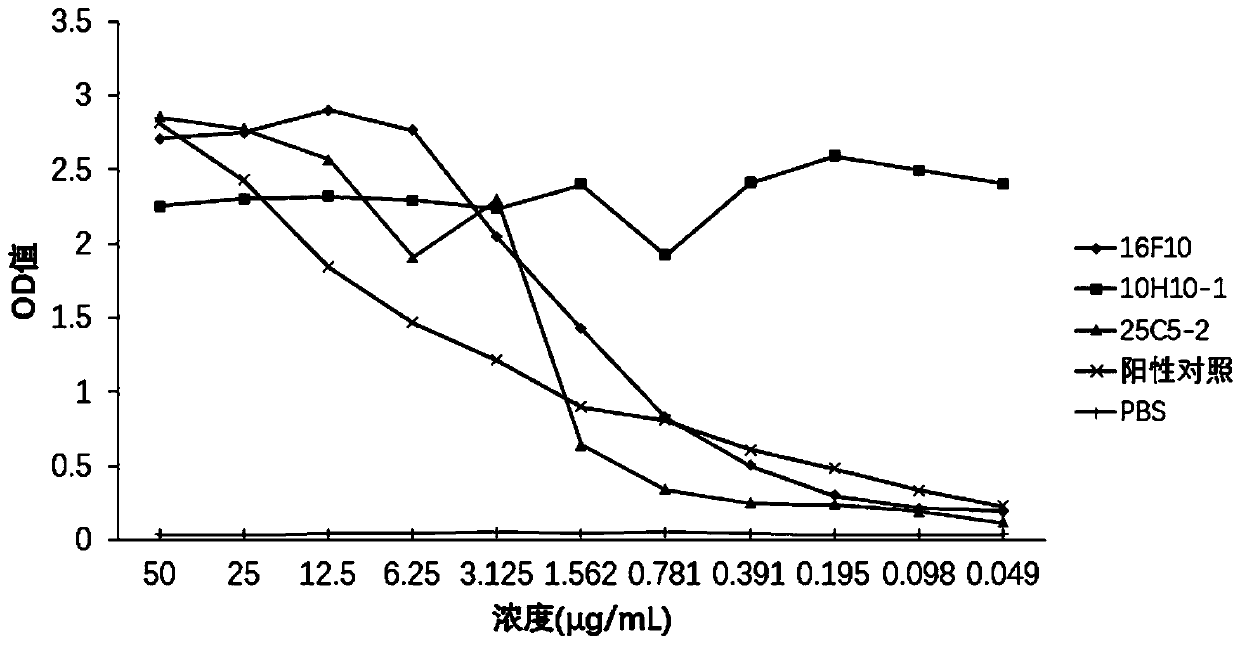
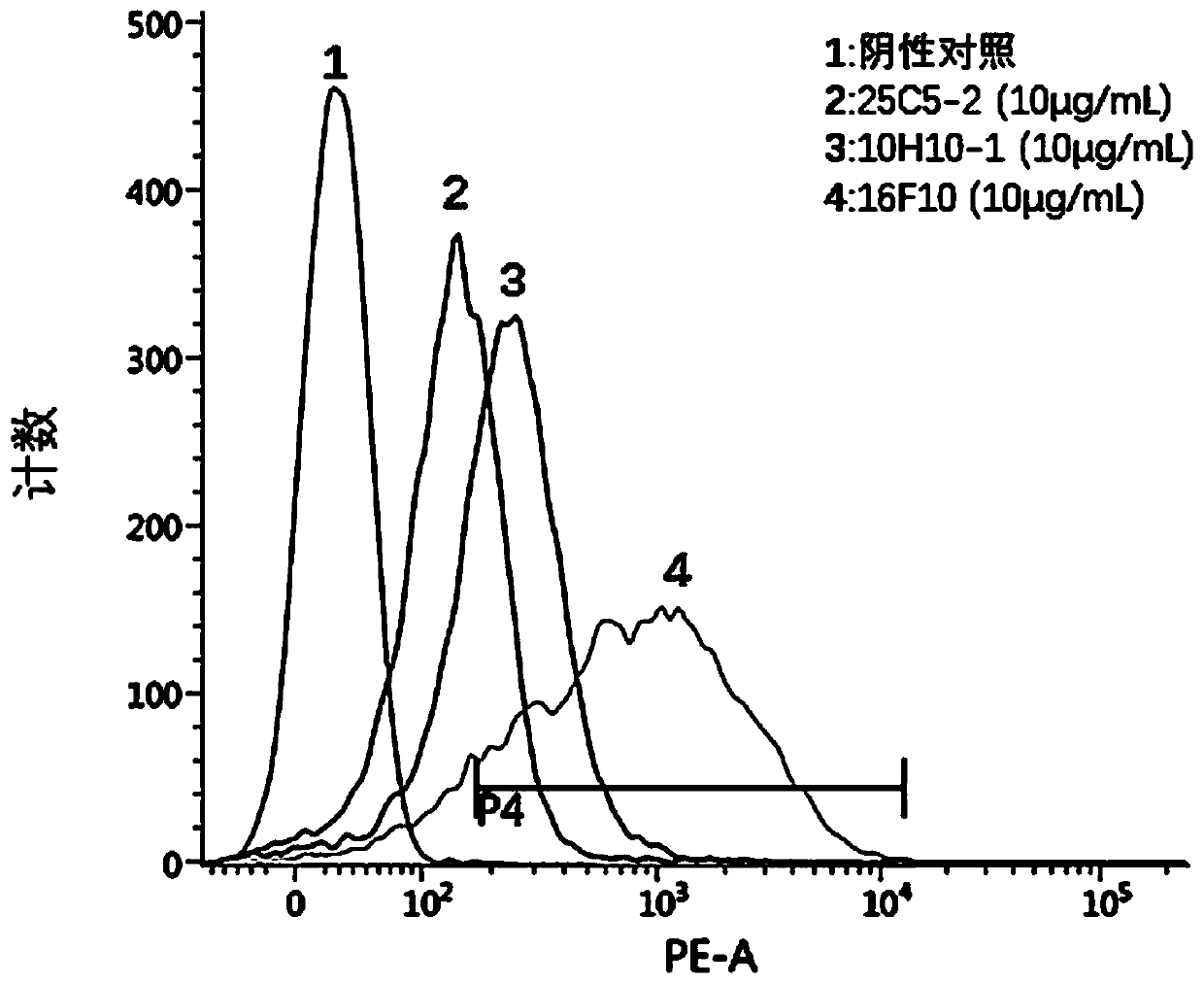
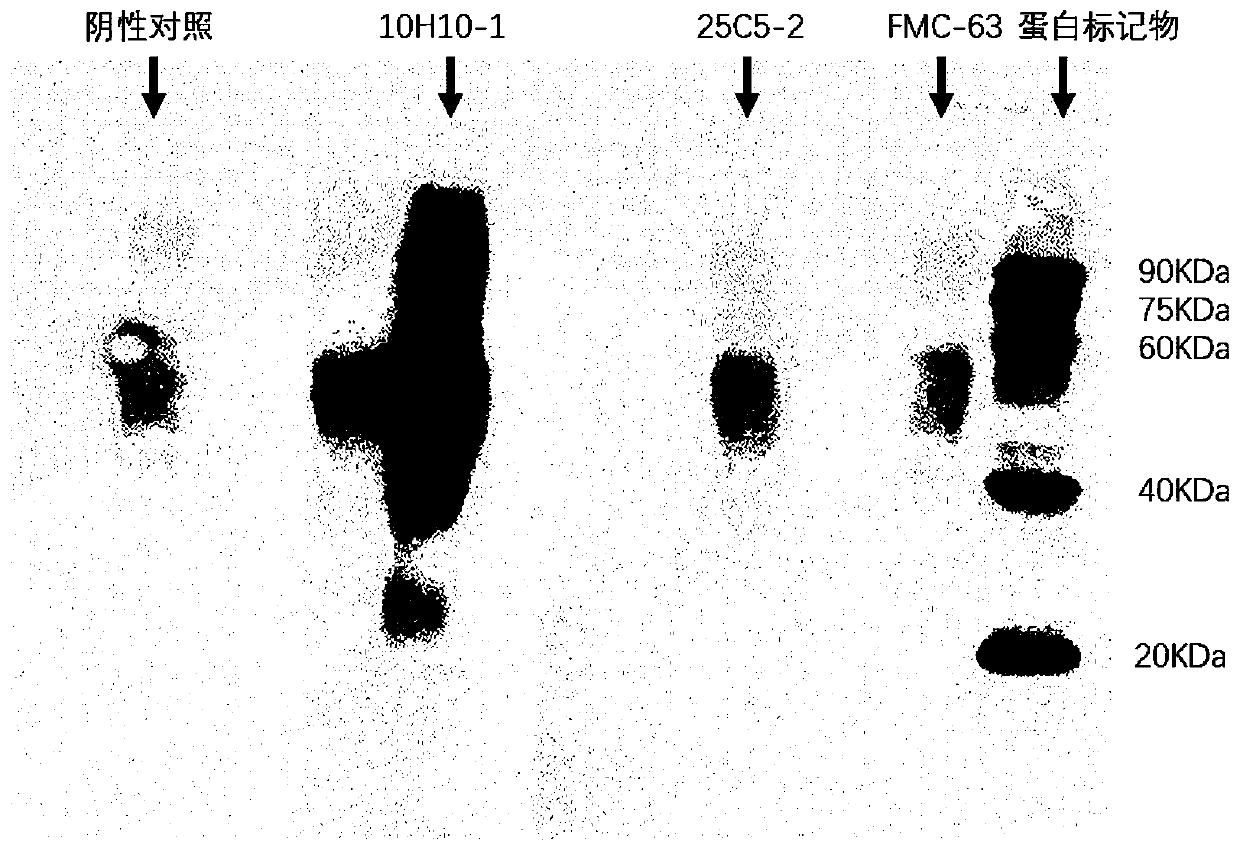
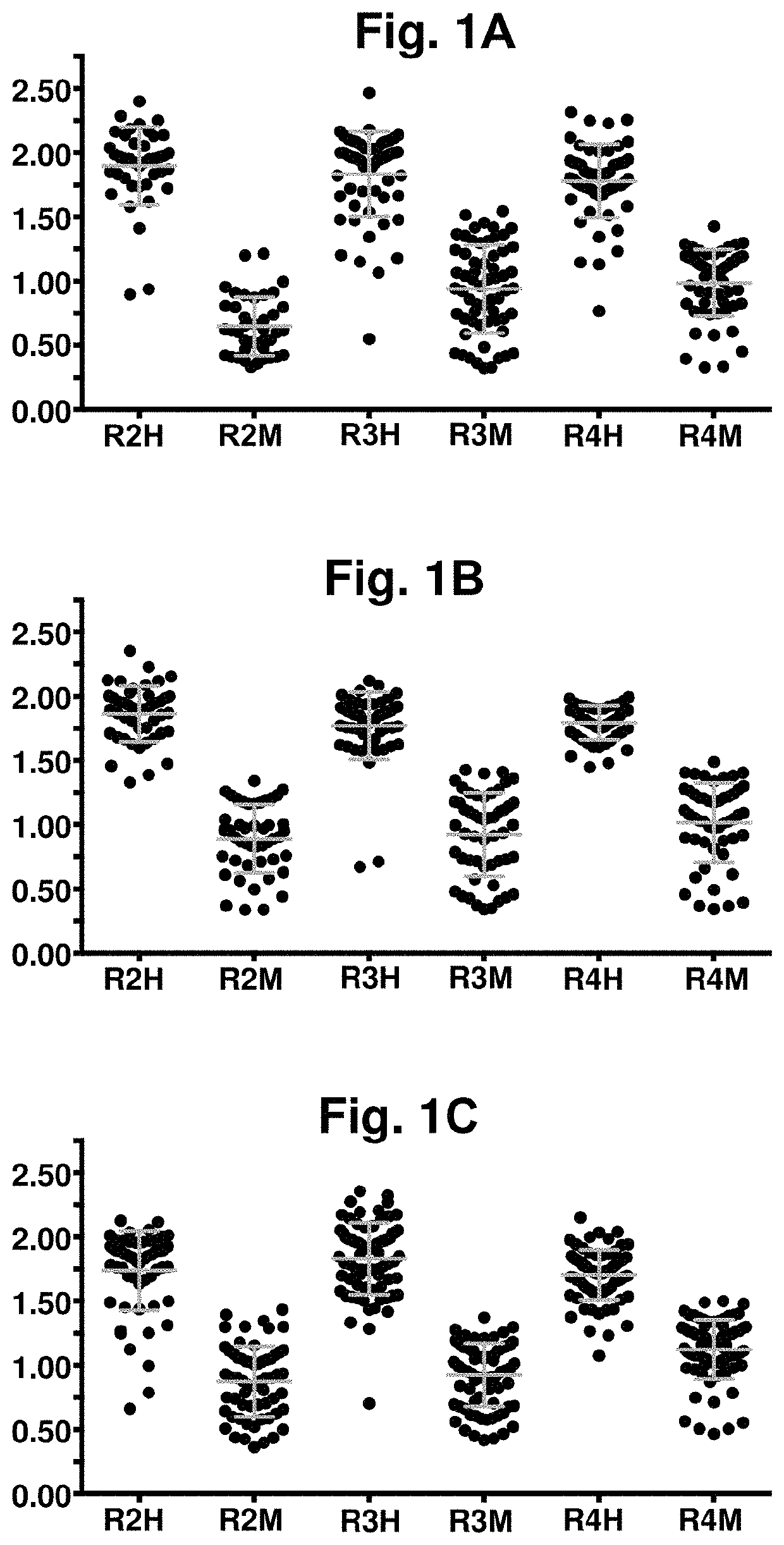
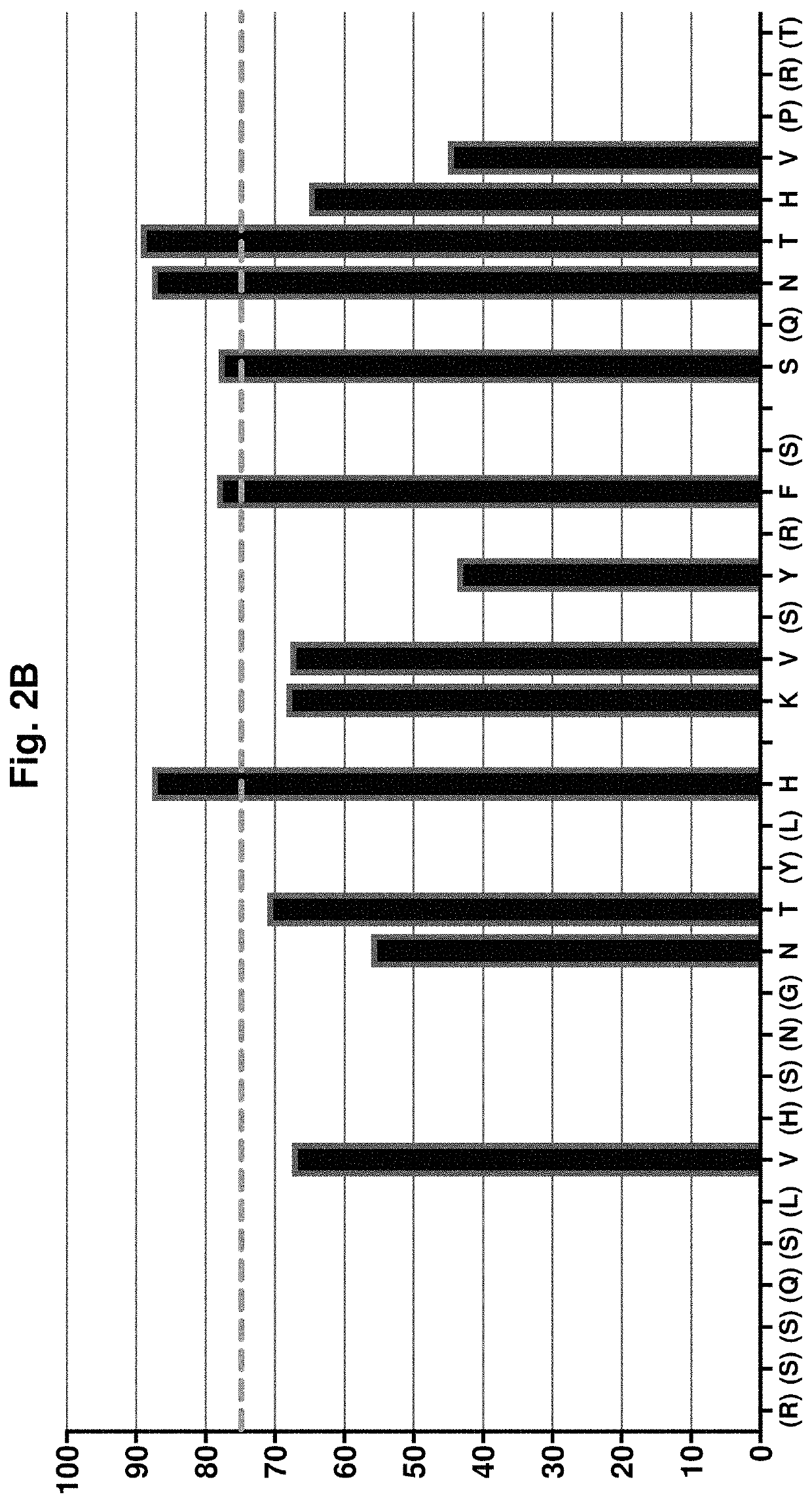
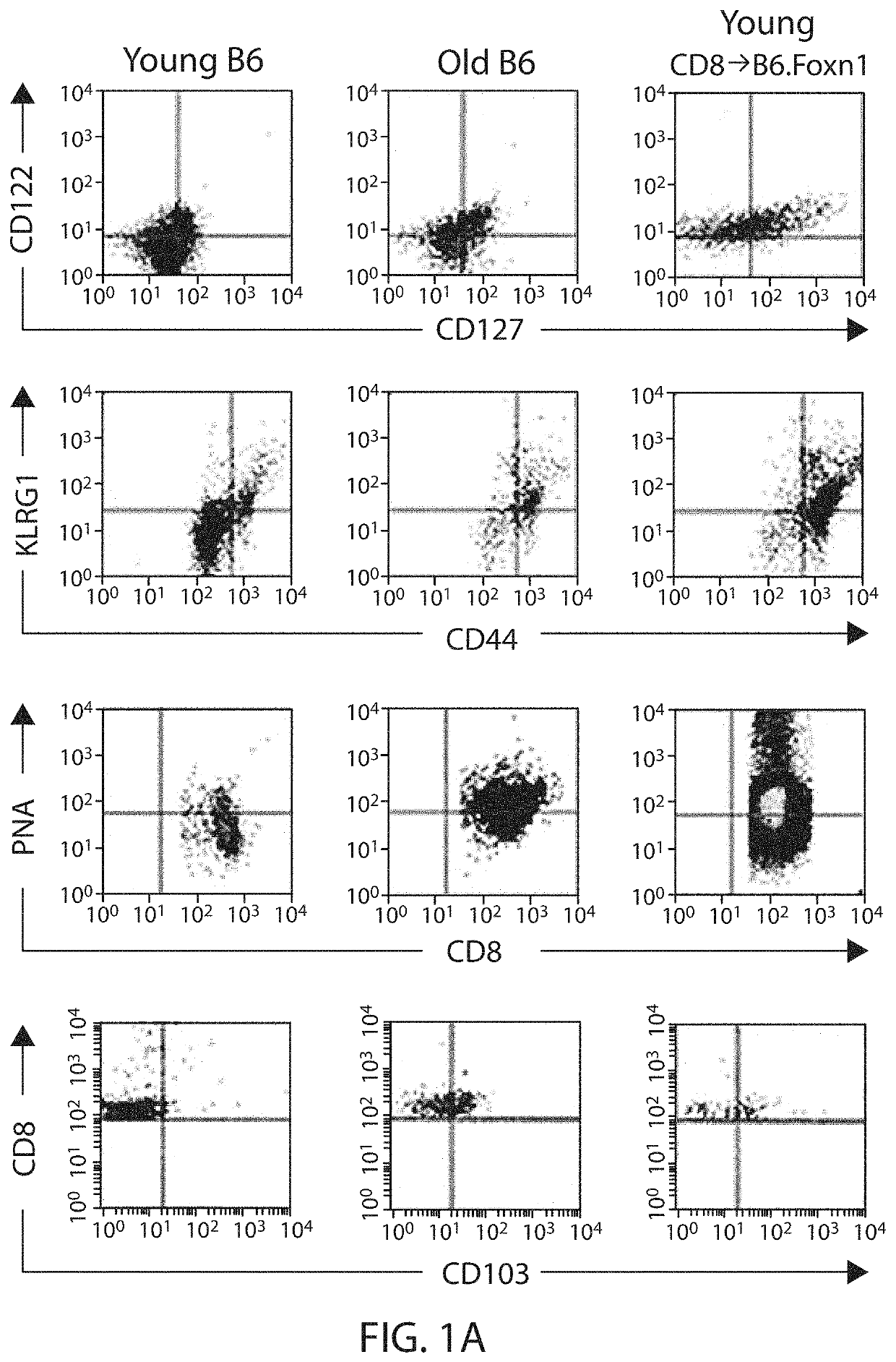
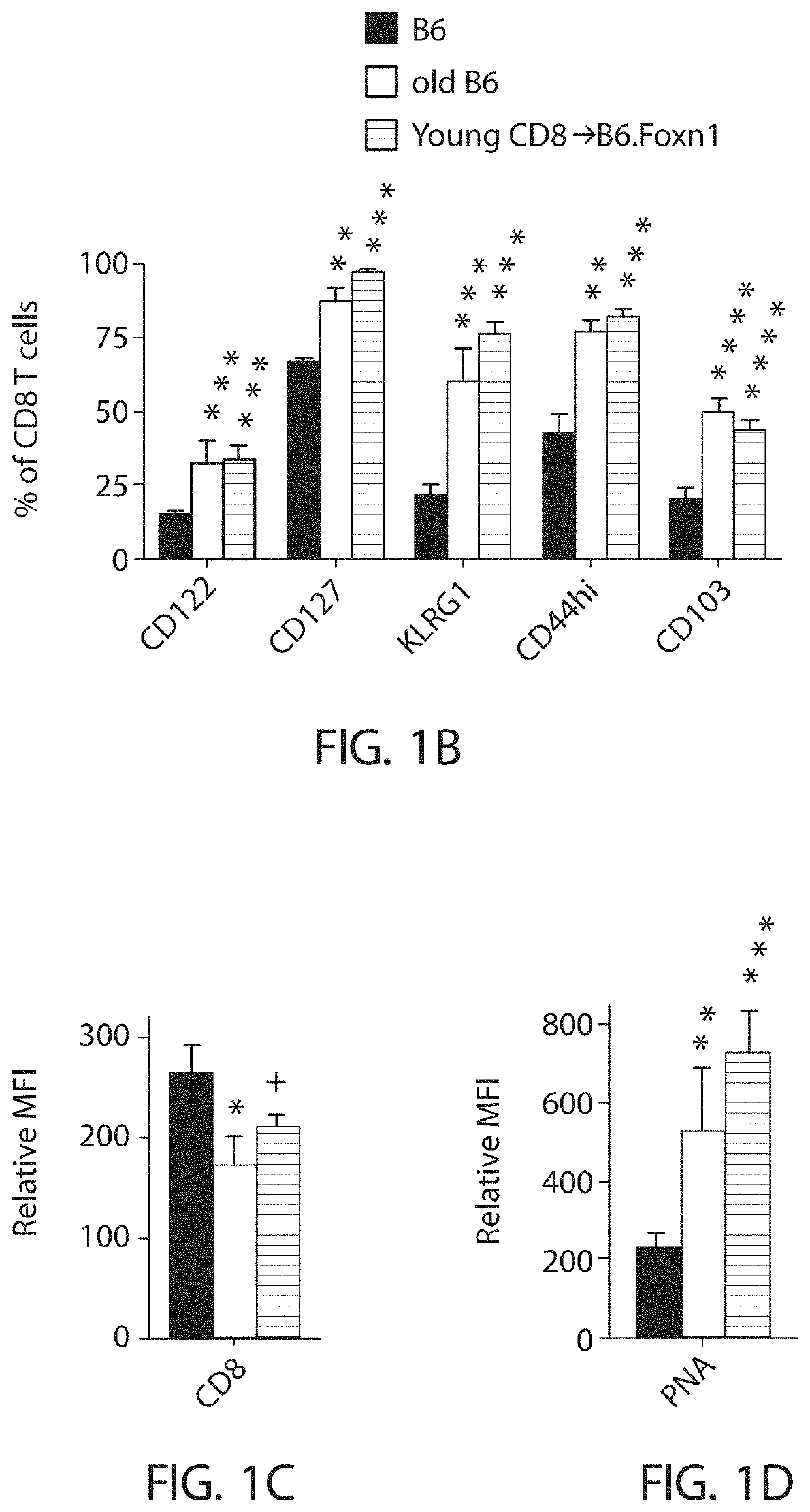
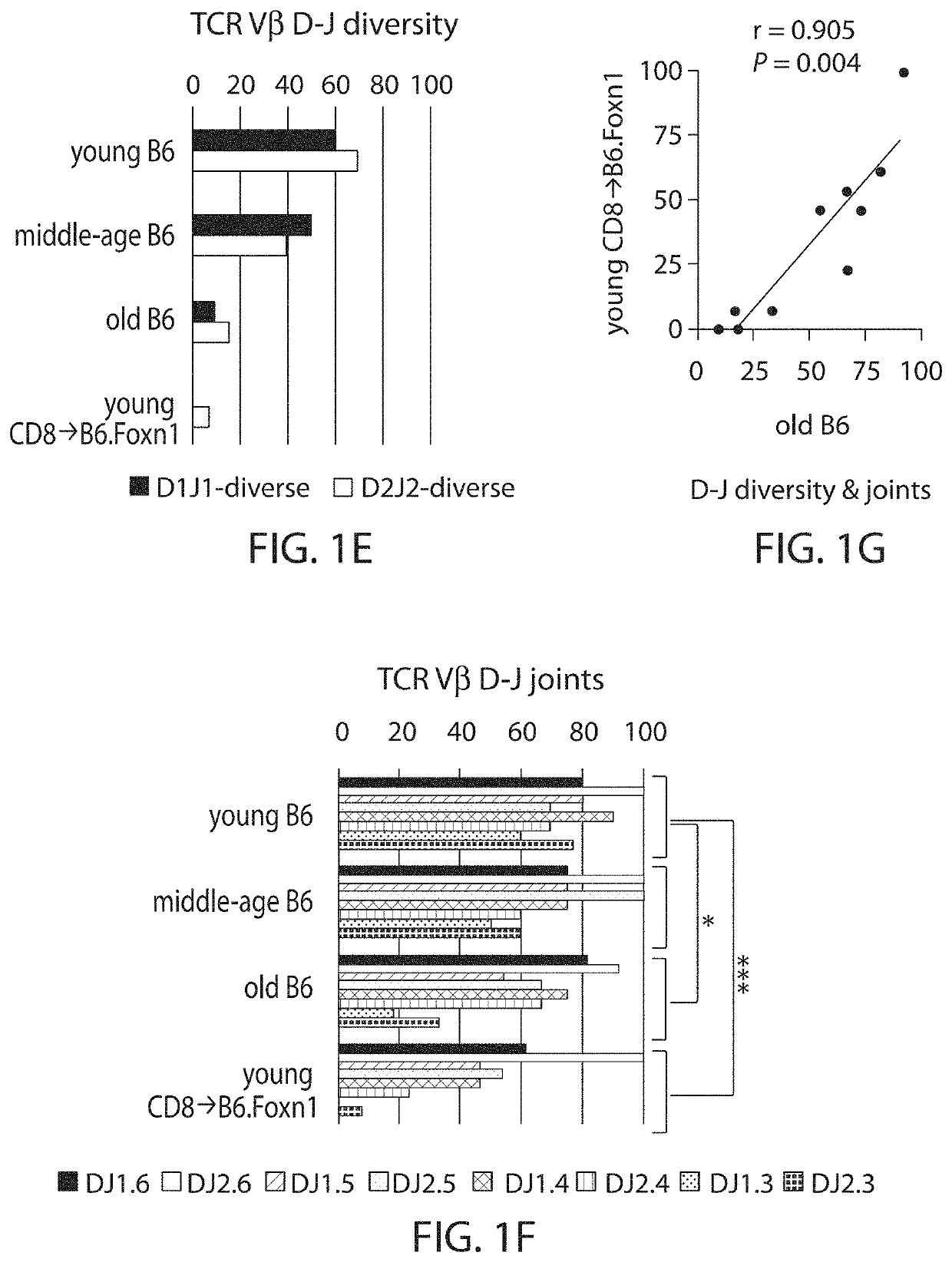
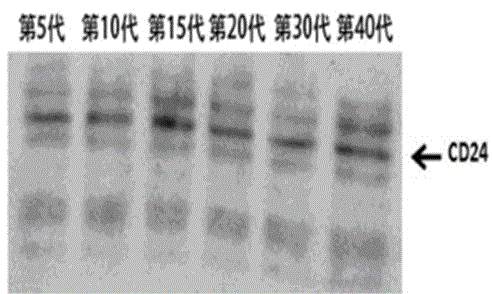
Patents
Literature
65 results about "Cluster of differentiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant and often abbreviated as CD) is a protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules providing targets for immunophenotyping of cells. In terms of physiology, CD molecules can act in numerous ways, often acting as receptors or ligands important to the cell. A signal cascade is usually initiated, altering the behavior of the cell (see cell signaling). Some CD proteins do not play a role in cell signaling, but have other functions, such as cell adhesion. CD for humans is numbered up to 371 (as of 21 April 2016).
Scd fingerprints
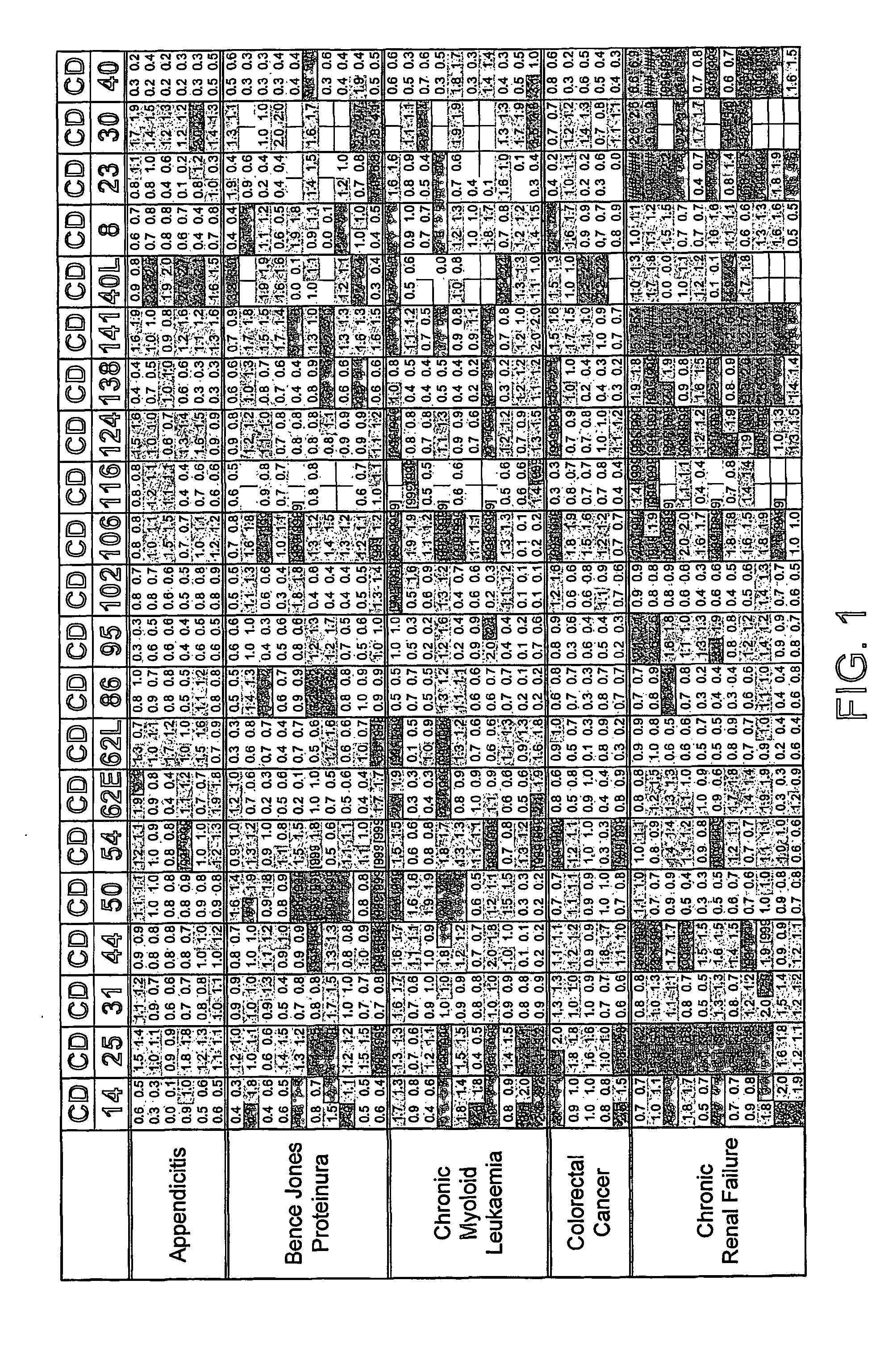
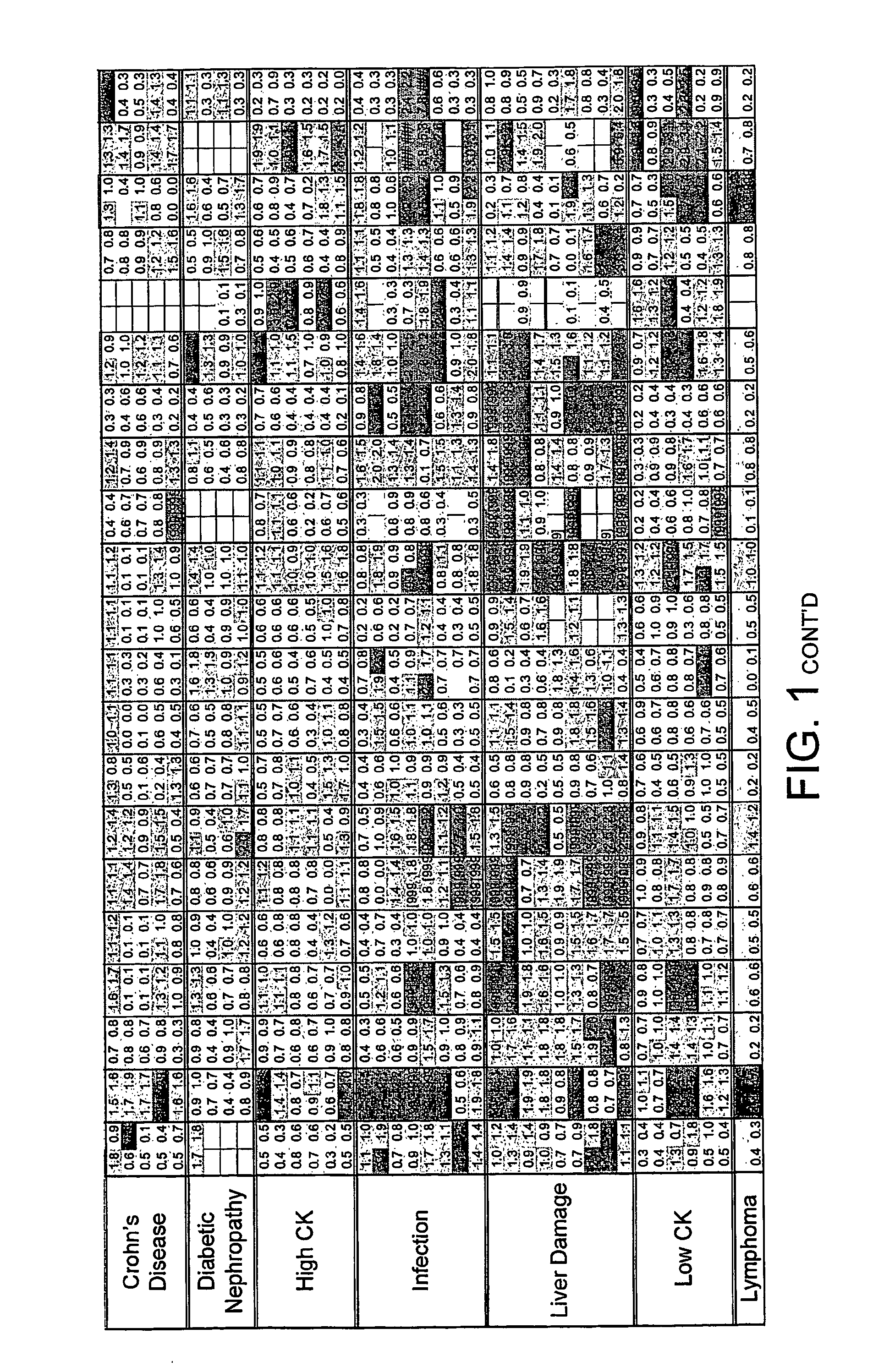
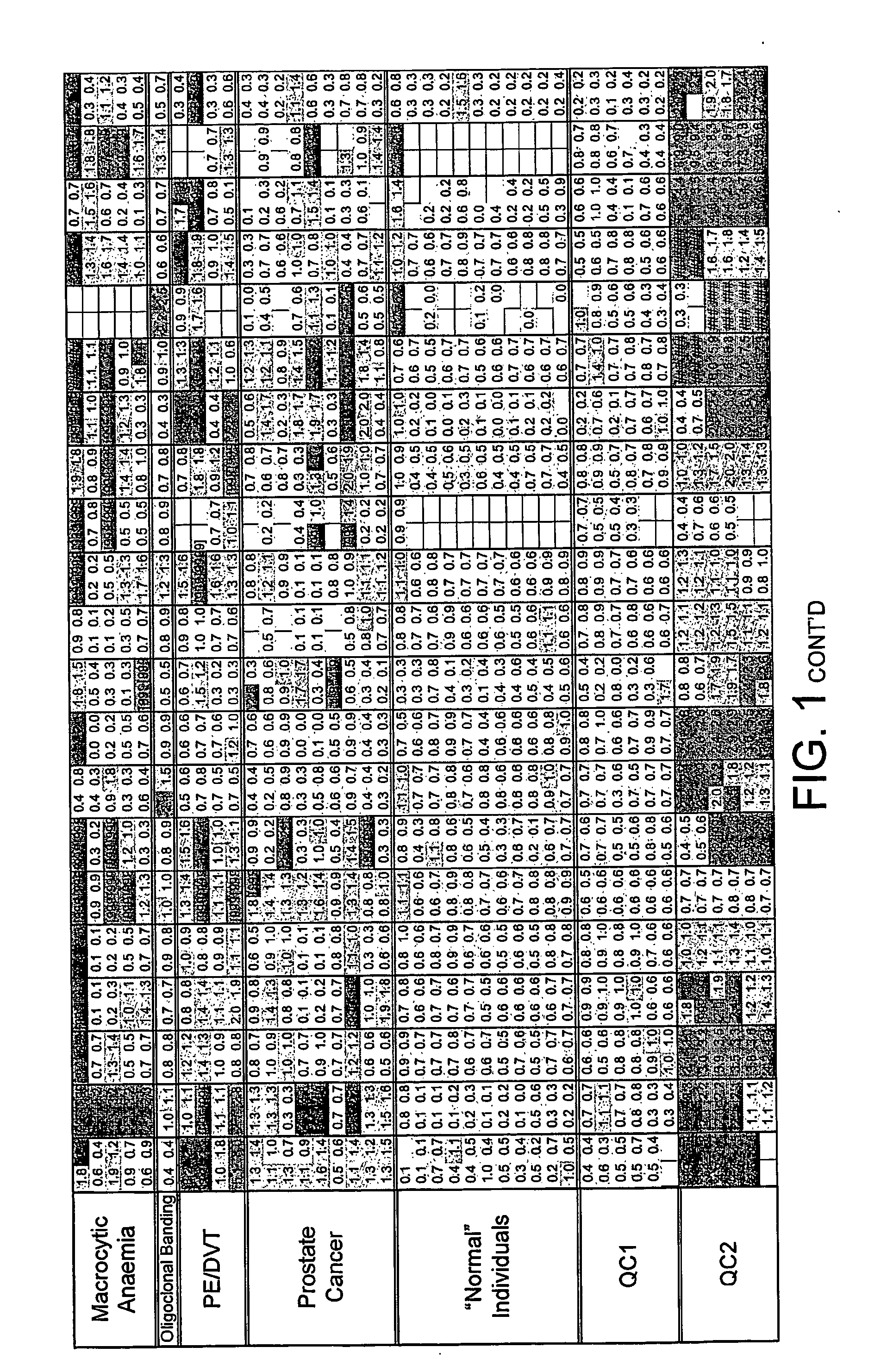
InactiveUS20070233391A1Complicate to obtainMinimize impactData processing applicationsBiological testingDiseaseCluster of differentiation
The present invention relates to the use of cluster of differentiation (CD) molecules in detecting the presence and progression of one or more disease states in an individual. In particular it relates to the use of profiles of shed CD (sCD) molecules in detecting and assessing the progression of one or more disease states in an individual. Further uses of sCD profiles according to the present invention are also described.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE UNIV TECH SERVICES LTD +2
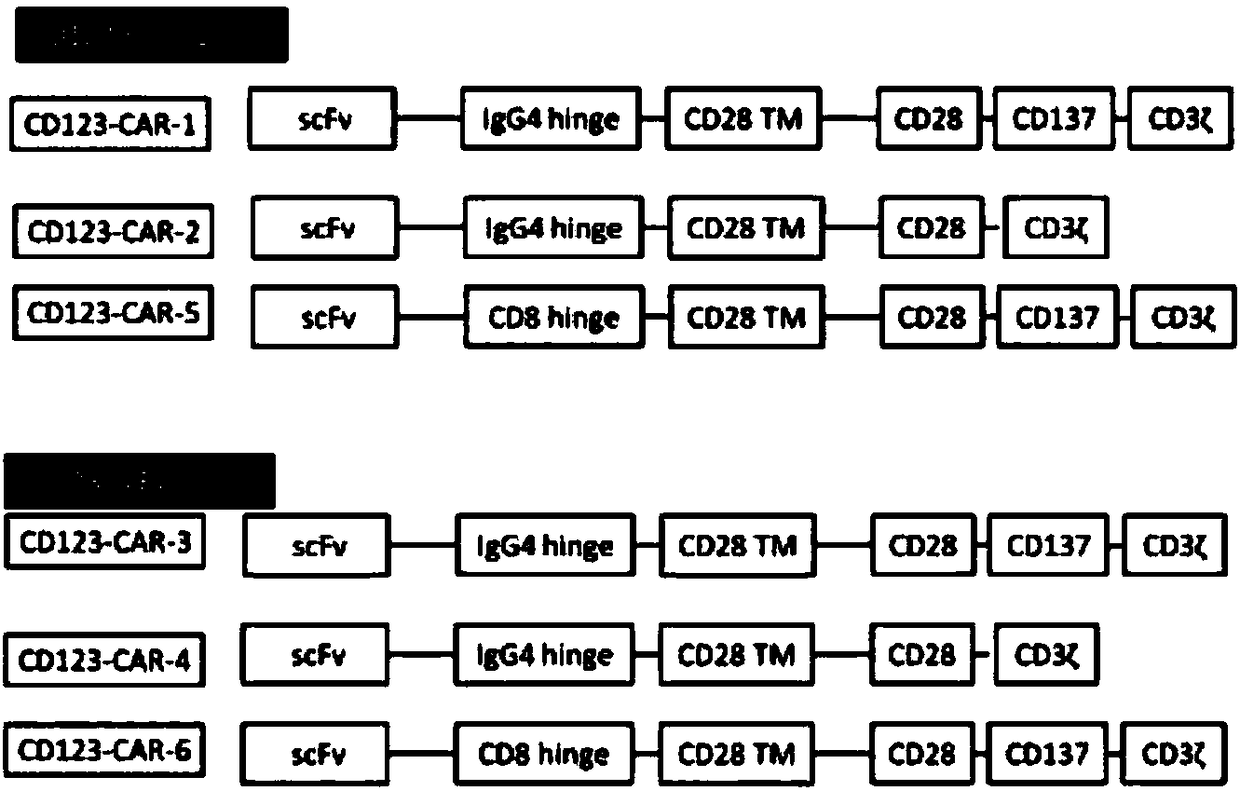
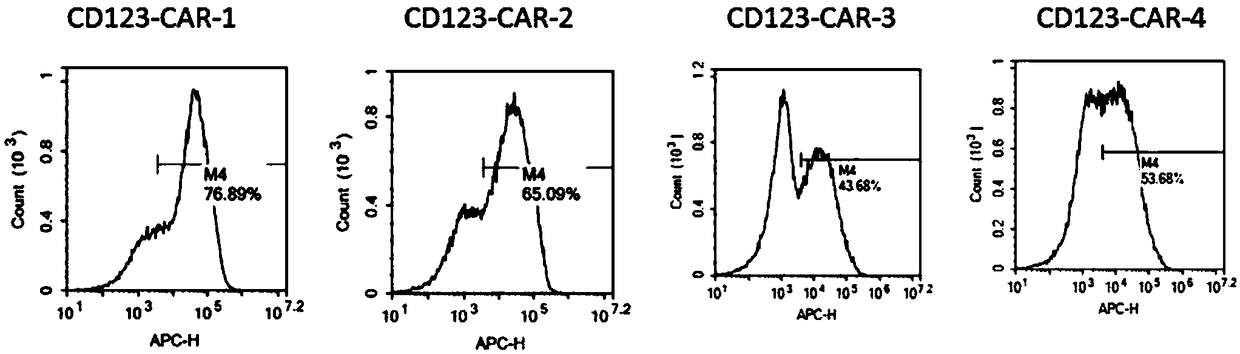
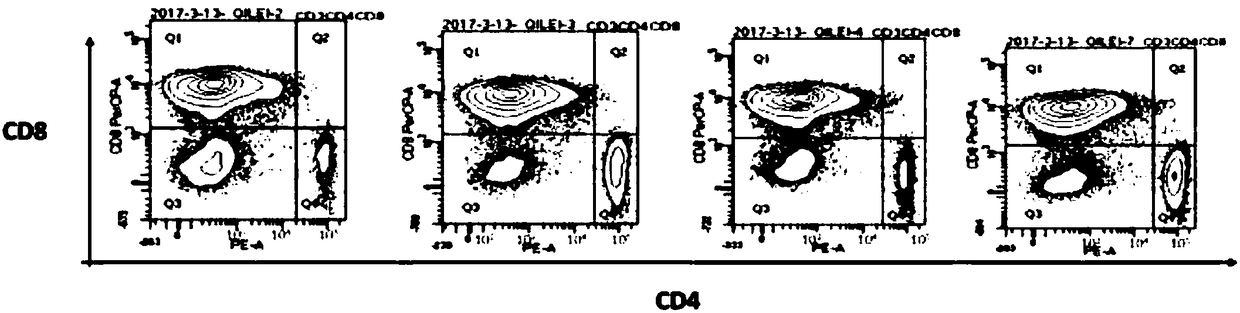
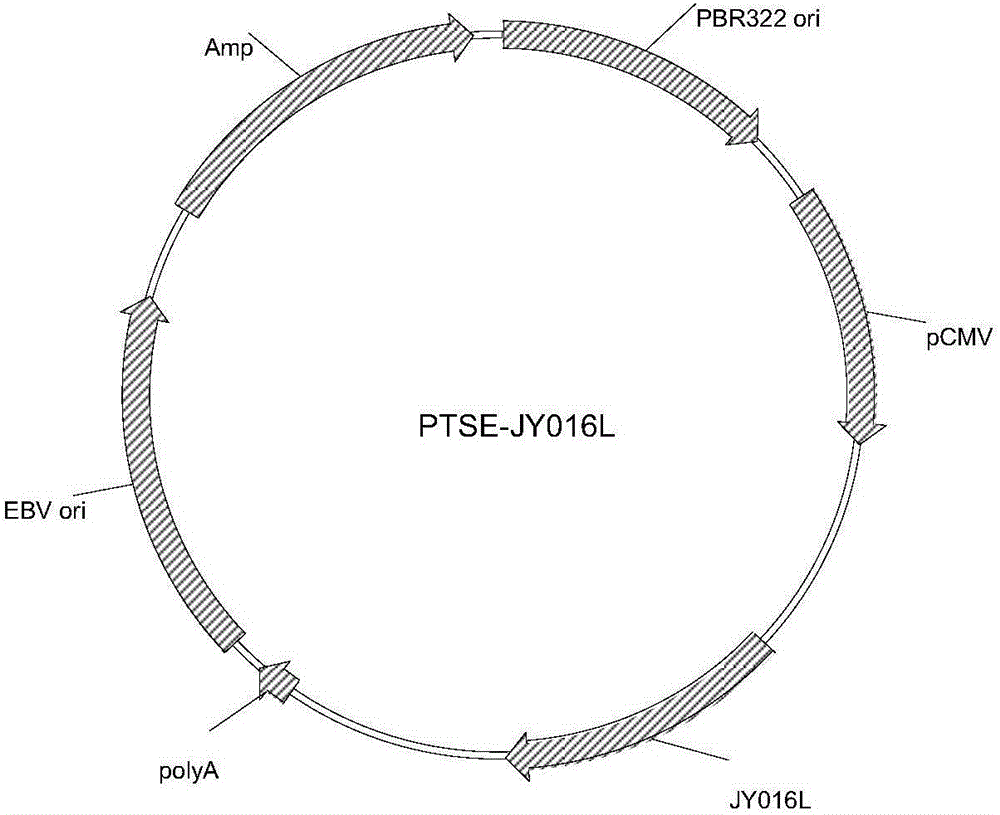
Anti-CD123 (anti-cluster of differentiation 123) single-chain antibody, chimeric antigen receptor combined by same and application thereof
ActiveCN108409840ANo mismatchImprove efficiencyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMammal material medical ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesHinge region
Owner:CHONGQING PRECISION BIOTECH CO LTD
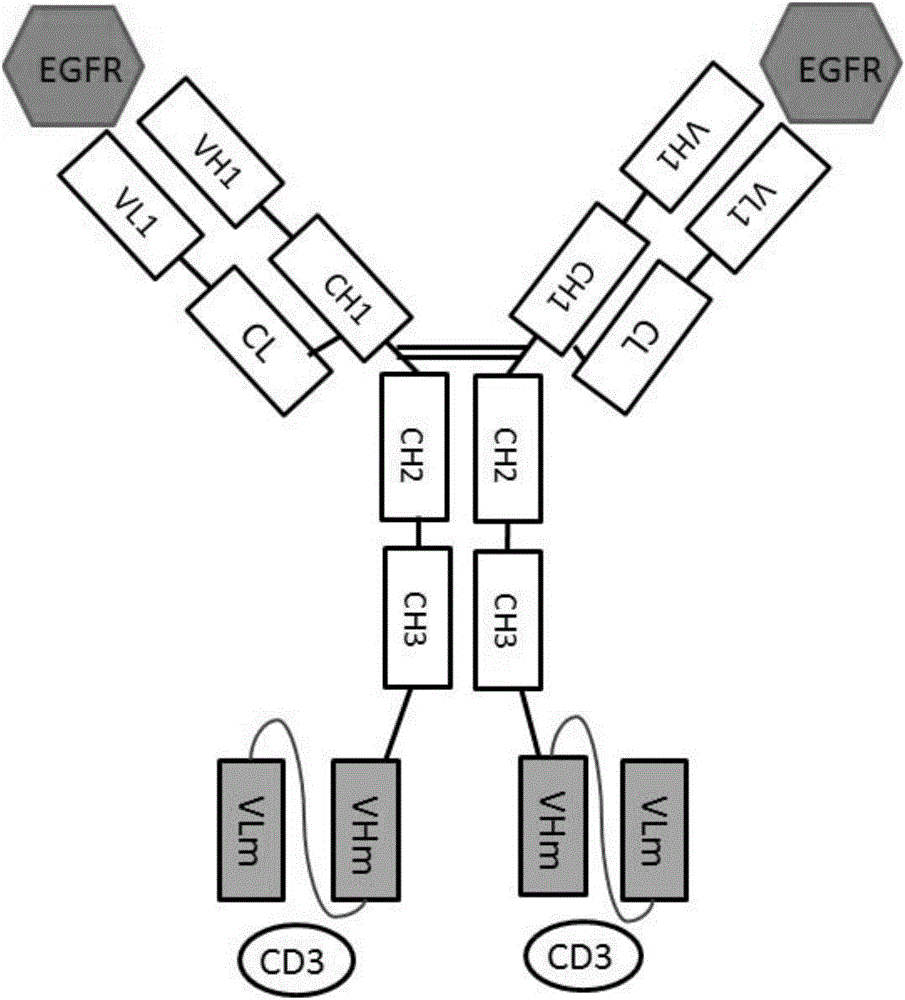
Anti-EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) and anti-CD3 (cluster of differentiation 3) bispecific antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN106632681AConducive to biological functionsConducive to biological functionHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseAntigen
Owner:BEIJING DONGFANG BIOTECH +1
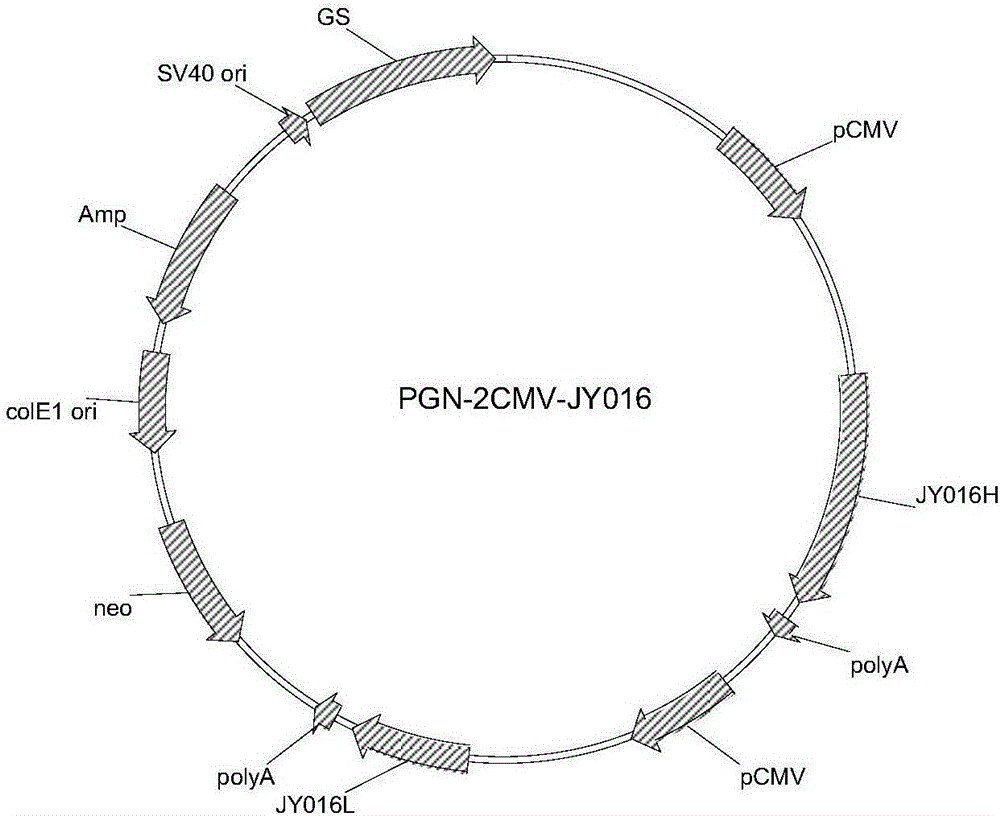
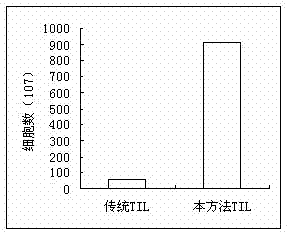
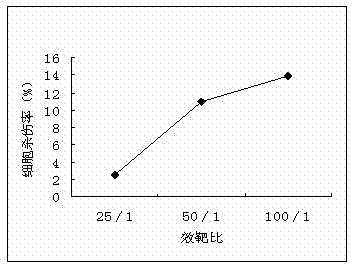
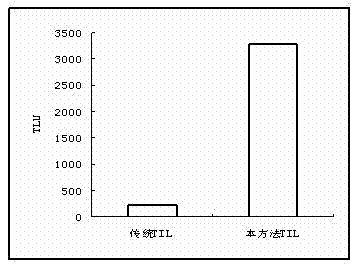
Method for effectively culturing tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs)
InactiveCN102174469AShorter hospital stayReduce the burden of hospitalizationBlood/immune system cellsAntineoplastic agentsClinical efficacyApoptosis Regulatory Proteins
The invention discloses a method for effectively culturing tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). The method comprises the following steps: extracting mononuclear cells from the pectoral ascite or tumor tissue of a patient, washing, inoculating into a culture bottle coated with recombinant human fibrin and cluster-of-differentiation-3 antibody, culturing for 24 hours, adding interleukin II, then using a serum-free culture medium containing the interleukin II and the supernatant pectoral ascite to enlarge and subculture every two or three days, and adding apoptosis-regulated protein survivin and mucoprotein-1 on the twelveth or thirteenth day to activate the killing activity; and harvesting cells on the fourteenth day. By adopting the method, the culture time, which is only 14 days, is greatly shortened, so that the hospital stays of the patient can be greatly shortened and the hospital burden of the patient can be reduced. Meanwhile, the problems that the cell proliferation speed is low and the proliferation ratio is low can be solved, thus the number of the cultured cells can meet the clinical requirement. The cultured TILs has strong cell specificity so as to enhance the clinical curative effect.
Owner:宋鑫 +1
Dosing for treatment with Anti-cd20/Anti-cd3 bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS20180134798A1Reduced effector functionOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCD20Disease
The invention provides methods of dosing for the treatment of cancers, such as B cell proliferative disorders, with anti-cluster of differentiation 20 (CD20) / anti-cluster of differentiation 3 (CD3) bispecific antibodies.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
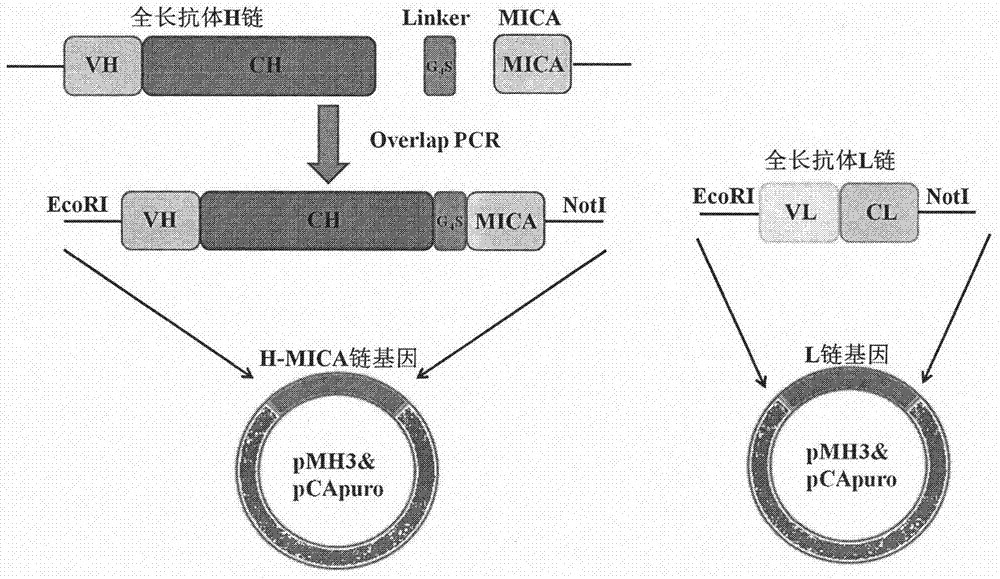
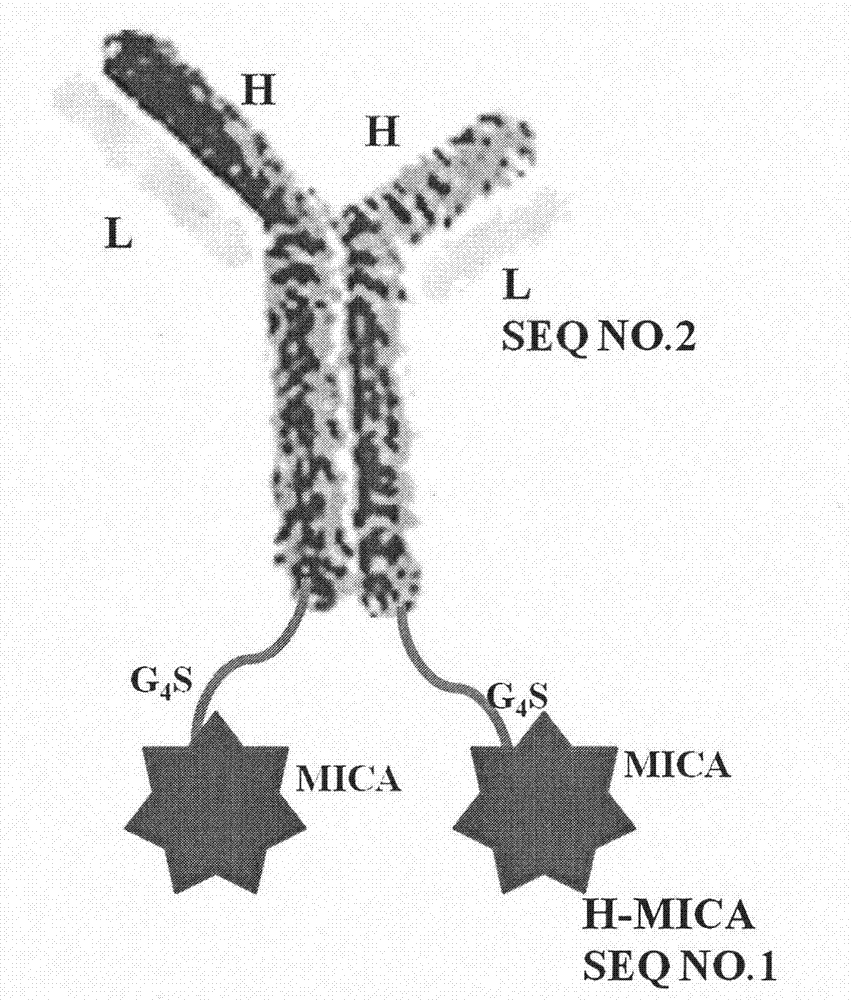
Preparation method and application of bispecific antibody targeting CD24 (cluster of differentiation 24) and activating NK cells (natural killer cells)
InactiveCN109678963AAvoid immune escapeEnhanced ADCC effectHybrid immunoglobulinsDigestive systemImmunocompetenceNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
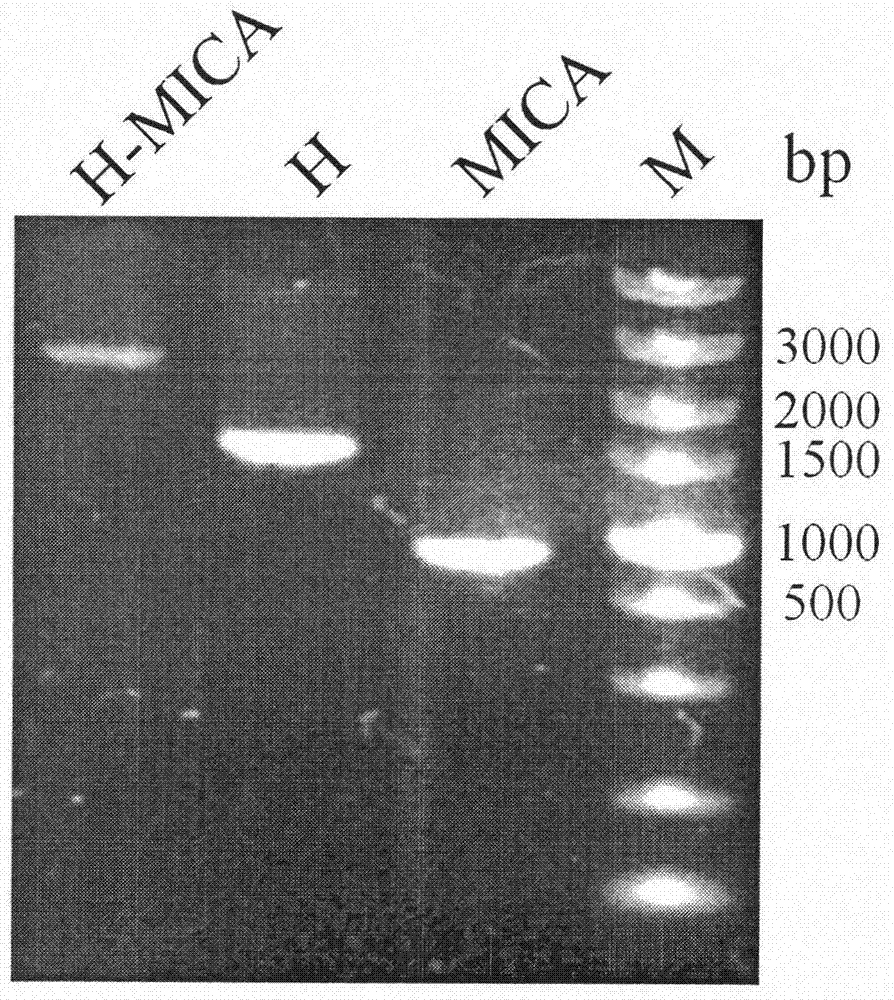
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering antibodies, and particularly relates to a preparation and application of a bispecific antibody targeting a CD24 (cluster of differentiation 24) and activating NK cells (natural killer cells). According to the preparation and application of the bispecific antibody, an anti-CD24 humanized chimeric antibody cG7 and an MICA molecule capable of recruiting and activating the activity of the NK cells are connected through flexible peptide (Gly4Ser) and are stably transferred to a CHO-s eukaryotic expression system, and a stable high-expression cell strain is selected for propagation and expression of cG7-MICA; the bispecific antibody cG7-MICA utilizes the function of remodeling the MICA by utilizing the targeting effect of the cG7 to selectively display the MICA on the surface of a CD24+ tumor cell, the immune surveillance effect of the NK cells is induced, in addition, the NK cells are further activated through the effect ofan Fc part, and the antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) is achieved; and through experimental verification, the immunocompetence of killing the CD24+ hepatocellular carcinoma cells is achieved in vitro and vivo.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
sCD Fingerprints
InactiveUS20080318836A1Complicate to obtainMinimize impactPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsDiseaseCluster of differentiation
The present invention relates to the use of cluster of differentiation (CD) molecules in detecting the presence and progression of one or more disease states in an individual. In particular it relates to the use of profiles of shed CD (sCD) molecules in detecting an assessing the progress of one or more disease states in an individual. Further uses of sCD profiles according to the present invention are also described.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD +1
Peptide mimotopes of the cd3 t-cell co-receptor epsilon chain and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190070248A1Optimization of binding propertyGenerate and inhibit immune responseImmunoglobulin superfamilyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenBinding domain
The present invention provides molecules that mimic antigenic determinants of the CD3 (cluster of differentiation 3) T-cell co-receptor epsilon chain (CD3ε). These molecules compete with CD3ε for binding to a CD3ε binding domain. e.g. a CD3ε binding domain of an antibody, and are capable of detecting antibodies against CD3ε. The mimotopes of the invention may be used to generate or inhibit immune responses in animals and preferably humans. Additionally, they may serve as tools for anti-CD3ε antibody purification and the detection of anti-CD3ε antibodies in biological samples.
Owner:JPT PEPTIDE TECH +1
Universal type lentivirus vector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106011174AUnaffected replicationNormal packagingNucleic acid vectorFermentationPeripheral blood mononuclear cellReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses a universal type lentivirus vector and a preparation method thereof, relates to a lentivirus vector and a preparation method thereof, and aims to solve the problems in a current CAR (Chimeric Antigen Receptor)-T preparation process that the vector construction steps are troublesome, the consumed time is too long, the lentivirus vector cannot be universally used, and the cost is high. The universal type lentivirus vector is characterized by taking pCDH-CMV-MCS-EF1-Puro plasmids as a framework and inserting the following elements of a CD8 (Cluster of Differentiation 8)alpha Leader DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence, a CD8alpha hinge region, a CD28 transmembrane region-intracellular region, a CD137 intracellular region and a CD3zeta in MCS (Multiple Cloning Sites) of the plasmid framework. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) designing a primer; (2) obtaining and activating a PBMNC (Peripheral Blood Mononulcear Cell); (3) extracting mRNA (Messenger Ribonucleic Acid) and carrying out an RT (Reverse Transcriptase) reaction; (4) preparing recombinant plasmids; (5) compounding a single-chain CD8alpha Leader DNA sequence; (6) connecting a linear vector, a target gene fragment and a CD8alpha Leader fragment, thus obtaining the universal type lentivirus vector. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is used for preparing the lentivirus vector.
Owner:天晴干细胞股份有限公司
Ginseng derived nano-particles, as well as preparation and application thereof
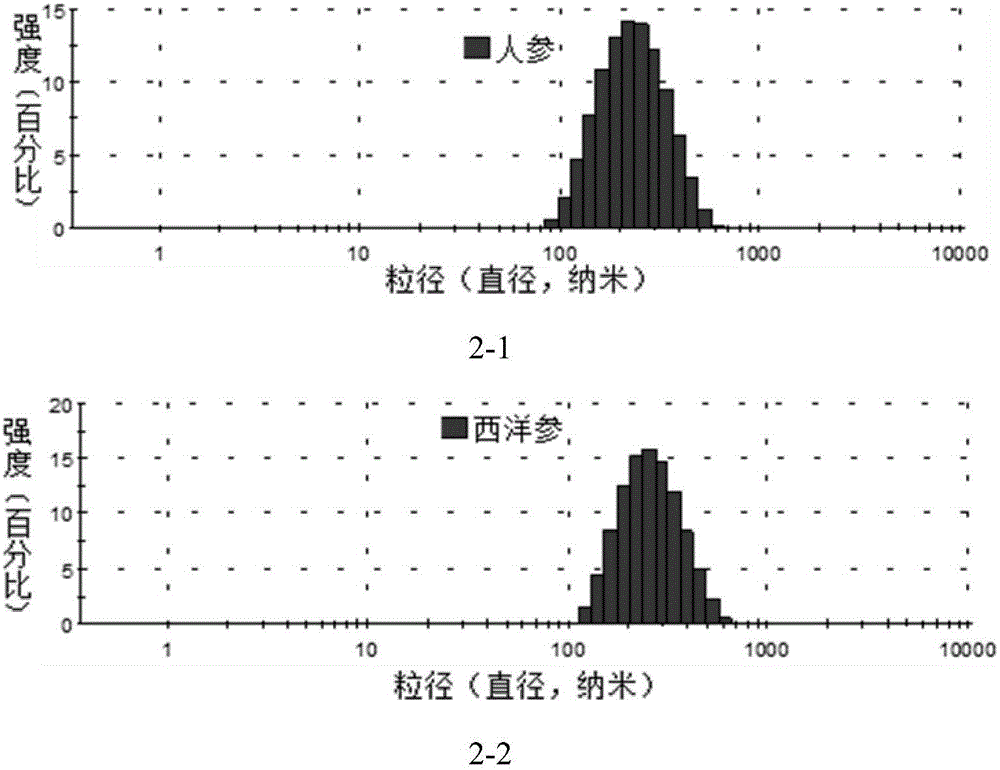
PendingCN106727810AWide variety of sourcesEasy to operateAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryInterleukin 6Impurity
The invention discloses ginseng derived nano-particles, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The ginseng derived nano-particles have a membrane structure, wherein the particle size range is 150 to 500nm, and the peak particle size is 280 to 350nm. The ginseng derived nano-particle is prepared by performing centrifugation and filtering impurity removal for many times. By the ginseng derived nano-particle, a bone marrow derived monocyte-macrophage can be effectively induced to be proliferated and activated, meanwhile, multiple surfactant molecules such as a TLR2 / 4 (toll-like receptor 2 / 4) and a CD80 (cluster of differentiation 80) are up-regulated, and cell factors such as a TNF-a (tumor necrosis factor-a) and an IL-6 (interleukin-6) are secreted. The ginseng derived nano-particle has broad application prospect in development of a medicament for preparing a natural immunoenhancer.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Humanized single-chain variable fragments of targeted B lymphoma cells
InactiveCN104558181AImprove biological activityAvoid HAMAsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering and protein engineering, in particular to DNA for encoding a recombinant fusion protein of a variable fragment which contains a humanized CD19 (Cluster of Differentiation 19) antibody, the fusion protein encoded by the DNA, a production method for the fusion protein, and the application of the fusion protein. The invention provides the protein which comprises a humanized CD19 single-chain variable fragment, which can combine targeted B lymphoma cells with the CD19, cannot combine the targeted B lymphoma cells without the CD19, shows specific targeted binding activity, and has a very good application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Composition for diagnosing liver cancer and methods of diagnosing liver cancer and obtaining information for diagnosing liver cancer
InactiveUS9518125B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCD43Cluster of differentiation
Provided is method of diagnosing liver cancer in a subject, the method comprising contacting a sample from a subject with a substance that specifically binds to transmembrane emp24 domain trafficking protein 2 (TMED2), cluster of differentiation 43 (CD43), or any combination thereof on the surface of a microvesicle; and measuring the level of the substance bound to microvesicles in the sample; and related methods and compositions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
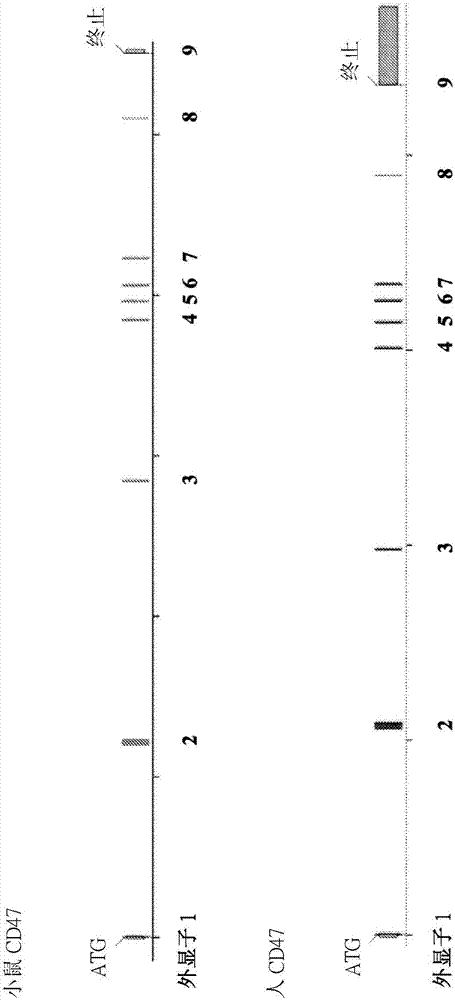
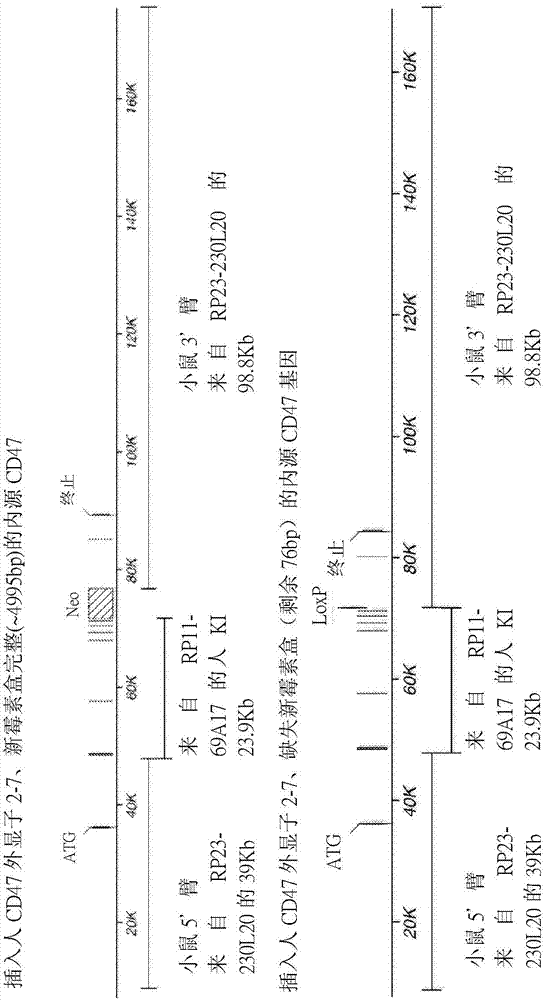
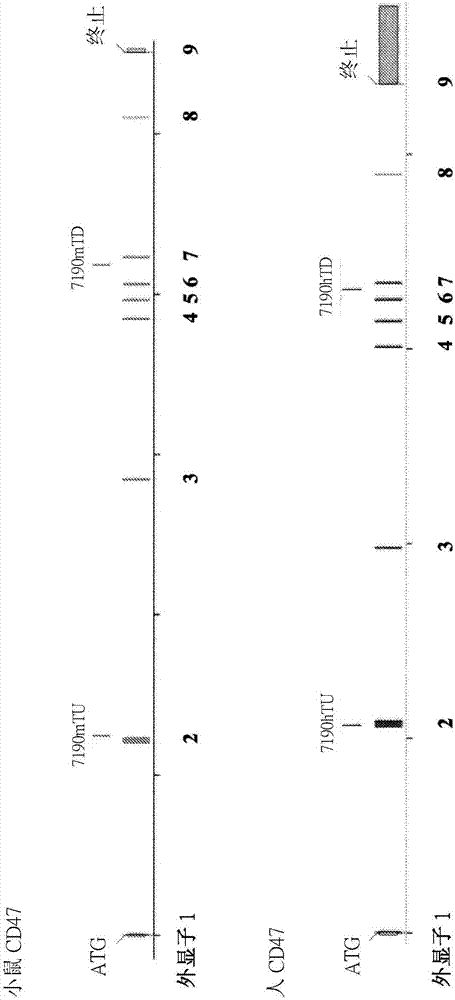
Non-human animals having humanized cluster of differentiation 47 gene
ActiveCN107205368APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCompounds screening/testingGeneEvolutionary biology
Non-human animals, and methods and compositions for making and using the same, are provided, wherein said non-human animals comprise a humanization of an endogenous cluster of differentiation (CD) gene, in particular a humanization of a CD47 gene. Said non-human animals may be described, in some embodiments, as having a genetic modification to an endogenous CD47 gene so that said non-human animals express a CD47 polypeptide that includes a human portion and a non-human portion (e.g., a murine portion).
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Anti-CD24 (cluster of differentiation 24) humanized antibody fusion protein
InactiveCN107226866AAssess the feasibilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulinsCell regionHumanized antibody
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering antibodies, in particular to a preparation method and application of a CD24 antibody fusion protein. The invention utilizes genetic engineering technology to link the CD24 humanized antibody hG7S with the extracellular 1-3 region of the MICA molecule through the G4S flexible peptide, and the mammalian eukaryotic expression system stably expresses hG7S-MICA; the CD24 antibody fusion protein hG7S-MICA can simultaneously Combined with CD24 molecules on the surface of tumor cells and the activated receptor NKG2D on the surface of NK cells, remodeling the immune surveillance effect of NK cells induced by NKG2D pathway on CD24+ tumor cells, and finally achieving the goal of activating the body's own immune system to effectively kill CD24+ tumor cells Purpose.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Method for detecting active tuberculosis
The present invention relates to a method of determining the presence or absence of active tuberculosis in a sample, in particular, comprising determining the levels of one or more biomarkers selectedfrom basic leucine zipper transcription factor ATF-like 2 (BATF2), cluster of differentiation 177 (CD177), haptoglobin (HP), immunoglobulin J chain (IGJ) and galectin 10 (CLC), in said sample. Uses of biomarkers of the invention and kits for performing the method of the invention are also described.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
Chinese medicinal preparation for treating acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102805810AImprove immune functionGood treatment effectAntiviralsPlant ingredientsCD4 LymphocyteSide effect
The invention discloses a Chinese medicinal preparation for treating acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and a preparation method thereof. The Chinese medicinal preparation is prepared from the following raw materials of baical skullcap root, sophora flower, astragalus, Chinese angelica, siberian solomonseal rhizome, prepared rehmannia root, liquoric root, weeping forsythia, Chinese caterpillar fungus and citric acid in a weight ratio. The Chinese medicinal preparation has the effects of clearing heat and removing toxicity, strengthening body resistance to eliminate pathogenic factors,activating blood circulation and tonifying qi, is used for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infected persons and AIDS patients, has an effect of improving cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) lymphocyte count, can reduce the HIV viral load of peripheral blood gradually, improve the symptoms of the patients obviously and improve liver functions of the patients, and does not have toxic or side effects of antiviral medicines in western medicines.
Owner:张林
Method capable of promoting Trichosanthes kirilowii tissue culture seedling differentiation
InactiveCN106962189ASpeed up the process of induction of differentiationWide variety of sourcesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsTrichosanthes kirilowiiDisinfectant
The invention mainly relates to the field of planting technology, and discloses a method for promoting the differentiation of Trichosanthes mellifera seedlings, including: selection and treatment of explants, preparation of medium, inoculation of explants, induction of differentiation and cultivation; Induced differentiation during basket tissue culture, after 16 days of culture in B5 medium, yellow-green cell protrusions began to appear, and then differentiated bud clusters appeared, which significantly shortened the time for induction of differentiation, improved planting efficiency, and increased economic income by 16.2%; As an explant, it will not cause damage to the Trichosanthes plant, does not affect the growth and results of Trichosanthes, and the source of young leaves is extensive, and tissue culture can be carried out at any time, and the planting efficiency is significantly improved; Salt water, acetic acid solution and nutrient solution treatment, avoid using too much disinfectant for repeated disinfection, save costs, and allow explants to continue absorbing and accumulating nutrients in a slightly acidic environment, speeding up the process of inducing differentiation of explants.
Owner:蚌埠清菲农业科技有限公司
Anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) gene engineering recombinant virus and preparation method thereof, and anti-HIV gene engineering medicament
InactiveCN102690792AEffective infectionAvoid infectionViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsAntiviralsHIV receptorHuman immunodeficiency
The invention relates to an anti-HIV gene engineering recombinant virus and a preparation method thereof, and an anti-HIV gene engineering medicament. The anti-HIV gene engineering recombinant virus comprises a constant region of a human antibody, and a cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) and a chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) which are connected with the constant region. The preparation method for the anti-HIV gene engineering recombinant virus comprises the steps as follows: obtaining a heavy chain constant region gene of the human antibody, a light chain constant region gene of the human antibody, a CD4 gene and a CCR5 gene; constructing a virus vector shuttle plasmid comprising the four genes; co-transforming the shuttle plasmid and a virus auxiliary plasmid to generate a recombinant virus plasmid; and transferring the recombinant virus plasmid to a cell strain for culturing and purifying the virus. The recombinant virus has both the CD4 and CCR5 capable of specifically binding with the CD4 site and CCR5 site of an HIV virus, an obviously enforced specific binding effect, and the function of doubly preventing the HIV virus from infecting a host cell. The preparation method is simple and practical. The anti-HIV gene engineering medicament with the recombinant virus can effectively act on the HIV virus, and can further effectively prevent and treat the infection of the HIV virus.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
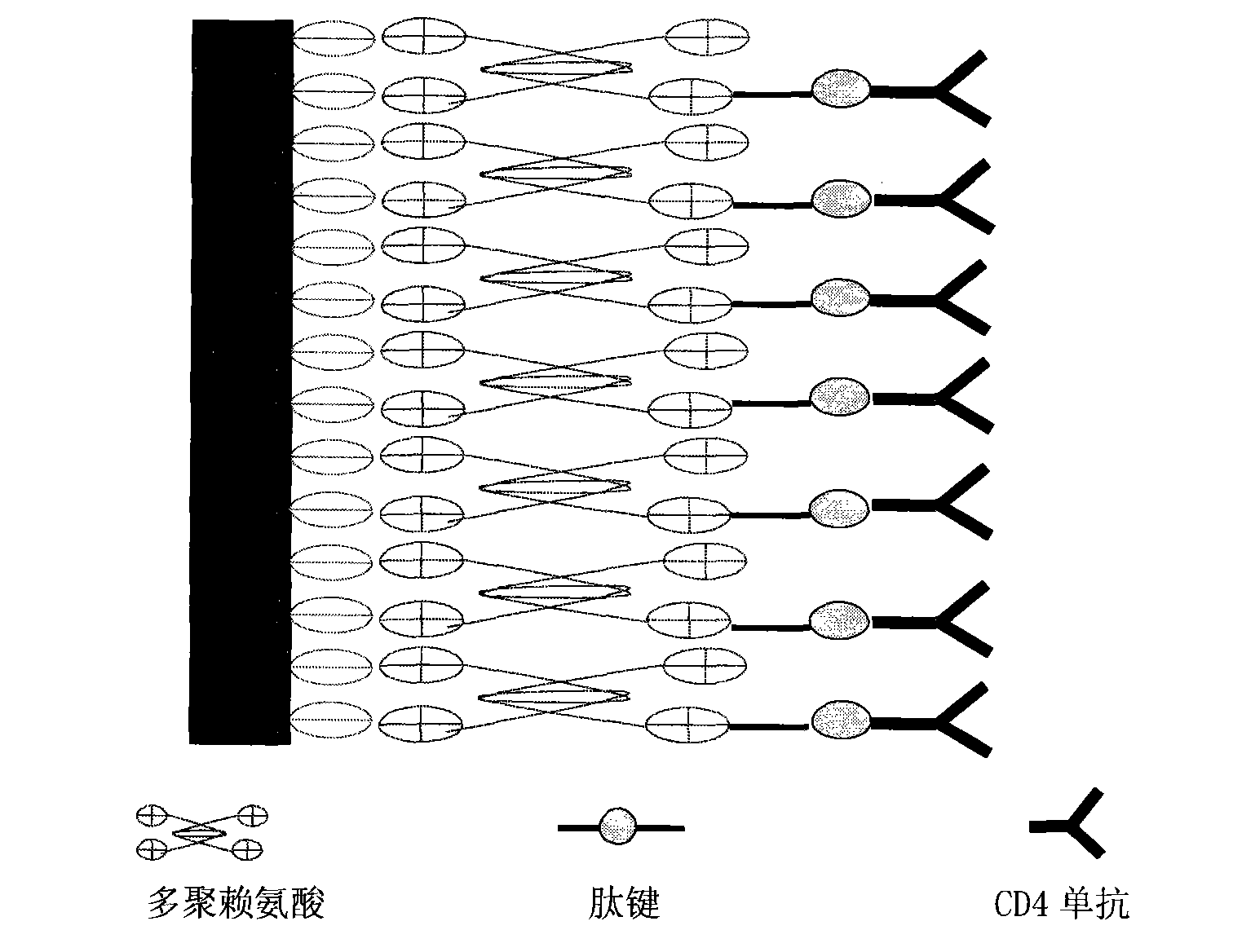
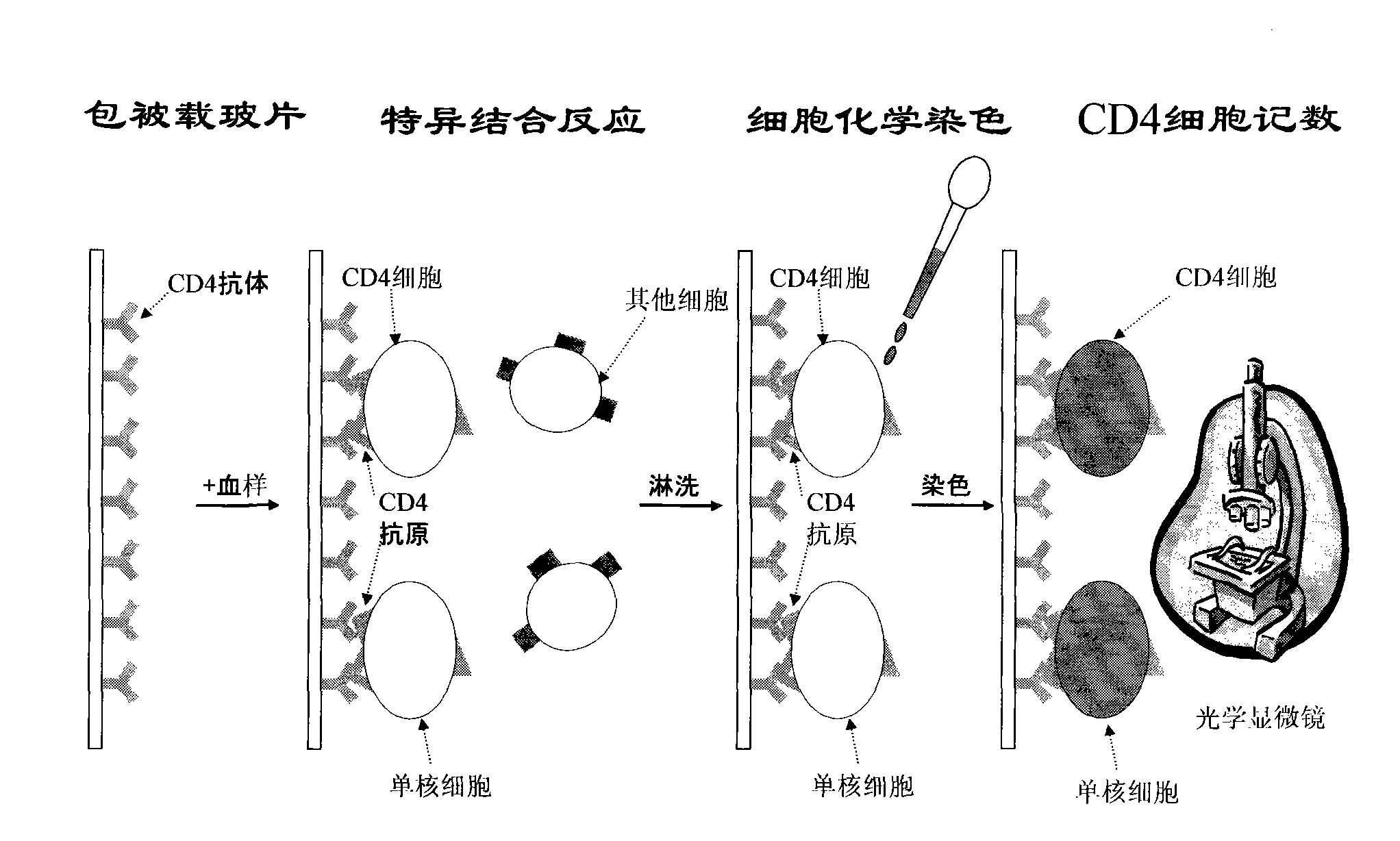
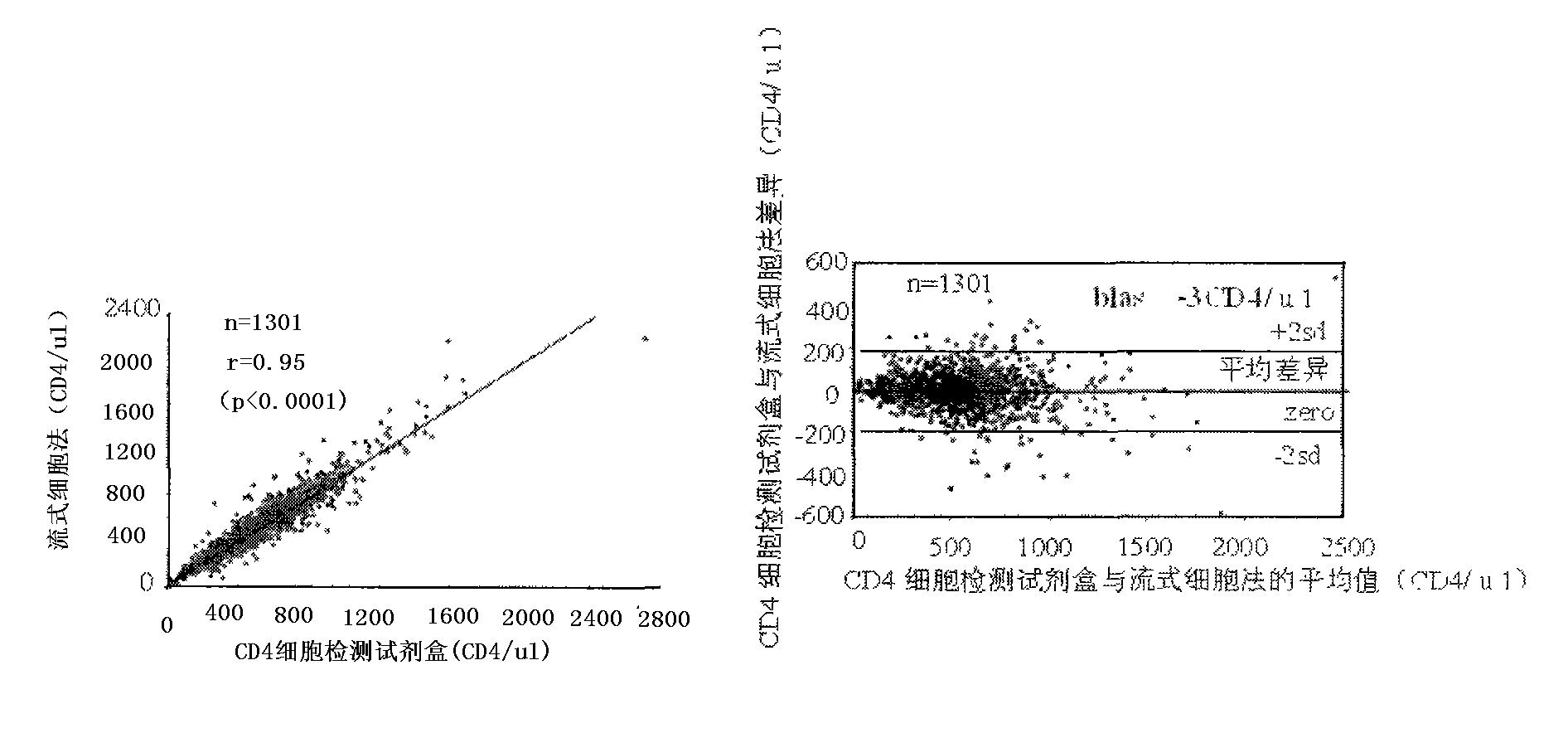
CD4 (Cluster of Differentiation 4) cell chip as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a CD4 (Cluster of Differentiation 4) cell chip which comprises a solid phase support and an antibody fixed on the support, wherein the antibody is a CD4 monoclonal antibody, and the solid phase support is a slide. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the CD4 cell chip, a CD4 cell assay kit containing the CD4 cell chip and a method for applying the CD4 cell chip to detection. The invention also discloses the application of the CD4 cell chip and the CD4 cell assay kit. The CD4 cell chip has the advantages of low cost and simple and convenient operation and is especially applicable to poverty-stricken zones seriously infected by AIDS viruses.
Owner:SHANGHAI SEMIBIO TECH
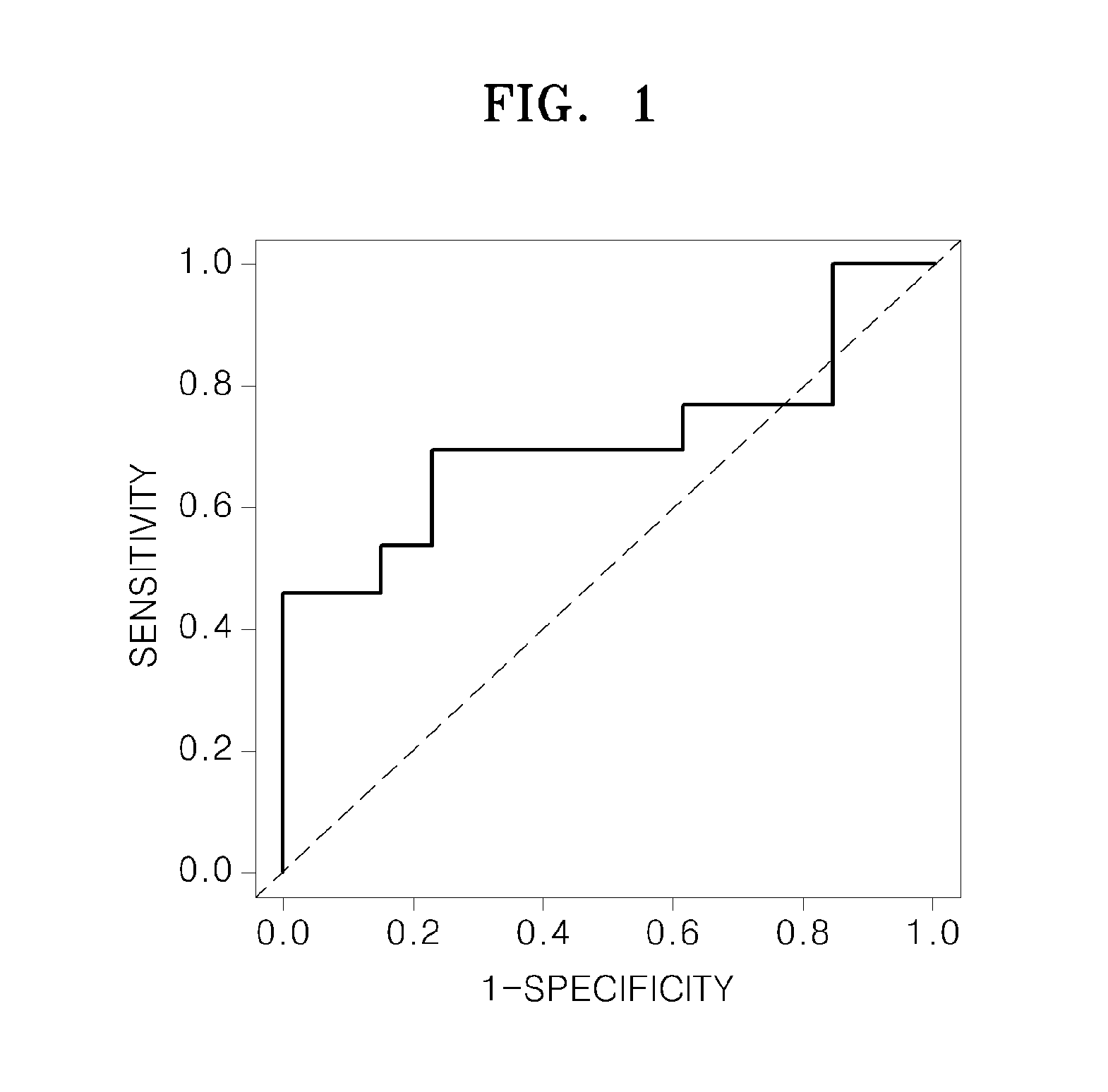
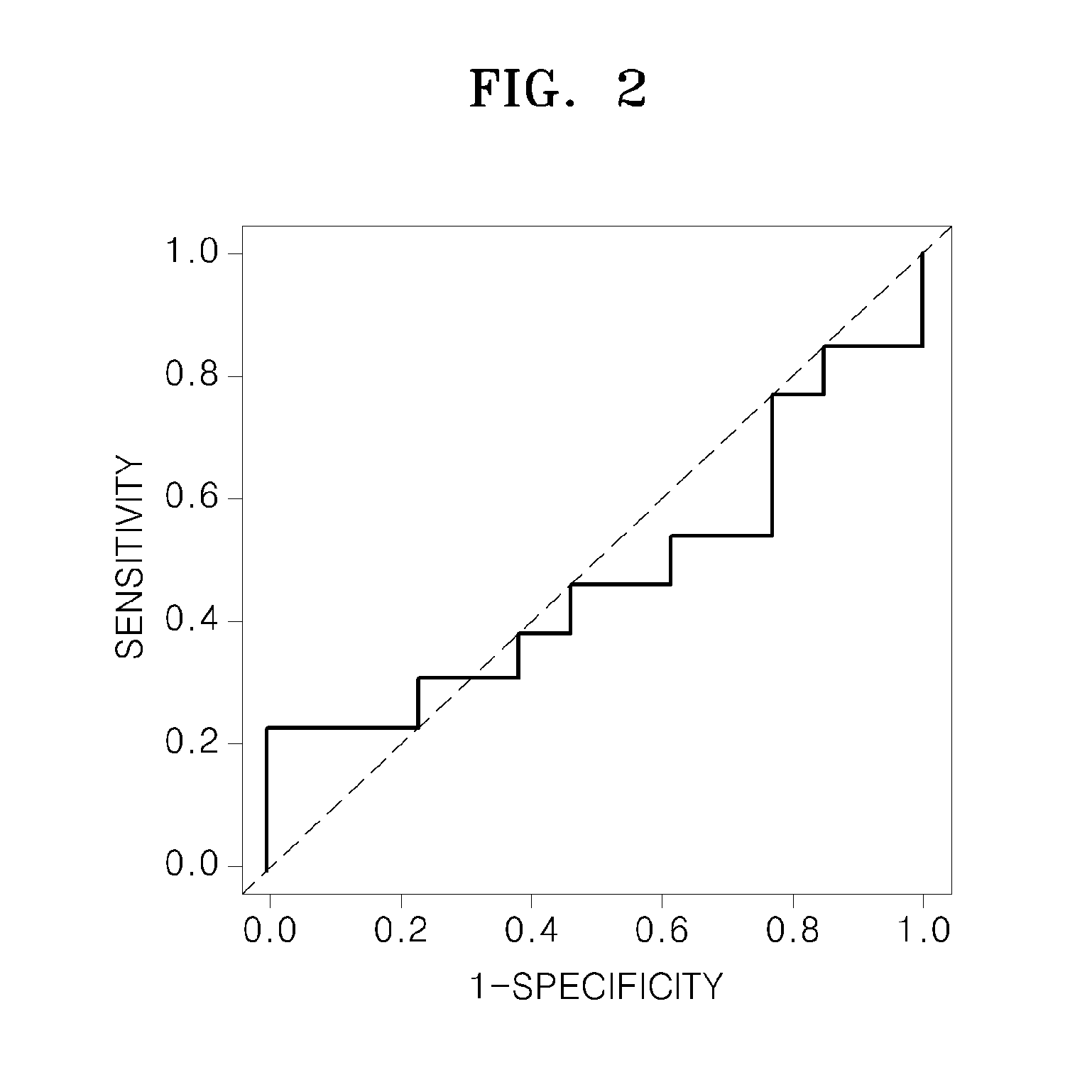
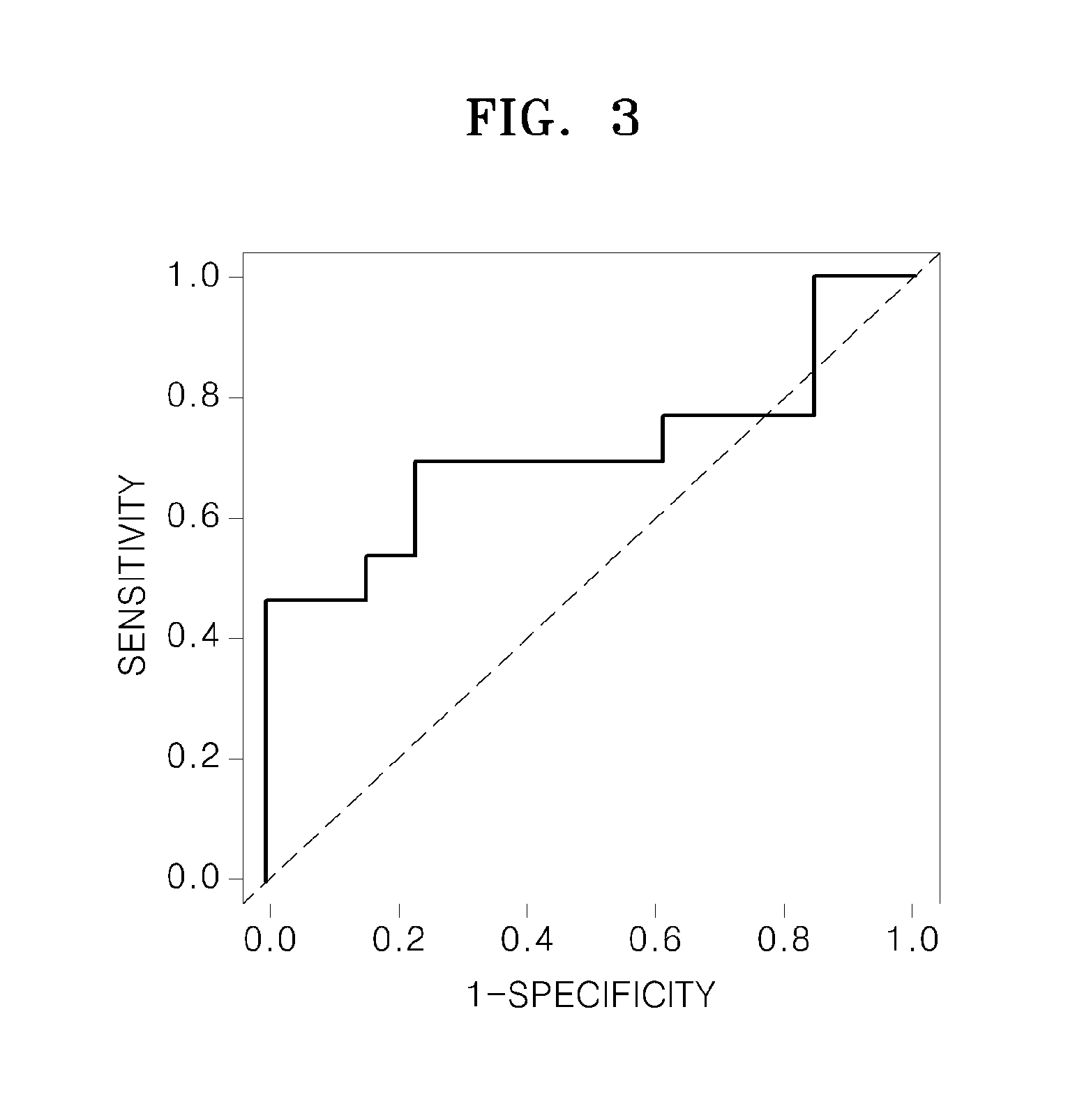
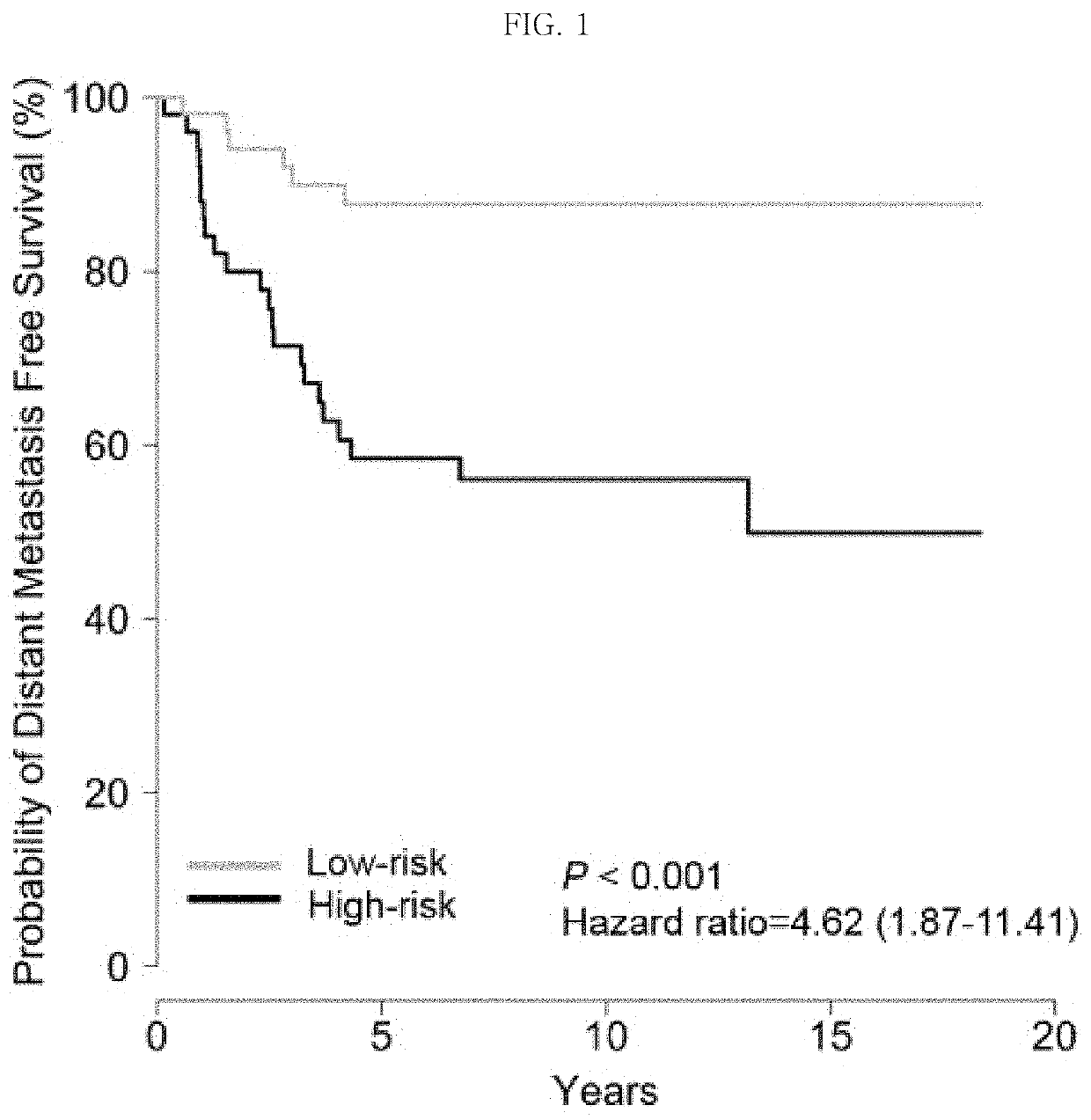
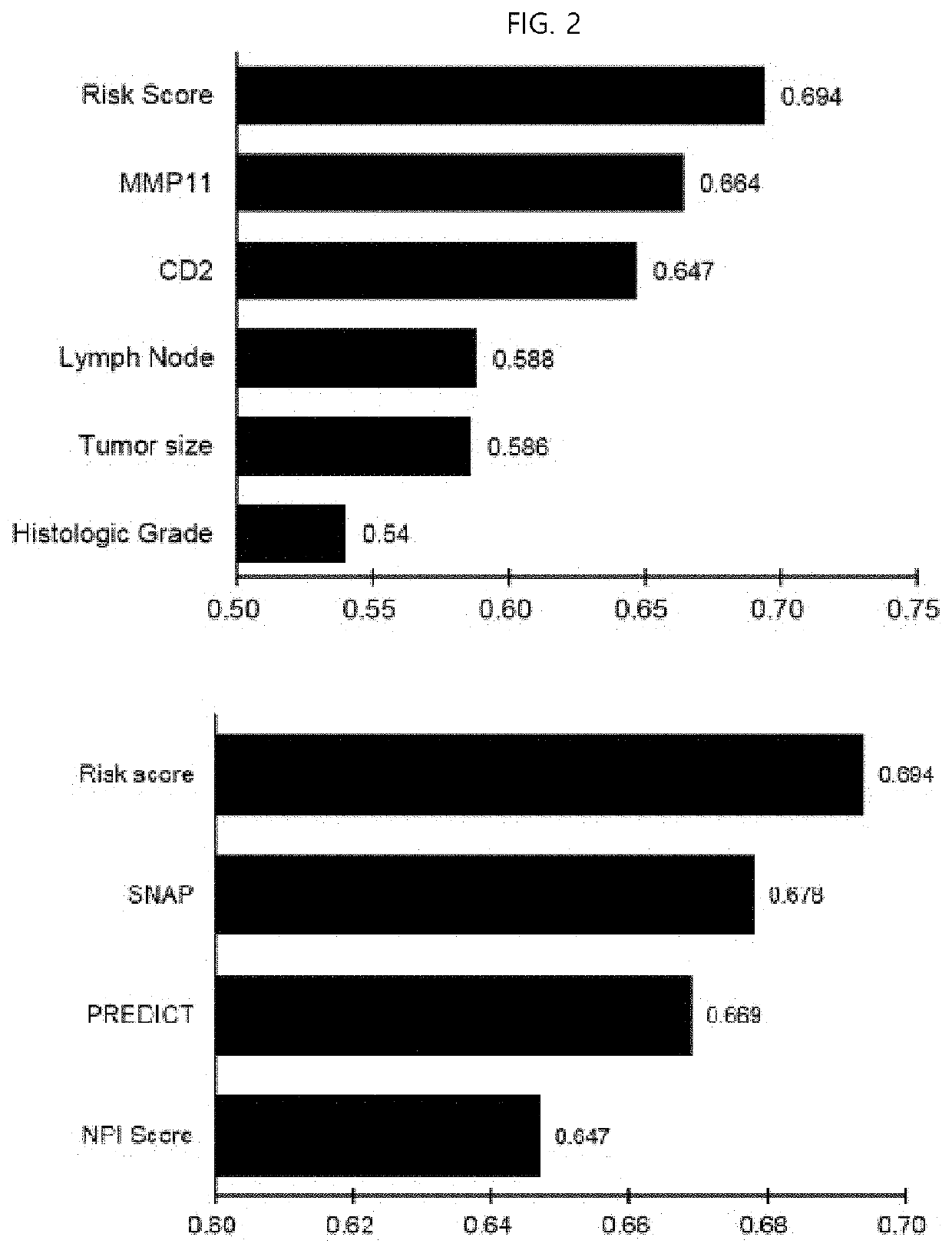
Method for predicting prognosis of breast cancer patient
The present invention relates to a method for predicting the prognosis of a breast cancer patient. More specifically, to provide information needed to predict the prognosis of a breast cancer patient, the method for predicting the prognosis of breast cancer including the following steps of the present invention comprises: (a) obtaining a biological sample from a breast cancer patient; (b) measuring the mRNA expression level of matrix metallopeptidase 11 (MMP11) and the mRNA expression level of cluster of differentiation 2 (CD2) from patient information or the sample of step (a); (c) normalizing the gene mRNA expression levels selected and measured in step (b); and (d) predicting the prognosis of breast cancer by combining the gene expression levels normalized in step (c), wherein overexpression of the MMP11 indicates a bad prognosis, and overexpression of CD2 indicates a good prognosis.The method of the present invention has an effect of being capable of more accurately predicting the future prognosis of metastasis, recurrence, or metastatic recurrence in breast cancer patients, and in particular, has a very excellent ability to predict the prognosis of HER2-type breast cancer, the prognosis of which is very poor, and thus can be usefully used to provide clues for the direction of future treatment of breast cancer.
Owner:GENCURIX
Dosing for treatment with anti-CD20/anti-CD3 bispecific antibodies
ActiveUS11466094B2Organic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCD20Disease
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Nanoparticle composition for use in targeting cancer stem cells and method for treatment of cancer
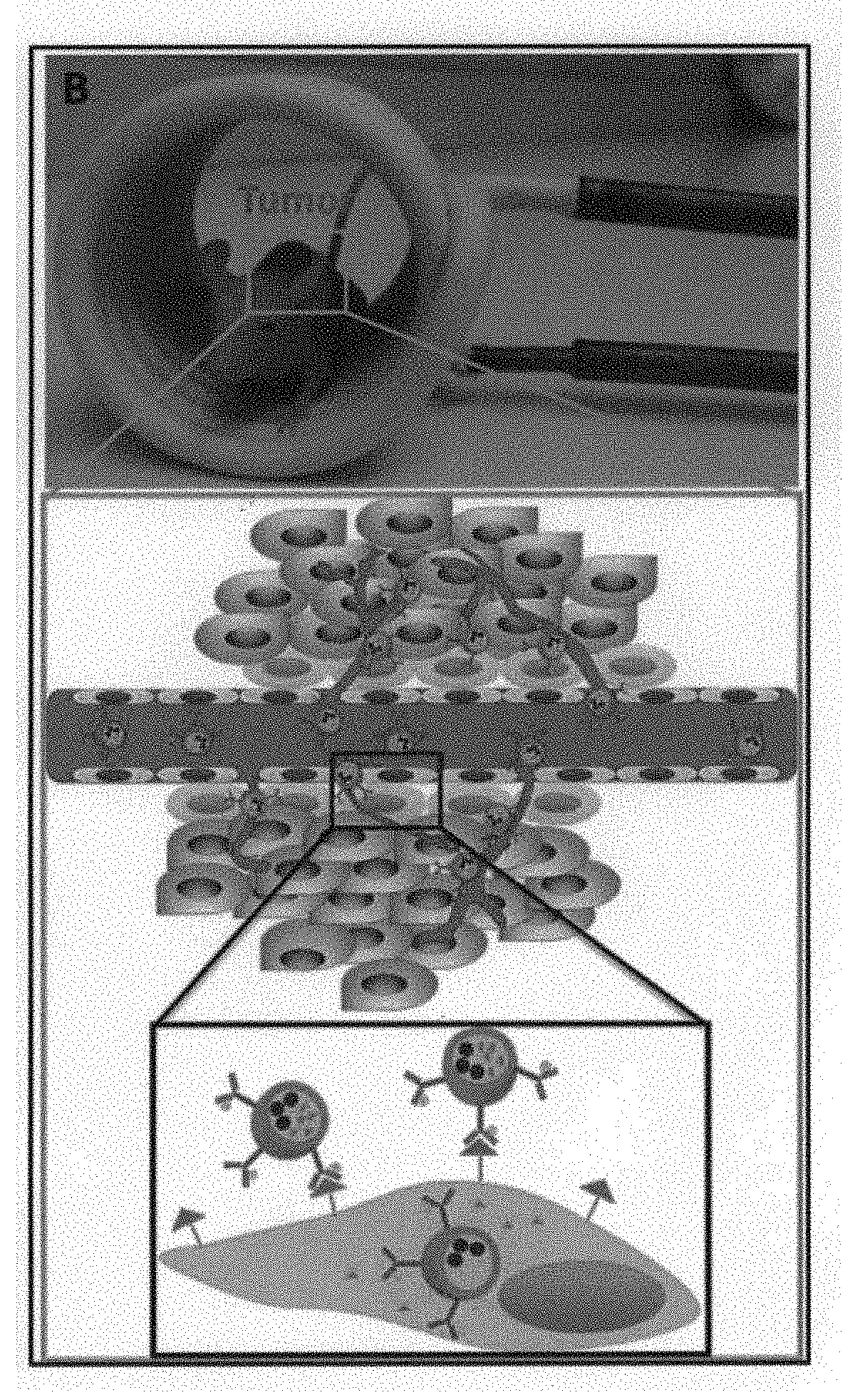
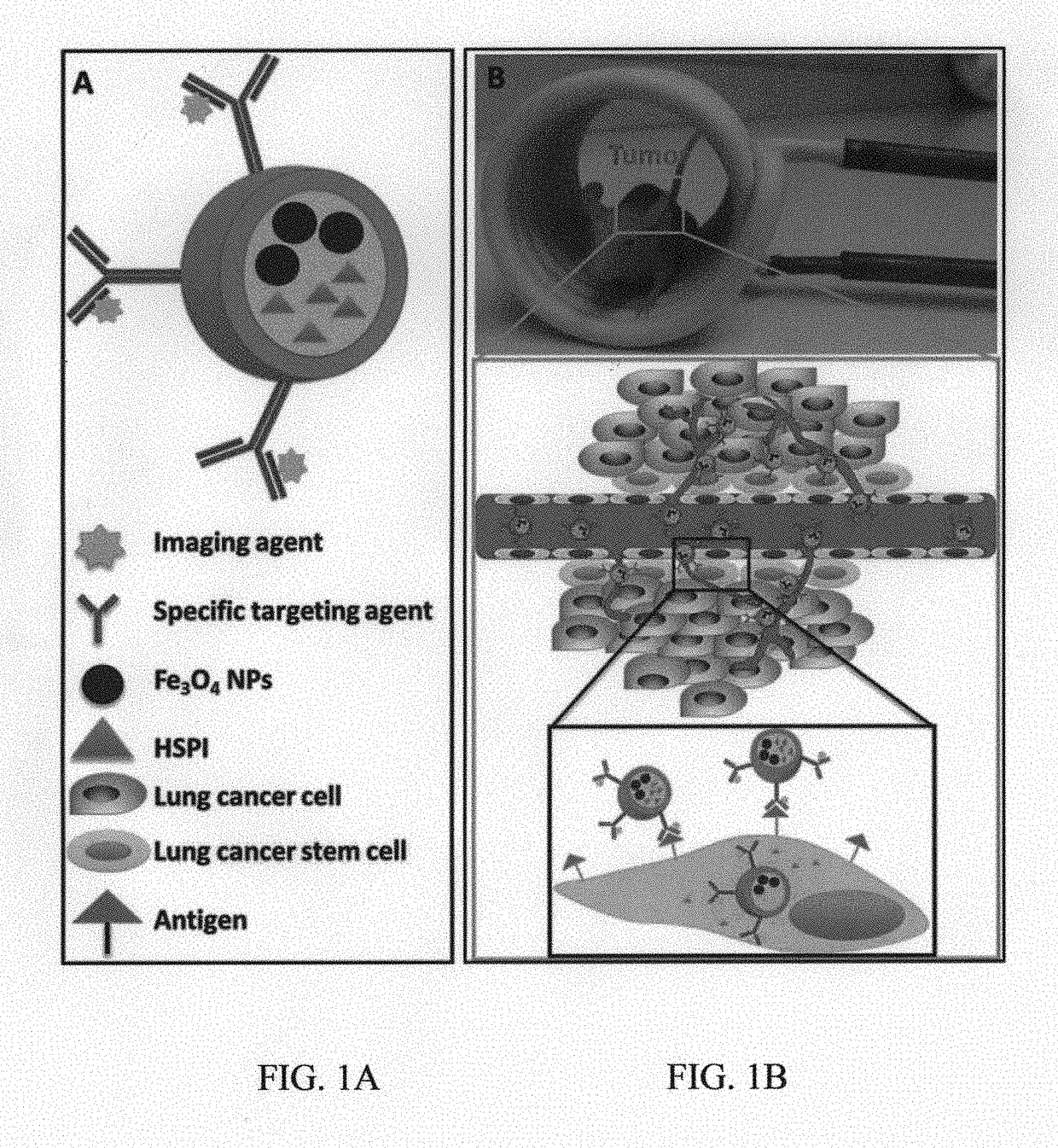
ActiveUS20180193485A1Growth inhibitionPowder deliveryElectrotherapyHeat Shock Protein InhibitorCancer targeting
There is disclosed a composition in the form of a nanoparticle. The nanoparticle composition has a diameter from 5 to 500 nanometers. The nanoparticle composition has i) a central core portion including magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles adapted to act as a heat source when subjected to a magnetic field and a chemotherapeutic agent configured to treat cancer tissues, ii)—a shell portion including a shell member encapsulating said core portion, and iii)—antibodies configured to target cancer stem cells and adhered to surface of said shell member. The chemotherapeutic agent is a heat shock protein inhibitor and is releasable on activation of the heat source due to the magnetic field, and the shell member is made of silica or a silica based material. Surface of the nanoparticle is modified with the antibodies capable of binding with a cluster of differentiation molecules on the cell surface of the target cancer stem cells, whereby by way of combination of specificity of the nanoparticle composition due to the antibody, thermo-therapeutic effect of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles, and release of the heat shock protein inhibitor on site at the target cancer stem cells, inhibition of the target cancer stem cells is synergistically and additionally enhanced is increased.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Cluster of differentiation 19 (CD19) antibody and application thereof
PendingCN111253487APeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenAntiendomysial antibodies
The application relates to an antibody which can be specifically bound to a cluster of differentiation 19 (CD19) or an antigen-binding fragment of the antibody, and the anti body is bound to CD19 protein with 3.5 [mu]g / mL or a smaller half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value. The application further relates to a use of the antibody or the antigen-binding fragment thereof in preparation of drugs.
Owner:SUNSHINE LAKE PHARM CO LTD
Anti-CD47 antibody molecules
ActiveUS10683350B2Improve the preparation effectImprove humanityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesAntigen binding
Owner:CENTESSA PHARM (UK) LTD
Binding agents
ActiveUS20190375840A1Improve the preparation effectImprove humanityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody medical ingredientsAntigen bindingIntegrin
The invention relates to antibody molecules and antigen-binding portions thereof which bind specifically to CD47 (Cluster of Differentiation 47, also known as integrin associated protein [IAP]). In aspects of the invention, the anti-CD47 antibody molecules and antigen-binding portions thereof specifically bind to human CD47 and cynomolgus monkey CD47. Medical uses of the anti-CD47 antibody molecules and antigen-binding portions of the invention are disclosed. The anti-CD47 antibody molecules and antigen-binding portions of the invention represent modified and optimised binding molecules compared with a VxP037 murine / humanized anti-CD47 antibody described in WO2014 / 093678A2.
Owner:CENTESSA PHARM (UK) LTD
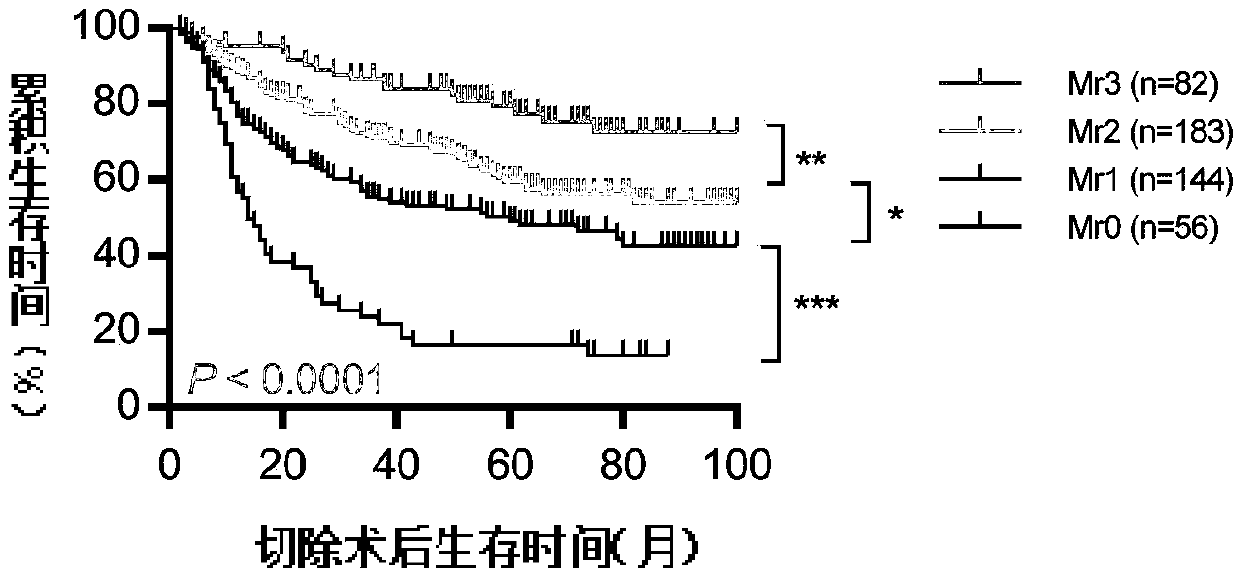
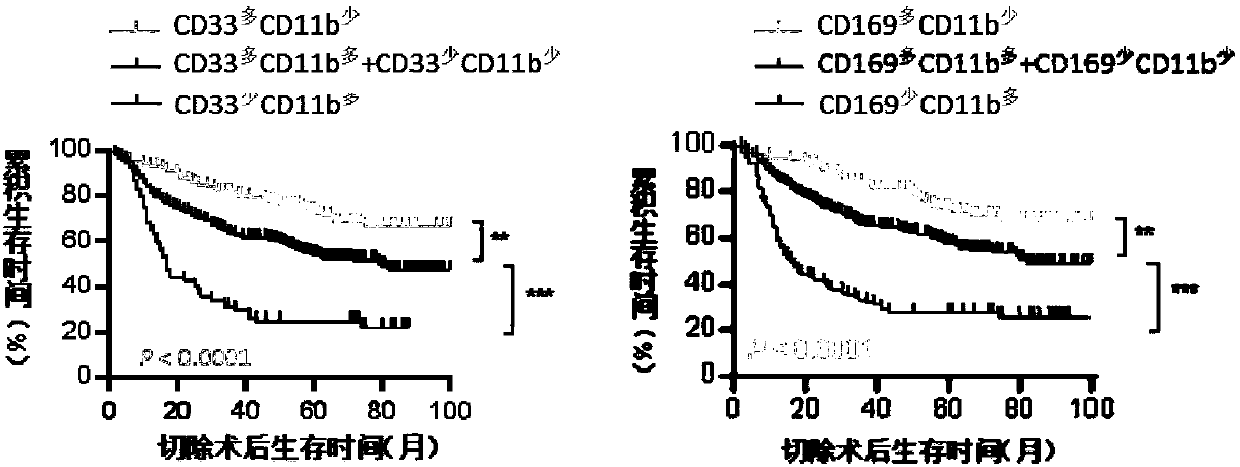
Immunohistochemical detection kit used for prognosis after hepatectomy
The invention relates to an immunohistochemical detection kit used for prognosis after hepatectomy. The immunohistochemical detection kit comprises a first antibody and a second antibody, the first antibody is two or combination of more than two selected from the following protein molecular markers of an antibody: CD33 (cluster of differentiation 33), CD11b (ITGAM), and CD169 (sialic acid adhesin). The kit employs a double antibody / tri-antibody combination index, prognosis condition of the patient after operation can be accurately predicted, so that appropriate treatment population and modes can be selected for doctors, and the kit provides more powerful support for effective diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
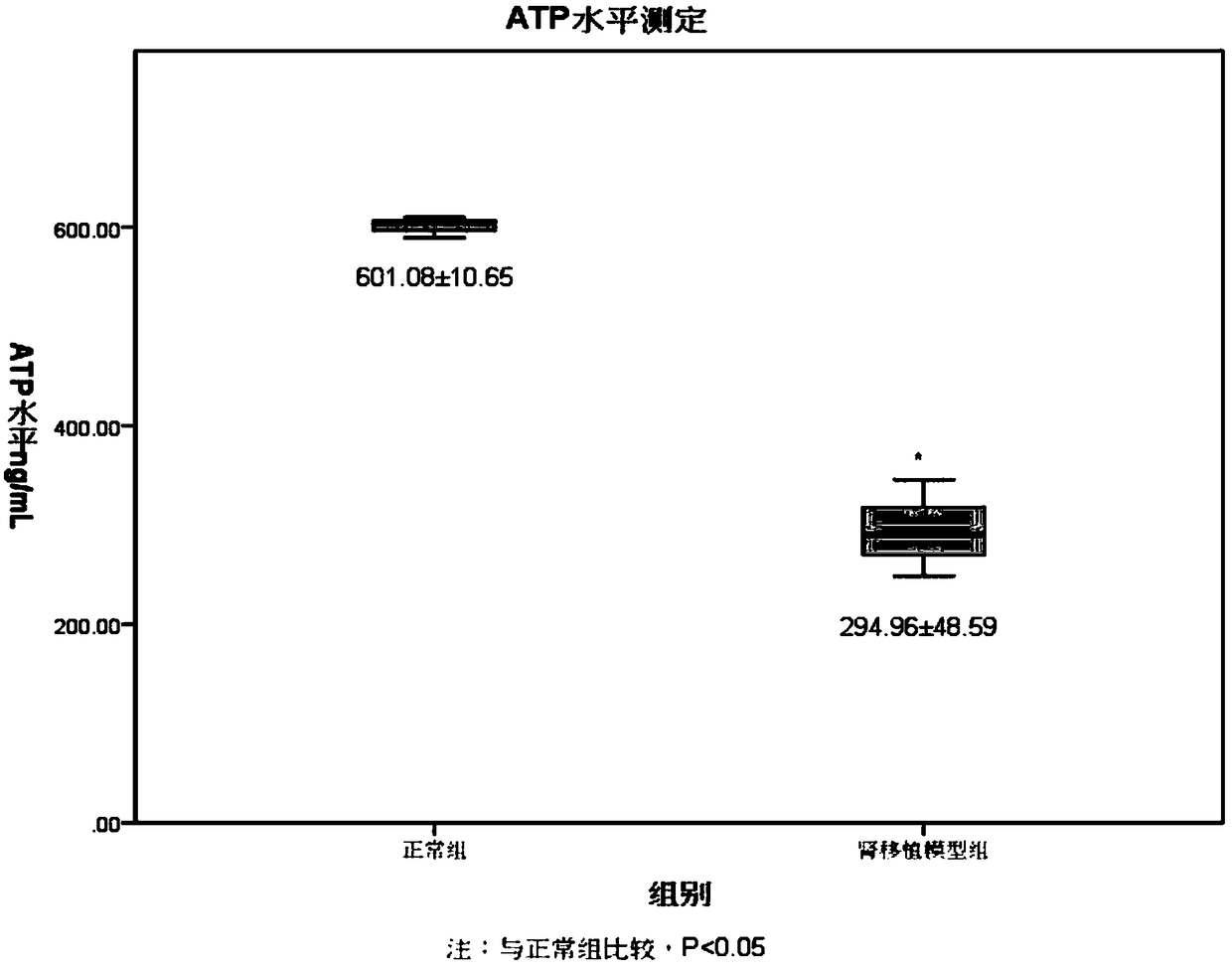
Rat CD4 (Cluster of Differentiation 4) antibody coated magnetic beads, preparation method and application therefor and kit containing magnetic beads
The invention provides a rat CD4 antibody coated magnetic beads, a preparation method and an application therefor and a kit containing magnetic beads. The method for preparing the magnetic beads comprises the following steps of: washing the magnetic beads multiple times through different reagents, and removing the supernatant. The rat CD4 antibody coated magnetic beads can be prepared according tothe preparation method. The prepared rat CD4 antibody coated magnetic beads can be used in the kit, and used for detecting immunological rejection after rat kidney transplantation. Compared with theprior art, the invention has the advantages that the rat CD4 antibody coated magnetic beads prepared by the method for preparing the rat CD4 antibody coated magnetic beads is combined with an immune cell function measurement kit ImmuKnow TW-Cylex , and can be used for detecting the immunological rejection after the rat kidney transplantation.
Owner:福建中医药大学附属人民医院(福建省人民医院)
Methods and systems for identification and treatment of pathological neurodegeneration and age-related cognitive decline
PendingUS20200400688A1Lower Level RequirementsReduce severityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDepressantT cell
Methods and systems for diagnosing, providing prophylaxis, and treating one or more age-related neurodegeneration or pathological cognitive impairment are provided. An increased presence of CD103+ resident memory CD8+ T cells (CD8+ TRM) can be detected in blood sample obtained from the human subjects with one or more symptoms of loss of short-term or long-term memory, decreased ability to maintain focus, and decreased problem-solving capacity. An increased presence of CD103+ CD8+ TRM can be compared to a value obtained from one or a pool of healthy human subjects with none of the one or more symptoms. One or more of a therapeutically effective amount of: an inhibitor of cluster of differentiation (CD103), an inhibitor of perforin-1, and an inhibitor of interferon gamma (IFNγ) can be administered as treatment of age-related neurodegeneration or pathological cognitive impairment. Pathological neurodegeneration can include Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, or Alzheimer' s disease.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Transformed and attenuated Listeria monocytogenes introducing human CD24 (cluster of differentiation 24) nucleotide sequence, and vaccine thereof
InactiveCN103820374AEfficient activationGood for preventing and treating tumorsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaNucleotideShuttle plasmid
The invention relates to a transformed and attenuated Listeria monocytogenes introducing a human CD24 (cluster of differentiation 24) nucleotide sequence, and a vaccine thereof. The transformed and attenuated Listeria monocytogenes is characterized in that human CD24 nucleotide is located on a shuttle plasmid PKSV7, and is duplicated and expressed in the attenuated Listeria monocytogenes or a progeny of the attenuated Listeria monocytogenes. The vaccine provided by the invention overcomes various defects in liver cancer treatment in the prior art, is used for clinic treatment and prevention of drug resistance of liver cancer to chemo-radiotherapeutic drugs and postoperative metastasis and relapse, and is relatively high in safety and reliability.
Owner:NANJING XINSAIERSI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Anti-cluster of differentiation 19 (CD-19) fully humanized antibody or antibody fragment and chimeric antigen receptor comprising same and application of fully humanized antibody or antibody fragment
ActiveCN111303286APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorAntibody fragments
The invention discloses an anti-cluster of differentiation 19 (CD-19) fully humanized antibody or antibody fragment and a chimeric antigen receptor comprising the same and application of the fully humanized antibody or antibody fragment. The antibody or antibody fragment or a nucleic acid coding the antibody or antibody fragment can be used for preparing host cells, lentiviral plasmids, tumor diagnosis drugs, targeted anti-tumor drugs and the like. The antibody or antibody fragment disclosed by the invention can be bound to humanized CD19 protein by high specificity.
Owner:CHANGZHOU VELOX PHARMA SCI & TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com