Self-discharge screening method for lithium ion phosphate battery
A technology of a lithium iron phosphate battery and a screening method, which is applied in the field of lithium ion batteries, can solve problems such as the inability to properly screen lithium iron phosphate batteries with large self-discharge, and achieve the effects of high reliability, improved consistency and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
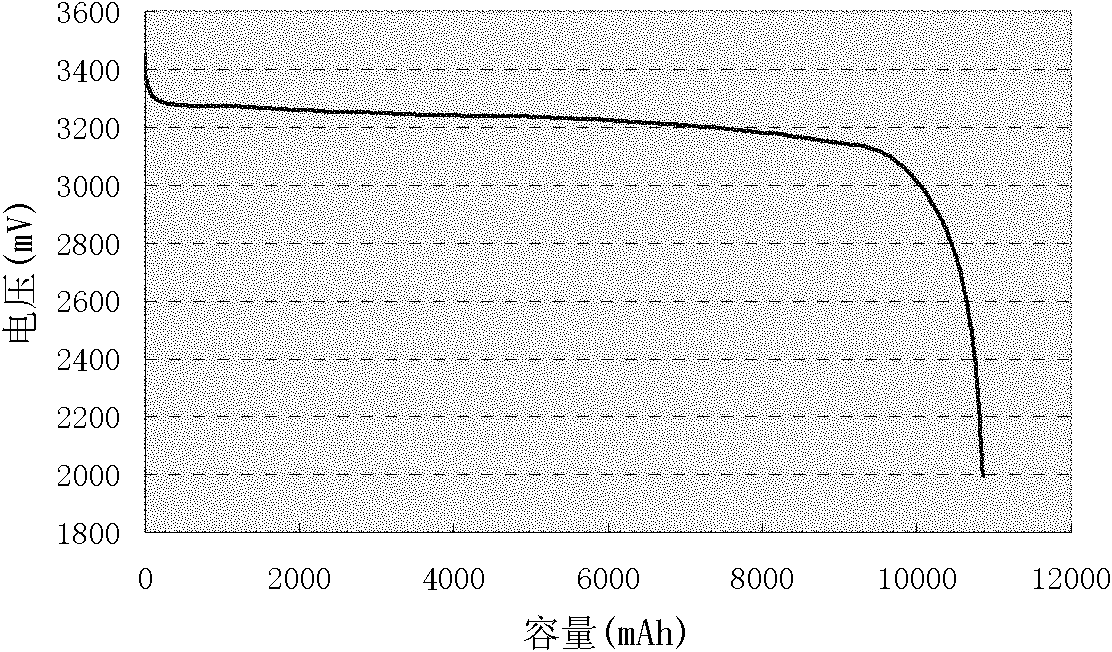
[0017] Example 1 In the composite positive electrode containing lithium iron phosphate, a layered lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide LiNi with a mass fraction of 3 wt% of lithium iron phosphate is added 0.4 co 0.2 mn 0.4 o 2 , with graphite as the negative electrode, assembled into a lithium iron phosphate battery. The battery discharge curve is as figure 2. Charge the battery with a constant current of 0.33C to 3.65V, and then charge it at a constant voltage of 3.65V until the current reaches the cut-off current of 0.02C, then stop charging; measure and record the voltage, and leave the battery at 25±2°C for 10 day, measure and record the voltage again; calculate the voltage difference and the voltage change value per unit time (K value), and determine the voltage difference of the self-discharging large battery for 10 days or the critical value of the voltage change per unit time is 40mV or 4mV / d , judging that the voltage difference or the voltage change per unit ti...
Embodiment 2
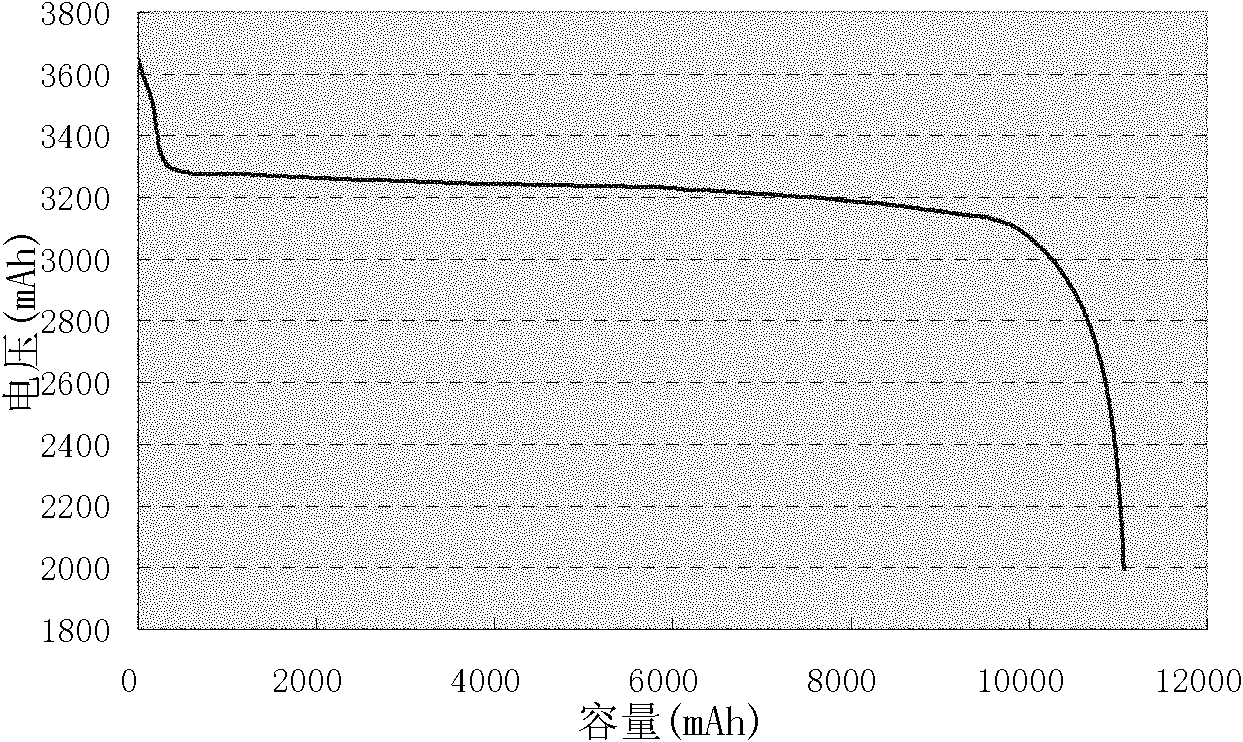
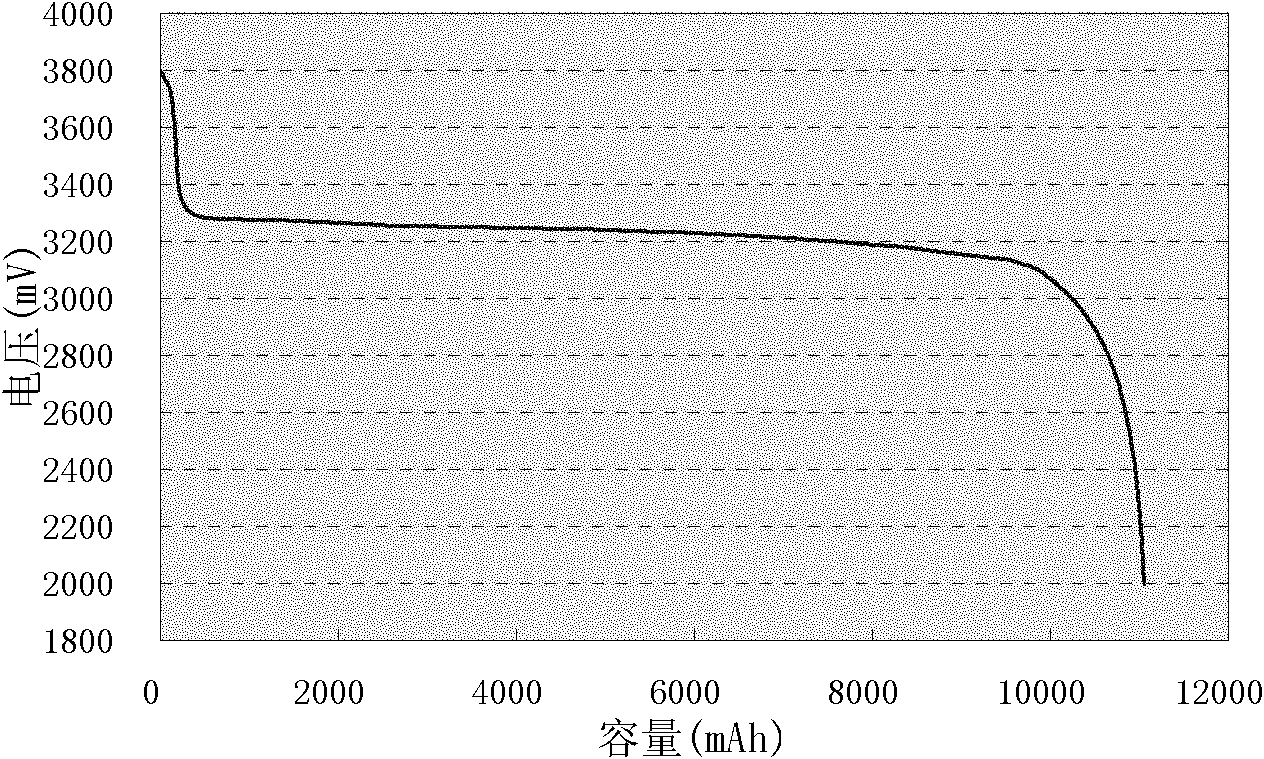
[0020] Example 2 In the composite positive electrode containing lithium iron phosphate, a spinel-like lithium manganese oxide LiMn with a mass fraction of 5 wt% of lithium iron phosphate is added 2 o 4 , with graphite as the negative electrode, assembled into a lithium iron phosphate battery. The battery discharge curve is as image 3. Charge the battery with a constant current of 0.33C to 3.8V, and then charge it at a constant voltage of 3.8V until the current reaches the cut-off current of 0.02C, then stop charging; measure and record the voltage, and leave the battery at 25±2°C for 10 day, measure and record the voltage again; calculate the voltage difference and the voltage change value (K value) per unit time, and determine the voltage difference of the self-discharging large battery for 10 days or the critical value of the voltage change per unit time is 40mV or 4mV / d, judging that the voltage difference or the voltage change per unit time is greater than the critical...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com