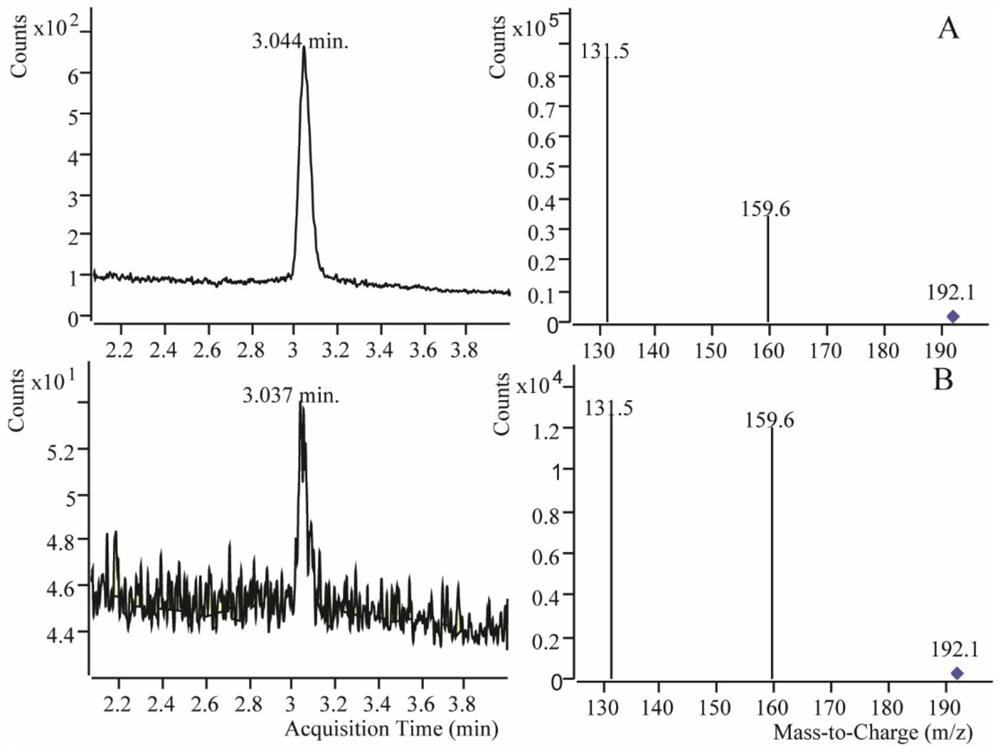
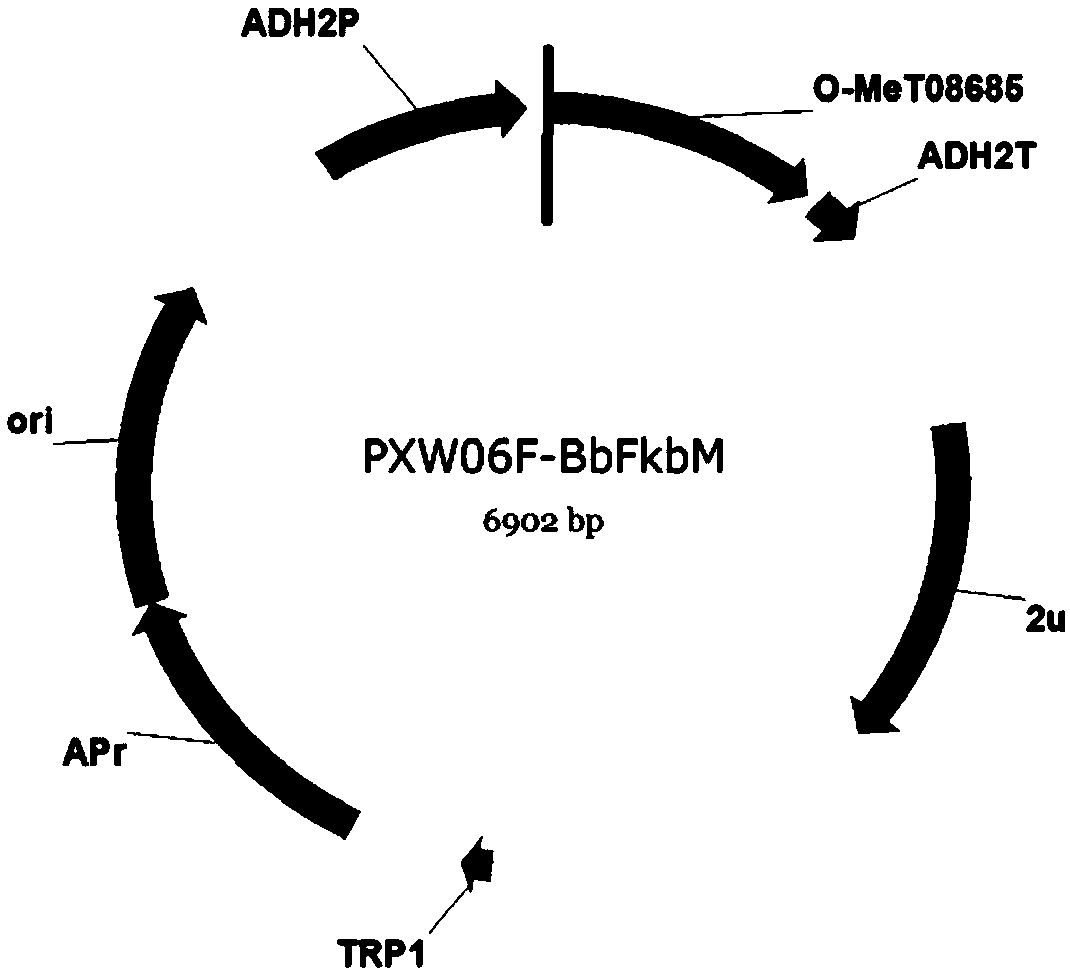
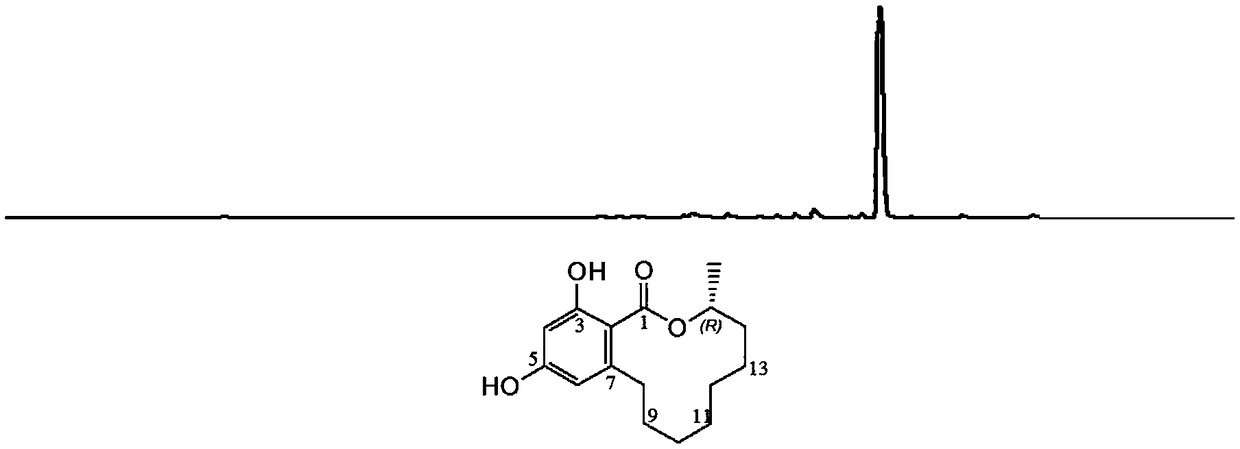
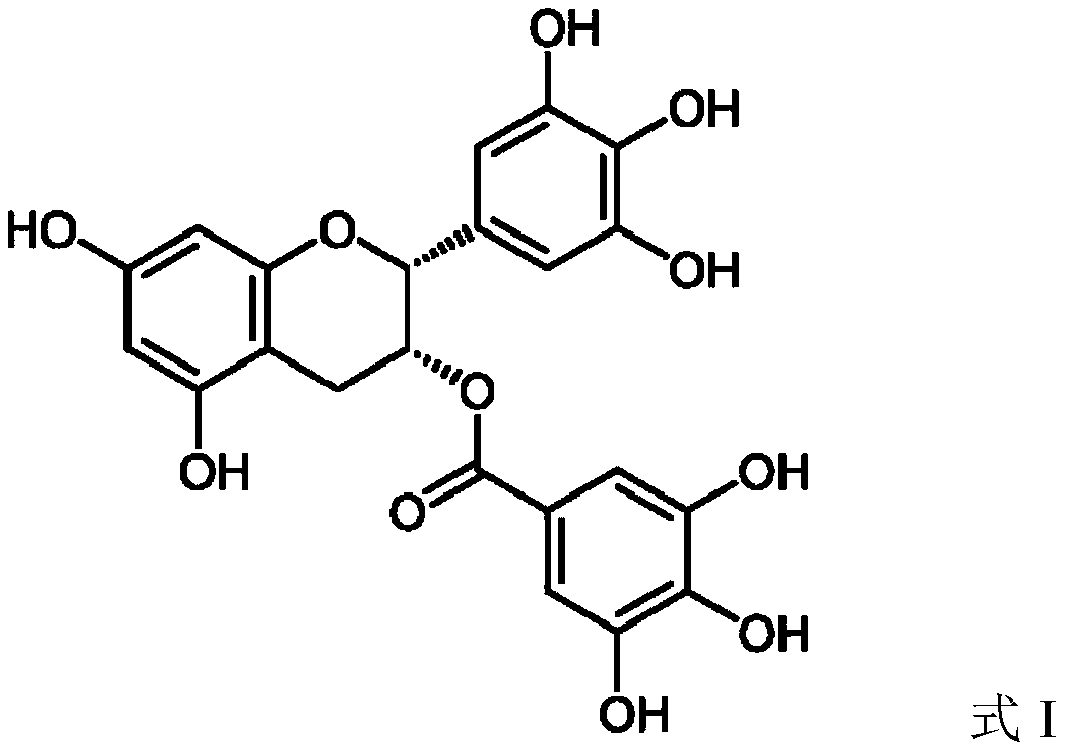
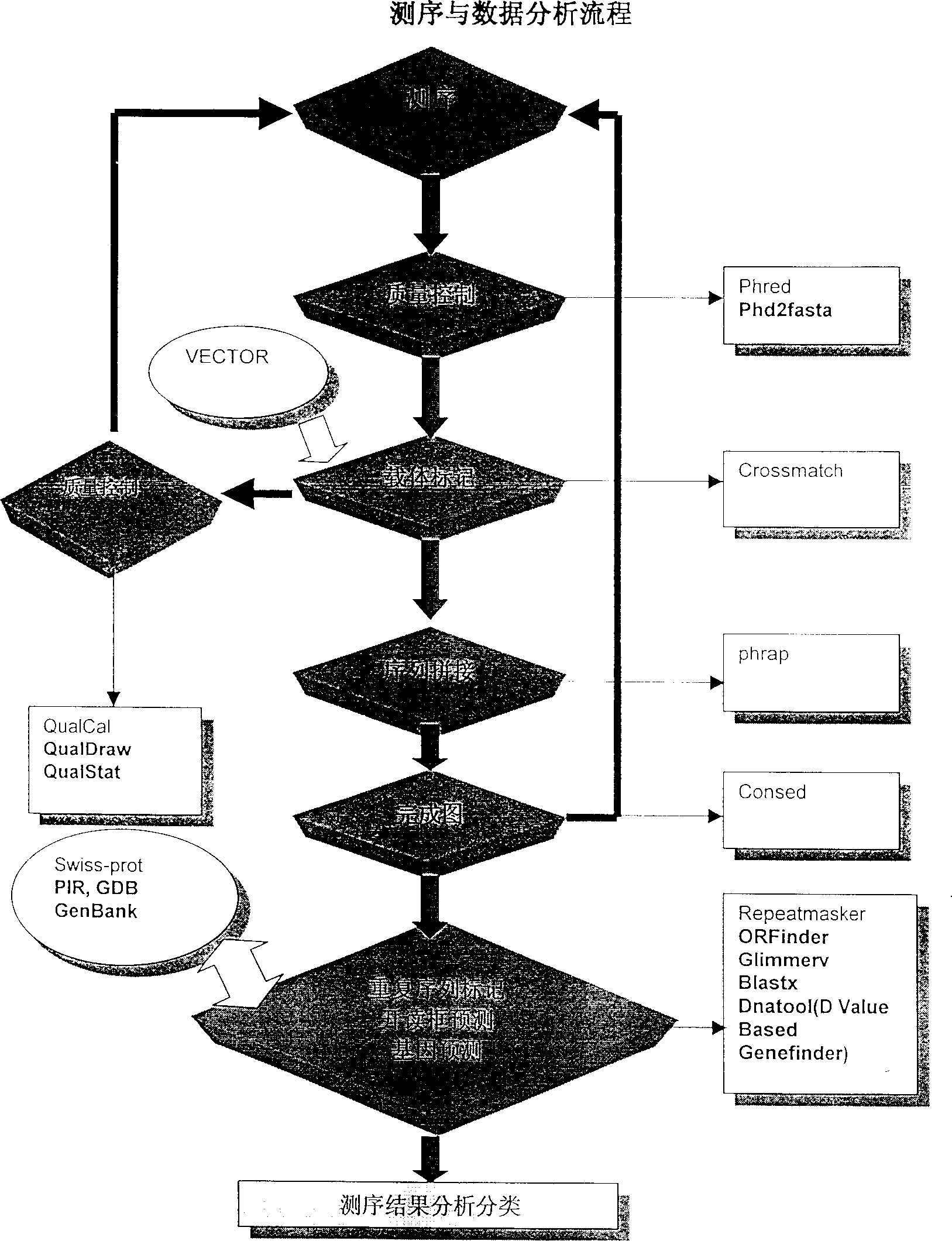
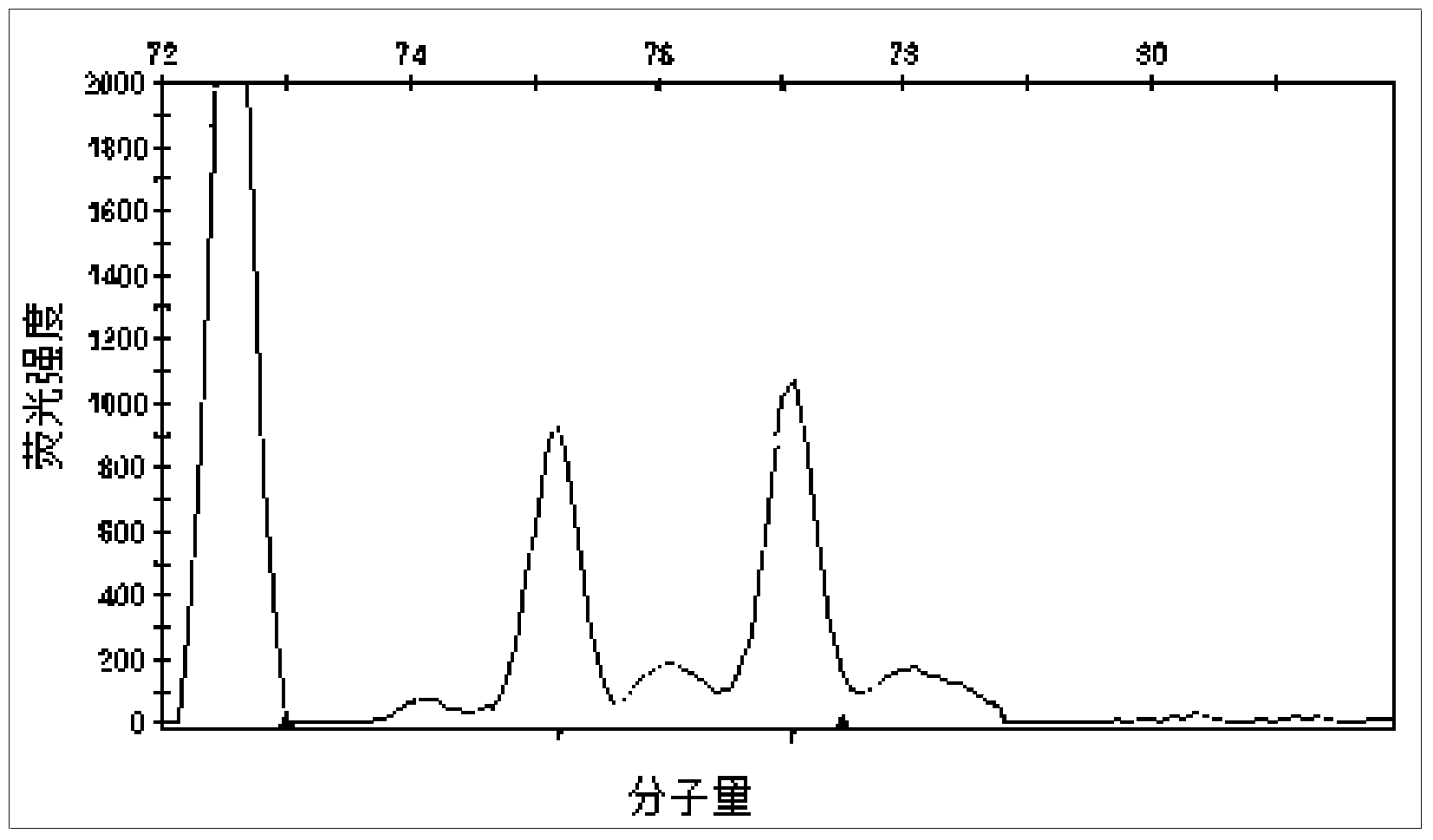
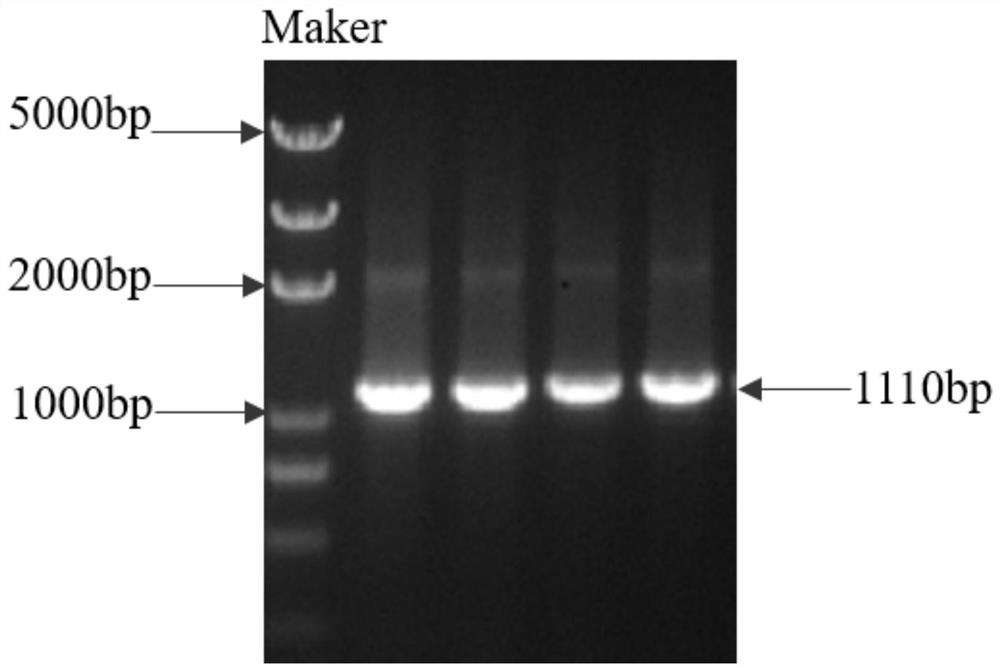
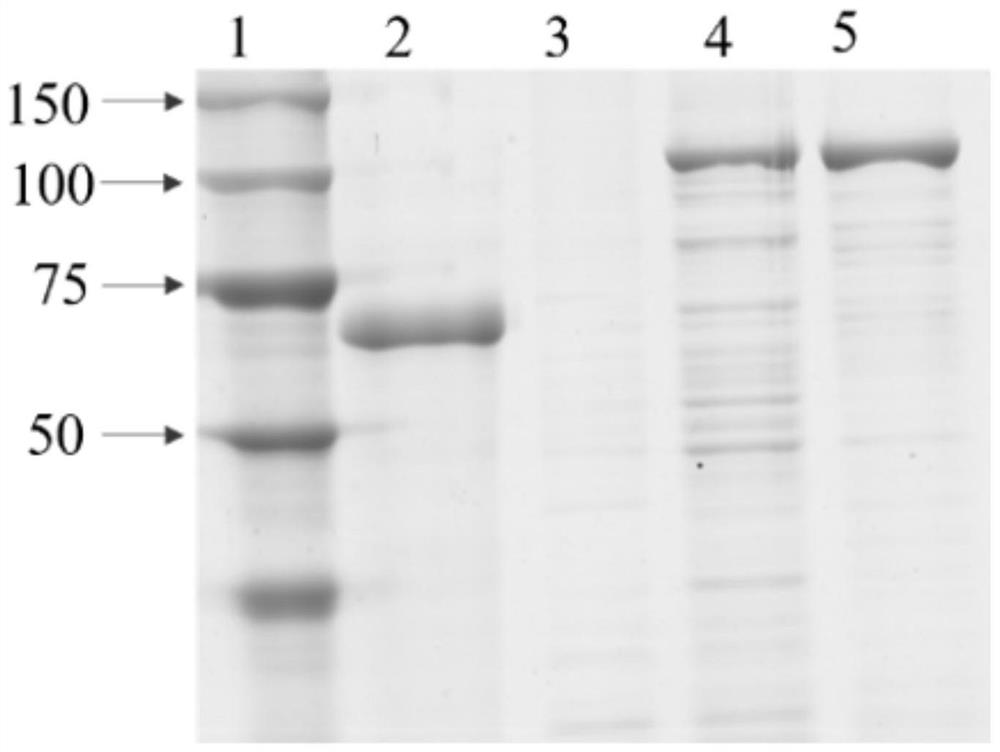
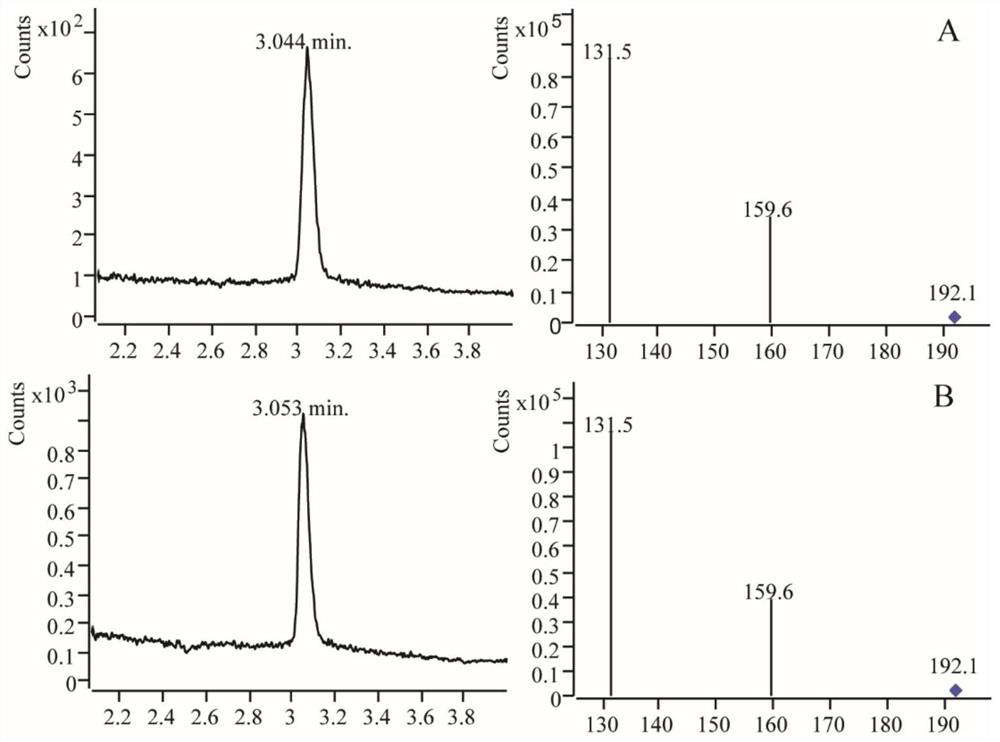
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Methyltransferase Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methyltransferase Genes encode Methyltransferases, a subclass of transferase class enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a methyl group from one compound to another. (NCI)
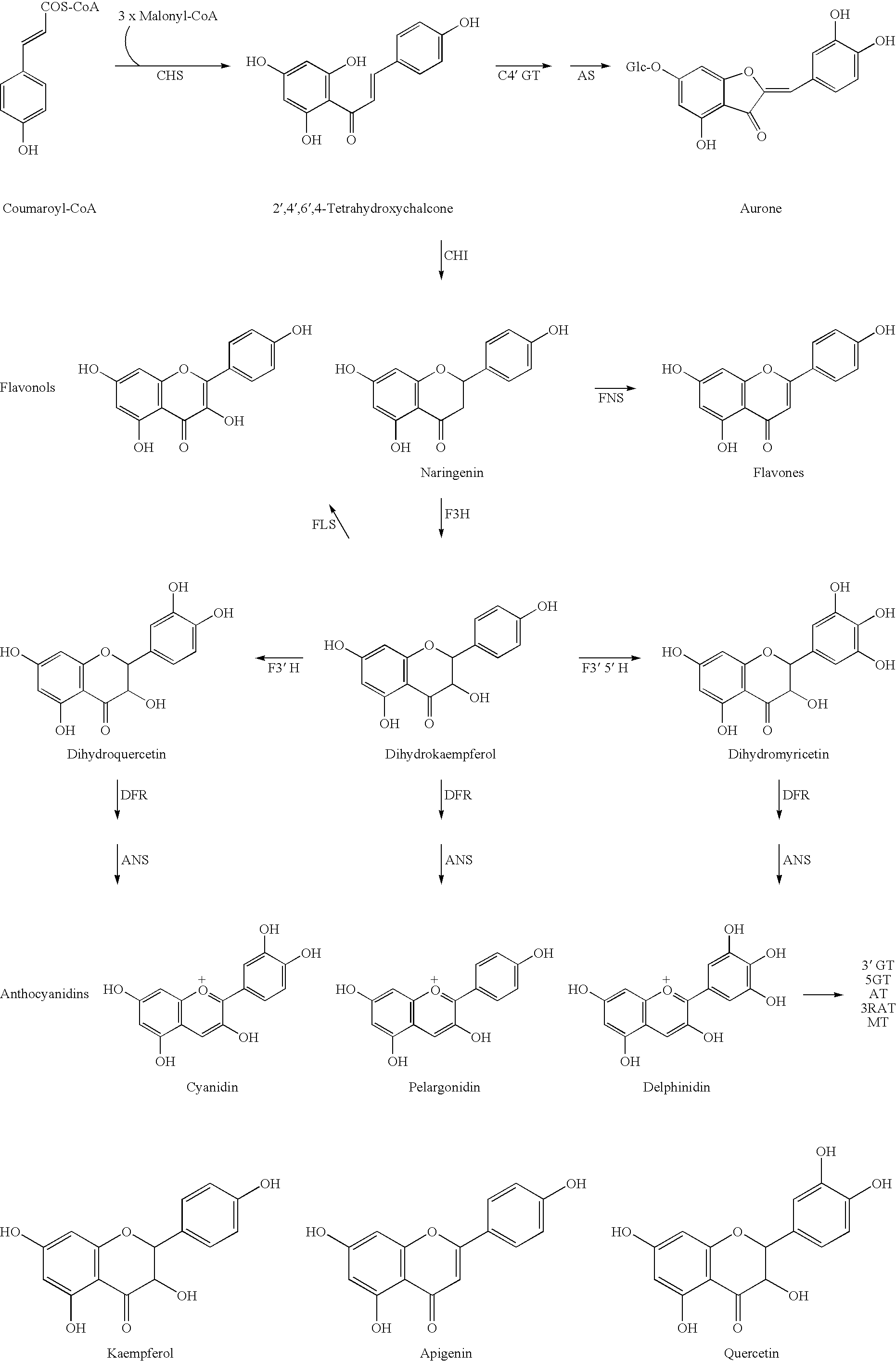
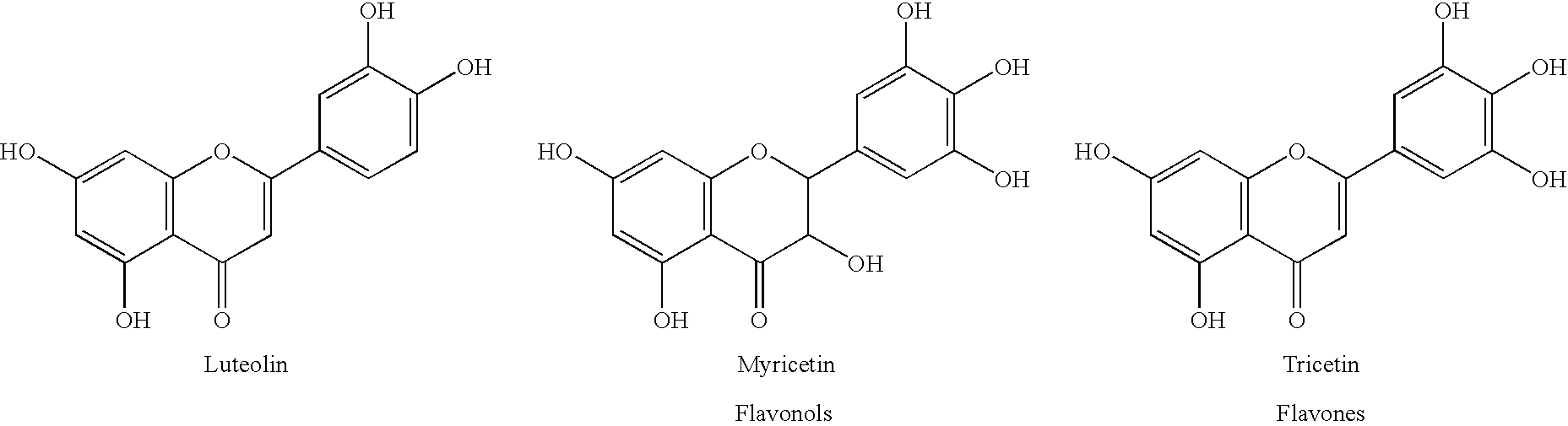
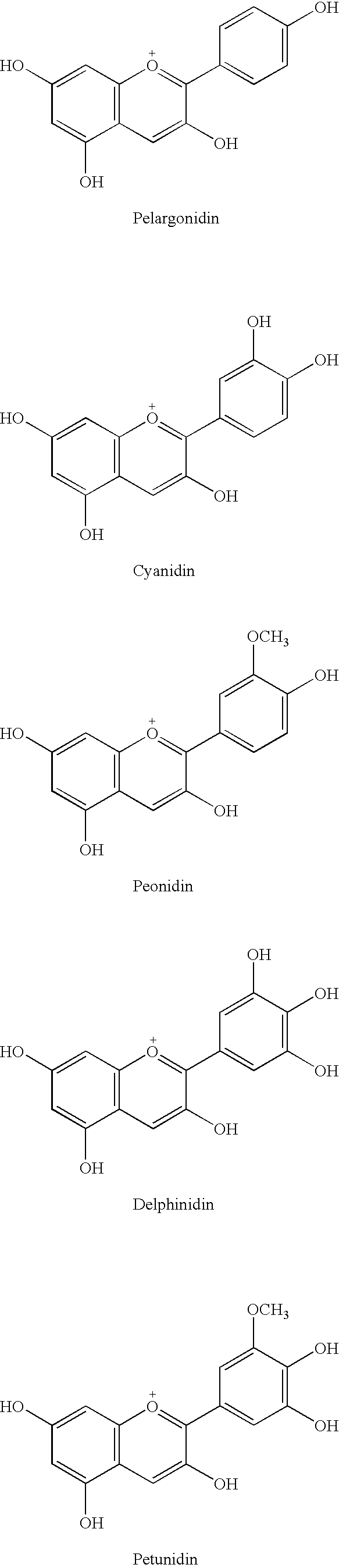
Rose containing flavone and malvidin, and method for production thereof
The invention provides a rose characterized by comprising a flavone and malvidin added by a genetic modification method. The flavone and malvidin are typically produced by expression of a transferred flavone synthase gene, pansy flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene and anthocyanin methyltransferase gene. The flavone synthase gene is, for example a flavone synthase gene of the family Scrophulariaceae,and specifically, the invention may be the flavone synthase gene of snapdragon of the family Scrophulariaceae, or the flavone synthase gene of torenia of the family Scrophulariaceae. The flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene is, for example, the pansy flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene. The anthocyanins methyltransferase gene is, for example, the methyltransferase gene of torenia of the family Scrophulariaceae.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
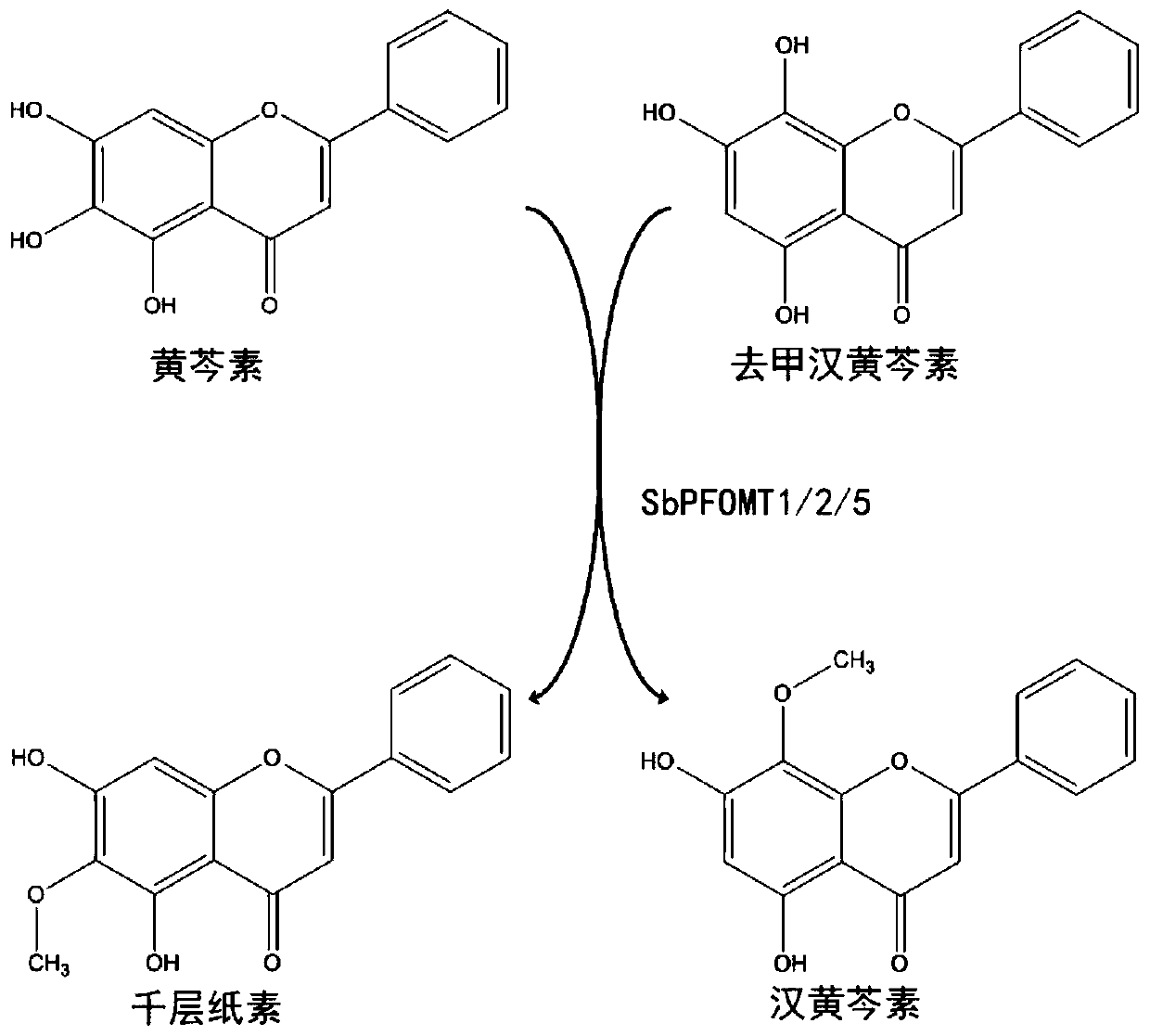
Radix scutellariae flavone phenylpropanoidand and flavonoid O-methyltransferase gene and vector construction and application thereof
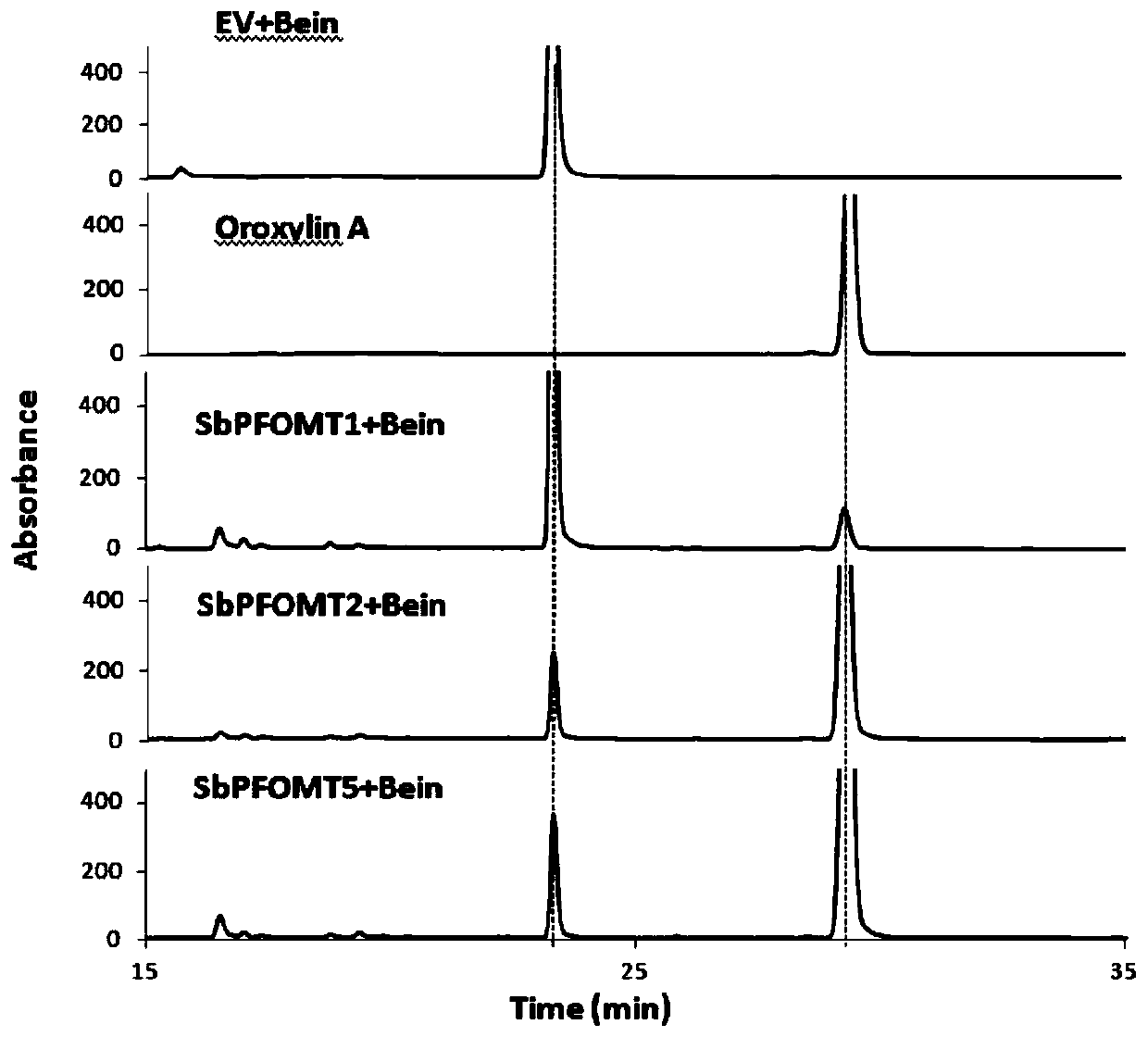
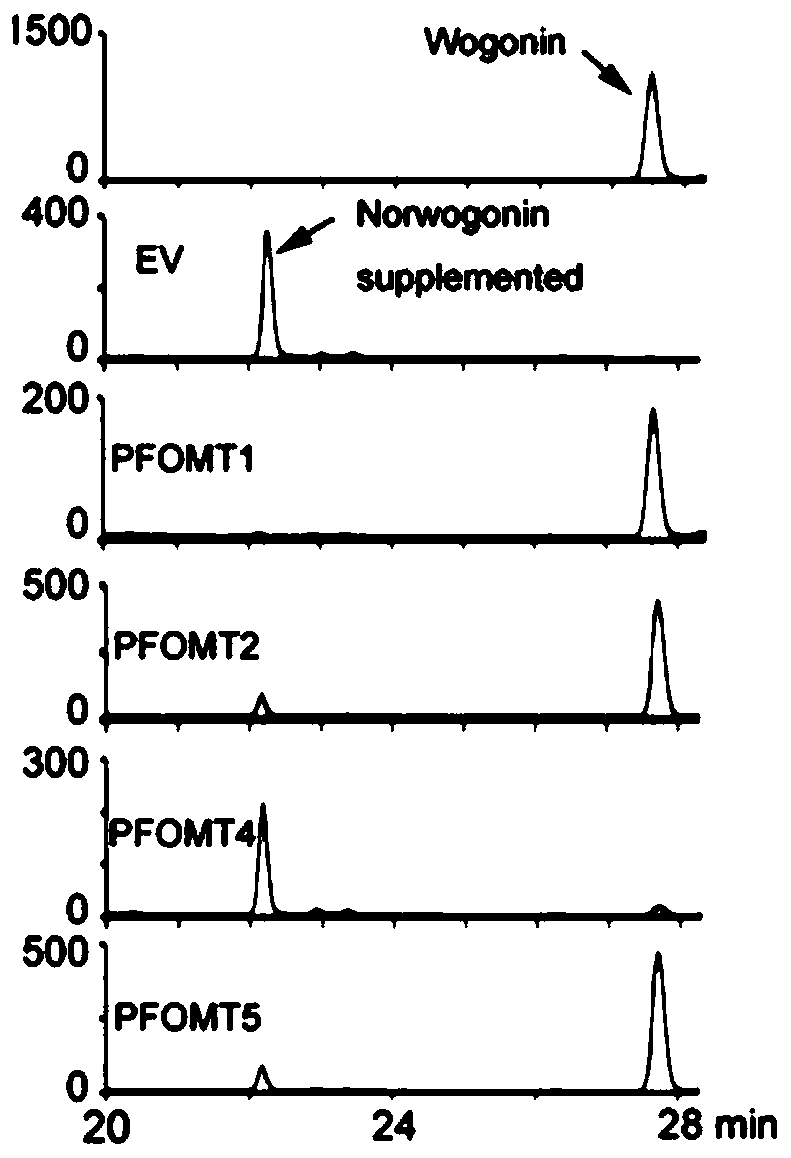
The invention provides a radix scutellariae flavone phenylpropanoidand and flavonoid O-methyltransferase gene. The radix scutellariae flavone phenylpropanoidand and flavonoid O-methyltransferase genecomprises at least one of SbPFOMT1, SbPFOMT2 and SbPFOMT5 genes, the gene sequence of the SbPFOMT1 is as shown in SEQID No.1, the gene sequence of the SbPFOMT2 is as shown in SEQID No.3, and the genesequence of the SbPFOMT5 is as shown in SEQID No.5; and a primer composition amplifying the gene, protein coded by the gene, a recombinant vector, a recombinant microorganism, a host cell, a transgenic cell line, transgenic plant tissue or a transgenic plant constructed by the gene, and an application of the recombinant vector, the recombinant microorganism, the host cell, the transgenic cell line, the transgenic plant tissue or the transgenic plant are provided. The methylation process of wogonin and similar flavonoid is analyzed, 3 flavone phenylpropanoidand and flavonoid O-methyltransferasegenes SbPFOMT1, SbPFOMT2 and SbPFOMT5 are obtained for the first time and cloned, besides, the function of enzymes coded by the gene is verified in an exogenous plant and a microorganism body, a theoretical basis is provided for methylation of wogonin and similar flavonoid in mass production, and a firm basis is also established for industrial production of other pertinent flavonoid compounds.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHENSHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN
Kit for genetic detection of breast cancer
InactiveCN101608225AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceEstrogen receptor
The invention discloses a kit for genetic detection of breast cancer. The kit comprises a specific primer pair and a specific probe pair which are used for detecting the mononucleotide polymorphism loci genotype of an estrogen receptor alpha gene (ER-alpha), a catechol-o-methyltransferas gene (COMT), a glutathione-s-transferase P1 gene (GSTP1), a human breast cancer susceptibility gene 1 (BRCA1), and a human breast cancer susceptibility gene 2(BRCA2), a fluorescent quantitative PCR general component and the like. The kit can evaluate the genetic risk of individuals suffered from the breast cancer by detecting the polymorphism loci genotype of the genes closely related to the genetic risk of the breast cancer at the same time.
Owner:XINBAXIANG SHANGHAI MOLECULAR MEDICAL TECH SHANGHAI
Metarhizium anisopliae o-methyltransferase and application thereof
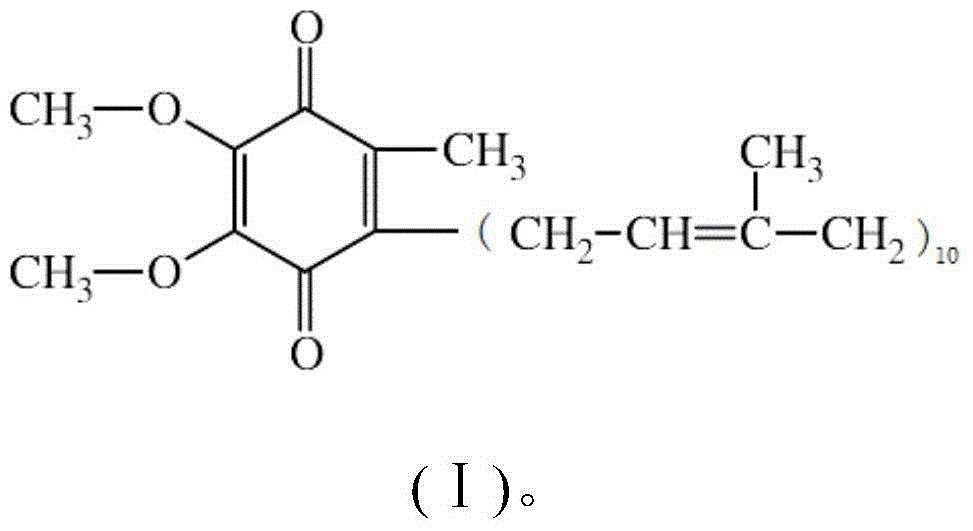
The invention provides an o-methyltransferase with a wide range of substrates, and can be applied to oxygen methyl transfer in a biosynthesis process of an organic compound. An experiment proves the catalytic activity of the o-methyltransferase, and shows that the o-methyltransferase can be applied to a plurality of substrates. The invention further provides a synthesis method for a hydroquinone lactone compound. The hydroquinone lactone compound is obtained by transforming an o-methyltransferase gene and a hydroquinone lactone synthetic gene into yeast cells, carrying out fermentation cultivation and extracting a product.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Genetically engineered bacteria and application thereof in production of coenzyme Q10
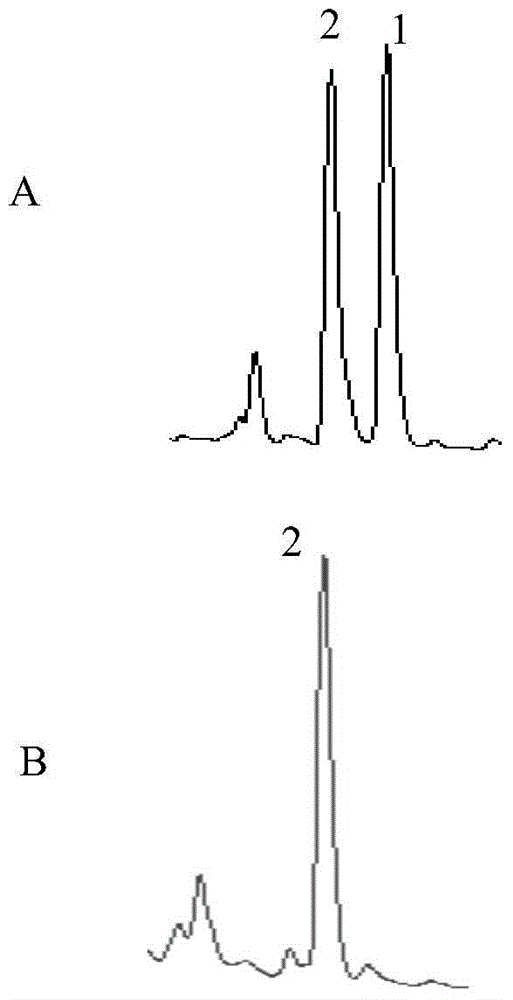
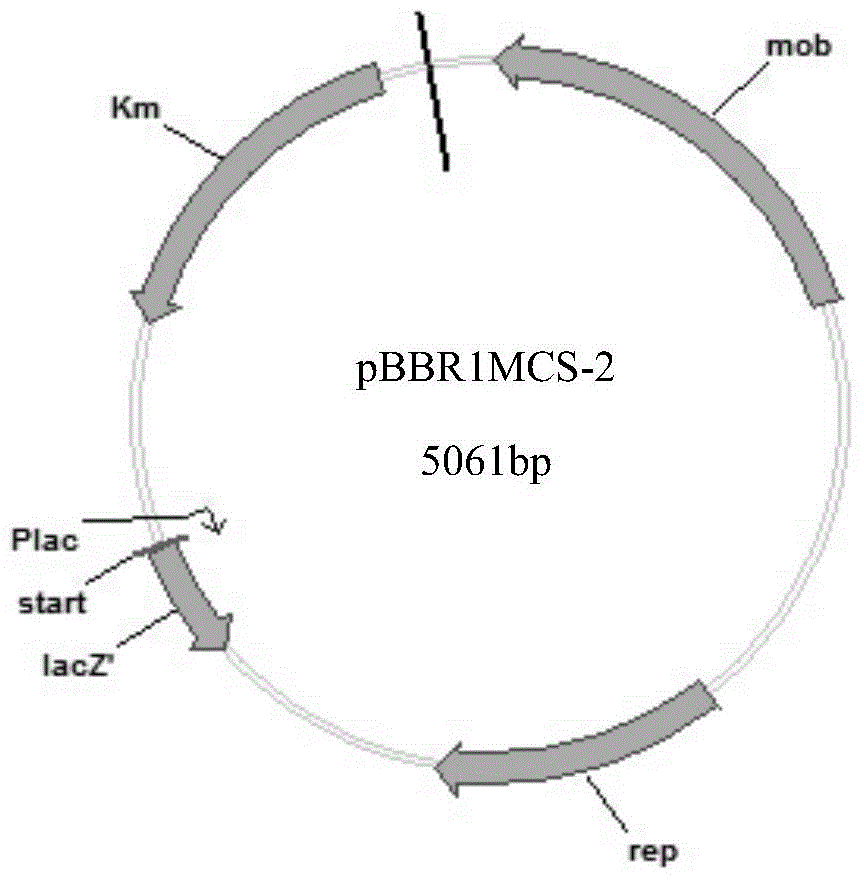
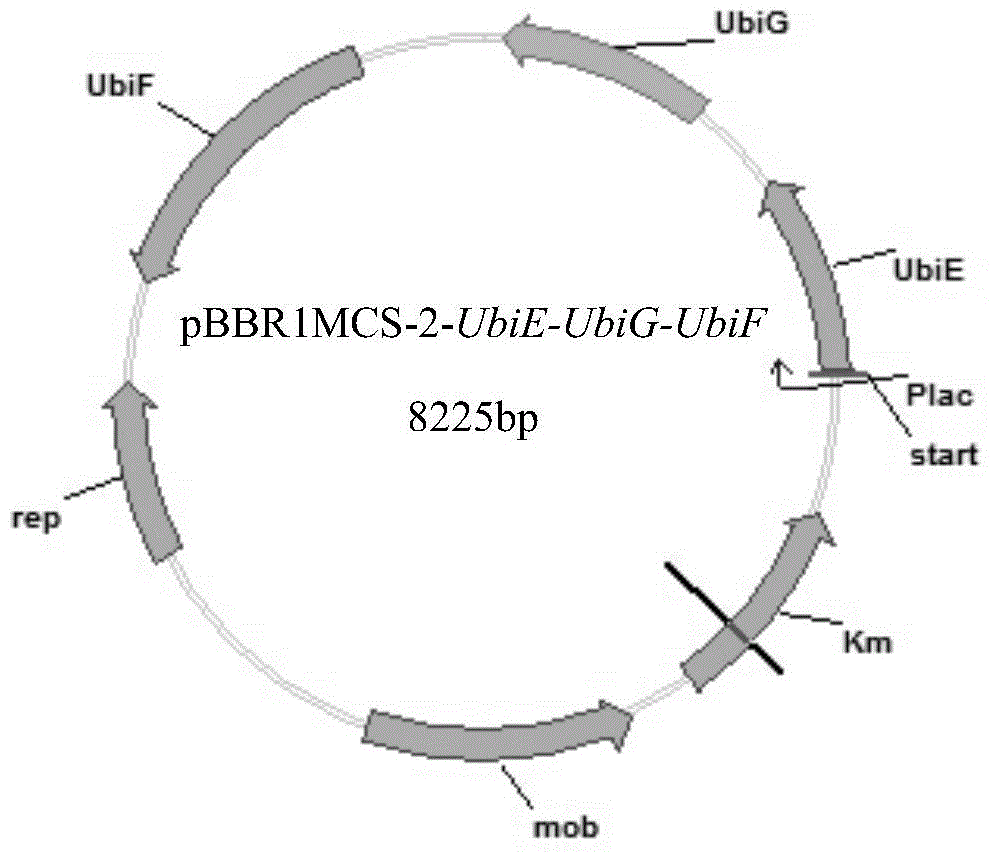
The present invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria and application thereof in production of coenzyme Q10. The genetically engineered bacteria comprises coenzyme Q10 producing bacteria and desired genes transferred into the coenzyme Q10 producing bacteria, and the desired genes are a demethylnaphthoquinone methyltransferase gene, a 2-octo isoprene-3-methyl-6-methoxy-1,4-hydroquinone hydroxylase gene and a 3-demethyl ubiquinone-93-methyl transferase gene. Rate-limiting enzyme genes UbiE, UbiG and UbiF in a coenzyme Q10 synthetic route are transferred into rhodobacter sphaeroides, and by in-series over-expression of the three rate-limiting enzyme genes UbiE, UbiG and UbiF, coenzyme Q10 synthesizing capability of the rate-limiting enzyme genes can be strengthened; and compared with the rhodobacter sphaeroides with no desired gene being transformed, by use of the genetically engineered bacteria for coenzyme Q10 producing, the yield of the coenzyme Q10 is increased by more than 20%.
Owner:SHANGYU NHU BIOCHEM IND
Method for regulating growth of plants and application thereof
InactiveCN101838665AMicroorganismsVector-based foreign material introductionGrowth plantMethyltransferase Gene
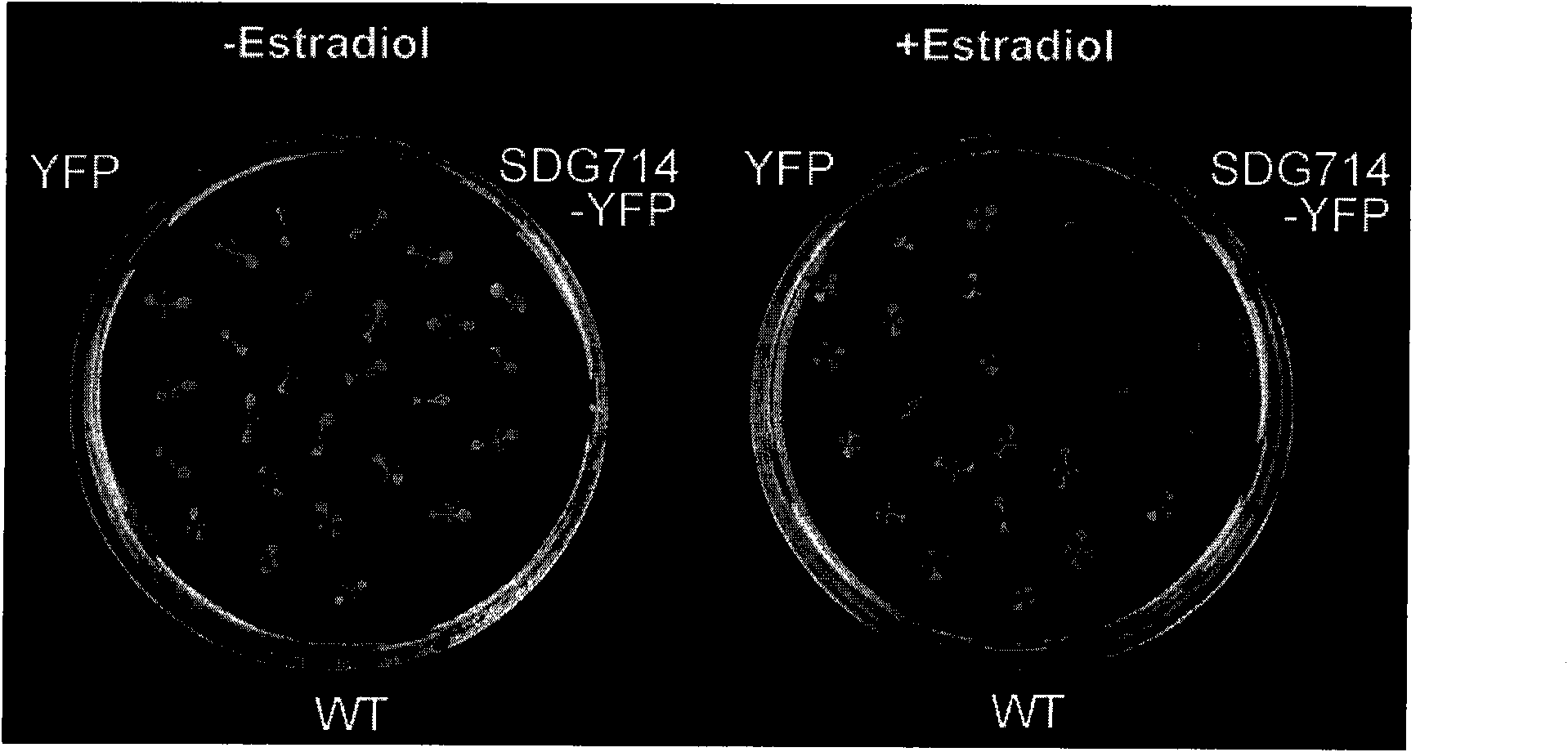
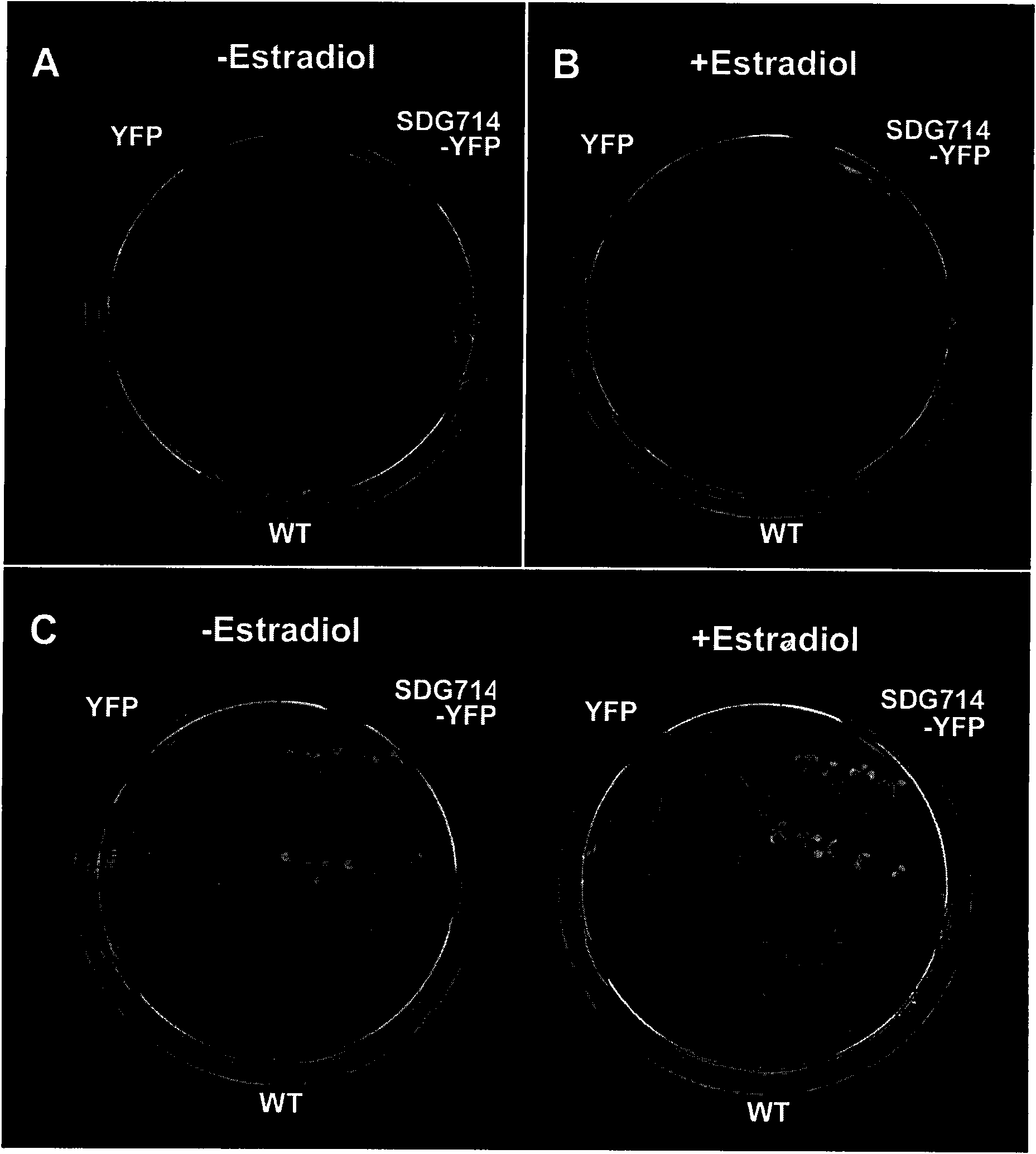
The invention belongs to the technical field of the biology, and relates to a method for regulating the growth of plants and an application thereof, in particular to an application of paddy rice Histone-lysine methyltransferase gene which is associated to the Epigenetics in the regulation of the plant growth. The name of the gene is SDG714, and the accession number is NM_001051801. Through a designed primer, a target gene entering plant expression carrier is obtained, and the plant Arabidopsis is transformed in an Agrobacterium rhizogenes medium transformation mode. Compared with a contrast group, in the plant of the over-expression SDG714, the methylation level of the histone H3K9 is obviously improved to cause the decrease of a great amount of genes which are related to the growth of the plant and to seriously inhibit the growth of the Arabidopsis; and once the SDG714 which is over-expressed is removed in the plant with the growth being inhibited, the plant can continue to grow. The method for regulating the growth of the plant has high real application value and promising application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
De novo DNA cytosine methyltransferase genes, polypeptides and uses thereof
De novo DNA cytosine methyltransferase polynucleotides and polypeptides and methods for producing said polypeptides are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for utilizing de novo DNA cytosine methyltransferase polynucleotides and polypeptides in diagnostic assays, for an in vitro DNA methylation application and therapeutic applications such as the treatment of neoplastic disorders.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Rose containing flavone and malvidin, and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20100281575A1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesMethyltransferase GeneTorenia
The invention provides a rose characterized by comprising a flavone and malvidin added by a genetic modification method. The flavone and malvidin are typically produced by expression of a transferred flavone synthase gene, pansy flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene and anthocyanin methyltransferase gene. The flavone synthase gene is, for example a flavone synthase gene of the family Scrophulariaceae, and specifically it may be the flavone synthase gene of snapdragon of the family Scrophulariaceae, or the flavone synthase gene of torenia of the family Scrophulariaceae. The flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene is, for example, the pansy flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene. The anthocyanin methyltransferase gene is, for example, the methyltransferase gene of torenia of the family Scrophulariaceae.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
De novo DNA cytosine methyltransferase genes, polypeptides and uses thereof
De novo DNA cytosine methyltransferase polynucleotides and polypeptides and methods for producing said polypeptides are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for utilizing de novo DNA cytosine methyltransferase polynucleotides and polypeptides in diagnostic assays, in vitro DNA methylation assays for screening agonists and antagonists, and therapeutic applications such as the treatment of neoplastic disorders.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Genetic engineering strain for accumulating emodin and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110527638AEfficient accumulationFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMethyltransferase Gene
The invention discloses a genetic engineering strain capable of accumulating emodin. An original strain of the genetic engineering strain is aspergillus terreus capable of producing emodin or downstream derivatives thereof, the genetic engineering strain is prepared by mutating O-methyltransferase genes (gedA) in the aspergillus terreus. Compared with the original strain, the genetic engineering strain can be used for accumulating emodin.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methyltransferase genes and uses thereof
The present invention relates to genes associated with the tocopherol biosynthesis pathway. More particularly, the present invention provides and includes nucleic acid molecules, proteins, and antibodies associated with genes that encode polypeptides that have methyltransferase activity. The present invention also provides methods for utilizing such agents, for example in gene isolation, gene analysis and the production of transgenic plants. Moreover, the present invention includes transgenic plants modified to express the aforementioned polypeptides. In addition, the present invention includes methods for the production of products from the tocopherol biosynthesis pathway.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
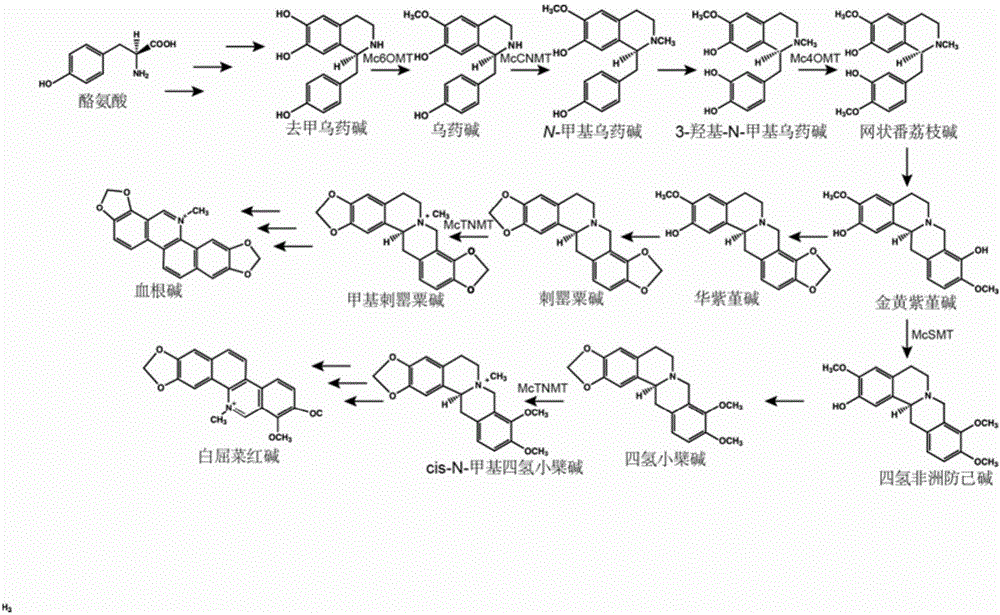
Transmethylase gene participating in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine in macleaya cordata and application of transmethylase gene
ActiveCN106085981AAchieve in vitro synthesisAchieve synthesisFungiTransferasesMethyltransferase GeneSanguinarine
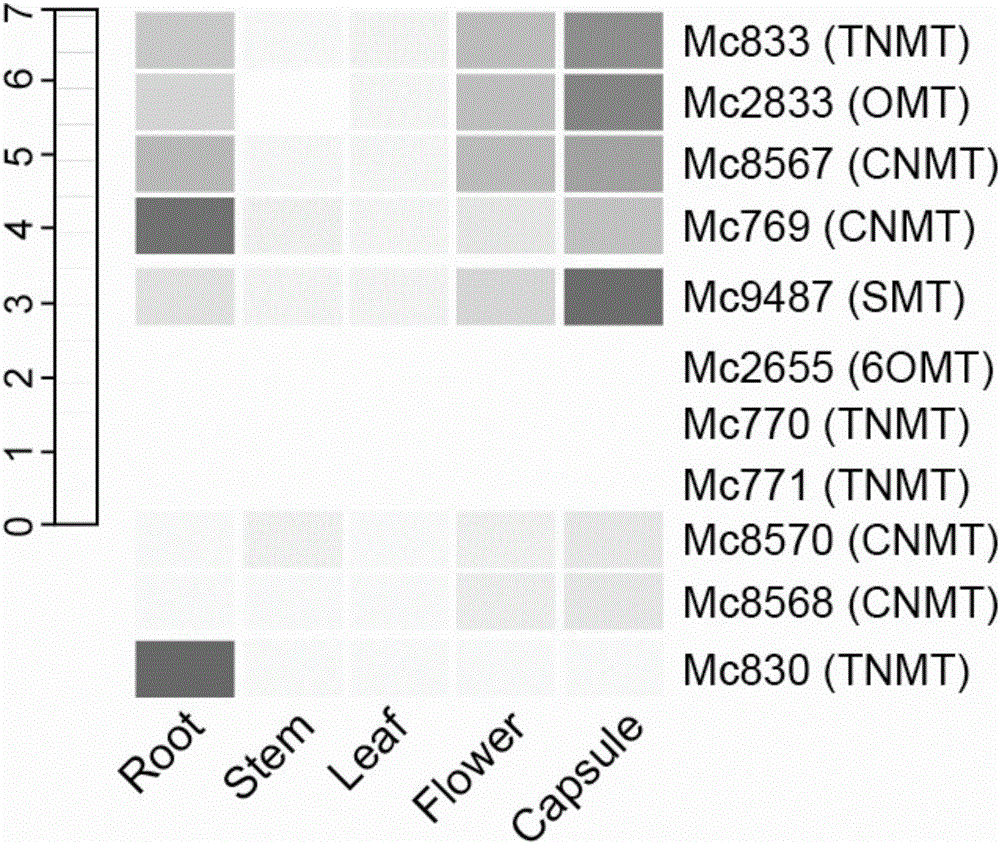
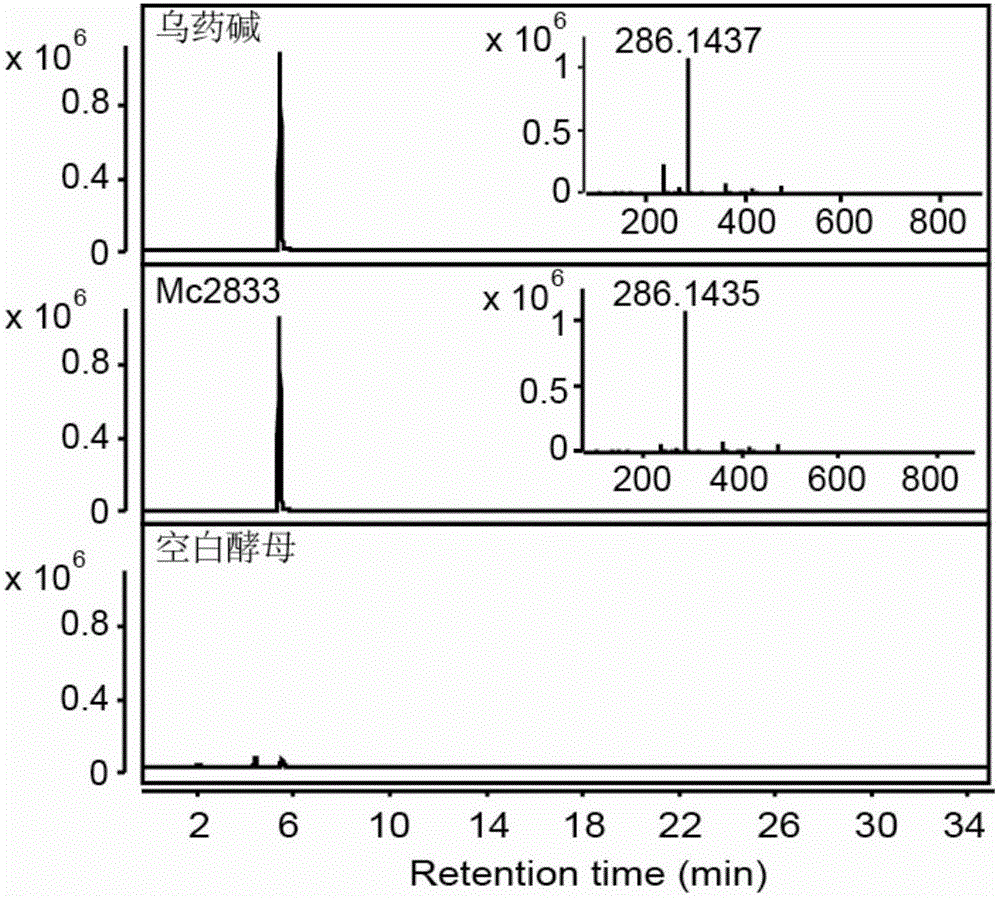
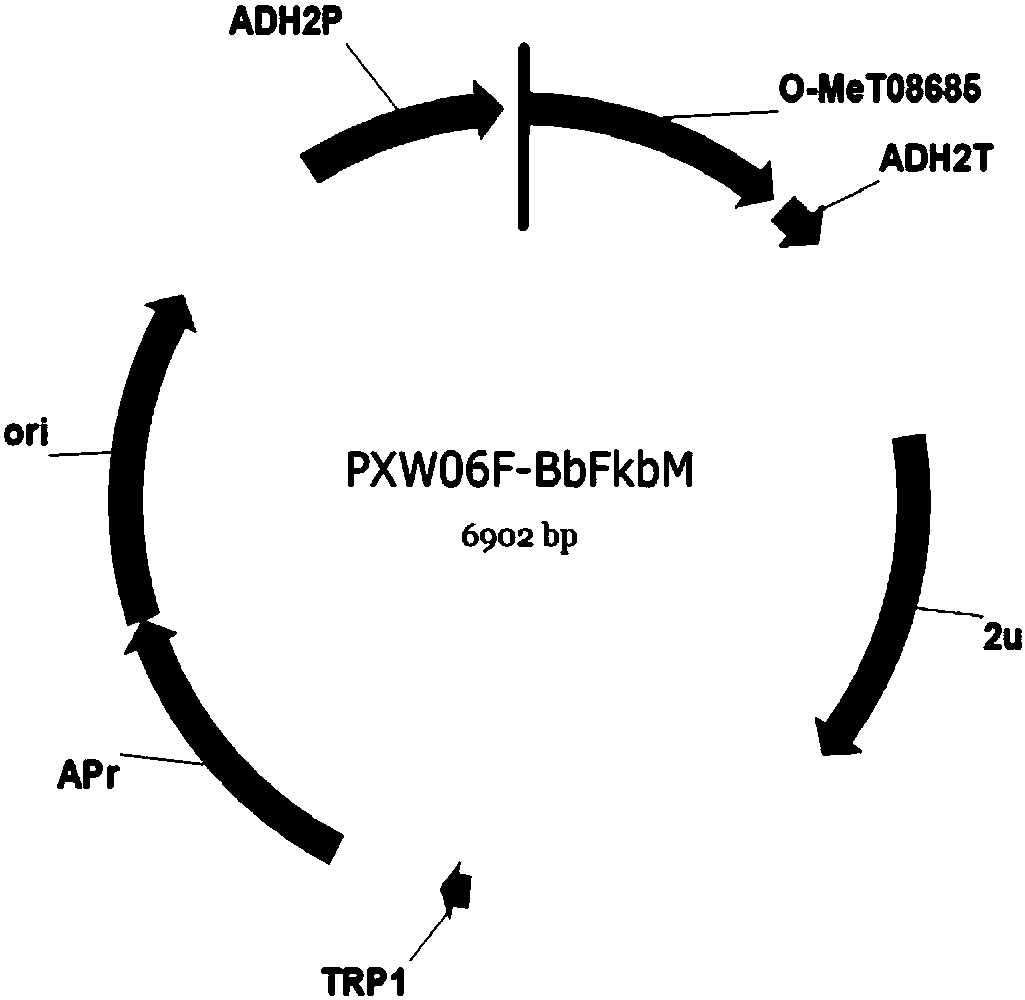
The invention discloses a transmethylase gene participating in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine in macleaya cordata and application of the transmethylase gene. Six transmethylase genes participating in synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine are found in a macleaya genome for the first time and comprise the Mc2833 gene, the Mc769 gene, the Mc8567 gene, the Mc833 gene, the Mc830 gene and the Mc9487 gene. A saccharomyces cerevisiae system is utilized for verifying, several steps of reactions are verified through upstream precursor feeding, and synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine intermediates can be achieved. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism of sanguinarine in synthesis of macleaya cordata, and theoretical bases and molecular assisted breeding objectives are provided for sanguinarine and chelerythrine content macleaya cordata breeding; meanwhile, valuable experience is provided for in-vitro artificial synthesis of sanguinarine and chelerythrine.
Owner:MICOLTA BIORESOURCE INC LTD
Methyltransferase gene of glycosides
The invention relates to a methyltransferase gene of glycosides. For the methyltransferase gene of glycosides, methylated modification can be carried out on four hydroxyl radicals of glycosyl in glycoside compounds in vitro, meanwhile, a synergistic effect can be achieved with glucosyltransferases, biosynthesis and bioconversion of different active substances including polyketides, flavonoids andanthraquinone are realized through combination, thus novel active compounds different from natural product structures are obtained, the oriented bioconversion of the compounds is realized, and the stability of the compounds is enhanced.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
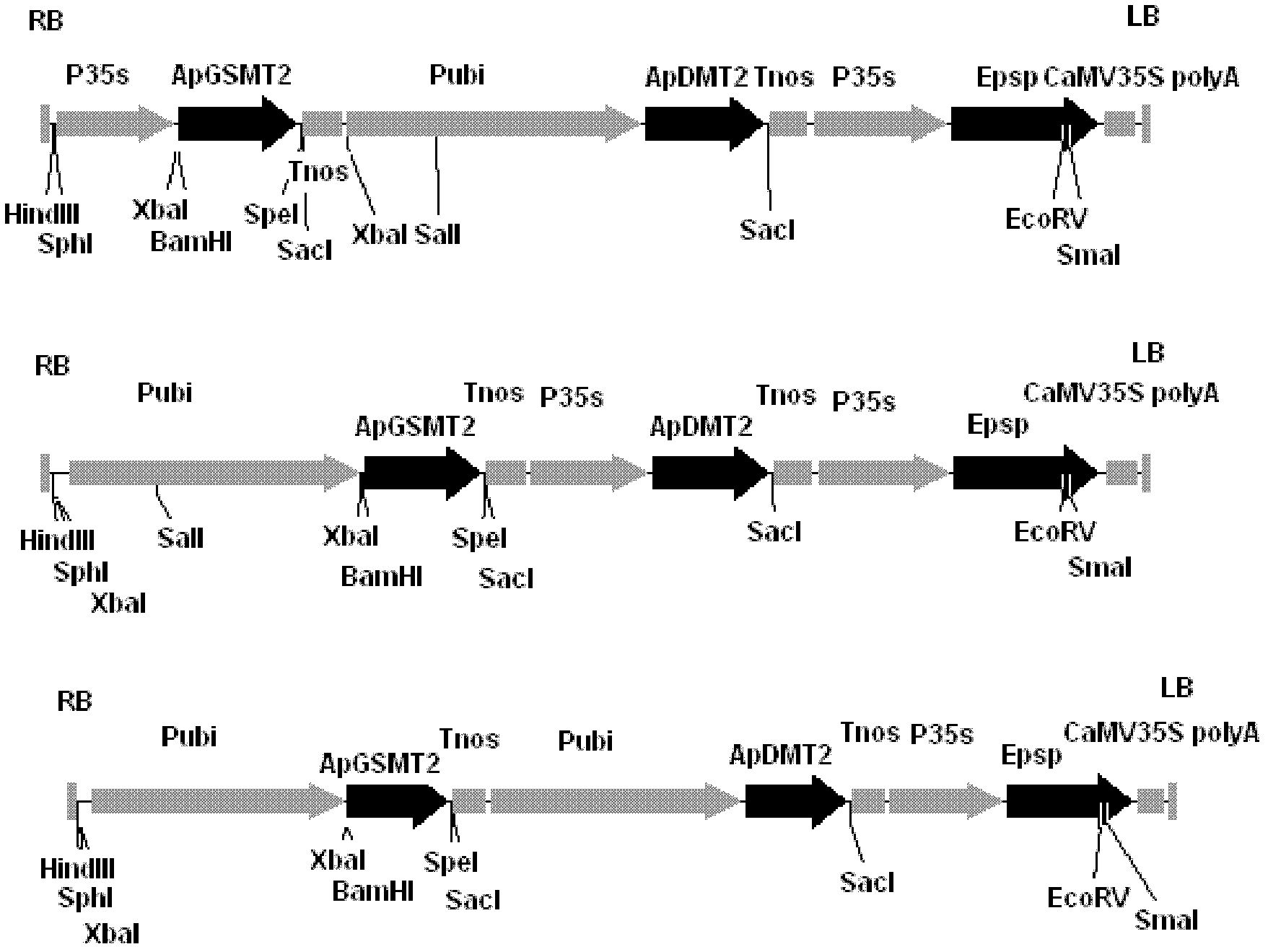
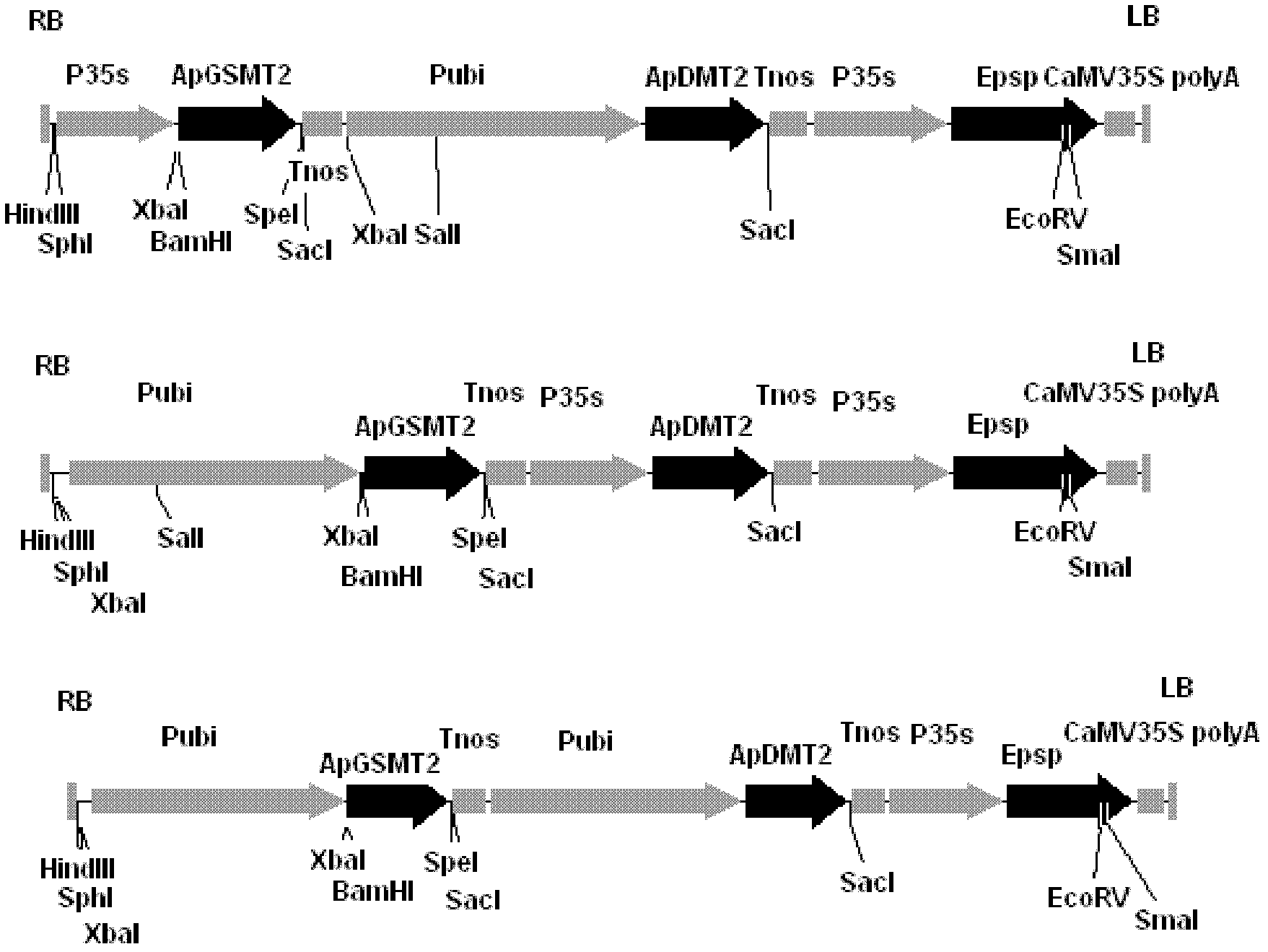
Methyltransferase gene in betaine synthetic pathway and application thereof
InactiveCN102604989AAchieve positioningFermentationGenetic engineeringHigh concentrationNicotiana tabacum
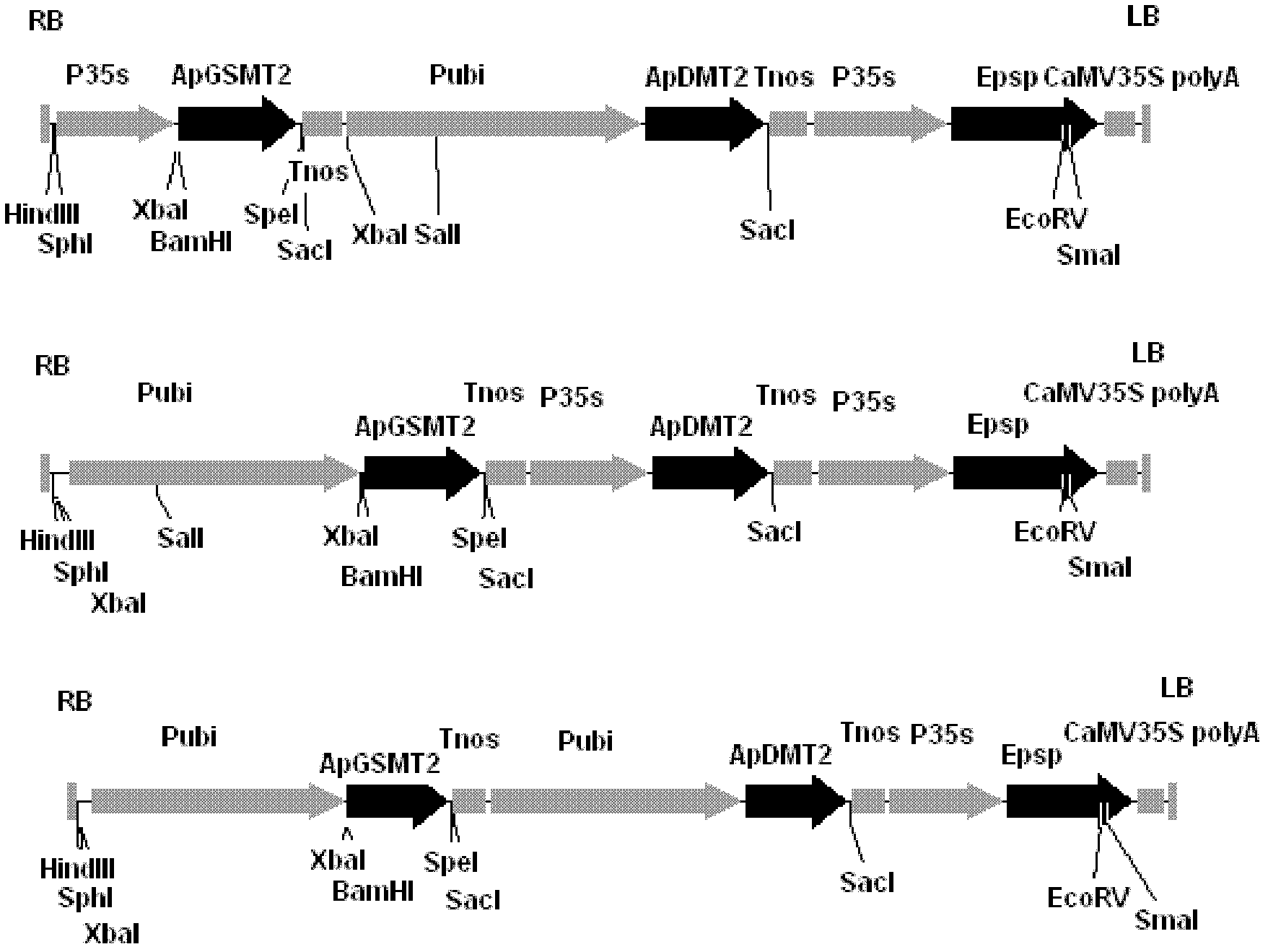
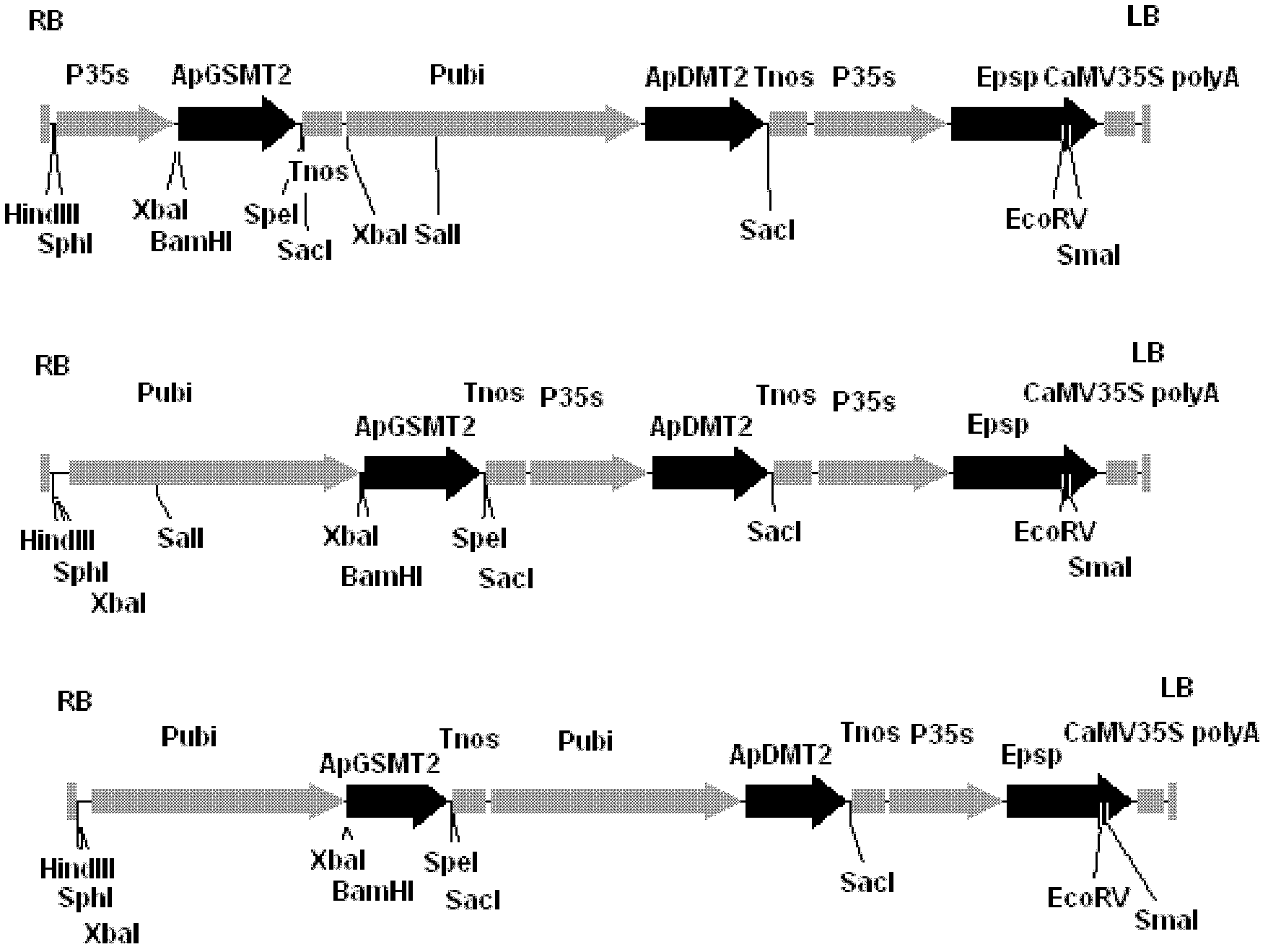
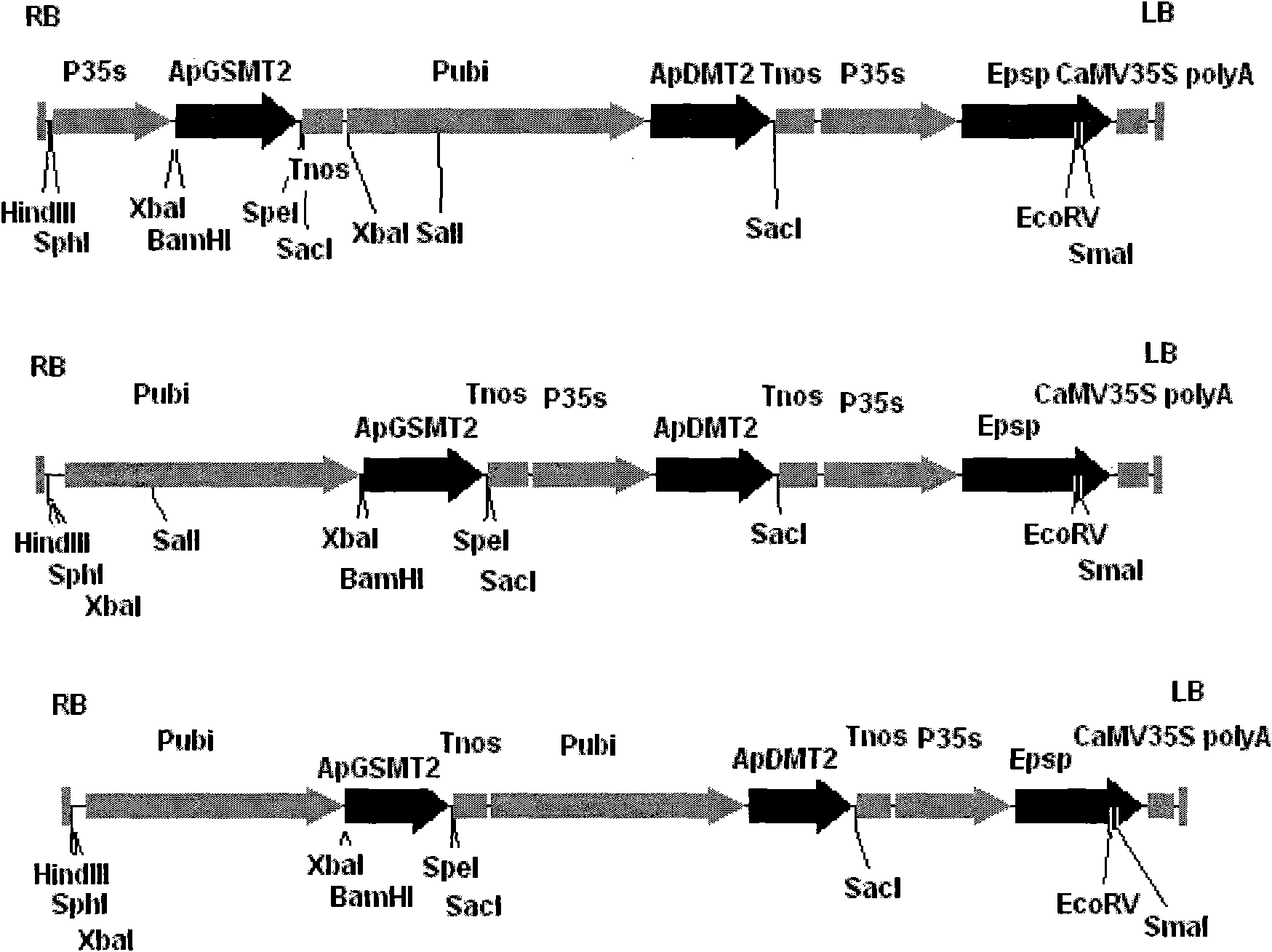
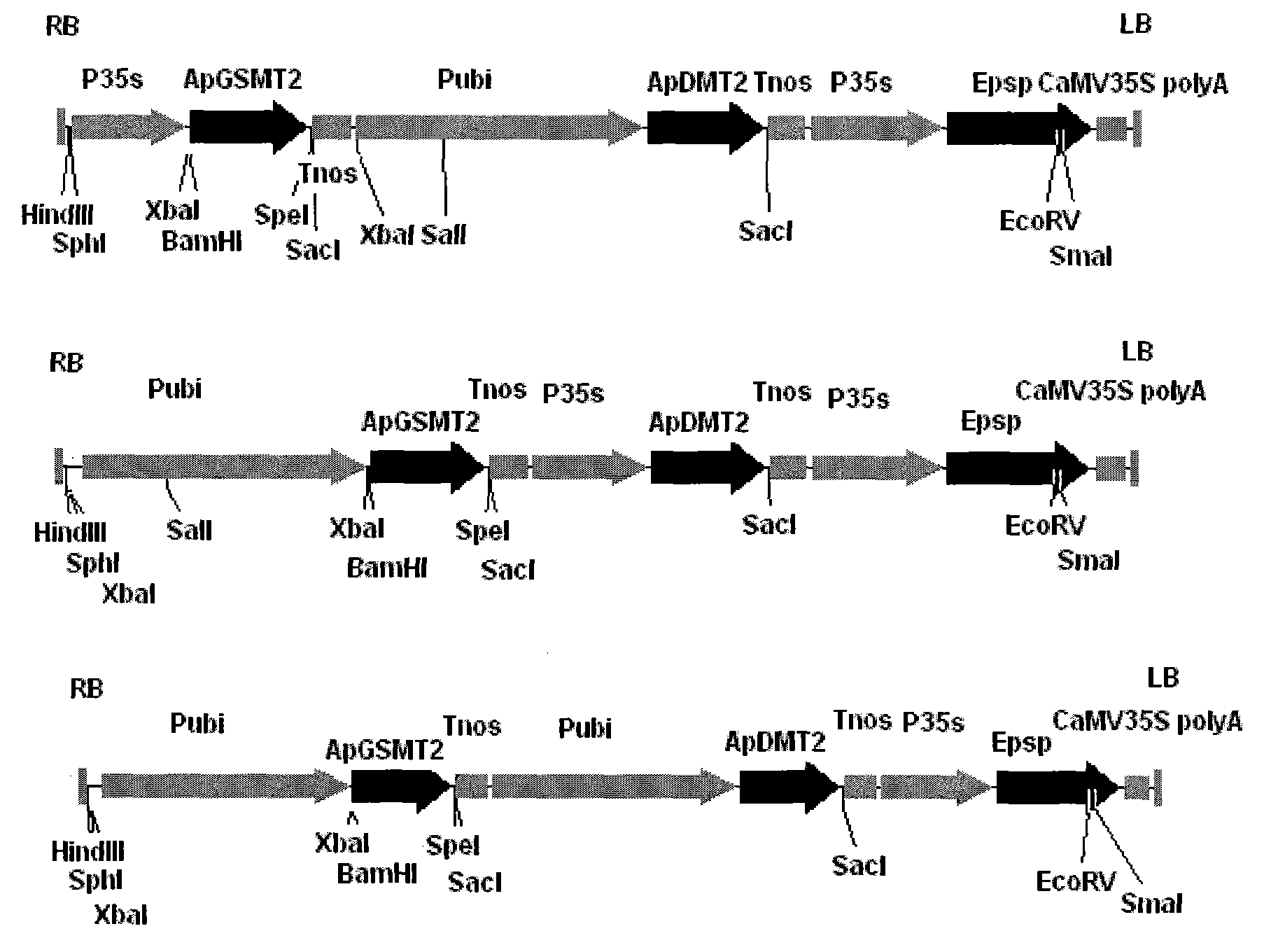
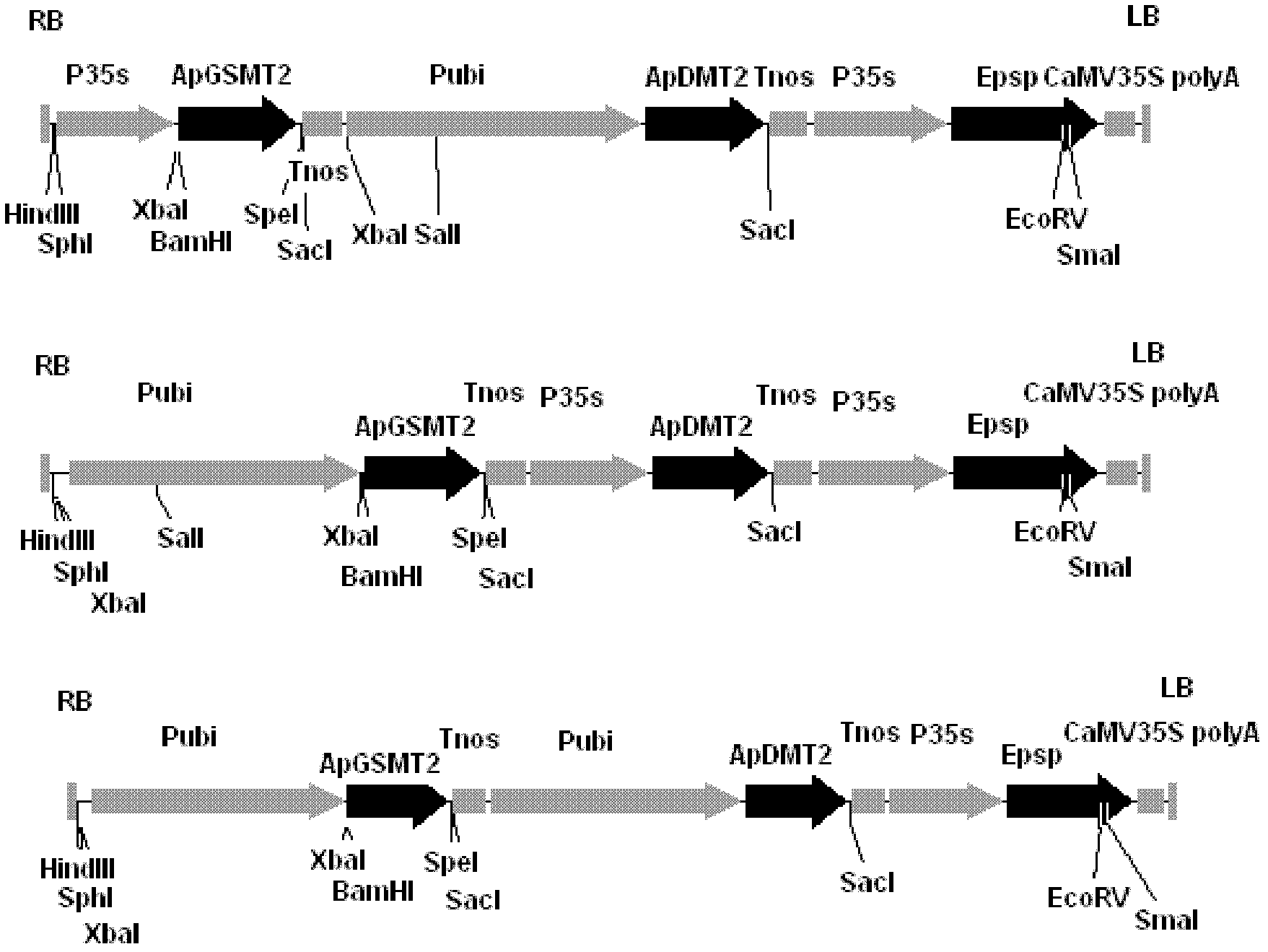
The invention discloses a methyltransferase gene in a betaine synthetic pathway and application thereof. A method for preparing the methyltransferase gene comprises the following steps of: cloning a glycylsarcosine N-methyltransferase gene (ApGSMT2) and a dimethylglycine N-methyltransferase gene (ApDMT2) from aphanothece halophytica; substituting a codon which is in the ApGSMT2 and the ApDMT2 andis relatively low in appearance chance in a higher plant by a codon which is favorable by the higher plant so as to generate the ApGSMT2d gene and the ApDMT2d gene; and constructing series genes of which the encoding products are respectively positioned in chondriosomes by the method for fusing a protein-positioned guide peptide sequence and the methyltransferase gene. The ApGSMT2 uses glycine and creatine as substrates to catalyze glycine methylation, the ApDMT catalyzes the methylation of dimethylglycine, and the ApGSMT2 and the ApDMT coordinate to catalyze the synthesis of the glycine betaine. The ApGSMT2 / ApDMT2 or modifying genes thereof are transplanted into crops, such as corns, wheat, cotton, bean, and tobacco in a synergistic way, and high concentration of glycine betaine is accumulatd ein cells, so that the stress resistance of plants is obviously improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Caffeic acid O-methyltransferase (COMT3) in Morus notabili and application thereof
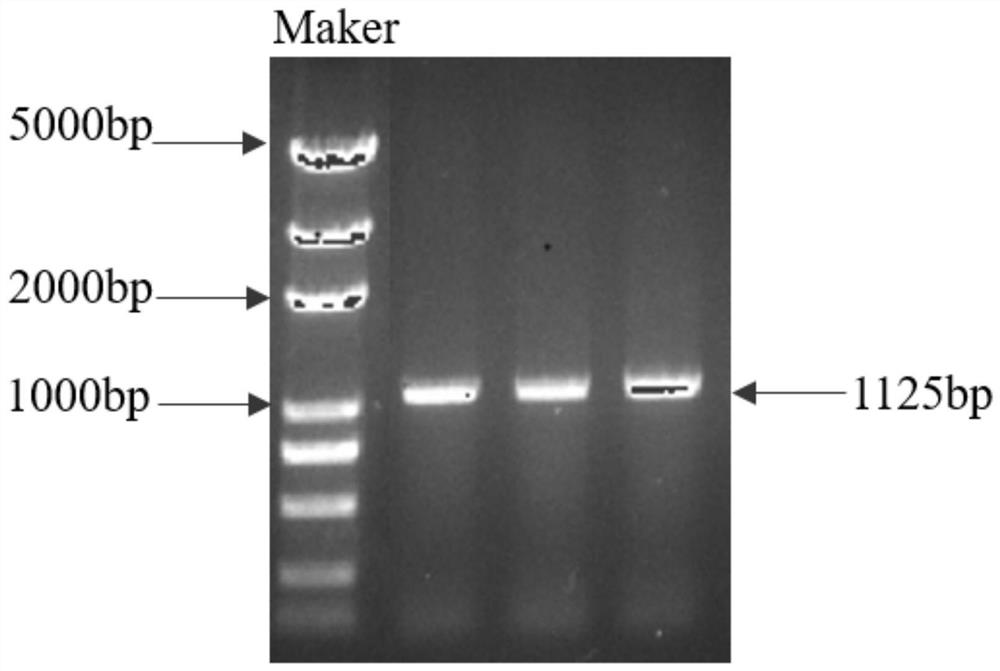
PendingCN111849935AIncrease enzyme activityTransferasesFermentationMethyltransferase GeneCaffeic acid
The invention discloses COMT3 in Morus notabili and application thereof. The COMT is prepared by coding 374 amino acids with a COMT3 gene having a full length of 1125 bp and a PI value of 4.98. The Morus notabili COMT3 gene is cloned, then a prokaryotic expression system is constructed, enzyme activity determination is carried out after recombinant expression, the activity of the COMT is measuredto be high, and therefore, the Morus notabili COMT gene can be used as a target gene of engineering bacteria, and the Morus notabili COMT3 can also be used for catalyzing conversion of 5-hydroxytryptamine into 5-methoxy-tryptamine or conversion of N-acetyl-5-hydroxytryptamine into melatonin in vitro and has good application prospects.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Methyltransferase gene for glycoside compounds
The invention relates to a methyltransferase gene for glycoside compounds. The methyltransferase gene can perform methylated modification on 4-position hydroxyls of glycosyls in the glycoside compounds; moreover, through a synergetic effect of the methyltransferase gene and glucosyltransferase, different active substances such as polyketones, flavonoids and anthraquinones can be converted throughcombined biosynthesis so as to obtain novel active compounds different from natural product structures, so that the oriented bioconversion of the compounds is achieved and the stability of the compounds is enhanced.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for methylating EGCG through enzymatic catalysis
InactiveCN110106213ATransferasesMicroorganism based processesMethyltransferase GeneRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention relates to a method for methylating EGCG through enzymatic catalysis. A crude enzyme solution is prepared from a culture of recombinant escherichia coli integrated with an O-methyltransferase gene from Benifuuki tea, and an enzymatic catalytic reaction is carried out under specific conditions, and then the effect of efficiently methylating EGCG is achieved.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +2
Method for creating phenotypic variation transgenic plant by utilizing methyltransferase gene
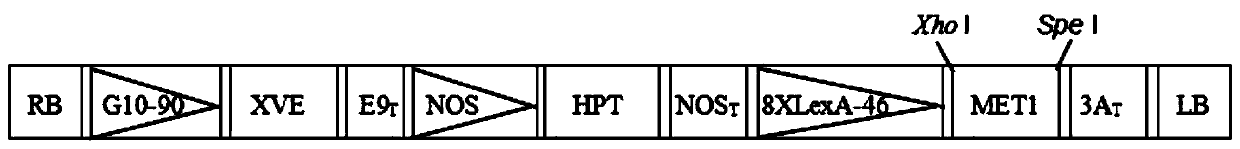
The invention belongs to the field of plant breeding, relates to the field of plant biotechnology breeding, and particularly relates to a method for creating a phenotypic variation transgenic plant byutilizing a methyltransferase gene. According to the method, an agrobacterium-mediated method is used for introducing a chemical induction promoter and the arabidopsis DNA methyltransferase gene AtMET1 into an 84K poplar genome to obtain an AtMET1 84K poplar plant, a sterile in-vitro leaf AtMET1 of the transgenic plant is induced to express for 3 hours, 12 hours and 24 hours by using estrogen, and then the leaf is induced to regenerate to obtain the phenotypic variant plant. According to the research, the chemical induction promoter is used for artificially promoting exogenous gene expression, phenotypic variation germplasm is created, and plant breeding resources are enriched.
Owner:INST OF FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Gene-engineering bacterium, construction method of same, and method of producing vanillin
ActiveCN106947727AEfficient accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesShikimate dehydrogenaseVanillin degradation
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and discloses a gene-engineering bacterium, a construction method of same, and a method of producing vanillin. In the gene-engineering bacterium, the metabolic pathway of 3-dehydro-shikimic acid is modified, wherein a shikimic acid dehydrogenase encoding gene is deleted and a vanillin degradation related gene is also deleted, so that the bacterial strain can accumulate a large amount of 3-dehydro-shikimic acid; in addition, expression on a 3-dehydro-shikimic acid dehydratase gene, an O-transmethylase gene and a vanillic acid reductase gene and two genes in the metabolic pathway of the 3-dehydro-shikimic acid are enhanced, so that yield of the vanillin is increased, degradation of the vanillin is reduced and quantity of the vanillin in a fermentation liquid is increased, thus improving the capability of fermenting production of the vanillin by the bacterial strain. A test proves that the gene-engineering bacterium uses glucose or glycerol as a substrate for producing the vanillin, wherein the yield of the vanillin is increased significantly. A vanillin fermentation liquid produced with the method is free of an isovanillin impurity, so that subsequent separation is easy to carry out.
Owner:BOTON SHANGHAI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
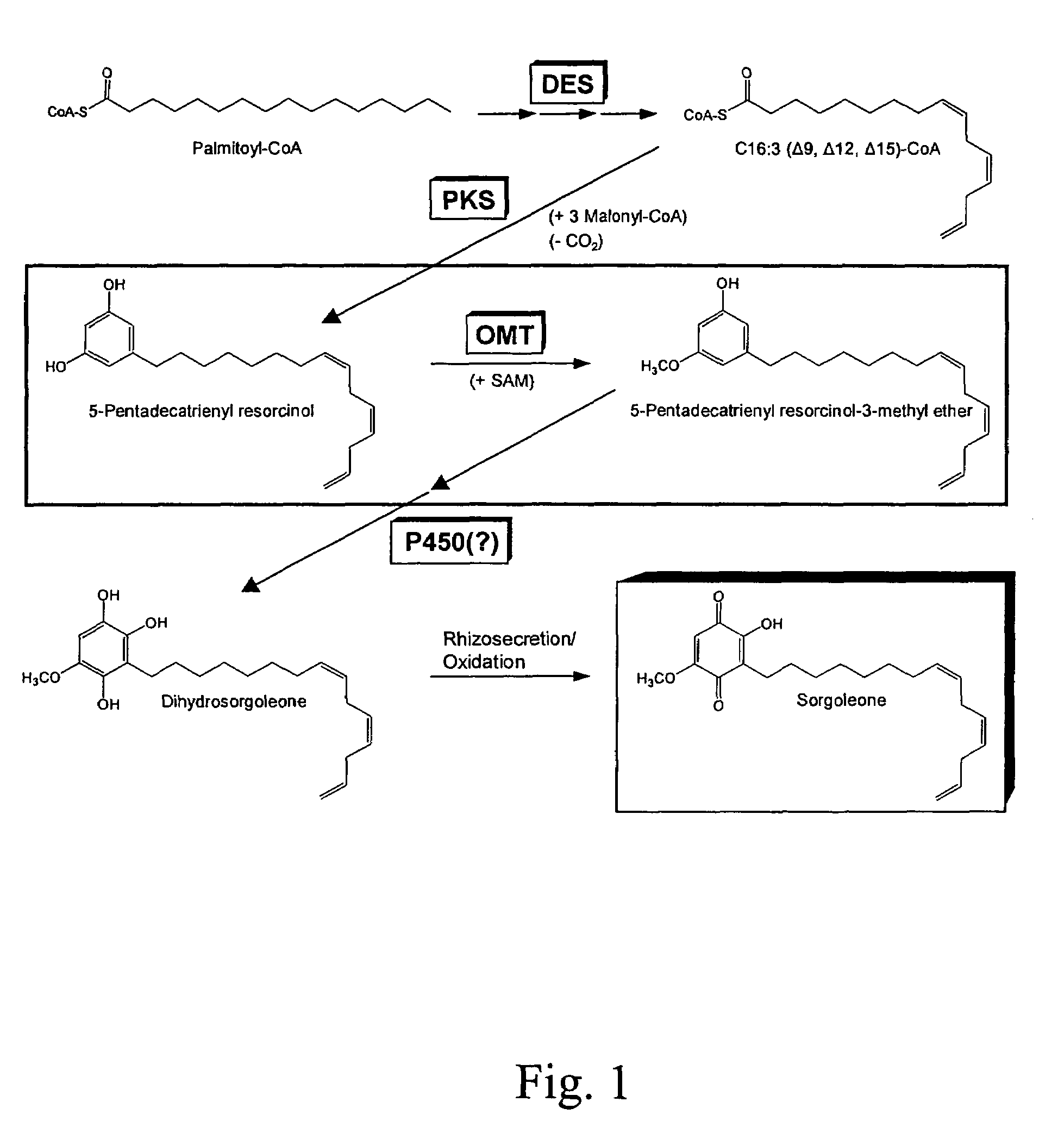
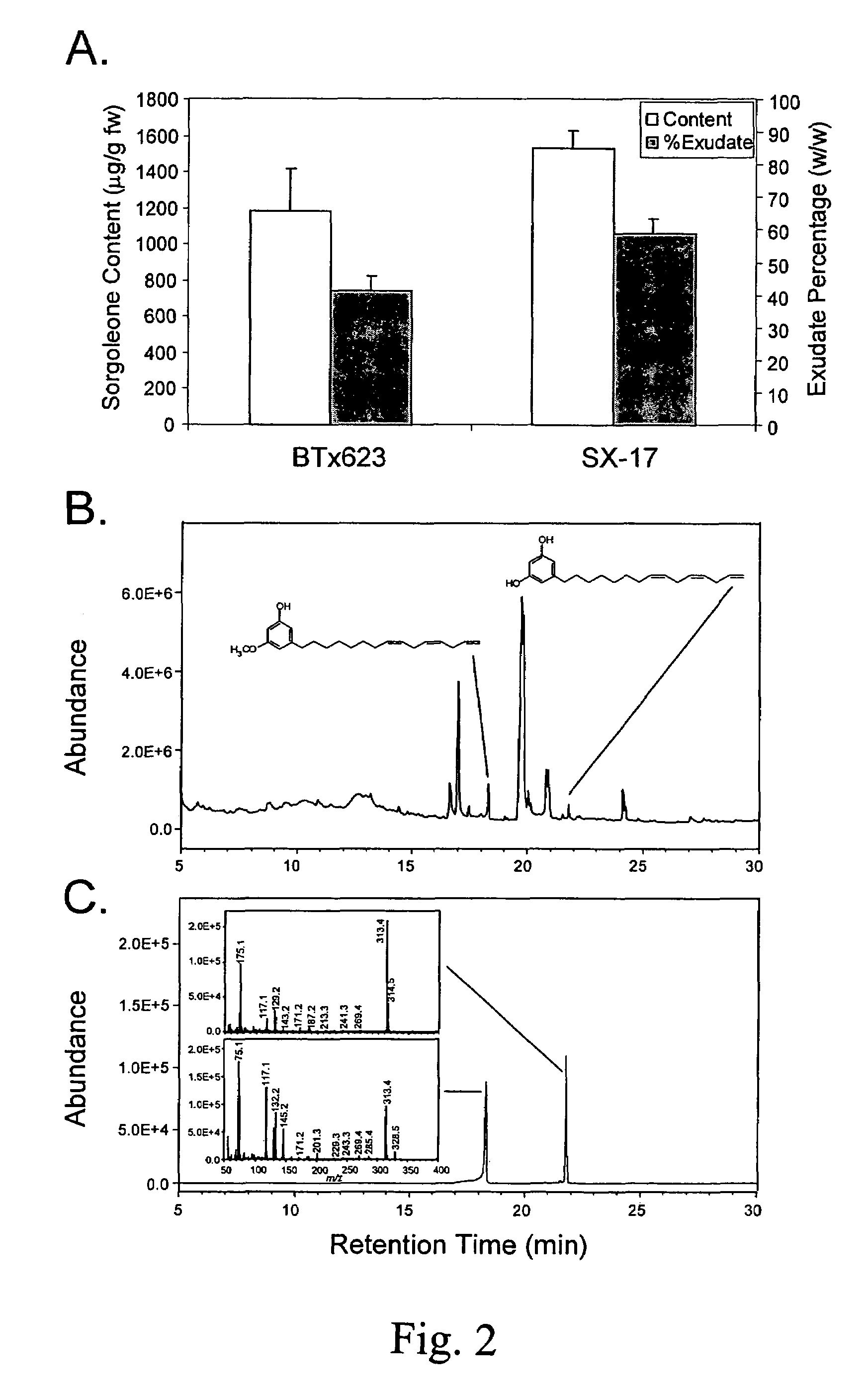
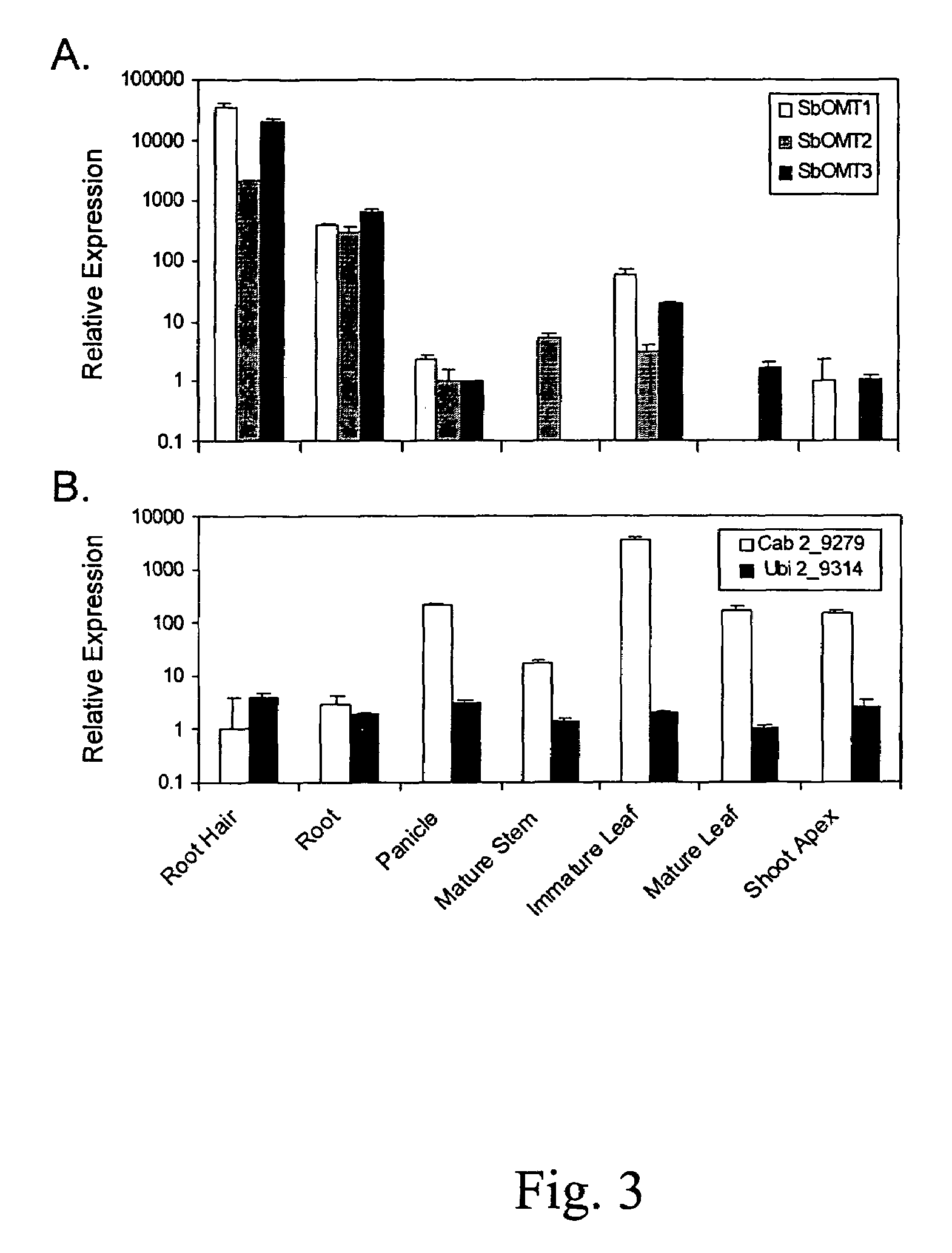
O-methyltransferase gene from sorghum cloning, expression, transformation and characterization
InactiveUS7732666B1Effective amountImprove the level ofImmunoglobulinsFermentationReal-Time PCRsSorgoleone
This invention relates to an O-methyltransferase gene cloned from sorghum, the sorghum O-methyltransferase-3 gene, SbOMT3. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR and recombinant enzyme studies with putative O-methyltransferase sequences obtained from an EST data set from sorghum have led to the identification of the novel root hair-specific O-methyltransferase designated SbOMT3. Transgenic plants which express SbOMT3 can convert resveratrol into pterostilbene in planta. SbOMT3 is also involved in the biosynthesis of sorgoleone.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Transmethylase gene in betaine synthesis process and application thereof
The invention discloses a transmethylase gene in a betaine synthesis process, and modification and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: cloning glycine sarcosine N-transmethylase gene (ApGSMT2) and dimethyl glycine N-transmethylase gene (ApDMT2) from aphanothece halophytica, substituting codons with lower occurrence possibility in higher plants in the ApGSMT2 and the ApDMT2 with higher plant preferred codons to generate a gene ApGSMT2d and a gene ApDMT2d, and constructing the serial genes, of which the coded products are respectively positioned in the chloroplast, byprotein locating targeting sequence and transmethylase gene fusion. Glycine and sarcosine are used as the substrates, the methylation of the glycine is catalyzed, the methylation of the dimethyl glycine is catalyzed by ApDMT, and the glycinebetaine is synthesized under the concerted catalysis. The ApGSMT2 / ApDMT2 or modifier genes thereof are synergically transferred into corn, wheat, cotton, soybean, tobacco and other crops, so high-concentration glycinebetaine is accumulated in the cells, thereby obviously enhancing the stress tolerance of the plant.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
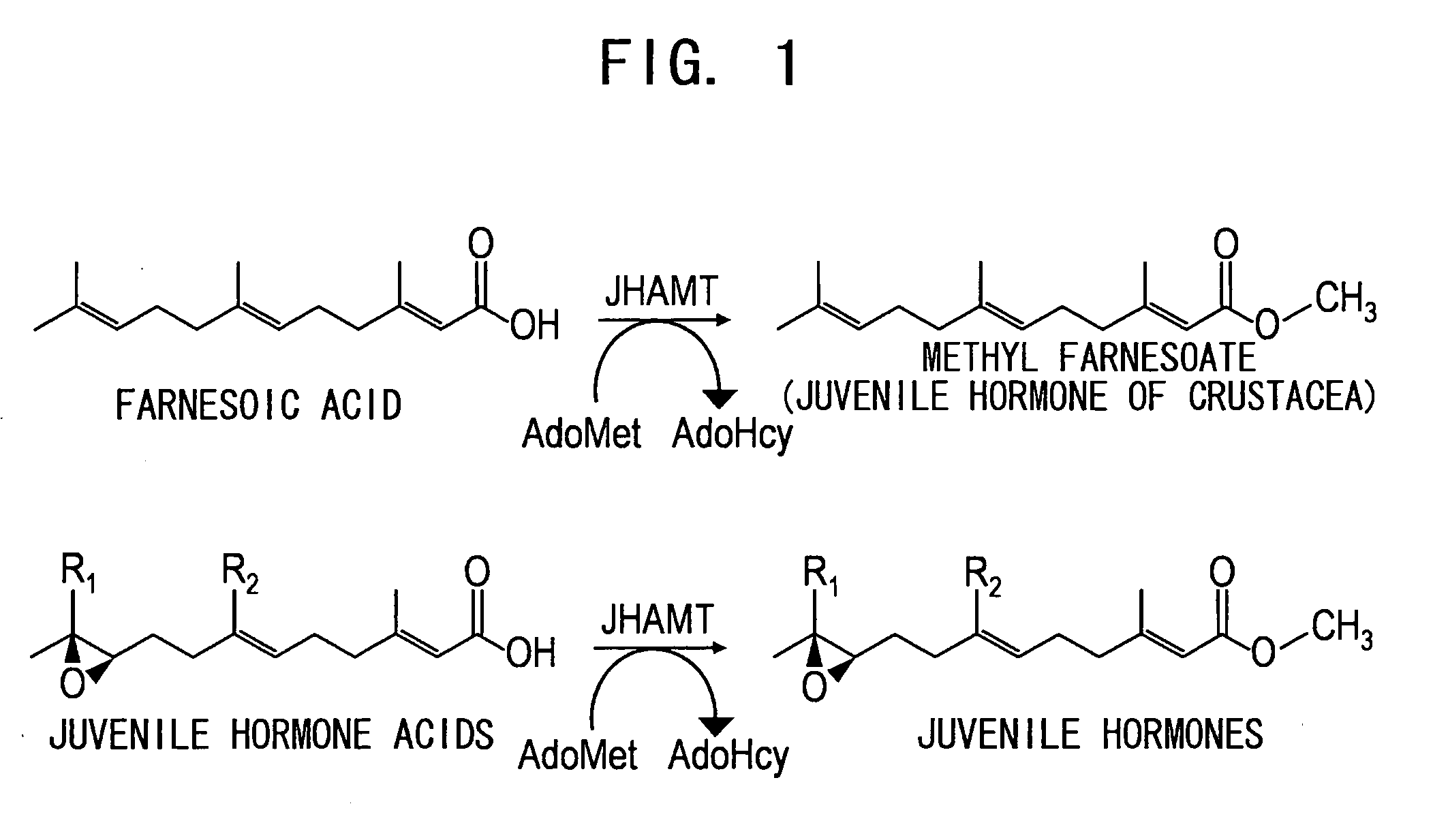
Juvenile hormone transmethylase genes and method of using the same
Juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase gene was cloned using a cDNA derived from the corpora allata of Bombyx mori by differential display methods. A recombinant protein expressed in Escherichia coli, which was transformed with a vector DNA incorporating the gene, was found to have juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase activity. Based on amino acid sequence homology, juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase genes were found from Drosophila melanogaster, Anopheles gambiae, Spodoptera litura, and Helicoverpa armigera. The proteins encoded by the juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase genes derived from Drosophila melanogaster, Spodoptera litura, and Helicoverpa armigera were found to have juvenile hormone acid methyltransferase activities.
Owner:INC ADMINISTRATIVE AGENCY NAT AGRI & BIO ORIENTED RES ORG
Refractory glutamic imine methyl transferase gene, polypeptide coded by it and preparing process
A refractory glutamic imine methyltransferase gene, the polypeptide coded by it and its preparing process are disclosed. On the basis of full-genom sequencing and analyzing of a thermophilic anaerobe, the said refractory glutamic imine methyltransferase gene is cloned and separated. It can be used to prepare the transgenic microbes or animal or plant for producing the said gene and recovering theenzyme coded by the said gene. The amino acid sequence for the polypeptide with activity of the said gene, the function-equal object and a process for preparing, separating and purifying the said polypeptide are also disclosed.
Owner:HUADA GENE RES & DEV CENT HANGZHOU
Detection method and detection kit of gene locus types of DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) methyltransferase 3 alpha
InactiveCN103993099ASimple purification processEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementMethyltransferase GeneGene type
The invention discloses a detection method and a detection kit of gene locus types of DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) methyltransferase 3 alpha. The method comprises the following steps of performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on genome DNA as a template to obtain a PCR amplification product; performing LDR (Ligase Detection Reaction) amplification on the PCR amplification product to obtain an LDR amplification product; analyzing the LDR amplification product by using the Genescan function of a sequenator, judging gene types of drug-resistant loci, and providing information of specific drug-related loci. According to the detection method and the detection kit, various gene types of DNMT3 alpha can be conveniently detected by adopting the PCR-LDR method; the detection method has the characteristics of being reliable and stable in result, simple to operate and quick; complicated steps of purifying the product, depositing and the like in a conventional PCR sequencing detection method are removed, the detection time is shortened, and a relatively high clinical application value is achieved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
N-acetyl-5-hydroxytryptamine O-methyltransferase (ASMT12) in Morus notabili and application thereof
PendingCN111849936AIncrease enzyme activityTransferasesFermentationMethyltransferase GeneProkaryotic expression
The invention discloses ASMT12 in Morus notabili and application thereof. The ASMT12 in Morus notabili is obtained by coding 370 amino acids with an ASMT12 gene having a full length of 1110 bp and a PI value of 6.57. The Morus notabili ASMT12 gene is cloned, then a prokaryotic expression system is constructed, enzyme activity determination is carried out after recombinant expression, the activityof the N-acetyltryptamine O-methyltransferase is measured to be high, and therefore, the Morus notabili ASMT12 gene can be used as a target gene of engineering bacteria, can also be used for catalyzing conversion of N-acetyl-5-hydroxytryptamine into melatonin or catalyzing conversion of 5-hydroxytryptamine into 5-methoxy-tryptamine in vitro, and has good application prospects.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Scopoloa acutangula 1,4-tetramethylenediamine-nitrogen-methyltransferase 1 and its coding protein and application
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Precorrin-2c(20)-methyltransferase mutants, mutant genes and their role in the production of vitamin b 12 application in
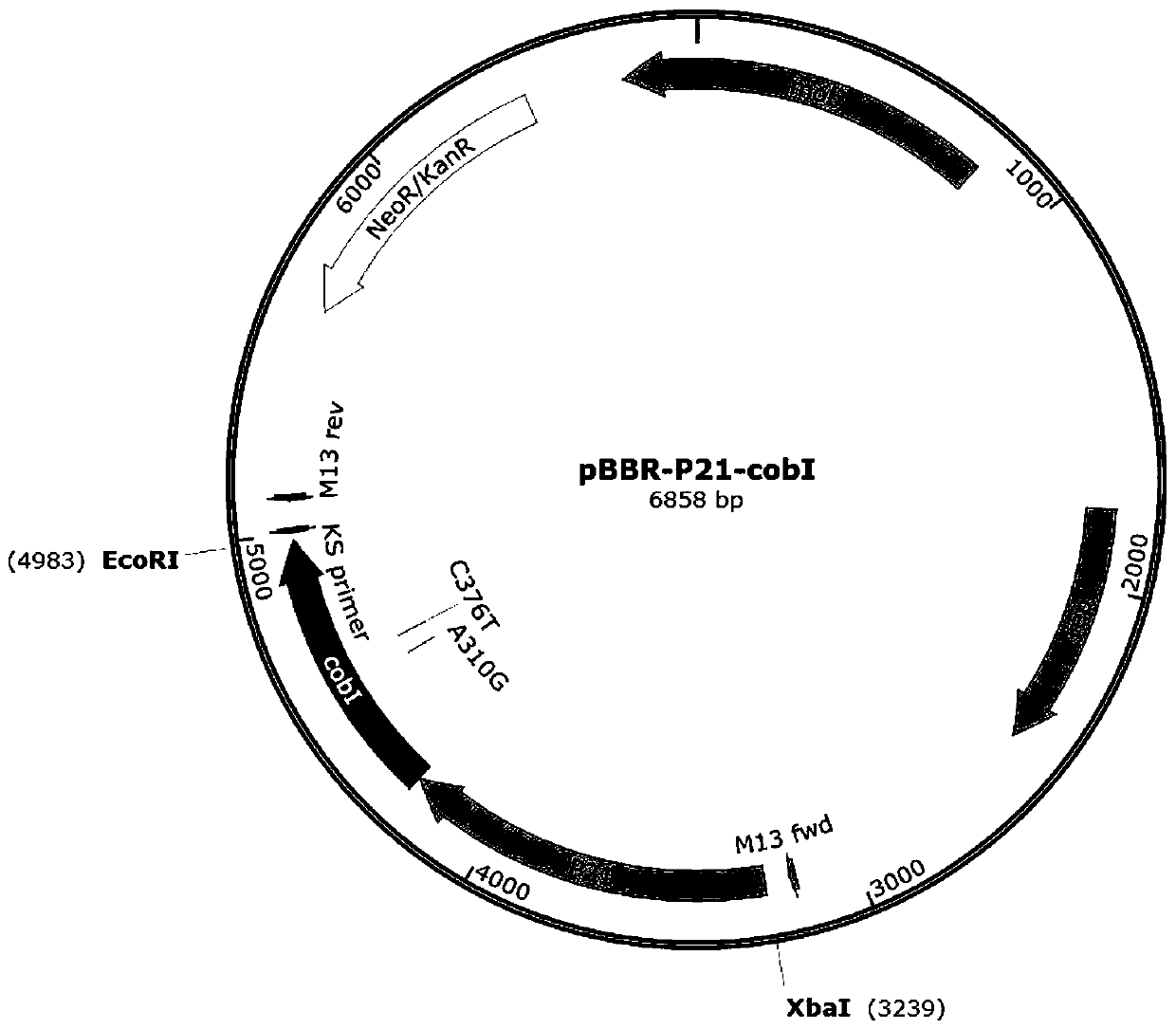
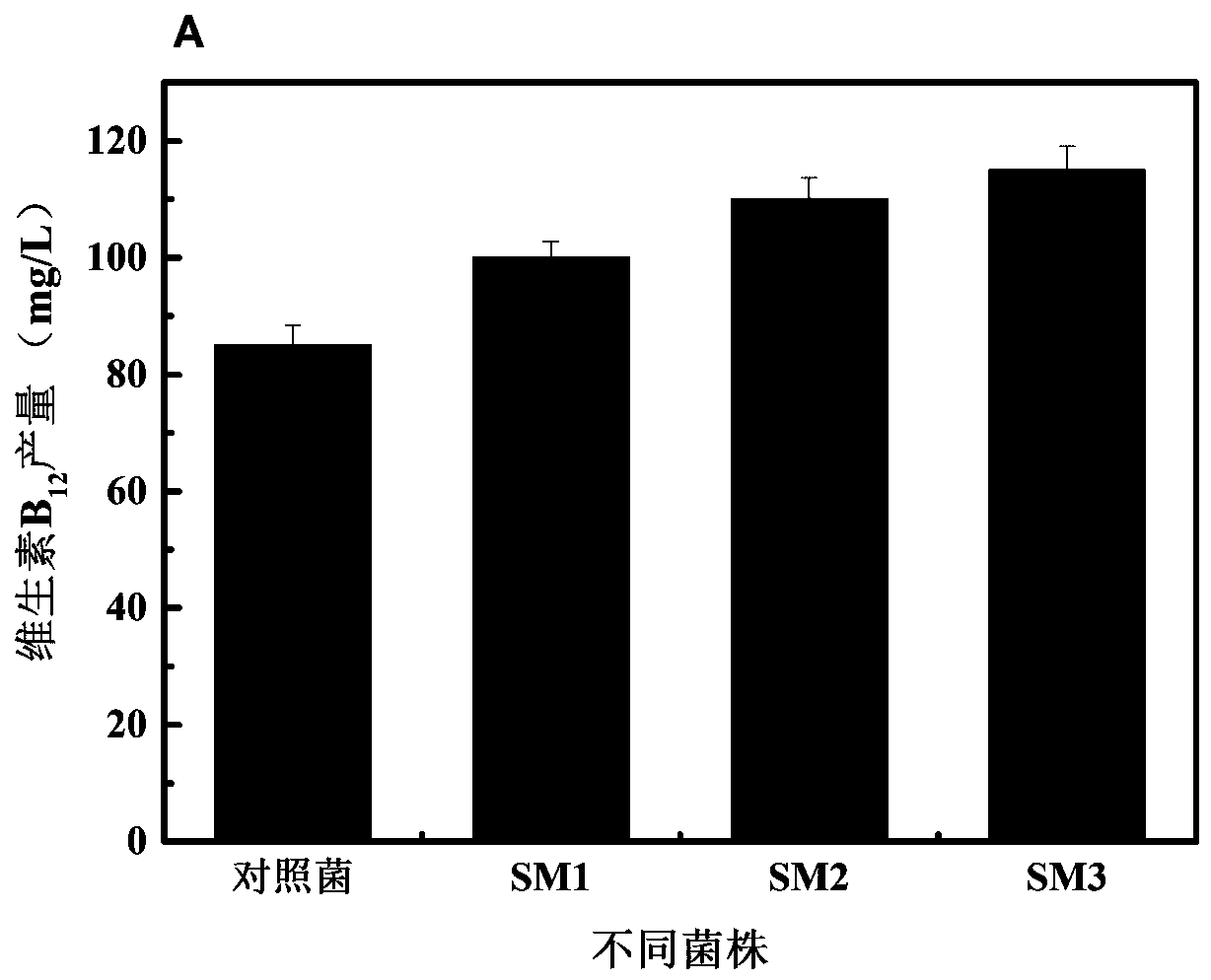
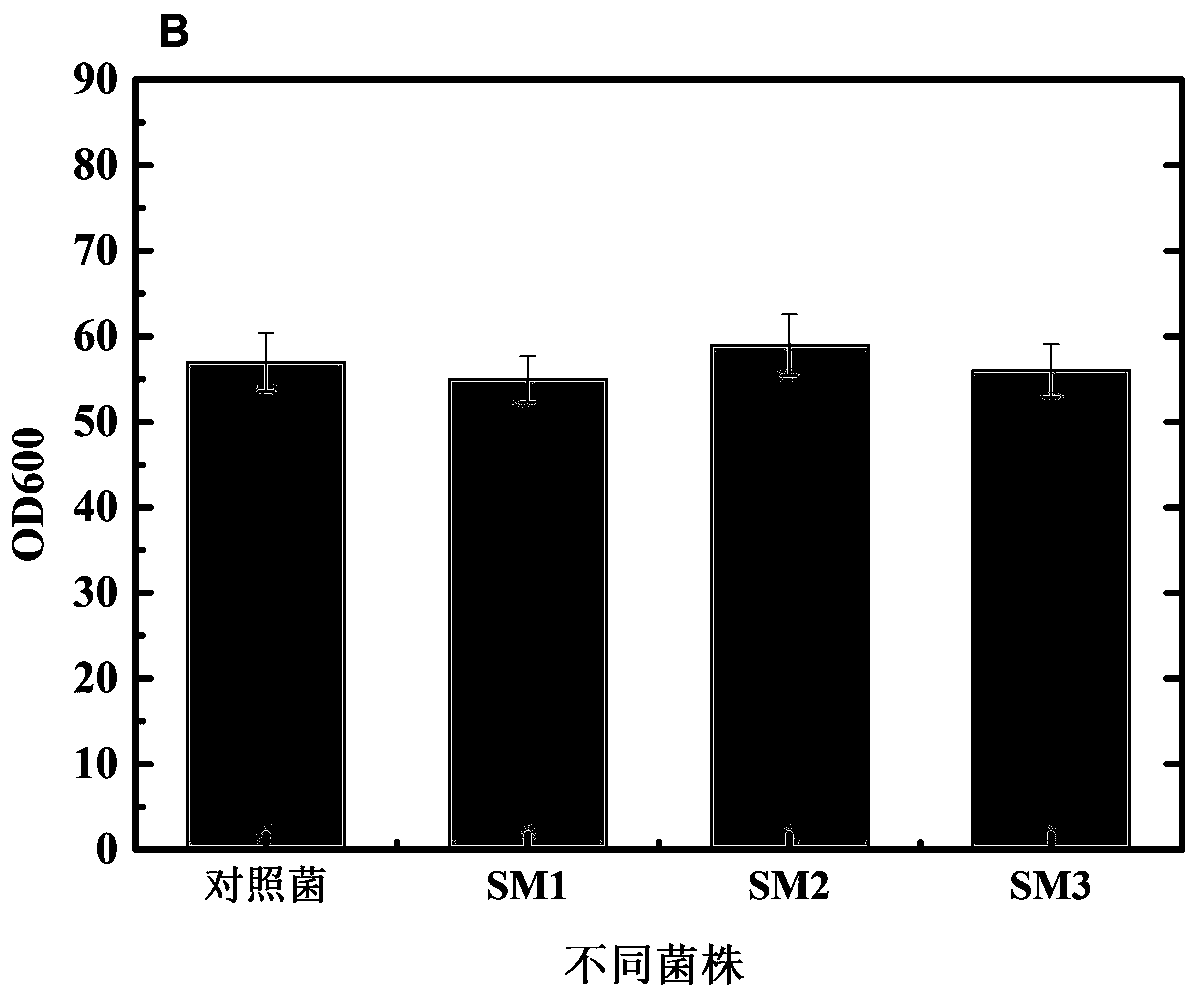
The invention discloses a precorrin-2C(20)-methyltransferase mutant and a mutant gene and application thereof in preparing vitamin B12. Through a genetically engineered bacteria overexpressing the precorrin-2C(20)-methyltransferase gene and the precorrin-2C(20)-methyltransferase mutant gene in Sinorhizobium meliloti, the ability of the Sinorhizobium meliloti to produce vitamin B12 is greatly improved, with great application and promotion value.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methyl transferase gene in betaine synthesis path and modification and application thereof
InactiveCN101805744AAchieve positioningMicroorganism based processesFermentationHigh concentrationNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a methyl transferase gene in a betaine synthesis path and modification and application thereof. The method for synthesizing betaineb by using the methyl transferase gene comprises the following steps: colonizing glycine sarcosine N-methyl transferase gene (ApGSMT2) and dimethylglycine N-methyl transferase gene (ApDMT2) from aphanothece halophytica; generating ApGSMT2 and ApDMT2 genes by substituting codons which has lower occurring probability in higher plants in the ApGSMT2 and ApDMT2 with codons preferred by higher plants; and constructing series gene of a coding product, which are respectively positioned on a chloroplast and a mitochondria by using a method for fusing a protein positioning targeting sequence with the N-methyl transferase gene; the ApGSMT2 catalyzes glycine to be methylated by taking glycine and sarcosine as substrates; the ApDMT2 catalyzes dimethyl glycine to be methylated; the ApGSMT2 and the ApDMT2 carry out concerted catalysis to synthesize glycine betaine. ApGSMT2 / ApDMT2 or modifier genes thereof are transferred under the synergism action into maize, wheat, cotton, soy beans, tobacco and other crops and high-concentration glycine betaine is accumulated in cells, so that the stress resistance of plants can be remarkably improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Methyltransferase genes and uses thereof
The present invention relates to genes associated with the tocopherol biosynthesis pathway. More particularly, the present invention provides and includes nucleic acid molecules, proteins, and antibodies associated with genes that encode polypeptides that have methyltransferase activity. The present invention also provides methods for utilizing such agents, for example in gene isolation, gene analysis and the production of transgenic plants. Moreover, the present invention includes transgenic plants modified to express the aforementioned polypeptides. In addition, the present invention includes methods for the production of products from the tocopherol biosynthesis pathway.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methyltransferase gene in betaine synthetic pathway and application thereof
InactiveCN102604989BAchieve positioningFermentationGenetic engineeringHigh concentrationNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a methyltransferase gene in a betaine synthetic pathway and application thereof. A method for preparing the methyltransferase gene comprises the following steps of: cloning a glycylsarcosine N-methyltransferase gene (ApGSMT2) and a dimethylglycine N-methyltransferase gene (ApDMT2) from aphanothece halophytica; substituting a codon which is in the ApGSMT2 and the ApDMT2 andis relatively low in appearance chance in a higher plant by a codon which is favorable by the higher plant so as to generate the ApGSMT2d gene and the ApDMT2d gene; and constructing series genes of which the encoding products are respectively positioned in chondriosomes by the method for fusing a protein-positioned guide peptide sequence and the methyltransferase gene. The ApGSMT2 uses glycine and creatine as substrates to catalyze glycine methylation, the ApDMT catalyzes the methylation of dimethylglycine, and the ApGSMT2 and the ApDMT coordinate to catalyze the synthesis of the glycine betaine. The ApGSMT2 / ApDMT2 or modifying genes thereof are transplanted into crops, such as corns, wheat, cotton, bean, and tobacco in a synergistic way, and high concentration of glycine betaine is accumulatd ein cells, so that the stress resistance of plants is obviously improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com