Method for detecting active tuberculosis
An active tuberculosis and non-tuberculosis technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, measuring devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0408] Example 1: Comparison of the blood transcriptome in active TB and after prolonged recovery
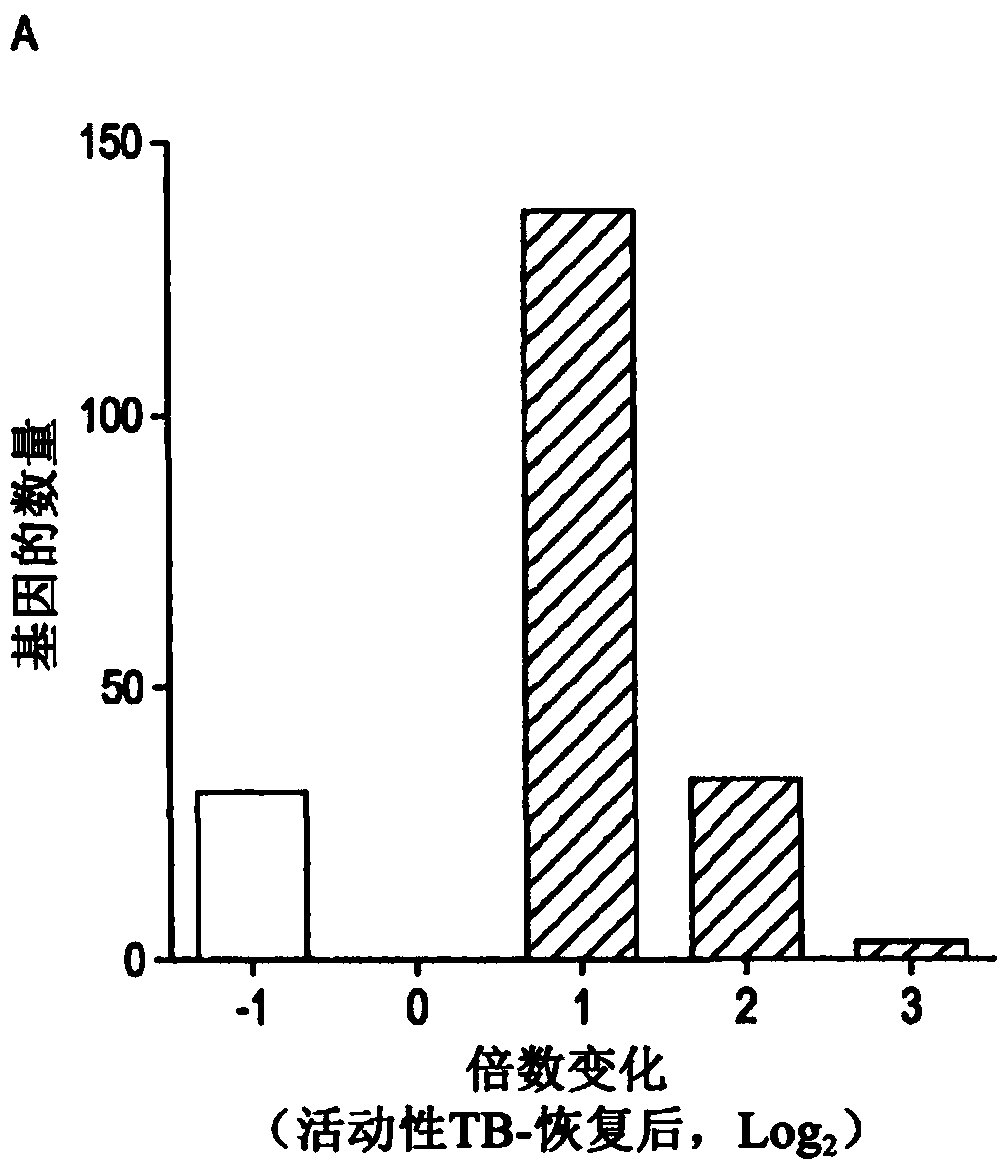
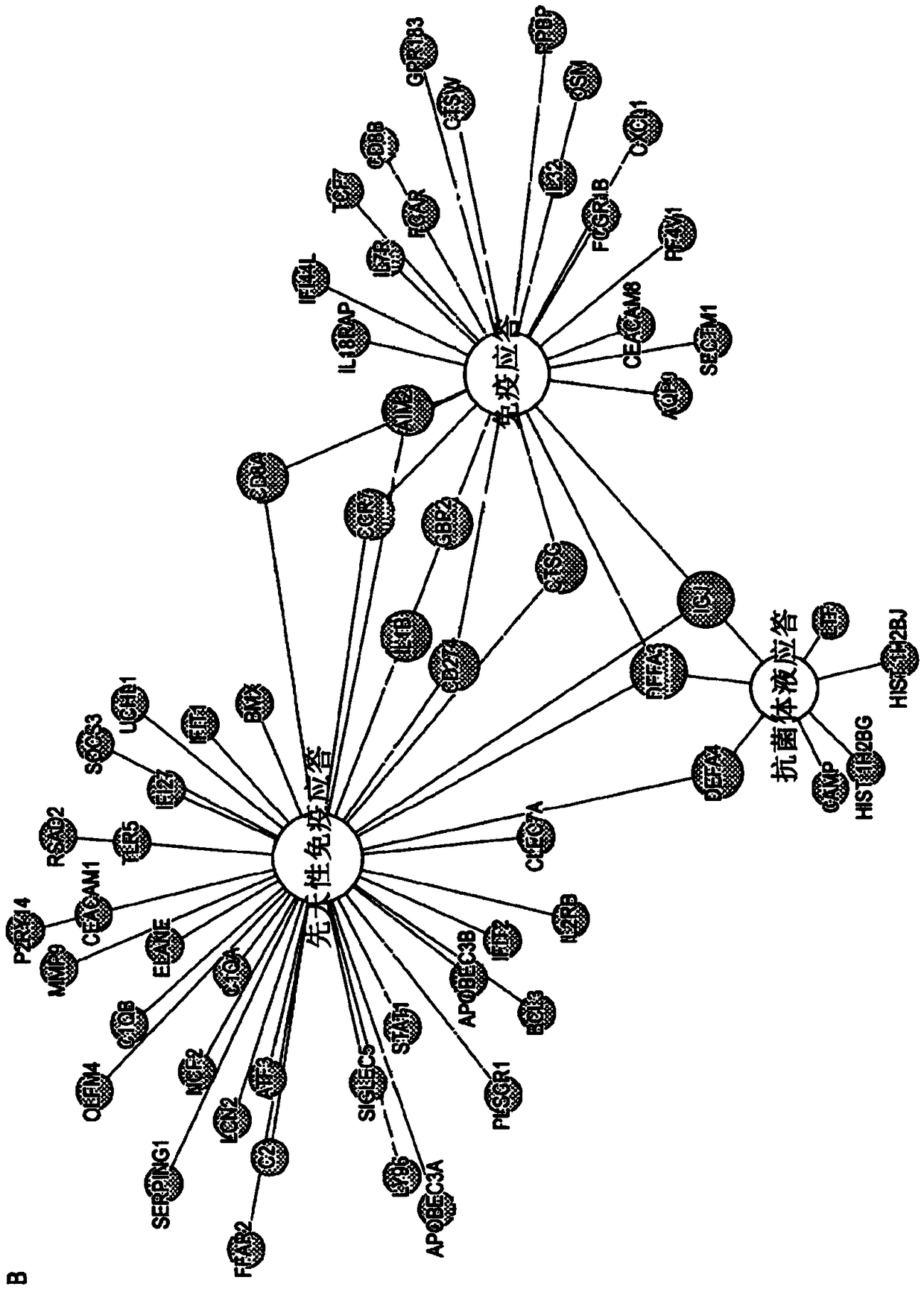
[0409] The AdjuVIT study population included HIV-negative patients with positive smears and cultures for pulmonary TB, in which, by comparison with recovered subjects drawn from the same cohort, two to four years after completion of TB treatment, The present invention seeks to identify the peripheral blood transcriptional signature of active TB in the above patients (Table 1). The analysis revealed statistically significant and >2-fold gene expression differences among 204 unique protein-coding transcripts ( figure 1 A). Consistent with other published data, active TB in this cohort was associated with increased expression of genes involved in the immune response ( figure 1 B). To assess the generality of this transcriptional signature in other patient cohorts with active TB, compared to healthy volunteers (Berry et al., 2010) or subjects with LTBI (Bloom et al., 2012) , the...
Embodiment 2
[0413] Example 2: Support Vector Machine Classification of Active TB by Comparison with Health Status
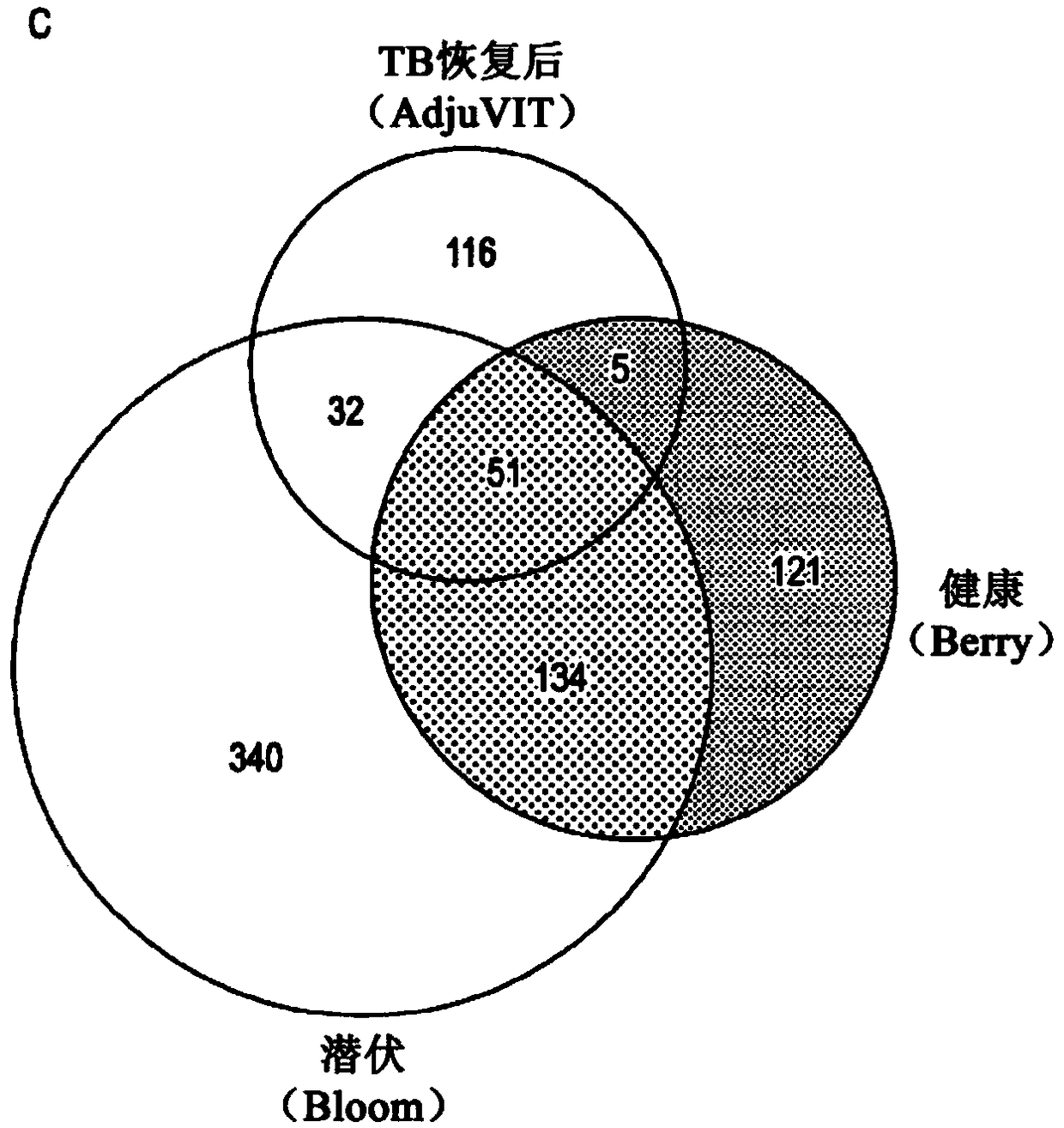
[0414] In order to distinguish individual cases by their blood transcriptome, the present invention uses SVM to obtain a discriminative model from the training data and classify the subsequent test cases. Using 51 transcripts differentially expressed in active TB compared to other healthy states in multiple cohorts ( figure 1 C), The present invention uses the AdjuVIT research dataset to train an SVM to distinguish active TB cases from recovered cases. The inventors then evaluated the performance of this SVM model in classifying samples from three independently published studies of HIV-negative subjects, including a total of 325 cases. These include the two studies mentioned above, including data from active TB and healthy volunteers (Berry cohort) (Berry et al., 2010) or active TB and latent TB (Bloom cohort) (Bloom et al., 2012) , and additional data from a multicenter A...
Embodiment 3
[0416] Example 3: BATF2 distinguishes active TB from healthy status in multiple study cohorts
[0417] Having identified peripheral blood BATF2 transcript levels in the AdjuVIT cohort as a biomarker of active TB, the present inventors sought to test its performance in multiple independent cohorts. Regardless of HIV status, BATF2 expression was significantly higher in patients with active TB than in healthy volunteers (Berry cohort) (Berry et al., 2010) and patients with LTBI (Bloom and Kaforou cohorts) (Bloom et al. , 2012; Kafourou et al., 2013) of BATF2 expression, representing data from a total of 402 patients ( image 3 A). In HIV-negative patients in these studies, peripheral blood BATF2 expression that differentiated active TB cases from various healthy cases was described with a ROCAUC score of 0.93 to 0.99 in each cohort ( image 3 B). In HIV-infected patients (ROC AUC of 0.84) in the Kaforou cohort, BATF2 levels were not well able to distinguish active TB cases fro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com