Method for removing antibiotic resistance genes through ionizing irradiation
A technology of antibiotic resistance and ionizing radiation, applied in the field of waste treatment, can solve the problems of land occupation, high moisture content of antibiotic residues, and low calorific value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
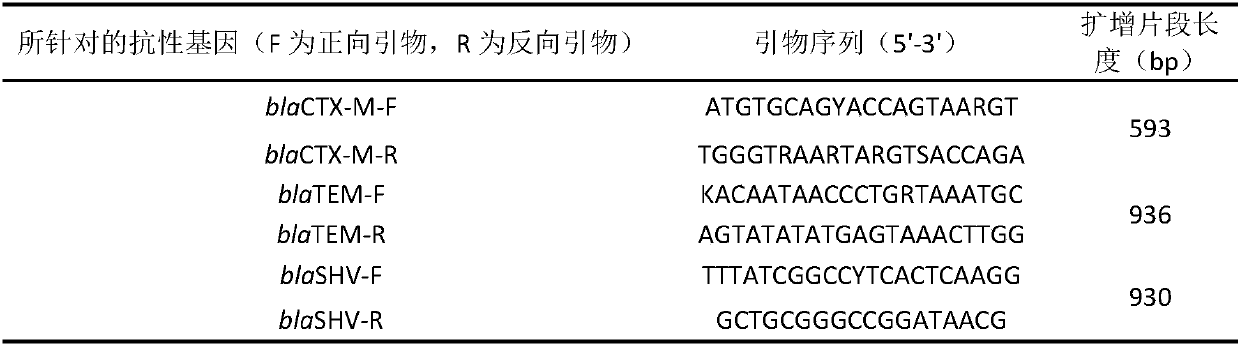
[0026] Get the solid-liquid mixture of erythromycin slag (the water content is 93%, the total suspended solids content is 72g / L, wherein the proportion of organic solids is 80%) to detect the concentration of erythromycin resistance gene and the active substance erythromycin The amount of prime A. Then put the solid-liquid mixture of the bacteria residue into the irradiation container, and use Co 60 Gamma rays (radiation activity 3.6×10 14 Bq), irradiated near the central channel, the dose rate is about 240Gy / min. The absorbed dose was controlled to be 5kGy and 10kGy by adjusting the irradiation time. After the irradiation, the concentration of erythromycin resistance gene and the concentration of residual active substance erythromycin A in the bacteria residue were detected under different absorbed doses.
[0027] The residual erythromycin in the bacterial residue was detected by high performance liquid chromatography. First use organic solvent to extract it from the bact...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Get the erythromycin thiocyanate bacterium residue solid-liquid mixture (water content is 92%, total suspended solids content is 75g / L, wherein the proportion of organic solids is 77%) to detect the concentration and activity of erythromycin resistance gene The amount of substance erythromycin A. It is then placed in an irradiation container with Co 60 Gamma rays (radiation activity 3.6×10 14 Bq), irradiated near the central channel, the dose rate is about 240Gy / min. The absorbed radiation dose was controlled to be 10kGy, 20kGy and 30kGy by adjusting the irradiation time. After the irradiation, the concentration of erythromycin A remaining in the residue of erythromycin thiocyanate and the amount of resistance gene were detected under different absorbed doses.
[0034] The residual erythromycin A in the bacteria residue was first extracted with organic solvent, and then detected by liquid chromatography. The specific detection method is the same as in Example 1.
...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Take penicillin slag solid-liquid mixture (water content is 88%, total suspended solids content is 116g / L, wherein the proportion of organic solid is 87%) to detect the concentration of penicillin resistance gene and the amount of penicillin. Then put the solid-liquid mixture of the bacteria residue into the irradiation container, and use Co 60 Gamma rays (radiation activity 3.6×10 14 Bq), irradiated near the central channel, the dose rate is about 240Gy / min. The absorbed radiation dose was controlled to be 5kGy and 10kGy by adjusting the irradiation time. After the irradiation, the residual penicillin concentration in the penicillin residue under different absorbed doses was detected and the qualitative detection of the resistance gene was carried out.
[0039] For the residual penicillin in the bacteria residue, it was first extracted with an organic solvent, and then detected by liquid chromatography. Wherein, the liquid chromatograph used is a high-performance li...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com