Methods for producing autologous t cells useful to treat b cell malignancies and other cancers and compositions thereof
A cell population and cell technology, applied in the direction of receptors/cell surface antigens/cell surface determinants, cell culture active agents, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems that are difficult to commercially apply and time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
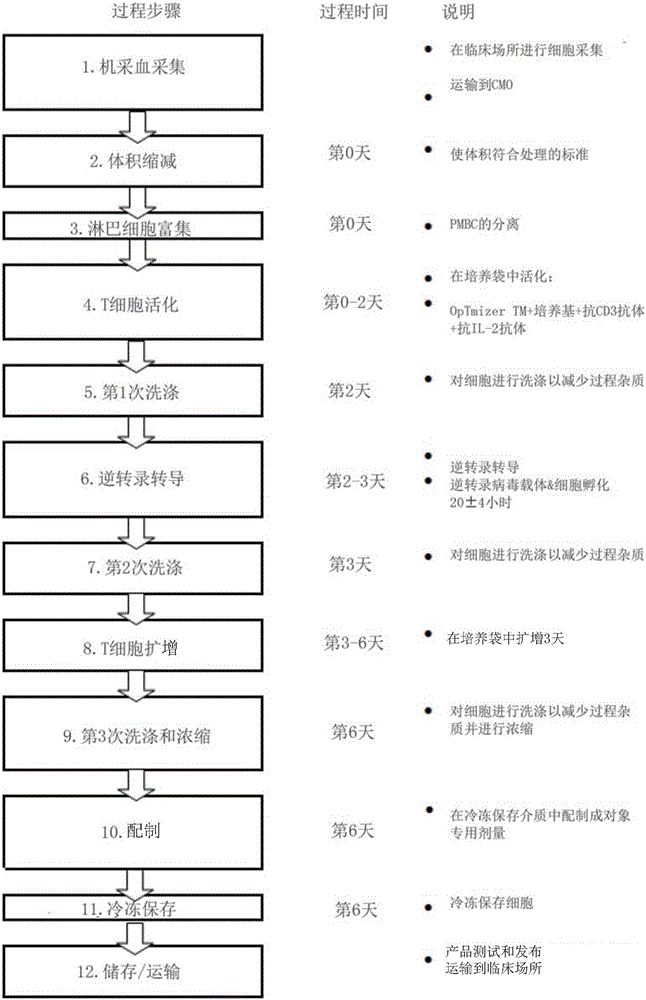
[0066] Example 1: Preparation of ex vivo genetically modified autologous cells
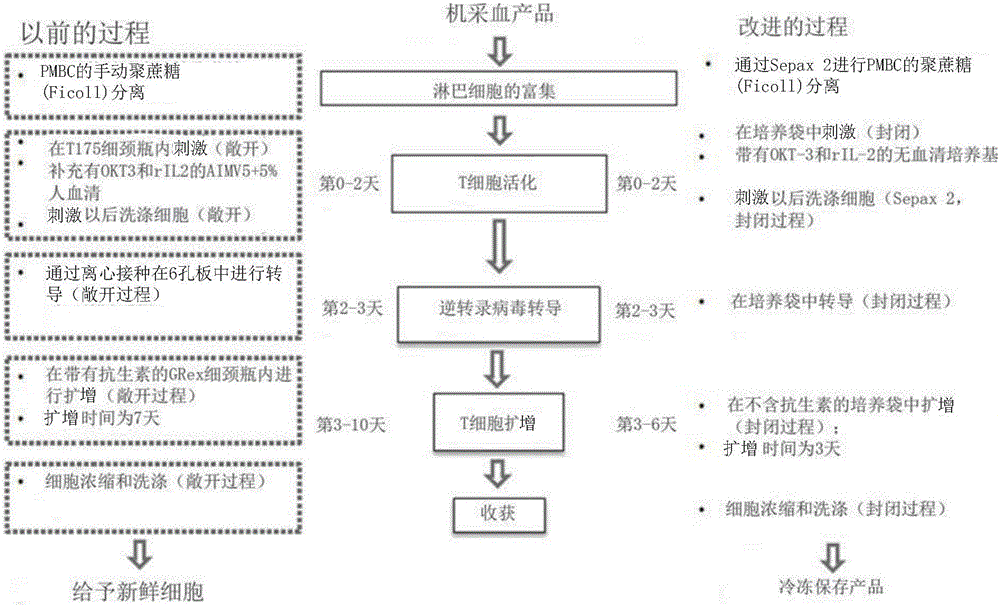
[0067] figure 1 A schematic diagram of an exemplary T cell production process ("improved" process) according to one embodiment is provided. This improved process also includes improvements to the traditionally used process for producing T cells (the "previous" process) (see the figure 2 ), while maintaining T cell product characteristics. Specifically, the improved process is a closed process that surprisingly avoids the use of serum. Moreover, this improved process uses a single cycle of transduction to produce a population of transduced T cells. Furthermore, cells subjected to a total expansion time of 6 days showed a more naïve immunophenotypic profile when using this procedure compared to cells subjected to an expansion time of 10 days. This process enables reproducible production of products with target numbers of transduced T cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) such as CD...
Embodiment 2
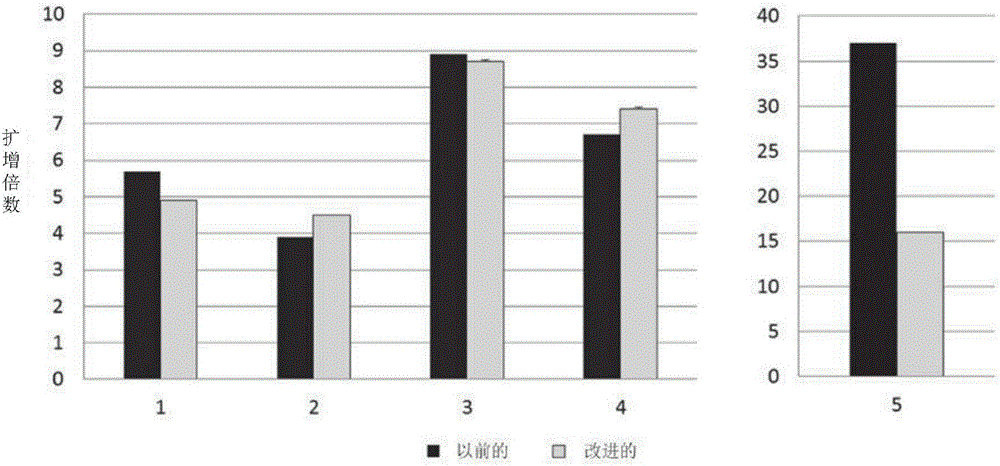
[0081] Example 2: Growth performance of T cells expanded in cell culture bags
[0082]Embodiments described herein provide a method for efficient production of engineered autologous T cell therapy within 6 days. The following improvements have been achieved over the existing technology: the process time has been shortened to 6 days instead of the 24, 14 or 10 days previously used (this reduces the number of tests (including RCR tests) required for product release); T cell products, including a higher proportion of naive T cells, achieve increased potency and effectiveness; larger numbers of cells can be used to initiate culture to compensate for shorter manufacturing times; closed systems are used to perform the methods described in the present invention identification of serum-free culture conditions that support T cell growth; single-cycle retroviral transduction in culture bags; cell culture activation and expansion in culture bags rather than vials; The product. These im...
Embodiment 3
[0102] Example 3: Development of transduction conditions in a closed system
[0103] Previously, transduction of PBMCs was performed in 6-well plates treated with non-tissue culture. These plates were incubated at 2-8°C with 10 μg / mL of Coating was performed overnight, or at room temperature for 2 hours. After incubation, remove Plates were blocked with 2.5% HSA for 30 minutes, followed by washing with HBSS+5mM HEPES. In the plate-based process, retroviral vectors are applied to coated wells and spun down in a centrifuge, followed by removal of approximately 75% of the viral supernatant, followed by addition of cells by spinnoculation for transduction .
[0104]In the present invention, three studies were performed to optimize the method for transducing PBMC in closed cell culture bags concentrations and to determine whether HSA washing and virus supernatant removal affected transduction. The first experiment was in Origen PermaLife TM PL07 culture bag, in which cel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com