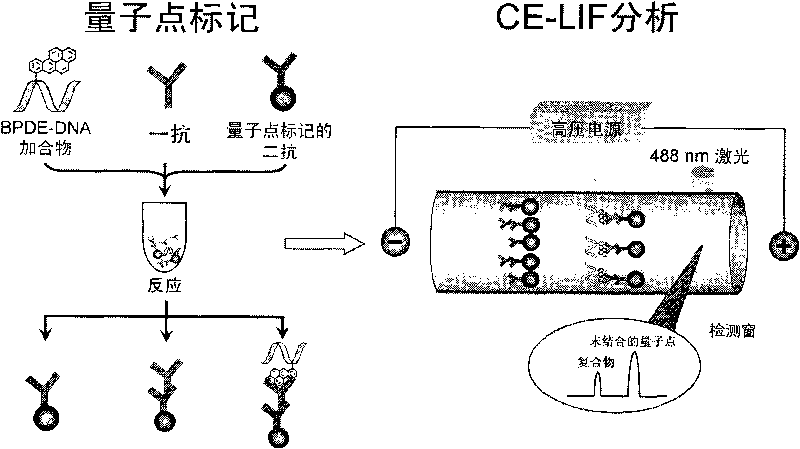
Method for analyzing quantum dot-enhanced high-sensitivity DNA adduct
A DNA adduct and analysis method technology, applied in the direction of analysis materials, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of DNA, low sensitivity, cumbersome operation, etc. tedious effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
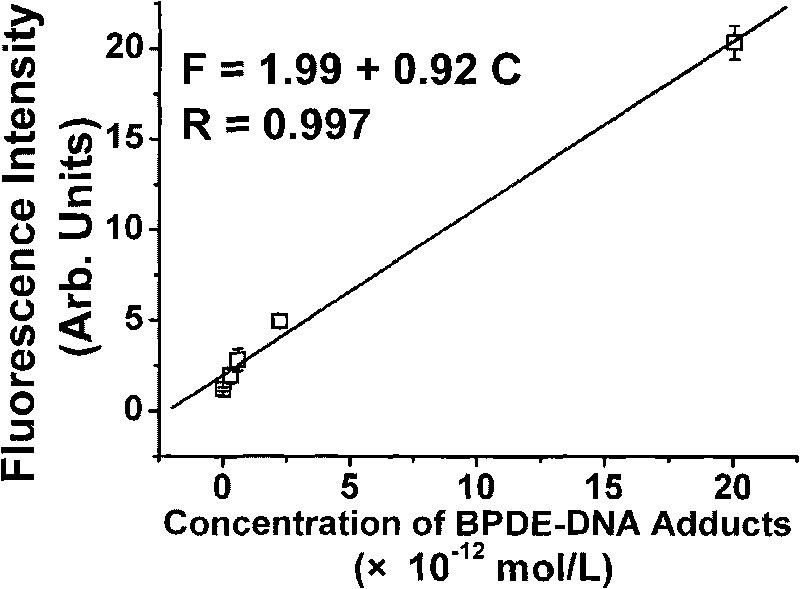
[0030] Example 1. Detection and analysis of BPDE-DNA adduct standard substance by quantum dot-enhanced immunocapillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence analysis technology.
[0031] In this example, the BPDE-DNA adduct is the target of analysis. BPDE-DNA adduct is the final metabolite o-diol epoxybenzo(a)pyrene (BPDE) activated by the highly carcinogenic environmental pollutant benzo(a)pyrene (B(a)P) in vivo. formed by covalent binding of DNA. The primary antibody used is a mouse-derived monoclonal antibody against BPDE-dG adduct, which can specifically recognize and bind to BPDE-dG adduct in single-stranded DNA; the secondary antibody is labeled with quantum dots Qdot 625 of anti-mouse IgG.
[0032] The DNA sample to be tested was heated at 95°C for 10 minutes to denature the double-stranded DNA into single-stranded DNA, and placed on ice for 10 minutes to prevent the single-stranded DNA from renaturing. The quenched DNA sample was mixed with the primary antibody...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2. Detection and analysis of BPDE-DNA adducts in genomic DNA of A549 cells after A549 cells were exposed to different concentrations of BPDE by quantum dot-enhanced immunocapillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence analysis.
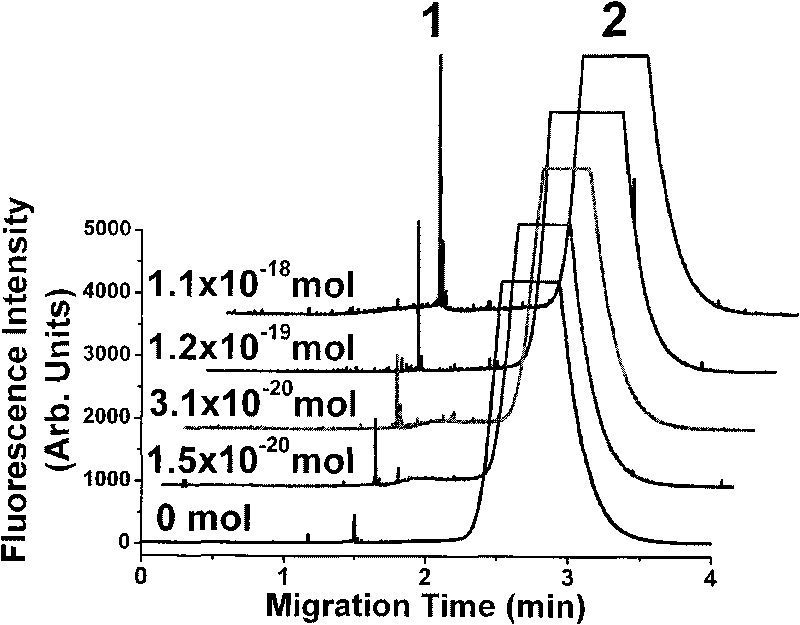
[0036] A549 cells were exposed to different concentrations of BPDE for 2 hours, and their genomic DNA was extracted as a sample to be tested. 100 μg / mL of cellular genomic DNA was quenched and then denatured into single-stranded DNA, mixed with primary antibody and quantum dot-labeled secondary antibody, and subjected to immunocapillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence analysis according to the conditions described in Example 1. attached Figure 4 Capillary electrophoresis chromatogram of the detection of BPDE-DNA adducts in genomic DNA of A549 cells exposed to 0.1 nMBPDE, wherein peak 1 is the peak of BPDE-DNA adduct-quantum dot-labeled antibody complexes, and peak 2 is the excess free The peak of the antibody (includi...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3. Detection and analysis of BPDE-DNA adducts in genomic DNA of A549 cells exposed to different concentrations of B(a)P by quantum dot-enhanced immunocapillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence analysis technology.
[0038] After exposure of different concentrations of B(a)P to A549 cells for 16 hours, the genomic DNA was extracted and used as a test sample. 100 μg / mL of cellular genomic DNA was quenched and then denatured into single-stranded DNA, mixed with primary antibody and quantum dot-labeled secondary antibody, and subjected to immunocapillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence analysis according to the conditions described in Example 1. attached Figure 5 Capillary electrophoresis-laser-induced fluorescence analysis spectrum for the detection of BPDE-DNA adducts in genomic DNA of A549 cells exposed to 1 nM B(a)P, in which peak 1 is the complex of BPDE-DNA adduct-quantum dot-labeled antibody Peak 2 is the peak of excess free antibody (i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com