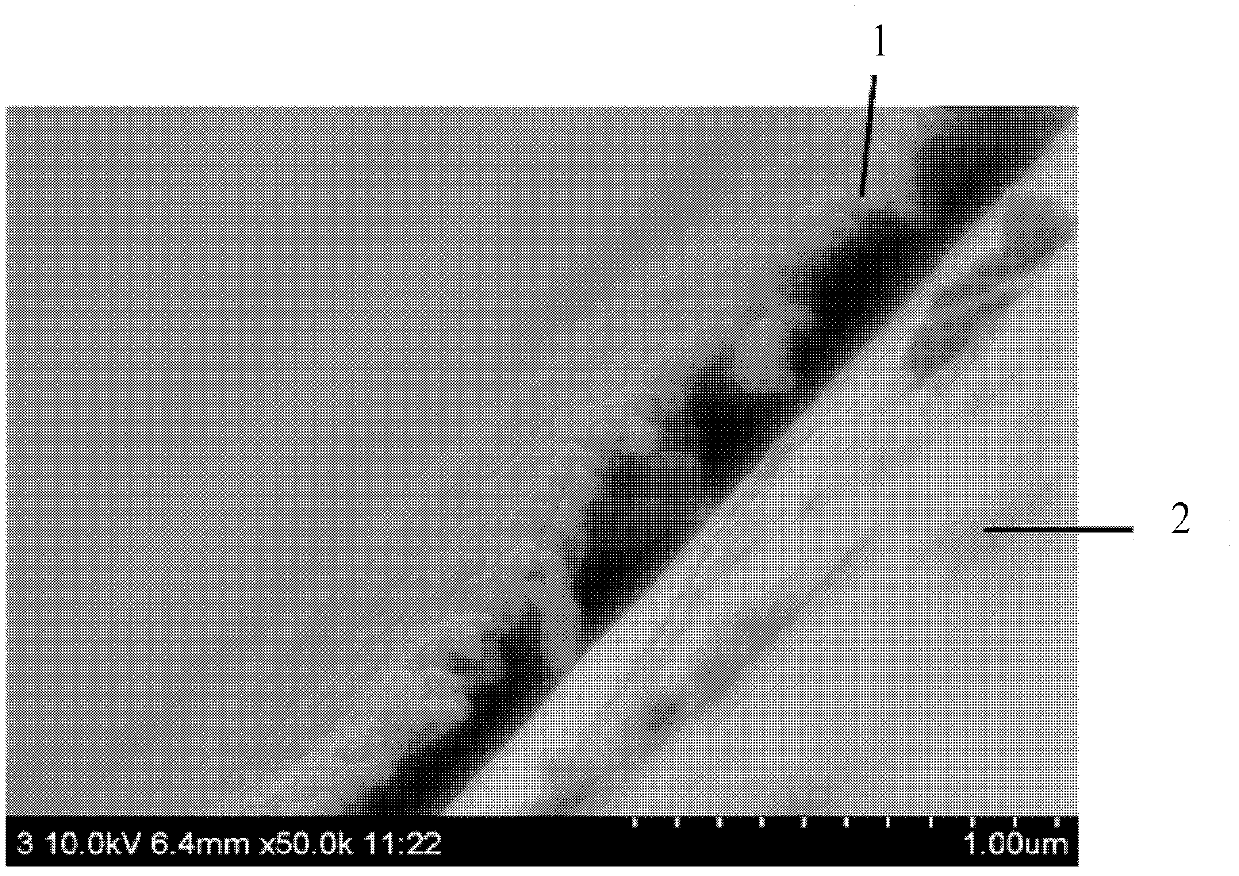
Method for detecting microstructure of reverse osmosis membrane separating layer
A technology of reverse osmosis membrane and microstructure, applied in semi-permeable membrane separation, chemical instruments and methods, membrane technology, etc., can solve the problem of inability to detect the section of the separation layer and the microstructure of its back surface, and achieves easy promotion and low equipment requirements. , the effect of strong practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
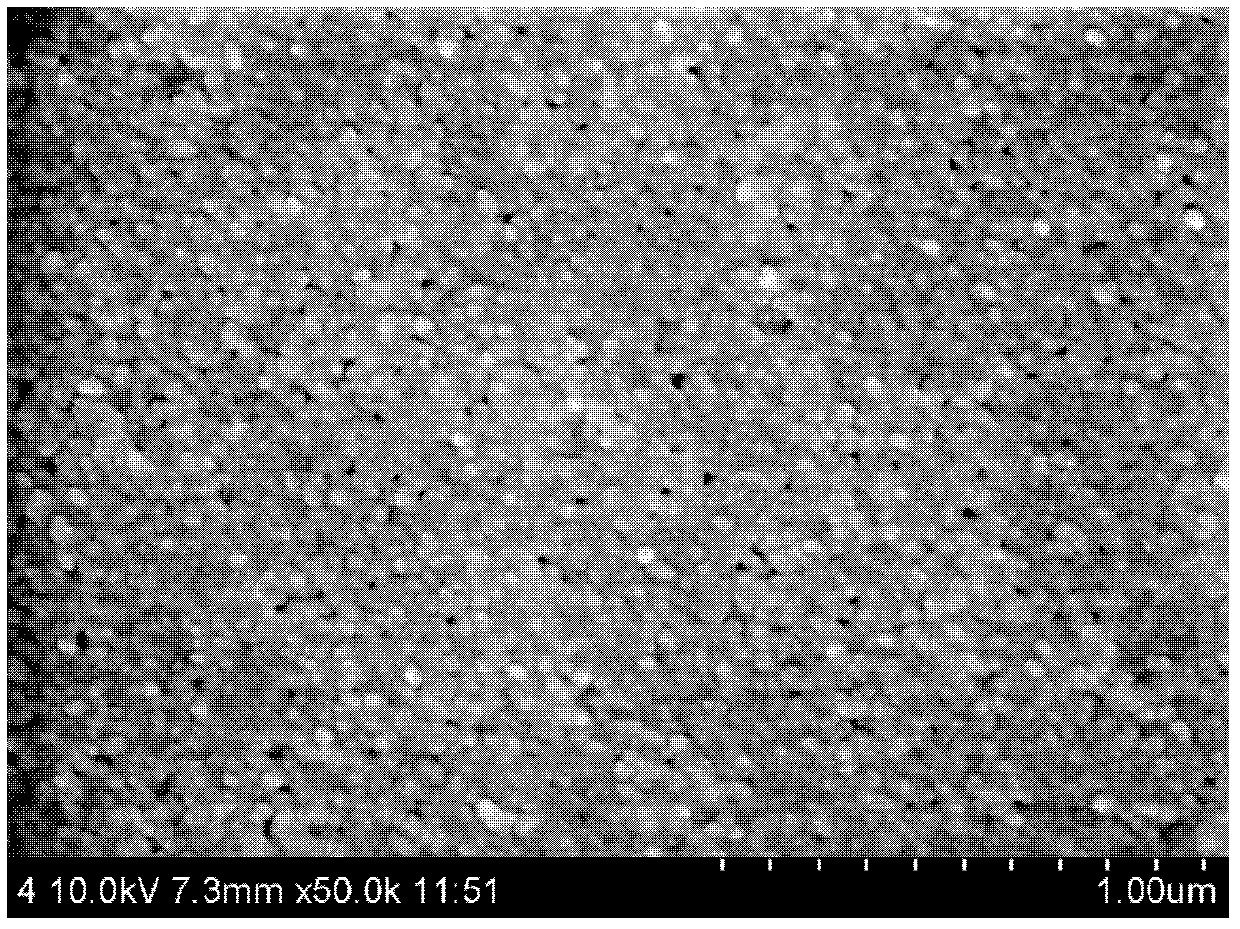
[0034] A 20mm×20mm low-pressure reverse osmosis membrane A is taken from the LP21 reverse osmosis membrane produced by Beijing Times Wharton Technology Co., Ltd.
[0035] Use tweezers to peel off the non-woven fabric layer of reverse osmosis membrane A, keep the separation layer and support layer, and paste it on the cover glass with the same size of 20mm×20mm with double-sided tape, so that the support layer faces On, place the separation layer in direct contact with the coverslip. In this way, it is ensured that in the process of washing and dissolving the supporting layer with an organic solvent, the organic solvent can directly contact with the supporting layer, so that the polysulfone supporting layer can be completely removed.
[0036] The coverslips were washed with distilled water and ethanol before use, and dried to remove surface-adhered pollutants. According to the difference in solubility between the separation layer and the support layer, a suitable volatile orga...
Embodiment 2
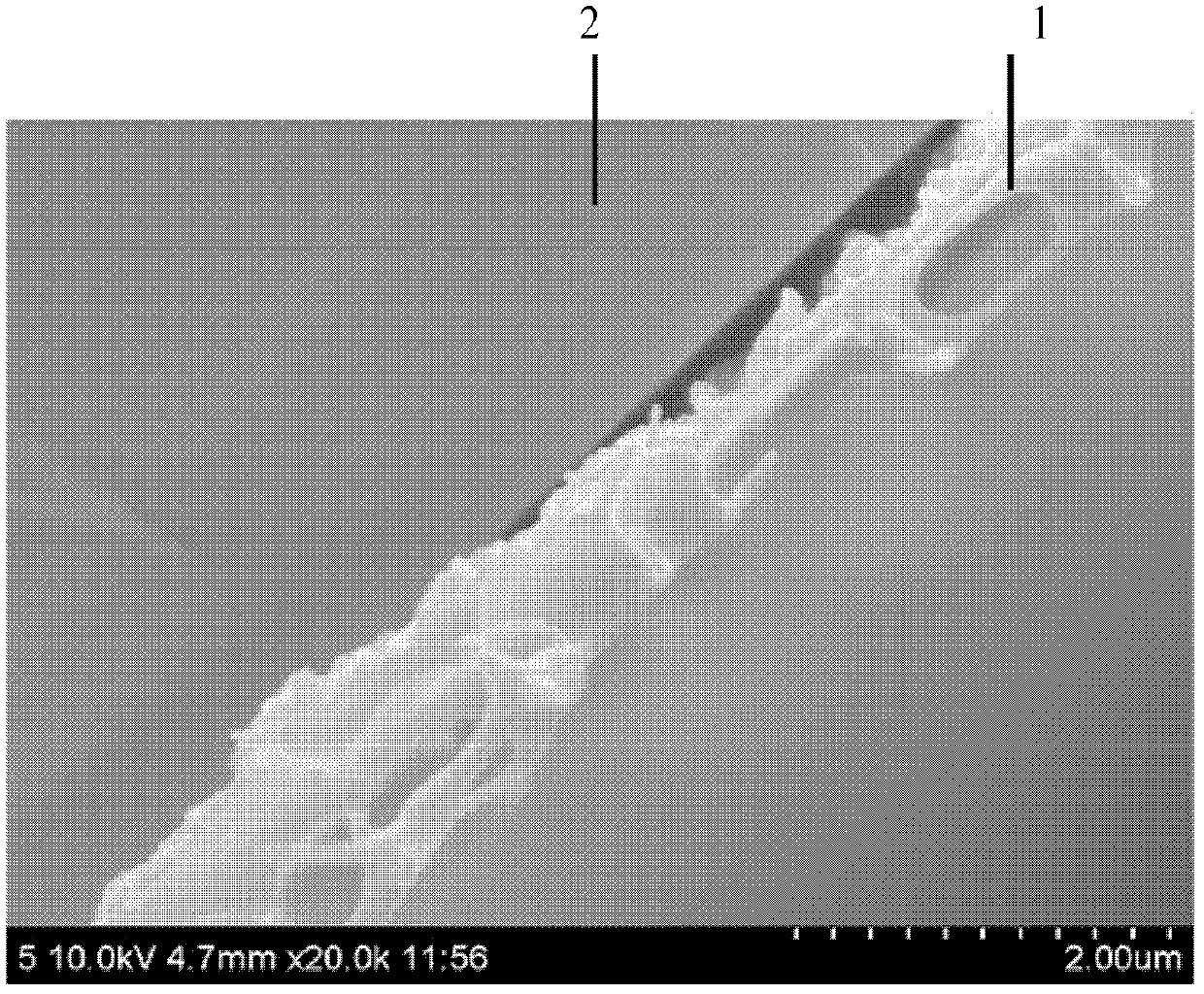
[0040] A 45mm×26mm ultra-low pressure reverse osmosis membrane B is taken from the ULP21 type reverse osmosis membrane produced by Beijing Times Wharton Technology Co., Ltd.
[0041] Use tweezers to peel off the non-woven fabric layer of reverse osmosis membrane B, keep the separation layer and support layer, and paste it on the cover glass with the same size of 45mm×26mm with double-sided tape, so that the support layer faces On, place the separation layer in direct contact with the coverslip. In this way, it is ensured that in the process of washing and dissolving the supporting layer with an organic solvent, the organic solvent can directly contact with the supporting layer, so that the polysulfone supporting layer can be completely removed.
[0042]The coverslips were washed with distilled water and ethanol before use, and dried to remove surface-adhered pollutants. According to the difference in solubility between the separation layer and the support layer, a suitable vo...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A pollution-resistant reverse osmosis membrane C of 25mm×75mm was taken. The pollution-resistant reverse osmosis membrane C was taken from the FR11 reverse osmosis membrane produced by Beijing Times Wharton Technology Co., Ltd.
[0047] Use tweezers to peel off the non-woven fabric layer of reverse osmosis membrane C, keep the separation layer and support layer, and paste it on a glass slide with the same specification of 25mm×75mm with double-sided tape, so that the support layer faces On, place the separation layer in direct contact with the glass slide. In this way, it is ensured that in the process of washing and dissolving the supporting layer with an organic solvent, the organic solvent can directly contact with the supporting layer, so that the polysulfone supporting layer can be completely removed.
[0048] The coverslips were washed with distilled water and ethanol before use, and dried to remove surface-adhered pollutants. According to the difference in solub...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com