Patents
Literature
266 results about "Microplasma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A microplasma is a plasma of small dimensions, ranging from tens to thousands of micrometers. Microplasmas can be generated at a variety of temperatures and pressures, existing as either thermal or non-thermal plasmas. Non-thermal microplasmas that can maintain their state at standard temperatures and pressures are readily available and accessible to scientists as they can be easily sustained and manipulated under standard conditions. Therefore, they can be employed for commercial, industrial, and medical applications, giving rise to the evolving field of microplasmas.
Remotely-excited fluorine and water vapor etch
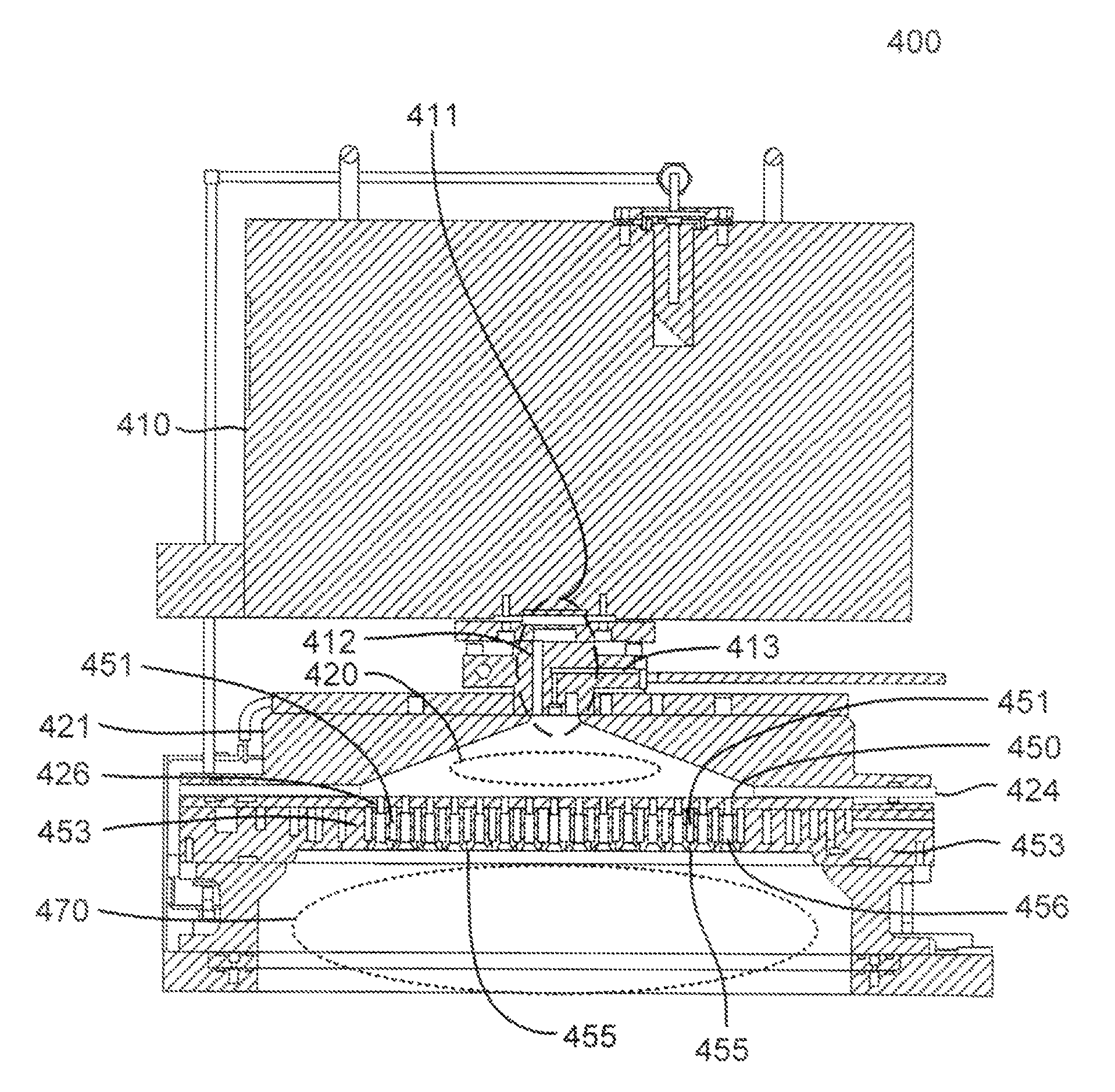
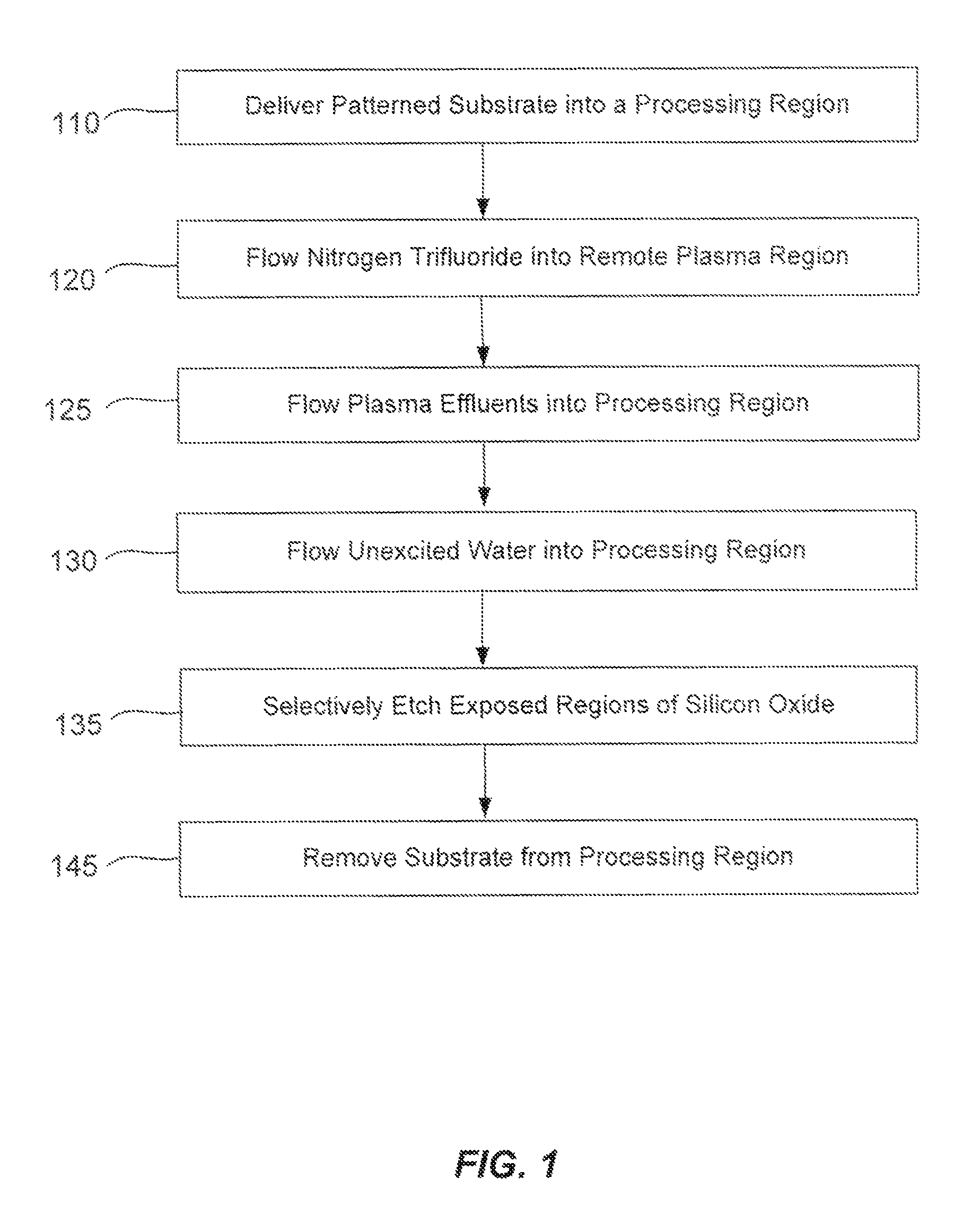
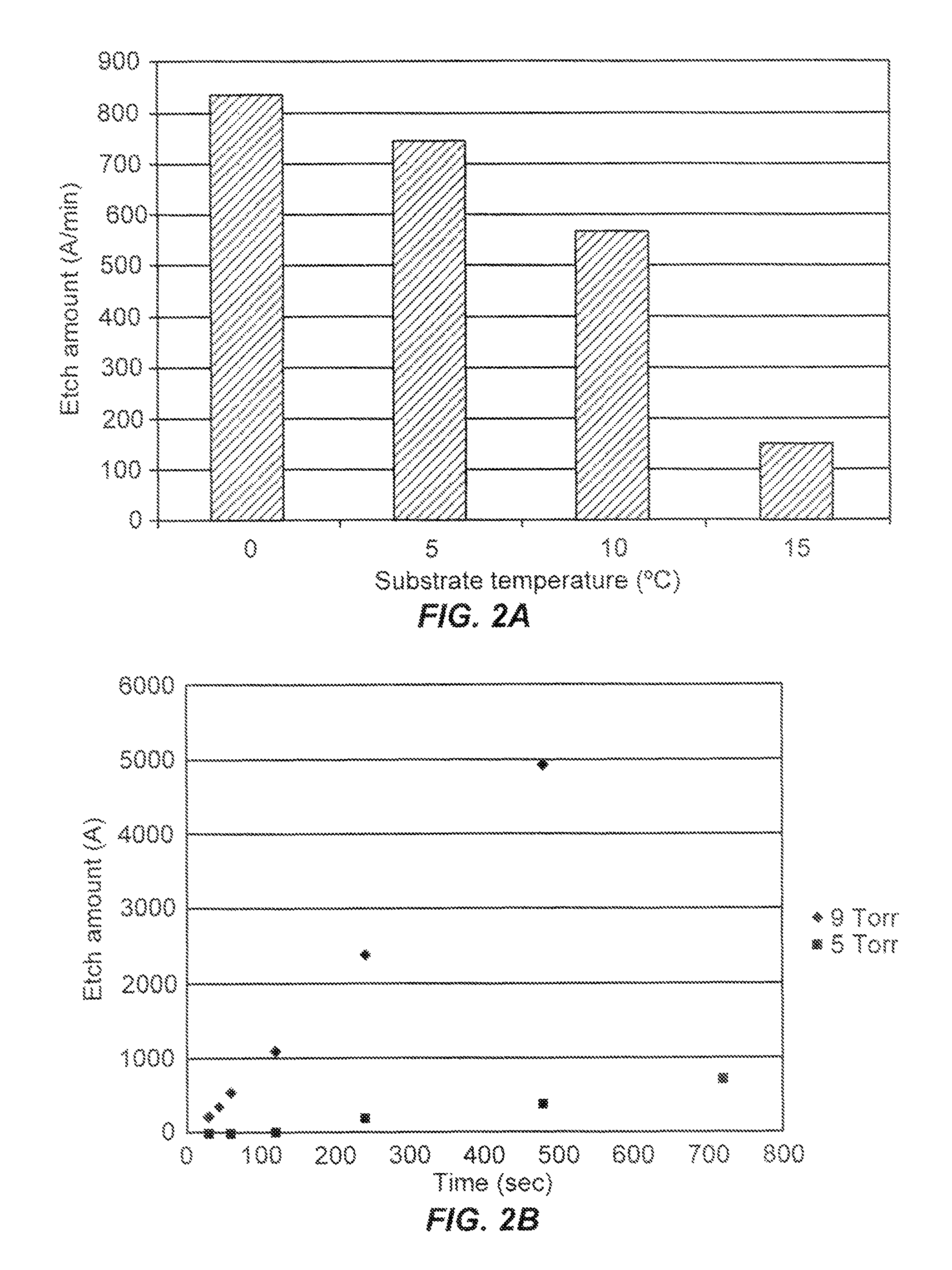
A method of etching exposed silicon oxide on patterned heterogeneous structures is described and includes a remote plasma etch formed from a fluorine-containing precursor. Plasma effluents from the remote plasma are flowed into a substrate processing region where the plasma effluents combine with water vapor. The chemical reaction resulting from the combination produces reactants which etch the patterned heterogeneous structures to produce, in embodiments, a thin residual structure exhibiting little deformation. The methods may be used to conformally trim silicon oxide while removing little or no silicon, polysilicon, silicon nitride, titanium or titanium nitride. In an exemplary embodiment, the etch processes described herein have been found to remove mold oxide around a thin cylindrical conducting structure without causing the cylindrical structure to significantly deform.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
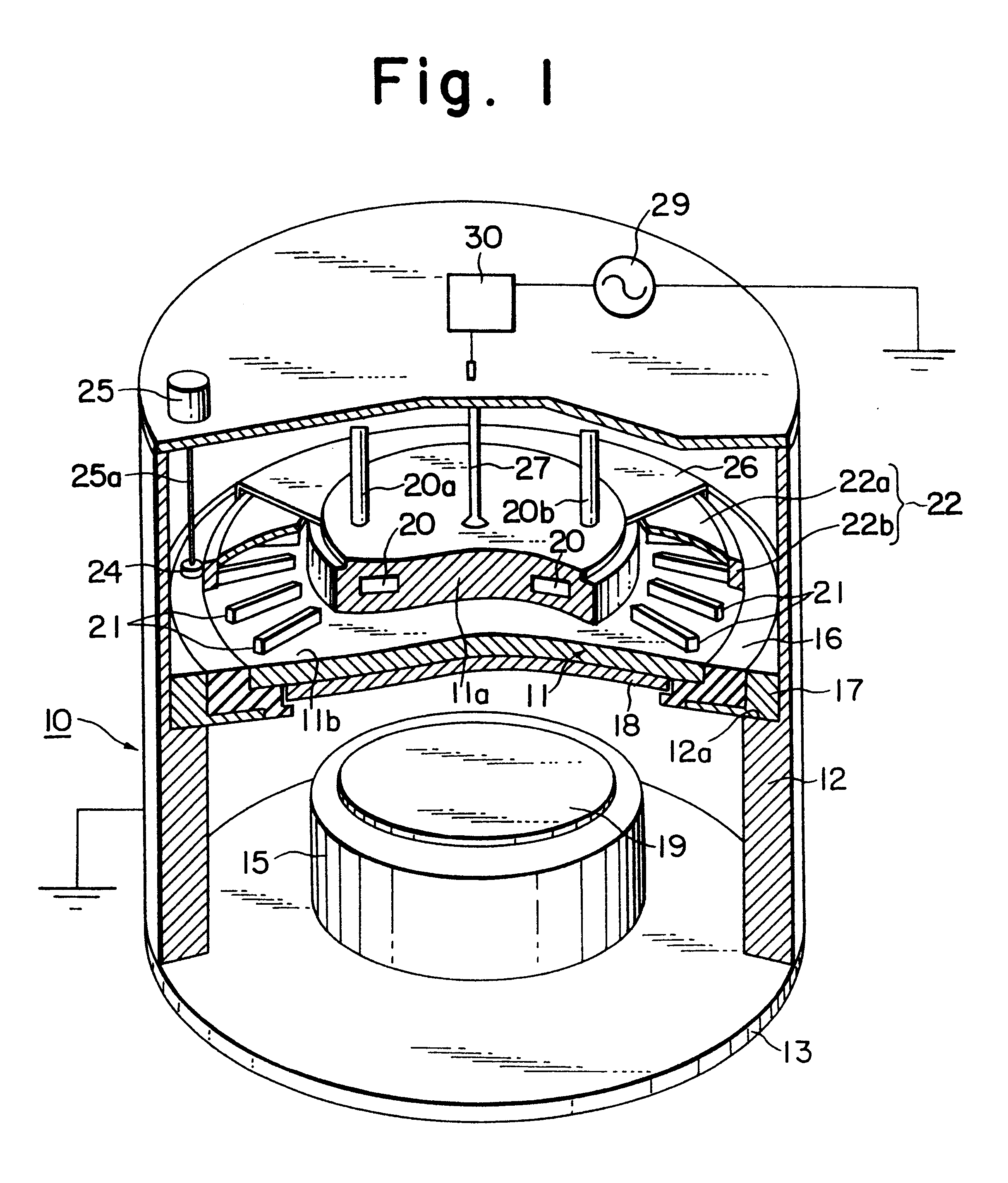
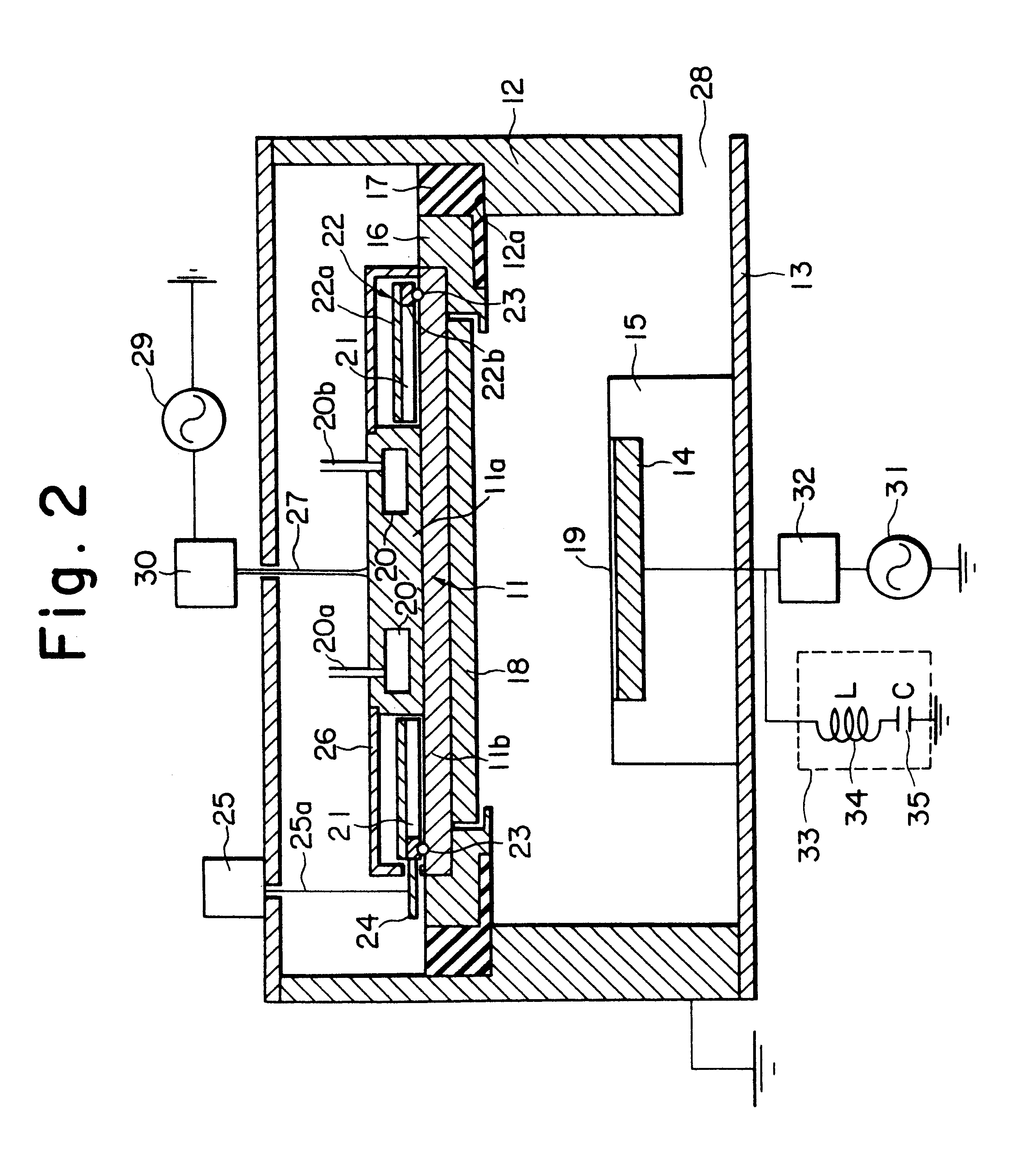
Plasma processing system for sputter deposition applications
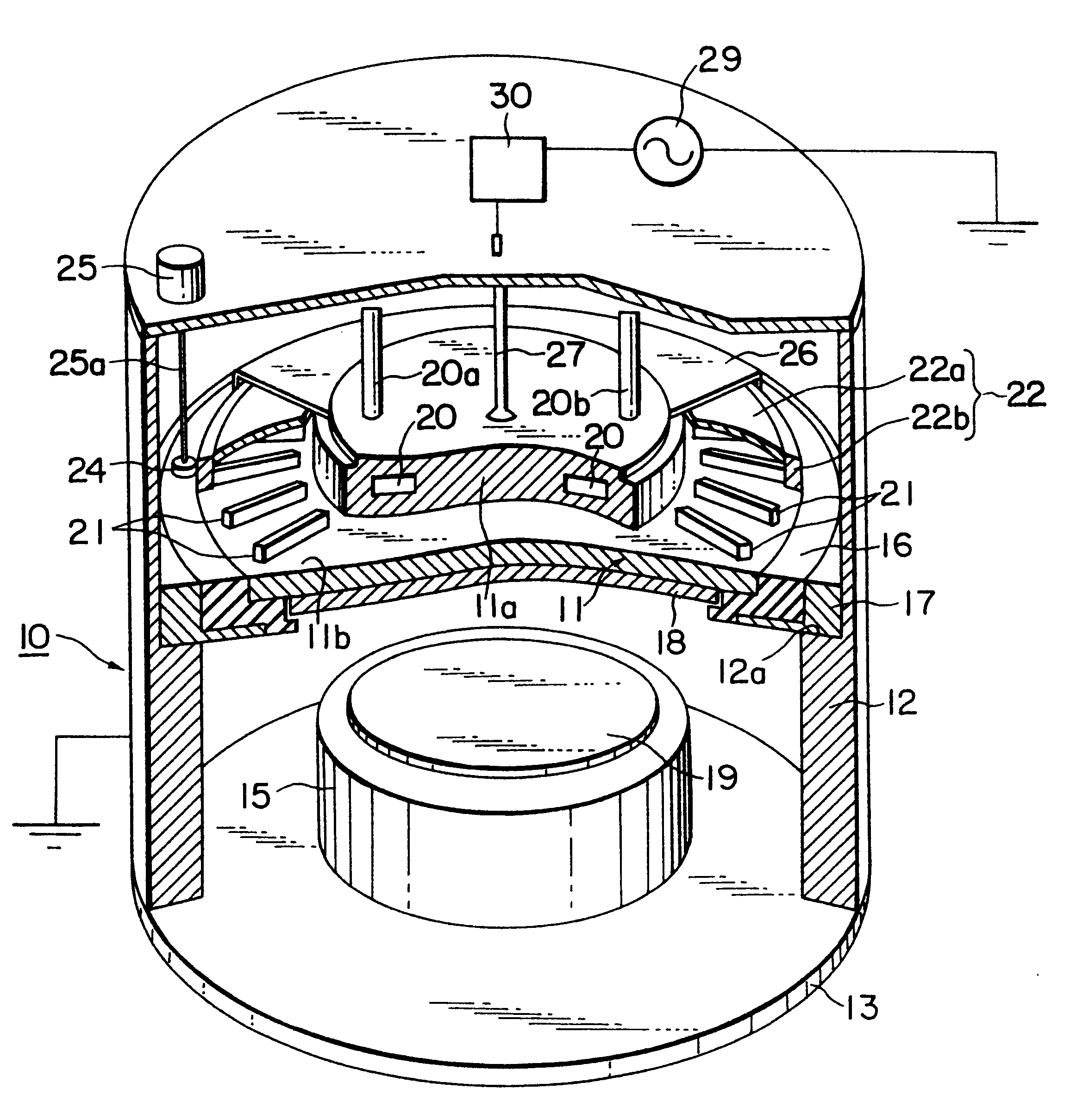
A plasma processing system for sputter deposition application is configured by a reactor including two parallel capacitively-coupled electrodes called upper and lower electrodes, and a multi-pole magnet arrangement over the outer region of the upper electrode. The magnets are assembled on a metal ring in order to rotate over the upper electrode. The target plate is fixed to the upper electrode which is given only a high-frequency rf current, or high-frequency rf current and a DC voltage together. The lower electrode where the substrate is placed, is given a MF, HF or VHF rf current in order to generate a negative self bias voltage on the lower electrode to extract ionized sputtered-atoms that fill contact-holes on the substrate surface.
Owner:ANELVA CORP
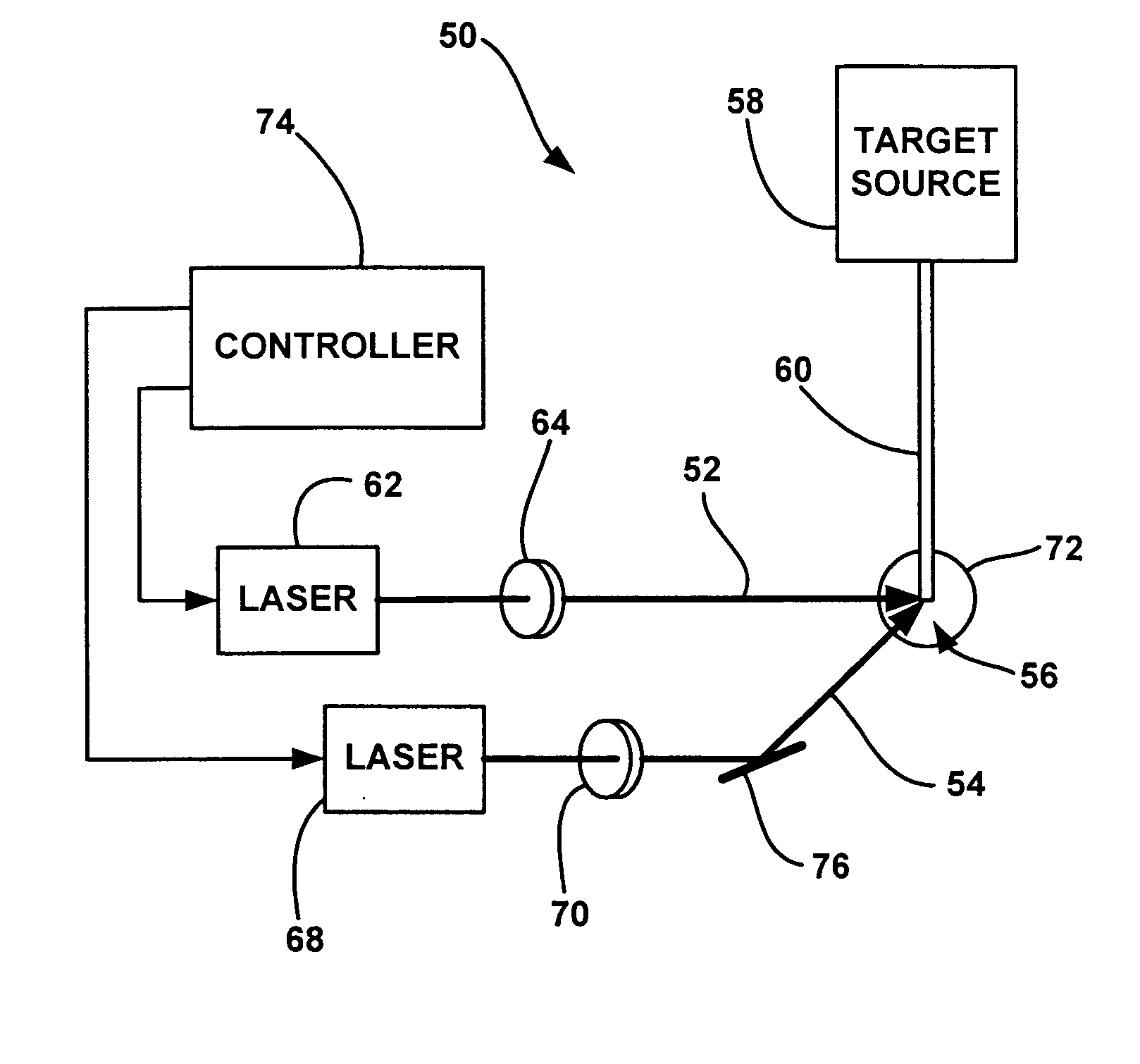
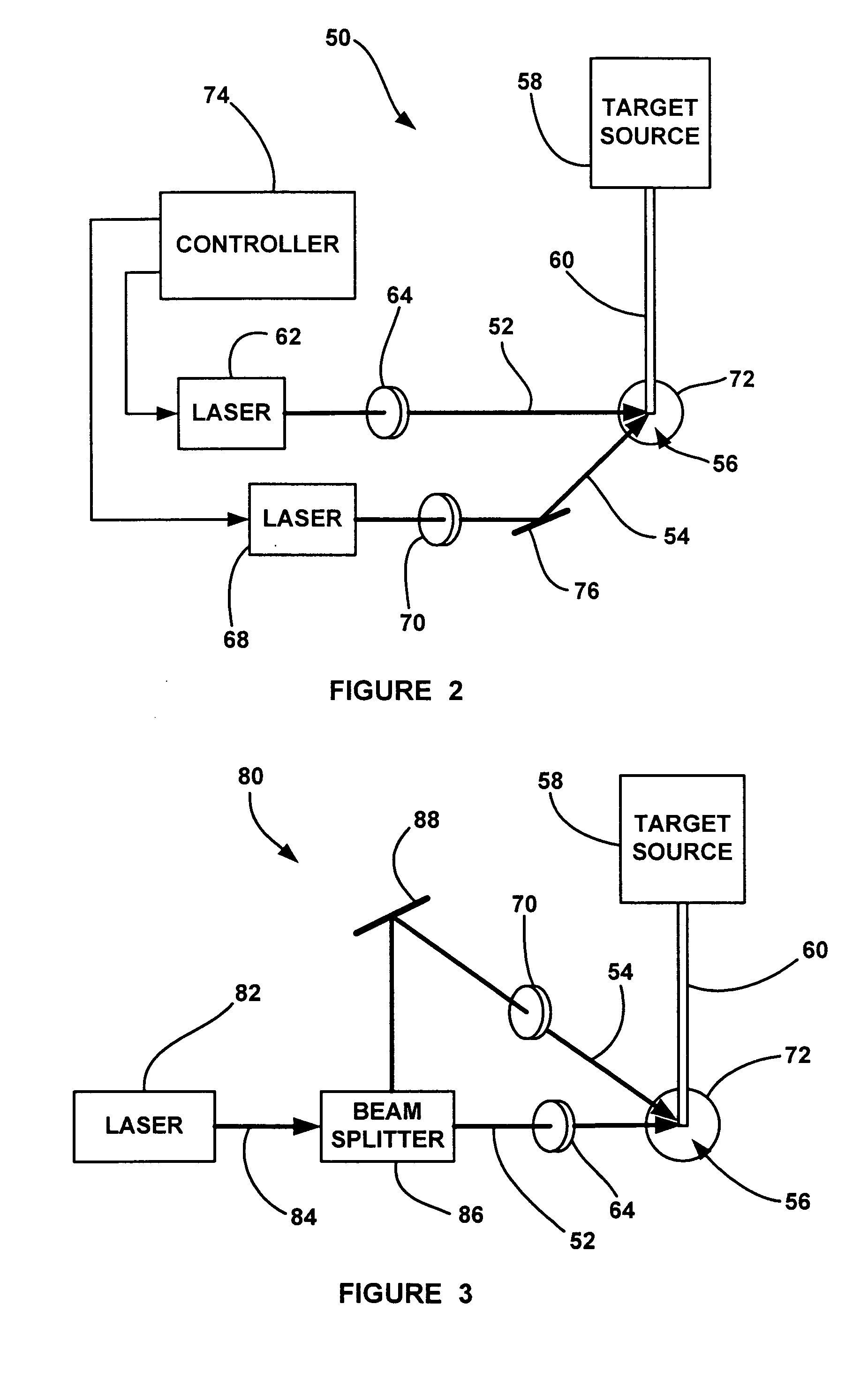
Laser-produced plasma EUV light source with pre-pulse enhancement
InactiveUS20040264512A1Laser using scattering effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBeam splitterHigh energy
An EUV radiation source that employs a low energy laser pre-pulse and a high energy laser main pulse. The pre-pulse generates a weak plasma in the target area that improves laser absorption of the main laser pulse to improve EUV radiation emissions. High energy ion flux is reduced by collisions in the localized target vapor cloud generated by the pre-pulse. Also, the low energy pre-pulse arrives at the target area 20-200 ns before the main pulse for maximum output intensity. The timing between the pre-pulse and the main pulse can be reduced below 160 ns to provide a lower intensity of the EUV radiation. In one embodiment, the pre-pulse is split from the main pulse by a suitable beam splitter having the proper beam intensity ratio, and the main pulse is delayed to arrive at the target area after the pre-pulse.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Surface plasmon resonance based nanoliter tear osmometer
ActiveUS20050159657A1Introduce errorEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMedicineMicroplasma
A medical diagnostic method utilizes a surface plasmon resonance apparatus provided with a sensing surface. A tear sample from an eye of a patient is placed into contact with the sensing surface. The surface plasmon resonance apparatus is then operated to determine osmolarity of the tear sample.
Owner:LACRISCI
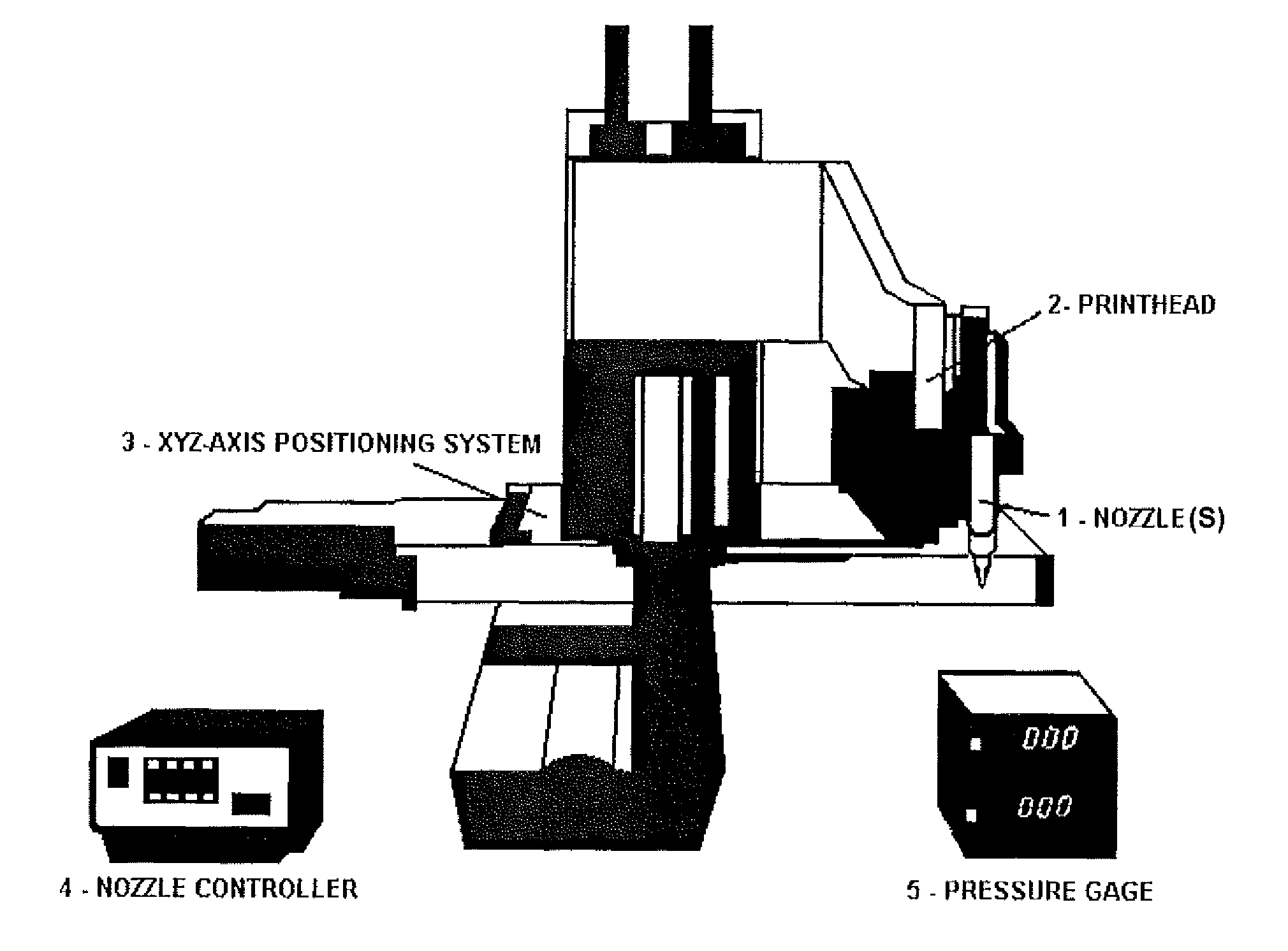
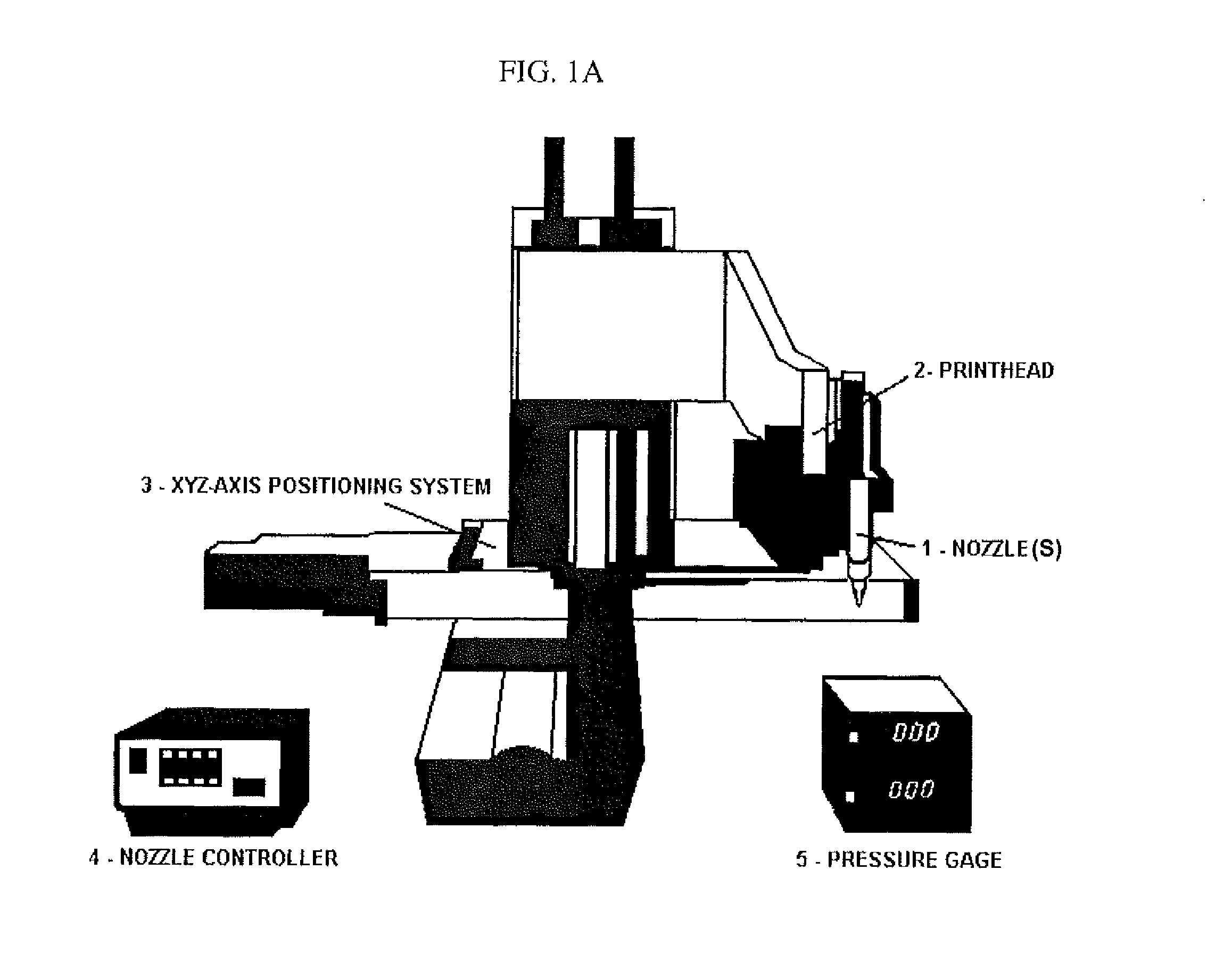
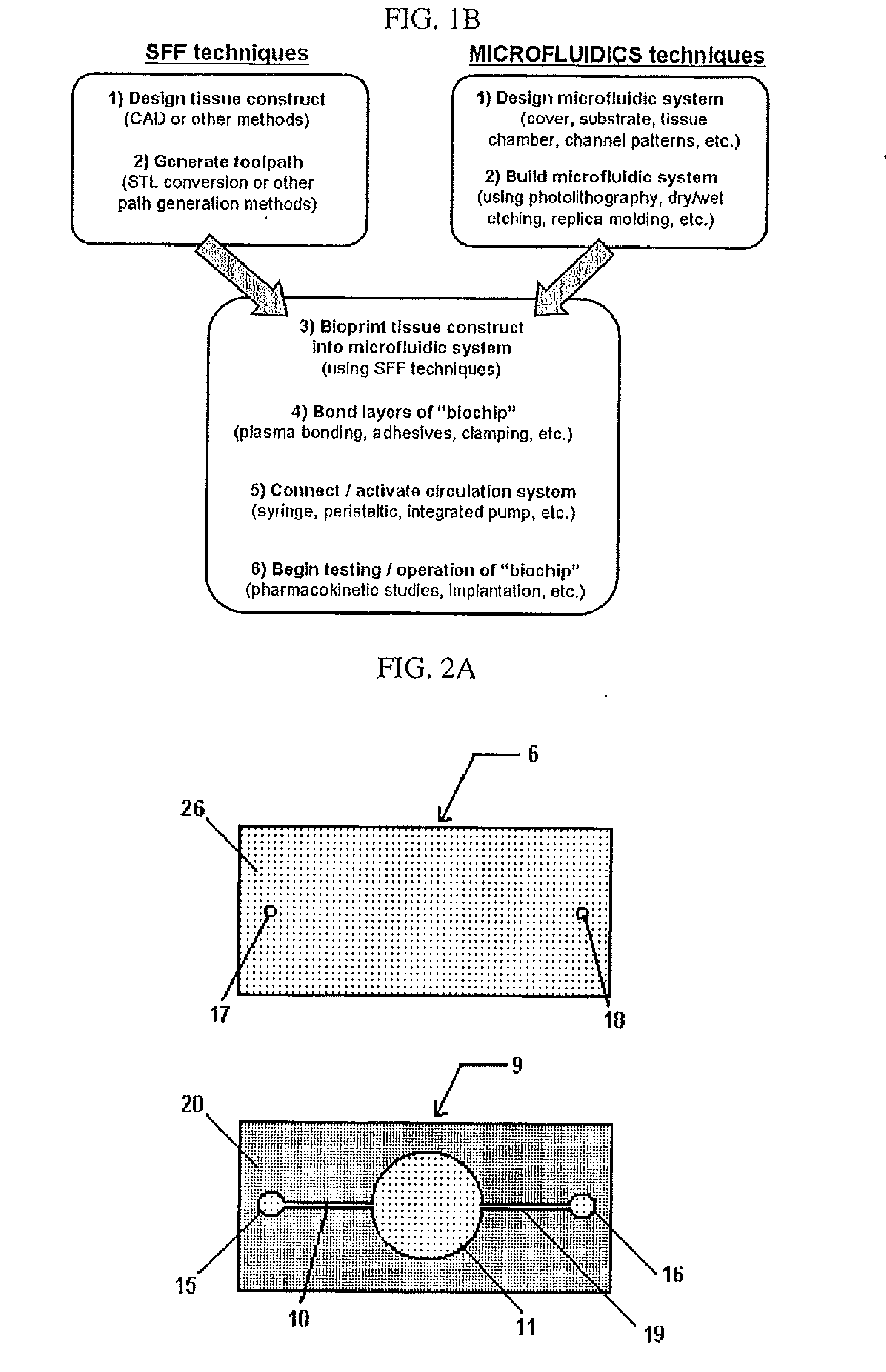
Compositions and Methods for Functionalized Patterning of Tissue Engineering Substrates Including Bioprinting Cell-Laden Constructs for Multicompartment Tissue Chambers
InactiveUS20110136162A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical treatmentDrug metabolism
The present invention relates to microfluidic systems and methods for monitoring or detecting a change in a characteristic of an input substance. Specifically, the invention relates to a model for in vitro pharmacokinetic study and other pharmaceutical applications, as well as other uses including computing, sensing, filtration, detoxification, production of chemicals and biomolecules, testing cell / tissue behavior, toxicology, drug metabolism, drug screening, drug discovery, and implantation into a subject. The present invention also relates to systems and methods of a microplasm functionalized surface patterning of a substrate. The present invention represents an improvement over existing plasma systems used to modify the surface of a substrate, as the present invention creates surface patterning without the use of a mask, stamp or a chemical treatment.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
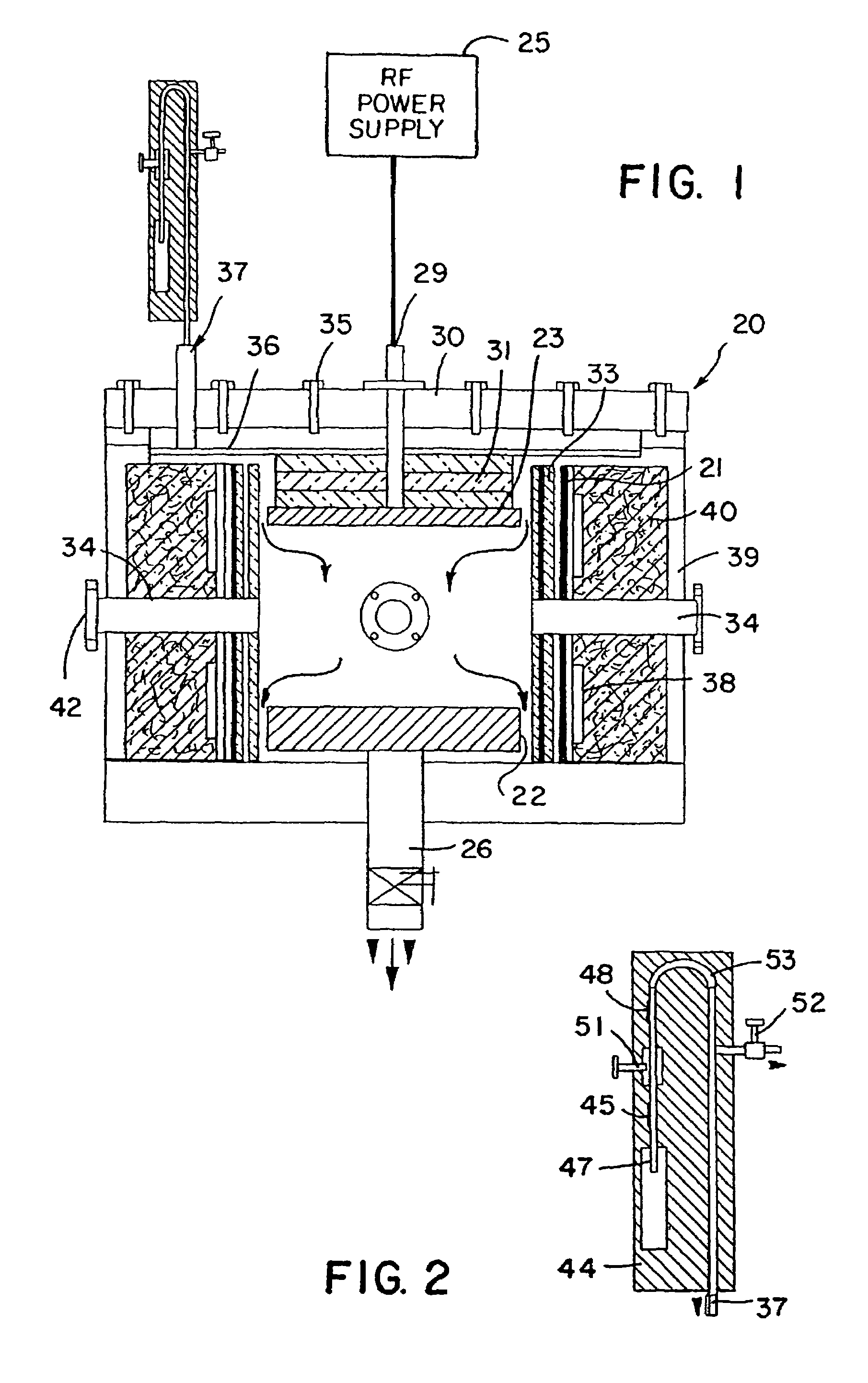
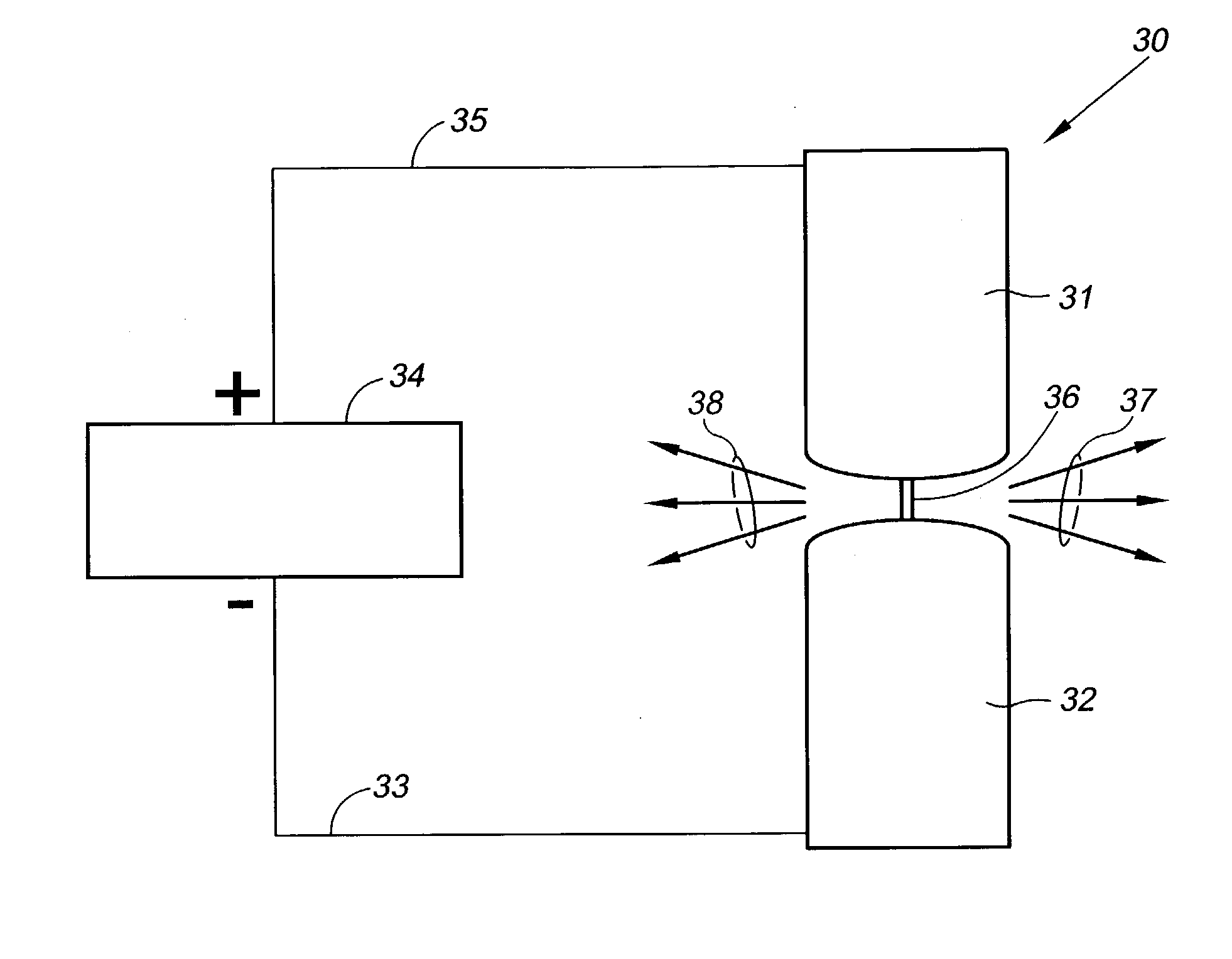
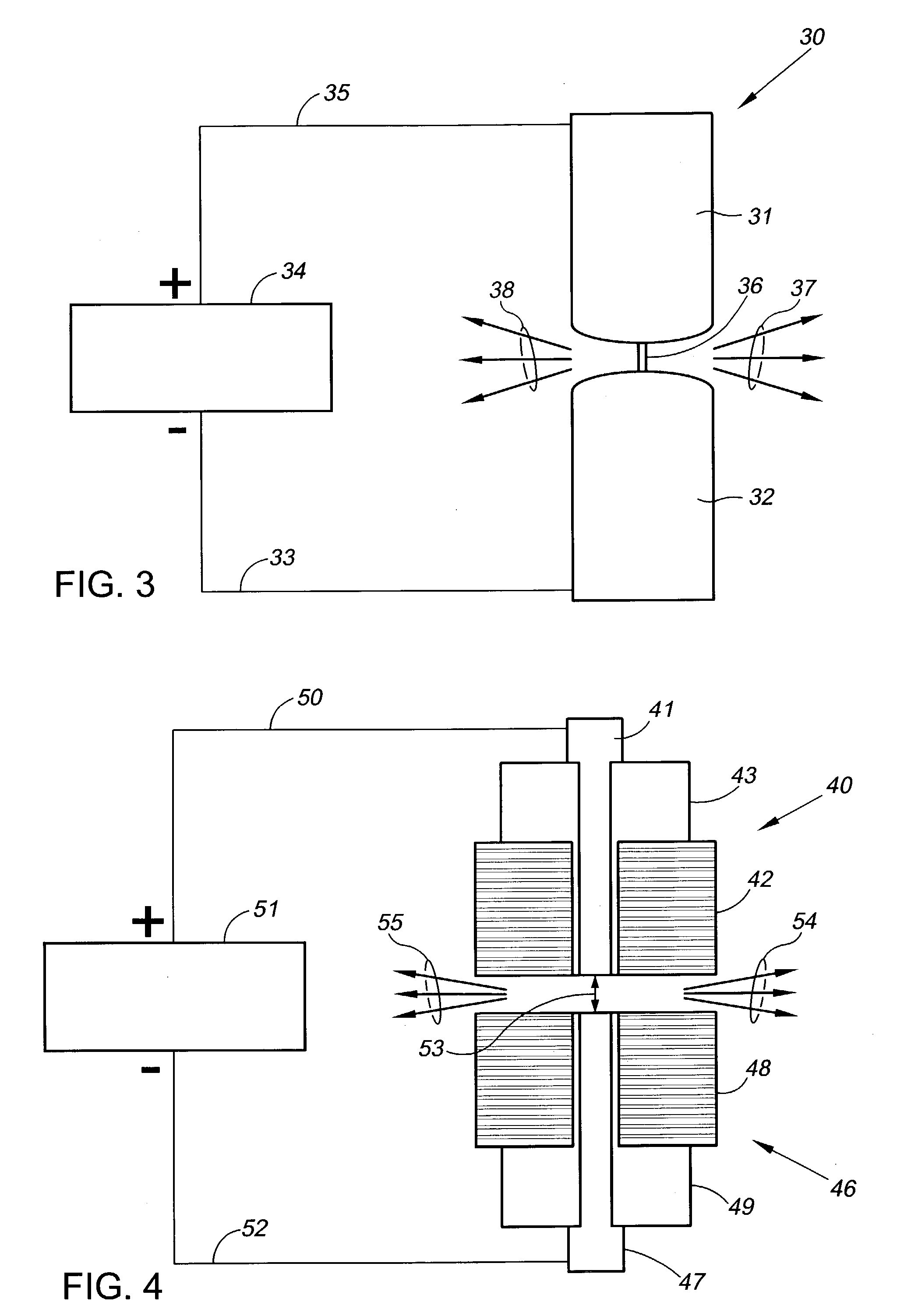
Method and device for creating a micro plasma jet
ActiveUS20060028145A1Reduce the possibilityIncrease electron densityElectric arc lampsArc welding apparatusDielectricPlasma jet
A microhollow cathode discharge assembly capable of generating a low temperature, atmospheric pressure plasma micro jet is disclosed. The microhollow assembly has at two electrodes: an anode and a cathode separated by a dielectric. A microhollow gas passage is disposed through the three layers, preferably in a taper such that the area at the anode is larger than the area at the cathode. When a potential is placed across the electrodes and a gas is directed through the gas passage into the anode and out the cathode, along the tapered direction, then a low temperature micro plasma jet can be created at atmospheric pressure.
Owner:MOHAMED ABDEL ALEAM H +2
In situ sterilization and decontamination system using a non-thermal plasma discharge
InactiveUS7192553B2Improve sterilization efficiencyReduce healthMechanical apparatusGas treatmentElectricityParticulates
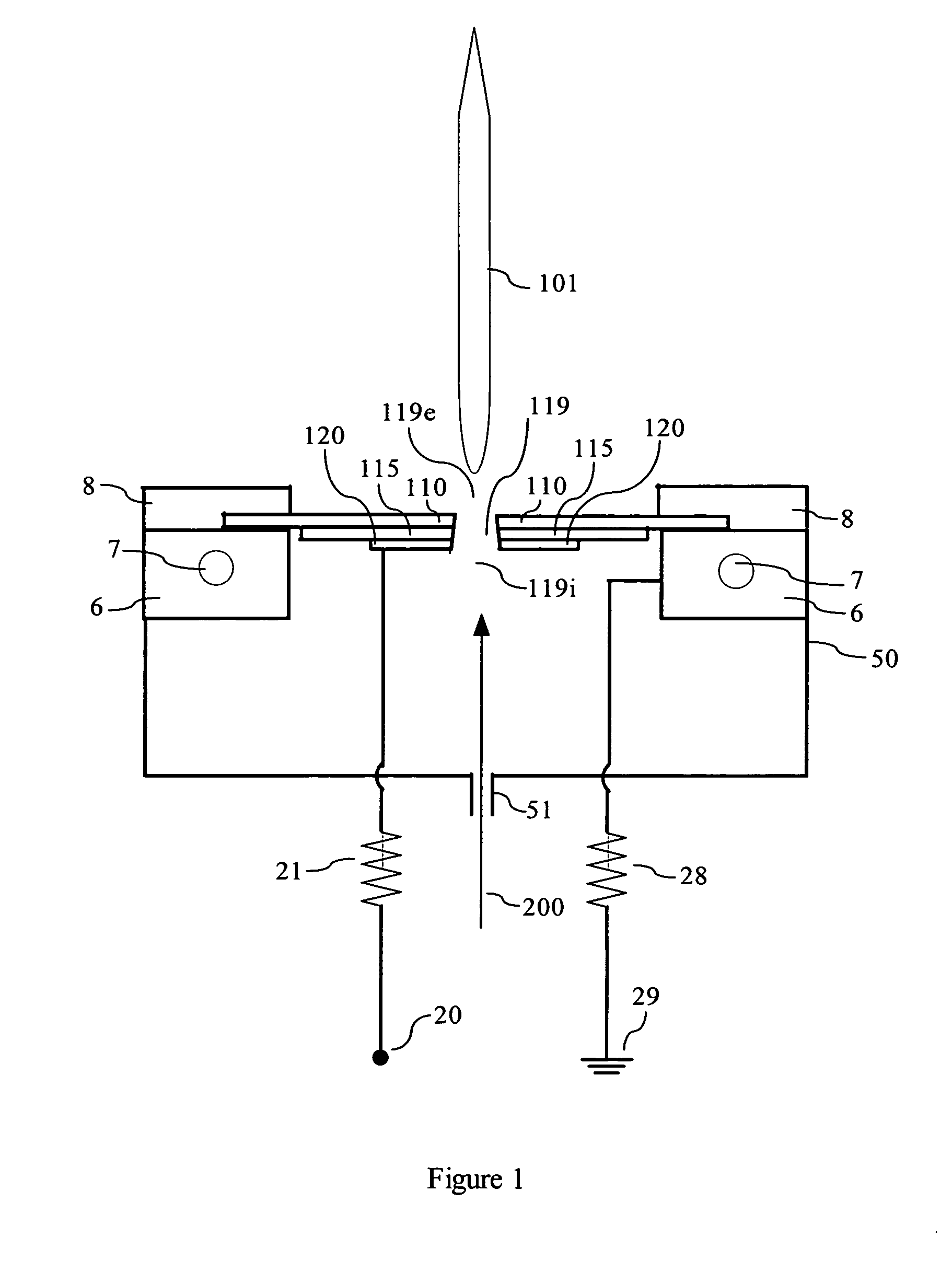
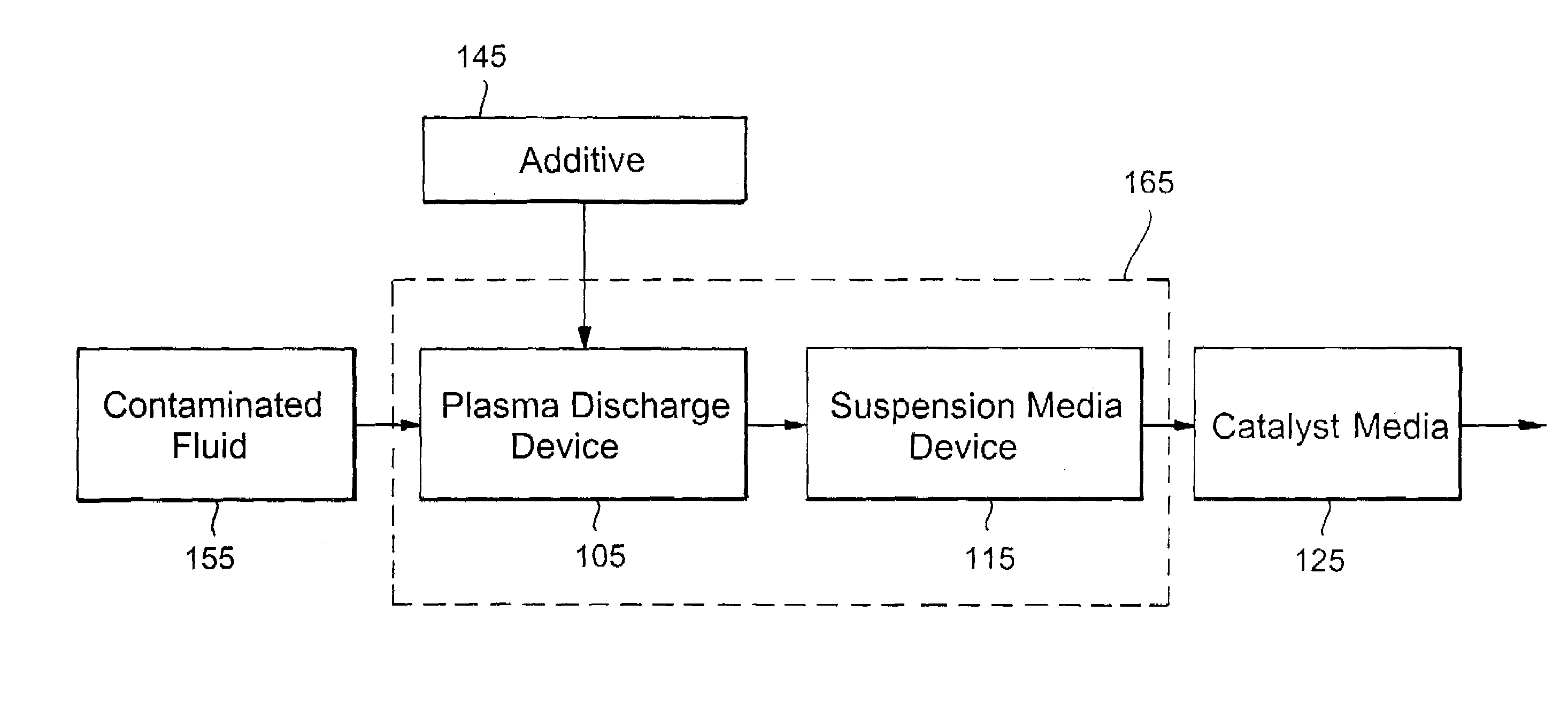
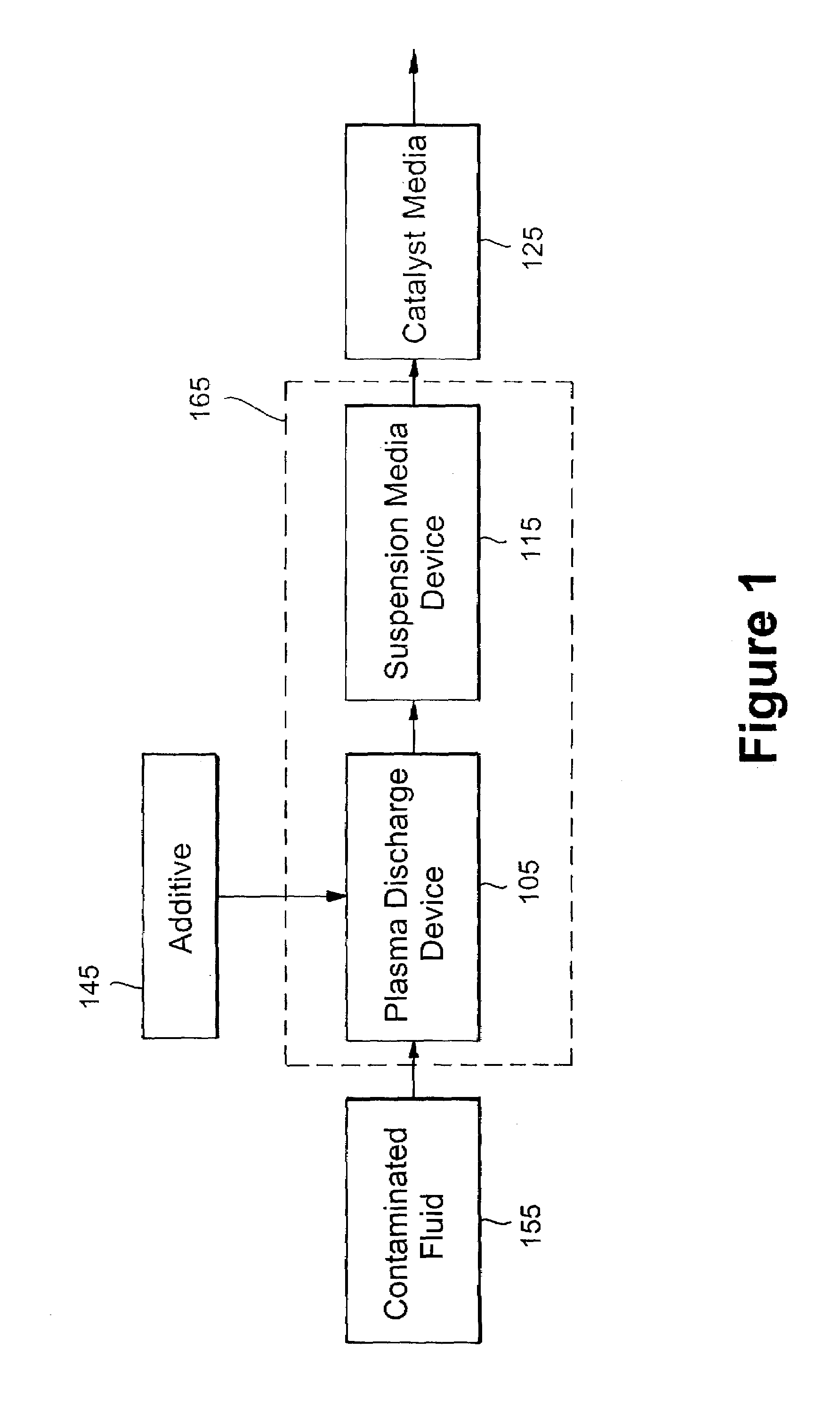
A sterilization and decontamination system in which a non-thermal plasma discharge device is disposed upstream of a suspension media (e.g., a filter, electrostatic precipitator, carbon bed). The plasma discharge device generates a plasma that is emitted through apertures (e.g., capillaries or slits) in the primary dielectric. Plasma generated active sterilizing species when exposed to contaminants or undesirable particulate matter is able to deactivate or reduce such matter in contaminated fluid stream and / or on objects. Thus, the undesirable contaminants in the fluid to be treated are first reduced during their exposure to the plasma generated active sterilizing species in the plasma region of the discharge device. Furthermore, the plasma generated active sterilizing species are carried downstream to suspension media and upon contact therewith deactivate the contaminants collected on the suspension media itself. Advantageously, the suspension media may be cleansed in situ. To increase the sterilization efficiency an additive, free or carrier gas (e.g., alcohol, water, dry air) may be injected into the apertures defined in the primary dielectric. These additives increase the concentration of plasma generated active sterilizing agents while reducing the byproduct of generated undesirable ozone pollutants. Downstream of the filter the fluid stream may be further treated by being exposed to a catalyst media or additional suspension media to further reduce the amount of undesirable particulate matter.
Owner:PLASMASOL CORP +1
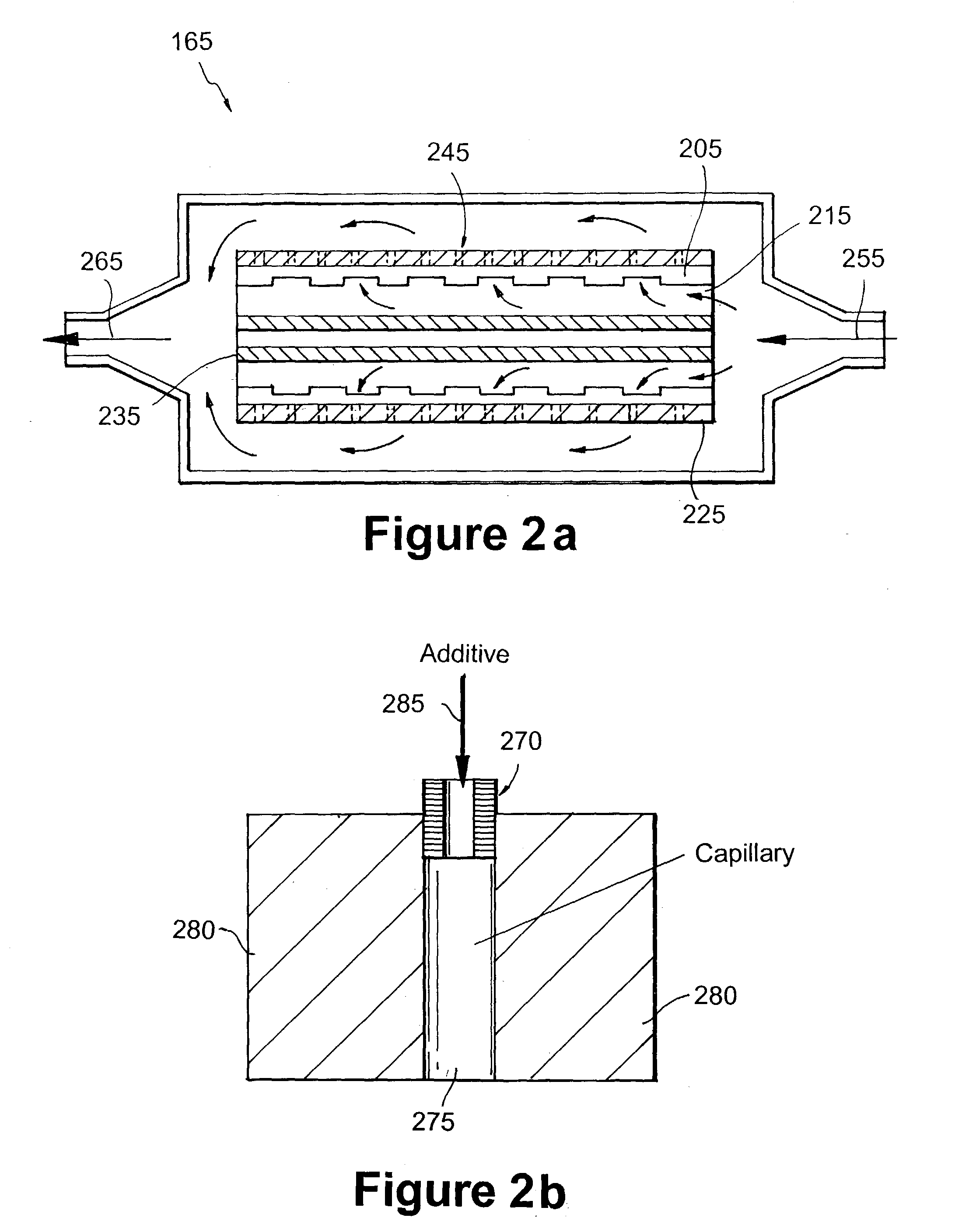
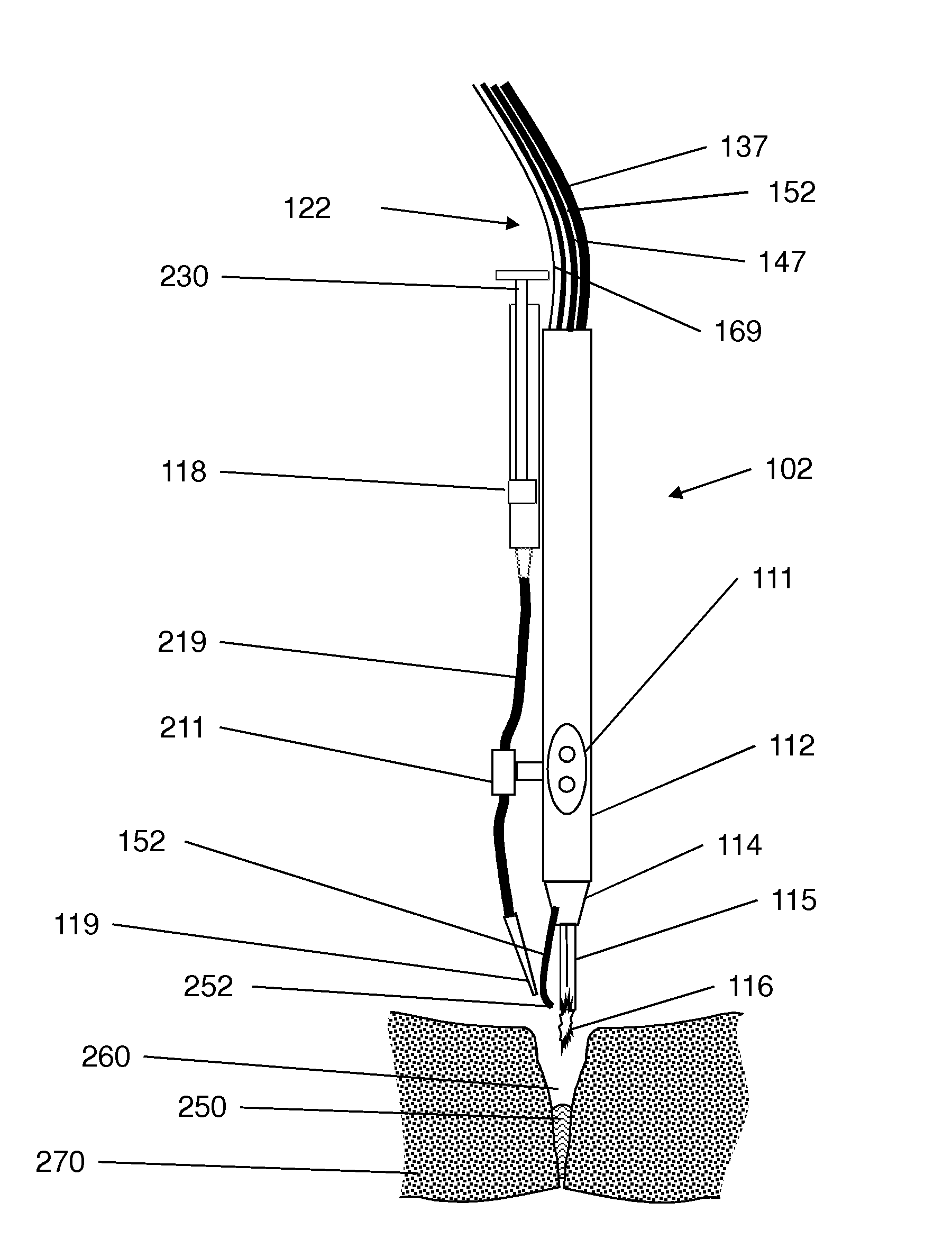
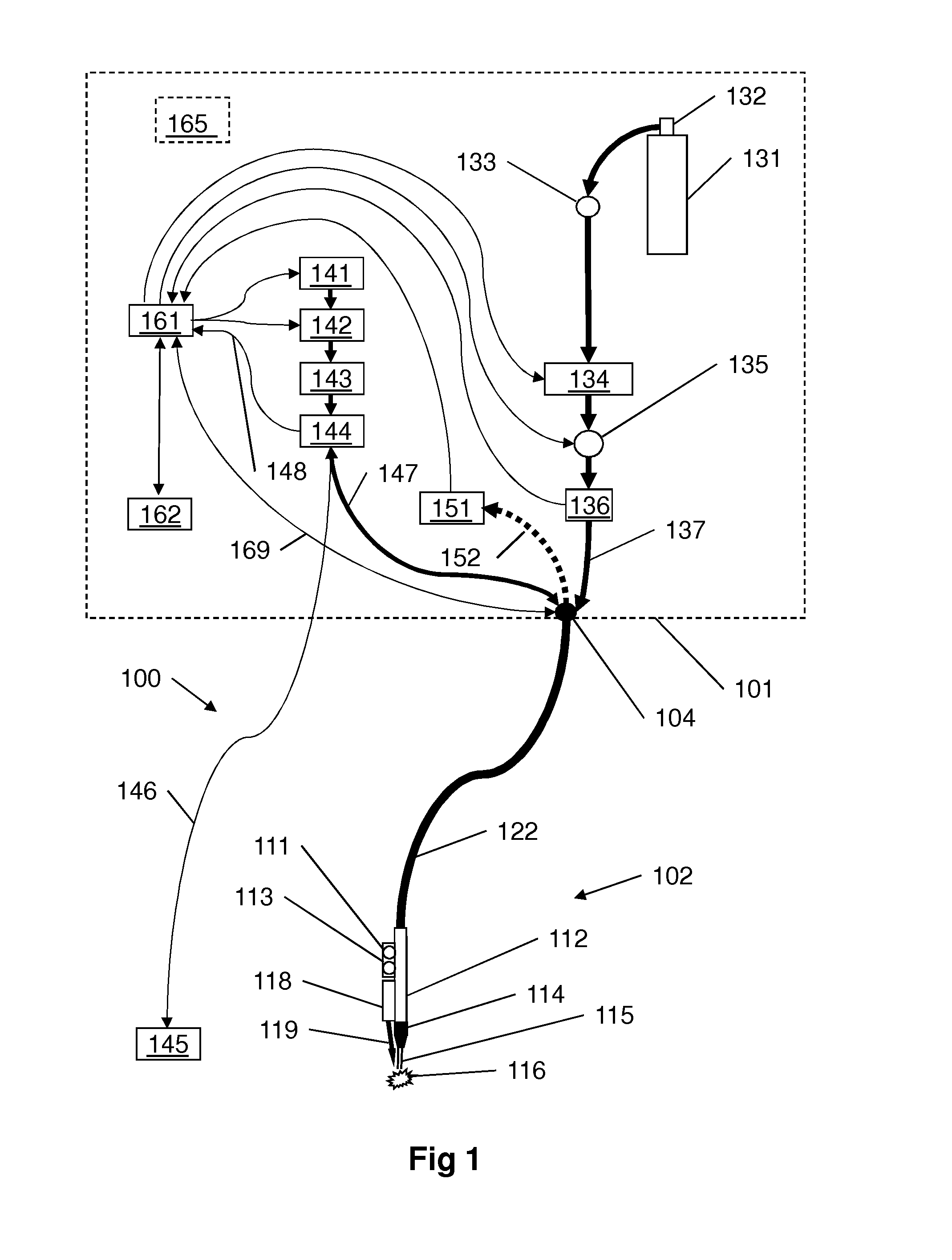
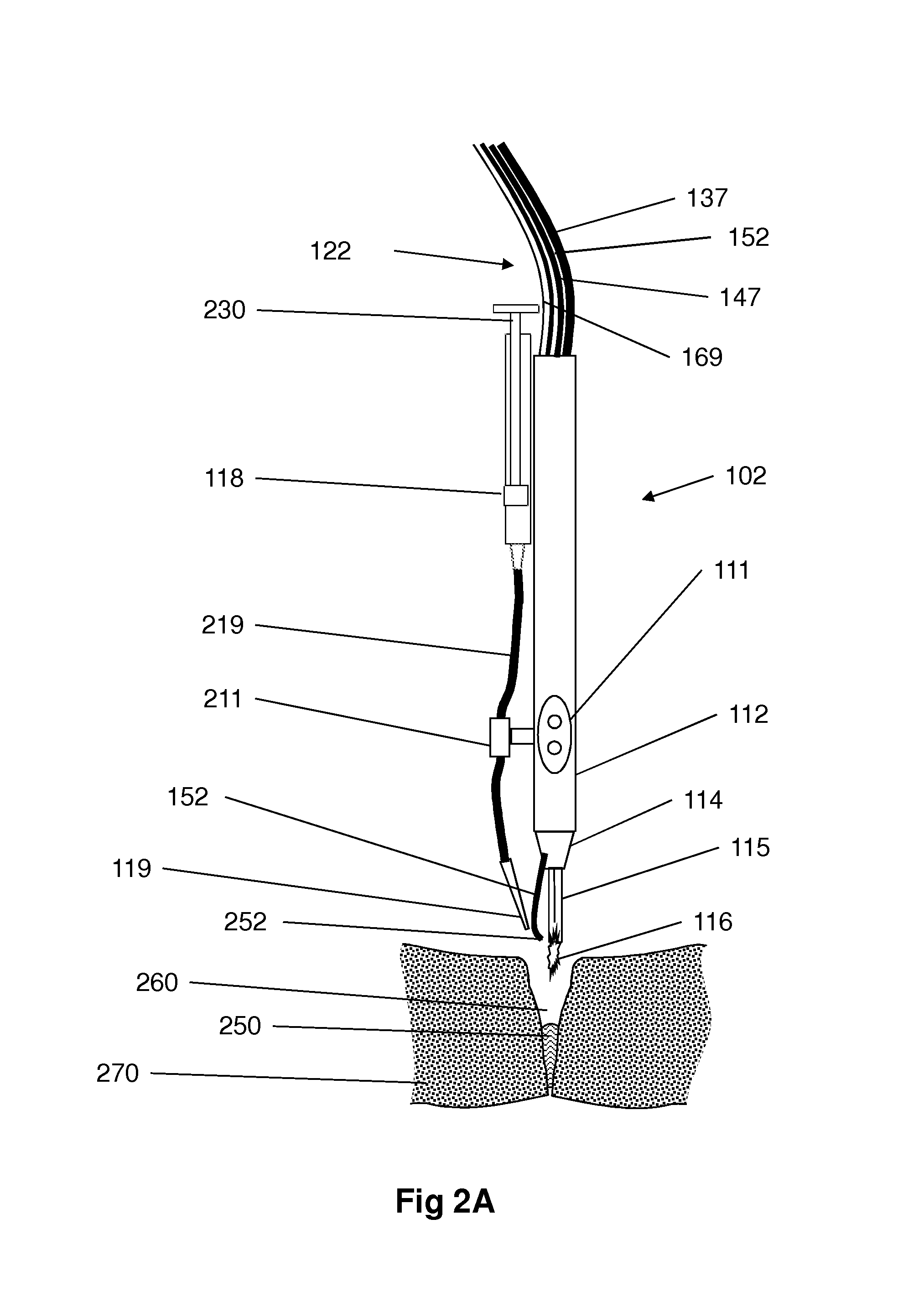
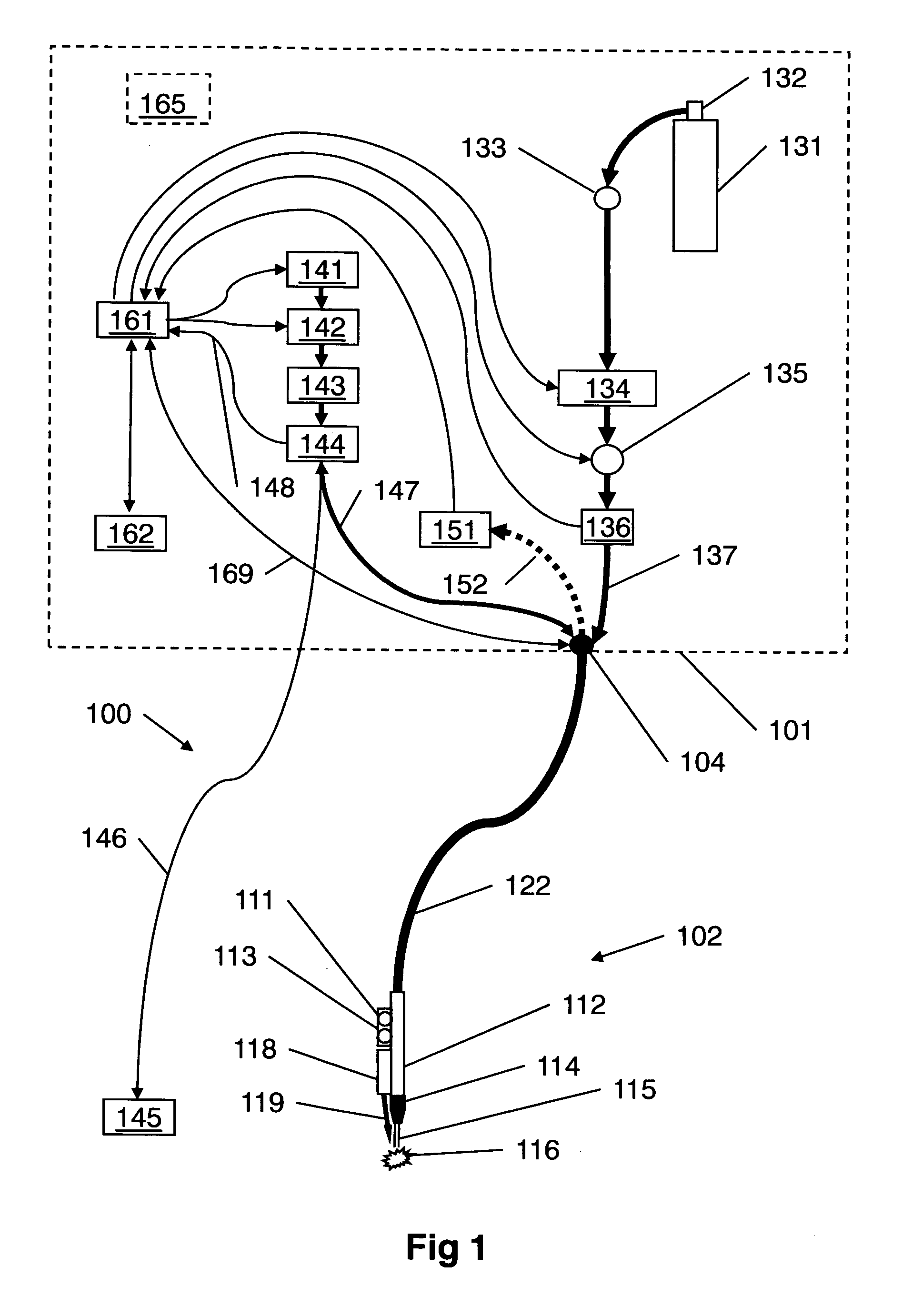
Tissue welding using plasma
A medical device (100) for tissue welding is provided that comprises at least one processor (161) configured to regulate cold plasma production in a plasma head (102) by controlling an RF power source (141) to supply RF plasma-producing power to the plasma head.
Owner:IONMED
Plasma-enhanced functionalization of carbon-containing substrates
ActiveUS7276283B2Improve environmental safetyLow costMaterial nanotechnologyLiquid surface applicatorsPolymeric surfaceDiamond-like carbon
Methods for producing plasma-treated, functionalized carbon-containing surfaces are provided. The methods include the steps of subjecting a carbon-containing substrate to a plasma to create surface active sites on the surface of the substrate and reacting the surface active sites with stable spacer molecules in the absence of plasma. Biomolecules may be immobilized on the resulting functionalized surfaces. The methods may be used to treat a variety of carbon-containing substrates, including polymeric surfaces, diamond-like carbon films and carbon nanotubes and nanoparticles.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Bonding apparatus and method for cleaning tip of a bonding tool
ActiveUS20080023028A1Easy to cleanSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceDevice material
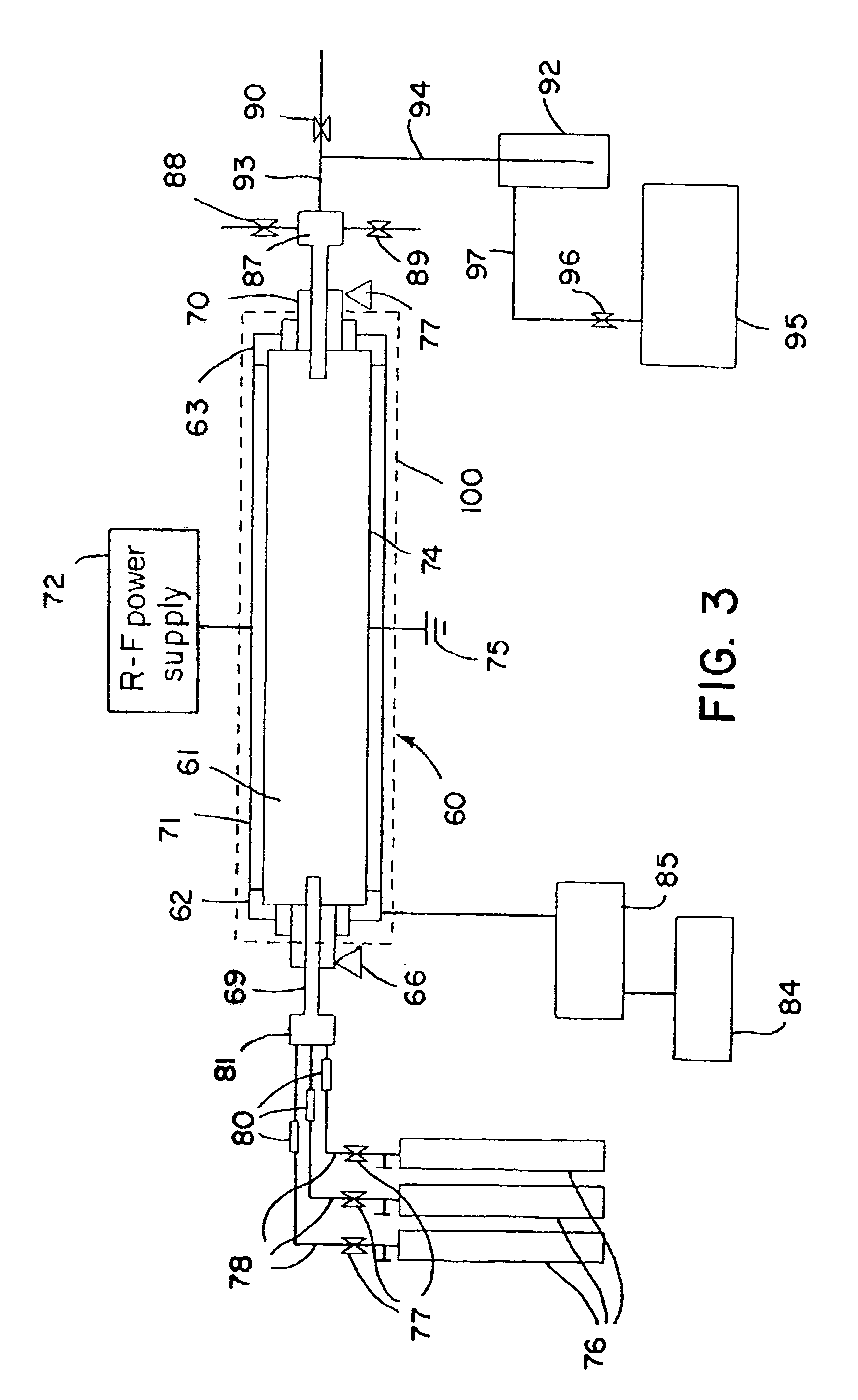
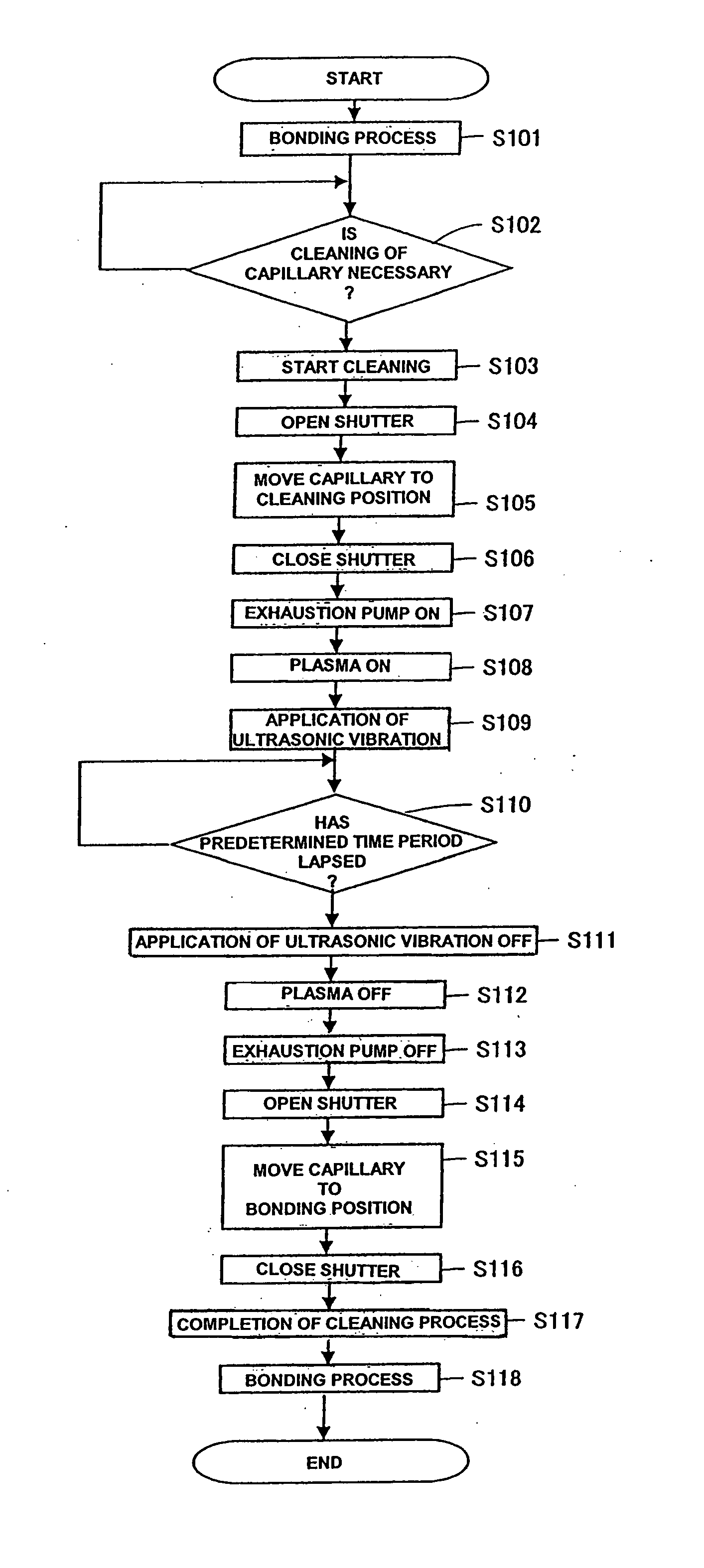
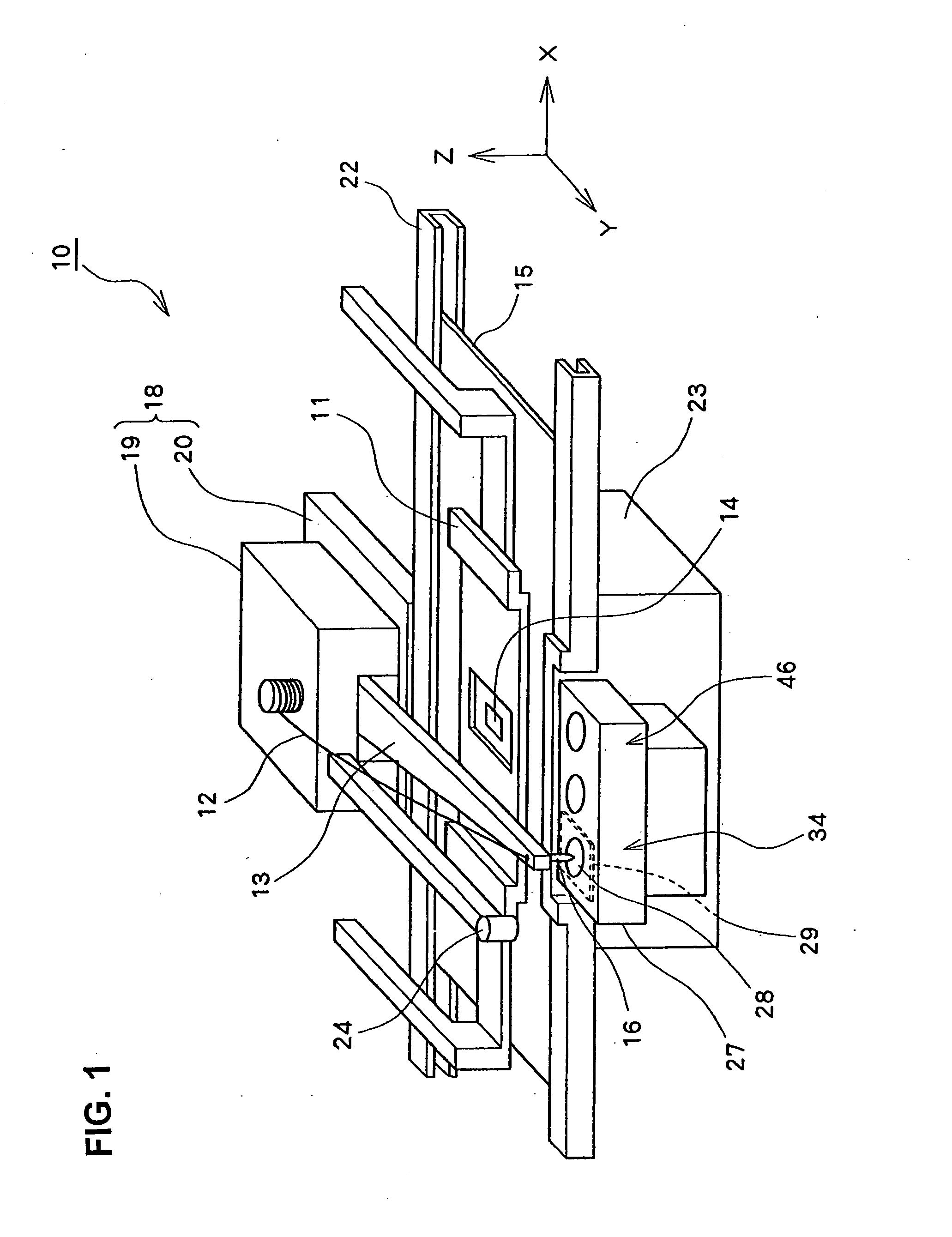
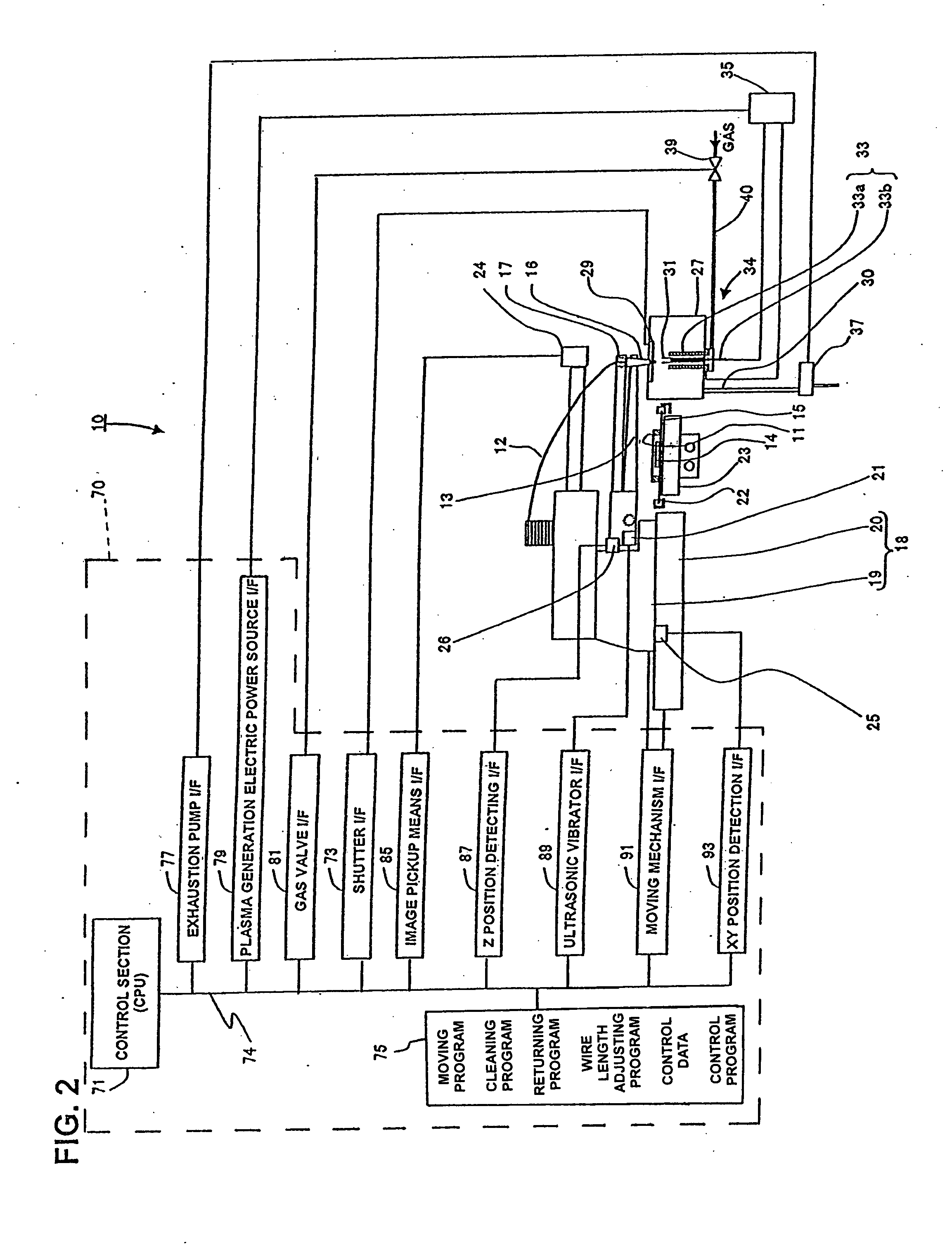
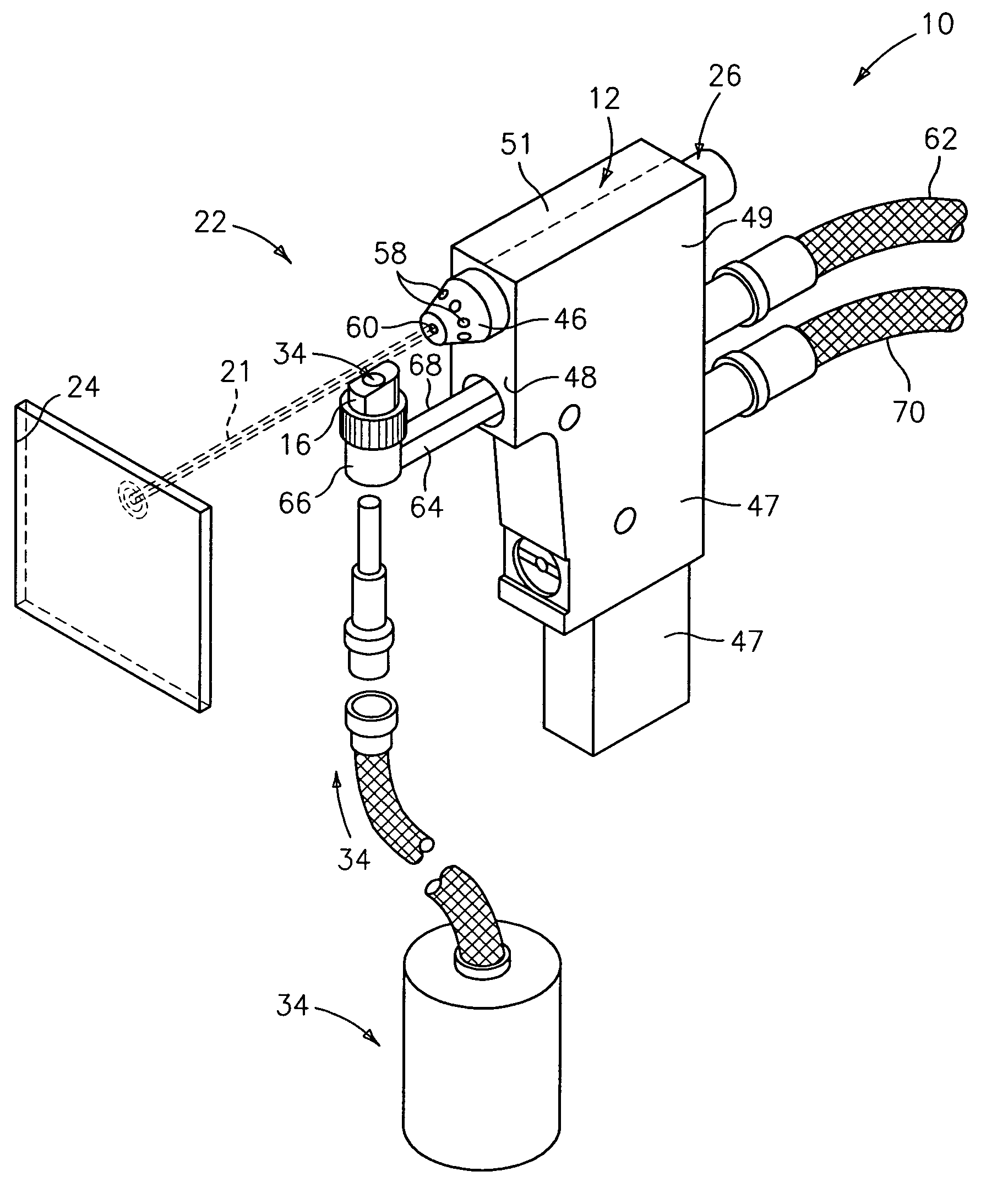
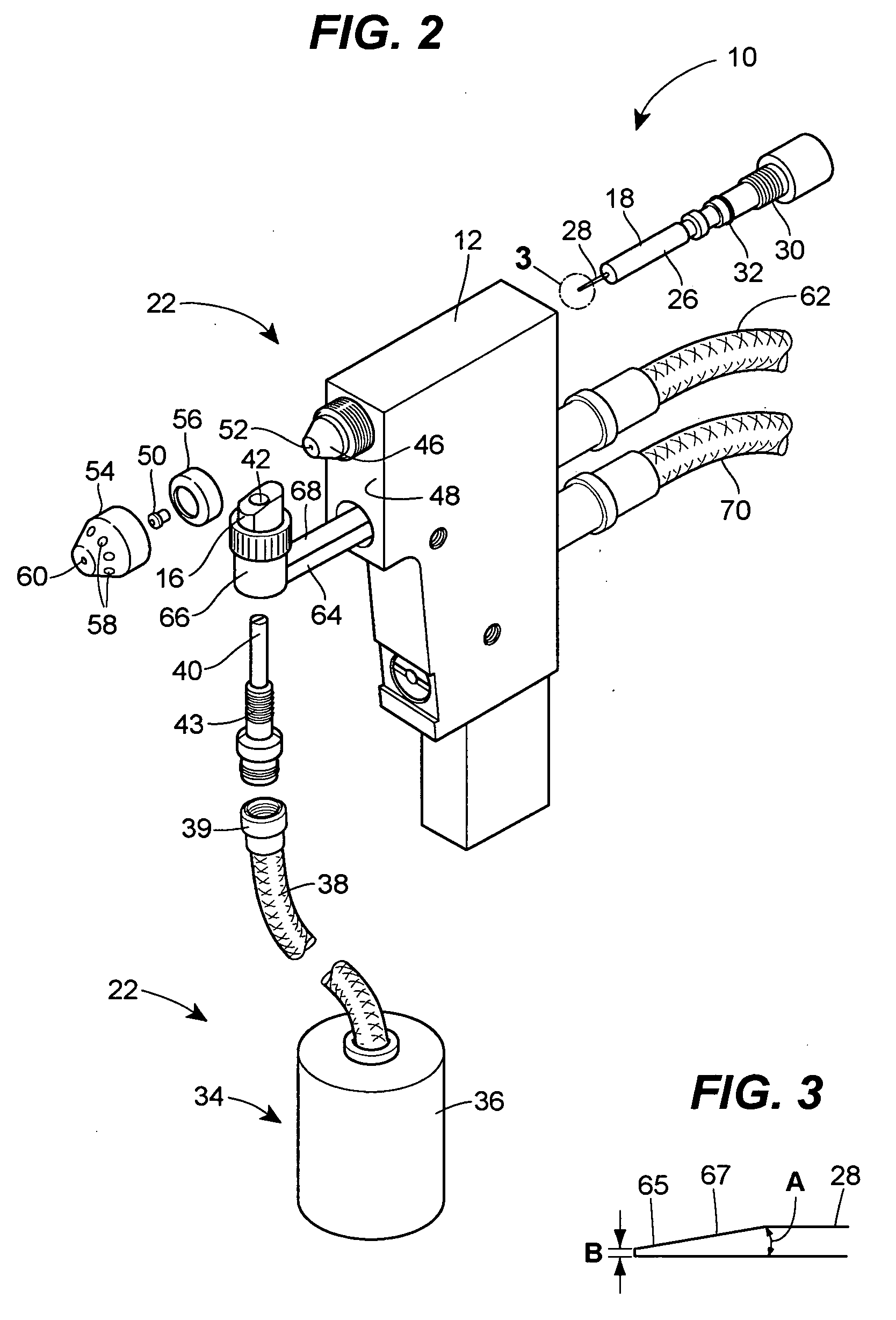
A wire bonding apparatus for manufacturing, for instance, semiconductor devices, including a cleaning case in which a microplasma generating section comprised of a plasma torch, which has a plasma nozzle 38 at the end, and capacitive coupling electrodes composed of an outer electrode and an inner electrode is fixed to the bottom of the cleaning case. The plasma nozzle is provided such that its center line is in alignment with the longitudinal center line of the capillary. Microplasma is ejected from below the capillary to clean its tip within the cleaning case. A shutter is provided on the top of the cleaning case and the wasted gas produced as a result of cleaning is exhausted out of the cleaning case through an exhaustion port of the cleaning case.
Owner:SHINKAWA CO LTD
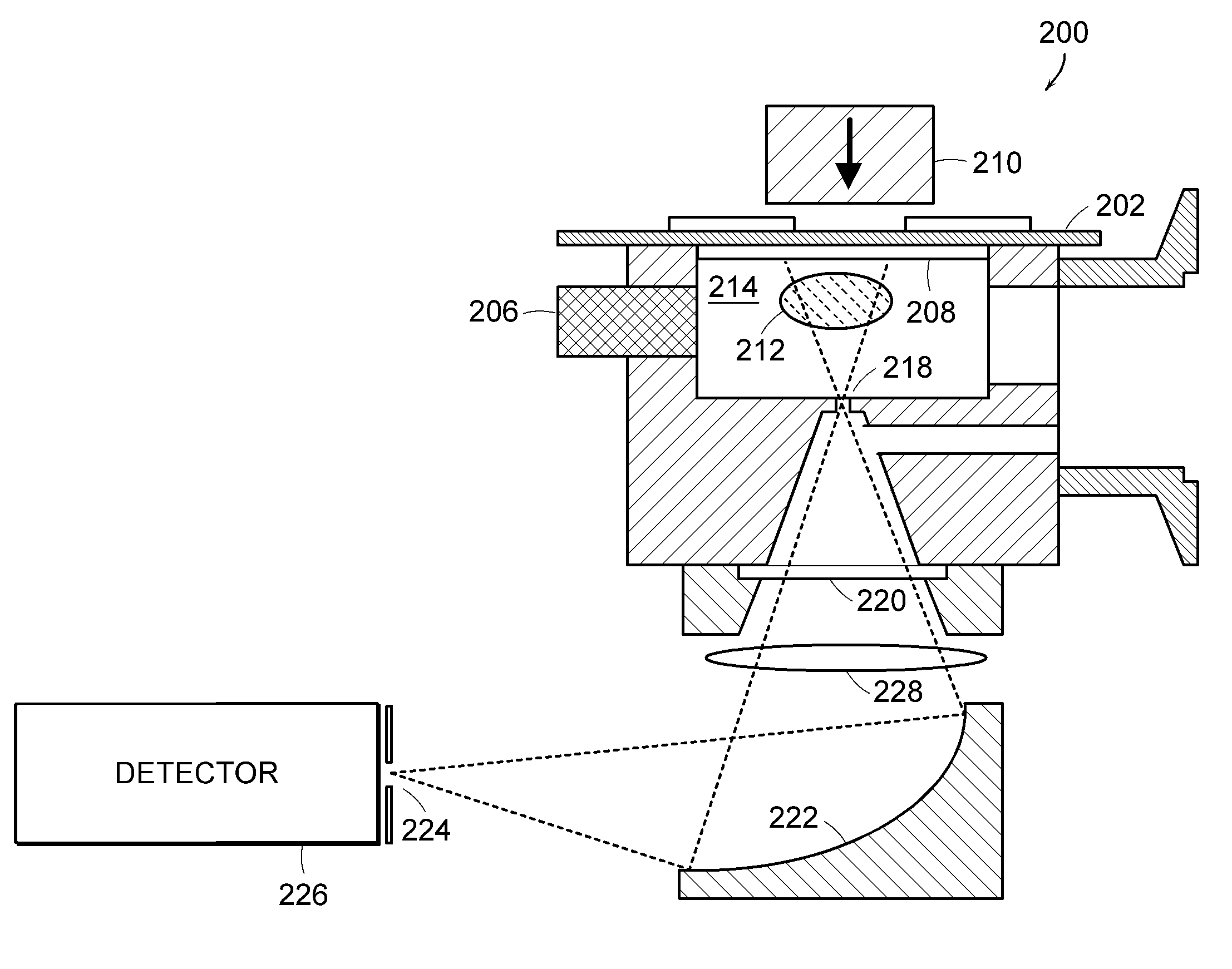
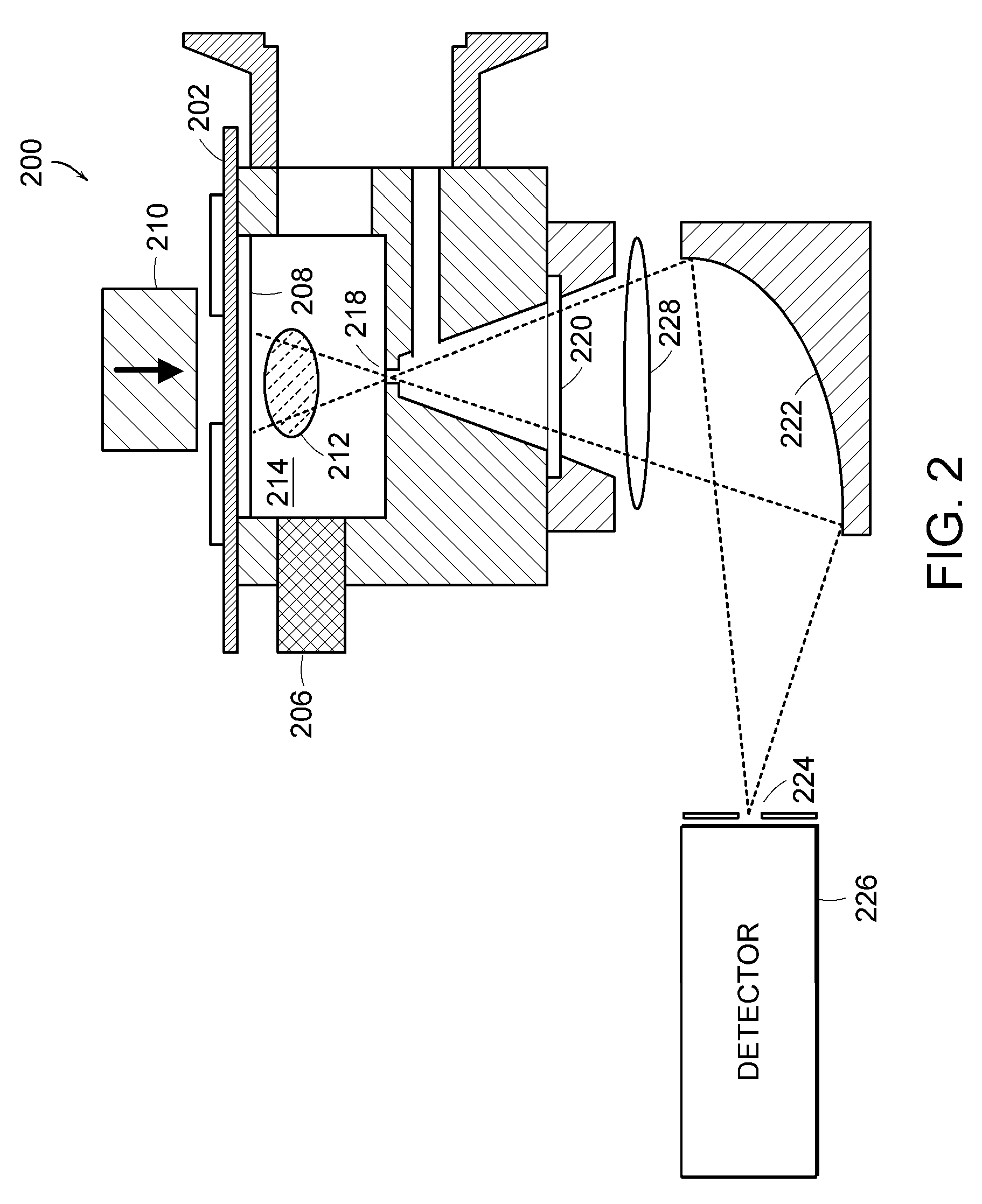
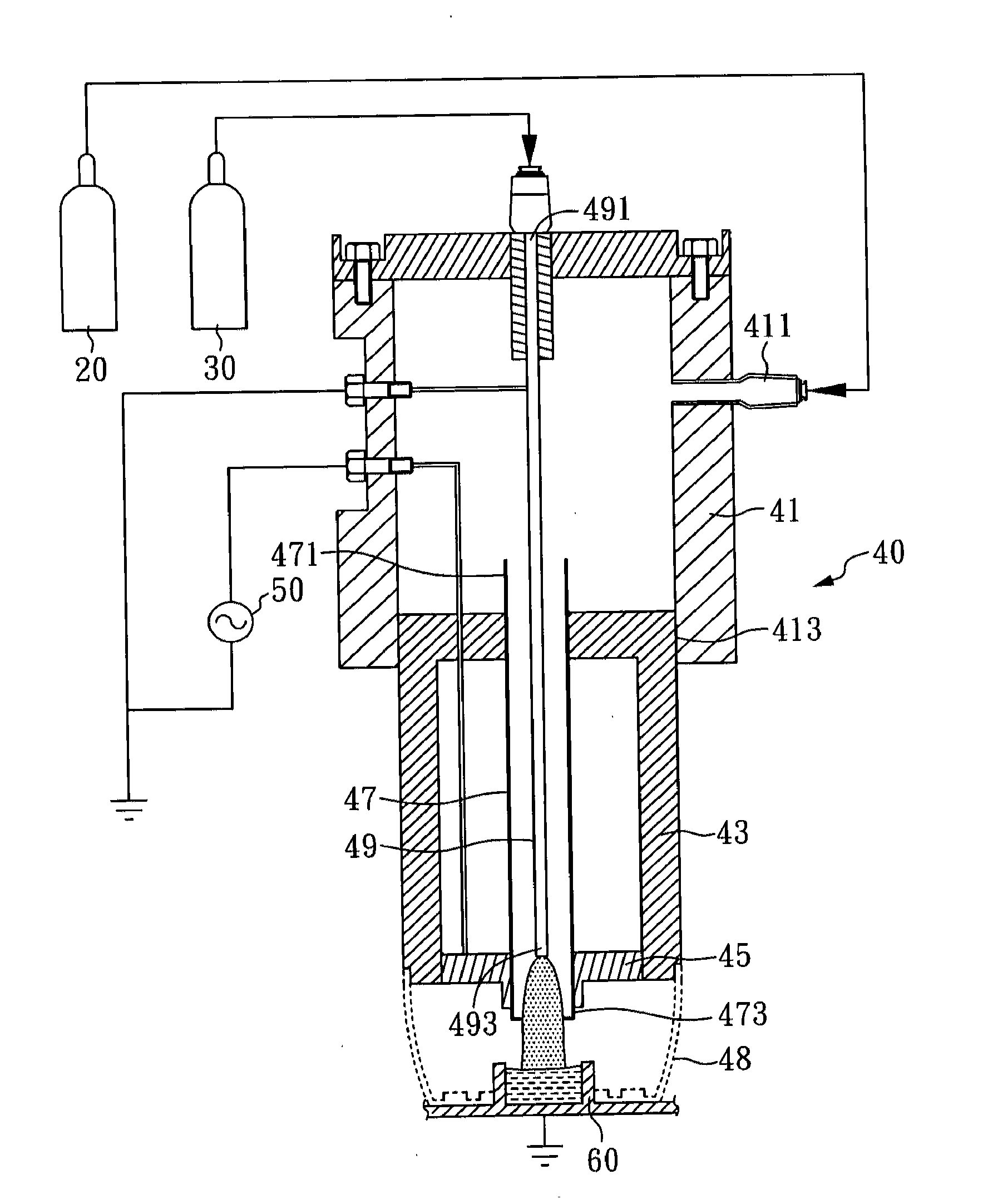
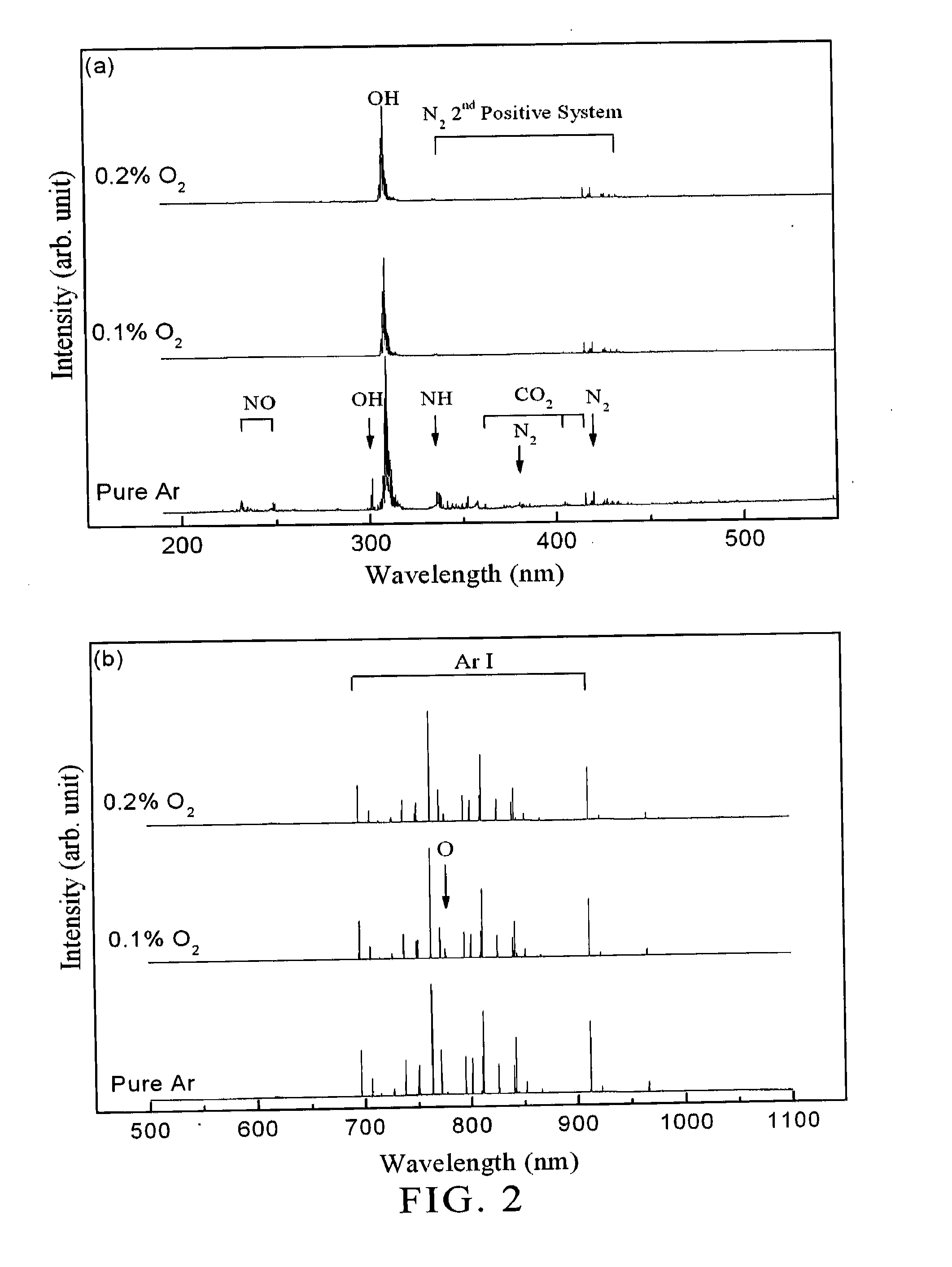
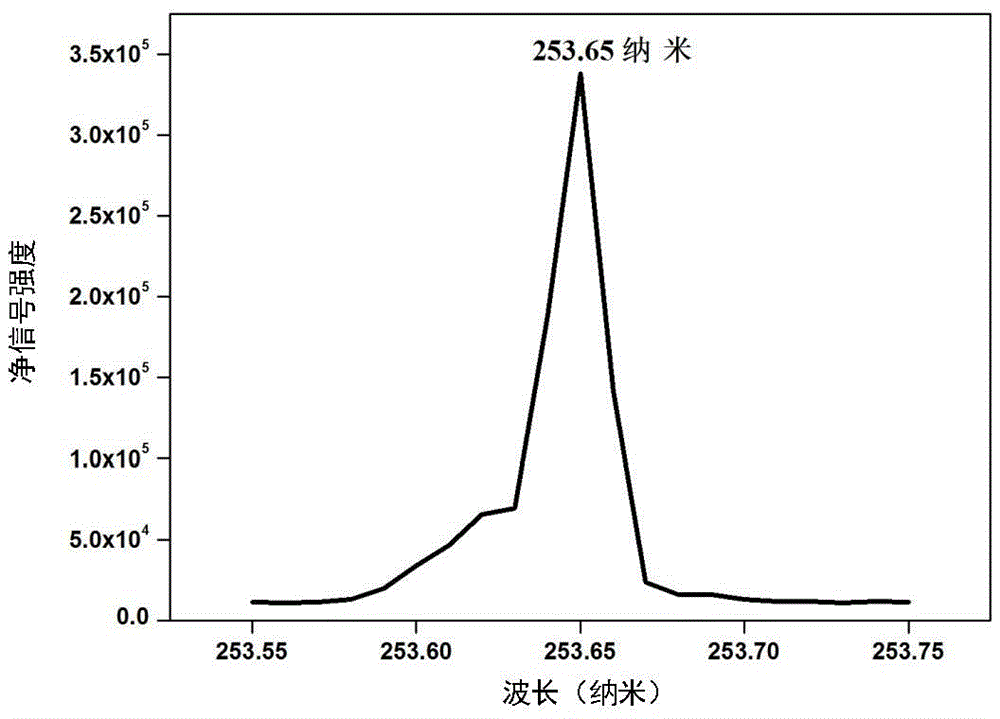
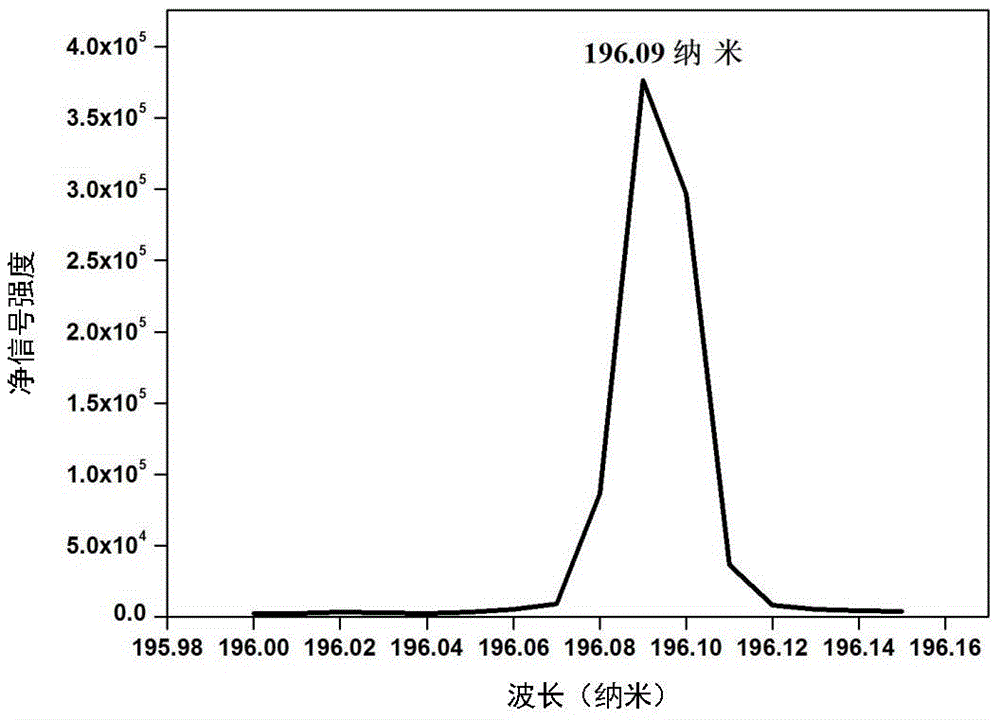
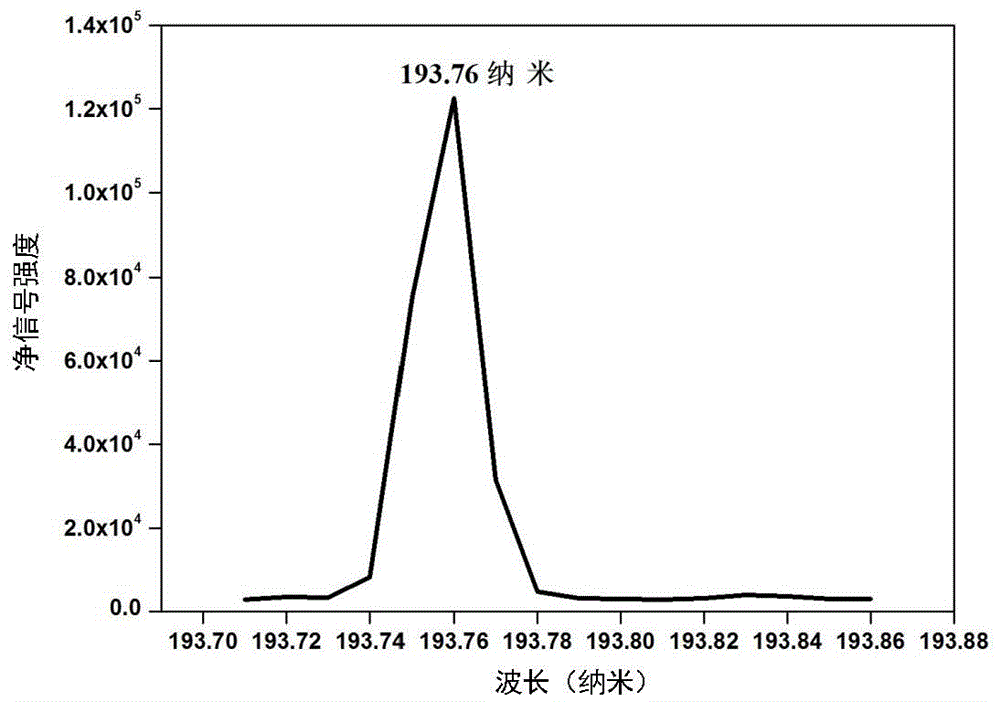
Microplasma emission spectrometer
A microplasma emission spectrometer is described that includes a chamber for confining a sample volume of gas. A microplasma source that includes a resonant antenna structure generates a microplasma in the chamber from the sample volume of gas. A RF power supply provides power to the resonant antenna structure that generates the microplasma from the sample volume of gas. A spectrally sensitive detector is optically coupled to the microplasma. The entrance of the spectrally sensitive detector has dimensions and is positioned so that emissions from at least one-tenth of a total volume of the microplasma are transmitted through the entrance of the spectrally sensitive detector.
Owner:INFICON INC
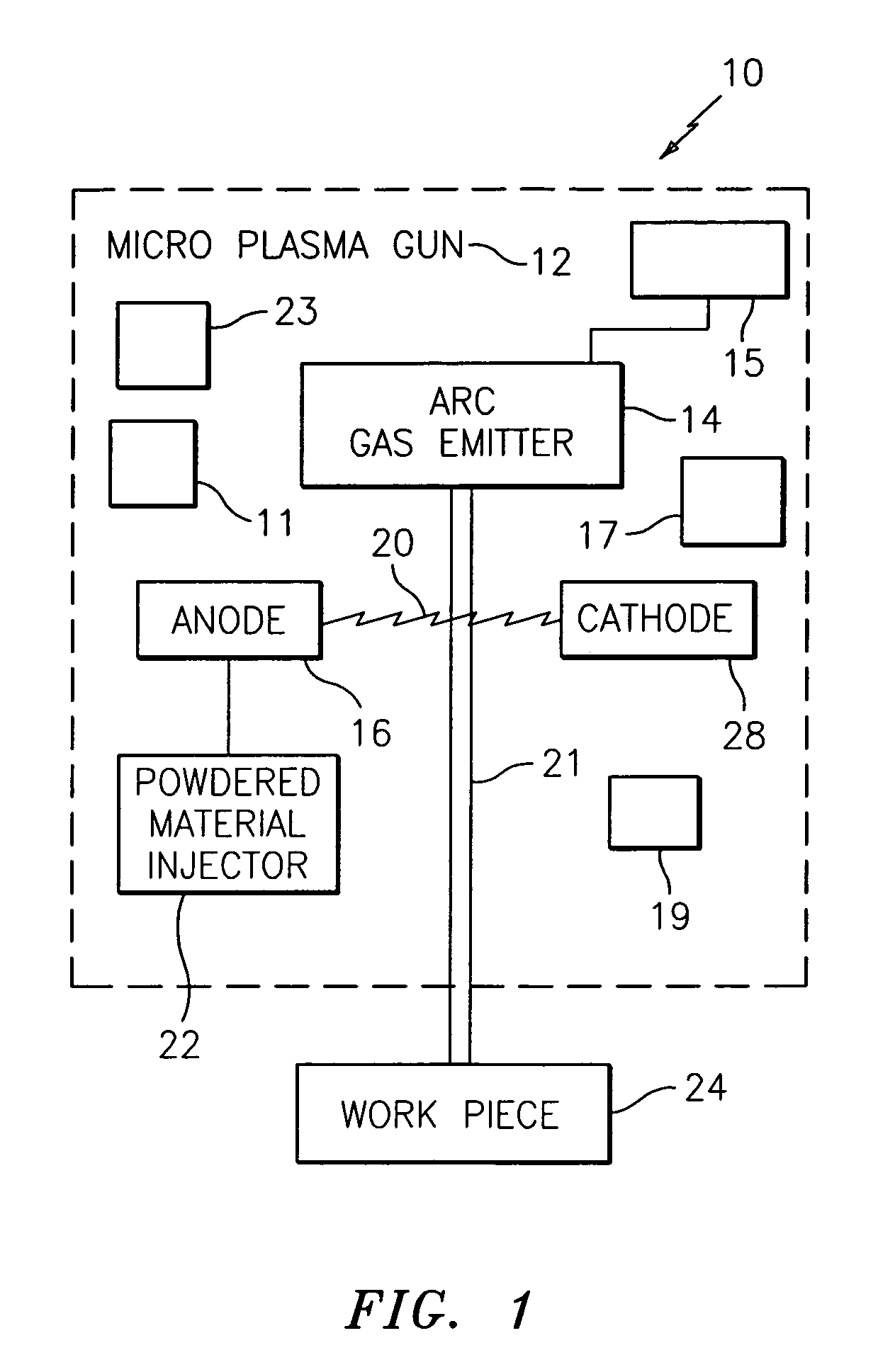
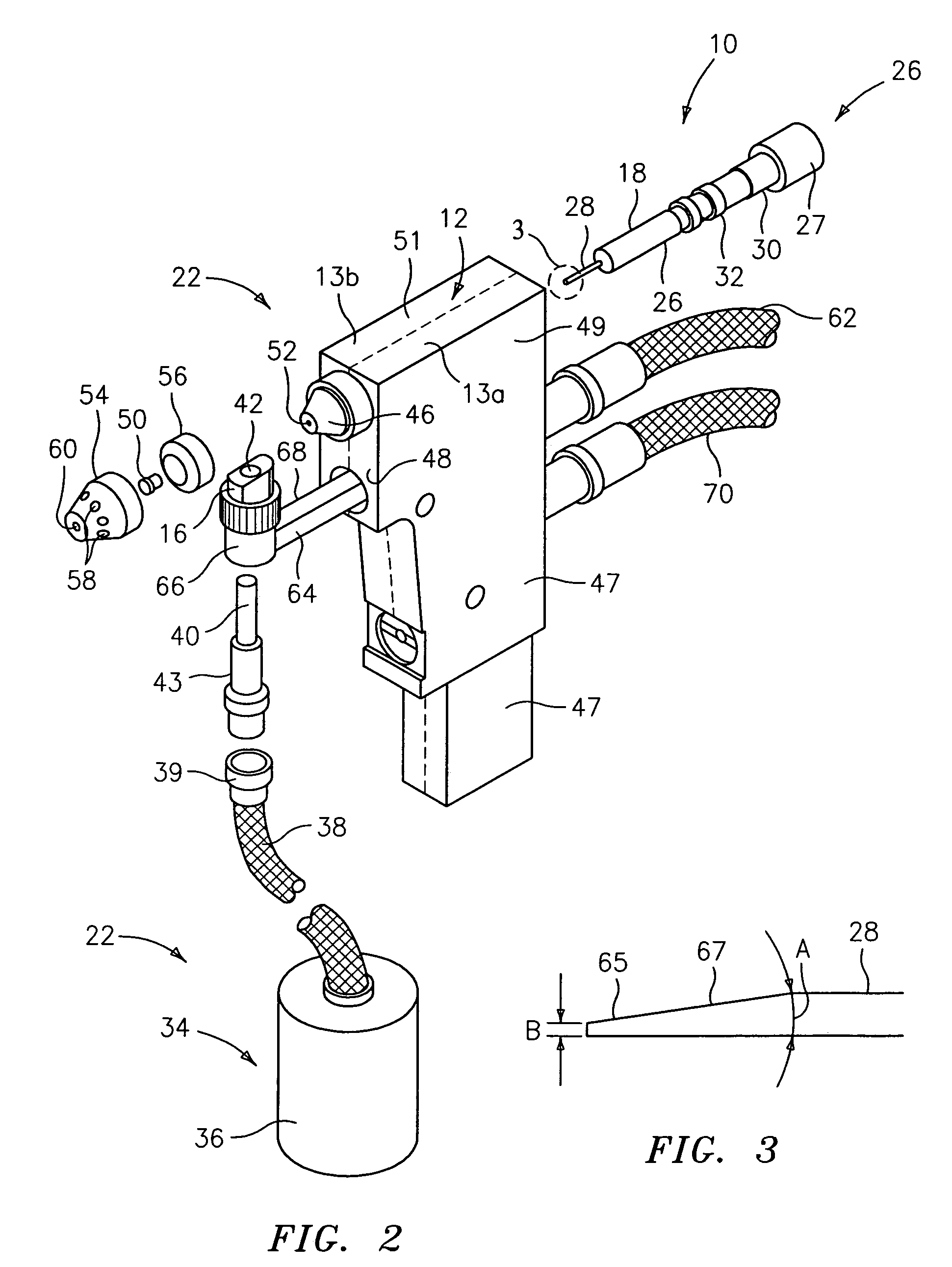
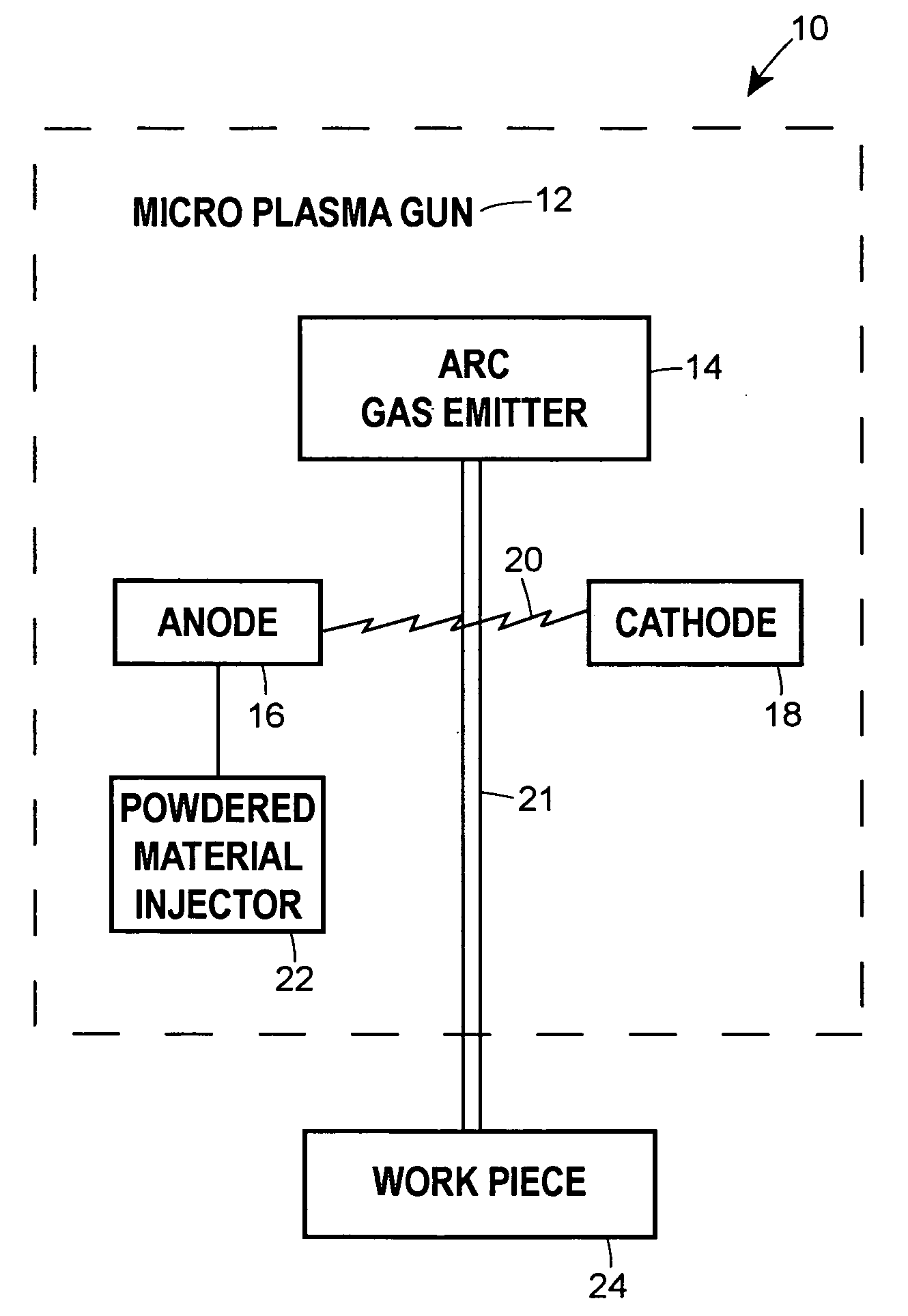
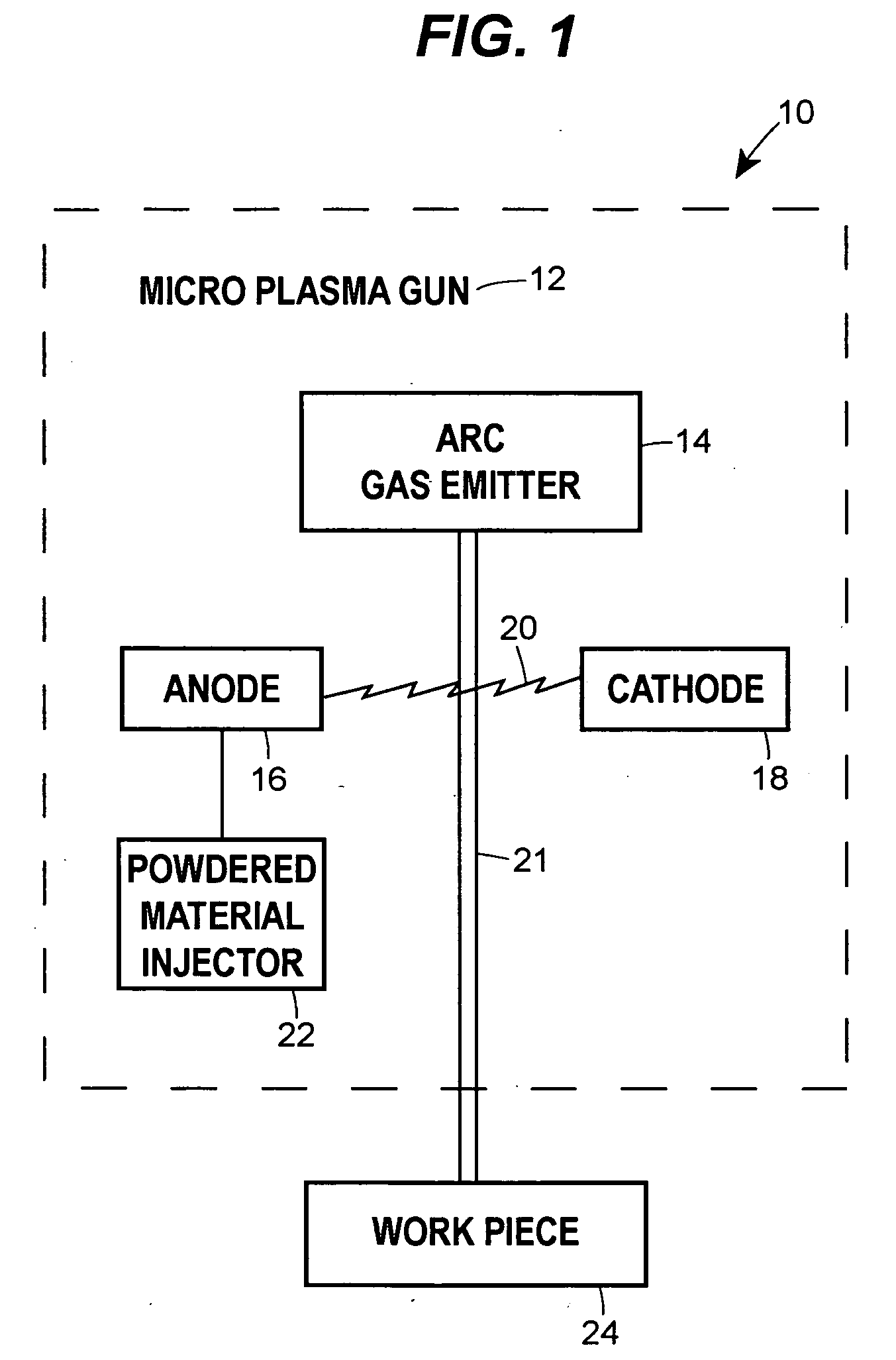
Microplasma spray coating apparatus
A portable, hand-held microplasma spray coating apparatus comprises an anode, a cathode and an arc gas emitter disposed in a housing, and a powder feeding system, a cooling system and a power source connected to the apparatus. The powder feeding system, cooling system and power source are detachably mounted on a mobile platform. The microplasma spray apparatus can be transported to on-site locations in the field to facilitate quick repair work.
Owner:RTX CORP
Plasma spray apparatus
A microplasma spray coating apparatus includes a microplasma apparatus with an anode, cathode, and an arc generator for generating an electric arc between the anode and cathode. An arc gas emitter injects inert gas through the electric arc. The electric arc is operable for ionizing the gas to create a plasma gas stream. A powder injector nozzle extends through the anode and injects powdered material into the plasma stream for transfer to the workpiece.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
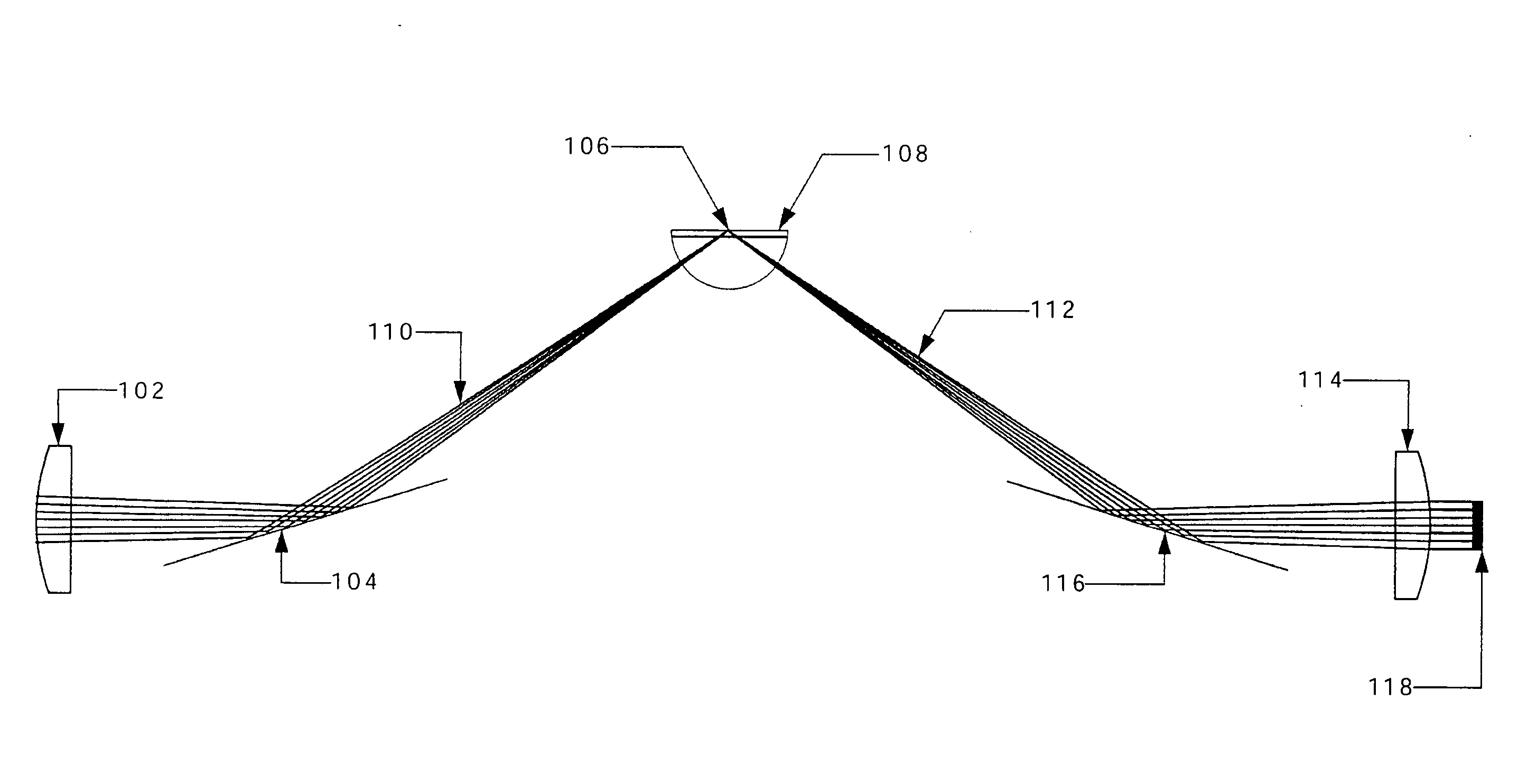
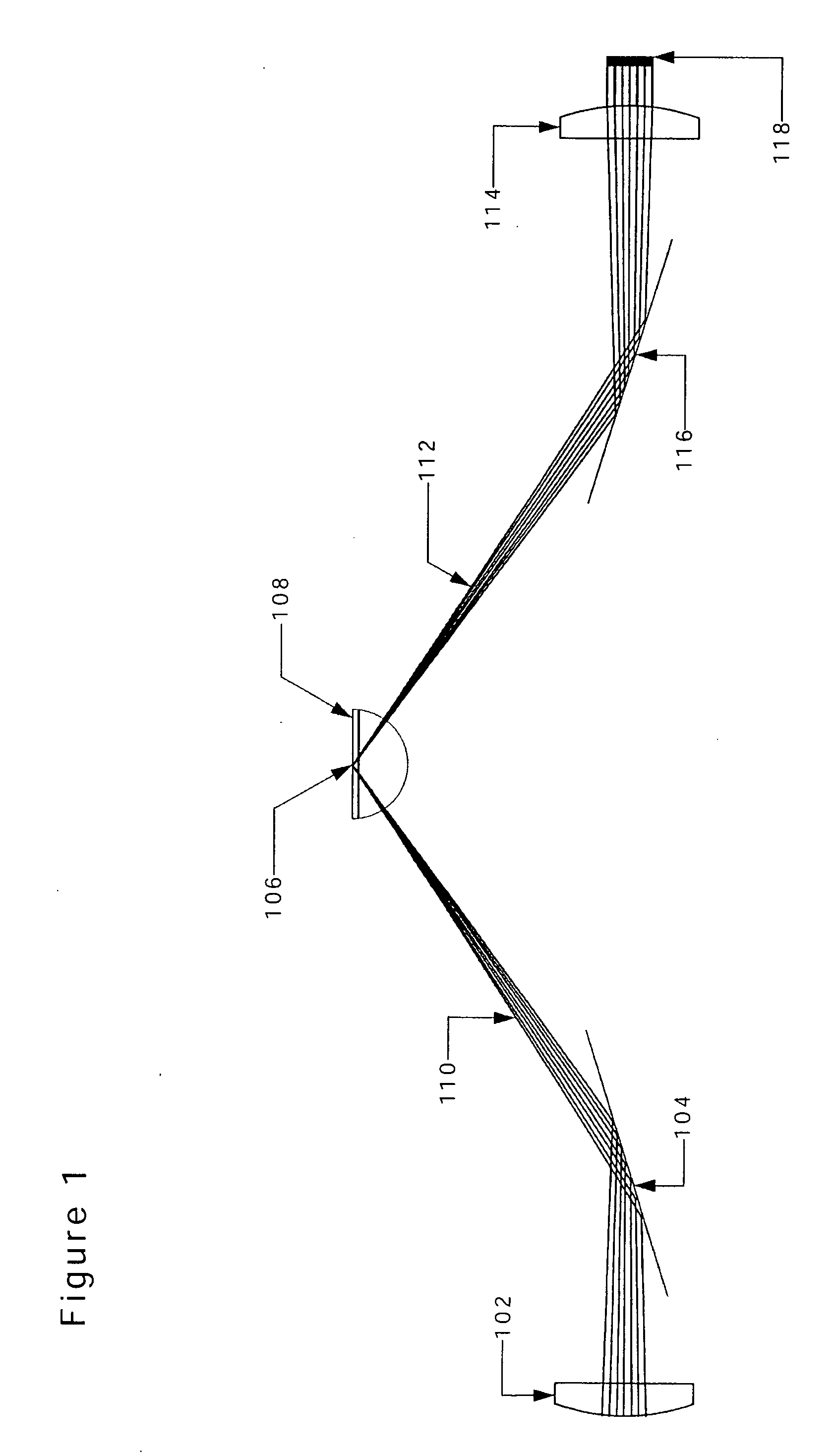
Analytical laser ablation of solid samples for ICP, ICP-MS, and FAG-MS analysis
InactiveUS20090073586A1High sensitivityReduce decreaseMirrorsAnalysis by thermal excitationMolecular analysisPath length
The present invention facilitates improvements in laser ablation of solid samples to be analyzed by an external inductively coupled plasma (ICP) emission spectrometer, ICP / mass-spectrometer (ICP-MS), or flowing afterglow (FAG) mass spectrometer (FAG-MS) for elemental analysis (ICP and ICP-MS) or molecular analysis (FAG-MS). A novel invention mirror-with-hole beam combiner eliminates chromatic aberration in the invention sample view and allows rad-hardening the laser ablation invention for use in a radiation hot cell for analysis of high activity nuclear waste. Many other novel invention rad-hardening attributes facilitate a comprehensive rad-hardened laser ablation system (the world's first). In other embodiments, invention novelties include unusually large homogeneous focused laser spot diameters, unusually long laser objective lens focal length, wide range operationally variable laser path length with built-in re-alignment, operationally variable demagnification ratio and diameter of the focused laser spot, the use of significantly higher powered SMR lasers in a large spot diameter to facilitate high sensitivity bulk analysis of solid samples, a demountable and gravitationally self-sealing stack assembly laser ablation cell, and the world's first auto-samplers (mechanized sample changers) for analytical laser ablation.
Owner:FRY ROBERT C +3
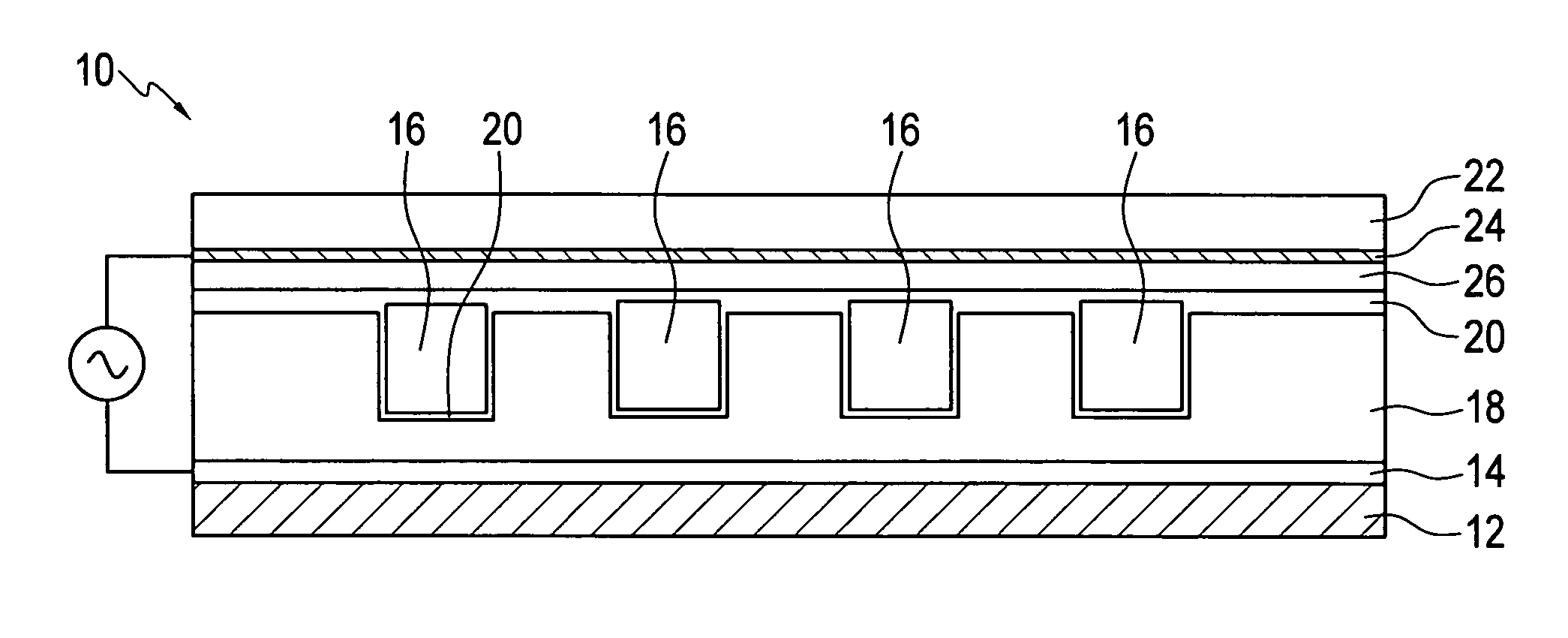
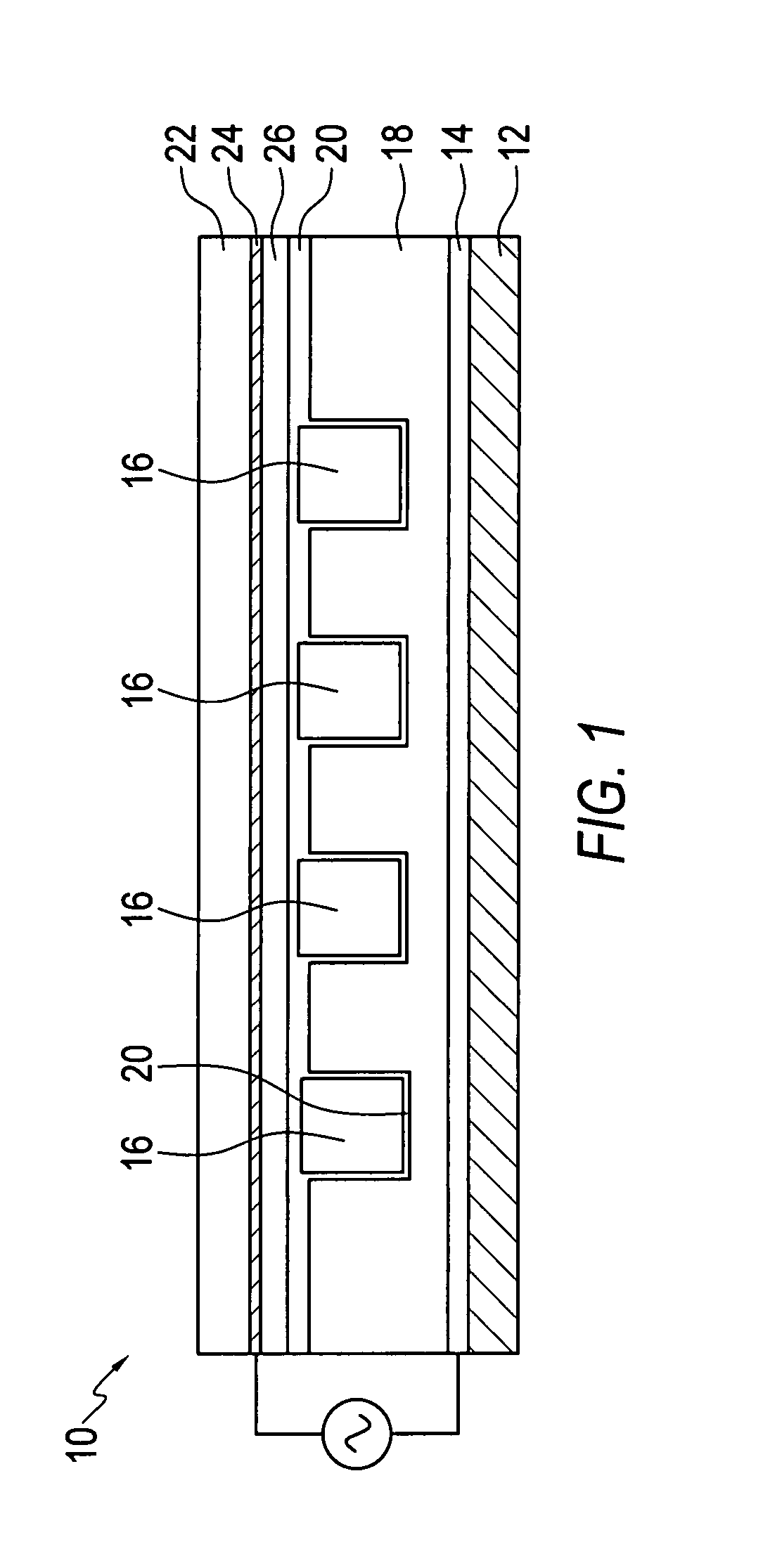
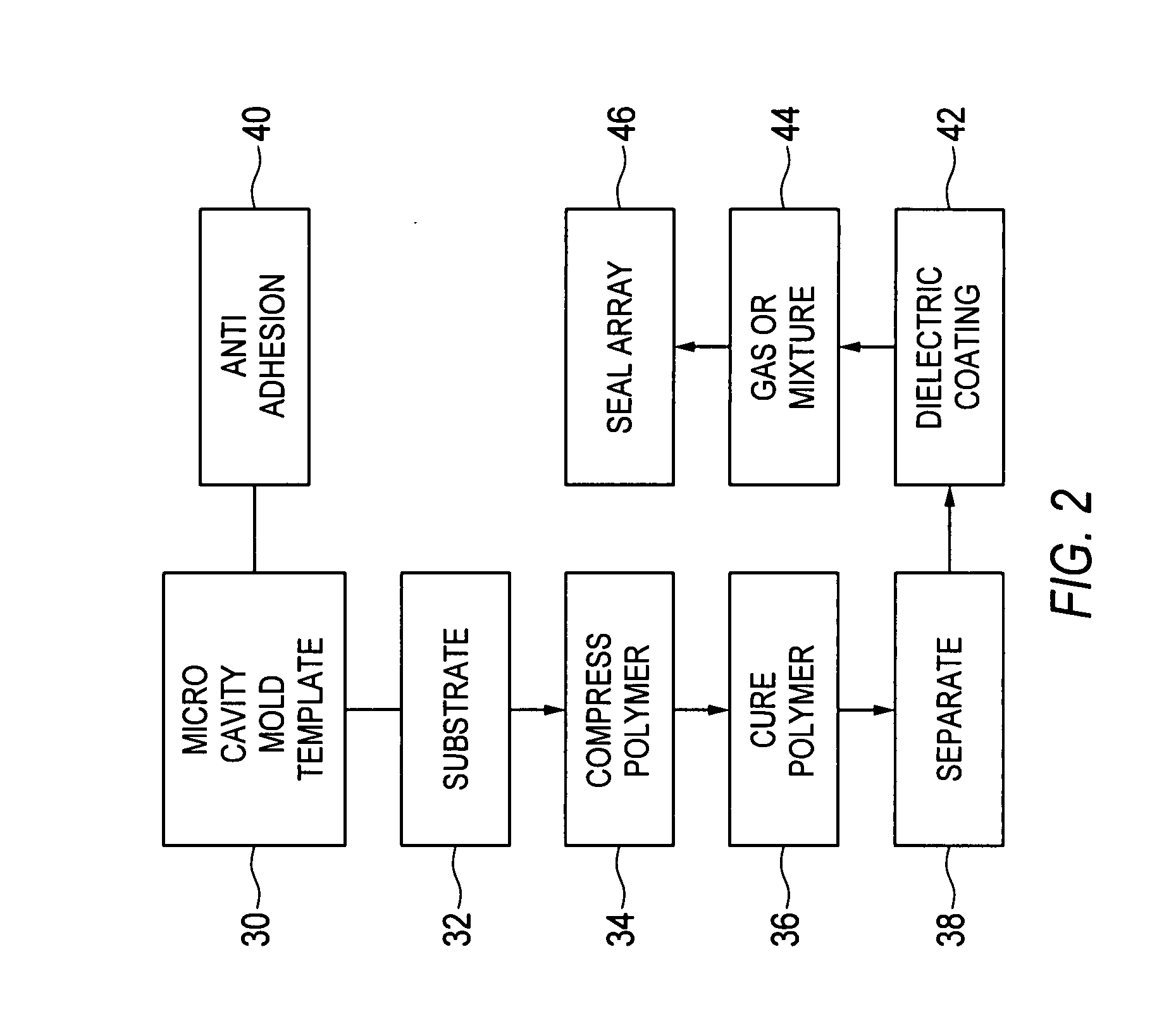
Polymer microcavity and microchannel devices and fabrication method
ActiveUS20070200499A1Alternating current plasma display panelsSolid cathode detailsPolymer sciencePolymer
A microplasma device includes a substrate and either or both of a microchannel or microcavity defined in a polymer layer supported by the substrate. Electrodes arranged with respect to the polymer material can excite a plasma in a discharge medium contained in the microchannel or the microcavity or both. A method of forming a microplasma device places a curable polymer material between a mold having a negative volume impression of microcavities and / or microchannels and a substrate. The polymer is cured and then the mold is separated from the solid polymer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Surface plasmon resonance based nanoliter tear osmometer
ActiveUS7395103B2Easy to useCost-effective patientBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMedicineSurface plasmon resonance imaging
Owner:LACRISCI
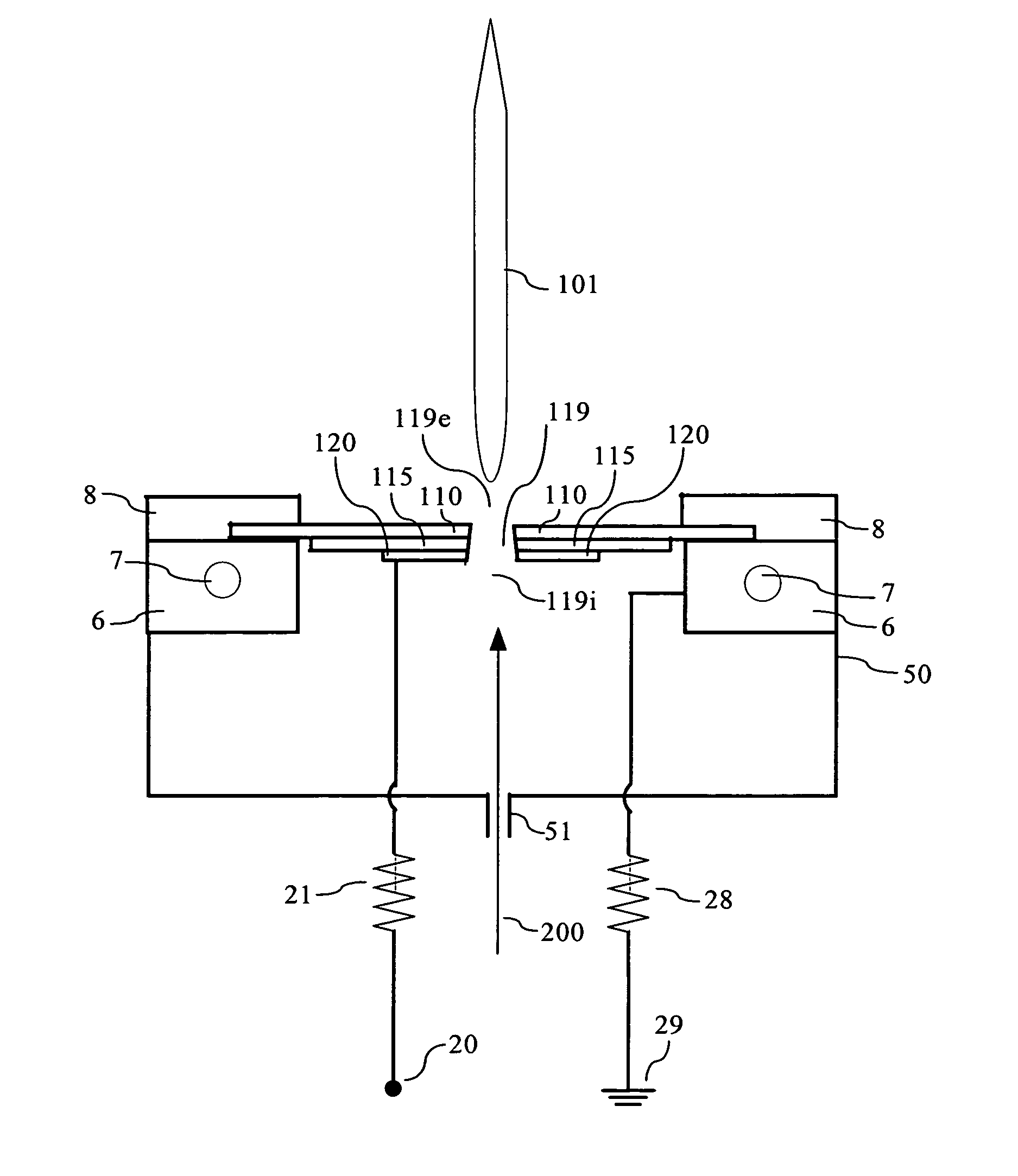
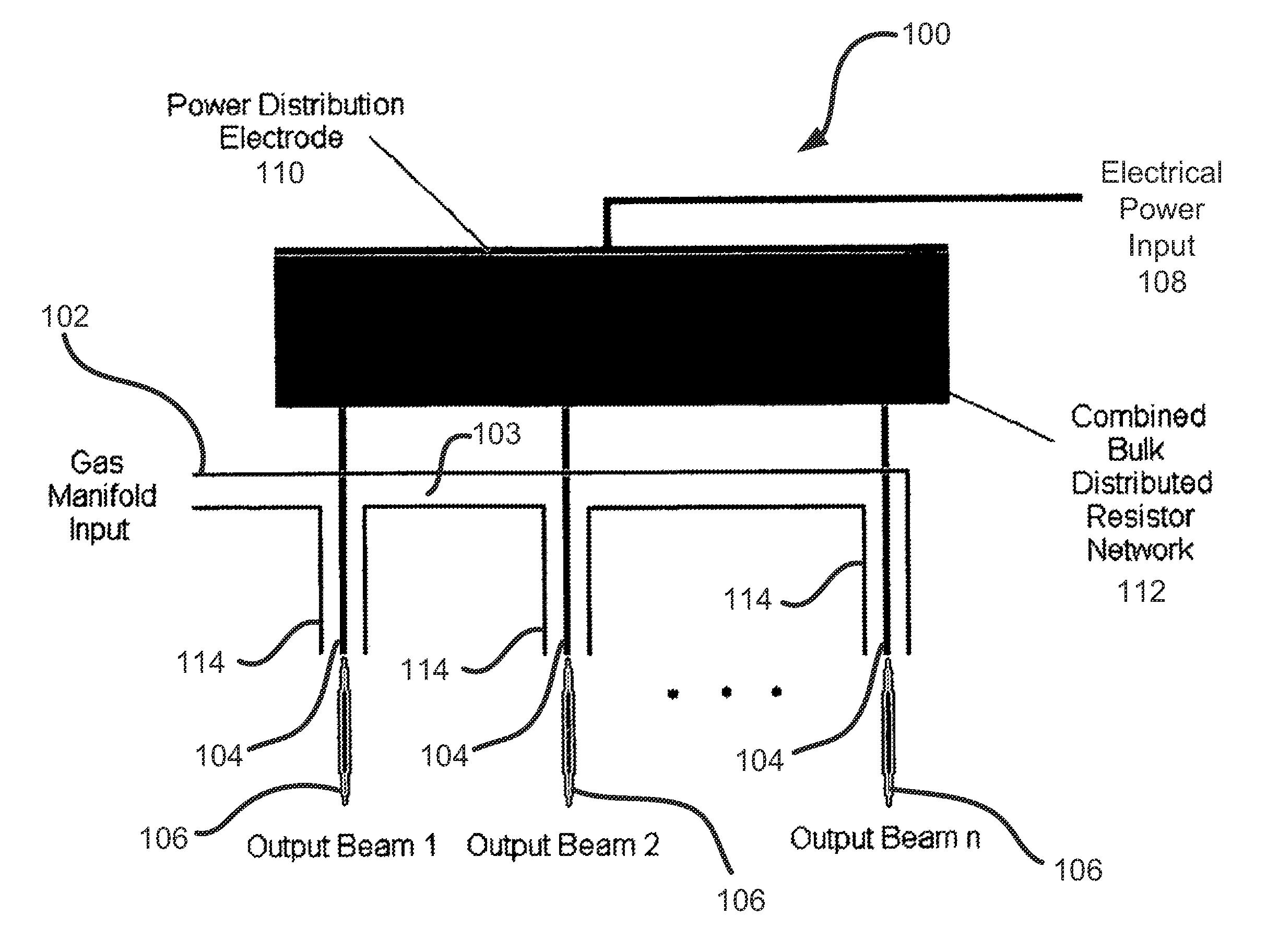
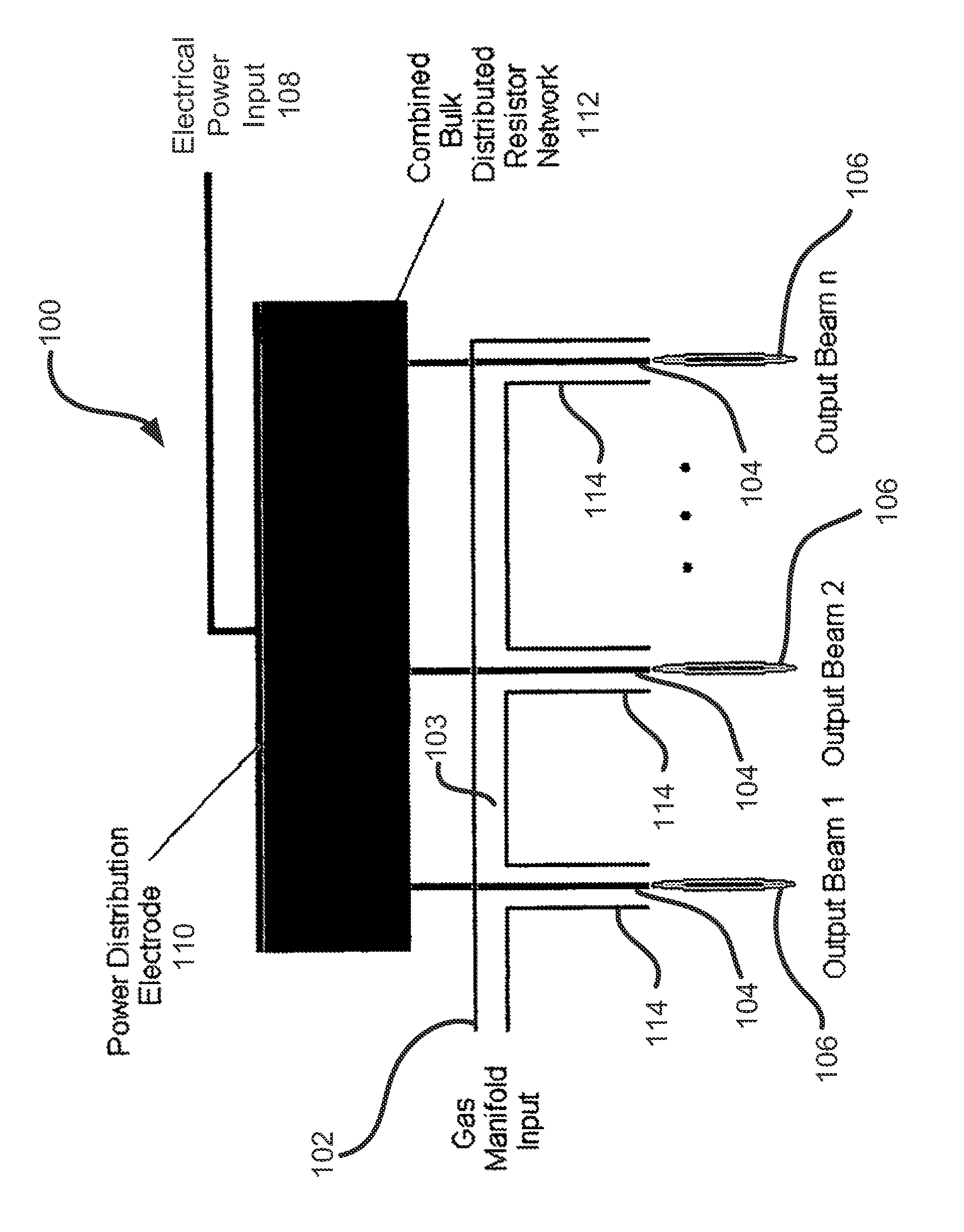
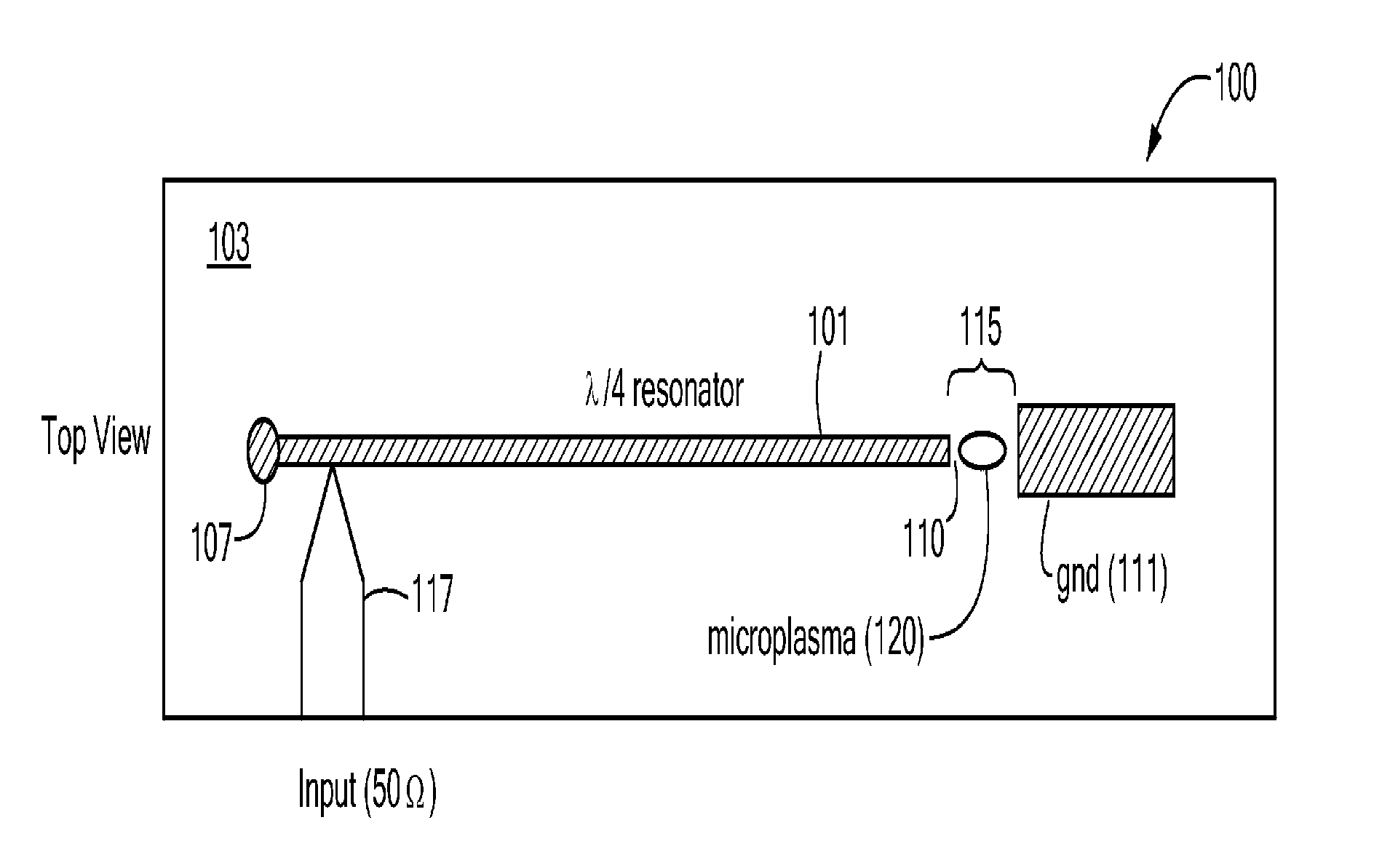
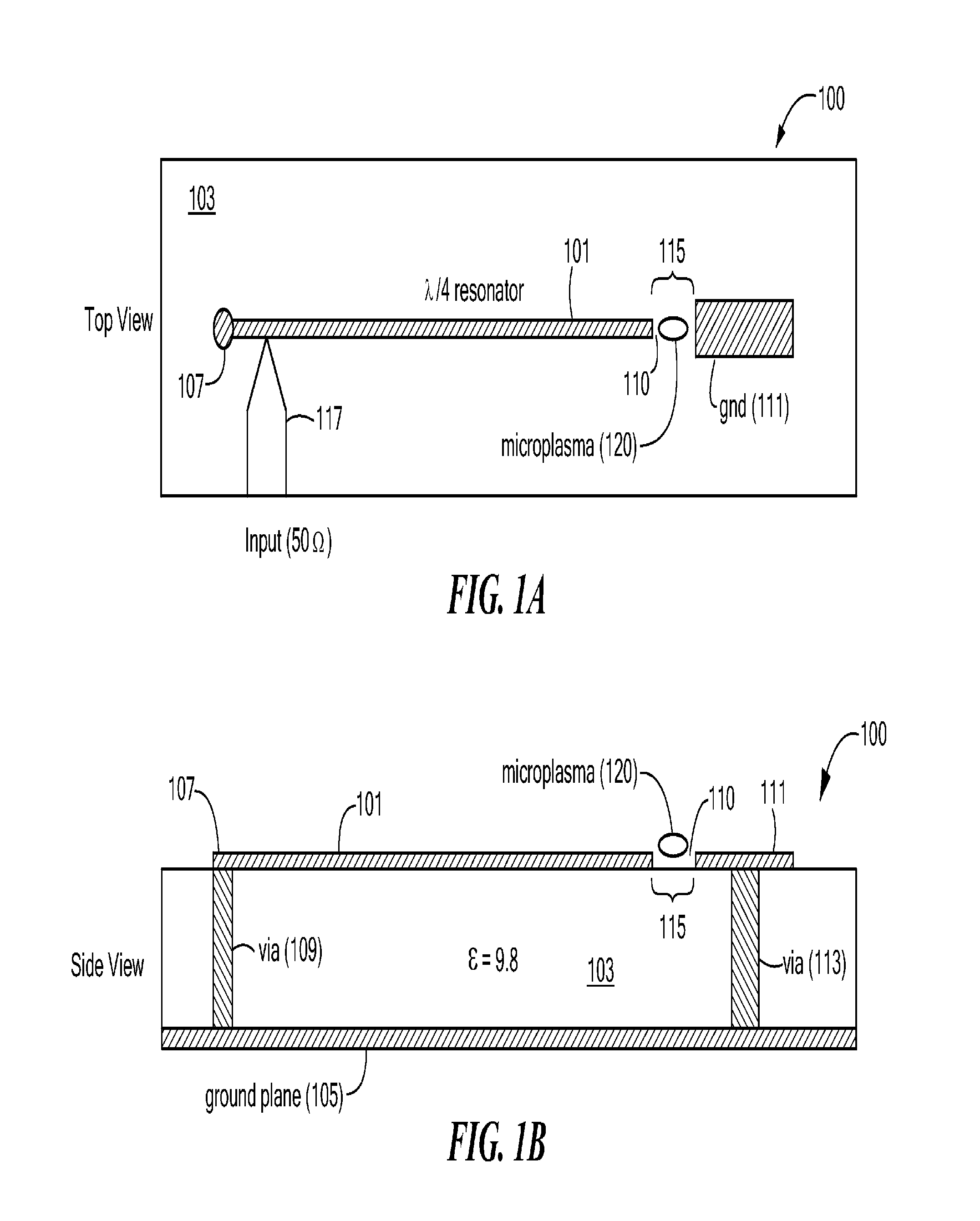
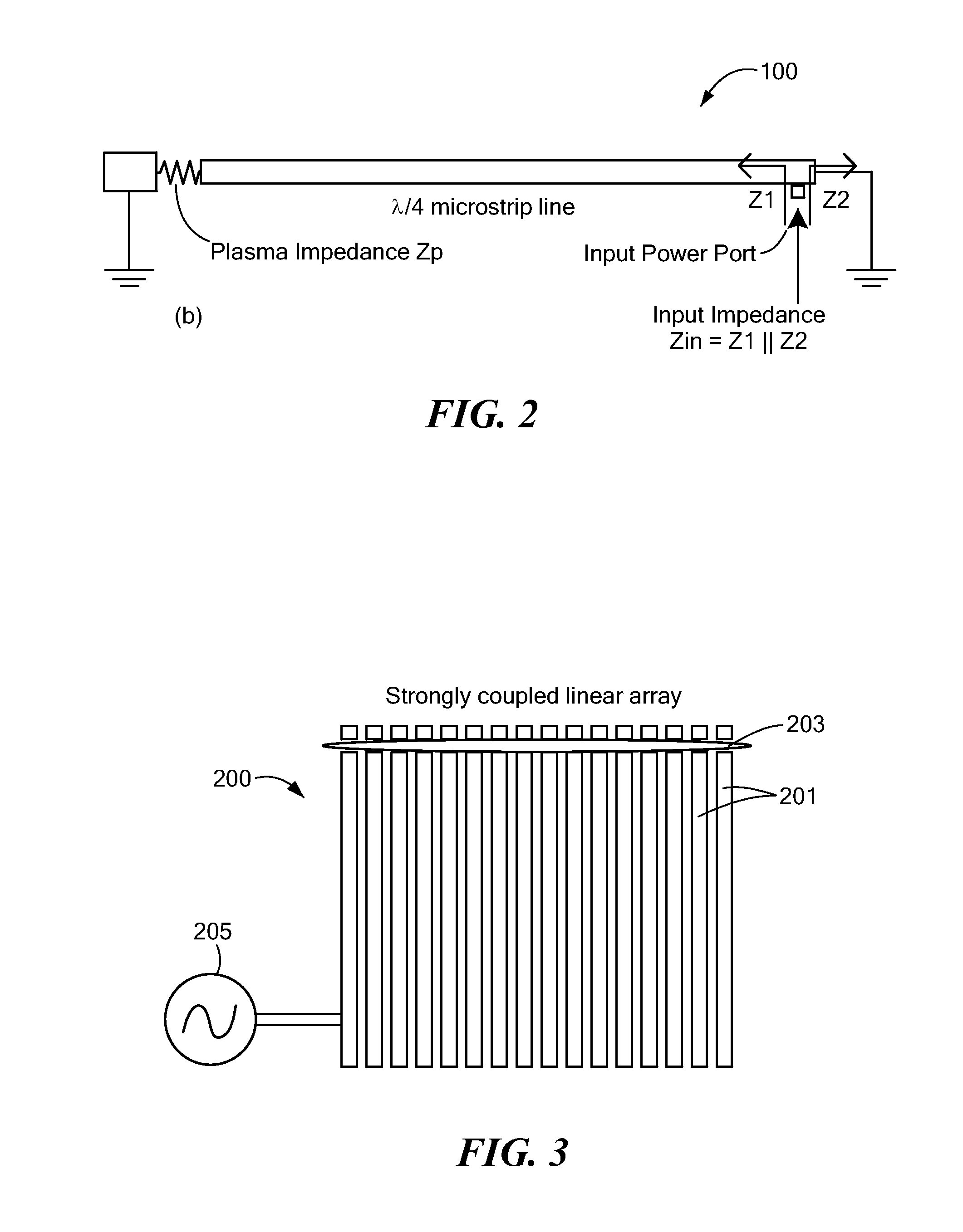
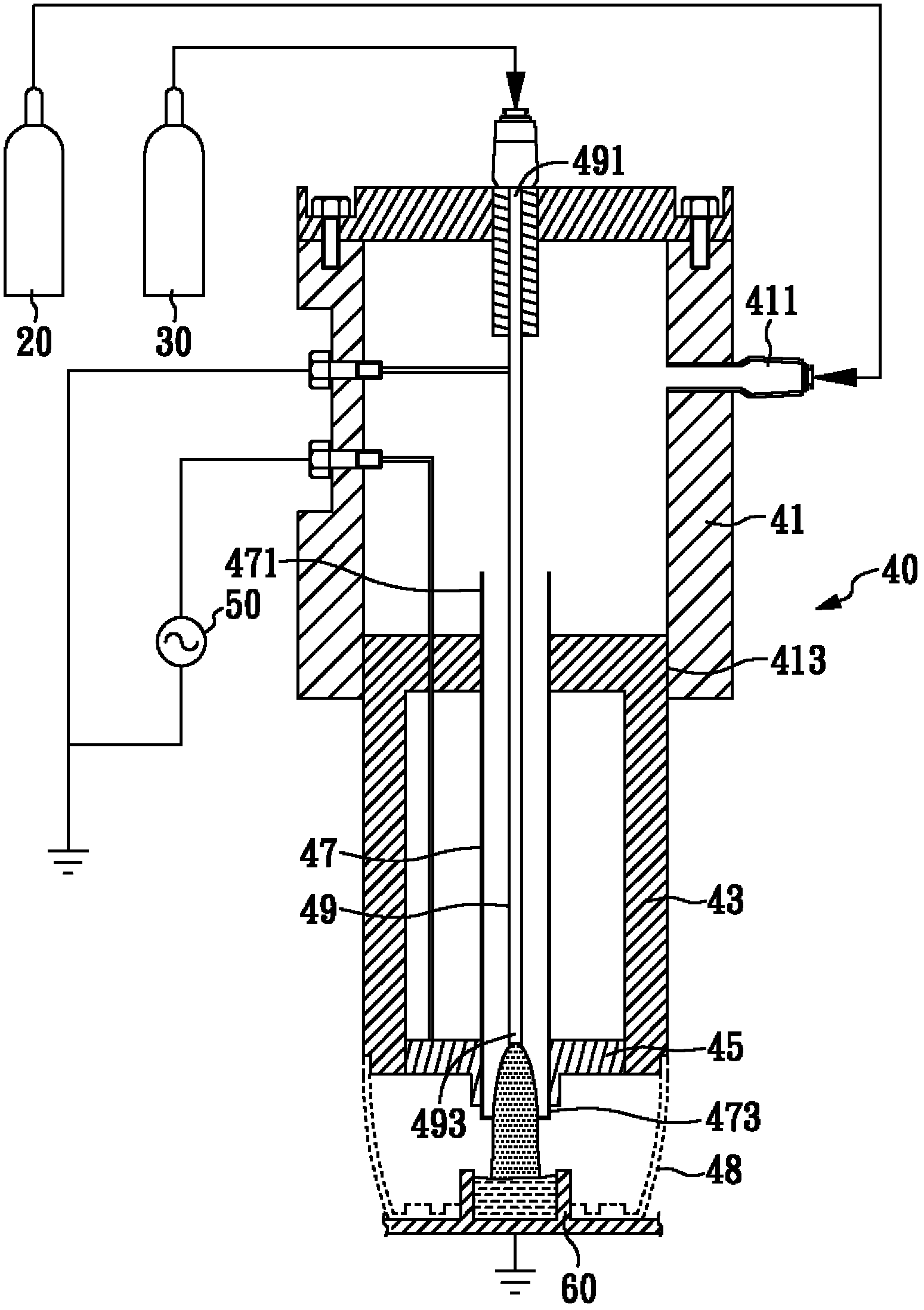
Microplasma generator and methods therefor
ActiveUS20120045863A1Low costEliminate needFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh frequency powerDielectric substrate
A low-temperature, atmospheric-pressure microplasma generator comprises at least one strip of metal on a dielectric substrate. A first end of the strip is connected to a ground plane and the second end of the strip is adjacent to a grounded electrode, with a gap being defined between the second end of the strip and the grounded electrode. High frequency power is supplied to the strip. The frequency is selected so that the length of the strip is an odd integer multiple of ¼ of the wavelength traveling on the strip. A microplasma forms in the gap between the second end of the strip and the grounded electrode due to electric fields in that region. A microplasma generator array comprises a plurality of strongly-coupled resonant strips in close proximity to one another. At least one of the strips has an input for high-frequency electrical power. The remaining strips resonate due to coupling from the at least one powered strip. The array can provide a continuous line or ring of plasma. The microplasma generator can be used to alter the surface of a substrate, such as by adding material (deposition), removal of material (etching), or modifying surface chemistry.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
Radial pulsed arc discharge gun for synthesizing nanopowders
A system and method for synthesizing nanopowder which provides for precursor material ablation from two opposing electrodes that are substantially axially aligned and spaced apart within a gaseous atmosphere, where a plasma is created by a high power pulsed electrical discharge between the electrodes, such pulse being of short duration to inertially confine the plasma, thereby creating a high temperature and high density plasma having high quench and / or reaction rates with the gaseous atmosphere for improved nanopowder synthesis.
Owner:NCC NANO LLC
Microplasma source and sterilization system including the same
ActiveUS20120063966A1Not need high power consumptionReduce power consumptionDisinfectionEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesElectricityEngineering
A microplasma source and a sterilization system including the same are disclosed. The microplasma source includes: a microplasma-generating unit including: a gas transmission chamber having a first inlet and a first outlet wherein the first inlet is used to import a first gas; a protection and heat dissipation chamber of which a side is connected to the inner wall of the first outlet; a dielectric inner tube having a second inlet and a second outlet and penetrating through the protection and heat dissipation chamber, wherein the second inlet is communicated to the gas transmission chamber; an electrode arranged outside at the second outlet and located in the protection and heat dissipation chamber; and a hollow metal tube disposed in the gas transmission chamber and the dielectric inner tube and having a third inlet and a third outlet, wherein the third inlet is used to import a second gas.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Electron injection-controlled microcavity plasma device and arrays
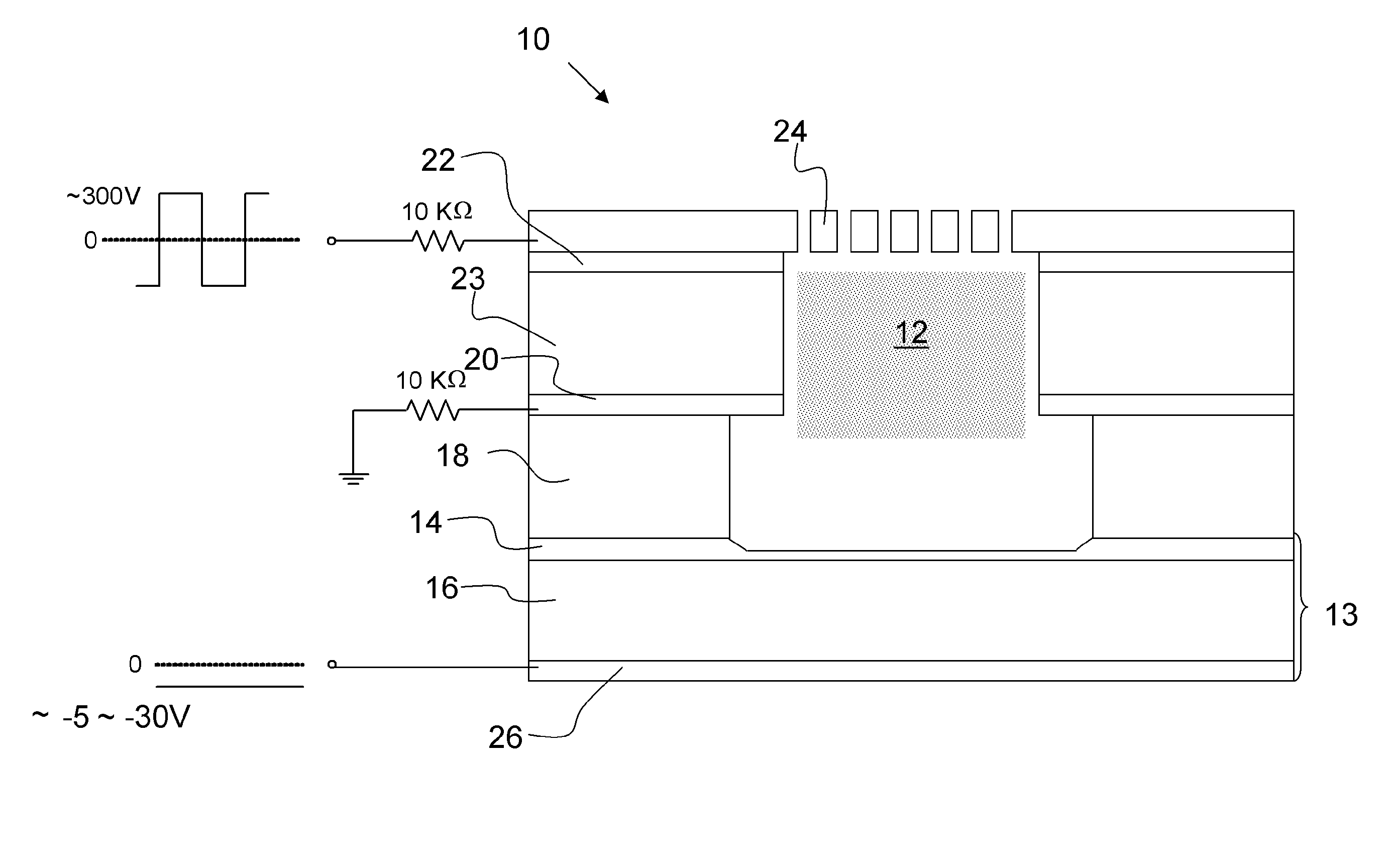
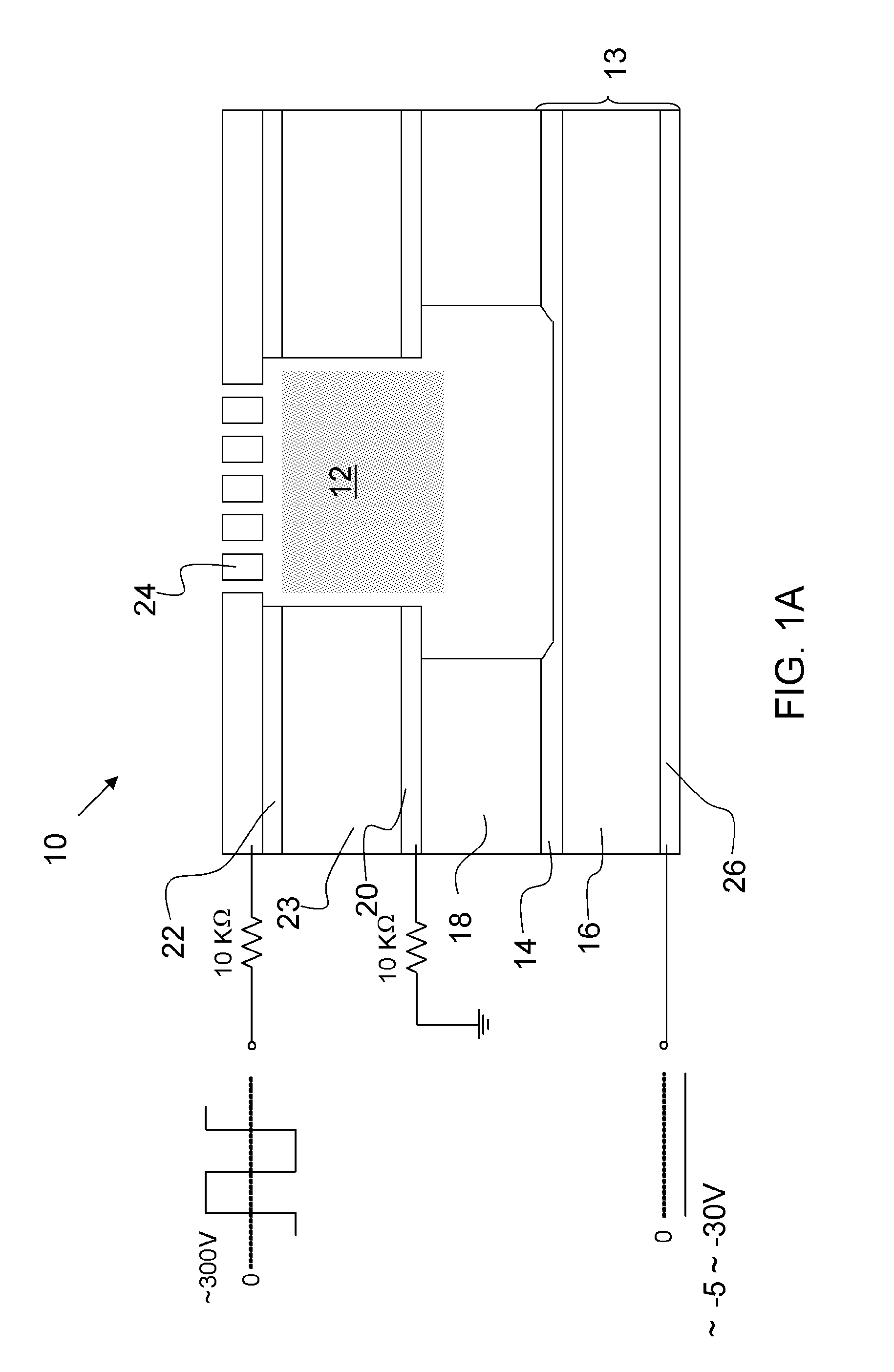
ActiveUS20100289413A1Increase speedSmall voltageAlternating current plasma display panelsElectric light circuit arrangementElectron injectionElectron source
An embodiment of the invention is a microcavity plasma device that can be controlled by a low voltage electron emitter. The microcavity plasma device includes driving electrodes disposed proximate to a microcavity and arranged to contribute to generation of plasma in the microcavity upon application of a driving voltage. An electron emitter is arranged to emit electrons into the microcavity upon application of a control voltage. The electron emitter is an electron source having an insulator layer defining a tunneling region. The microplasma itself can serve as a second electrode necessary to energize the electron emitter. While a voltage comparable to previous microcavity plasma devices is still imposed across the microcavity plasma devices, control of the devices can be accomplished at high speeds and with a small voltage, e.g., about 5V to 30V in preferred embodiments.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Plasma preclean with argon, helium, and hydrogen gases
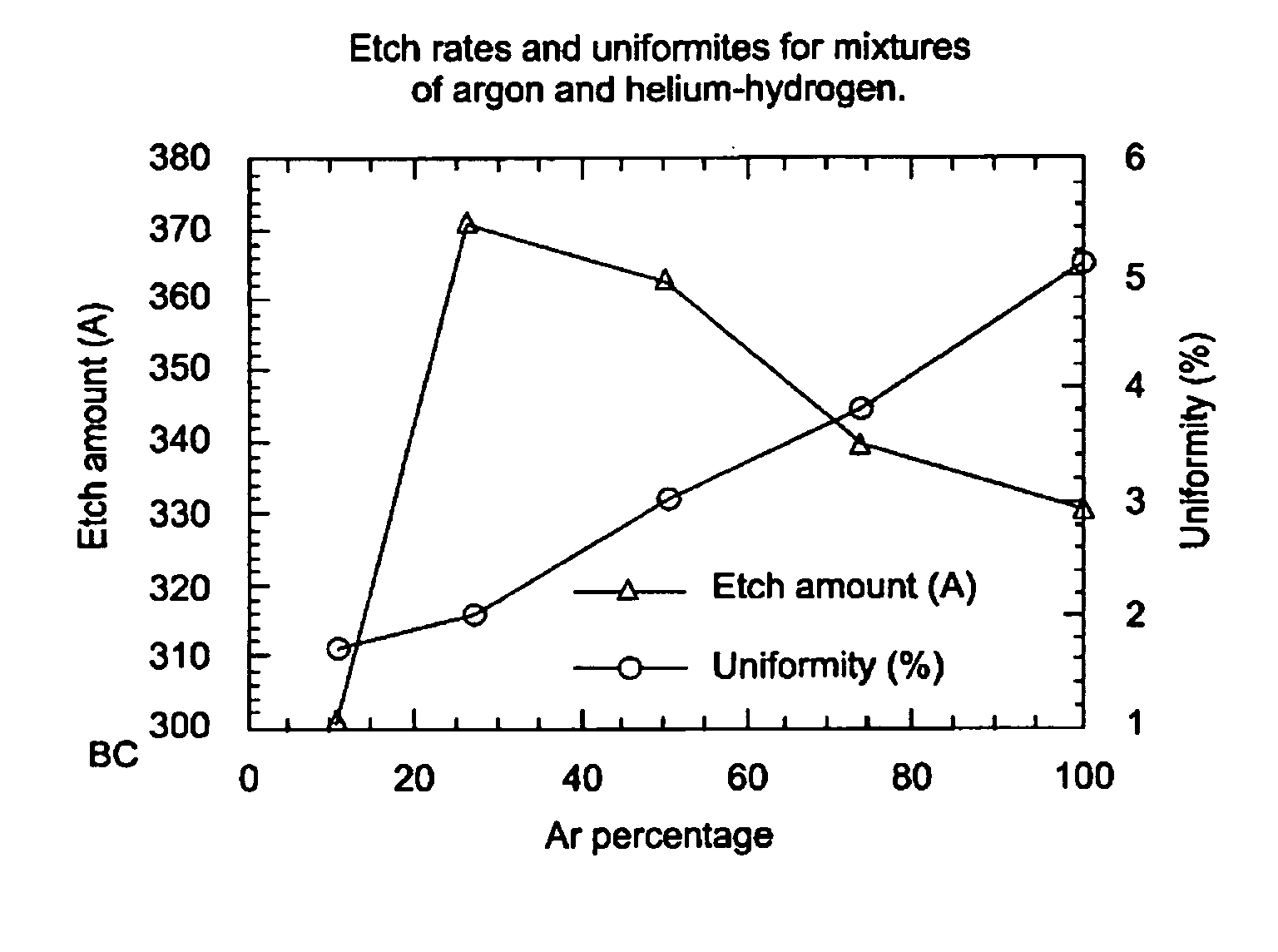
InactiveUS7053002B2Increase etch rateHigh aspect ratioVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenPatterned substrate
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for precleaning a patterned substrate with a plasma comprising a mixture of argon, helium, and hydrogen. Addition of helium to the gas mixture of argon and hydrogen surprisingly increases the etch rate in comparison to argon / hydrogen mixtures. Etch rates are improved for argon concentrations below about 75% by volume. RF power is capacitively and inductively coupled to the plasma to enhance control of the etch properties. Argon, helium, and hydrogen can be provided as separate gases or as mixtures.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
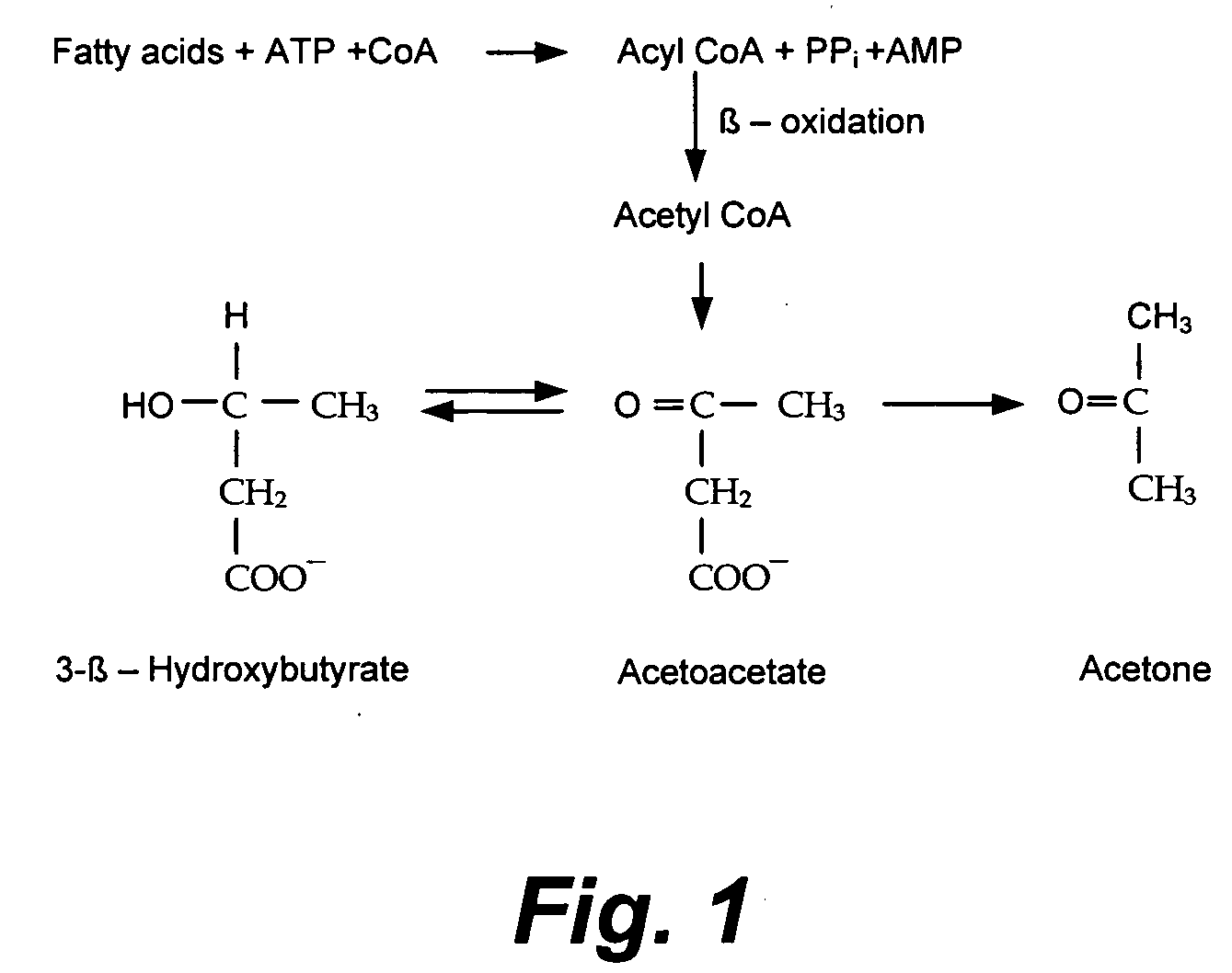
Apparatus and method for monitoring breath acetone and diabetic diagnostics
An apparatus and method for monitoring diabetes through breath acetone detection and quantitation employs a microplasma source in combination with a spectrometer. The microplasma source provides sufficient energy to produce excited acetone fragments from the breath gas that emit light. The emitted light is sent to the spectrometer, which generates an emission spectrum that is used to detect and quantify acetone in the breath gas.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Electrosurgical apparatus to generate a dual plasma stream and method thereof
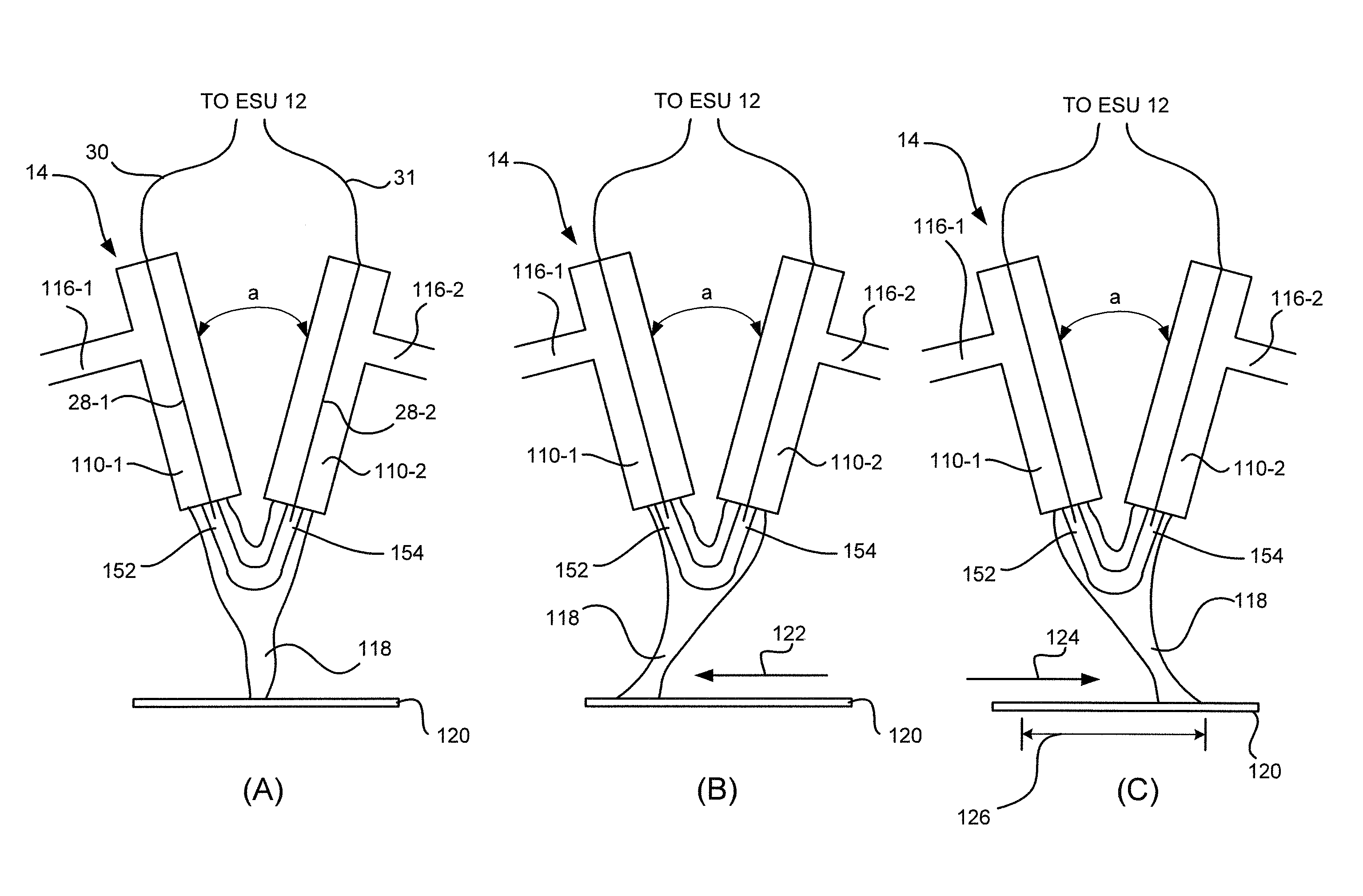
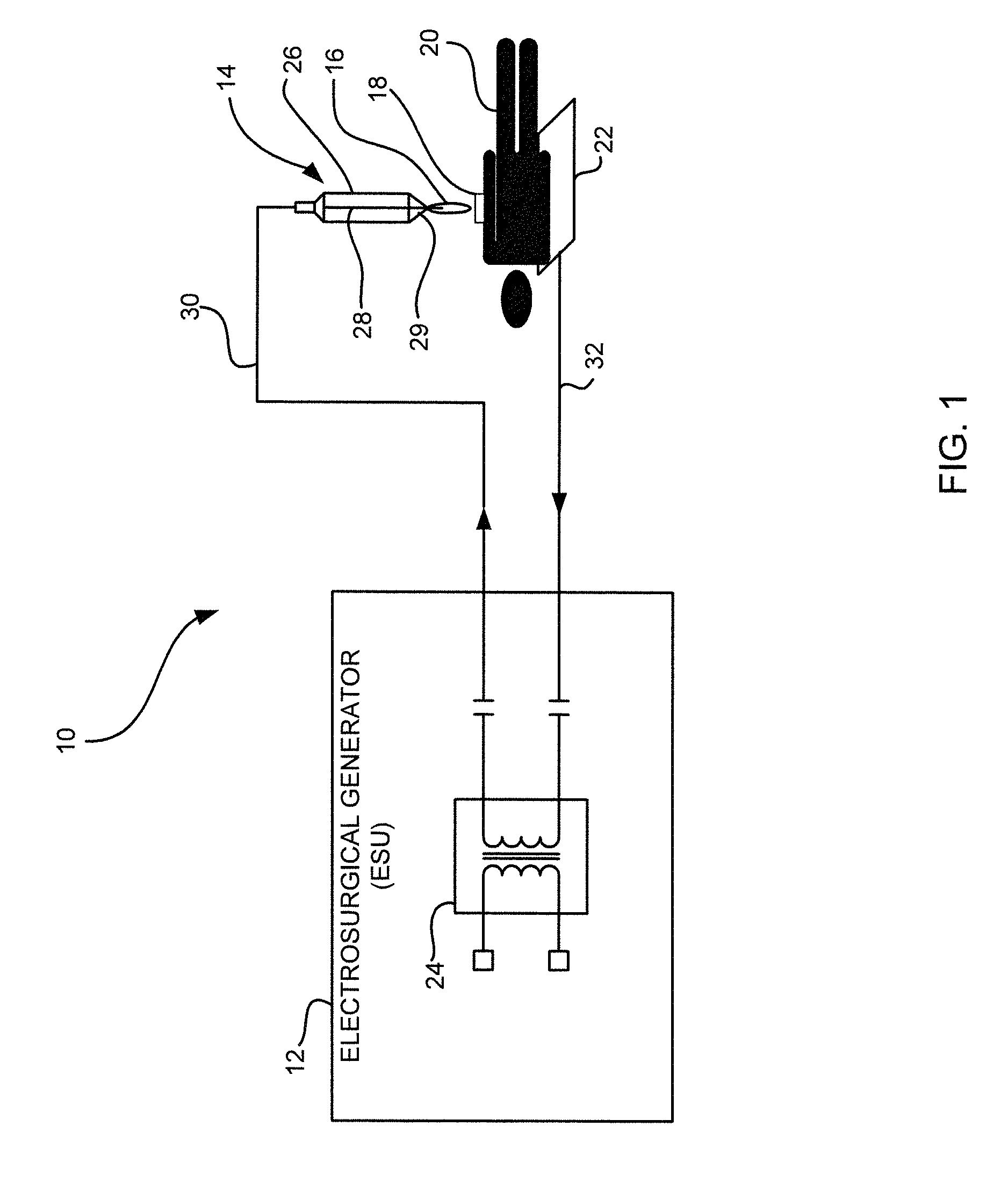
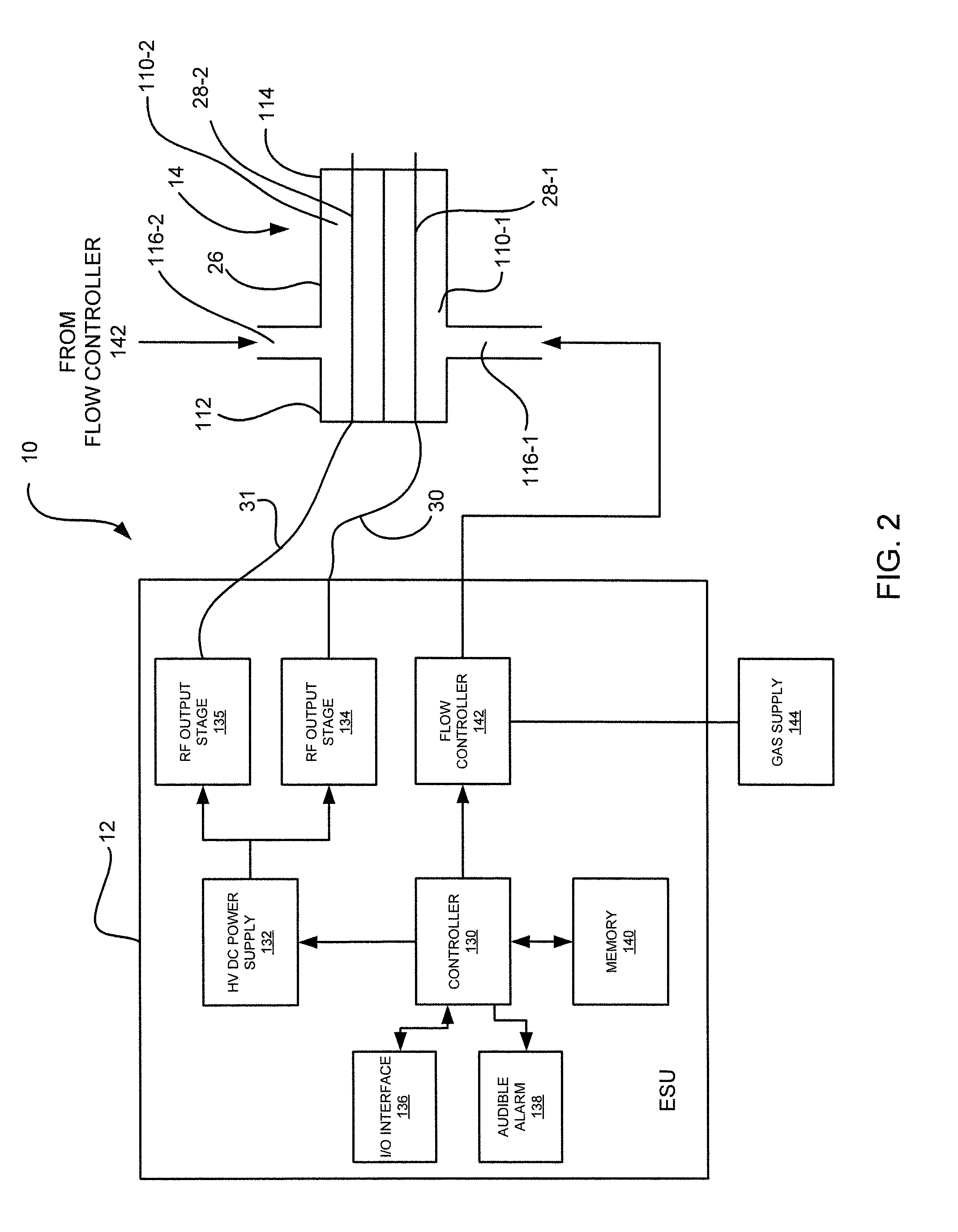
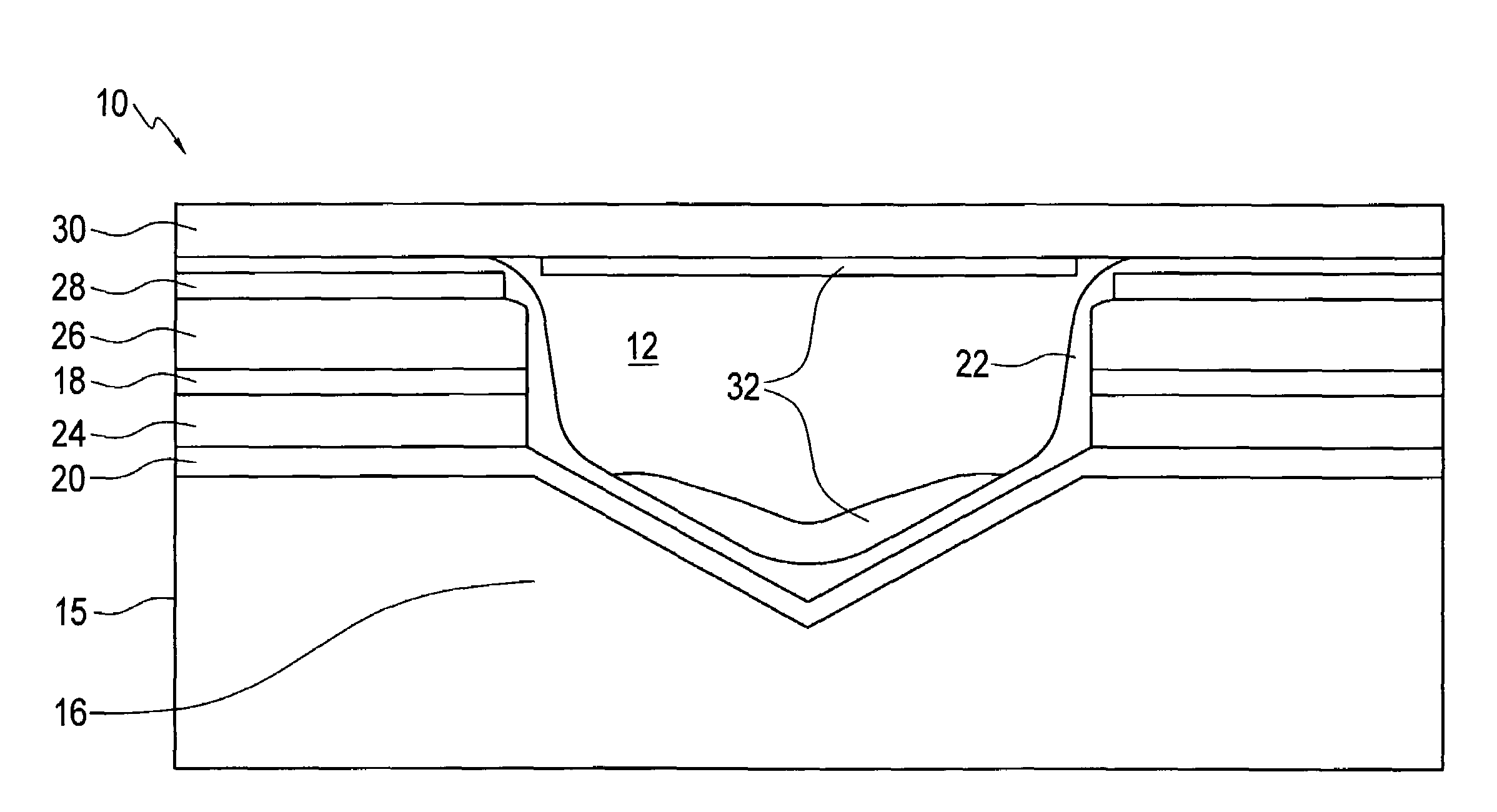
ActiveUS8795265B2Small equivalent capacitanceGood effectSurgical instruments for heatingPlasma currentElectrosurgery
The present disclosure relates to an electrosurgical apparatus to generate a dual plasma stream to perform electrosurgery on a surgical site on a patient. The apparatus and method of the present disclosure generates a hot gas jet to a surgical site by generating two plasma beams that are electrically up to 180 degrees out of phase from each other. Since each beam uses the other beam to establish plasma currents at a load, the combined dual plasma stream can be used on non-conductive surfaces, e.g., a tissue at the surgical site. Furthermore, by applying different flow rates to the plasma beams, various scanning effects by the hot gas jet can be achieved.
Owner:BOVIE MEDICAL CORPORATION
Low voltage microcavity plasma device and addressable arrays
ActiveUS20080129185A1Low excitation voltageReduce crosstalkDischarge tube luminescnet screensLighting and heating apparatusLow voltageHalf cycle
Microcavity plasma devices and arrays of microcavity plasma devices are provided that have a reduced excitation voltage. A trigger electrode disposed proximate to a microcavity reduce the excitation voltage required between first and second electrodes to ignite a plasma in the microcavity when gas(es) or vapor(s) (or combinations thereof) are contained within the microcavity. The invention also provides symmetrical microplasma devices and arrays of microcavity plasma devices for which current waveforms are the same for each half-cycle of the voltage driving waveform. Additionally, the invention also provides devices that have standoff portions and voids that can reduce cross talk. The devices are preferably also used with a trigger electrode.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Apparatus and method for monitoring breath acetone and diabetic diagnostics
An apparatus and method for monitoring diabetes through breath acetone detection and quantitation employs a microplasma source in combination with a spectrometer. The microplasma source provides sufficient energy to produce excited acetone fragments from the breath gas that emit light. The emitted light is sent to the spectrometer, which generates an emission spectrum that is used to detect and quantify acetone in the breath gas.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Laser Heated Discharge Plasma EUV Source With Plasma Assisted Lithium Reflux
InactiveUS20090224182A1Ultraviolet radiation is enhancedAvoid dischargeRadiation pyrometryX-ray tube with very high currentRefluxLength wave
A self-magnetically confined lithium plasma that has an applied axial magnetic field is irradiated at sub-critical density by a perpendicularly oriented carbon dioxide laser to generate extreme ultraviolet photons at the wavelength of 13.5 nm with high efficiency, high power and small source size. Lithium reflux is facilitated by ionization, electric field induced drift toward, and capture on surfaces intersected perpendicularly by the applied axial magnetic field.
Owner:PUREX
Device and method for the detection of heavy metal elements
ActiveCN105842230ASimple structureEasy to installAnalysis by electrical excitationTitaniumSpectrometer
The invention relates to a device and a method for the detection of heavy metal elements. The device comprises a hydride generator unit, a liquid negative electrode glow discharge spectrometer unit and a connection unit connected to the hydride generator unit and the liquid negative electrode glow discharge spectrometer unit. The hydride generator unit makes a sample to be measured generate heavy metal hydride to be measured ; the heavy metal hydride to be measured generated by the hydride generator unit is transported to a positive electrode of a hollow titanium tube via the connection unit, and is lead from the positive electrode of the titanium tube to a glow discharge microplasma, and is excited to generate a characteristic emission spectrum. The device has simple structure, the method is convenient for operation and low in cost, and can conveniently, timely detect heavy metal elements and improve the sensitivity and selectivity to heavy metal elements.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Microplasma source and sterilization system including the same
InactiveCN102404927AEasy to operateReduce energy consumptionLavatory sanitoryDisinfectionEngineeringGenerating unit
A microplasma source and a sterilization system including the same are disclosed. The microplasma source includes: a microplasma-generating unit including: a gas transmission chamber having a first inlet and a first outlet wherein the first inlet is used to import a first gas; a protection and heat dissipation chamber of which a side is connected to the inner wall of the first outlet; a dielectric inner tube having a second inlet and a second outlet and penetrating through the protection and heat dissipation chamber, wherein the second inlet is communicated to the gas transmission chamber; an electrode arranged outside at the second outlet and located in the protection and heat dissipation chamber; and a hollow metal tube disposed in the gas transmission chamber and the dielectric inner tube and having a third inlet and a third outlet, wherein the third inlet is used to import a second gas.
Owner:廖峻德
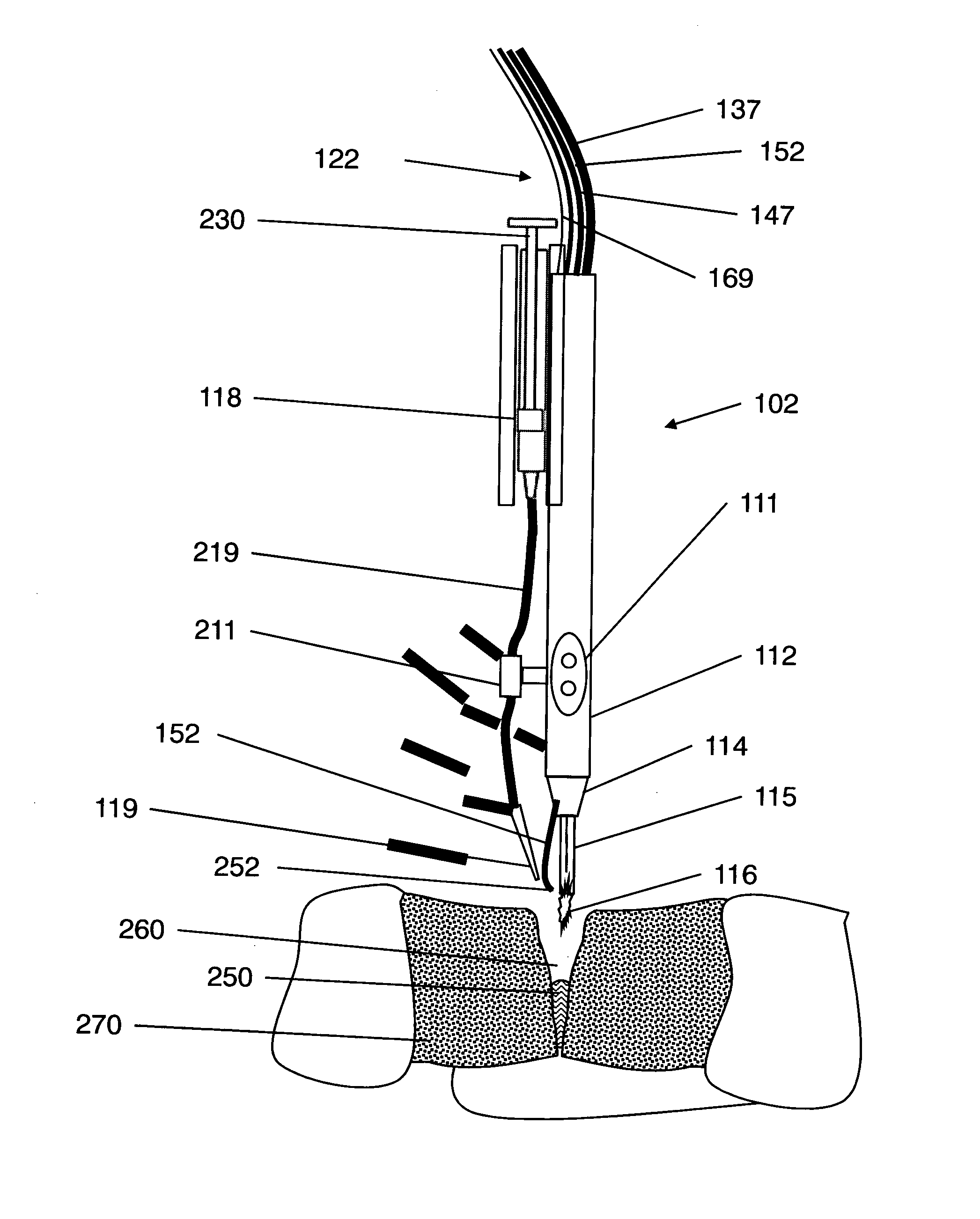
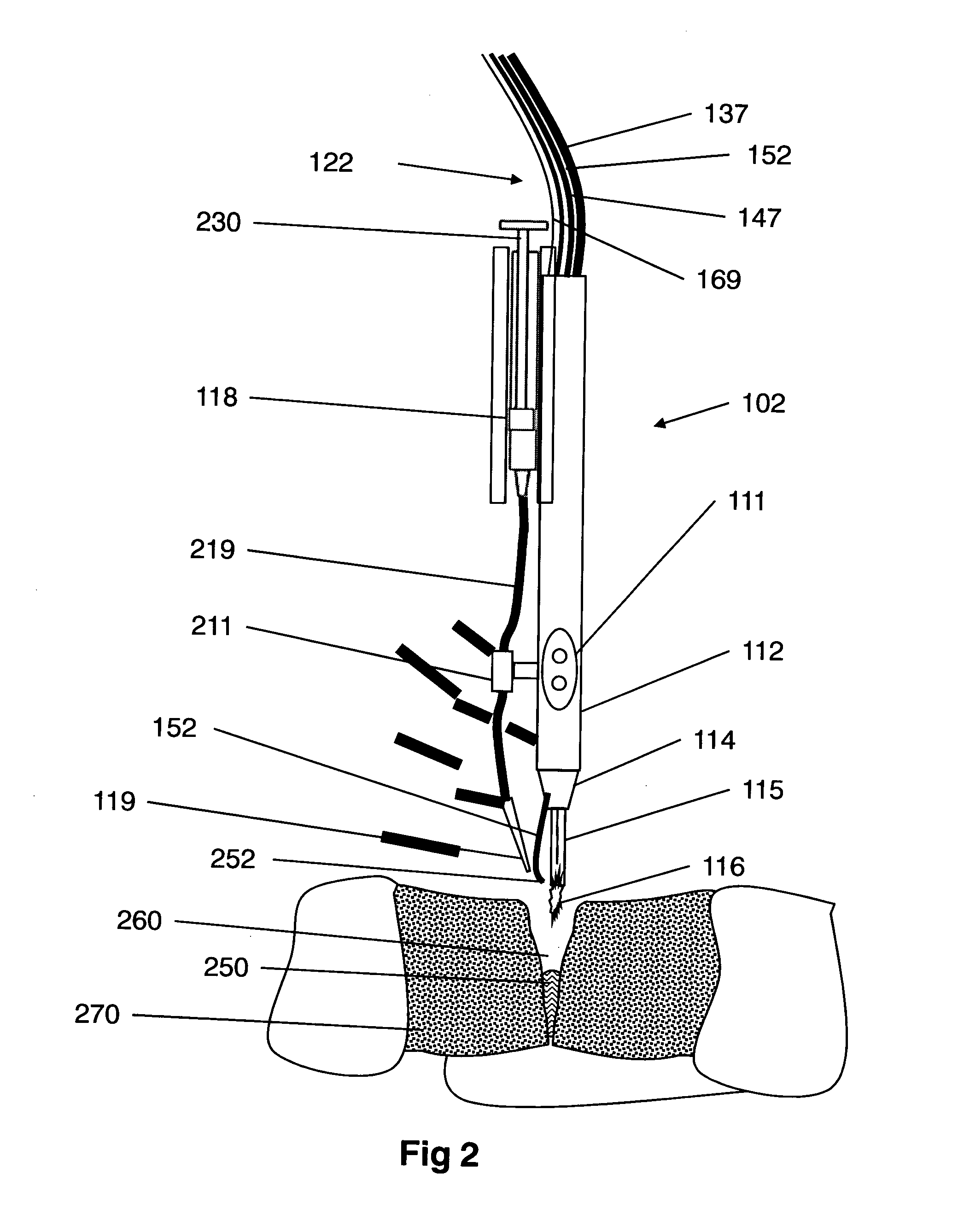
Plasma head for tissue welding
InactiveUS9060750B2Easy to adjustIncreasing RF power/frequencyDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingAlbumin solutionHand held
A compact medical device for tissue welding is provided. The hand-held plasma heads are configured for deep cuts and long cuts. A bio-compatible liquid capable of solidifying in response to application of plasma, such as an albumin solution, is applied to the wound. Plasma created from a gas such as helium is then applied to said bio-compatible liquid to solidify it and seal the wound. An additional polymerizing gas may also be applied. A feedback mechanism may maintain the temperature of said plasma. A wiper fort removal of excess liquid may also be provided.
Owner:IONMED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com