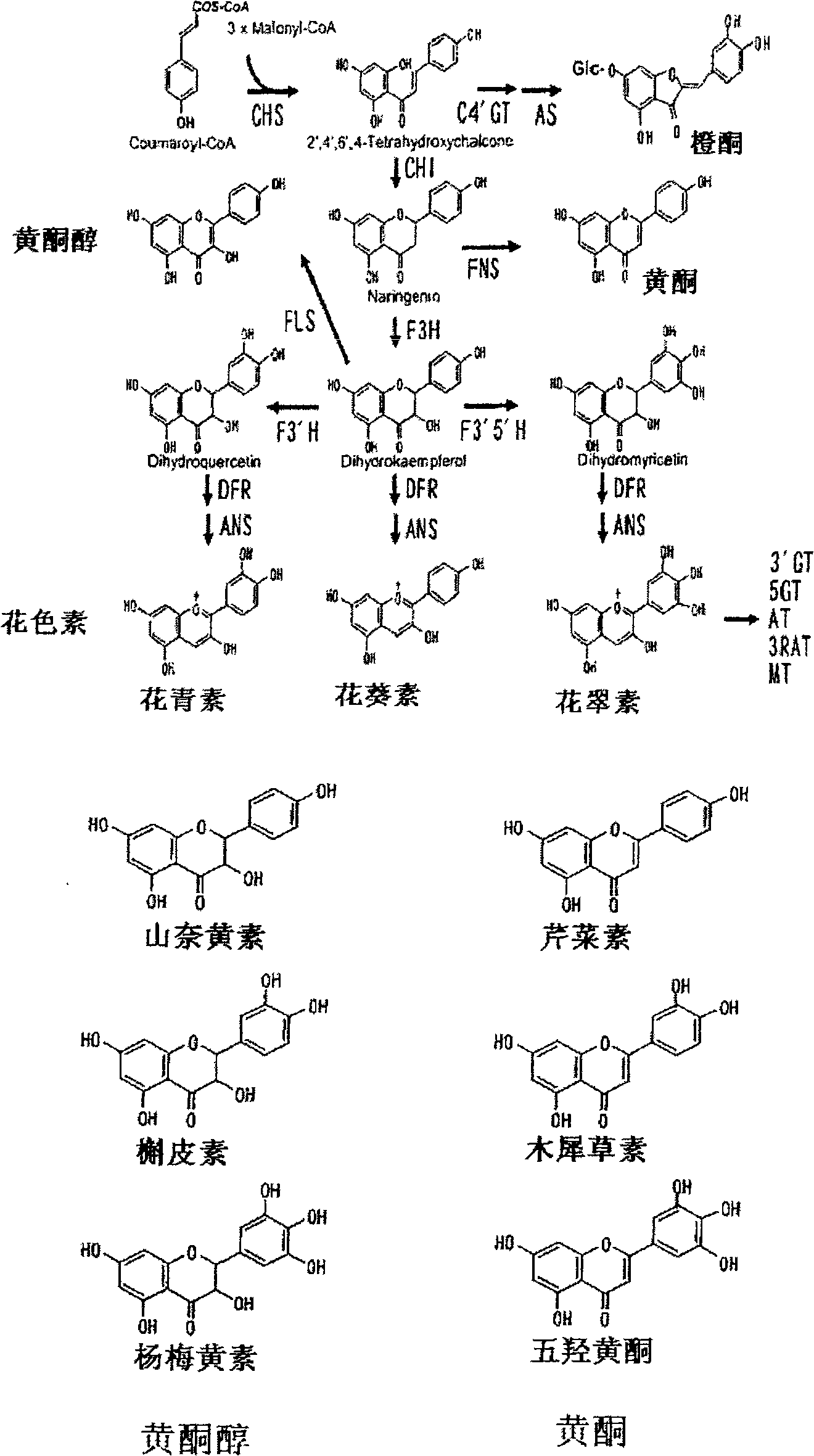
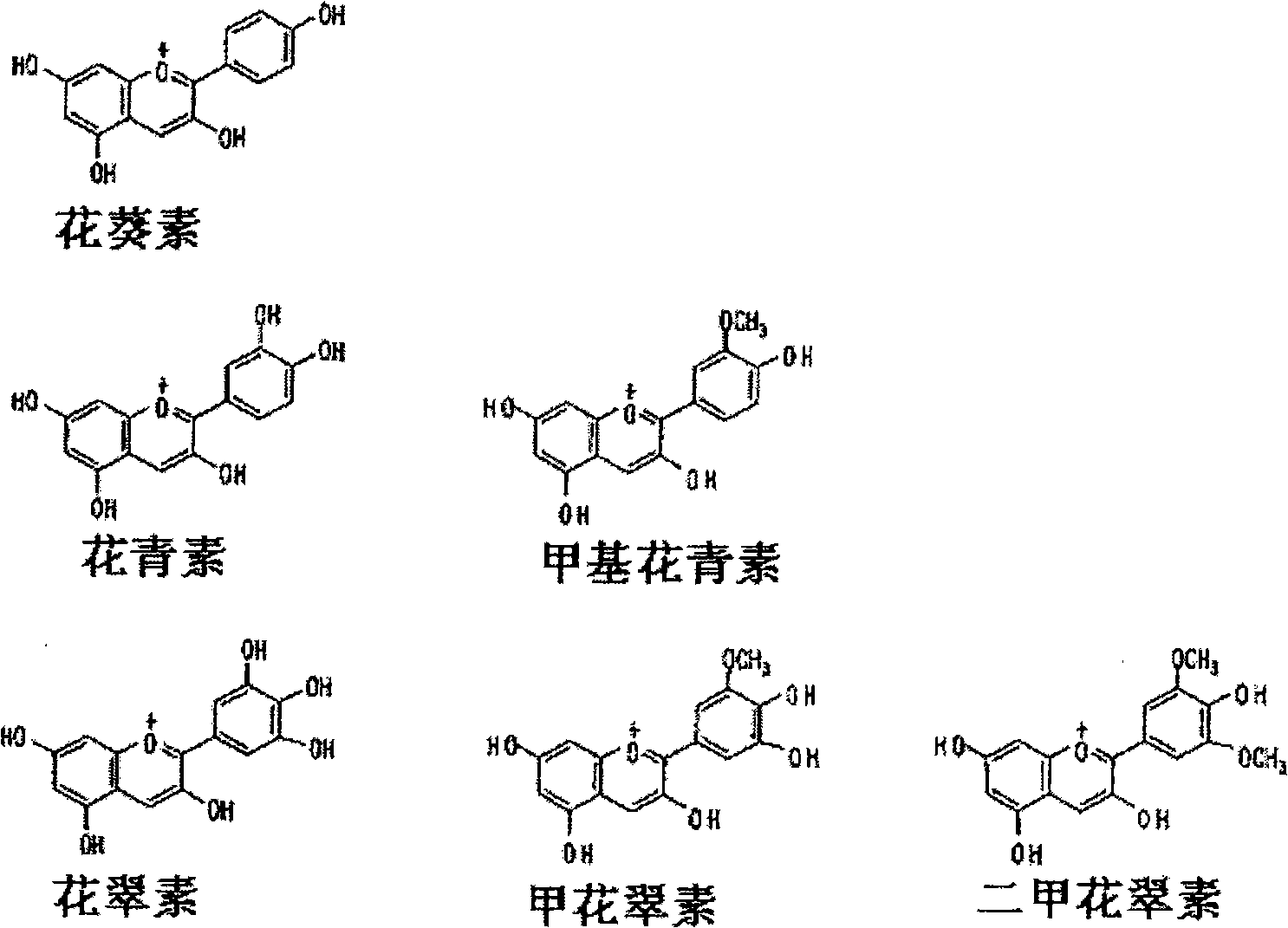
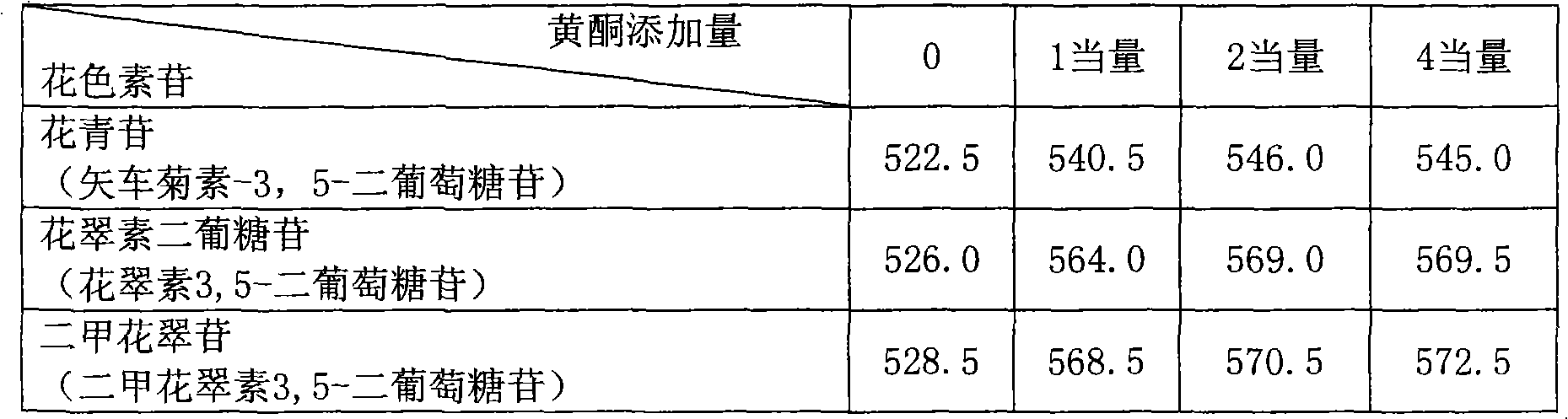
Rose containing flavone and malvidin, and method for production thereof
A rose and flavonoid technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, botanical equipment and methods, enzymes, etc., can solve problems such as unobtained
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0108] Example 1 : Simulation of the Cochrome Effect of Flavonoids on Anthocyanins
[0109] In order to simulate the co-coloring effect of flavonoids on anthocyanins, anthocyanins were first prepared. Cyanin is extracted and purified from the petals of the Chinese rose variety "Rote Rose" (rose cv. "Rote Rose"). Delphin is obtained from Verbena species "Tapien Violet" (vberbena cv. "Tapien Violet" or vberbena variety Sunmaref TP-V ("Tapien Violet") ("Tapien" is a Trade Mark registered in The pigment extracted from the petals of Japan)) is purified by alkaline hydrolysis. Malvin and Luteolin 7-O-glucoside were purchased from Funakoshi Co., Ltd., Japan.
[0110]To the various anthocyanins thus prepared, flavone (Luteolin 7-O-glucoside) was added at a molar concentration ratio of 0, 1, 2, and 4 equivalents in a pH 5.0 buffer, and the absorption spectrum was measured. As anthocyanins, Cyanin (Cyanidin 3,5-diglucoside (Cyanidin 3,5-diglucoside)), Delphin (Delphin 3, 5-Delph...
Embodiment 2
[0119] Embodiment 2 (reference example) : Introducing F3'5' from pansy to the rose variety "Lavande" H#40 Gene and Flavone Synthase Gene from Perilla
[0120] The plasmid pYFS3 containing the flavone synthase gene from perilla described in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2000-279182, pYFS3 was digested with XbaI, blunted at the end, and further digested with BamHI to obtain perilla flavone synthase of about 1.8 kb Gene fragment. On the other hand, pSPB906 described in WO2005 / 017147 was digested with XhoI, blunted at the end, and further digested with BamHI. Between the blunt end and the BamHI cleavage site, the flavone synthase gene fragment of perilla was inserted to obtain 906-pYFS3. 906-pYES3 was inserted into the El 2 There is a perilla-derived flavone synthase gene between the 35S promoter and the D8 terminator (both described in WO2005 / 017147).
[0121] The BamHI and SalI sites of pSPB176 described in the report of Ueyama et al. (Ueyama et al. Plant Sci...
Embodiment 3
[0129] Example 3 : Introducing the F3'5'H#40 gene from Pansy into the rose variety "Lavande" and the flavone synthase gene from Butterfly
[0130] The Butterfly plant-derived flavone synthase gene described in the report of Akashi et al. (Plant Cell Physiol 40, 1182-1186, 1999) was inserted into the EcoRI and XhoI sites of plasmid pBluescript II SK(-), and the obtained plasmid was designated as pSPB426. After it was digested with KpnI, the end was blunted, and further digested with BamHI to obtain a flavone synthase gene fragment of about 1.7 kb from Butterfly. On the other hand, pSPB906 described in WO2005 / 017147 was digested with XhoI, blunted at the end, and further digested with BamHI. Between the blunt end and the BamHI cleavage site, the above-mentioned flavone synthase gene fragment of Butterfly grass was inserted to obtain 906-426.
[0131] The BamHI and SalI sites of pSPB176 described in the report of Ueyama et al. (Ueyama et al. Plant Science, 163, 253-263, 20...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com