Patents
Literature
49 results about "Dna interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein–DNA interactions. Protein–DNA interactions occur when a protein binds a molecule of DNA, often to regulate the biological function of DNA, usually the expression of a gene. Among the proteins that bind to DNA are transcription factors that activate or repress gene expression by binding to DNA motifs and histones that form part of ...
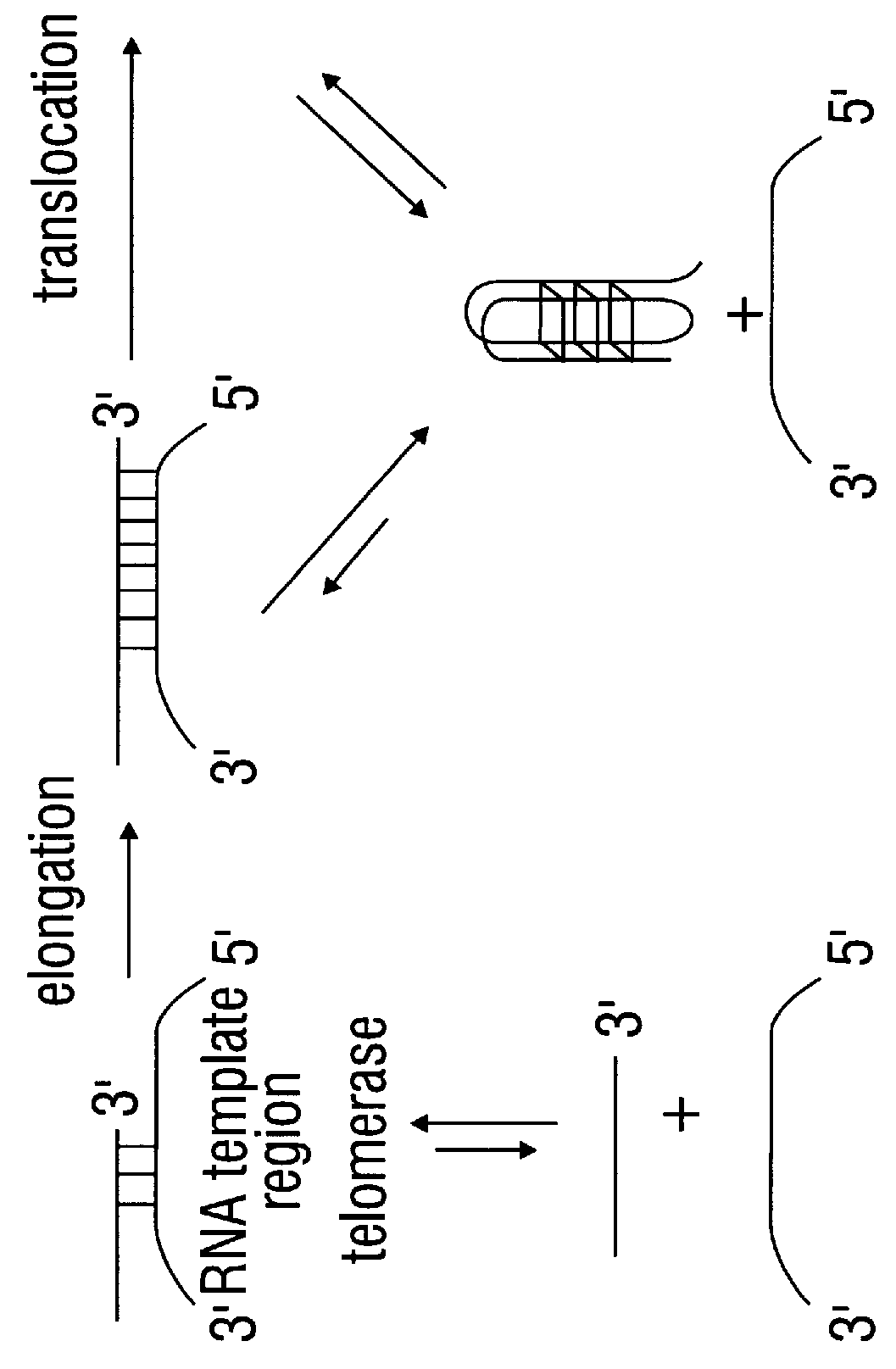
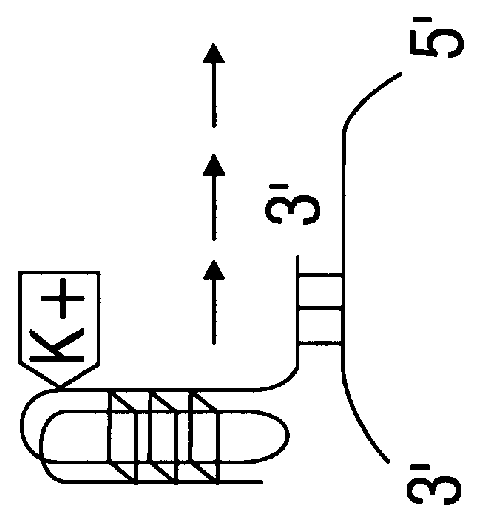
Porphyrin compounds as telomerase inhibitors
InactiveUS6087493ARegulating telomerase functionModulating tumor proliferation and mortalitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTelomeraseDna interaction
The present invention has identified compounds with extended aromatic chromophores that bind the G-quadruplex formed by the folding of single-stranded human telomeric DNA. These compounds have been shown to be effective telomerase inhibitors and are contemplated to be useful in developing cancer treatments. A model of cationic porphyrin interaction with quadruplex DNA by intercalation has been established and in combination with structure activity relations has provided novel porphyrin compounds that exhibit discrimination between binding duplex and quadruplex DNA and show improved activity against telomerase.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Wireless CMOS Biosensor
System and methods for detection and measurement of interactions in microarrays or within a human body are described. The system includes a CMOS sensor which can be placed in a fluidic environment, and is capable of measuring DNA interactions and protein binding kinetics, as well as cellular interactions and signals within the body. The sensor can be placed in close proximity with the sample and eliminates the need for optics, and in some embodiments is a wireless device.
Owner:ANWAR M MEKHAIL +2
Array systems and methods
Methods, kits, arrays, and biosensors for detecting proteins, modified-proteins, protein-protein interactions, protein-DNA interactions, autoantibodies, and protein-small molecule interactions, are disclosed. A representative method of detecting proteins of the present invention includes exposing a solid support to a solution containing proteins; conjugating proteins to the solid support; exposing the solide support to a plurality of types of DNA-conjugated antibodies, wherein each type of DNA-conjugated antibody has an affinity for a specified protein; forming a complex between a protein conjugated with the solid support and a type of DNA-conjugated antibody when the protein is the specified protein for which the DNA-conjugated antibody has an affinity; separating the complex from the solution of proteins and the DNA-conjugated antibodies; releasing DNA from the DNA-conjugated antibodies; and detecting the DNA, wherein each DNA indicates the presence of the specified proteins.
Owner:HUANG RUO PANG
Preparation method of deoxyribonucleic acid electrochemical nanometer sensor
InactiveCN1525163AHigh detection sensitivityImprove detection limitBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesDna interactionElectrochemistry
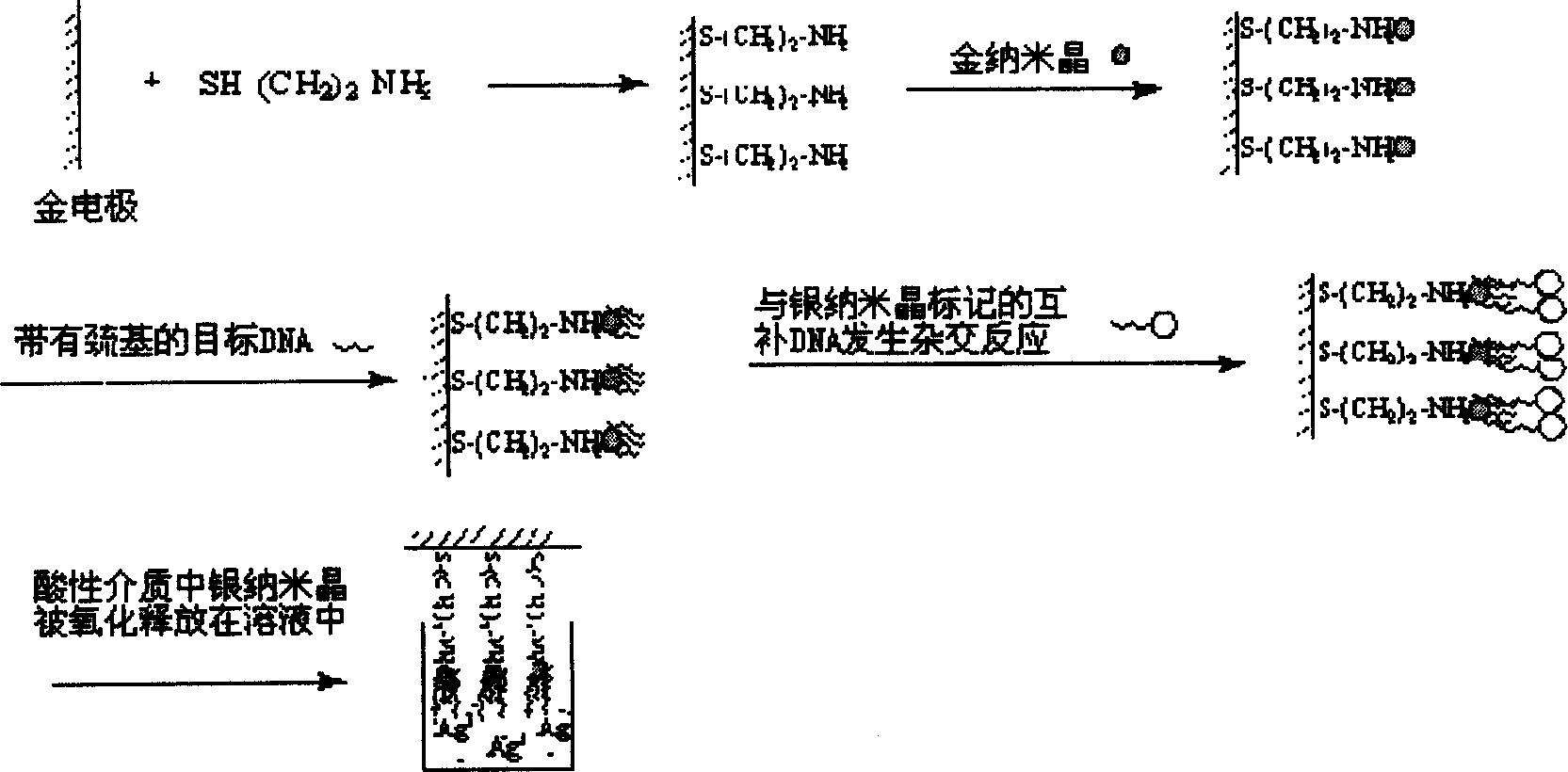
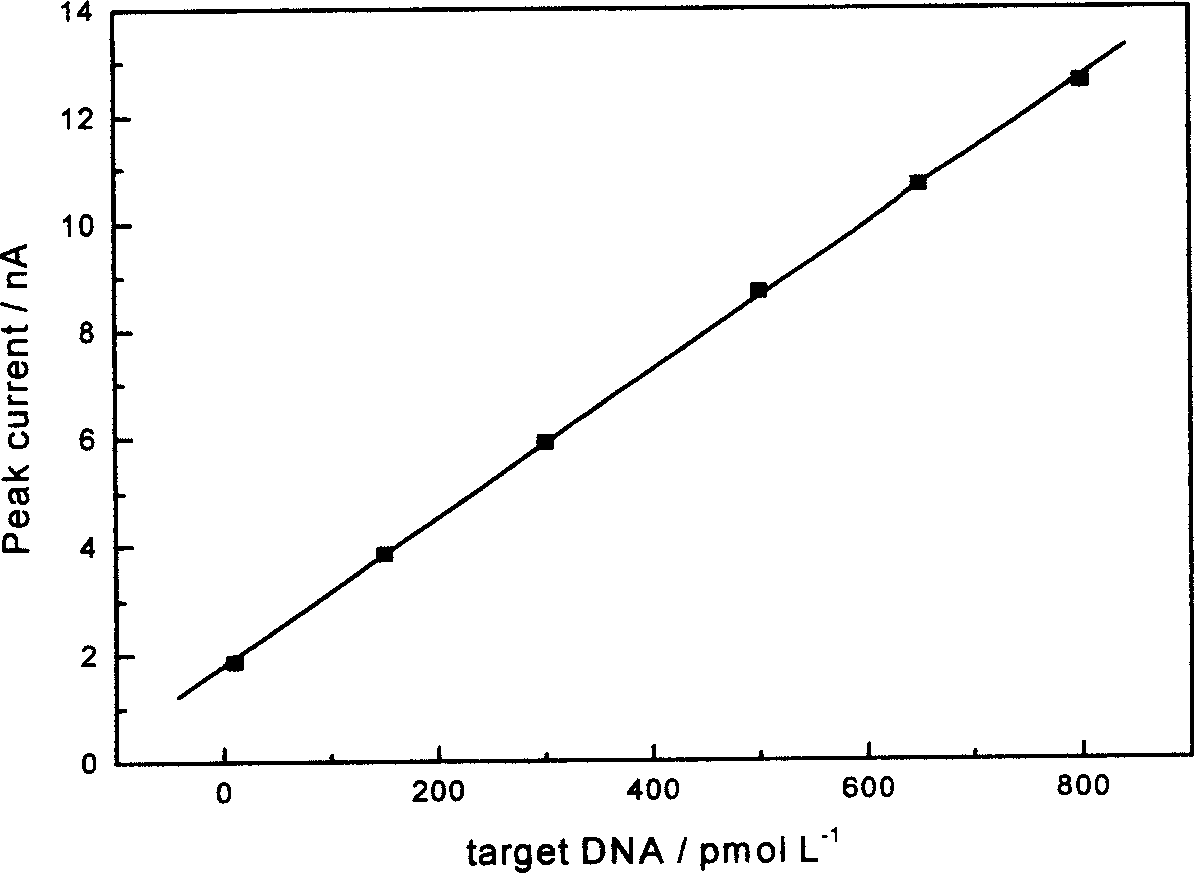
The invention belongs to a method of preparing deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) electrochemical nano sensor. It fixes the nano gold crystal on the surface of the gold electrode, uses the property that nano gold crystal and mercapto functional group containing DNA can interact to fix sequence- known target single-string DNA (ssDNA) on the surface of the gold electrode. The nano silver crystal labeled compensatory DNA and the target ssDNA make cross reaction. In an acidic medium, oxidize and release the nano silver crystal to make the nano silver crystal exist in the solution in an ion state. It detects the quantity of silver ions by electrochemical method, thus detecting that of the target DNA. The sensor has very strong selectivity and very high sensitivity.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
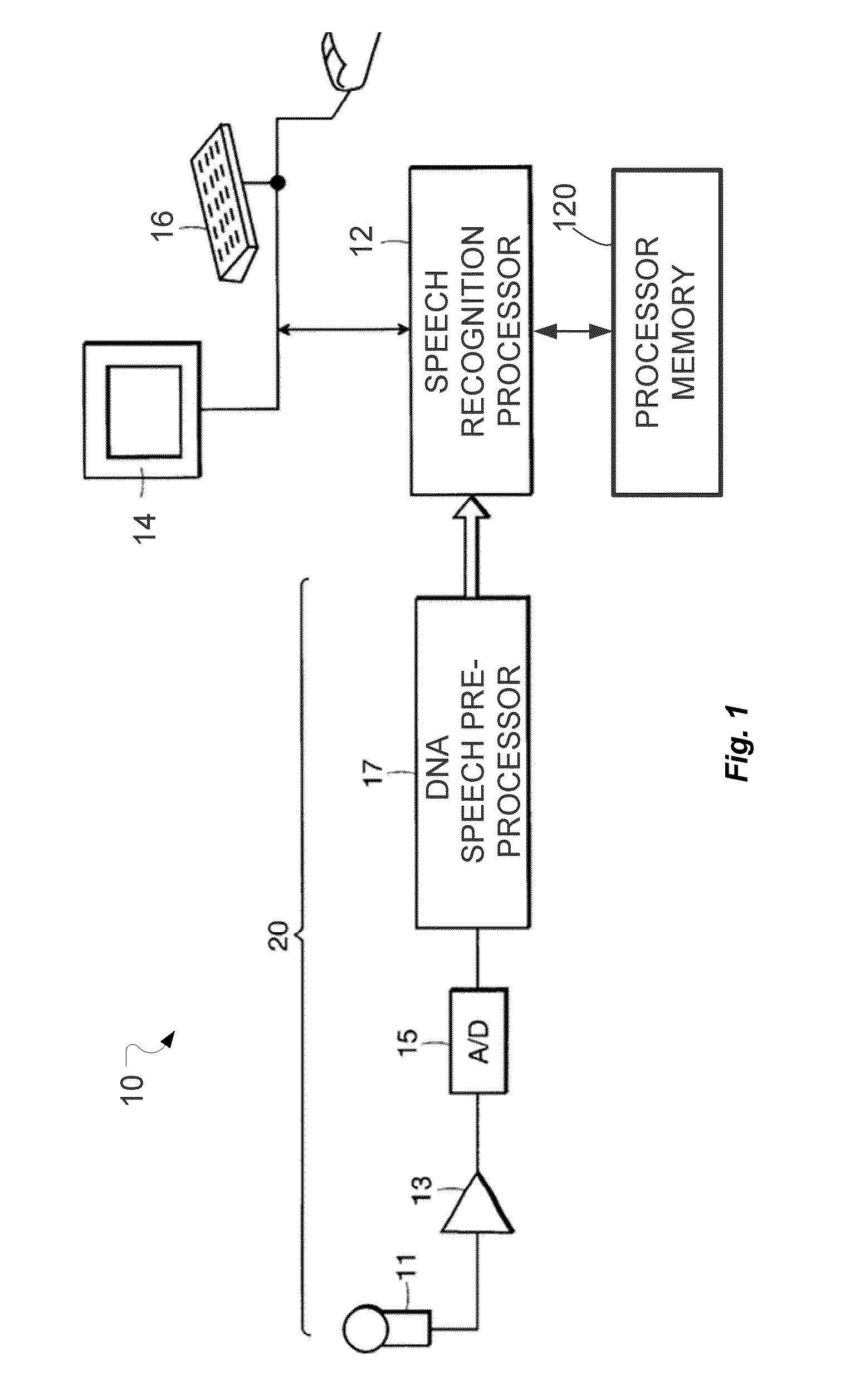
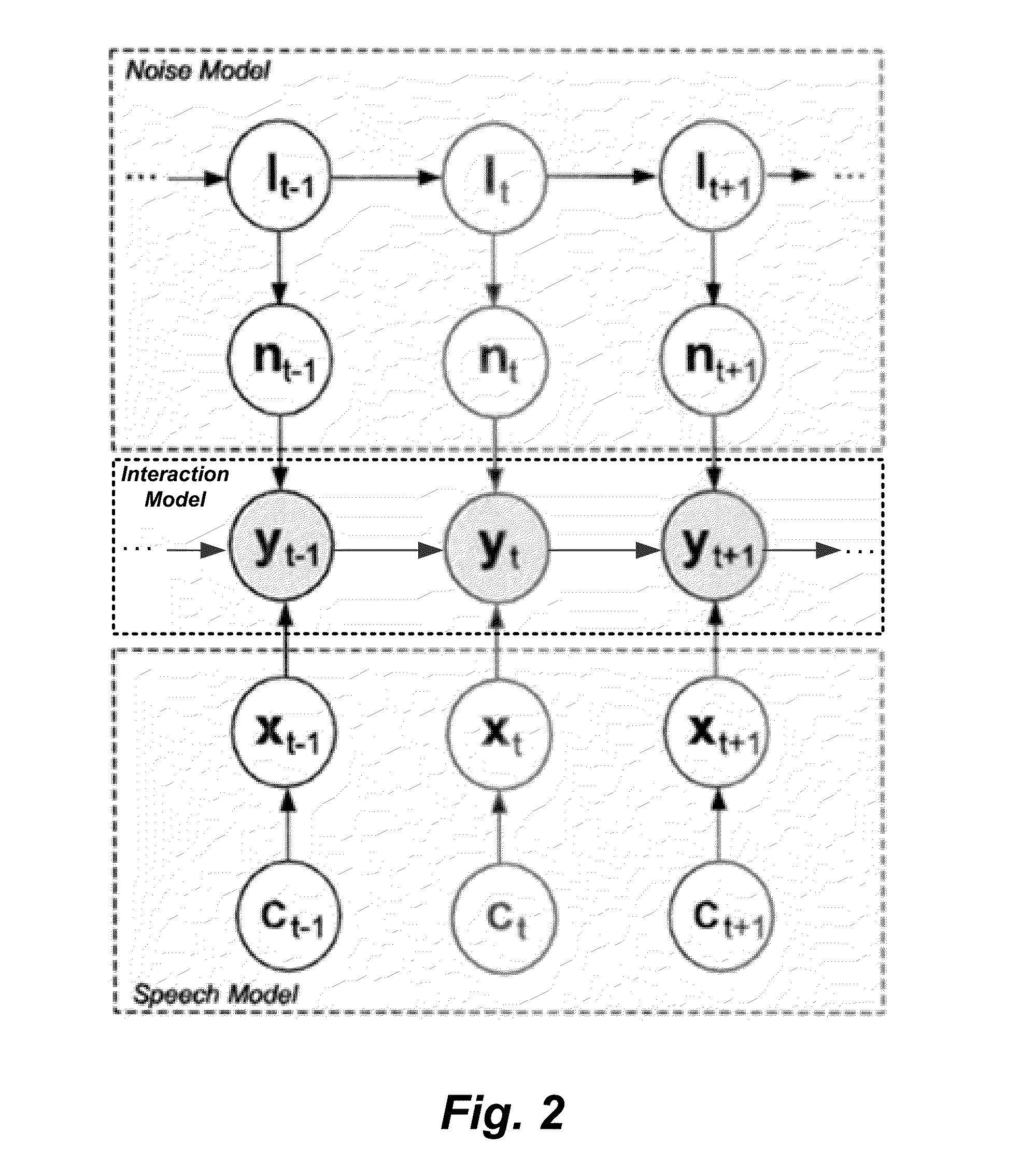
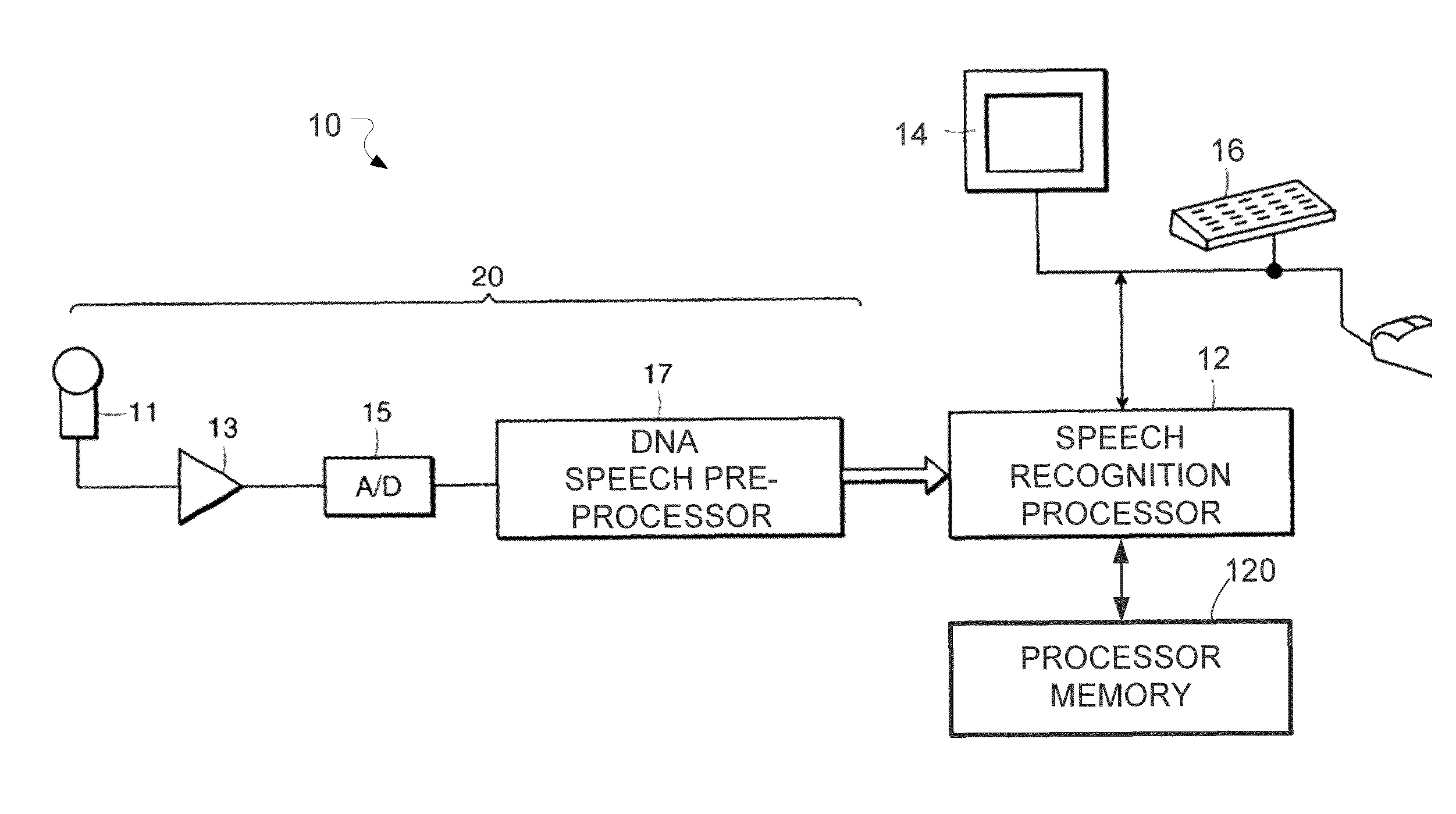
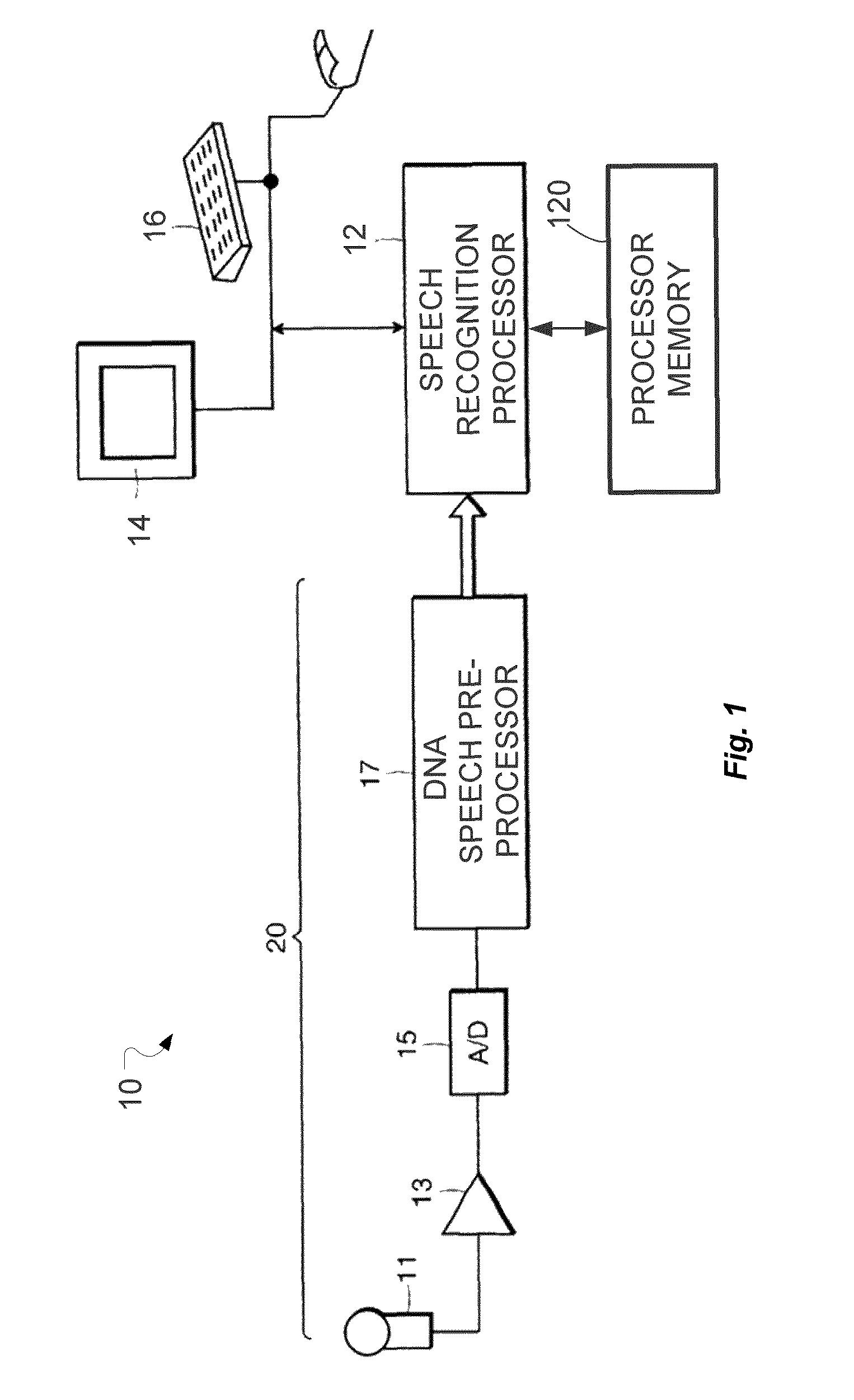
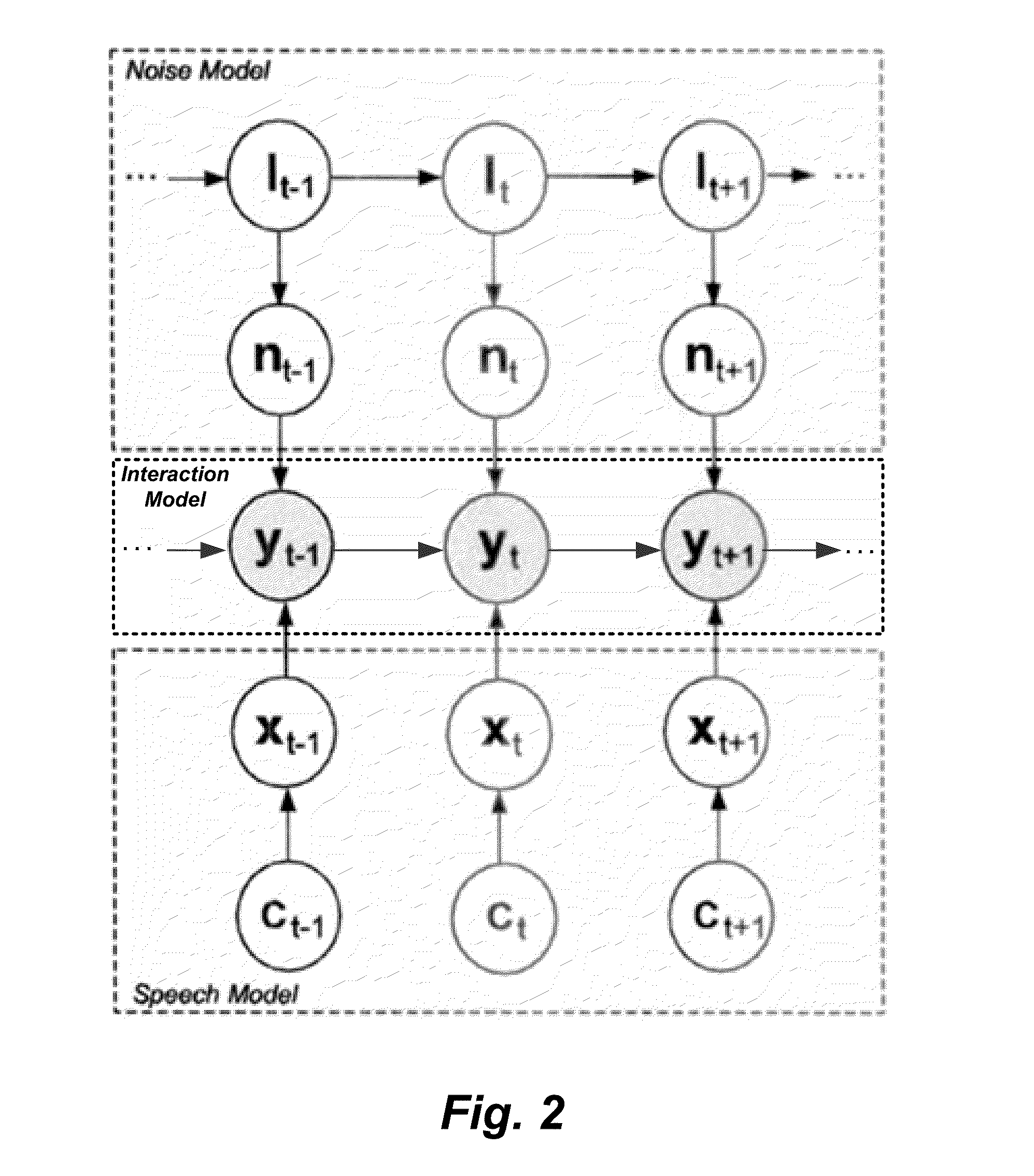
System and Method for Dynamic Noise Adaptation for Robust Automatic Speech Recognition
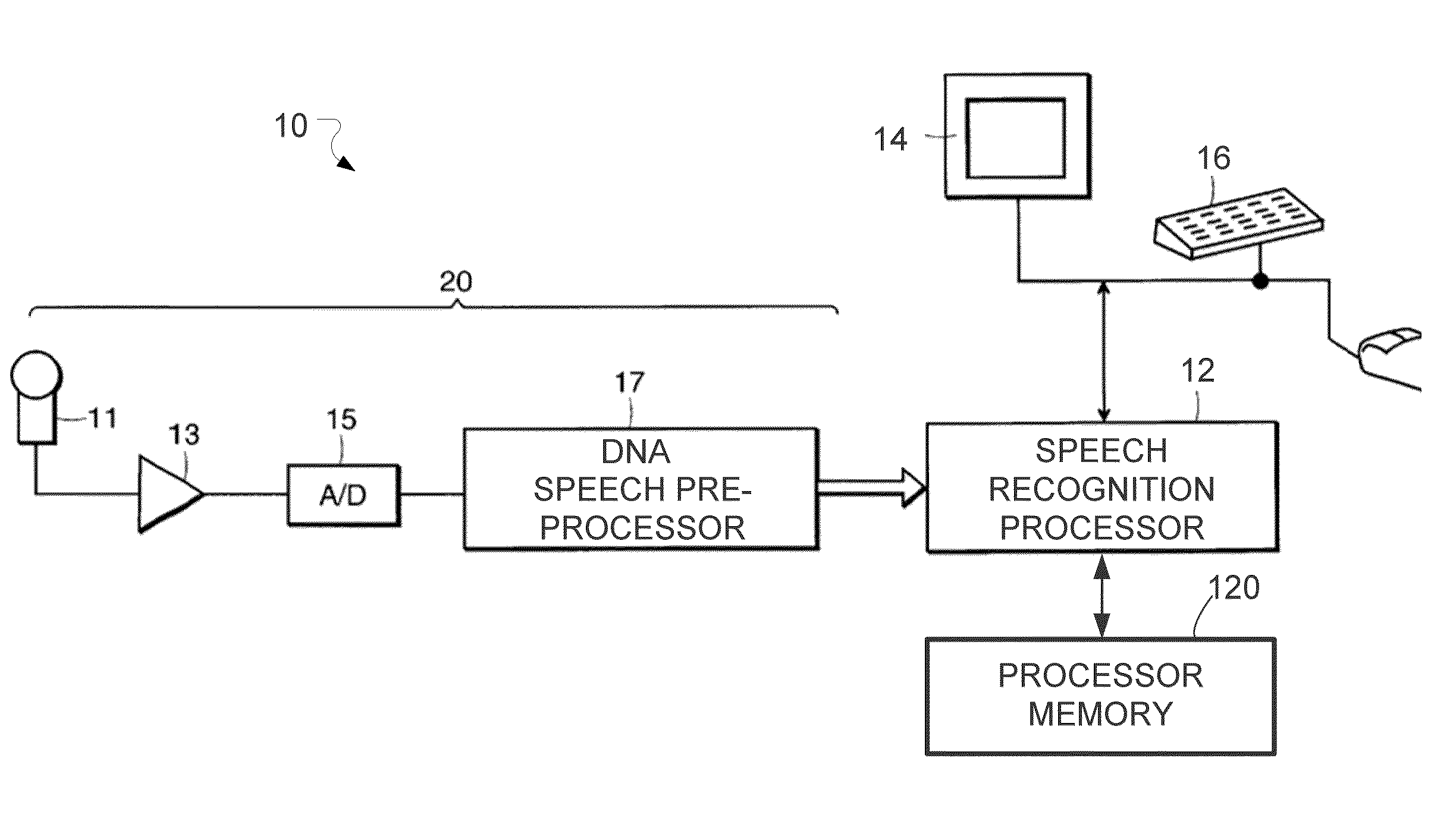
A speech processing method and arrangement are described. A dynamic noise adaptation (DNA) model characterizes a speech input reflecting effects of background noise. A null noise DNA model characterizes the speech input based on reflecting a null noise mismatch condition. A DNA interaction model performs Bayesian model selection and re-weighting of the DNA model and the null noise DNA model to realize a modified DNA model characterizing the speech input for automatic speech recognition and compensating for noise to a varying degree depending on relative probabilities of the DNA model and the null noise DNA model.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
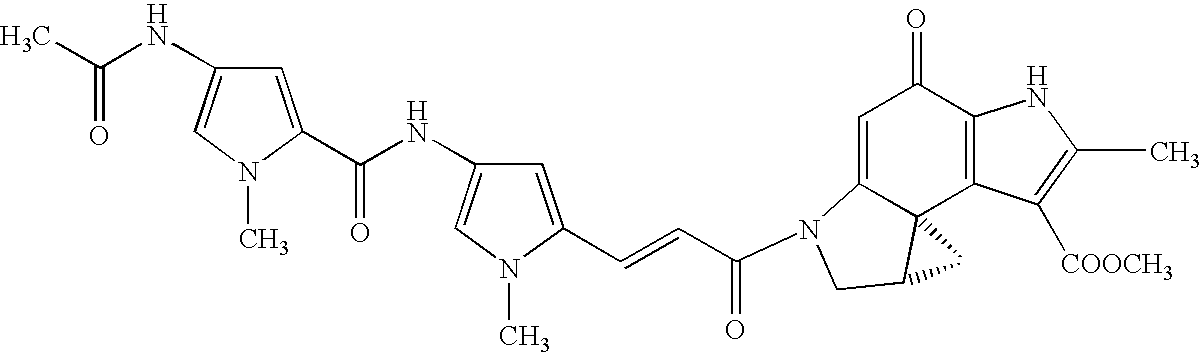
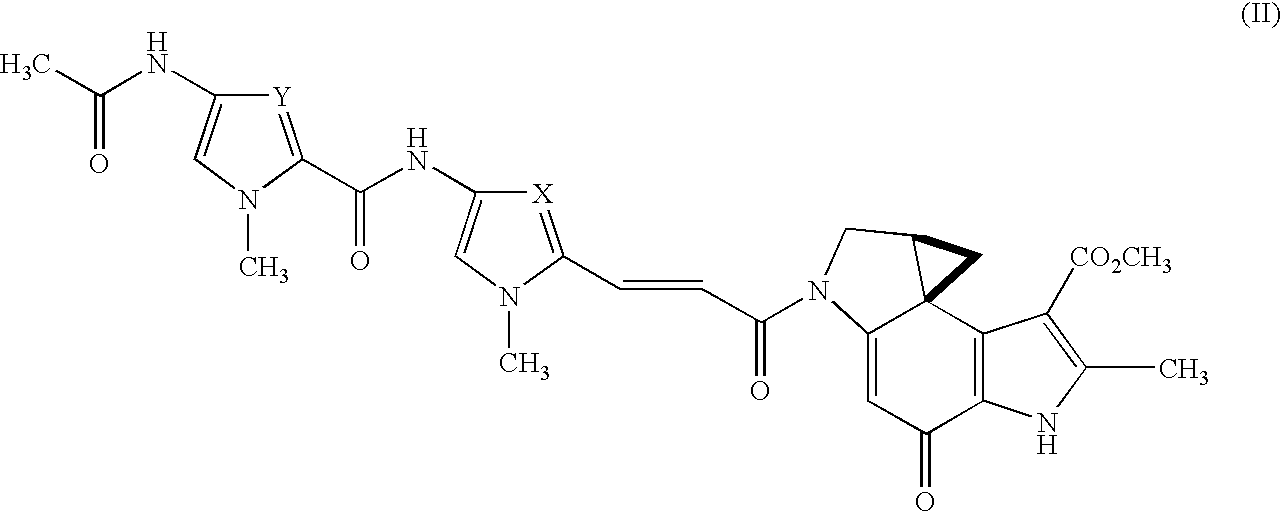
7-fluoro-substituted Isaindigotone derivatives and preparation method thereof, and application of 7-fluoro-substituted Isaindigotone derivatives in preparing anticancer drugs
ActiveCN106220631APrevent proliferationBroad anti-tumor effectOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsProtein targetDna interaction
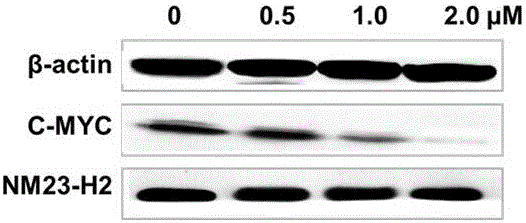
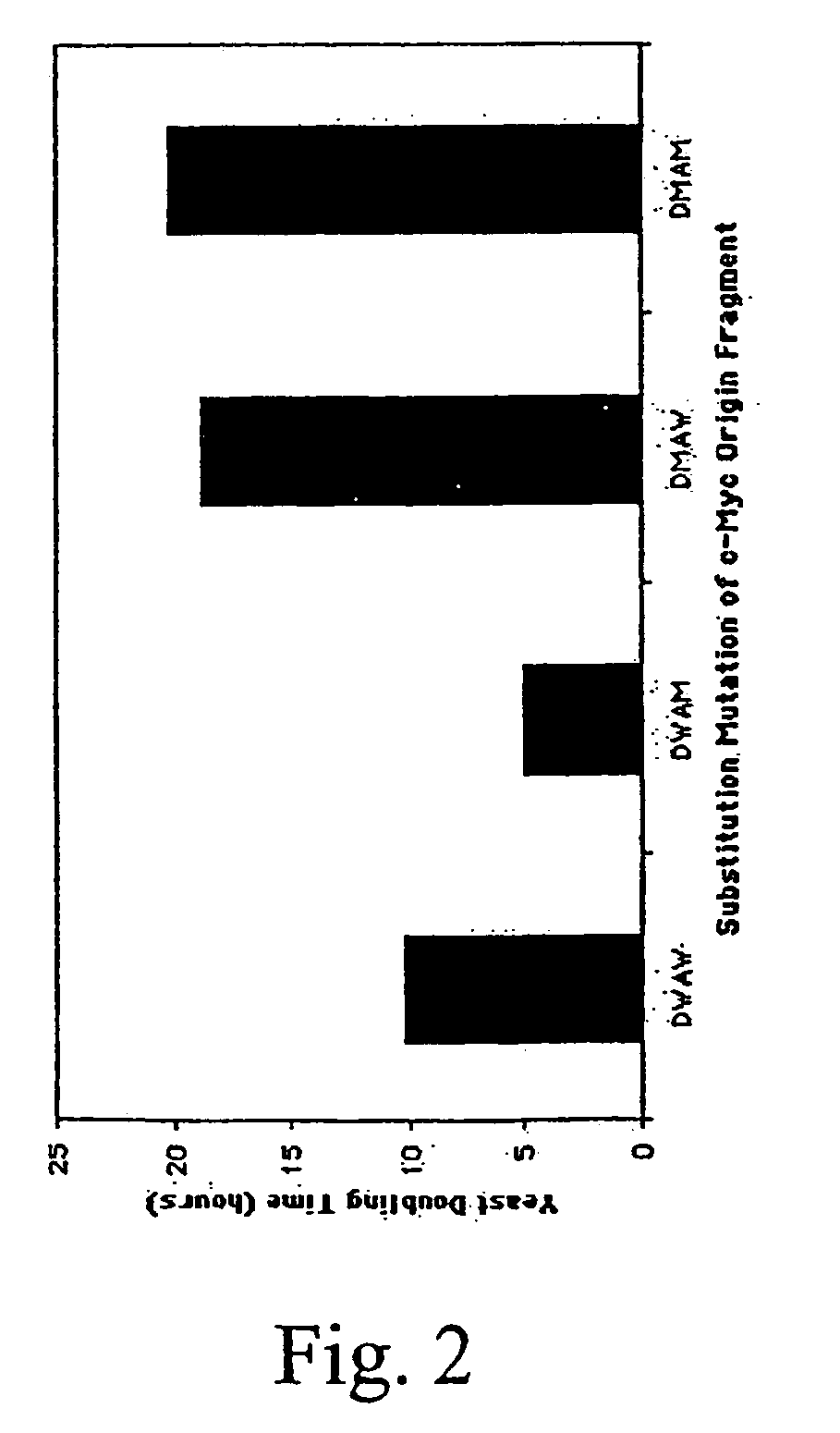
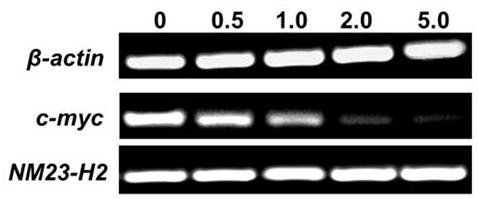
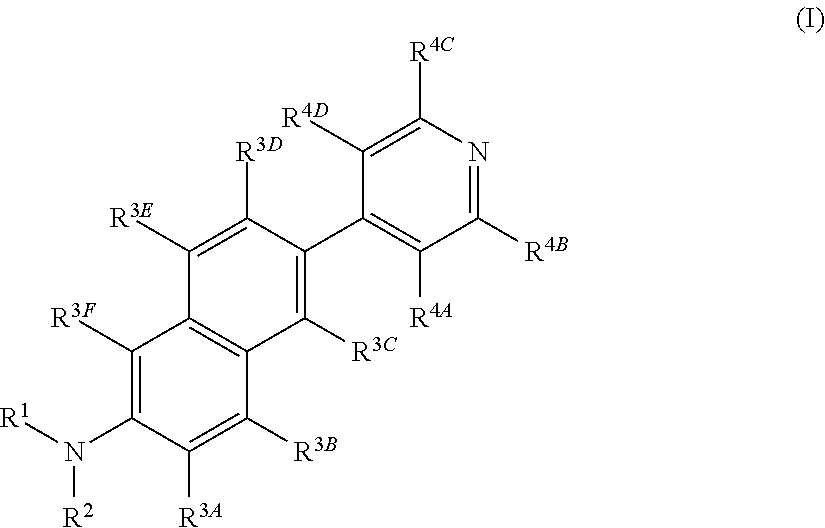
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, and particularly discloses 7-fluoro-substituted Isaindigotone derivatives. The structural formula of the derivatives is disclosed as Formula (I) or Formula (II), wherein X is C or N; R1 is hydrogen, amino, substituted amino, orpenta- or hexa-heterocyclic radical; R2 is hydrogen, hydroxy, amino, C1-C8 alkyl, or C1-C8 alkoxy or halo; R3, R5 and R6 are defined the same as R2; and R4 is hydrogen, hydroxy, amino, phenyl, C1-C8 cycloalkyl, C1-C8 alkyl, C1-C8 alkoxy, C1-C6 alkyl acyloxy, C1-C6 alkynyl, halo, or penta- or hexa-heterocyclic radical. The fluoro-substituted Isaindigotone derivatives can bebondedwith NM23-H2 protein and block the interaction between the NM23-H2 protein and c-myc G-quadruplex DNA, thereby causing the reduction of protooncogene c-myc transcription and translation, and inhibiting the proliferation of multiple tumor cell strains. The fluoro-substituted Isaindigotone derivatives have wide antitumor effects. The fluoro-substituted Isaindigotone derivatives are a novel NM23-H2-protein-targeted transcription regulation blocker, and have wide application space in preparing anticancer drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for isolating specific genomic regions
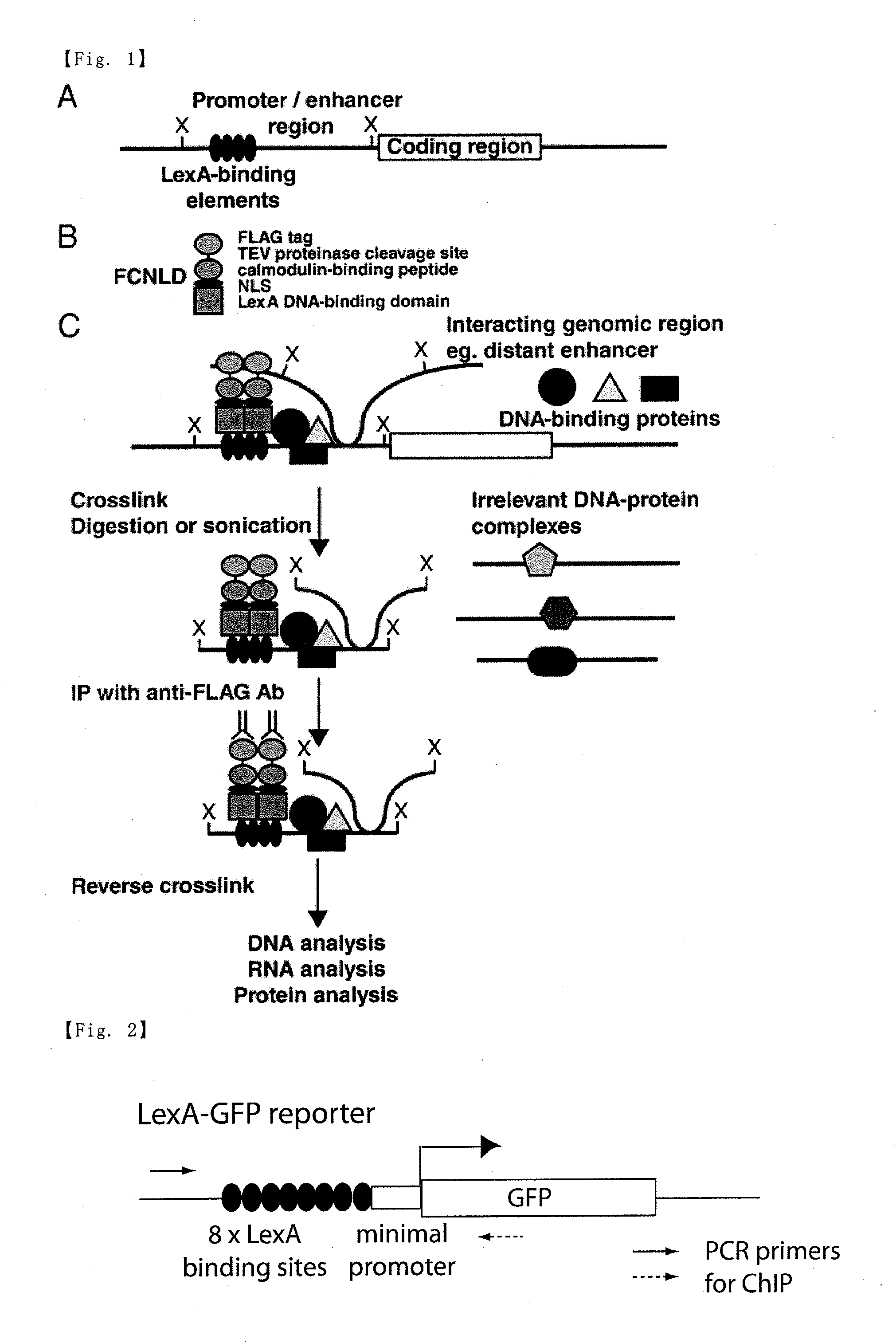
Provided is a method for specifically isolating any genomic region while maintaining interaction of the genomic region with its interacting molecule(s). According to the method comprising the following steps 1 to 5:Step 1:preparing a cell in which a DNA fragment having a recognition sequence(s) for an exogenous DNA-binding molecule is inserted in genomic DNA of a genomic region to be isolated;Step 2:bringing genomic DNA of the cell into contact with an exogenous molecule at least having a DNA-binding domain of the exogenous DNA-binding molecule;Step 3:performing a treatment for maintaining interaction of the genomic DNA of the cell with a molecule(s) interacting with the genomic DNA;Step 4:performing a treatment for fragmenting the genomic DNA; andStep 5:allowing a complex to be formed by binding of a molecule capable of specifically binding to the exogenous molecule, and then collecting the complex,specific genomic regions can be specifically isolated while kept interacting with their interacting molecules.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
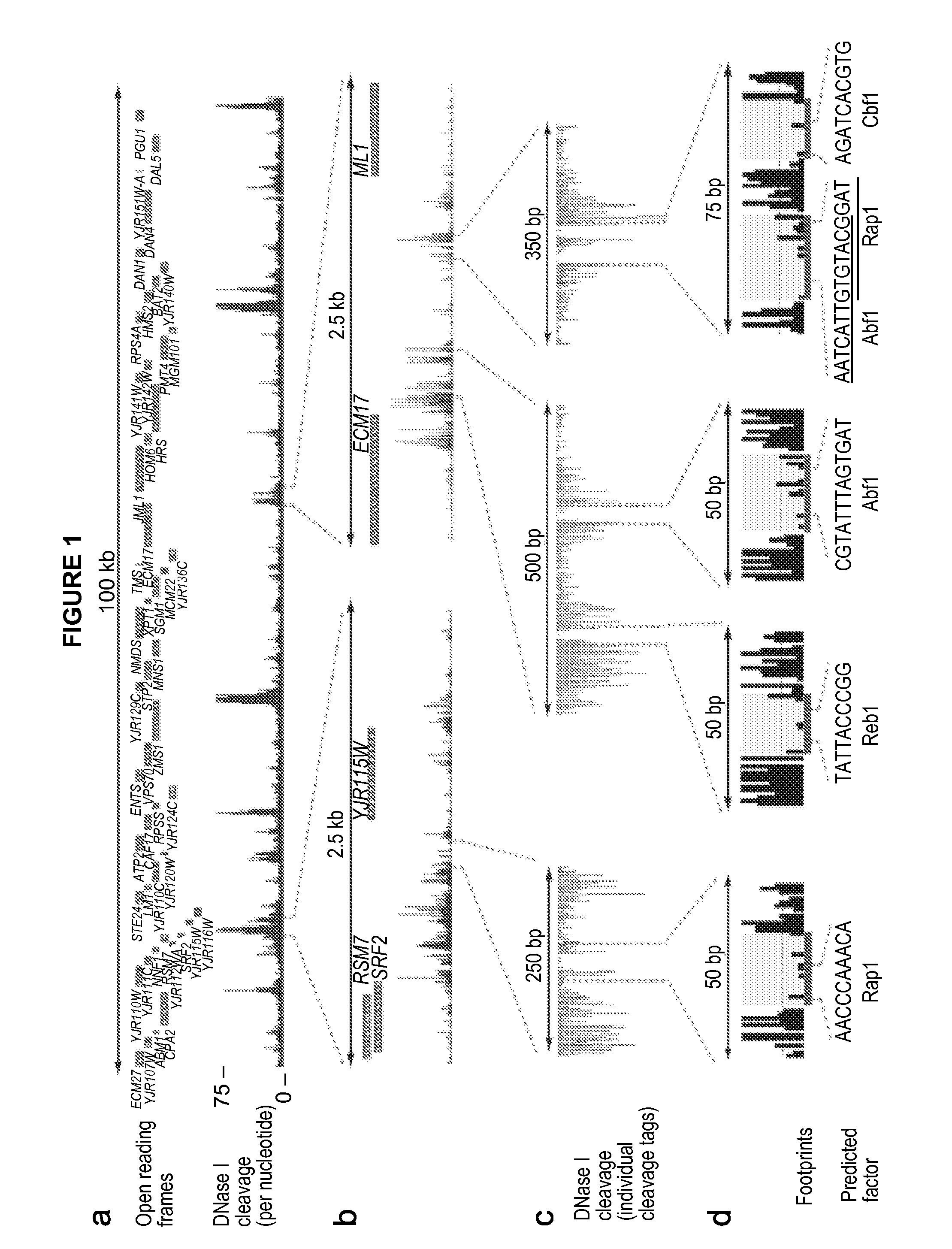
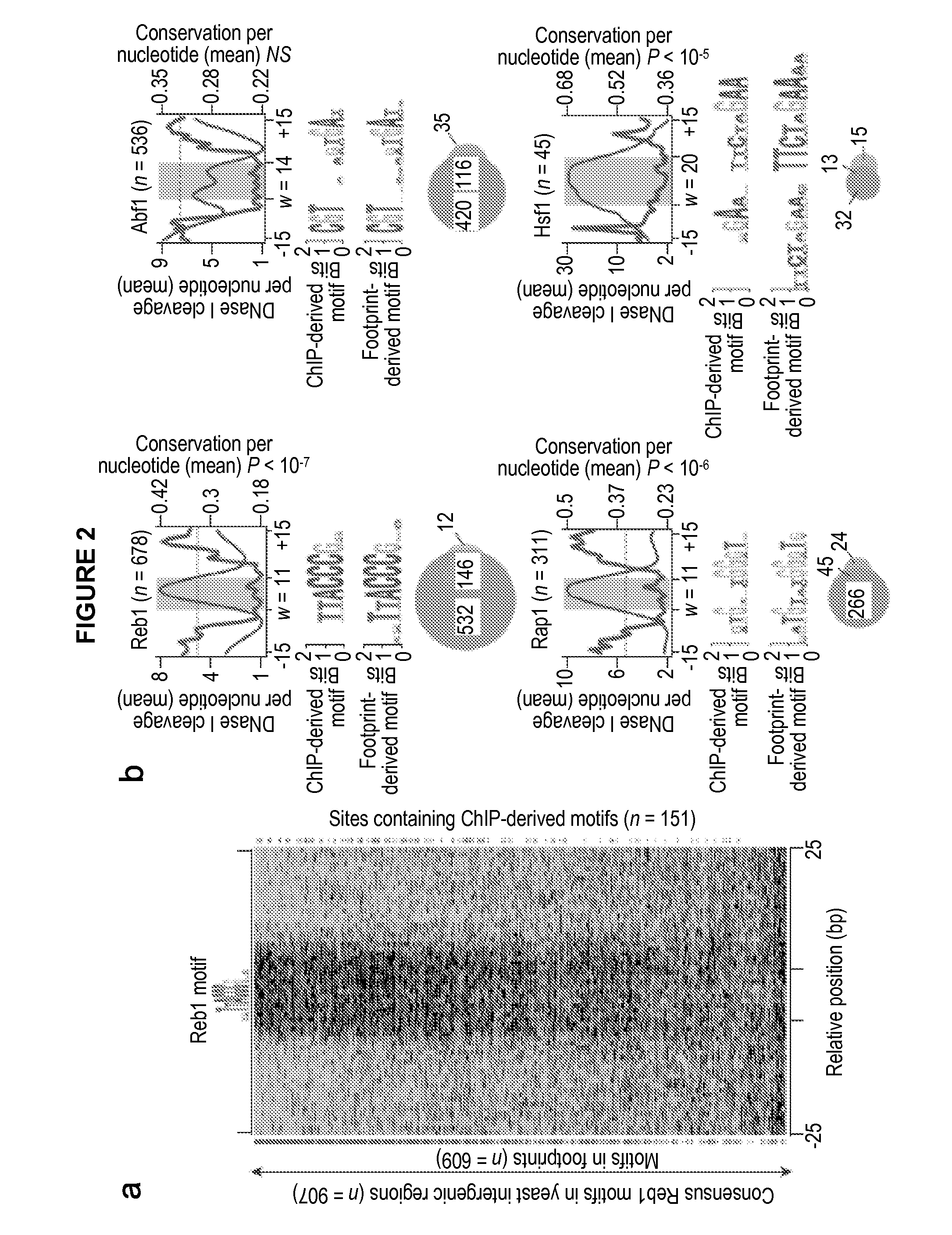
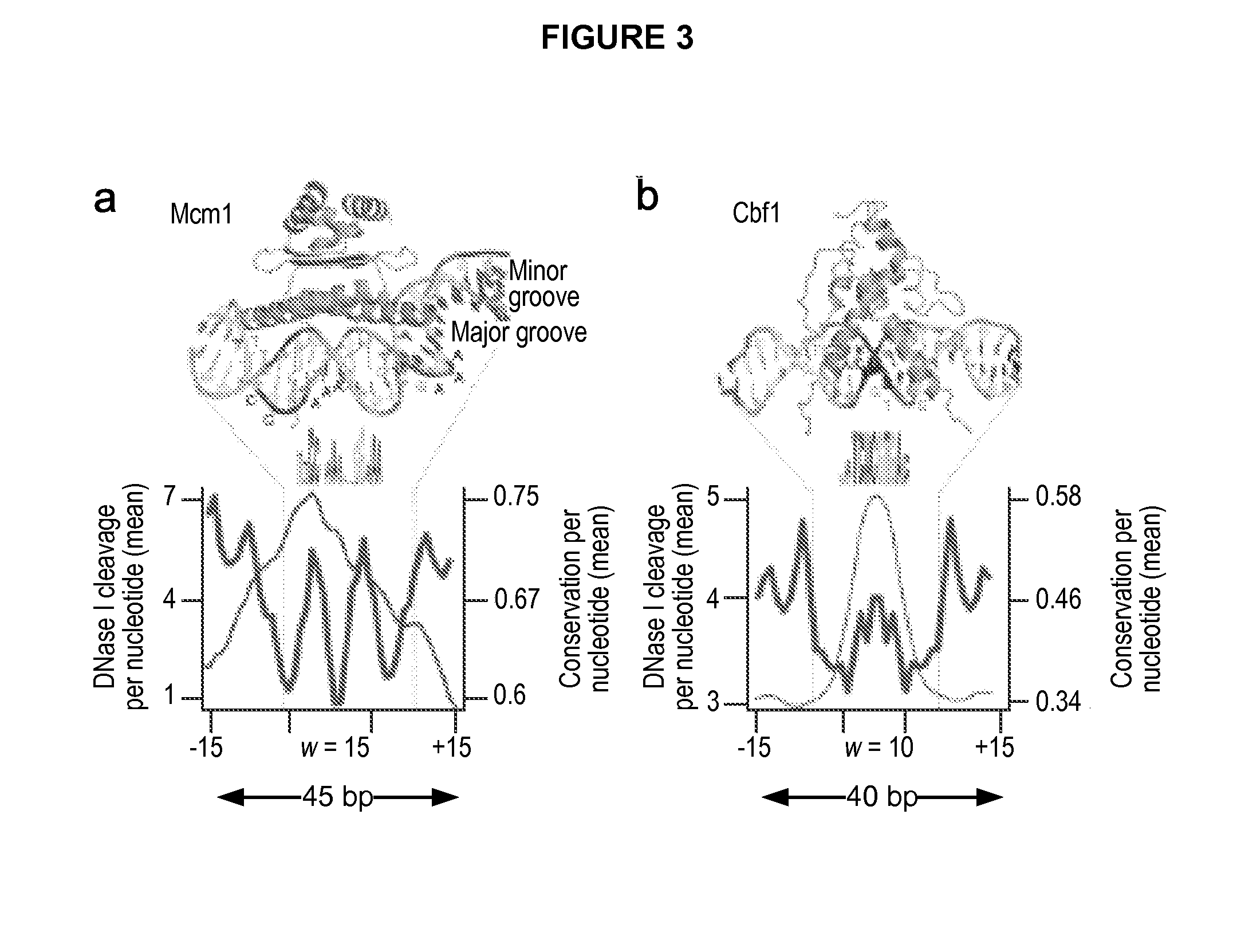
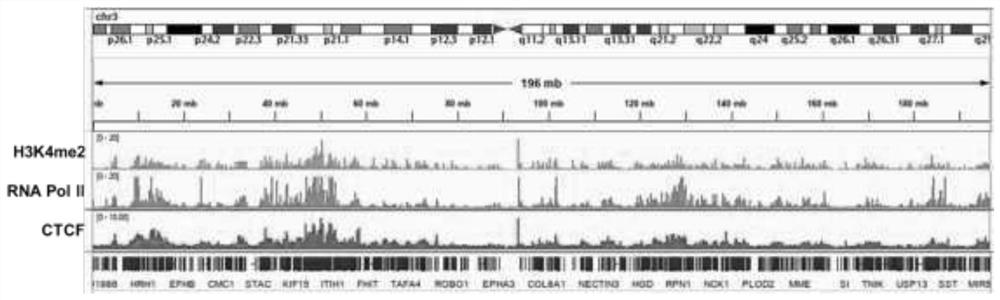
Global mapping of protein-dna interaction by digital genomic footprinting
The present invention provides a method for globally mapping a genome for its protein-binding pattern. A computer system useful for this purpose is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
System and method for dynamic noise adaptation for robust automatic speech recognition
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Research method and tool for multi-target protein-DNA interaction
The invention provides a targeting transposon complex with an oligonucleotide tag and application of the targeting transposon complex to research of interaction of multiple-target molecule-DNA.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
Method for determining transcriptional control complex
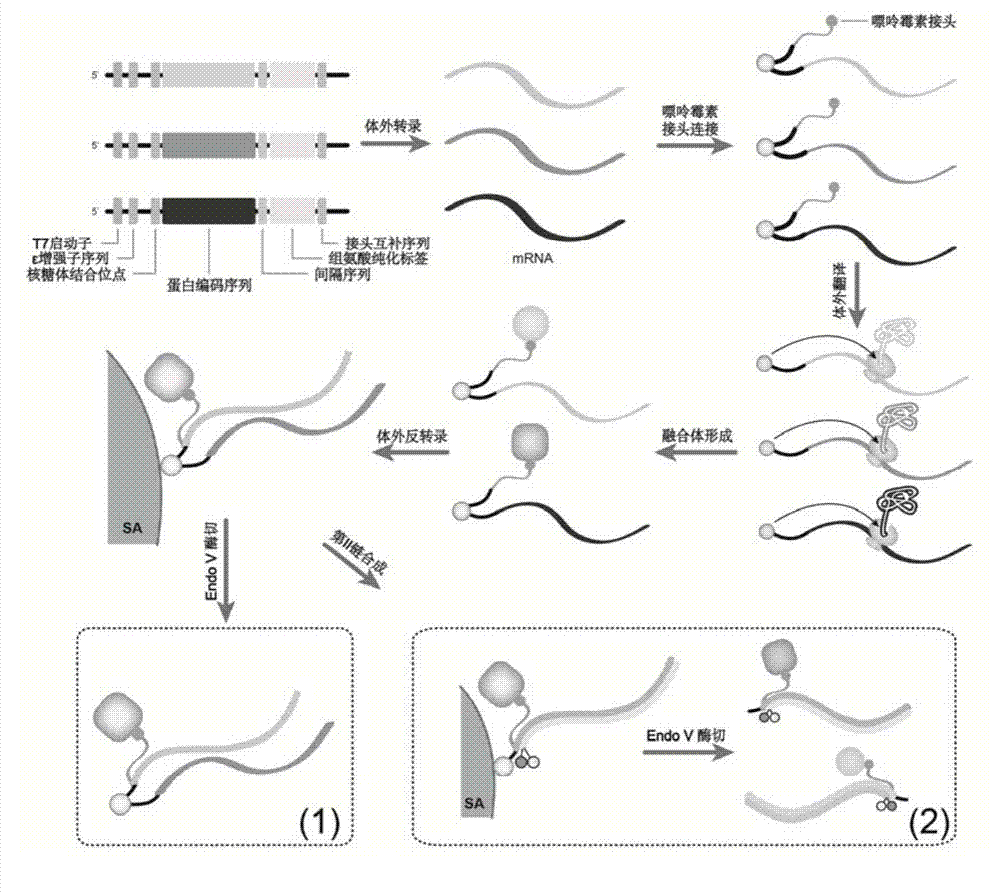
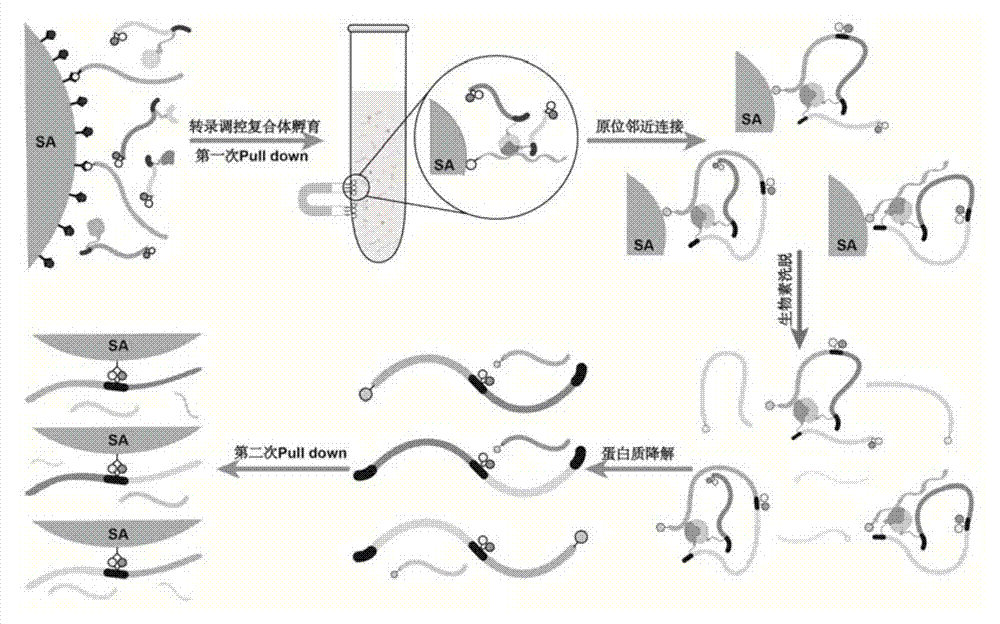
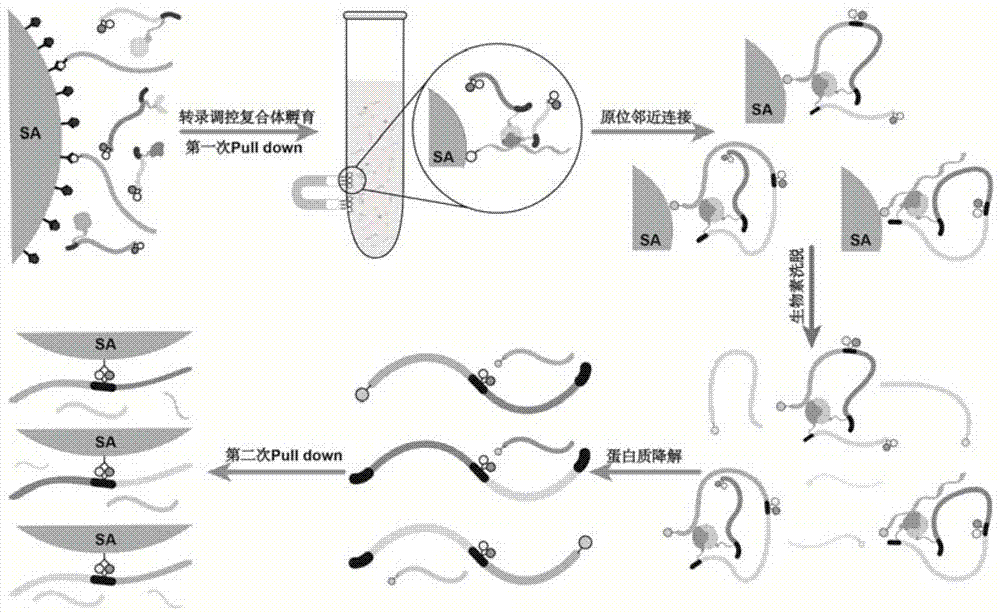
ActiveCN104774923AIncrease library capacityMitigate incompatibilitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementDna interactionProtein–DNA interaction
The invention relates to a method for determining a transcriptional control complex, and belongs to the field of molecular biology. The method for determining the transcriptional control complex includes the following steps: preparation of a bait DNA sequence, preparation of a DNA sequence for encoding a bar code protein, construction of a bar code protein library, screening of the transcriptional control complex, and in situ adjacent connection capture of the transcriptional control complex, and the identification of the transcriptional control complex. The invention combines cDNA display technology and the adjacent connection technology to establish a novel method for determining the transcriptional control complex; the determination of transcriptional control complex involves simultaneous determination of a variety of interaction effects of protein-protein and protein-DNA; and the method can realize simultaneous determination of a variety of interaction effects of protein-protein and protein-DNA in a same experimental system, and effectively solve the incompatibility of the determination methods for the protein-protein interaction and protein-DNA interaction in the same experimental system in the prior art.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
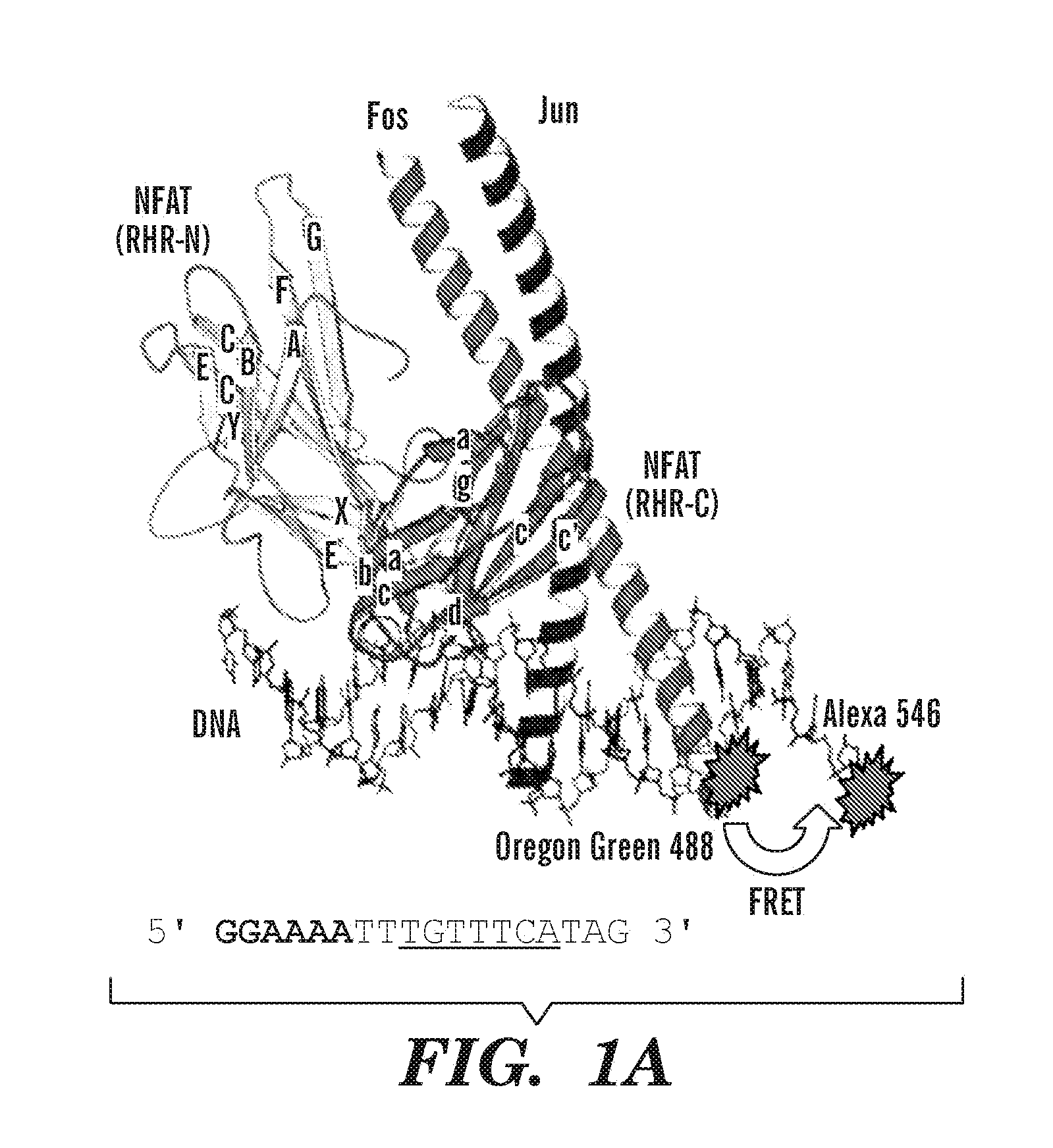
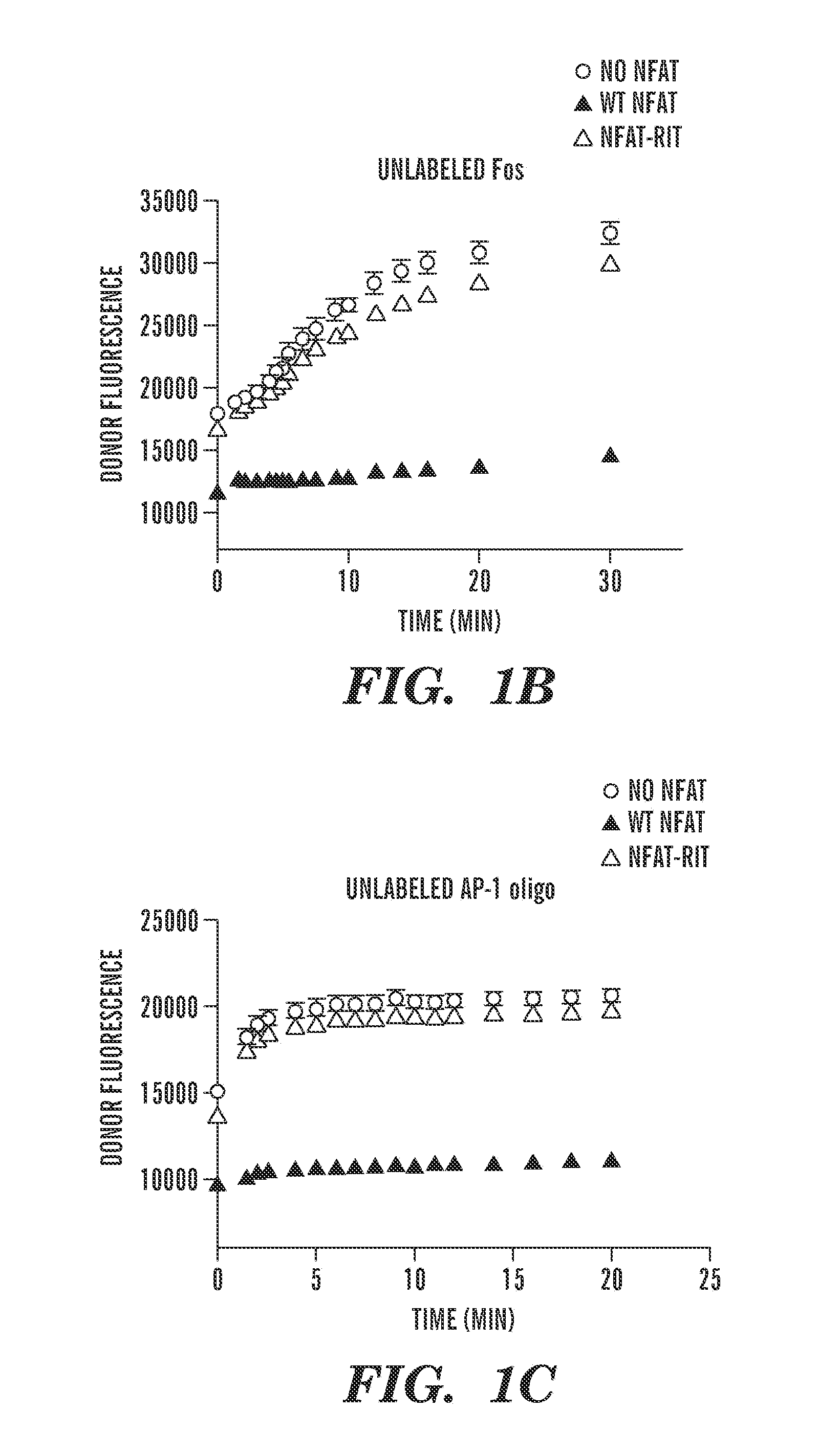
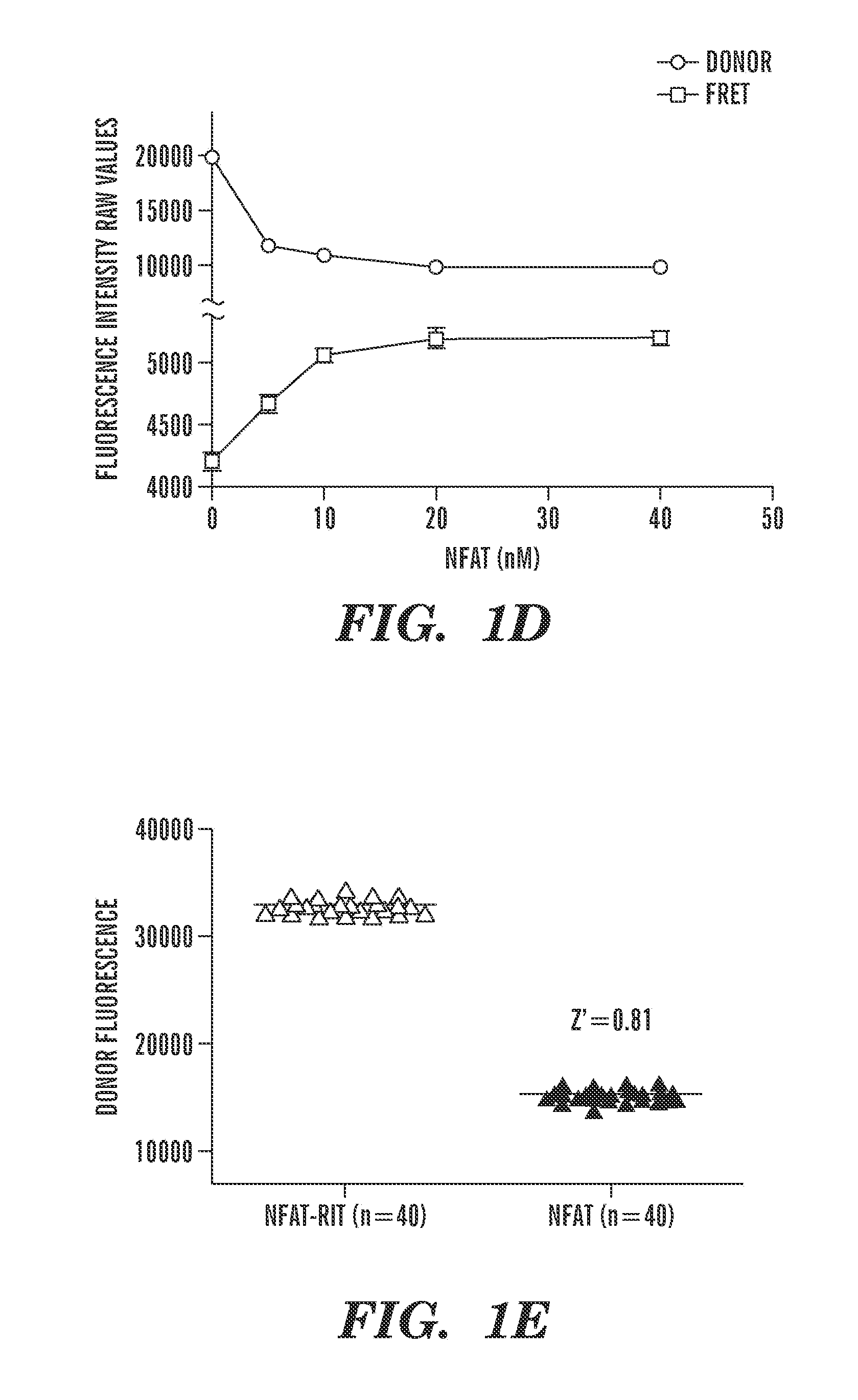
Small molecule screen for inhibitors of nfat: ap-1: DNA interactions
The invention provides a screening assay for selecting inhibitors of NFAT:Transcription factor interactions. The invention also provides compositions and methods for inhibiting immune response in a subject.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Compositions and methods comprising the use of cell surface displayed homing endonucleases
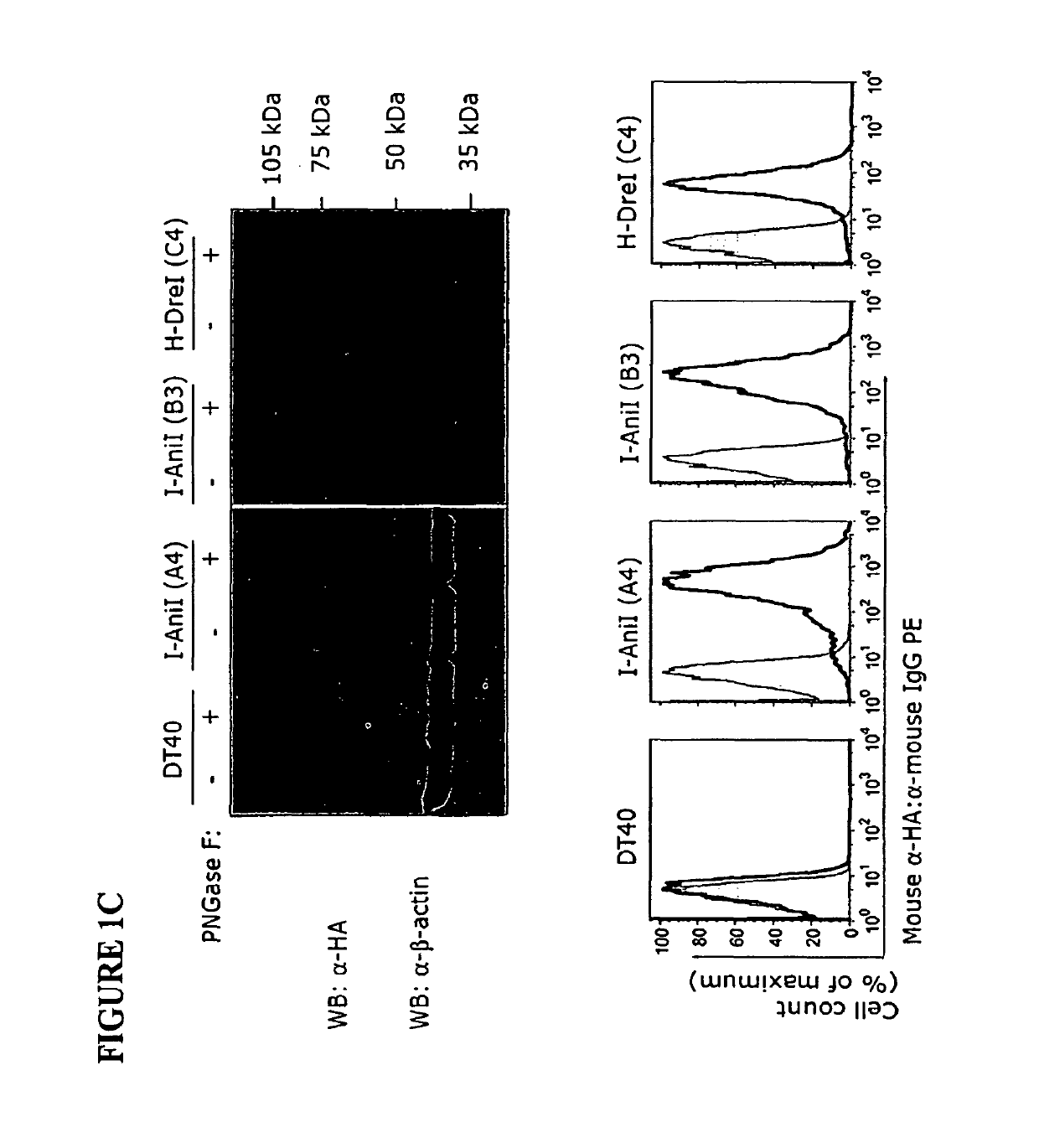
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Method for testing hormonal effects of substances
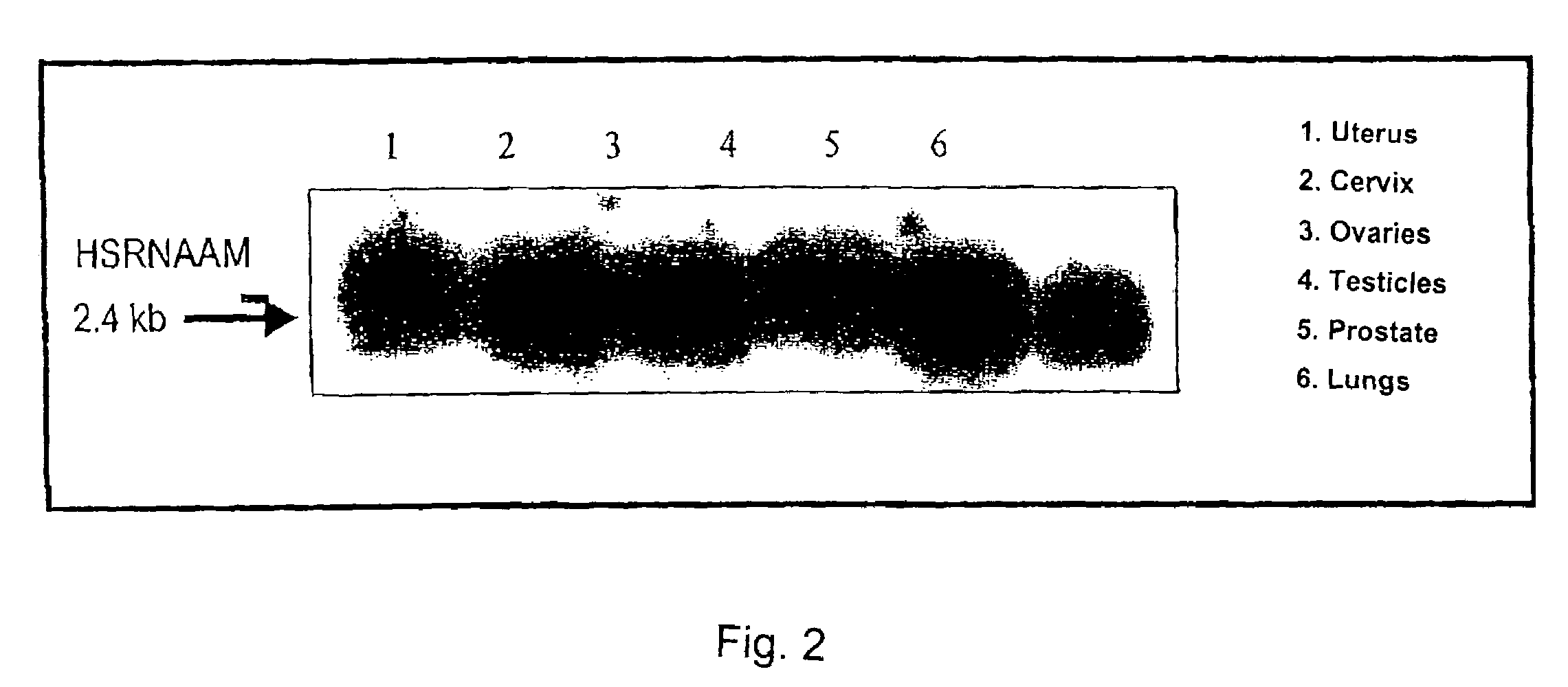
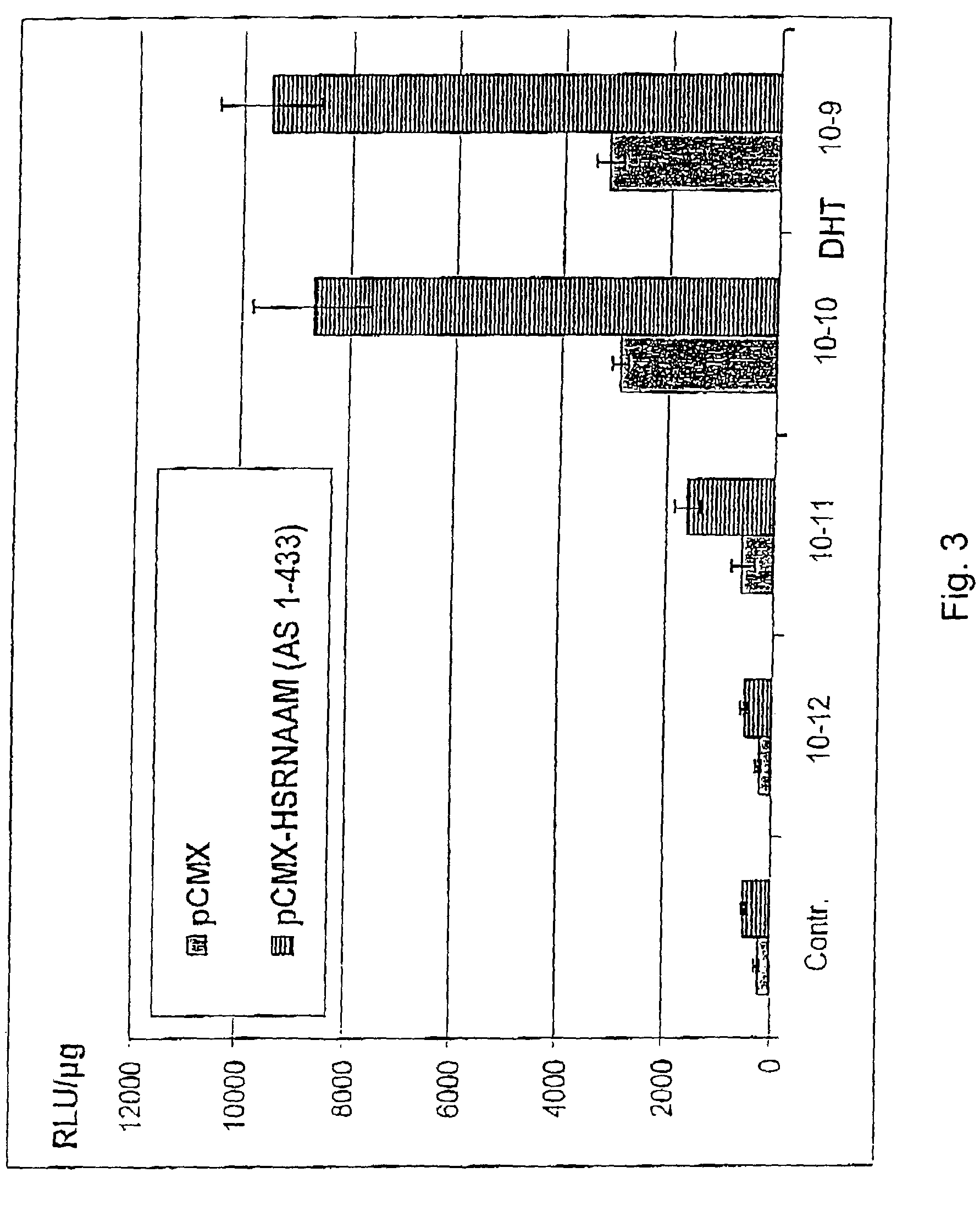
InactiveUS7074566B2Reduce HSRNAAM titerHigh potencyMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyTwo-vectorAnti-Androgen Effect
The method for testing of substances for hormonal effects, especially for androgenic or anti-androgenic effects, includes exposing cells transfected with two vectors to the substances, wherein one vector contains a DNA, which codes for a nuclear receptor protein, or a fragment thereof, especially a human nuclear receptor protein, or a fragment thereof, and the other vector contains a DNA, which codes for the HSRNAAM co-modulator, or a fragment thereof; and measuring transcription activity, which the nuclear receptor protein, or its fragment, activates or releases in the presence of the HSRNAAM co-modulator, or its fragment, and / or measuring the influence of the substance on the interaction between the nuclear receptor protein, or its fragment, and the HSRNAAM co-modulator, or its fragment, by protein-protein interaction or by protein-protein-DNA interaction. Also a method for determining interference in the co-modulation mechanism between androgen receptor protein and HSRNAAM co-modulator is described.
Owner:SCHERING AG
Compositions and methods comprising the use of cell surface displayed homing endonucleases
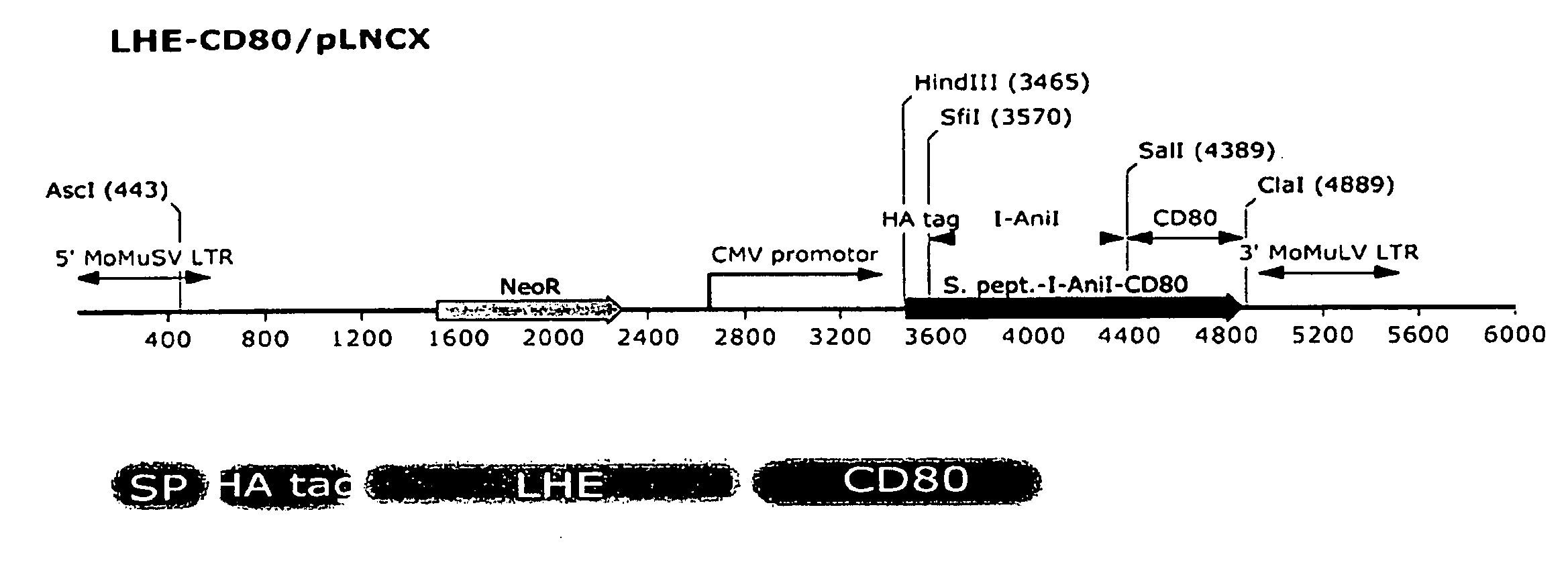
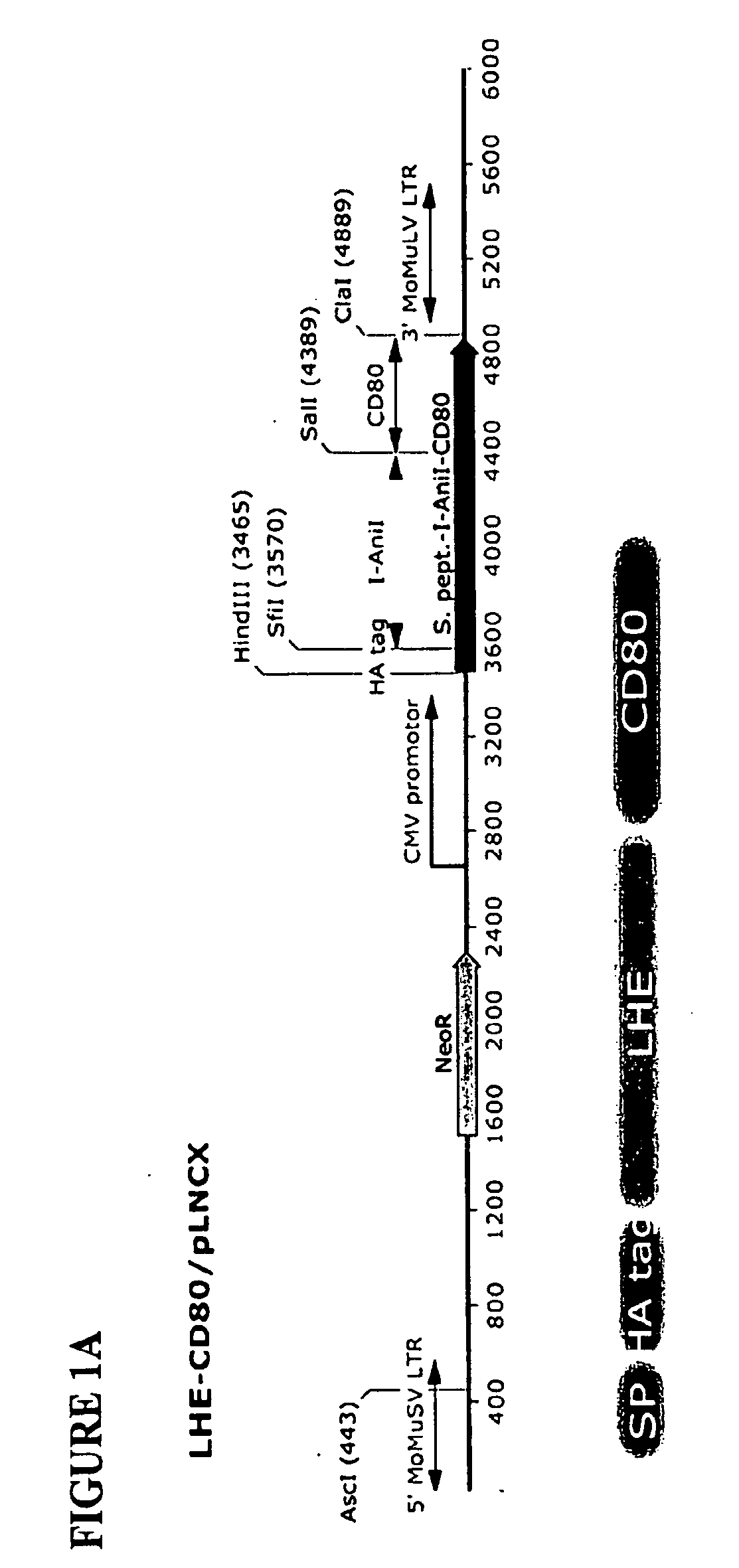
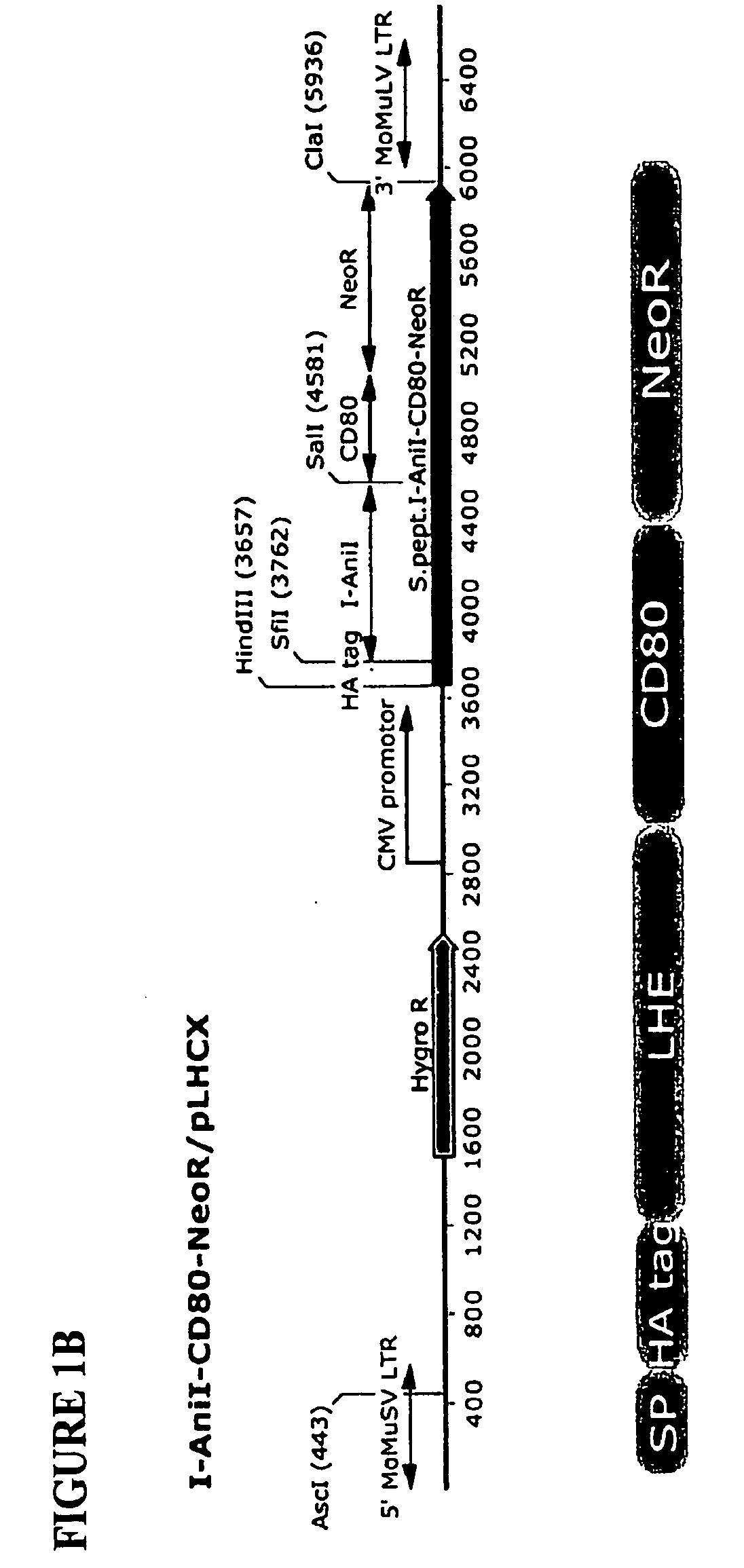
According to particular exemplary aspects, DNA target site binding and cleavage properties of native, variant or modified homing endonucleases (HE) (e.g., LAGLIDAG (LHE), HNH, His-Cys Box, GIY-YIG, I-SspI-type, and fusions, muteins or variants thereof) in solution are recapitulated on the cell surface (e.g., as assessed by flow cytometric analysis) to provide for novel cells expressing one or more cell surface HEs (e.g., expressing one or more HE binding and / or cleavage specificities), novel cell libraries, and high-throughput methods for assessing target site binding, target site cleavage. The rapid analysis of HE and LHE-DNA interactions on the cell surface with concurrent sorting options provides for high-throughput library screening affording rapid identification, analysis and isolation of novel HEs or LHEs having novel sequence specificities. Such novel sequence specificities, obtained by said methods provide novel methods for introducing targeted DNA-strand cleavage events, and novel chromatin immunoprecipitation methods (CHIP methods).
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
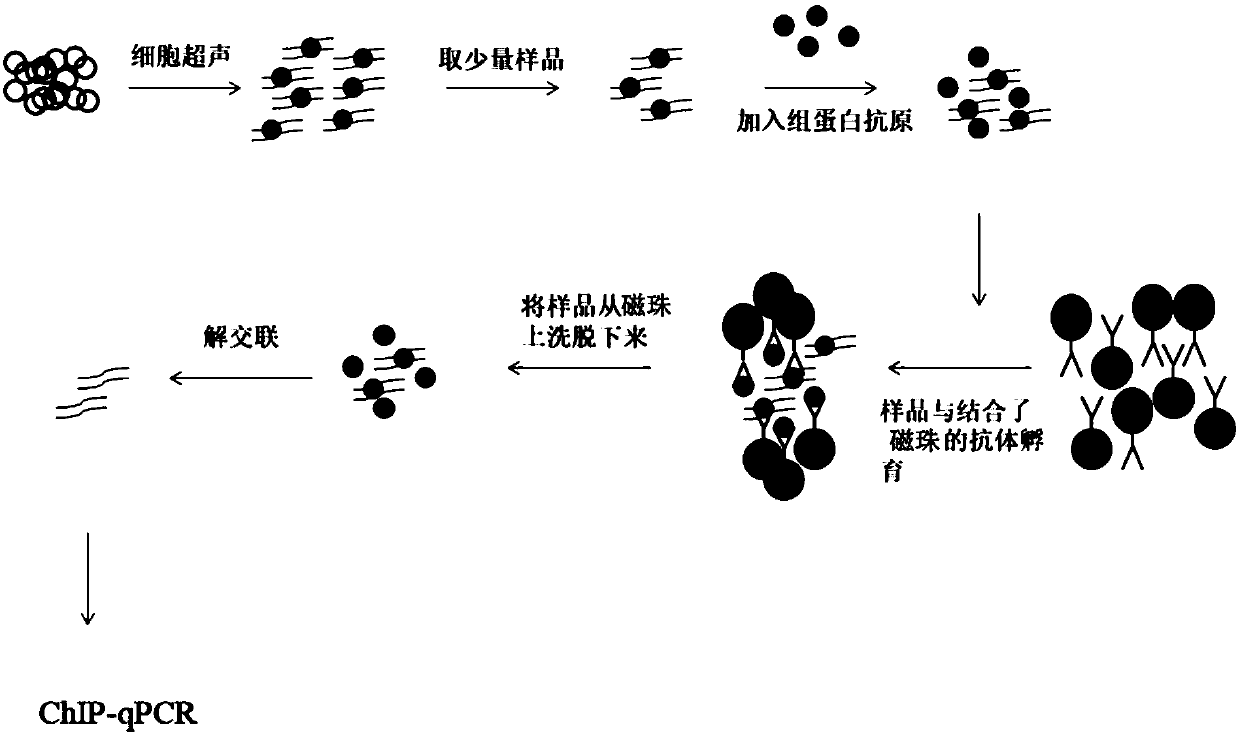
Kit and method for detecting interaction between proteins and DNA, and applications of kit and mehod
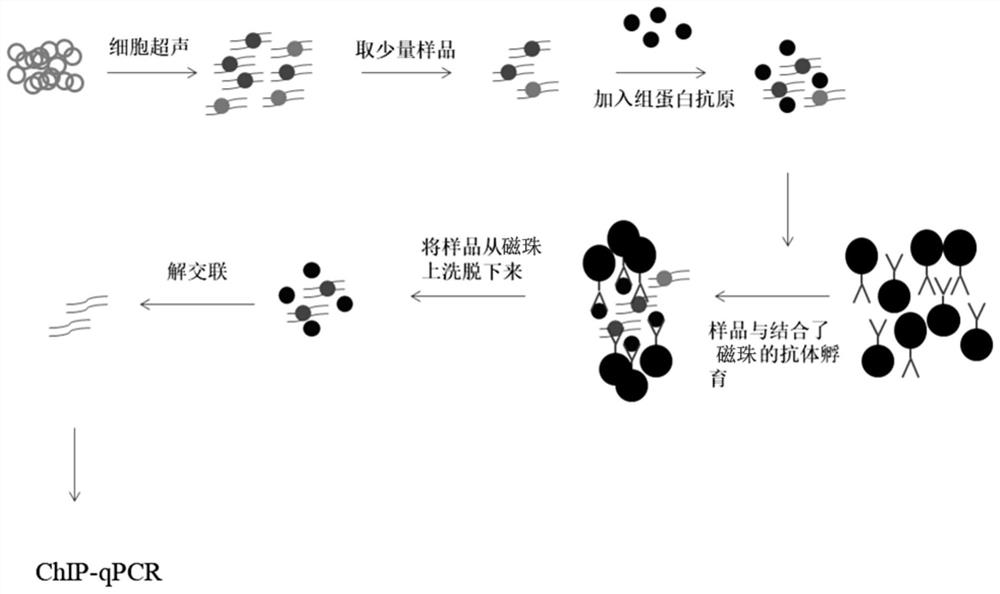
ActiveCN108680757AReduce lossesImprove the efficiency of immunoprecipitation reactionsBiological testingDNA preparationAntigenHistone antigen
The invention discloses a kit for detecting the interaction between proteins and DNA, wherein the kit at least includes an exogenous histone antigen. The invention also discloses an application of thekit in detecting the interaction between a small number of proteins and the DNA, and the required sample amount can be as low as 1000 cells. The invention also discloses a method for detecting the interaction between the proteins and the DNA and an application thereof. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, sample loss is reduced and the efficiency of immunoprecipitation reaction is improved by additionally adding a corresponding antigen of histone requiring to be researched and interacting with DNA into a small number of initial samples. The kit has the following advantages: 1, the minimum required sample number is 1000 cells, and the kit is more suitable for detection and analysis of the interaction of a small number of proteins and DNA from the samples; and 2, a ChIP experiment does not require specific kits and experimental equipment, the cost is low, and the kit has high universal applicability.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
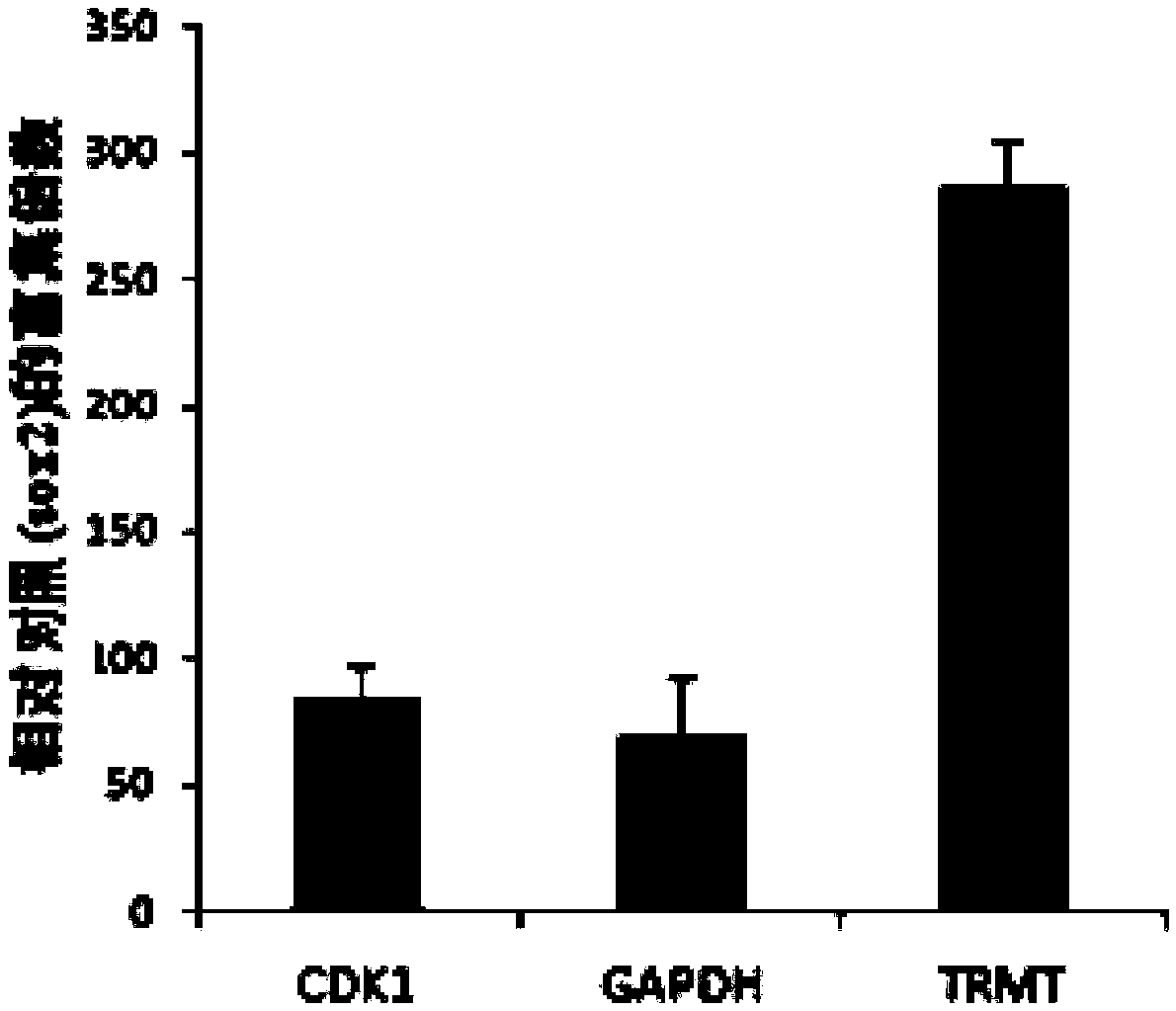
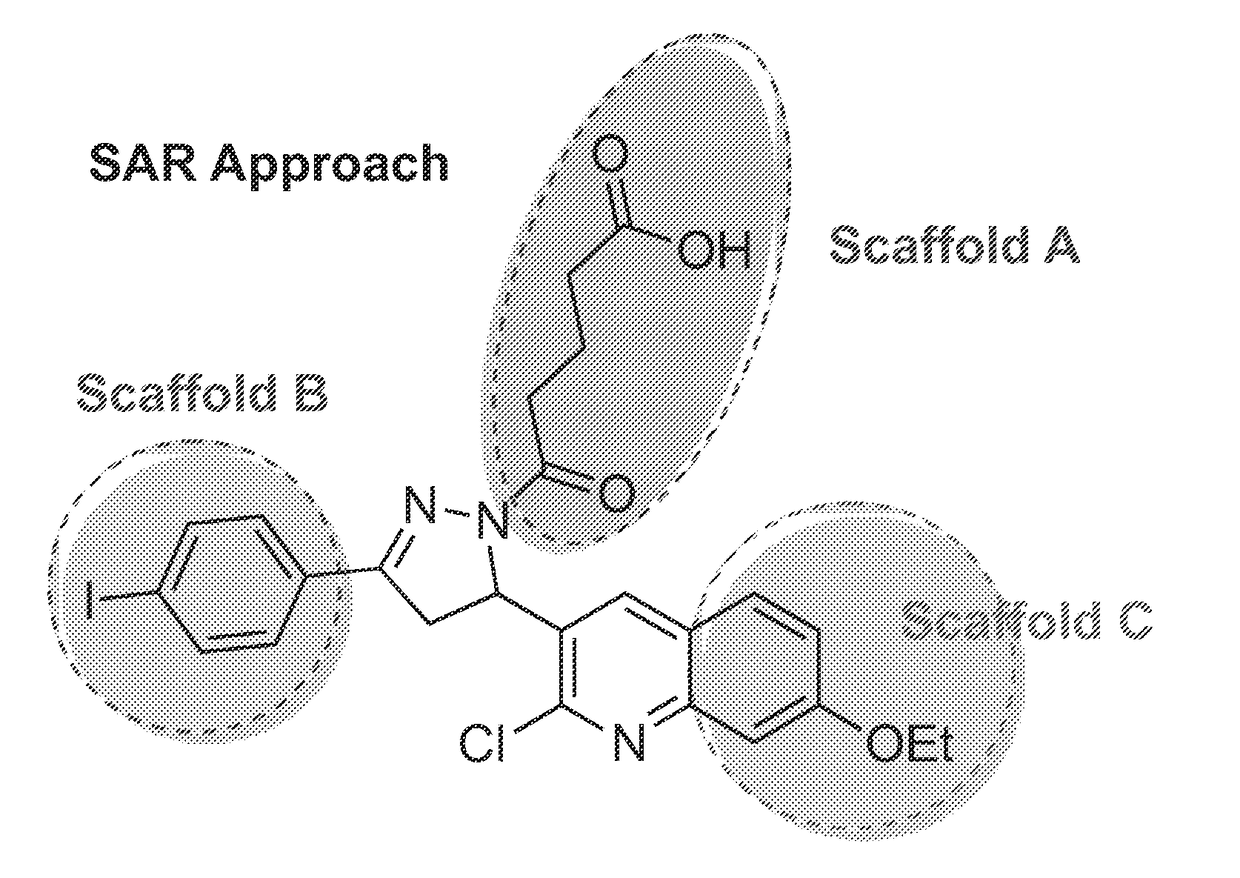
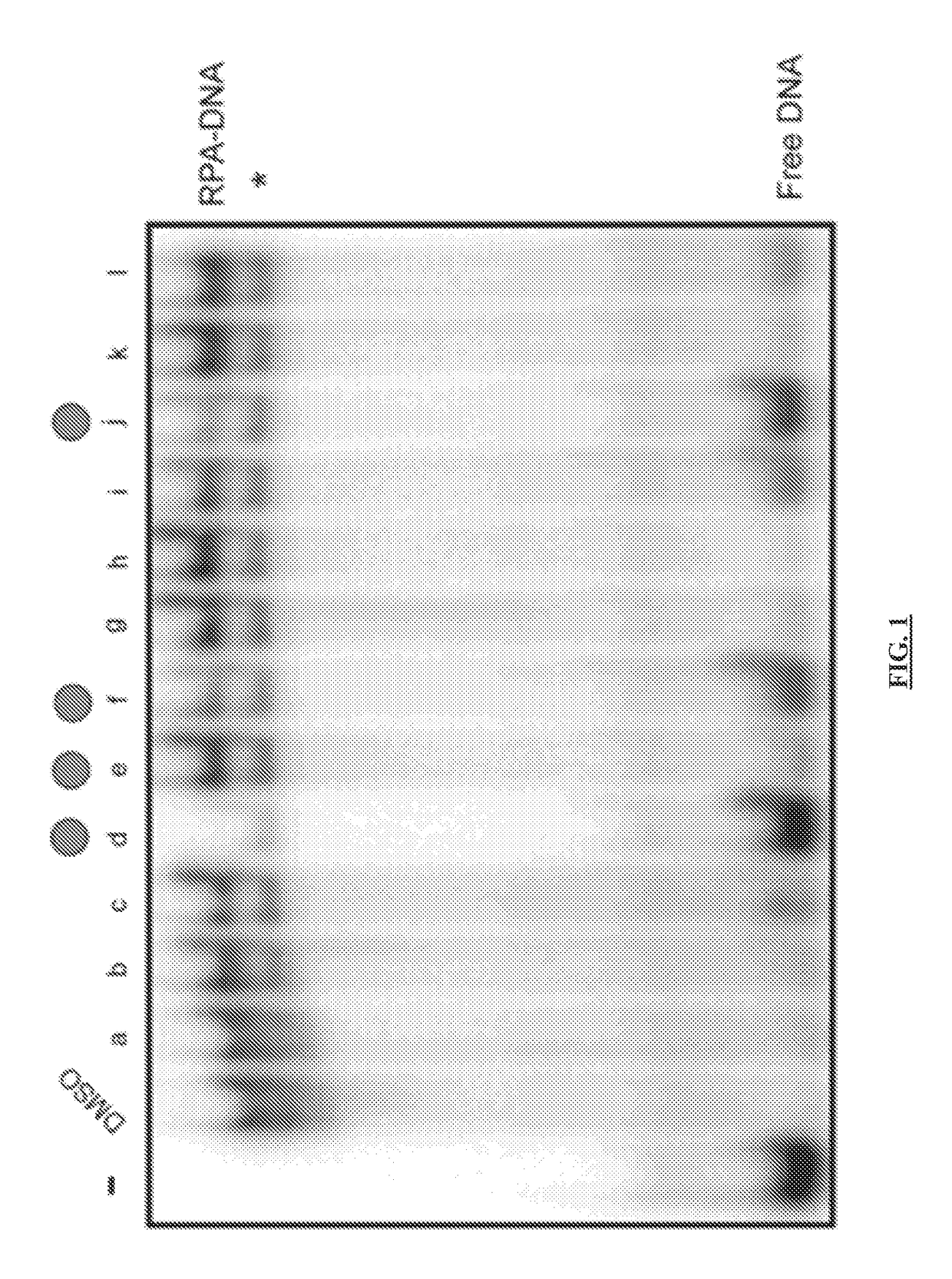
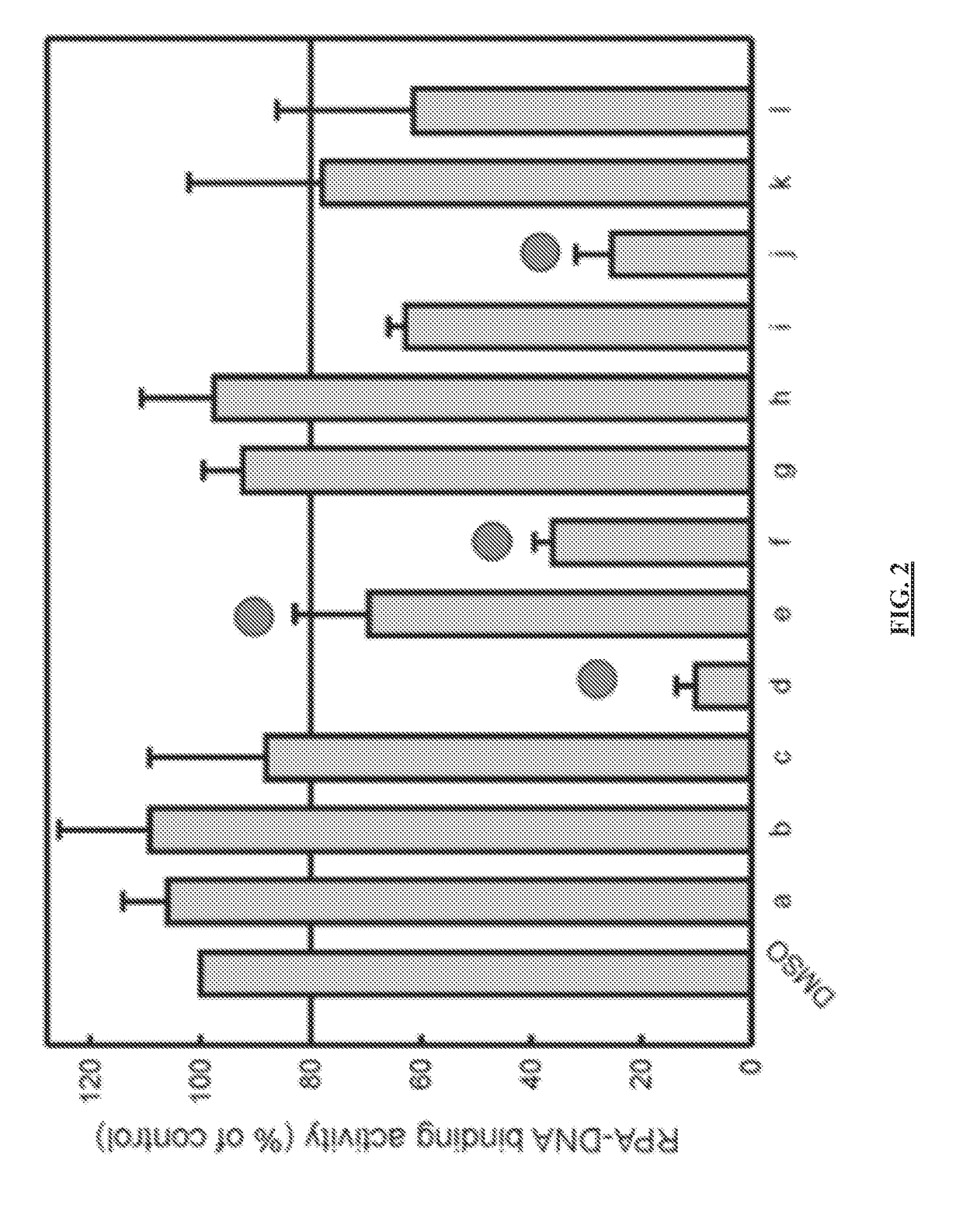
Materials and method for inhibiting replication protein a and uses thereof
ActiveUS20180305330A1Simple designReduced effectivenessOrganic chemistryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCytotoxicitySingle strand
Targeting uncontrolled cell proliferation and resistance to DNA damaging chemotherapeutics with at least one reagent has significant potential in cancer treatment. Replication Protein A, the eukaryotic single-strand (ss) DNA binding protein, is essential for genomic maintenance and stability via roles in both DNA replication and repair. Reported herein are small molecules that inhibit the in vitro, in vivo, and cellular ssDNA binding activity of RPA, thereby disrupting the eukaryotic cell cycle, inducing cytotoxicity and increasing the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents damage DNA, and / or disrupt its replication and / or function. These results provide new insights into the mechanism of RPA-ssDNA interactions in chromosome maintenance and stability. This represents a molecularly targeted eukaryotic DNA binding inhibitor and demonstrates the utility of targeting a protein-DNA interaction as a means of studying the cell cycle and providing a therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Development of method for screening physiologically active pyrrole imidazole derivative
A method for screening the effect of a segment A (chemical species A) on a substance (for example, a cell) containing DNA or RNA by using artificial chemical species. Namely, a method of detecting or identifying the function of a chemical species A on a substance containing DNA or RNA by using one or more chemical species represented by the following general formula (I) which are capable of recognizing a DNA base sequence; a kit therefor; and a plate to be used therein: B-L-A (I) wherein B represents a chemical structure containing an non-natural base capable of recognizing a DNA base sequence; A represents a chemical structure having an interaction with DNA; and L represents a linker whereby the chemical structures A and B can be linked together.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
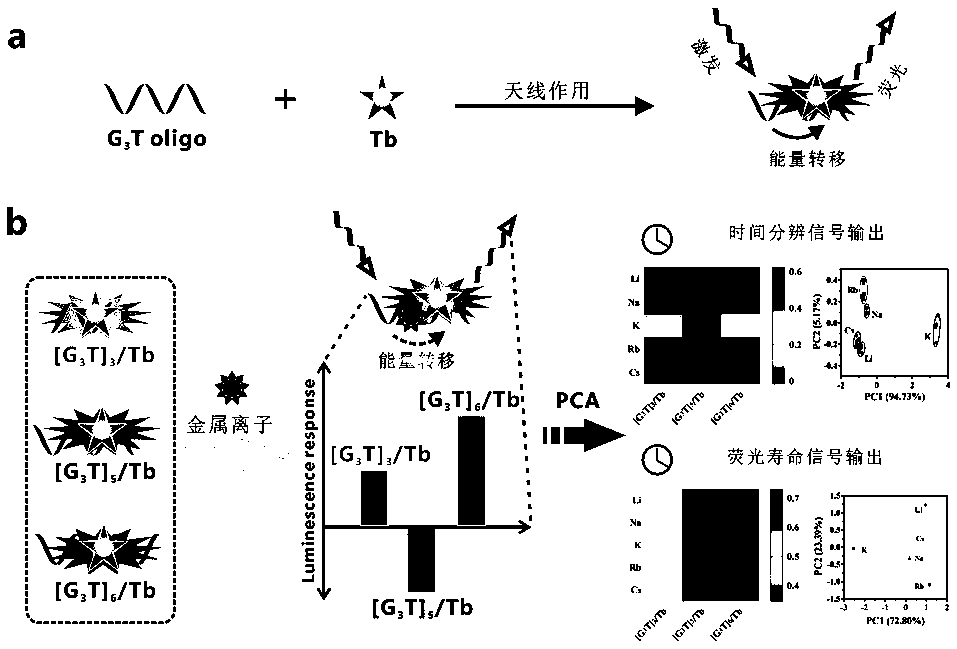
Fluorescent sensor formed on the basis of DNA combining terbium ion, and application thereof for distinguishing and detecting metal ions
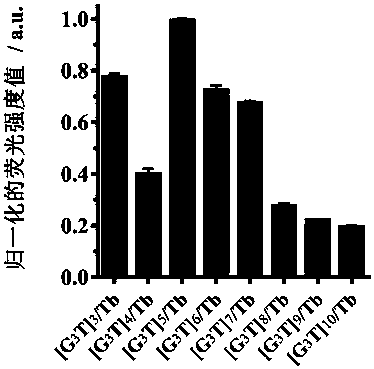
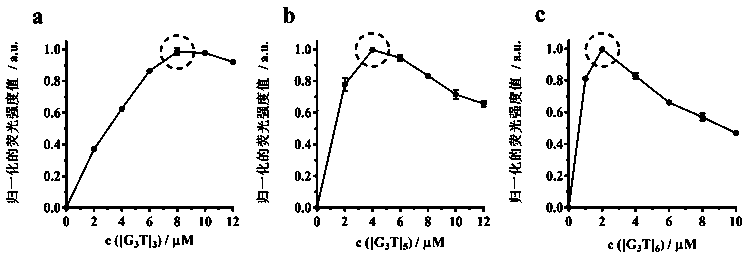
ActiveCN108444955AChange the distinctionSaving methodFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntenna effectAlkaline earth metal
The invention discloses a fluorescent sensor formed on the basis of DNA combining terbium ion, and an application thereof for distinguishing and detecting metal ions, wherein distinguish and detectionon large-scale metal ions are achieved by means of a time resolution fluorescent method. A method includes the steps of: screening three single-chain DNAs, which are rich in guanine (G) and thymine (T) and are in different lengths, as ligands, and forming the fluorescent sensor (DNA / Tb) by sensitizing the terbium through an antenna effect; then dissolving the DNA / Tb in a buffer solution and adding 49 metal ions, comprising alkali metal ions, alkaline-earth metal ions, transition / late-transition metal ions, and rare earth metal ions, wherein the antenna effect is influenced due to interactionbetween the metal ions and DNA, so that the DNA / Tb can acquire different time resolution fluorescent signals and fluorescent service life under different metal ion conditions; finally performing principal component analysis (PCA) to analyze the fluorescent signals and fluorescent service life to achieve the distinguish and detection on metal ions. The method also achieves semi-quantitative detection on metal in river water.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
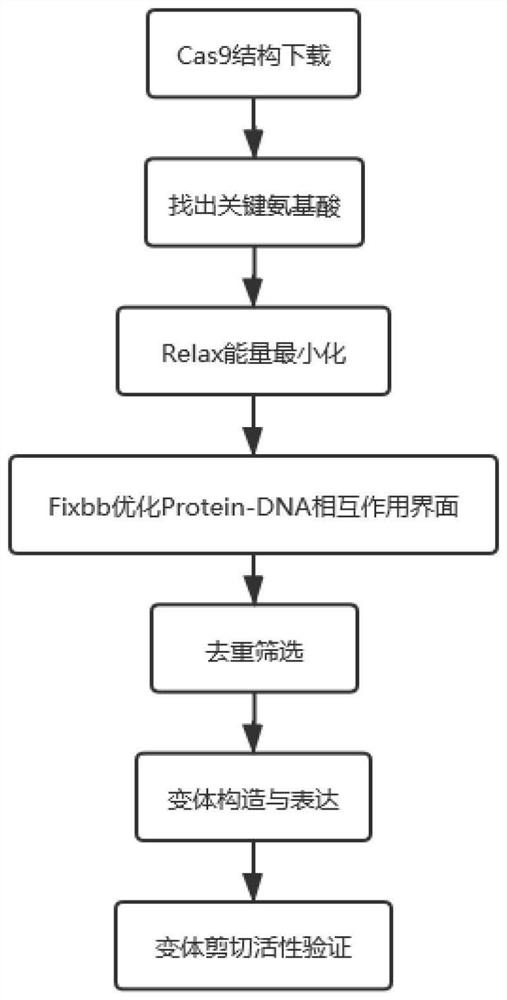
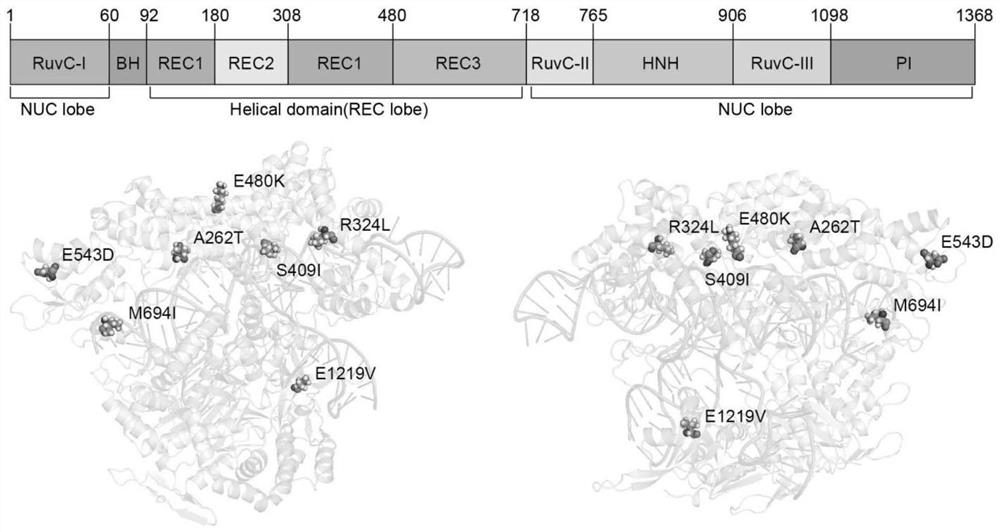
Optimum design method of structure-based CRISPR protein
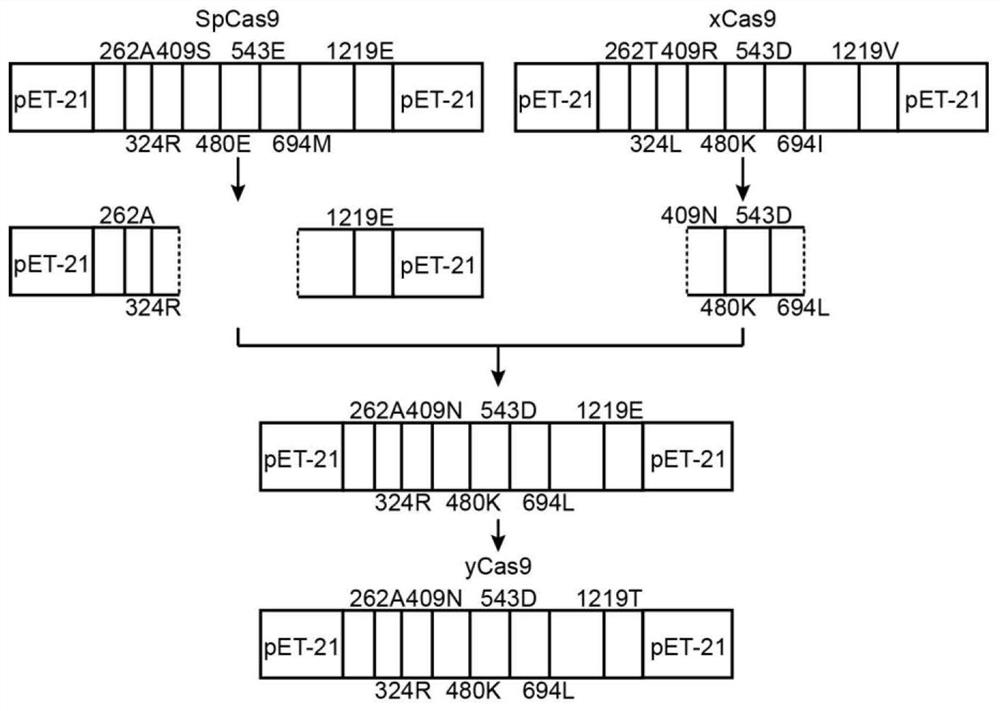
The invention belongs to the technical field of protein engineering, and specifically relates to an optimum design method of a structure-based CRISPR protein. The optimum design method comprises the following steps: carrying out analysis and comparison based on an analyzed CRISPR protein structure, so as to find out an amino acid site greatly influencing a certain function of Cas9; and optimizinga Protein-DNA interaction interface of the Cas9 through combination with Rosetta, finally carrying out designing to successfully obtain a novel mutant yCas9. The mutant has shearing activities equal to xCas9: the mutant has a wide PAM recognition range, is capable of recognizing NGG, NGA, NGT, NGC, GAA and GAT and is low in missing rate during gene editing. Therefore, the yCas9 functionally keepspace with the xCas9 and is a gene editing tool with a potential application value, thereby proving the validity and practicability of the design method.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for predicting protein-RNA interaction sites
InactiveCN109949859AExcellent final resultImprove accuracyProteomicsGenomicsDna interactionProtein–DNA interaction
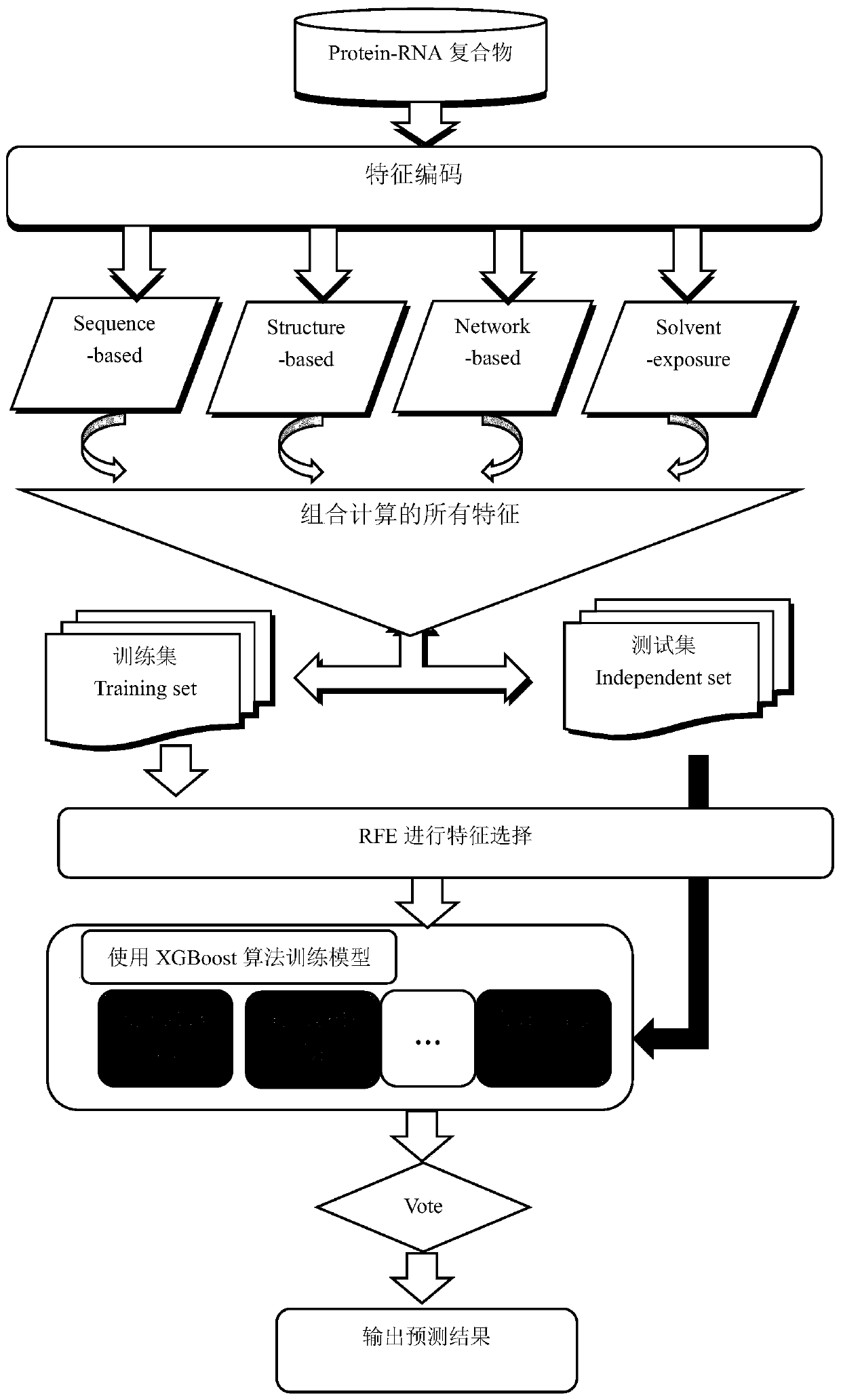
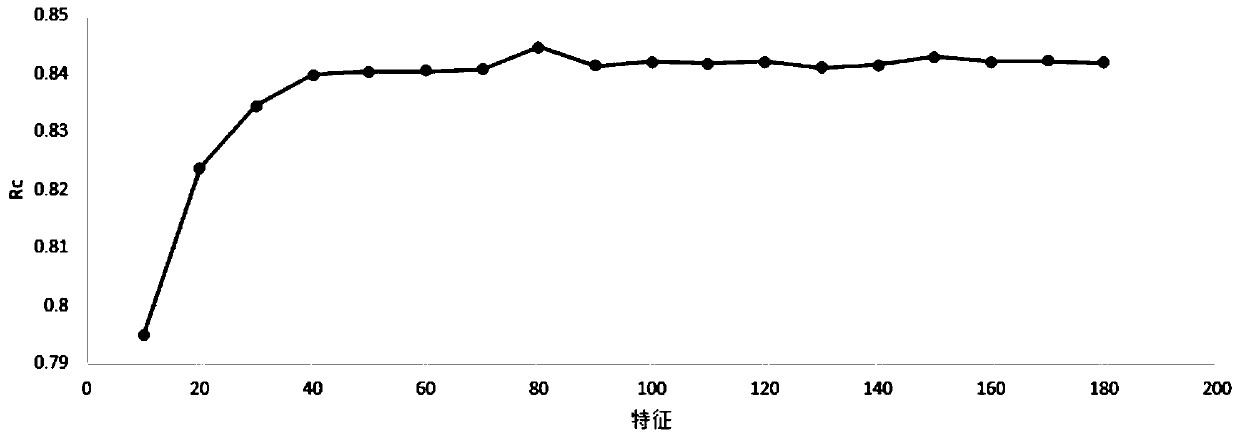
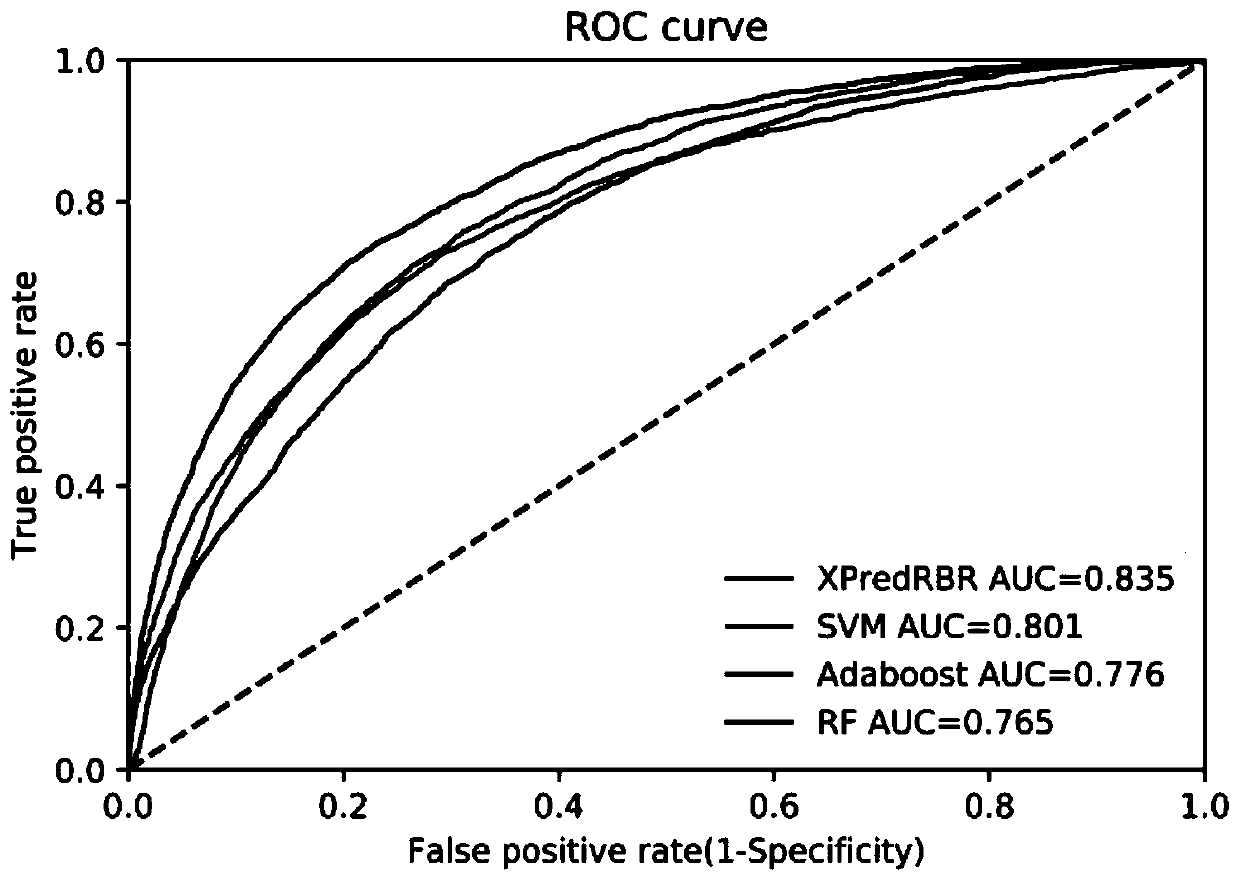
The invention discloses a method for predicting protein-RNA interaction sites. Multiple kinds of characteristic data of a protein-RNA compound are combined for forming a complicated multidimensional characteristic set. Then an effective characteristic with high weight is selected through a characteristic selecting algorithm. Finally a protein-RNA interaction site is predicted through a machine learning algorithm. Compared with the prior art, the method is advantageous in that more and more effective characteristics are fused; a more advanced algorithm is used; the more effective characteristics are selected; and besides consideration of prediction of the protein-RNA interaction sites which are proved by experiments, more data can be integrated, such as protein-DNA interaction sides. According to the method of the invention, through fusing more effective algorithm and more characteristic data, the protein-RNA interaction sites can be more accurately predicted than previous technology. Furthermore multiple pairs of protein-RNA interaction sites can be predicted in one time in a large scale manner, thereby effectively settling problems of blindness and high cost of a biological experiment method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Small molecule compounds targeting pbx1 transcriptional complex
ActiveUS20180118688A1Nervous disorderOrganic chemistryPervasive developmental disorderAutoimmune disease
In accordance with one or more embodiments, the present invention provides a compound of formulas I, II, and III, for use in methods of inhibition of PBX1-DNA interaction in a mammalian cell or population of cells, and for use in the treatment of medical conditions including but not limited to cancers, developmental disorders, inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, or neuro-degenerative disorders.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
A method for assaying transcriptional regulatory complexes
ActiveCN104774923BImprove stabilityLow efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDna interactionProtein–DNA interaction
The invention relates to a method for determining a transcriptional control complex, and belongs to the field of molecular biology. The method for determining the transcriptional control complex includes the following steps: preparation of a bait DNA sequence, preparation of a DNA sequence for encoding a bar code protein, construction of a bar code protein library, screening of the transcriptional control complex, and in situ adjacent connection capture of the transcriptional control complex, and the identification of the transcriptional control complex. The invention combines cDNA display technology and the adjacent connection technology to establish a novel method for determining the transcriptional control complex; the determination of transcriptional control complex involves simultaneous determination of a variety of interaction effects of protein-protein and protein-DNA; and the method can realize simultaneous determination of a variety of interaction effects of protein-protein and protein-DNA in a same experimental system, and effectively solve the incompatibility of the determination methods for the protein-protein interaction and protein-DNA interaction in the same experimental system in the prior art.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A kit, method and application for detecting the interaction between protein and dna
ActiveCN108680757BReduce lossesImprove the efficiency of immunoprecipitation reactionsBiological testingDNA preparationAntigenHistone antigen
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
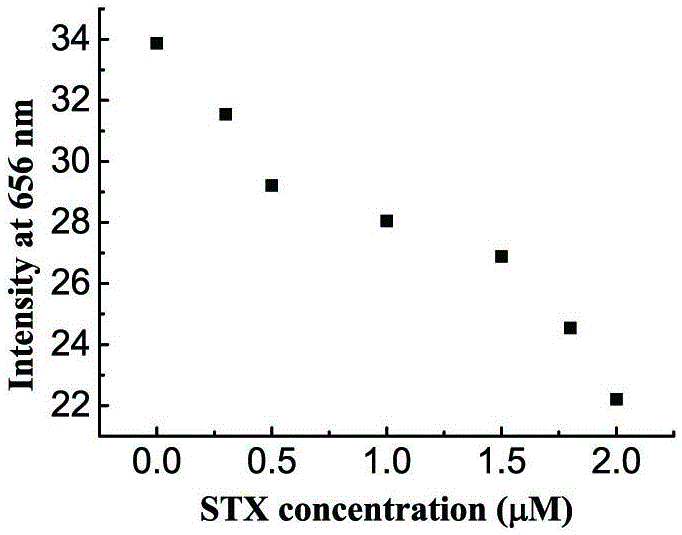
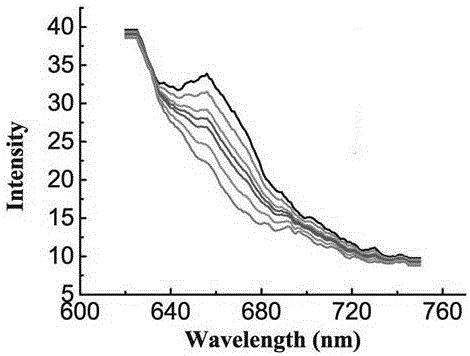
Method for detecting saxitoxin on basis of embedded dye and DNA interaction
InactiveCN107179305ARealize quantitative determinationAvoid complexityFluorescence/phosphorescenceInteraction timeDna interaction
The invention discloses a method for detecting saxitoxin on the basis of embedded dye and DNA interaction. The method comprises the following specific steps: dissolving DNA in a buffer solution at first, then adding the saxitoxin in the buffer solution, carrying out interaction on the saxitoxin and DNA for 25-35 minutes, when interaction time is up, adding the embedded dye in the buffer solution, waiting for 25-35 minutes, then carrying out fluorescence spectrometry, and calculating the concentration of the saxitoxin through the peak value of the measured spectrum according to a standard curve. The concentration of the saxitoxin can be measured quantitatively through measurement to fluorescent light, complicated instruments and construction of a detecting platform are not required, the detection mode is simple, rapid and accurate, therefore, the technological difficulty that traditional measurement depends on complicated and high-cost instruments is avoided, and complexity on fixing of DNA and construction of the detecting platform is avoided.
Owner:HEFEI NORMAL UNIV
DNA binding protein
InactiveUS20060084108A1Preventing and decreasing proliferationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDna interactionDNA replication
Methods of screening for compounds which are, for example, capable of modulating amino acid-DNA interaction, modulating DNA replication, modulating cell proliferation, and for identifying compounds which inhibit cellular proliferation caused by cancer, are provided.
Owner:WRIGHT STATE UNIVERSITY
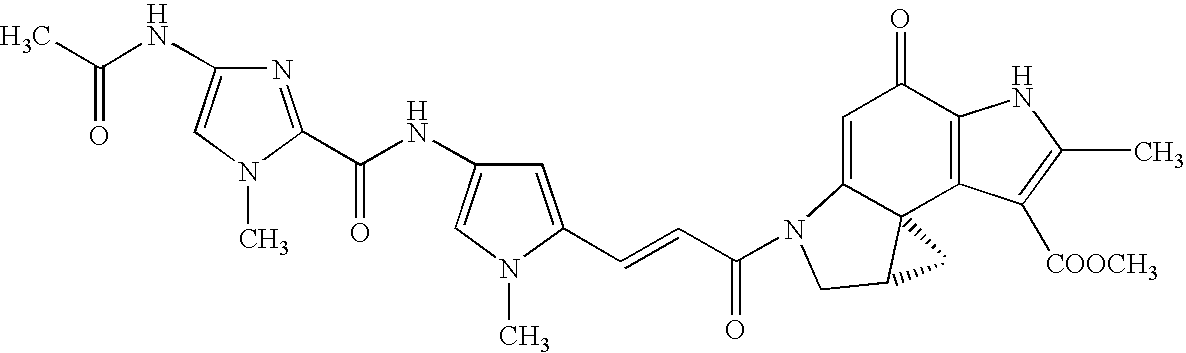
A 7-position fluorine-substituted isaindigotone derivative and its preparation method and application in the preparation of anticancer drugs
ActiveCN106220631BGrowth inhibitionInhibit expressionOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsProtein targetHydrogen
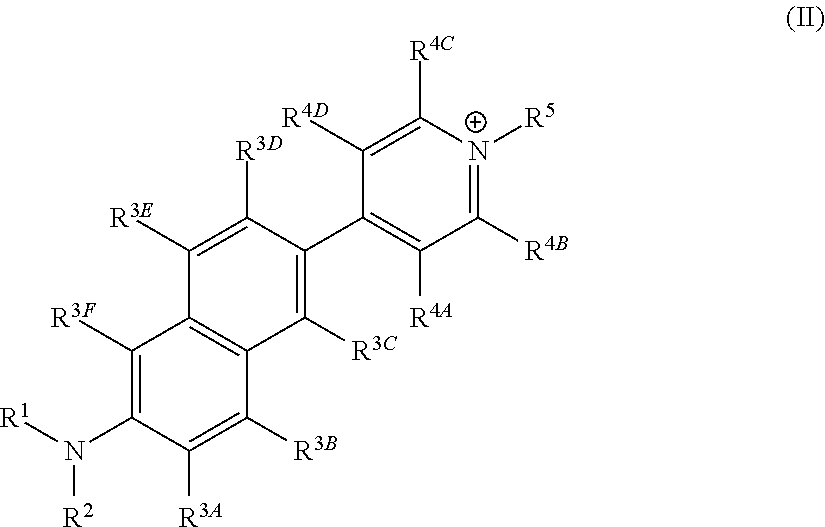
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, and particularly discloses 7-fluoro-substituted Isaindigotone derivatives. The structural formula of the derivatives is disclosed as Formula (I) or Formula (II), wherein X is C or N; R1 is hydrogen, amino, substituted amino, orpenta- or hexa-heterocyclic radical; R2 is hydrogen, hydroxy, amino, C1-C8 alkyl, or C1-C8 alkoxy or halo; R3, R5 and R6 are defined the same as R2; and R4 is hydrogen, hydroxy, amino, phenyl, C1-C8 cycloalkyl, C1-C8 alkyl, C1-C8 alkoxy, C1-C6 alkyl acyloxy, C1-C6 alkynyl, halo, or penta- or hexa-heterocyclic radical. The fluoro-substituted Isaindigotone derivatives can bebondedwith NM23-H2 protein and block the interaction between the NM23-H2 protein and c-myc G-quadruplex DNA, thereby causing the reduction of protooncogene c-myc transcription and translation, and inhibiting the proliferation of multiple tumor cell strains. The fluoro-substituted Isaindigotone derivatives have wide antitumor effects. The fluoro-substituted Isaindigotone derivatives are a novel NM23-H2-protein-targeted transcription regulation blocker, and have wide application space in preparing anticancer drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
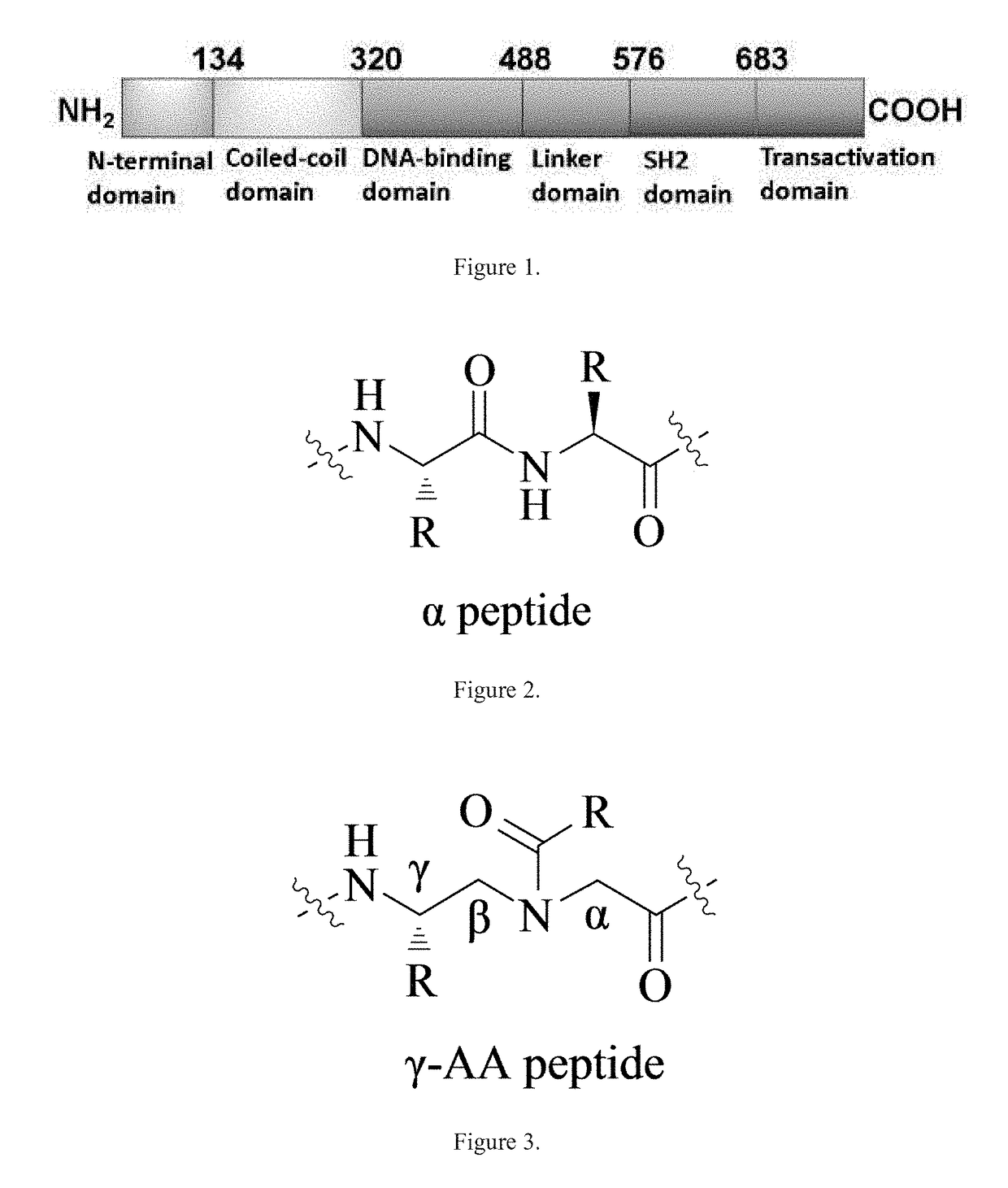
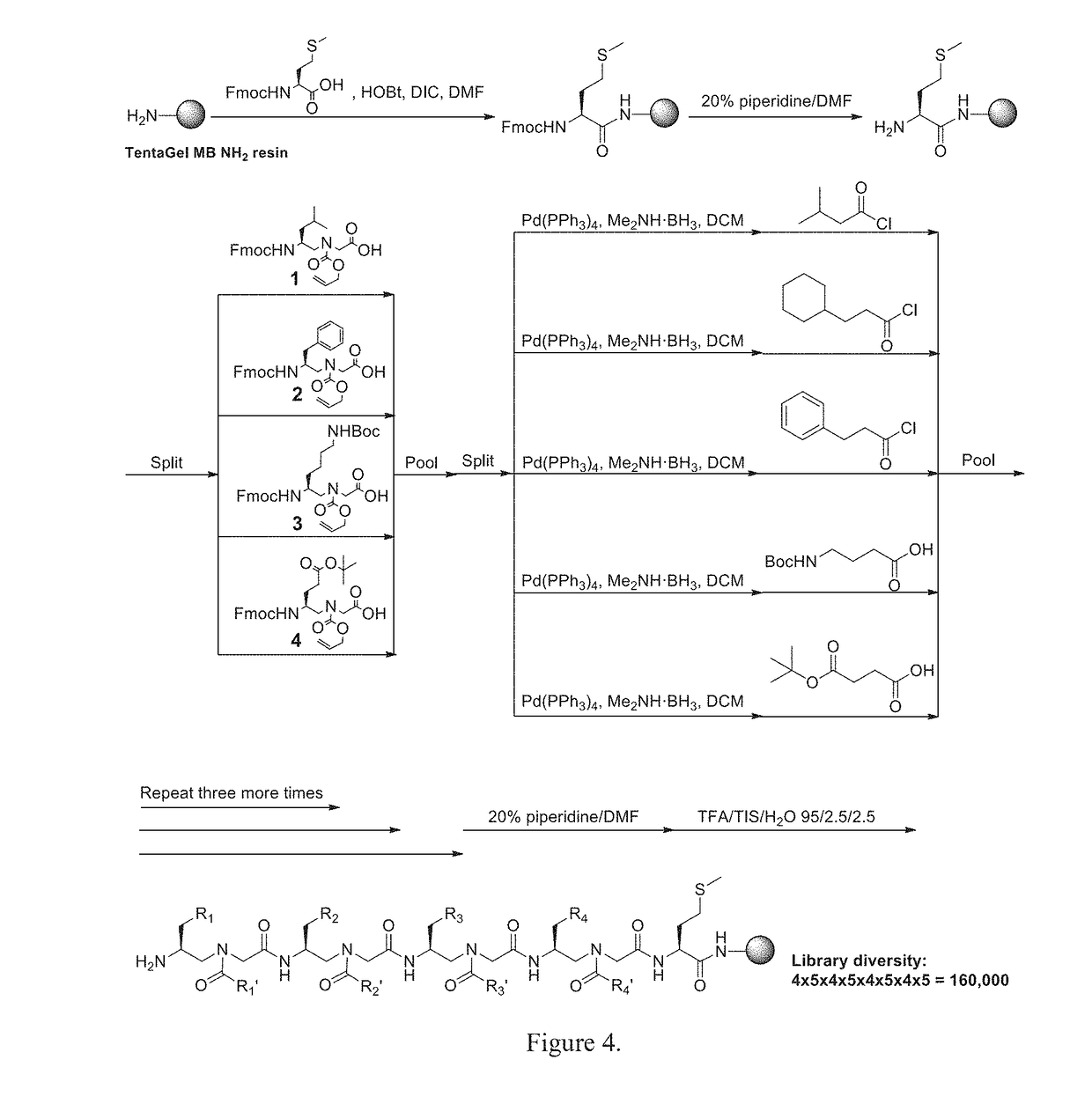
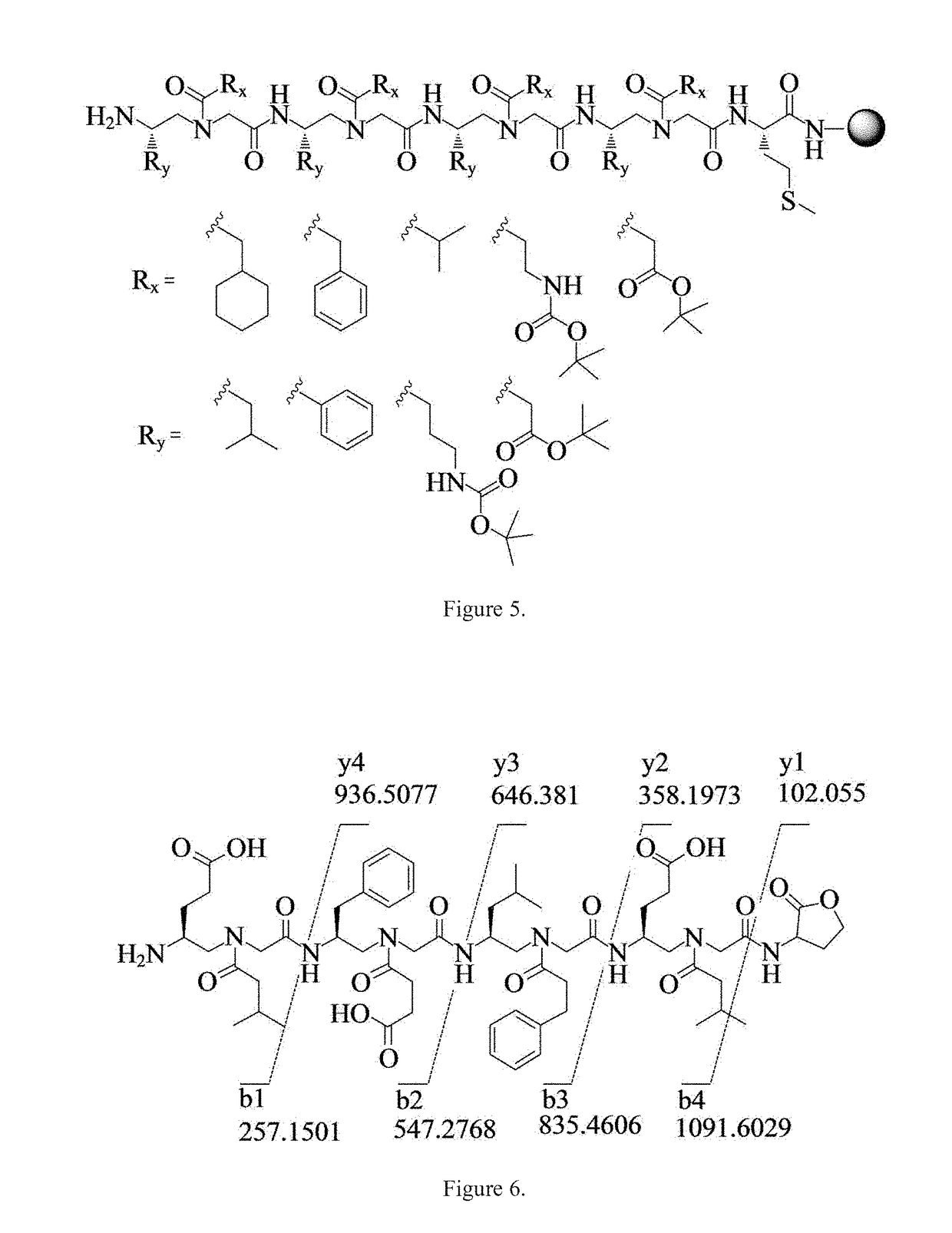
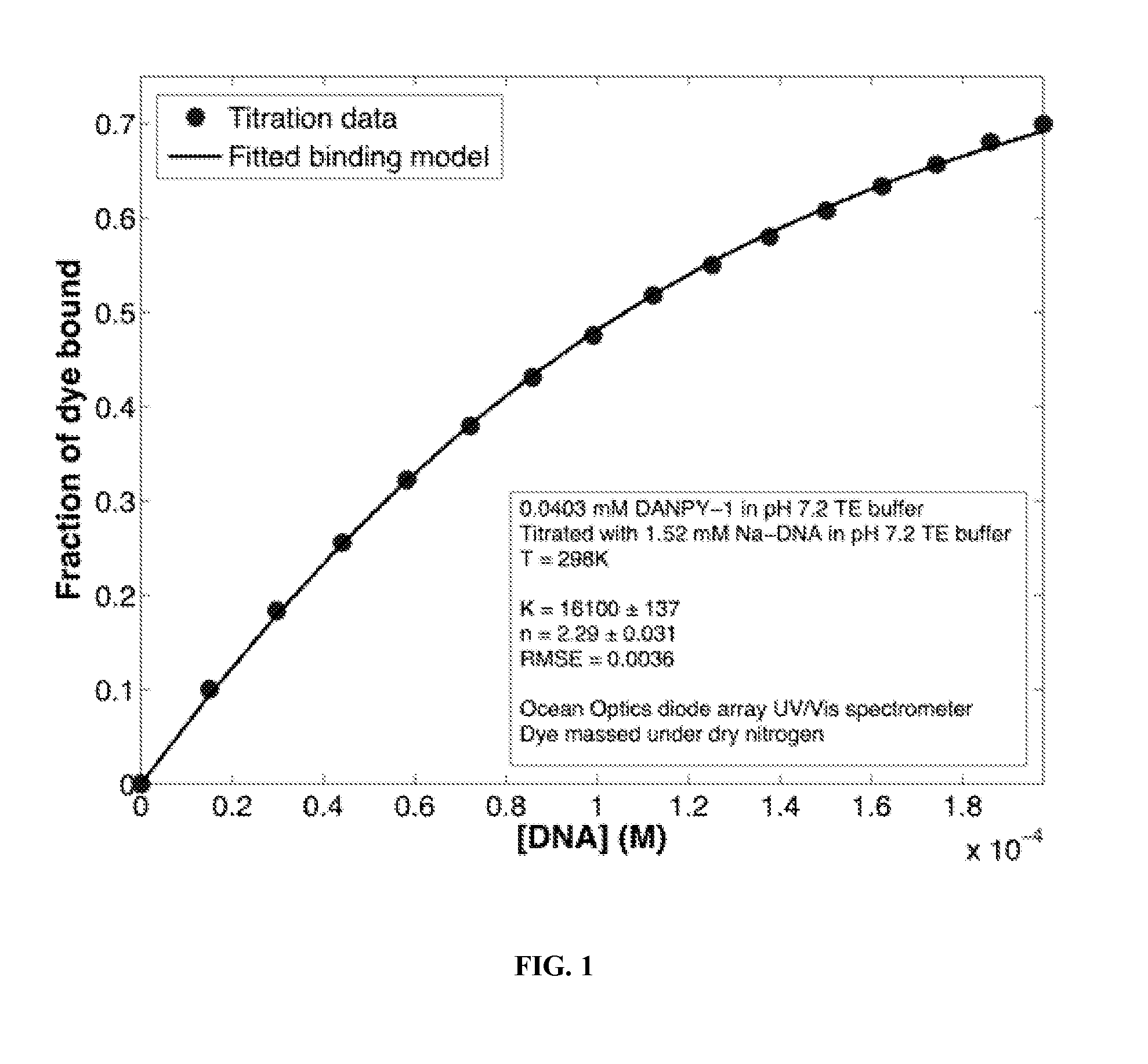
Gamma-aa-peptide stat3/dna inhibitors and methods of use
ActiveUS20180244719A1Antineoplastic agentsPeptides with abnormal peptide linkDNA-binding domainGene expression level
STAT3 hyperphosphorylation, dimerization and DNA binding are required for its ability to contribute to malignant transformation. As such, STAT3 has been recognized as a promising target for cancer therapy. Although a number of inhibitors of STAT3-STAT3 dimerization have been reported, molecular ligands that prevent interactions between STAT3 and DNA are very rare. The γ-AApeptide-based one-bead-one-compound (OBOC) combinatorial library was used, and identified γ-AApeptides that can selectively inhibit STAT3 / DNA interaction and suppress the expression levels of STAT3 target genes in intact cells. The results not only validate γ-AApeptides as novel inhibitors of STAT3 signaling pathway, but also demonstrate that in addition to the SH2 domain, the DNA binding domain of STAT3 is targetable for the development of new generation of anti-cancer therapeutics. This also validates the approach of OBOC combinatorial library for the identification of ligands targeting traditionally recognized “undruggable targets”.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
Fluorescent Dyes and Related Methods
Fluorescent dyes with affinity for nucleic acids and related methods are provided. Dielectric or semiconducting films including fluorescent dyes with affinity for nucleic acids and related methods are also provided. Coumarin-based surfactants conjugated to the fluorescent dyes with affinity for nucleic acids and related methods are provided. Fluorescent compounds capable of interacting with DNA can be used for a variety of applications.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
A method for the determination of lysozyme based on the interaction between carboxylated carbon nanoparticles and DNA
ActiveCN103399005BRealize determinationHigh selectivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAptamerDna interaction
The invention provides a lysozyme content detection method which is used for detecting lysozyme content in cells and biological samples and belongs to the technical field of a chemiluminiscence aptasensor. The lysozyme content detection method comprises the following steps of: modifying amination magnetic beads by using carboxylation carbon nanoparticles so as to obtain carbon nanoparticle modified magnetic beads; and modifying lysozyme aptamer by using a chemiluminiscence agent ABEI (3-aminophthalic acid cyclic hydrazide) so as to prepare a marked aptamer; combining the marked aptamer and the lysozyme in the presence of lysozyme, mixing a solution, which is subjected to the action of the lysozyme-marked aptamer, with the carbon nanoparticle modified magnetic beads, wherein liquid supernatant generates chemiluminiscence in the presence of H2O2 and Co<2+> after magnetic separation, thus realizing the detection of the lysozyme. The lysozyme content detection method is simple and low in cost.
Owner:凯惠睿智生物科技(上海)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com