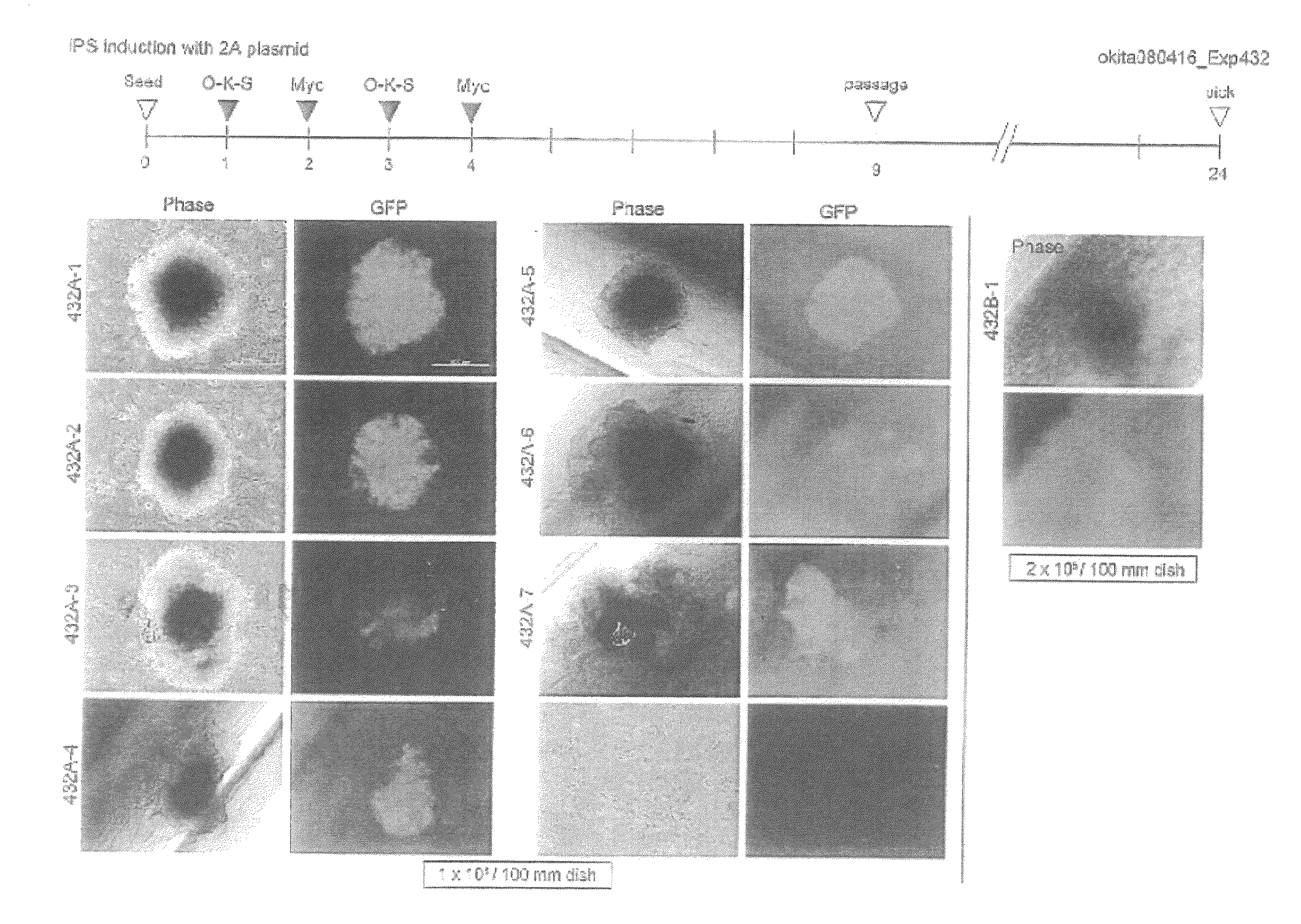
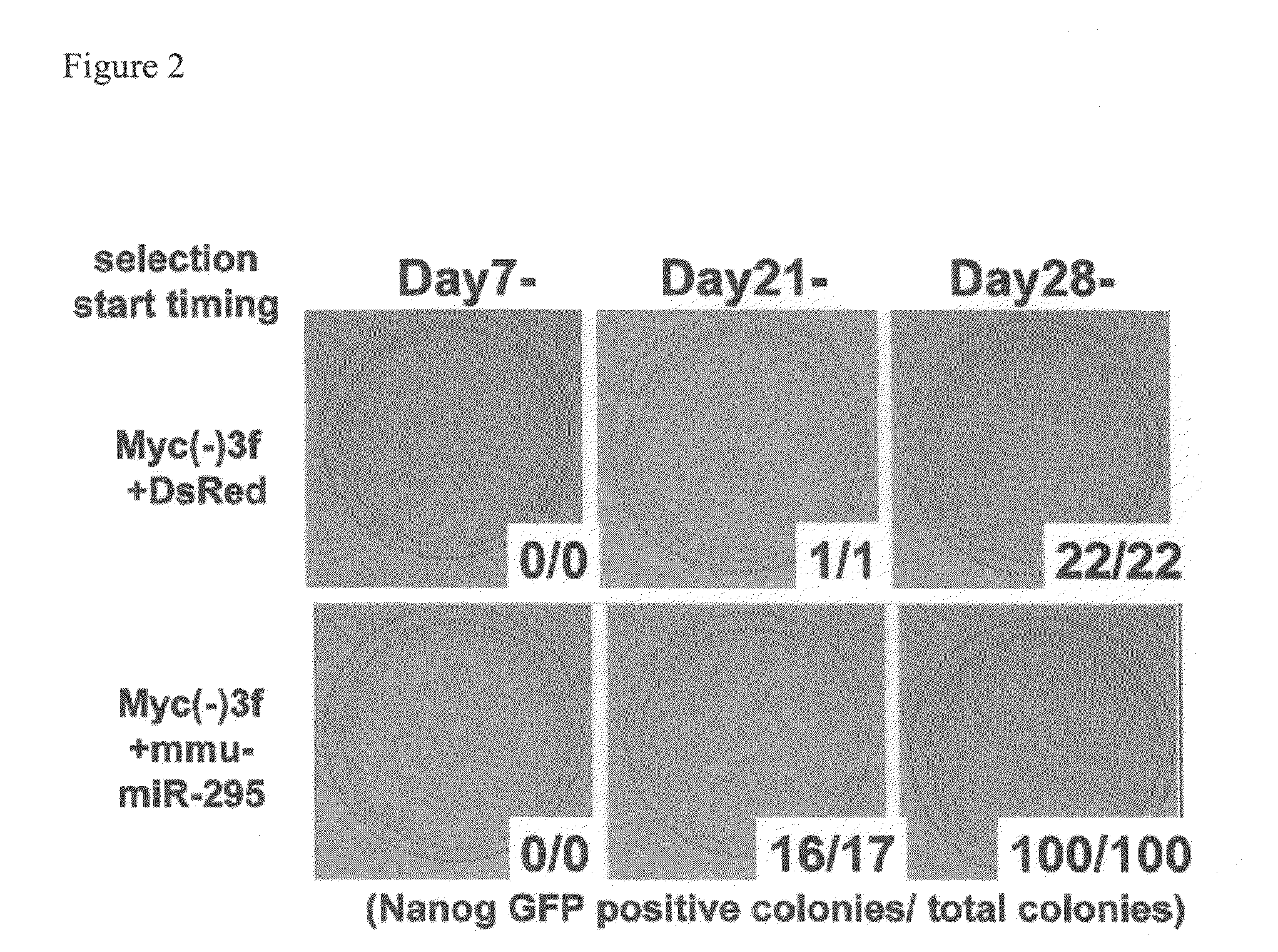
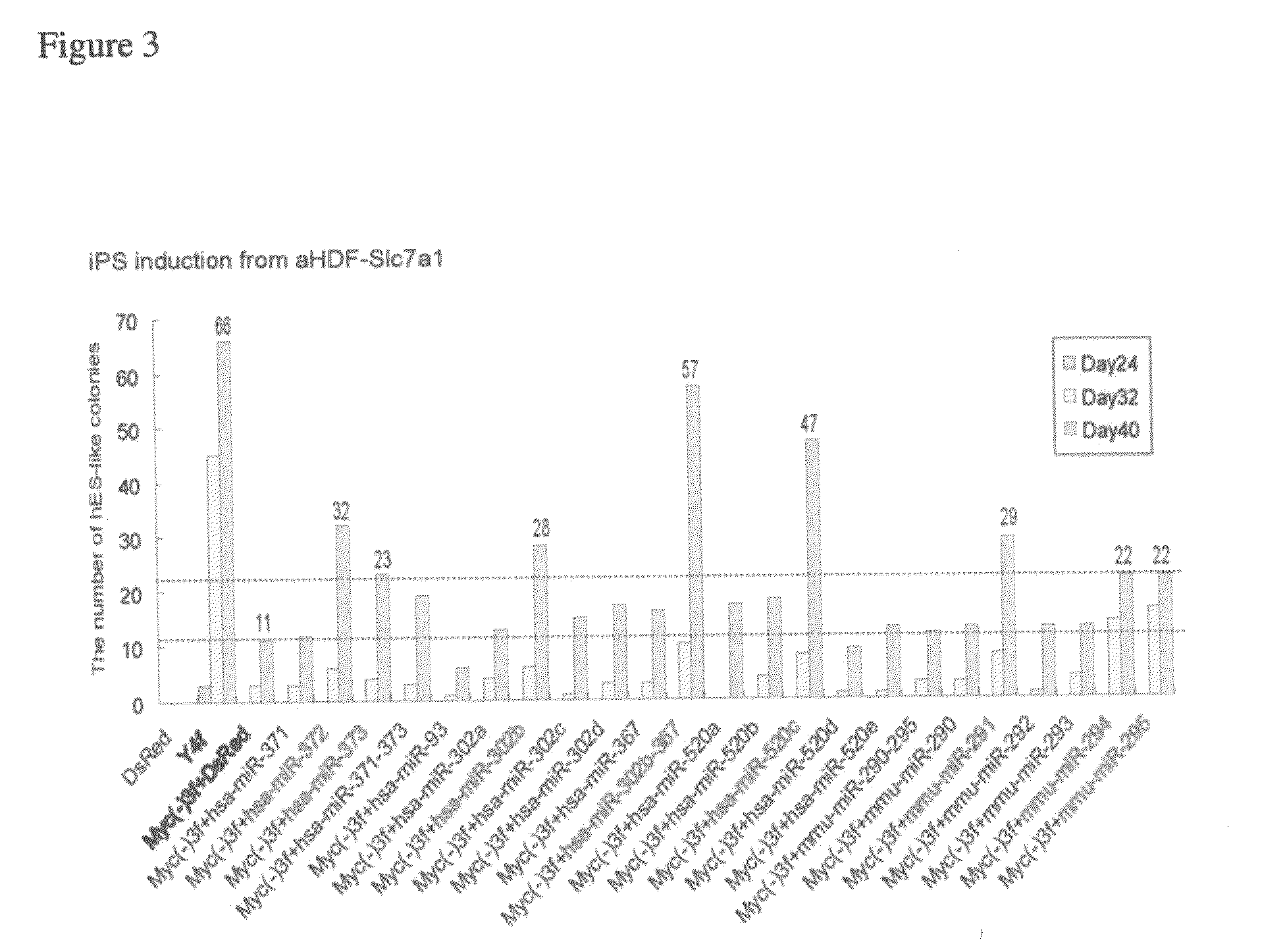
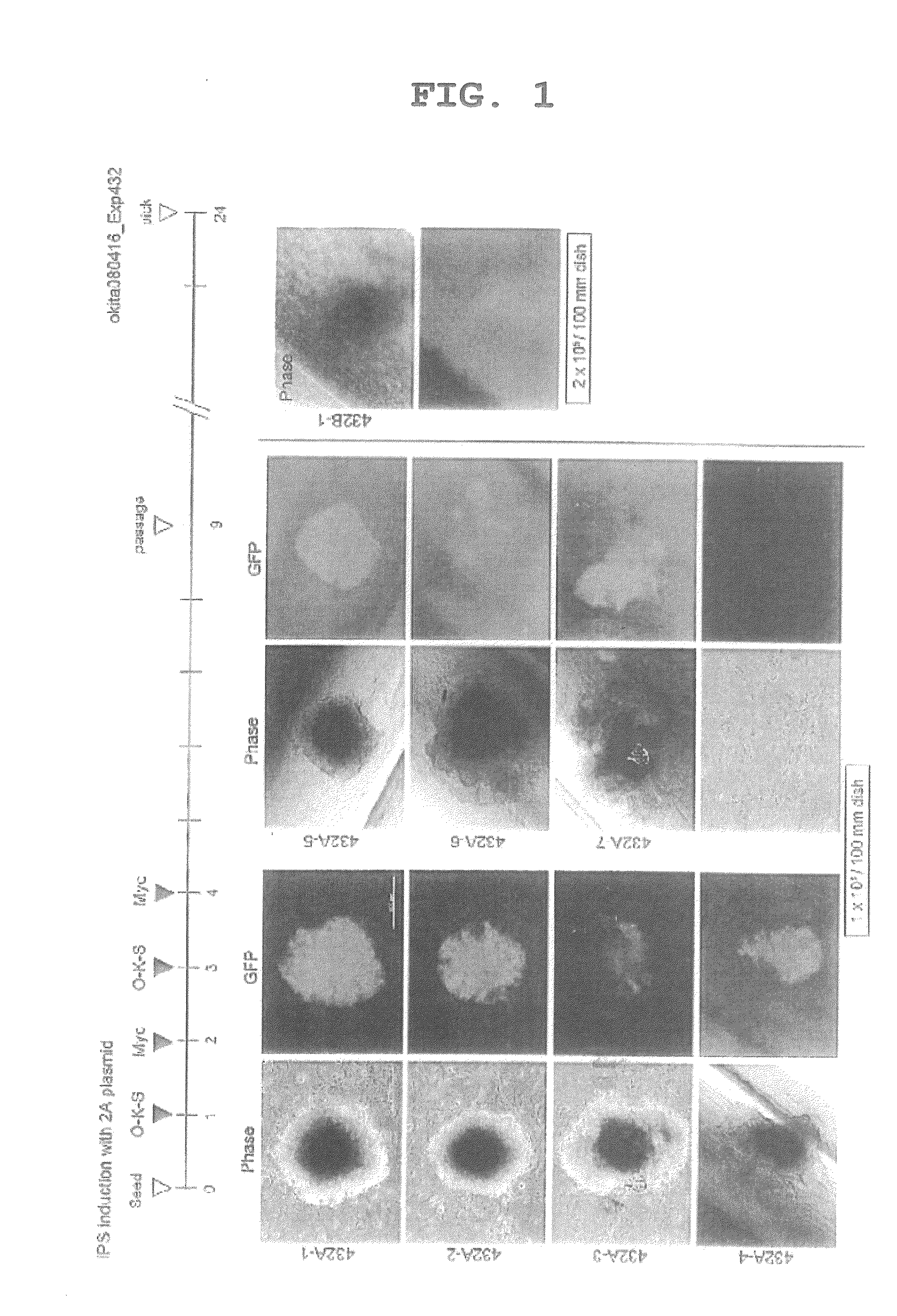
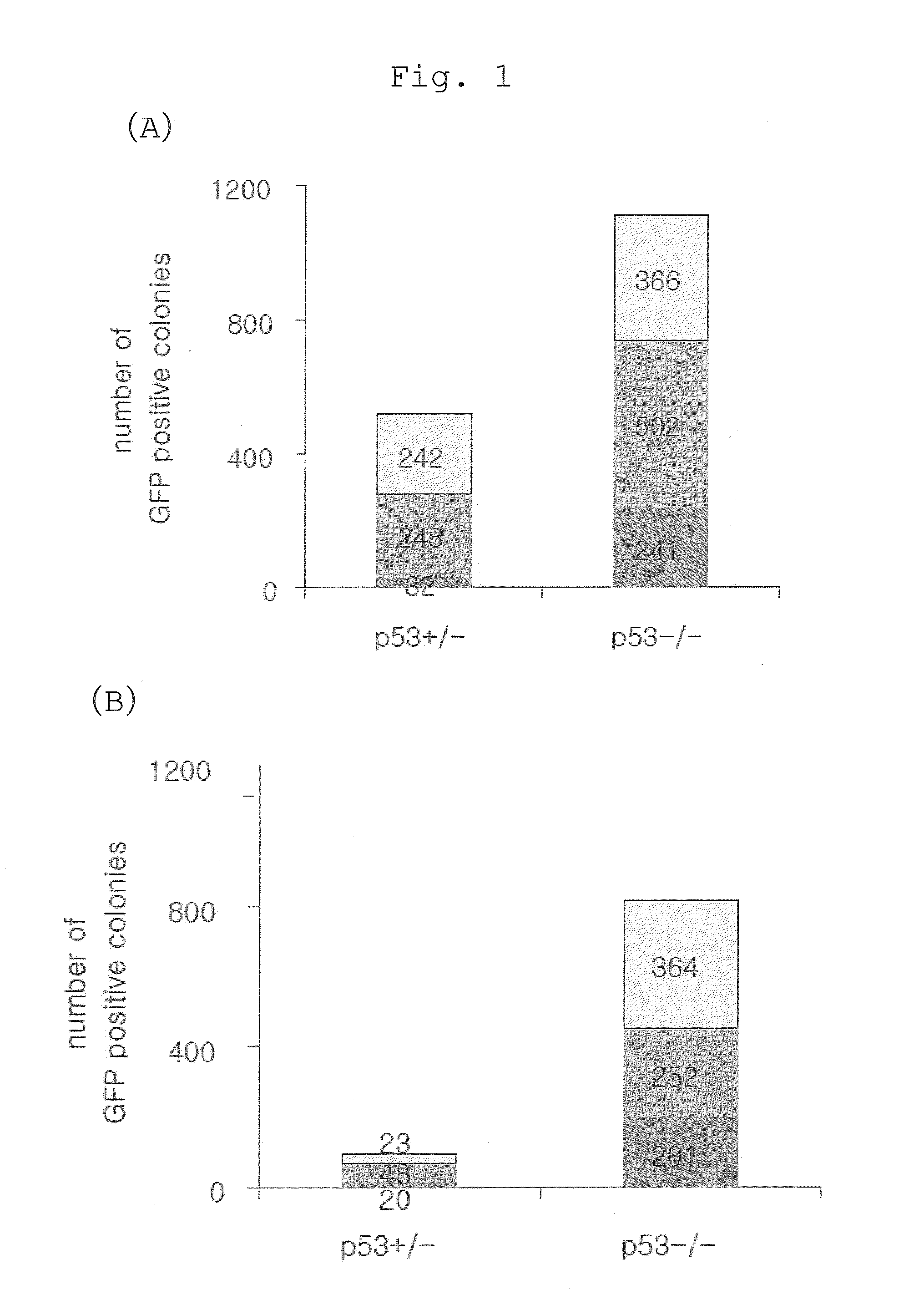
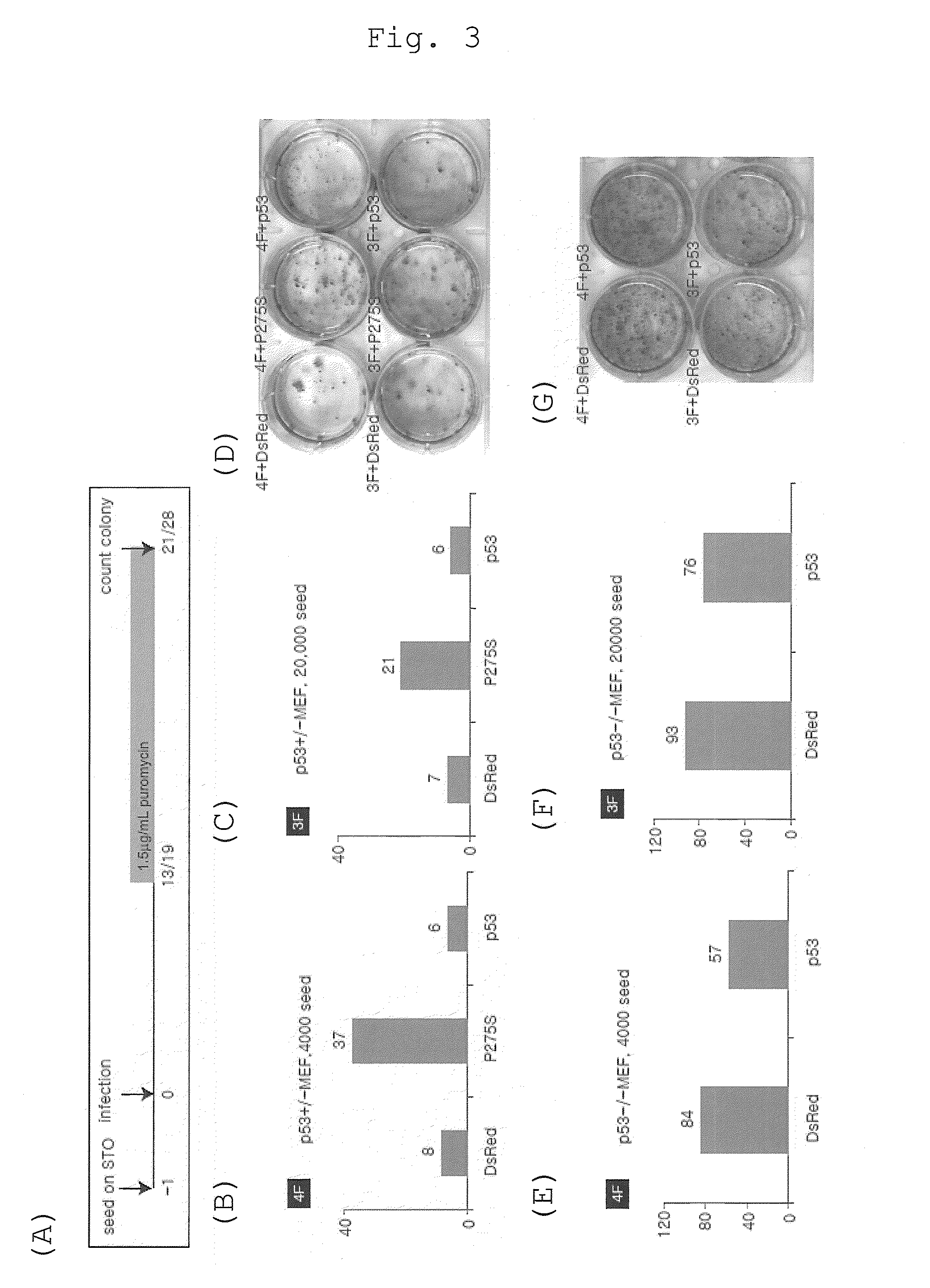
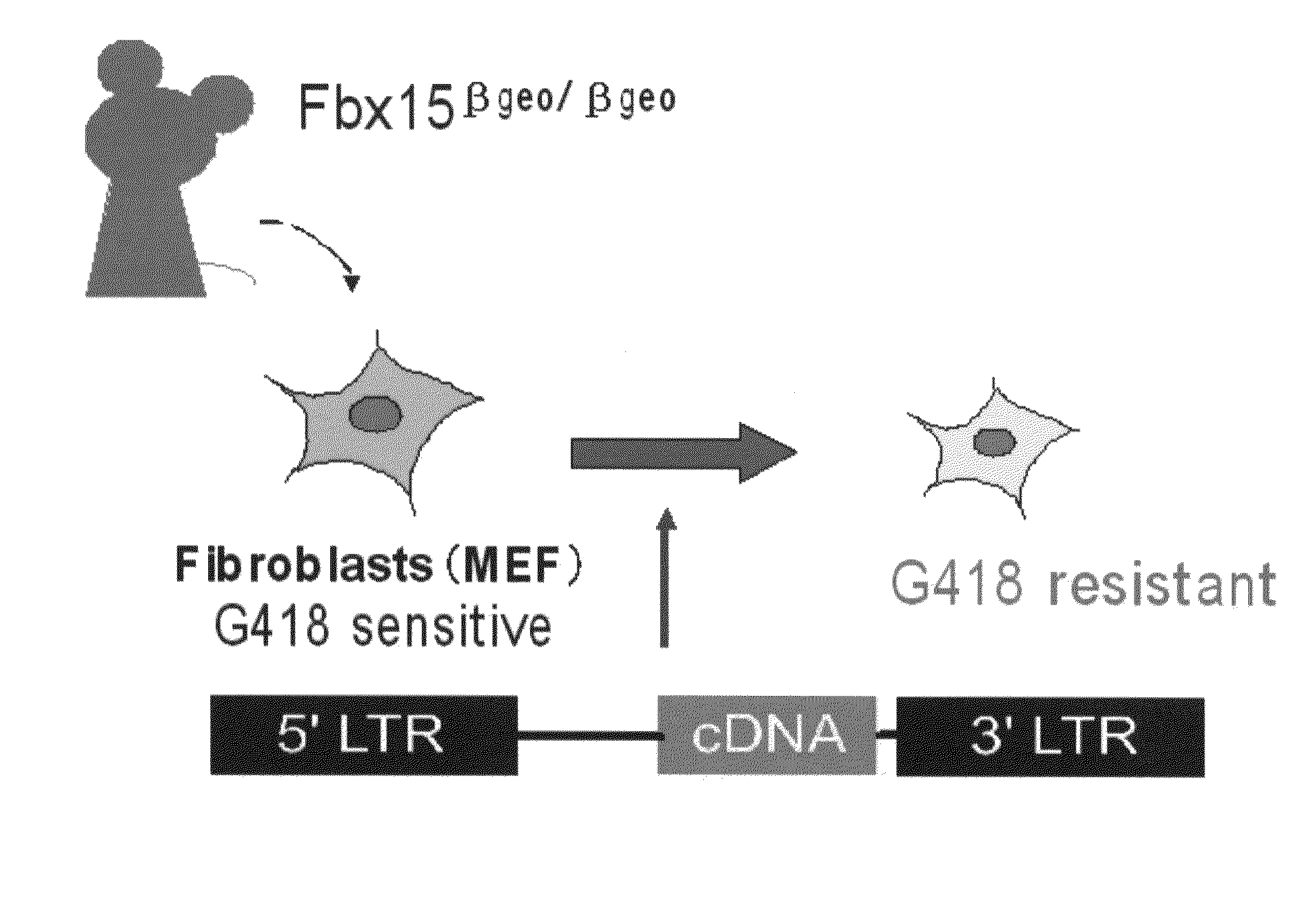
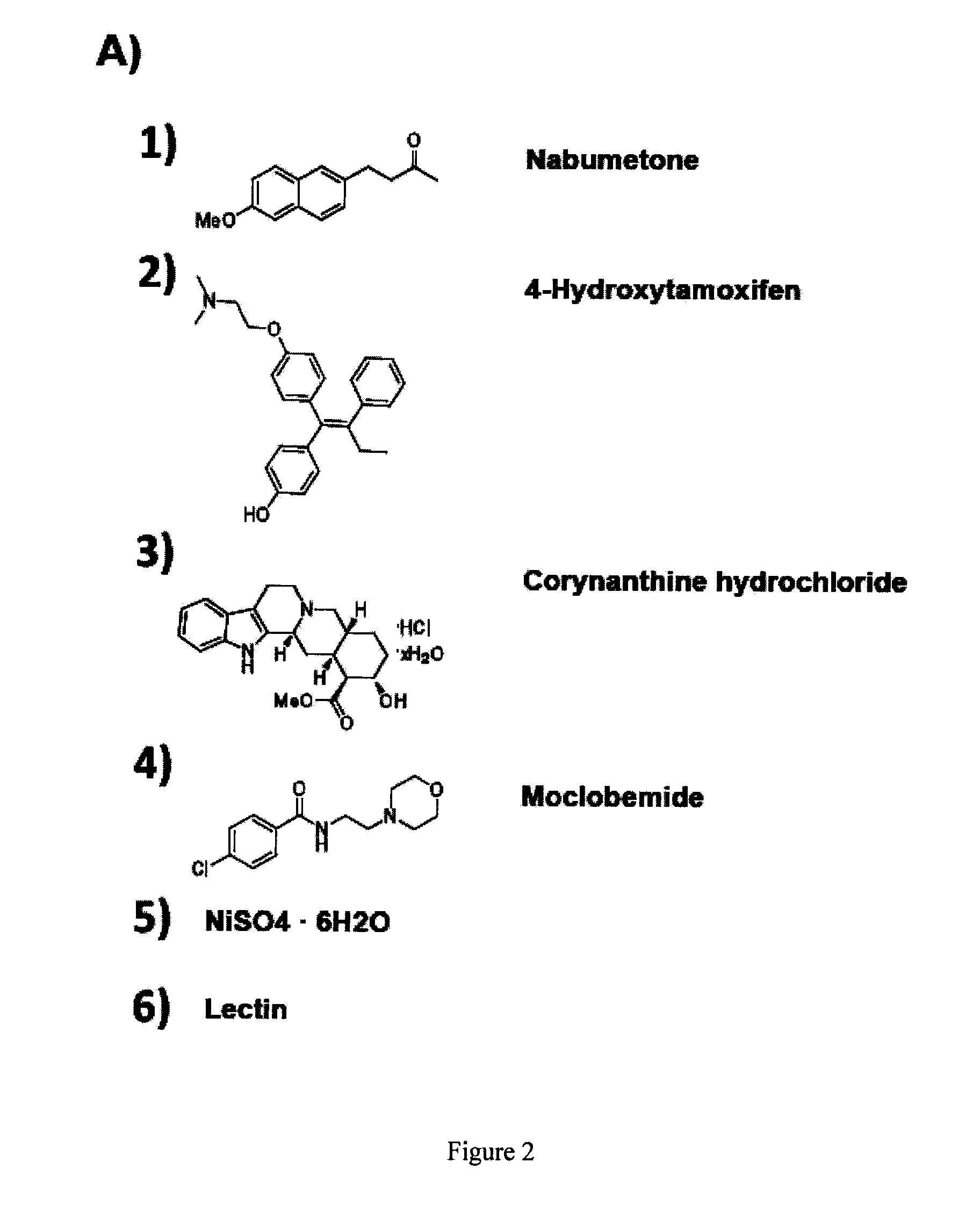
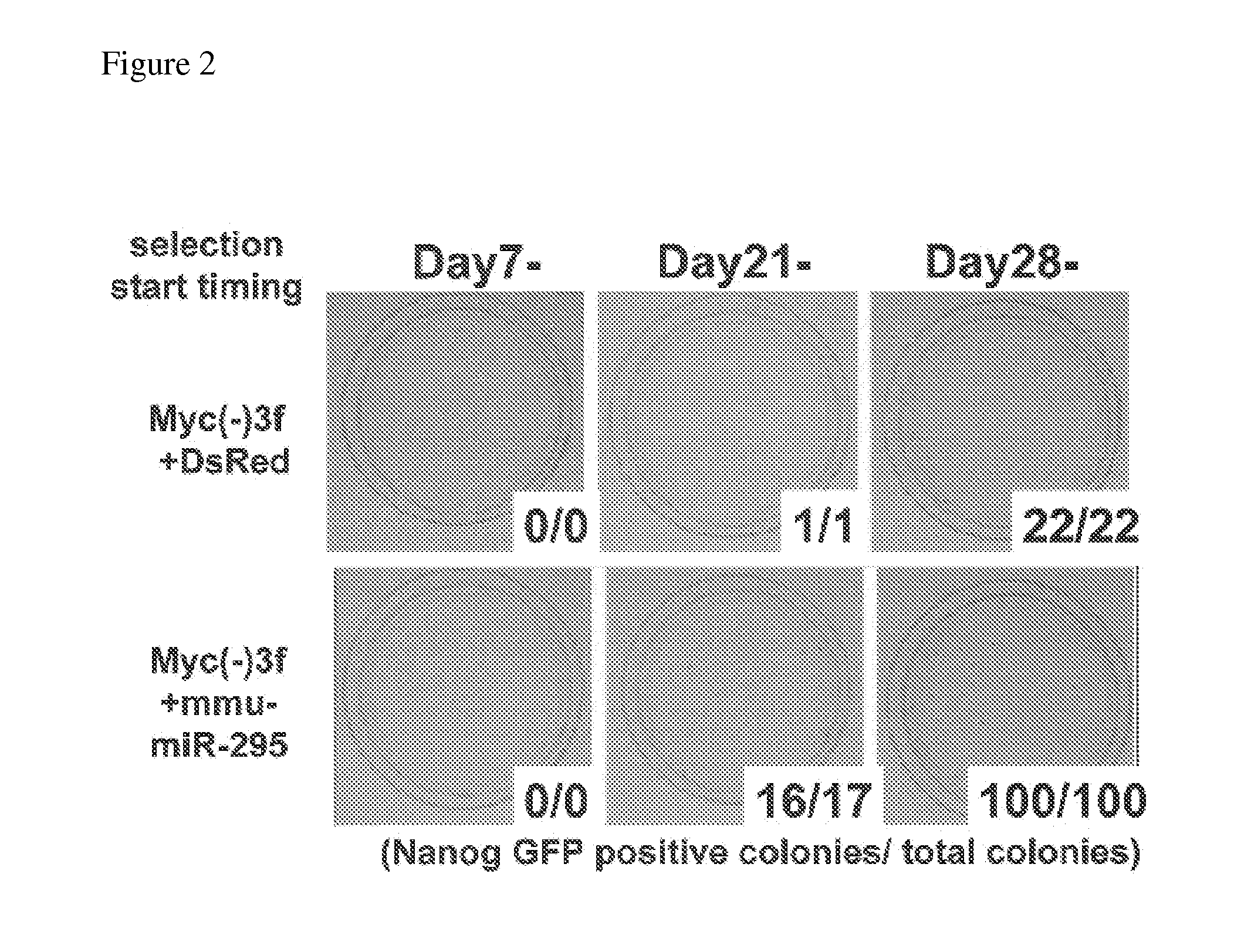
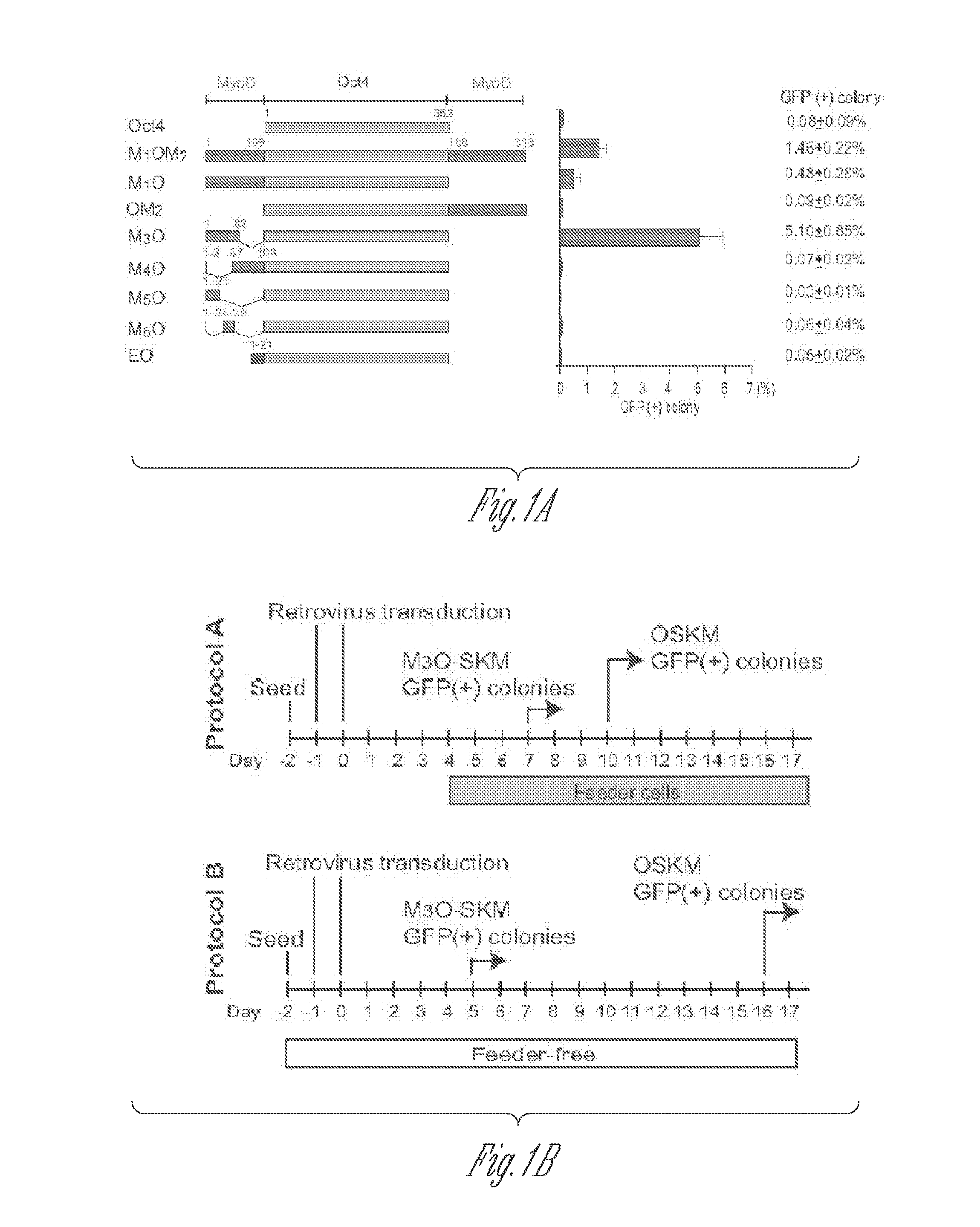
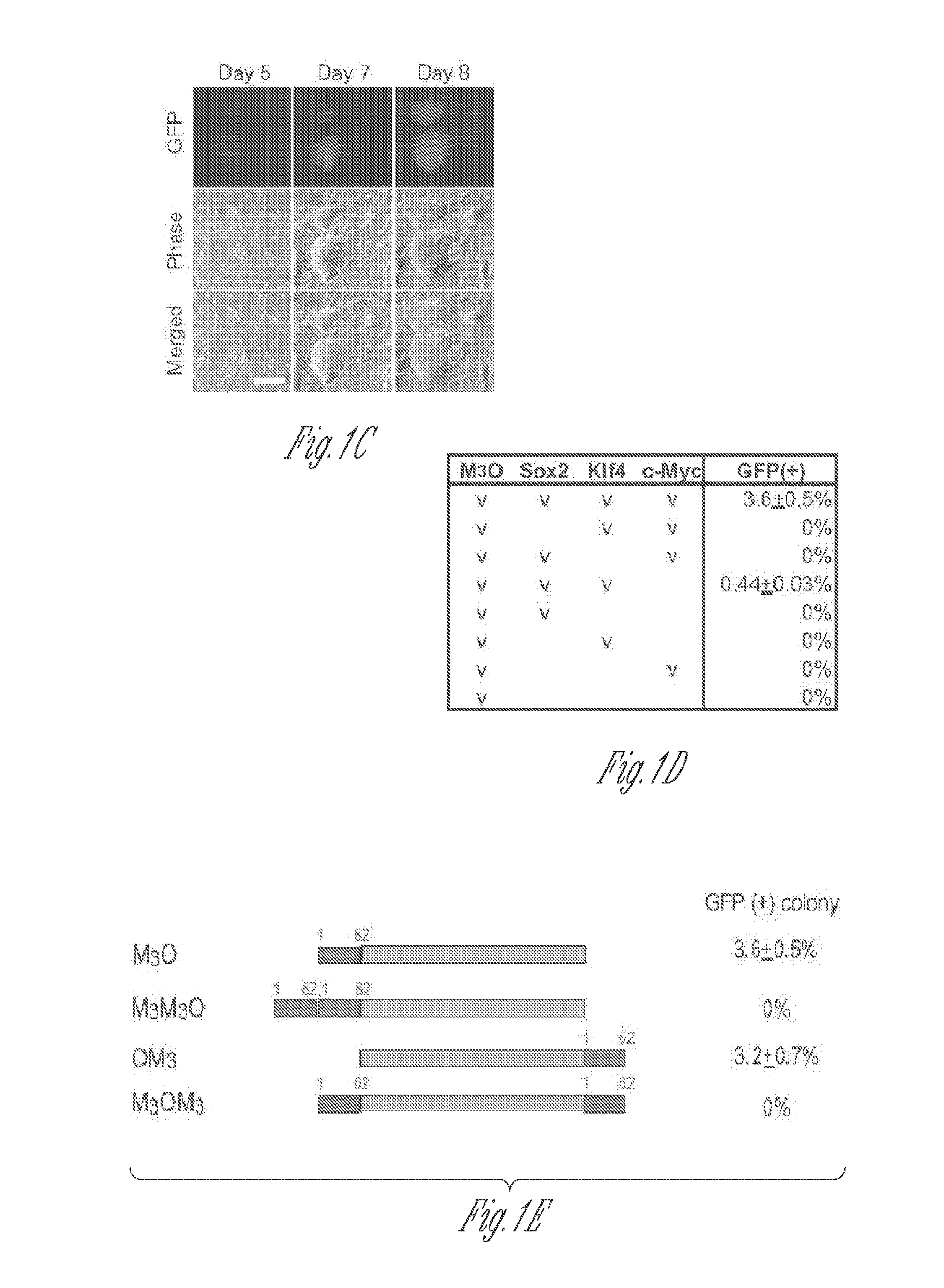
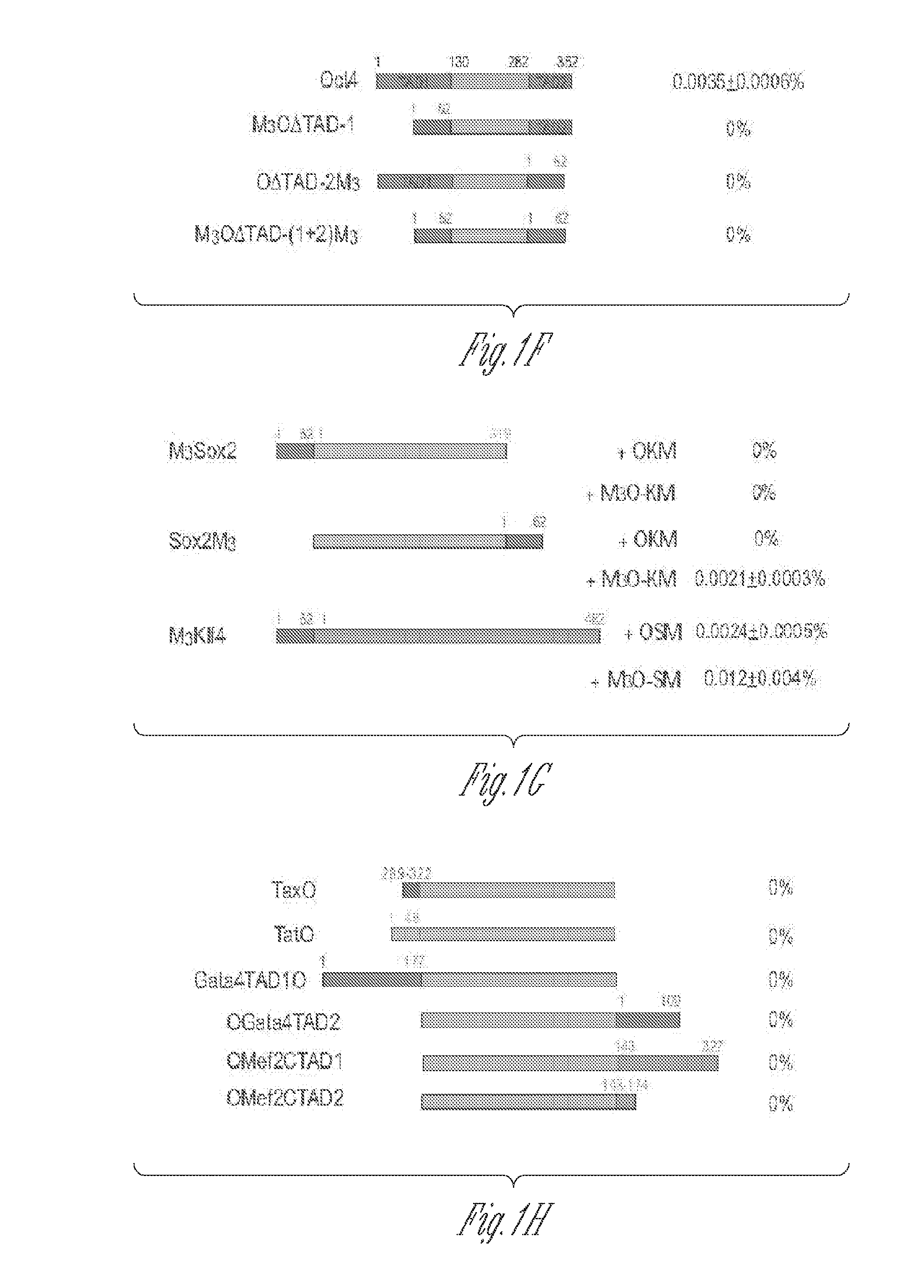
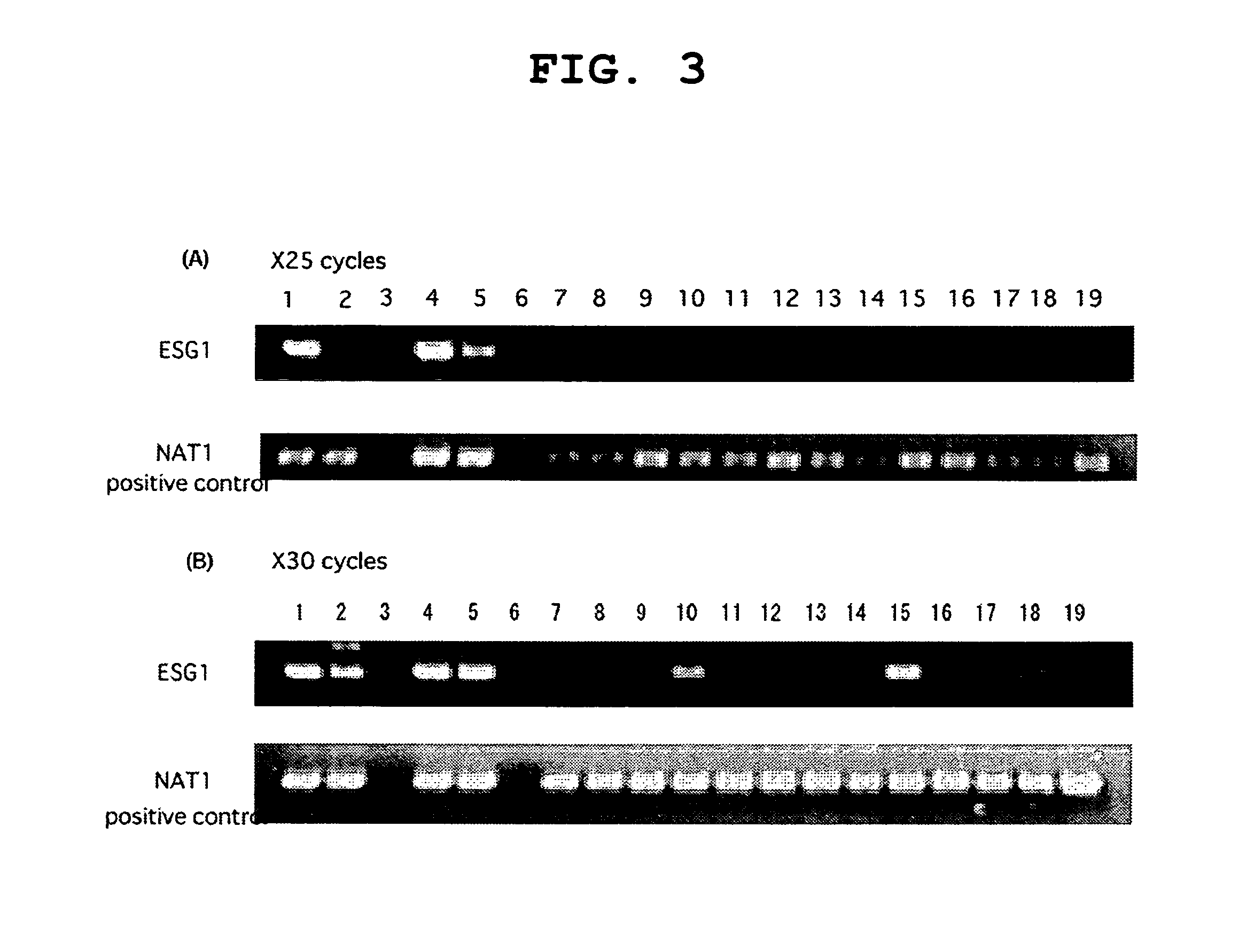
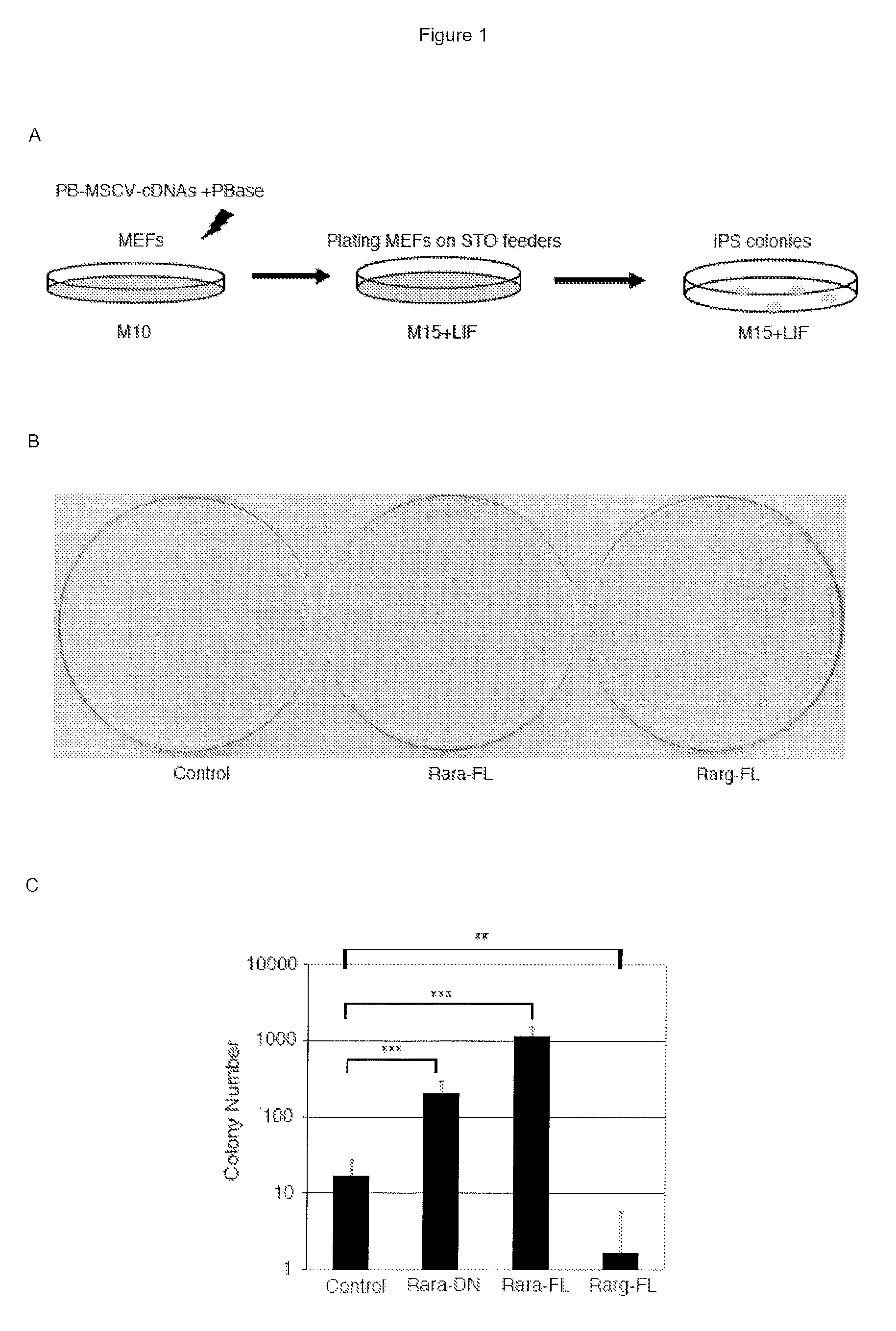
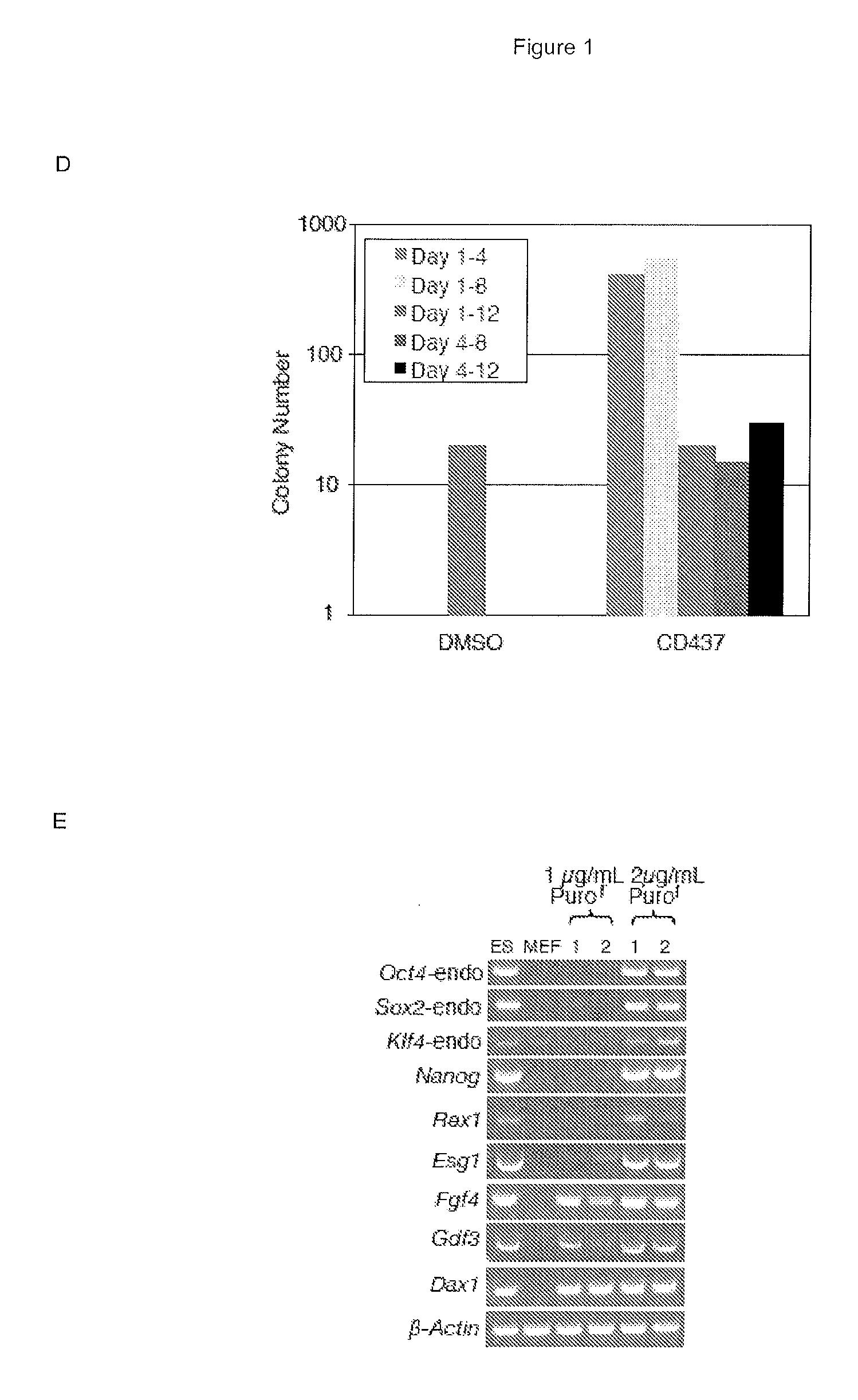
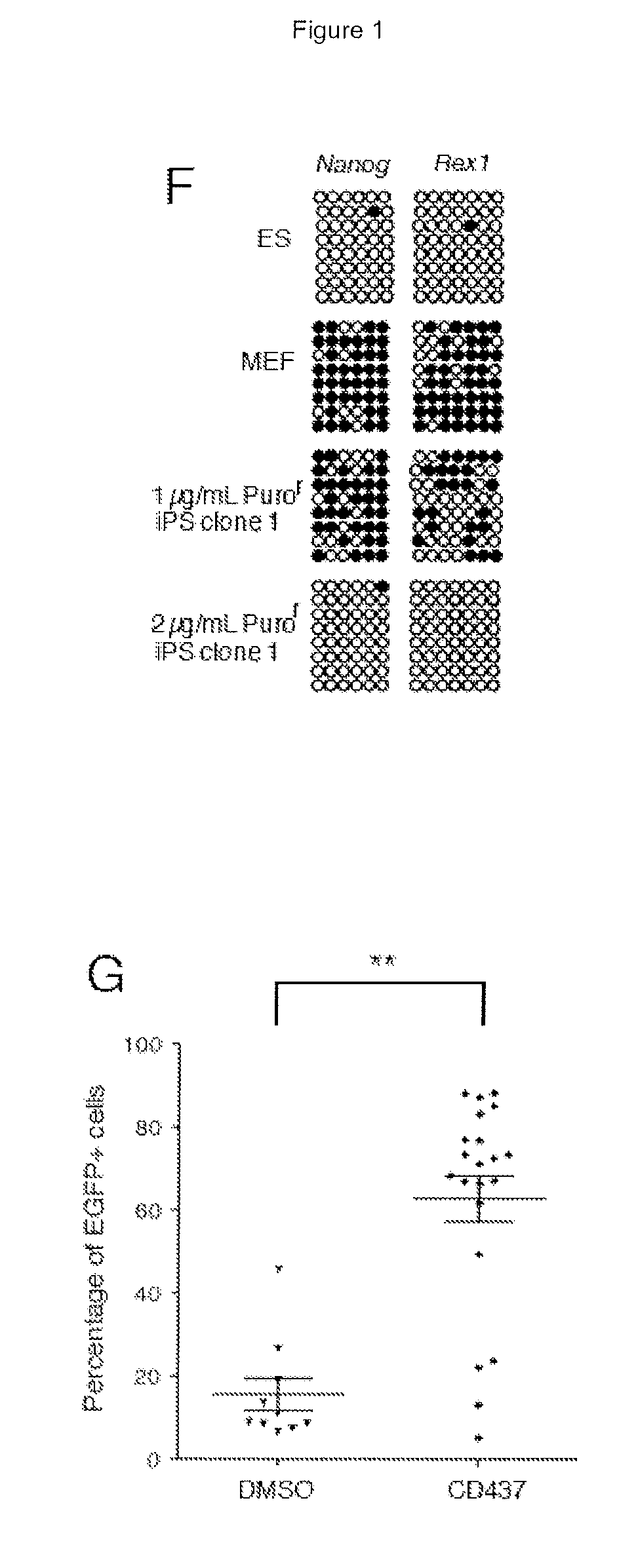
Patents
Literature
69 results about "Nuclear reprogramming" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nuclear Reprogramming Factor
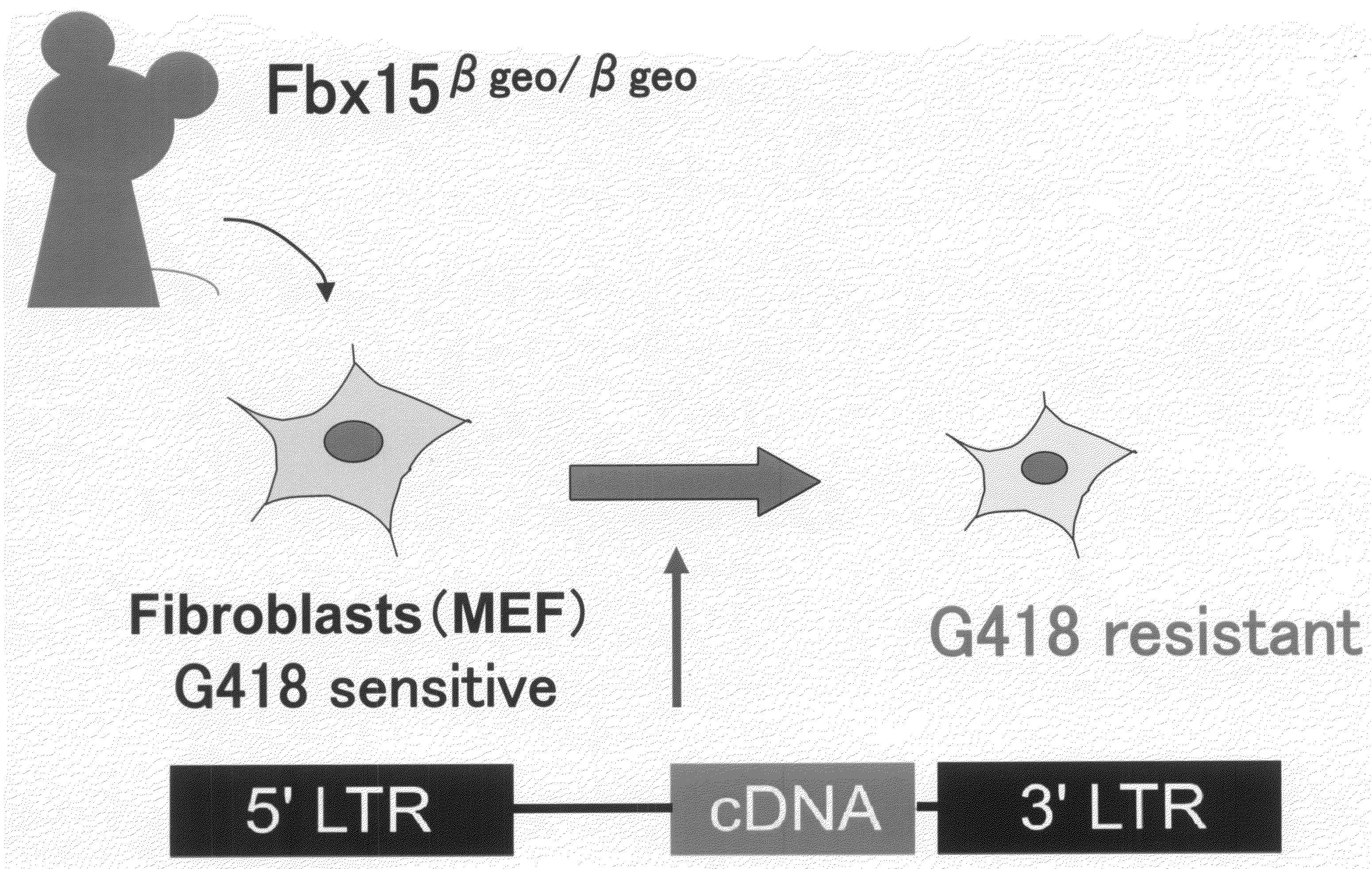
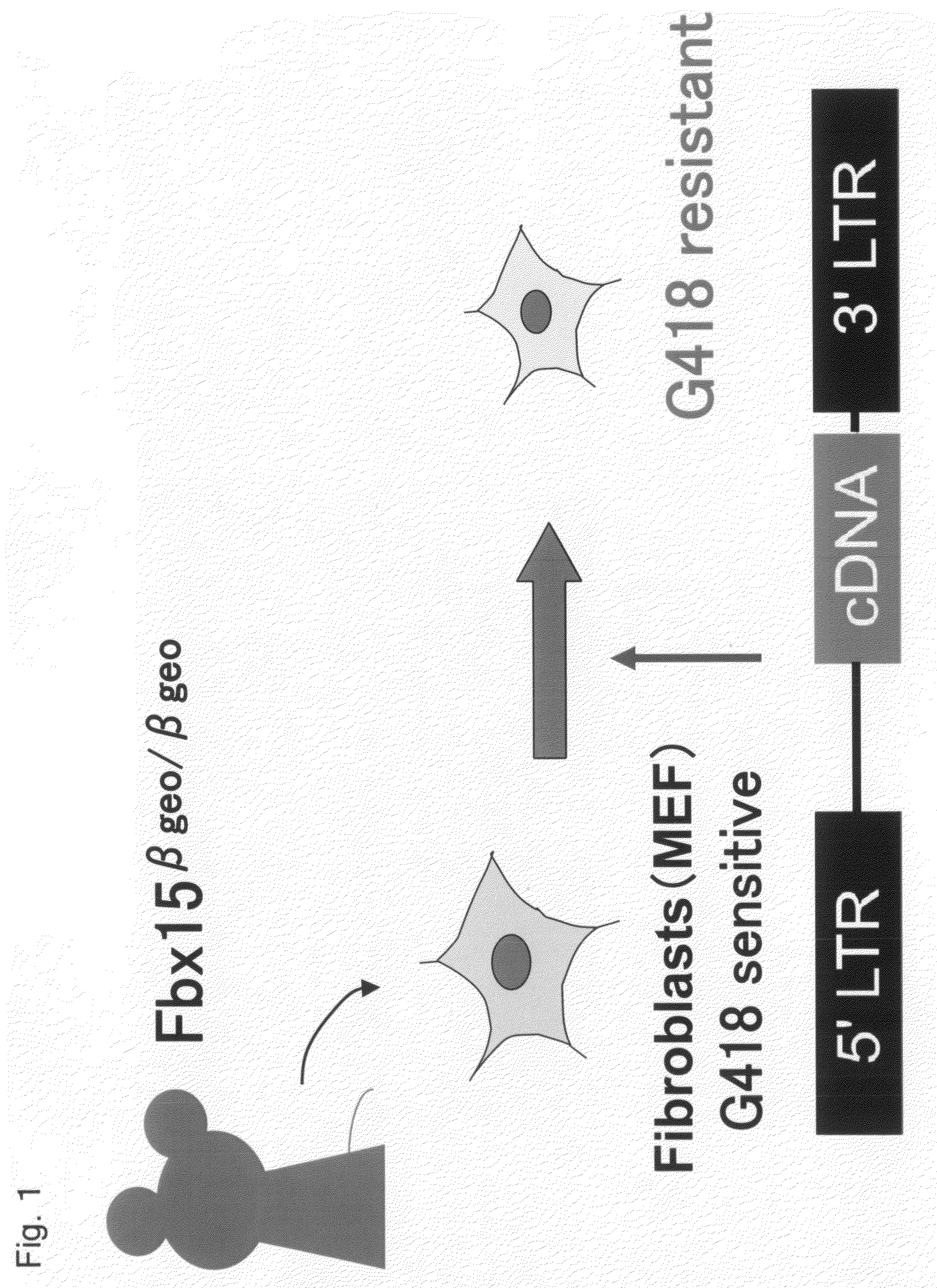
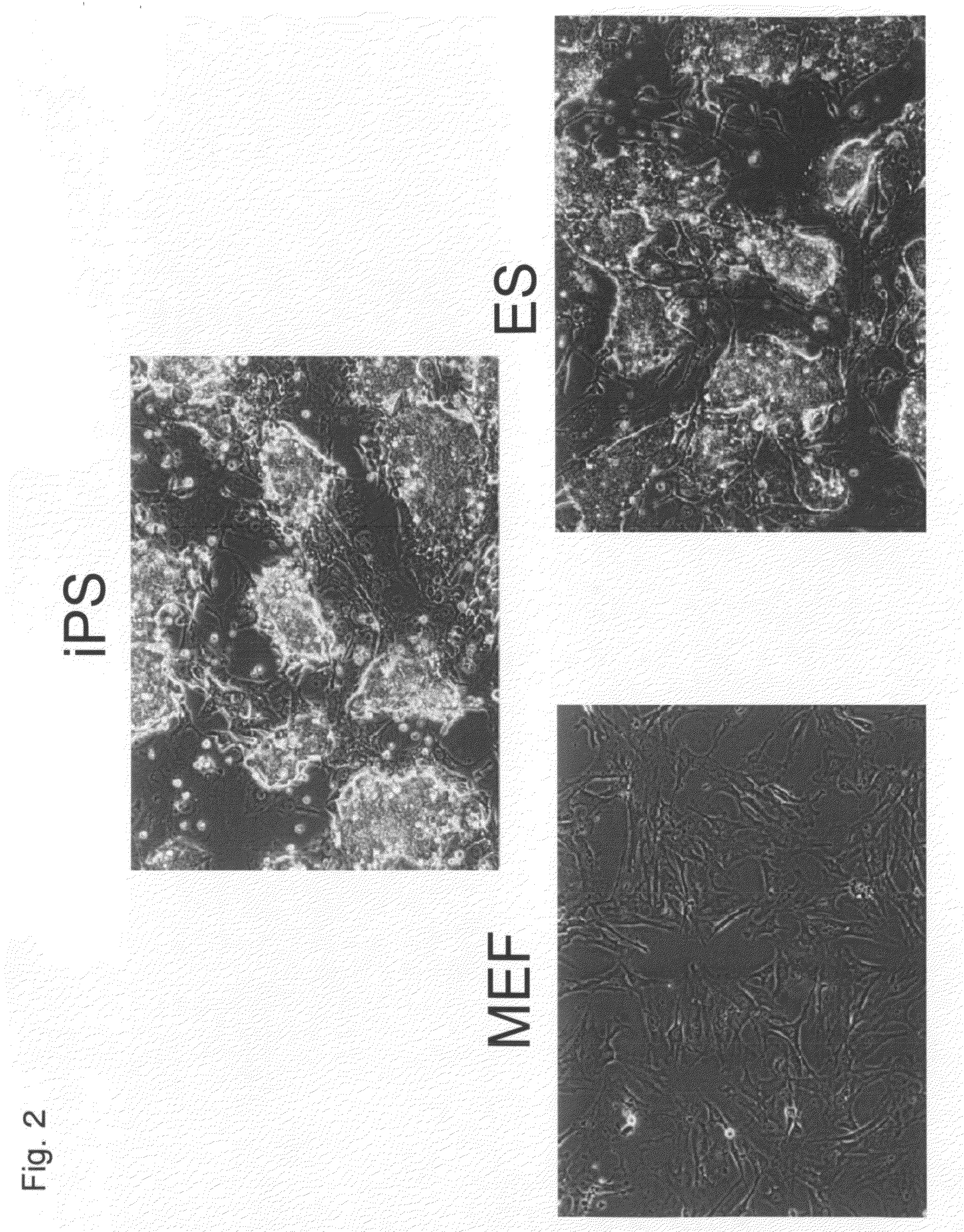
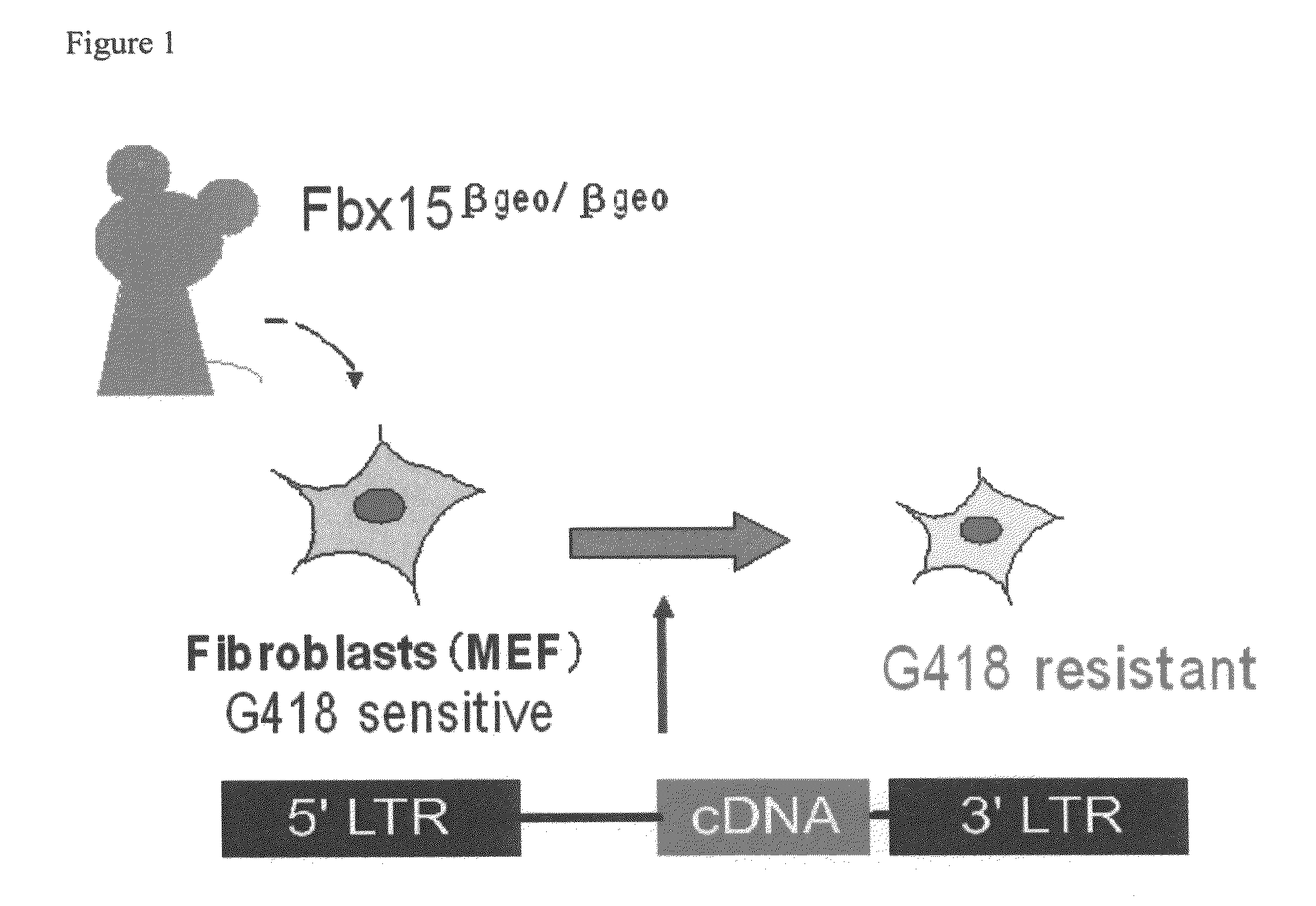
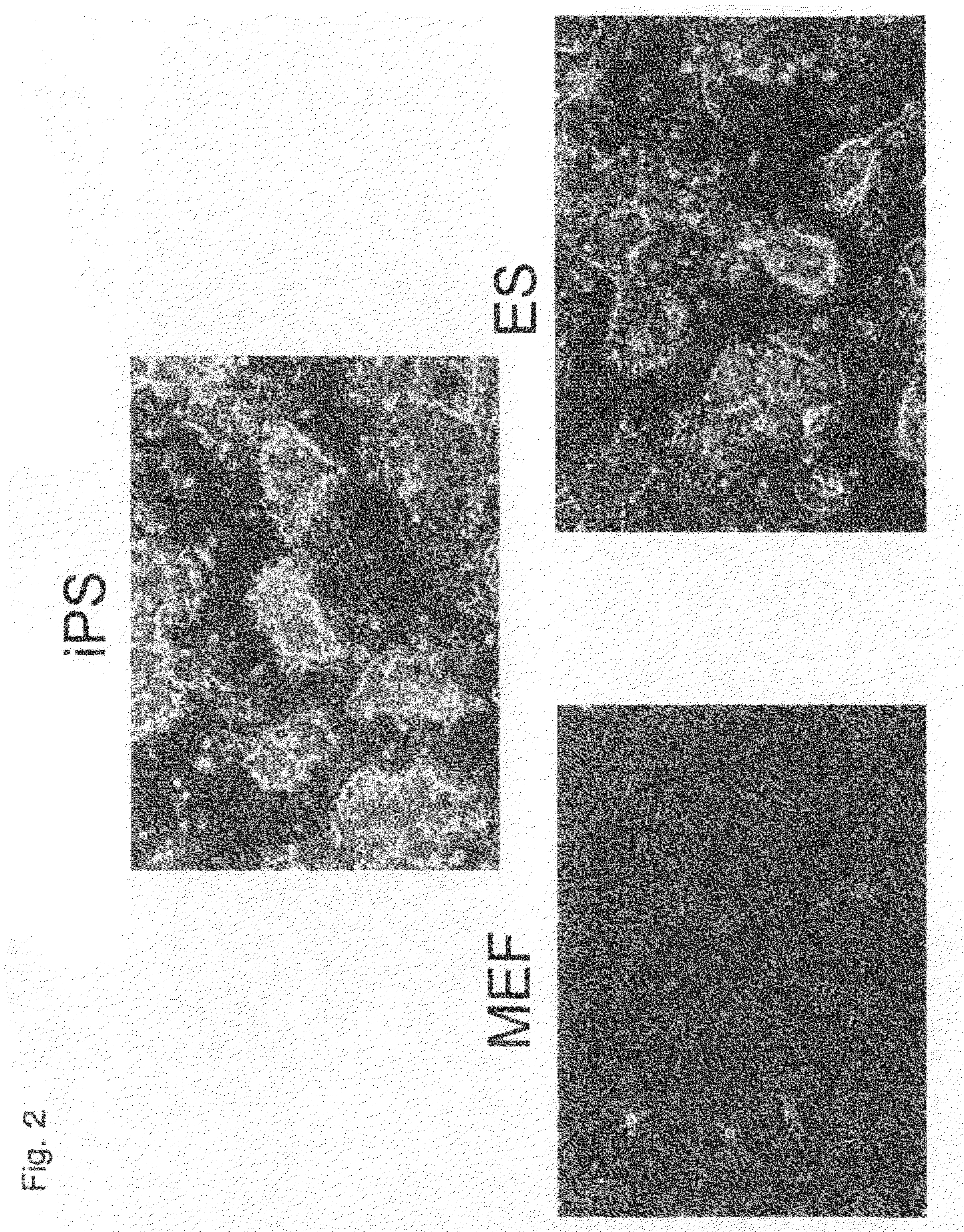
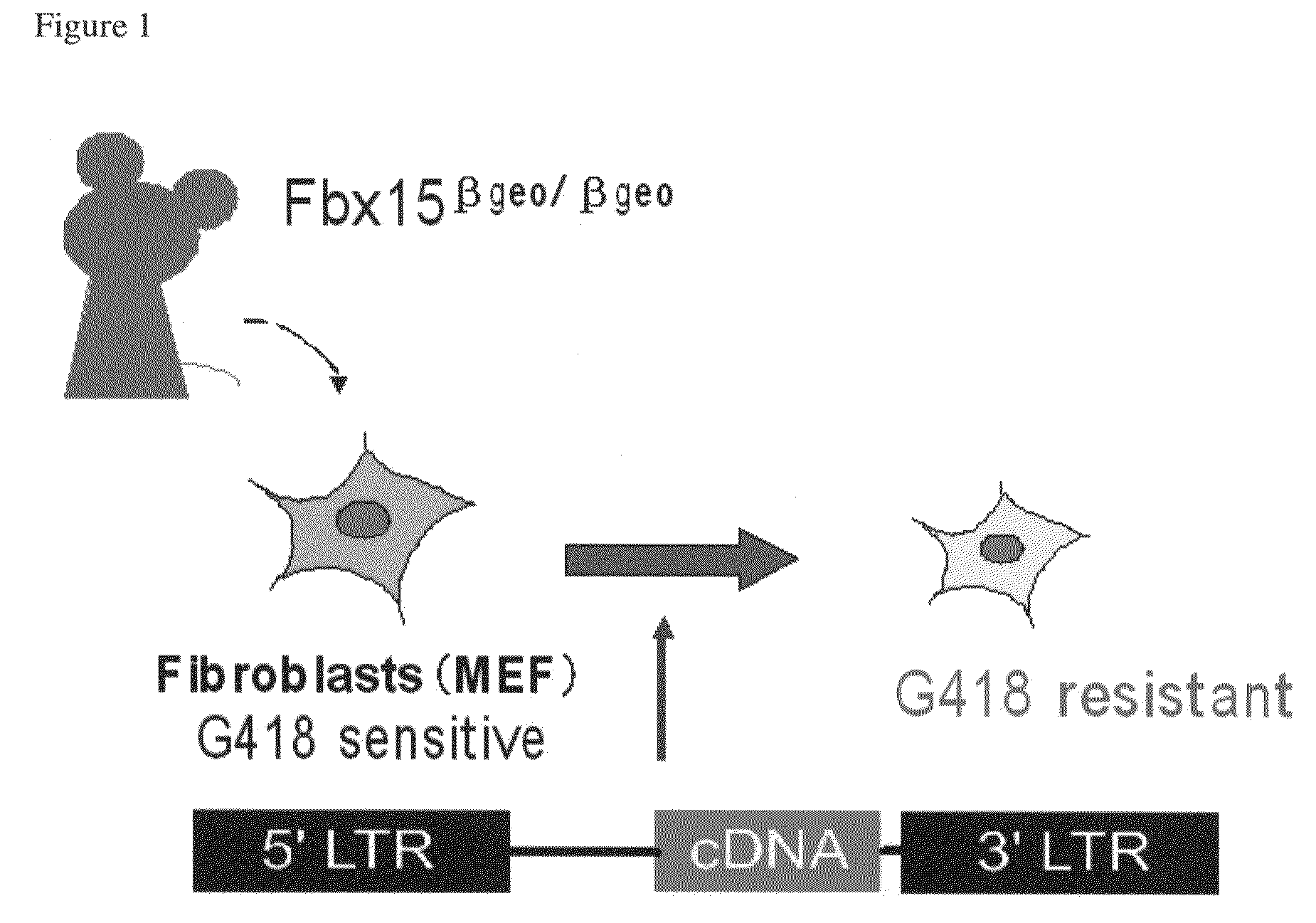
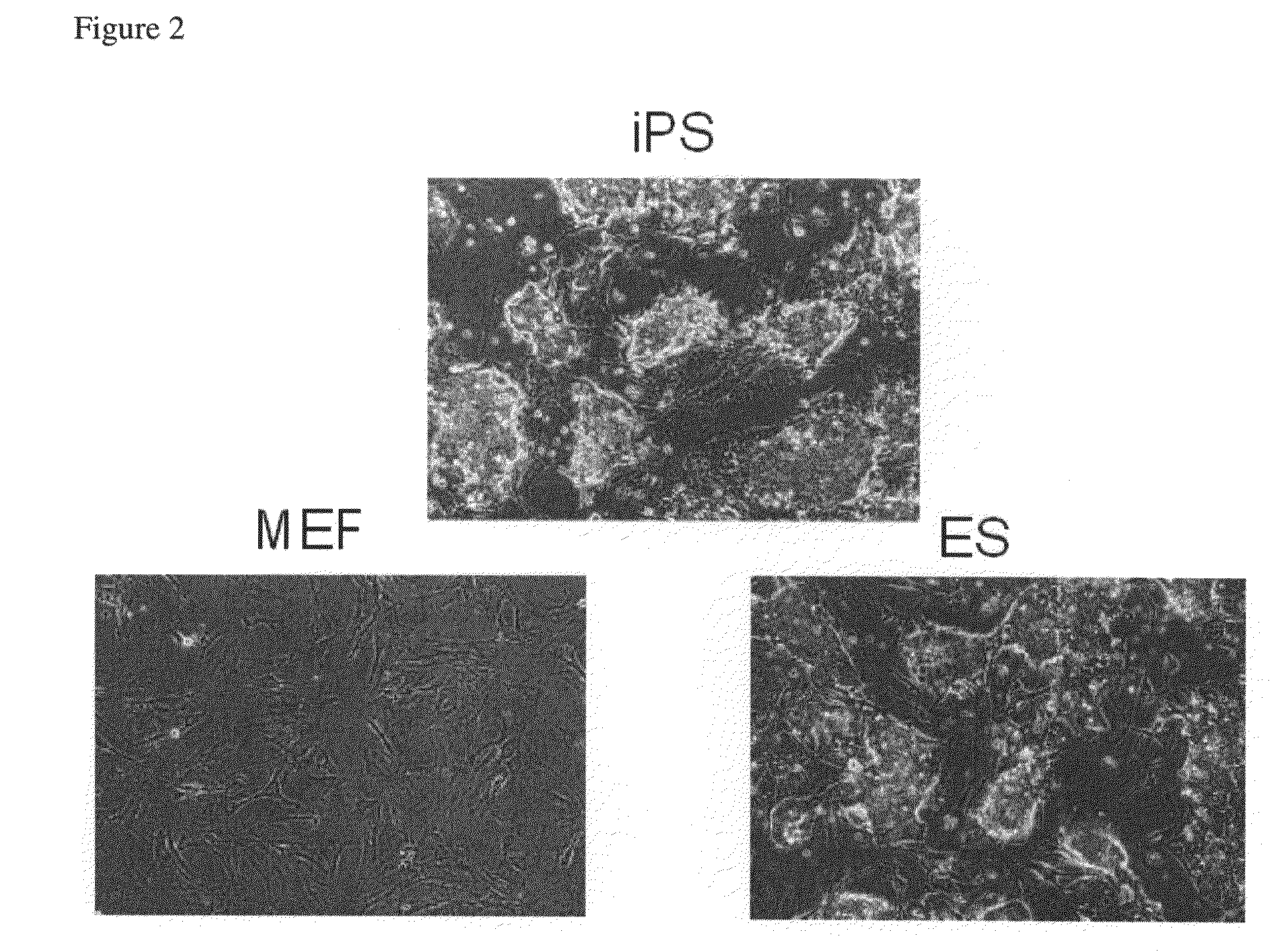
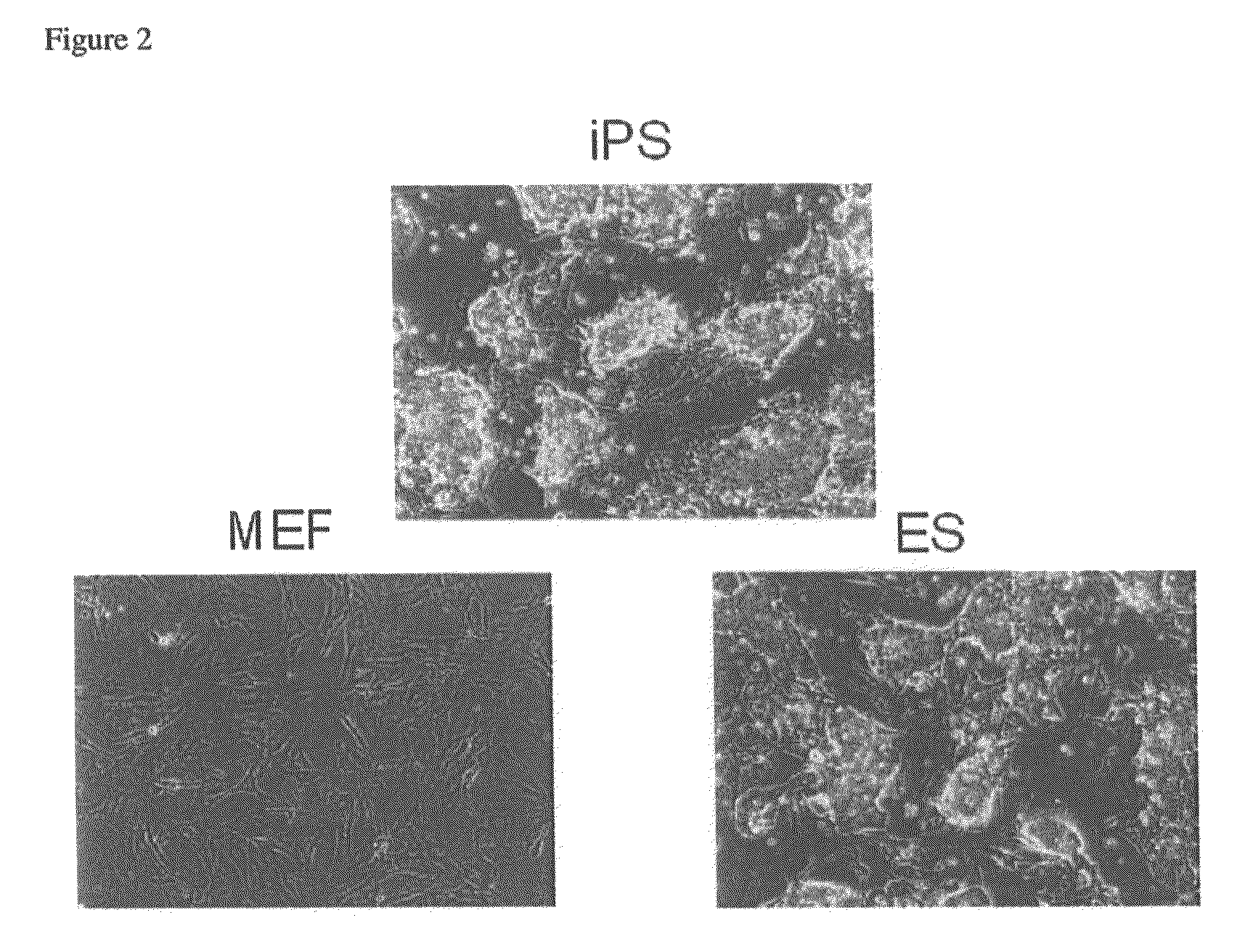
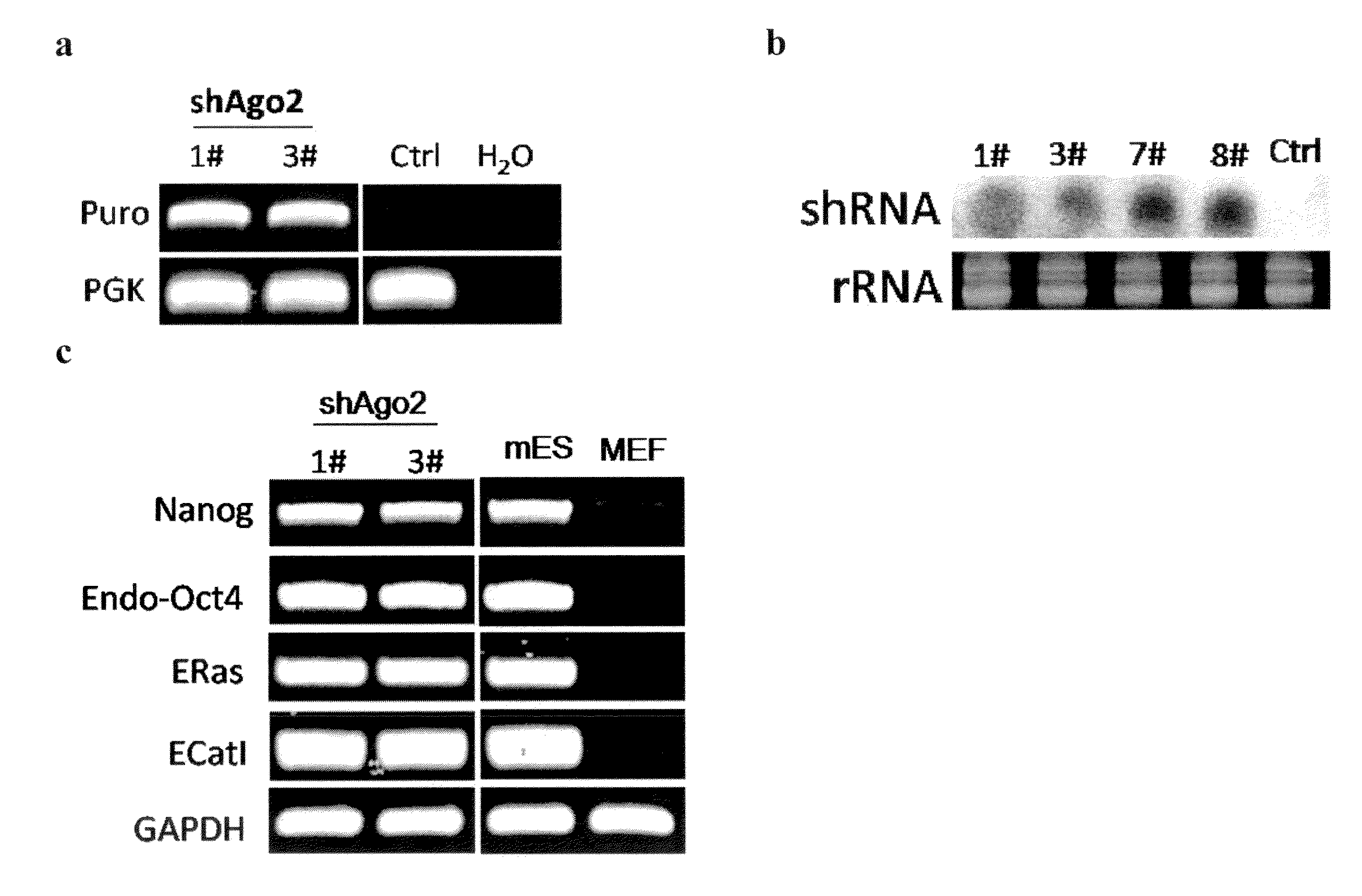
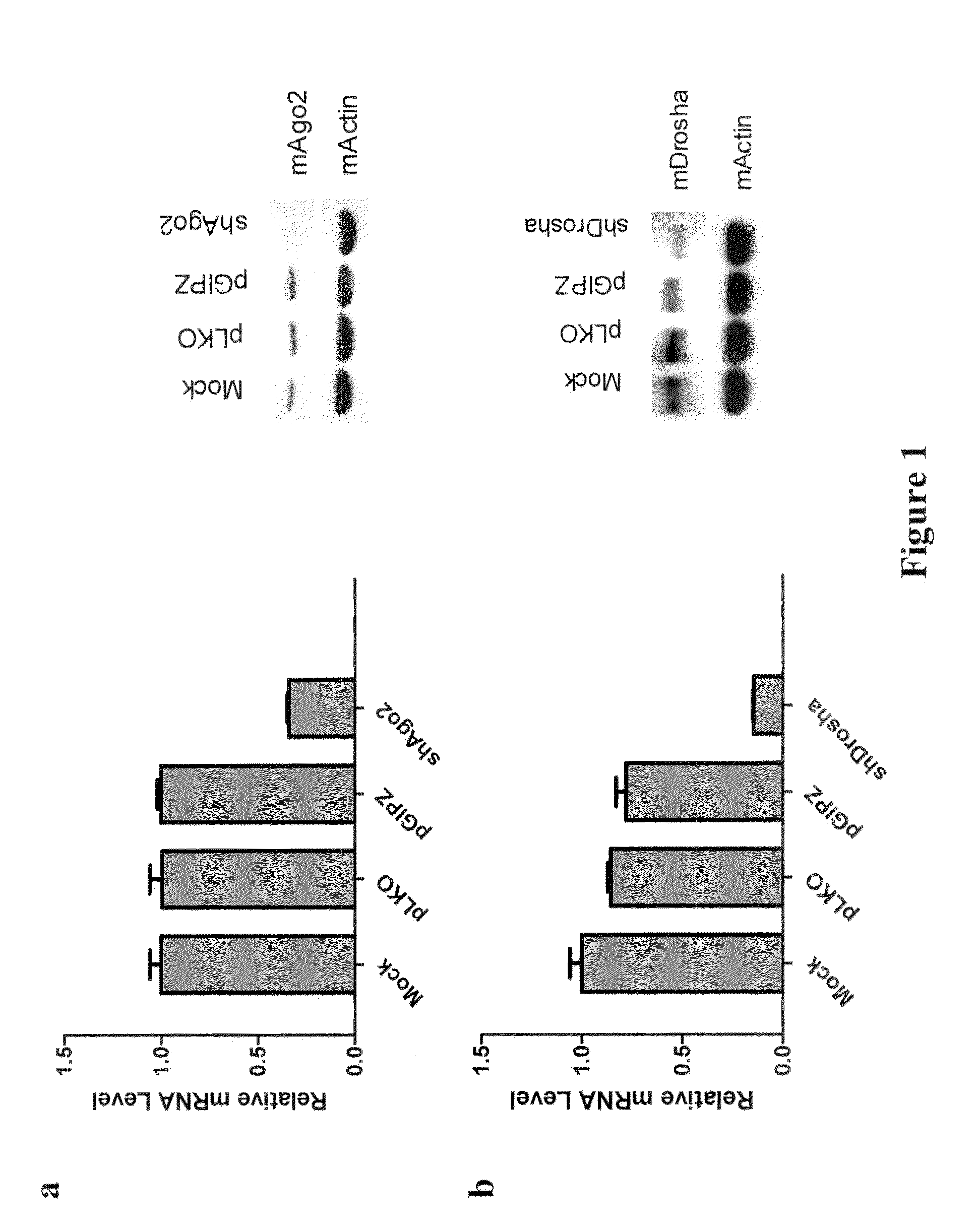
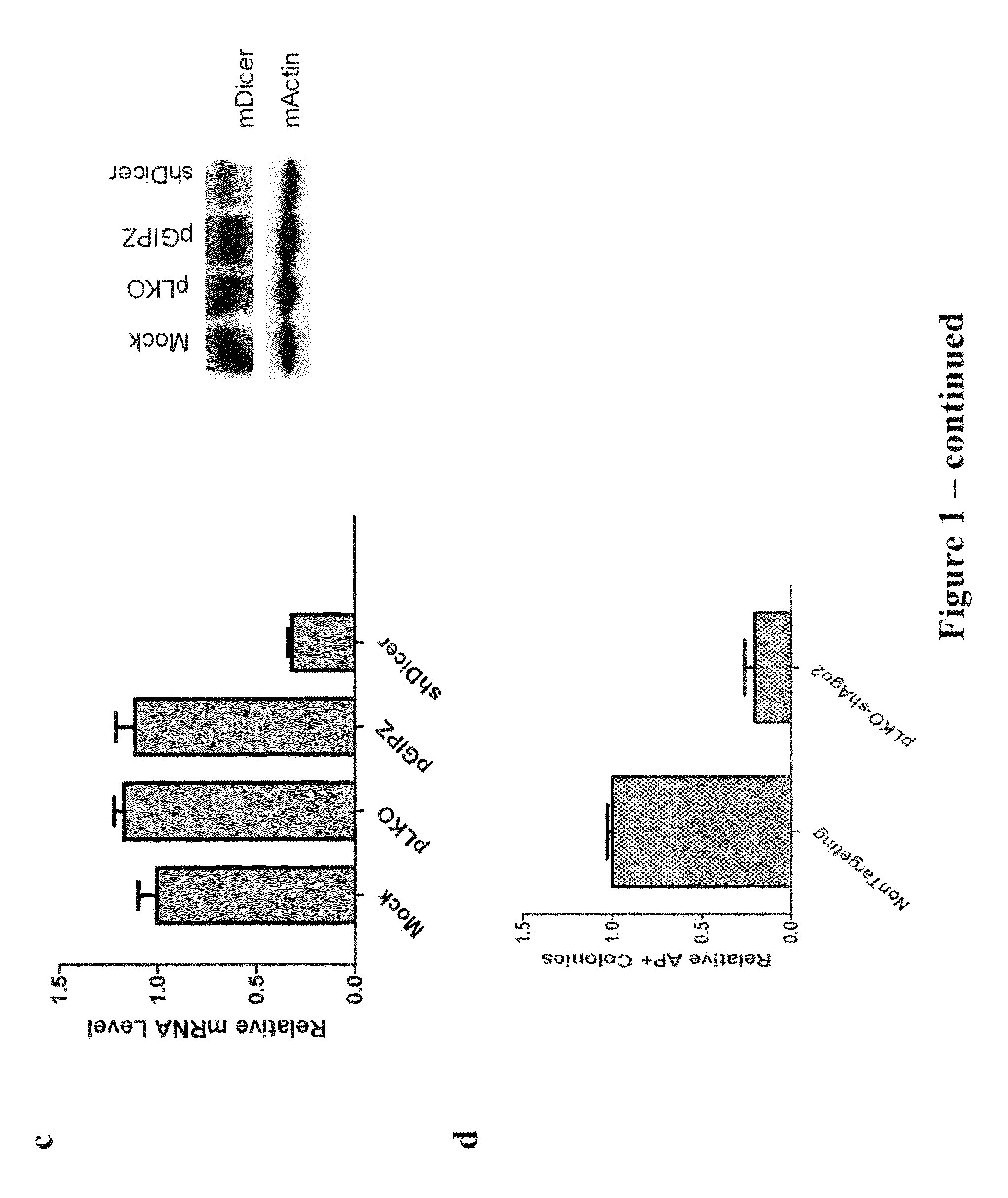
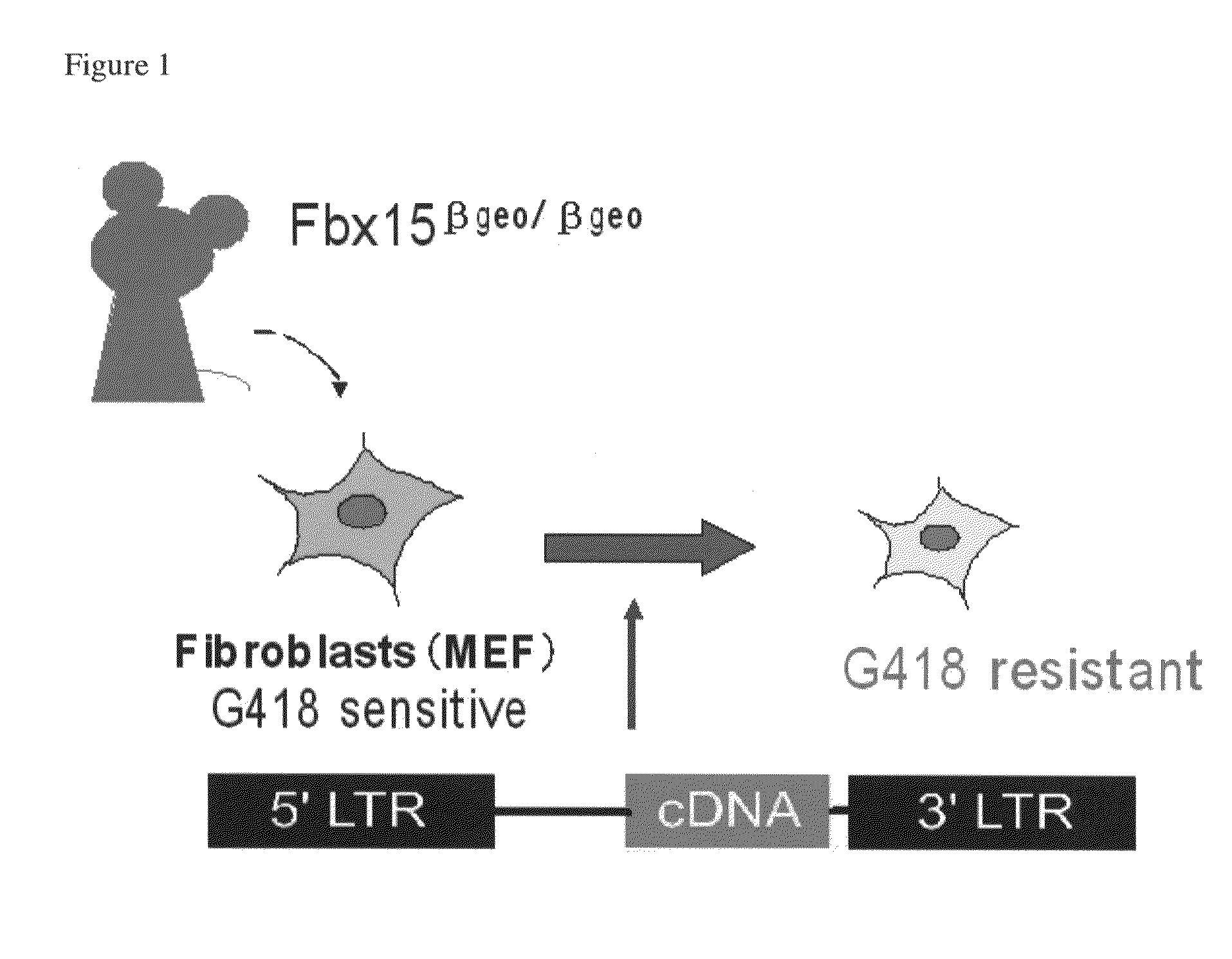
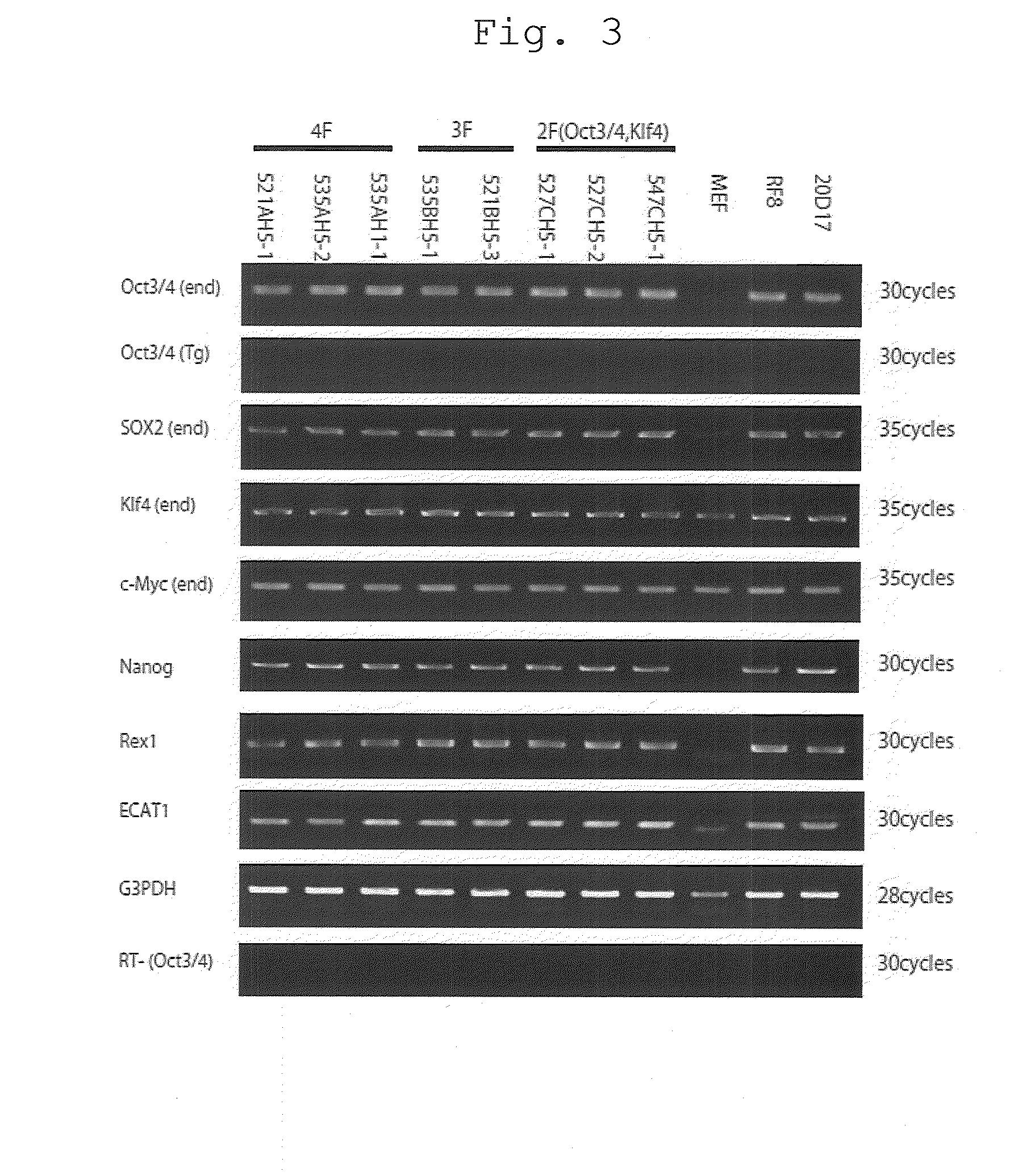
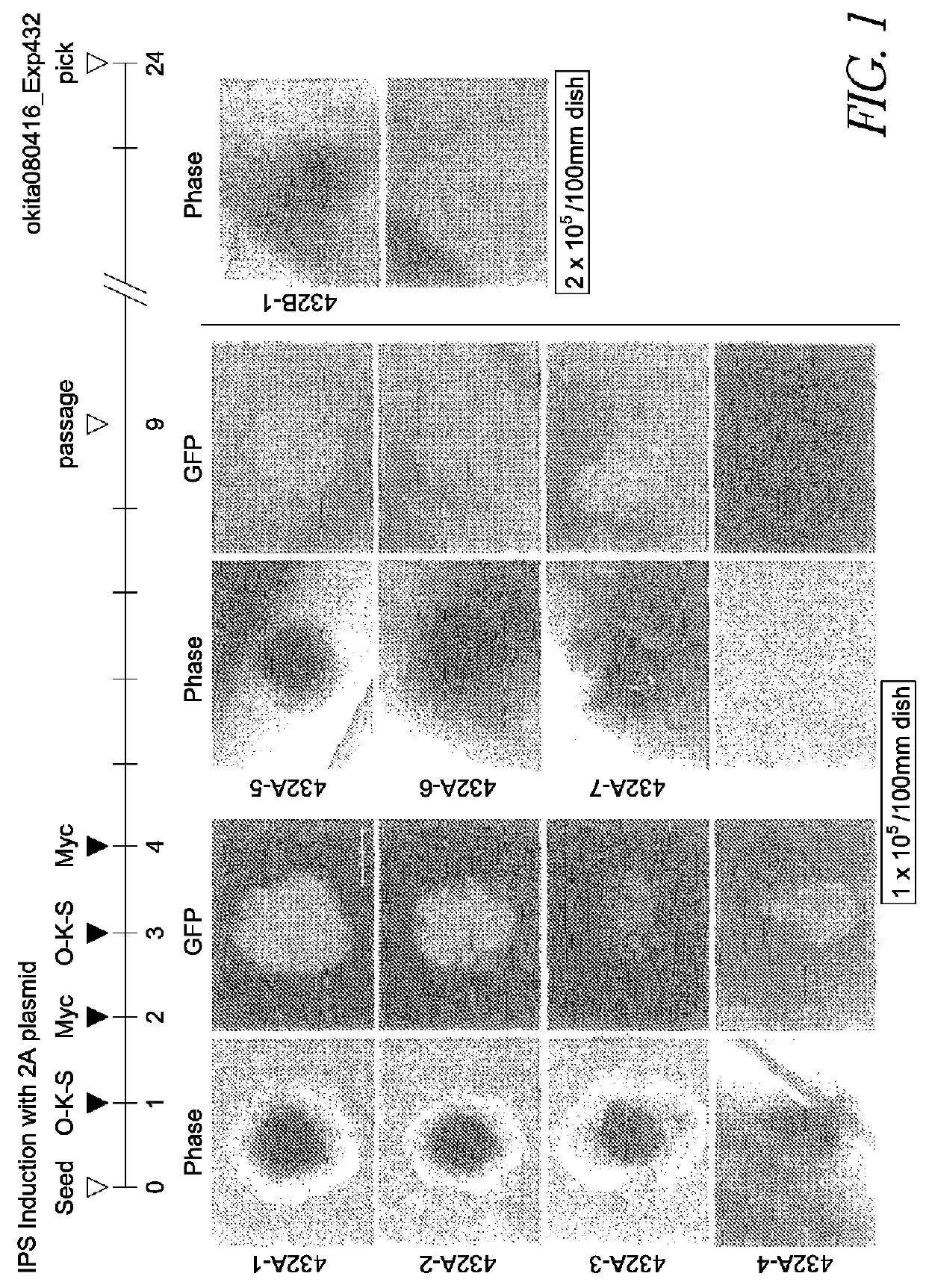
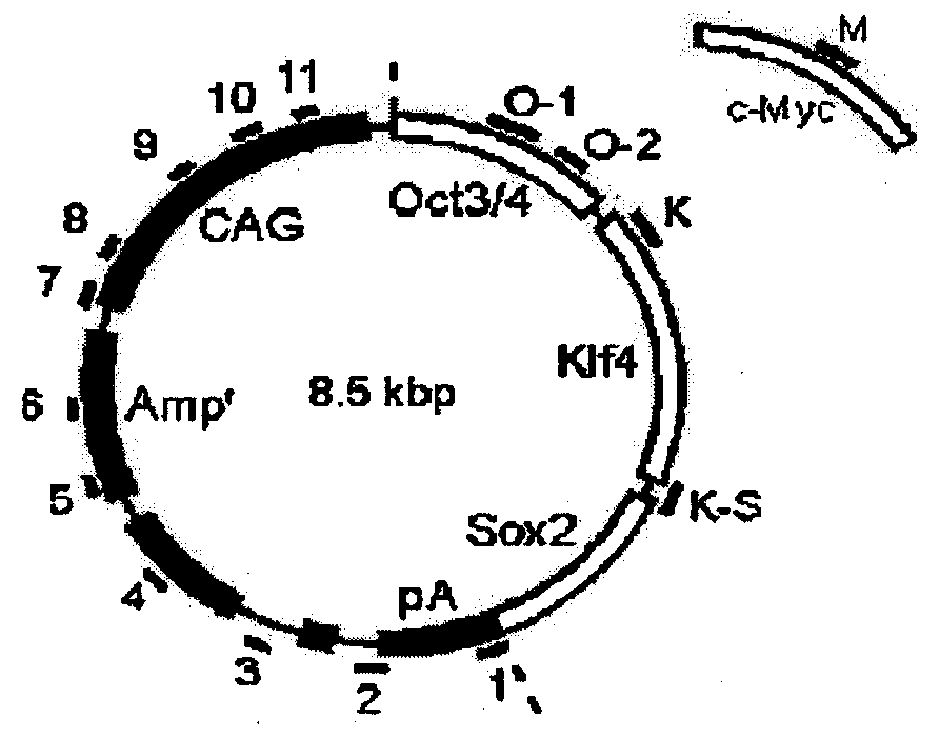
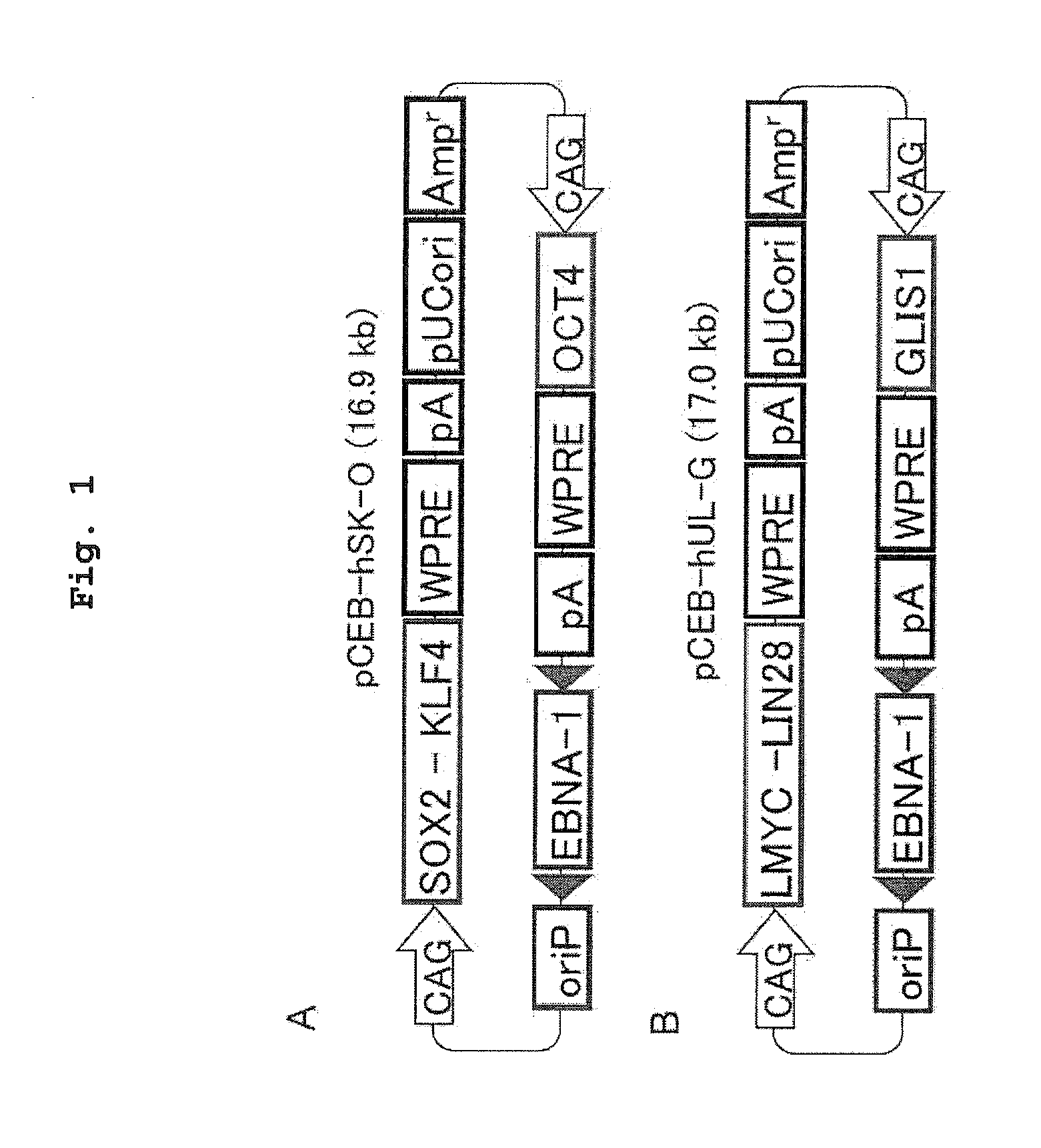
There is provided a nuclear reprogramming factor for a somatic cell, which comprises a gene product of each of the following three kinds of genes: an Oct family gene, a Klf family gene, and a Myc family gene, as a means for inducing reprogramming of a differentiated cell to conveniently and highly reproducibly establish an induced pluripotent stem cell having pluripotency and growth ability similar to those of ES cells without using embryo or ES cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20090227032A1Easy to prepareEffective isolationGenetically modified cellsPeptidesNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Nuclear reprogramming factor
ActiveUS8048999B2Improve abilitiesPromote growthNervous disorderVirusesGene productNuclear reprogramming
There is provided a nuclear reprogramming factor for a somatic cell, which comprises a gene product of each of the following three kinds of genes: an Oct family gene, a Klf family gene, and a Myc family gene, as a means for inducing reprogramming of a differentiated cell to conveniently and highly reproducibly establish an induced pluripotent stem cell having pluripotency and growth ability similar to those of ES cells without using embryo or ES cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Somatic cell reprogramming by retroviral vectors encoding Oct3/4. Klf4, c-Myc and Sox2
ActiveUS8129187B2Easy to prepareEffective isolationGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Efficient method for nuclear reprogramming
InactiveUS20100075421A1Efficient preparationImprove efficiencyGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsNuclear reprogrammingBiology
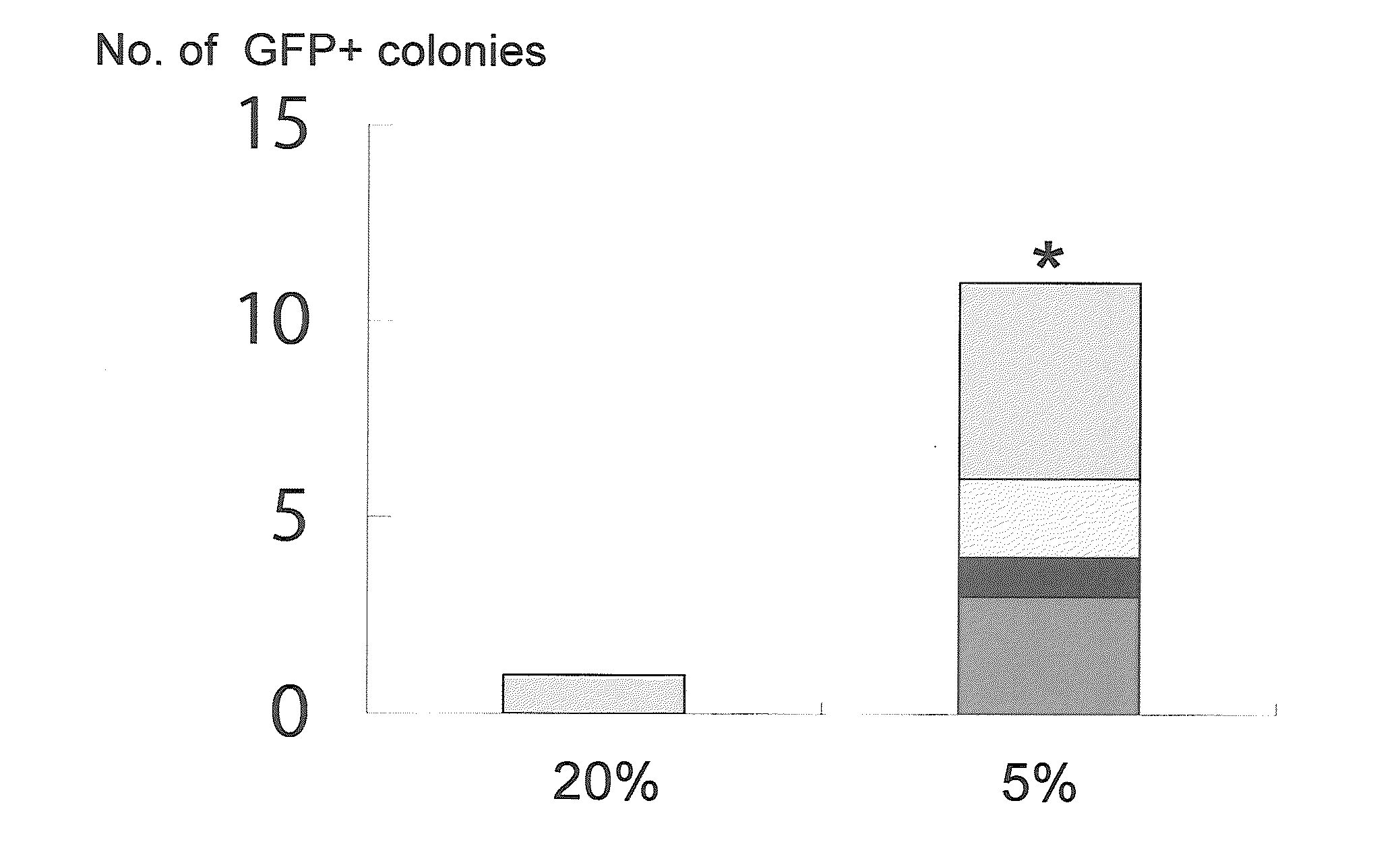
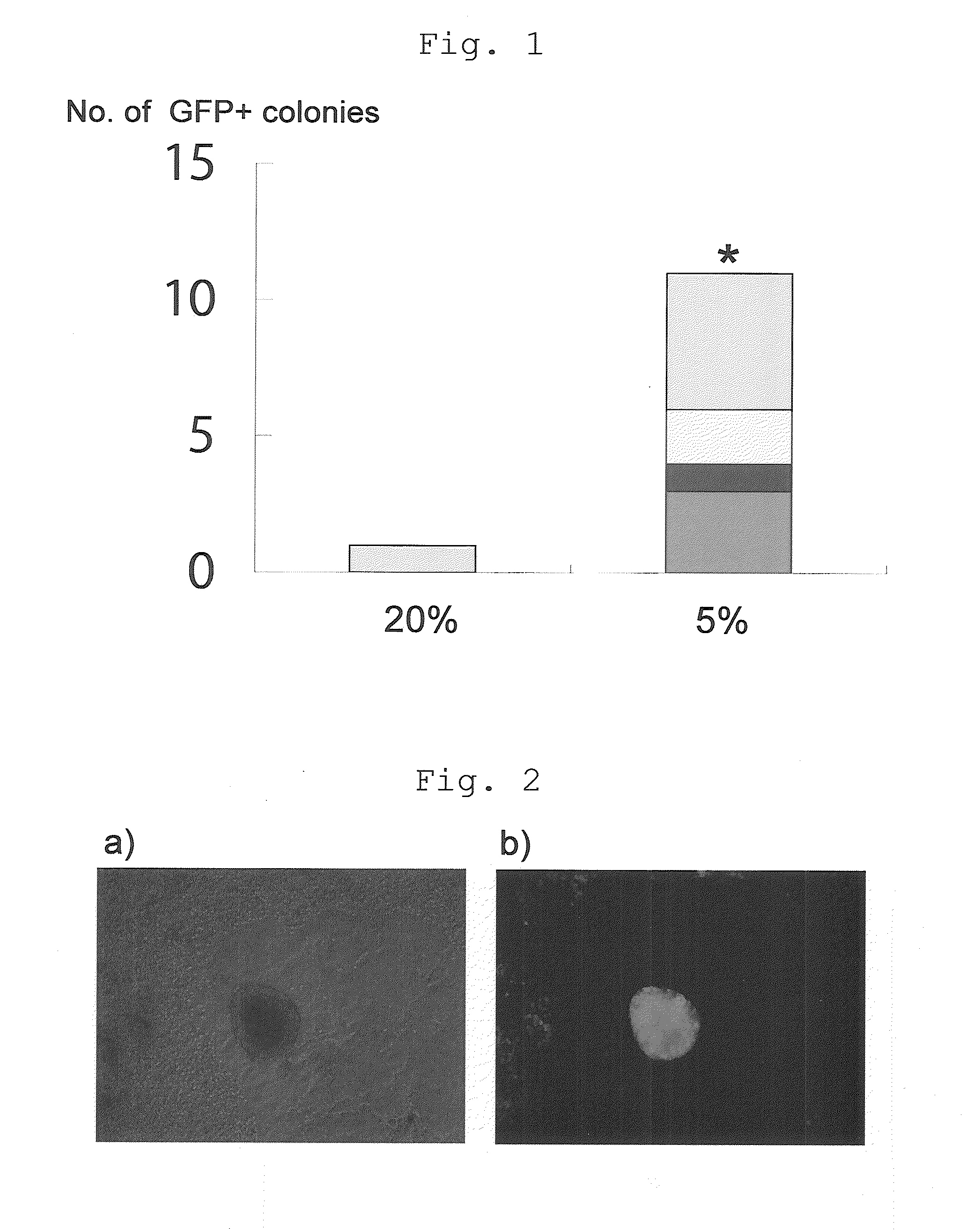
A method of preparing induced pluripotent stem cells, comprising a nuclear reprogramming step with a nuclear reprogramming factor in the presence of miRNA, wherein said miRNA has a property of providing a higher nuclear reprogramming efficiency in the presence of said miRNA than in the absence thereof.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20100062533A1Easy to prepareEffective isolationGenetically modified cellsPeptidesNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method for generation and regulation of ips cells and compositions thereof
InactiveUS20110189137A1Avoid immune rejectionIncrease the number ofBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsMicroRNANuclear reprogramming
The present invention provides methods for generating induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells having an increased efficiency of induction as compared with conventional methods. The method includes treating a somatic cell with a nuclear reprogramming factor in combination with an agent that alters microRNA levels or activity in the cell and / or a p21 inhibitor. The invention further provides iPS cells generated by such methods, as well as clinical and research uses for such iPS cells.
Owner:SANFORD BURNHAM MEDICAL RES INST
Method of nuclear reprogramming
InactiveUS20100279404A1Easy to useElectric discharge tubesGenetically modified cellsPlasmid VectorNuclear reprogramming
This invention provides a method of producing an induced pluripotent stem cell comprising the step of introducing at least one kind of non-viral expression vector (more preferably a plasmid vector) incorporating at least one gene that encodes a reprogramming factor into a somatic cell. An induced pluripotent stem cell wherein no exogenous genes induced is integrated into the cellular genome is also provided.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
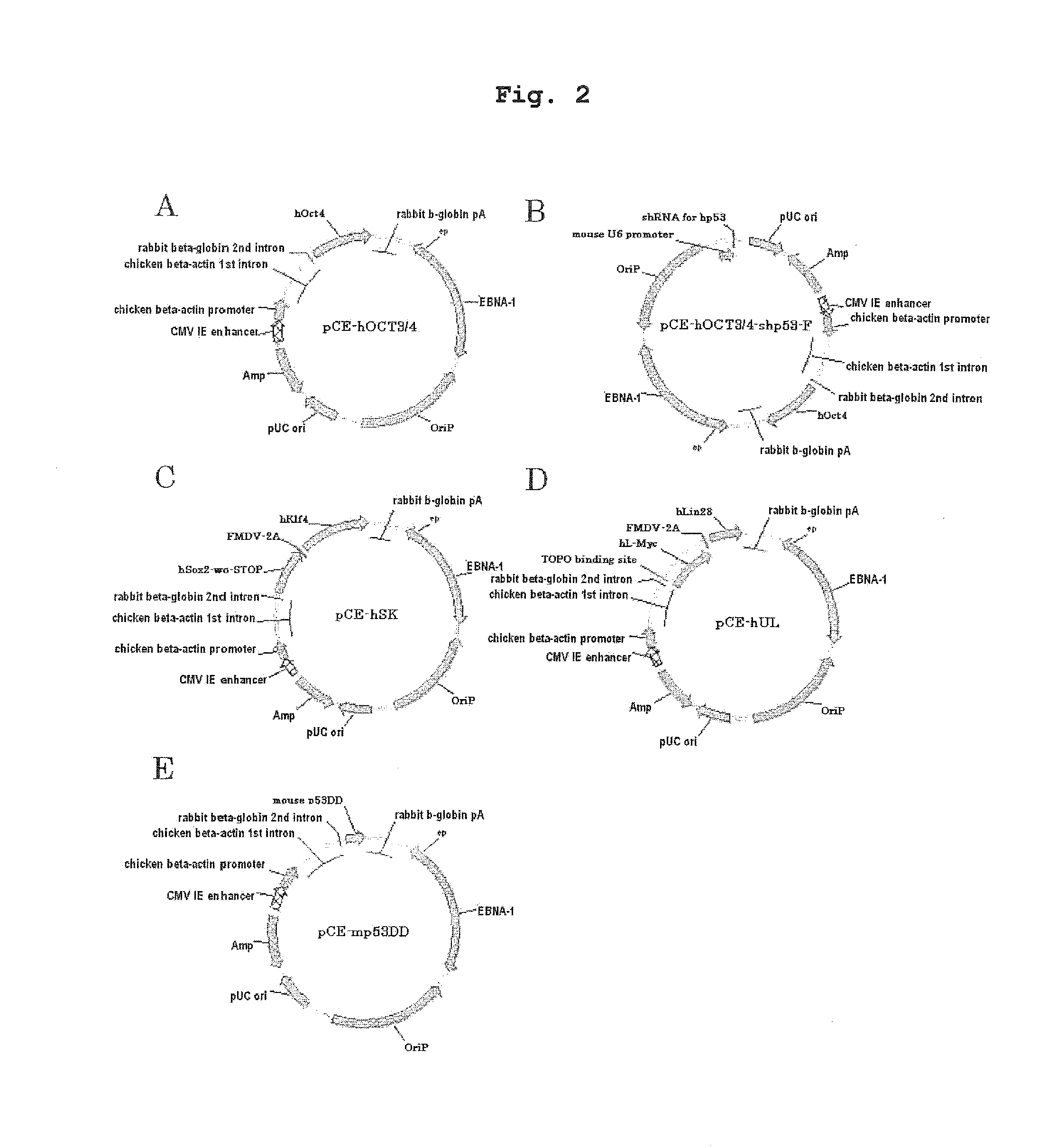
ActiveUS20110223669A1Improve setup efficiencyEfficient productionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsNuclear reprogrammingBiology
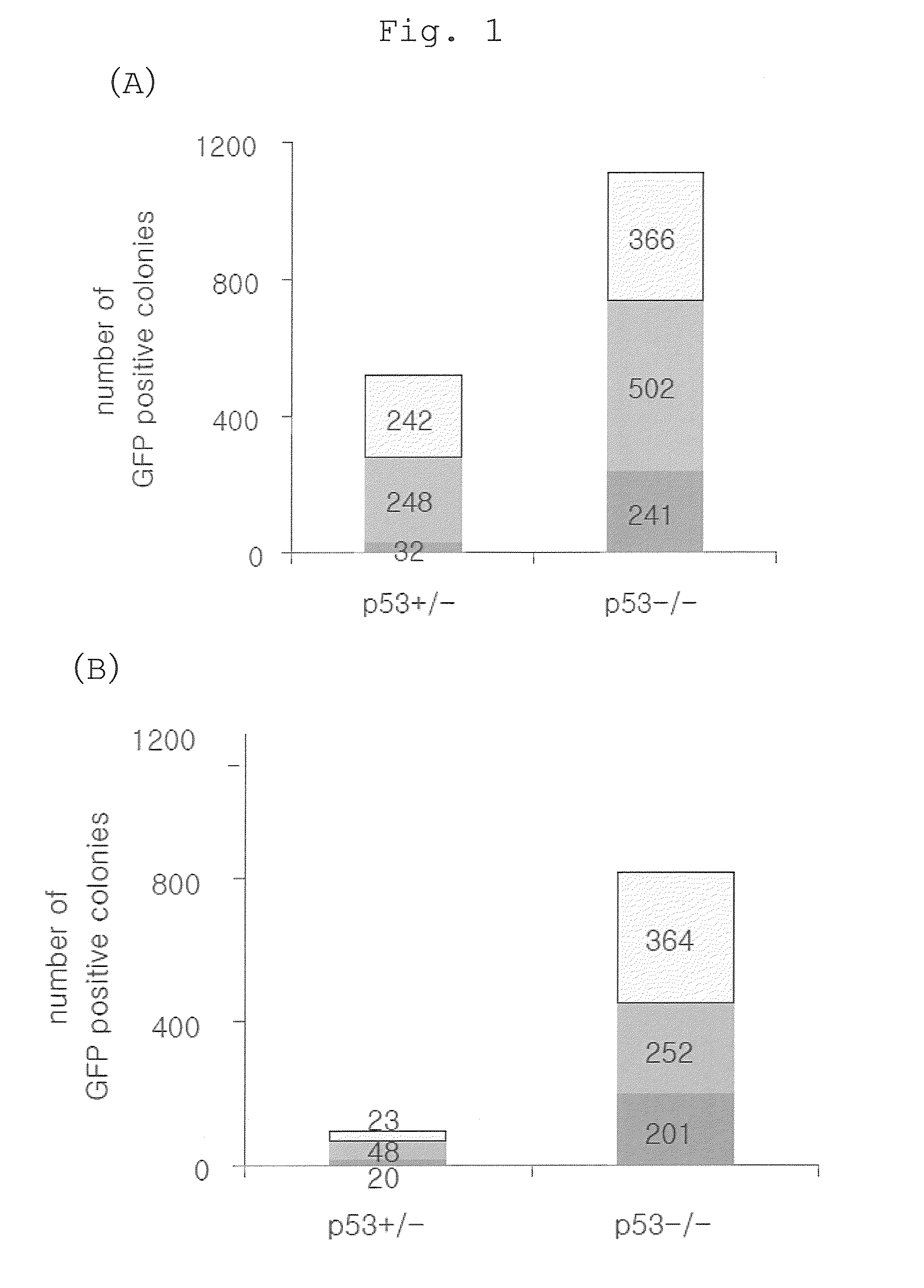
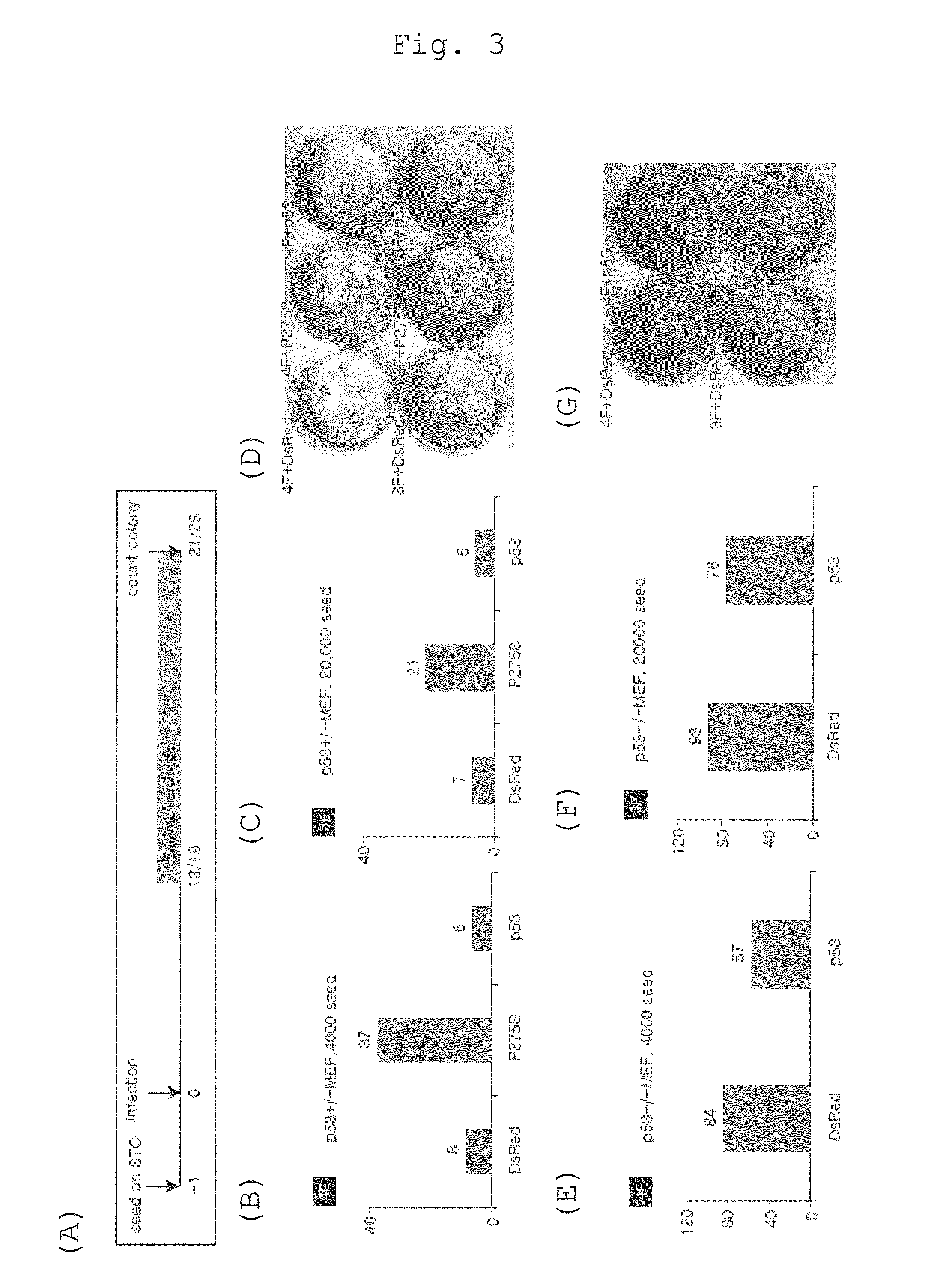
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, comprising inhibiting the p53 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The inhibition of p53 function is achieved by bringing a substance selected from the group consisting of (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors, into contact with a somatic cell, and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of iPS cells, the agent comprising an inhibitor of p53 function, particularly (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors. The present invention further provides a method of producing an iPS cell, comprising bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p53 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20100216236A1Effective isolationEasy to prepareGenetically modified cellsPeptidesNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20110039338A1Improve setup efficiencyImprove efficiencyGenetically modified cellsCulture processNuclear reprogrammingHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Provided is a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem cells, comprising culturing somatic cells under hypoxic conditions in the step of nuclear reprogramming thereof.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS8530238B2Genetically modified cellsBlood/immune system cellsNuclear reprogrammingCancer research
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, comprising inhibiting the p53 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The inhibition of p53 function is achieved by bringing a substance selected from the group consisting of (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors, into contact with a somatic cell, and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of iPS cells, the agent comprising an inhibitor of p53 function, particularly (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors. The present invention further provides a method of producing an iPS cell, comprising bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p53 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method of nuclear reprogramming
ActiveUS20130065311A1Easy to useElectric discharge tubesGenetically modified cellsNuclear reprogrammingHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
A method of producing an induced pluripotent stem cell includes introducing into a somatic cell one or more non-viral expression vectors. The vectors include one or more of an Oct family gene, a Klf family gene, a Sox family gene, a Myc family gene, a Lin family gene, and Nanog gene. The somatic cell is then cultured in a medium that supports pluripotent stem cells. At least a portion of the one or more introduced non-viral expression vectors is not substantially integrated in the chromosome.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Screening Method for Somatic Cell Nuclear Reprogramming Substance
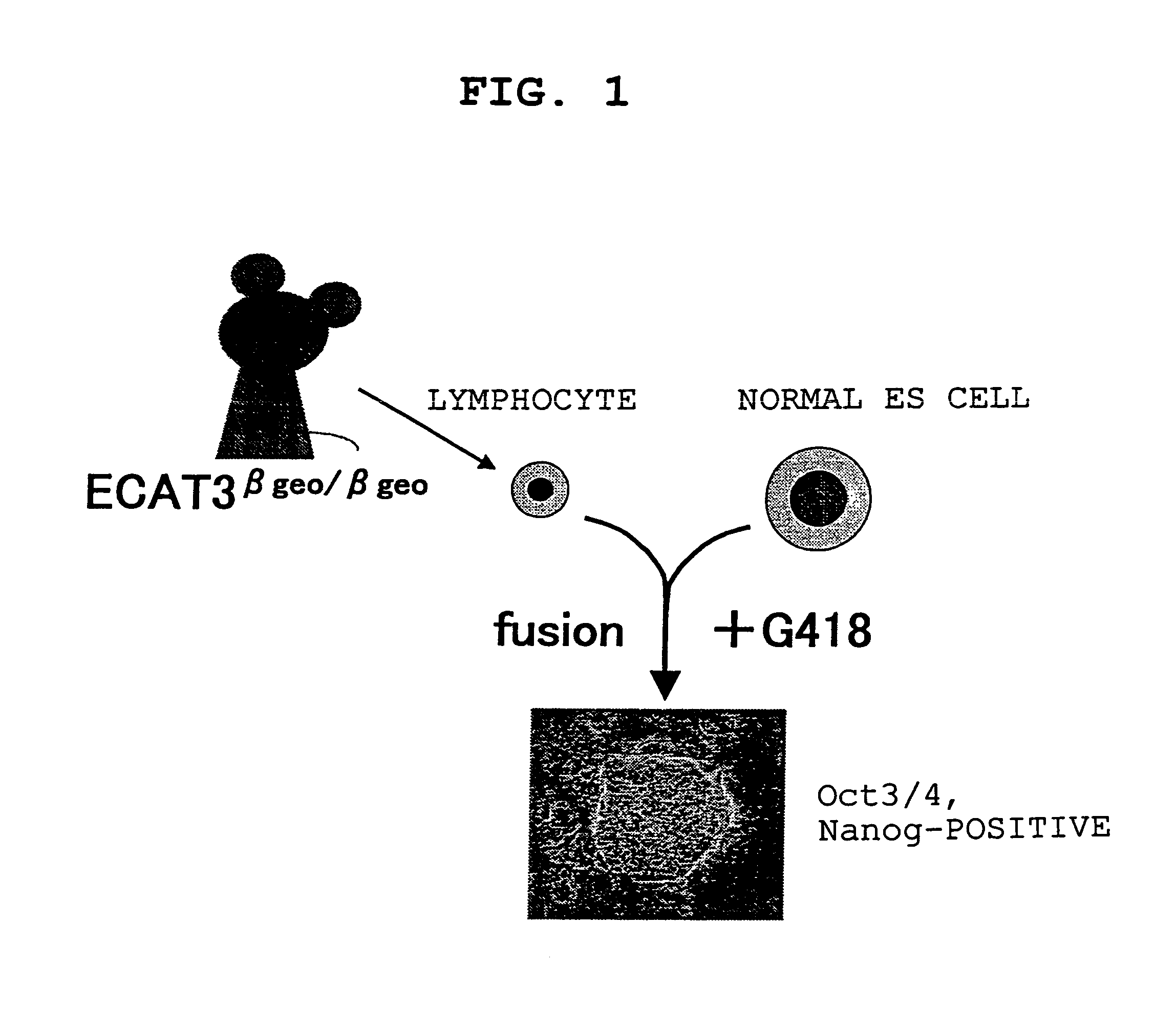
ActiveUS20080274914A1Valid choiceEasy to monitorPeptide librariesPeptidesScreening methodNuclear reprogramming
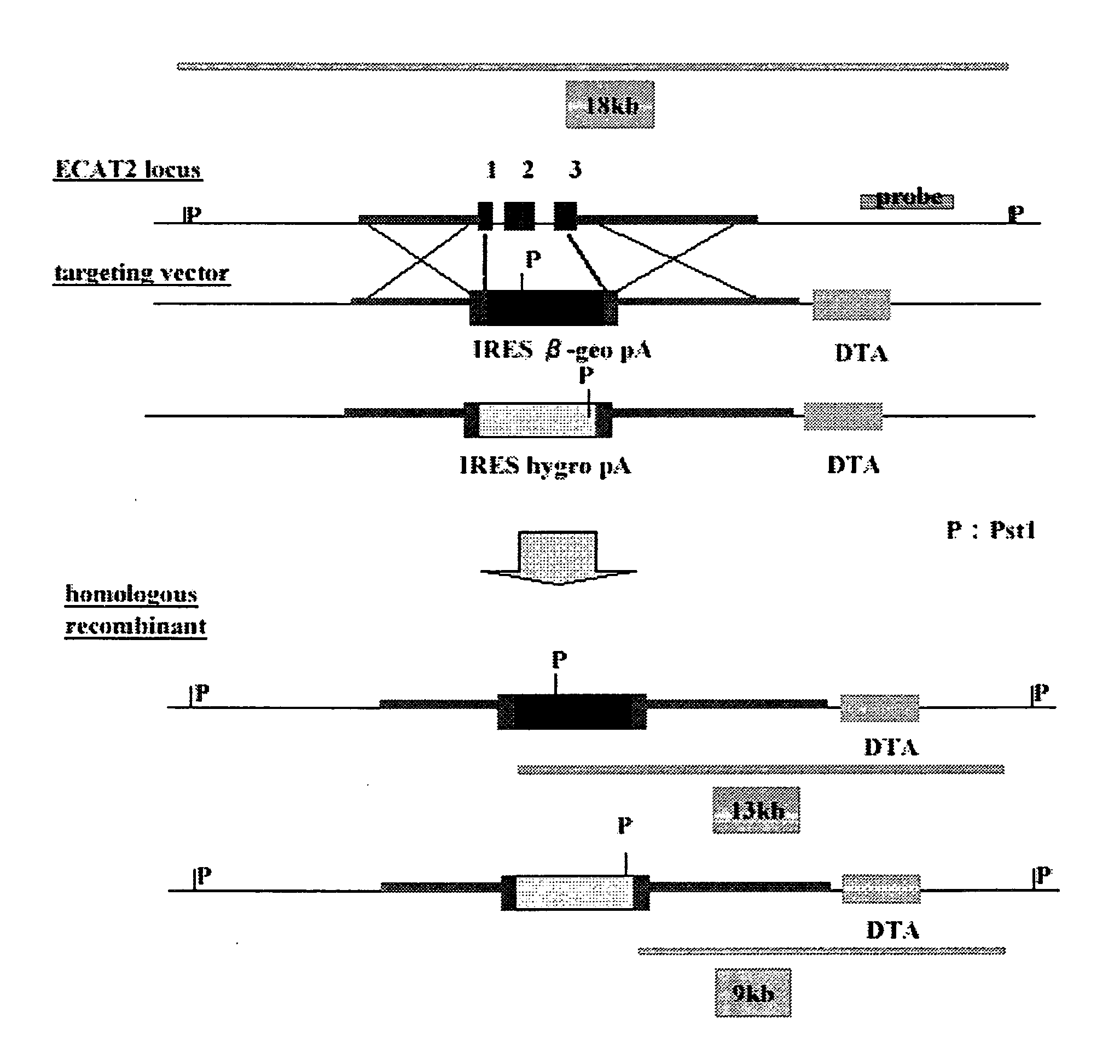
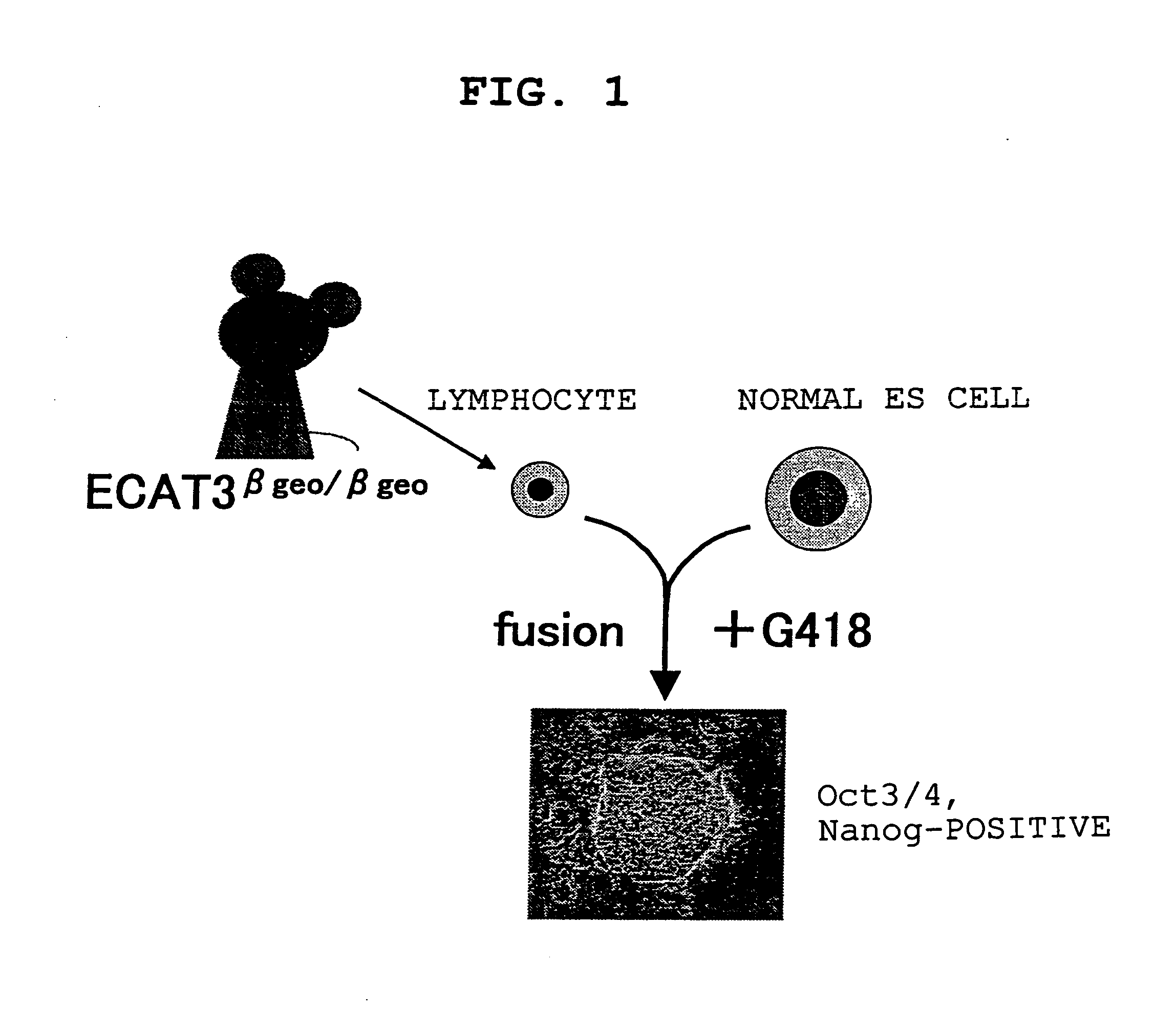
The present invention provides a screening method for somatic cell nuclear reprogramming substances, which comprises (a) a step for bringing into contact with each other a somatic cell comprising a gene wherein a marker gene is present at a position permitting expression control by the expression control region of an ECAT gene, and a test substance, and (b) a step following the aforementioned step (a), for determining the presence or absence of the emergence of cells expressing the marker gene, and selecting a test substance allowing the emergence of the cells as a somatic cell nuclear reprogramming substance candidate, and the like.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
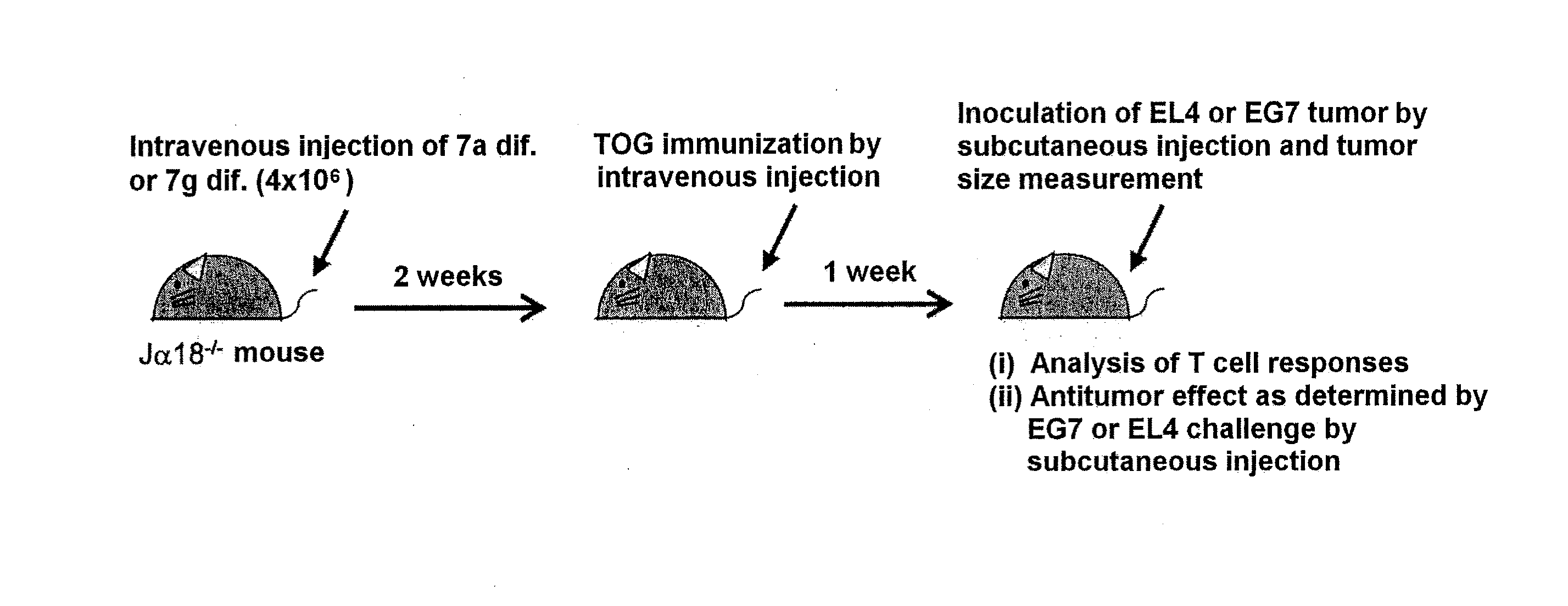
NKT CELL-DERIVED iPS CELLS AND NKT CELLS DERIVED THEREFROM
Provided are an iPS cell derived from a somatic cell such as an NKT cell, having the α-chain region of the T cell antigen receptor gene rearranged to uniform Vα-Jα in an NKT cell receptor-specific way, NKT cells differentiated from the iPS cell, a method of creating the same, and an immune cell therapy agent prepared using cells differentiated from the iPS cell. Also provided are an iPS cell having TCRα rearranged to NKT-TCR (NKT-iPS cell), obtained by contacting a somatic cell, such as an NKT cell, having the α-chain region of the T cell antigen receptor gene rearranged to uniform Vα-Jα in an NKT cell receptor-specific way, with nuclear reprogramming factors, isolated NKT cells obtained by differentiating the iPS cell ex vivo (iPS-NKT cell), a method of generating CD4 / CD8-double positive NKT cells (DP-NKT cells) and mature NKT cells from NKT-iPS cells by altering the combination of feeder cells and / or cytokines, a method of expanding the iPS-NKT cells, and an NKT cell cytotherapy agent comprising NKT cells activated with α-galactosyl ceramide (α-GalCer), or iPS-NKT cells, and α-GalCer in combination.
Owner:RIKEN
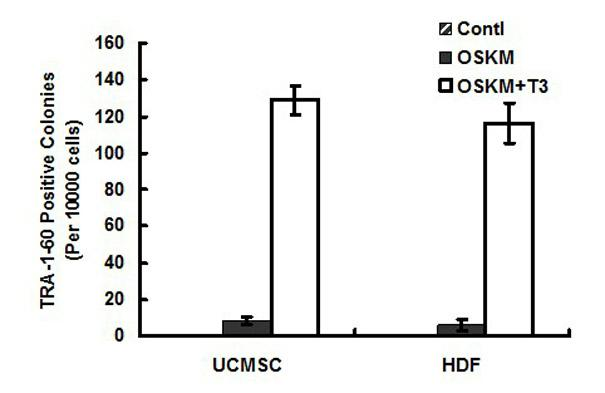
Method for efficiently inducing reprogramming of human body cells into pluripotent stem cells
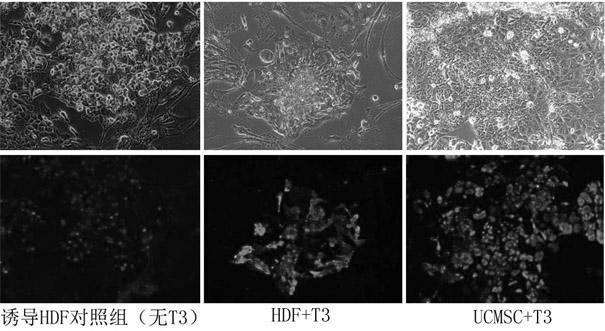
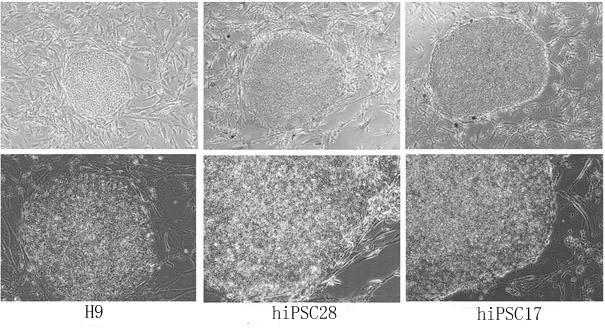
ActiveCN102093981AImprove the efficiency of inducing iPSCsShort induction periodVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsNuclear reprogrammingExpression gene
The invention provides a method for efficiently inducing reprogramming of human body cells into pluripotent stem cells, belonging to the field of biomedicine. The method provided by the invention comprises the following step: before carrying out nuclear reprogramming on body cells, culturing the body cells for 2-4 days in a culture medium containing thyroid hormone T3. The method provided by the invention can increase the iPSC (induced pluripotent stem cell) induction efficiency by 20-100 times to about 1.2%, and shorten the induction cycle to 12-16 days; and meanwhile, different clones of the iPSC obtained by induction have uniform cellular morphology, multiplication capacity and pluripotent gene expression, and can be used for researching human diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN BEIKE BIOTECH
Highly efficient method for establishing induced pluripotent stem cell
ActiveUS20150175973A1Improve setup efficiencyEfficient supplyGenetically modified cellsVirus peptidesNuclear reprogrammingHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
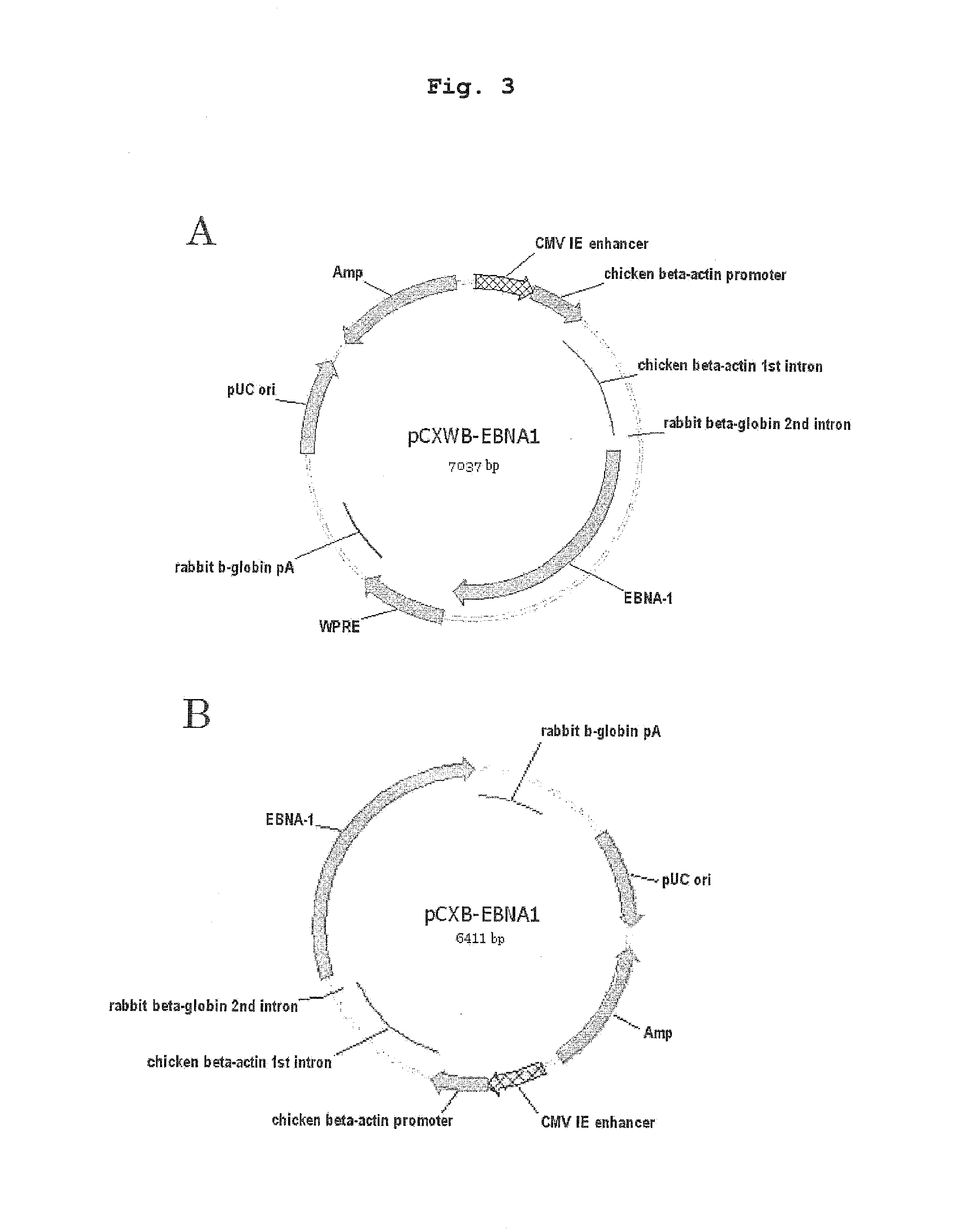
The present invention provides a production method of iPS cell, including a step of introducing the following (1) and (2):(1) an episomal vector containing a nuclear reprogramming factor; and(2) an episomal vector containing EBNA-1, which is different from (1),into a somatic cell, as well as a method for improving iPS cell establishment efficiency. The present invention also provides an agent for improving iPS cell establishment efficiency, which contains an episomal vector containing a nucleic acid encoding EBNA-1, and a kit for producing an iPS cell further containing an episomal vector containing a nucleic acid encoding a nuclear reprogramming factor.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
B cell-derived ips cells and application thereof
InactiveUS20110231944A1Low costLow cost productionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsMonoclonal antibodyImmunodeficient Mouse
Provided are a B cell-derived iPS cell generated using a convenient technique, a technology for providing a human antibody at low cost using the iPS cell, an immunologically humanized mouse prepared using cells differentiated from the iPS cell, and the like. Also provided are a cloned cell obtained by contacting a B cell with nuclear reprogramming factors excluding C / EBPα and Pax5 expression inhibiting substances, particularly nucleic acids that encode Oct3 / 4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc, wherein the cloned cell has an immunoglobulin gene rearranged therein and possesses pluripotency and replication competence (B-iPS cell). Still also provided are a method of producing a monoclonal antibody against a specified antigen, comprising recovering an antibody from a culture of B cells obtained by differentiating a B-iPS cell derived from a B cell immunized with the specified antigen, and a method of generating an immunologically humanized mouse, comprising transplanting to an immunodeficient mouse a human immunohematological system cell obtained by differentiating a B-iPS cell.
Owner:RIKEN
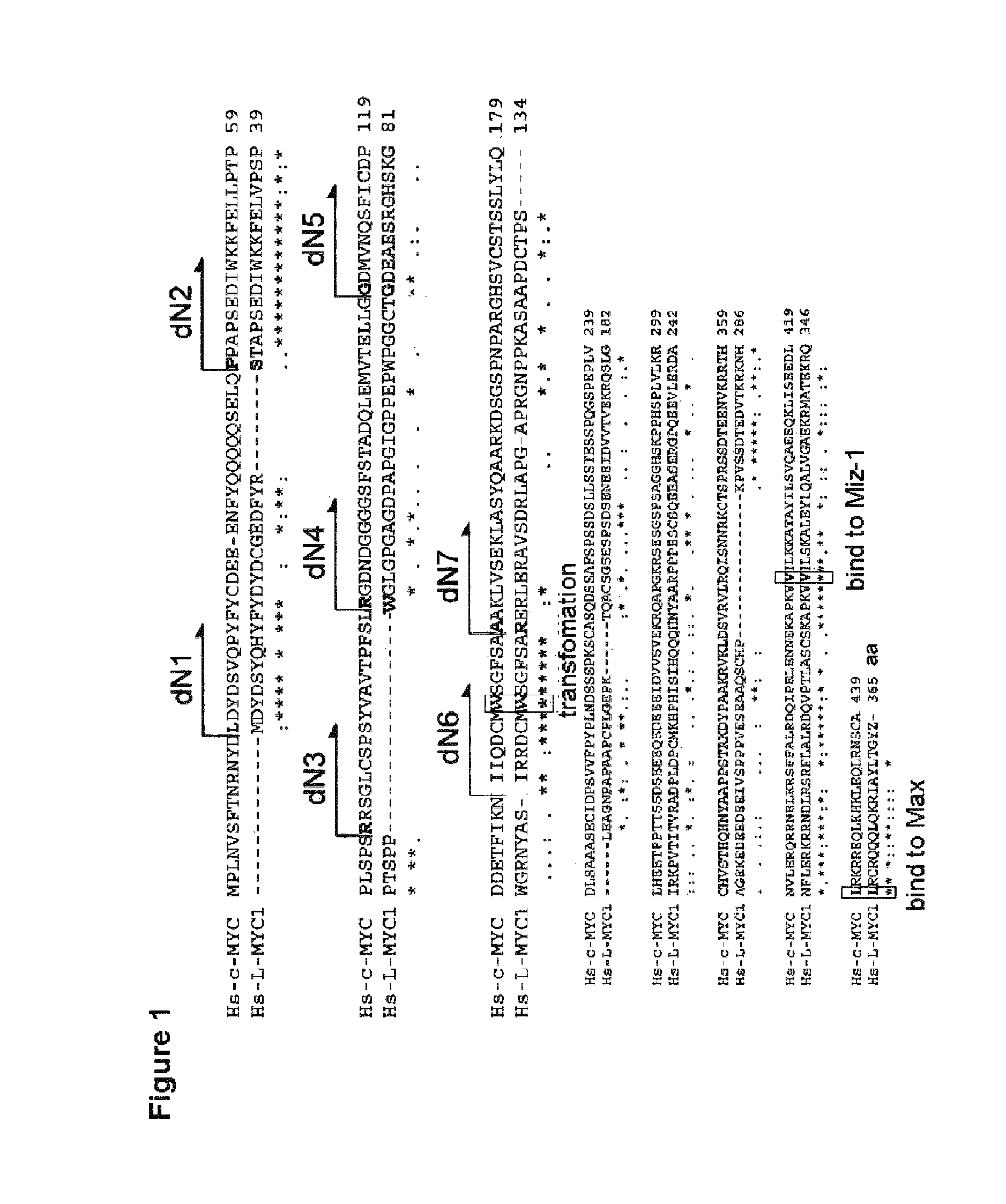
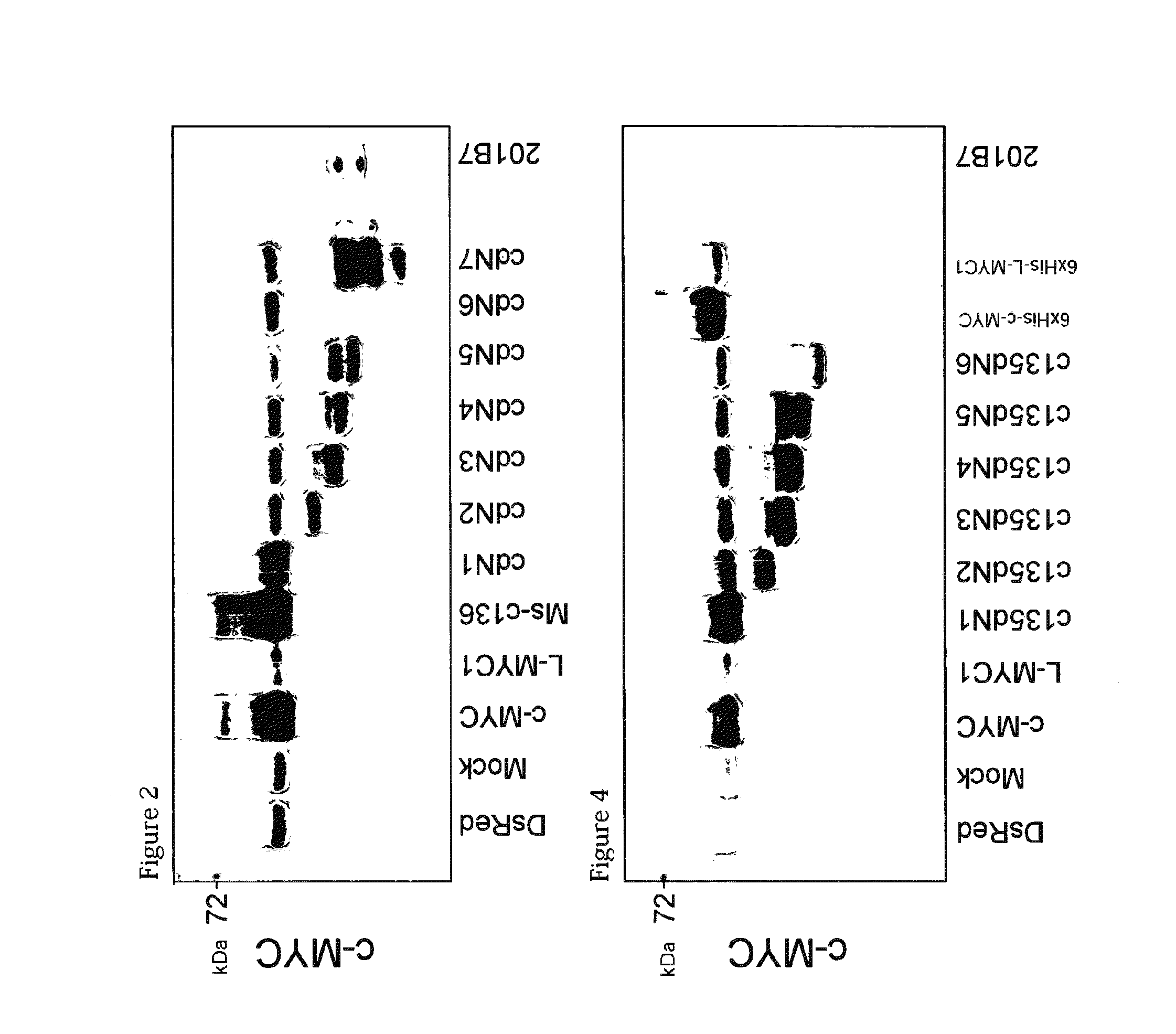
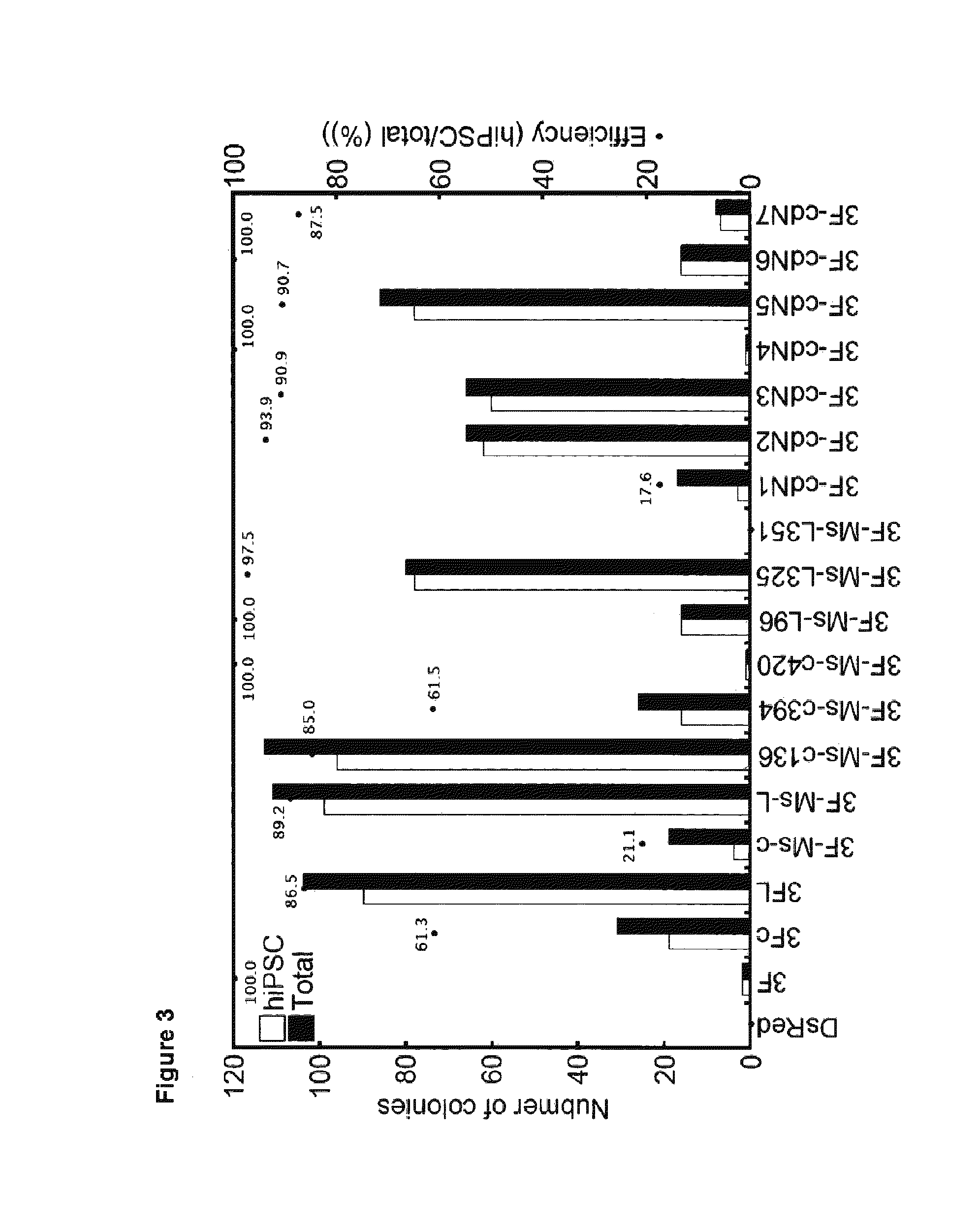
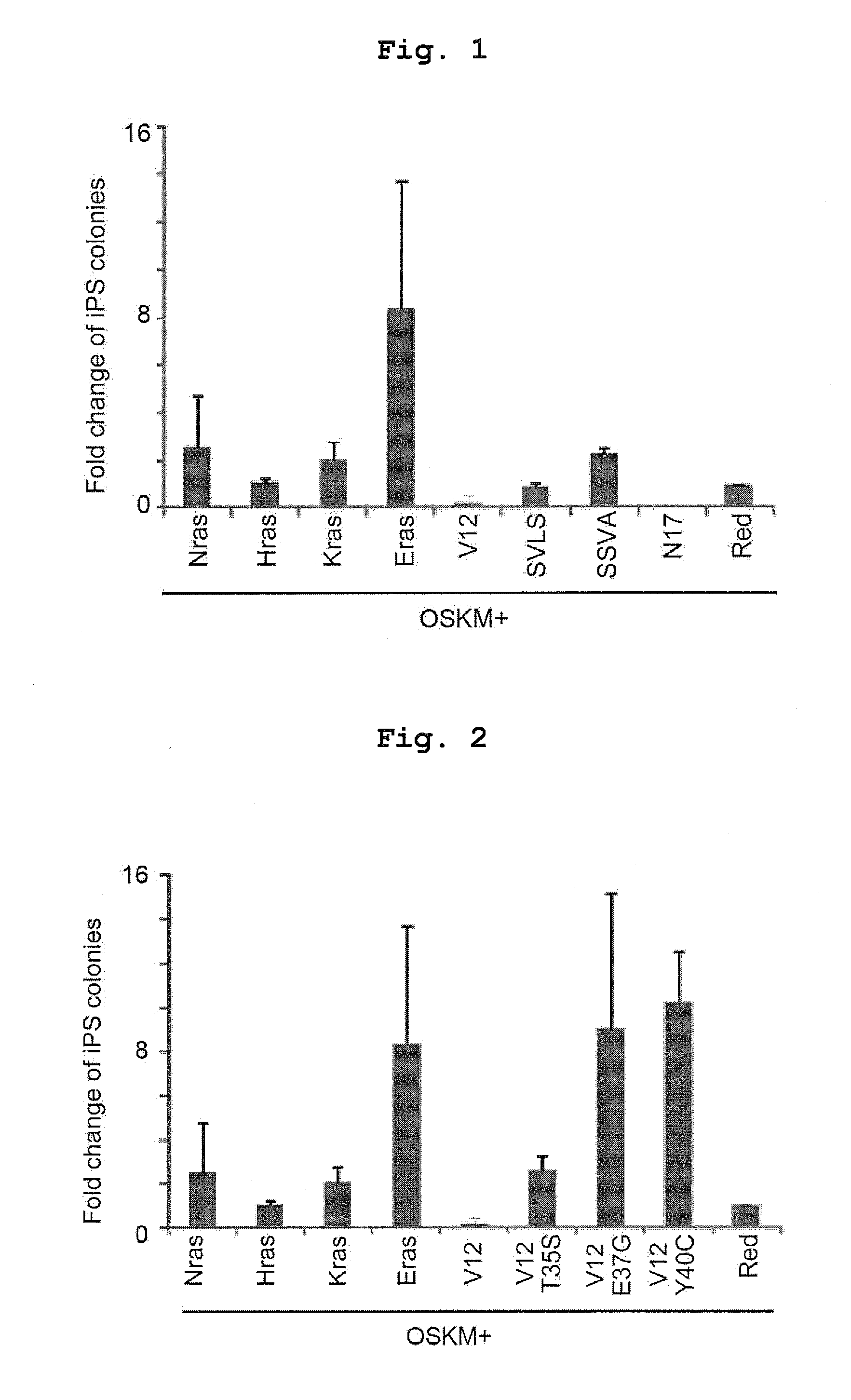
Myc variants improve induced pluripotent stem cell generation efficiency
ActiveUS9005967B2Improve power generation efficiencyHigh activityArtificial cell constructsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsNuclear reprogrammingMultipotential stem cell
The present invention provides a method for improving iPS cell generation efficiency, which comprises a step of introducing a Myc variant having the following features: (1) having an activity to improve iPS cell generation efficiency which is comparative to, or greater than that of c-Myc; and (2) having a transformation activity which is lower than that of c-Myc; or a nucleic acid encoding the variant, in a nuclear reprogramming step. Also, the present invention provides a method for preparing iPS cells, which comprises a step of introducing the above Myc variant or a nucleic acid encoding the variant and a combination of nuclear reprogramming factors into somatic cells. Moreover, the present invention provides iPS cells comprising the nucleic acid encoding the Myc variant which can be obtained by the above method, and a method for preparing somatic cells which comprises inducing differentiation of the iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
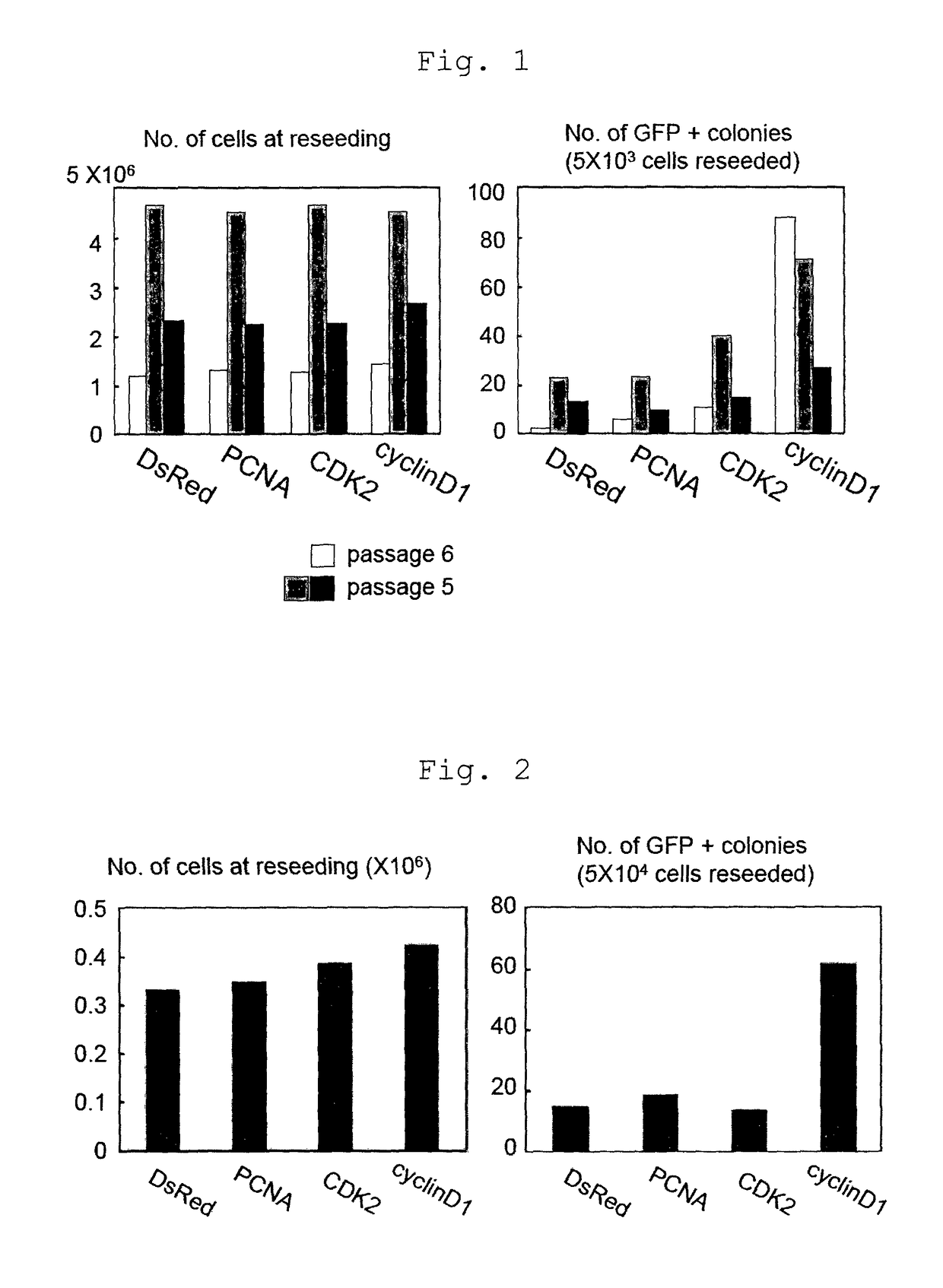
ActiveUS9637732B2Improve setup efficiencyEfficient productionHydrolasesTransferasesNuclear reprogrammingHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
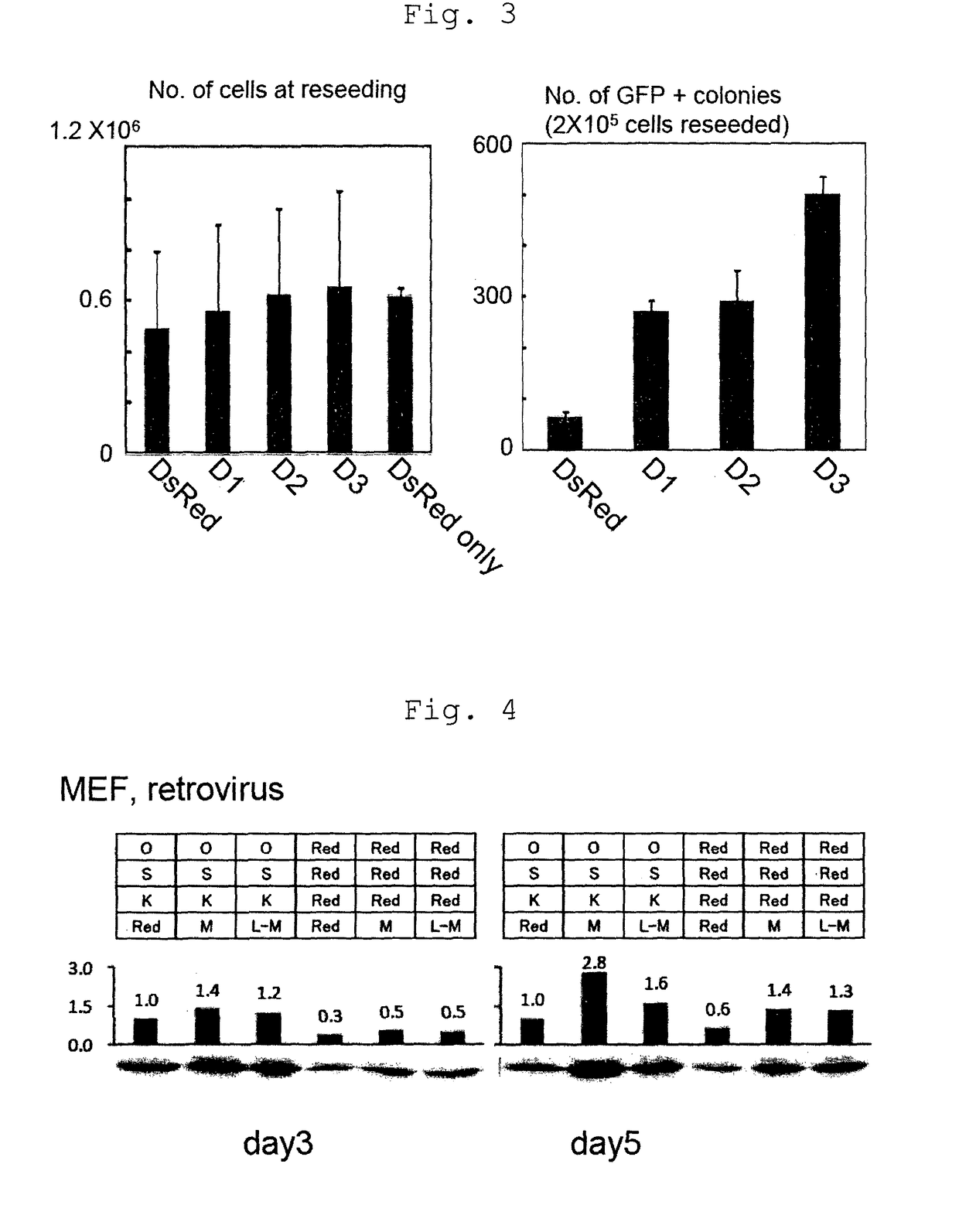
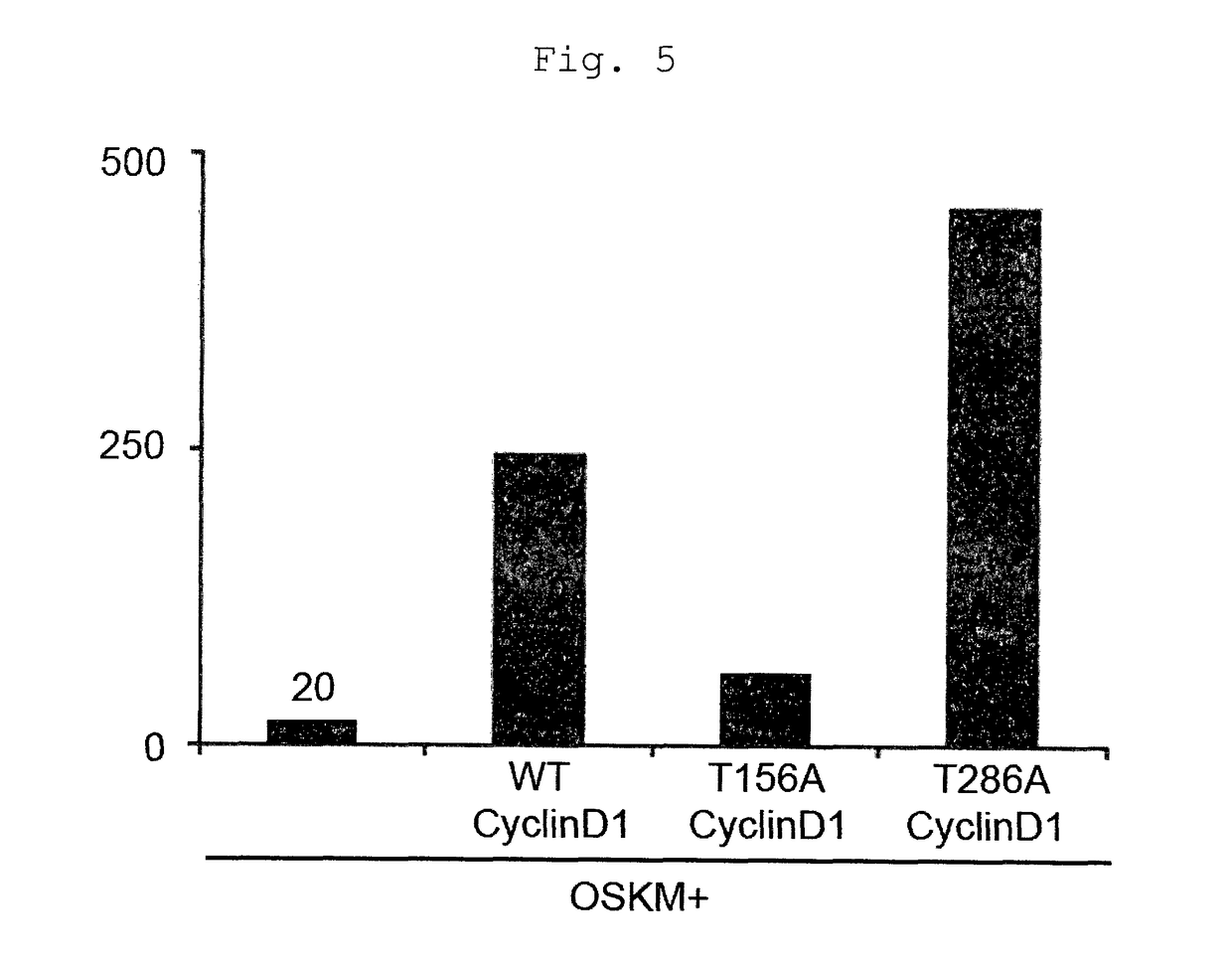
Provided is a method of improving the efficiency of iPS cell establishment, comprising bringing one or more factors selected from the group consisting of proteins belonging to cyclin D family and nucleic acids that encode the same into contact with a somatic cell, in the step of nuclear reprogramming of the somatic cell. Also provided are a method of producing an iPS cell comprising the step of bringing the factor(s) and nuclear reprogramming substance(s) into contact with a somatic cell, an iPS cell comprising a nucleic acid that encodes a protein belonging to cyclin D family that can be obtained by the method of producing an iPS cell, and a method of somatic cell production by forcing the iPS cell to differentiate.
Owner:TANABE KOJI
METHOD AND COMPOUNDS FOR GENERATION OF iPSCs
InactiveUS20120213746A1Avoid immune rejectionIncrease the number ofBiocideLibrary screeningGenomicsCell specific
The present invention is based on the seminal concept of combining genomics and chemical biology to identify new agents useful for induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) generation. The invention provides a method of generating an iPSC utilizing agents that antagonize a cell specific gene or upregulate expression or activity of a nuclear reprogramming gene, as well as a method of screening for such agents.
Owner:SANFORD BURNHAM PREBYS MEDICAL DISCOVERY INST
Generating a mature NKT cell from a reprogrammed somatic cell with a T-cell antigen receptor α-chain region rearranged to uniform Va-Ja in a NKT-cell specific way
Provided are an iPS cell derived from a somatic cell such as an NKT cell, having the α-chain region of the T cell antigen receptor gene rearranged to uniform Vα-Jα in an NKT cell receptor-specific way, NKT cells differentiated from the iPS cell, a method of creating the same, and an immune cell therapy agent prepared using cells differentiated from the iPS cell. Also provided are an iPS cell having TCRα rearranged to NKT-TCR (NKT-iPS cell), obtained by contacting a somatic cell, such as an NKT cell, having the α-chain region of the T cell antigen receptor gene rearranged to uniform Vα-Jα in an NKT cell receptor-specific way, with nuclear reprogramming factors, isolated NKT cells obtained by differentiating the iPS cell ex vivo (iPS-NKT cell), a method of generating CD4 / CD8-double positive NKT cells (DP-NKT cells) and mature NKT cells from NKT-iPS cells by altering the combination of feeder cells and / or cytokines, a method of expanding the iPS-NKT cells, and an NKT cell cytotherapy agent comprising NKT cells activated with α-galactosyl ceramide (α-GalCer), or iPS-NKT cells, and α-GalCer in combination.
Owner:RIKEN
Efficient method for nuclear reprogramming
ActiveUS20130102768A1Efficient preparationImprove efficiencySugar derivativesGenetically modified cellsNuclear reprogrammingBiology
A method of preparing induced pluripotent stem cells, comprising a nuclear reprogramming step with a nuclear reprogramming factor in the presence of miRNA, wherein said miRNA has a property of providing a higher nuclear reprogramming efficiency in the presence of said miRNA than in the absence thereof.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20130195812A1Increased chromatin accessibilityEasy to recruitBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransdifferentiationNuclear reprogramming
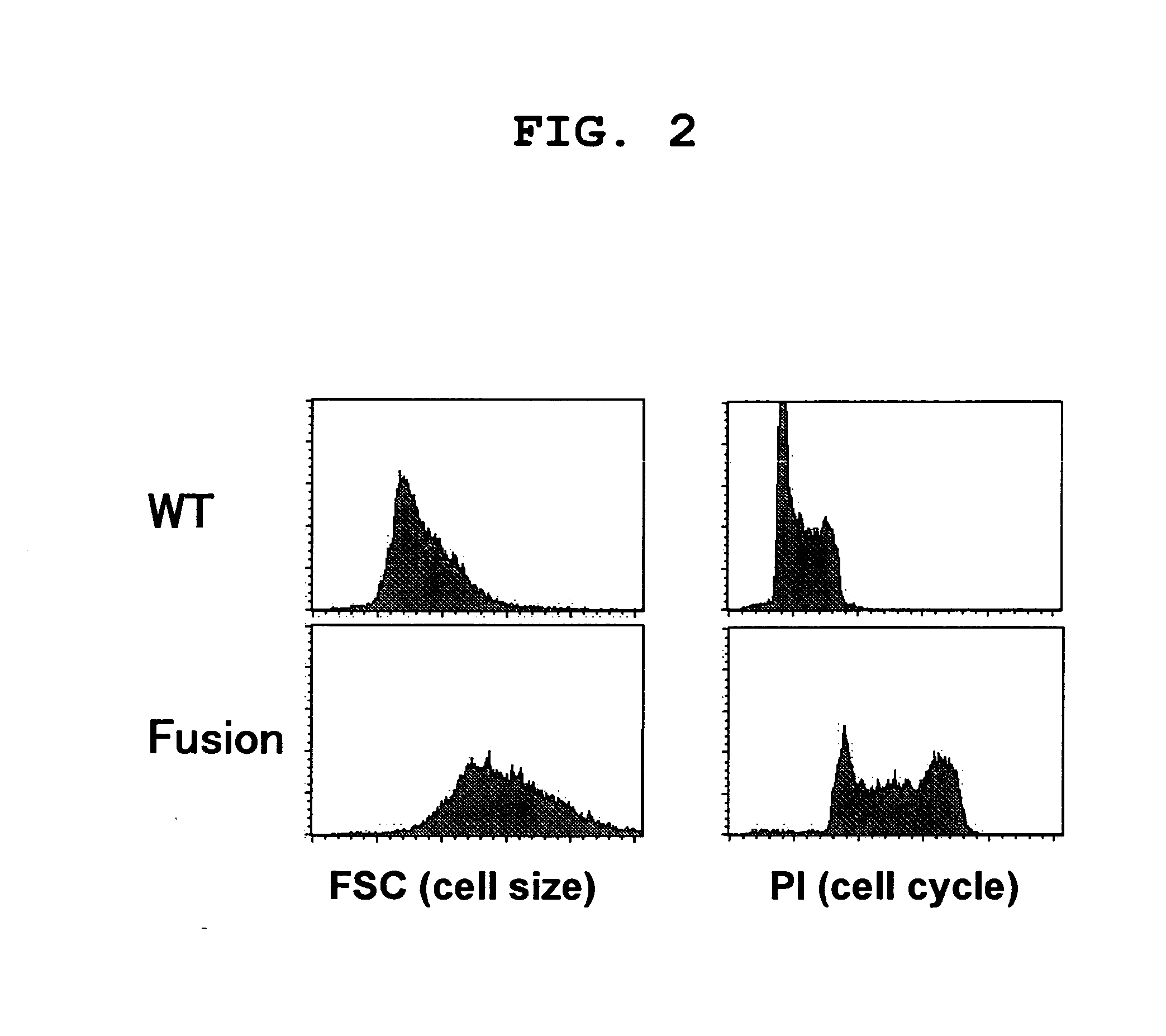
Described herein is a major breakthrough in nuclear reprogramming and induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology. Fusion of the powerful transcription activation domain (TAD) of MyoD to the Oct4 protein makes iPSCs generation faster, more efficient, purer, safer and feeder-free. Also, disclosed herein is the first report of the use of a TAD fused to a transcription factor as a method for making iPSCs. By combining transcription factors and TADs, this approach to nuclear reprogramming can have a range of applications from inducing pluriopotency to inducing transdifferentiation without transitioning through iPSCs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
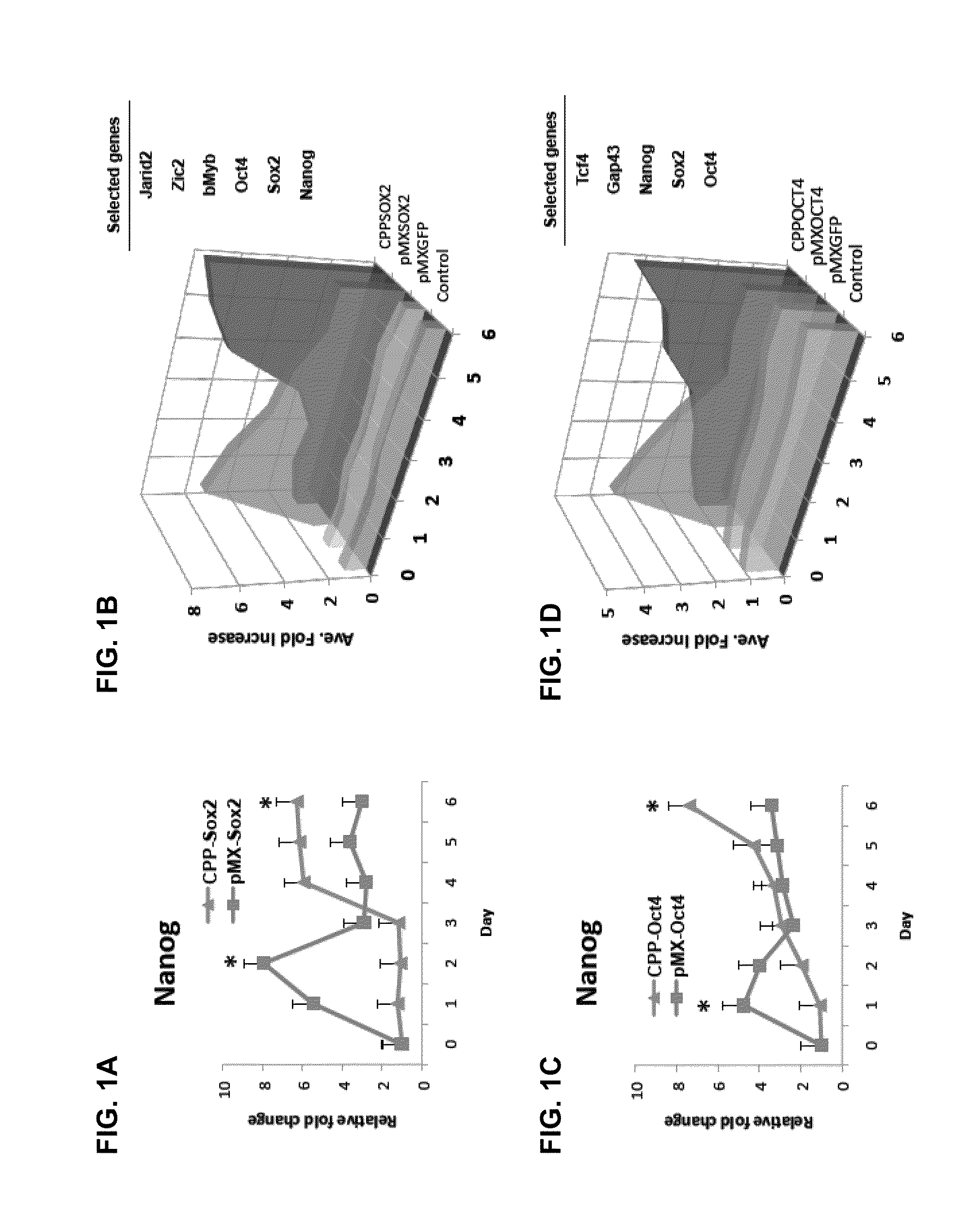
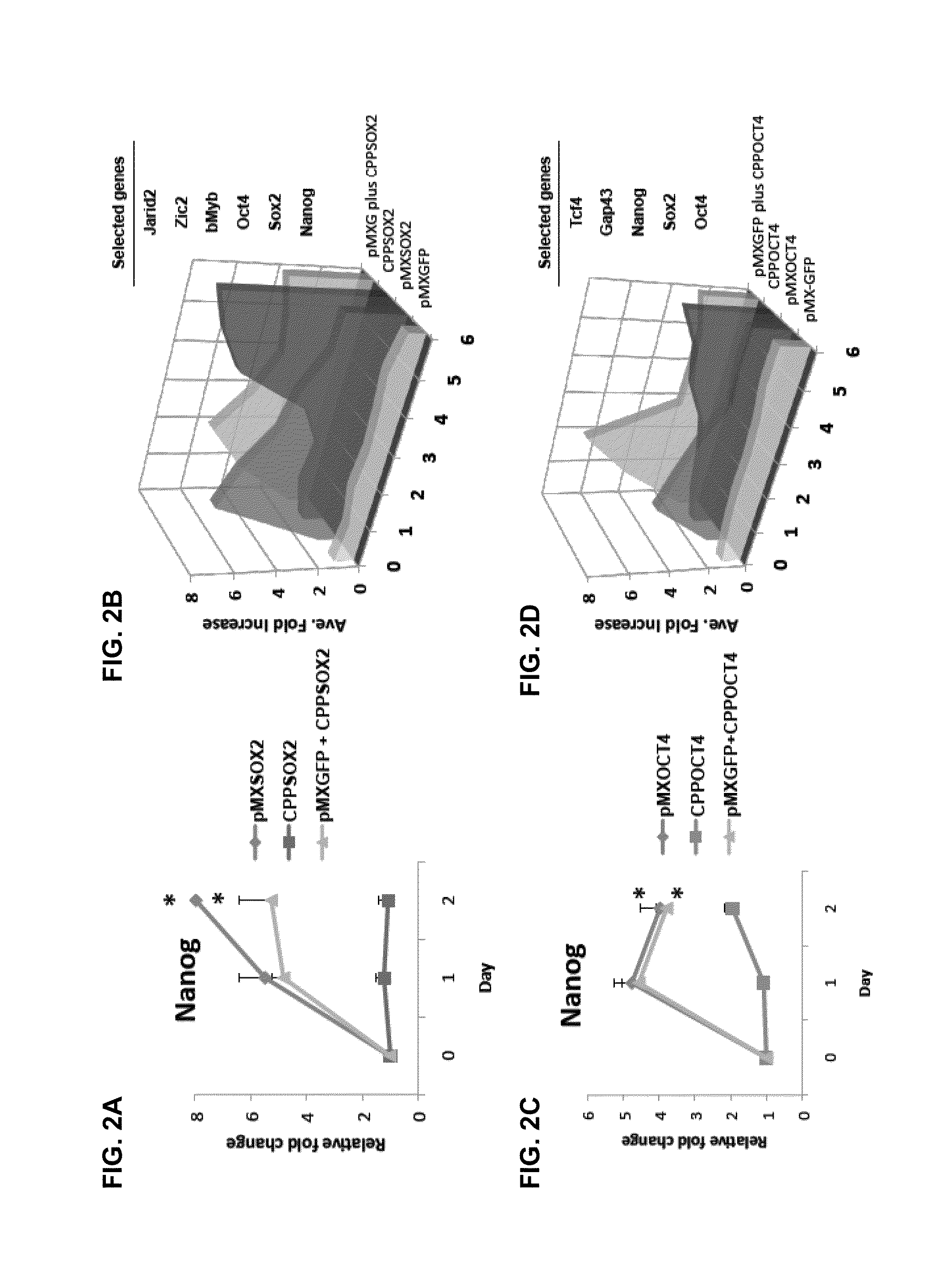
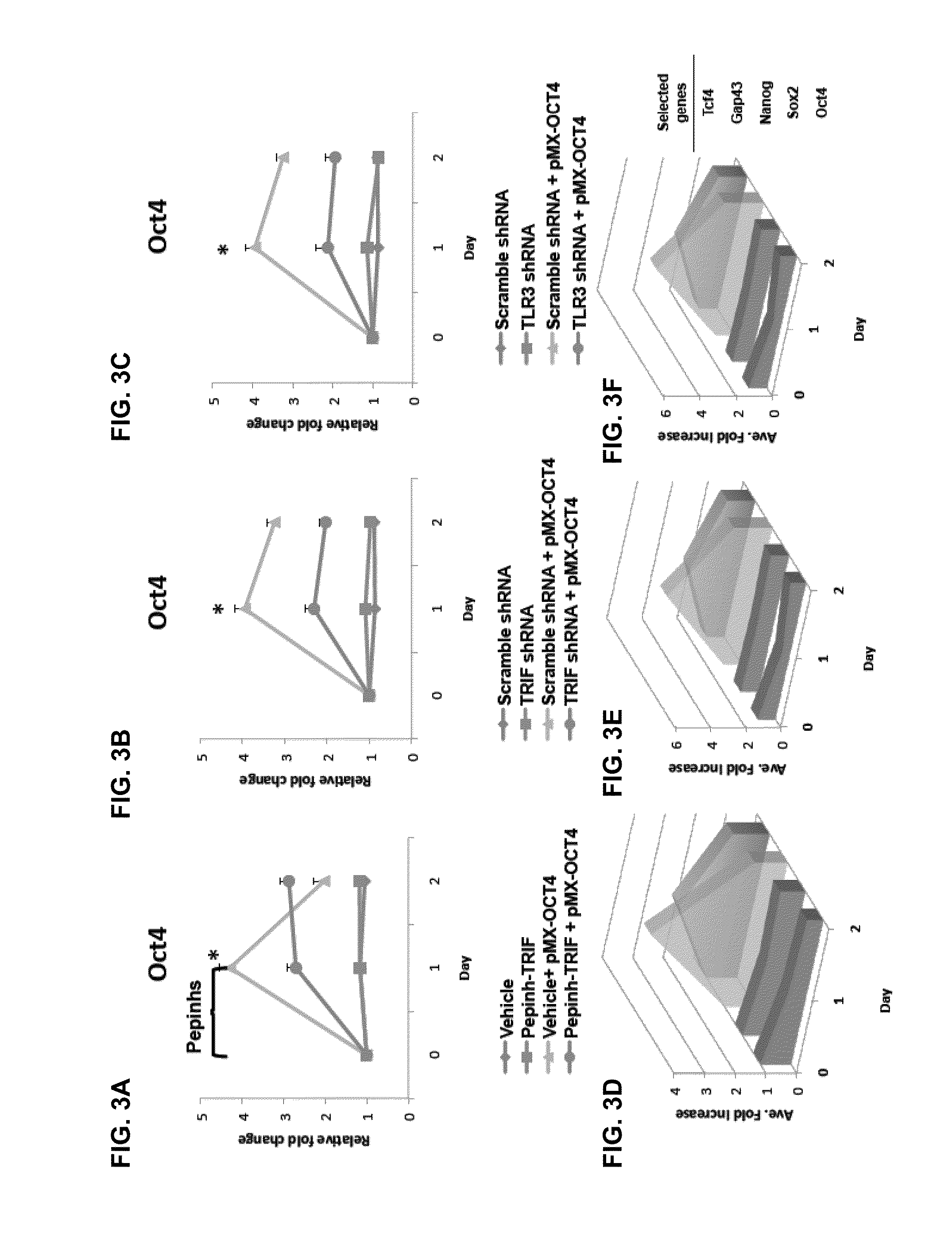
Activation of innate immunity for nuclear reprogramming of somatic cells
InactiveUS20130202649A1Enhances reprogrammingIncrease productionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsToll-like receptorNuclear reprogramming
The nuclear reprogramming of somatic cells with non-integrating factors is shown to be greatly accelerated by activation of innate immune responses in the somatic cell. Methods of activating innate immunity include activation of toll-like receptors, e.g. TLR3. Somatic cells with activated innate immune responses can be reprogrammed to induced pluripotent cells or to transdifferentiated cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Efficient method for establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
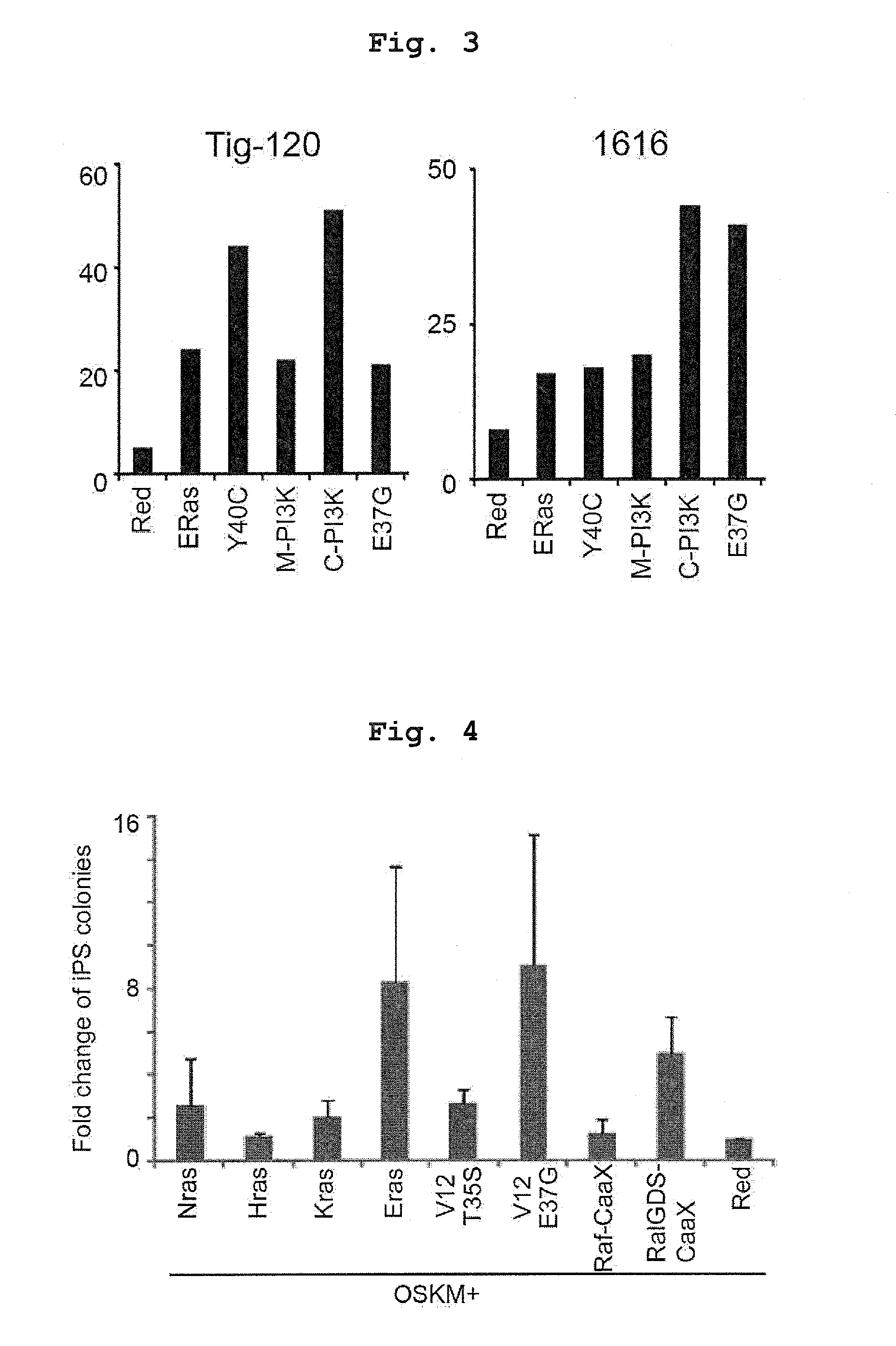
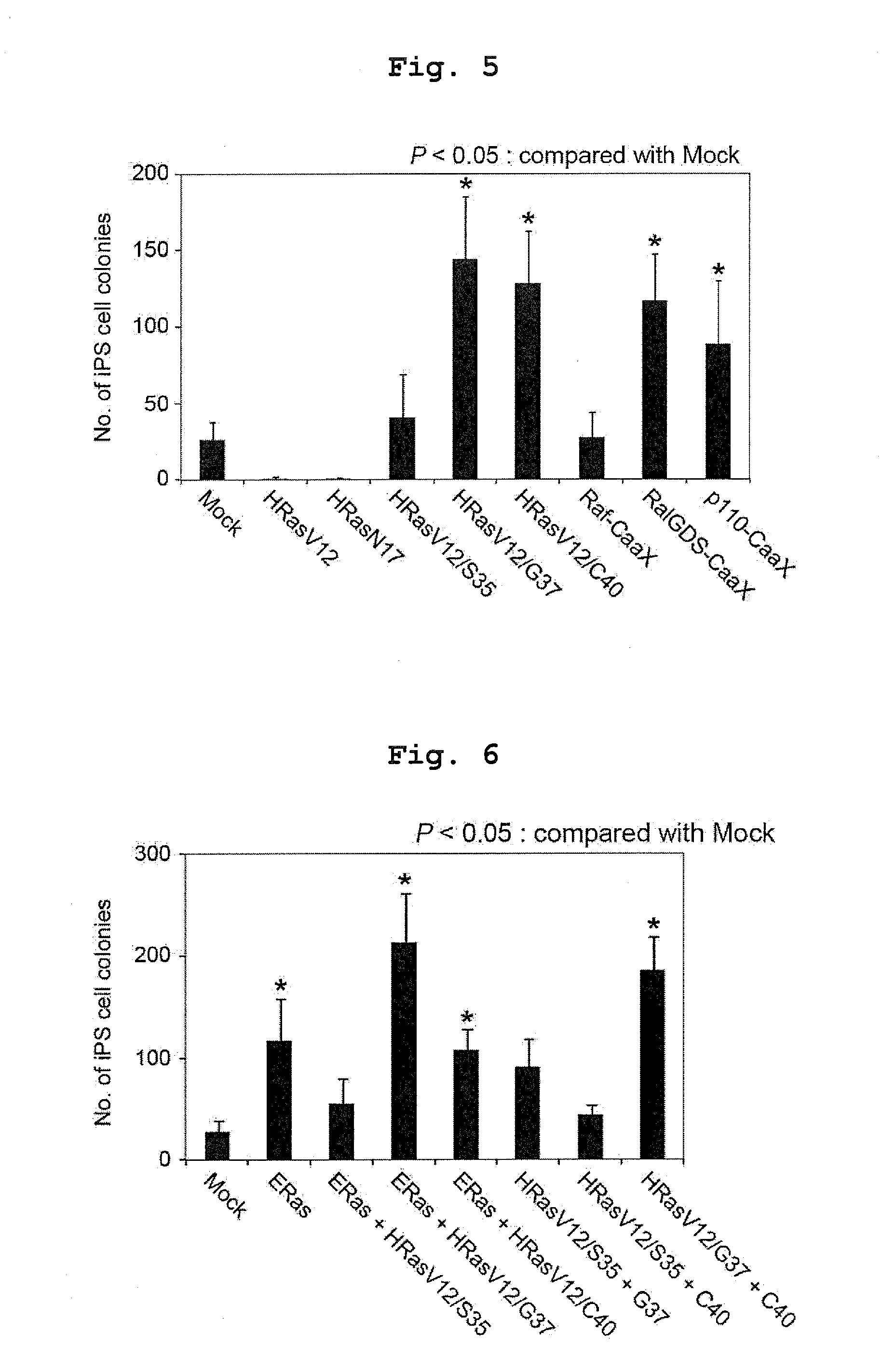
ActiveUS20130267030A1Improve setup efficiencyIncreased level of activationHydrolasesTransferasesRHEBNuclear reprogramming
The invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem cells by increasing, in a nuclear reprogramming step of somatic cell, the level of activated form of one or more proteins selected from the group consisting of Ras family members, PI3 kinase, RalGEF, Raf, AKT family members, Rheb, TCL1 and S6K. The invention also provides a method of producing induced pluripotent stem cells by contacting a somatic cell with a nuclear reprogramming substance and one or more of such proteins and nucleic acids that encode such proteins. The invention further provides an induced pluripotent stem cell that has an exogenous nucleic acid encoding such a protein, as well as agents for use in the aforesaid methods.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Effective nuclear reprogramming in mammals using CDK2 inhibitors
InactiveUS6906238B2Convenient timeOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureMammalGenetic Materials
The present invention provides methods of producing a cloned non-human mammalian nuclear transfer (NT) embryo and methods for producing a cloned non-human mammal. Embodiments of the methods include introducing donor genetic material into a metaphase I oocyte; introducing donor genetic material into a non-enucleated oocyte; introducing donor genetic material obtained from a donor cell that is at metaphase into an oocyte; introducing donor genetic material into an oocyte, and naturally activating the oocyte or the NT embryo; and introducing donor genetic material obtained from a donor cell that is at late G1 phase into an oocyte.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Screening method for somatic cell nuclear reprogramming substance affecting ECAT2 and ECAT3
InactiveUS7964401B2Valid choiceEasy to monitorPeptide librariesPeptidesNuclear reprogrammingCell nucleus
The present invention provides a screening method for somatic cell nuclear reprogramming substances, which comprises (a) a step for bringing into contact with each other a somatic cell comprising a gene wherein a marker gene is present at a position permitting expression control by the expression control region of an ECAT gene, and a test substance, and (b) a step following the aforementioned step (a), for determining the presence or absence of the emergence of cells expressing the marker gene, and selecting a test substance allowing the emergence of the cells as a somatic cell nuclear reprogramming substance candidate, and the like.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Cells and methods for obtaining them
InactiveUS20120315703A1High reprogramming efficiencyQuality improvementDrug compositionsFermentationRetinoic acid receptorGene product
Reprogrammed somatic cells, methods for reprogramming, reprogramming factors for somatic cells and uses of such factors and cells are described. Nuclear reprogramming factors [NRF] described comprise one or more of a gene product or a polynucleic acid encoding a gene product from a retinoic acid receptor (RAR / RXR) family member, or an agonist or antagonist thereof; a gene product from an Lrh1 family member; or an agonist thereof; retinoic acid or a gene product involved in synthesizing or metabolizing retinoic acid; or an agonist or antagonist thereof; or a gene product that is involved in transporting a retinoic acid family member.
Owner:GENOME RES LTD
Methods for nuclear reprogramming of cells
ActiveUS20150086649A1BiocideNervous disorderNuclear reprogrammingHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
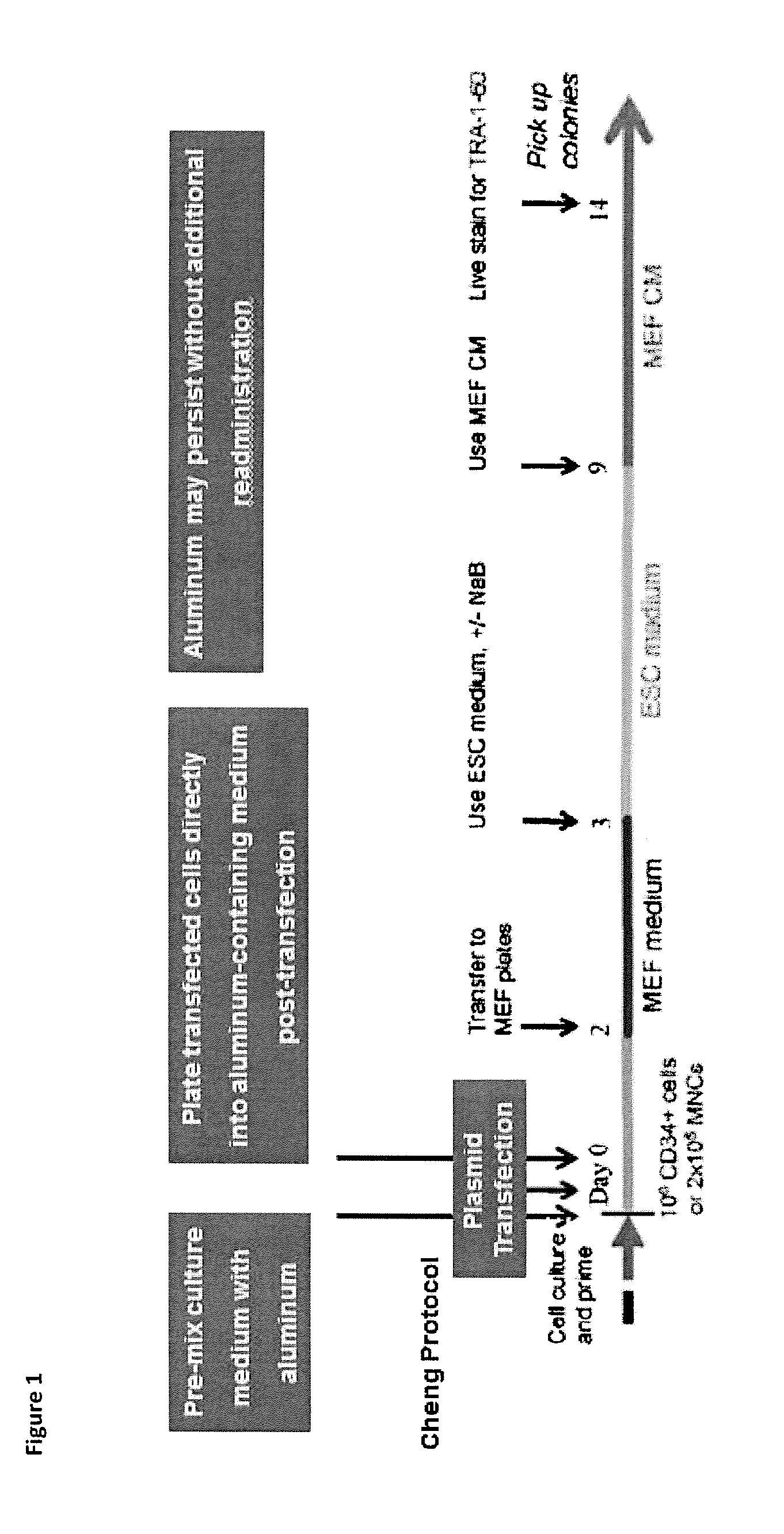
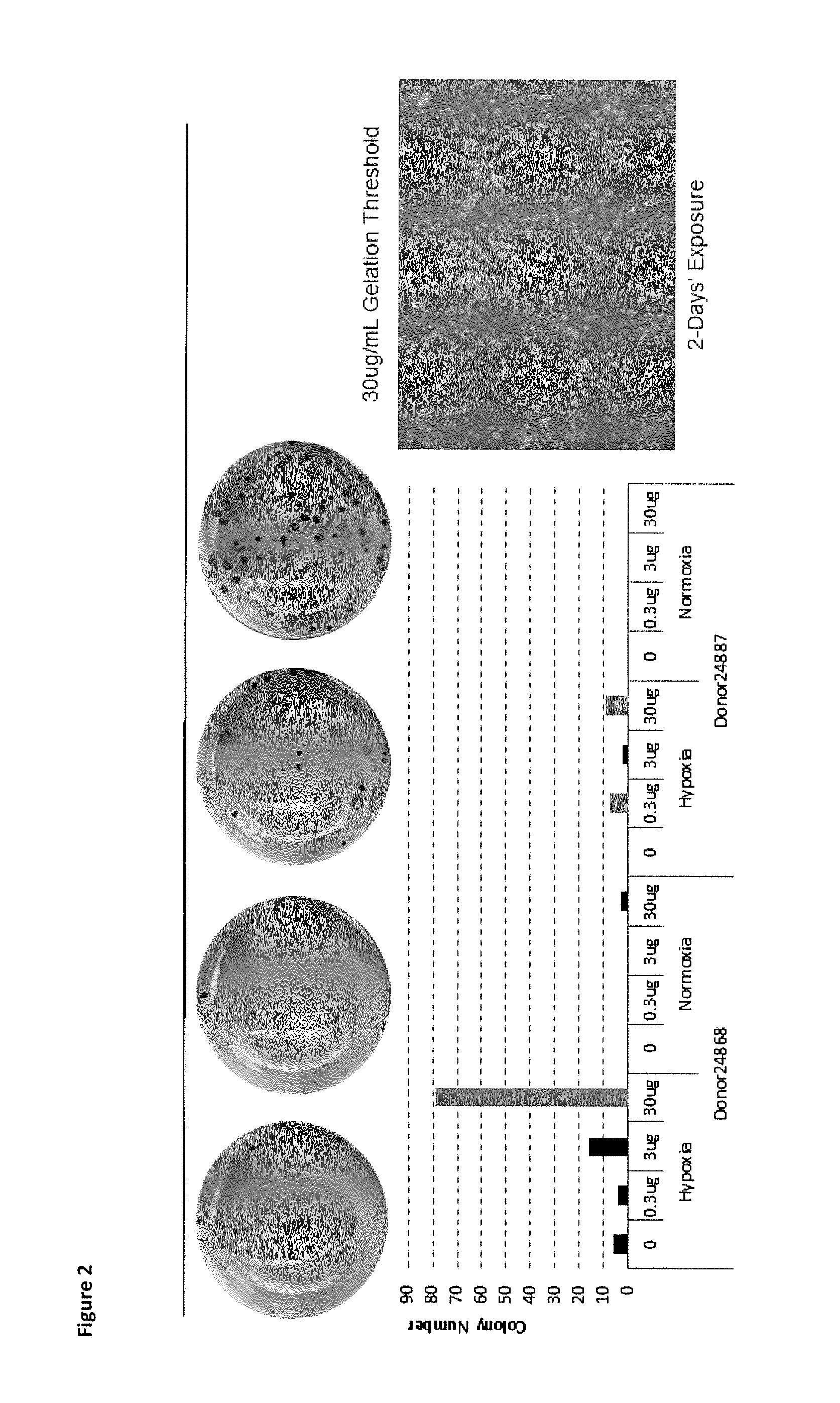
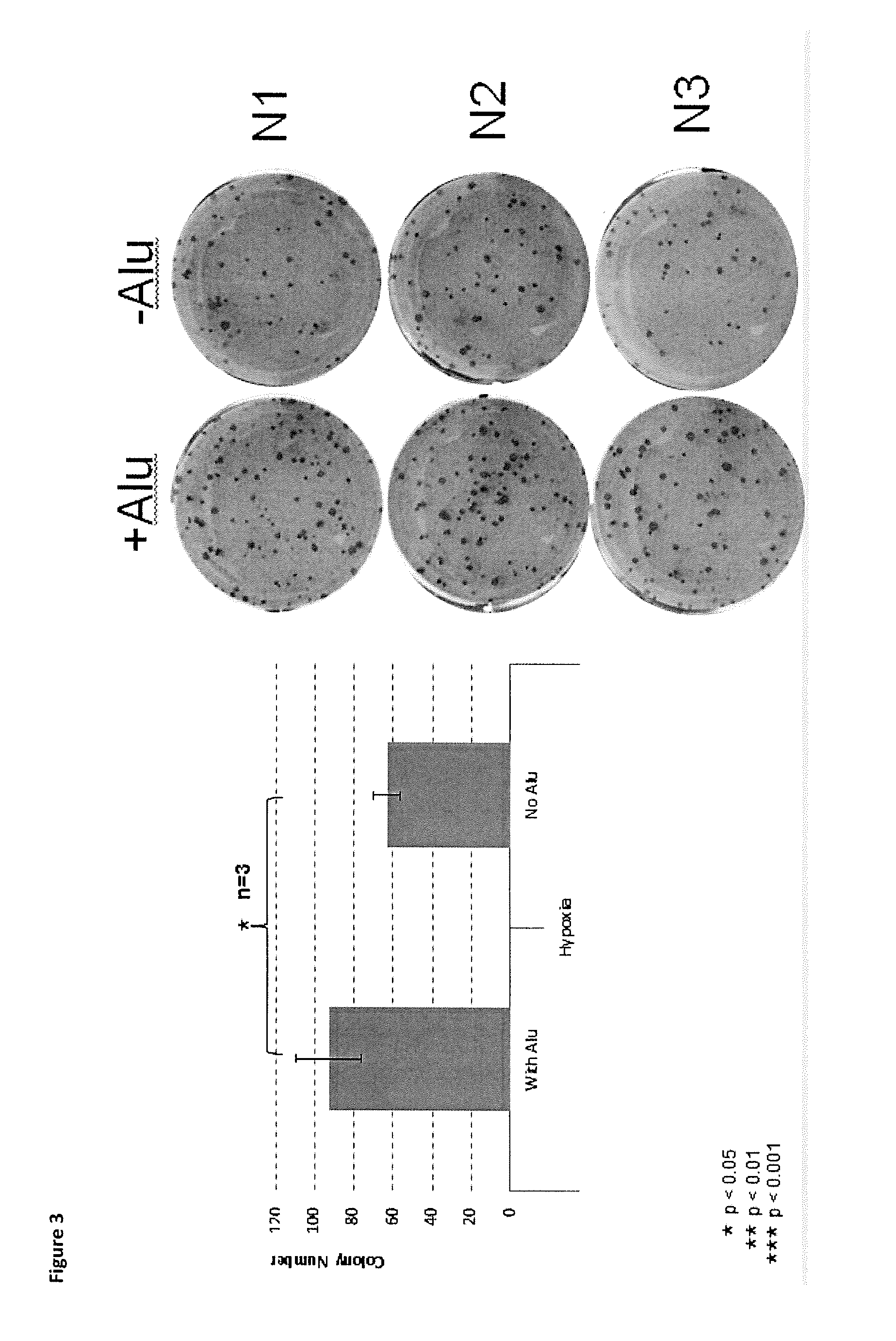
Described herein are methods for enhancing the nuclear reprogramming of somatic cells to become induced pluripotent stem cells. In particular, the methods disclosed herein involve the use of damage-associated molecular pattern molecules (DAMP). In certain embodiments the DAMPs are aluminum compositions such as aluminum hydroxide. Such DAMPs have unexpectedly and surprisingly been found to enhance the nuclear reprogramming efficiency of the reprogramming factors commonly used to induce somatic cells to become induced pluripotent stem cells. Accordingly, this disclosure describes methods of nuclear reprogramming as well as cells obtained from such methods along with therapeutic methods for using such cells for the treatment of disease amendable to treatment by stem cell therapy; as well as kits for such uses.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com