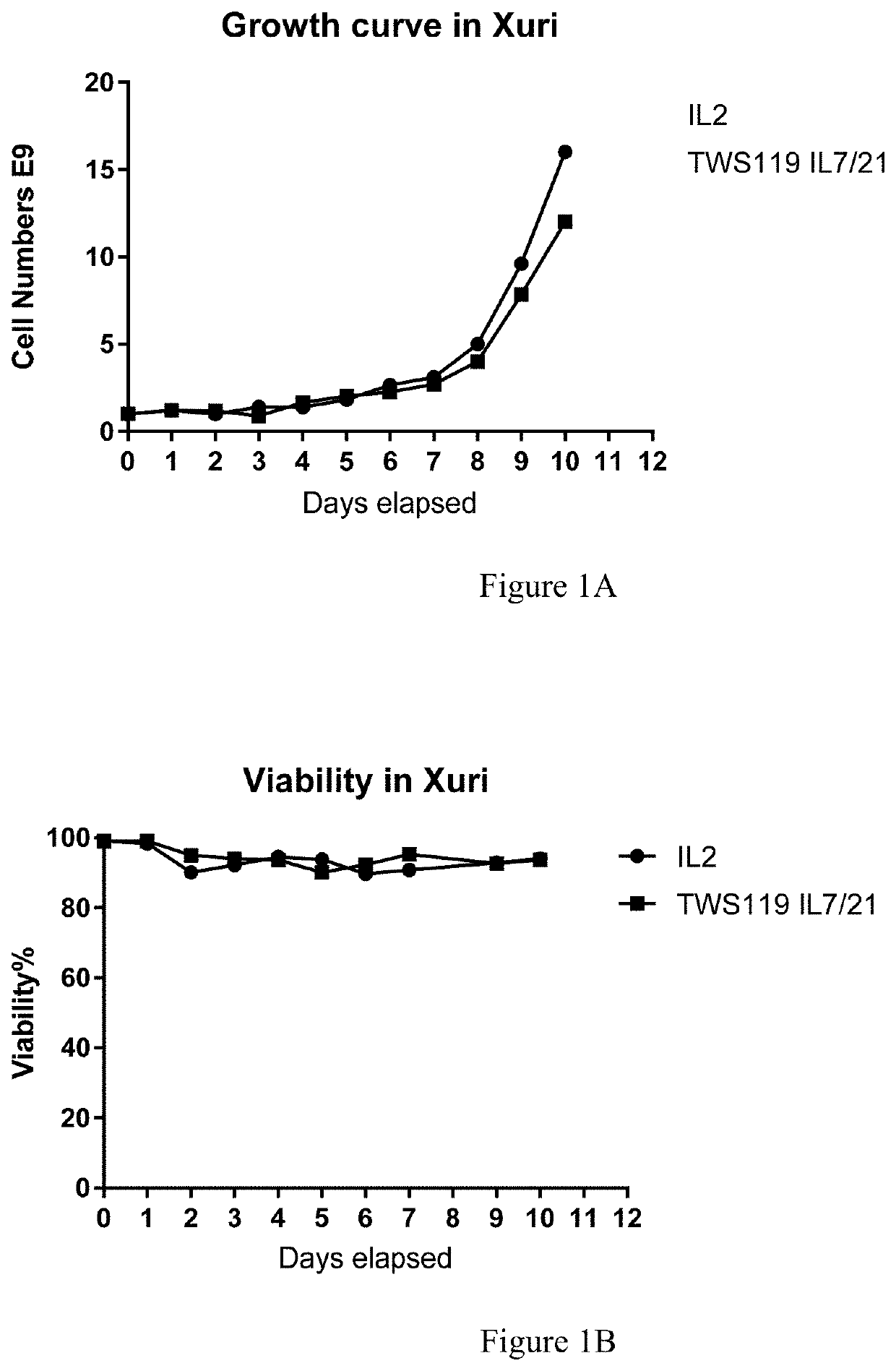
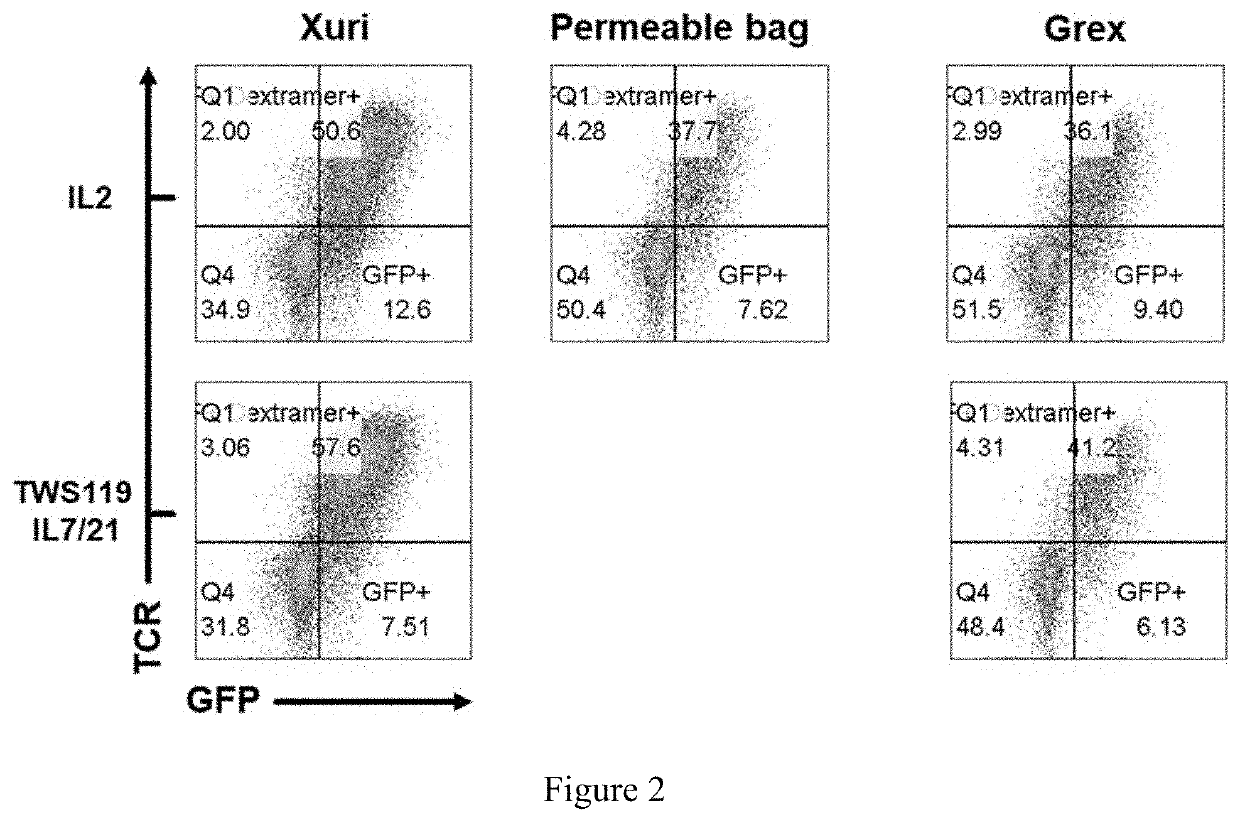
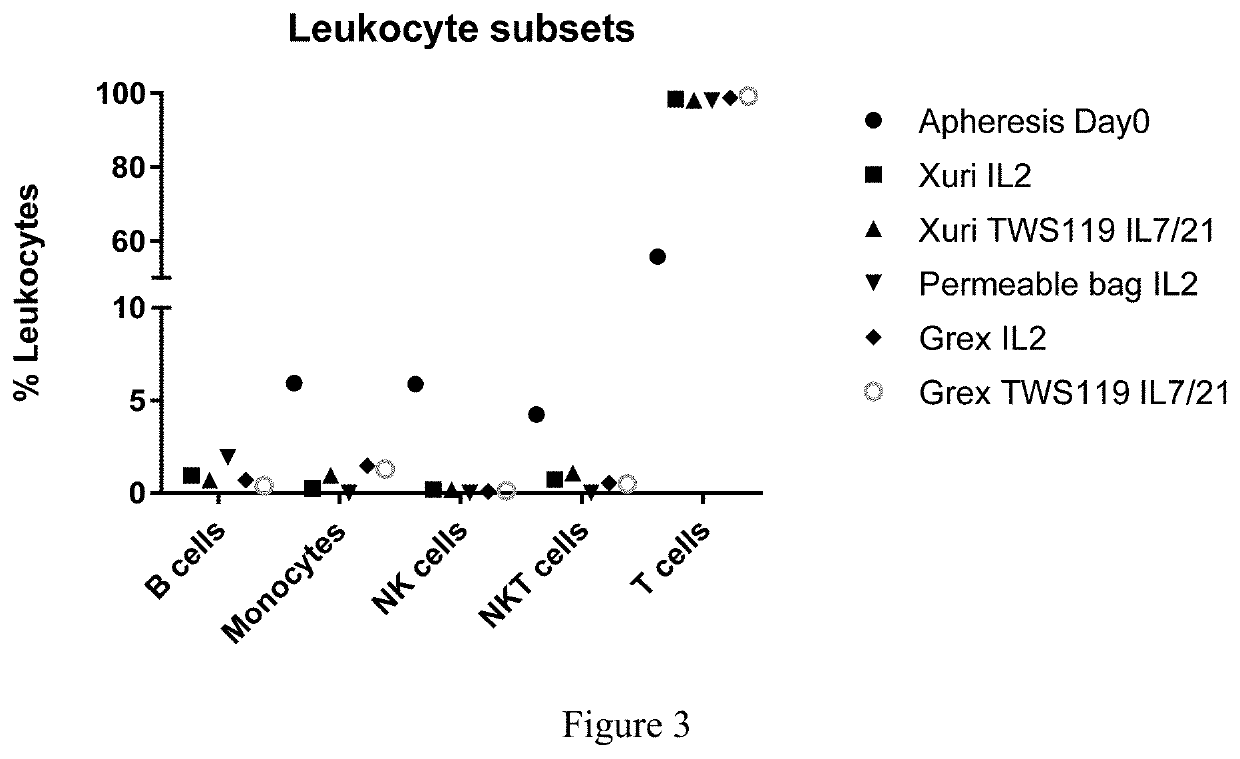
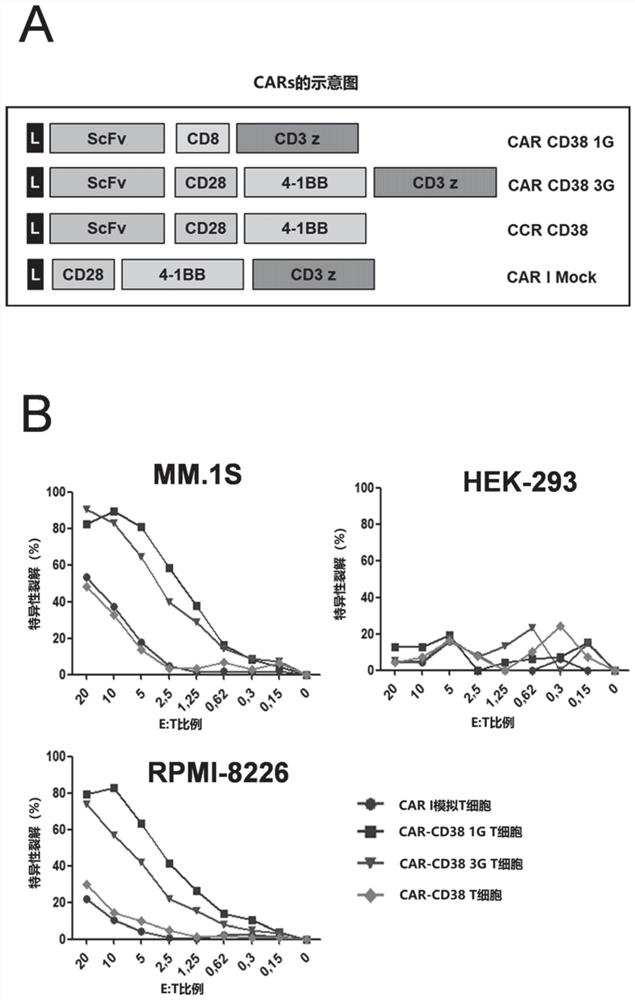
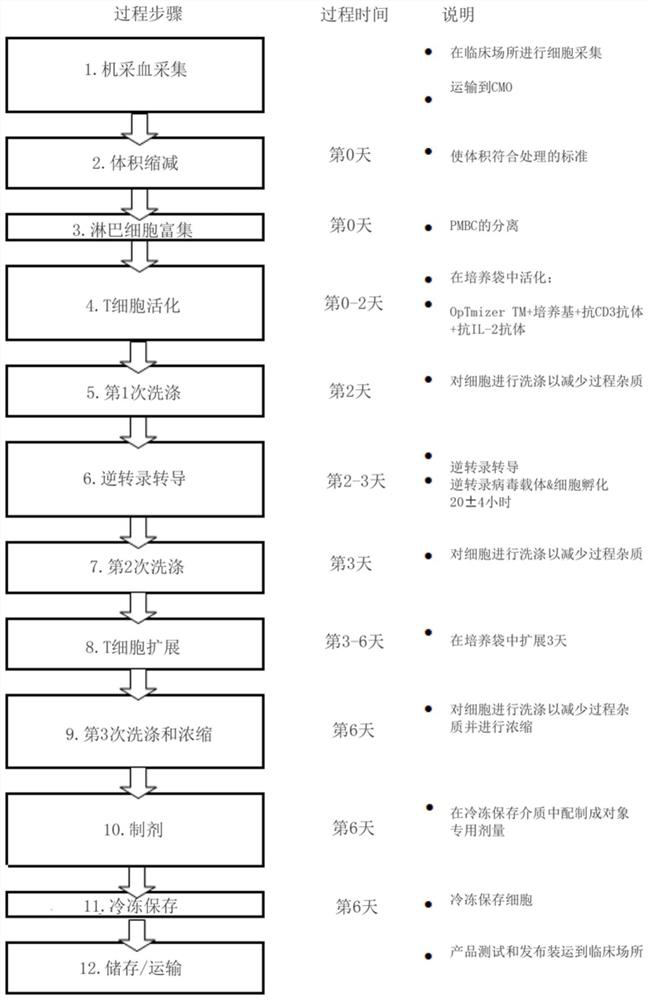
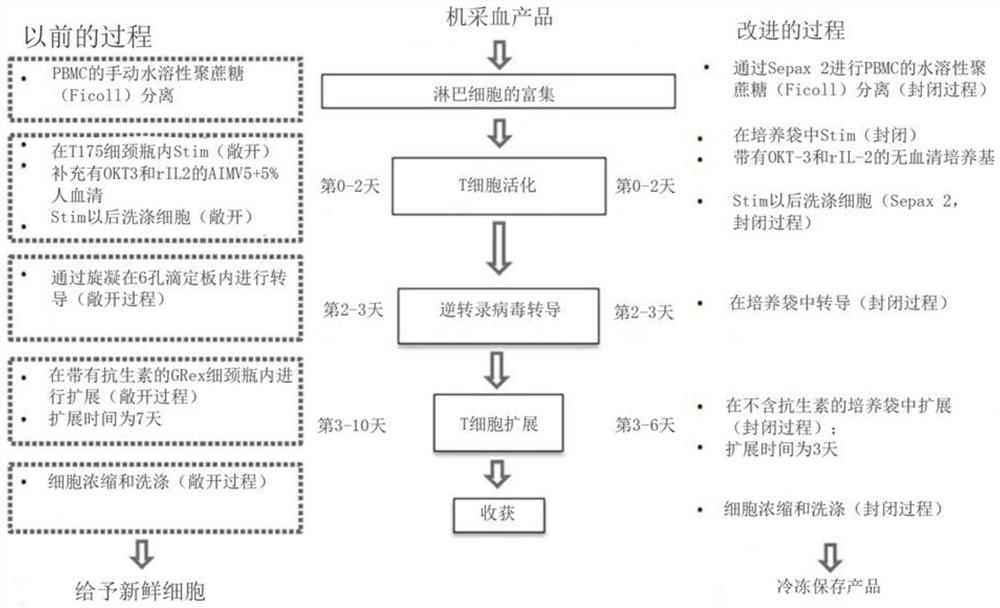
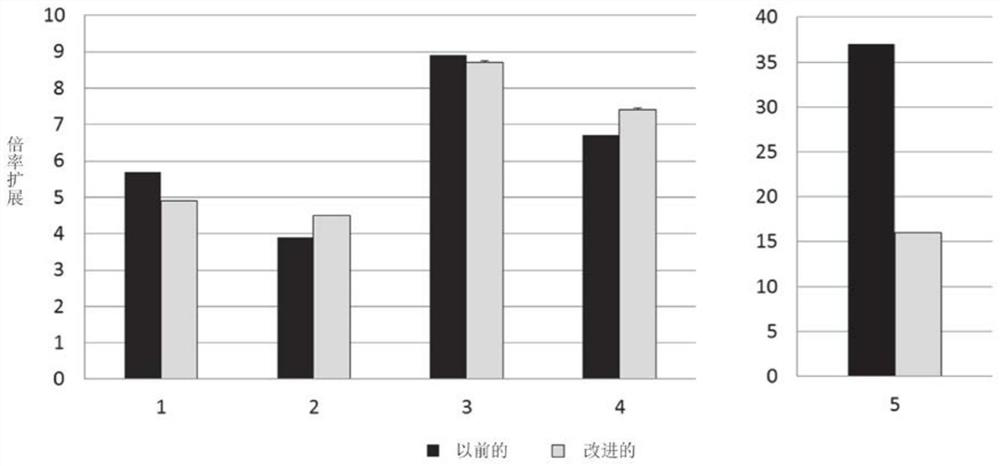
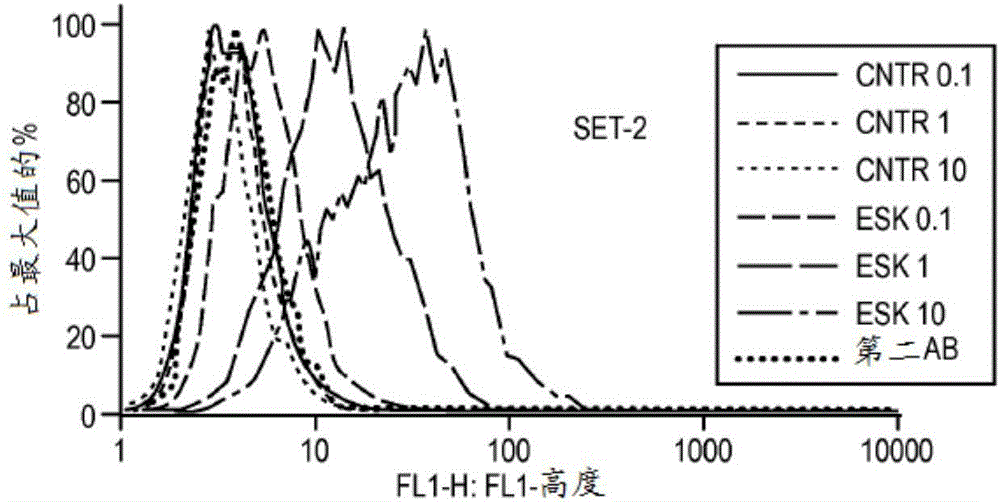
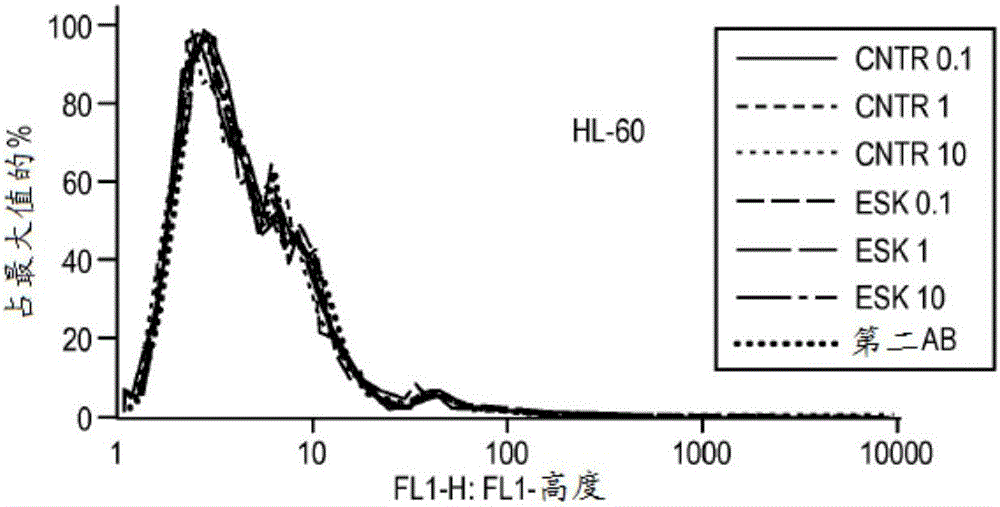
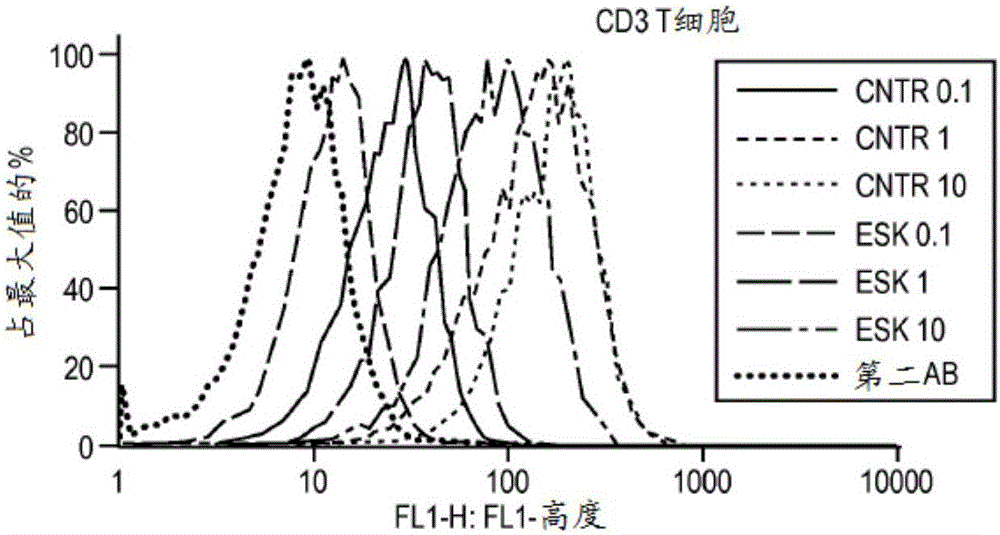
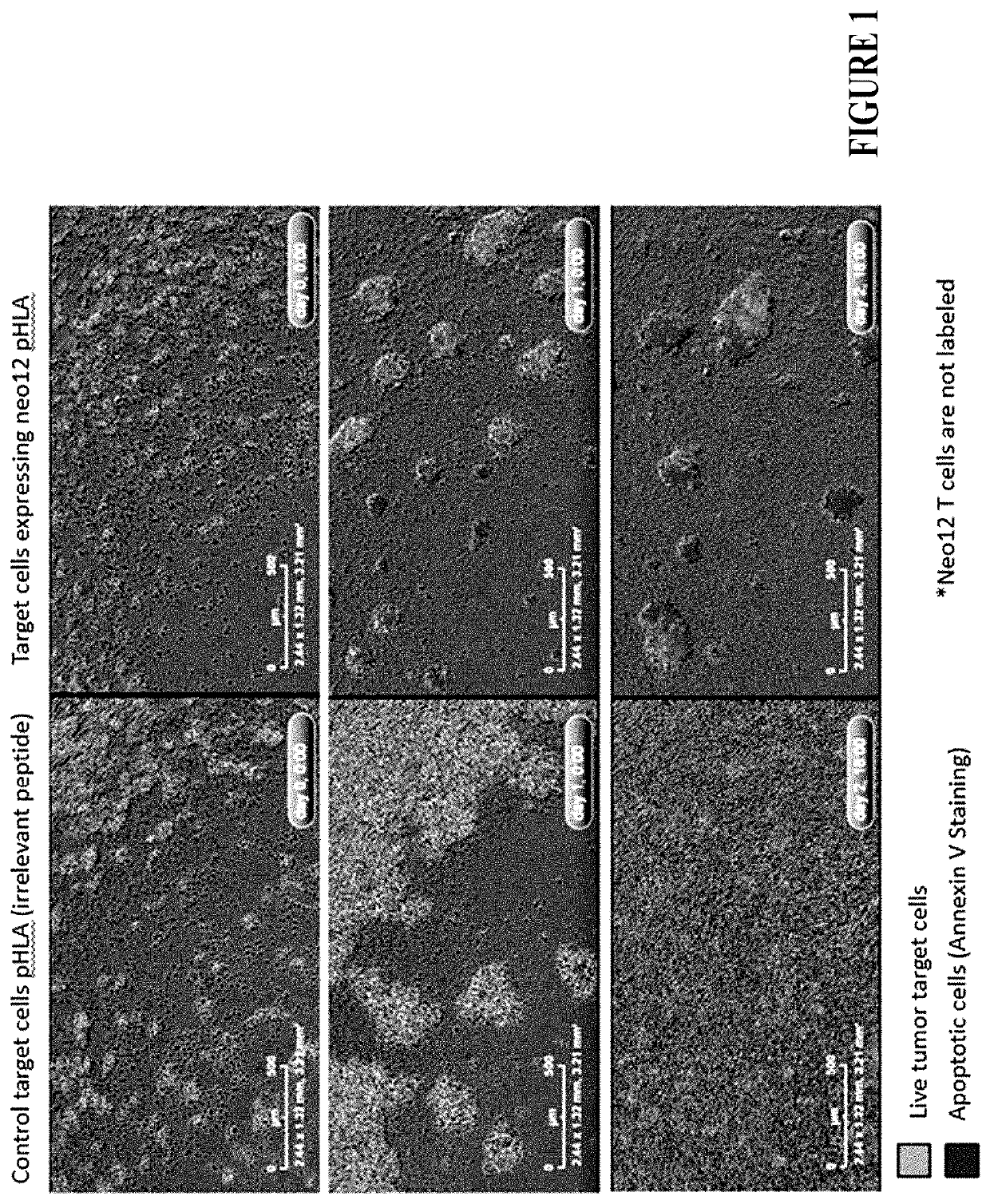
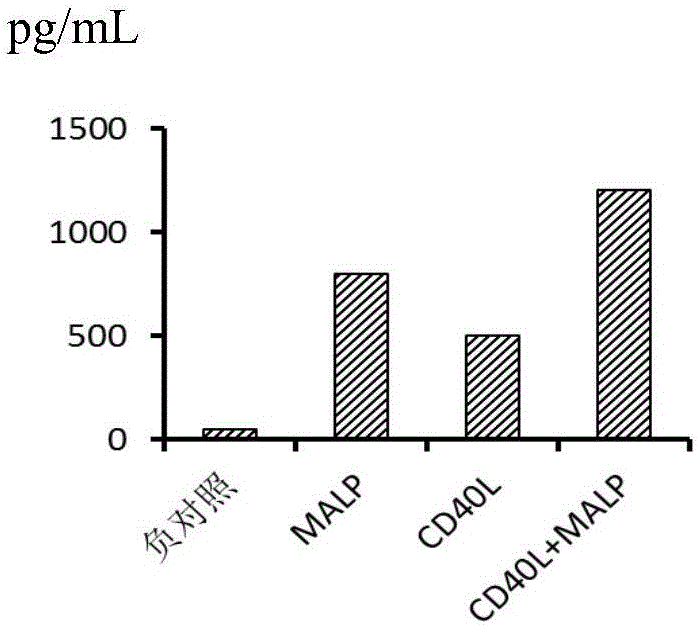Patents
Literature
36 results about "Autologous T-cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Adoptive cell therapy with young T cells
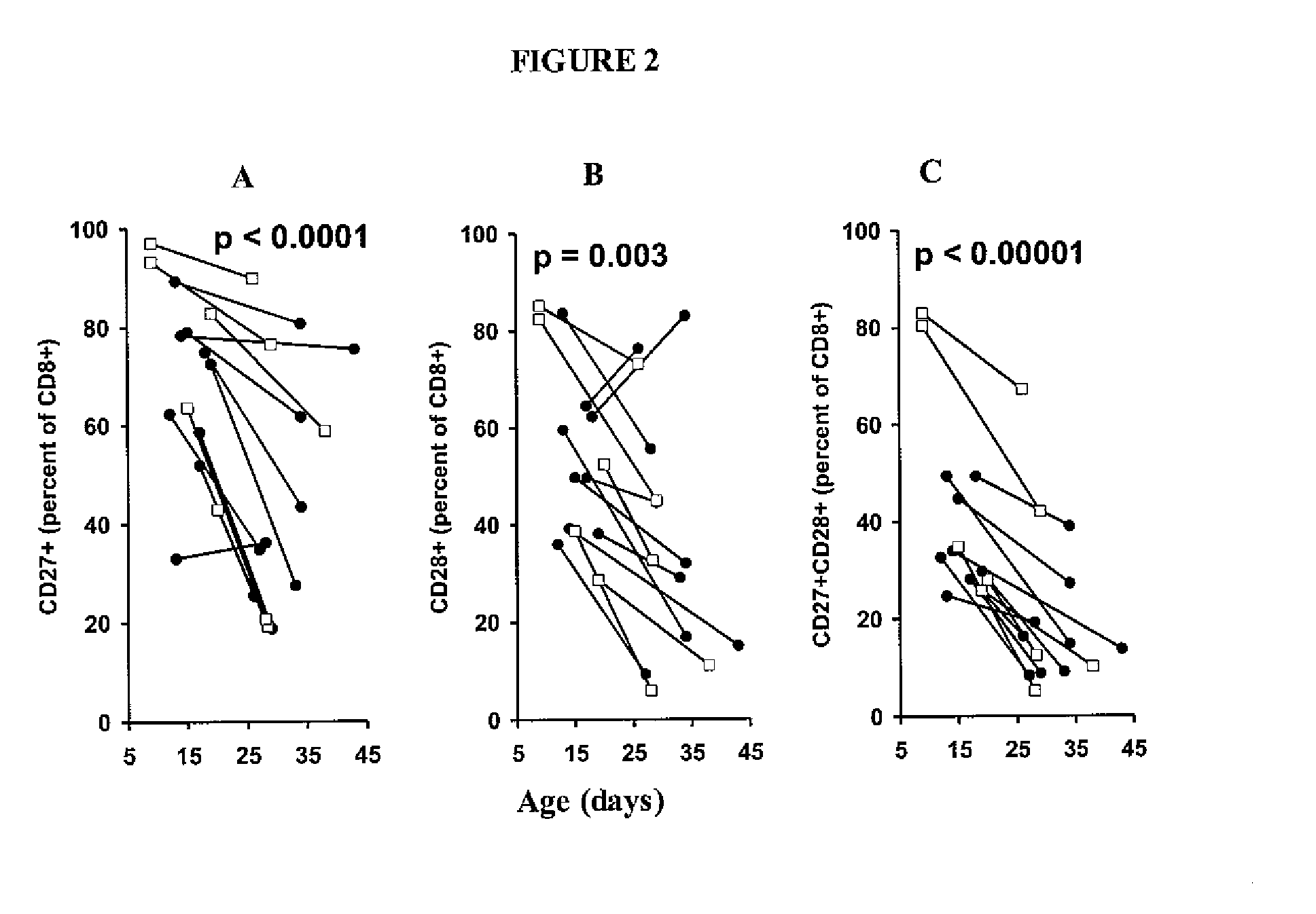
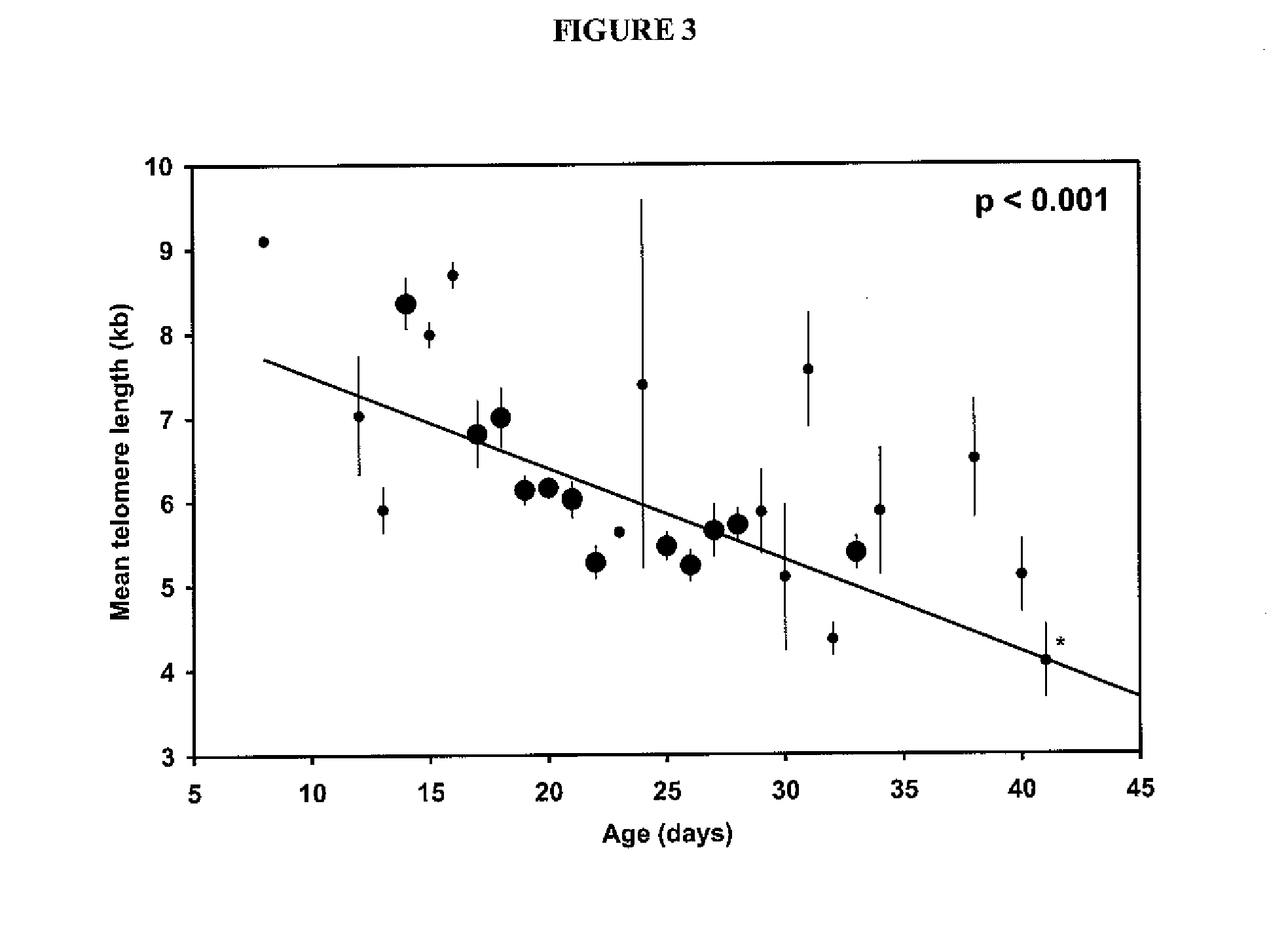
The invention provides a method of promoting regression of a cancer in a mammal comprising (i) culturing autologous T cells; (ii) expanding the cultured T cells; (iii) administering to the mammal nonmyeloablative lymphodepleting chemotherapy; and (iv) after administering nonmyeloablative lymphodepleting chemotherapy, administering to the mammal the expanded T cells, wherein the T cells administered to the mammal are about 19 to about 35 days old and have not been screened for specific tumor reactivity, whereupon the regression of the cancer in the mammal is promoted.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Adoptive cell therapy with young t cells
The invention provides a method of promoting regression of a cancer in a mammal comprising (i) culturing autologous T cells; (ii) expanding the cultured T cells; (iii) administering to the mammal nonmyeloablative lymphodepleting chemotherapy; and (iv) after administering nonmyeloablative lymphodepleting chemotherapy, administering to the mammal the expanded T cells, wherein the T cells administered to the mammal are about 19 to about 35 days old and have not been screened for specific tumor reactivity, whereupon the regression of the cancer in the mammal is promoted.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Methods of isolating t cell receptors having antigenic specificity for a cancer-specific mutation
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Process of expanding t cells
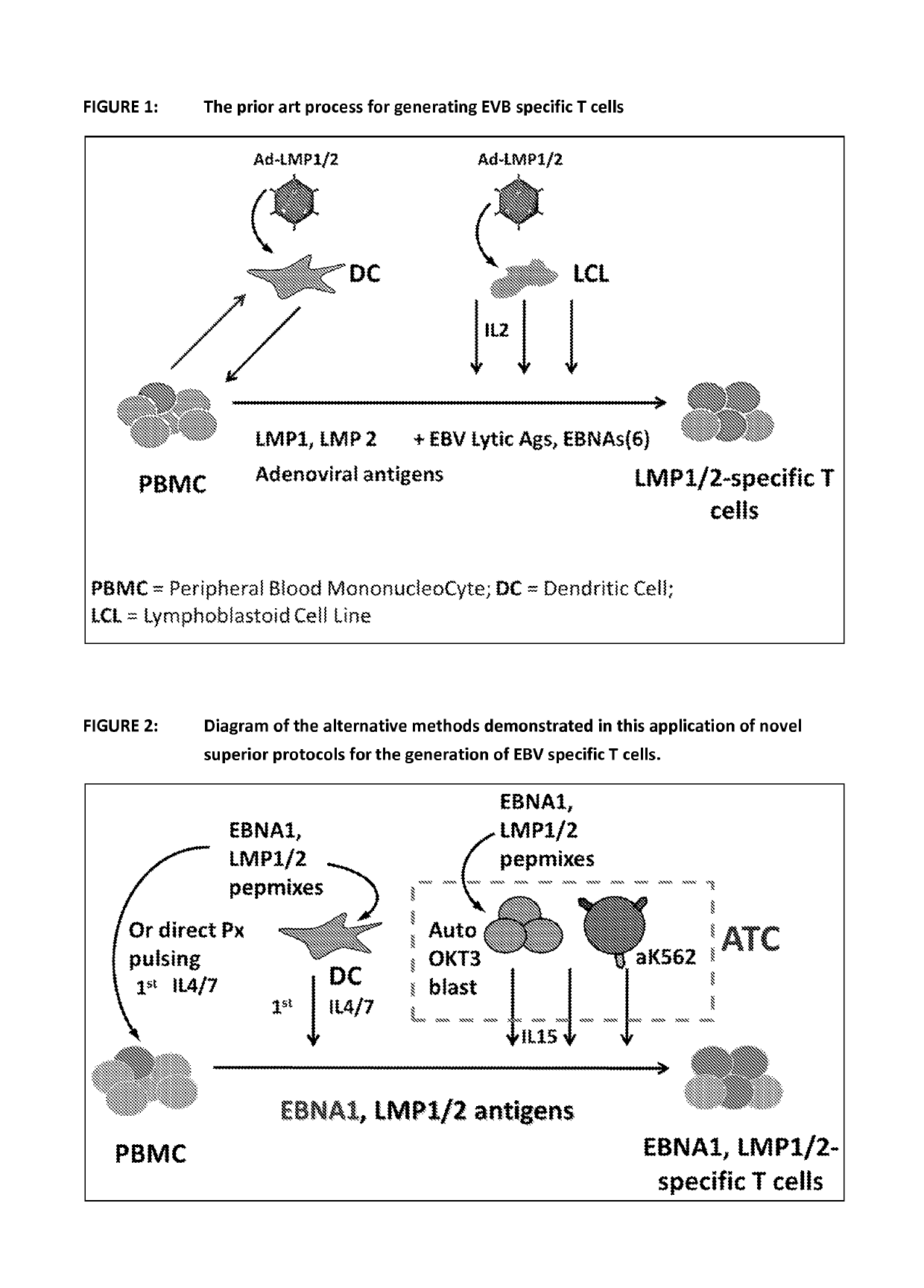
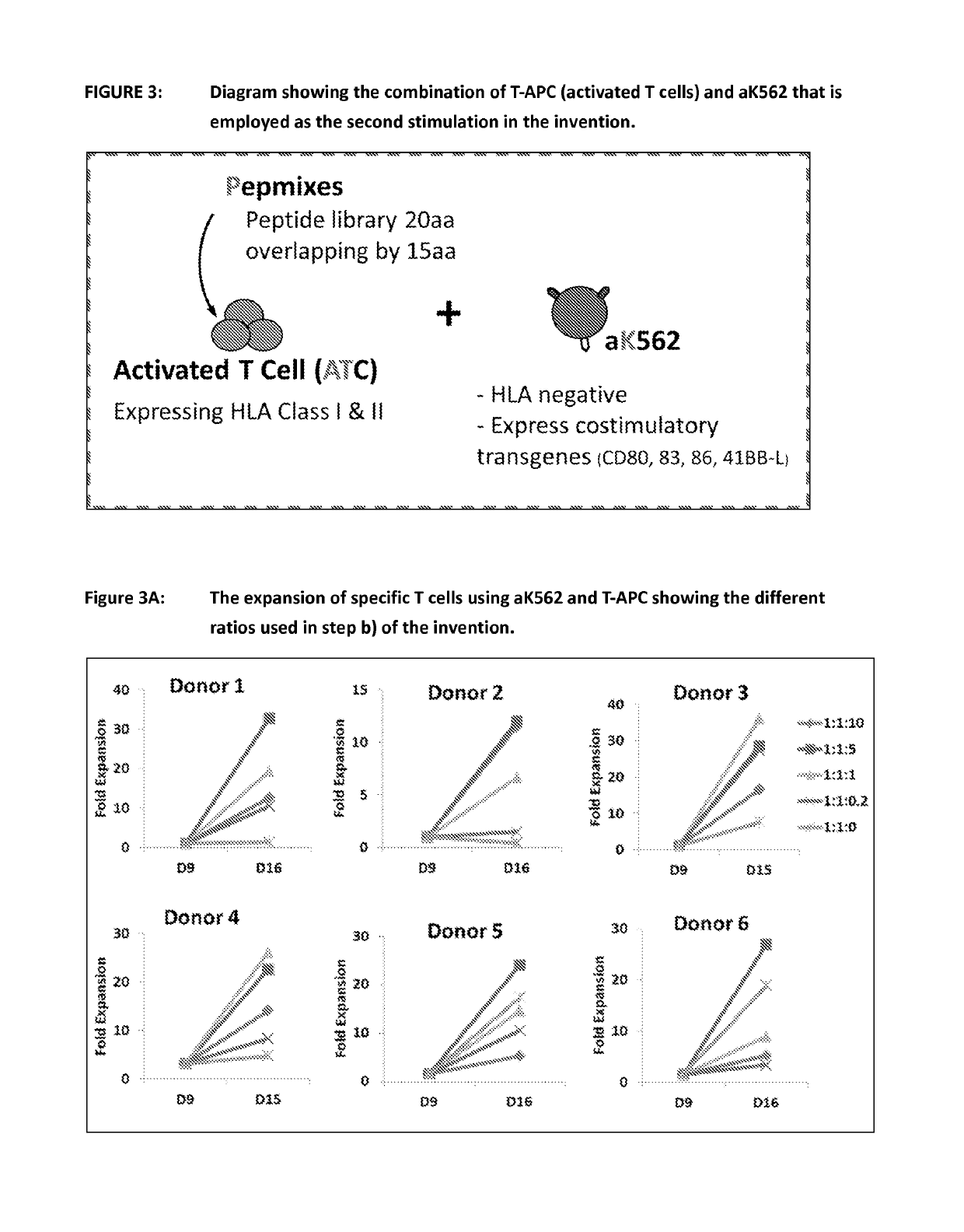
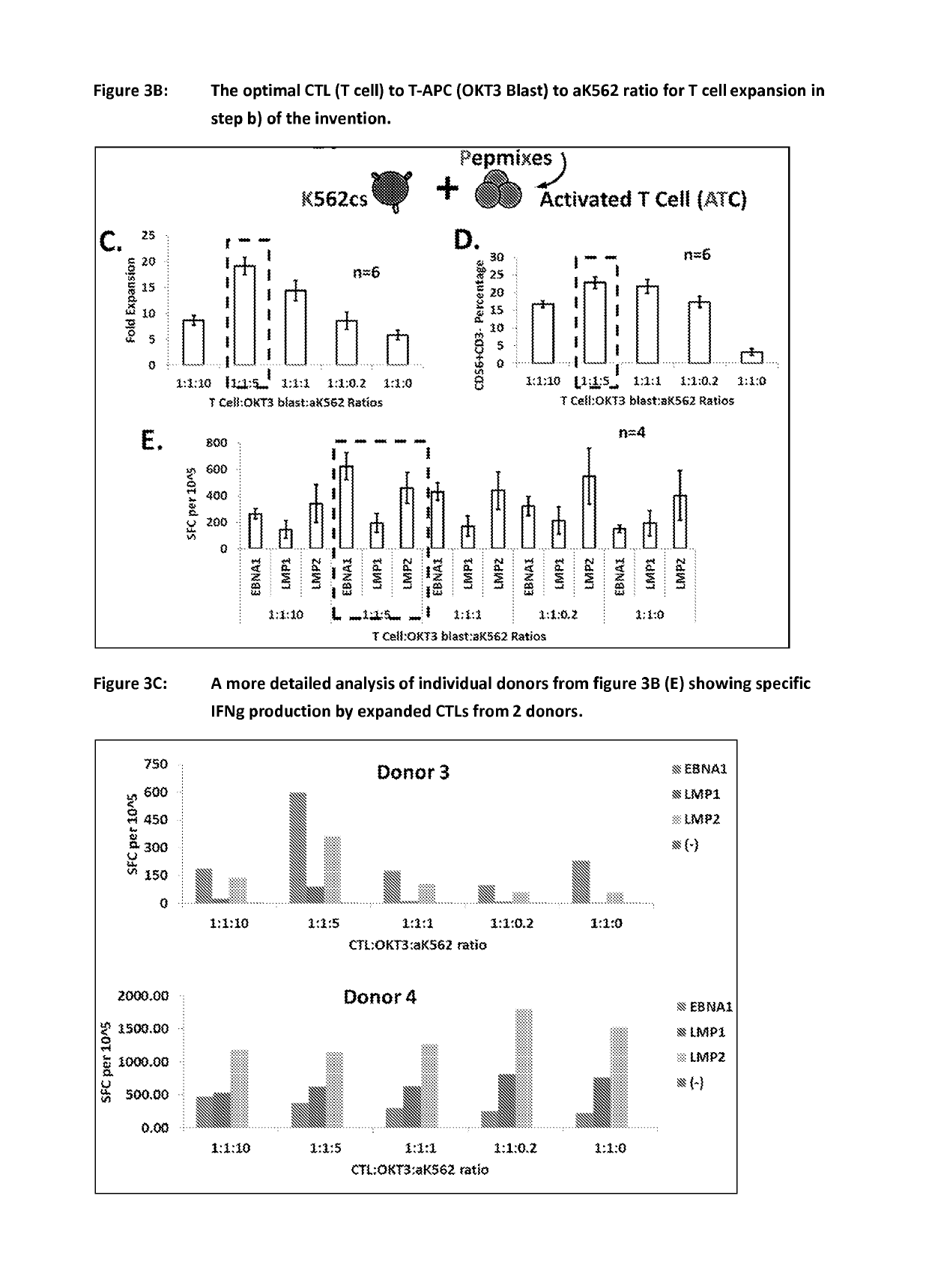
ActiveUS20150017723A1Minimises opportunity for contaminationMinimised of interventionGenetically modified cellsMammal material medical ingredientsImmune compromisedAutologous T-cells
The present disclosure relates to a novel process for expanding T cells, such as autologous T cells, cell populations therefrom, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the said cell populations and use of the cells and compositions for treatment, particular the treatment or prophylaxis of virus infection and / or cancer, for example in immune compromised or immune competent human patients.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
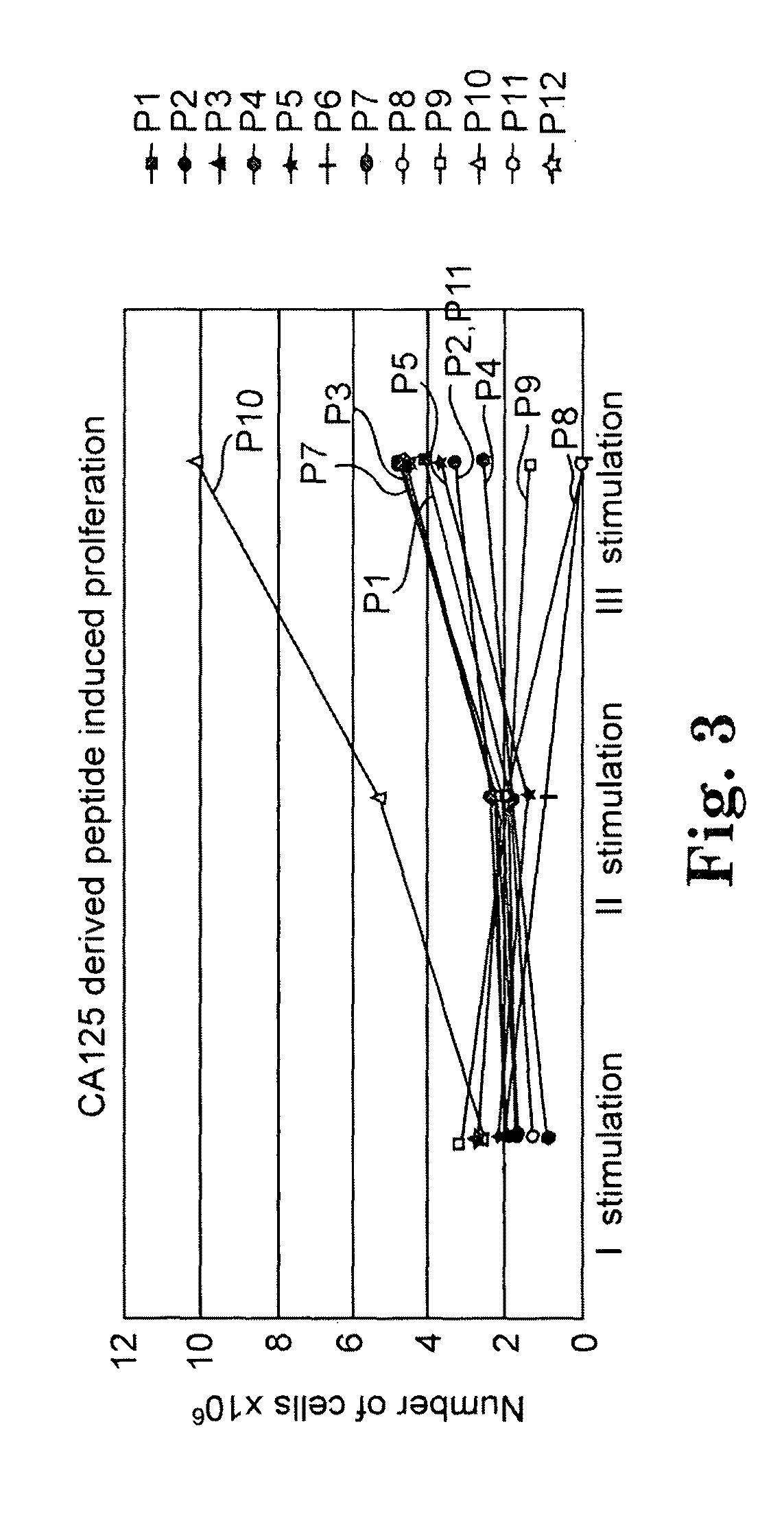
Target peptides for ovarian cancer immunotherapy
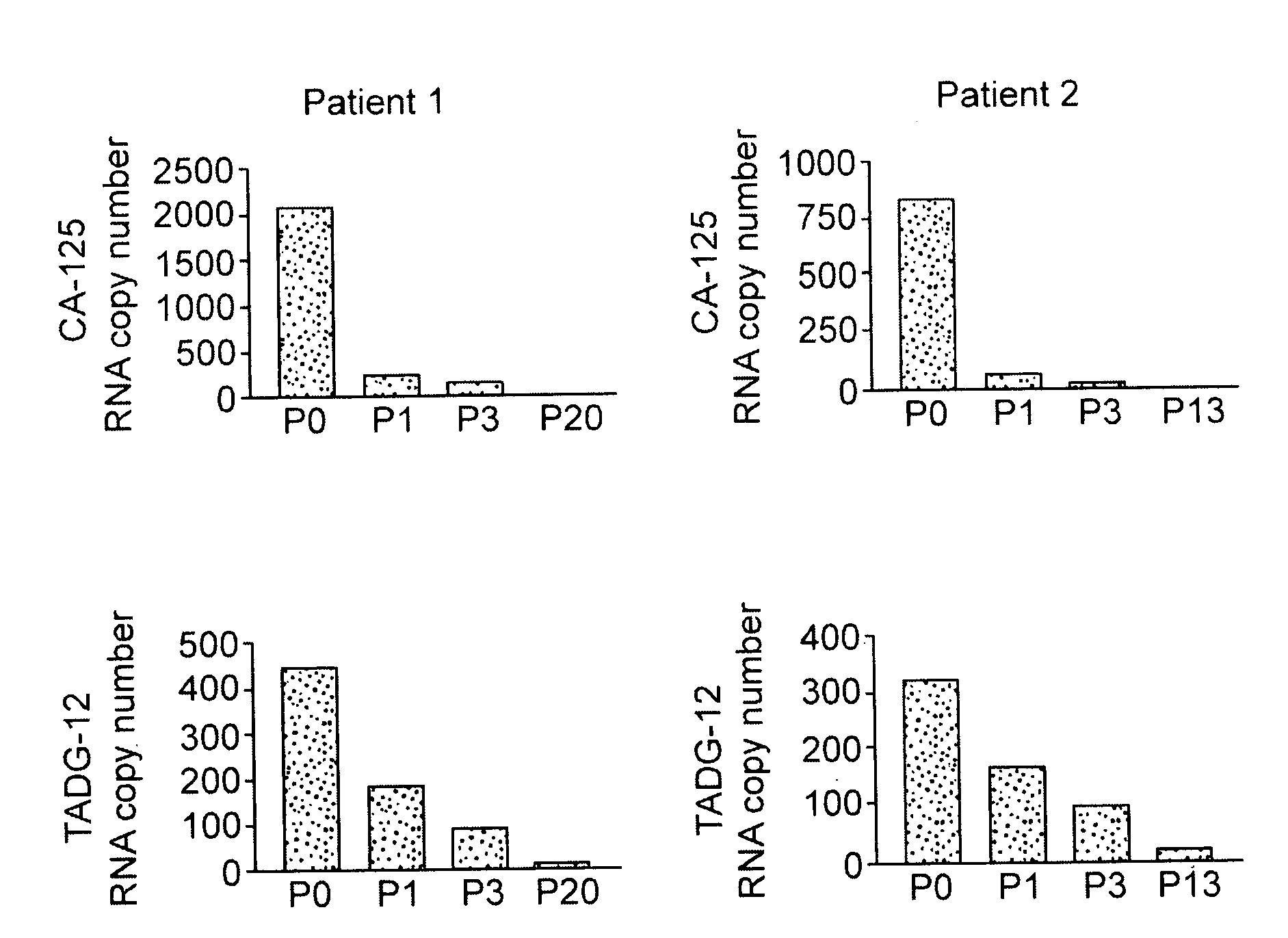
TADG-12 and CA125 are two proteins expressed with high specificity in ovarian cancer tumors. They thus would be potential antigens for immunotherapy in ovarian cancer. The invention is based on the discovery of peptides in TADG-12 and CA125 that can be used to induce an autologous T cell response that lyses ovarian cancer cells expressing TADG-12 or CA125. The peptides are contacted with dendritic cells in vitro to generate peptide-loaded dendritic cells. The peptide-loaded dendritic cells are contacted with T cells in vitro to amplify CD8+ T cells that recognize the peptide. At least one CA125 peptide and at least one TADG-12 peptide were found that amplified CD8+ T cells, even from cancer patients, that lysed autologous CA125-expressing or TADG-12-expressing tumor cells. The peptide-loaded dendritic cells can be administered to a cancer patient to amplify CD8+ T cells in vivo that attack the cancer cells. Alternatively, autologous CD8+ T cells can be amplified ex vivo and then infused into the cancer patient.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Monitoring mantle cell lymphoma clonotypes in peripheral blood after immunotransplant
InactiveUS20150299800A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDiseaseAutologous T-cells
The invention is directed to a method of monitoring a mantle cell lymphoma residual disease in an immunotransplant patient by post-treatment analysis of clonotype profiles from patient blood samples. In some embodiments, methods of the invention comprising steps of (a) treating a patient by immunotransplanting the patient with vaccine-primed autologous T cells; (b) obtaining a peripheral blood sample from the patient comprising B-cells and / or cell-free nucleic acids; (c) amplifying molecules of nucleic acid from the B-cells of the sample and / or cell-free nucleic acids in the sample, the molecules of nucleic acid comprising recombined DNA sequences from immunoglobulin genes; (d) sequencing the amplified molecules of nucleic acid to form a clonotype profile; and (e) determining from the clonotype profile a presence, absence and / or level of the one or more patient-specific clonotypes correlated with the mantle cell lymphoma, including phylogenic clonotypes thereof.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Methods of isolating t cell receptors having antigenic specificity for a cancer-specific mutation
Disclosed are methods of isolating a TCR having antigenic specificity for a mutated amino acid sequence encoded by a cancer-specific mutation, the method comprising: identifying one or more genes in the nucleic acid of a cancer cell of a patient, each gene containing a cancer-specific mutation that encodes a mutated amino acid sequence; inducing autologous APCs of the patient to present the mutated amino acid sequence; co-culturing autologous T cells of the patient with the autologous APCs that present the mutated amino acid sequence; selecting the autologous T cells; and isolating a nucleotide sequence that encodes the TCR from the selected autologous T cells, wherein the TCR has antigenic specificity for the mutated amino acid sequence encoded by the cancer-specific mutation. Also disclosed are related methods of preparing a population of cells, populations of cells, TCRs, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating or preventing cancer.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Adoptive cell therapy with young t cells
ActiveUS20140030806A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAdoptive cellular therapyTumor response
The invention provides a method of promoting regression of a cancer in a mammal comprising (i) culturing autologous T cells; (ii) expanding the cultured T cells; (iii) administering to the mammal nonmyeloablative lymphodepleting chemotherapy; and (iv) after administering nonmyeloablative lymphodepleting chemotherapy, administering to the mammal the expanded T cells, wherein the T cells administered to the mammal are about 19 to about 35 days old and have not been screened for specific tumor reactivity, whereupon the regression of the cancer in the mammal is promoted.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Isolation and identification of t cells
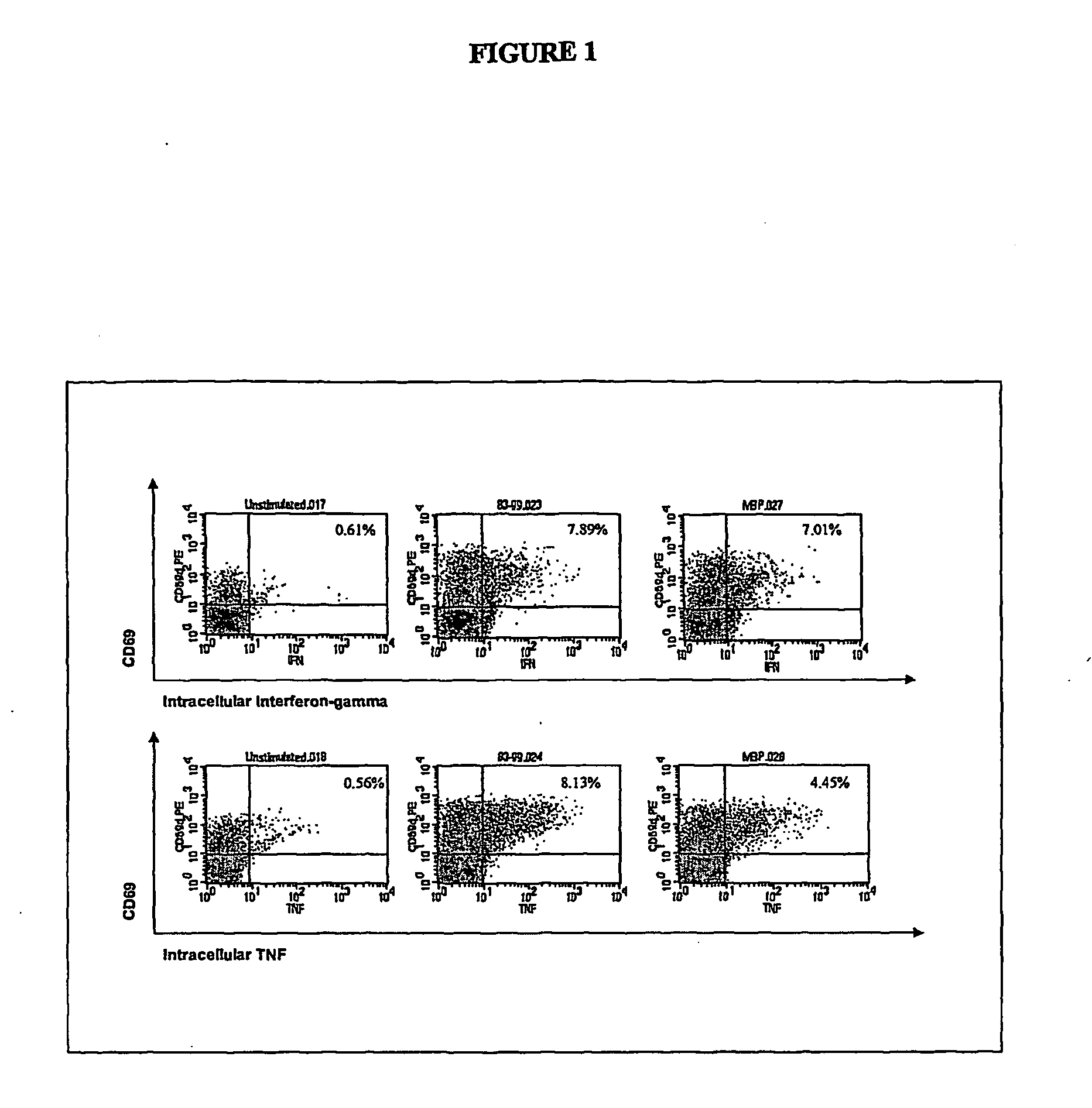
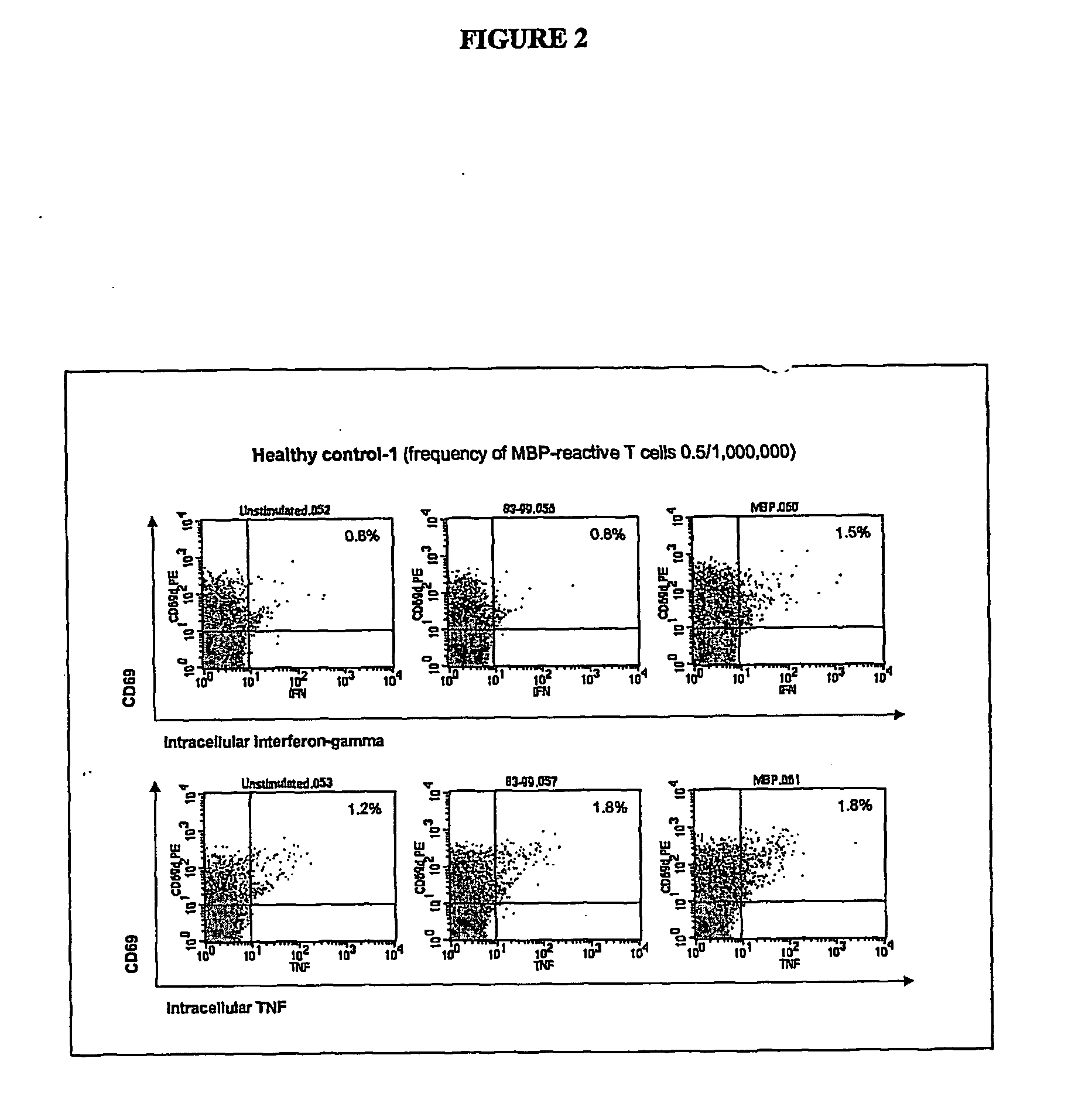
The present invention relates to improved autologous T cell vaccines and improved methods for their production. The invention is also directed to methods for treating autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis or rheumatoid arthritis using autologous T cell vaccines. The invention is further directed to the diagnosis of T cell associated diseases.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
Target CA125 peptides for cancer immunotherapy
TADG-12 and CA125 are two proteins expressed with high specificity in ovarian cancer tumors. They thus would be potential antigens for immunotherapy in ovarian cancer. The invention is based on the discovery of peptides in TADG-12 and CA125 that can be used to induce an autologous T cell response that lyses ovarian cancer cells expressing TADG-12 or CA125. The peptides are contacted with dendritic cells in vitro to generate peptide-loaded dendritic cells. The peptide-loaded dendritic cells are contacted with T cells in vitro to amplify CD8+ T cells that recognize the peptide. At least one CA125 peptide and at least one TADG-12 peptide were found that amplified CD8+ T cells, even from cancer patients, that lysed autologous CA125-expressing or TADG-12-expressing tumor cells. The peptide-loaded dendritic cells can be administered to a cancer patient to amplify CD8+ T cells in vivo that attack the cancer cells. Alternatively, autologous CD8+ T cells can be amplified ex vivo and then infused into the cancer patient.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
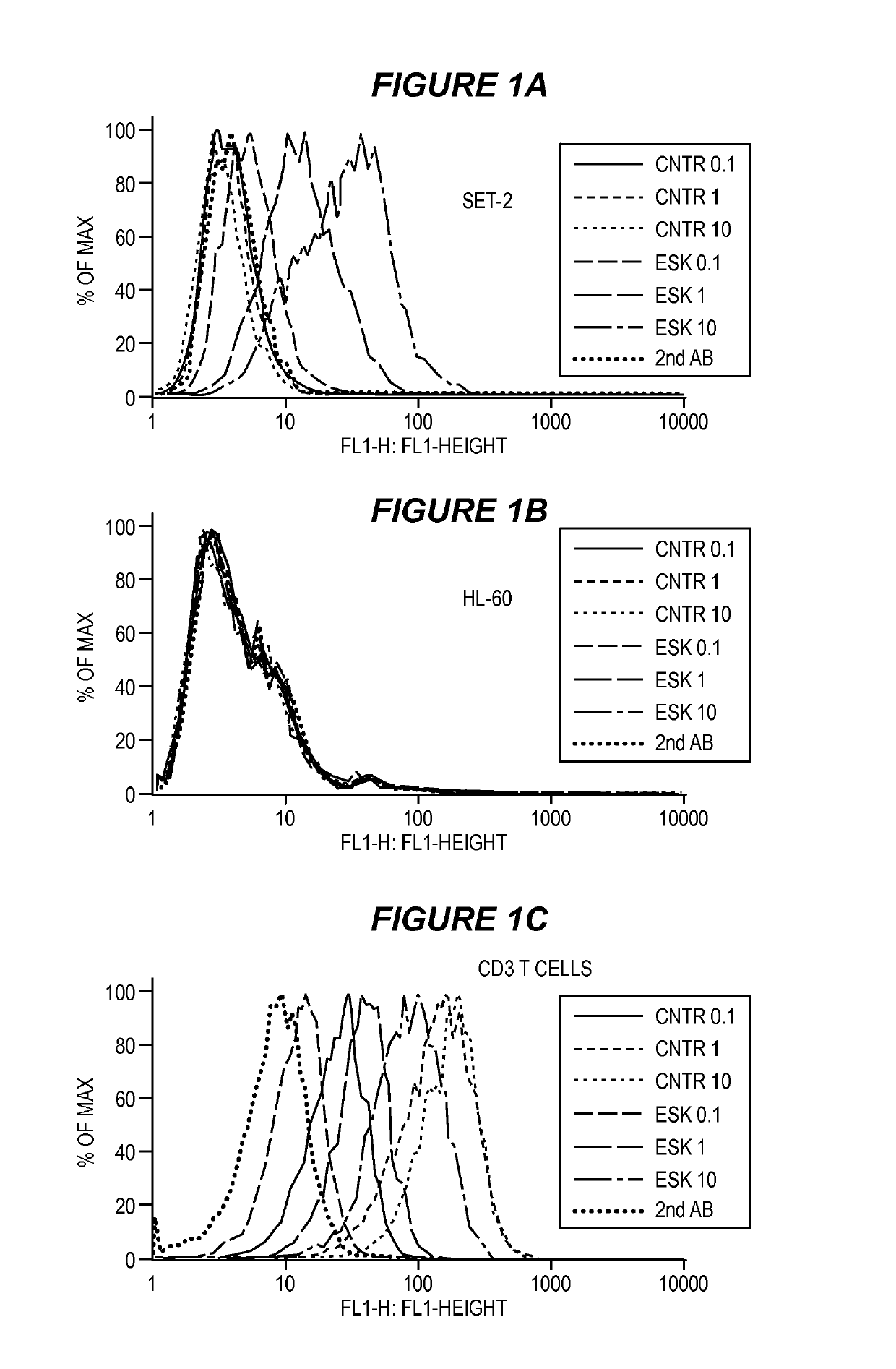
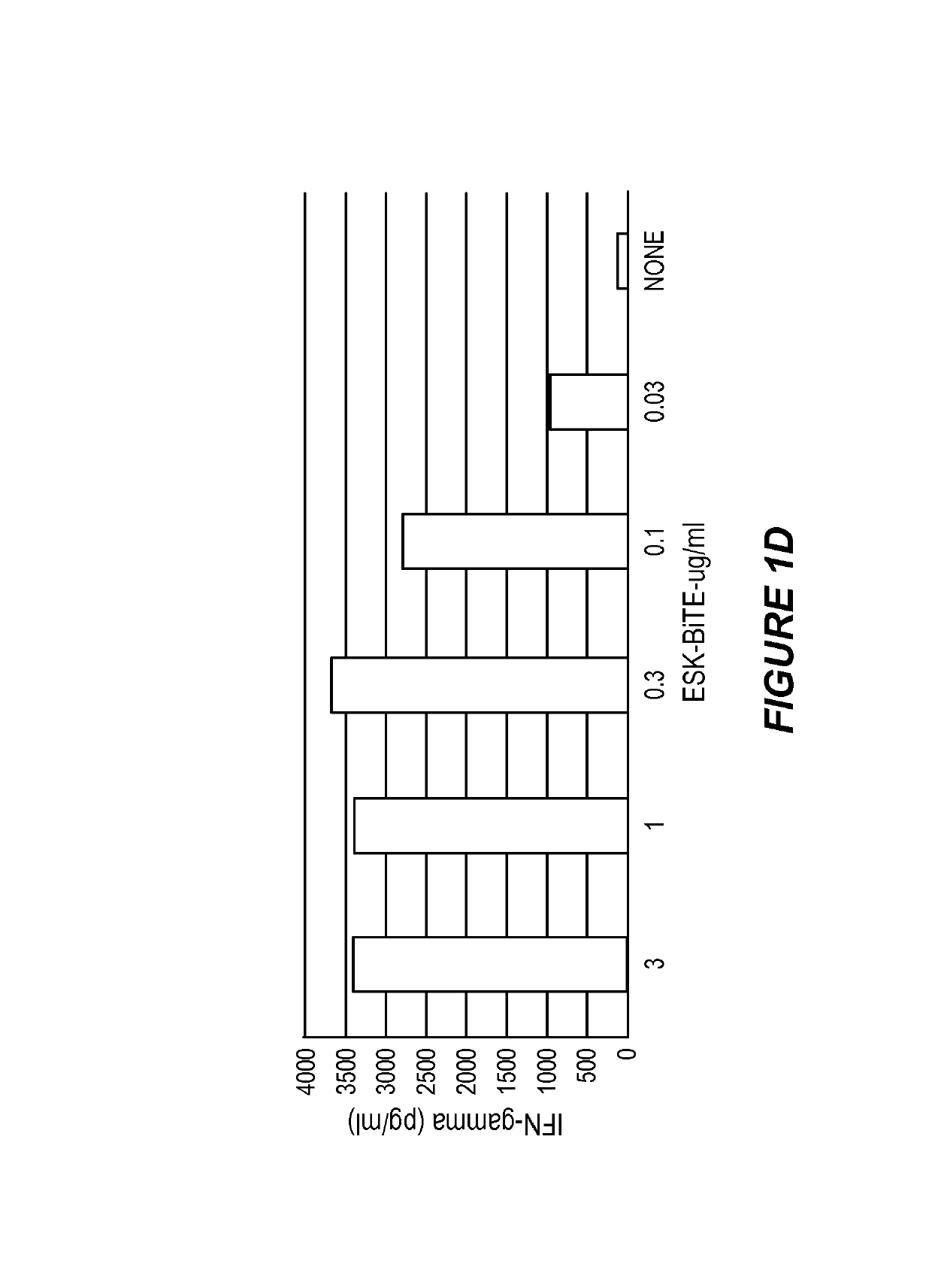
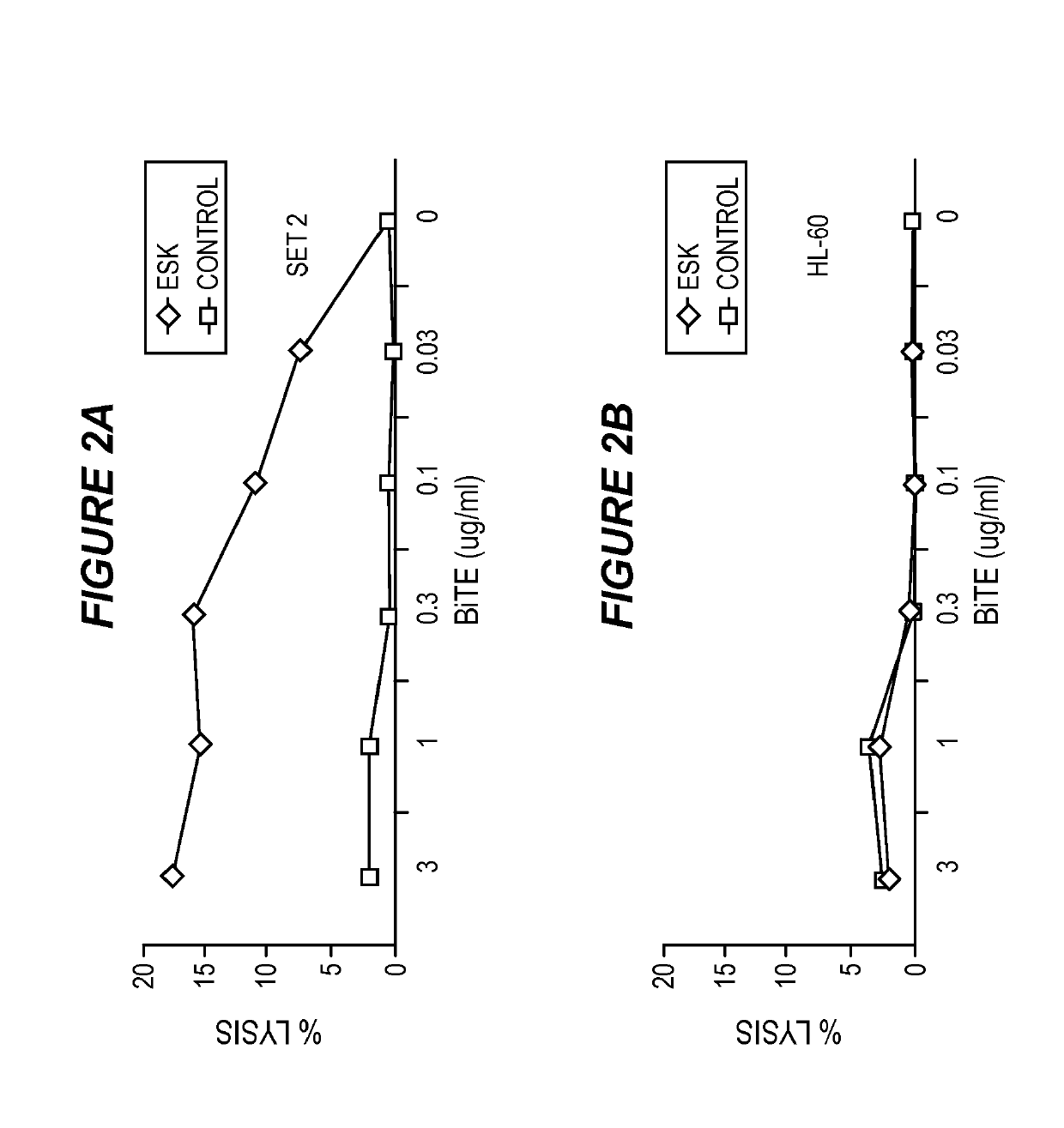
Anti-WT1/HLA bi-specific antibody
ActiveUS10239952B2Potent therapeutic activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsMyeloid leukemiaAntiendomysial antibodies
Disclosed herein is a bi-specific form of a T cell receptor mimic (TCRm) mAb with reactivity to human immune effector cell antigen and a WT1 peptide / HLA-A epitope. This antibody selectively bound to leukemias and solid tumor cells expressing WT1 and HLA-A as well as activated resting human T cells to release interferon-(IFN-γ) and to kill the target cancer cells in vitro. Importantly, the antibody mediated autologous T cell proliferation and directed potent cytotoxicity against fresh ovarian cancer cells. Therapeutic activity in vivo of the antibody was demonstrated in NOD SCID SCID Yc*(NSG) mice with three different human cancers expressing WT1 / HLA-A2 including disseminated Ph+ acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), disseminated acute myeloid leukemia, and peritoneal mesothelioma. In both of the leukemia xenograft models, mice that received the antibody and T cells also showed longer survival and delayed limb paralysis. Also provided are methods for stimulating a primary T cell response comprising stimulating cytotoxic T cells against a first tumor antigen and a secondary T cell response comprising stimulating effector T cells and / or memory T cells against a first tumor antigen and / or against a second tumor antigen using the bi-specific antibodies described herein.
Owner:EUREKA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Process of expanding T cells
ActiveUS10351824B2Efficient and robust 2-step culture processImprove propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetically modified cellsImmune compromisedImmunocompetence
The present disclosure relates to a novel process for expanding T cells, such as autologous T cells, cell populations therefrom, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the said cell populations and use of the cells and compositions for treatment, particular the treatment or prophylaxis of virus infection and / or cancer, for example in immune compromised or immune competent human patients.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
Combination factor for promoting maturity of dendritic cells and method for cultivating dendritic cells
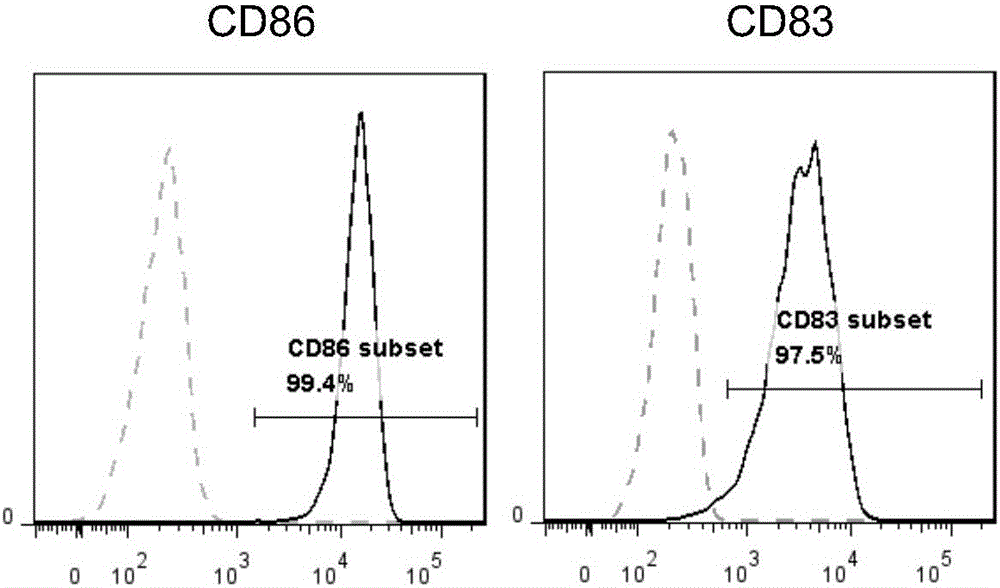
InactiveCN106701680AMature and efficientFully matureCulture processBlood/immune system cellsDendritic cellAutologous T-cells
The invention belongs to the field of cell biology and discloses a combination factor for promoting maturity of dendritic cells and a method for cultivating the dendritic cells. The combination factor comprises CD40L and MPLA. The combination factor is utilized to stimulate the dendritic cells, efficiently activate autologous T cells thereof and induce the dendritic cells to mature fully. According to the method for cultivating the dendritic cells, the combination factor for promoting maturity of the dendritic cells is used to stimulate immature dendritic cells. According to the method, the dendritic cells can be induced to mature fully and have the capability of efficiently activating the autologous T cells thereof, the operation method is simple, the cost is low, cultivated mature DC cells can be extensively used for preparing tumor immunotherapy medicines or vaccines to play an important role in the field of tumor immunotherapy.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
GBS Toxin Receptor Compositions and Methods of Use
InactiveUS20090221804A1Ameliorate any conditionReduce severityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCancer antigen ingredientsAutologous T-cellsImmunocompatibility
Methods are provided for preventing or attenuating pathoangiogenic conditions by administering at least one GBS toxin receptor polypeptide or at least one immunogenic fragment thereof. Also provided are a composition that includes a GBS toxin receptor polypeptide and a method for making such a composition. In another embodiment of the invention, immunized animals also receive GBS toxin, immunocompatible antibodies to the GBS toxin receptor, and / or expanded autologous T cells to the GBS toxin receptor. Also included in this invention are methods of identifying additional GBS toxin receptors.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Methods for producing autologous t cells useful to treat b cell malignancies and other cancers and compositions thereof
Provided herein are methods for manufacturing T cells. In certain embodiments, methods for manufacturing T cells which express a cell surface receptor that recognizes a specific antigenic moiety on the surface of a target cell are provided. Such methods may include, but are not limited to, steps of (1 ) enriching a population of lymphocytes obtained from a donor subject; (2) stimulating the population of lymphocytes with one or more T-cell stimulating agents to produce a population of activated T cells, wherein the stimulation is performed in a closed system using serum-free culture medium; (3) transducing the population of activated T cells with a viral vector comprising a nucleic acid molecule which encodes the cell surface receptor, using a single cycle transduction to produce a population of transduced T cells, wherein the transduction is performed in a closed system using serum-free culture medium; and (4) expanding the population of transduced T cells for a predetermined time to produce a population of engineered T cells, wherein the expansion is performed in a closed system using serum-free culture medium. Also provided herein are populations of engineered T cells produced by the methods described herein and pharmaceutical compositions thereof.
Owner:凯德药业公司 +1
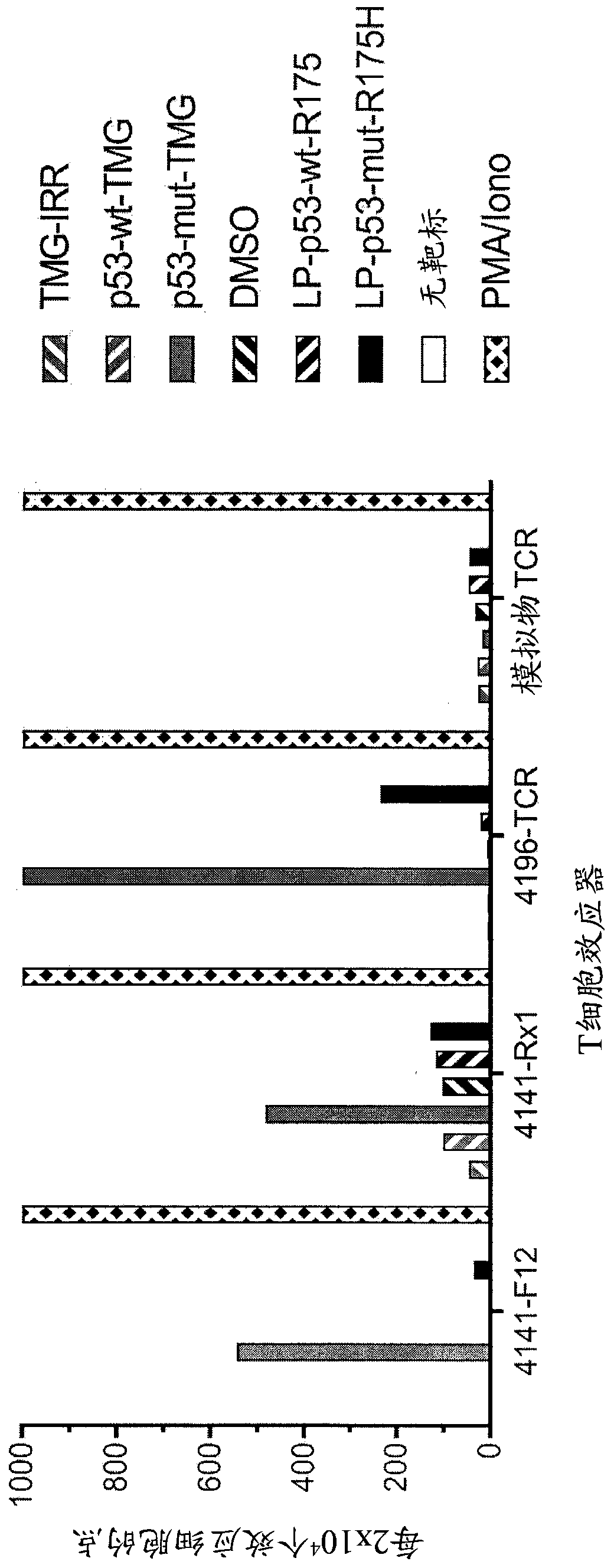
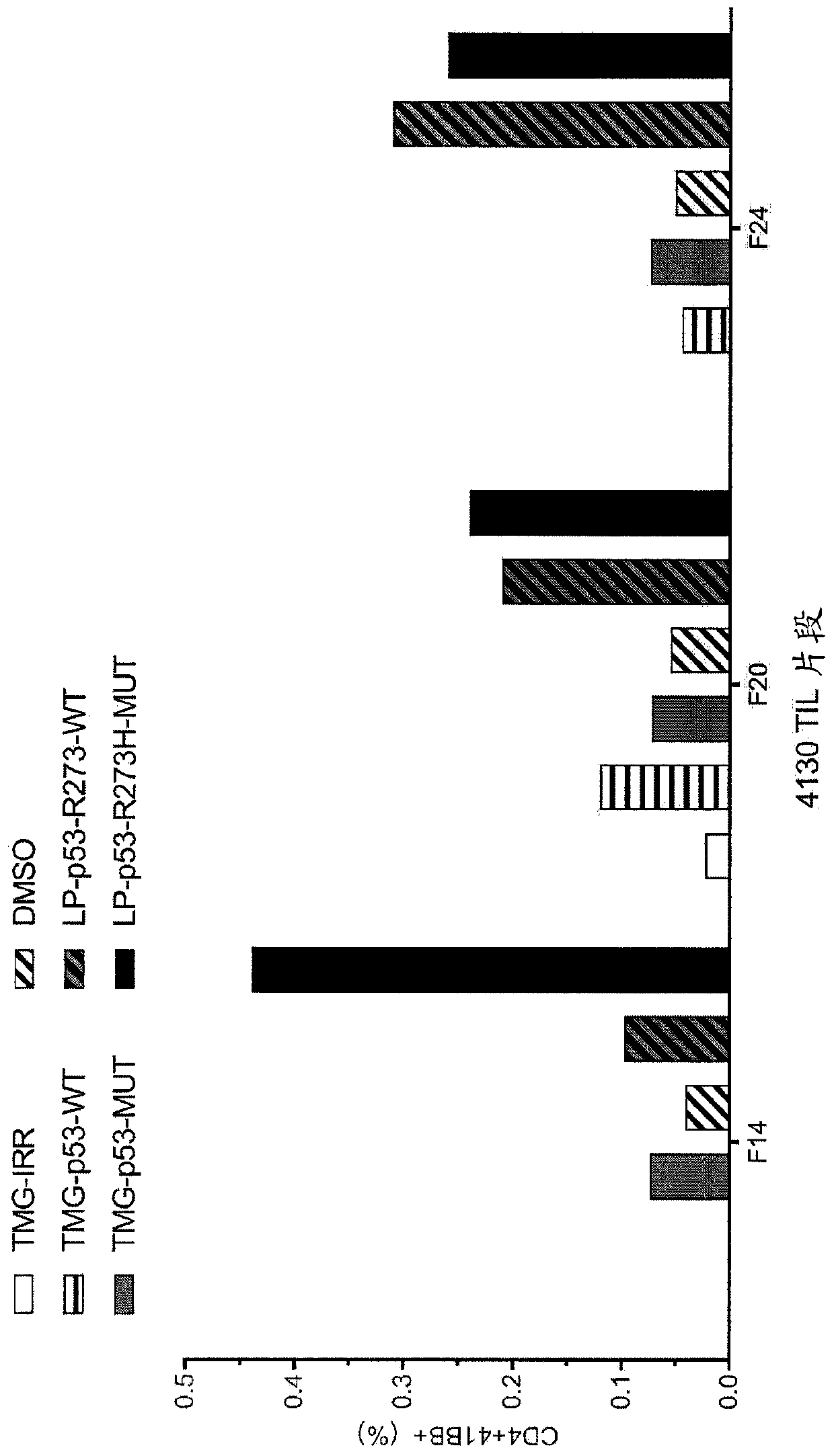
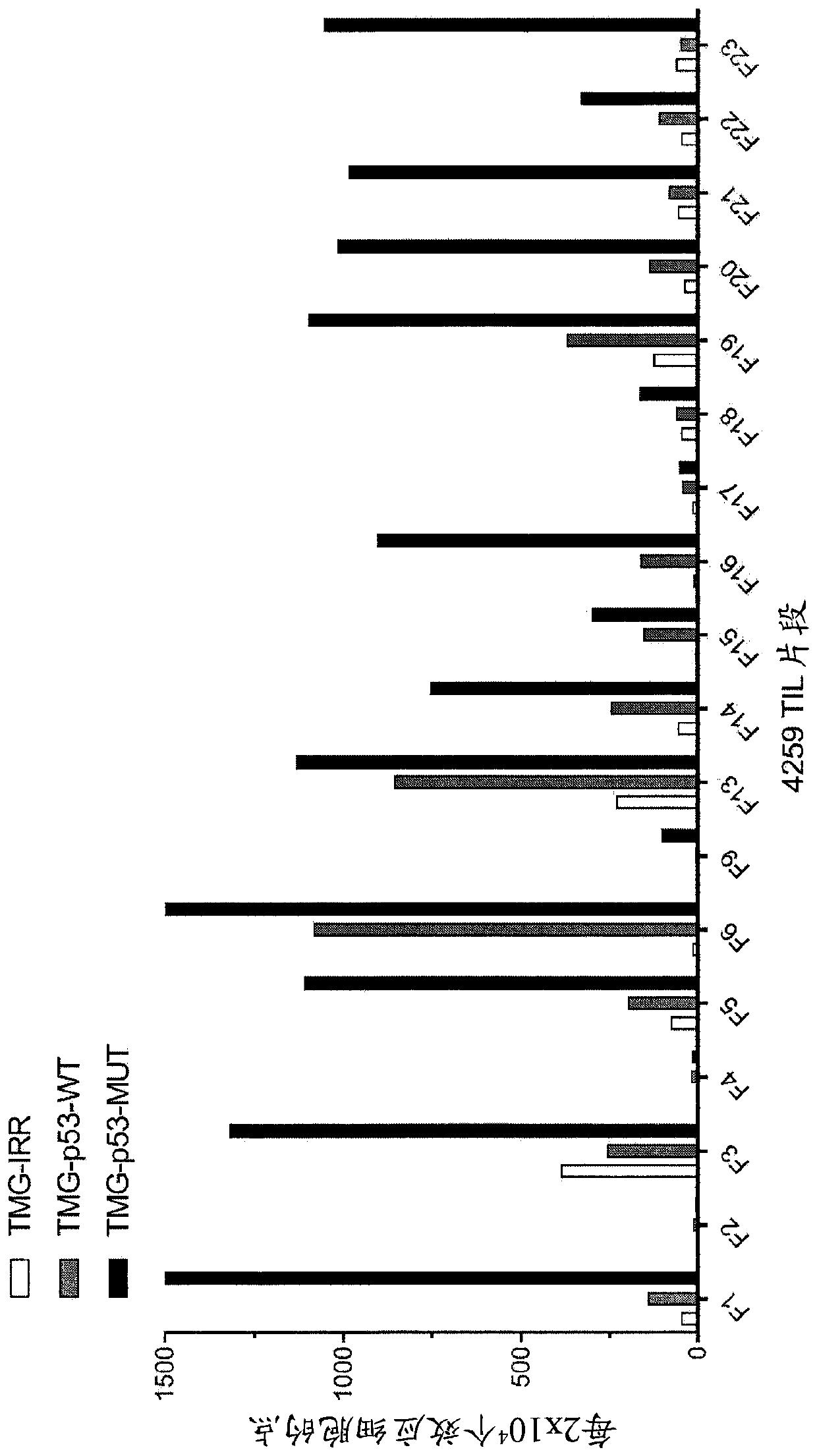
Methods of isolating T cells having antigenic specificity for P53 cancer-specific mutation
Disclosed are methods of isolating T cells having antigenic specificity for a mutated p53 amino acid sequence encoded by a cancer-specific p53 mutation, the method comprising: inducing autologous APCsof the patient to present the mutated p53 amino acid sequence; co-culturing autologous T cells of the patient with the autologous APCs that present the mutated p53 amino acid sequence; and selectingthe autologous T cells. Also disclosed are related methods of preparing a population of cells, populations of cells, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating or preventing cancer.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method for reconstructing colorectal cancer organoid immune microenvironment
PendingCN112143699AStrong lethalityIncrease lethalityCulture processCell culture supports/coatingOncologyErythroid cell
The invention provides a method for reconstructing a colorectal cancer organoid immune microenvironment. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a colorectal cancer organoid by using fresh colorectal cancer tissue; obtaining peripheral blood, then performing erythrocyte lysis, and separating lymphocytes by adopting a lymphocyte separating medium; enriching CD3 <+> T cells; and digesting the organoids into single cells, co-culturing the single cells and the cultured CD3 <+> T cells according to a ratio of 1: (10-30), and constructing the colorectal cancer patient-derived organoids immune microenvironment according to the steps. According to the method for reconstructing the colorectal cancer organoid immune microenvironment provided by the invention, fresh colorectal cancer tissue from the same individual and CD3 <+> T cells from peripheral blood are co-cultured to obtain the organoid immune microenvironment, it is, from cellular morphology and ATP values, shown that immune cells have an obvious killing effect on organoids of CRC patients, and an in-vitro experimental basis is provided for immunotherapy of clinical autologous T cell transfusion.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
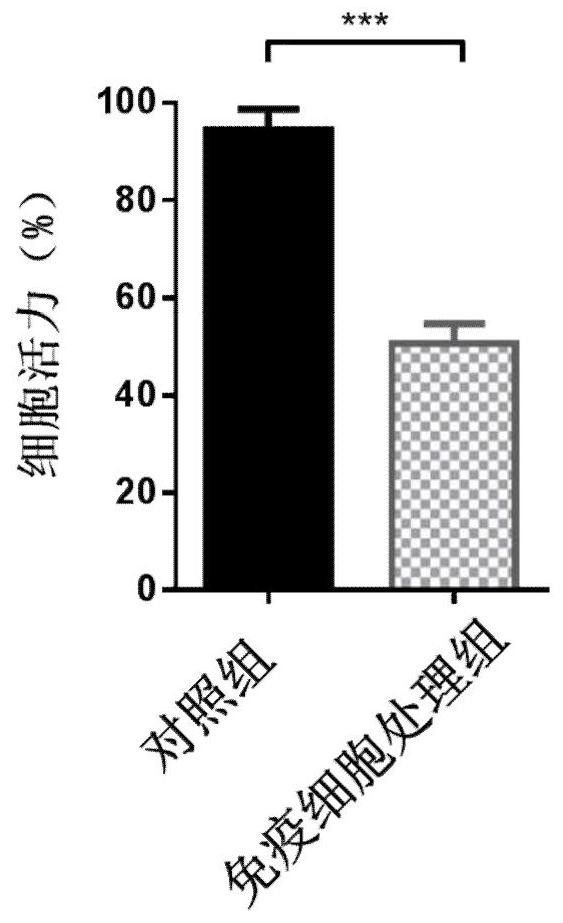
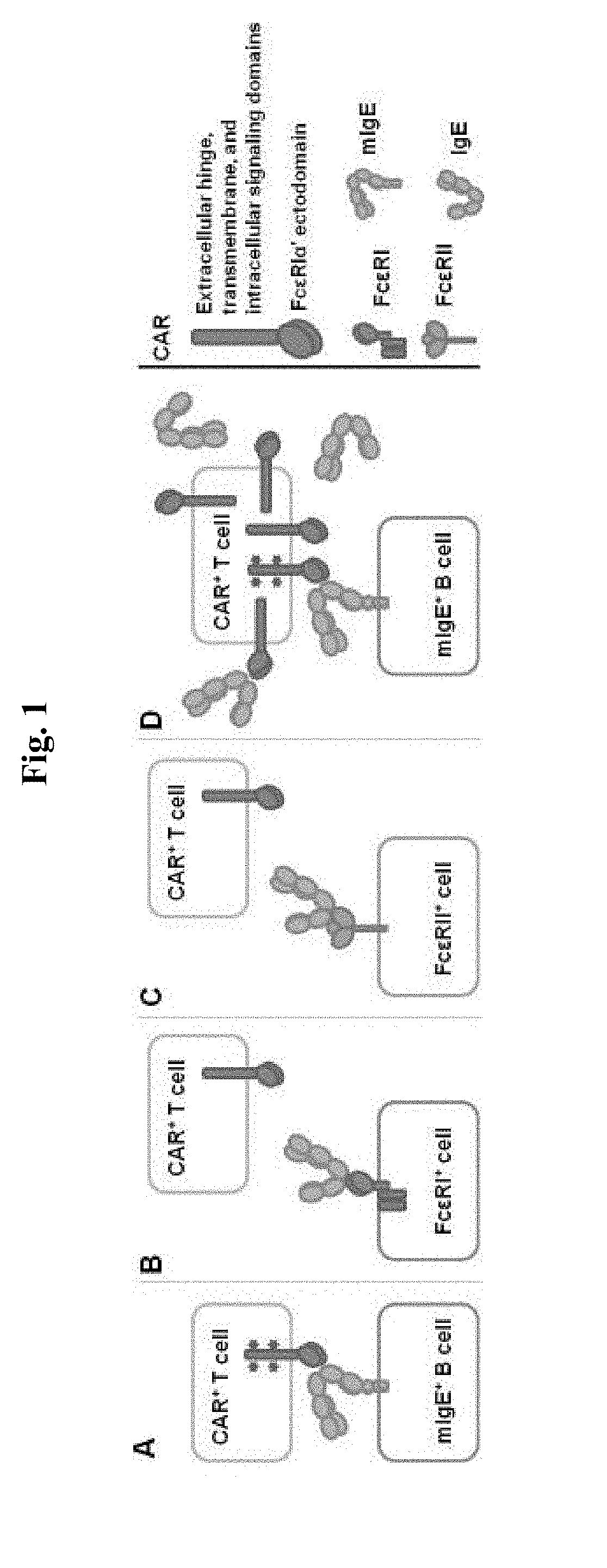
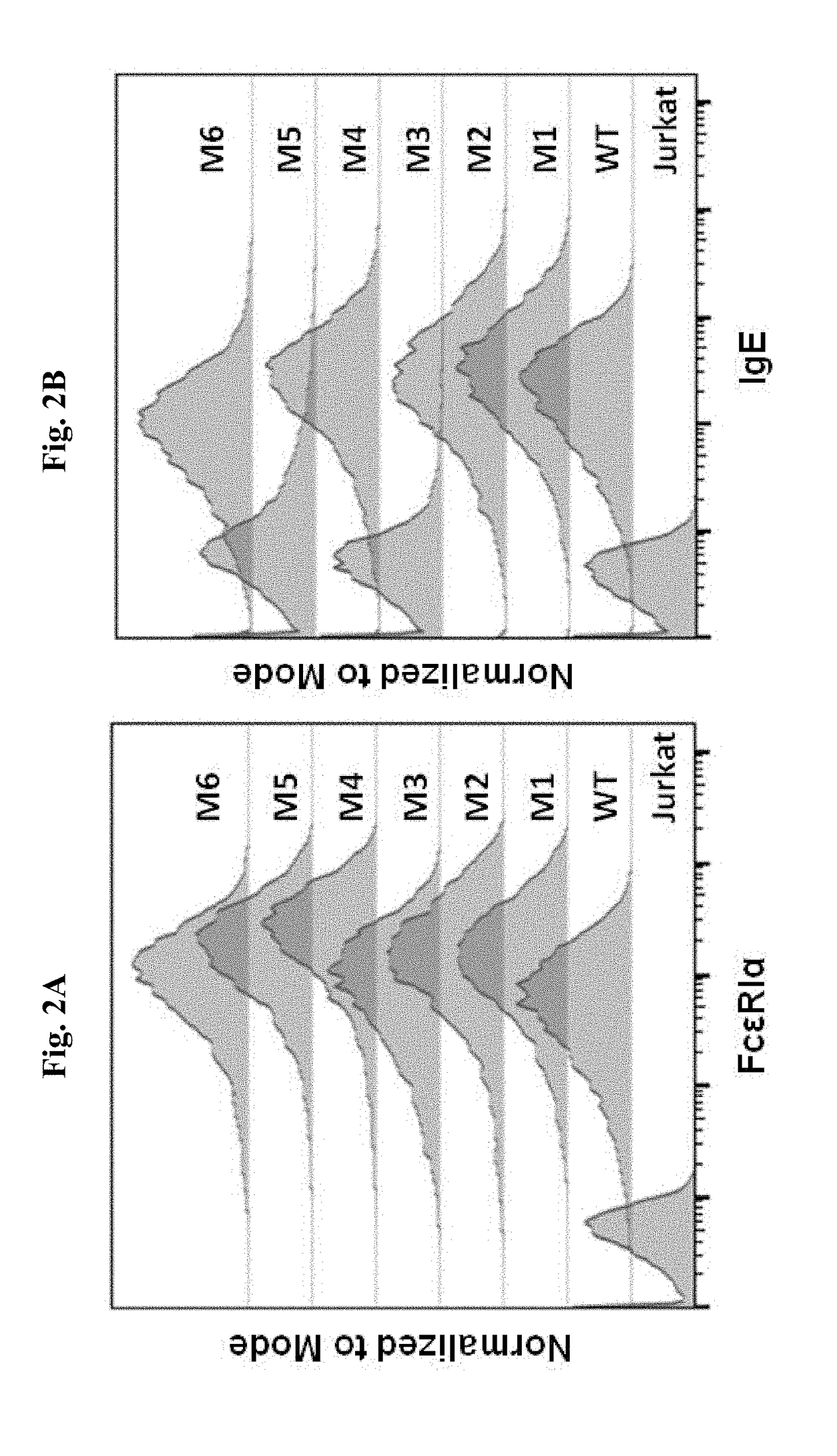
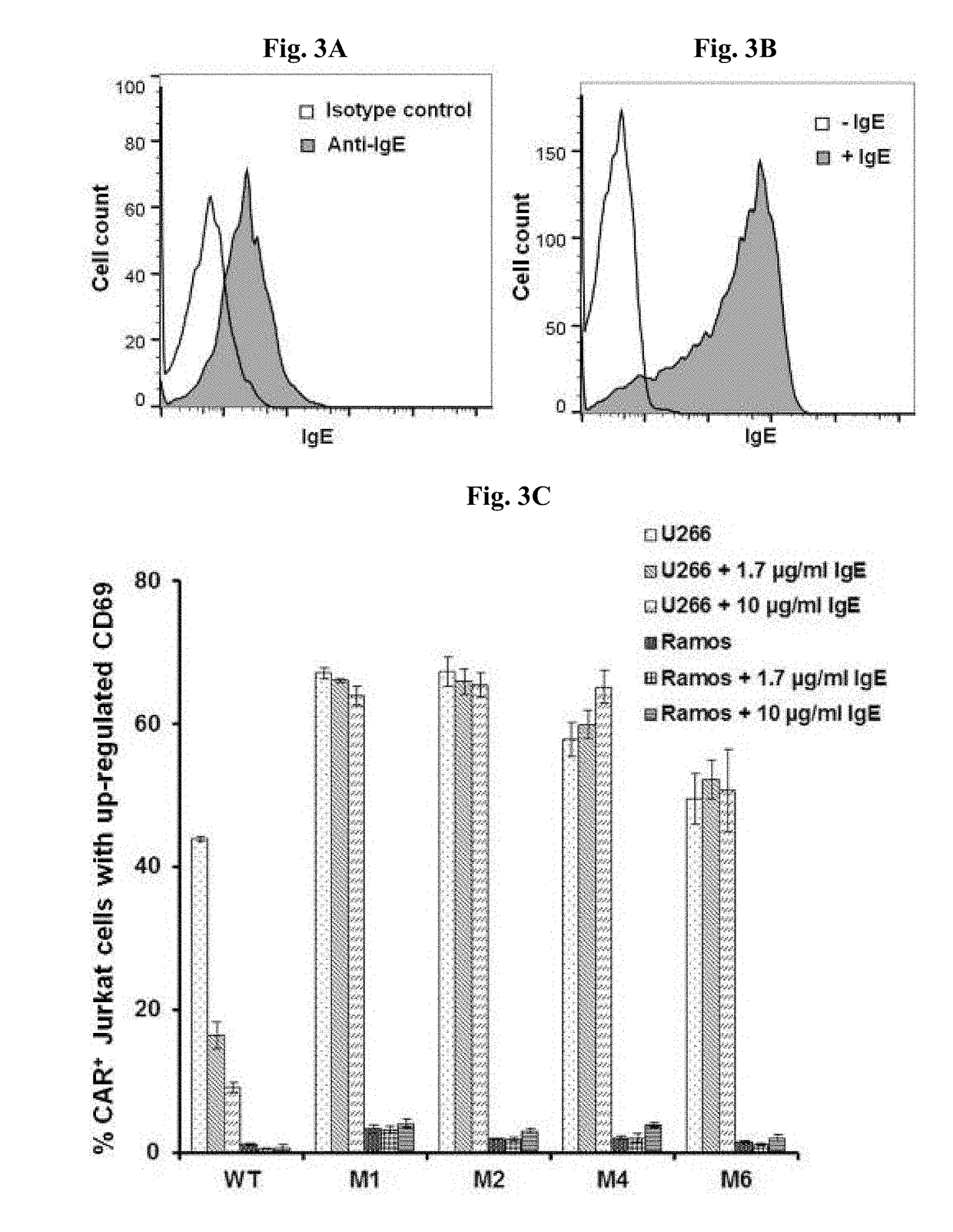
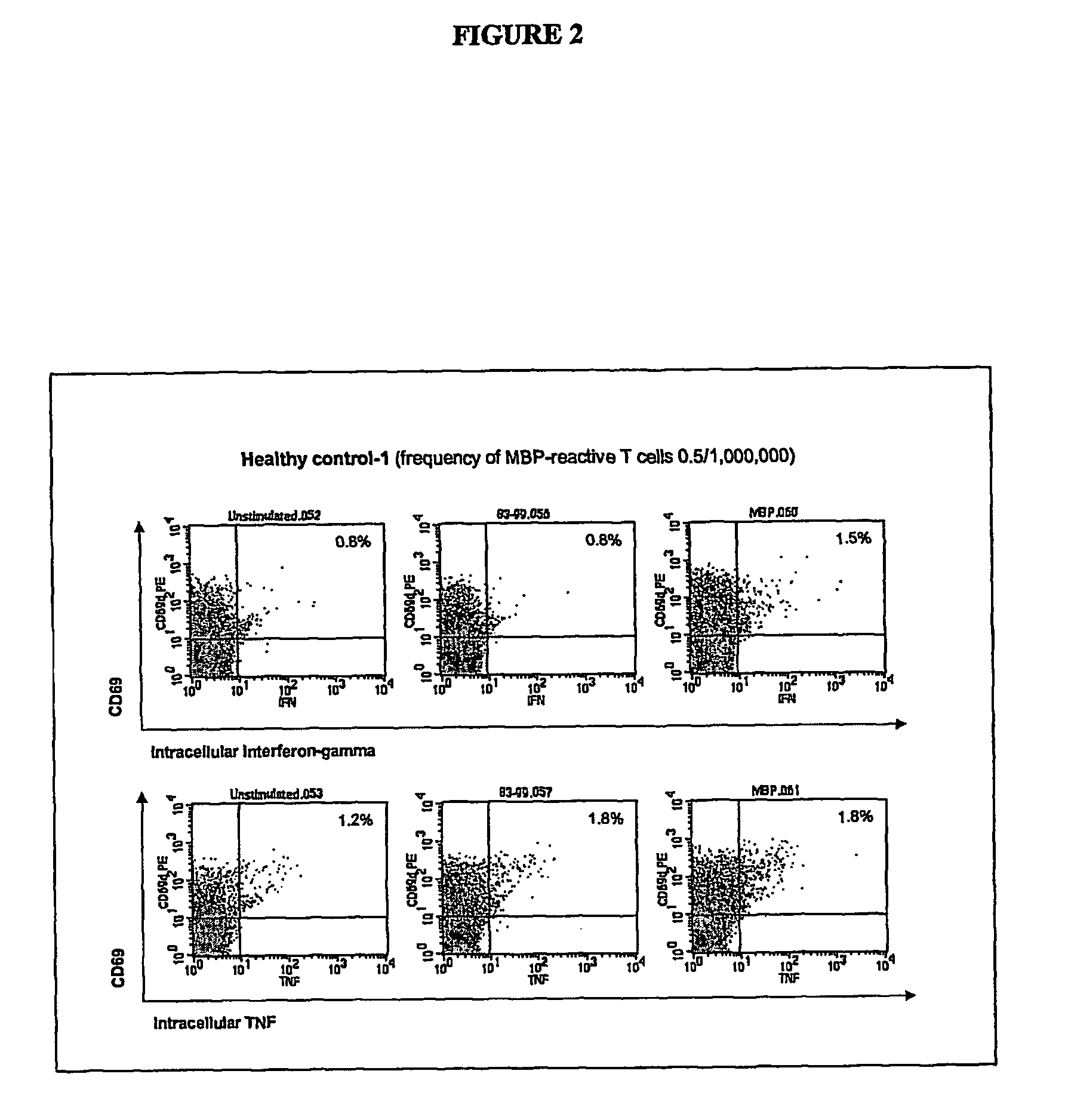
ADOPTIVE T-CELL THERAPY USING FceRI-BASED CHIMERIC ANTIGEN RECEPTORS FOR TREATING IgE-MEDIATED ALLERGIC DISEASES
ActiveUS20180193452A1Stimulate immune responsePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigenDisease
A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) contains a human FcεRIα extracellular domain or a mutant FcεRIα extracellular domain that has a reduced binding affinity for human IgE compared to wild type human FcεRIα extracellular domain. The CAR further contains an intracellular signaling domain comprising at least one immunoreceptor-based activation motif (ITAM). The CAR may further comprise a costimulatory signaling domain, such as an intracellular domain of at least one of the costimulatory molecules 4-1BB, CD27, CD28, CD134 or ICOS. T cells transduced with vectors encoding the CAR are used in CAR-based adoptive T-cell therapy for targeting IgE-expressing B cells and treating IgE-mediated allergic diseases.
Owner:THE NEMOURS FOUND
Method for enhancing production of genetically engineered autologous t cells
PendingUS20210324333A1High transduction efficiencyIncrease volumeImmunoglobulin superfamilyGenetically modified cellsAutologous T-cellsEngineered genetic
The present invention relates to a method for enhancing production of autologous genetically engineered T cells for use in cell therapy applications.
Owner:AMGEN INC
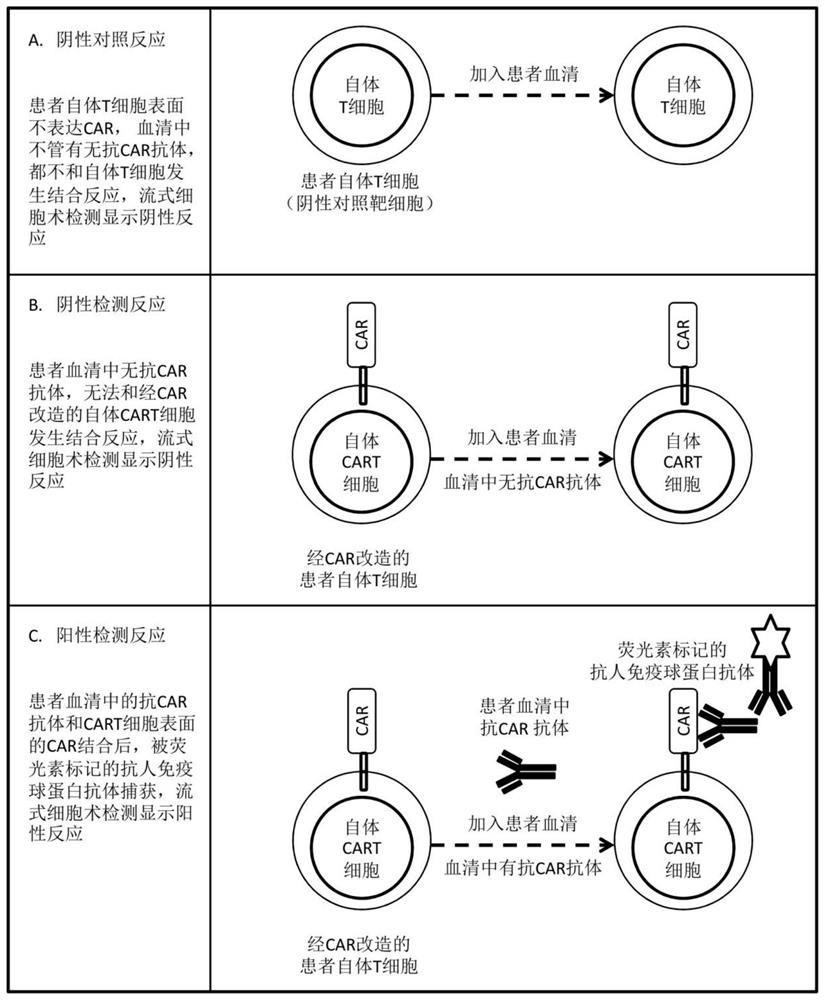
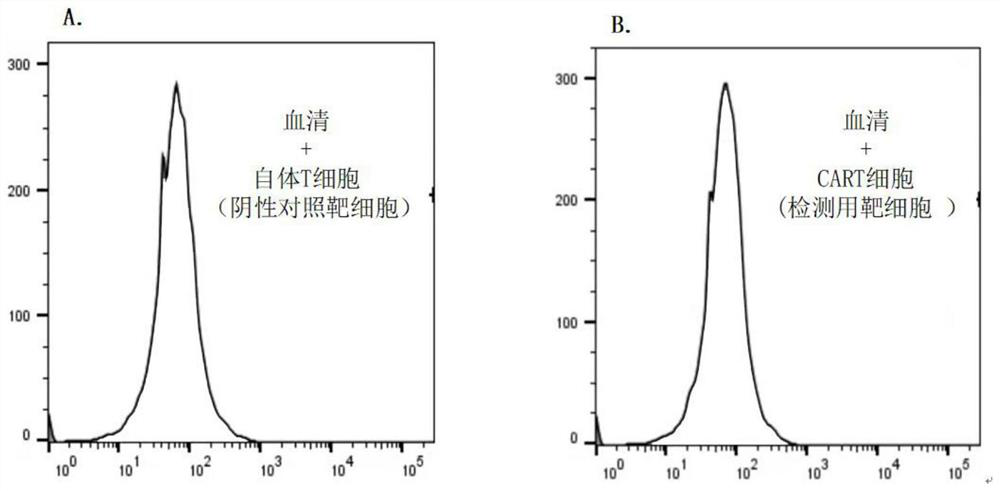
Method for detecting humoral immunogenicity of autologous CART cells
PendingCN113109572AAvoid treatment failureGood treatment effectBiological testingImmunoassaysAntiendomysial antibodiesTreatment effect
The invention provides a method for detecting the humoral immunogenicity of autologous CART cells. According to the invention, autologous T cells, which are not modified by CAR, of a testee are used as negative control target cells, autologous CART cells, which are modified by CAR, of the testee are used as target cells for detection, and the reactivity difference between the detected serum sample of the testee and the two target cells is determined through comparison through a flow cytometry, so that whether the anti-CAR antibody exists in the detected serum sample of the testee or not is judged; and the method not only can help a clinician to screen a CAR transformation method which is not easy to cause generation of an anti-CAR antibody for a patient before CART treatment is carried out on the patient, but also can be used as an etiological detection means for dynamically monitoring CART treatment failure possibly caused by induction of the anti-CAR antibody in CART cell treatment, so that CART cells play the maximum treatment effect.
Owner:苏州才博医学科技有限公司
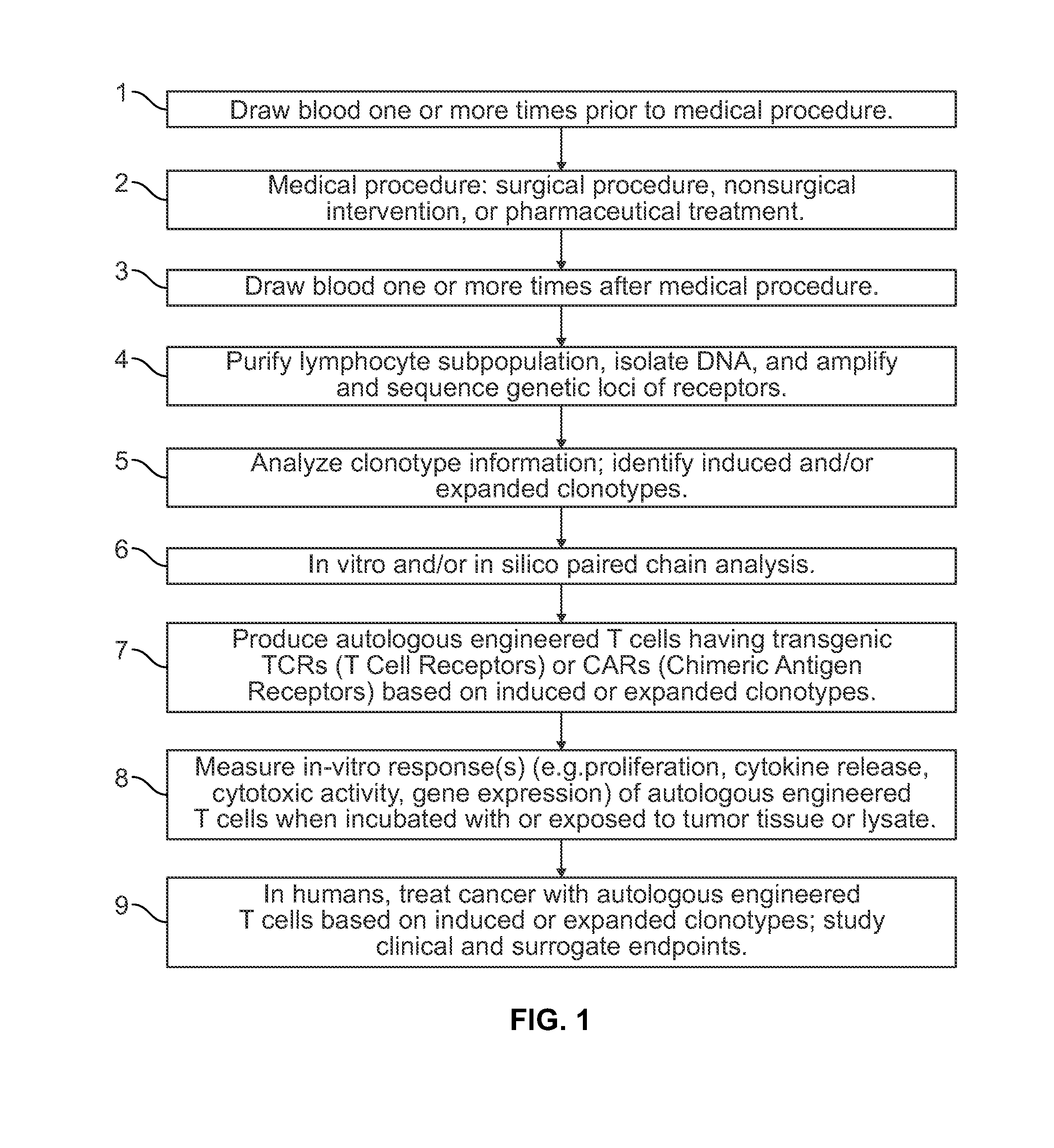
Method to augment immune system in response to disease or injury
InactiveUS20140065098A1Microbiological testing/measurementAntibody ingredientsImmune recognitionLymphocyte
In one example, the present invention comprises a deliberate insult or the recognition that an insult has occurred in a patient, which insult induces an immune recognition event. The T cell repertoire is catalogued from samples of the patient's lymphocytes from before and after the insult in order to detect and sequence the TCR alpha and beta loci of highly expanded T cell clonotypes. In some examples, this information is used in turn to generate autologous T cells or to create autologous genetically-engineered T cells, either of which include TCR sequences that target the individual's disease or injury, resulting in cure or amelioration of symptoms.
Owner:BARKEN ISRAEL +1
Isolation and identification of T cells
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
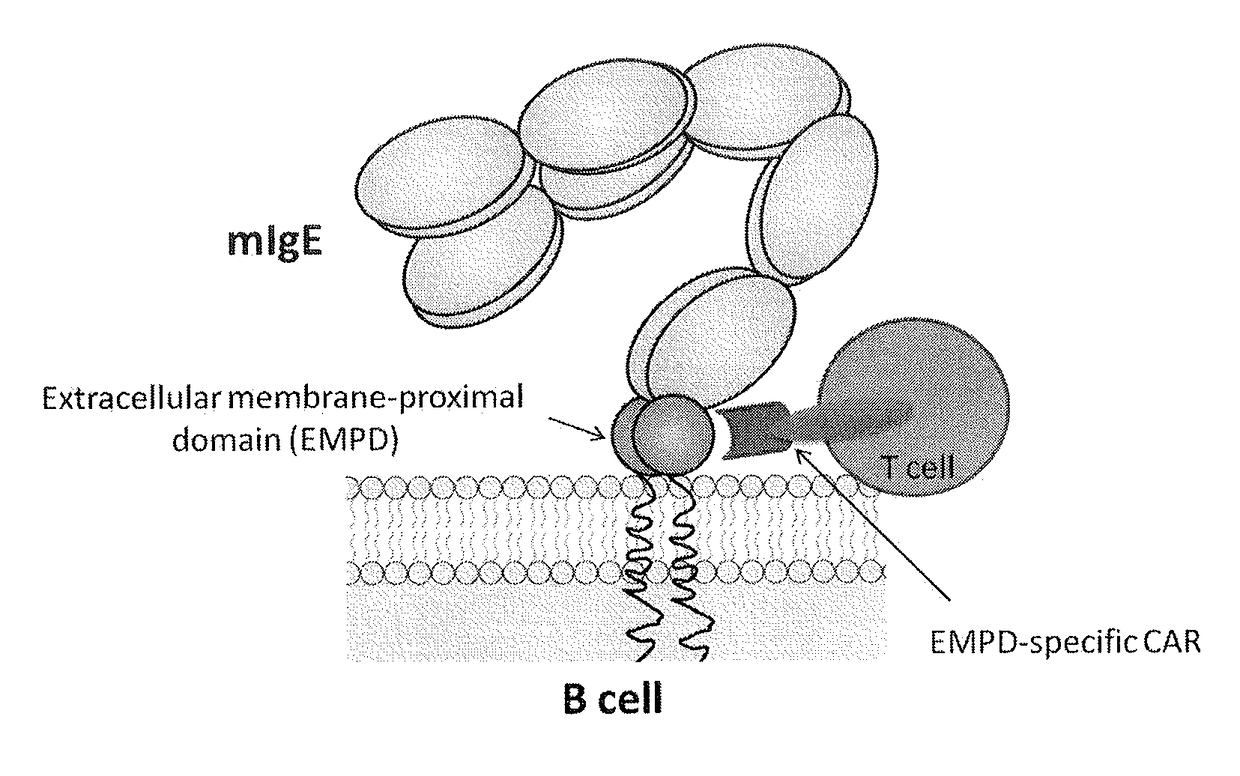
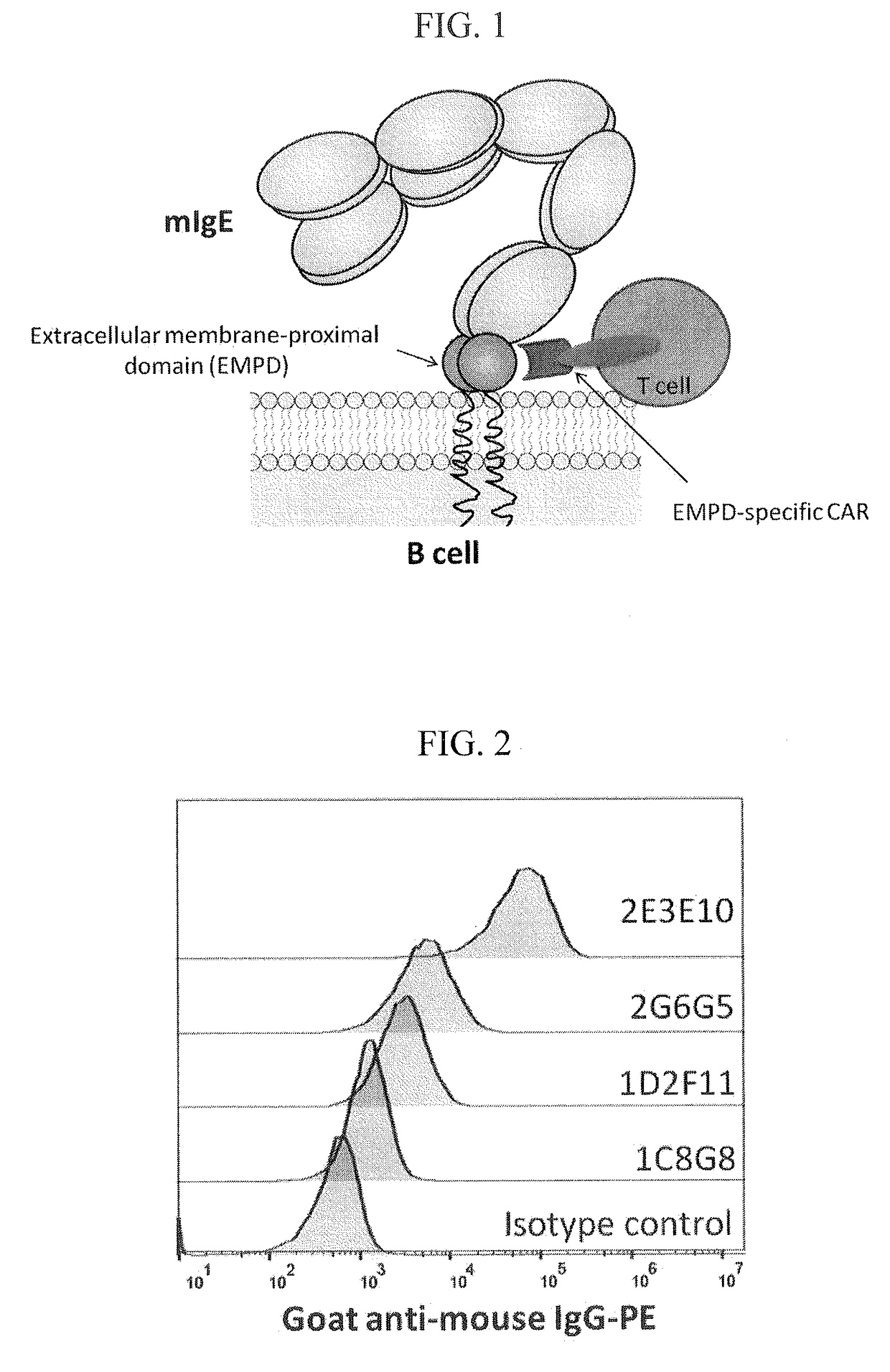
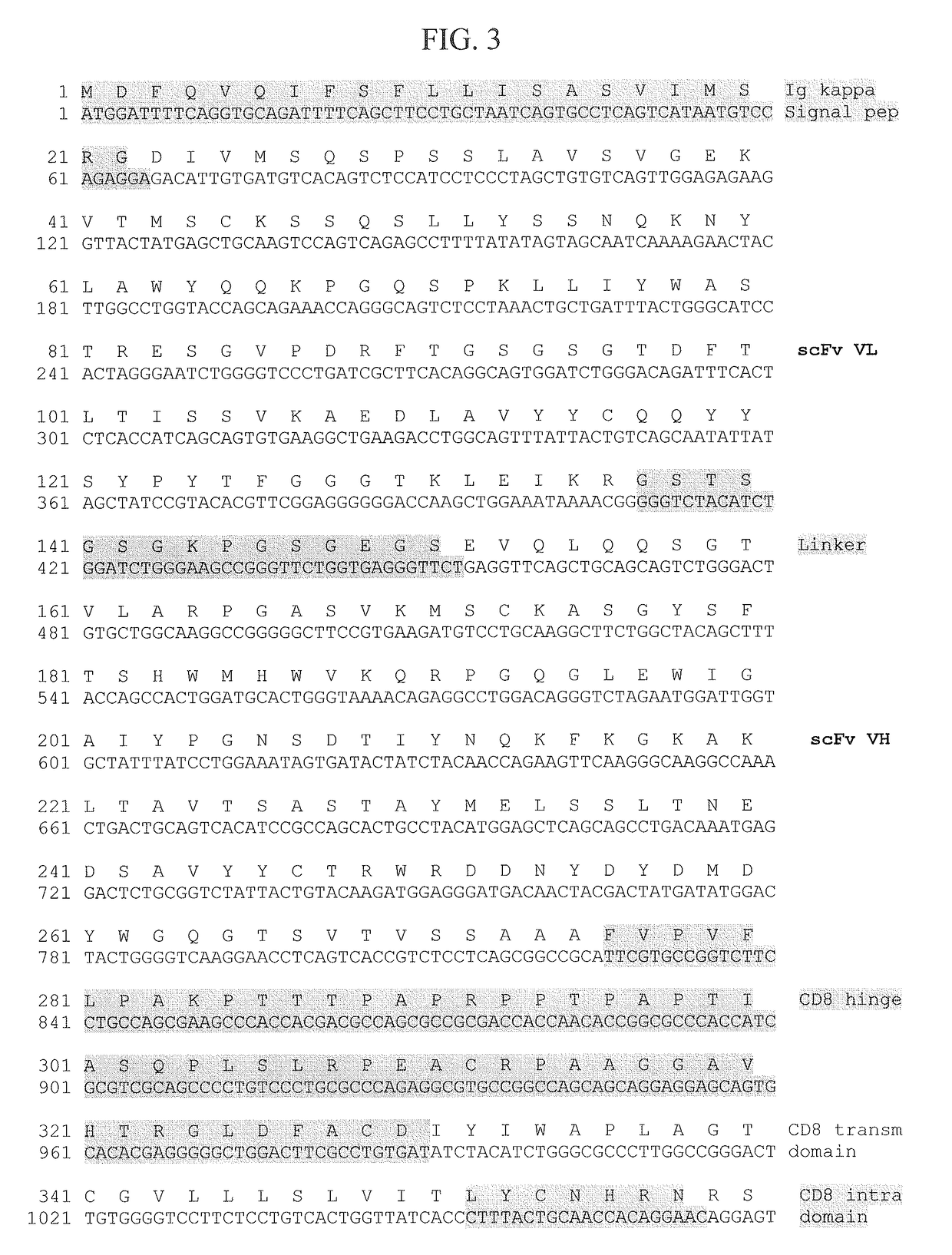
ADOPTIVE T-CELL THERAPY USING EMPD-SPECIFIC CHIMERIC ANTIGEN RECEPTORS FOR TREATING IgE-MEDIATED ALLERGIC DISEASES
ActiveUS20180022826A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenAntigen receptors
A chimeric antigen receptor specific for the extracellular membrane-proximal domain (EMPD) of membrane-bound IgE (mIgE) is provided. The EMPD-specific chimeric antigen receptor comprises an extracellular ligand binding domain capable of binding EMPD, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain that mediates T cell activation upon EMPD binding. Nucleic acids and vectors encoding the EMPD-specific chimeric antigen receptor are provided. T cells transduced with such vectors find use in chimeric antigen receptor-based adoptive T-cell therapy for targeting IgE-expressing B cells and treating IgE-mediated allergic diseases.
Owner:THE NEMOURS FOUND
Methods of isolating T cells having antigenic specificity for a cancer-specific mutation
ActiveUS10973894B2Increase the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestive systemCancer preventionCancer cell
Disclosed are methods of isolating T cells having antigenic specificity for a mutated amino acid sequence encoded by a cancer-specific mutation, the method comprising: identifying one or more genes in the nucleic acid of a cancer cell of a patient, each gene containing a cancer-specific mutation that encodes a mutated amino acid sequence; inducing autologous APCs of the patient to present the mutated amino acid sequence; co-culturing autologous T cells of the patient with the autologous APCs that present the mutated amino acid sequence; and selecting the autologous T cells. Also disclosed are related methods of preparing a population of cells, populations of cells, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating or preventing cancer.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Antibodies specific for cd38 and uses thereof
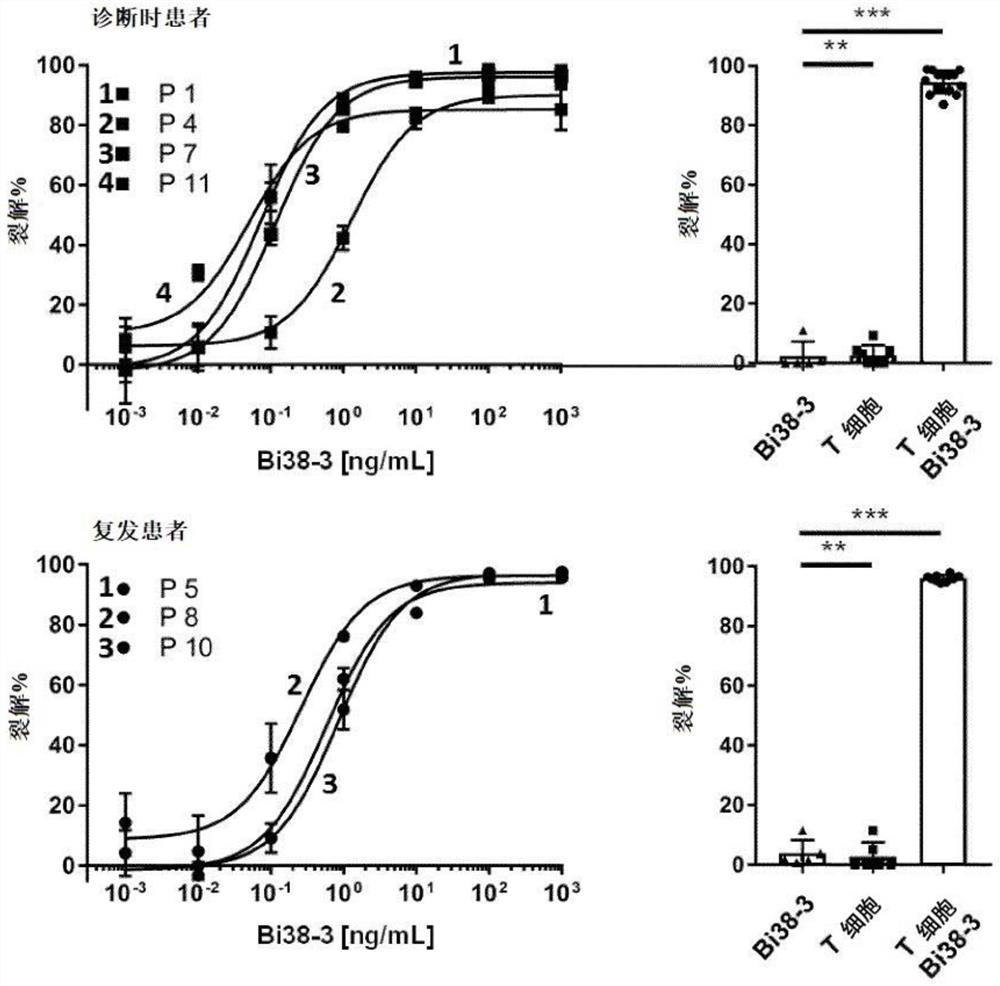
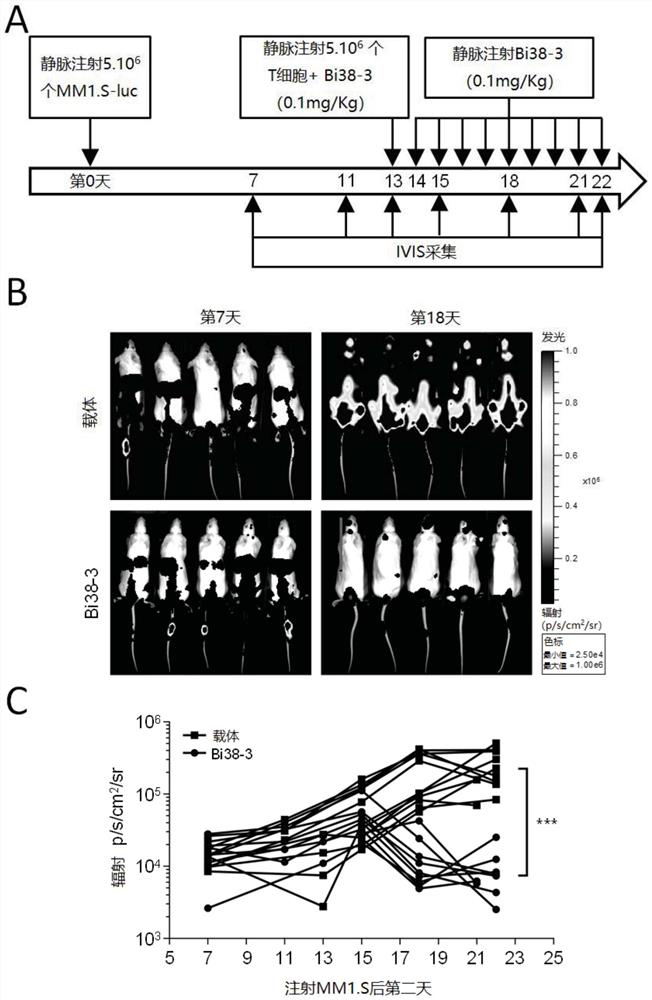
CD38 is also expressed in a variety of hematological malignancies, including multiple myeloma. In the present invention, the inventors have obtained a novel antibody against CD38, which can be suitable for the production of bispecific antibodies as well as CAR-T cell populations. In particular, the inventors report the development of Bi38-3, which is a novel bispecific T cell binding agent that targets CD38 on MM cells and establishes cytotoxic T cells through CD3 epsilon. The Bi38-3 lacks the Fc region of the natural mAb, while the Fc region contributes to the resistance process, but elicits T cell proliferation, release of cytokines and lysis of CD38 positive MM cells in vitro. Similarly, Bi38-3 induces autologous T cells to eliminate tumor plasma cells isolated from MM patients at the time of diagnosis and recurrence. The cytotoxicity caused by Bi38-3 is only limited to cells expressing high-level CD38, and the integrity of T, B and NK lymphocytes is maintained in vitro. More importantly, the Bi38-3 can be used for rapidly reducing tumor cells in an MM1. S xenotransplantation mouse model of human MM. In conclusion, the result shows that the antibody is an effective reagent for specifically removing CD38 positive malignant cells, does not obviously influence CD38 low-expression cells, and is a novel immunotherapy tool expected to treat hematological malignancies, especially multiple myeloma.
Owner:INSERM法国国家健康医学研究院 +1
Methods of production of autologous t cells for treatment of b-cell malignancies and other cancers and compositions thereof
The present invention relates to the field of T cells and provides methods of producing autologous T cells and compositions thereof for the treatment of B-cell malignancies and other cancers. A method of making T cells expressing a cell surface receptor that recognizes a specific antigen moiety on the surface of a target cell, the method comprising enriching a population of lymphocytes; stimulating the population of lymphocytes with one or more T cell stimulators to produce a population of activated T cells, the stimulation being performed in a closed system using a serum-free culture medium; transduction of the activated population of T cells with a viral vector comprising a nucleic acid molecule encoding a cell surface receptor, producing a transduction population of T cells using single cycle transduction, the transduction being performed in a closed system using a serum-free culture medium; the transduced population of T cells is expanded for a predetermined time resulting in an engineered population of T cells, the expansion being performed in a closed system using a serum-free culture medium. The methods and processes described herein can be completed in significantly shorter time.
Owner:凯德药业公司 +1
Anti-wt1/hla bi-specific antibody
ActiveCN106414500AHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMyeloid leukemiaSpecific antibody
Disclosed herein is a bi-specific form of a T cell receptor mimic (TCRm) mAb with reactivity to human immune effector cell antigen and a WT1 peptide / HLA-A epitope. This antibody selectively bound to leukemias and solid tumor cells expressing WT1 and HLA-A as well as activated resting human T cells to release interferon-(IFN-gamma) and to kill the target cancer cells in vitro. Importantly, the antibody mediated autologous T cell proliferation and directed potent cytotoxicity against fresh ovarian cancer cells. Therapeutic activity in vivo of the antibody was demonstrated in NOD SCID SCID Yc*(NSG) mice with three different human cancers expressing WT1 / HLA-A2 including disseminated Ph+ acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), disseminated acute myeloid leukemia, and peritoneal mesothelioma. In both of the leukemia xenograft models, mice that received the antibody and T cells also showed longer survival and delayed limb paralysis. Also provided are methods for stimulating a primary T cell response comprising stimulating cytotoxic T cells against a first tumor antigen and a secondary T cell response comprising stimulating effector T cells and / or memory T cells against a first tumor antigen and / or against a second tumor antigen using the bi-specific antibodies described herein.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT +1
Methods of treatment using a genetically modified autologous t cell immunotherapy
InactiveUS20210205363A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAutologous T-cellsTreatment use
Owner:ADOC SSF LLC
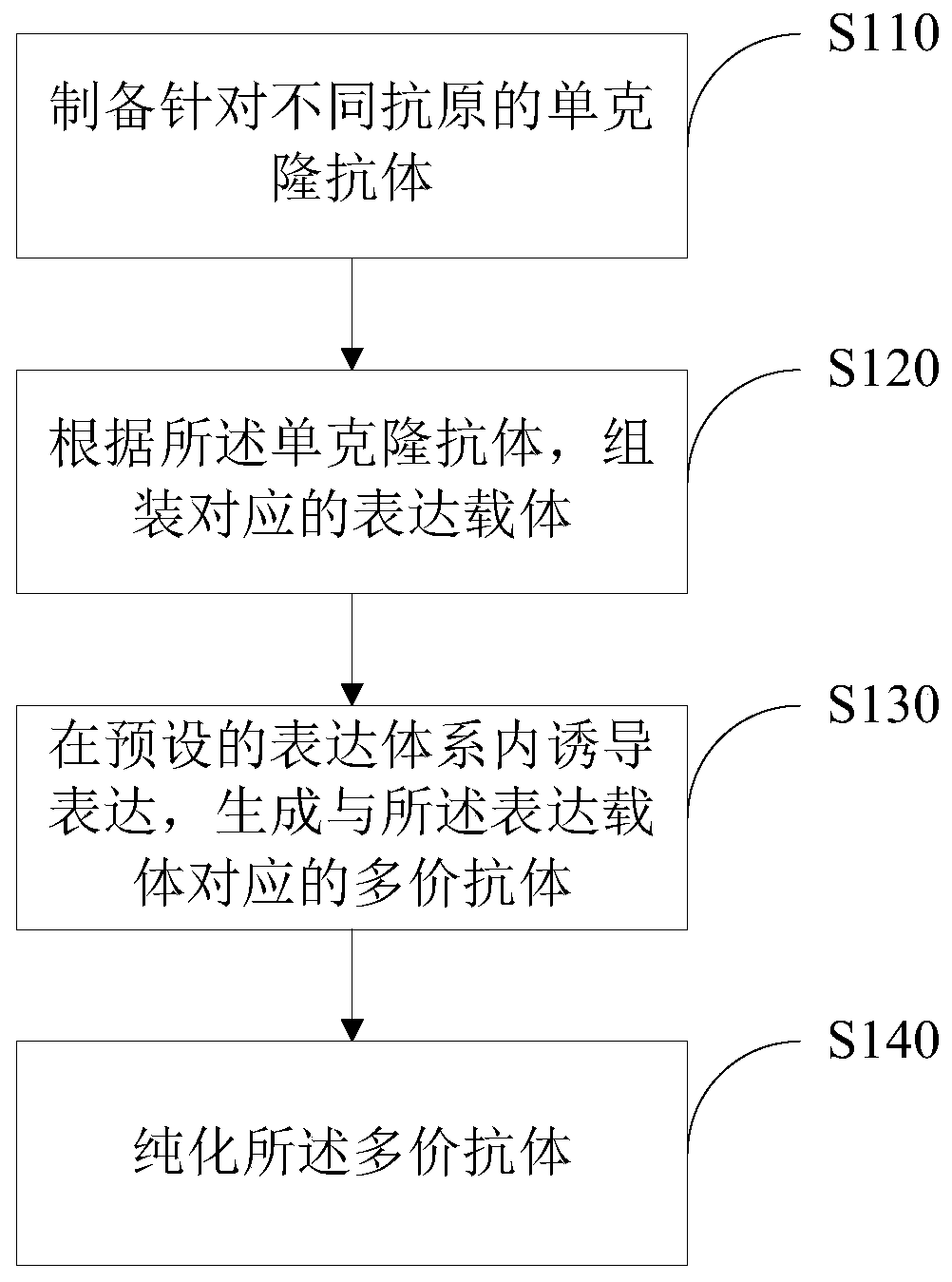
Polyvalent antibody and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110698563ABroad-spectrumEliminate the risk of infectionHybrid immunoglobulinsHybrid peptidesCancer cellBinding site
The embodiment of the invention discloses a polyvalent antibody and a preparation method thereof. The polyvalent antibody includes a plurality of antigen-binding sites, wherein the antigen-binding sites are connected to a human-source antibody core fragment; and the antigen-binding sites at least include antigen-binding sites specifically bound with tumor cells and antigen-binding sites specifically bound with immunocyte. The polyvalent antibody is obtained through reformation in a genetic engineering manner, and can enable the immunocyte to be bound to the cancer cells to arouse attack of theimmunocyte on the cancer cells. Compared with a conventional CAR-T treatment method, a treatment method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the polyvalent antibody has broad spectrum,does not depend on autologous T cells of patients, and can be in mass production. In addition, waiting time does not exist, and the polyvalent antibody can be immediately prepared for use. Relying ona mature antibody production technology, risk infected by other pathogens can be eliminated in the manner of GMP and the like, and the polyvalent antibody has lower treatment fees.
Owner:深圳容金科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com