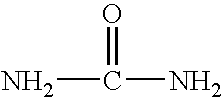Patents
Literature
56 results about "Damage dna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
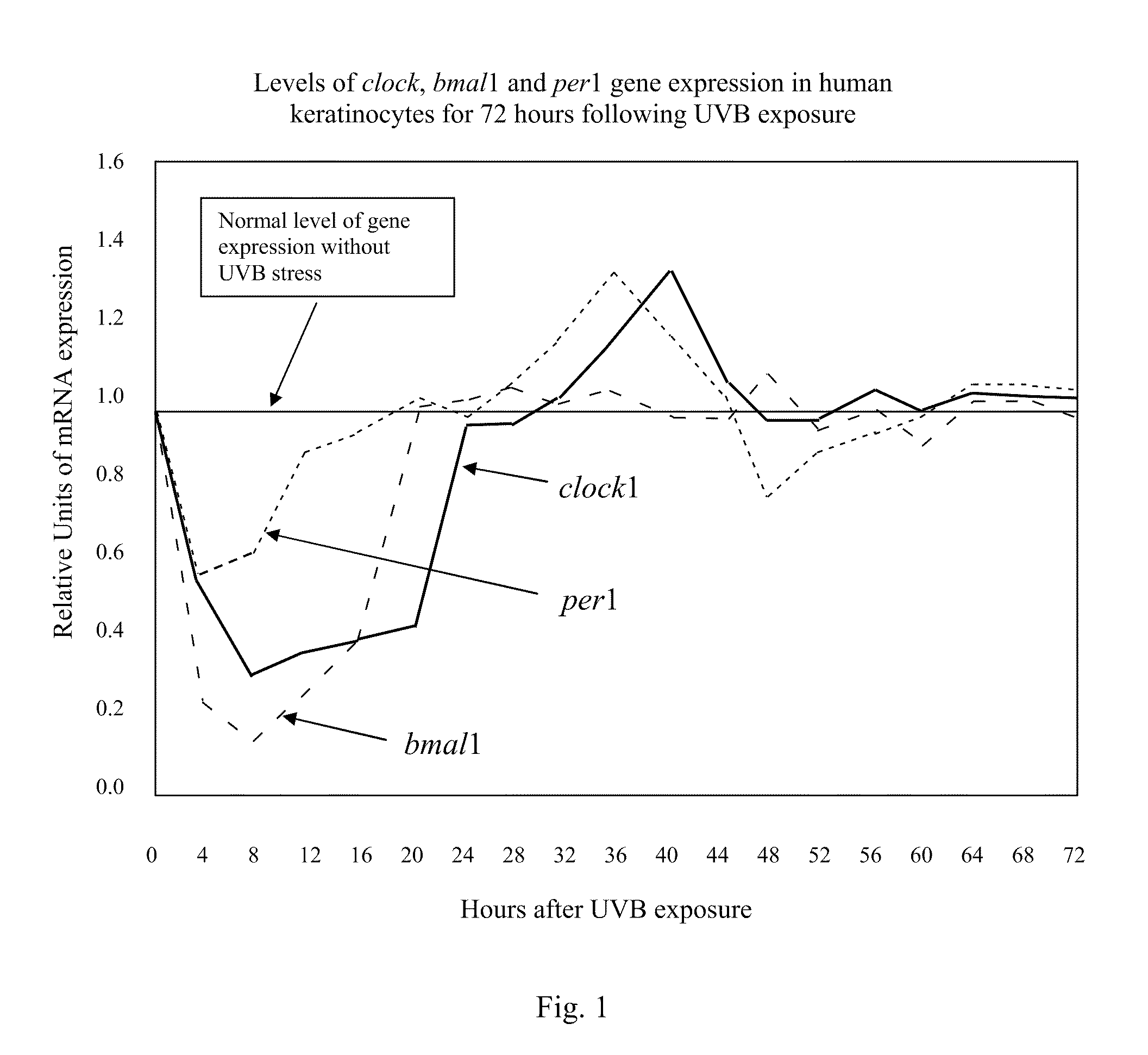
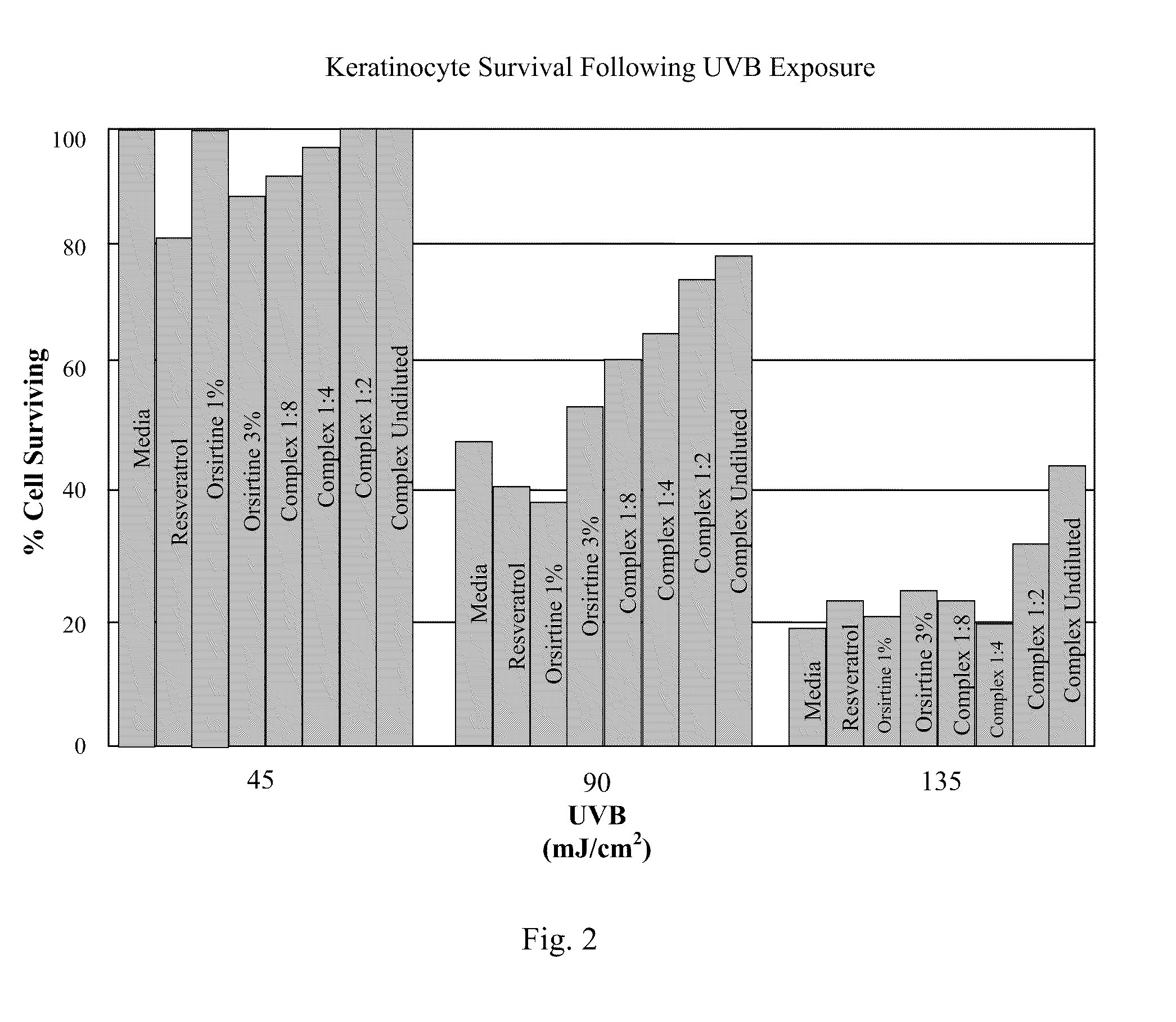
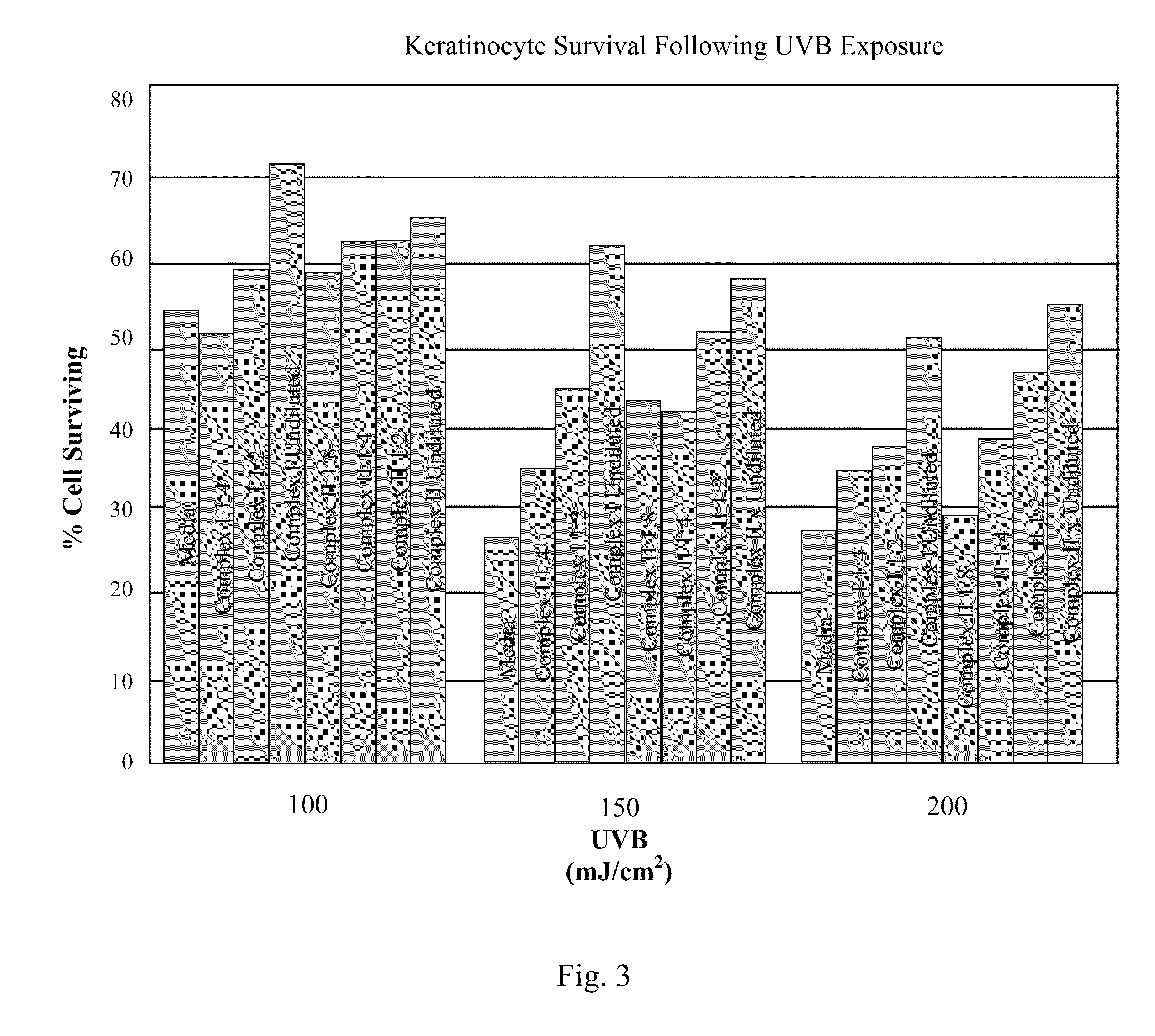
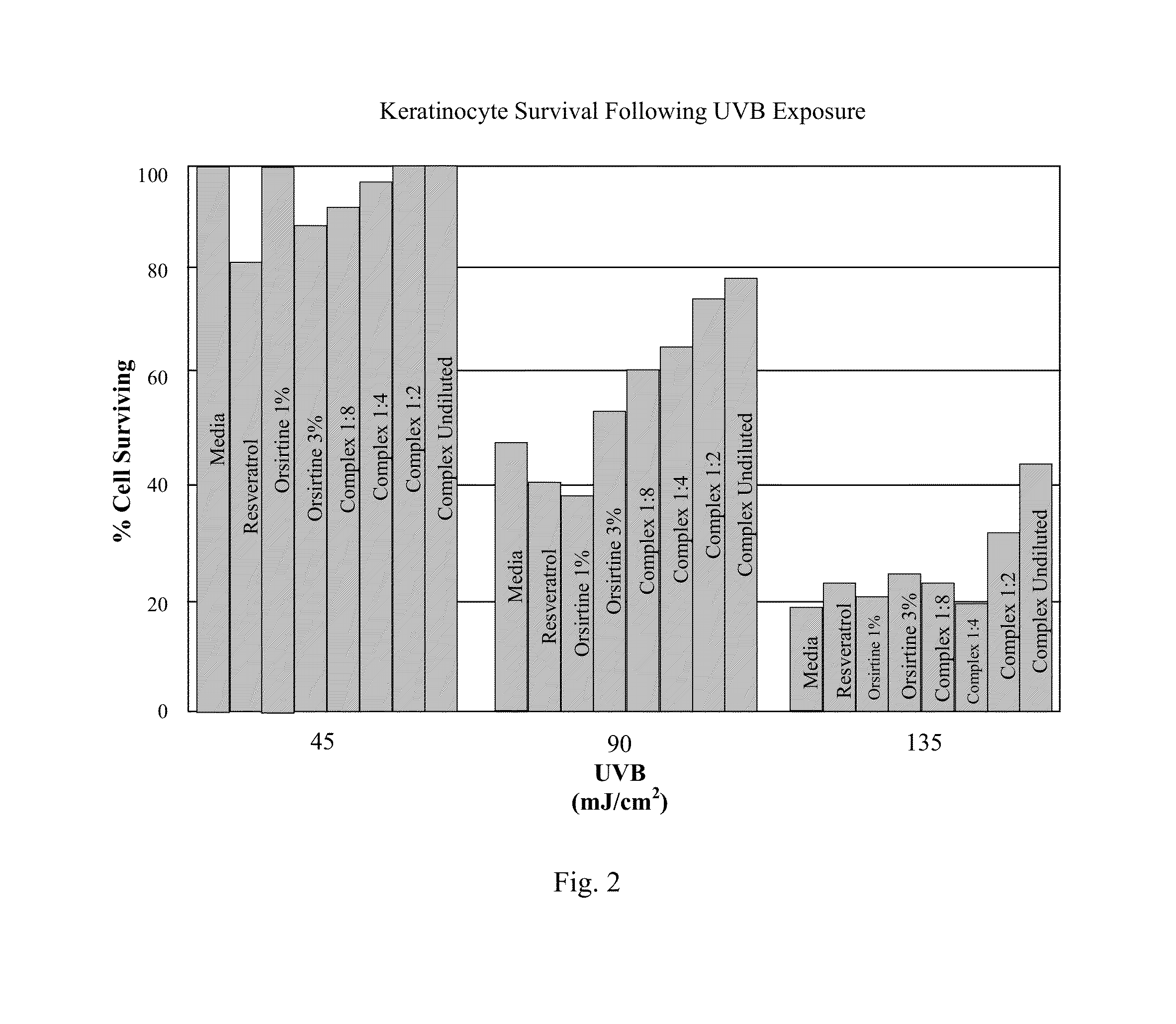
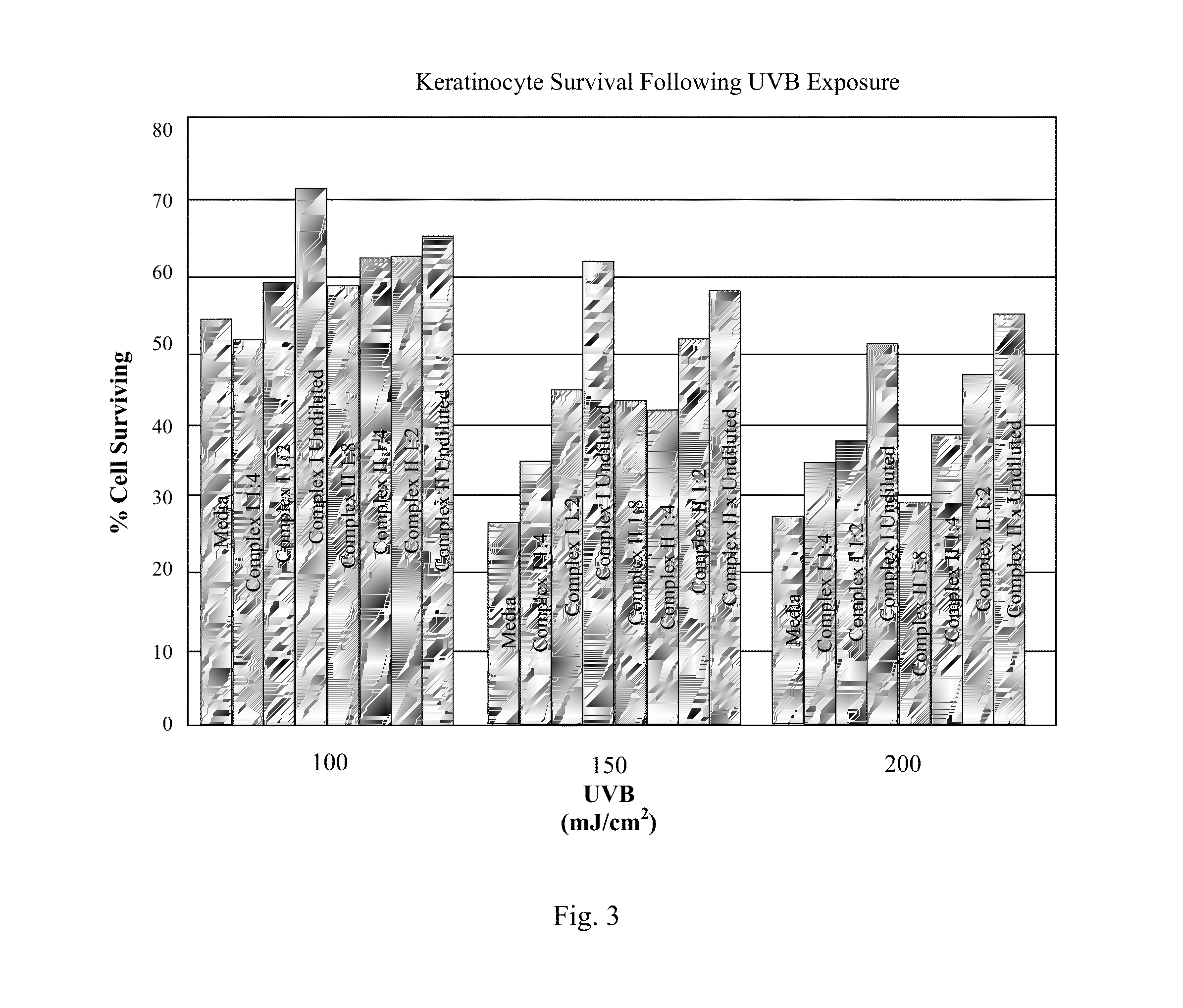
Skin Repair Compositions Comprising Circadian Gene Activators And A Synergistic Combination Of Sirt1 Gene Activators
ActiveUS20100028317A1Enhance cell viabilityPromote cellular longevityBiocideCosmetic preparationsPersonal careCircadian clock gene
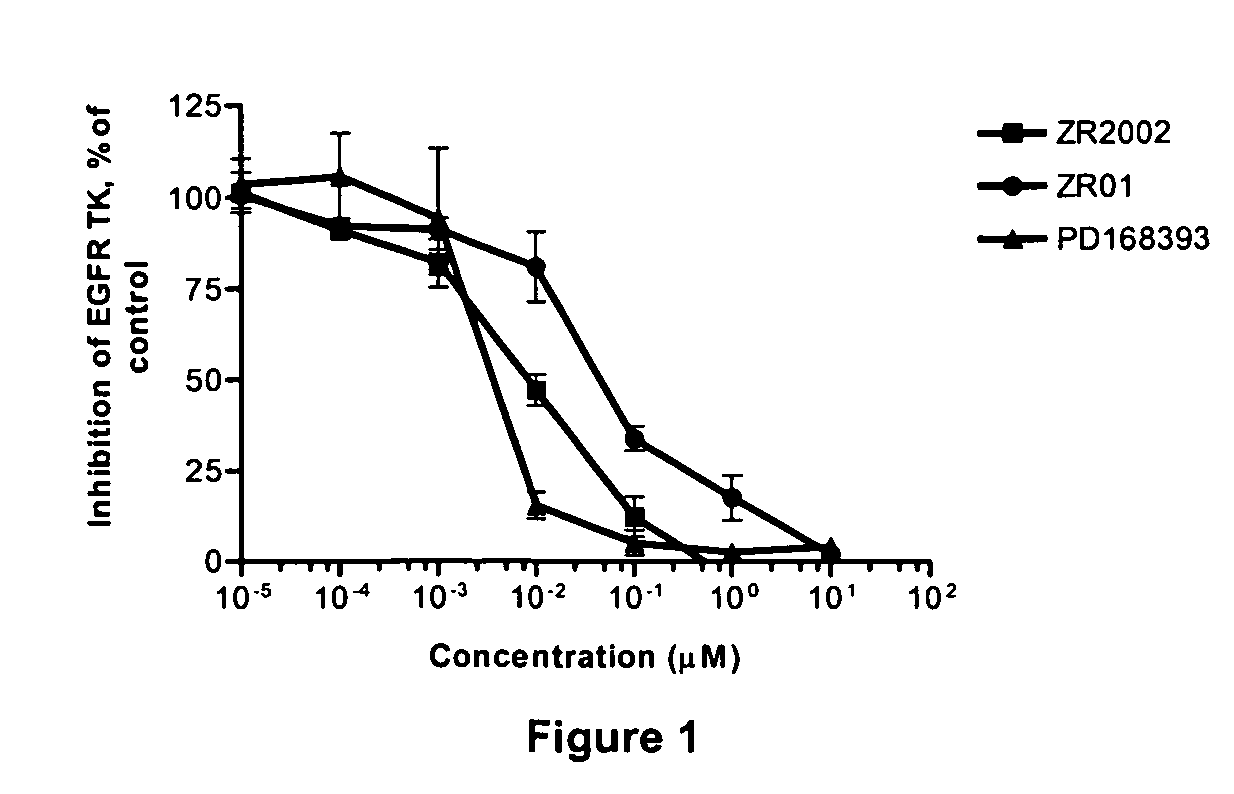
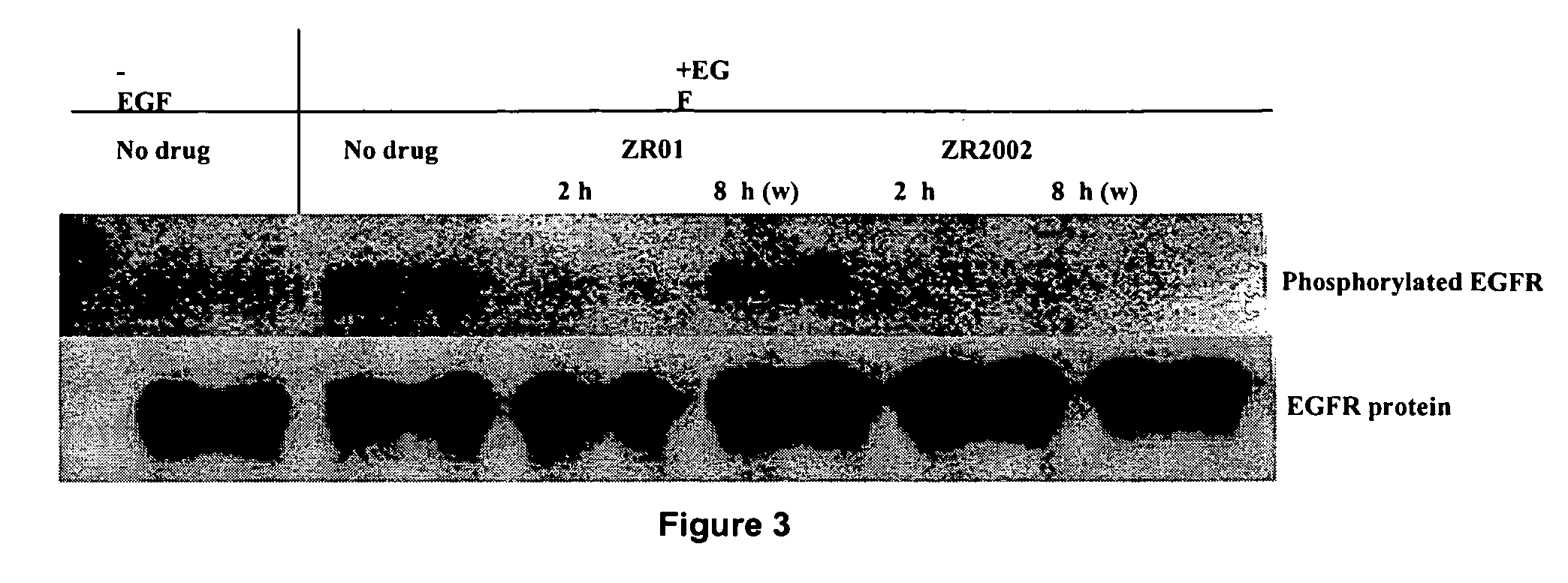
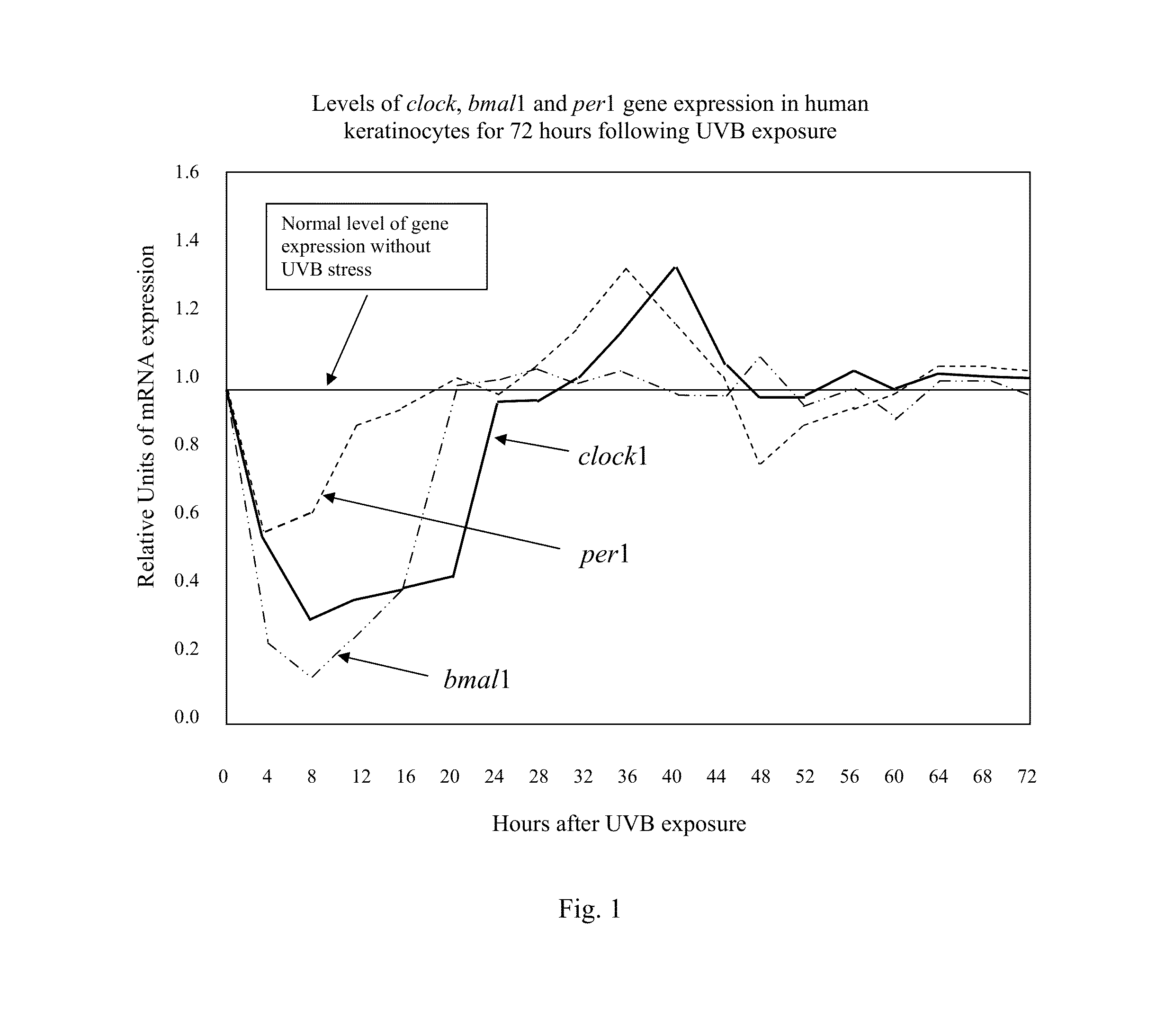
Compositions and methods for enhancing repair of damaged DNA in skin cells. Topical compositions comprising at least one agent that upregulates circadian gene expression in skin cells and at least one non-circadian agent that delays mitosis in skin cells. Preferably, such compositions comprise one or more keratinocyte clock and per1 gene activators, along with SIRT1 or one or more sirt1 activators. More preferably, the sirt1 activator is a synergistic combination of specific peptidic sirt1 activators and resveratrol. Preferably, such compositions are easy to use, efficacious, cosmetically acceptable, chemically, thermodynamically and light stable, safe for topical use, have little or no side effects, and commercially feasible in a personal care marketplace.
Owner:ELC MANAGEMENT LLC
Germicidal and acaricidal dust collector
ActiveCN103142186AEasy to cleanInhibit large currentSuction nozzlesElectric equipment installationUltravioletEngineering
The invention discloses a germicidal and acaricidal dust collector. The dust collector mainly comprises a machine body as well as a housing cover, an axial-flow suction fan, a circuit board and a dust collection box, which are buckled at the upper end of the machine body, wherein a brush bin is horizontally arranged on the machine body on the rear side in a lamp bin; a shaft brushing clamping frame is arranged on two sides in the brush bin; an unpowered rolling brush is arranged on the shaft brushing clamping frame; a dust extraction port is formed in the middle of the brush bin on the back side of the unpowered rolling brush; a slant dust collecting plate is arranged on the two sides of the dust extraction port, in the brush bin; the outside of the slant dust collecting plate stretches to a brushing wheel part; a bottom sealing plate is buckled at the front end of the bottom of the machine body, and divides the lamp bin and the brush bin into independent spaces; brushing hole grooves and a wheel hole groove for the extending out of brushings and brushing wheels are formed on the bottom sealing plate in the front of the brush bin; the circuit board comprises a power supply unit; and the power supply unit is connected to a control unit. The germicidal and acaricidal dust collector can effectively utilize ultraviolet to sterilize and damage DNA of an acarid by circuit control, and a flapping device and the unpowered rolling brush can act together to flap out or brush out the acarid to be cleaned and removed together with dust, so that the germicidal and acaricidal dust collector has the cleaning functions of flapping, sterilizing, acarid removing, sweeping, dust collecting and the like.
Owner:北京福玛特科技有限公司
Methods and Compositions for Amplification of DNA
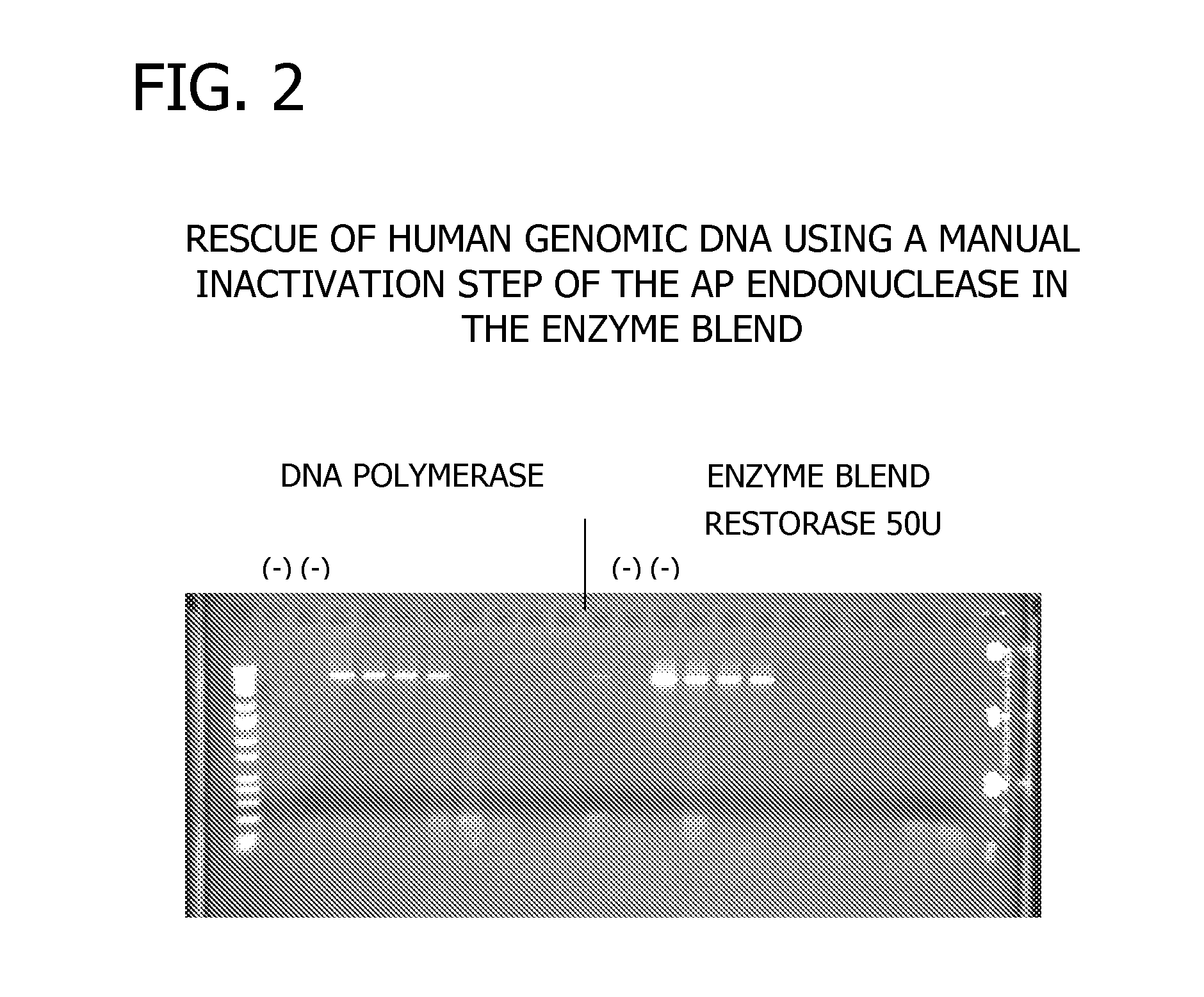
Compositions for the amplification of damaged nucleic acids are disclosed. The compositions generally comprise a mesophilc polymerase, a thermostable polymerase, and an AP endonuclease. Methods of using the same for the amplification of damaged DNA are also disclosed.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Methods for single-stranded nucleic acid library preparation
ActiveUS20180119216A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationLibrary preparationDiagnostic information
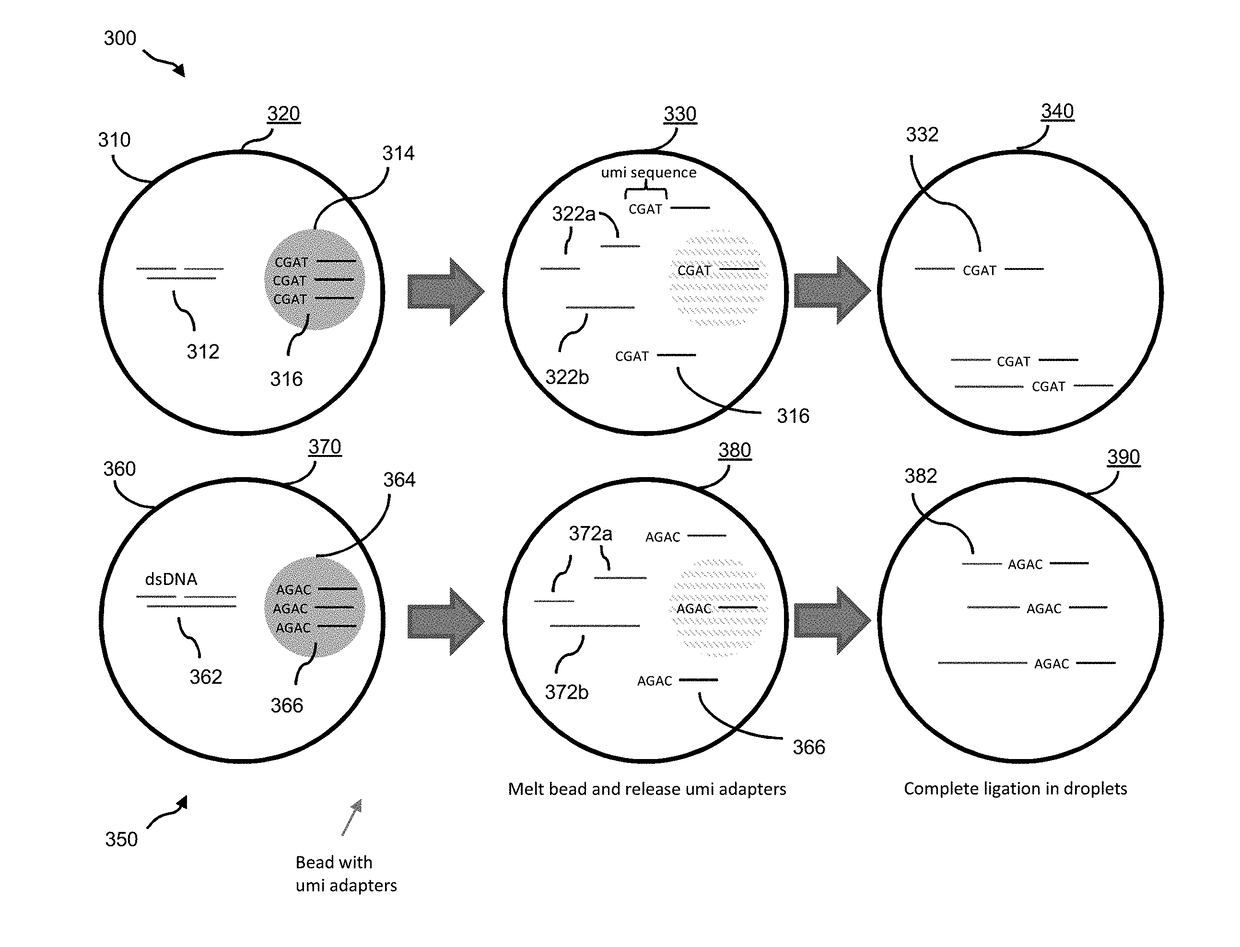
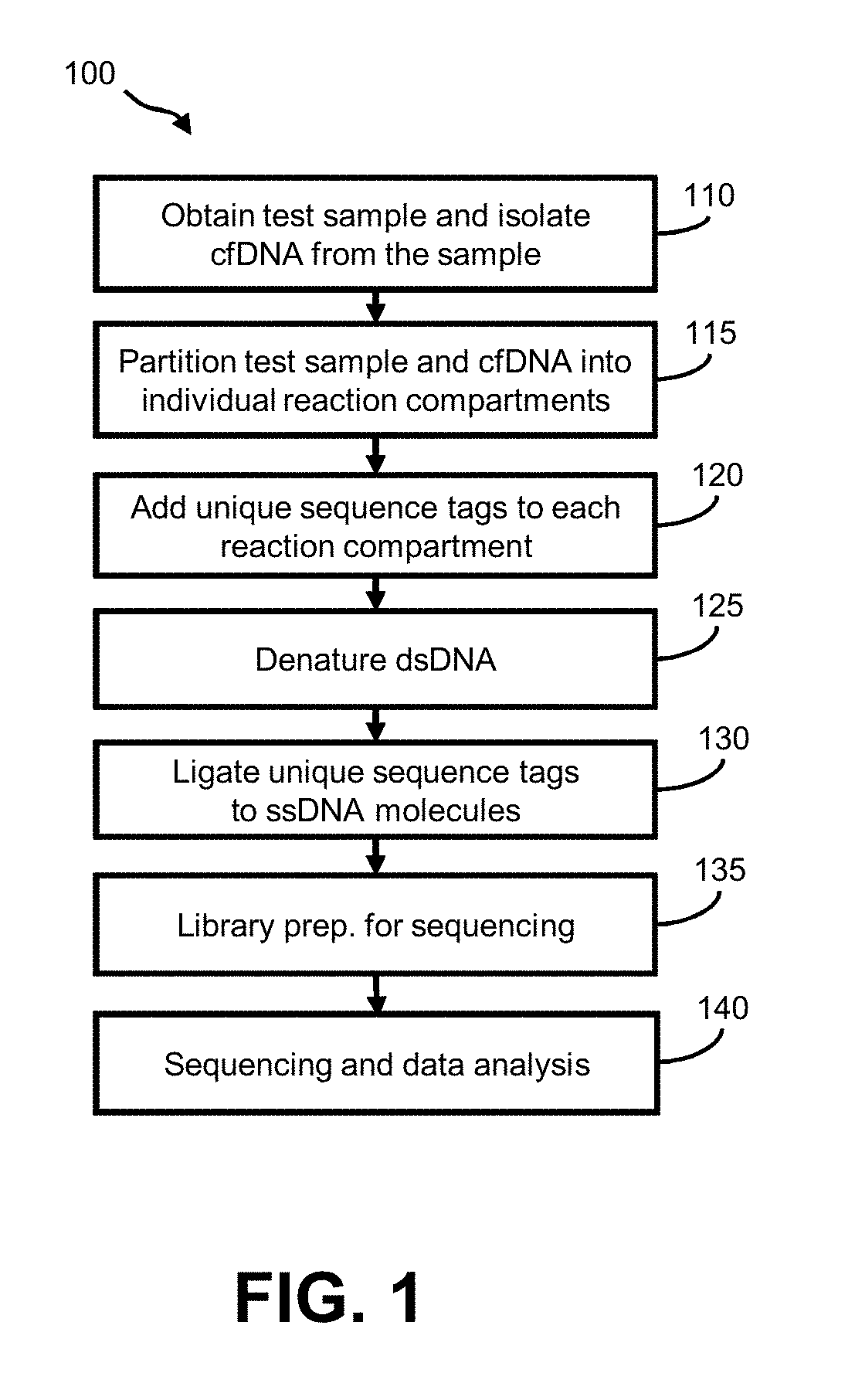
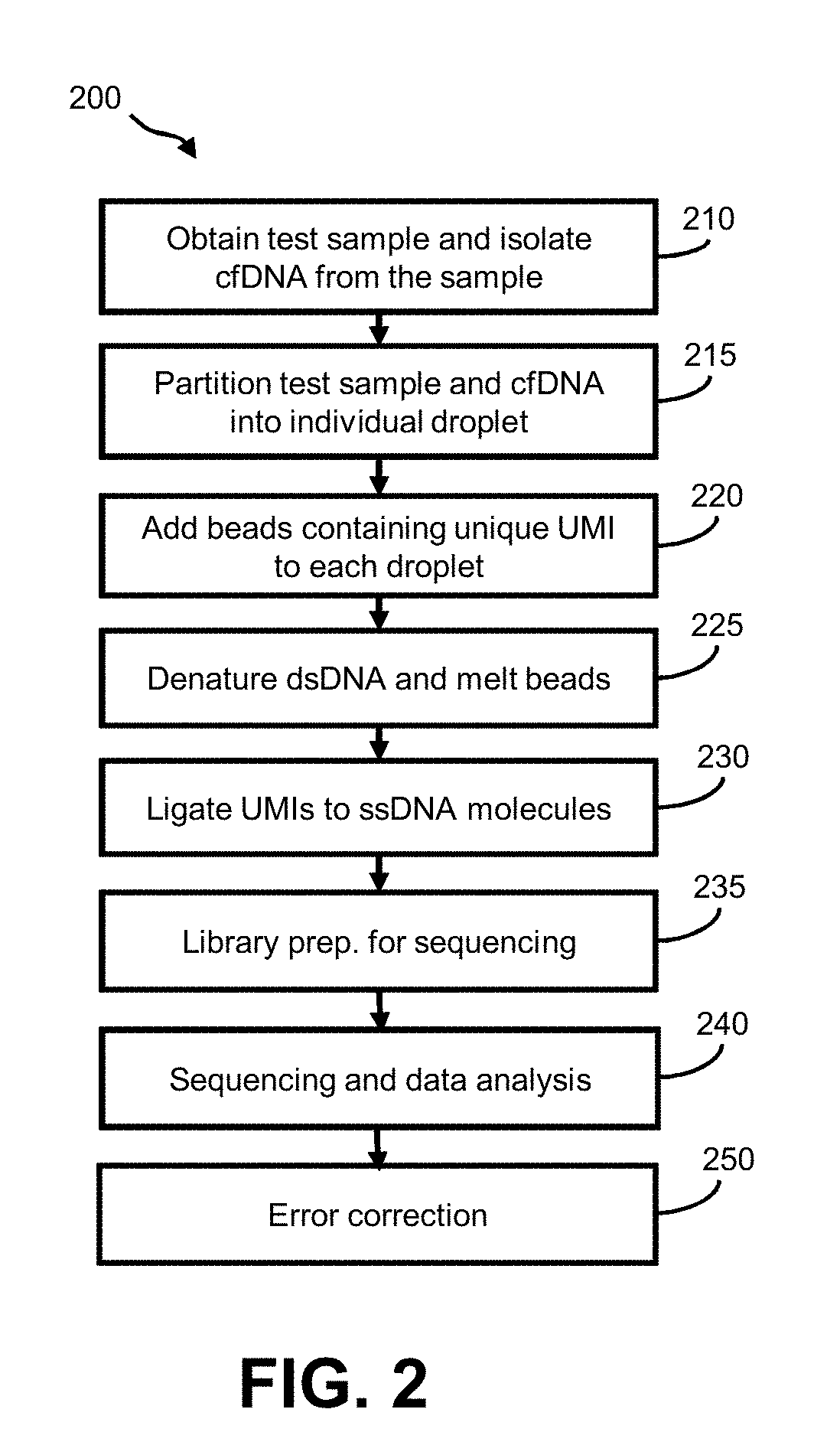
Aspects of the invention relate to methods and compositions for preparing and analyzing a single-stranded sequencing library from a double-stranded DNA (e.g., double-stranded cfDNA) sample. In some embodiments, the sample includes double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) molecules, and damaged dsDNA (e.g., nicked dsDNA) molecules. In some embodiments, the sample includes single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) molecules. The subject methods facilitate the collection of information, including strand-pairing and connectivity information, from dsDNA, ssDNA and damaged DNA (e.g., nicked DNA) molecules in a sample, thereby providing enhanced diagnostic information as compared to sequencing libraries that are prepared using conventional methods.
Owner:GRAIL LLC
Method for analyzing quantum dot-enhanced high-sensitivity DNA adduct
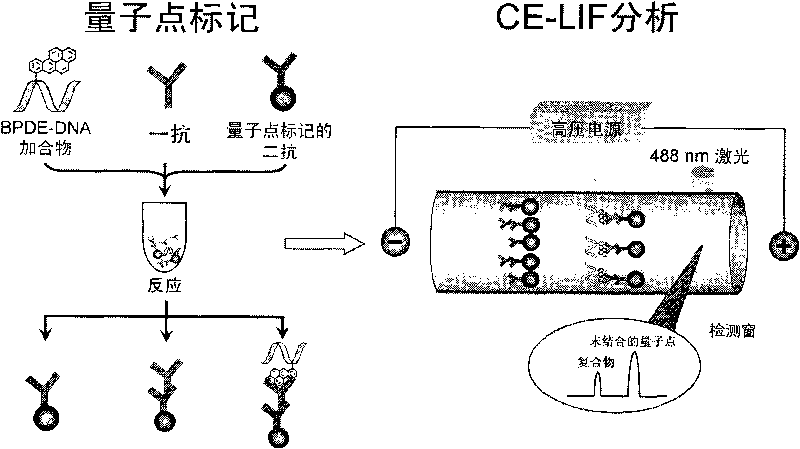
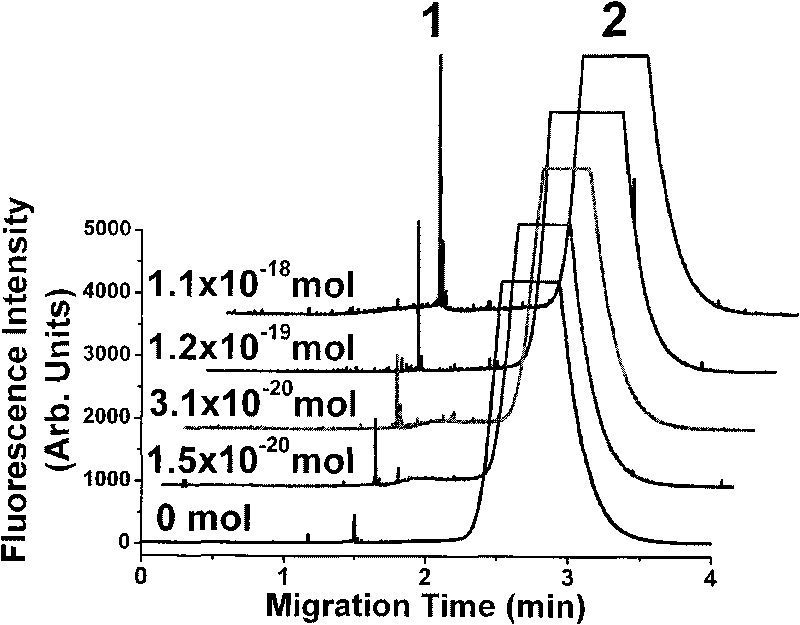
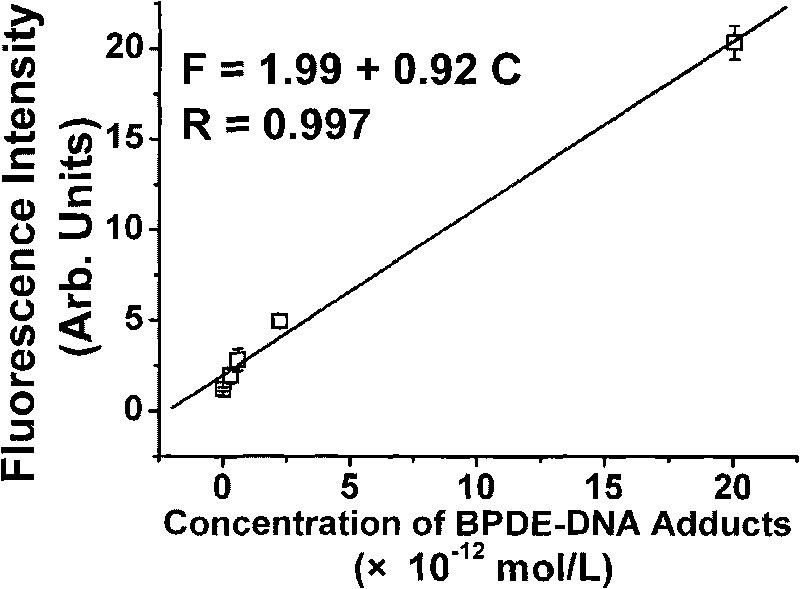
The invention relates to a method for analyzing quantum dot-enhanced high-sensitivity DNA adduct, comprising the following steps: using an antibody marked by a quantum dot as a fluorescence probe, combining with the immuno-capillary electrophoresis (CE)-laser induced fluorescence (LIF) detection technology and developing the method for analyzing high-sensitivity DNA adduct. The invention adopts the immuno-capillary electrophoresis (CE)-laser induced fluorescence (LIF) detection technology to separate and detect the compound formed by the antibody marked by the quantum dot and the DNA adduct to determine the content of the DNA adduct in the sample, and has the advantages of high detection sensitivity, little DNA usage amount, rapid analysis speed, strong specificity and the like. Therefore, the invention can be used for quantitative detection on trace DNA adduct generated by organism in an interlocking manner under the condition of environmental pollutant exposion, can be used for studying formation and restoration mechanism of the damaged DNA under the condition of lower-level exposion, and evaluates potential ecological risk for environmental carcinogens and heath hazard for human beings.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for removing antibiotic resistance genes through ionizing irradiation
The invention discloses a method for removing antibiotic resistance genes through ionizing irradiation. Antibiotic mushroom dregs are treated with an ionizing irradiation technology (including gamma-rays and high-power electron beams generated by an electronic accelerator) to damage DNA of microbial cells, so that the resistance genes are effectively removed, and residual antibiotics can be decomposed simultaneously. The method is efficient and wide in application range; radiation can be performed at the normal temperature, no chemical reagents or only a few chemical reagents are required to be added, and no secondary pollution can be caused. The method can be applied to removal of the resistance genes in the antibiotic mushroom dregs, can be applied to removal of the resistance genes in water, soil and sludge and has wide application prospects in the environmental field.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for evaluating protective action of Chinese herbal medicine to DNA oxidation damnify
ActiveCN101382545AProtection from oxidative damageMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisHerbal preparationsMicrosphere
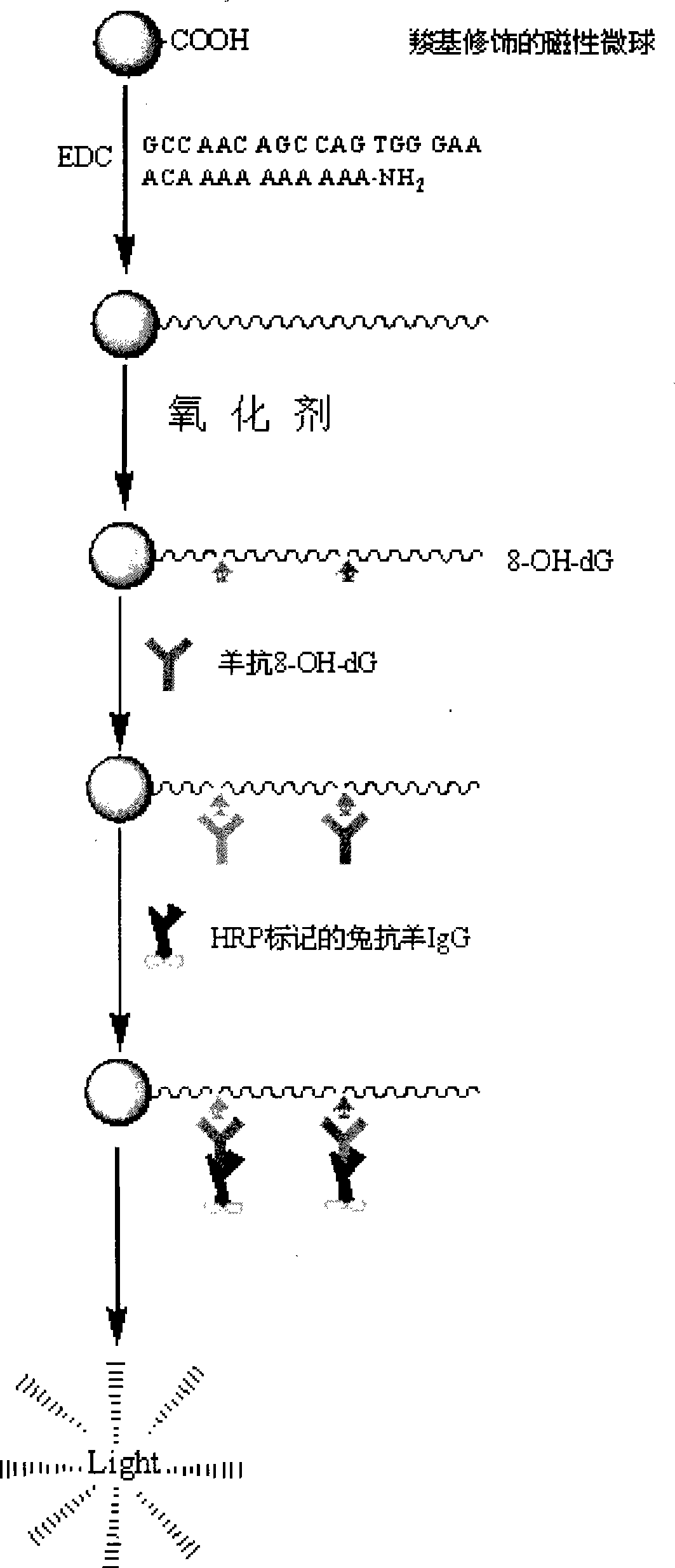
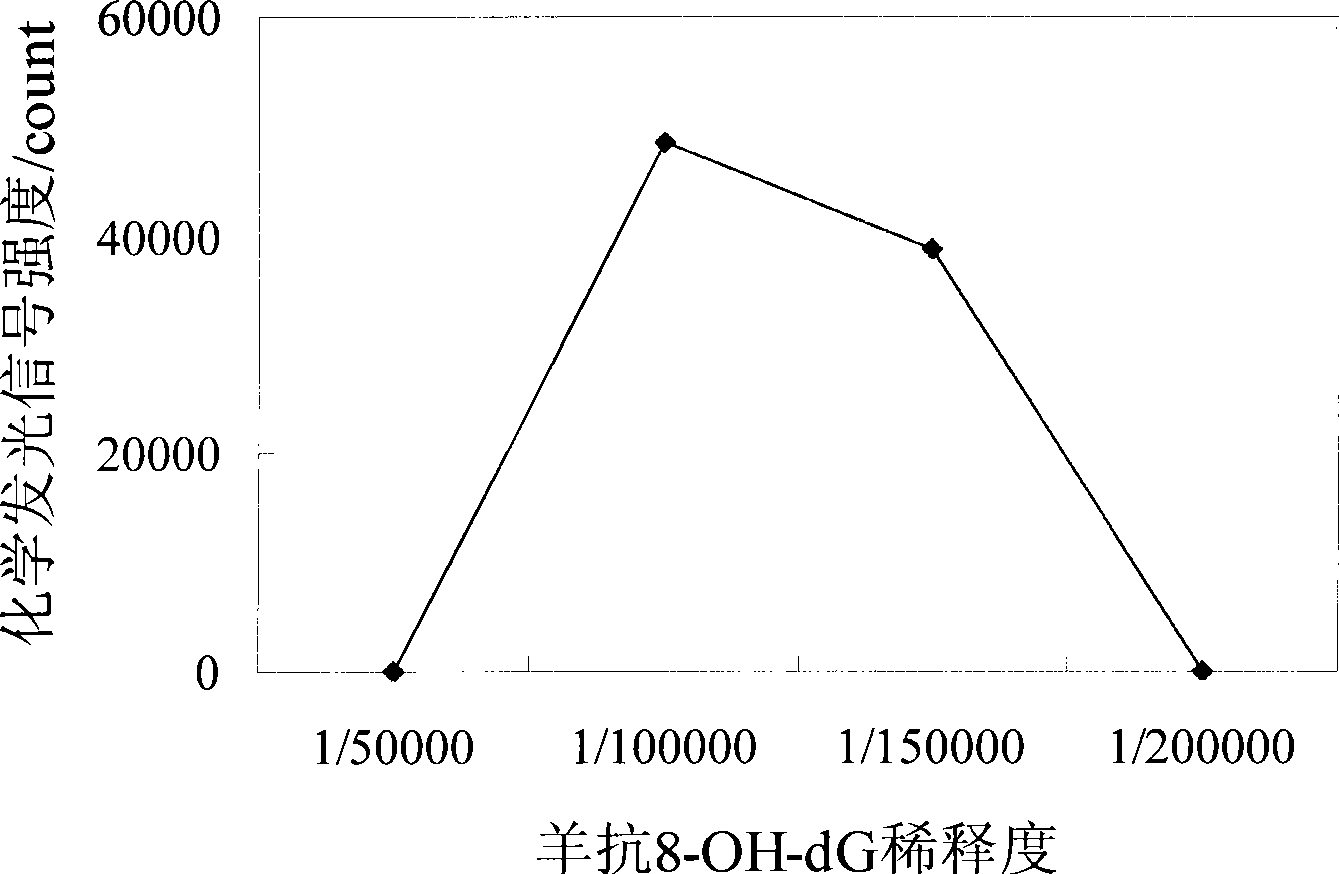
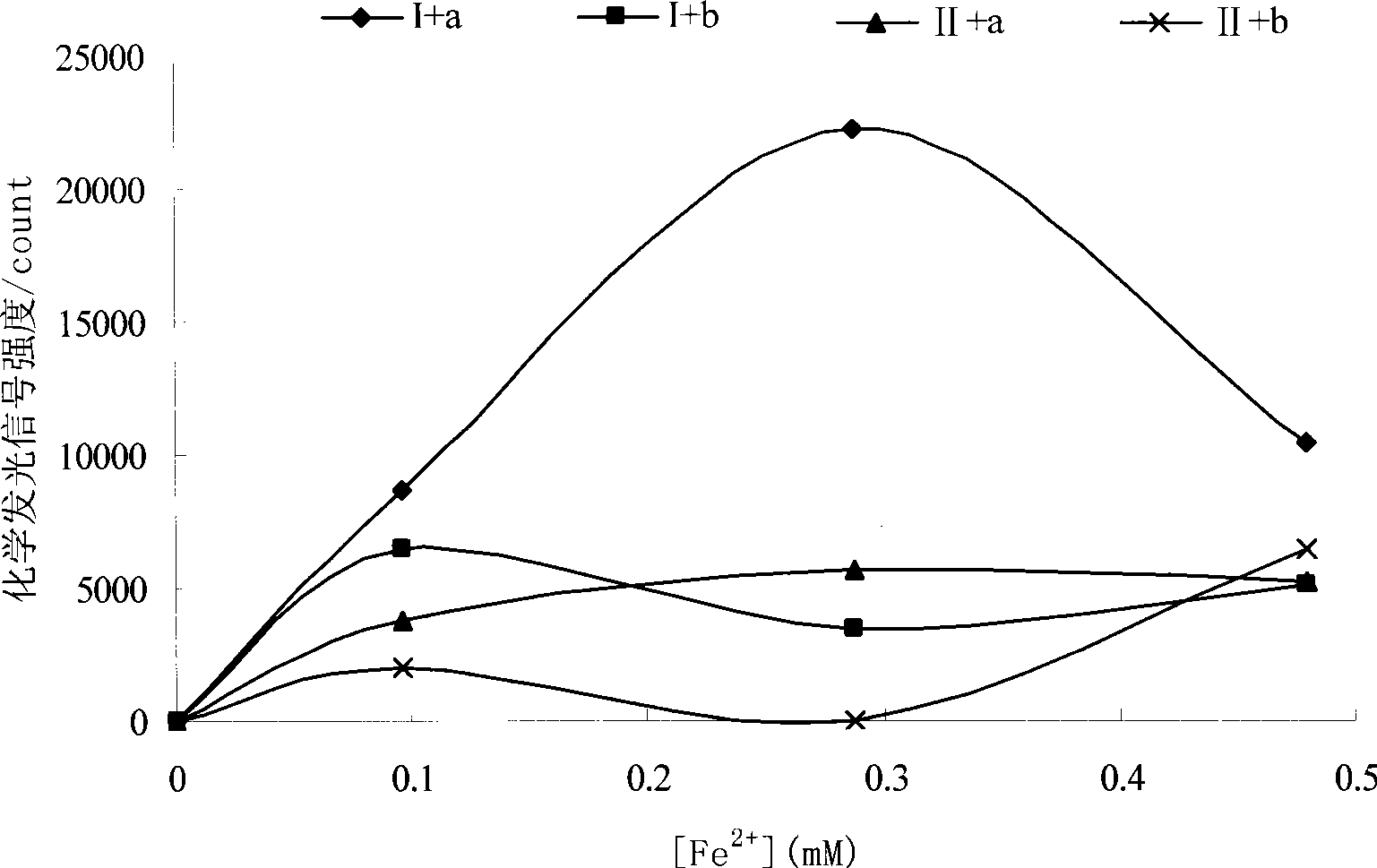
The invention relates to an assessment method on the protective action of Chinese medicinal herb to the DNA oxidative damage, which comprises the steps that: DNA is fixed on the surface of a magnetic bead microsphere by covalent bonds; Chinese medicinal herb solution is added; the fixed DNA infects toxicity in vitro; magnetic bead separation is carried out to oxidize the components but reserve the oxidation-damaged DNA; 8-OH-dG antibodies are added to carry out immunoreaction with the 8-OH-dG generated by oxidative damage; enzyme-labeled second antibodies are added to react with the obtained product; and a luminous substrate is added, the high-sensitivity chemiluminescence method is adopted to detect the generated 8-OH-dG by DNA damage; the detection result is analyzed according to the detection result of the control group so as to judge whether the Chinese medicinal herb has the function of inhibiting the DNA oxidative damage to generate 8-OH-dG. The invention can detect and assess the protective action of Chinese medicinal herb to the DNA oxidative damage, and can be used for screening and developing high-efficiency and safe Chinese herbal preparations to protect the organism DNA from suffering oxidative damage.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ZHEJIANG IND
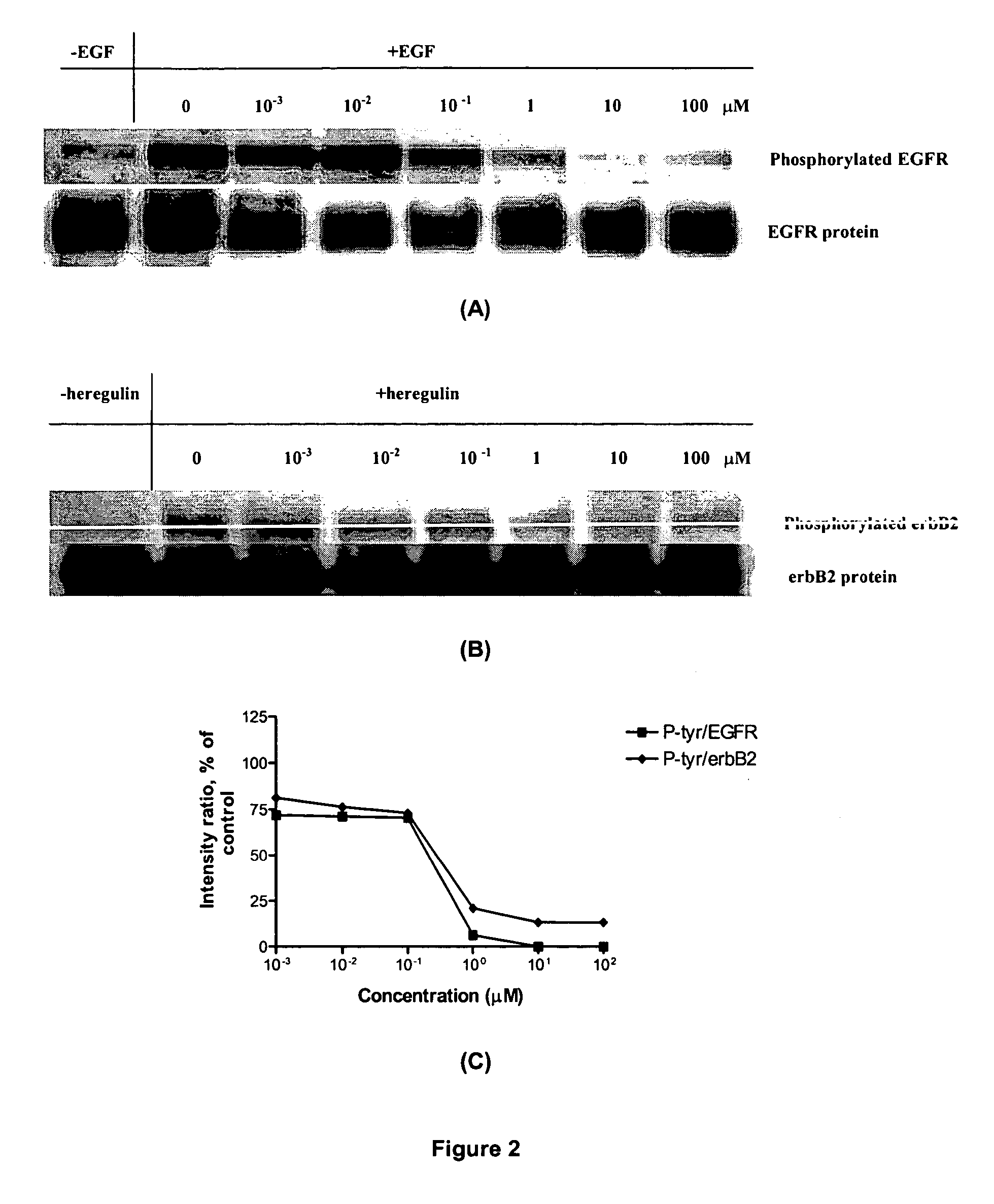
Novel combi-molecules having EGFR and DNA targeting properties
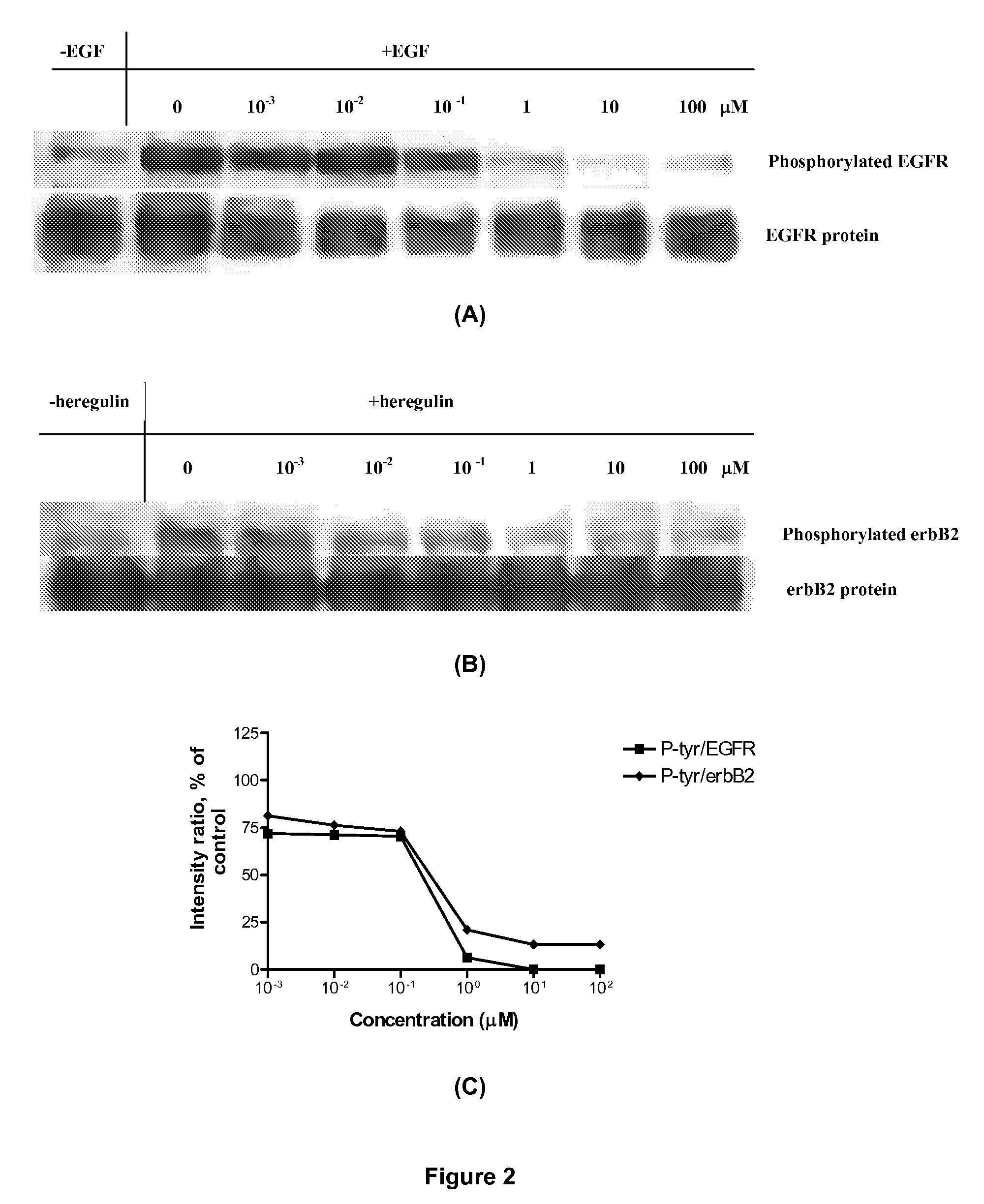
InactiveUS20060003970A1Inhibit phosphorylationInhibits downstream signallingOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAbnormal tissue growthDna targeting
A series of new chemical agents that demonstrate anti-tumor activity are described. The new chemical agents combine two major mechanisms of anti-tumor action. In an embodiment, the agents are capable of both inhibiting EGFR and damaging DNA while also, upon degradation, degrading to an inhibitor of EGFR and to an agent capable of damaging DNA. Moreover, a novel series of molecules capable of releasing two moles of EGFR inhibitor and a potent bi-functional alkylating agent are also described.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Methods for co-encapsulation of combination drugs and co-encapsulated combination drug product
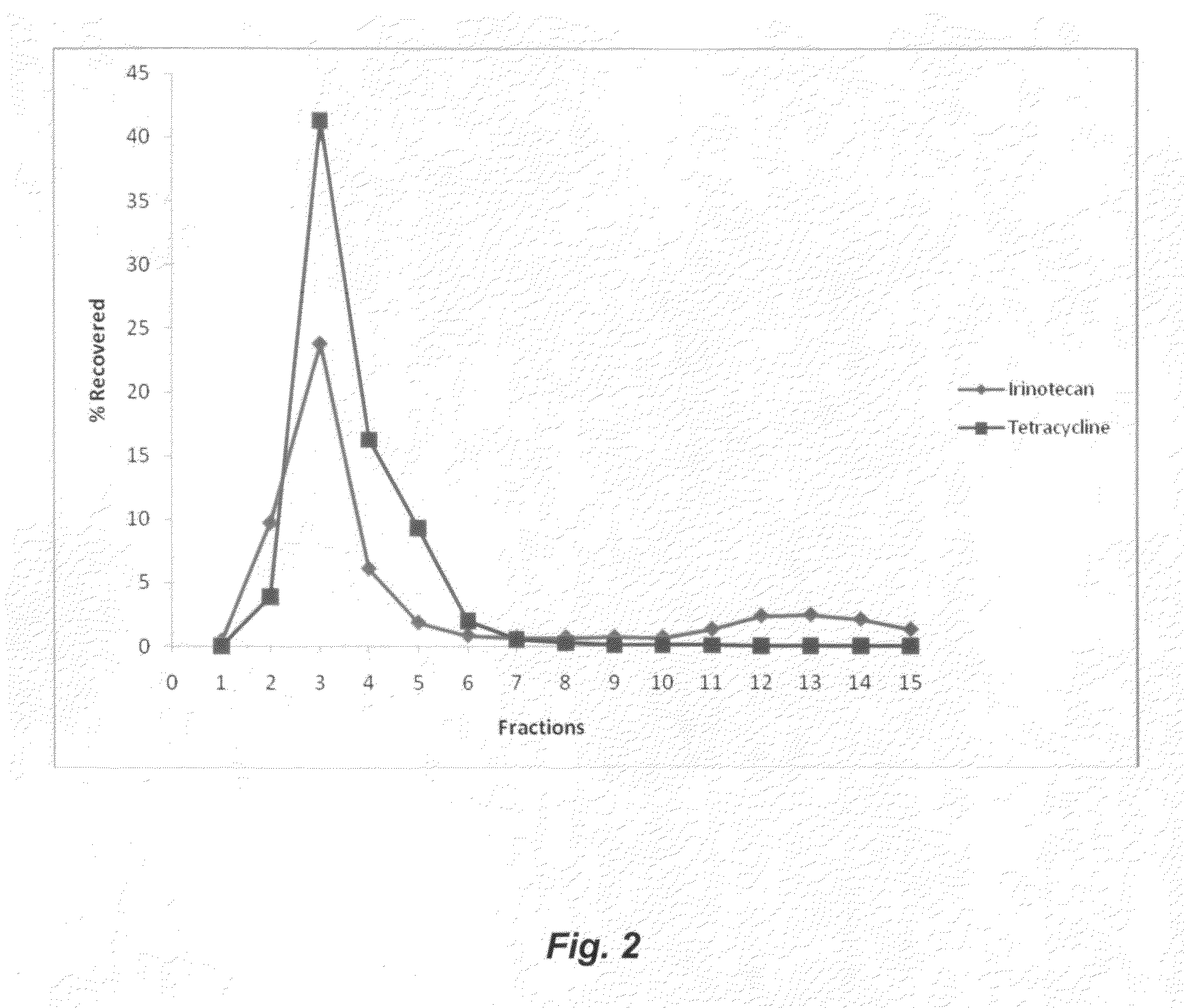
ActiveUS20100247620A1Reduce processing stepsShorten the timeOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAnticarcinogenPhospholipid
This invention is for an improved process to co-encapsulate hydrophobic drugs and hydrophilic drugs in phospholipid liposomes. Non-toxic supercritical or near-critical fluids with / without polar cosolvents are utilized to solubilize phospholipid materials and hydrophobic drugs, and form uniform liposomes to encapsulate hydrophobic drugs and hydrophilic drugs.DNA topoisomerase I (Top1) is the target of camptothecin, and novel Top1 inhibitors are in development as anticancer agents. Top1 inhibitors damage DNA by trapping covalent complexes between the Top1 catalytic tyrosine and the 3′-end of the broken DNA. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1) can repair Top1-DNA covalent complexes by hydrolyzing the tyrosyl-DNA bond. Inhibiting Tdp1 has the potential to enhance the anticancer activity of Top1 inhibitors and to act as antiproliferative agents. It has been recently reported that neomycin inhibits Tdp1 more effectively than the related aminoglycosides paromomycin and lividomycin A. Inhibition of Tdp1 by neomycin is observed both with single- and double-stranded substrates but is slightly stronger with duplex DNA, which is different from aclarubicin, which only inhibits Tdp1 with the double-stranded substrate. Inhibition by neomycin can be overcome with excess Tdp1 and is greatest at low pH. Aminoglycoside antibiotics and the ribosome inhibitors thiostrepton, clindamycin-2-phosphate, and puromycin are the first reported pharmacological Tdp1 inhibitors. The development of Tdp1 inhibitors as anticancer agents can be envisioned as combinations of Tdp1 and Top1 inhibitors. Moreover, Tdp1 inhibitors might also be effective by themselves as anticancer agents. In addition, Tdp1 inhibitors might be valuable as anti-infectious agents.This invention can produce a co-encapsulated combination drug product consisting of a topoisomerase 1 inhibitor such as camptothecins including neat camptothecin and its derivatives irinotecan, topotecan and other derivatives, and a tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1) such as aminoglycoside antibiotics including neomycin and tetracycline, and the ribosome inhibitors thiostrepton, clindamycin-2-phosphate, and puromycin.
Owner:APHIOS
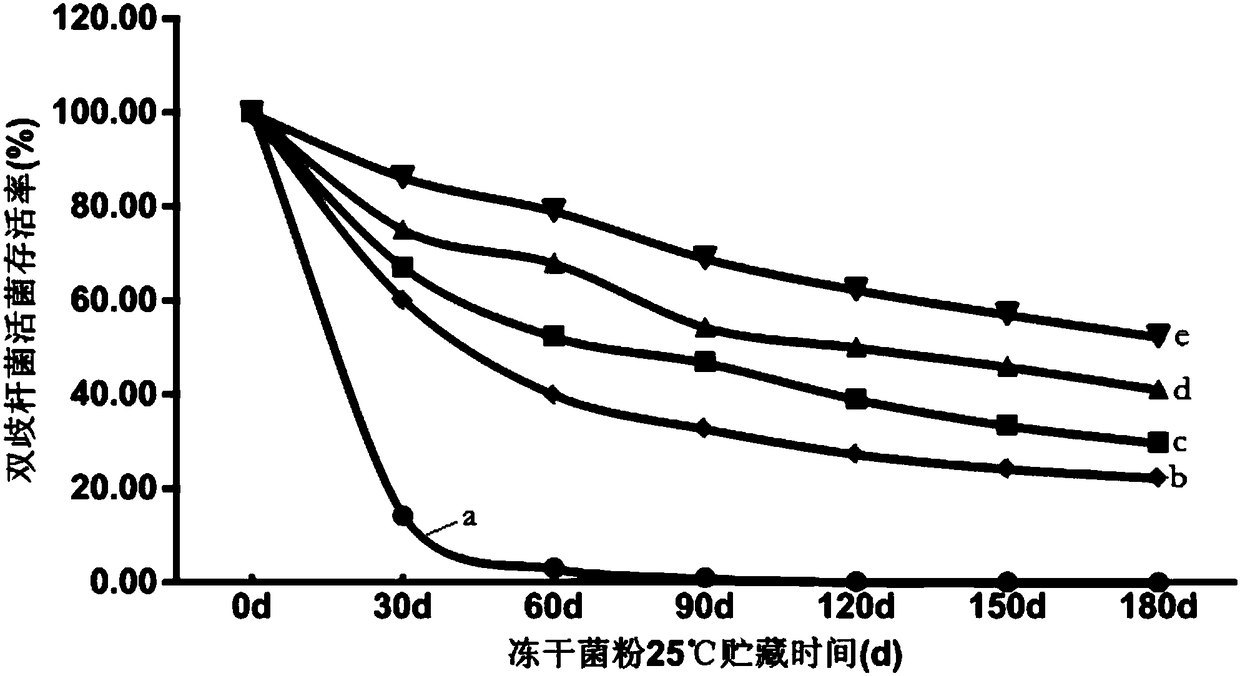
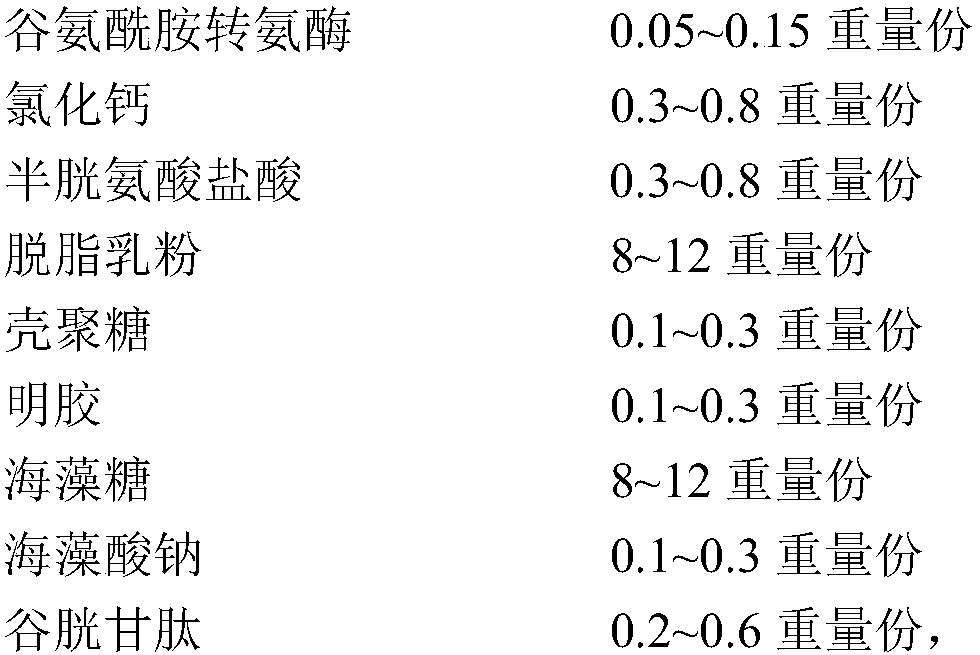
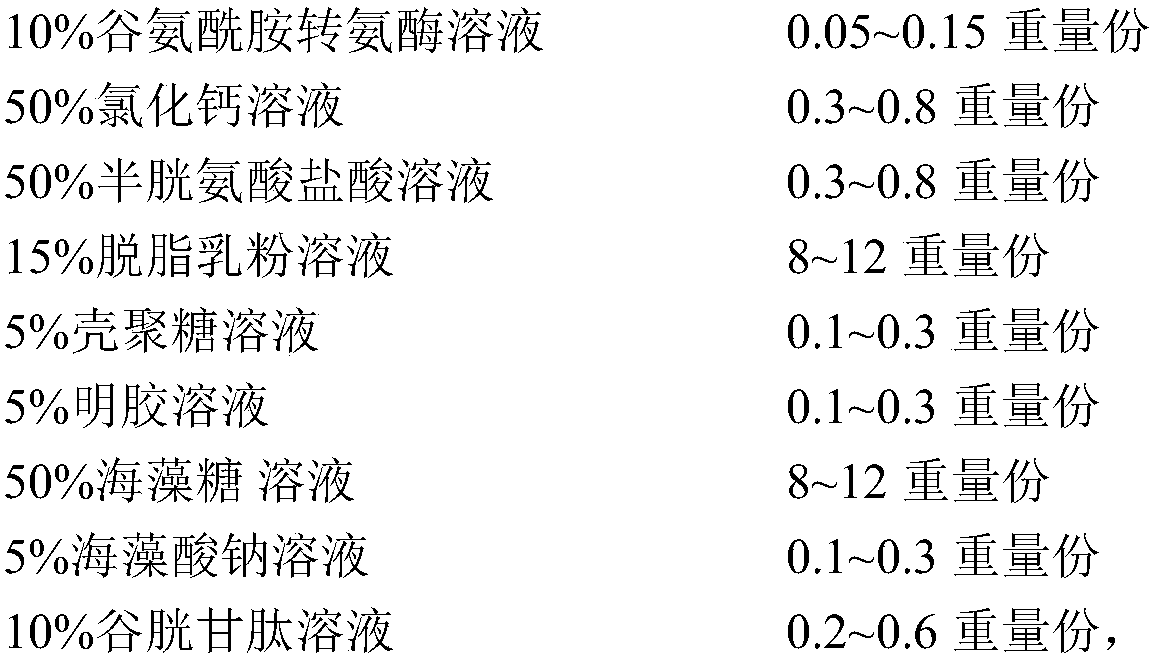
A Bifidobacterium lactis strain, Bifidobacterium lactis freeze-dried powder and a preparing method thereof
ActiveCN108220193ANot easy to inactivateAvoid interactionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBifidobacteriumAntioxidant
The invention provides a Bifidobacterium lactis strain (that is Bifidobacterium lactis BL9) with an accession number of CGMCC No.14536. The invention also provides a preparing method of Bifidobacterium lactis freeze-dried powder. The method includes performing embedding and freeze-drying treatment in an anaerobic environment, and before freeze-drying treatment, a plurality of antioxidants are adopted to perform embedding treatment on the Bifidobacterium lactis in steps, thus effectively preventing interactions between oxygen and a cytomembrane system of the Bifidobacterium lactis, preventing behaviors damaging DNA synthesis, and clearing free radicals generated before freeze drying of the strain, and therefore oxidation damage in a drying process is prevented, and the Bifidobacterium lactis is not liable to be deactivated under room-temperature storage conditions. The invention also provides Bifidobacterium lactis freeze-dried powder prepared by the method.
Owner:金华银河生物科技有限公司
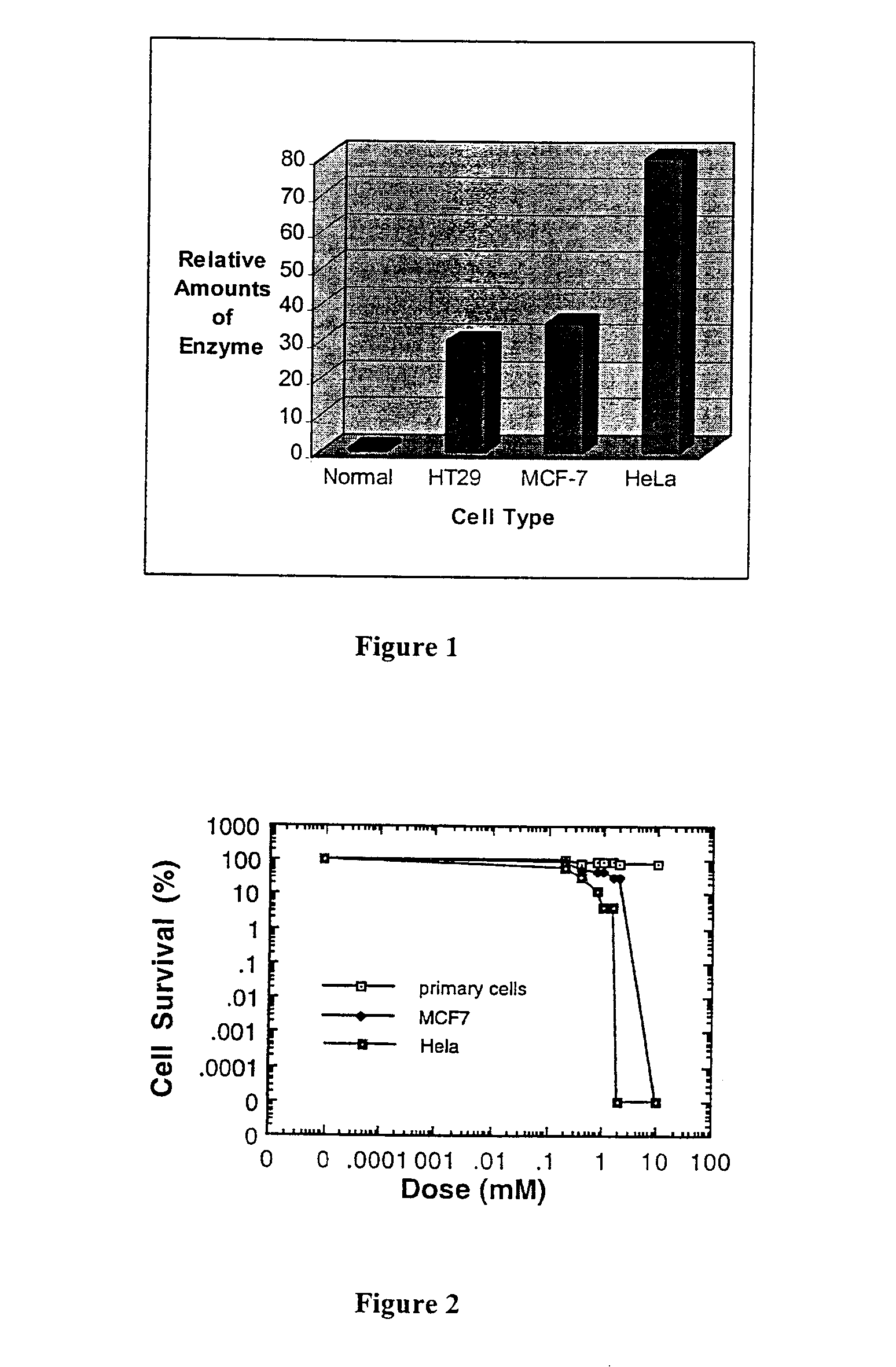
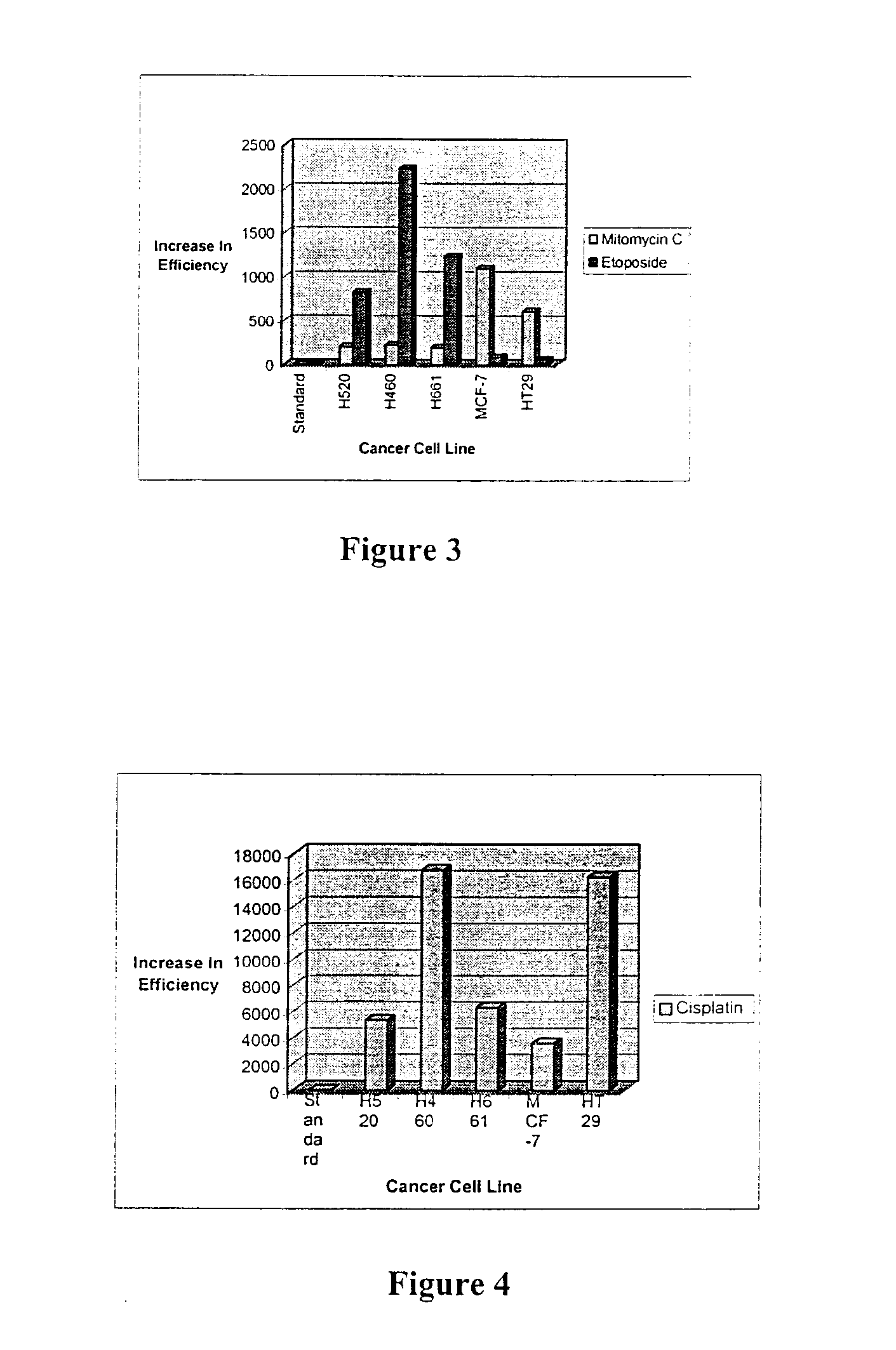
Inhibitors of endo-exonuclease activity for treating cancer
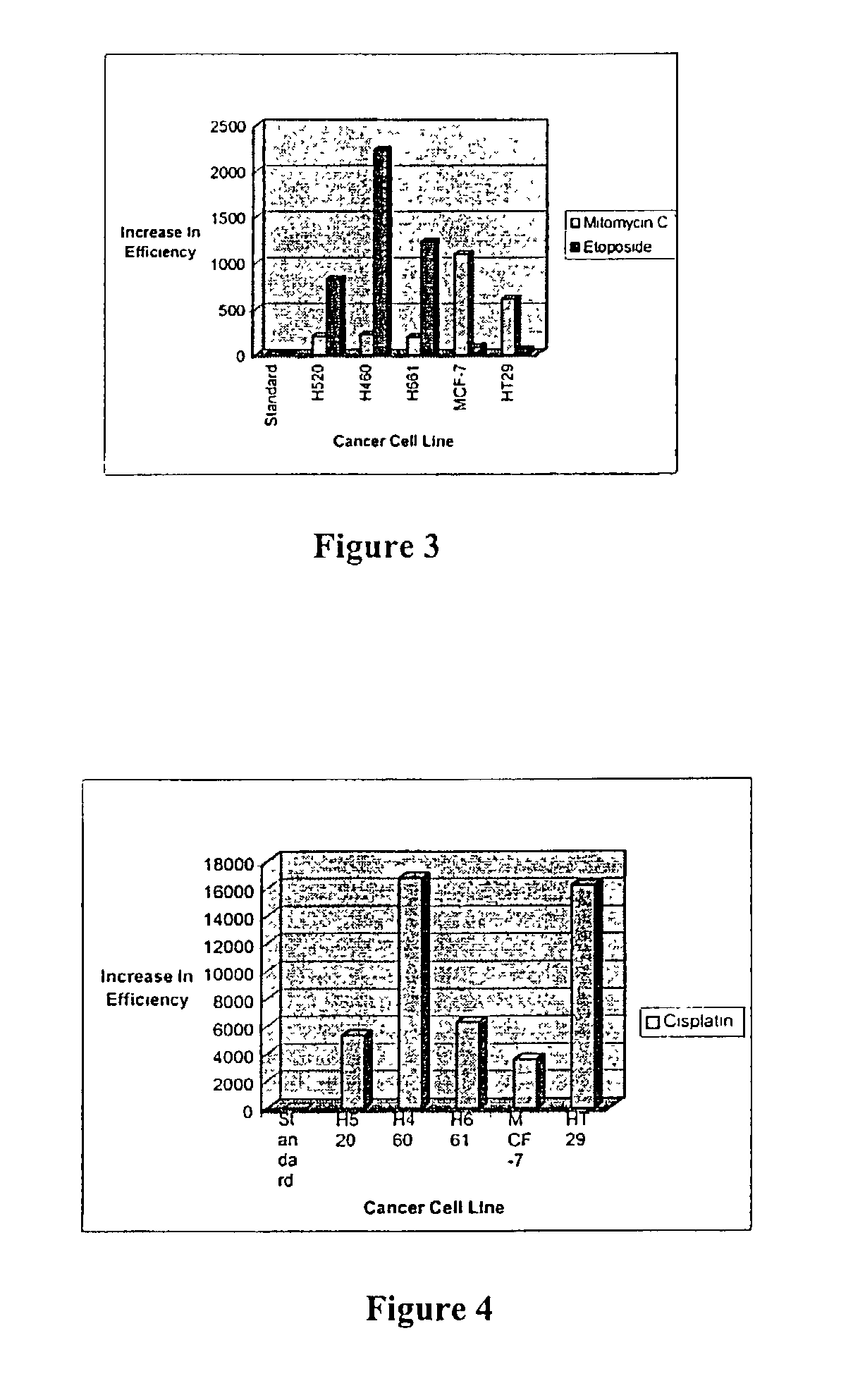
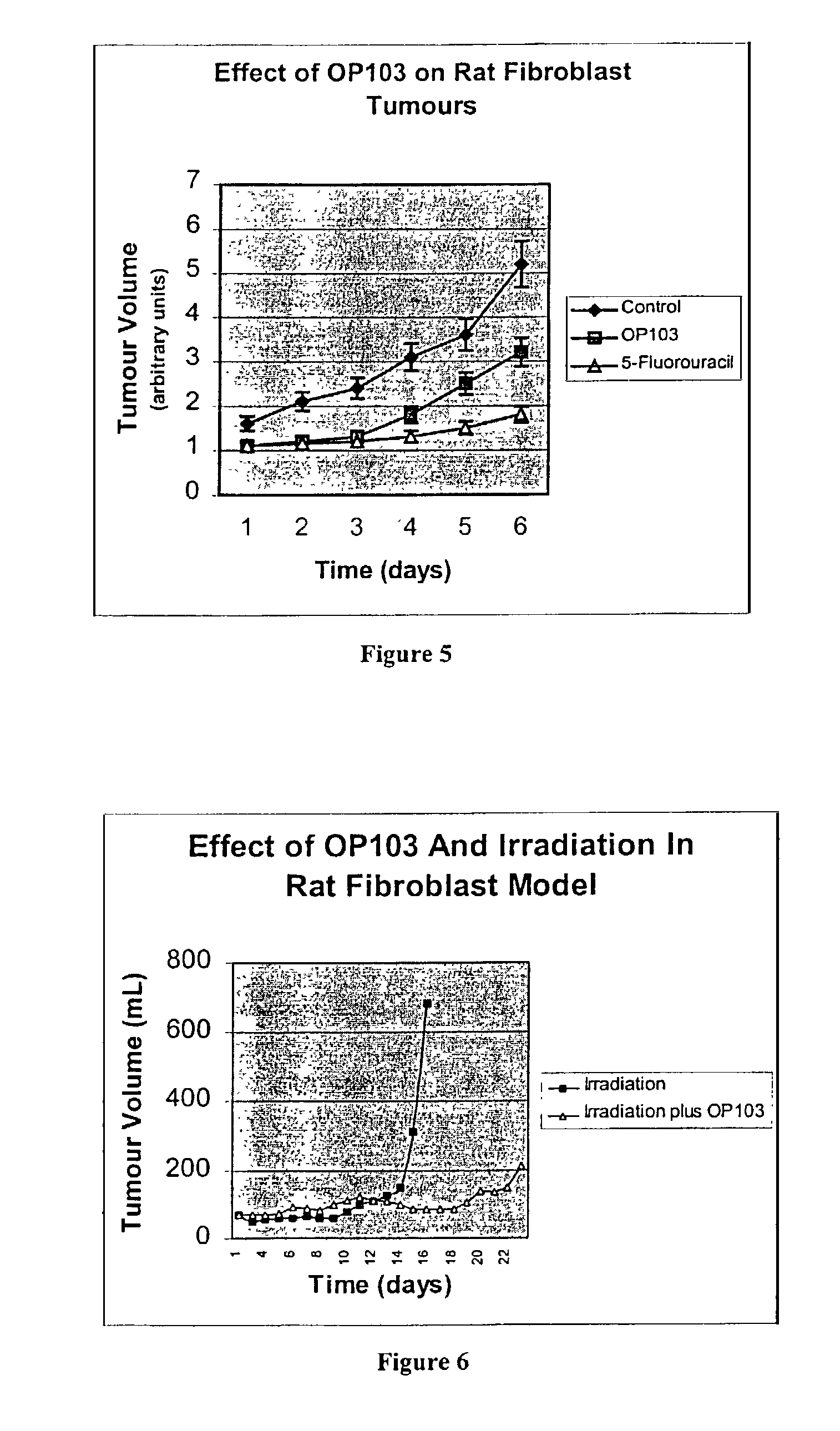
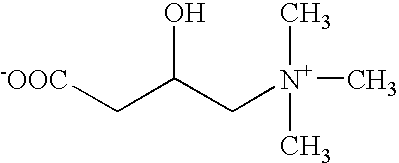
InactiveUS7115665B1Increase concentrationPrevent proliferationBiocideNitro compound active ingredientsDna breakageSerum ige
The present invention relates to the treatment of cancer with compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease. Endo-exonuclease has been shown to be necessary for the repair of damaged DNA. Compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease have been shown to be particularly effective for treating cancer when used in combination with drugs that induce DNA breaks such as cisplatin and mitomycin C. These compounds have a synergistic effect when used in combination for inhibiting tumour growth. The invention includes pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting tumour growth comprising a compound that inhibits endo-exonuclease activity. These pharmaceutical compositions preferably include compounds that induce DNA breaks. The invention includes methods of treating cancer with these pharmaceutical compositions and uses of these compositions to treat cancer. The preferred compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease have low toxicity. One such compound is pentamidine. The invention also includes a method for diagnosing cancer and monitoring its progression. This aspect of the invention involves isolating serum from a patient; measuring the concentration of endo-exonuclease in said serum and determining whether said concentration is above a predetermined mean.
Owner:ONCOZYME PHARMA
Composition and method for treating skin conditions
InactiveUS20060058387A1Reducing hair growthFiner and large irregularityBiocideCosmetic preparationsCelluliteDamage dna
Compositions and methods for treatment of skin conditions, such as age spots, liver spots, photodamaged skin, skin folds, diminished hair growth, non-infectious cellulite and “orange skin”, or for repairing damaged DNA in a skin cell, utilize a formulation including about 0.01-1 part by weight tretinoin, and about 1-45 parts by weight dimethylfsulfoxide. Compositions may include about 5-40 parts by weight urea, and about 45-90 parts by weight carrier.
Owner:AEBI ALBERT
Method and Kits for Repairing Nucleic Acid Sequences
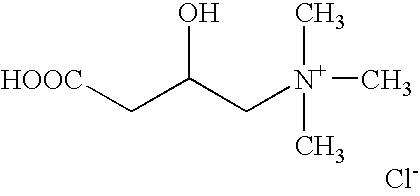
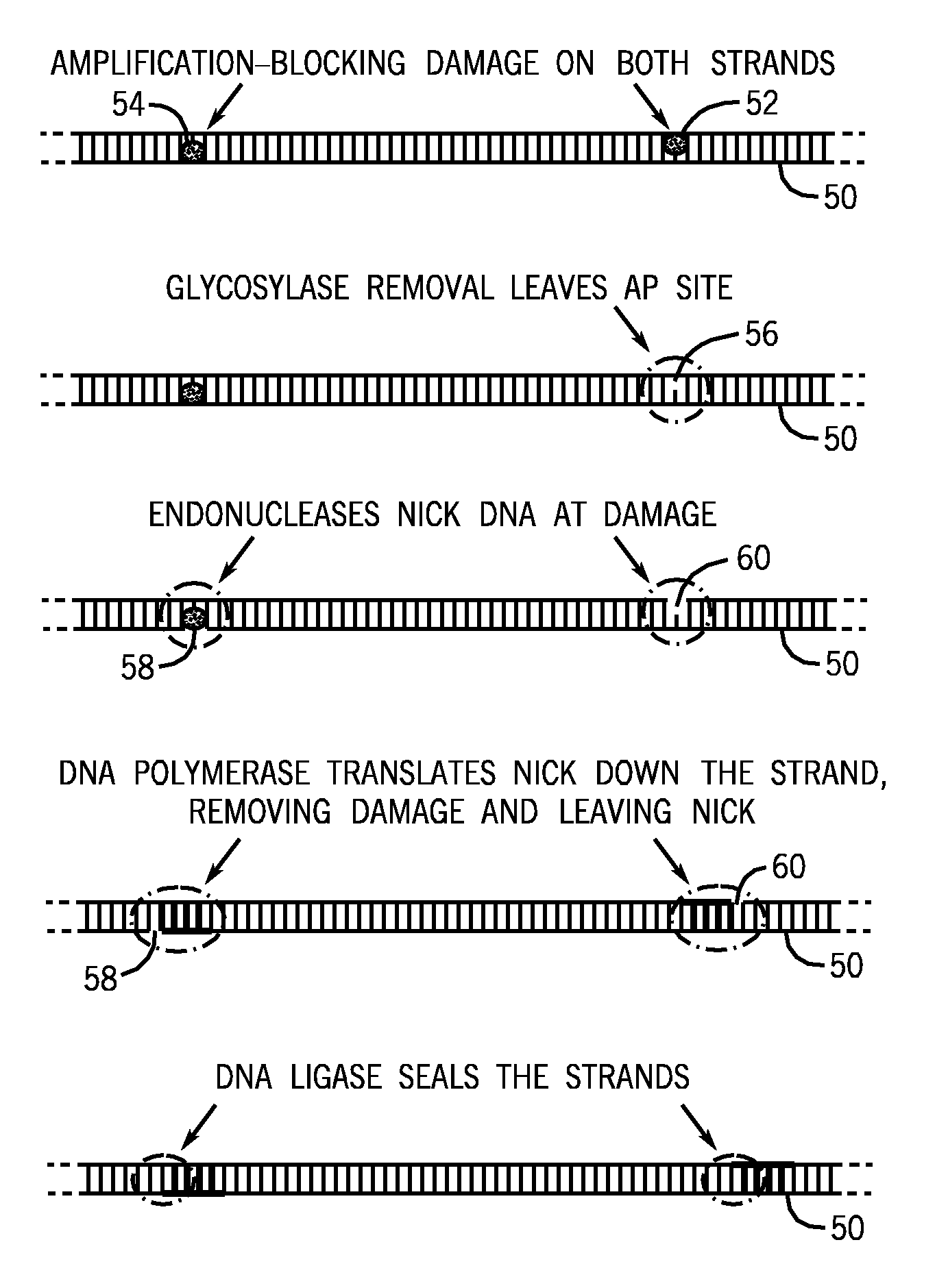
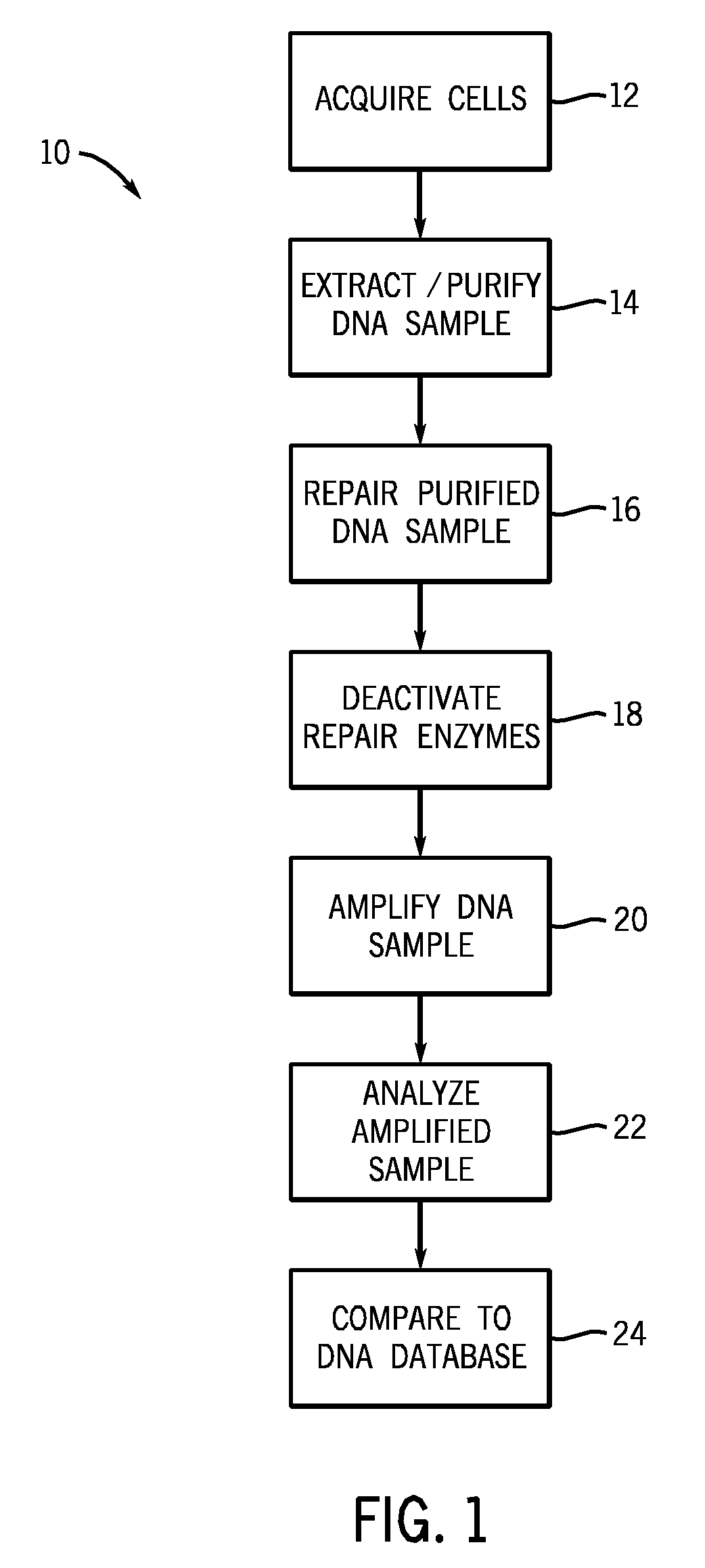
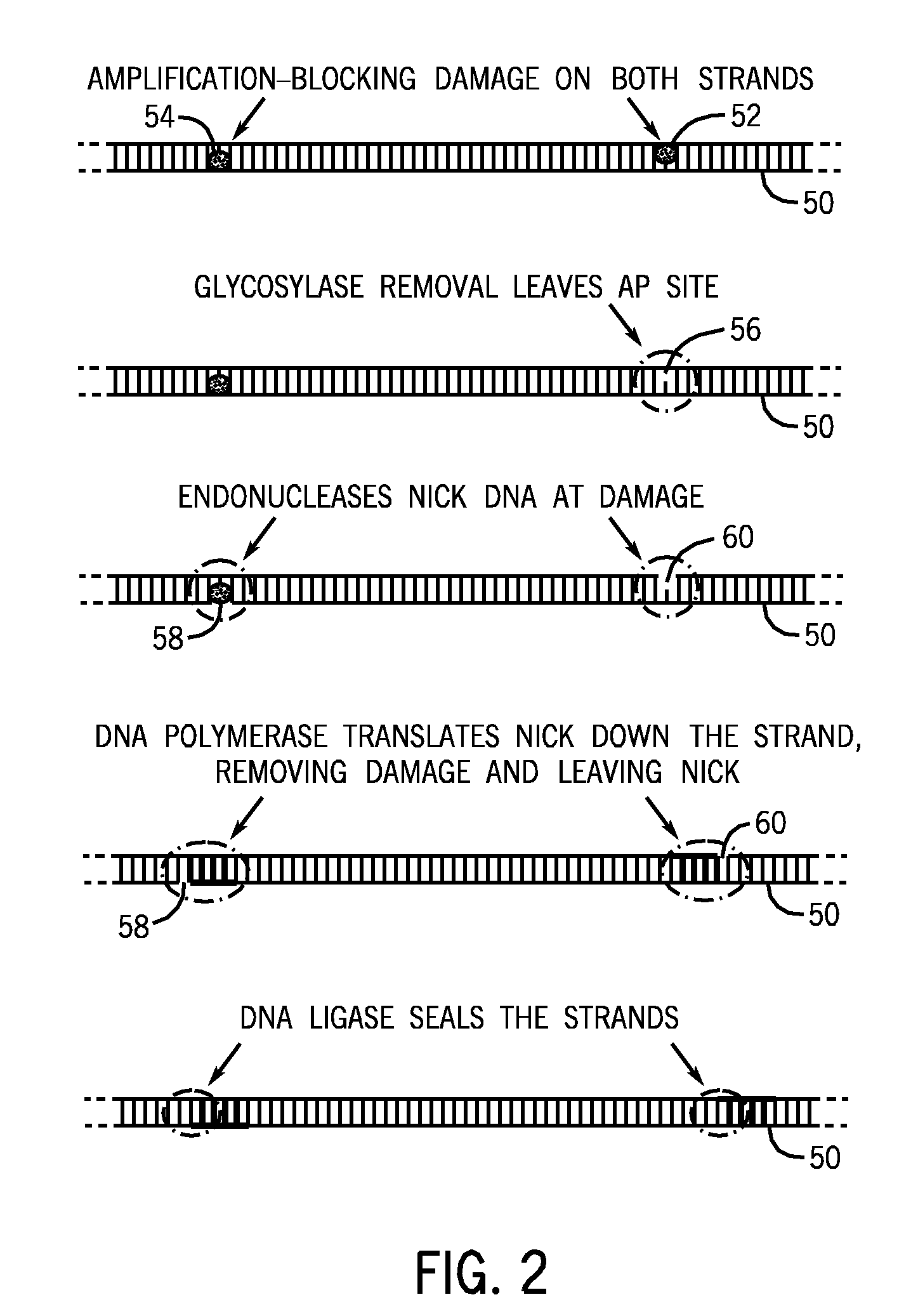
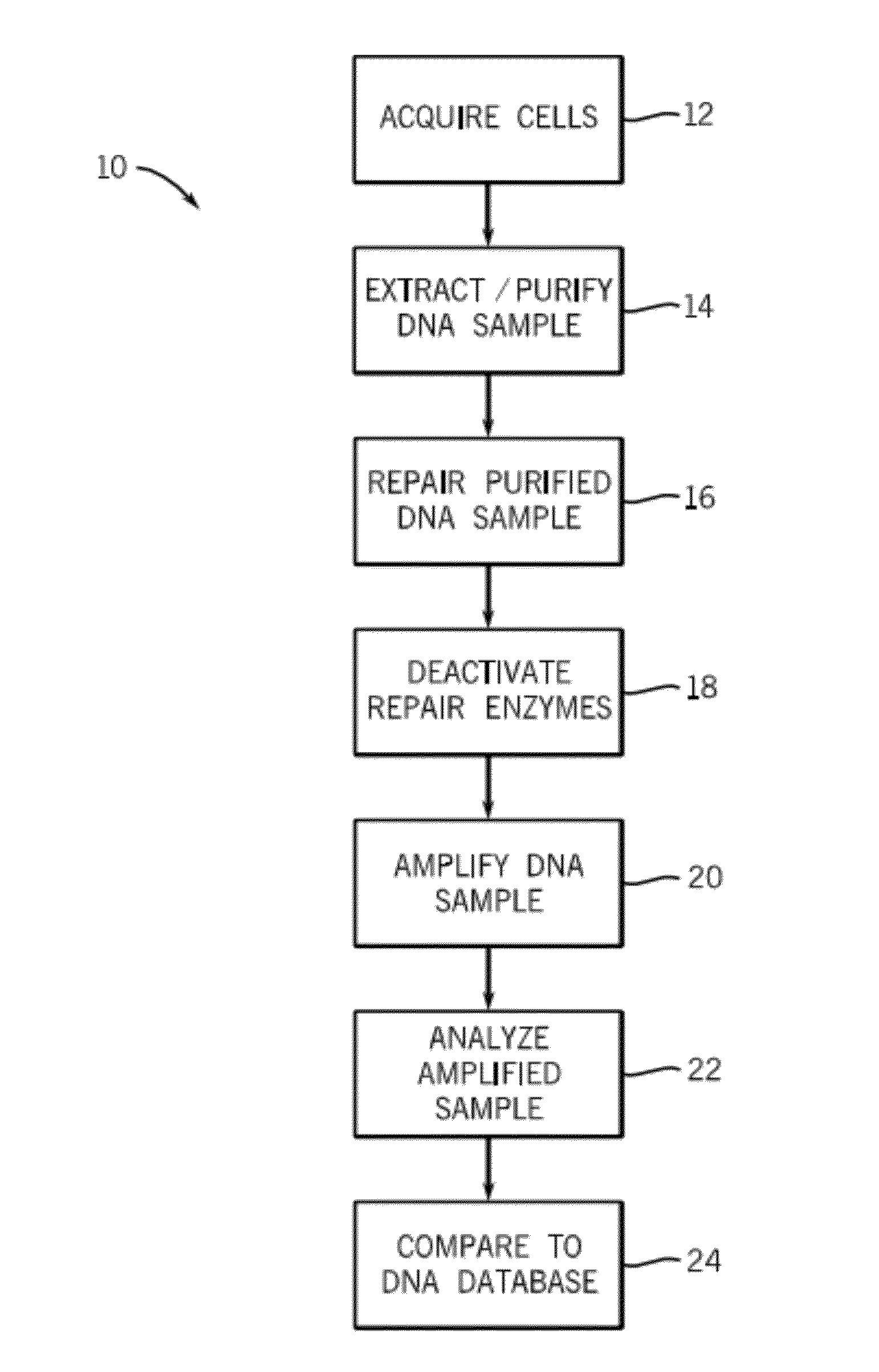
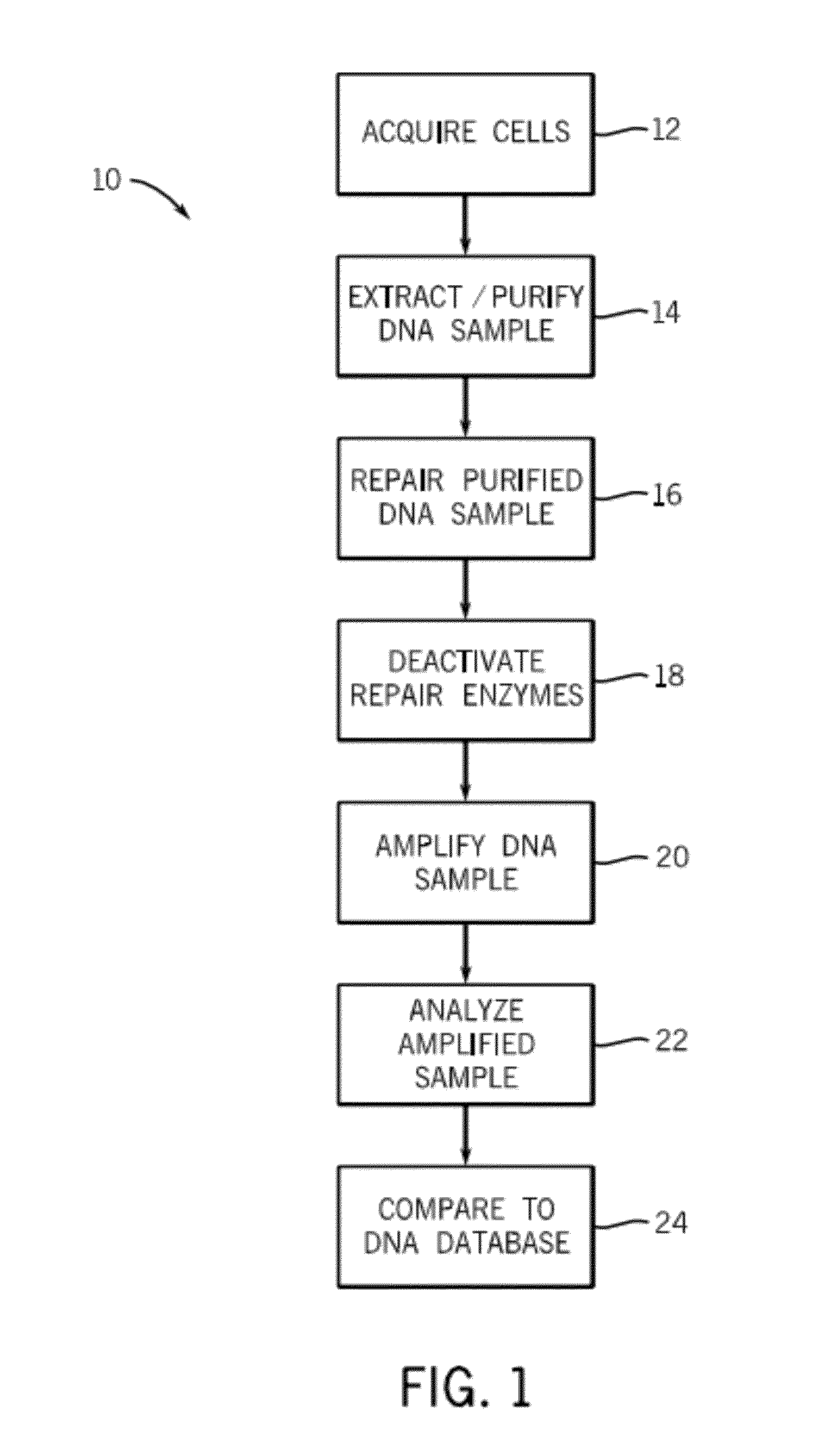
Methods and kits for DNA repair are provided. The methods and kits described herein repair multiple types of DNA damage. The kit may include a plurality of enzymes to repair a greater variety of lesions than any single enzyme is capable of repairing. Repair of damaged DNA may include releasing damaged bases from the DNA strand, nicking the DNA at the damaged sites, translating the nicks via 5′-3′ exonuclease activity, and sealing the nicks. The enzymes employed in the repair process may then be heat-inactivated, thereby obviating a purification process. The repaired DNA may then be analyzed using a variety of DNA analysis methods.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
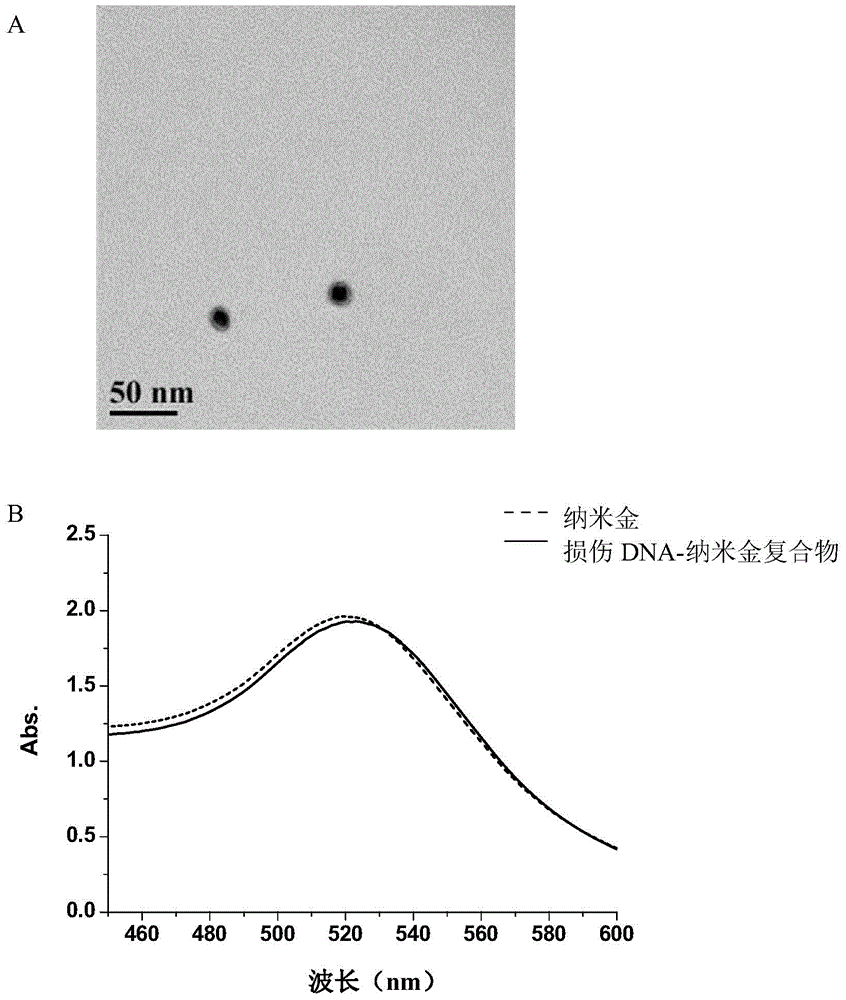
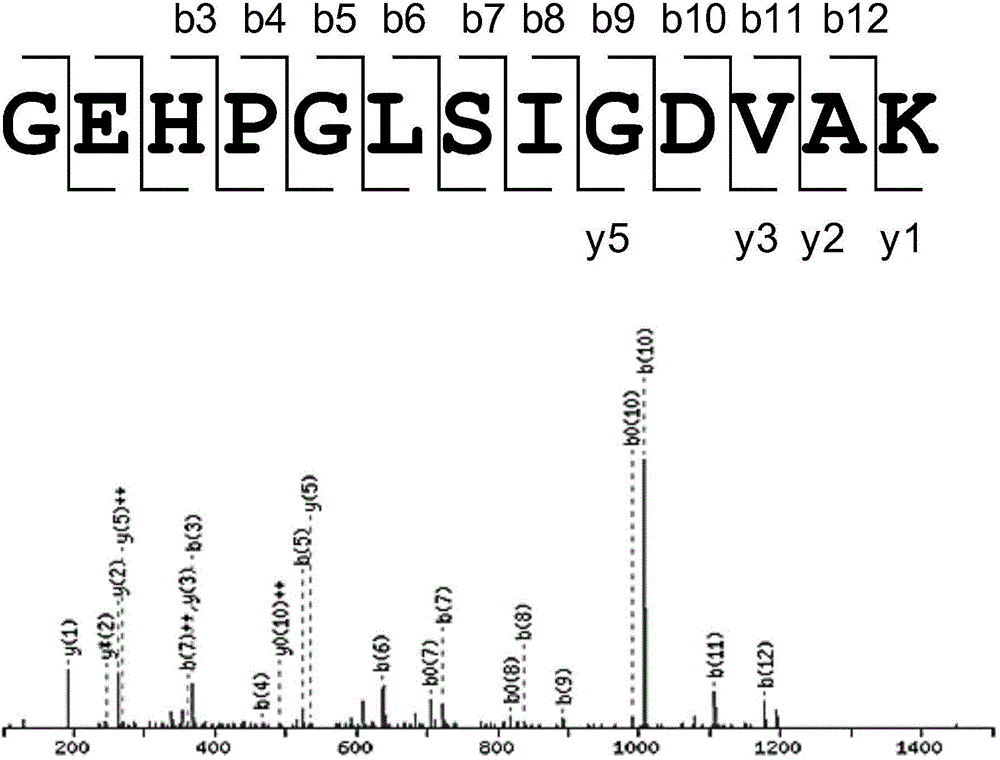
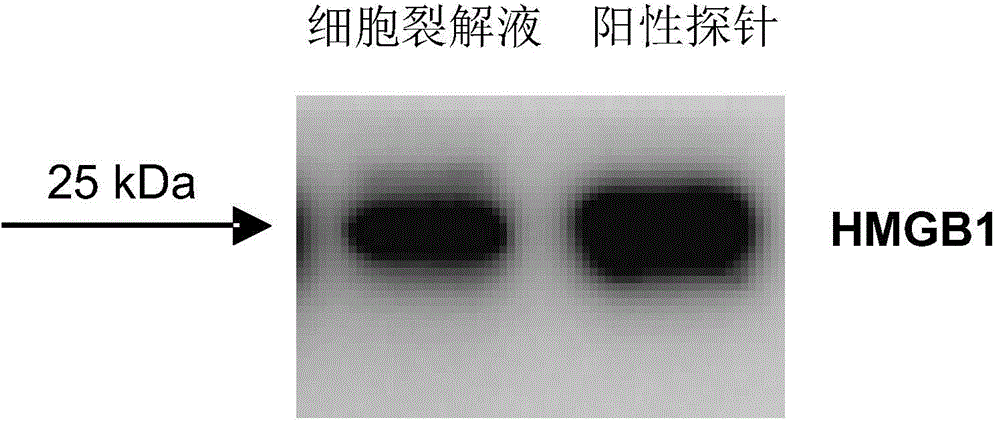
Damaged DNA-nanometer gold compound and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN104861037AAchieve captureHigh capture specificityPeptide preparation methodsBiological testingCentrifugationPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses a damaged DNA-nanometer gold compound and its preparation method and use in drug-damaged DNA response protein capture and / or identification, and a method for capturing a drug-damaged DNA response protein by the damaged DNA-nanometer gold compound. In the damaged DNA-nanometer gold compound, a mole of nanometer gold and 7-12 moles of the drug-damaged double-chain DNA are bonded. The damaged DNA-nanometer gold compound can realize high-specificity capture of the drug-damaged DNA response protein only by a less amount of a cell lysate. In capture of the drug-damaged DNA response protein, through the damaged DNA-nanometer gold compound, the captured drug-damaged DNA response protein can be separated from other proteins by a simple centrifugation process so that processes are simplified.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
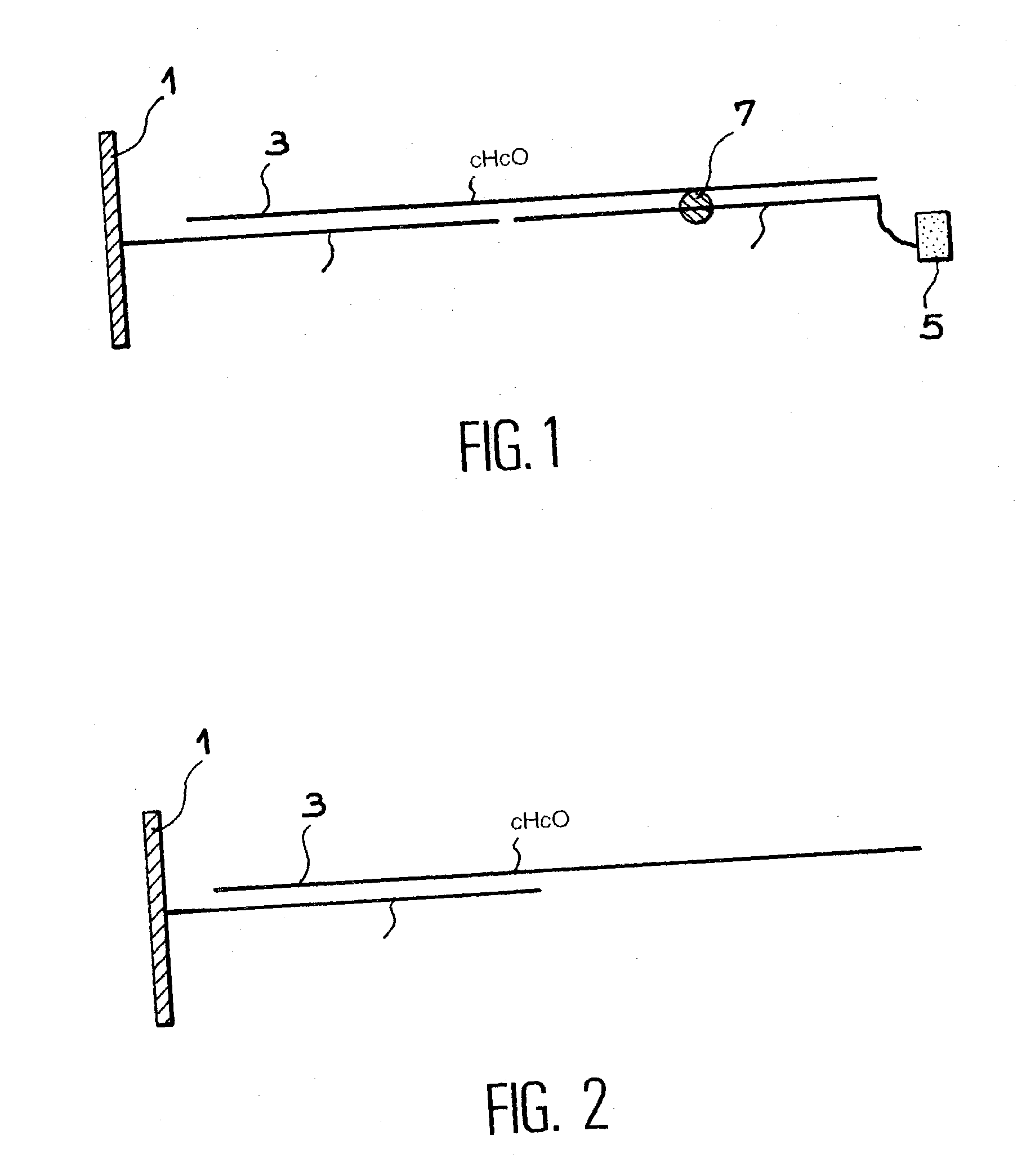
Method for detecting and characterising activity of proteins involved in lesion and dna repair
InactiveUS20030104446A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyProtein activityLesion
The invention relates to a method for detecting and characterising the activity of protein(s) involved in the repair of DNA, comprising the following steps: a) fix a known damaged DNA O comprising a lesion (7) onto a solid support (1) b) subject this damaged DNA to the action of a repair composition that may contain at least one protein contributing to the repair of this damaged DNA, and c) determine the activity of this protein for the repair, by measuring the variation of the signal emitted by a marker (5) that is fixed onto or is eliminated from the support in step b).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
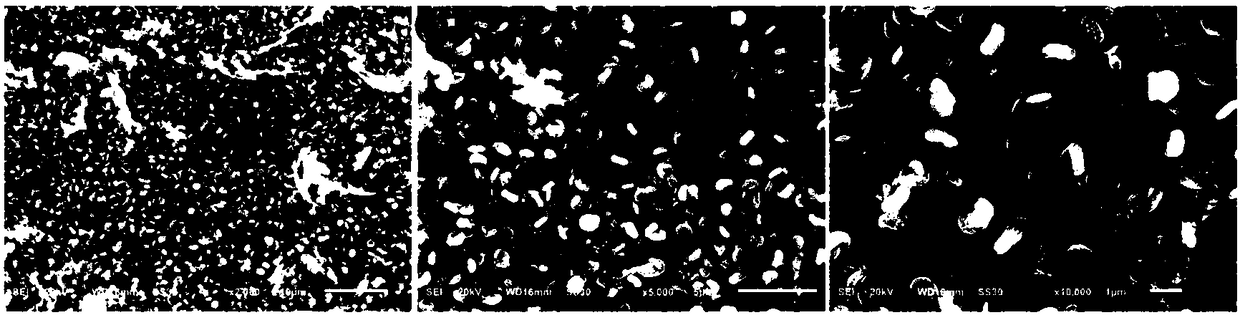
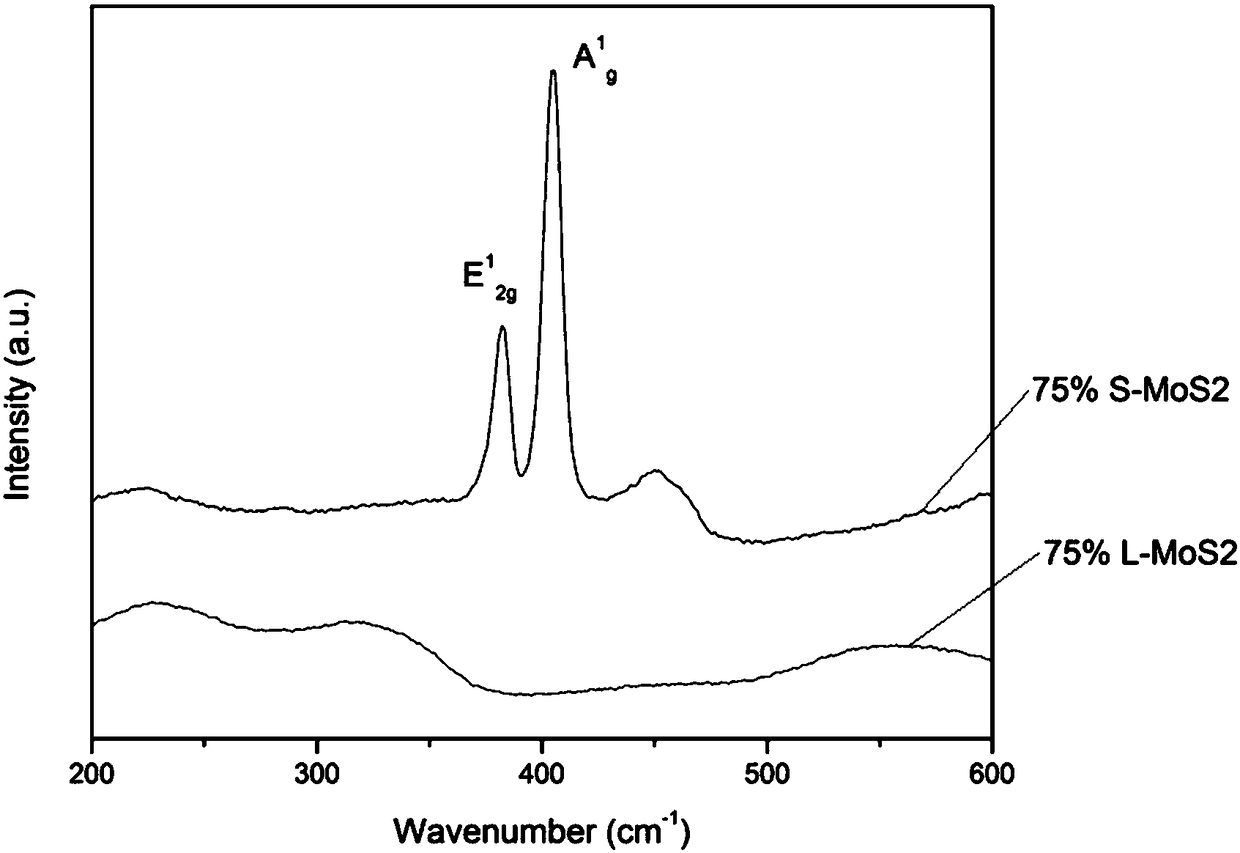
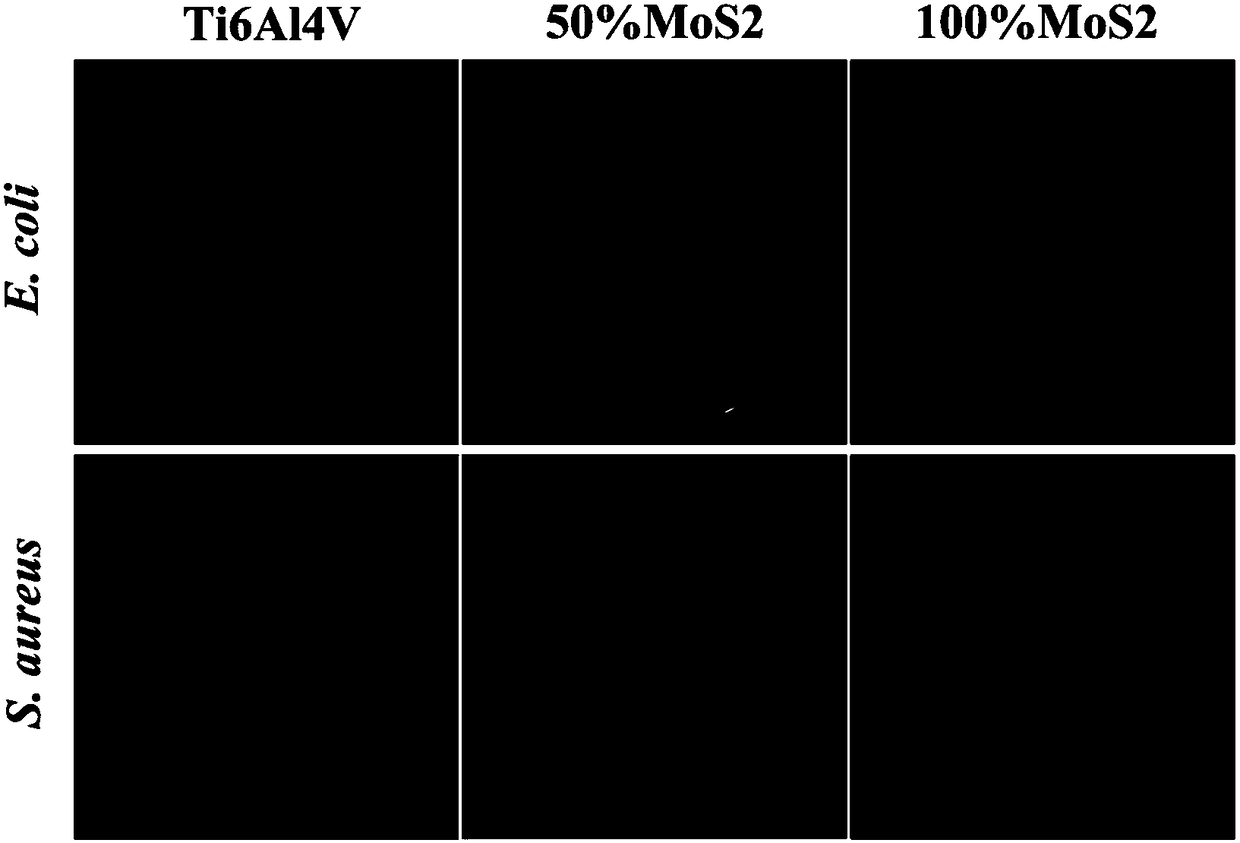
Preparation method of HA/MoS2 biological composite coating, with photocatalytic activity, on surface of titanium alloy
InactiveCN108355165ALong-term stabilityEasy accessMetallic material coating processesTissue regenerationOsseointegrationCell membrane
The invention discloses a method of preparing a hydroxyapatite / molybdenum disulfide biological composite coating, with the photocatalytic activity, on the surface of titanium alloy. The method endowsthe coating with excellent biocompatibility, bone formation performance and photocatalytic sterilization. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, preparing an HA / MoS2 suspension liquid, performing ultrasonic treatment, and dropwise adding the suspension liquid on the surface, subjected to polishing treatment, of Ti6Al4V with a pipette to form a preset coating; then performing laser treatment to enable the preset coating to be firmly combined with a base; and finally, performing sulphur treatment on a sample after laser cladding through a CVD furnace to prepare the HA / MoS2 biological composite coating. The method has the advantages that through a preparation method by combining a laser cladding technology with a CVD phase, except that combination of the coating and the Ti6Al4Vbase is firm, HA in the coating can effectively exert the advantages of the biocompatibility, bone formation and osseointegration, and meanwhile, MoS2 in the coating can produce a photocatalytic product through illumination with 660nm laser light, can effectively oxidize cell walls and cytomembranes of bacteria and damage DNA of the bacteria so as to cause bacteria apoptosis.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
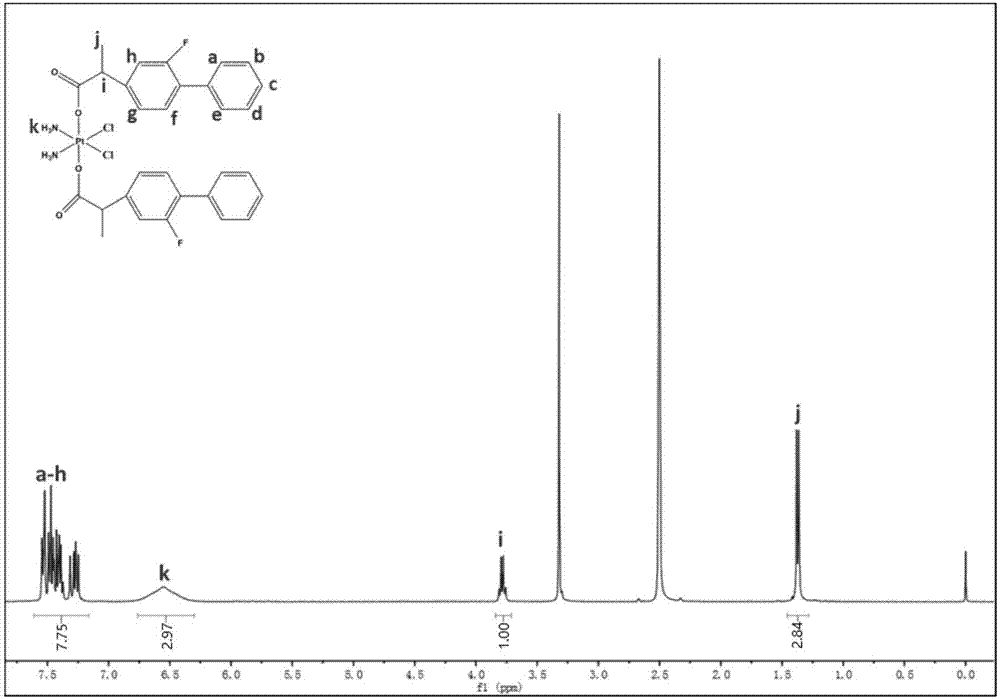
Cisplatin-flurbiprofen prodrug, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107445818AReverse drug resistanceImprove anti-tumor effectHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsOxalyl chlorideTumor cells
The invention provides a cisplatin-flurbiprofen prodrug, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The cisplatin-flurbiprofen prodrug is a tetravalent platinum prodrug, and an anti-inflammatory drug flurbiprofen is connected to the two axial positions of tetravalent platinum. The preparation method of the cisplatin-flurbiprofen prodrug comprises the following steps: (1) enabling the flurbiprofen to react with oxalyl chloride to obtain flurbilofenyl chloride; (2) enabling the flurbilofenyl chloride to react with dihydroxyl diamineplatinum dichloride to obtain the cisplatin-flurbiprofen prodrug. The prepared cisplatin-flurbiprofen prodrug can be reduced by a reducing molecular such as glutathione in a cell in a cellular environment to release monomolecular cisplatin and bimolecular flurbiprofen, DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) are damaged by the cisplatin, the flurbiprofen has an anti-inflammatory effect, and the cisplatin and the flurbiprofen are simultaneously released at the same position in the cell in a prodrug connecting manner to reverse the drug resistance of tumor cells to the cisplatin, thereby synergistically killing tumors and enhancing an anti-tumor effect.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
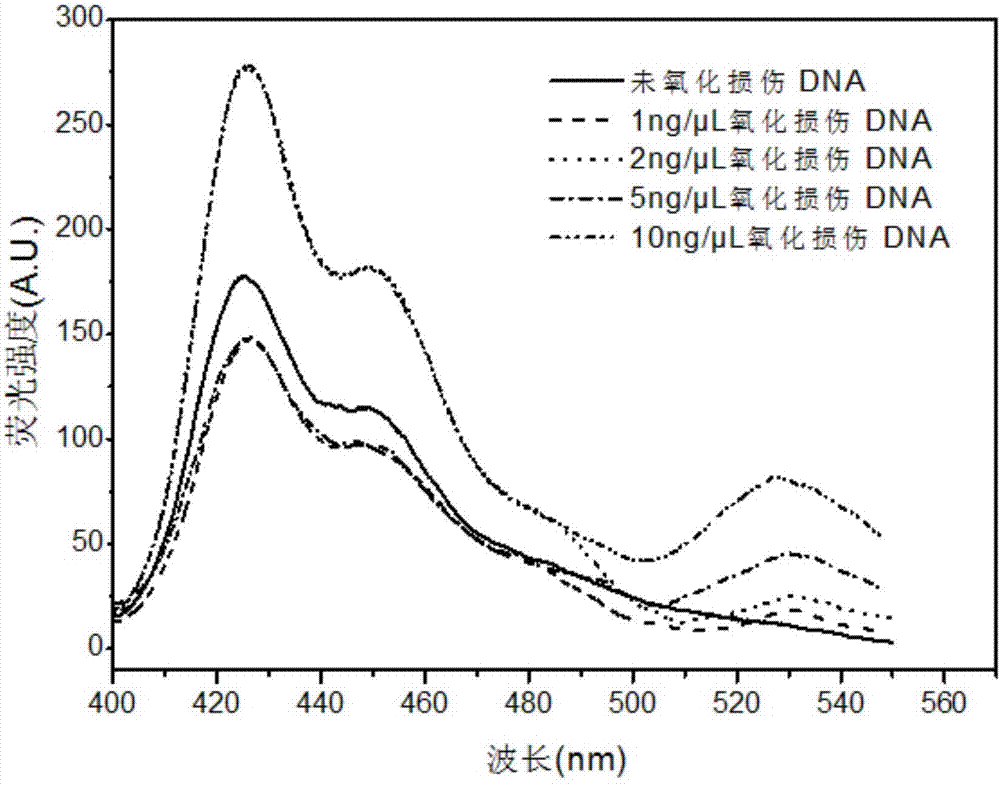
Oxidative damage DNA detection method
InactiveCN106939336AInjury mitigation steps are cumbersomeEase sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateNucleotide
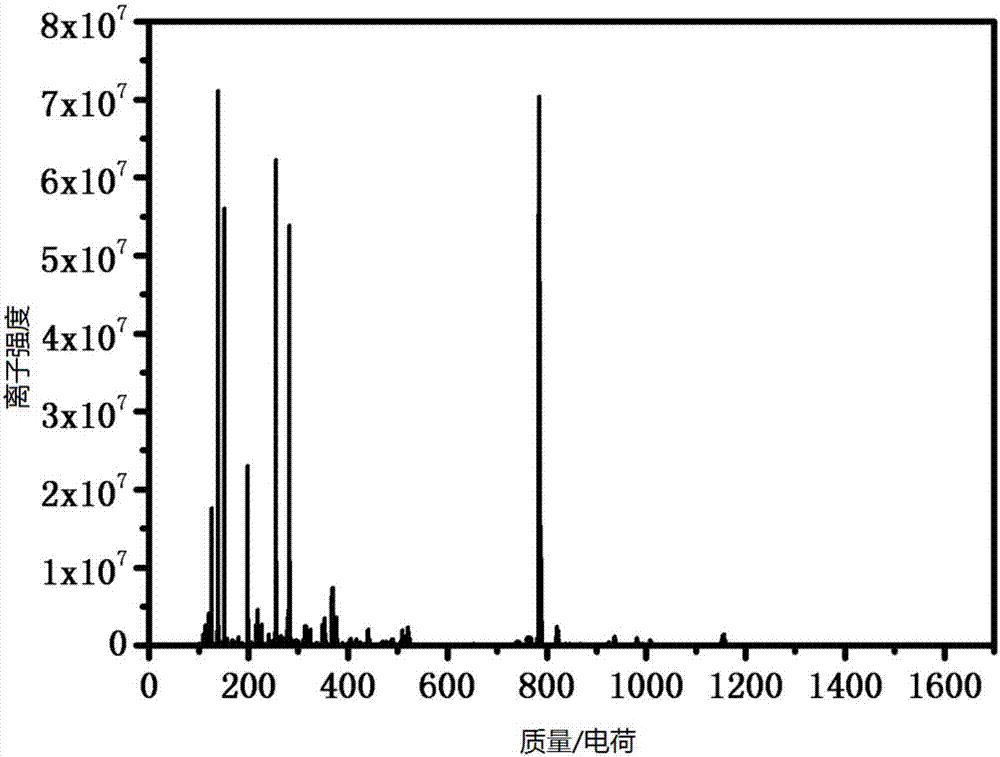
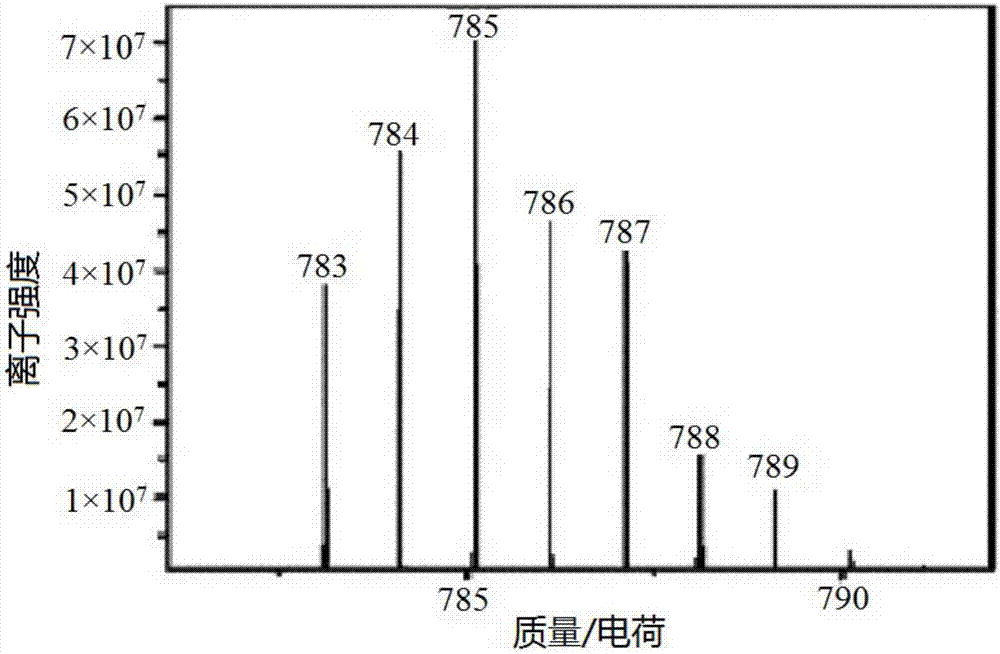
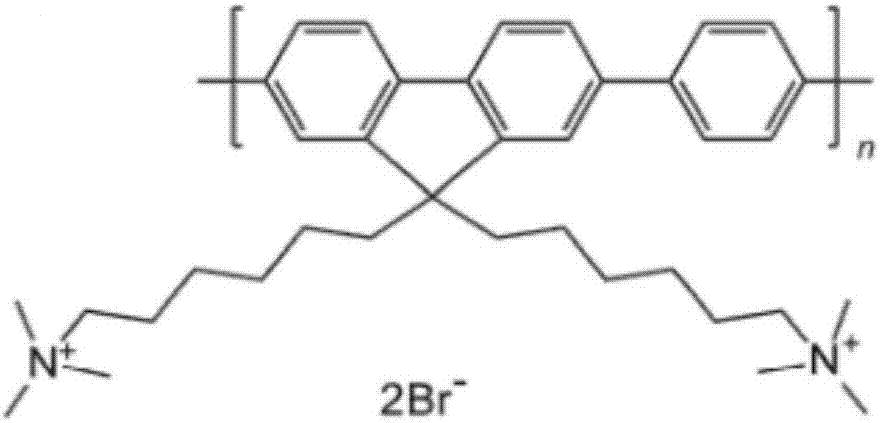
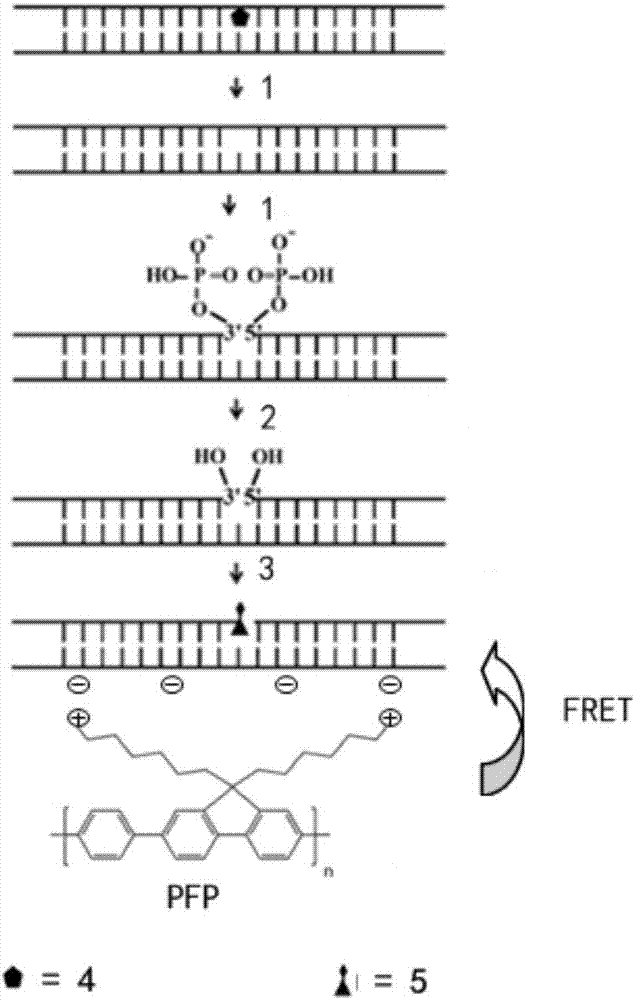
The invention discloses an oxidative damage DNA detection method, and relates to the technical field of DNA oxidative damage detection. The method comprises (a) obtaining of DNA containing 3 ', 5'-phosphate group nucleotide voi, to be more specific, adding a DNA repair enzyme for recognition and cutting of oxidized DNA bases; (b) introduction of hydroxyl into 3 ', 5' site, to be more specific, adding alkaline phosphatase for dephosphorylation to obtain the DNA containing 3 ', 5'-hydroxyl group nucleotide voids; (c) introduction of a fluorescent marker, to be more specific, adding DNA polymerase I and the fluorescent marker to obtain fluorescence-labeled DNA; (d) formation of a PFP-DNA complex, to be more specific, adding PFP to obtain the PFP-DNA complex; and (e) oxidative damage DNA detection, to be more specific, detecting damage DNA by FRET. The method alleviates the disadvantages of tedious steps, low sensitivity and low selectivity of DNA damage detection in the prior art. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity and high accuracy.
Owner:CHINA INST OF SPORT SCI
DNA optical prosthetic instrument
An optical DNA prosthetic apparatus for prostheting the damaged DNA of skin tissue and delaying skin sanility is composed of microcomputer, optical spectrum and intensity control unit, and full-spectrum therapeutic lamp with 400-5600 nm of spectrum range, 100-6000 W of electric power and 20 mJ-40 mJ / sq.cm of output energy.
Owner:郭勇
Inhibitors of endo-exonuclease activity for treating cancer
InactiveUS20060276548A1Increase concentrationPrevent proliferationBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsMitomycin CCisplatin
The present invention relates to the treatment of cancer with compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease. Endo-exonuclease has been shown to be necessary for the repair of damaged DNA. Compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease have been shown to be particularly effective for treating cancer when used in combination with drugs that induce DNA breaks such as cisplatin and mitomycin C. These compounds have a synergistic effect when used in combination for inhibiting tumour growth. The invention includes pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting tumour growth comprising a compound that inhibits endo-exonuclease activity. These pharmaceutical compositions preferably include compounds that induce DNA breaks. The invention includes methods of treating cancer with these pharmaceutical compositions and uses of these compositions to treat cancer. The preferred compounds that inhibit the activity of endo-exonuclease have low toxicity. One such compound is pentamidine. The invention also includes a method for diagnosing cancer and monitoring its progression. This aspect of the invention involves isolating serum from a patient; measuring the concentration of endo-exonuclease in said serum and determining whether said concentration is above a predetermined mean.
Owner:ONCOZYME PHARMA
Method and kits for repairing nucleic acid sequences
Methods and kits for DNA repair are provided. The methods and kits described herein repair multiple types of DNA damage. The kit may include a plurality of enzymes to repair a greater variety of lesions than any single enzyme is capable of repairing. Repair of damaged DNA may include releasing damaged bases from the DNA strand, nicking the DNA at the damaged sites, translating the nicks via 5′-3′ exonuclease activity, and sealing the nicks. The enzymes employed in the repair process may then be heat-inactivated, thereby obviating a purification process. The repaired DNA may then be analyzed using a variety of DNA analysis methods.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS OPERATIONS UK LTD
Extraction preparation method of star-of-Bethlehem stem cell cambium and anticancer composition
The invention provides an extraction preparation method of star-of-Bethlehem stem cell cambium and an anticancer composition. As stem cells from the cambium are in undifferentiated state, cells can be massively cultured in long-term culture because cell growth and mode are stably maintained without variation. Functional anticancer foods in forms of oral liquid preparations, beverages and the like are prepared by ethanol extraction, centrifugal separation, rotary low temperature vacuum concentration and vacuum freezing and drying. The foods have strong inhibiting and killing activities to more than 20 types of tumor cells with different specificities. Meanwhile, the foods have better inhibiting effect to prevent differentiated cells from turning to tumor cells, and further have the better functional effects of resisting oxidation, reducing blood fat and sugar, reducing cholesterol, resisting radiation, enhancing the immunity and activating damaged DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid).
Owner:林树芳
Clinical use of an Alu element based bioinformatics methodology for the detection and treatment of cancer
ActiveUS9932640B1Microbiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsBiomarker (petroleum)Human genetics
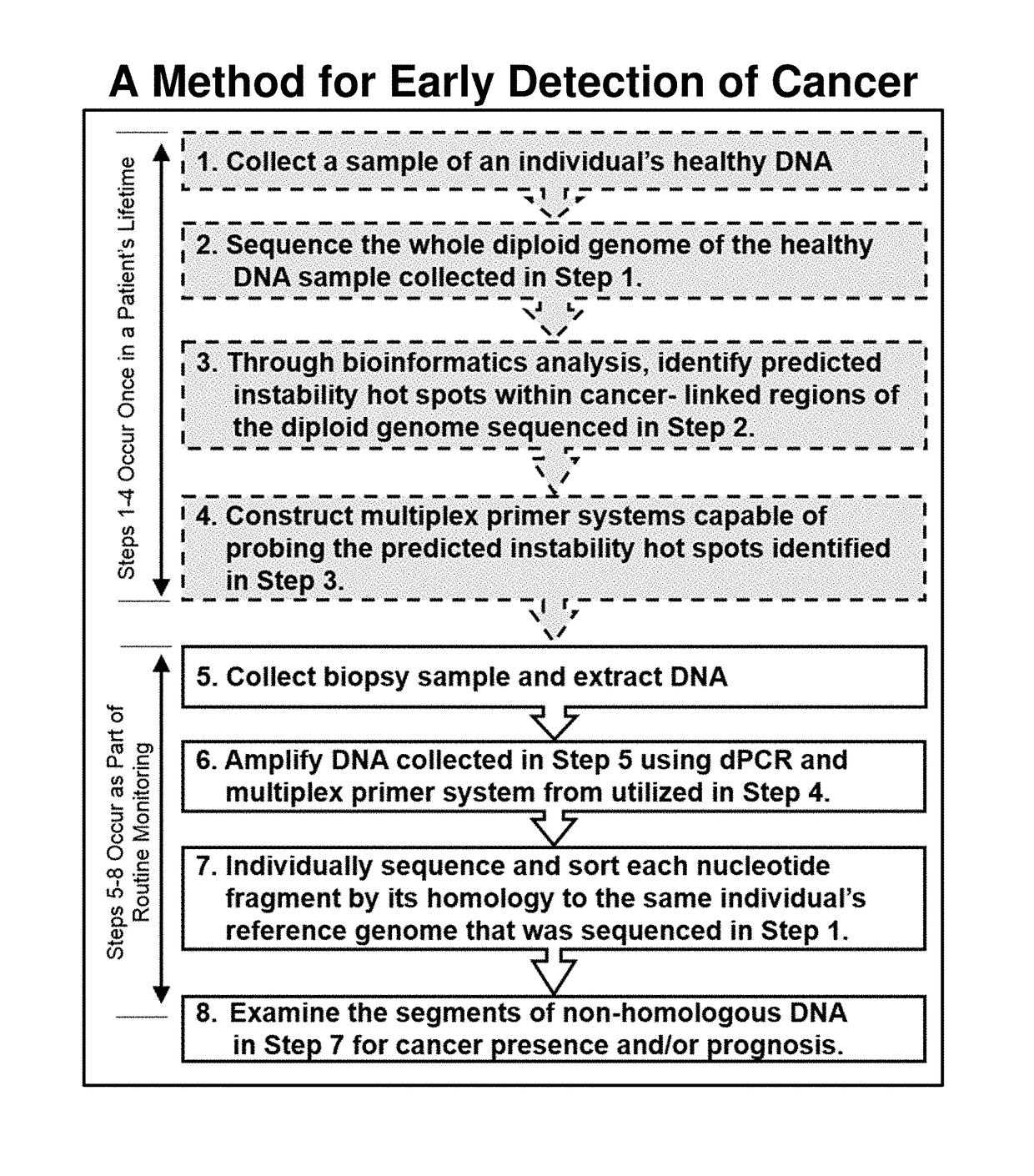
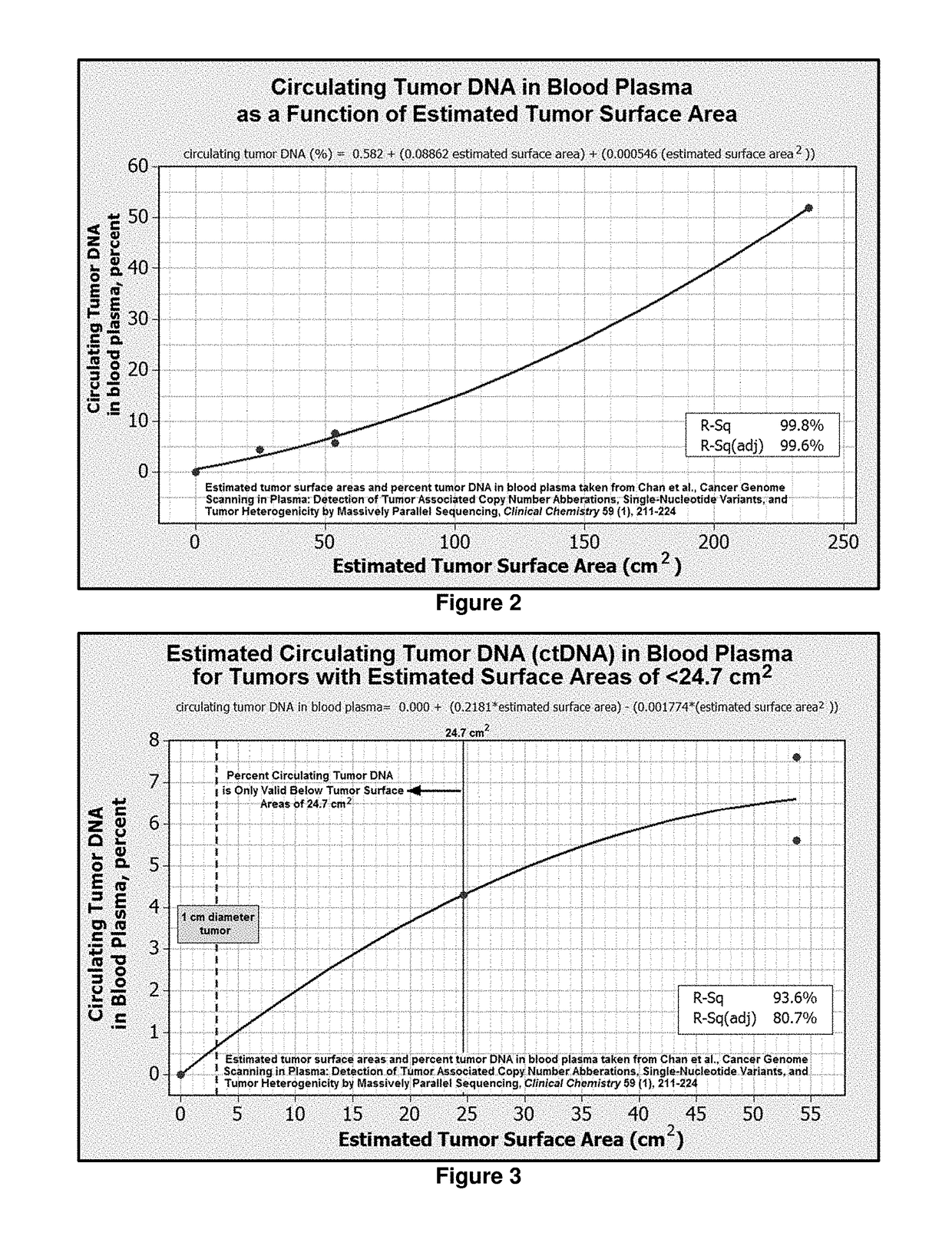
The present invention relates generally to the field of human genetics. More specifically, this invention relates to the clinical application of a bioinformatics methodology described in patent application Ser. No. 14 / 154,303 for the early detection of cancer. Said clinical application relates to obtaining the genome sequence from an individual's healthy tissue and comparing it to the DNA sequence obtained from that same individual's body tissues, wastes and / or fluids. Said method inspects the DNA sequence obtained from body tissues, wastes and / or fluids for the presence of DNA damage at bioinformatically predicted genetically unstable loci within cancer-linked regions of the patients healthy DNA. The identification of DNA damage within a predicted locus is considered to be evidence of cancer. Said method then uses the unique signature of any damaged DNA sequence which has occurred at predicted unstable cancer-linked loci to construct patient-specific cancer biomarker(s). These biomarkers can be used for monitoring the progression of cancer and for treatment of the cancer in a patient.
Owner:COOK JR GEORGE WYNDHAM
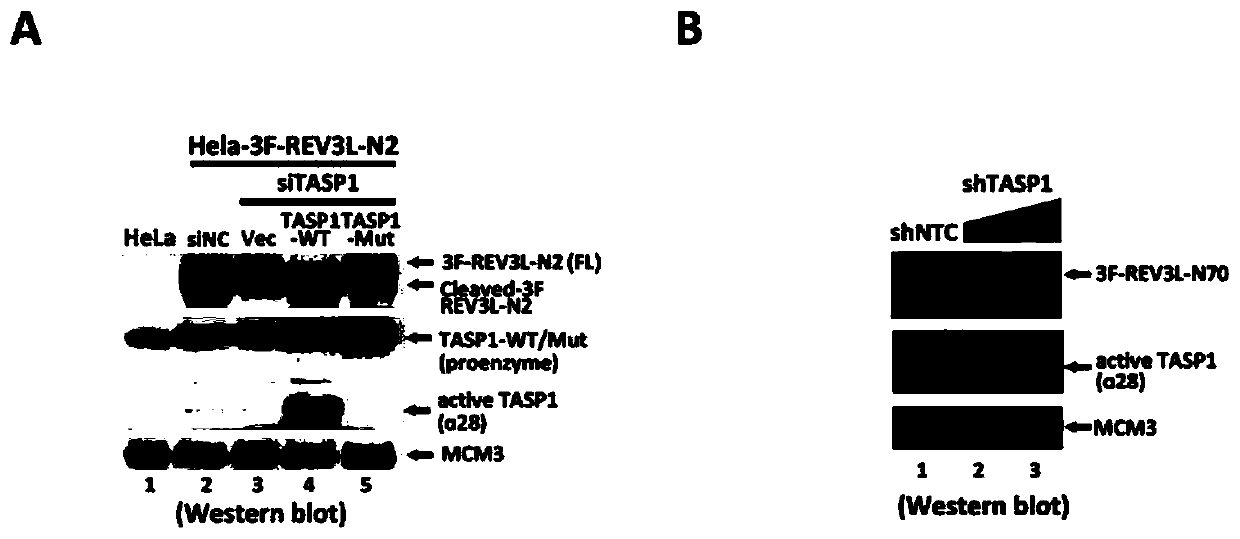
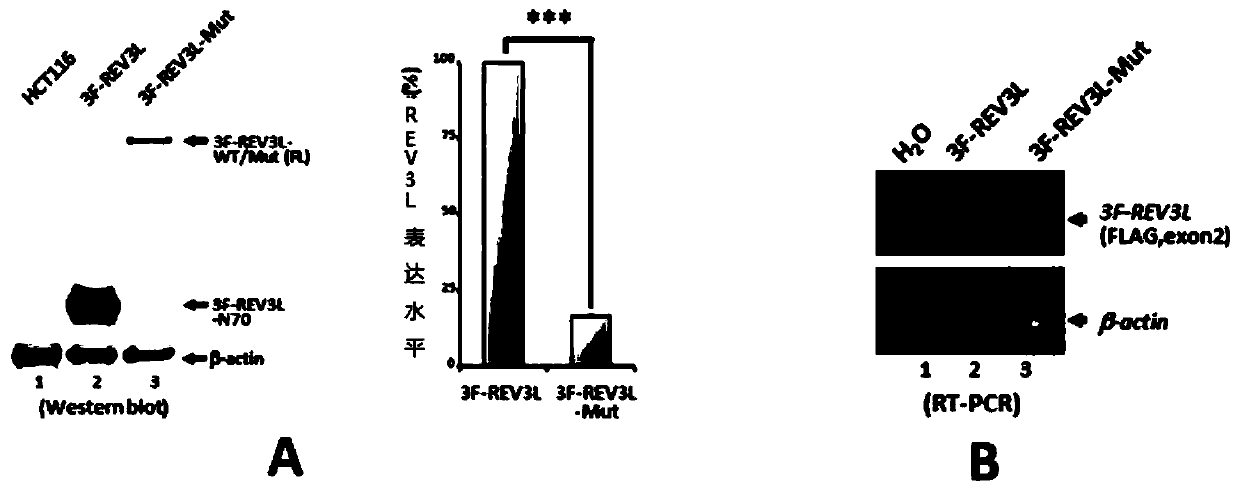
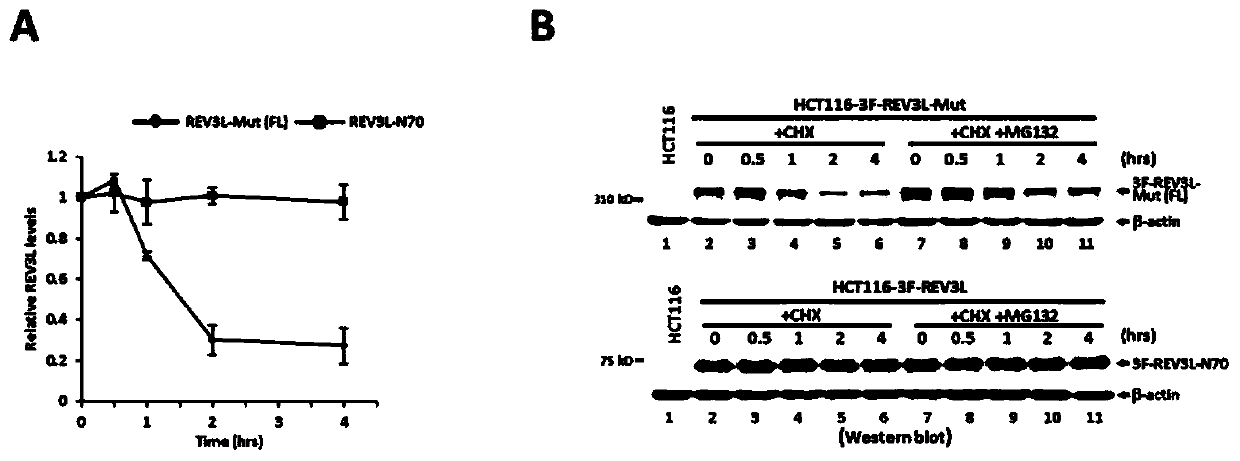
Human REV3L protein cleavage inhibitor and application thereof
InactiveCN111467493AIncreased sensitivityDelay drug resistanceHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseDrug target
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine, and particularly relates to a human REV3L protein cleavage inhibitor and application thereof. The invention discloses a drug for improvingsensitivity of tumor cells to DNA damage and controlling drug resistance of tumor cells. The action target of the drug is obtained by a protease TASP1 mediated human REV3L protein position specific cleavage event. The inventor finds that the human REV3L protein has a TASP1 mediated sequence dependent protein cleavage event; polyubiquitination modification of REV3L protein and proteasome mediated degradation can be effectively promoted by interfering the REV3L protein cleavage event, so that low-fidelity cross-damage DNA synthesis activity in tumor cells is further reduced, DNA mutation inducedby DNA damage is reduced, sensitivity of tumor cells to DNA damage is remarkably improved, and therefore, a new potential drug target is provided for enhancing the radiotherapy and chemotherapy effects of tumors and other diseases taking induction of DNA damage as a molecular basis and controlling generation of drug resistance.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Support for fixing nucleotide and process for producing the same
InactiveCN1396954AEffective generationEasy to fixSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideRestriction site
A support for fixing a nucleotide which contributes to the efficient clarification of DNA without damaging the terminal parts of the DNA and, therefore, is useful in the fields of molecular biology, biochemistry and the like. This support for fixing a nucleotide is a chemically modified substrate on which oligonucleotides are immobilized characterized in that the oligonucleotides have a restriction enzyme cleavage site. This support is produced by chemically modifying the substrate, immobilizing a single-stranded oligonucleotide thereon, then hybridizing the single-stranded oligonucleotide with another single-stranded oligonucleotide having a base sequence complementary thereto, and ligating an oligonucleotide having a restriction enzyme site at the end thereof.
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD
Recombinant bacteria for characterizing genotoxicity and its construction method and application
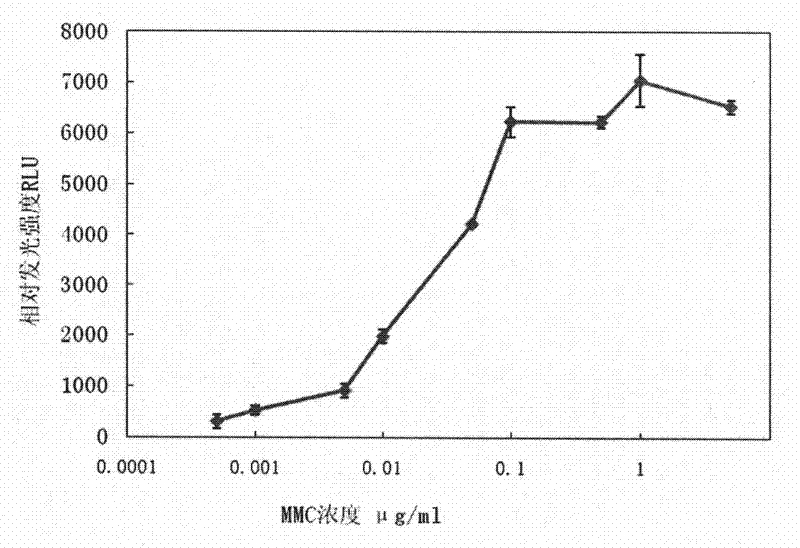
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium characterizing genotoxicity, its construction method and application. The recombinant bacterium is Acinetobacter sp. ADP1 containing a reporter gene in the recA gene of the chromosome; the reporter gene and the recA gene have a common promoter. The recA gene may also contain a screening marker gene, which is located at the 3' end of the reporter gene; the screening marker gene has a promoter. After the recombinant bacteria are exposed to genotoxic substances or radiation with DNA damage ability, the reporter gene expression produces a reporter product, and the amount of the reporter product has a dose-effect relationship with the genotoxicity, which can be used to evaluate the genotoxicity of the sample and the DNA of the radiation damage intensity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Materials and method for inhibiting replication protein a and uses thereof
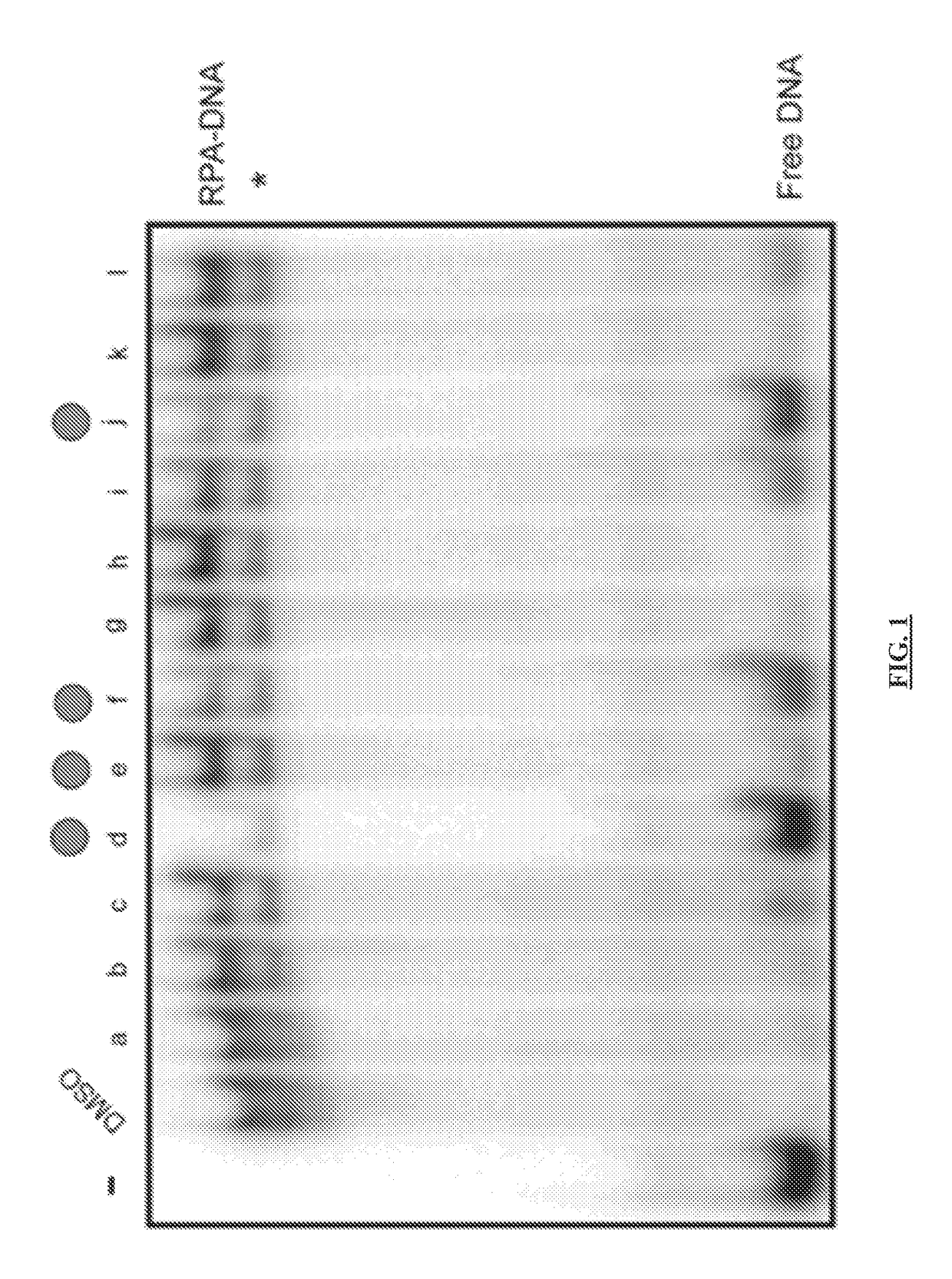
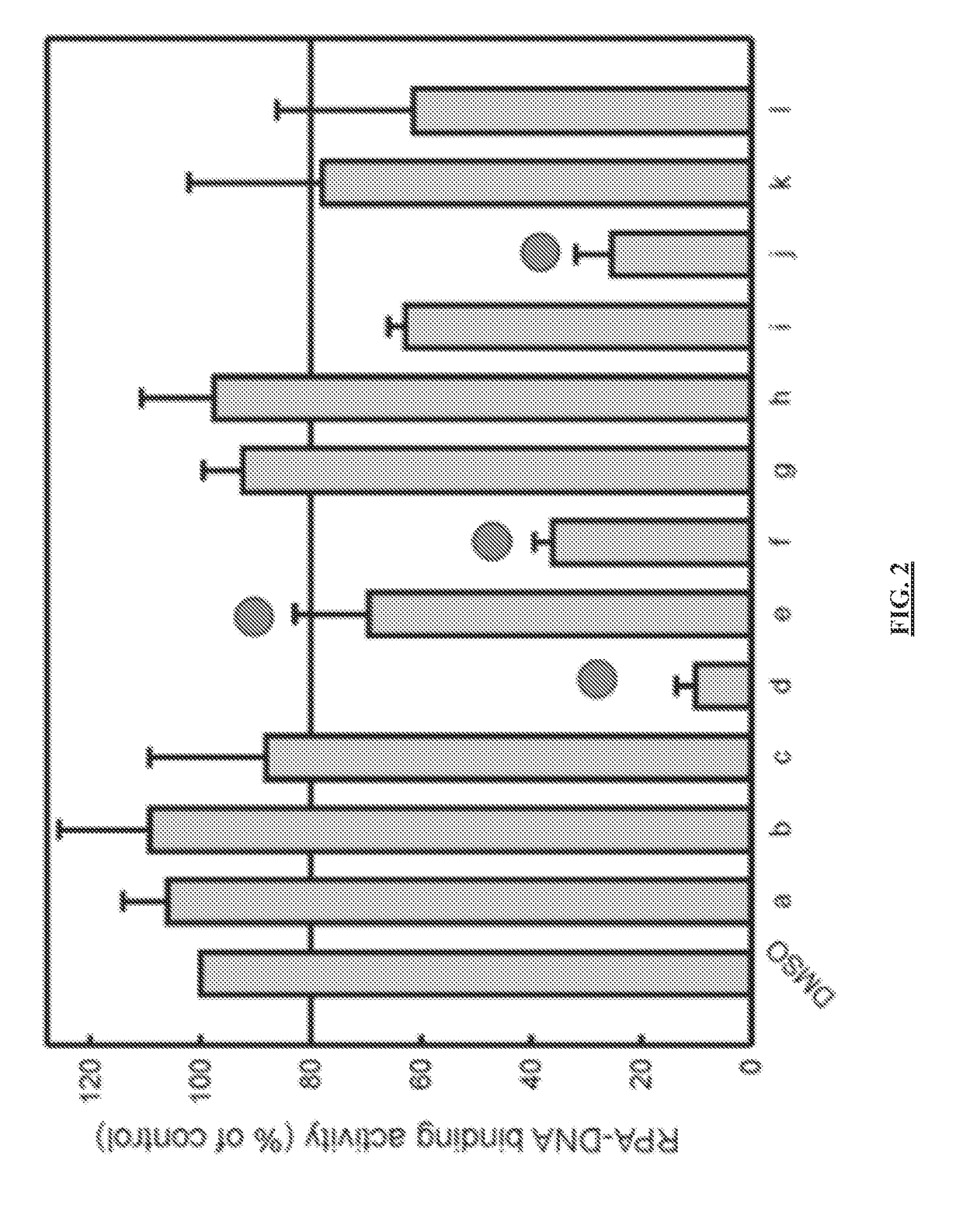
ActiveUS20180305330A1Simple designReduced effectivenessOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCytotoxicitySingle strand
Targeting uncontrolled cell proliferation and resistance to DNA damaging chemotherapeutics with at least one reagent has significant potential in cancer treatment. Replication Protein A, the eukaryotic single-strand (ss) DNA binding protein, is essential for genomic maintenance and stability via roles in both DNA replication and repair. Reported herein are small molecules that inhibit the in vitro, in vivo, and cellular ssDNA binding activity of RPA, thereby disrupting the eukaryotic cell cycle, inducing cytotoxicity and increasing the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents damage DNA, and / or disrupt its replication and / or function. These results provide new insights into the mechanism of RPA-ssDNA interactions in chromosome maintenance and stability. This represents a molecularly targeted eukaryotic DNA binding inhibitor and demonstrates the utility of targeting a protein-DNA interaction as a means of studying the cell cycle and providing a therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Combi-molecules having EGFR and DNA targeting properties
A series of new chemical agents that demonstrate anti-tumor activity are described. The new chemical agents combine two major mechanisms of anti-tumor action. In an embodiment, the agents are capable of both inhibiting EGFR and damaging DNA while also, upon degradation, degrading to an inhibitor of EGFR and to an agent capable of damaging DNA. Moreover, a novel series of molecules capable of releasing two moles of EGFR inhibitor and a potent bi-functional alkylating agent are also described.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Skin repair compositions comprising circadian gene activators and a synergistic combination of Sirt1 gene activators
ActiveUS8703161B2Restore levelDelaying mitosisCosmetic preparationsBiocidePersonal careCircadian clock gene
Compositions and methods for enhancing repair of damaged DNA in skin cells. Topical compositions comprising at least one agent that upregulates circadian gene expression in skin cells and at least one non-circadian agent that delays mitosis in skin cells. Preferably, such compositions comprise one or more keratinocyte clock and per1 gene activators, along with SIRT1 or one or more sirt1 activators. More preferably, the sirt1 activator is a synergistic combination of specific peptidic sirt1 activators and resveratrol. Preferably, such compositions are easy to use, efficacious, cosmetically acceptable, chemically, thermodynamically and light stable, safe for topical use, have little or no side effects, and commercially feasible in a personal care marketplace.
Owner:ELC MANAGEMENT LLC
Tumor microenvironment response type nucleus-targeting platinum nanoparticles as well as preparation method and application
ActiveCN110624111AImprove specific targeting aggregationImprove tumor treatment effectPowder deliveryInorganic active ingredientsPolymer modifiedPlatinum salts
The invention discloses tumor microenvironment response type nucleus-targeting platinum nanoparticles comprising platinum nanoparticles and nucleus-targeting peptide and amphiphilic polymer modified on the platinum nanoparticles. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the tumor microenvironment response type nucleus-targeting platinum nanoparticles. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: a platinum salt precursor and a blocking agent are dissolved in water to form a precursor solution, and a strong reducing agent is added for a reduction reaction to obtain subminiature platinum nanoparticles; amphiphilic polymers are dissolved in a good solvent, a modifier is added, and stirring reaction is conducted to obtain a n amphiphilic polymer is obtained; the subminiature platinum nanoparticles and nucleus-targeting polypeptide are dissolved in water, and stirring reaction is conducted to prepare nucleus-targeting platinum nanoparticles; and the nucleus-targeting platinum nanoparticles and the amphiphilic polymer are dissolved in water, and stirring reaction is conducted to obtain the tumor microenvironment response type nucleus-targeting platinum nanoparticles. The tumor microenvironment response type nucleus-targeting platinum nanoparticles can specifically target tumor cells, center cell nucleus to damage DNA and kill tumor cells.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com