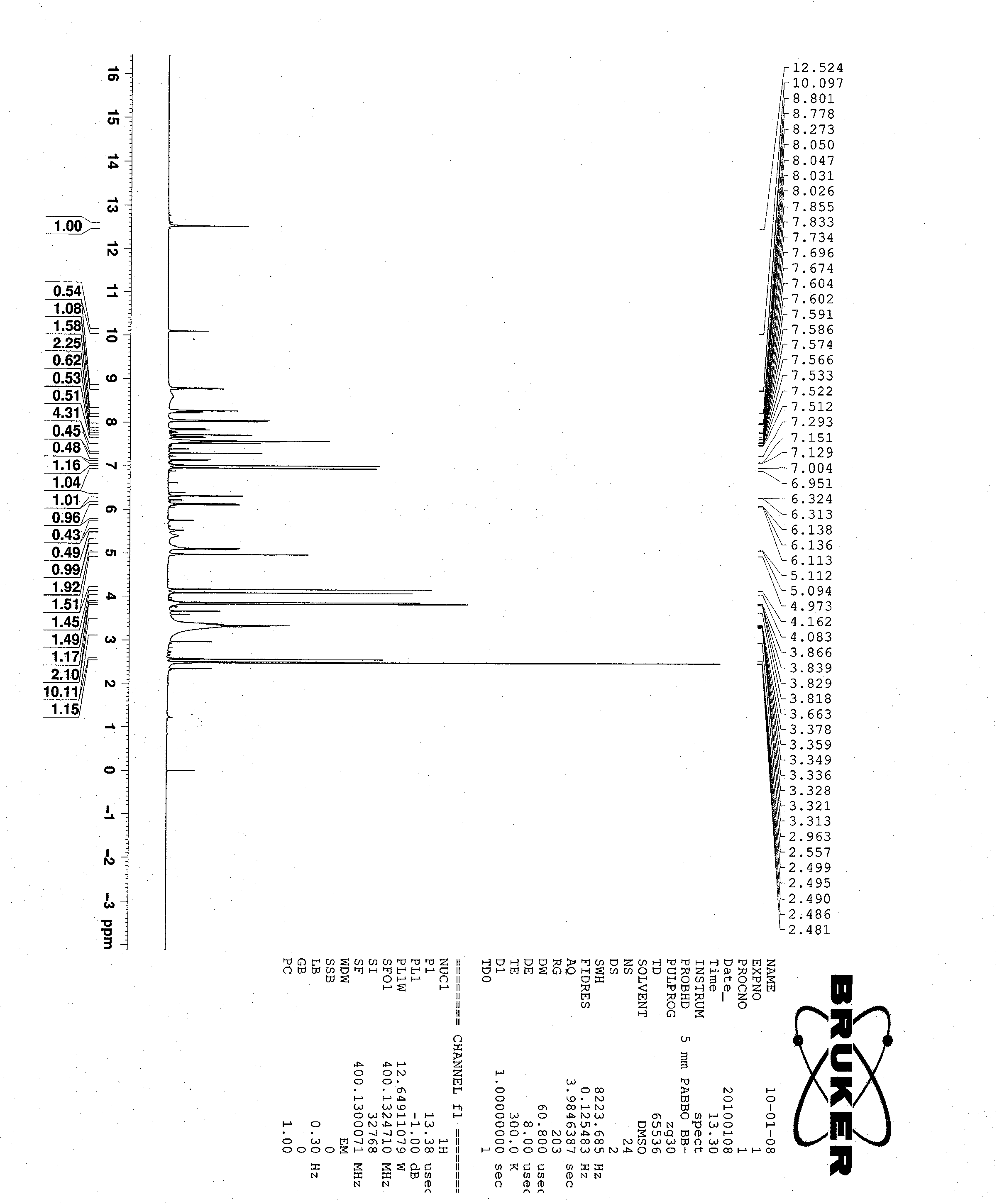
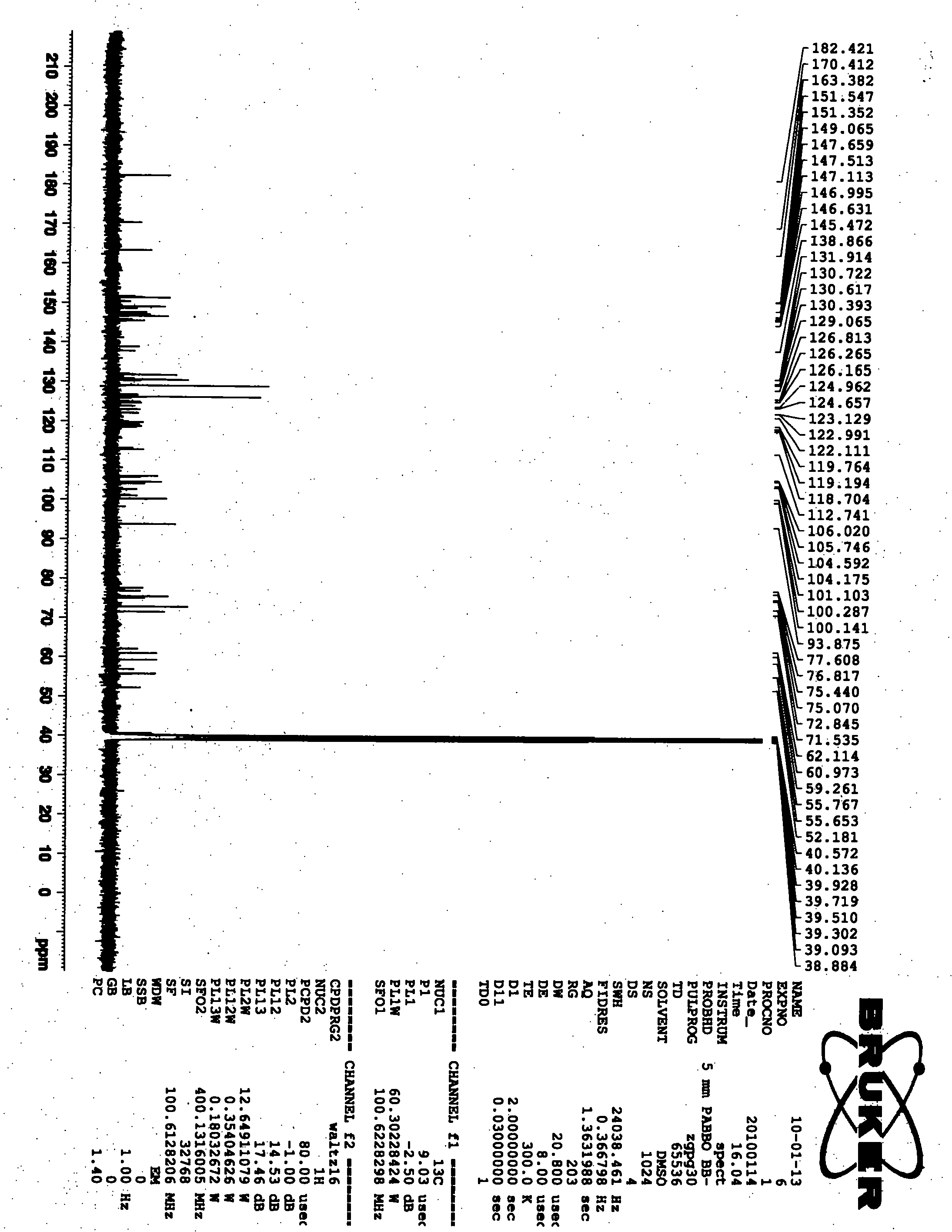
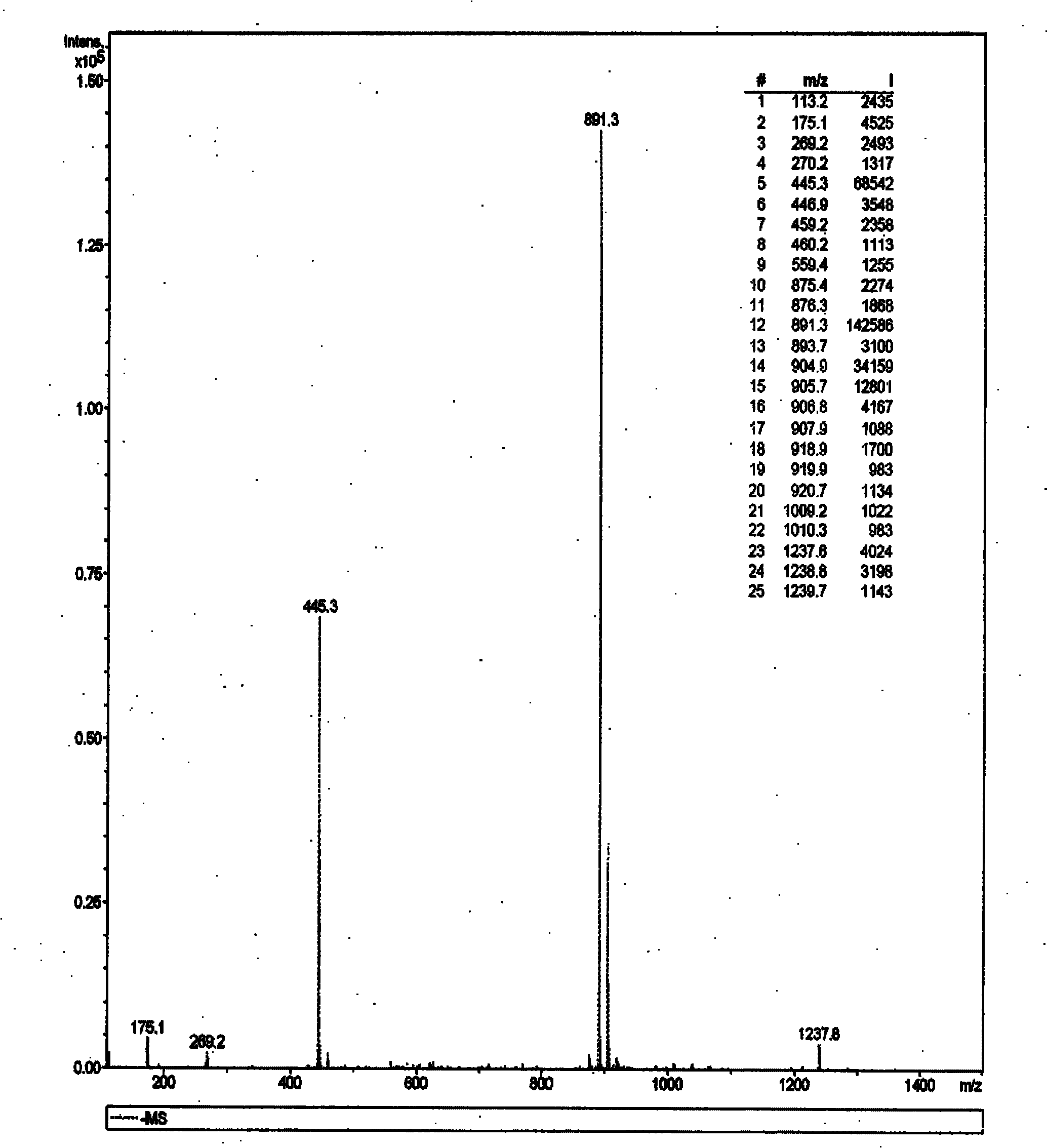
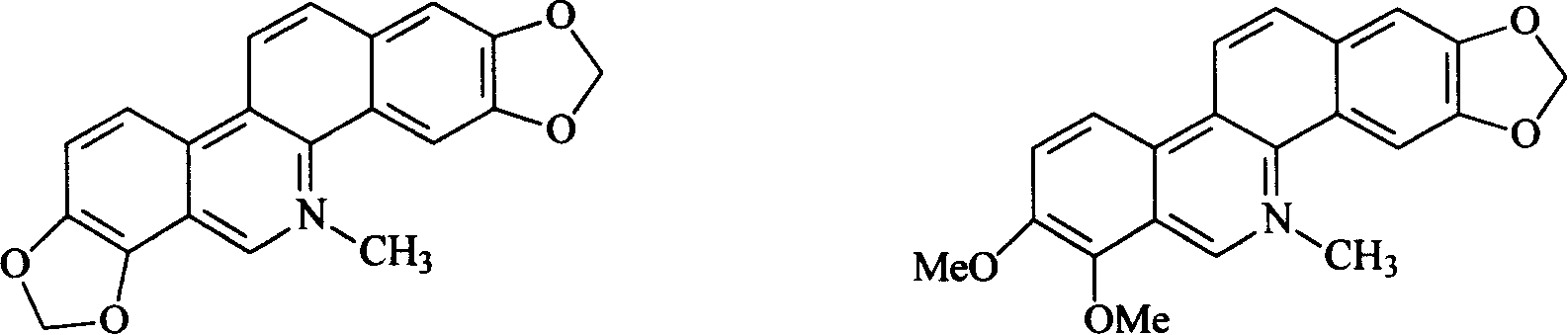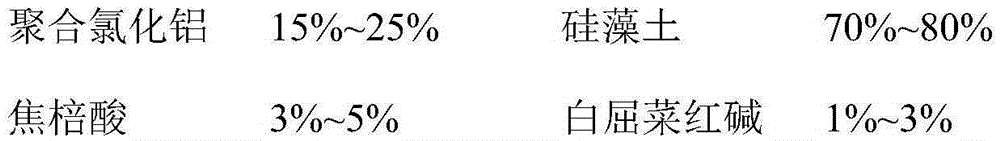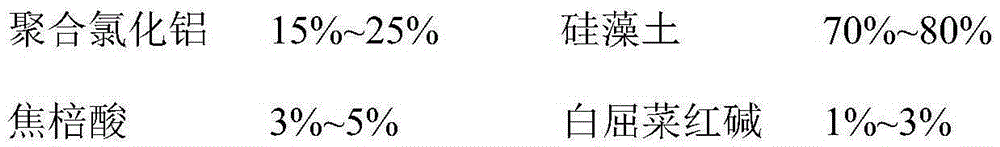Patents
Literature
65 results about "Chelerythrine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
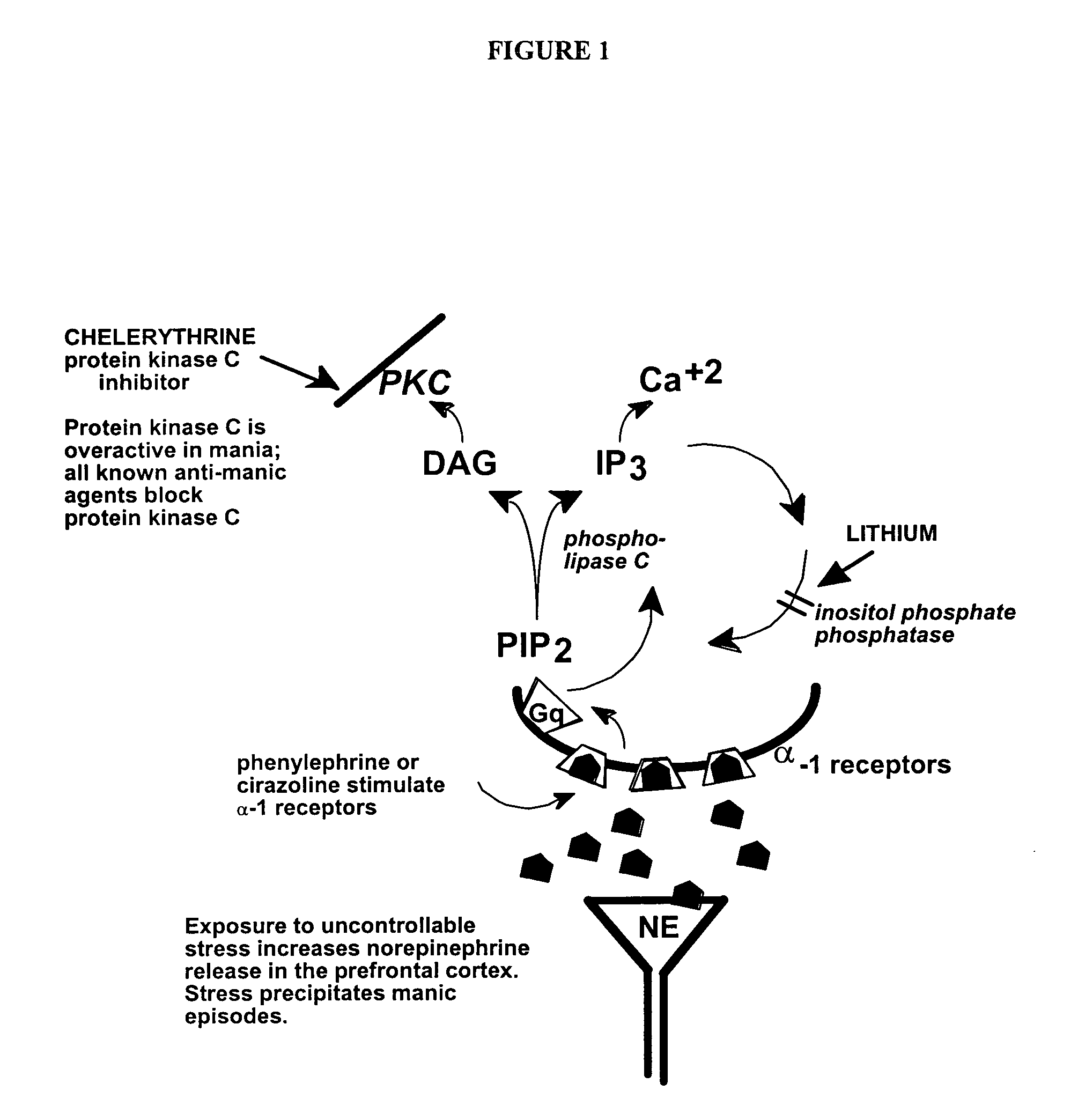
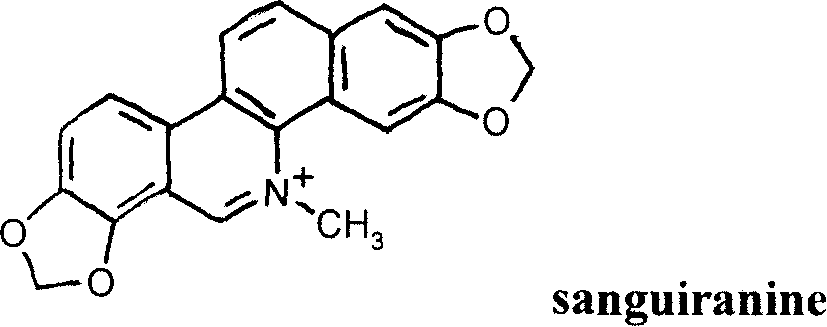
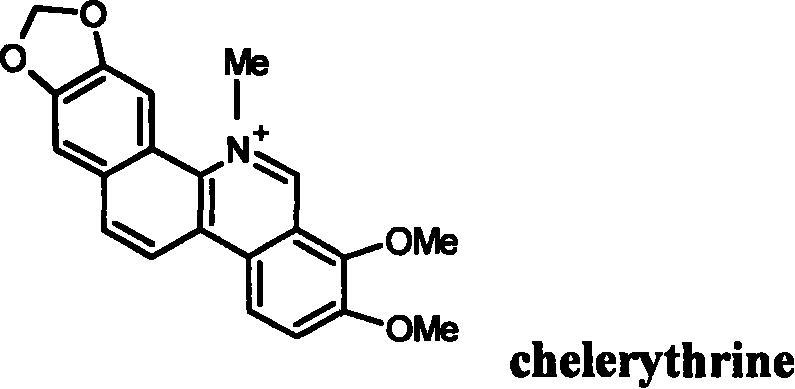
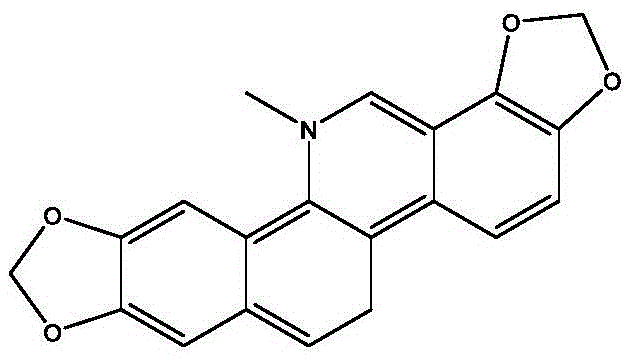
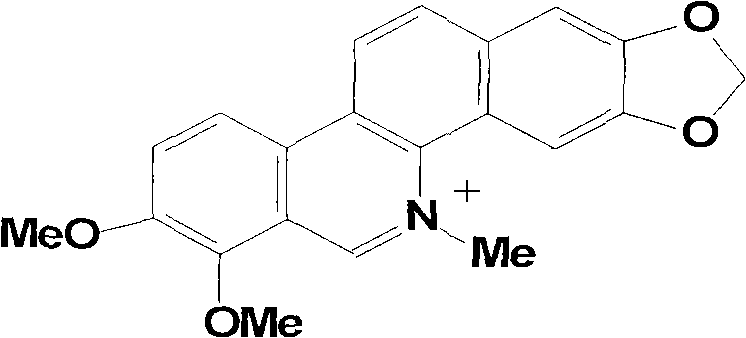
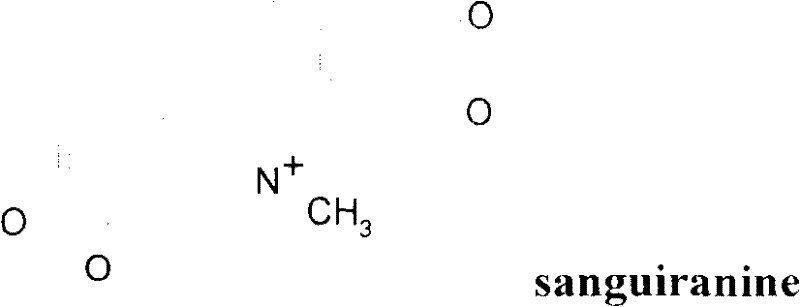
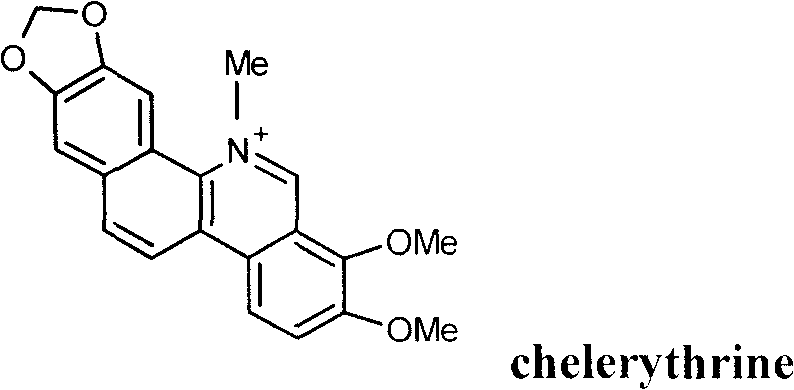
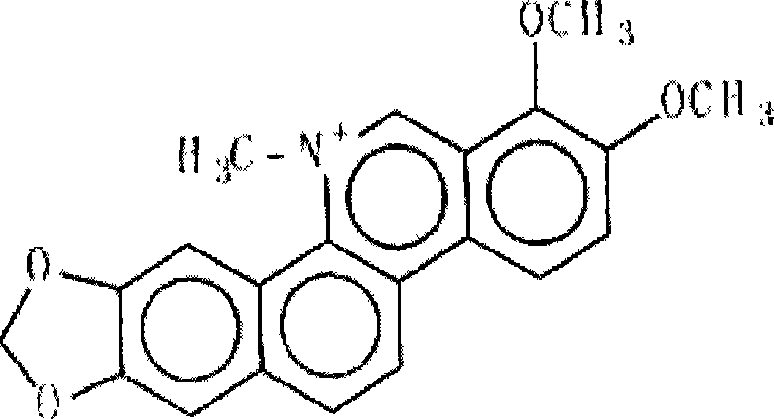
Chelerythrine is a benzophenanthridine alkaloid present in the plant Chelidonium majus (greater celandine). It is a potent, selective, and cell-permeable protein kinase C inhibitor in vitro. And an efficacious antagonist of G-protein-coupled CB1 receptors. It is also found in the plants Zanthoxylum clava-herculis and Zanthoxylum rhoifolium, exhibiting antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and other human pathogens.
Preparation method of macleaya cordata extracts
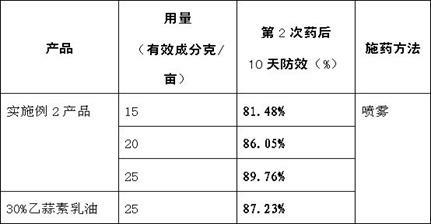
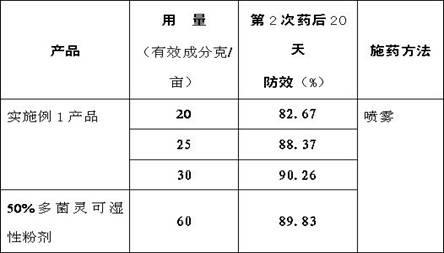
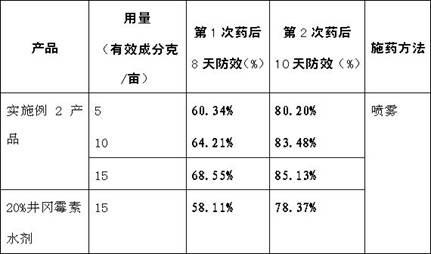
ActiveCN101849994AAddress process complexitySolve the large consumption of solventPlant ingredientsActivated carbonAlcohol
The invention relates to a preparation method of macleaya cordata extracts, which comprises the following steps: carrying out diacolation on macleaya cordata medical materials by an acid solution; adding alkali into diacolation liquid for regulating the solution to the alkaline solution for carrying out alkali deposition; dissolving precipitates by low-carbon alcohol; adding a proper amount of active carbon for back flowing extraction; adding acid for generating salt after the recovery of partial solvents from extraction liquid, and separating out orange crystalline precipitates; filtering the precipitates; using alcohol to wash remained acid; and obtaining the macleaya cordata extracts after drying. The extracts have the main ingredients of benzophen anthridine alkaloid salt with sanguinarine and chelerythrine as the representatives, and the total content is not lower than 60 percent through being metered by raw alkali, wherein the content of the sanguinarine is not lower than 40 percent, and the content of the chelerythrine is not lower than 18 percent. The preparation of the macleaya cordata extracts of the invention has the advantages of simple method and equipment, stable process, short production period and little environment pollution. The obtained extracts have high yield, low cost and stable product quality.
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
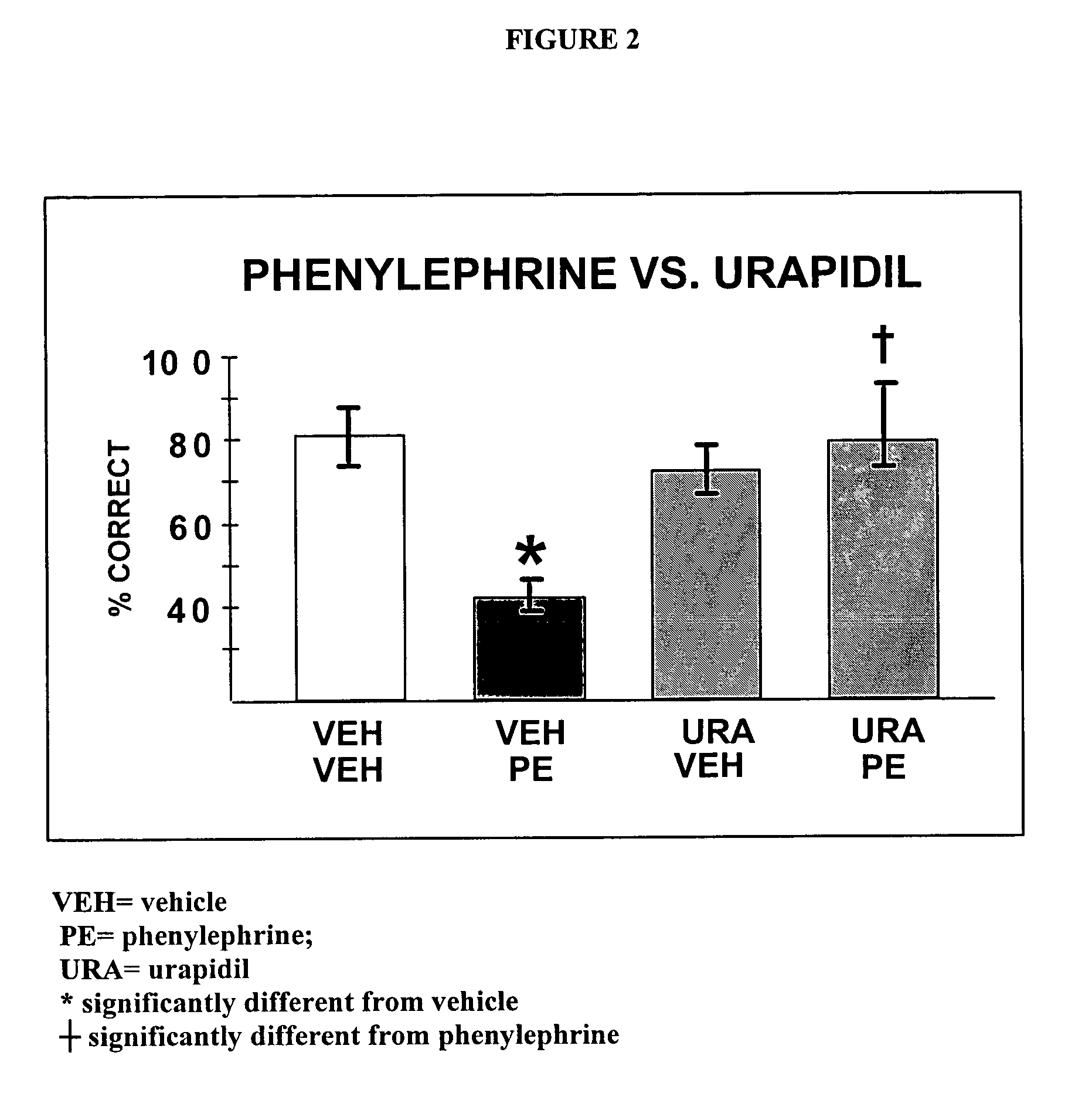
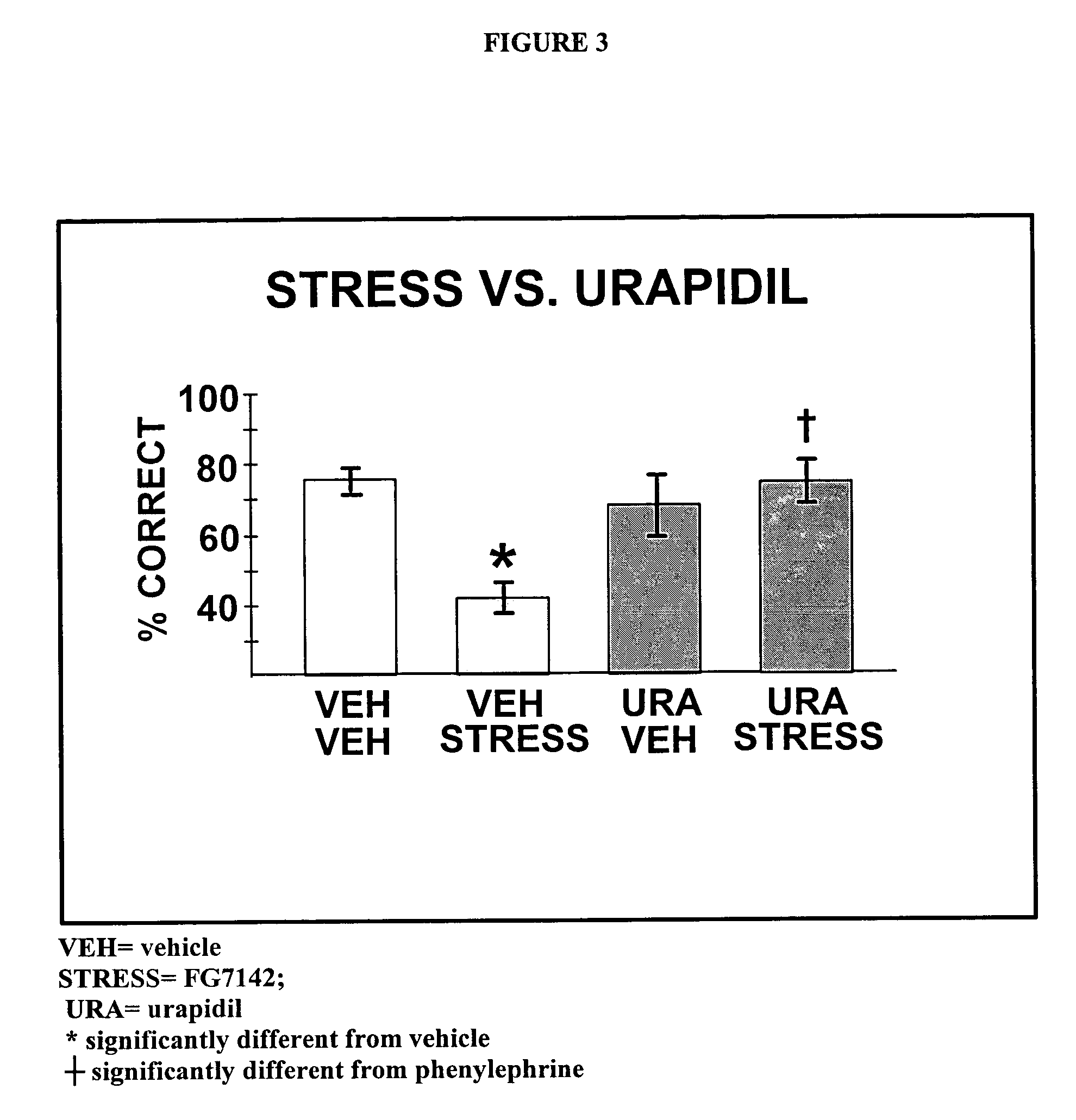
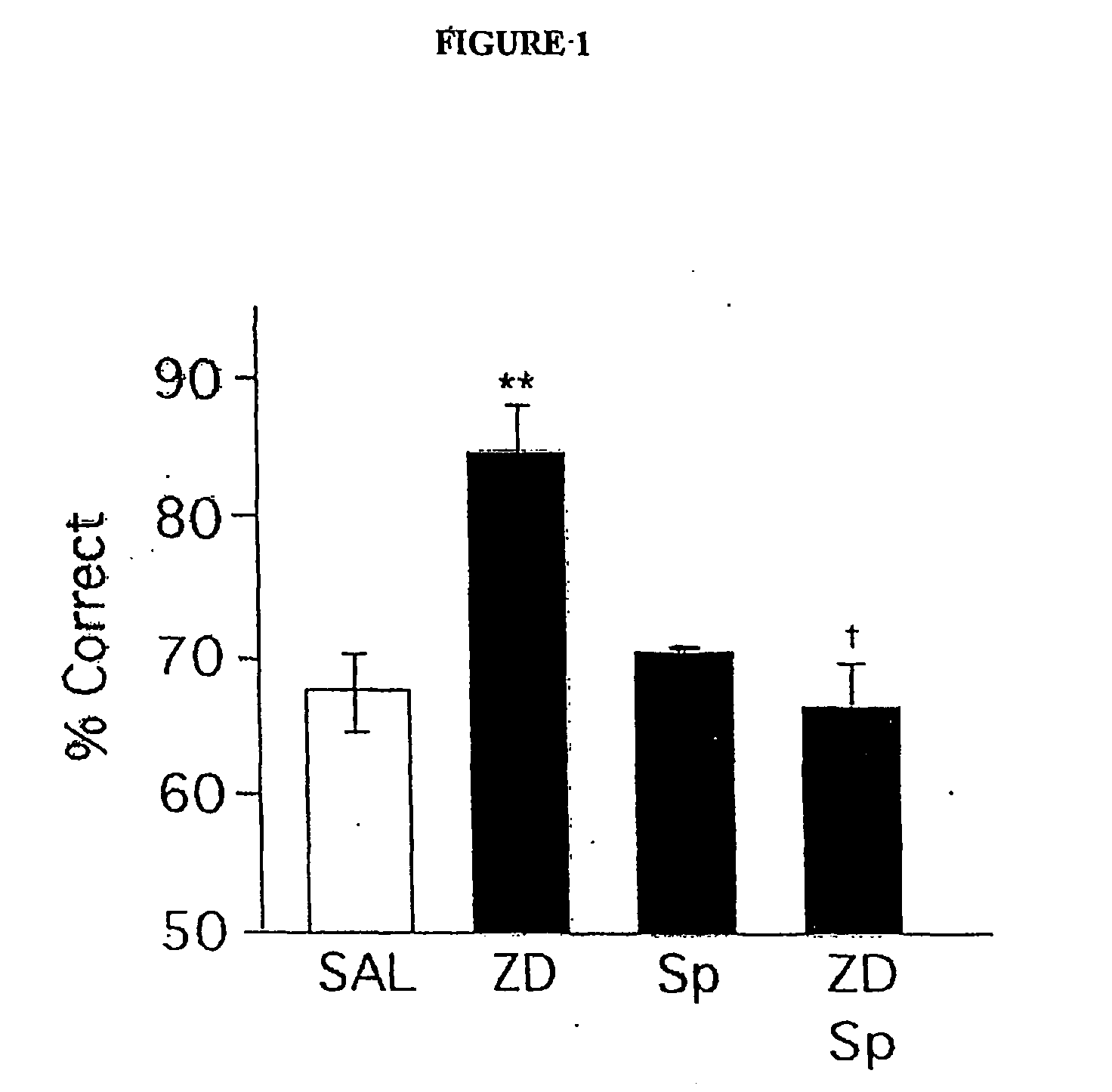
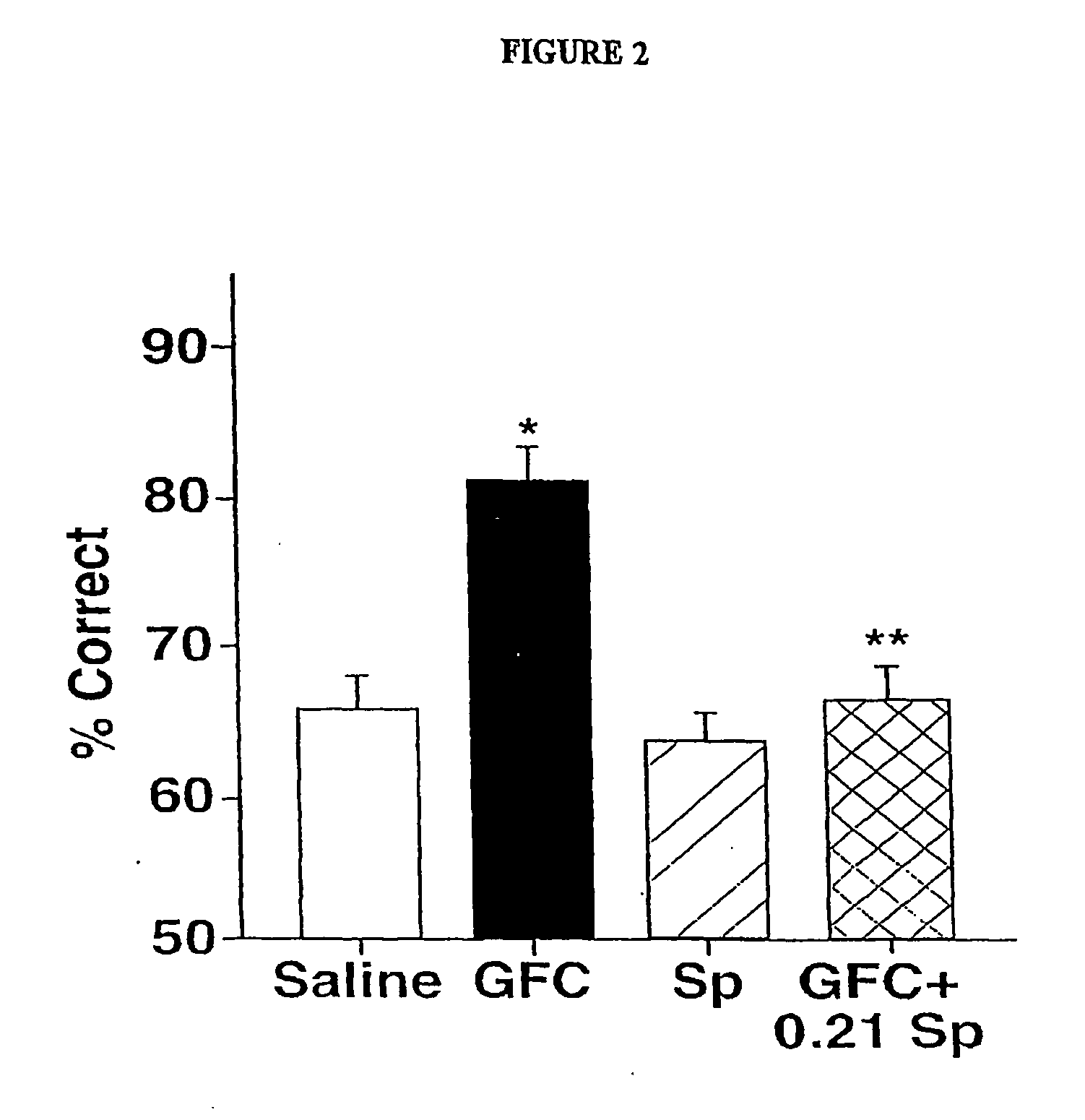
Chelerythrine, analogs thereof and their use in the treatment of bipolar disorder and other cognitive disorders
InactiveUS20050070565A1Impaired delayed alternation performanceSlow performanceBiocideNervous disorderBipolar mood disorderCognitive diseases
The present invention relates to the use of chelerythrine and chelerythrine analogs in pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of prefrontal cortical cognitive disorders, including bipolar disorder, among others.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Application of sanguinarine or toddaline in prevention and cure of schistosomiasis
ActiveCN101209043APrevent schistosomiasisSafe and efficient killingBiocideOrganic active ingredientsOncomelaniaMedicine
The invention relates to application of a sanguinarine or a chelerythrine for preventing and curing of schistosomiasis. The invention applies the sanguinarine and the chelerythrine on killing an oncomelania, a snail egg, a Japanese blood fluke cercaria, a schistosome and the prevention and cure of schistosomiasis. The inventor discovers that the sanguinarine or the chelerythrine can kill the oncomelania and the snail egg safely and effectively and can kill the Japanese blood fluke cercaria as well as a schistosomulum and an imago of the schistosome under a lower concentration, which has the functions of preventing and curing the schistosomiasis and does not pollute the environment.
Owner:长沙世唯科技有限公司
High polarity polystyrene adsorption resin preparation method and its uses in separating bocconine
InactiveCN1970592ASimple processReduce manufacturing costOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesOrganic solventElectrical polarity
The invention discloses a making method of polyphenylacetylene typed adsorption resin with high-polarity group and application to bocconine alkaloid, which is characterized by the following: synthesizing new-typed adsorption resin based on polyphenylacetylene as frame with high-polarity group content according to structural feature of sanguinarine and toddaline; utilizing the synergic effect of resin dipole action and hydrophobic action; separating sanguinarine and toddaline from resin.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
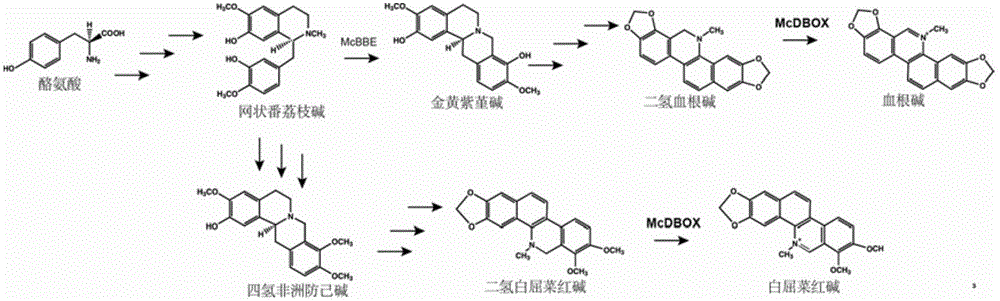
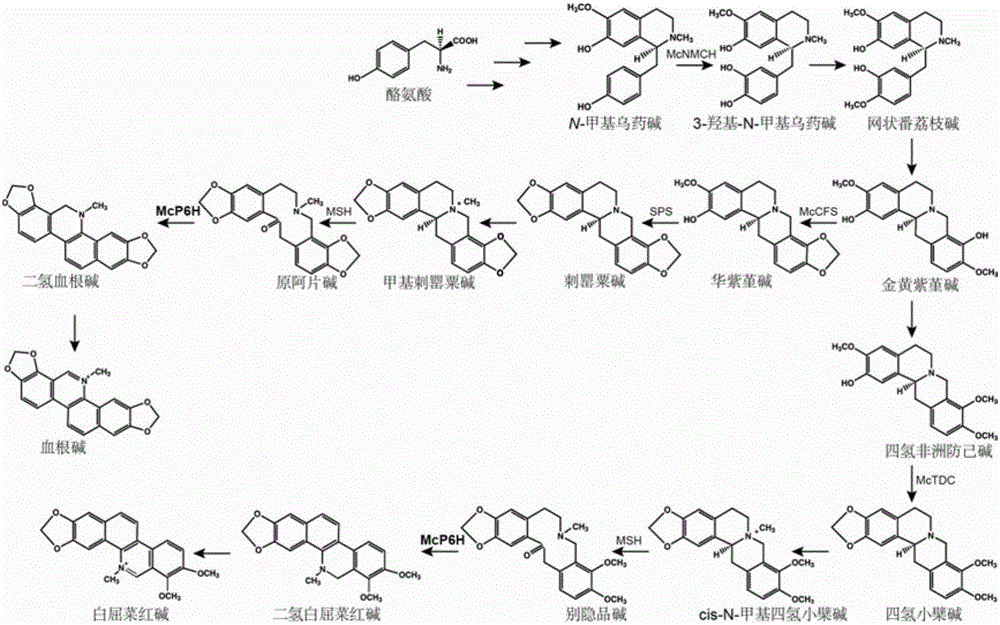
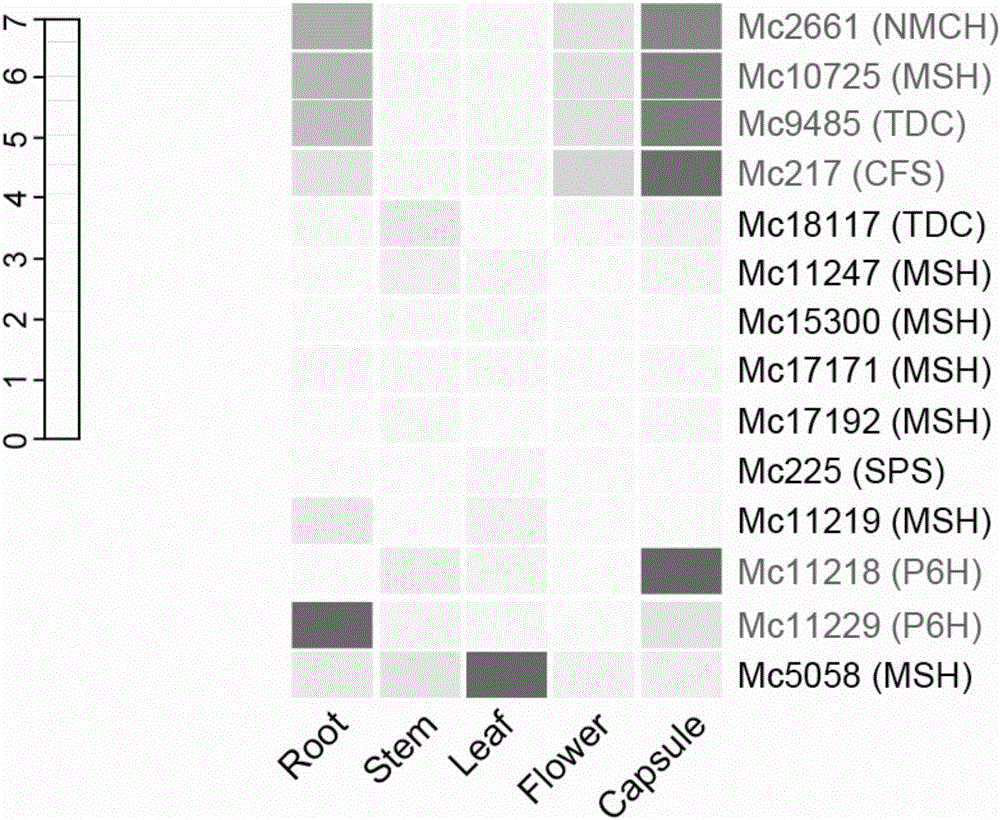
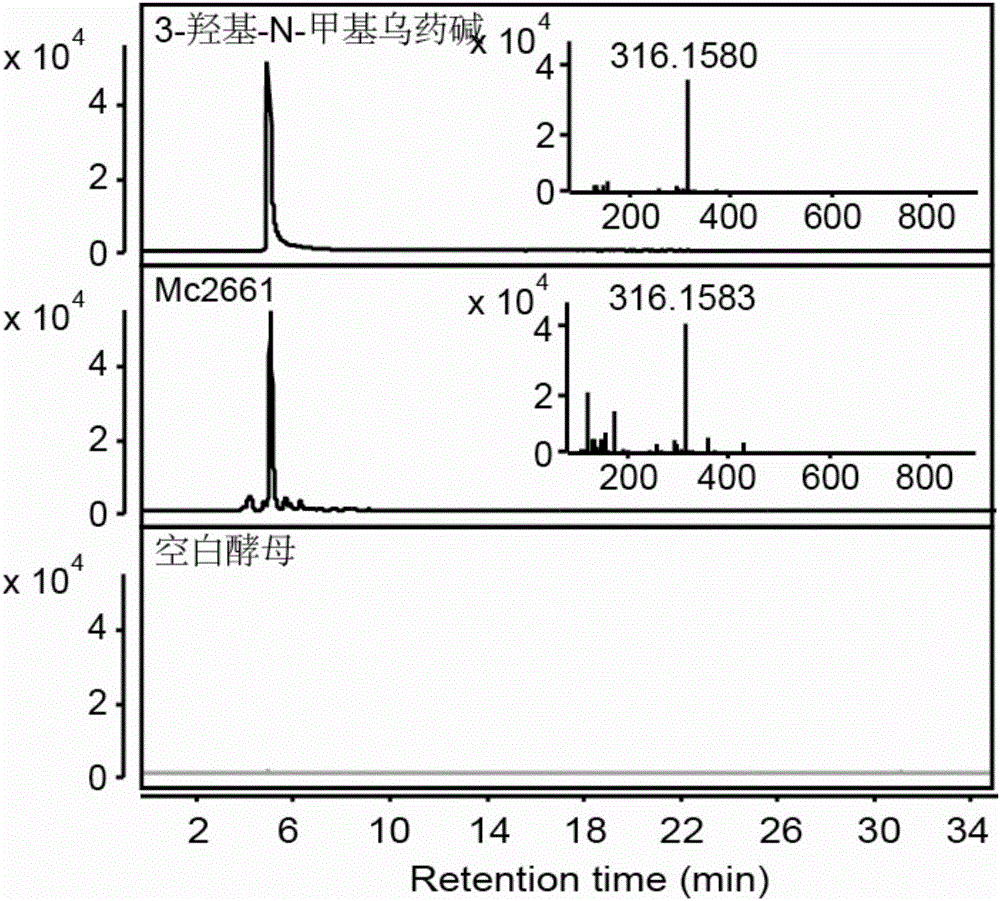
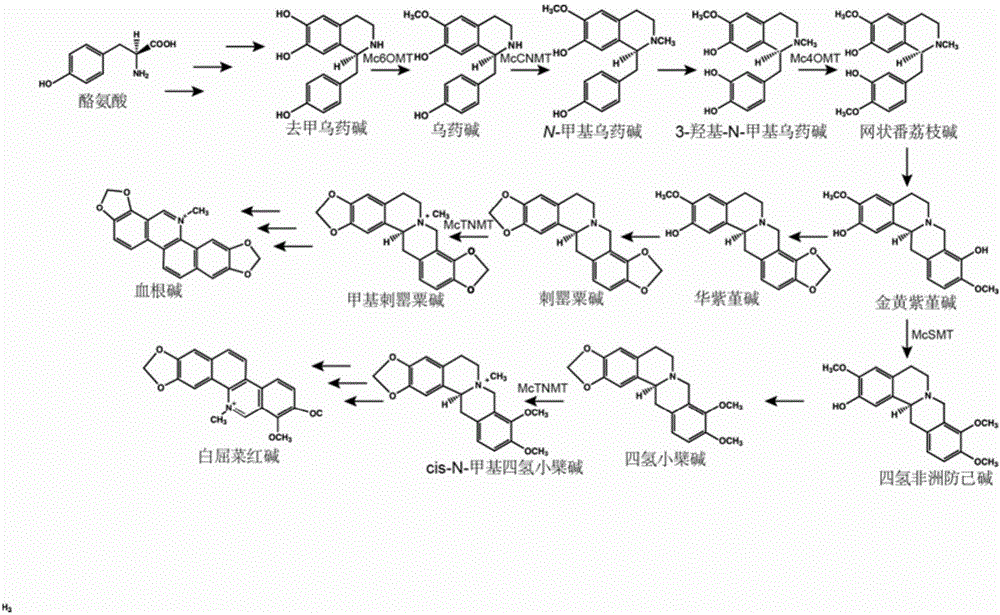
Flavoprotein oxidase genes of macleaya cordata in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine and application of flavoprotein oxidase genes
ActiveCN106047904AAchieve synthesisAchieve in vitro synthesisOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringHeterologousFlavoprotein
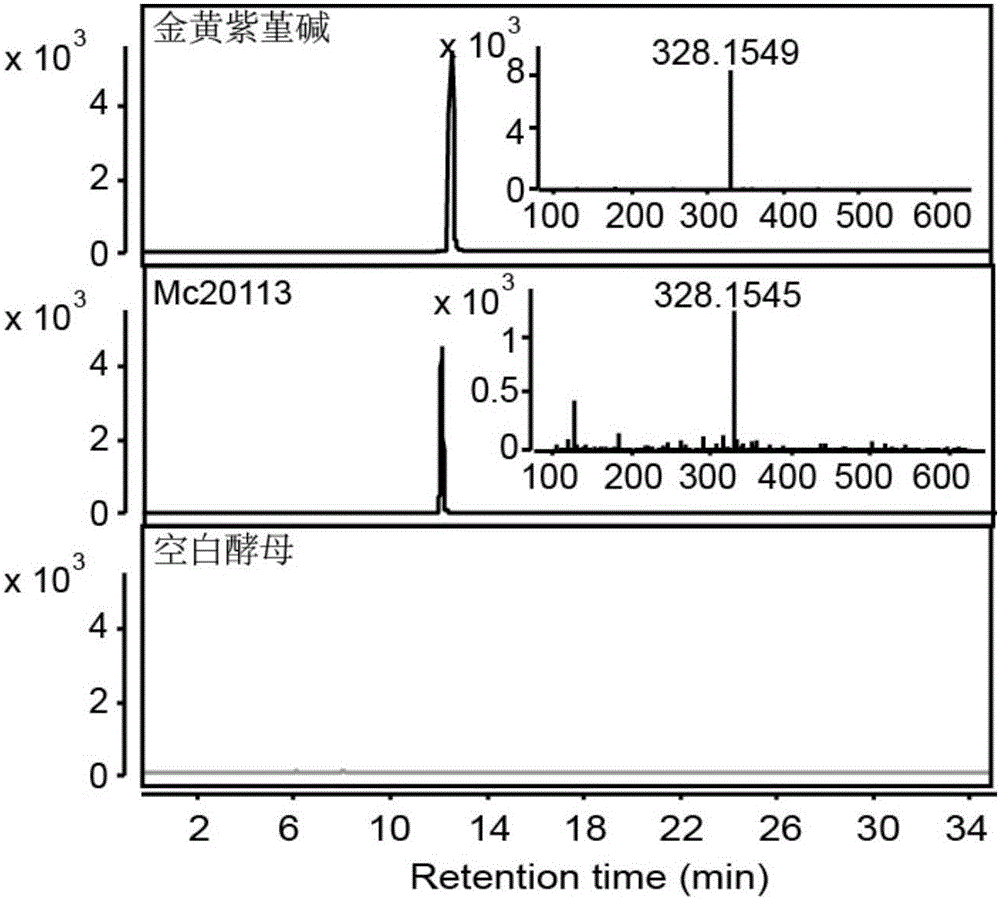
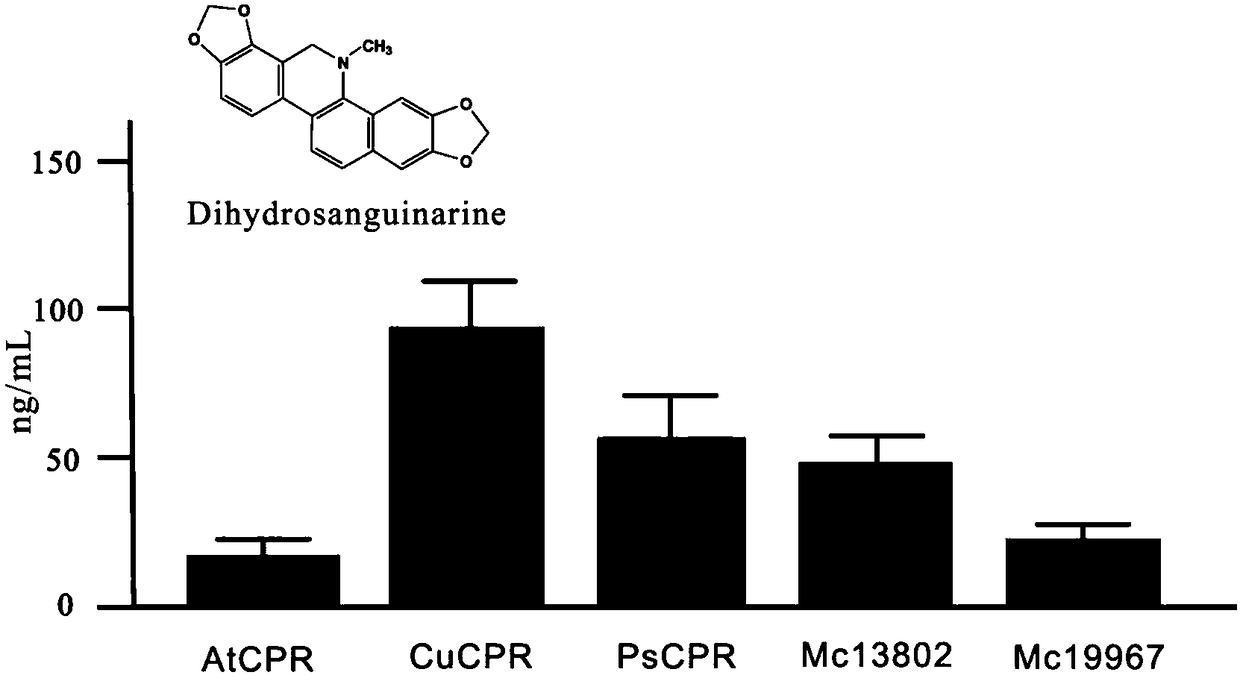
The invention discloses flavoprotein oxidase genes of macleaya cordata in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine and application of the flavoprotein oxidase genes. Three flavoprotein oxidase genes joining in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine are found in a macleaya cordata genome for the first time, including genes Mc20113, Mc6407 and Mc6408. Steps of reaction are respectively verified by using a brewer's yeast system through upstream precursor feeding, and synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine and midbodies can be achieved. The conversion efficiency of same functional genes of macleaya cordata and opium poppy is further compared by using a brewer's yeast heterologous expression system, and the result shows that the conversion rate of the gene of macleaya cordata is remarkably higher than that of opium poppy. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism of synthesis of sanguinarine in macleaya cordata, and a theoretic basis and molecular assistant breeding targets are provided for breeding of macleaya cordata with high contents of sanguinarine and chelerythrine; and meanwhile, precious experience is provided for in-vitro artificial synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine.
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
Sanguinarine alcoholate and chelerythrine alcoholate and preparation method and application thereof in animal acaricidal drugs
InactiveCN102180885ALower resistanceGood treatment effectBiocideOrganic chemistryTreatment effectChelerythrine
The invention relates to a sanguinarine alcoholate and a chelerythrine alcoholate and a preparation method and application thereof in acaricidal drugs for animals. Livestock and poultry acariasis is an in vitro parasitic disease which can cause serious damage to the animal health, and serious stress response of animals to influence ingestion, feed efficiency and weight gain, even cause death. At present, the control of the animal acariasis mainly relies on drugs for killing ticks and mites, and the ticks and mites can produce resistance to the drugs after the drugs are used for a long time, so that the drugs can cause adverse environmental and ecological effects, and can only drive and kill polypides instead of ova. The sanguinarine alcoholate and the chelerythrine alcoholate are derived from natural compounds-sanguinarine and chelerythrine alcoholate, and exist in the form of free alkaloids in the acaricidal drugs for animals. The sanguinarine alcoholate and the chelerythrine alcoholate have the characteristics of low toxicity, low residue and not easy production of resistance to the drugs of natural drugs, and have remarkable acaricidal activity and good treatment effect on the acariasis of animals when the sanguinarine alcoholate and the chelerythrine alcoholate are applied as the acaricidal drugs for animals.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Anti-coronavirus macleaya cordata benzylisoquinoline alkaloid and resveratrol composition and application thereof
InactiveCN110960532AEnhanced inhibitory effectHydroxy compound active ingredientsAntiviralsQuinolineChelerythrine
The invention discloses an anti-coronavirus macleaya cordata benzylisoquinoline alkaloid and resveratrol composition and application thereof. The macleaya cordata benzylisoquinoline alkaloid and resveratrol composition is prepared from five compositions including sanguinarine, chelerythrine, protopine, alpha-allocryptoxine and trans-resveratrol. The macleaya cordata benzylisoquinoline alkaloid andresveratrol composition has unique binding activity on a coronavirus related protein target, has a remarkable anti-coronavirus effect, and is expected to become a raw material of a drug for treatingpneumonia caused by human infection of Covid-19 coronavirus especially when concerning to the inhibition effect on Covid-19 coronavirus. The composition can be used for preparing medicines or other products for resisting diseases caused by coronavirus infection.
Owner:金晓飞
Pharmaceutical composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107441086AGood curative effectImprove qualityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseReflux extraction
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of medicines. The pharmaceutical composition consists of the following components in parts by weight: 800-1200 parts of berberine hydrochloride, 1-3 parts of chelerythrine and 300-500 parts of pulsatilla saponin B4. An agent consists of the pharmaceutical composition and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or adjuvants. The preparation method of the pharmaceutical composition comprises the following steps: mixing herba chelidonii, Chinese pulsatilla root and cortex fraxini, and implementing reflux extraction by virtue of a 30-70% (vol%) ethanol solution for 1-2 times, wherein each time lasts for 1-5h, combining filtrates which are obtained from the extraction, and condensing the combined filtrate, so that a first clear paste is obtained; and mixing 20-30 parts by weight of berberine hydrochloride with the first clear paste. According to the preparation method, the contents of the chelerythrine, the pulsatilla saponin B4 and aesculin in the extract (the pharmaceutical composition) can be effectively improved, so that the efficacy of the pharmaceutical composition and the agent on treating such diseases as diarrhoea, dysentery and the like can be improved.
Owner:HARBIN ZHENBAO PHARMA +1
Cytochrome P450 enzyme gene for taking part in sanguinarine and chelerythrine synthesis in macleaya cordata and application of cytochrome P450 enzyme gene
ActiveCN106119265AAchieve synthesisAchieve in vitro synthesisTransferasesOxidoreductasesSanguinarineChelerythrine
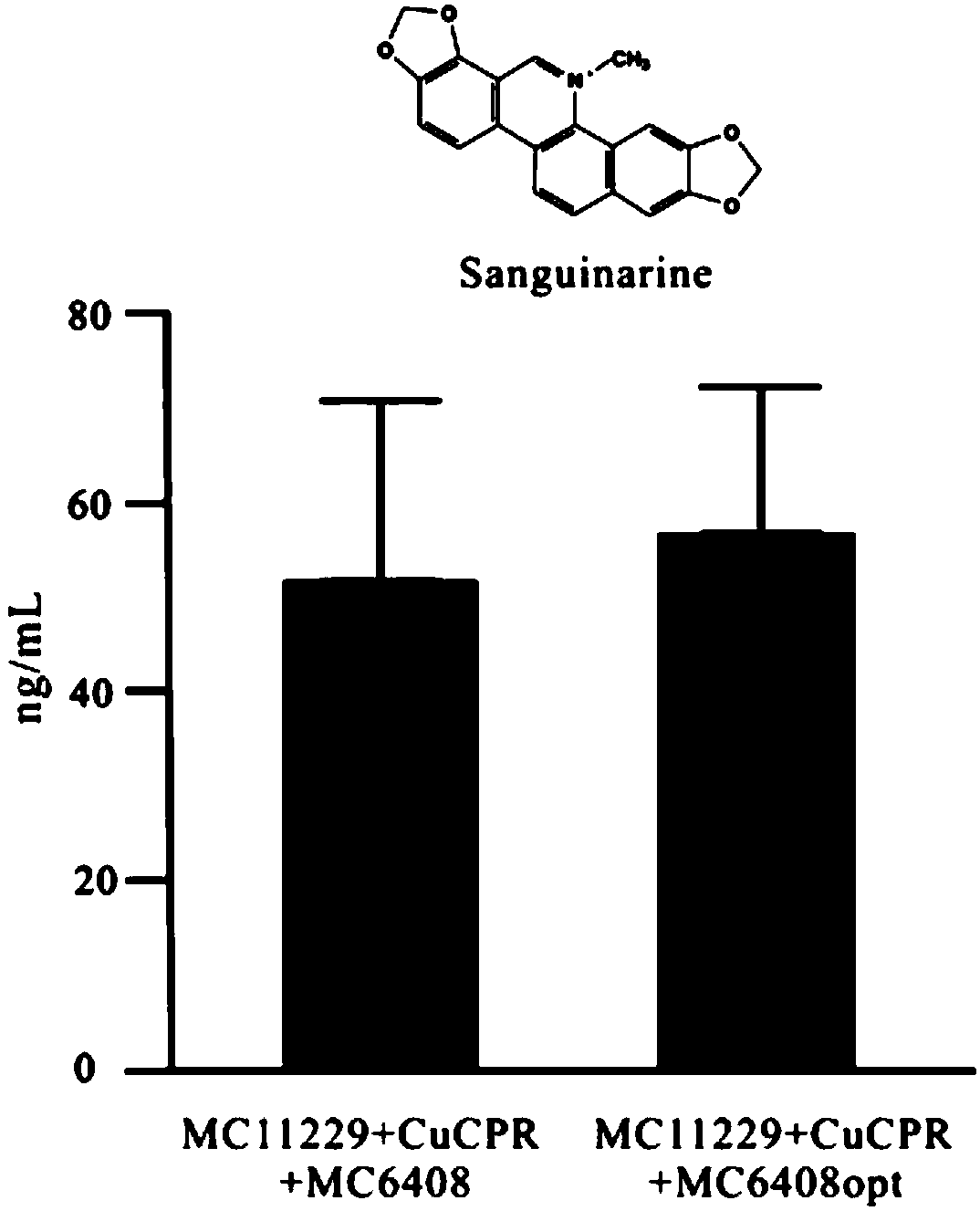
The invention discloses cytochrome P450 enzyme gene for taking part in sanguinarine and chelerythrine synthesis in macleaya cordata and application of the cytochrome P450 enzyme gene. For the first time, five cytochrome P450 enzyme genes taking part in sanguinarine and chelerythrine synthesis are found in macleaya cordata genome and comprise gene Mc9485, gene Mc2661, gene Mc217, gene MC11229 and gene Mc11218. A brewer's yeast system verifies that the steps of reaction are respectively verified by upstream precursor feeding and synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine intermediate is achieved. According to the cytochrome P450 enzyme gene, the conversion efficiencies of the same function genes in the macleaya cordata, the papaver somniferum and the eschscholzia californica are compared by the brewer's yeast heterogeneous expression system, and the conversion efficiency of the macleaya cordata is obviously higher than those of the papaver somniferum and the eschscholzia californica. According to the cytochrome P450 enzyme gene, a molecular mechanism of the sanguinarine synthesis in the macleaya cordata is further revealed. Thus, a theoretical basis and a molecular assistant breeding target are provided for the breeding of the macleaya cordata with high sanguinarine and chelerythrine content. Meanwhile, valuable experience is provided for in-vitro artificial synthesis of the sanguinarine and the chelerythrine.
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
Novel method for quickly extracting and separating five types of alkaloids from macleaya cordata
The invention relates to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicines and in particular relates to a novel method for quickly extracting and separating five types of alkaloids from macleaya cordata. The method comprises the following steps of 1) performing solvent extraction on dry macleaya cordata powder, thus obtaining an extracted solution; 2) extracting the extracted solution sequentially by utilizing ethyl acetate and normal butanol, thus obtaining an ethyl acetate extract and a normal butanol extract respectively; 3) treating the ethyl acetate extract, thus obtaining high-purity sanguinarine and chelerythrine; and 4) treating the normal butanol extract, thus obtaining high-purity protopine, cryptopine and allocryptopine. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity in operation, high efficiency, low cost, high product purity and product recovery rate and suitability for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
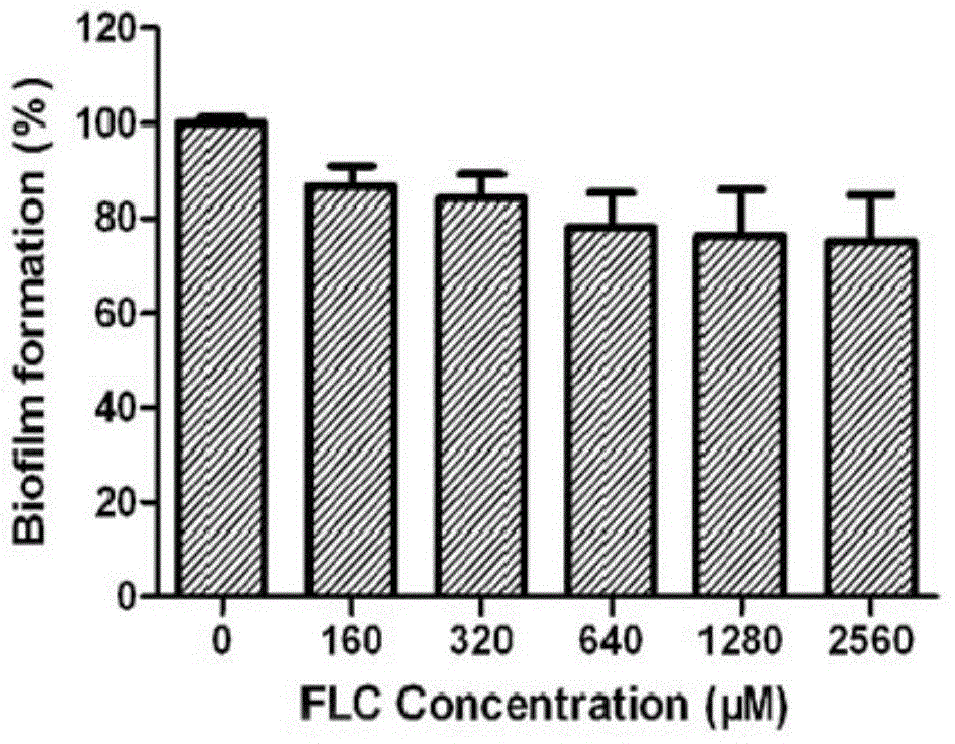
Application of chelerythrine in preparation of antifungal biofilm medicines
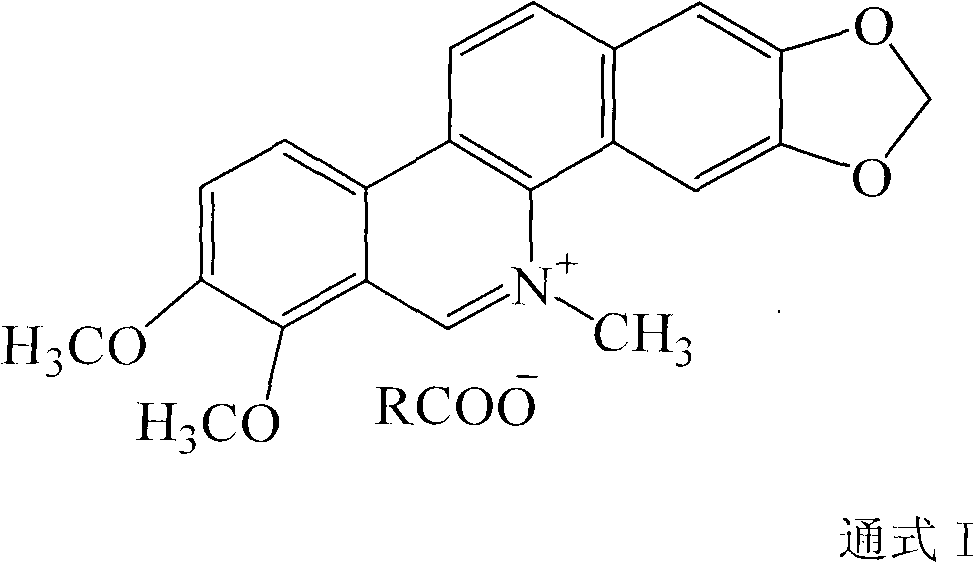
InactiveCN104145966AGrowth inhibitionEfficient killingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideIsoquinolineChelerythrine
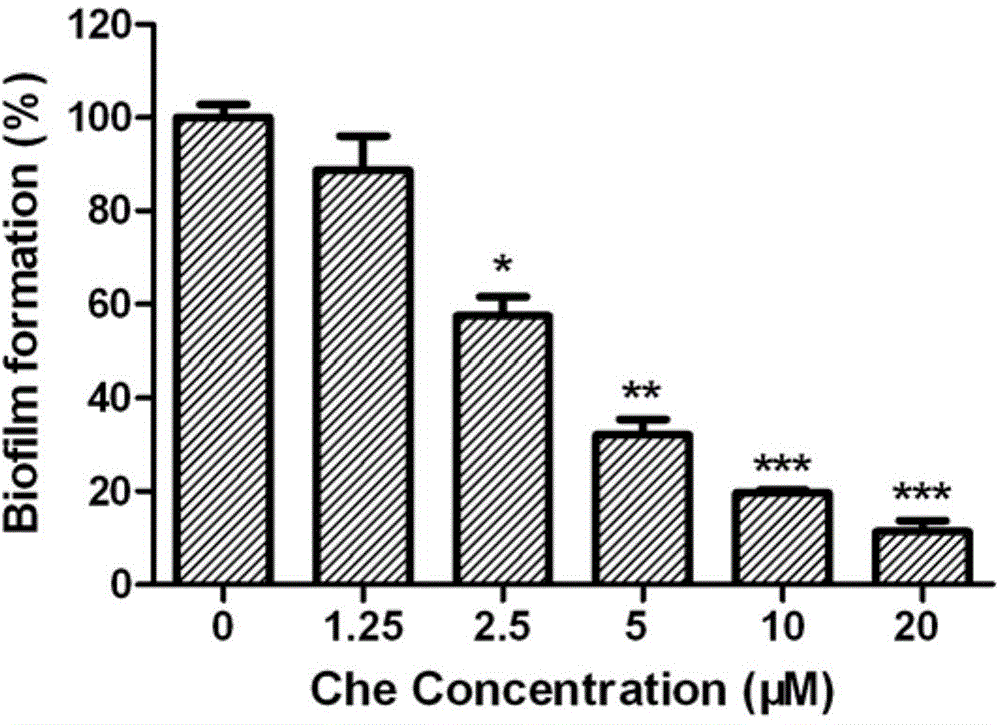
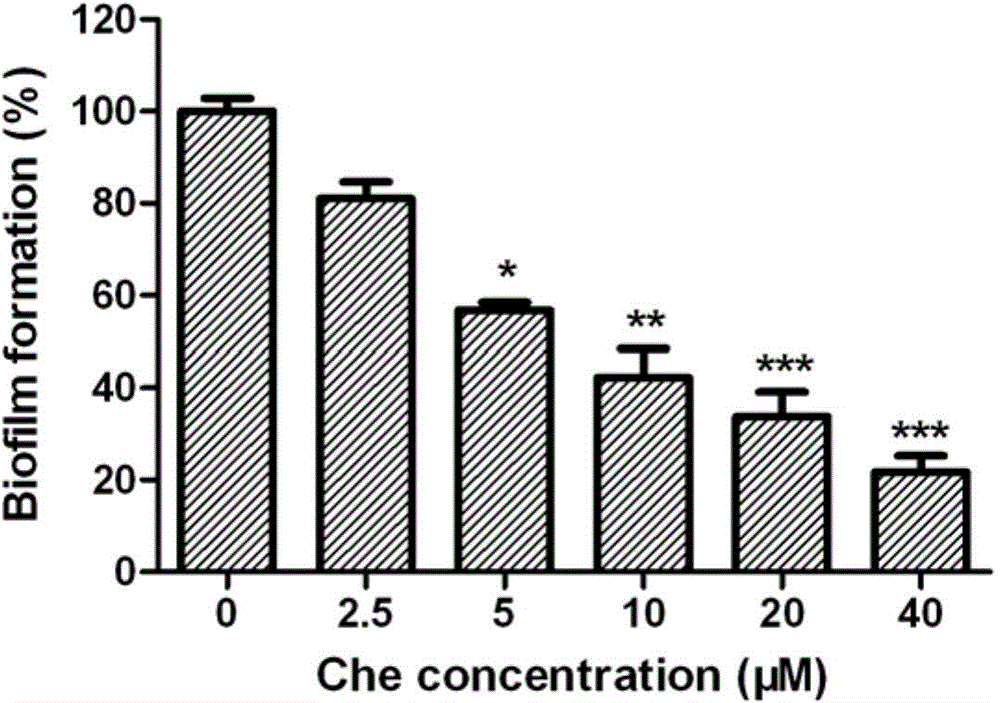
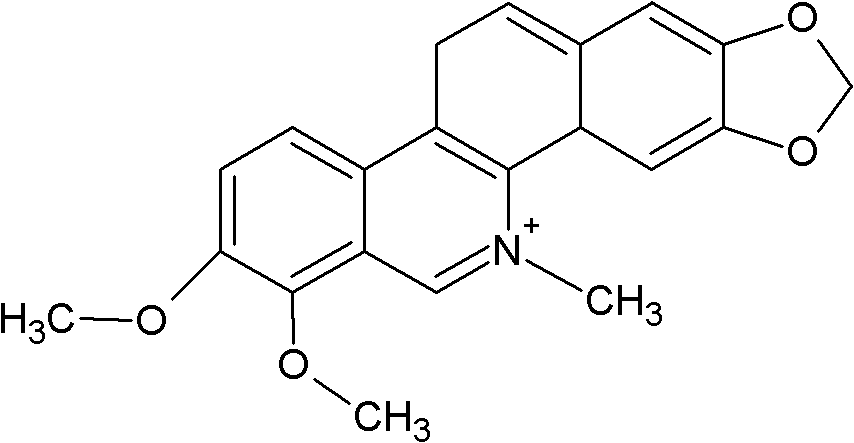
The invention relates to the technical field of medicine. Chelerythrine is isoquinoline-type alkaloid existing in plants such as celandine and macleaya cordata, and the structural formula of chelerythrine is shown in (I) described in the specification. The invention provides applications of chelerythrine in preparation of antifungal biofilm medicines, medical equipment or medical materials and the like. Experiments prove that chelerythrine has better antifungal biofilm activity both in vitro and in vivo, can effectively inhibit the growth and proliferation of fungal biofilms, and can effectively inhibit mature biofilms.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
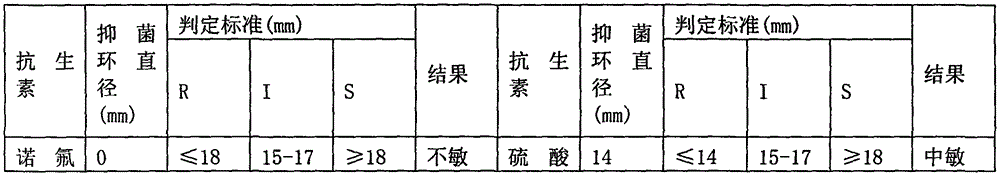
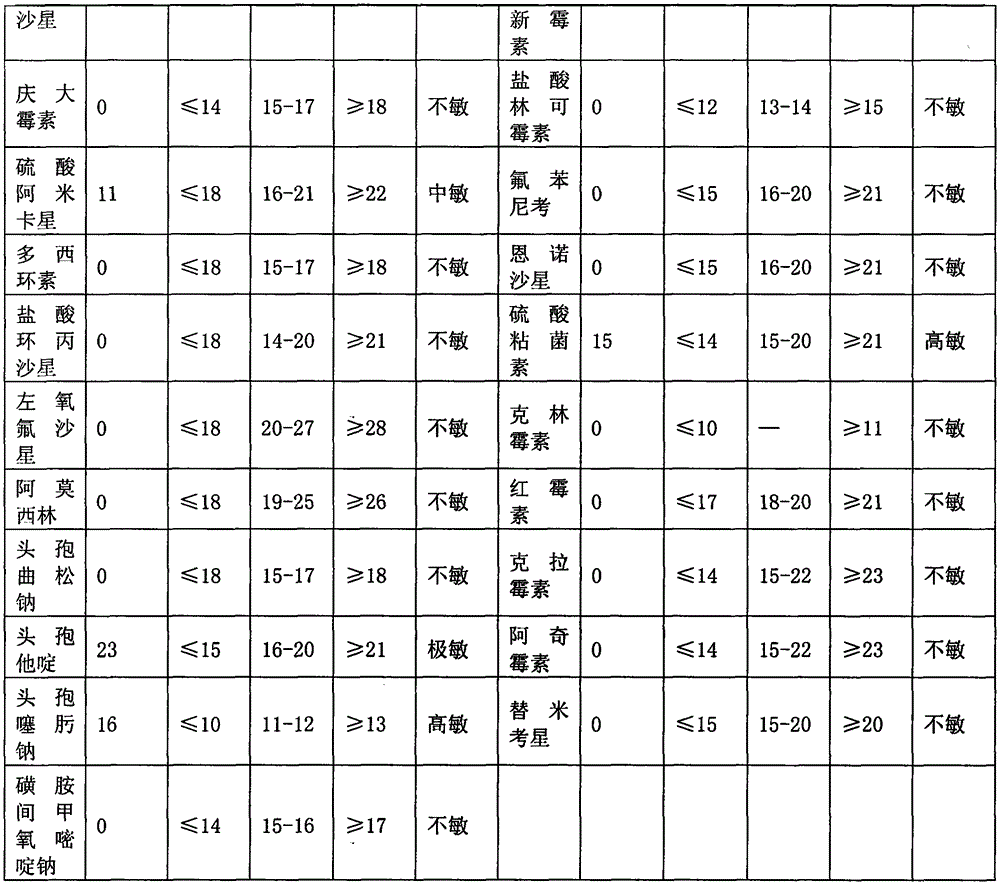
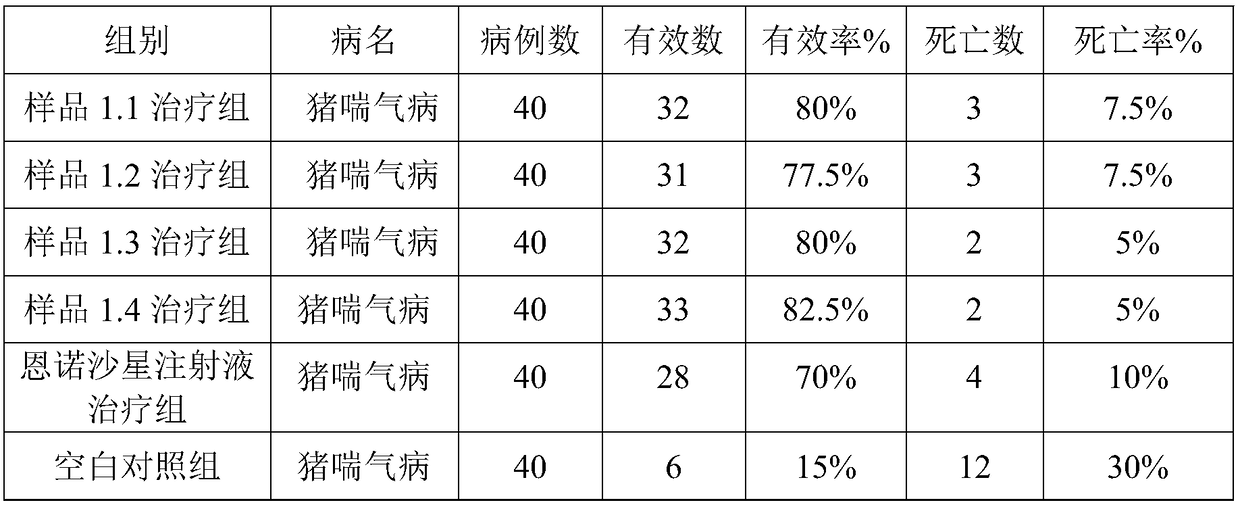
Application of chelerythrine to treatment of poultry drug-resisting colibacillosis
InactiveCN106138054AGood inhibitory effectGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliAdjuvant
The invention relates to application of chelerythrine to the treatment of poultry drug-resisting colibacillosis and in particular relates to a medicine which is prepared from the chelerythrine and other ministerial drugs and adjuvant drugs and is used for treating the poultry drug-resisting colibacillosis. The medicine provided by the invention can be prepared into suitable traditional Chinese medicine dosage forms including tablets, capsules, granules, pills, powder, ointment, sublimed preparations, powdered preparations, solutions, injections and the like according to market requirements and production conditions. The medicine provided by the invention has the characteristics of low medicine cost, simple production process, controllable quality and the like. The effective rate on the poultry drug-resisting colibacillosis reaches 93.5 percent, the death and culling rate can be reduced, the uniformity of chicken flocks is improved and the feed reward is increased; meanwhile, the medicine is environmentally friendly and has no pollution.
Owner:SHENYANG VICA ANIMAL HUSBANDRY TECH
Preparation method for high content macleaya cordata alkaloid
The invention relates to a method for preparing total alkaloid from macleaya cordata and further separating the total alkaloid to obtain high content alkaloid, particularly a preparation method for high content sanguinarine and chelerythrine. The preparation method comprises: atomizing and extracting a macleaya cordata raw material by acid water, adsorbing and eluting an extraction liquid by weakly polar macroporous resin, and recovering a solvent from an eluant and drying the eluant to obtain the total alkaloid, the content of which is not less than 60%; dissolving the total alkaloid in low-degree ethanol, carrying out secondary adsorption by using polar macroporous resin, carrying out stepwise elution by using 60% and 80% ethanol, and recovering a solvent from an eluant and drying the eluant to separately obtain the chelerythrine and the sanguinarine, the contents of which are not less than 90%. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple in process step, short in production period, high in product yield and less in use level of solvent, the environment is slightly polluted, and the obtained product is high in content, stable in quality and low in cost.
Owner:长沙博拓生物科技有限公司
Biological bactericide chelerythrine suspending agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102657192AEfficient control effectHeat-clearing and detoxifyingBiocideFungicidesDiseaseSulfonate
The invention discloses a biological bactericide chelerythrine suspending agent and a preparation method thereof. The biological bactericide is mainly prepared from chelerythrine, sodium lignin sulfonate, sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate and glycol in a certain weight ratio. The biological bactericide has a high-efficiency bactericidal and disease preventing properties, and is wide in application range and good in effect for controlling crop diseases and pests.
Owner:芜湖市嘉创生物科技有限责任公司
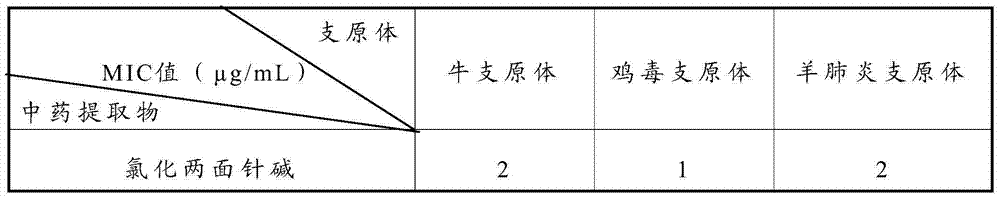
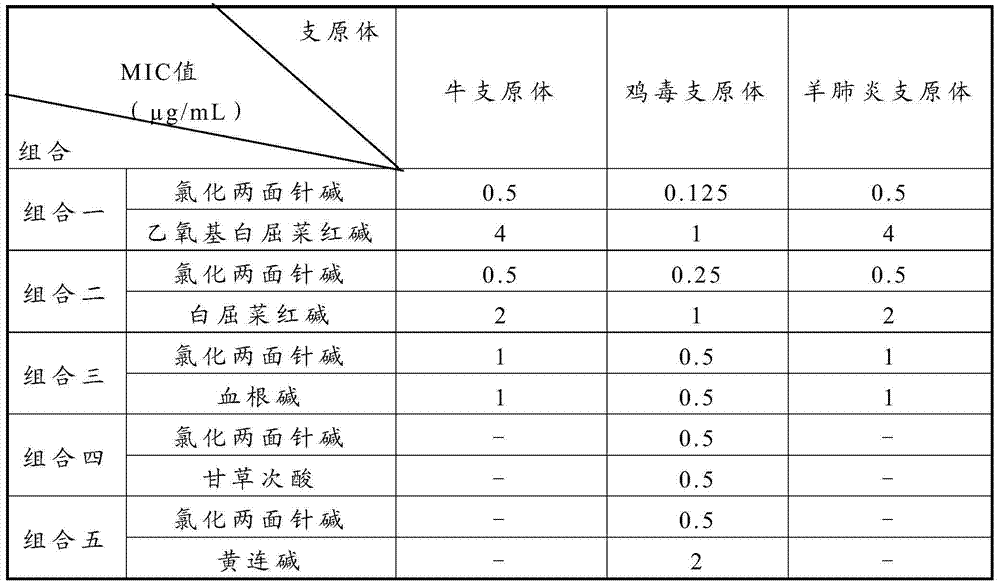
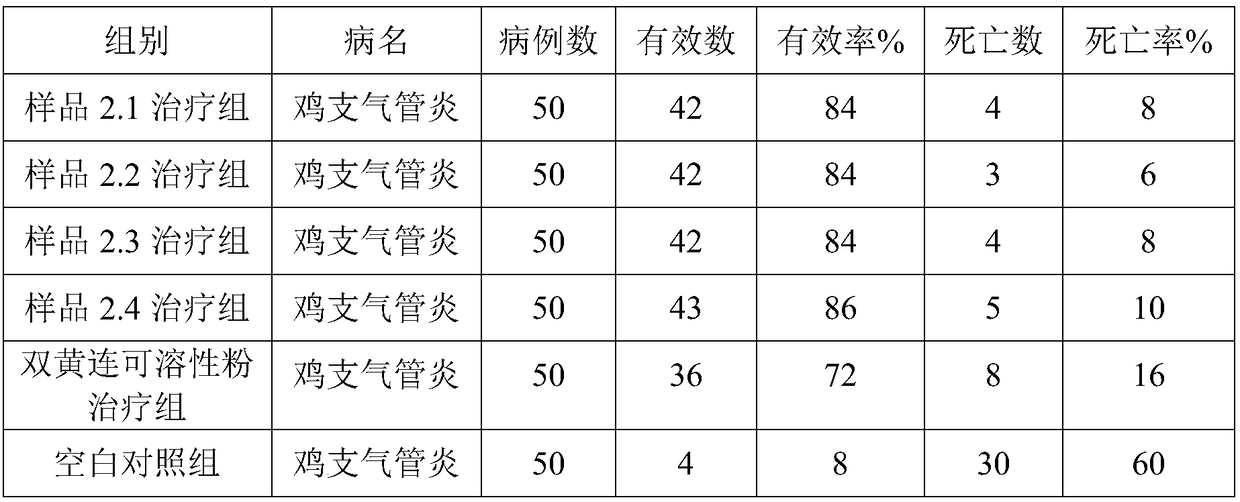
Traditional Chinese medicine extract and traditional Chinese medicine composition having poultry and livestock mycoplasma resistant activity
ActiveCN103690538ARelieve respiratory symptomsEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCoptisineNitidine chloride
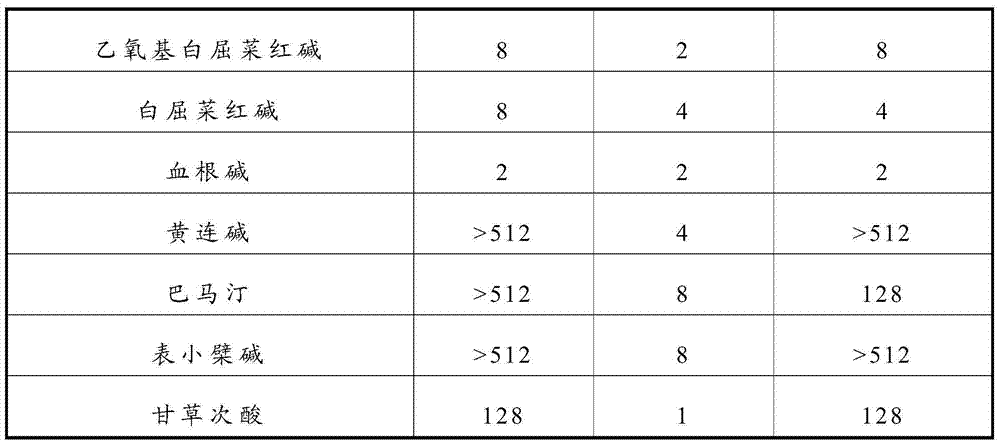
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine extract having poultry and livestock mycoplasma resistant activity. The traditional Chinese medicine extract contains any one or more of the following components: 1-512 mu g / mL of nitidine chloride, 1-512 mu g / mL of ethoxychelerythrine, 1-512 mu g / mL of chelerythrine, 1-512 mu g / mL of sanguinarine, 1-512 mu g / mL of coptisine, 1-512 mu g / mL of palmatine, 1-512 mu g / mL of epiberberine, and 1-512 mu g / mL of glycyrrhetinic acid. The invention further provides a traditional Chinese medicine composition having poultry and livestock mycoplasma resistant activity. Both the traditional Chinese medicine extract and the traditional Chinese medicine composition provided by the invention have the stronger effect for inhibiting poultry and livestock mycoplasma activity in vitro, are safe, green and free from medicine residue, and can be applied to treating and preventing poultry and livestock mycoplasma diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNNY BIO TECH CO LTD +1
Fly killing agent containing macleaya cordata and cyromazine
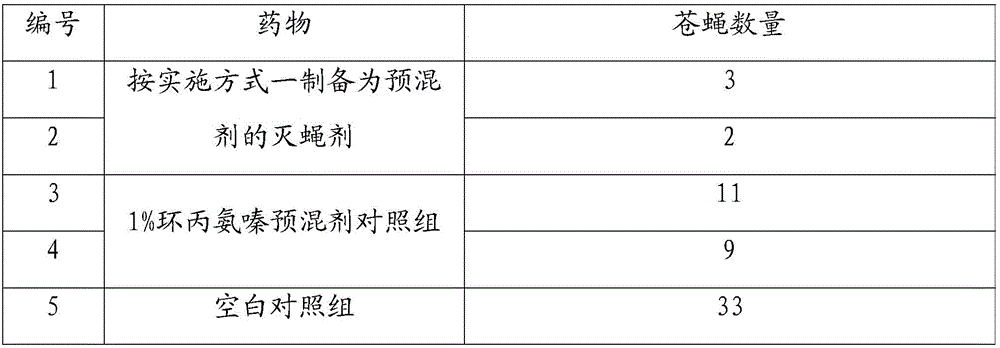
InactiveCN106614764AInhibition hatchingReduce usageBiocideDead animal preservationFeed conversion ratioActive component
The invention relates to the technical field of veterinary drugs and discloses a fly killing agent containing macleaya cordata and cyromazine. Macleaya cordata and cyromazine are used as active components of the fly killing agent; according to percentage by weight, the weight percentage range of macleaya cordata is 1-5%, and the weight percentage range of cyromazine is 1-10%; in macleaya cordata, the weight percentage of sanguinarine is not less than 1.50%; the total weight percentage of sanguinarine and chelerythrine is not less than 2.25%. Macleaya cordata and cyromazine are matched in use; the cyromazine is used while a certain amount of chelerythrine is added, so that the effects of killing and controlling flies can be improved; the consumption of cyromazine is reduced; the influence on animal organism and environment is reduced; the effects of killing and controlling flies of the fly killing agent are greatly improved; the consumption of cyromazine is effectively reduced; drug pollution and residue can be reduced; the fly killing agent also has the advantages of accelerating parturition, reducing feed conversion ratio, improving animal parturition performance and reducing feeding cost, and has a wide application prospect in the animal farming industry.
Owner:FOSHAN STANDARD BIO TECH
Method for extracting high-purity sanguinarine and chelerythrine by using chromatographic technique
ActiveCN105541856AOvercome the disadvantage of low preparation puritySolve the shortcomings of small sample loading and high costOrganic chemistrySepharoseSanguinarine
The invention discloses a method for extracting high-purity sanguinarine and chelerythrine by using a chromatographic technique. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving a macleaya cordata extract and then filtering; (2) preparing a corresponding buffer solution A and a corresponding buffer solution B; (3) injecting a macleaya cordata solution obtained through the filtering into a chromatographic column filled with SP-Sepharose FF fillers for adsorption; (4) flushing the chromatographic column by using the buffer solution A by 1 to 3 column volumes firstly, then eluting impurities in the chromatographic column by using the buffer solution B, and then eluting a target object from the chromatographic column by using the buffer solution B. The method provided by the invention is simple to operate, small in energy consumption, low in cost, and high in purity, and sanguinarine and chelerythrine with the purity above 98 percent can be obtained.
Owner:LISUI TECH SUZHOU
Method for efficient enzyme catalytic synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine
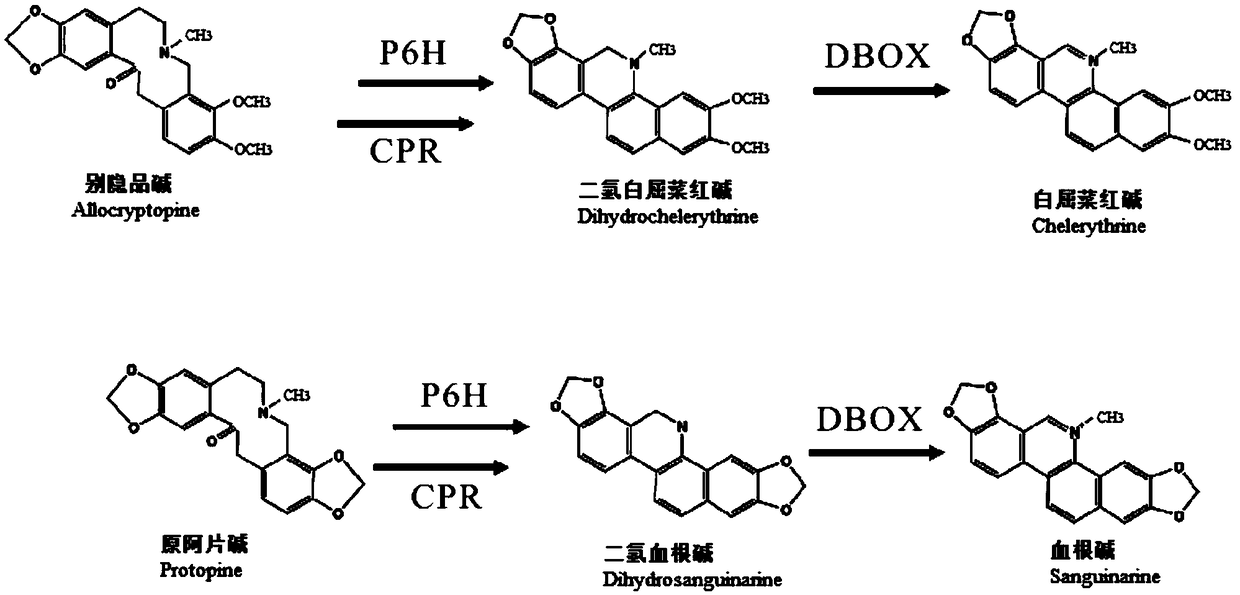
ActiveCN109468351AIncrease contentReduce manufacturing costFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCytochrome P450 reductase
The invention discloses a method for efficient enzyme catalytic synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine. The method comprises the following steps: respectively screening optimal genes with high expression efficiency from a known protopine-6-hydroxylase gene, a dihydrobenzophen anthridine oxidase gene and a cytochrome P450 reductase gene through heterologous expression and result comparison andanalysis, and carrying out codon optimization on selected optimal genes; establishing optimal gene sequences on expression carriers, transferring into a yeast engineering bacterium, and carrying outtransformation so as to obtain a recombinant yeast engineering strain; finally feeding the recombinant yeast engineering strain with a macleaya cordata leaf raw material liquid precursor to carry outfermentation, thereby obtaining sanguinarine and chelerythrine. By adopting the method, the enzyme catalysis efficiency of the sanguinarine and the chelerythrine is improved from multiple aspects suchas gene levels and fermentation processes, fumarine and allocryptopine which are high in alkaloid content in leaves can be transformed into sanguinarine and chelerythrine with high values, and comprehensive utilization of macleaya cordata resources can be achieved.
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
Alga inhibiting and eliminating drug
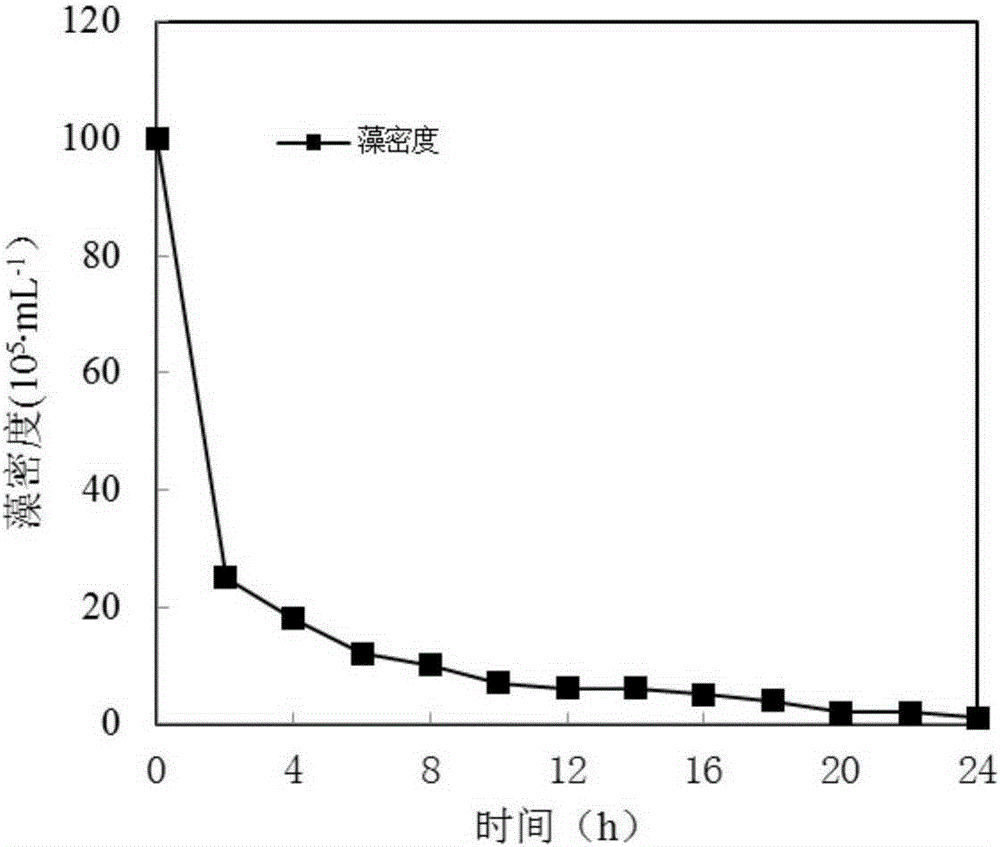
ActiveCN105293651ALow costNo growth phenomenonWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationChelerythrinePollution
The invention discloses an alga inhibiting and eliminating drug. The alga inhibiting and eliminating drug comprises, by mass, 15 to 25% of polymeric aluminum, 70 to 80% of diatomite, 3 to 5% of pyrogallic acid and 1 to 3% of chelerythrine. The alga inhibiting and eliminating drug has the following beneficial effects: (1) good effect and fast action; (2) small secondary pollution; and (3) long-lasting alga inhibiting effect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Ion-pair compound of chelerythrine from Chinese medicine extracts, preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101775022AReduce hydrophilicityImprove lipophilicityAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBenzoic acidChlorogenic acid
The invention relates to an ion-pair compound of chelerythrine from Chinese medicine extracts, a preparation method and application thereof. Organic acids of the invention mainly comprise chlorogenic acid, gallic acid, shikimic acid, oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, benzoic acid, salicylic acid, tartaric acid, lactic acid, sorbic acid, fumaric acid, malic acid, citric acid, maleic acid, glycyrrhizic acid, glycyrrhetinic acid, carnosic acid, P-hydroxycinnamic acid, rosmarinic acid, succinic acid, ferulic acid, protocatechuic acid, cinnamic acid, caffeic acid, chicoric acid or cortex pseudolaricis acetic acid. The ion-pair compound prepared from the chelerythrine and the organic acids has the antibacterial biological activity. The invention relates to the application of the ion-pair compound of the chelerythrine to medicine, animal remedy or daily use cosmetics.
Owner:曾建国
Macleaya cordata leaf extract as well as preparation method and product thereof
ActiveCN108837006APromote recoveryReduce mortalityOrganic active ingredientsClimate change adaptationChelerythrineRespiratory disease
The invention provides a macleaya cordata leaf extract as well as a preparation method and a product thereof. In the macleaya cordata leaf extract, the content of fumarine is not lower than 0.1%, thecontent of allocryptopine is not lower than 0.1%, and the sum of content of sanguinarine and chelerythrine is not lower than 0.2%. The preparation method comprises the following steps: extracting macleaya cordata leaves with an acidic aqueous solution, adding alkali into the extracting solution to regulate the pH value to be alkaline, performing alkaline precipitation, and drying the precipitate,thereby obtaining the product. The invention further provides application of the macleaya cordata leaf extract in preparation of medicines for preventing and treating respiratory diseases of livestockand poultry. The extract prepared in the invention is prepared into an oral preparation, and can be used for preventing and treating the respiratory diseases of livestock and poultry, promoting rapidrehabilitation of the livestock and poultry and effectively reducing the death rate of sick livestock and poultry.
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
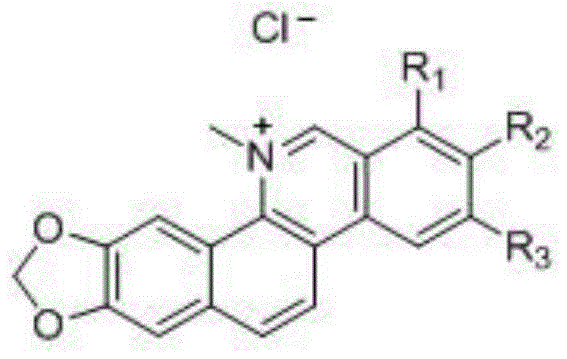
Nitidine chloride, derivative thereof, and applications of nitidine chloride and derivative of nitidine chloride in preparing medicines used for preventing and treating dermatosis
ActiveCN104800216AGood effectImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsDermatological disorderEmulsionChelerythrine
The invention discloses nitidine chloride, a derivative thereof, and applications of nitidine chloride and the derivative of nitidine chloride in preparing medicines used for preventing and treating dermatosis. Nitidine chloride and the derivative of nitidine chloride comprise nitidine chloride, sanguinarine, and chelerythrine; the medicine can be capsules, tablets, emulsions, cream preparations, gel preparations, or ointments; and weight content of nitidine chloride and the derivative of nitidine chloride ranges from 1 to 99%. Nitidine chloride and the derivative of nitidine chloride are capable of inhibiting human skin abnormal proliferative cell proliferation; effect is excellent; and safety is high.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
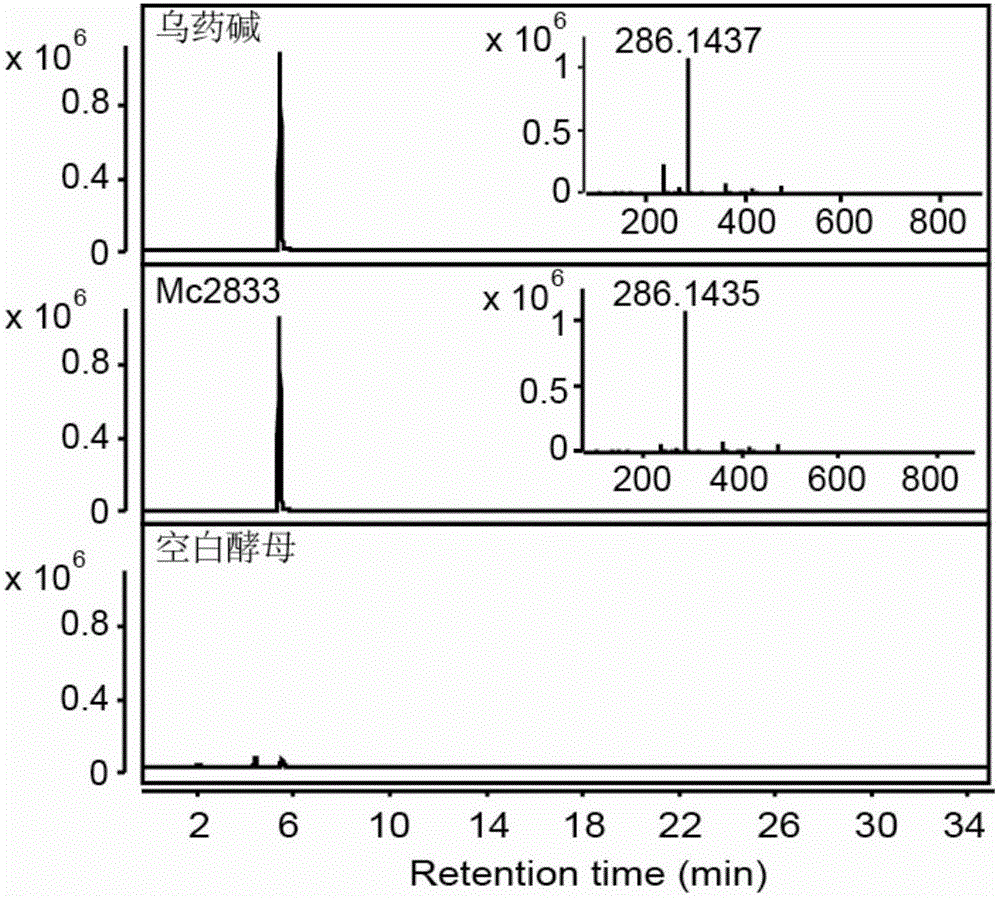
Transmethylase gene participating in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine in macleaya cordata and application of transmethylase gene
ActiveCN106085981AAchieve in vitro synthesisAchieve synthesisFungiTransferasesMethyltransferase GeneSanguinarine
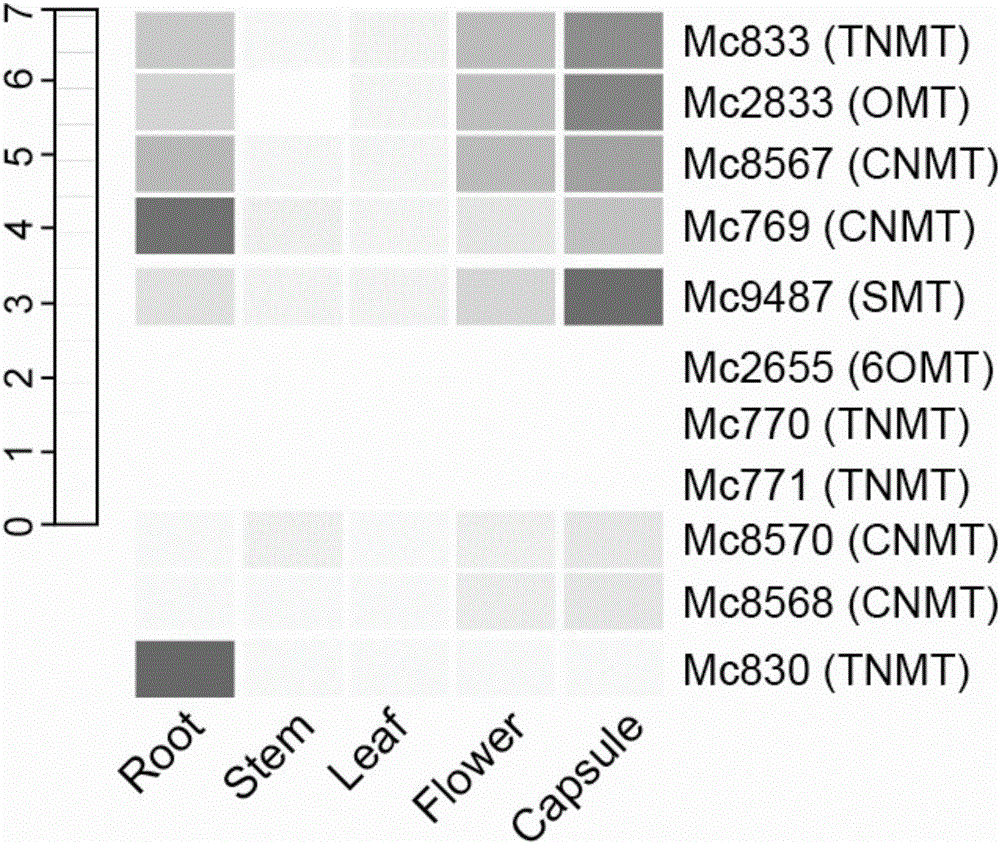
The invention discloses a transmethylase gene participating in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine in macleaya cordata and application of the transmethylase gene. Six transmethylase genes participating in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine are found in a macleaya genome for the first time and comprise the Mc2833 gene, the Mc769 gene, the Mc8567 gene, the Mc833 gene, the Mc830 gene and the Mc9487 gene. A saccharomyces cerevisiae system is utilized for verifying, several steps of reactions are verified through upstream precursor feeding, and synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine intermediates can be achieved. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism of sanguinarine in synthesis of macleaya cordata, and theoretical bases and molecular assisted breeding objectives are provided for sanguinarine and chelerythrine content macleaya cordata breeding; meanwhile, valuable experience is provided for in-vitro artificial synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine.
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
Cultivation method of high-yield radish sprouting having high phenolic substance content
InactiveCN108887125AImprove qualityReduce bitternessMagnesium fertilisersSeed and root treatmentChelerythrineNutrient solution
The invention belongs to the technical field of radish sprouting cultivation and particularly provides a cultivation method of a high-yield radish sprouting having high phenolic substance content. Thecultivation method comprises the following specific steps that 1, irradiation treatment is conducted on radish seeds by using 60 Co-gama rays, the radish seeds are immersed in a magnesium chloride solution for soaking, constant stirring is performed, draining is performed, the seeds are taken out and are flushed with clear water for 3-4 times, the seeds are immersed in a warm glucose nutrient solution for heat preserved soaking, draining is performed, the seeds are taken out, and treated radish seeds are obtained; 2, the treated radish seeds are sowed in a seedling raising medium, the sowingdepth is 1.1-1.3 cm, and the obtained seedling raising medium is prepared from the following raw materials: sunflower seed shells, pear residue, leaf mold, hyodeoxycholic acid, chelerythrine, perillapolysaccharide and thistle polysaccharide. Vigorous growth of stems and leaves of radish sprouts can be effectively promoted, the bitter taste of the radish sprouts can be reduced, the content of total phenols can be increased, the fresh weight of upper-portion parts can be increased, high-yield and high-quality radish sprouts are produced, human health is effectively promoted, and the economic benefits of radish sprouts are increased.
Owner:界首市鑫康家庭农场
Application of sanguinarine or toddaline in prevention and cure of schistosomiasis
The invention relates to application of a sanguinarine or a chelerythrine for preventing and curing of schistosomiasis. The invention applies the sanguinarine and the chelerythrine on killing an oncomelania, a snail egg, a Japanese blood fluke cercaria, a schistosome and the prevention and cure of schistosomiasis. The inventor discovers that the sanguinarine or the chelerythrine can kill the oncomelania and the snail egg safely and effectively and can kill the Japanese blood fluke cercaria as well as a schistosomulum and an imago of the schistosome under a lower concentration, which has the functions of preventing and curing the schistosomiasis and does not pollute the environment.
Owner:长沙世唯科技有限公司
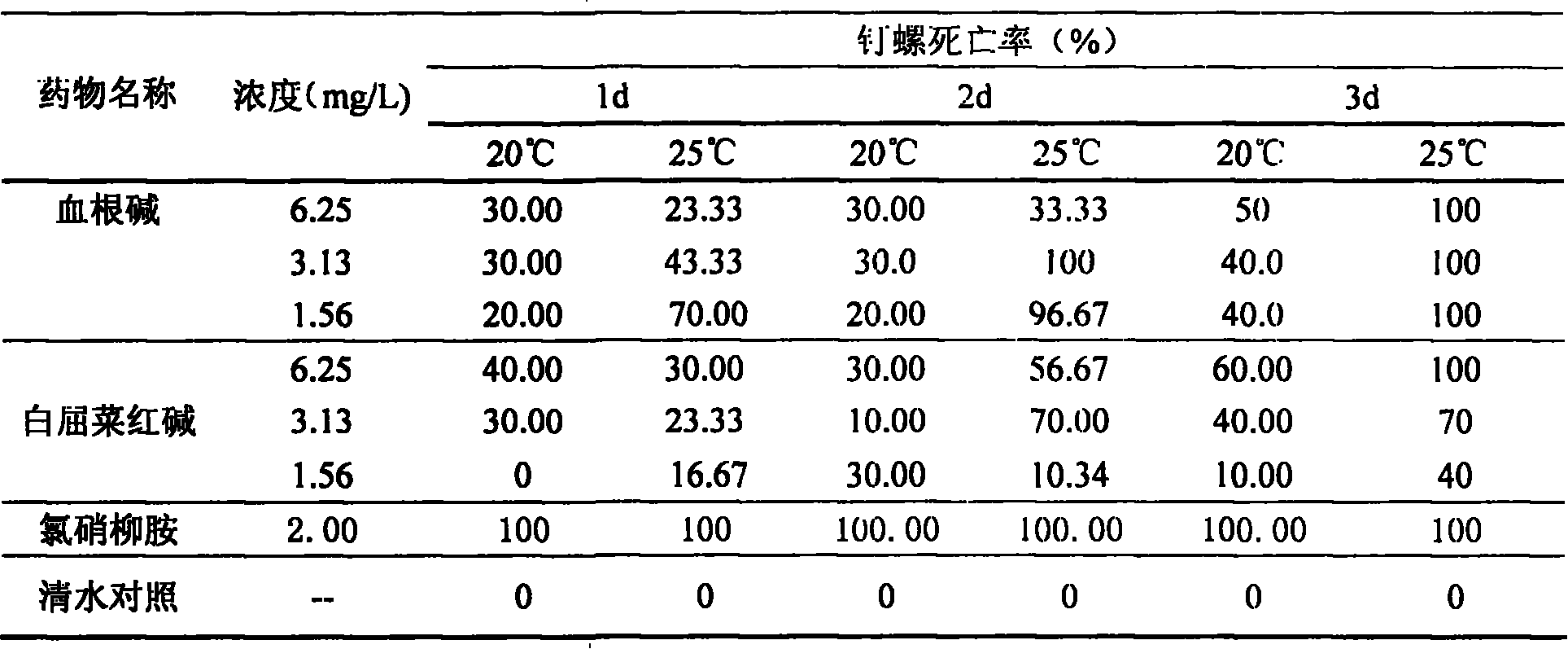
Use of chelerythrine extracted from plant for killing snall
InactiveCN101069510AWide variety of sourcesReduce pollutionBiocideMolluscicidesChelerythrineAqueous solution
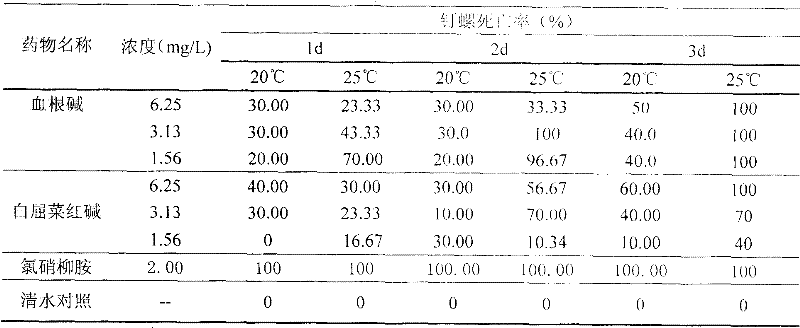
The present invention relates to an application of chelerythrine extracted from plant for killing oncomelaniae. It is characterized by that the chelerythrine can be prepared into aqueous solution whose concentration is 1.5-100.0mg / L, said chelerythrine aqueous solution can be used for soaking oncomelaniae for 96h, its killing rate for killing oncomelaniae can be up to 44-10%.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
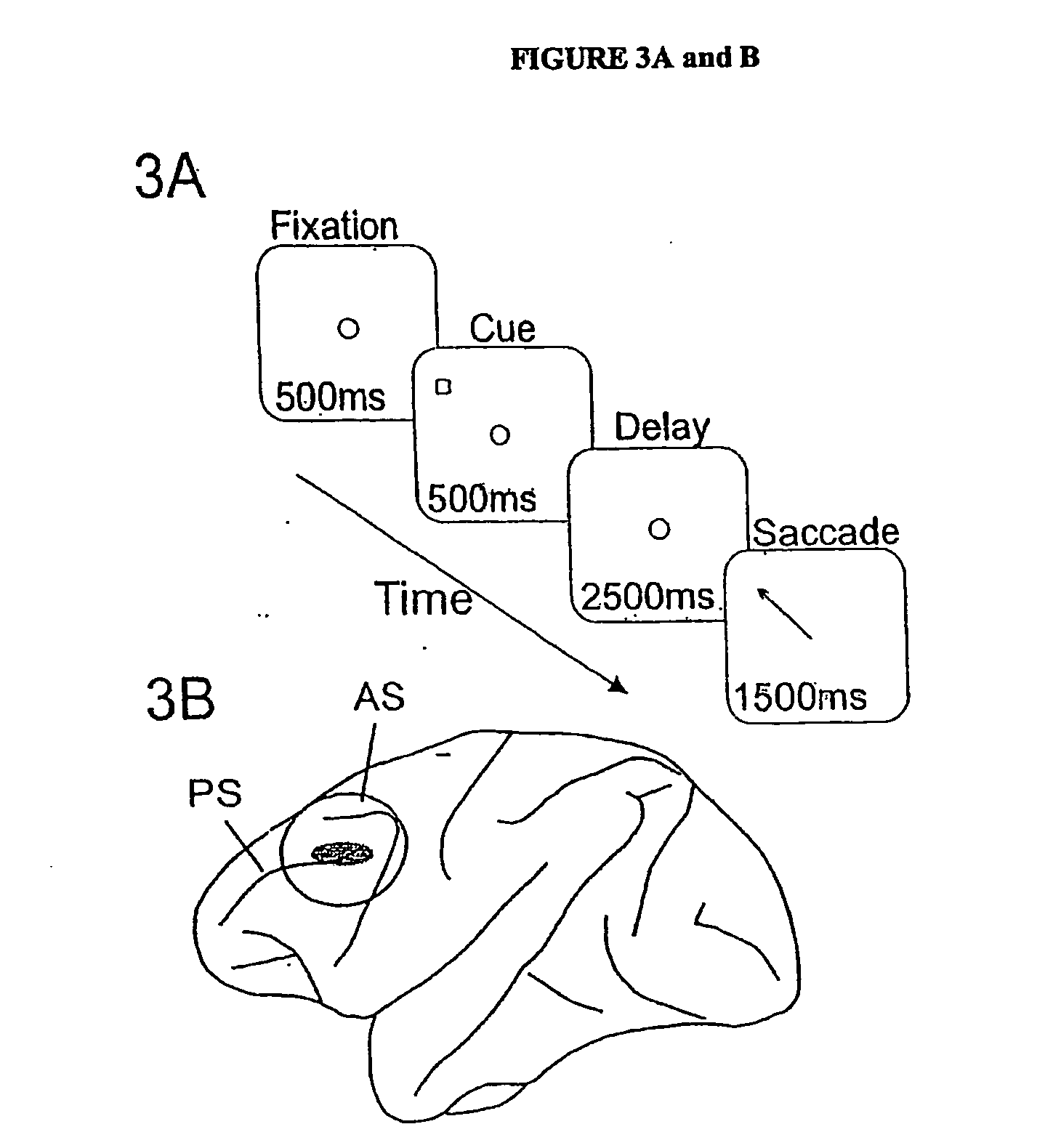
Compositions and Methods for Treating Cognitive Disorders
The present invention relates to the use of inhibitors or blockers of Ih (hyperpolarization-activated cationic current) channels in the treatment of cognitive disorders. In preferred aspects of the present invention, an effective amount of a compound is administered to a patient in need, wherein the compound has the chemical structure: Where R1 is H, or an optionally substituted C1-C3 alkyl, preferably a C2 alkyl (ethyl) group; R2 is an optionally substituted C1-C3 alkyl group, preferably a methyl group; R3 is H, an optionally substituted C1-C3 alkyl (preferably methyl), a halogen or 0(Ci-Ca) alkyl; R4 is an optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl, C(O)—(C1-C5)alkyl, C(O)-aryl, C(O)O—(C1-C4)alkyl, C(O)O-aryl, or an optionally substituted heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl group; R4 is H or an optionally substituted C1-C6 (preferably a C1-C3) alkyl; R5, R6 and R7 are each independently H, halogen, an optionally substituted C1-C6 alkyl (preferably, an optionally substituted C1-C3 alkyl), 0-(C1-C3) alkyl, or an optionally substituted heterocyclic, aryl or heteroaryl group; Y− is an anion of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt (a physiologically acceptable anion, preferably a Cl−, Br−, I−, OAc−); or a solvate or polymorph thereof, optionally, in combination with guanfacine and / or chelerythrine, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, additive or excipient to a patient in need of therapy.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Composition for preventing respiratory diseases of livestock and poultry and preparation method of composition
ActiveCN108635422AEasy to useReduce mortalityClimate change adaptationRespiratory disorderDiseaseRespiratory tract disease
The invention provides a composition for preventing respiratory diseases of livestock and poultry and a preparation method of the composition. The composition is prepared from the following componentsby weight percent: 50 to 90 percent of folium macleayae cordatae extract, 5 to 30 percent of rhizoma coptidis extract, and 5 to 30 percent of dandelion herb extract, wherein in the folium macleayae cordatae extract: the weight content of fumarine is not less than 0.1 percent, the weight content of allocryptopine is not less than 0.1 percent, and the sum of the weight content of sanguinarine and chelerythrine is not less than 0.2 percent. The invention also provides a preparation method of the composition. The medicine composition provided by the invention is used for preventing the respiratory diseases of the livestock and poultry, can promote the rapid rehabilitation of the livestock and poultry, and can effectively reduce the death rate of the ill livestock and poultry.
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
Salt of chelerythrine derivative
InactiveCN103374008APractical therapeutic activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryChelerythrinePharmacology
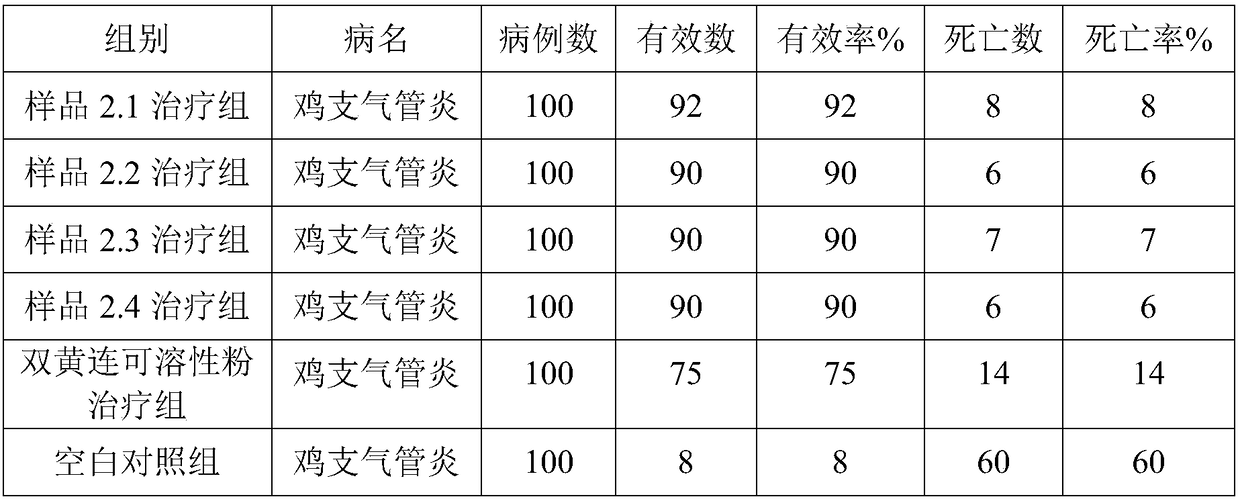
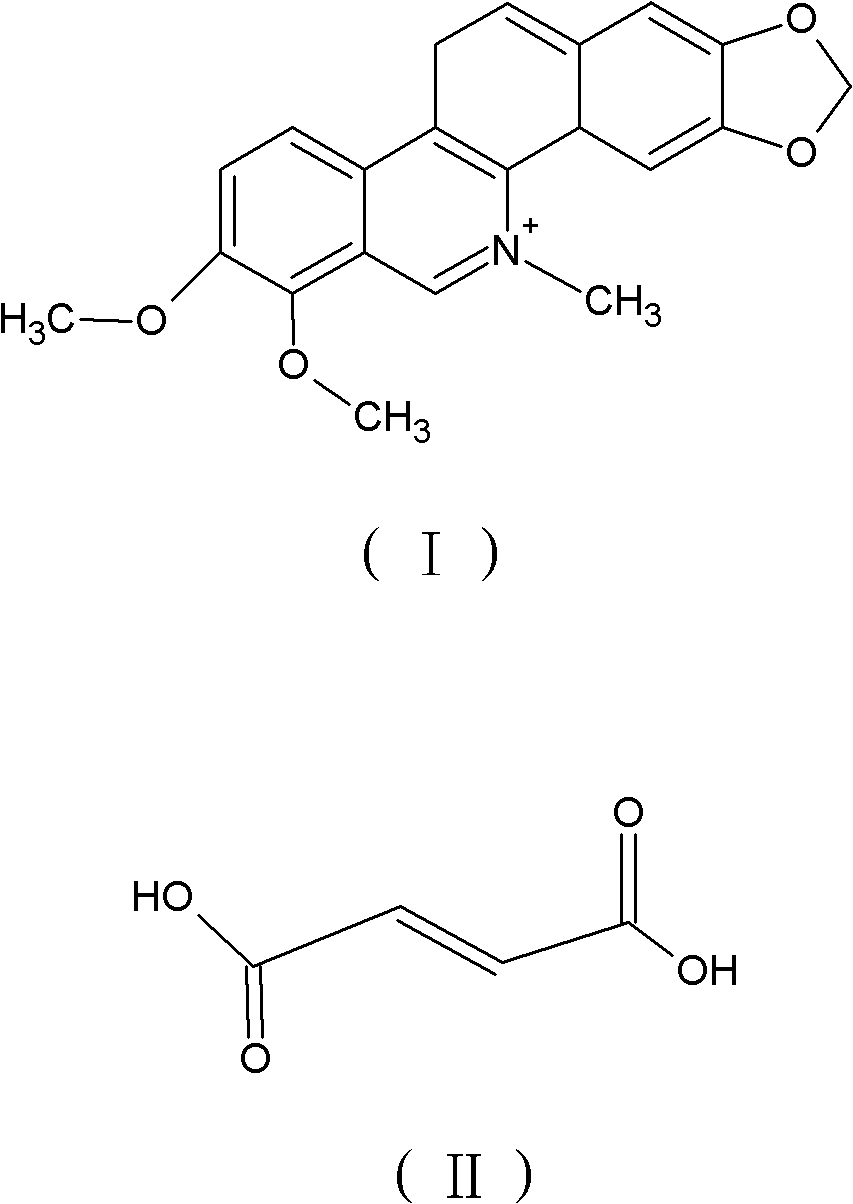
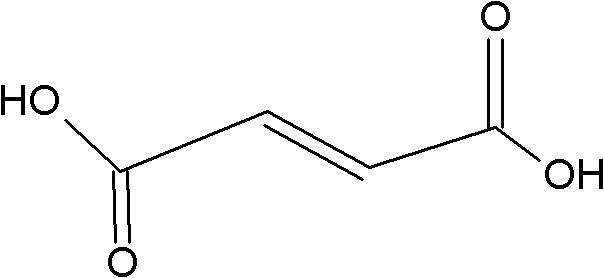
The invention relates to chelerythrine, fumarate of a derivative of the chelerythrine or a pharmaceutically acceptable solvate of the chelerythrine and applications of the chelerythrine, the fumarate and the solvate in preparation of medicaments for treating hepatitis B.
Owner:SHANGHAI YIZHI MEDICAL TECH
Baicalin ion pair medicine from traditional Chinese medicine of baikal skullcap root as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101824061AReduce hydrophilicityImprove lipophilicityOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsHuman medicineChelerythrine
The invention relates to a novel baicalin ion pair compound which is an ion pair compound having the structure of a formula (I) and containing baicalin. The baicalin ion pair compound is an ion pair compound generated by the baicalin and chelerythrine. The spectrum analysis of 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, MS, IR and UV proves that the molecular formula of the ion pair compound is C42H35015N. By the sieving of the antibacterial activity, the ion pair compound has the antibacterial activity, and the activity is obviously better than that of the baicalin. The invention also relates to a human medicine, a veterinary medicine or a daily health product of the baicalin ion pair compound in the antibacterial aspect.
Owner:曾建国
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com