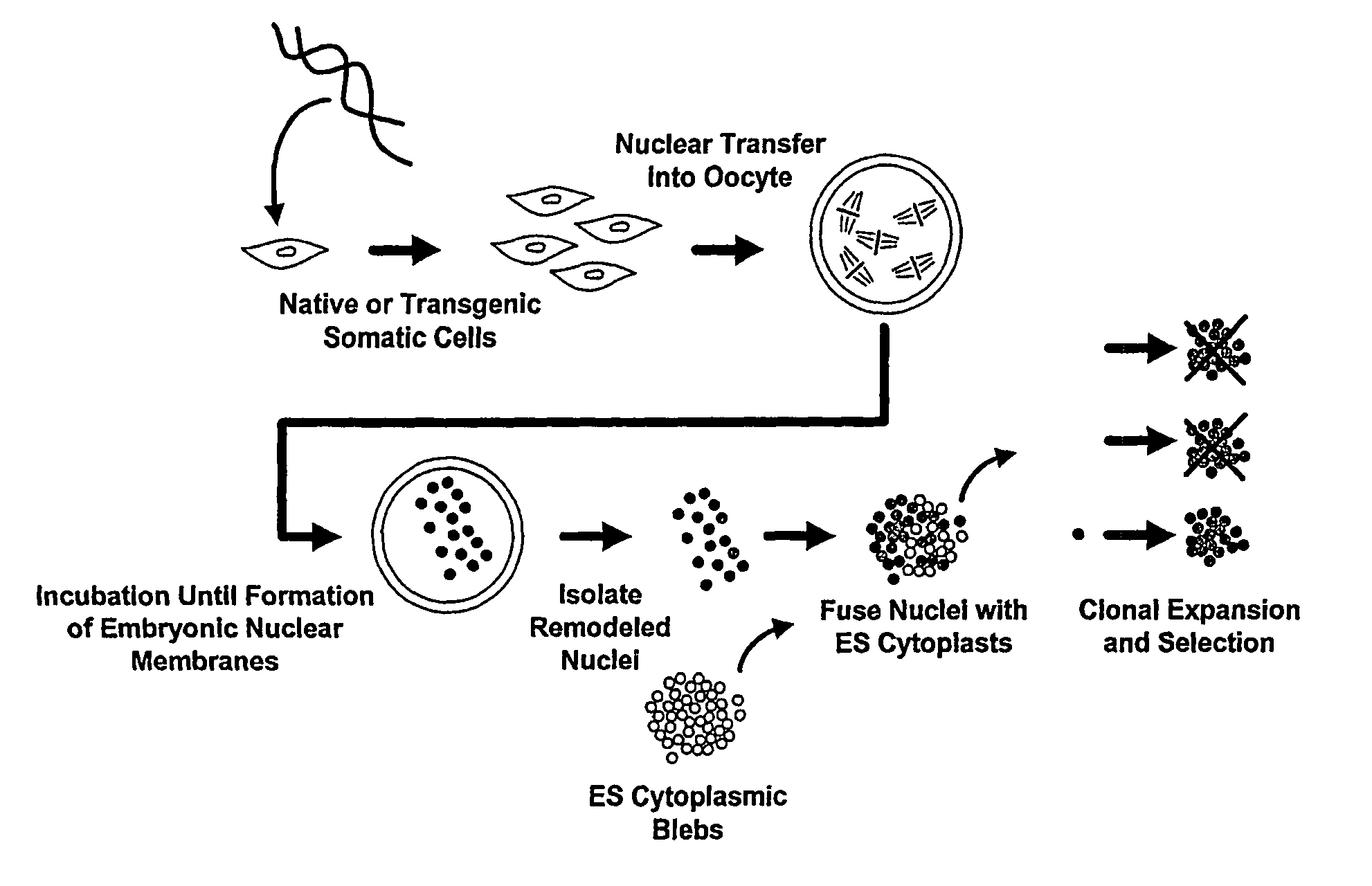
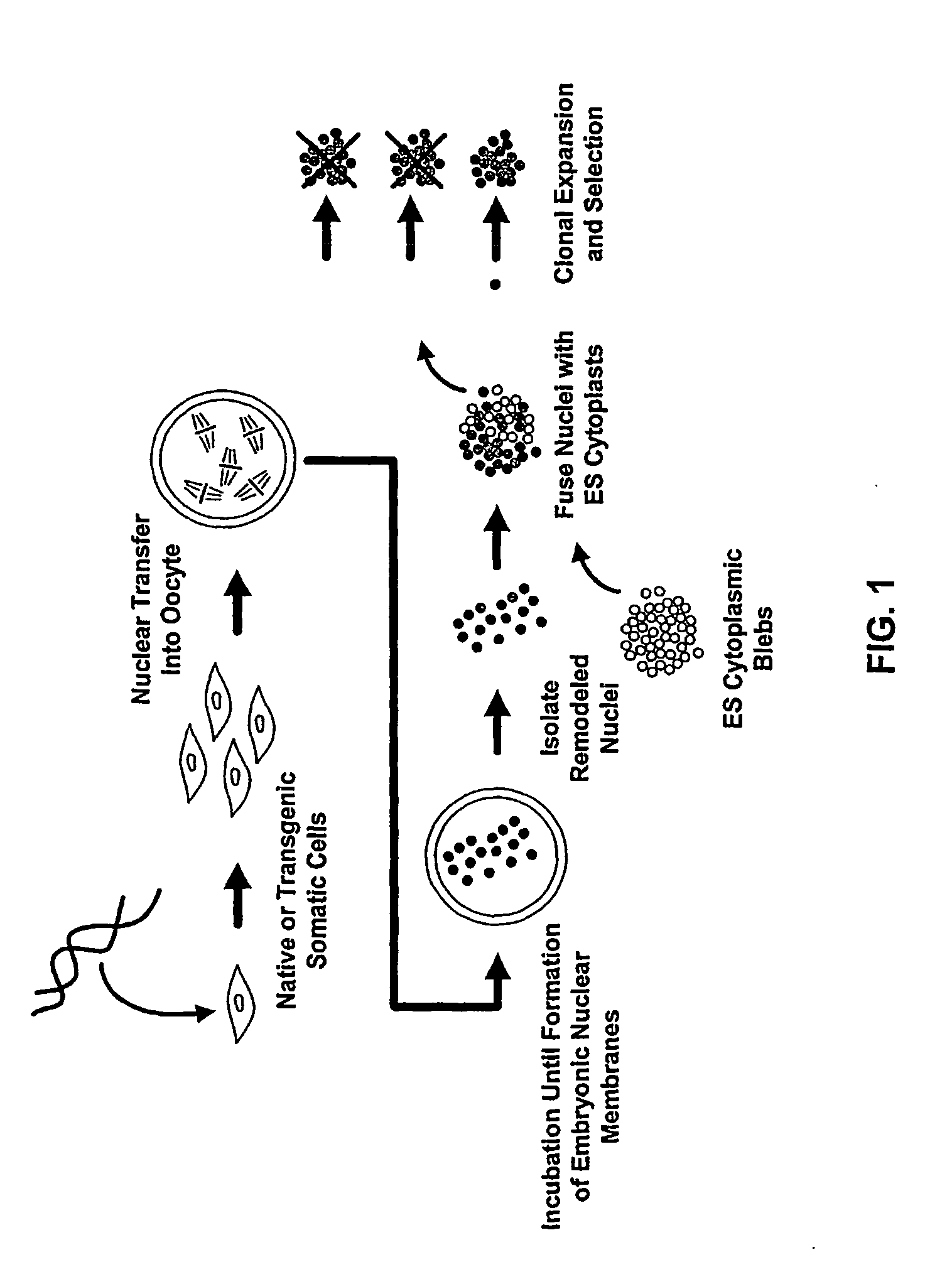
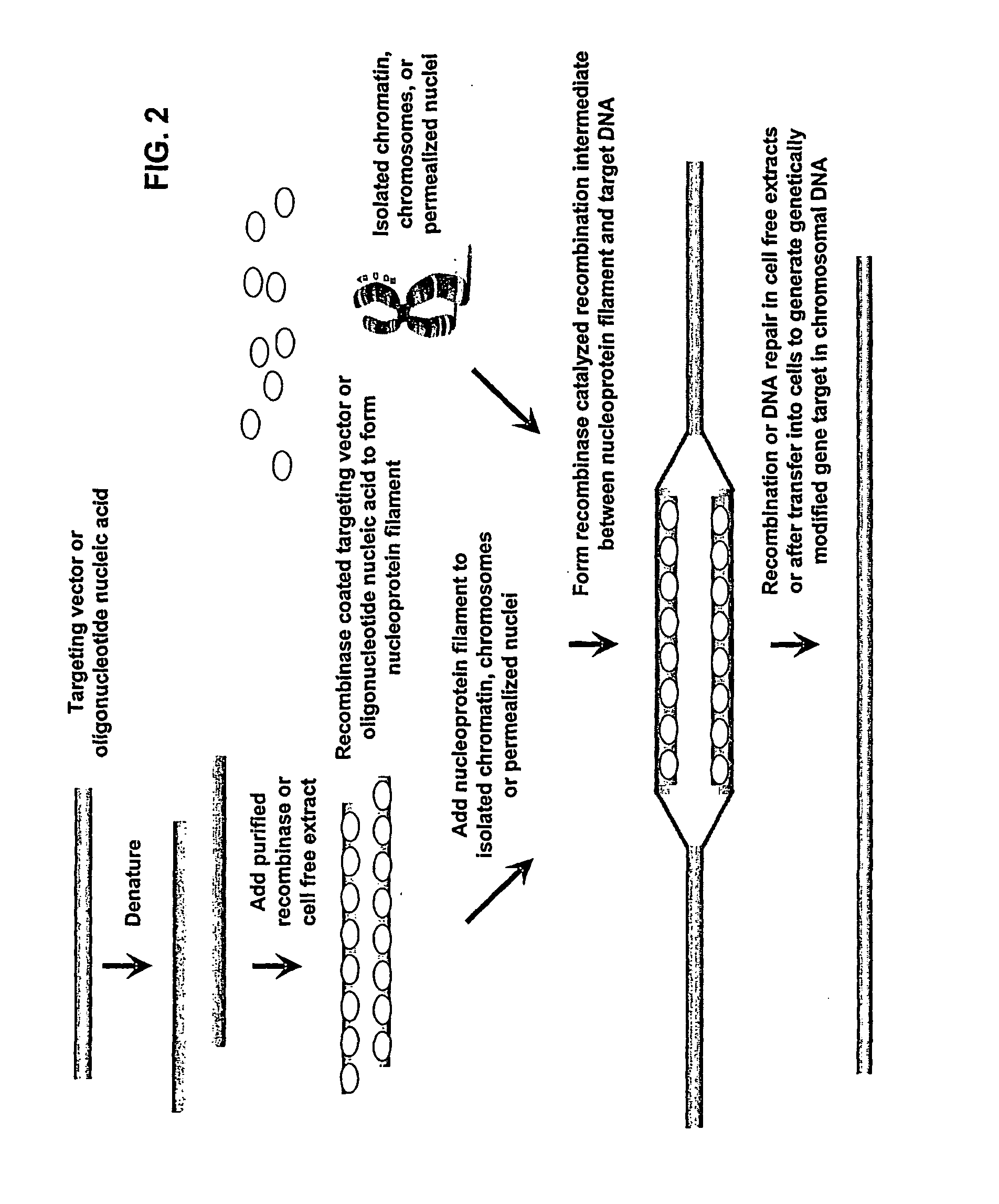
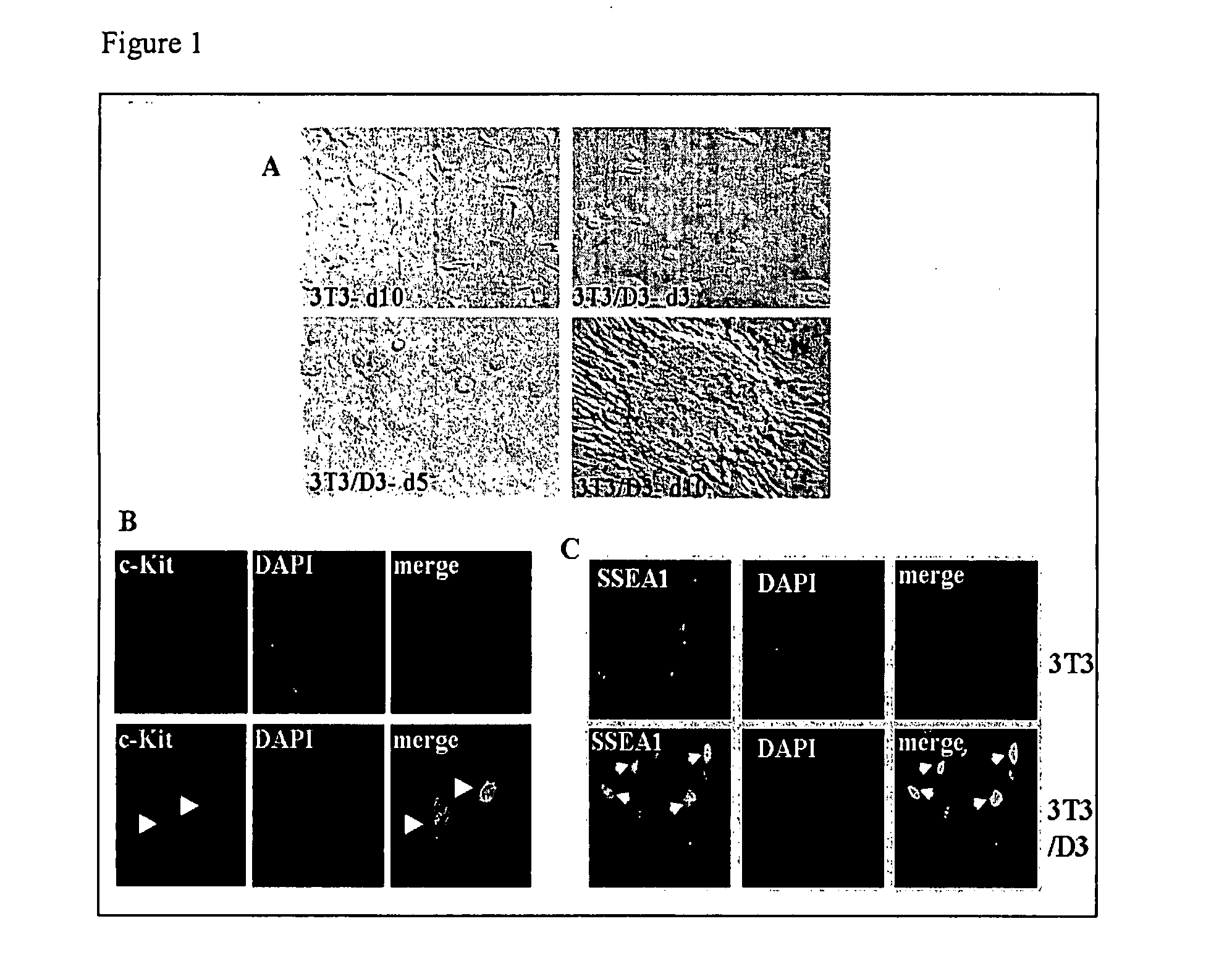
Patents
Literature
73 results about "Somatic portion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Somatic (biology), referring to the cells of the body in contrast to the germ line cells. Somatic nervous system, the portion of the vertebrate nervous system which regulates voluntary movements of the body.
Nuclear Reprogramming Factor
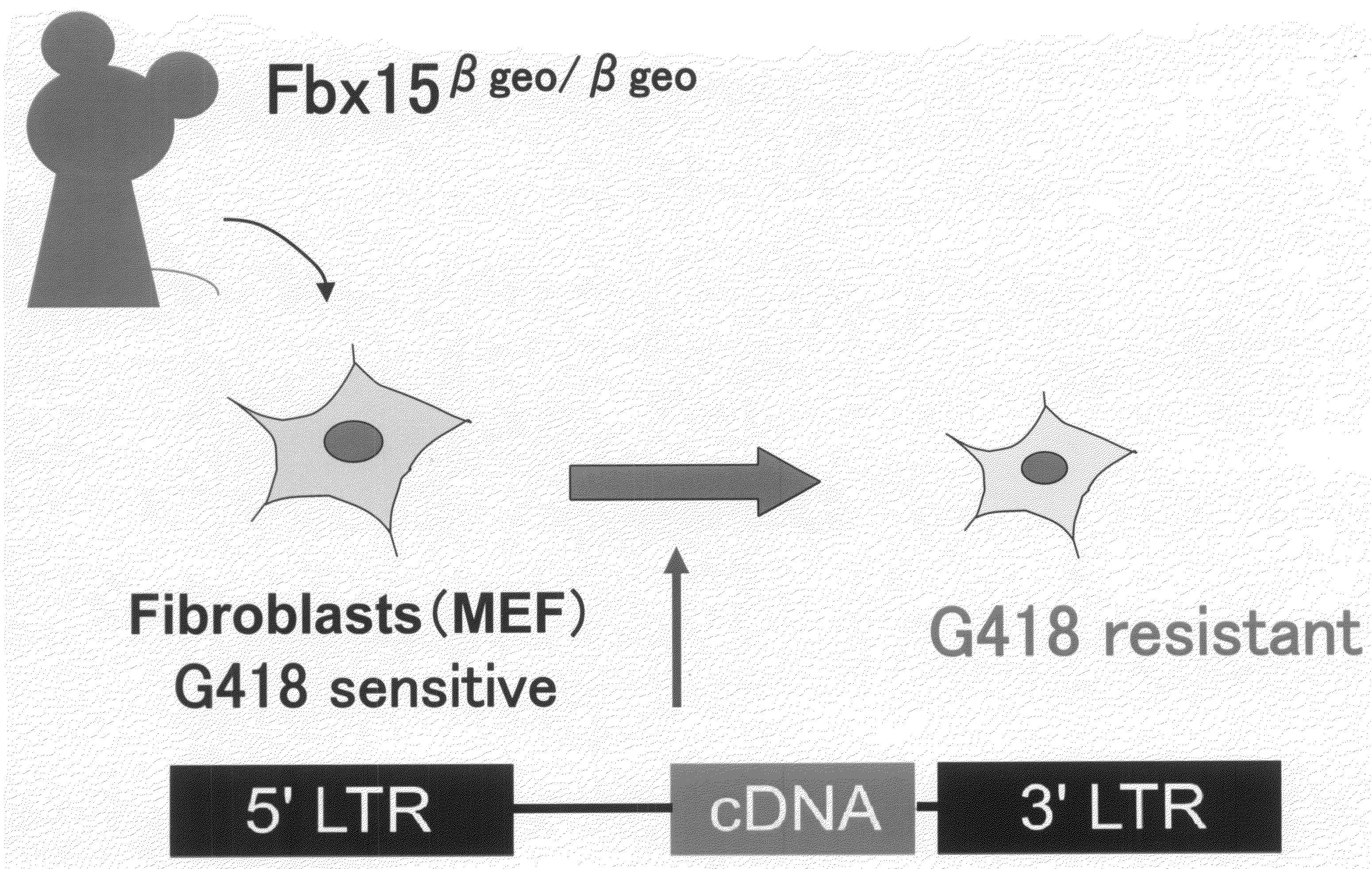
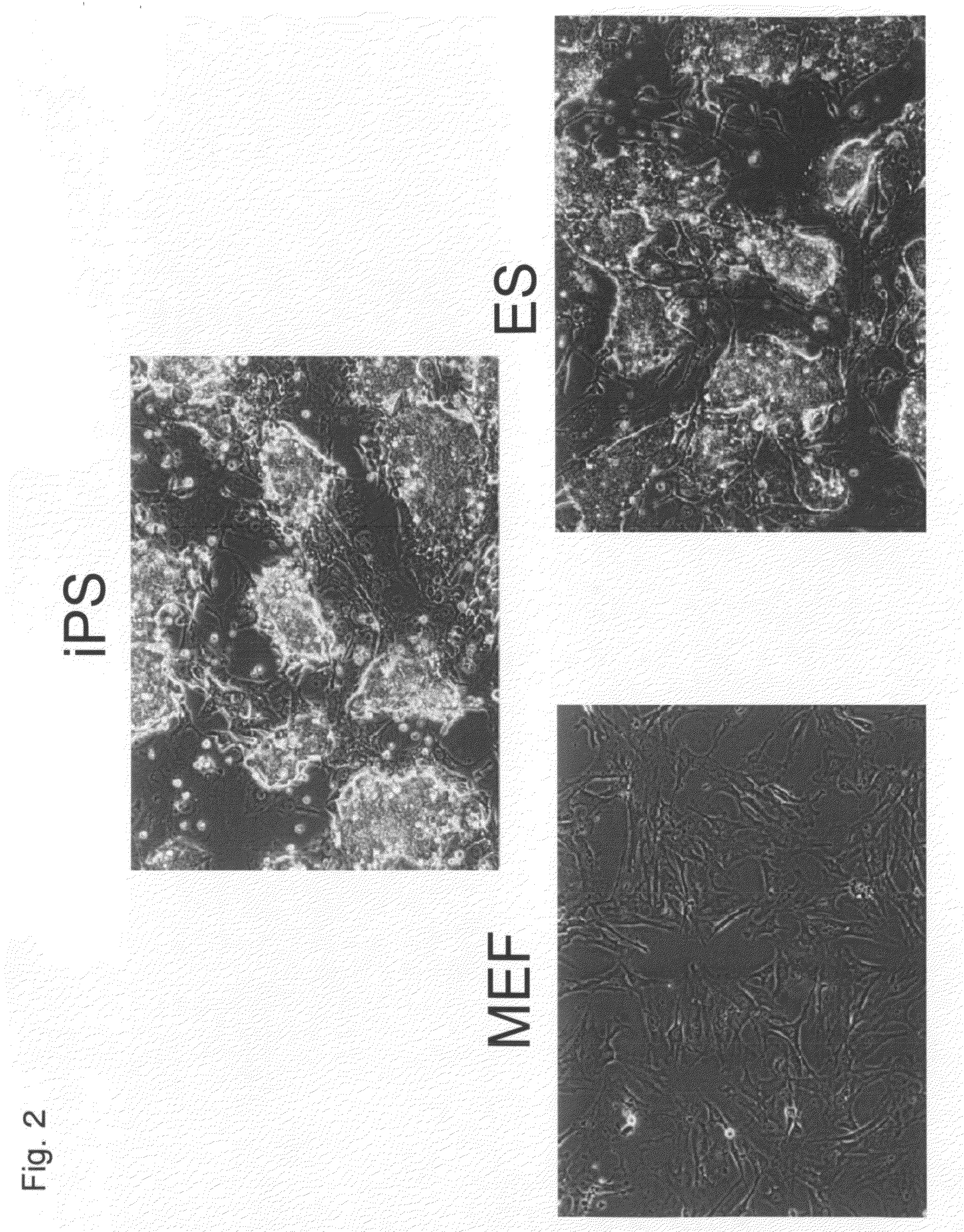
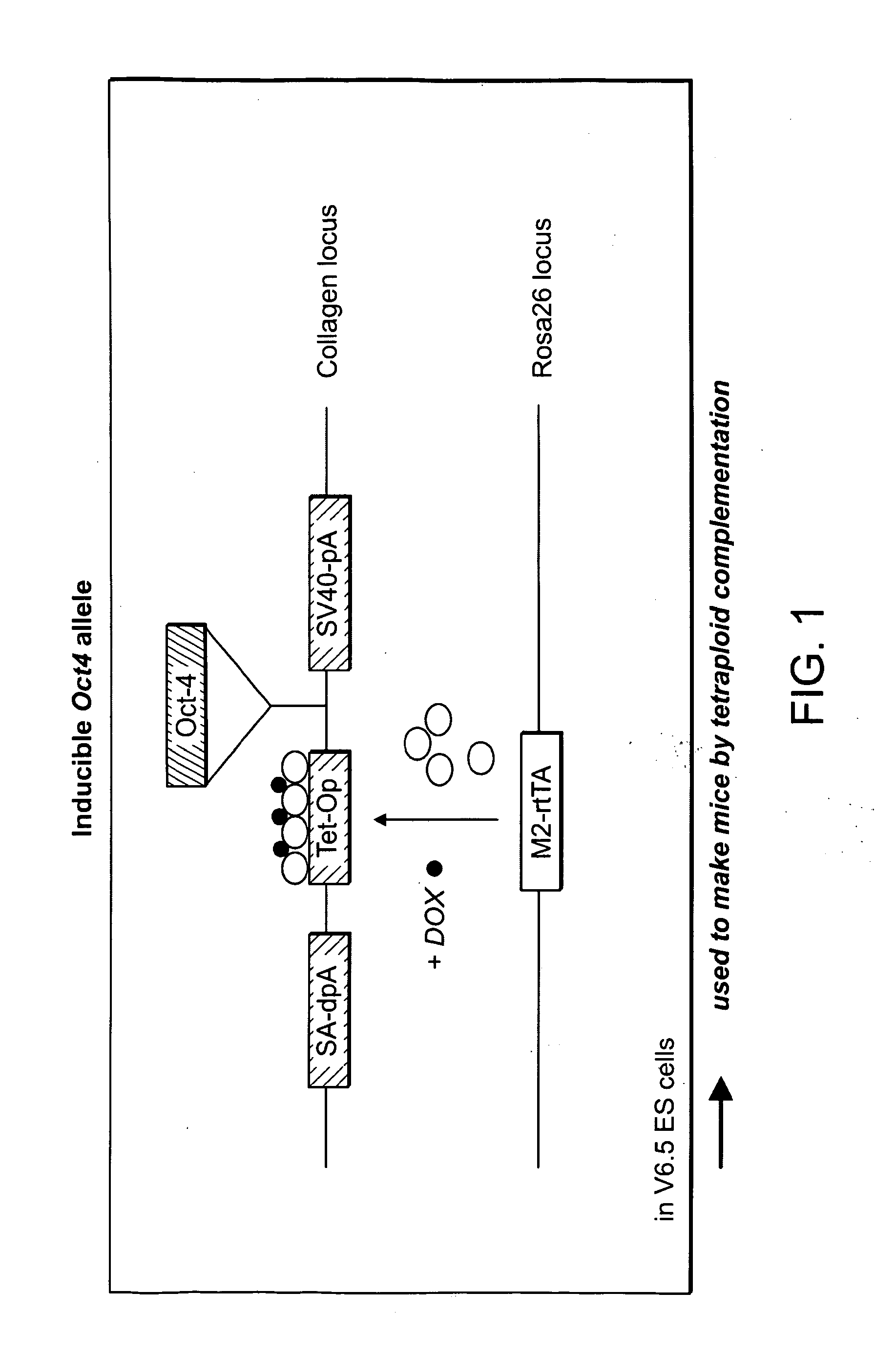
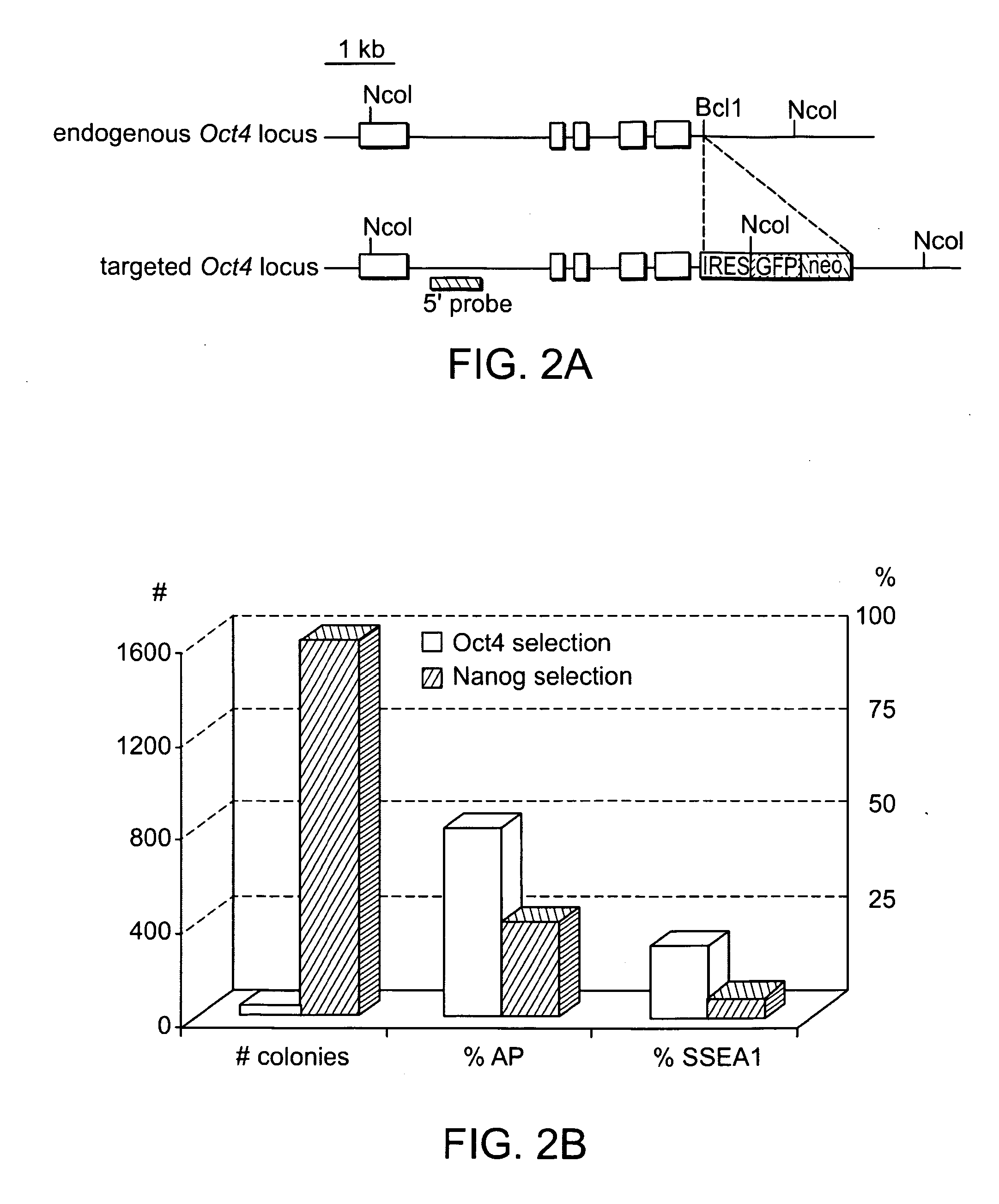
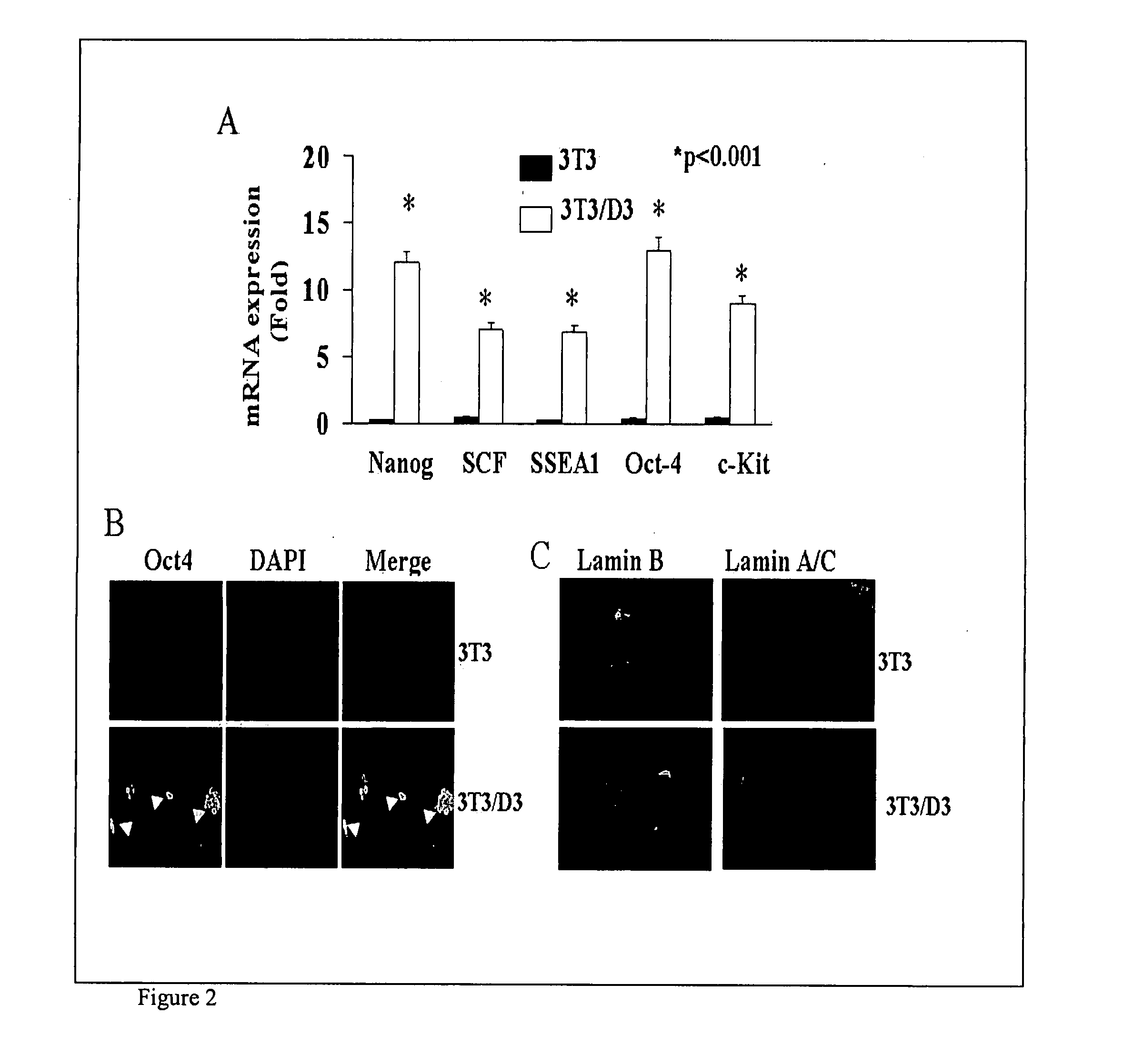
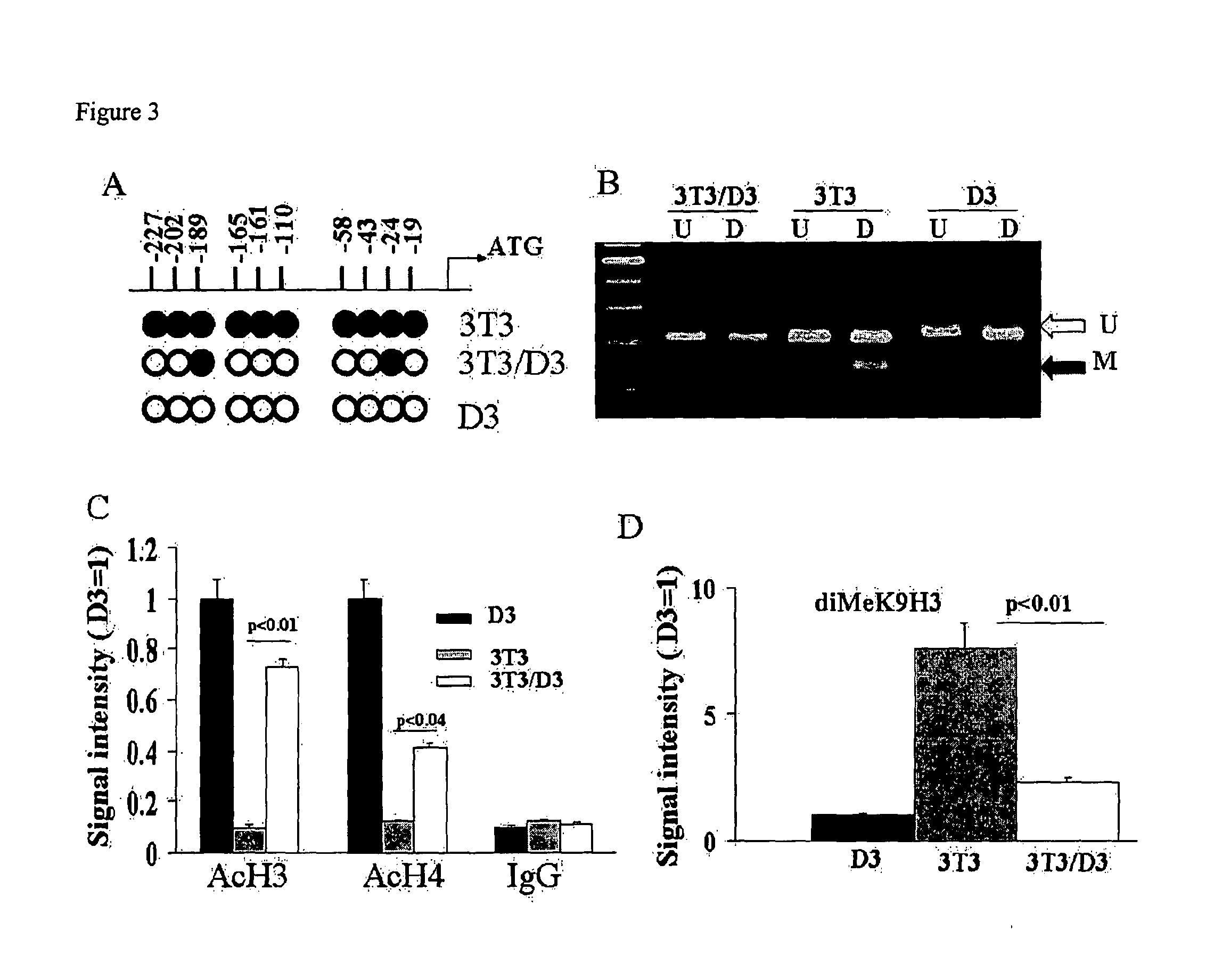
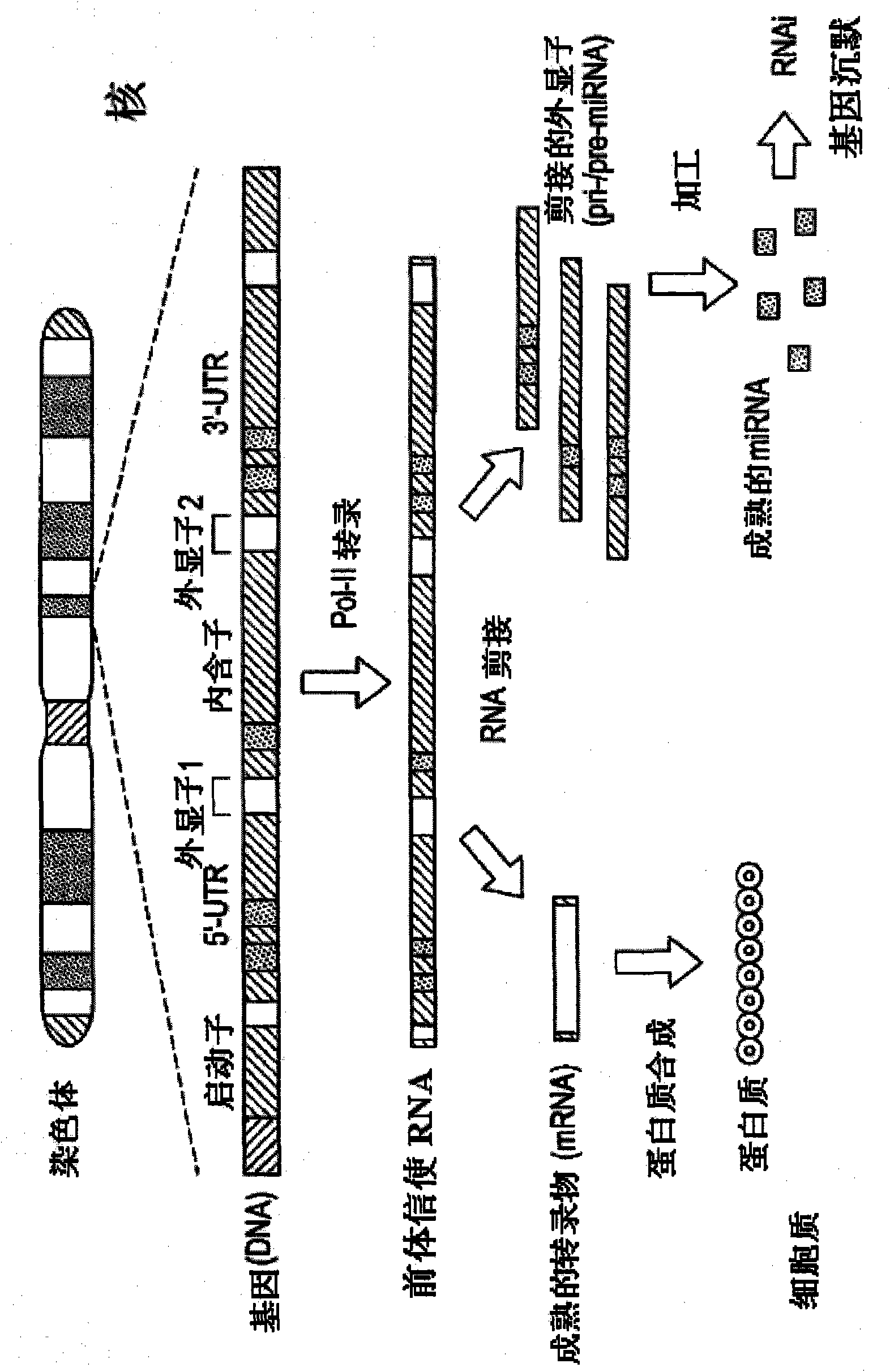
There is provided a nuclear reprogramming factor for a somatic cell, which comprises a gene product of each of the following three kinds of genes: an Oct family gene, a Klf family gene, and a Myc family gene, as a means for inducing reprogramming of a differentiated cell to conveniently and highly reproducibly establish an induced pluripotent stem cell having pluripotency and growth ability similar to those of ES cells without using embryo or ES cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Reprogramming of somatic cells
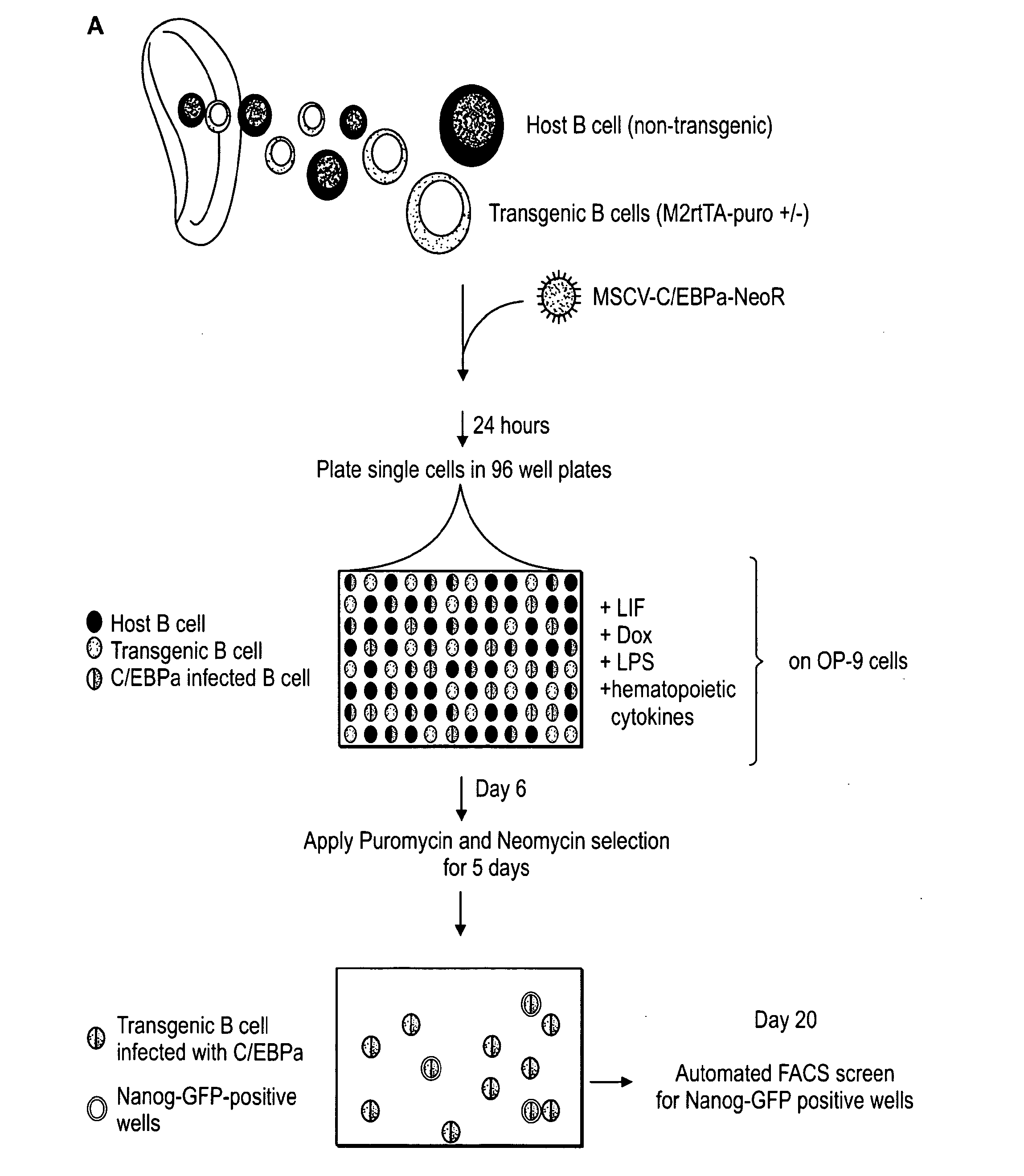
The disclosure relates to a method of reprogramming one or more somatic cells, e.g., partially differentiated or fully / terminally differentiated somatic cells, to a less differentiated state, e.g., a pluripotent or multipotent state. In further embodiments the invention also relates to reprogrammed somatic cells produced by methods of the invention, to uses of said cells, and to methods for identifying agents useful for reprogramming somatic cells.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Generation of tumor-free embryonic stem-like pluripotent cells using inducible recombinant RNA agents
InactiveUS20090203141A1Improve target specificityReduce the number of copiesVectorsFermentationCancer cellMammal
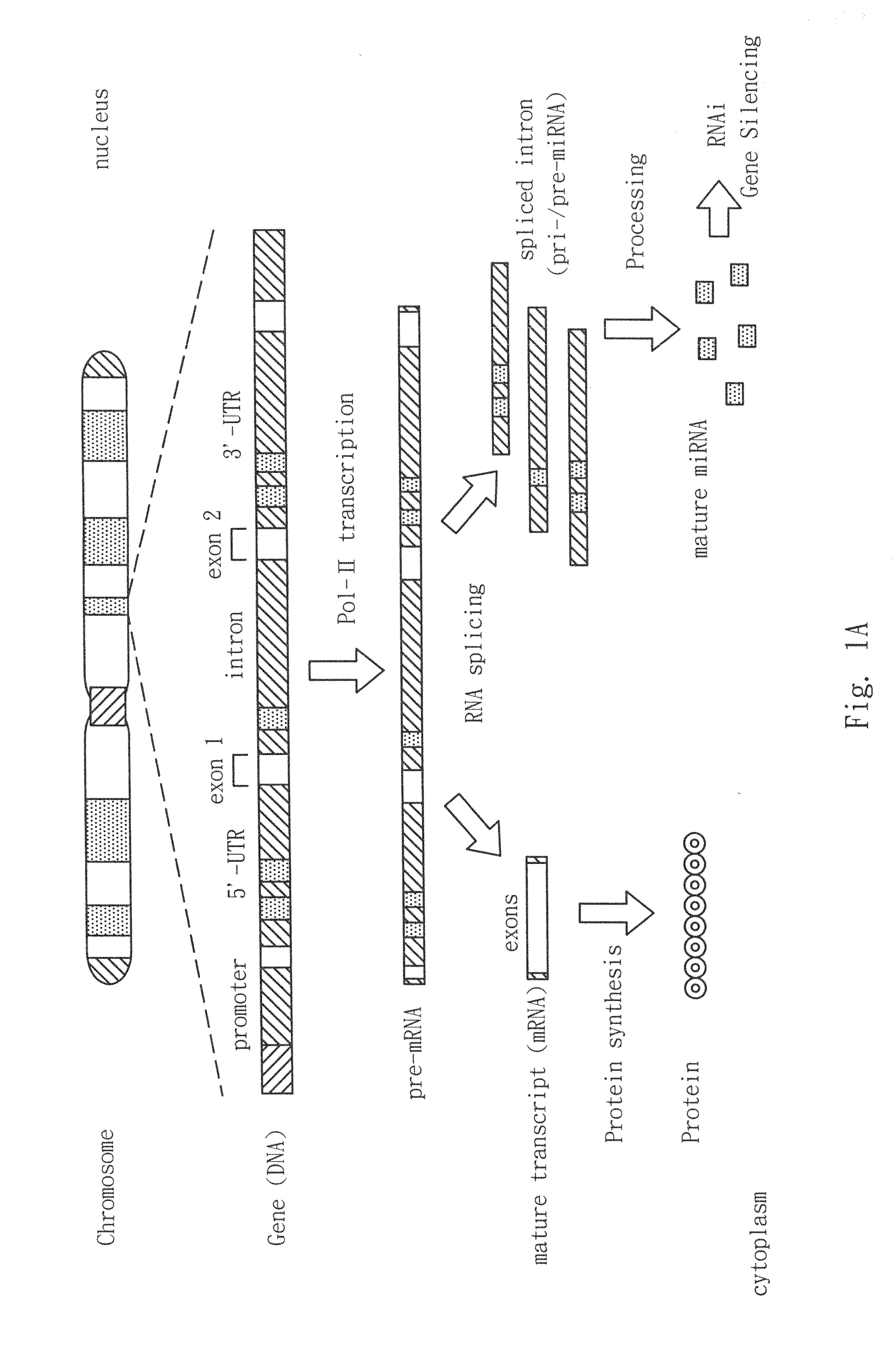
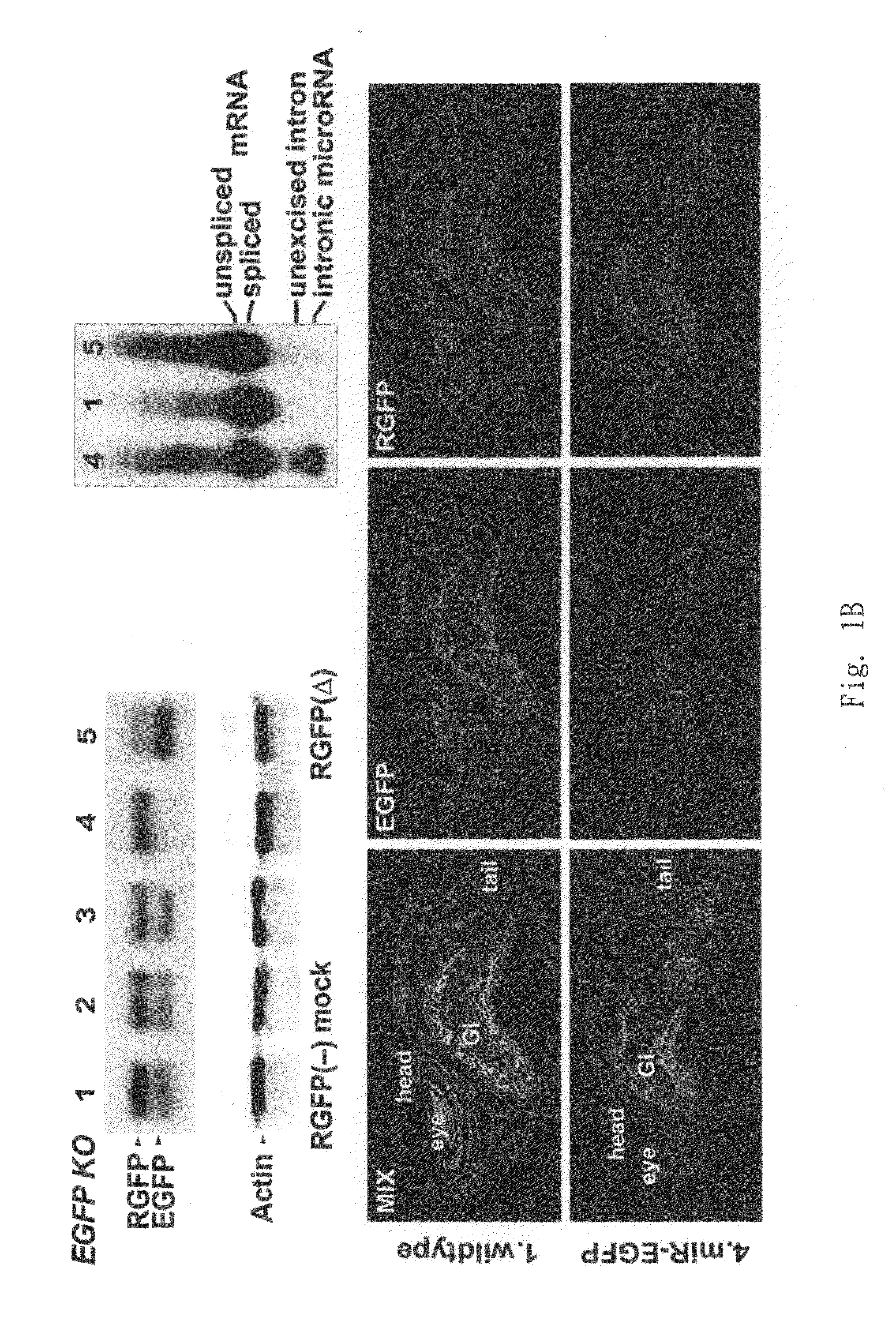
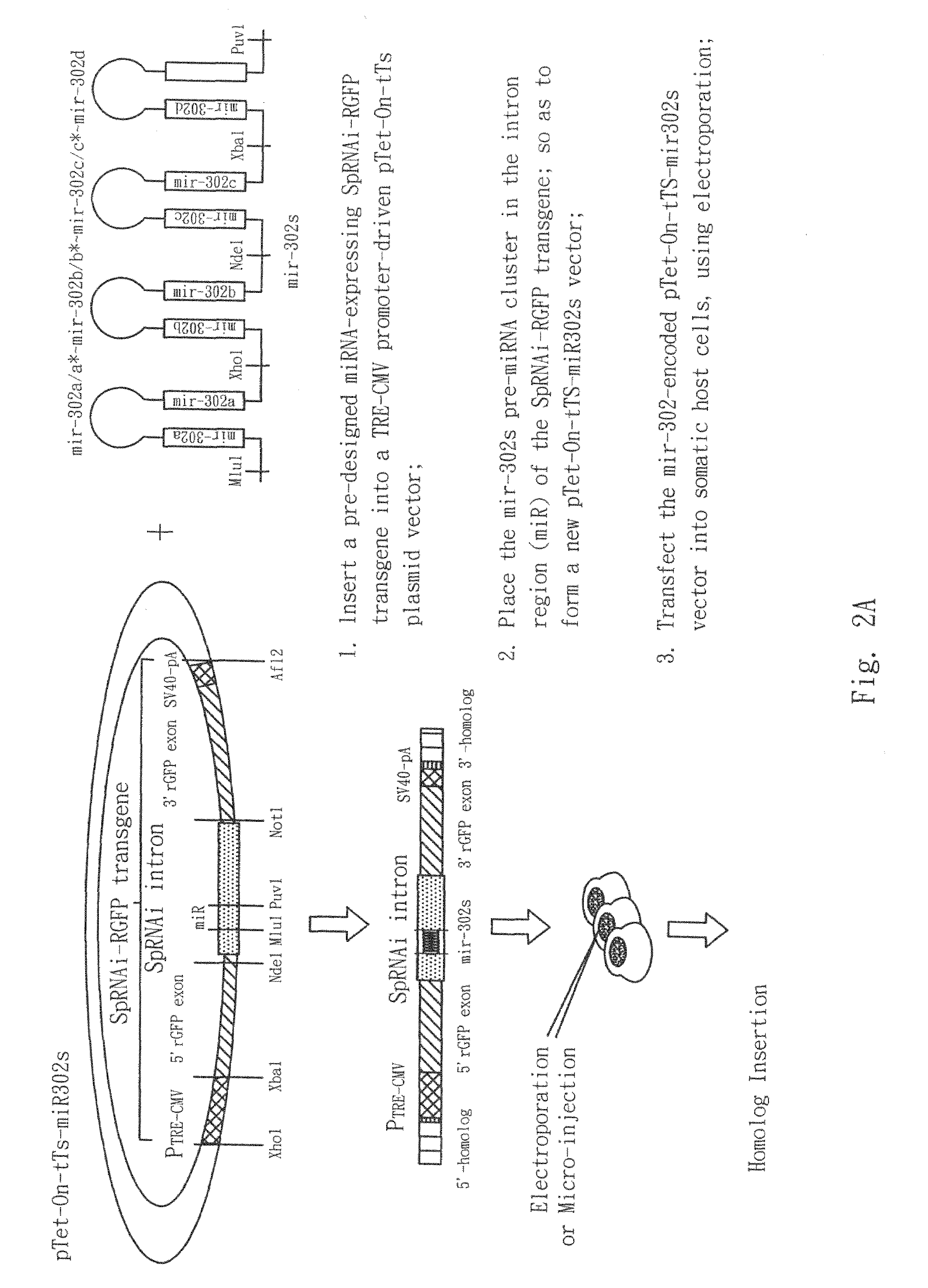
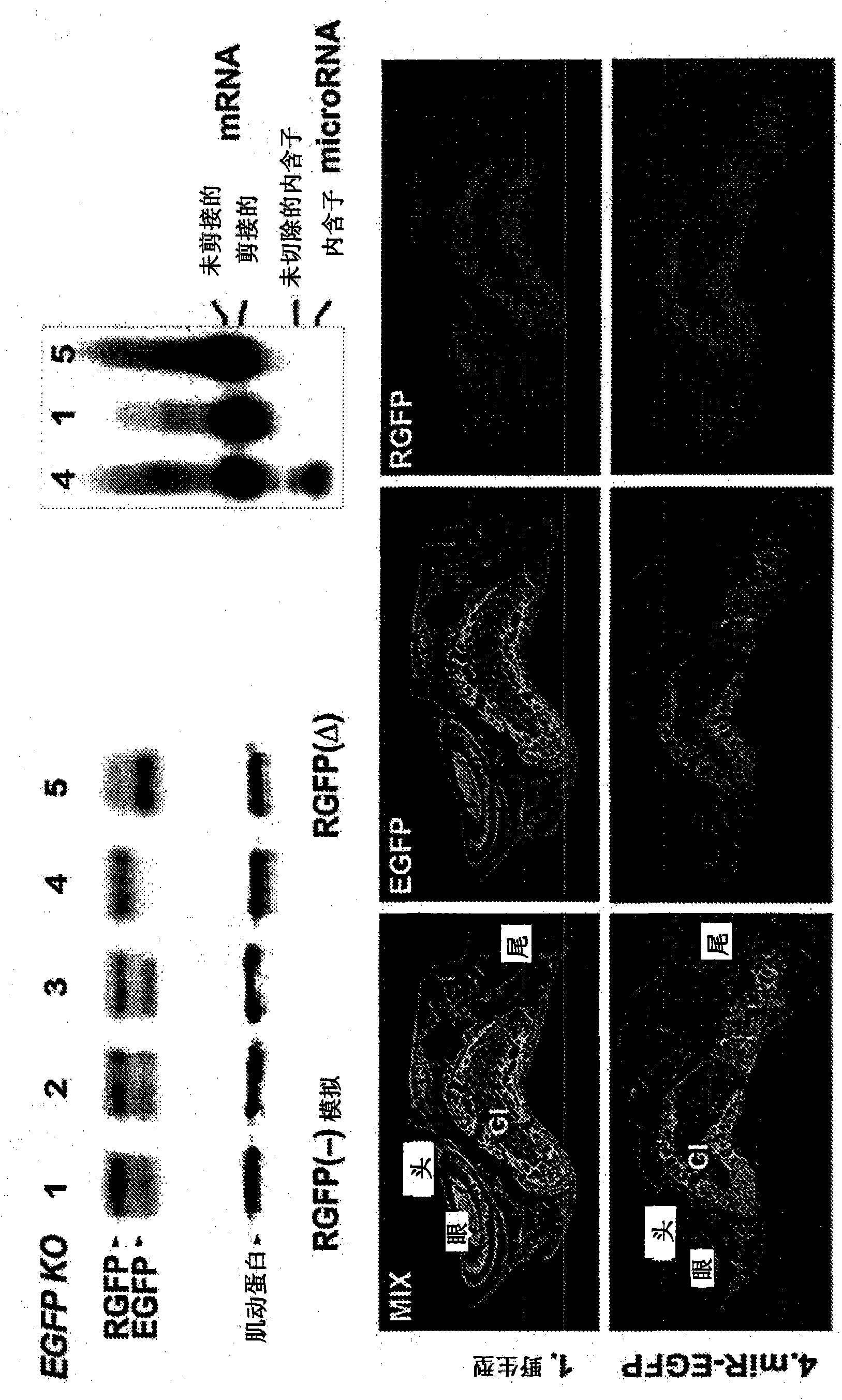
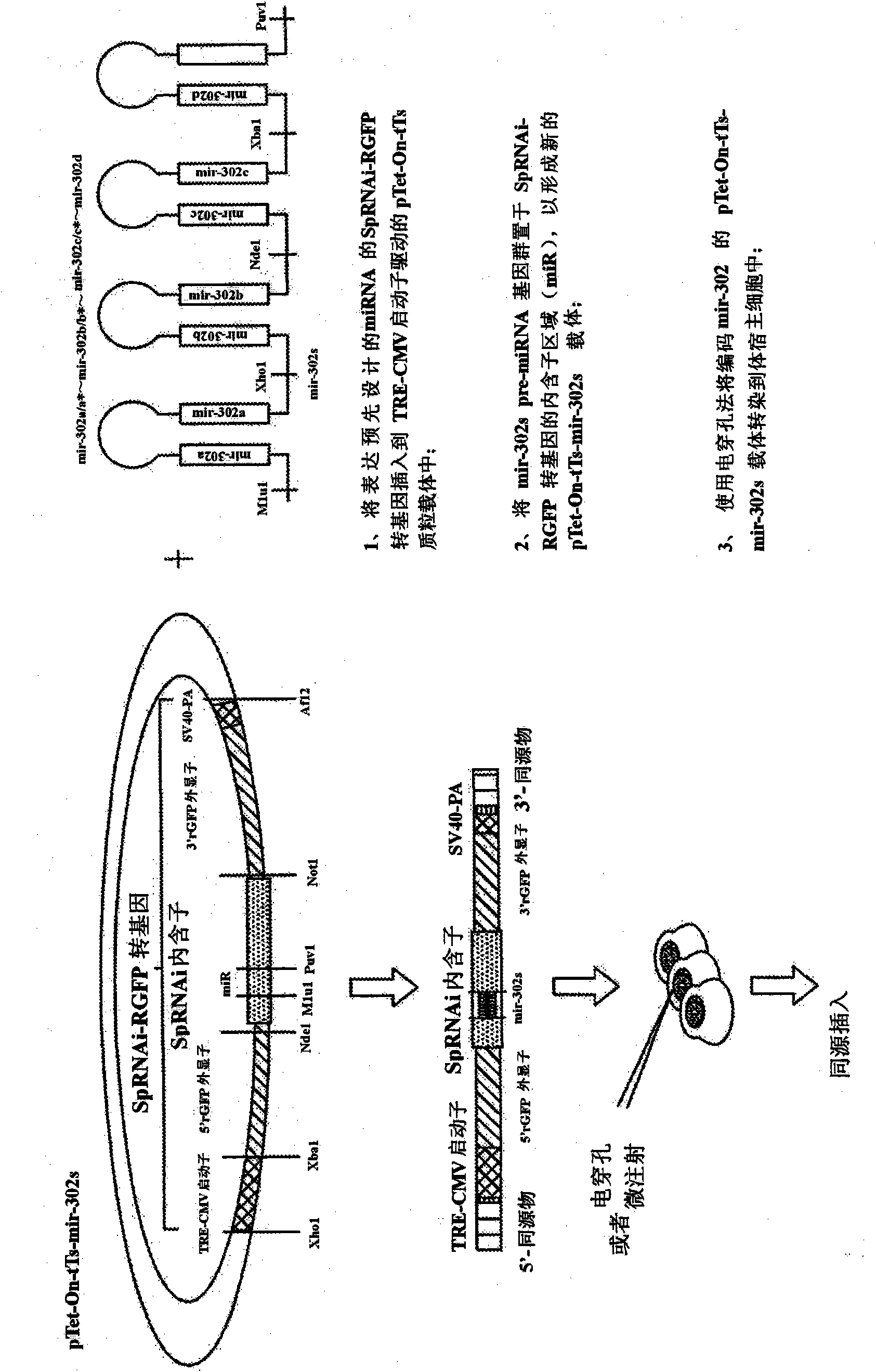
The present invention generally relates to a method for developing, generating and selecting tumor-free embryonic stem (ES)-like pluripotent cells using electroporation delivery of an inducible tumor suppressor mir-302 agent into mammalian cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method and composition for generating a Tet-On / Off recombinant transgene capable of expressing a manually re-designed mir-302 microRNA (miRNA) / shRNA agent under the control of doxycyclin (Dox) in human somatic / cancer cells and thus inducing certain specific gene silencing effects on the differentiation-associated genes and oncogenes of the cells, resulting in reprogramming the cells into an ES-like pluripotent state.
Owner:LIN SHI LUNG +1
Difference-weighted somatic spectroscopy
InactiveUS20080009689A1Improved real-time feedbackLow delivery of oxygenDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSpectroscopySomatic portion
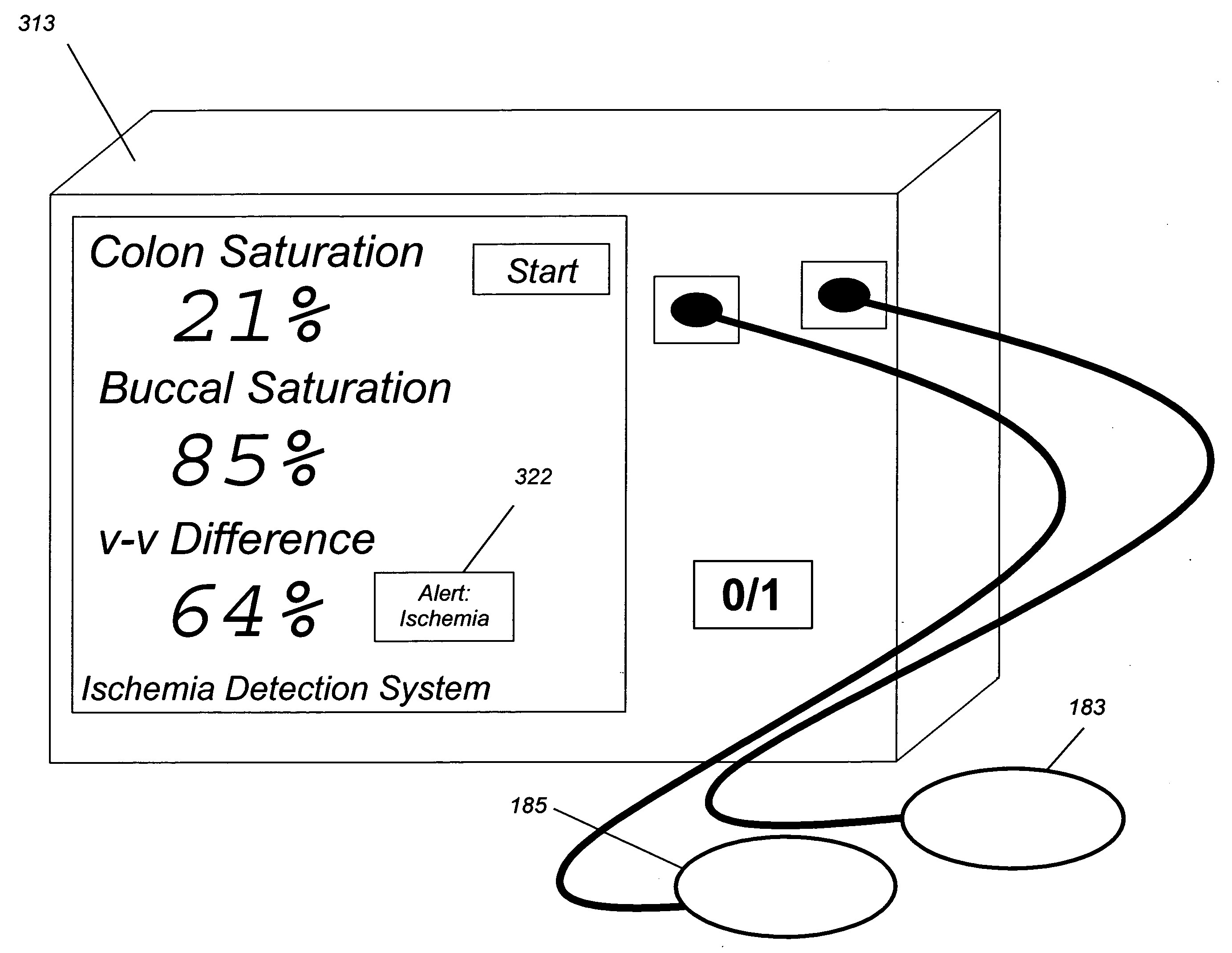
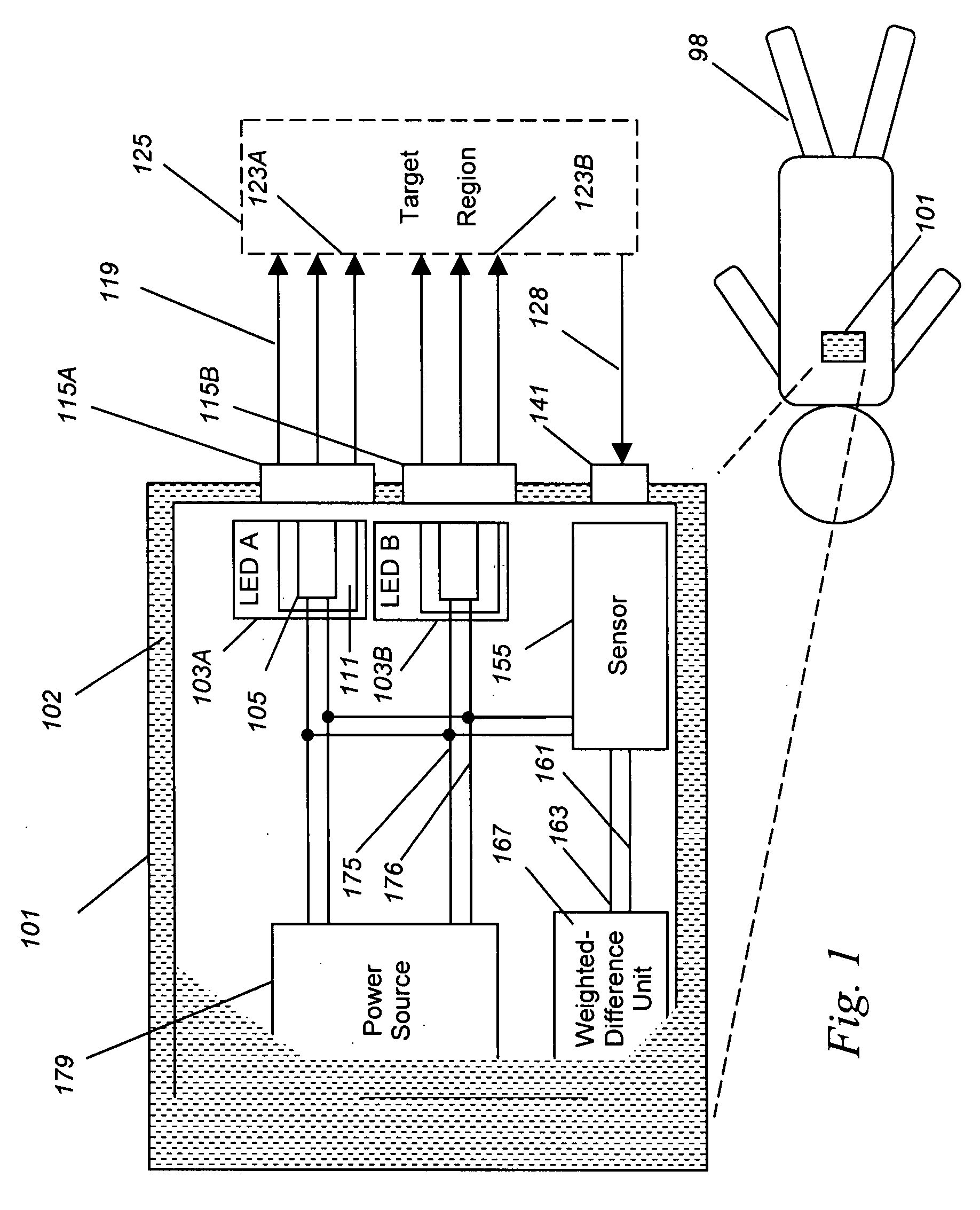
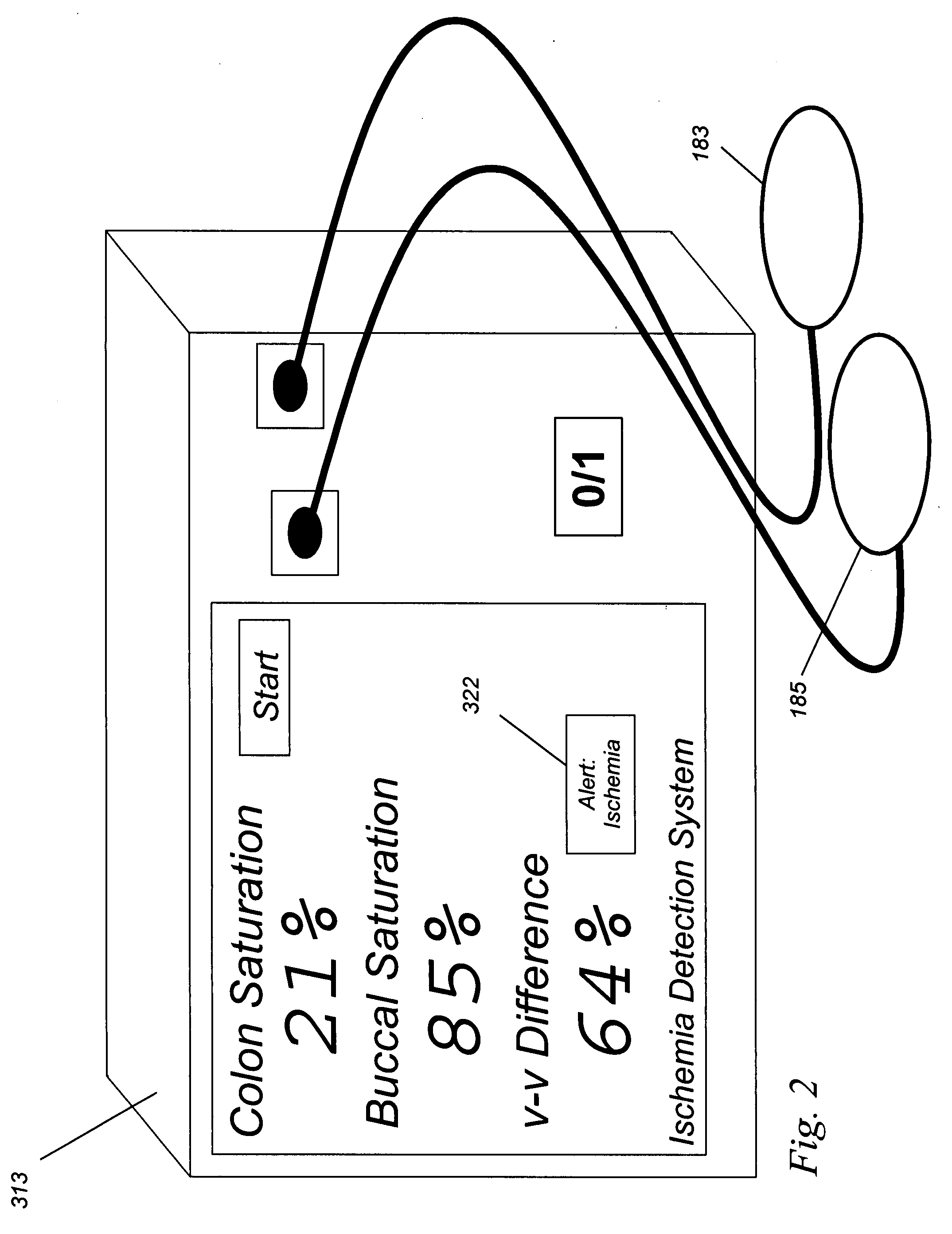
An ischemia detection system in two or more somatic measures, collected simultaneously or near-simultaneously, are provided for direct or computational comparison, in which light from light source A (103A) and source B (103B) is detected by a sensor (155), and a difference-weighted value is determined (167), thereby enhancing the value of the spectroscopic measurements over values taken individually and singly.
Owner:J FITNESS LLC
Trans-differentiation and re-differentiation of somatic cells and production of cells for cell therapies
The invention provides a method for effecting the trans-differentiation of a somatic cell, i.e., the conversion of a somatic cell of one cell type into a somatic cell of a different cell type. The method is practiced by culturing a somatic cell in the presence of at least one agent selected from the group consisting of (a) cytoskeletal inhibitors and (b) inhibitors of acetylation, and (c) inhibitors of methylation, and also culturing the cell in the presence of agents or conditions that induce differentiation to a different cell type. The method is useful for producing histocompatible cells for cell therapy.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Soybean selection system based on AEC-resistance
InactiveUS7525013B2Improve featuresOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationHeterologousAntibiotic resistance
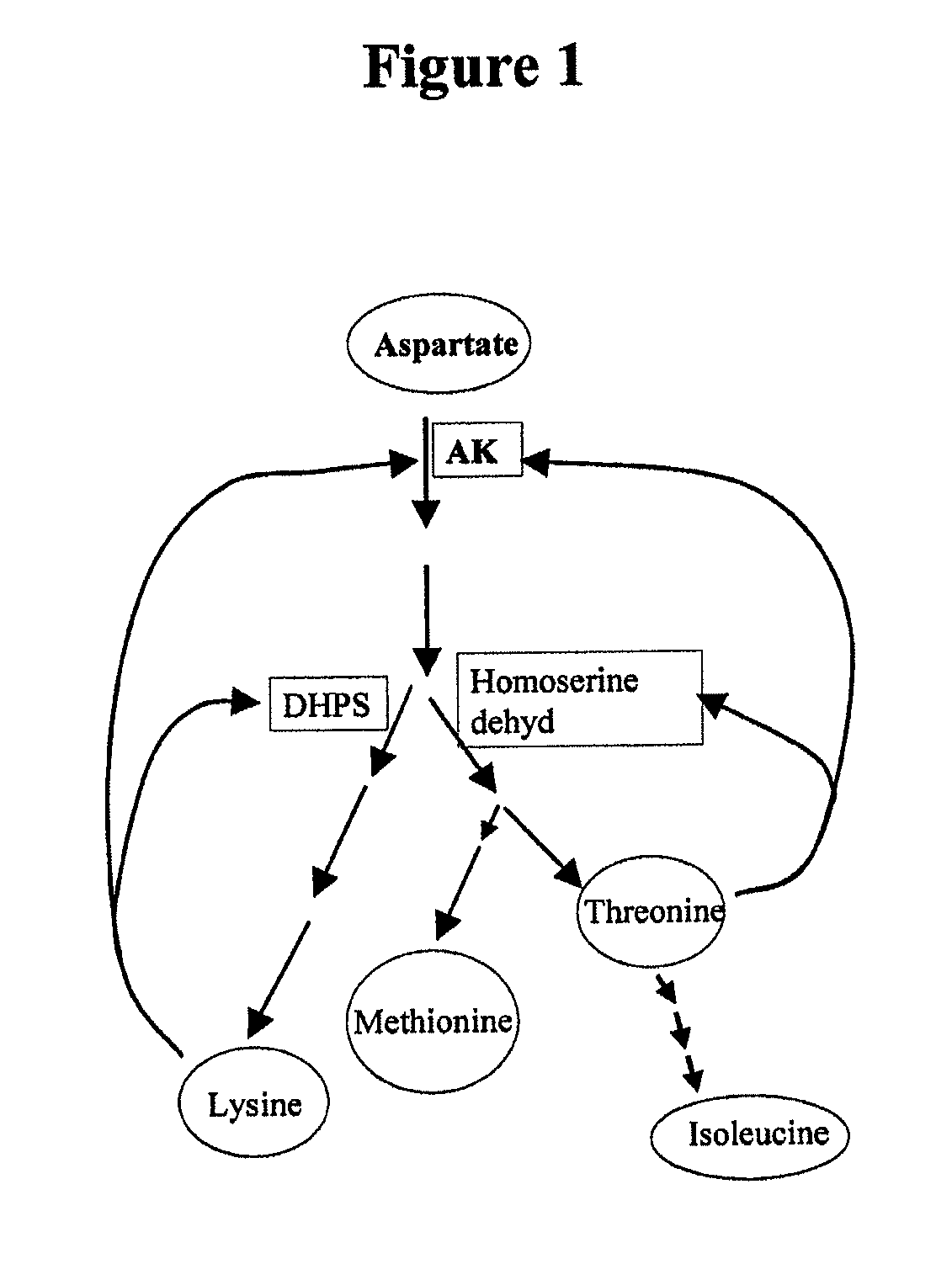
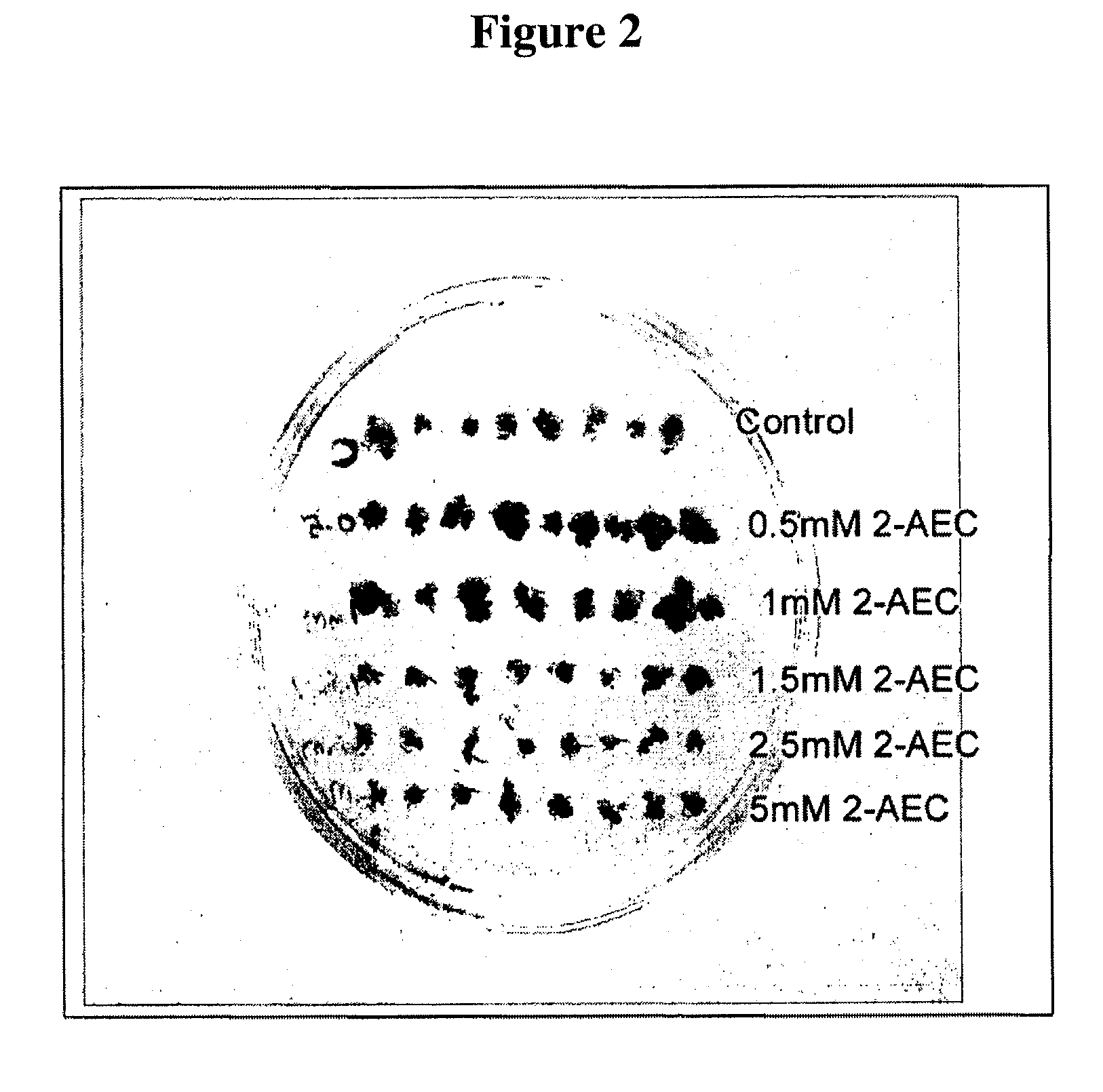
A method for generating a transgenic soybean plant comprising in its genome a heterologous nucleic acid sequence of interest, comprises introducing into a soybean somatic embryo a polynucleotide encoding a functional dihydrodipicolinate synthase (DHPS) polypeptide, and a polynucleotide encoding a heterologous polypeptide of interest, operably linked to expression control sequences, wherein DHPS expressed from the introduced DHPS-encoding polynucleotide is effective to render the embryo resistant to S-2-aminoethylcysteine (2-AEC), and contacting the embryo with 2-AEC, under conditions effective for an embryo which expresses the DHPS to grow selectably and mature into a soybean plant that expresses a desired trait, and preferably includes no antibiotic resistance marker sequence.
Owner:UNITED SOYBEAN BOARD
Vegf-C or Vegf-D Materials and Methods for Stimulation of Neural Stem cells
InactiveUS20080057028A1Easy to identifyTherapy is simpleOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsOligodendrocytePrecursor cell
The present invention relates to VEGF-C or VEGF-D materials and methods for promoting growth and differentiation of neural stem cells, neuronal and neuronal precursor cells, oligodendrocytes and oligodendrocyte precursor cells and materials and methods for administering said cells to inhibit neuropathology.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Methods of Reprogramming Animal Somatic Cells
InactiveUS20100167404A1Extend the lifespanExtending telomere lengthCell differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalEmbryo
This invention generally relates to methods to obtain mammalian cells and tissues with patterns of gene expression similar to that of a developing mammalian embryo or fetus, and the use of such cells and tissues in the treatment of human disease and age-related conditions. More particularly, the invention relates to methods for identifying, expanding in culture, and formulating mammalian pluripotent stem cells and differentiated cells that differ from cells in the adult human in their pattern of gene expression, and therefore offer unique characteristics that provide novel therapeutic strategies in the treatment of degenerative disease.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Methods for Reprogramming Adult Somatic Cells and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20100135970A1Easy to produceReduce probabilityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsSomatic cellSomatic portion
As described below, the present invention features methods for reprogramming somatic cells and related therapeutic compositions and methods.
Owner:STEWARD RES & SPECIALTY PROJECTS
Somatic sensory controlled upper limb exoskeleton mirrored rehabilitation robot
ActiveCN106618958AImprove real-time performanceEasy to trainChiropractic devicesSomatosensory systemRobotic arm
The invention discloses a somatic sensory controlled upper limb exoskeleton mirrored rehabilitation robot. The robot comprises a Kinect sensor, a main control computer, a three degree-of-freedom exoskeleton wearable mechanical arm and a somatic sensory controlled system for the mechanical arm. The Kinect sensor is used for collecting information about a joint angle of the upper limb on the uninjured side of the human body; the exoskeleton wearable mechanical arm comprises an elbow bend and stretch structure, a shoulder flexion and extension structure and a shoulder abduction and adduction structure. The robot has the characteristic of being directly controlled by the somatic sensory, no signal collection device needs to be worn, and the robot is convenient to operate; the injured limb of a patient can be driven by the movement of the health limb of the patient to carry on novel bilateral mirrored synchronous rehabilitation training with the assistance of the robot, and in addition, master-slave type rehabilitation training can be carried out through the movement of the limb, on the same side of the injured limb of the patient, of a physical therapist.
Owner:南通大学技术转移中心有限公司
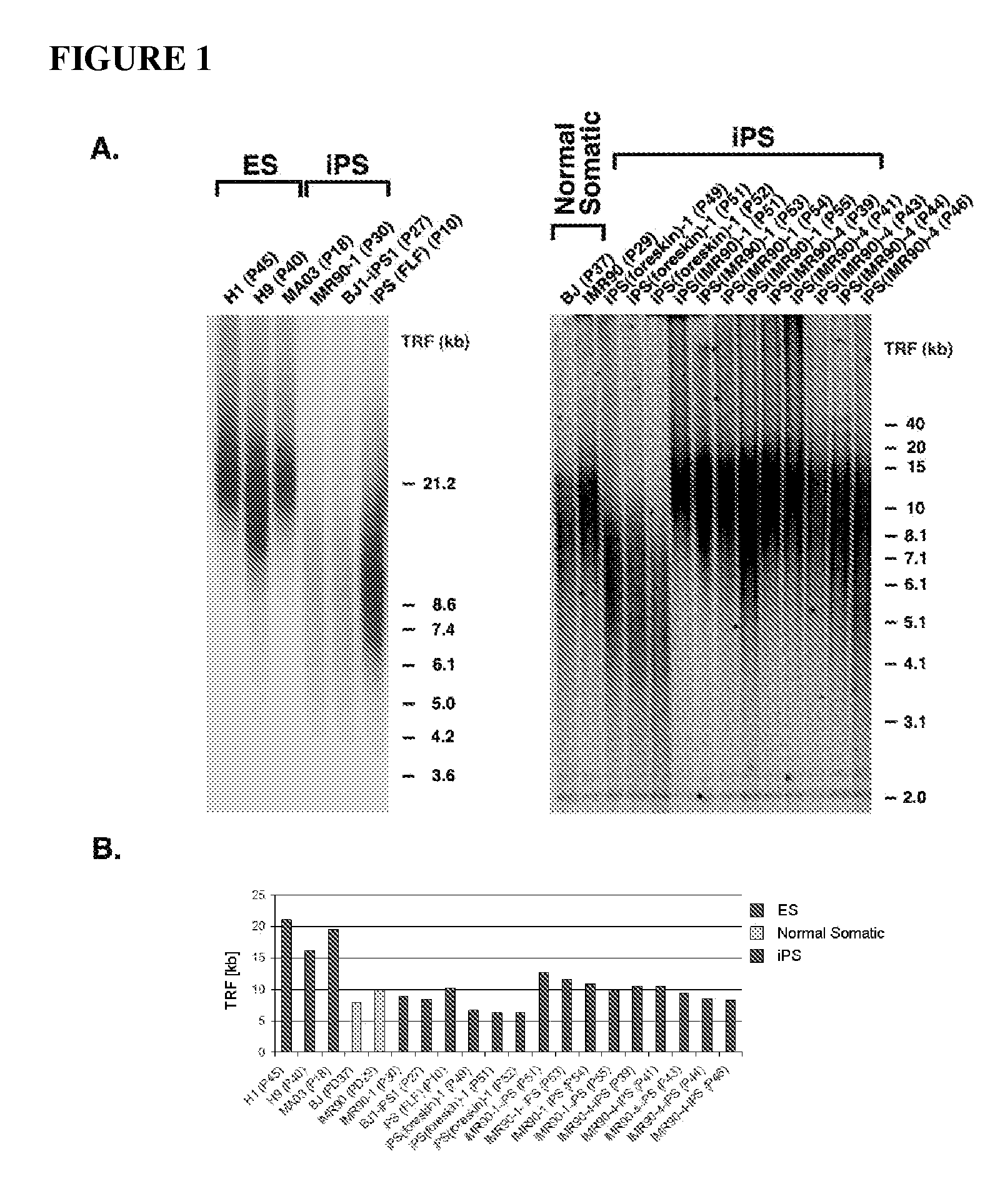
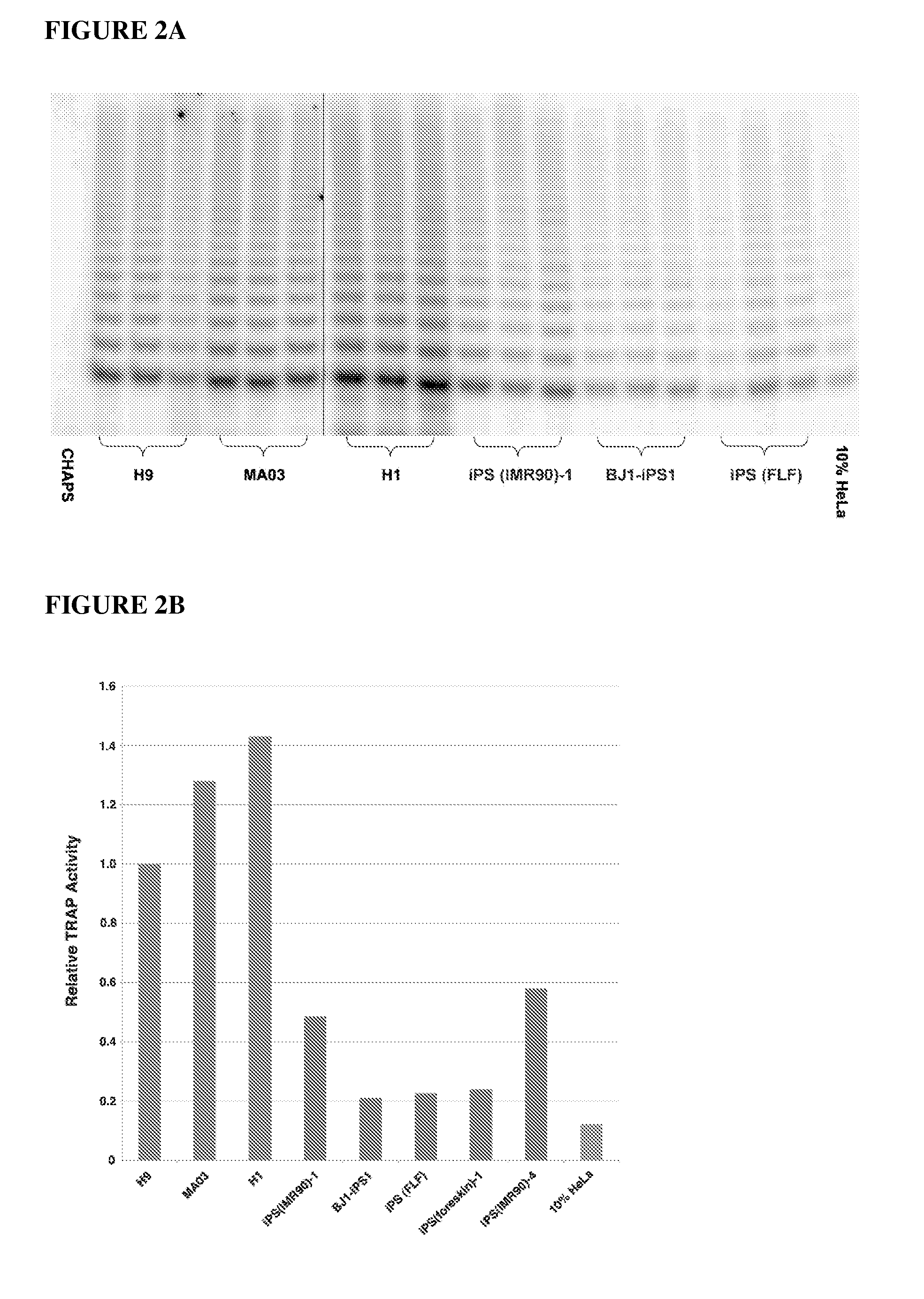
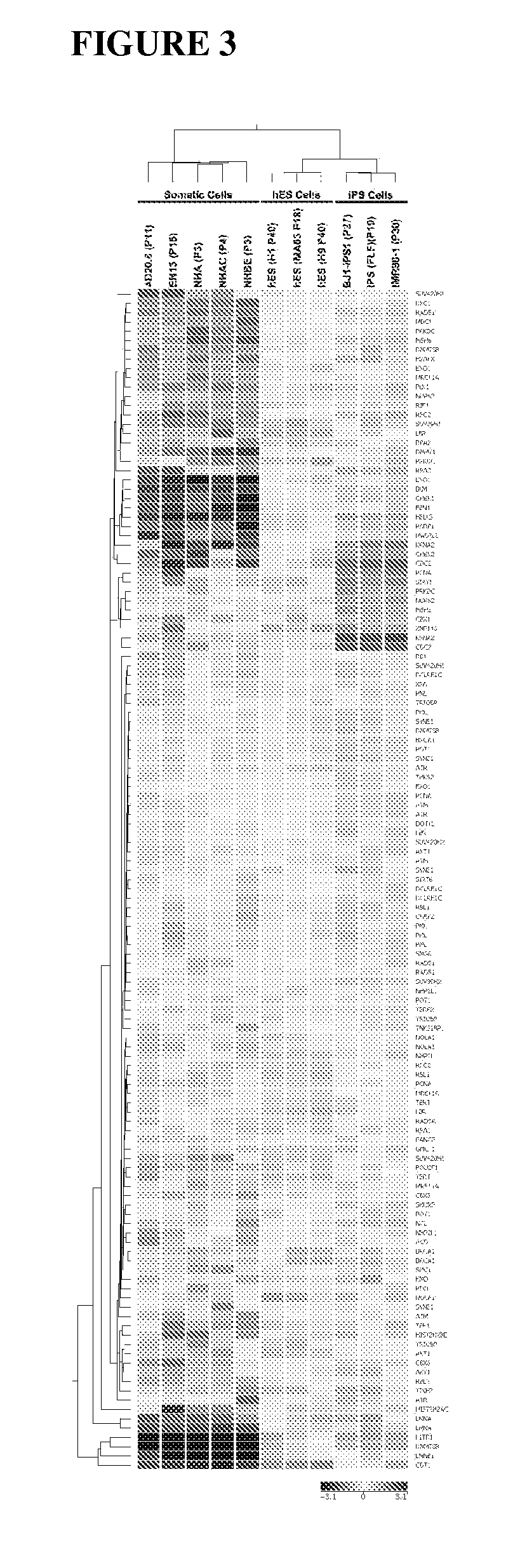
Methods for telomere length and genomic DNA quality control and analysis in pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20130011918A1Reduce riskDesired phenotypeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPluripotential stem cellClinical grade
The generation of clinical-grade cell-based therapies from human embryonic stem cells or cells reprogrammed to pluripotency from somatic cells, requires stringent quality controls to insure that the cells have long enough telomeres and resulting cellular lifespan to be clinically useful, and normal gene expression and genomic integrity so as to insure cells with a desired and reproducible phenotype and to reduce the risk of the malignant transformation of cells. Assays useful in identifying human embryonic stem cell lines and pluripotent cells resulting from the transcriptional reprogramming of somatic cells that have embryonic telomere length are described as well as quality control assays for screening genomic integrity in cells expanded and banked for therapeutic use, as well as assays to identify cells capable of abnormal immortalization,
Owner:LINEAGE CELL THERAPEUTICS INC
Multifunctional child somatic sensation educating system
InactiveCN103377568AImprove knowledge literacyImprove accuracyElectrical appliancesSomatosensory systemCognition
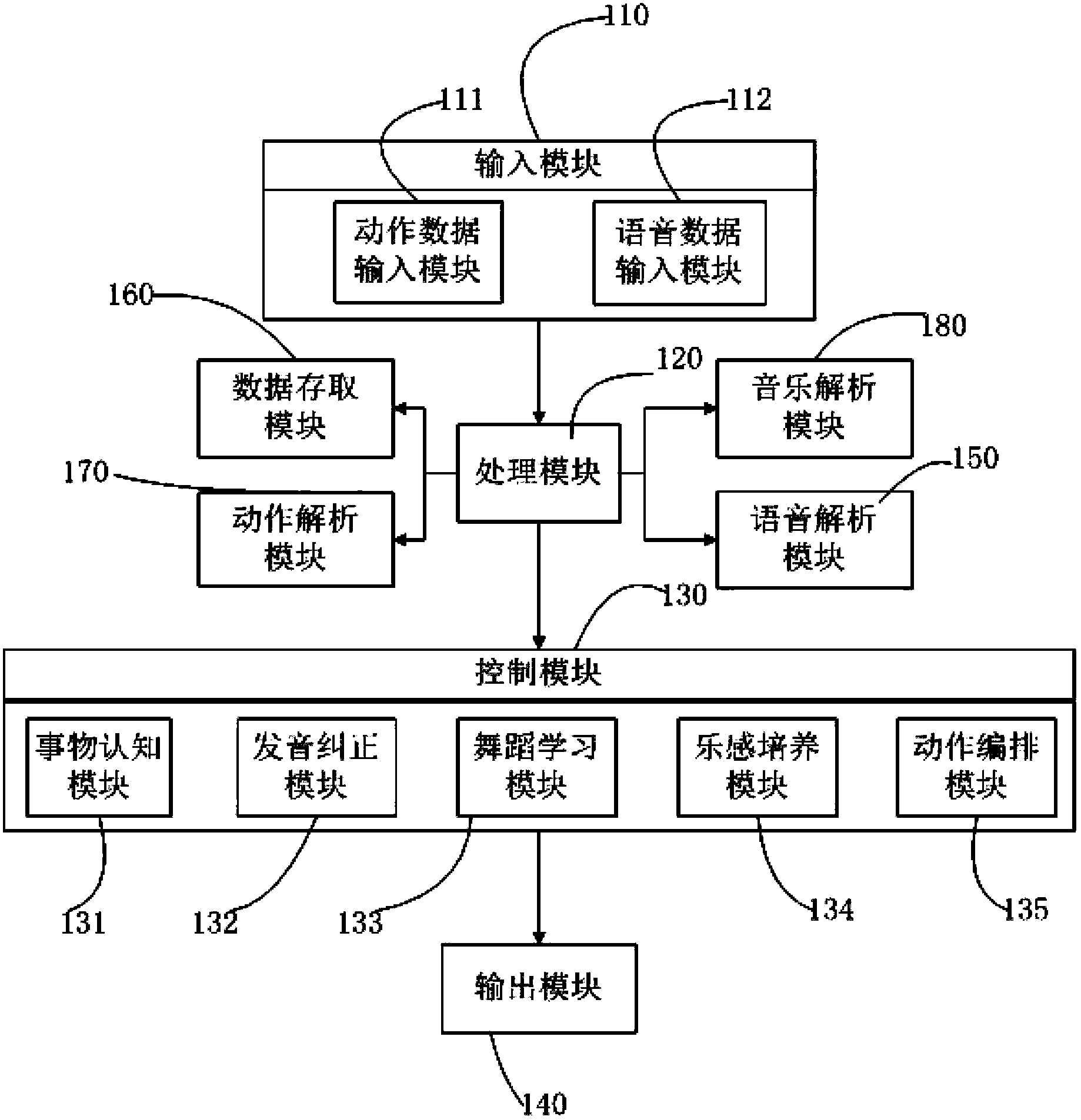
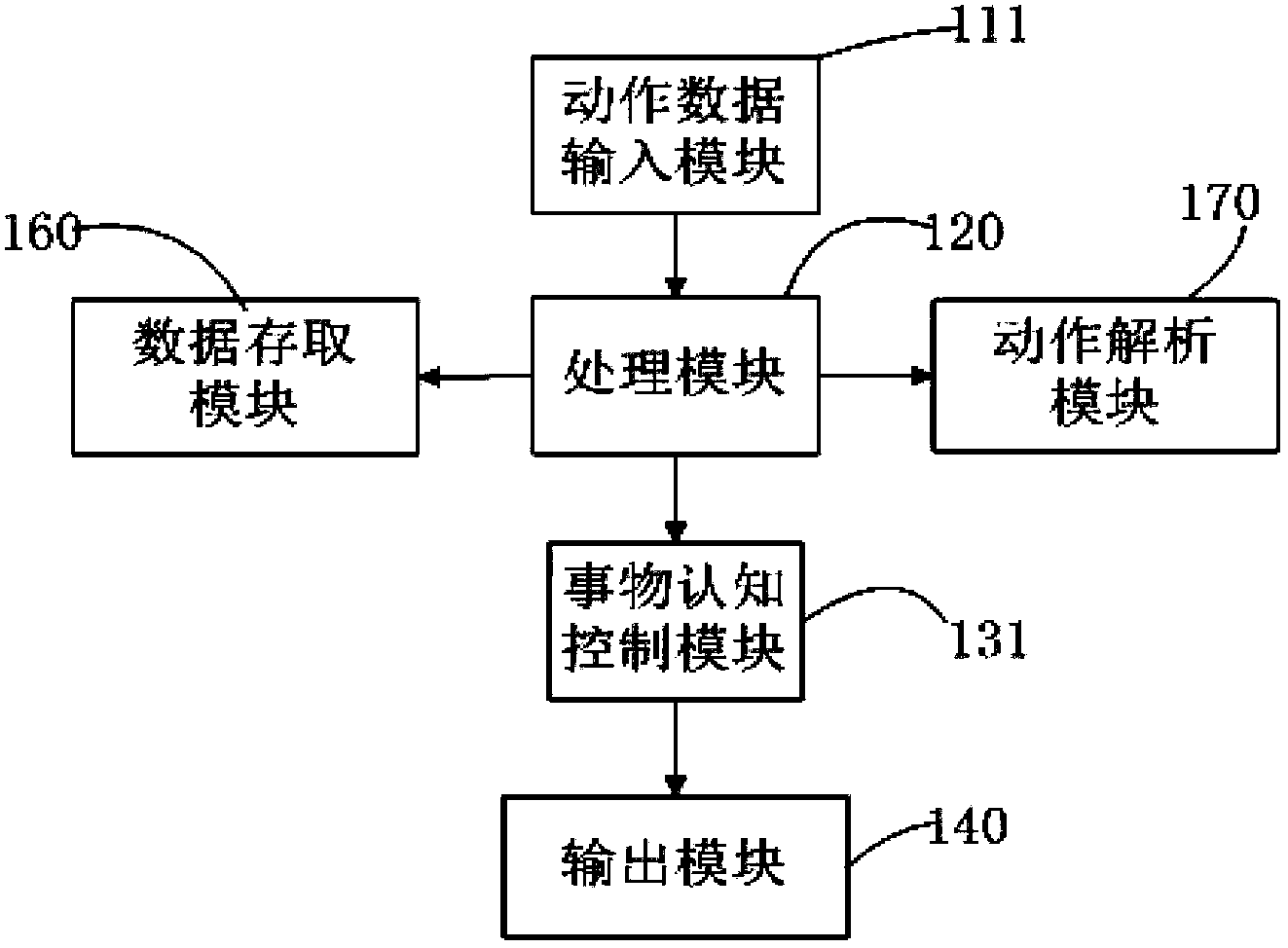
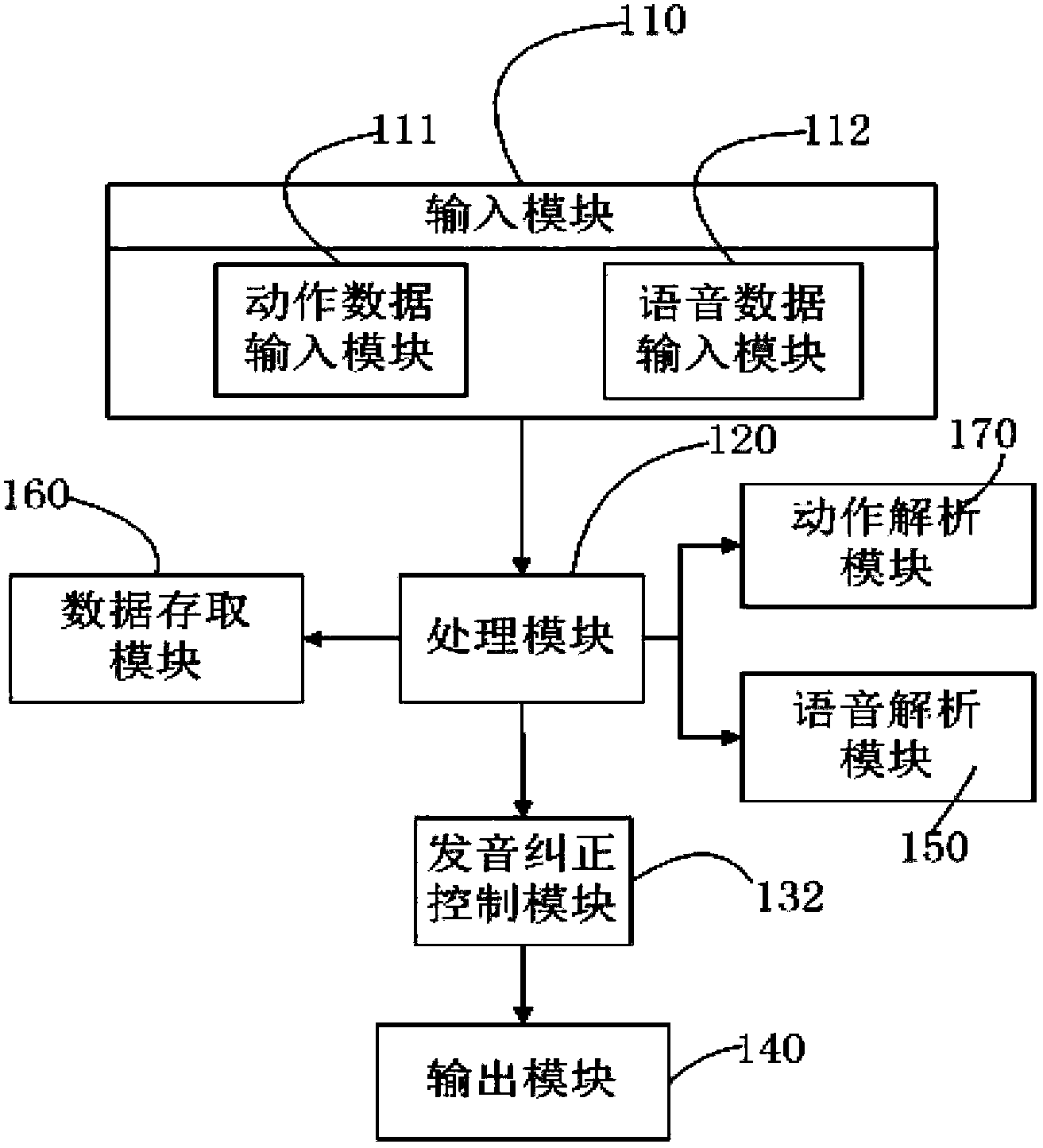
The invention discloses a multifunctional child somatic sensation educating system which comprises an input module, a processing module, a control module and an output module. The multifunctional child somatic sensation educating system is further characterized by further comprising a data access module, a movement analysis module, a voice analysis module and a music analysis module. The control module comprises an object cognition control module, a pronunciation correction control module, a dance learning control module, a musicality cultivation control module and a movement arrangement control module. The input module, the processing module, the control module and the output module are connected mutually in sequence, and the data access module, the movement analysis module, the voice analysis module and the music analysis module are respectively connected with the processing module. The multifunctional child somatic sensation educating system has the advantages that the educating system has educational modes of object cognition, pronunciation correction, dance learning, musicality cultivation and movement arrangement at the same time, the educational modes are rich and varied, and the educating system not only can help children to learn knowledge, but also can help the children to do physical exercise, mold character and stimulate imagination.
Owner:浙江大学软件学院(宁波)管理中心(宁波软件教育中心)
Method for inducing plant regeneratation using somatic embryo of picea koraiensis nakai
InactiveCN101228848AShorten the breeding cycleRich breeding cycleHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSomatic embryogenesisPicea koraiensis
A plant regeneration method inducted by a somatic embryo of Korean spruce relates to a method for inducing the plant to regenerate with the somatic embryo of Korean spruce, which solves the problems that the conventional breeding of Korean spruce is of long period and low reproduction rate. The method is that: I. callus culture with zygotic embryo; II. Culturing the somatic embryo to be mature and drying the mature somatic embryo; III. Culturing the mature somatic embryo till the germination of the somatic embryo; IV. Continuing to culture until the root and stem forms, thus acquiring the regeneration plant of Korean spruce. The plant regeneration method inducted by the somatic embryo of Korean spruce of the invention uses the immature seed of Korean spruce as an explant induction somatic embryo to acquire the regeneration plant, thus shortening the breeding period of Korean spruce, the cycle is increased by 3 to 6 times compared with cottage grafting vegetative propagation, and the reproduction rate is high.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Mesenchymal stem cell induction differentiation medium and method
InactiveCN103881973APromote growthShorten the growth cycleNervous disorderNervous system cellsMesenchymal stem cellPrecursor cell
The invention provides a mesenchymal stem cell induction differentiation medium and method. The mesenchymal stem cell induction differentiation medium is prepared by adding 10-30ng / mL cerebrospinal fluid into a basic medium. The invention also provides the method for induction differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into neural precursor cells by use of the medium. According to the medium and the culture method, in consideration of time, the growth cycles of neural stem cells and neurons can be greatly shortened, cells grow well, differentiated cells are mainly neuronal cells and are long in service life is, an efficient xenogeneic animal component-free clinical neural precursor cell transplantation technology platform is provided, and the method is simple, and less in spend.
Owner:曾因明
Generation of tumor-free embryonic stem-like pluripotent cells using inducible recombinant rna agents
ActiveCN101970664AIncrease translation efficiencyStrong gene silencing effectGenetically modified cellsCell culture active agentsCancer cellMammal
The present invention generally relates to a method for developing, generating and selecting tumor-free embryonic stem (ES)-like pluripotent cells using electroporation delivery of an inducible tumor suppressor mir-302 agent into mammalian cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method and composition for generating a Tet-On / Off recombinant transgene capable of expressing a manually re-designed mir-302 microRNA (miRNA) / shRNA agent under the control of doxycyclin (Dox) in human somatic / cancer cells and thus inducing certain specific gene silencing effects on the differentiation-associated genes and oncogenes of the cells, resulting in reprogramming the cells into an ES-like pluripotent state.
Owner:林希龙 +1
Process For Producing Hematopoietic Stem Cells Or Vascular Endothelial Precursor Cells
InactiveUS20080095746A1Inhibition effectMethod is limitedCompound screeningBiocideVascular endotheliumHematopoietic Tissue
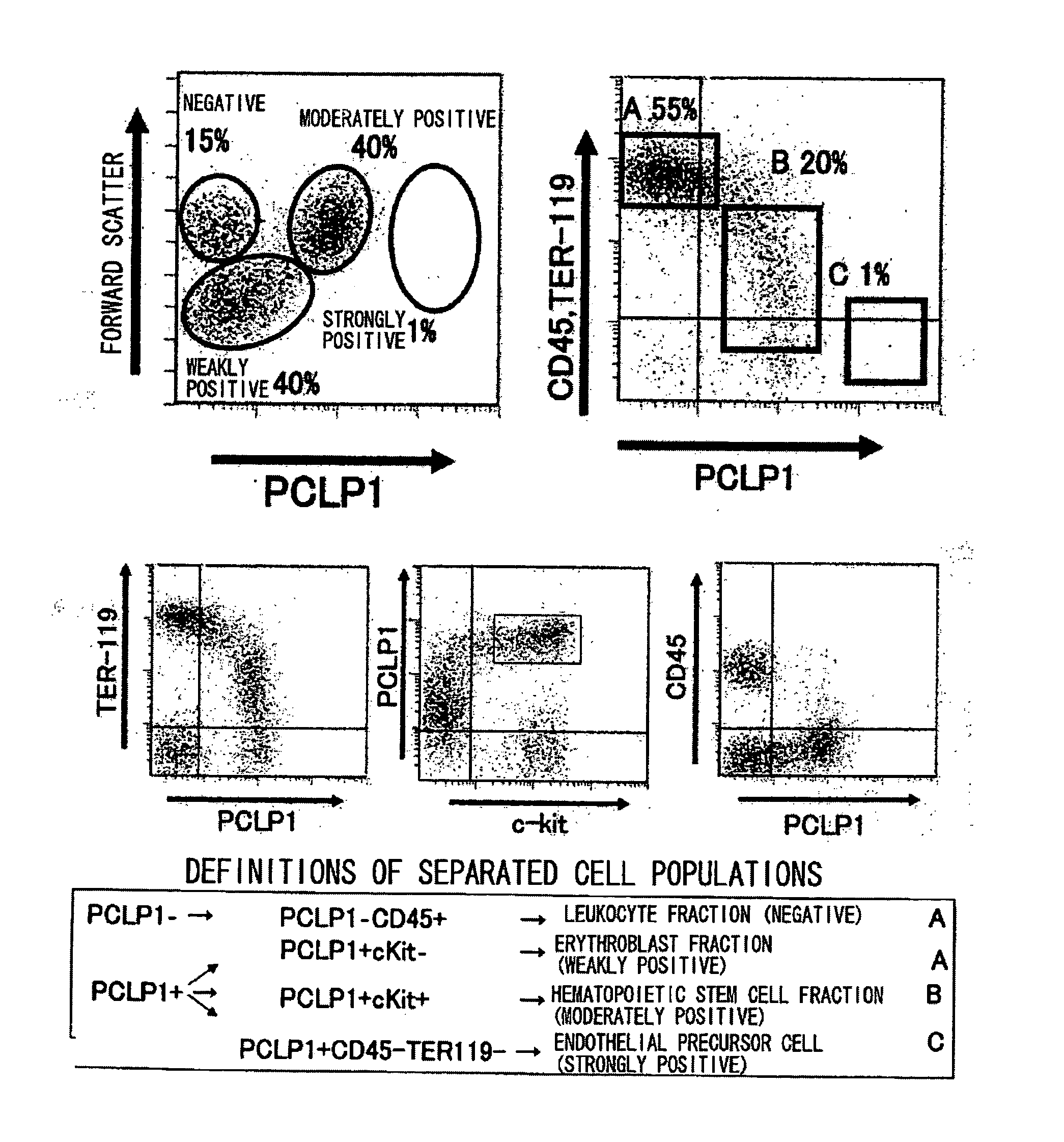
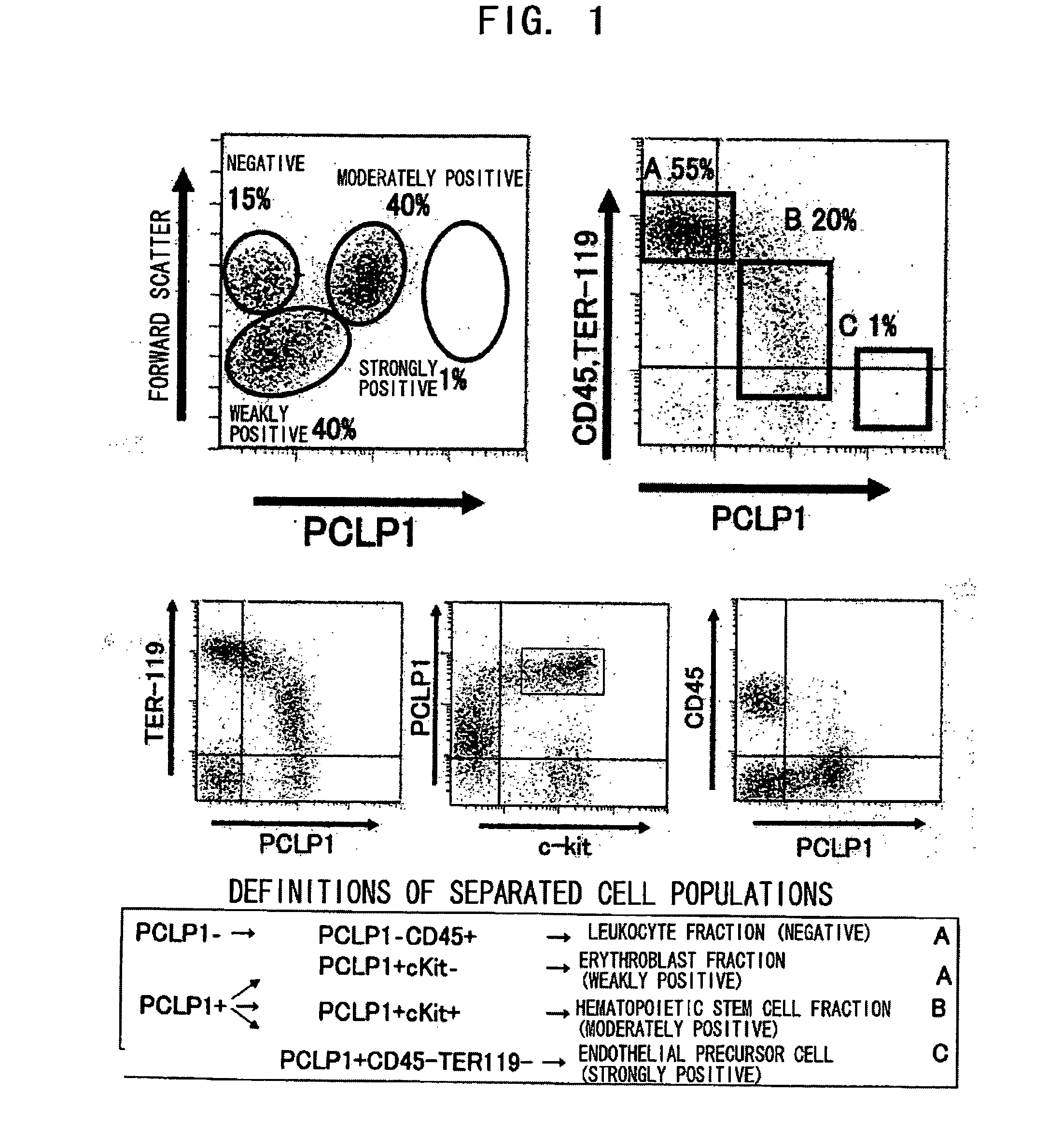
The present invention provides methods for producing hematopoietic stem cells or vascular endothelial precursor cells, wherein the methods comprise the step of separating PCLP1-positive cells from the hematopoietic tissues of an individual, and then culturing the obtained cells. PCLP1-positive cells obtained from the hematopoietic tissues of an individual can be cultured for a long time, and during culture they produce large quantities of hematopoietic stem cells or vascular endothelial precursor cells. The hematopoietic stem cells or vascular endothelial precursor cells obtainable by the present invention can be utilized for regenerative medicine.
Owner:TOUDAITLO LTD +1
Cinnamomum kanahirai hay body embryo culture medium and tissue culture rapid propagation method
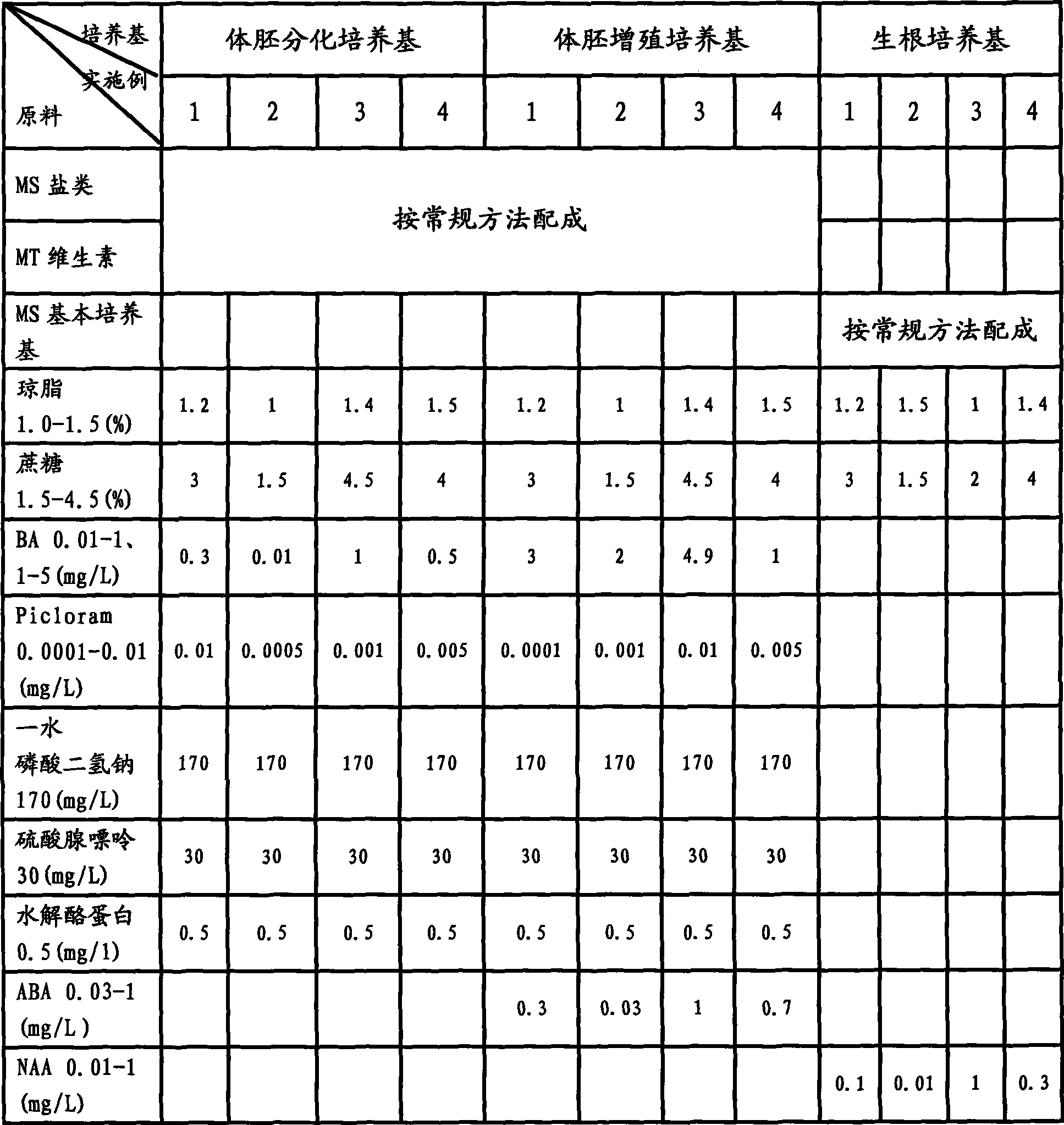
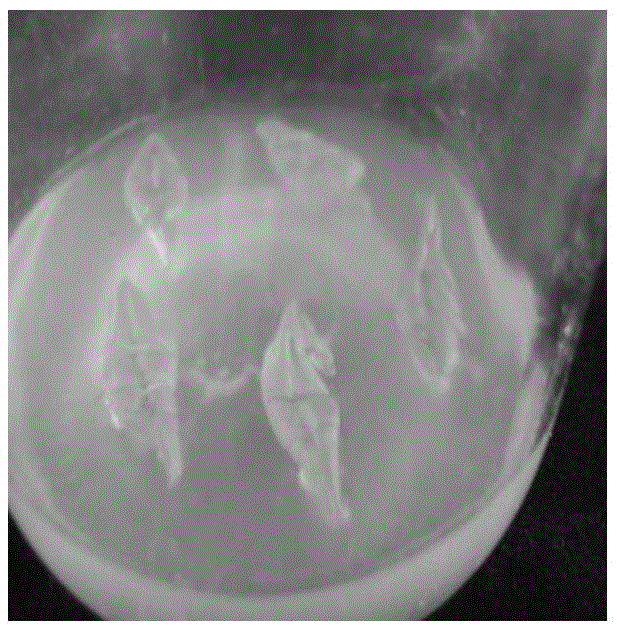
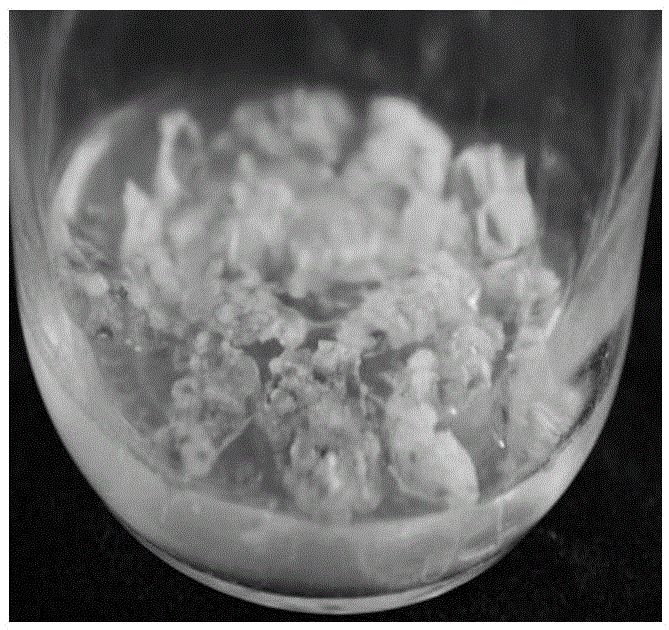
The invention discloses a Cinnamonum kanehirae Hayata somatic embryo culture medium, which contains MS as a basic culture medium or MS salts and MT vitamin, and also contains growth regulators such as BA, Picloram, ABA and NAA, 170mg / L sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate,30mg / L adenine sulfate, 0.5g / L caseinhydrolysate, 1.2 percent agaragar, and 3 percent saccharose, wherein three culture media for somatic embryogenesis, somatic embryo proliferation and embryo differentiation, and embryo rooting are prepared respectively. The tissue culture and rapid propagation method of Cinnamonum kanehirae Hayata by using the culture media comprises the following four steps: 1. the acquisition and disinfection of an explant; 2. the induction of a somatic embryo; 3. the somatic embryo proliferation and embryo differentiation; and 4. root induction and transplanting. The invention initially creates a complete set of method for Cinnamonum kanehirae Hayata somatic embryos to reproduce seedlings, saves the endangered species resource, lays a foundation for further exploring the gene engineering of somatic embryos, broadening explant materials and so on, and provides adequate wood for the mass production of Antrodia camphorata with extremely high economic value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Chinese scholartree detached leaf somatic embryo induction rapid-breeding method
ActiveCN105660396AConvenient inductionInduced fastPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budGermplasm
The invention discloses a Chinese scholartree detached leaf somatic embryo induction rapid-breeding method. The method comprises selecting Chinese scholartree tender twigs, disinfecting the tender twigs, taking stems with axillary buds or terminal buds, inoculating a bud initial medium with the axillary buds or terminal buds, inducing germination of the axillary buds or terminal buds, removing base leaves of the produced young sprouts, carrying out cutting to obtain stem sections with axillary buds or terminal buds, inoculating a test-tube plantlet multiplication medium with the stem sections with axillary buds or terminal buds to obtain sterile test-tube plantlets, taking leaves of the sterile test-tube plantlets, inoculating a somatic embryo inducing medium with the leaves of the sterile test-tube plantlets, carrying out culture to obtain callus, inoculating an adventitious bud induction medium with the callus, carrying out culture to obtain multiple shoots, cutting the multiple shoots to obtain callus blocks, inoculating a test-tube plantlet multiplication medium or an adventitious bud induction medium with the callus blocks, carrying out culture, transferring the cultured multiple shoots into a shoot strengthening medium, carrying out shoot strengthening culture and carrying out seedling hardening and transplanting. The method has a high regeneration rate, a large budding rate, a plant transplanting survival rate of 95% or more, produces strong seedlings and effectively solves the problem of degeneration of excellent seedling germplasm.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREST SCI RES INST
Method for inductively producing snow lotus somatic embryo
The invention relates to a method for inducing the body embryo of saussurea involucrate, which is: inducing the callus of saussurea involucrate seeds, and getting the body embryo of saussurea involucrate by the body embryo induction. According the leaflet regenerating principle, taking seedling cotyledons as explants, then inducing them by solid and liquid suspension culturing to get the body embryo of saussurea involucrate, laying the foundation of producing artificial seeds.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Peanut somatic embryo induction and plant regeneration method
InactiveCN101965798ANumber of regenerated plantsHigh regeneration rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureInorganic saltsSomatic embryogenesis
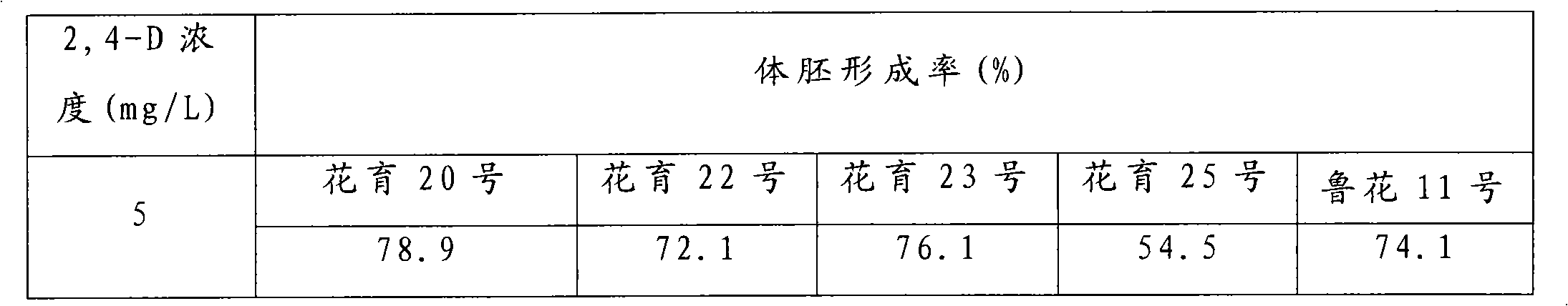
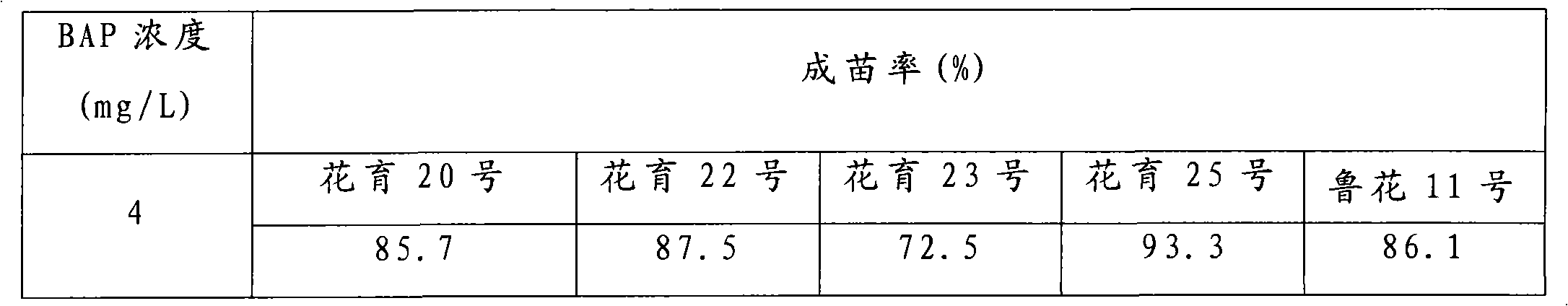
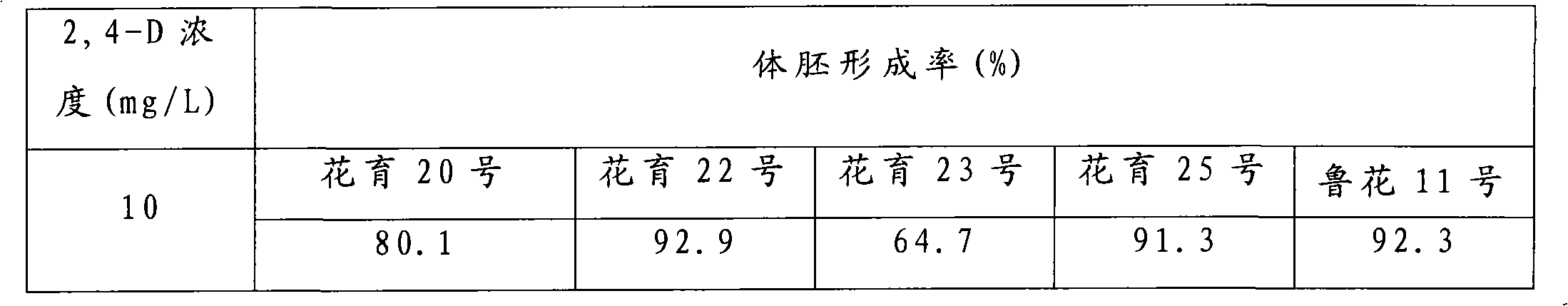
The invention provides a peanut somatic embryo induction and plant regeneration method, which can solve the problem of low plant regeneration frequency in the prior art. The method of the invention comprises the following main steps: separating embryonic leaflet from a peanut embryo which is treated by surface sterilization and soaked, and inoculating the embryonic leaflet to an induction culture medium to which 2,4-D (5-10mg / L) is added for culturing a somatic embryo; then transferring the somatic embryo to a somatic embryo germinating culture medium to which BAP (4mg / L) is added, and subculturing twice to obtain regenerated plants; and cutting the somatic embryo at the bottom after the somatic embryo germinates and elongates, and transferring the cut somatic embryo to a 1 / 2MS inorganic salt and B5 organic rooting culture medium to which NAA (0.2-0.5mg / L) is added for inducing rooting to obtain complete plants. By taking the embryonic leaflet of peanut mature seeds as explant, and using the induction culture medium of 2,4-D (5-10mg / L) and the somatic embryo germinating culture medium of BAP (4mg / L), the somatic embryo induction rate and plant regeneration rate are high, and simultaneously the somatic embryo is derived from one cell, and the chimerism of regenerated plants is avoided.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
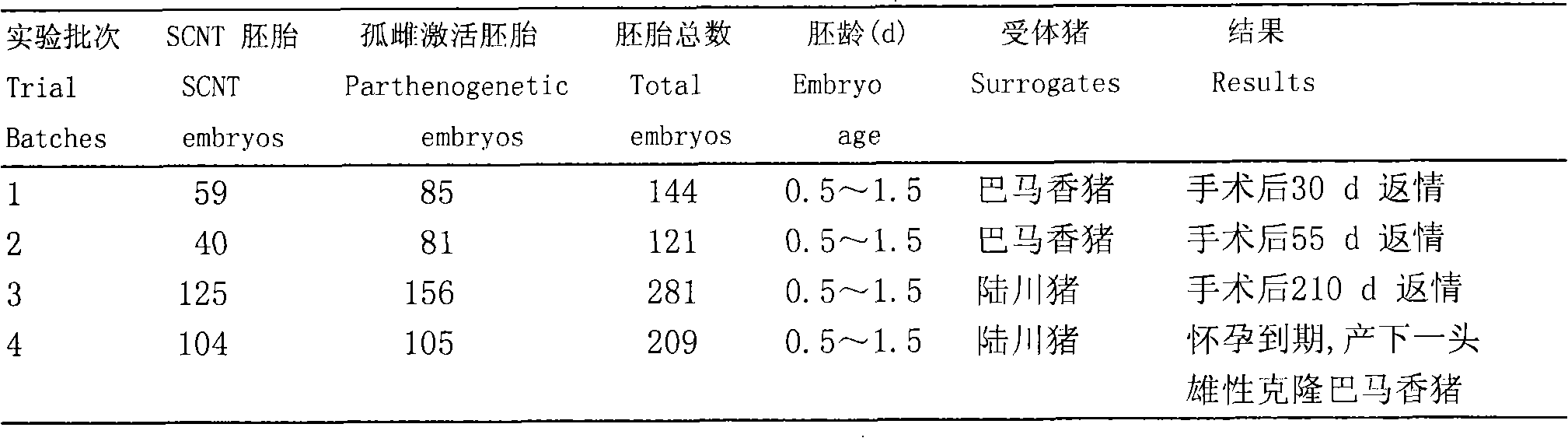
Bama miniature pig somatic cell cloning method
InactiveCN101857878ASolve the introductionSolve species conservationAnimal reproductionFermentationAnimal scienceOrgan transplantation
The invention discloses a Bama miniature pig somatic cell cloning method, which comprises the following steps: 1) preparing related agents; 2) cultivating Bama miniature pig somatic cells; 3) freezing the Bama miniature pig somatic cells; 4) unfreezing the frozen somatic cells; 5) acquiring and externally cultivating pig oocytes; 6) transplanting nucleus; and 7) transplanting embryos. The invention has the advantages of speeding up the research on domestic transgenosis pig technology and human heterogeneous organ transplantation, accelerating the development of animal husbandry in Guangxi even the whole country, and academically filling the gap in China.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Tissue-culturing quick propagation method of wild rhizoma panacis japonici
InactiveCN1883259AFast growthSolve insufficient resourcesHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEmbryoSkin callus
The invention relates to a method for tissue culture and rapid reproduction of wild P.japonicus, comprising (1)selection and sterilization of explants: selecting stems and leaves of wild P.japonicus, surfacely sterilizing same, as explants for tissue culture; (2)callus culture; (3)callus proliferation to form embryogenic callus; (4)somatic embryos differentiation: somatic embryos differentiate from the surface of embryogenic callus; (5)somatic embryo proliferation to differentiate somatic embryos further; (6)plants regeneration culture to form full plants with roots, stems and leaves; (7)strong seedlings culture; (8)plants transplantation. The invention is provided with high frequency of regeneration plants, fast speed of proloferation, and no shortcoming of easy variation of offspring reproduced by normal seeds.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for inducing extended self-renewal of functionally differentiated somatic cells
InactiveUS20120156179A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSomatic cellSomatic portion
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Composition for treating ischemic diseases or neurogenic inflammation, containing, as active ingredient, neural progenitor cells or secretome thereof
PendingCN106714814APromote generationInhibit the inflammatory responseCulture processPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProgenitorNervous system
The present invention provides a composition for treating ischemic diseases or neurogenic inflammation. PSA-NCAM-positive neural progenitor cells used in the present invention promote angiogenesis in injected tissue and inhibit an inflammatory response. The PSA-NCAM-positive neural progenitor cells can be simply isolated by using an anti-PSA-NCAM-antibody, and exhibit excellent angiogenic and anti-inflammatory activities compared with mesenchymal stem cells, and thus can be useful as a composition for effectively treating ischemic diseases caused by a vascular injury and nerve damage diseases caused by inflammation. In addition, a secretome of the neural progenitor cells of the present invention reduces the ischemic injury site and allows a neurological function to recover, and thus can be used as an agent for treating ischemic diseases and degenerative nervous system disorders such as nerve damage diseases caused by inflammation.
Owner:S-BIOMEDICS CO LTD
Indefinite culture of human adult glia without immortalization and therapeutic uses thereof
Cell culture conditions for the isolation, maintenance, and indefinite expansion of human glia are established favoring the growth of neural precursor cells. Cultured cells proliferate indefinitely, express catalytic telomerase, and retain a non-immortalized phenotype. Compositions allow for the indefinite expansion of non-immortalized neural tissue for bioassay applications and restorative neuroscience.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods for conditioning plant somatic embryos
InactiveUS20070087438A1Promote physiological maturationImprove germination rateSeed and root treatmentFermentationEmbryoSomatic cell
The present invention provides methods for conditioning plant somatic embryos. The methods include the step of exposing the somatic embryos to a gas stream having a selected moisture content for a period of time sufficient to change the moisture content of the somatic embryo to a desired moisture content, wherein the gas stream is produced using an ionomeric membrane.
Owner:WEYERHAEUSER NR CO
Culture medium for overcoming variety and genetype restriction in regeneration culture of alfalfa high frequency somatic embryos
InactiveCN101703002AOvercome different breedsOvercoming the genotype restriction problemHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSucroseSaccharum
The invention discloses a culture medium for overcoming variety and genetype restriction in regeneration culture of alfalfa high frequency somatic embryos. The culture medium comprises seedling growth and acclimatization culture medium, a somatic cell embryo occurrence and induction culture medium, an embryo subgeneration formation culture medium and an embryo maturing and sprouting culture medium. The seedling growth and acclimatization culture medium is half modified MS+20g / L white sugar+0.7% agaragar; the somatic cell embryo occurrence and induction culture medium is modified SH+6-10mg / L2,4-D+0.2-0.5mg / L 6-BA+30g / L cane sugar+0.3% phytagel; the embryo subgeneration formation culture medium is modified SH+2-5 mg / L 2,4-D+0.2-0.5mg / L6-BA+500mg / L hydrolyzed casein+50g / L cane sugar+0.35% phytagel; and the embryo maturing and sprouting culture medium is modified MS+500mg / L hydrolyzed casein+30g / L white sugar+0.7% agaragar. The invention can effectively overcome the variety and genetype restriction in regeneration culture of alfalfa high frequency somatic embryos, vastly improve somatic cell embryo occurrence frequency and regeneration plant frequency, and enhance breeding efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY +1
Method for mutagenizing anti-chlorosulfuron somatic mutant of rice
InactiveCN1582639AIncrease the frequency of induced mutationsImprove selection efficiencyPlant phenotype modificationPlant tissue cultureAlcoholHusk
A method for inducing the chlorsulfuron-resistant somatic mutant of paddy rice includes such steps as removing husk from the health seeds, immersing in alcohol and then in mercury chloride solution, flushing by aseptic water, inducing culture, secondary culturing, screening culturing by adding chlorsulfuron, differential culturing and redifferential culturing.
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Kit and method for detecting anthurium andraeanum SERK gene expression status
InactiveCN102925550AStrong design specificityHigh rate of callus inductionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceEmbryoPcr ctpp
The invention relates to a kit and a method for detecting an anthurium andraeanum SERK gene expression status, and belongs to the field of plant molecular biology. According to the invention, a just-expended young leaf of an anthurium andraeanum potted variety Alabama mature plant is adopted as an explant, and anthurium andraeanum embryogenic callus induction is carried out; non-embryogenic callus and embryogenic callus obtained in two induction stages are subjected to cytological observation; a full-length sequence of cDNA gene of anthurium andraeanum somatic embryo SERK gene is obtained by cloning; primers with relatively high specificity are designed; and researches and analysis upon changes of expression amount of SERK gene transcriptional level of anthurium andraeanum somatic embryo induction and development stages are carried out by using a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR technology, such that a low-cost and high-specificity kit used for detecting anthurium andraeanum SERK gene expression status is obtained, and a method thereof is provided.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Somatic sensation simulation device having cold touch, and somatic sensation simulation system
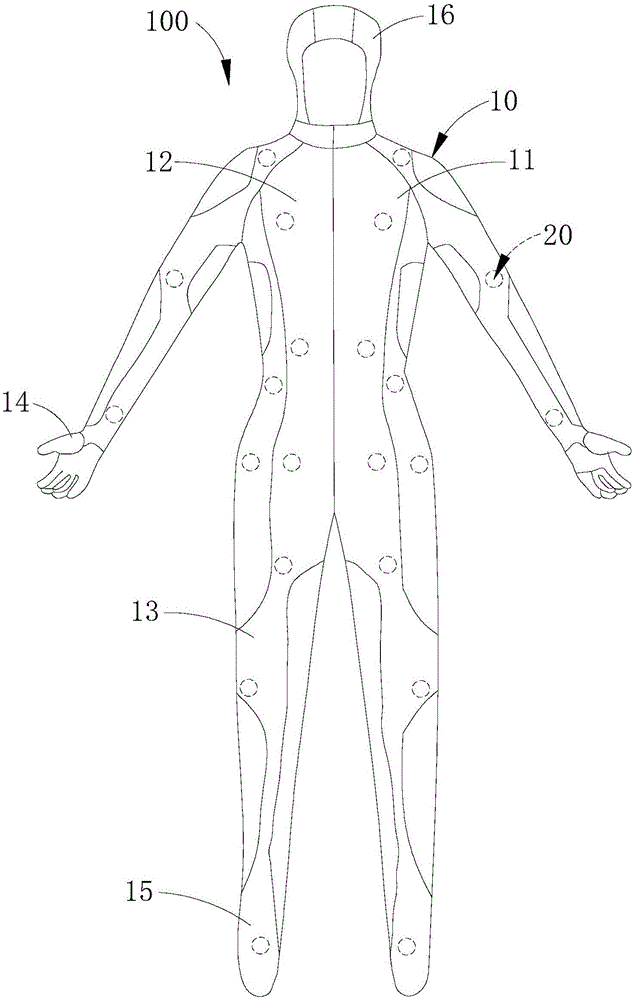
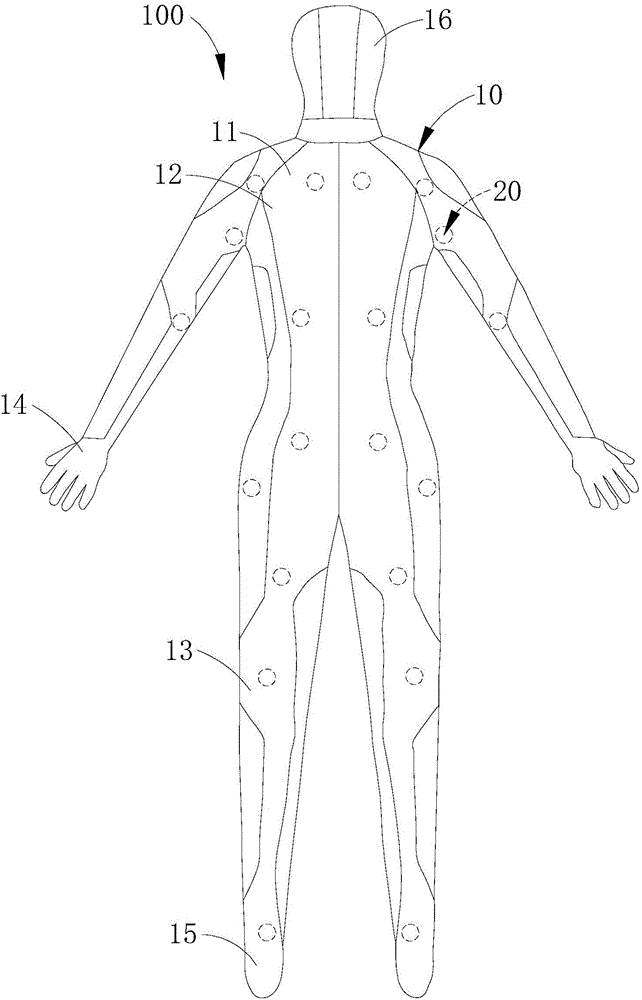
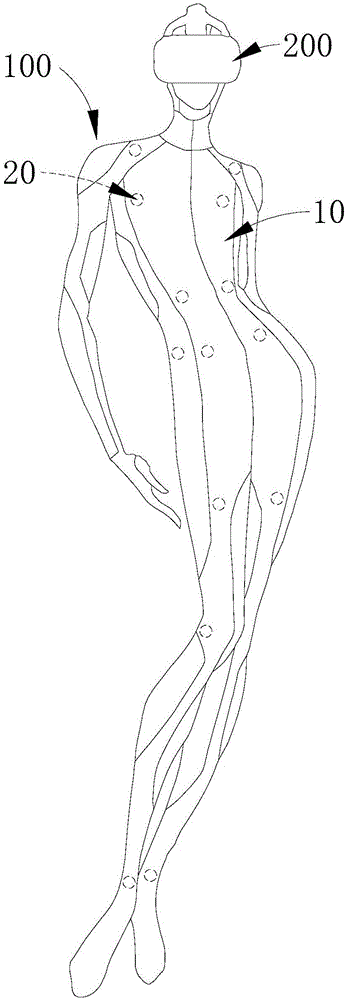
InactiveCN106406546AImprove effectivenessImprove realismInput/output for user-computer interactionVideo gamesSomatosensory systemWhole body
The invention relates to a somatic sensation simulation device having cold touch. The somatic sensation simulation device comprises a wearable body, a plurality of somatic sensation simulation components and a control unit; the wearable body is used for wrapping the whole body of a user; the plurality of somatic sensation simulation components are arranged on the wearable body; furthermore, each somatic sensation simulation component at least comprises a cold touch functional module; and the control unit is separately connected with each somatic sensation simulation component electrically. Because the wearable body used for wrapping the whole body is adopted and the plurality of somatic sensation simulation components are arranged in the wearable body, various areas in the whole body of the user can generate corresponding somatic sensation according to requirements of an application scene; not just a single or individual body part is stimulated; therefore, the somatic sensation simulation validity and the user feel real degree are greatly improved; simultaneously, because the plurality of somatic sensation simulation components each can simulate a cold effect, various parts of the body of the user can feel somatic sensation stimulation of cold touch; and thus, requirements and real experiences of users on the cold touch can be ensured.
Owner:包磊
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com