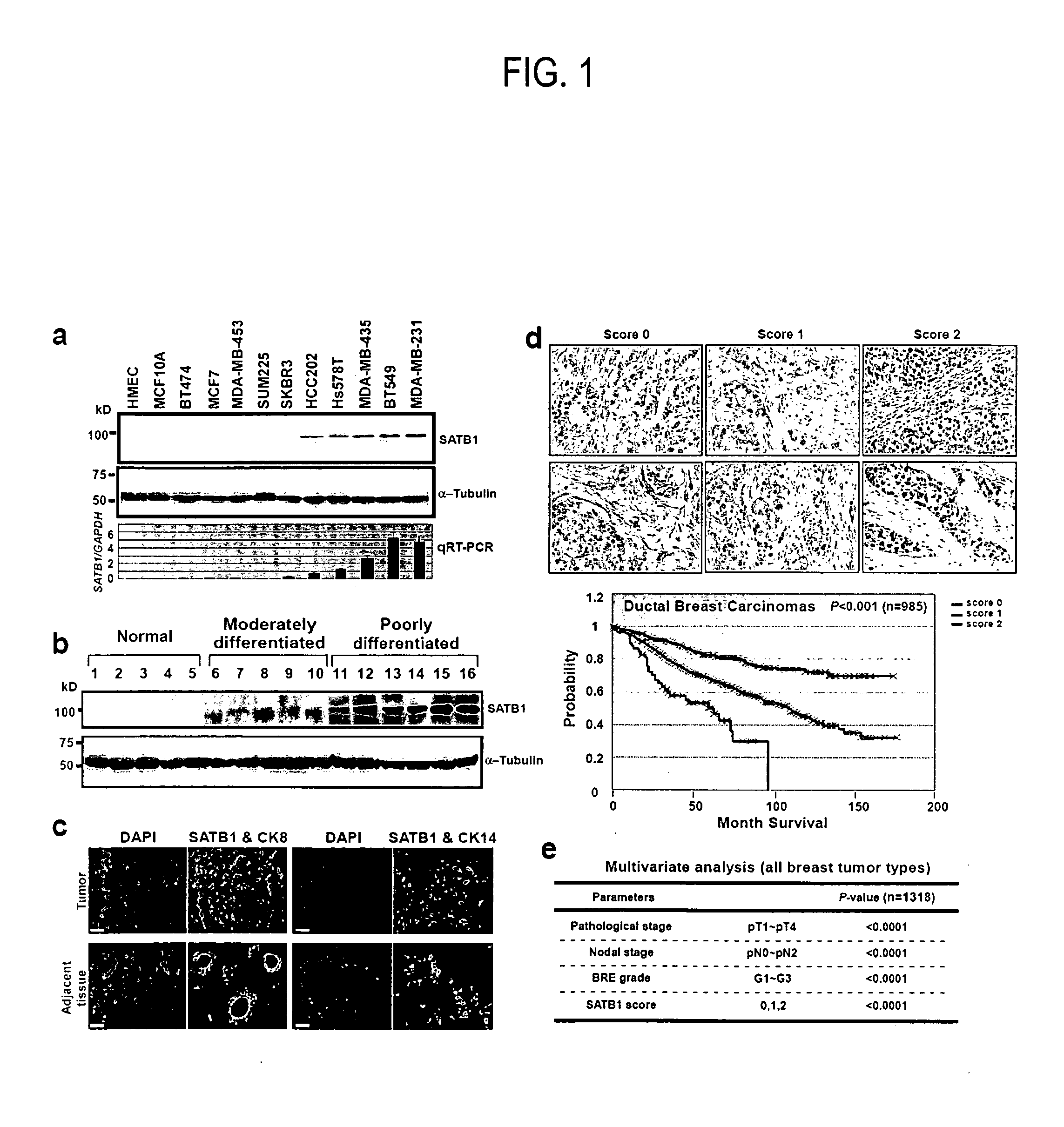
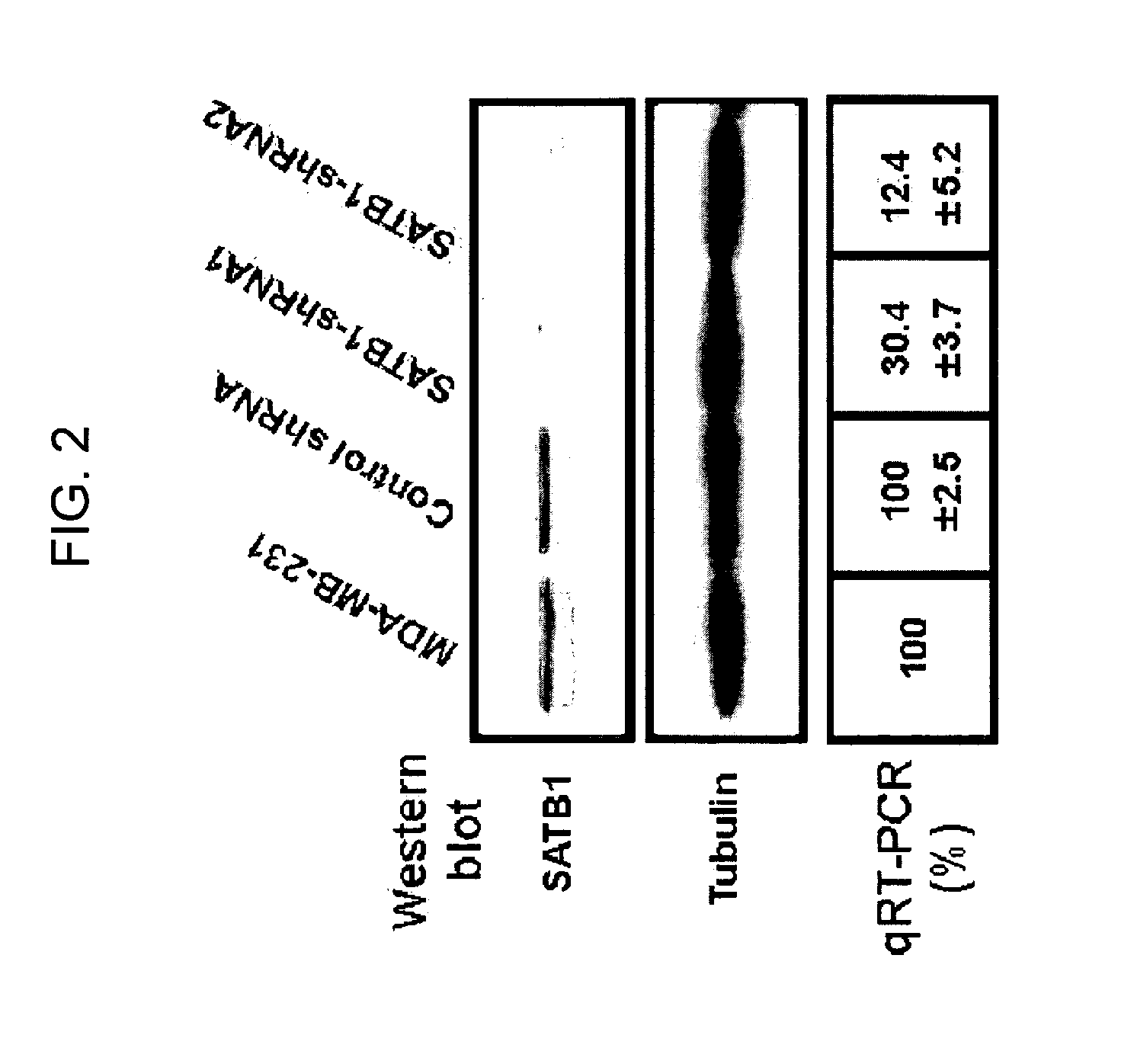
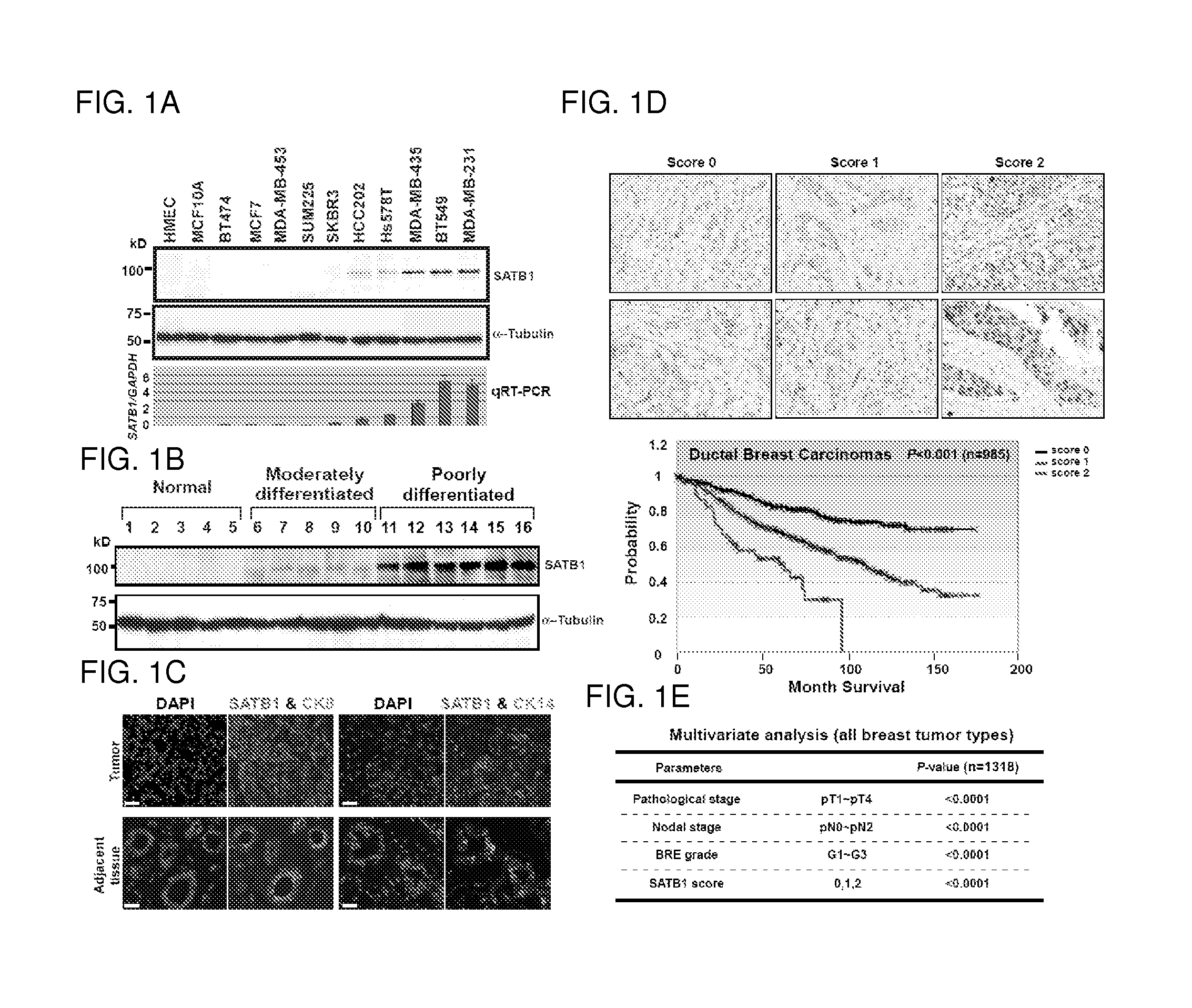
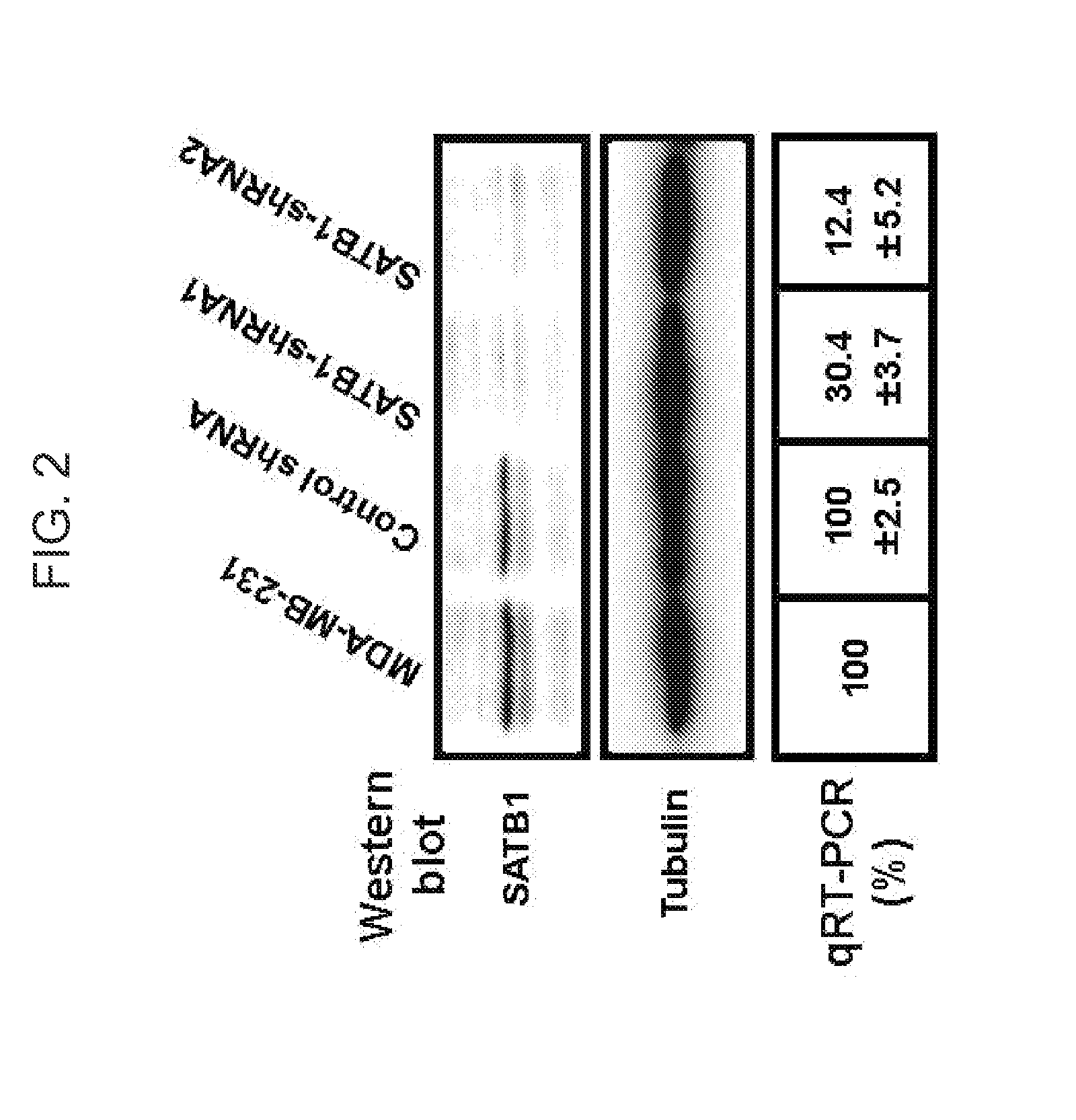
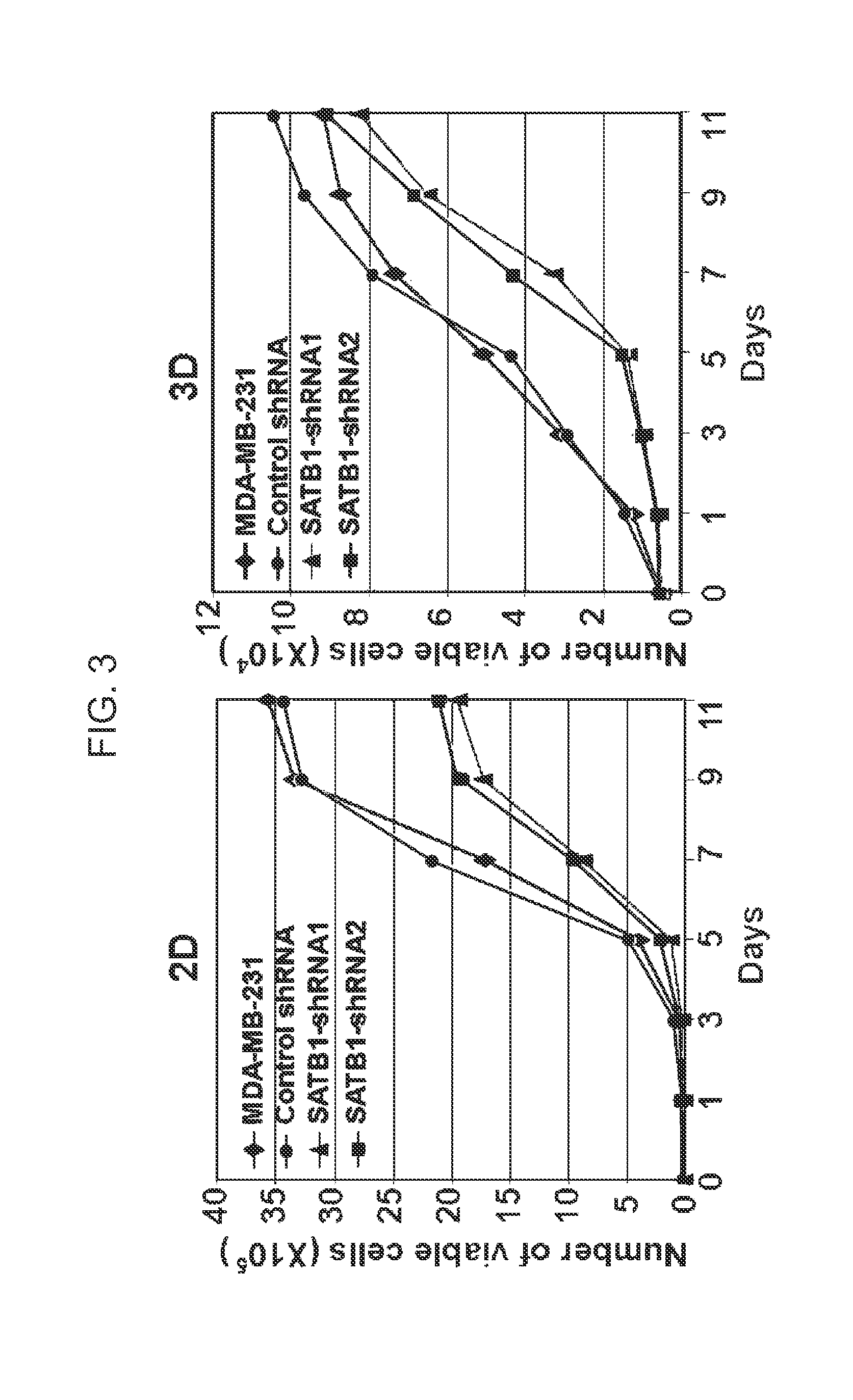
Satb1: a determinant of morphogenesis and tumor metastasis
InactiveUS20080280298A1Reliable diagnosisReliable prognosisOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCancer cellLymphatic Spread
It is proposed that cancer cells express SATB1, and that SATB1 acts as a determinant for the acquisition of metastatic activity by controlling expression of a specific set of genes that promote metastatic activity. In order for cancer cells to gain the ability to metastasize, SATB1 re-organizes or re-packages genomic sequences in a specific manner to allow a switch in the pattern of gene expression. SATB1 expression was found restricted mainly to aggressive cancer cells where it may regulate the genetic and epigenetic changes that program the steps involved in the metastatic process. The present invention describes reagents and tools to detect the SATB1 protein for use in diagnosis and prognosis of aggressive cancers and therapeutics to inhibit SATB1 protein to deplete its expression in metastatic and aggressive cancers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
NK Cell Receptor Conjugates for Treating Malignancies
InactiveUS20100047169A1Promoting internalizationPromote cell deathVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsNK Cell Receptors
The present invention relates generally to compositions useful in therapies involving the selective destruction of tumor cells in vivo. In particular, this invention relates to a conjugate which comprises a target recognition segment and an active cytotoxic segment. The target recognition segment comprises a receptor specific to NK cells, wherein the receptor binds to a cellular ligand expressed on the surface of a tumor cell, and the active segment comprises an agent capable of exerting a cytotoxic effect on the tumor cell. The target recognition segment derived form the natural killer receptor NKp30 has been found to be particularly effective in vivo.
Owner:NATSPEARS
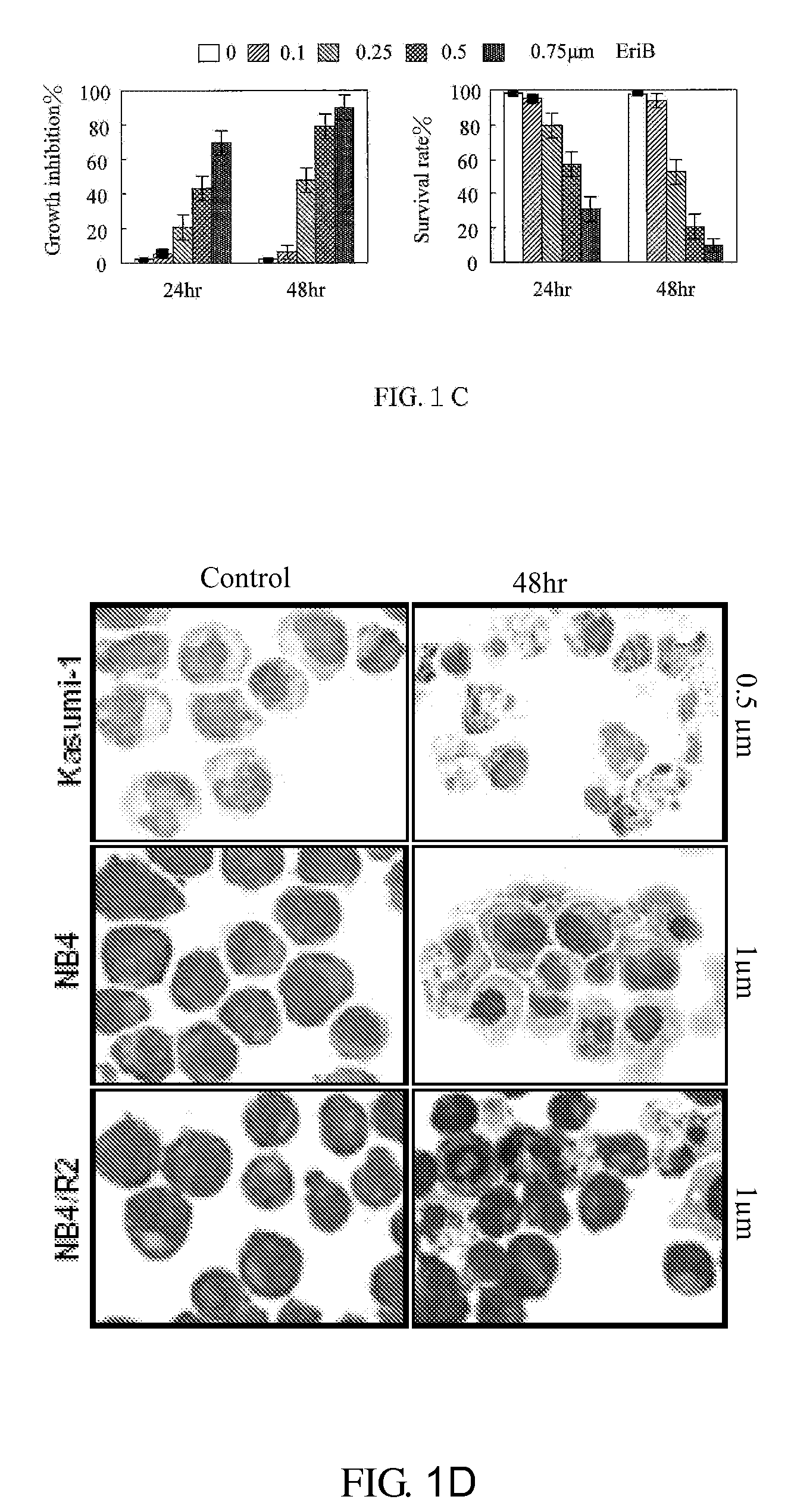
Application of Eriocalyxin B in the Manufacture of Medicaments For Treating Leukemia
InactiveUS20080300299A1Promote cell survivalLower the thresholdBiocideAnimal repellantsPhosphorylationTumor transplantation
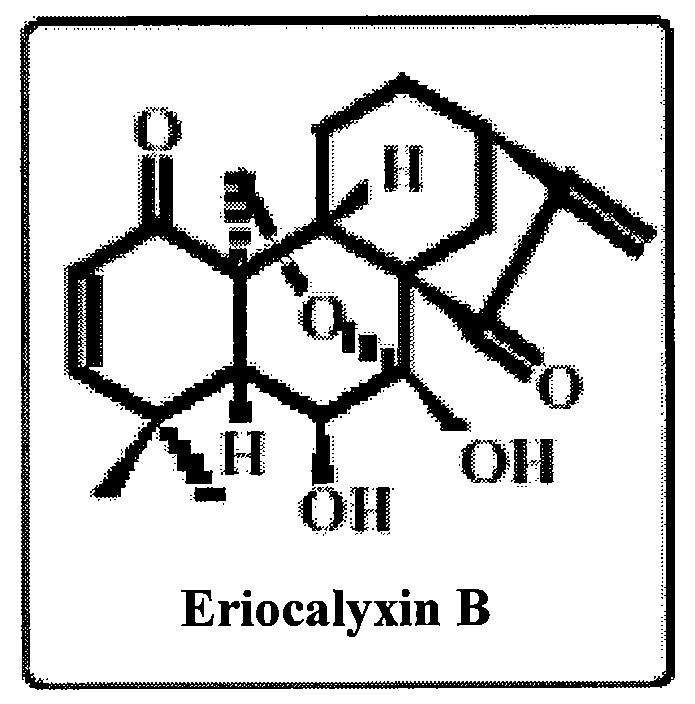
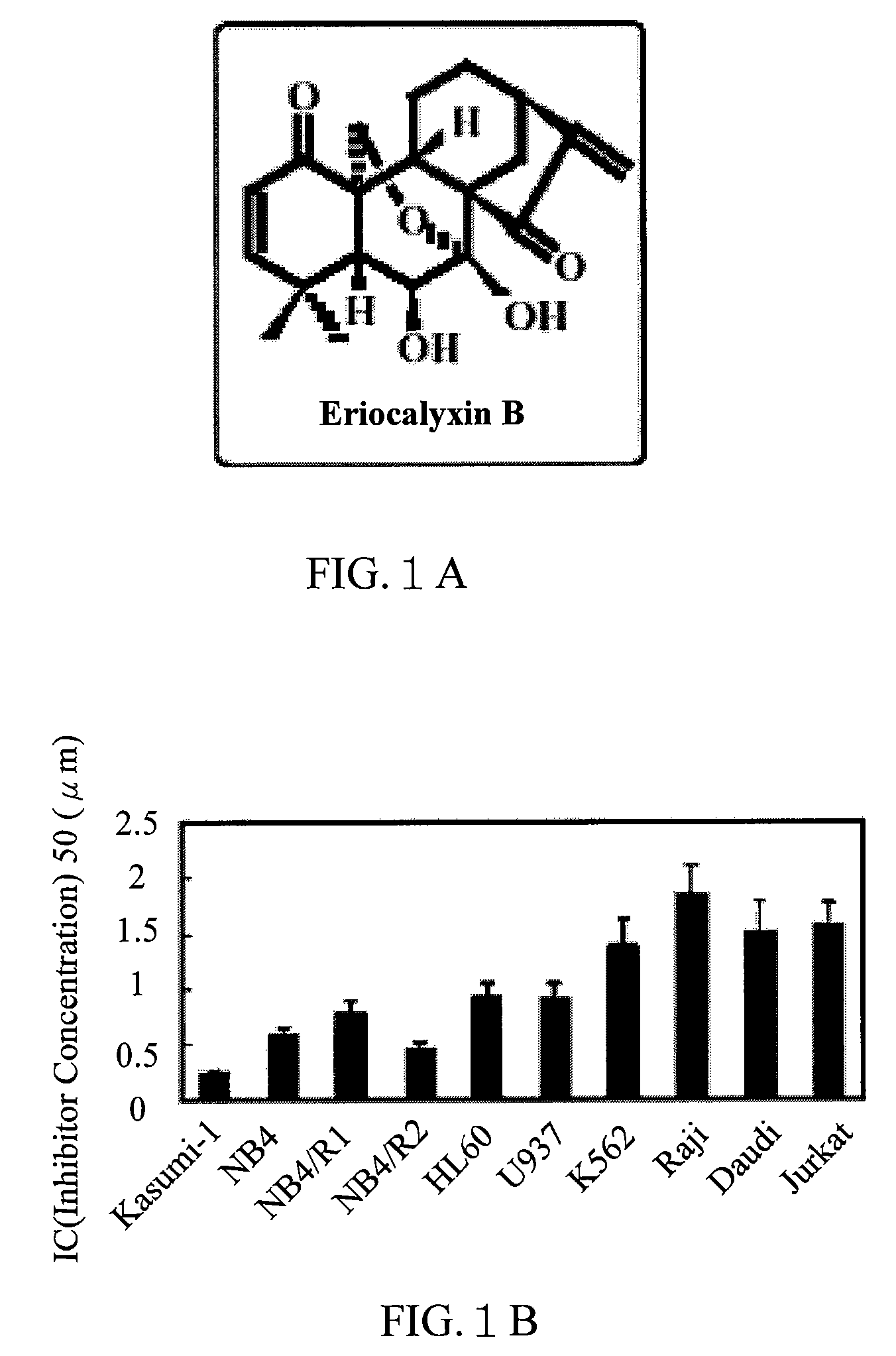
The use of eriocalyxin B in the manufacture of medicaments for treating leukemia, wherein the leukemia include leukemia containing AML1-ETO fusion protein, acute promyelocytic leukemia, acute myelocytic leukemia and lymphocytic leukemia. Eriocalyxin B increases the level of peroxidate and influences the phosphorylation and degradation of IκBα to prevent NF-κB from getting into the nucleus in order to inhibition NF-κB pathway. Eriocalyxin B can decrease the phosphorylation of ERI1 / 2 and inhibit MAPK pathway. Eriocalyxin B can extend the life span of mice and decrease tumor volume in mice model of C57 leukemia and tumor transplantation.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO SHANGHAI NO 2 MEDICALUNIV +1
ITE for Cancer Intervention and Eradication
ActiveUS20130310429A1Good curative effectInhibit angiogenesisPhotovoltaic supportsBiocideProstate cancerCarrier system
A method of cancer intervention or eradication by administering an effective amount of an endogenous ligand for the aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor (AhR) named ITE or one of its analogs (the active ingredient) to a subject with cancer is disclosed. An effective dose and dosing frequency of the active ingredient are determined by measuring its blood levels of the subject after dosing. The active ingredient formulated with a carrier system is applied topically, enterally, or parenterally to the subject. The formulated drug can also be administered together with one or more of other cancer therapeutic agents. A maintenance dosing is provided after the subject is free of cancer to insure the cancer eradication. Subjects with cancers of prostate, liver, lung, ovarian, and breast are preferably accepted for treatment.
Owner:ARIAGEN INC
Satb1: a determinant of morphogenesis and tumor metastatis
InactiveUS20150323536A1Reliable diagnosisReliable prognosisOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCancer cellMorphogenesis
It is proposed that cancer cells express SATB1, and that SATB1 acts as a determinant for the acquisition of metastatic activity by controlling expression of a specific set of genes that promote metastatic activity. In order for cancer cells to gain the ability to metastasize, SATB1 re-organizes or re-packages genomic sequences in a specific manner to allow a switch in the pattern of gene expression. SATB1 expression was found restricted mainly to aggressive cancer cells where it may regulate the genetic and epigenetic changes that program the steps involved in the metastatic process. The present invention describes reagents and tools to detect the SATB1 protein for use in diagnosis and prognosis of aggressive cancers and therapeutics to inhibit SATB1 protein to deplete its expression in metastatic and aggressive cancers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Protein logic gates
ActiveUS20050004347A1Easily interfaceFew catalytic activityPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesConstitutively activeHeterologous
Protein logic gates are made from autoregulated fusion proteins comprising an output domain and a plurality of input domains, wherein at least one of the input domains is heterologous to the output domain, and the input domains interact with each other to allosterically and external, ligand-dependently regulate the output domain. The output domain may be constitutively active, and in the absence of the ligand, the input domains interact to inhibit the output domain. The activity of the output domain is user discretionary, and may include activities that are catalytic, label-generative, metabolic-regulative, apototic, specific-binding, etc. Multiple input domains can cooperatively regulate the fusion protein in a wide variety of functionalities, including as an OR-gate, an AND-gate, and an AND-NOT-gate. The gates may be incorporated into cells and therein used to modulate cell function.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Antibodies against prostate specific membrane antigen
InactiveUS8629247B2Reduce the overall heightPromote cell deathAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulinsProstate specific membraneAntigen Binding Fragment
Antibodies (Ab) and antigen binding fragments capable of binding to prostate specific membrane antigen and which may be used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes are provided herein. Formulation anti-PSMA antibodies which are stable under extreme storage condition are also provided.
Owner:PROSCAN RX PHARMA
Use of adrenergic beta-E-receptor blockers in cancer treatment
ActiveUS9622996B2Reduce in quantityReduce expressionBiocideNervous disorderAdrenergicCancer treatment
Owner:LIN SHUGUANG +1
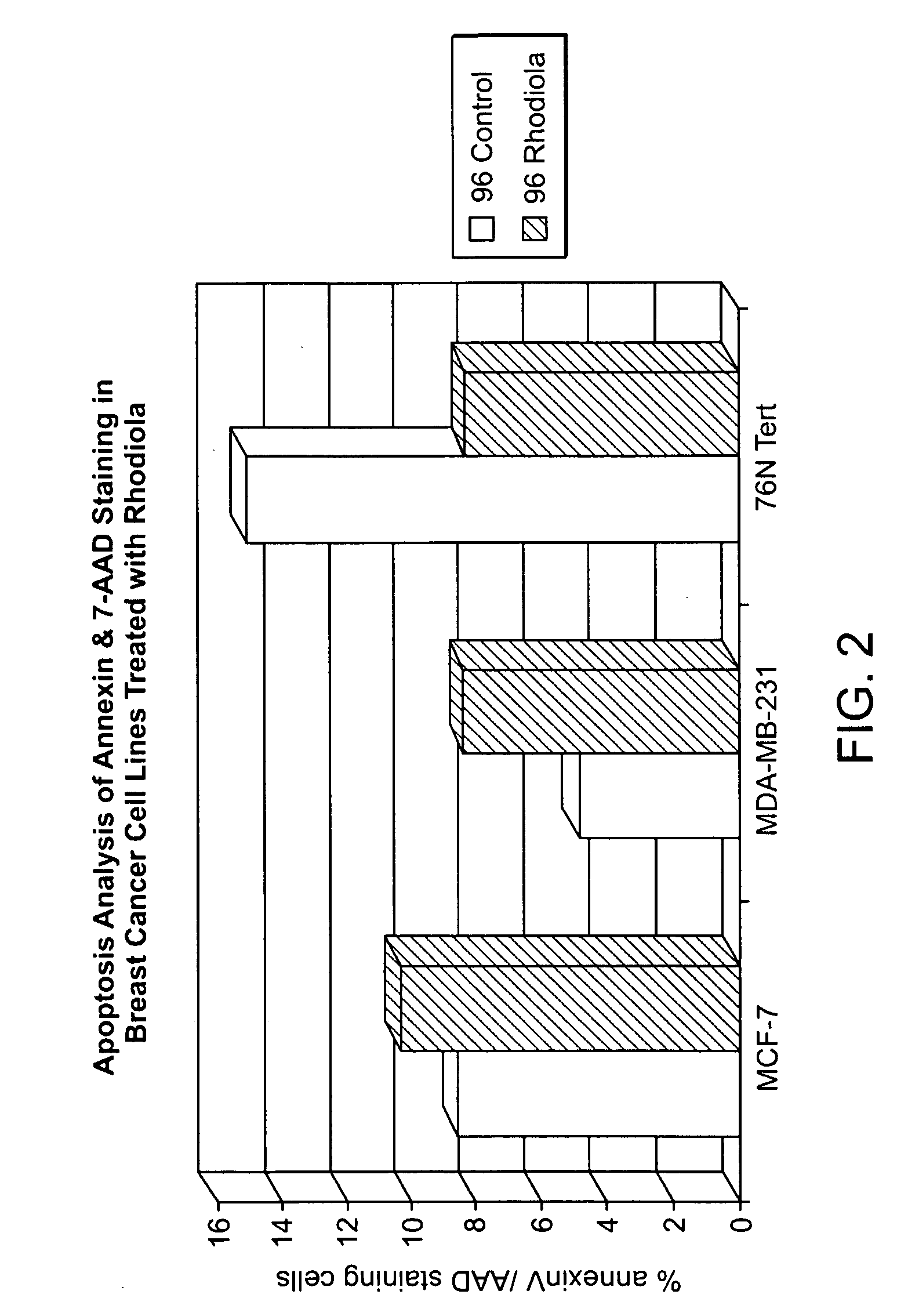
Pharmaceutical formulations of rhodiola crenulata and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080118589A1High activityDecreasing AKT phosphorylationBiocideAnimal repellantsTelomeraseRetinoid
Isolated extracts of Rhodiola crenulata and their constituents sensitize tumor cells to cancer therapies, such as tamoxifen, retinoids, and radiation, and act to potentiate radiation therapy in the treatment of cancer, with or without adjuvant chemotherapy. Methods are provided for inhibiting the P13kinase / AKT pathway in cancer cells, a general survival pathway which leads to resistance of many tumors to typical therapies; decreasing cyclooxygenase (COX) activities in cancer cells, another pathway known to increase resistance to tumors; inhibiting telomerase activity in cancer cells, an activity notable for its ability to increase the life span of the cells; enhancing the ATM (Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated) response in cells, which is involved in DNA damage sensing and repair; modulating cellular response to oxidation, which effects the other signaling pathways on numerous levels; and altering usage of metabolic energy pathways.
Owner:BAYSTATE HEALTH SYST
Protein logic gates
ActiveUS7604805B2Few catalytic activityEasily circuitryLogic circuits using specific componentsAntibody medical ingredientsHeterologousConstitutively active
Protein logic gates are made from autoregulated fusion proteins comprising an output domain and a plurality of input domains, wherein at least one of the input domains is heterologous to the output domain, and the input domains interact with each other to allosterically and external, ligand-dependently regulate the output domain. The output domain may be constitutively active, and in the absence of the ligand, the input domains interact to inhibit the output domain. The activity of the output domain is user discretionary, and may include activities that are catalytic, label-generative, metabolic-regulative, apototic, specific-binding, etc. Multiple input domains can cooperatively regulate the fusion protein in a wide variety of functionalities, including as an OR-gate, an AND-gate, and an AND-NOT-gate. The gates may be incorporated into cells and therein used to modulate cell function.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Use of adrenergic beta-e-receptor blockers in cancer treatment
ActiveUS20130197091A1Increase in mitophagyReduce decreaseBiocideNervous disorderAdrenergicCancer treatment
A method for treating an cancer disease is disclosed comprising administering to a subject a pharmaceutical composition comprising an adrenergic beta-3-receptor blocker.
Owner:LIN SHUGUANG +1
Bacteriophage and prophage proteins in cancer gene therapy
InactiveUS20090117084A1Improve leakagePromote cell deathBiocideAntimycoticsCancer genesNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to the use of a polypeptide having a proliferation inhibitory activity or a cell death inducing activity on animal cells. The invention provides further means and methods to use said polypeptide and the corresponding nucleic acids sequence containing the coding regions of said polypeptide. The invention further relates to vectors expressing said polypeptide, to pharmaceutical compositions and therapeutic methods for treating proliferative disorders or diseases like cancer. Last but not least the invention provides a method for a gene therapeutic approach using said polypeptide having a proliferation inhibitory activity or a cell death inducing activity on animal cells.
Owner:ZIEL BIOPHARMA LTD
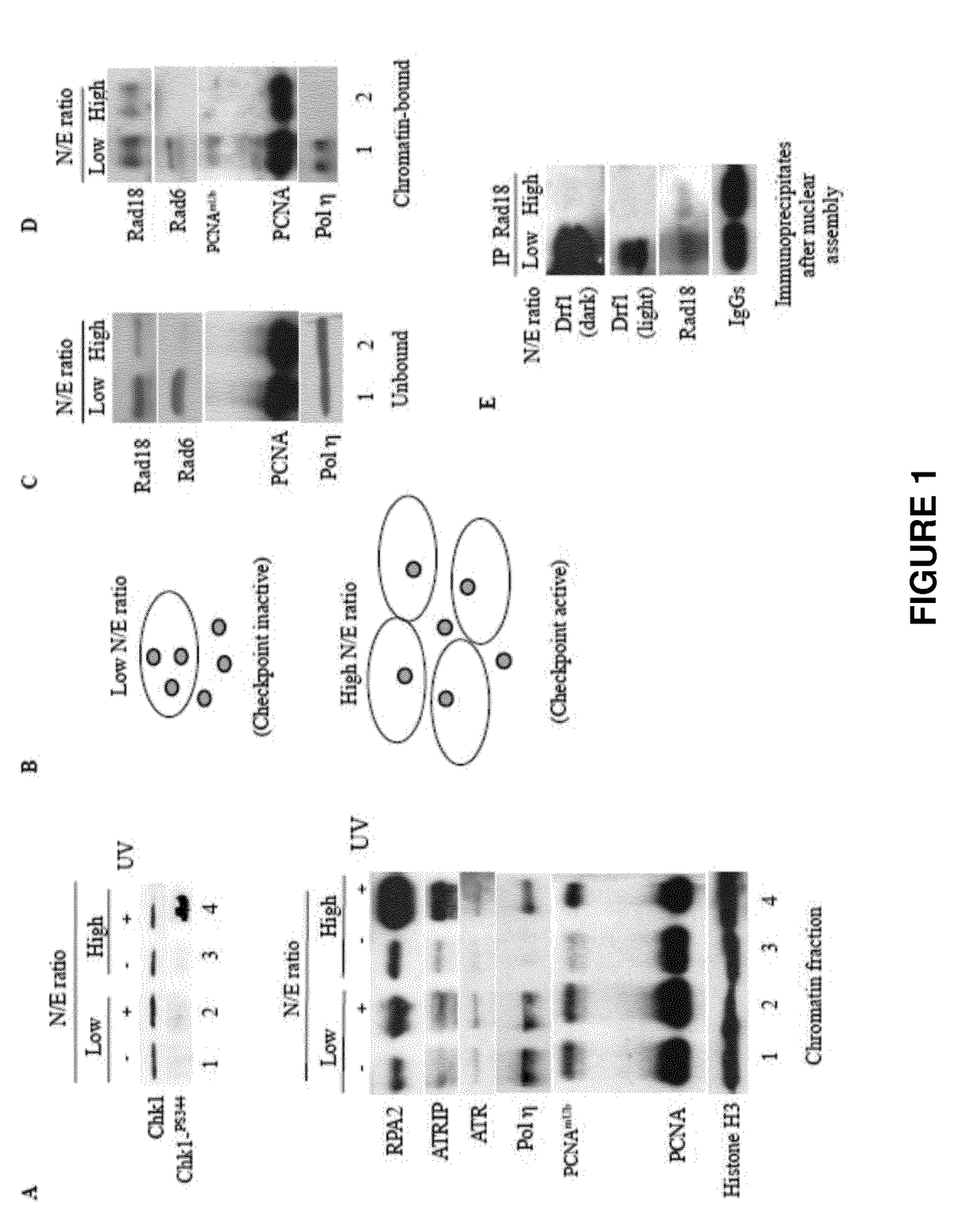
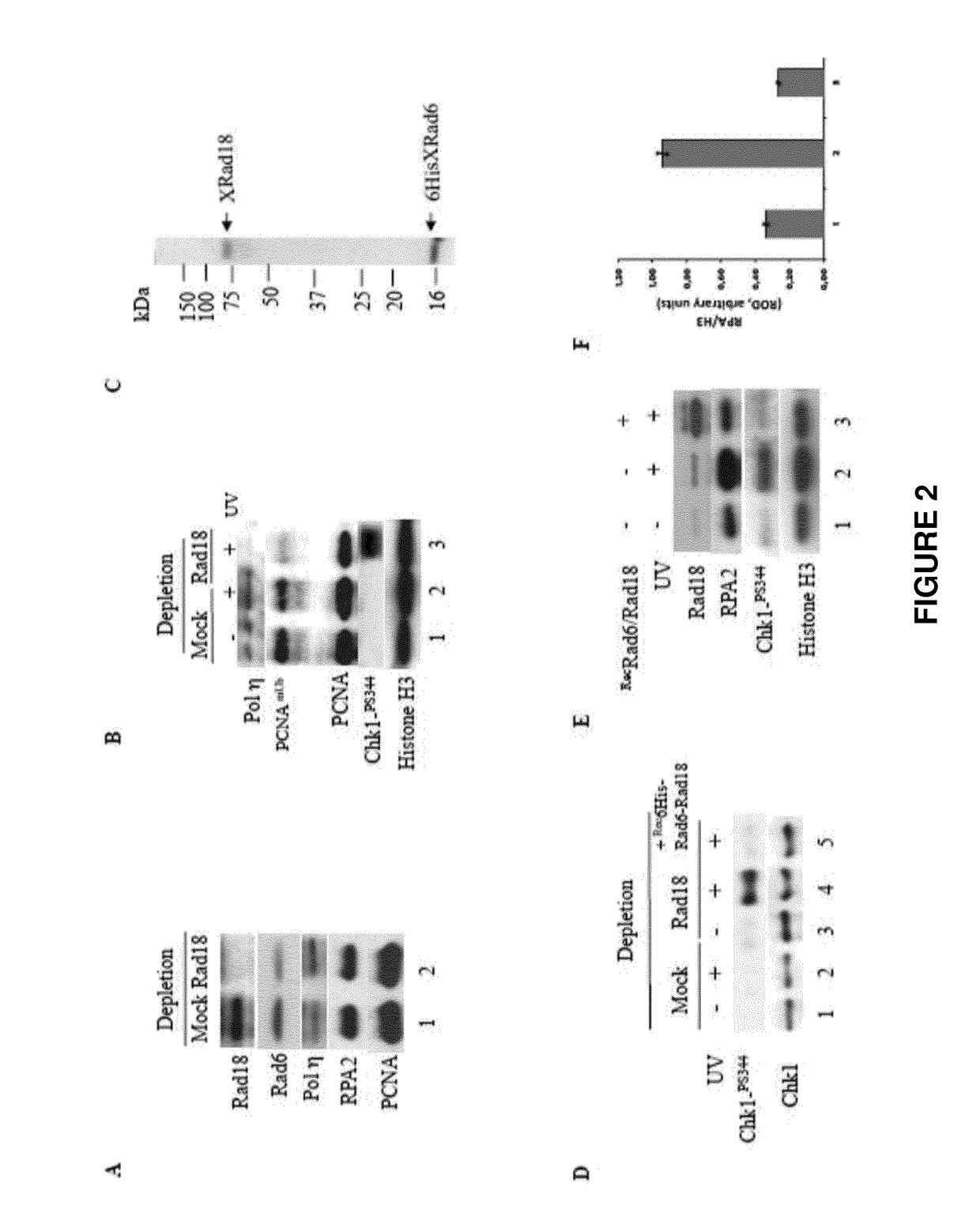
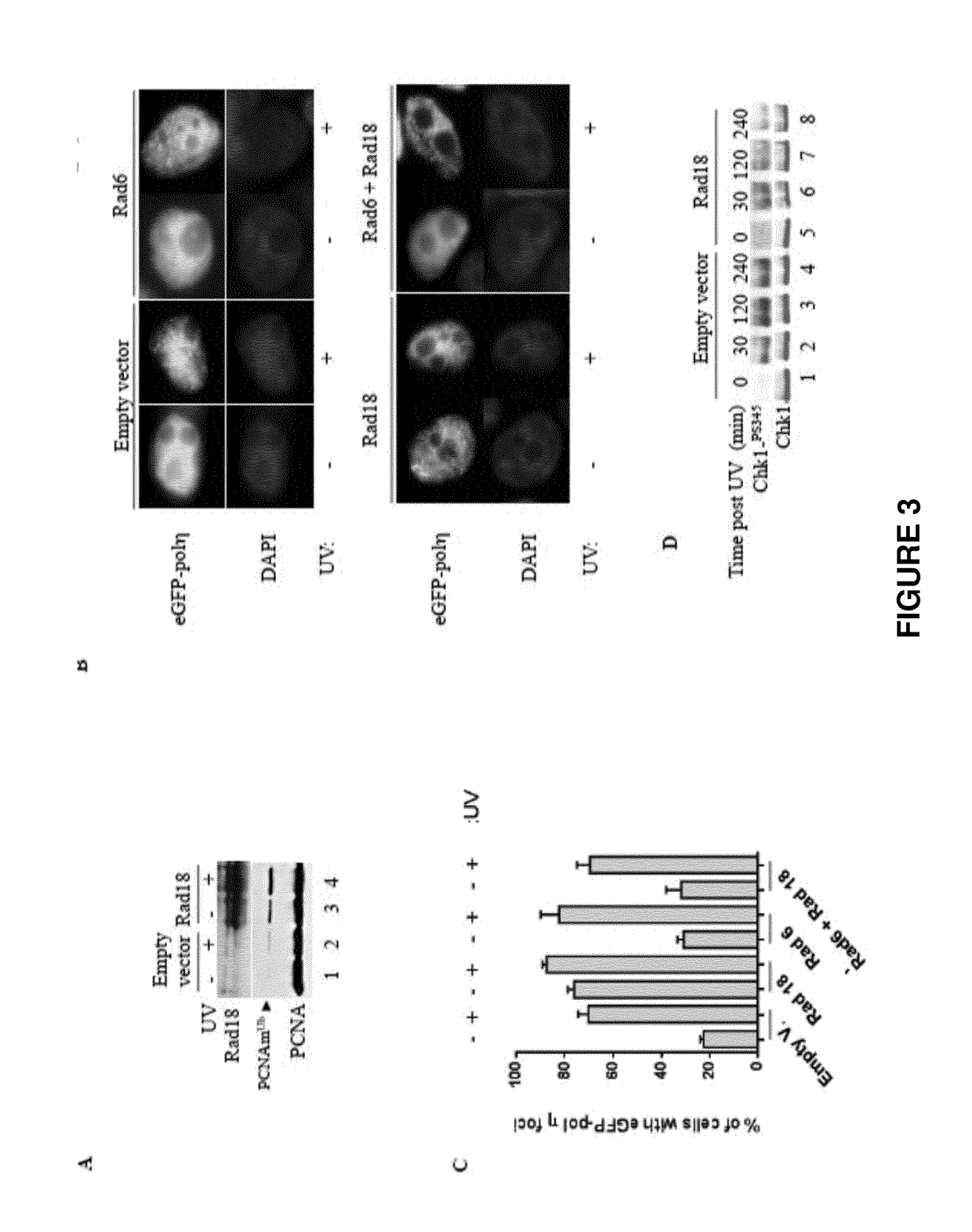
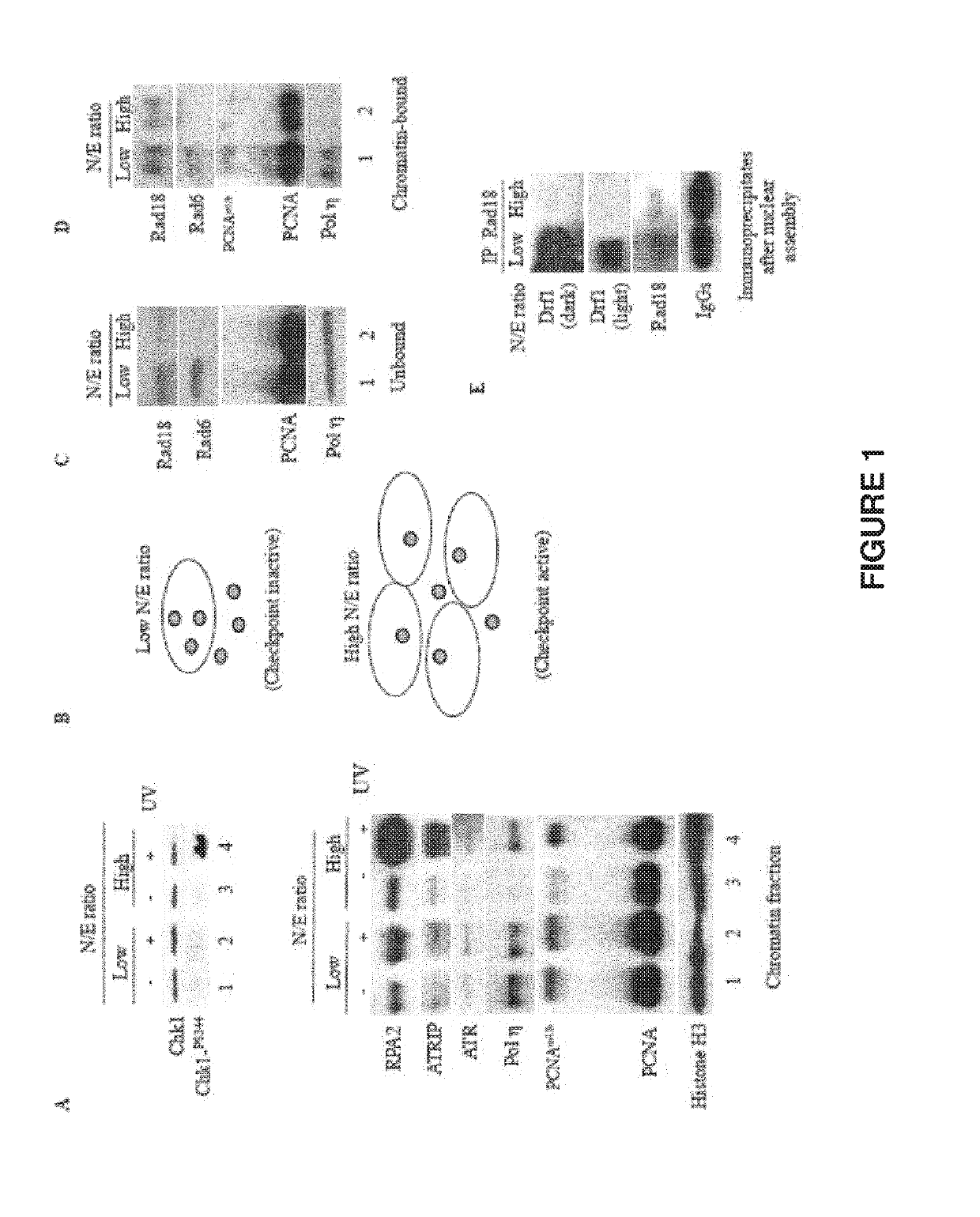
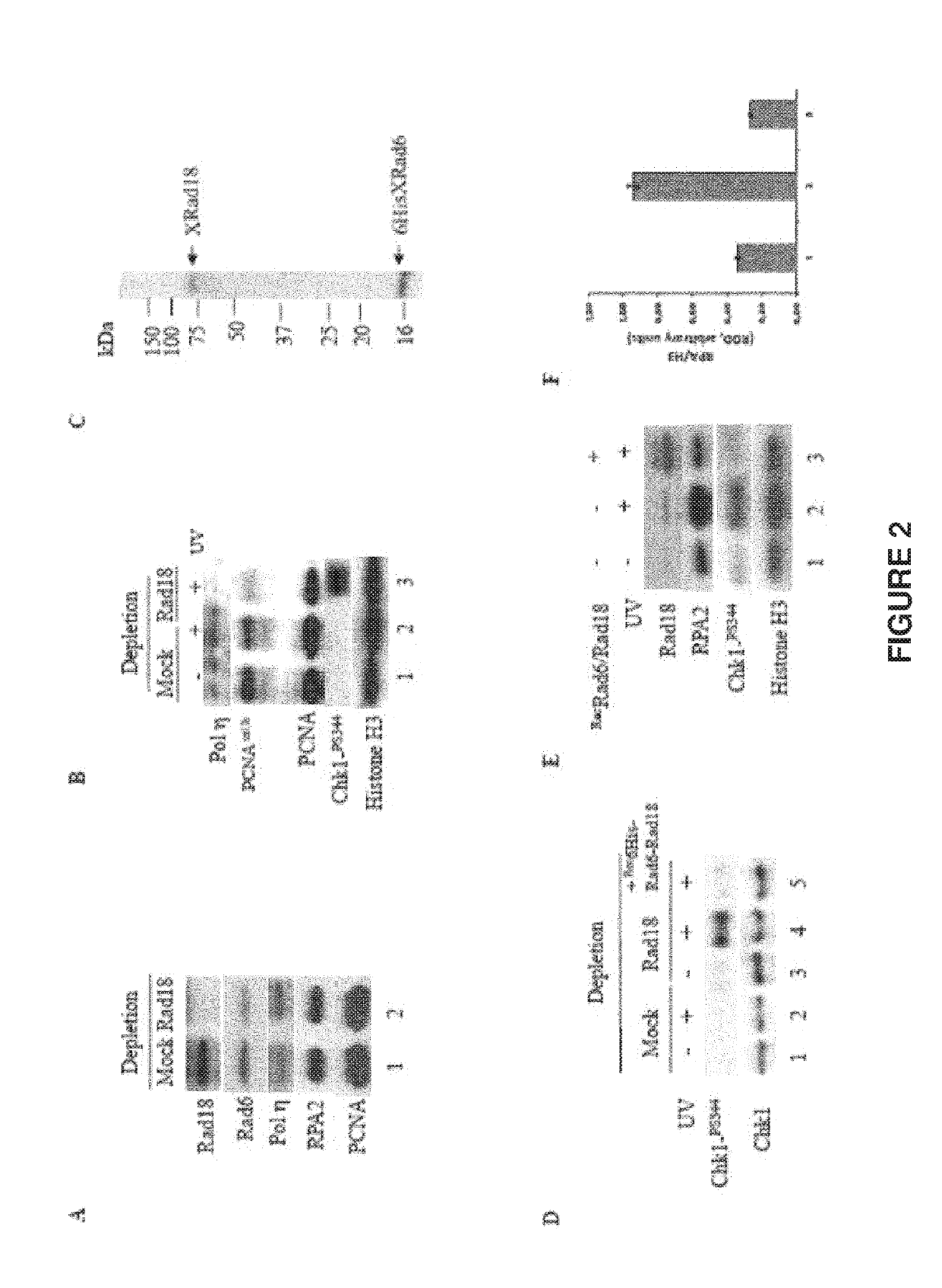
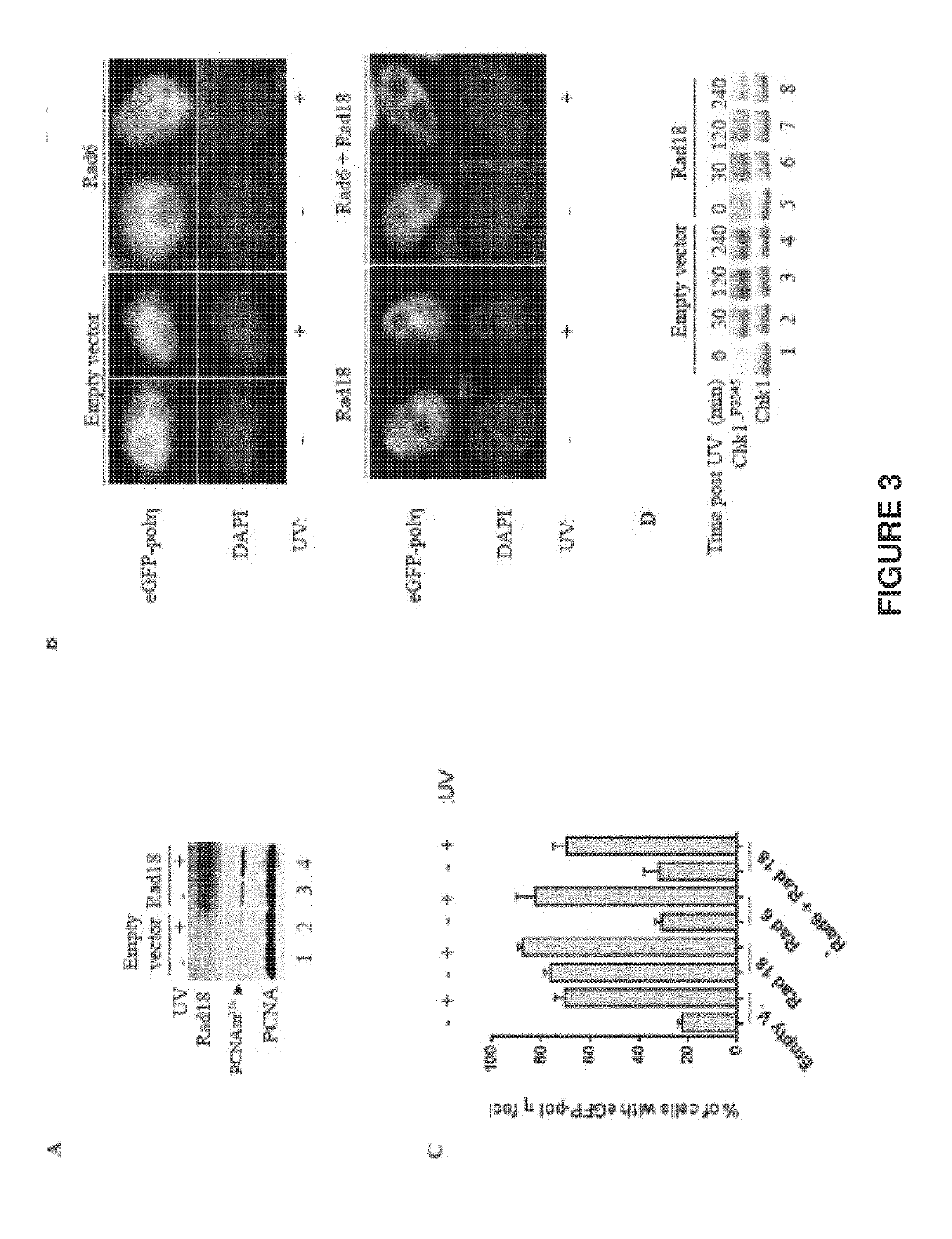
Use of rad18 inhibitors in the treatment of tumors
InactiveUS20170362593A1Reduce riskReduces self renewalOrganic active ingredientsInorganic active ingredientsTumor therapyOncology
The present invention relates to the use of an inhibitor of Rad18 expression or activity, in treating a tumor or in sensitizing a patient affected with a tumor, to a treatment with an antineoplastic agent that is a DNA damaging chemotherapeutic agent so to both reduce the self renewal of cancer stem cells and increase the DNA damage response thus boosting apoptotic cell death.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
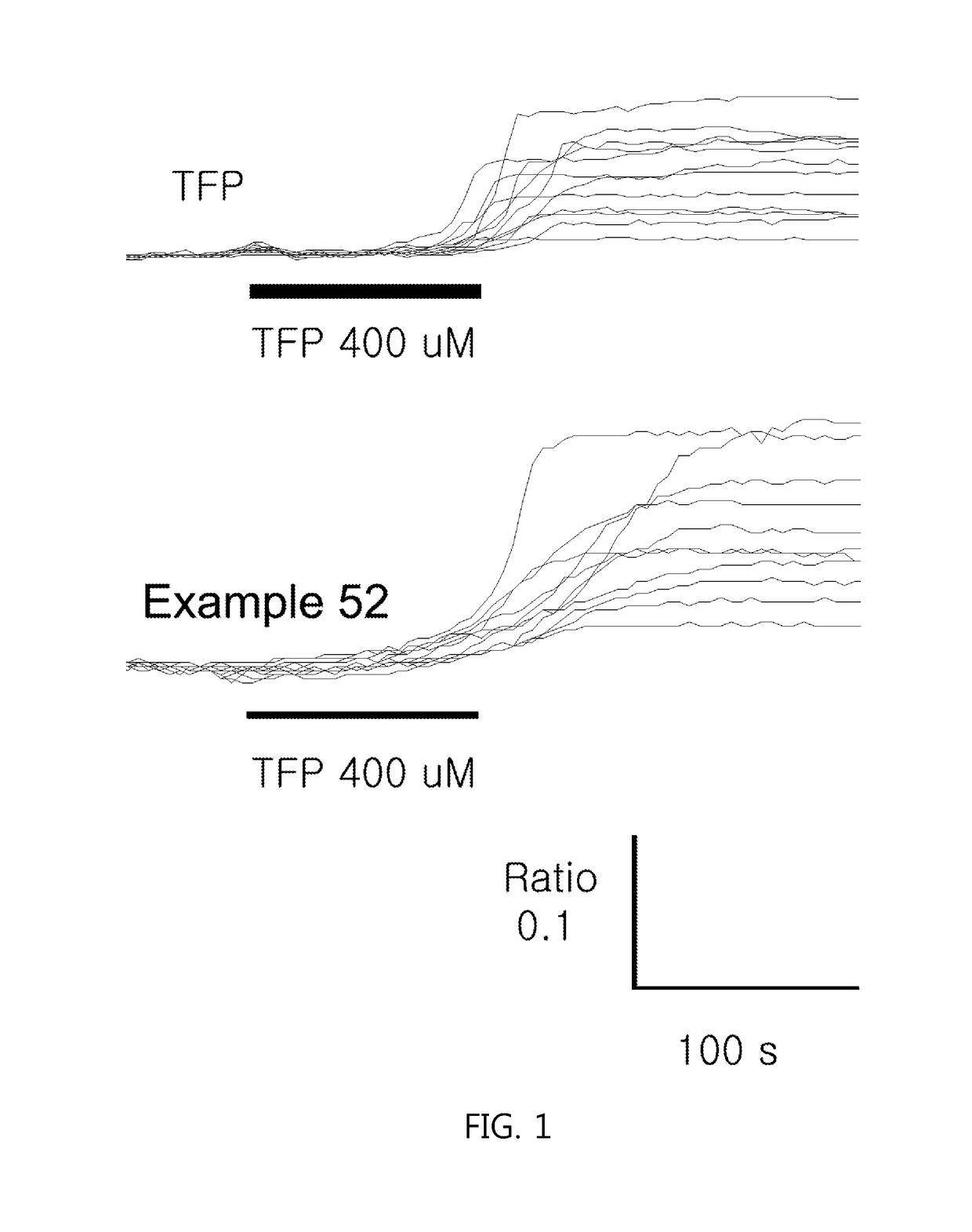
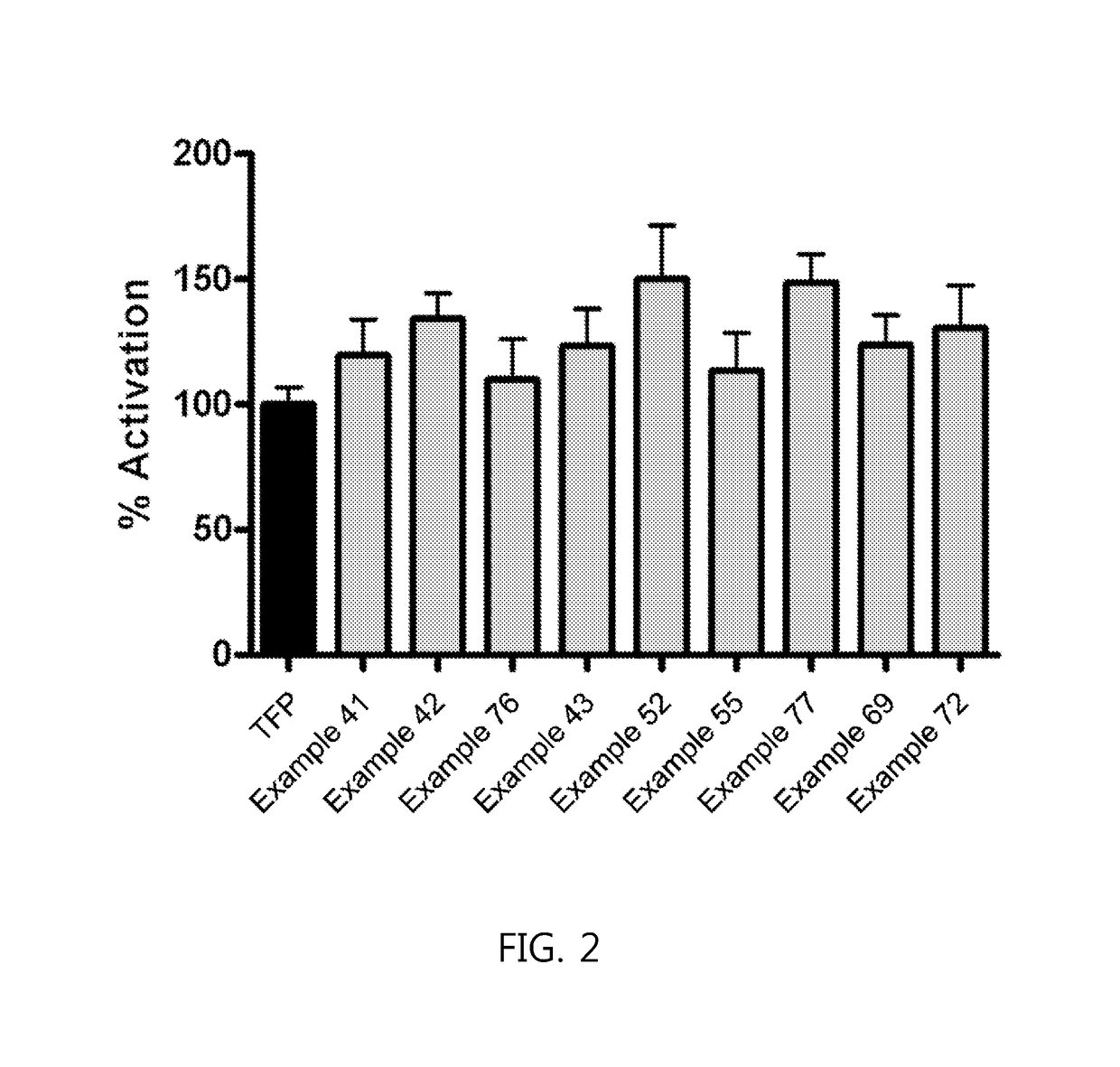
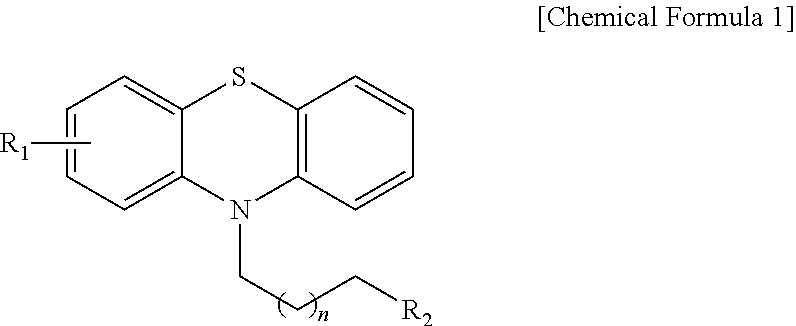
Phenothiazine derivatives having CaM inhibitory activity
The present invention provides a phenothiazine derivative or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a method of preparing a compound selected therefrom and a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound as an active ingredient. The phenothiazine derivative according to the present invention has an effect of inhibiting calmodulin (CaM; calcium-modulated protein) and thus helps cell death by maintaining the intracellular level of calcium in lung cancer cells at high concentration. Accordingly, the phenothiazine derivative according to the present invention can be usefully used to prevent or treat malignant tumors such as lung cancer.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Use of rad18 inhibitors in the treatment of tumors
ActiveUS20190194664A1Reduce self renewalImprove responseHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsTumor therapyOncology
The present invention relates to the use of an inhibitor of Rad18 expression or activity, in treating a tumor or in sensitizing a patient affected with a tumor, to a treatment with an antineoplastic agent that is a DNA damaging chemotherapeutic agent so to both reduce the self renewal of cancer stem cells and increase the DNA damage response thus boosting apoptotic cell death.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
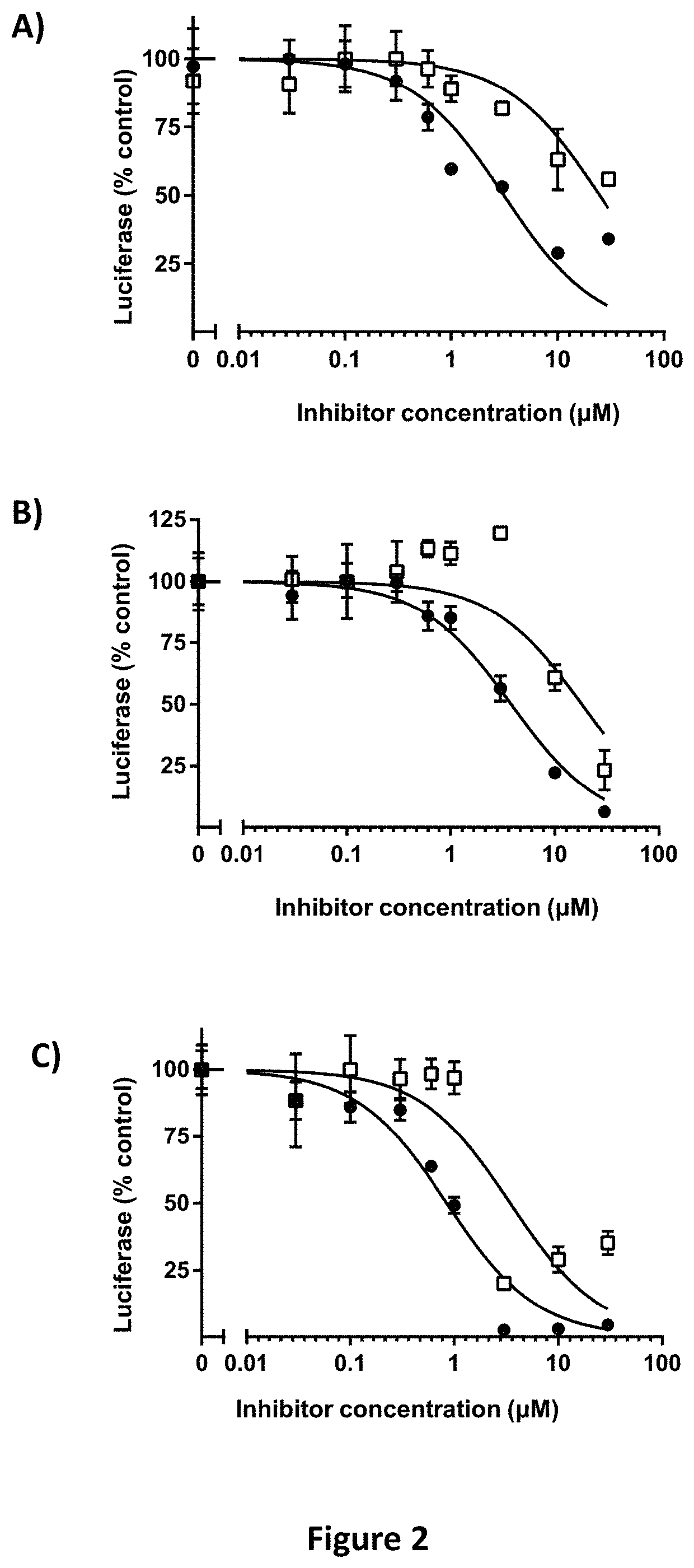
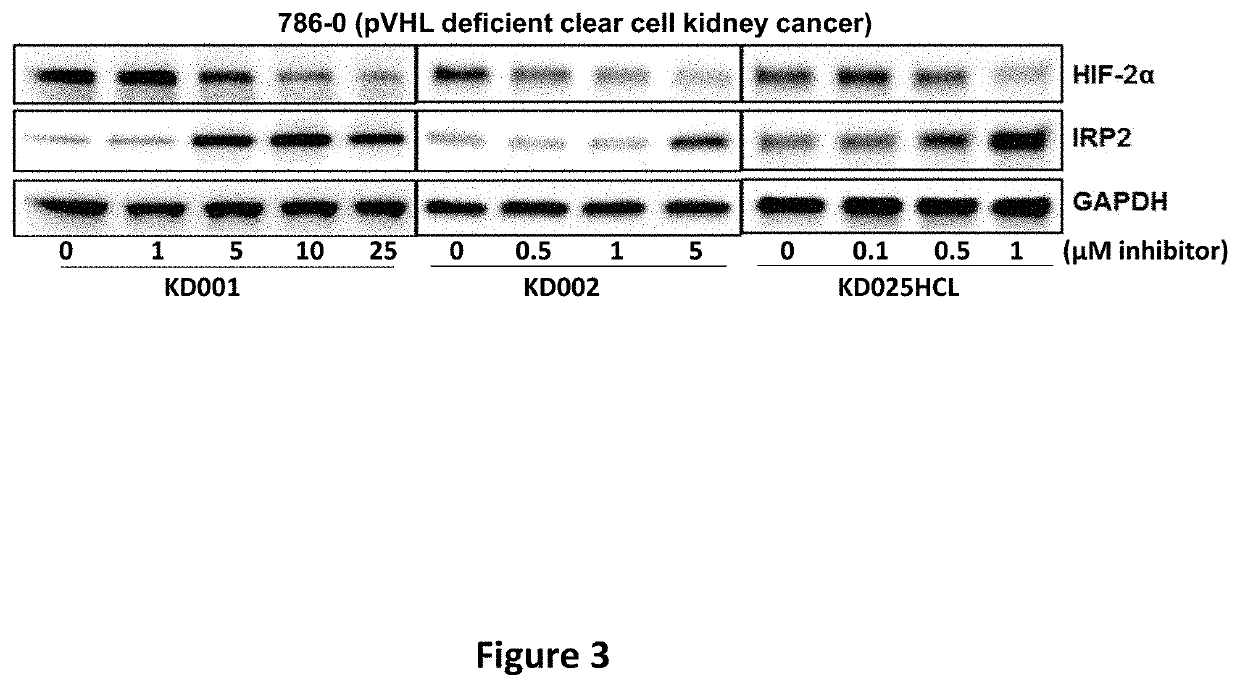
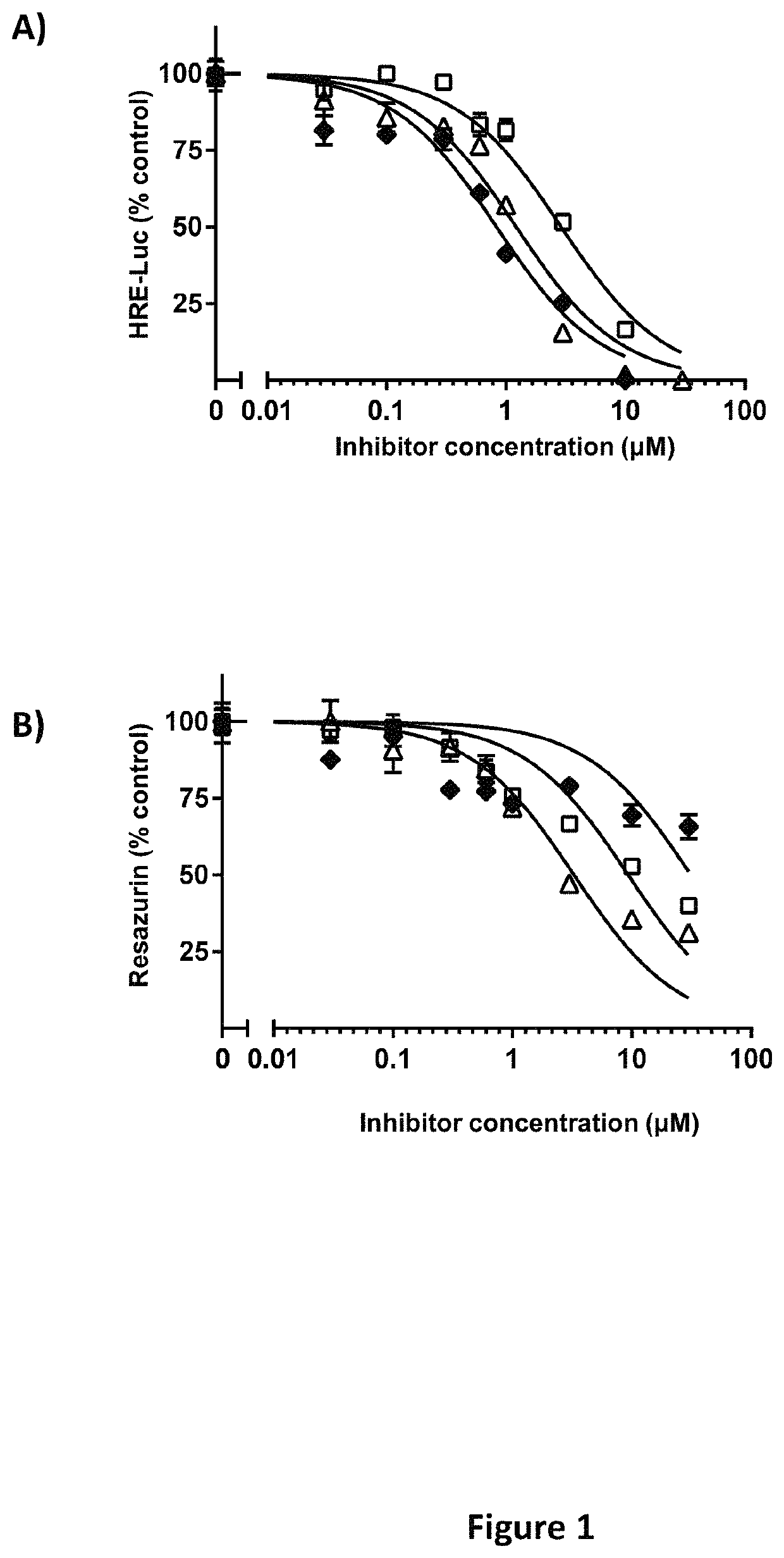
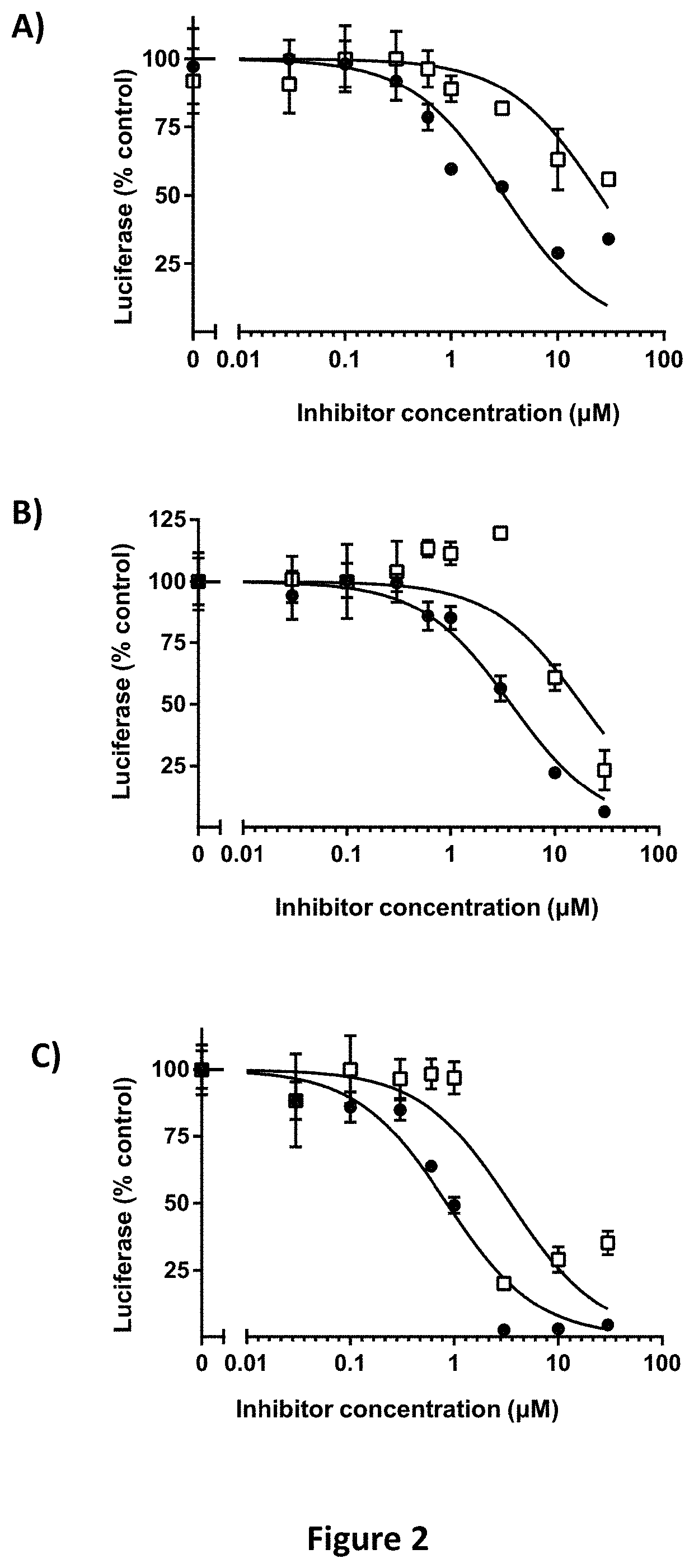
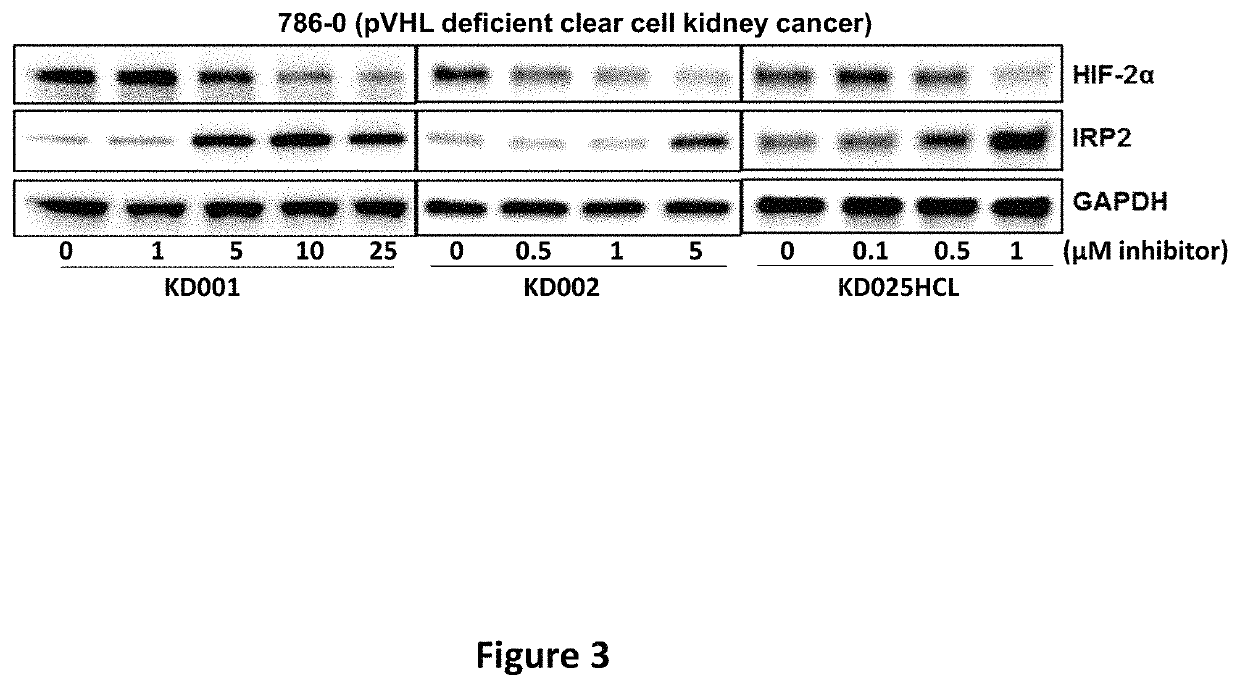
Imidazopyridine and Oxazolopyridine Derivatives and Analogs Thereof, Methods of Preparation Thereof, Methods of HIF-2A Pathway Inhibition, and Induction of Ferroptosis
ActiveUS20220281862A1High in ironEasy to operateOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsPharmaceutical drugFerroptosis
Novel substituted imidazopyridine and oxazolopyridine compounds that are useful as inhibitors of HIF-2α and inducers of ferroptosis through perturbations in iron metabolism, synthetic methods for making said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and methods of using the compounds and compositions to treat disorders associated with dysfunction of HIF-2α or iron metabolism.
Owner:KUDA THERAPEUTICS INC
Imidazopyridine and oxazolopyridine derivatives and analogs thereof, methods of preparation thereof, methods of HIF-2A pathway inhibition, and induction of ferroptosis
ActiveUS11447482B1High in ironEasy to operateOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsPharmaceutical drugFerroptosis
Novel substituted imidazopyridine and oxazolopyridine compounds that are useful as inhibitors of HIF-2α and inducers of ferroptosis through perturbations in iron metabolism, synthetic methods for making said compounds, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and methods of using the compounds and compositions to treat disorders associated with dysfunction of HIF-2α or iron metabolism.
Owner:KUDA THERAPEUTICS INC
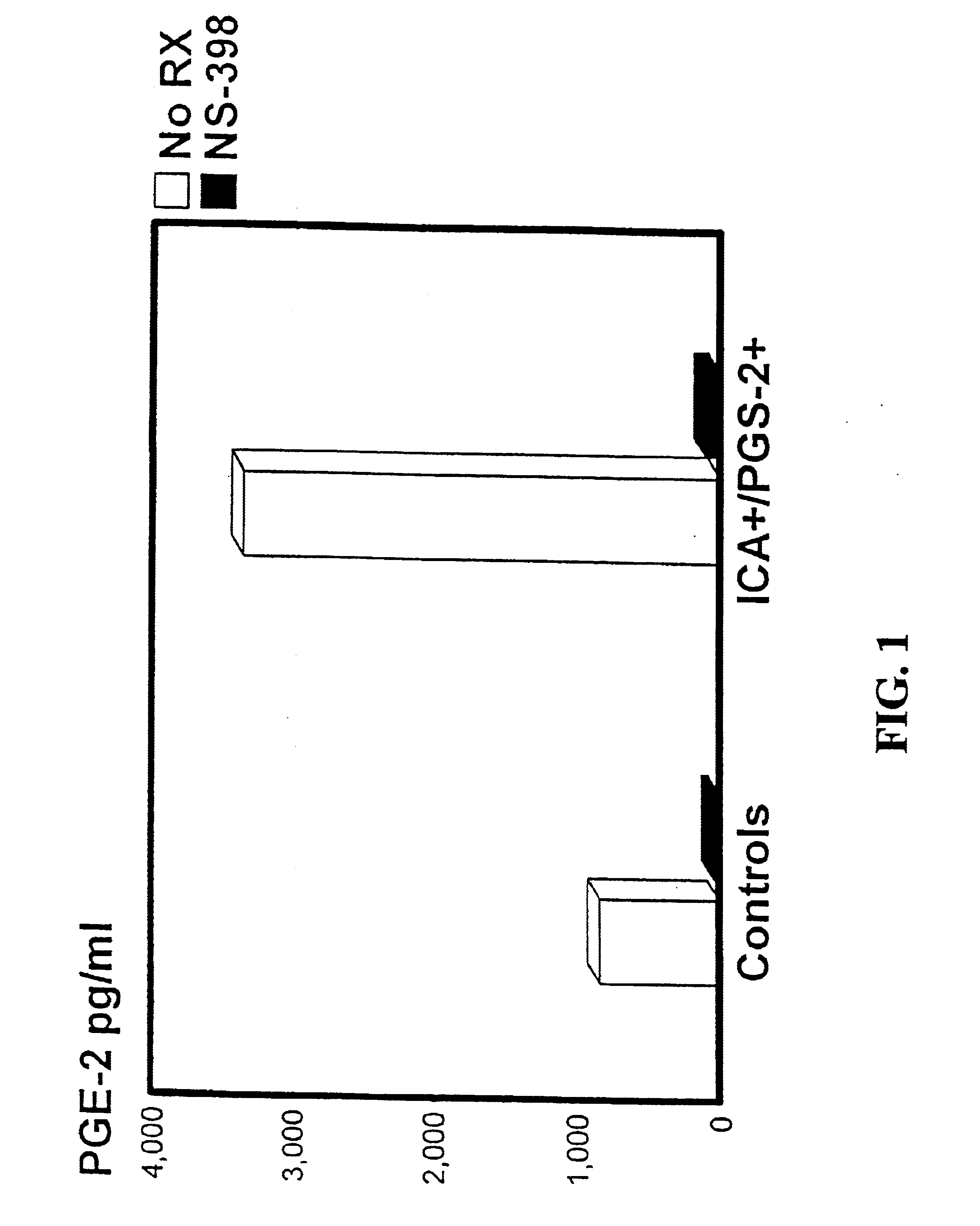
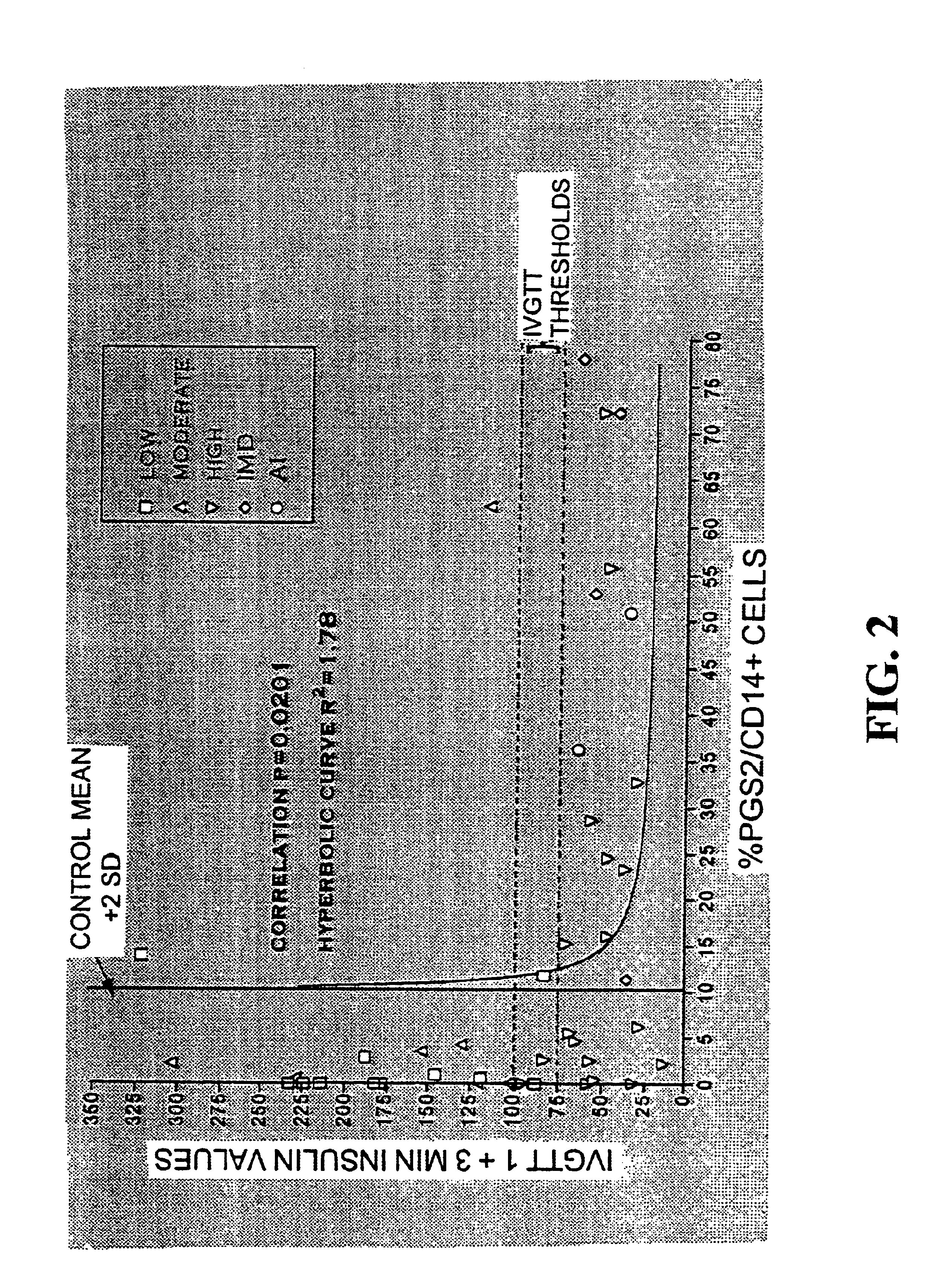
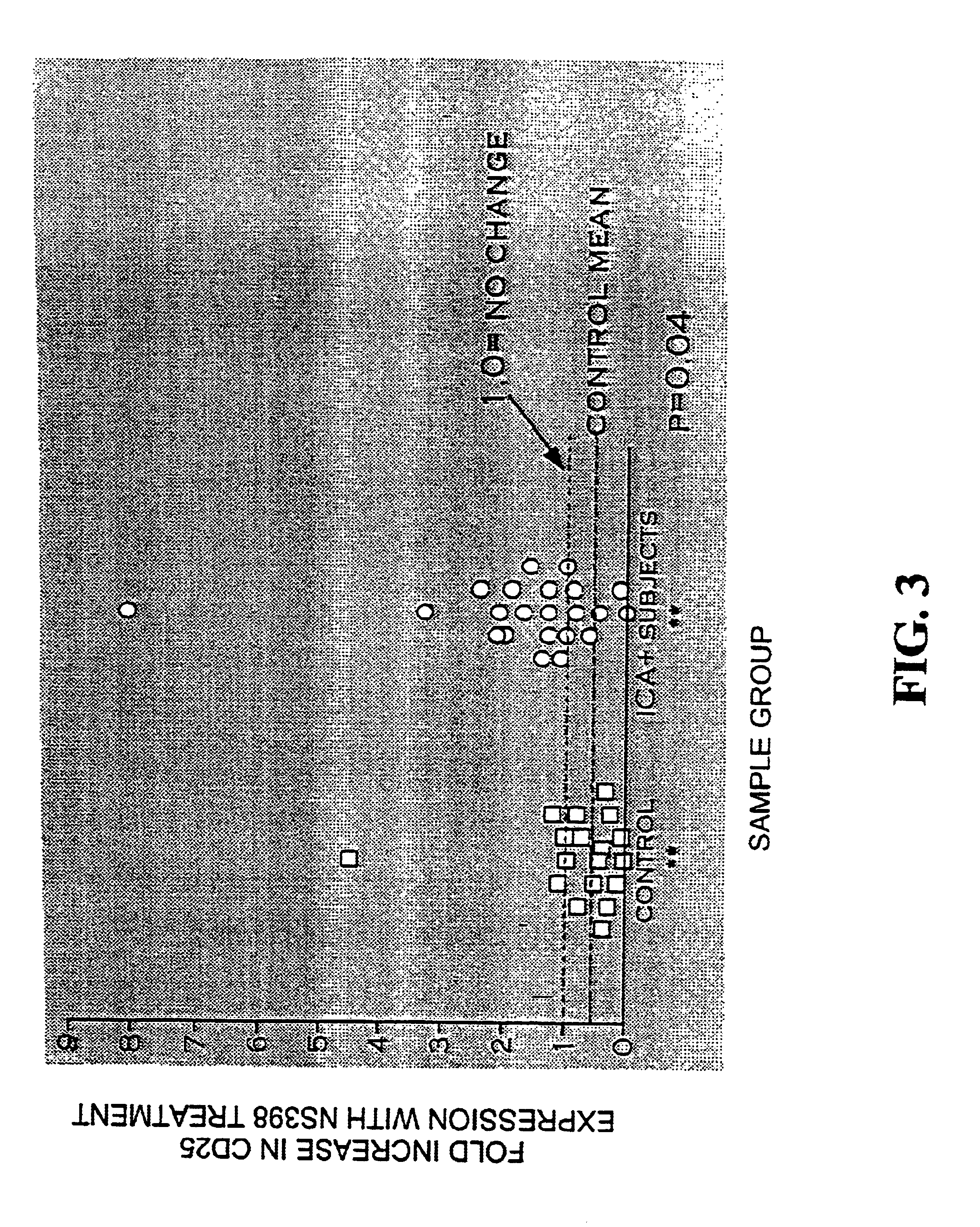
Materials and methods for detection and treatment of immune system dysfunctions
InactiveUS6953578B2Enhanced inhibitory effectEfficacy of therapy can be monitoredPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The subject invention concerns novel materials and methods for the treatment and / or prevention of autoimmune disease. In a specific embodiment, elevated production of prostaglandin synthase-2 (PGS-2) is correlated with autoimmune dysfunction.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods of regulating growth and death of cancer cells
InactiveUS20070155689A1Reduce expressionTested and reliableOrganic active ingredientsCompound screeningCancer cellAnticarcinogen
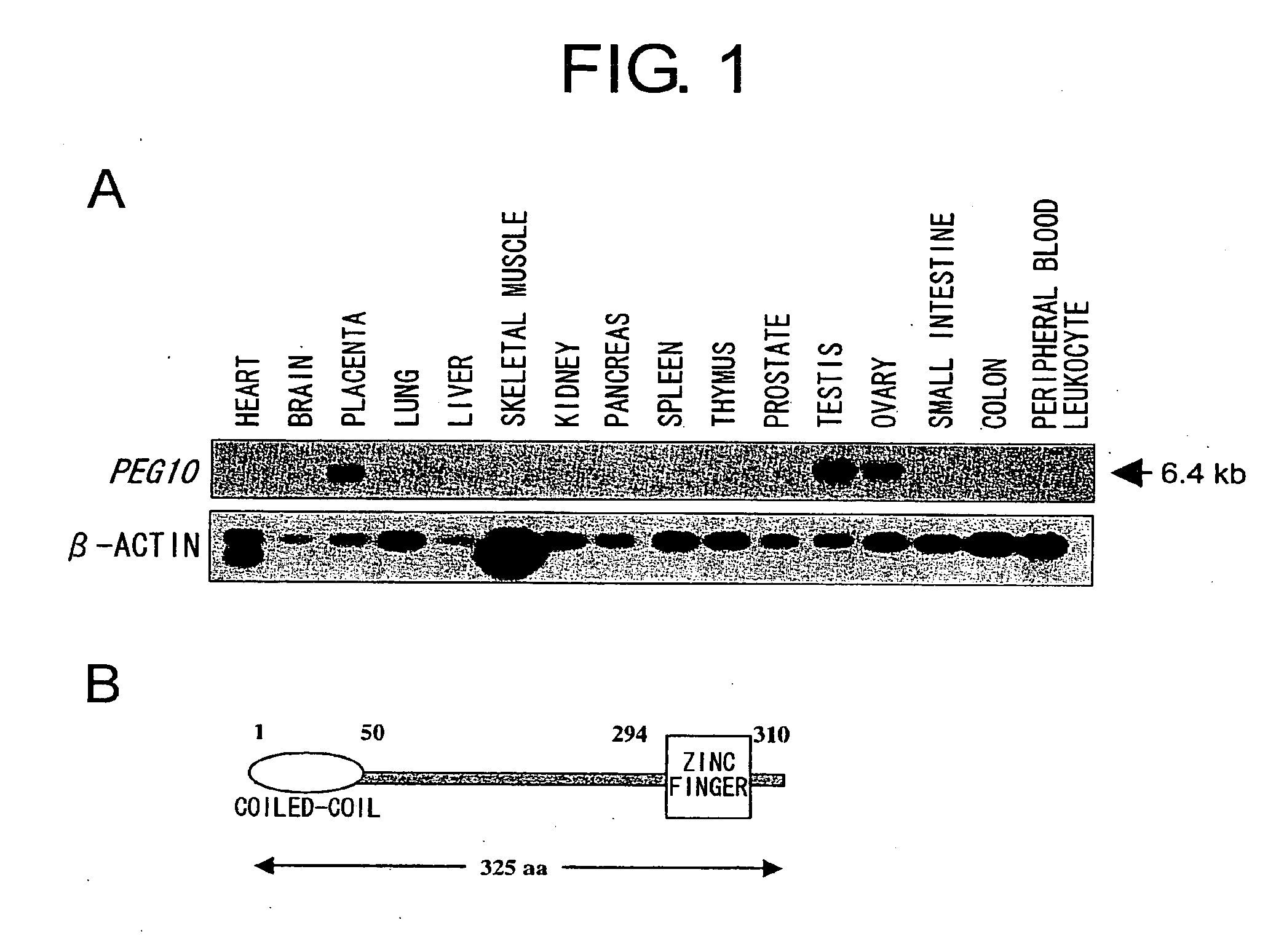
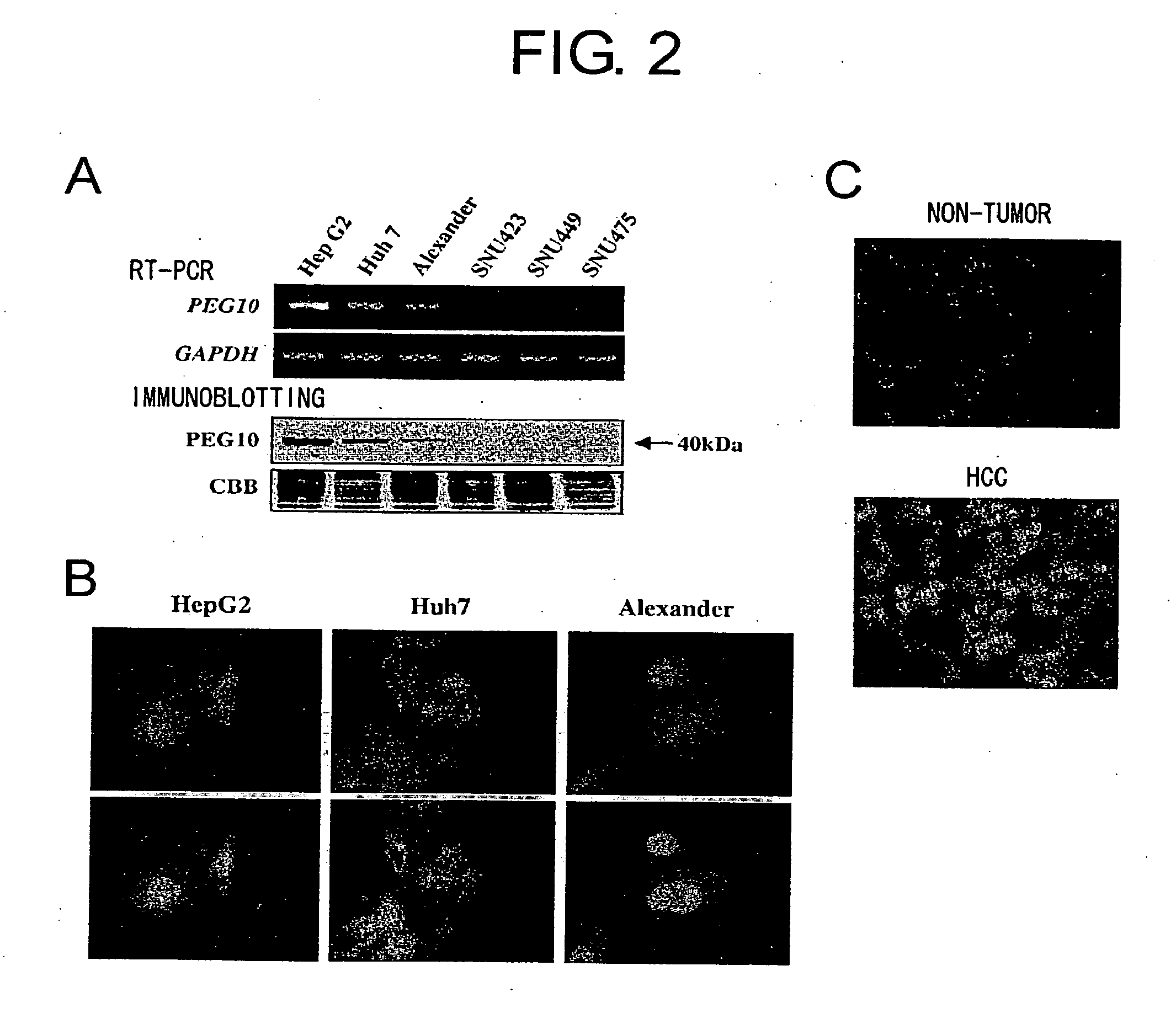
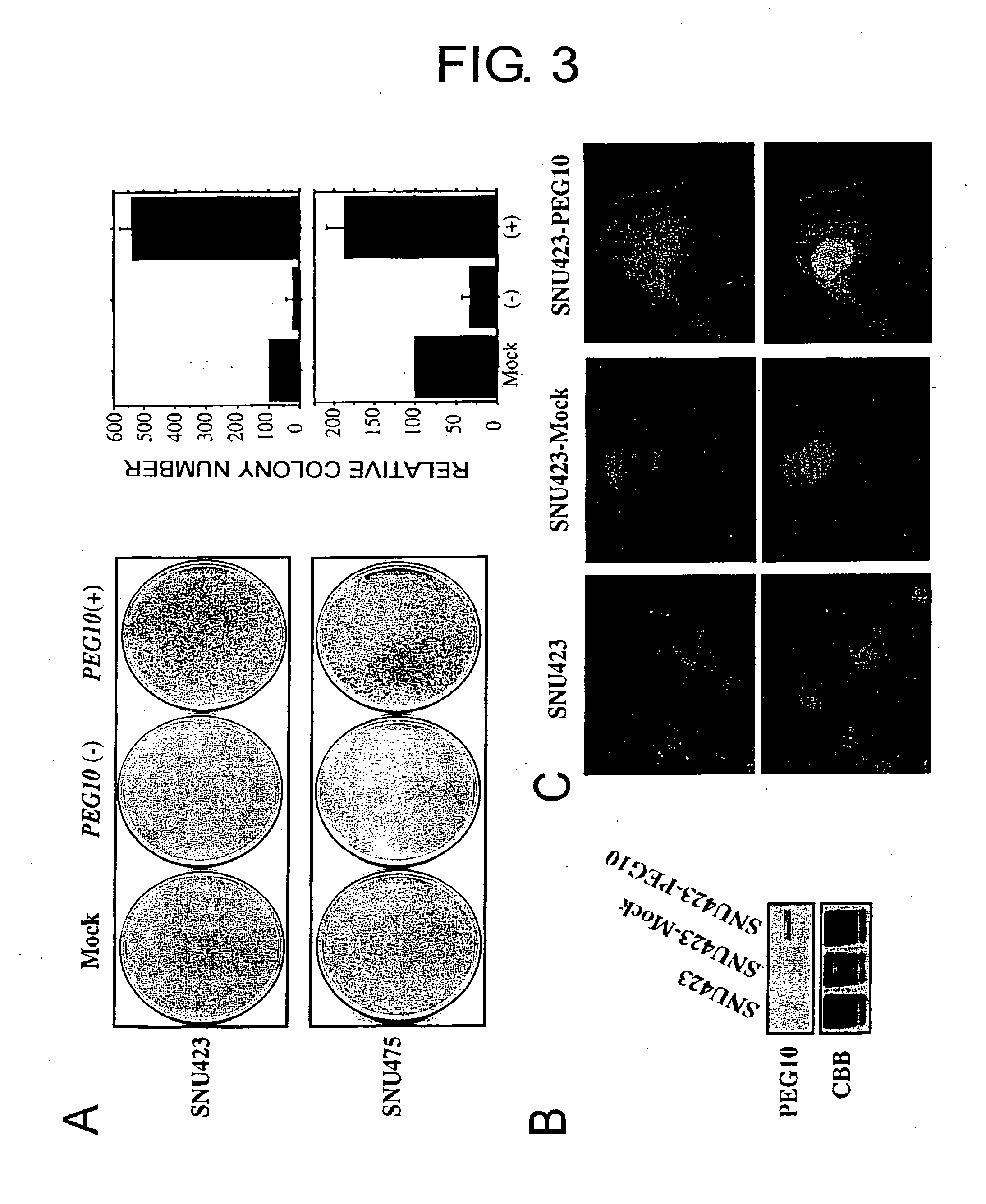
This invention demonstrates that the PEG10 protein suppresses apoptosis and promotes cancer cell growth. Furthermore, PEG10 protein was found to be degraded through interaction with SIAH1 protein. This invention provides methods of regulating cell growth and cell death using the PEG10 protein. Furthermore, the present invention provides methods of screening for novel anticancer agents which use the PEG10 protein. The screening of this invention enables development of pharmaceutical agents that induce apoptosis and suppress cell growth by specifically targeting cancer cells. In particular, since the PEG10 protein is specifically expressed in hepatoma cells, it is an ideal target molecule for diagnosis and treatment of hepatoma.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Cancer treatment using BMP inhibitor
ActiveUS9505763B2Promote growthEasy SurvivalOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCancer cellCell growth
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com