Non-human animals having humanized cluster of differentiation 47 gene
A gene, alpha gene technology, applied in the field of non-human animals with humanized differentiation cluster 47 gene
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
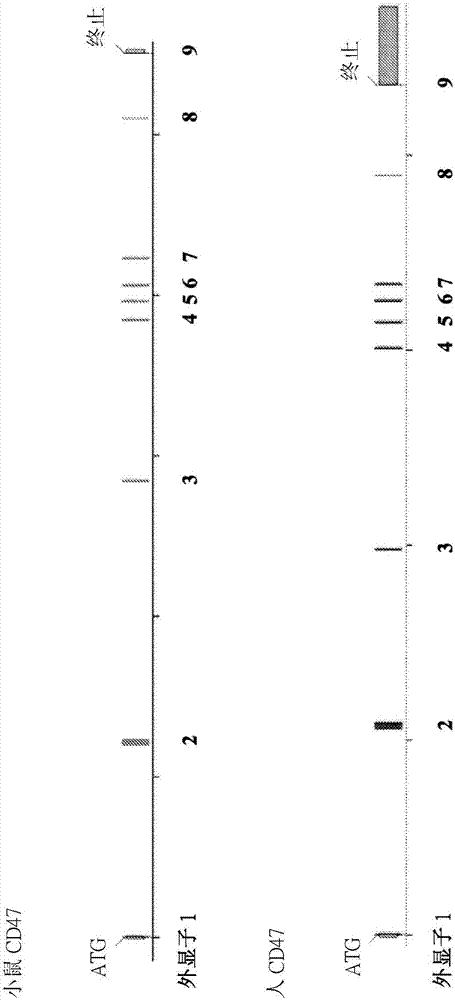
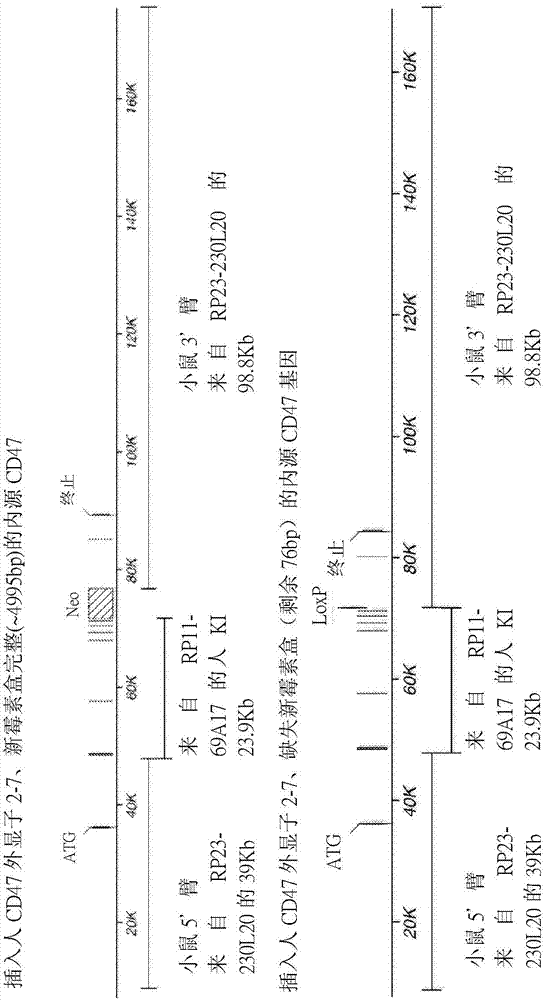
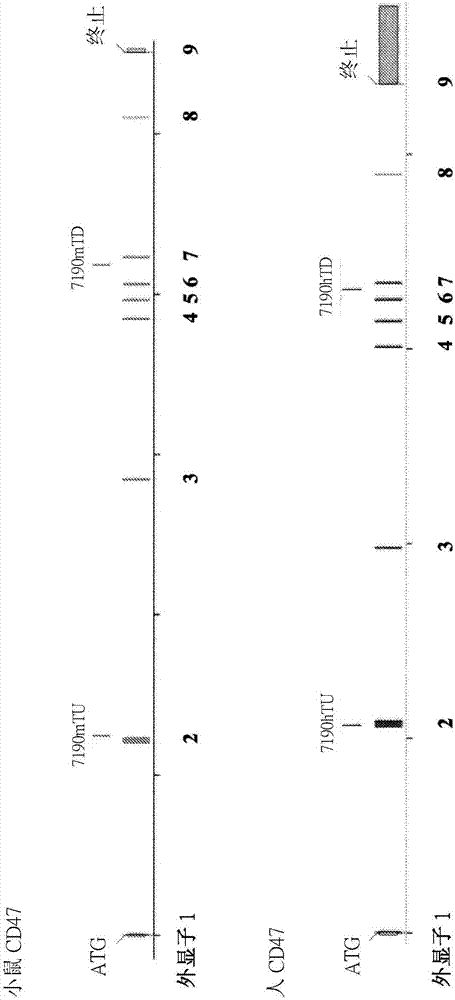
[0214] Example 1. Humanization of the Endogenous Cluster of Differentiation 47 (CD47) Gene
[0215] This example illustrates exemplary methods for humanizing an endogenous gene encoding cluster of differentiation 47 (CD47) in a non-human mammal, such as a rodent (eg, mouse). The methods described in this example can be used to humanize the endogenous CD47 gene of a non-human animal using any human sequence or combination of human sequences (or sequence fragments) as described. In this example, the human CD47 gene present in bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone RP11-69A17 was used to humanize the endogenous CD47 gene in mice.
[0216] use technology to construct a targeting vector for humanizing the genetic material encoding the extracellular N-terminal IgV domain and five transmembrane domains of the endogenous CD47 gene (see, e.g., U.S. Patent No. 6,586,251 and Valenzuela et al. (2003) High-throughput engineering of the mouse genome coupled with high-resolution expr...
Embodiment 2
[0223] Example 2. Expression of humanized CD47 polypeptide by mouse erythrocytes.
[0224] This example demonstrates that non-human animals (e.g., rodents) modified to contain a humanized CD47 gene according to Example 1 can be used to screen for CD47 modulators (e.g., anti-CD47 antibodies) and to determine various properties such as drug Kinetic and safety properties. In this example, multiple anti-CD47 antibodies were screened on mouse red blood cells (RBC) isolated from rodents prepared according to Example 1 expressing a humanized CD47 polypeptide as described herein.
[0225] Briefly, 2 mL of whole blood (n=2) from humanized CD47 mice was transferred to a 15 mL tube and centrifuged at 200 x g for 10 min at 4°C. Aspirate the plasma and buffy coat, then add 15 mL of PBS and mix the cells gently. Centrifuge the mixture again at 200 x g for five minutes at 4 °C. Aspirate the supernatant and wash the cells two more times. Resuspend the pelleted RBCs in a final volume of 10...
Embodiment 3
[0231] Example 3. Hemagglutination of mouse erythrocytes expressing humanized CD47 polypeptide.
[0232] This example also demonstrates that non-human animals (e.g., rodents) modified to contain a humanized CD47 gene according to Example 1 can be used in various assays (e.g., hemagglutination assays) to screen for modulators of CD47 ( For example, anti-CD47 antibody) and determine various properties such as pharmacokinetic and safety profiles. In this example, several anti-CD47 antibodies were screened on mouse red blood cells (RBC) expressing a humanized CD47 polypeptide as described herein to determine the concentration of the antibody that promotes hemagglutination.
[0233] Briefly, RBCs (n=2) from wild-type and humanized CD47 mice were prepared as described in Example 2. Twenty (20) μL of anti-CD47 antibody (5-fold serial dilution) was added to wells 1-12 of a 96-well V-bottom plate, followed by 80 μL of 0.5% mouse RBCs to all wells of the plate. Tap the plate to mix an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com