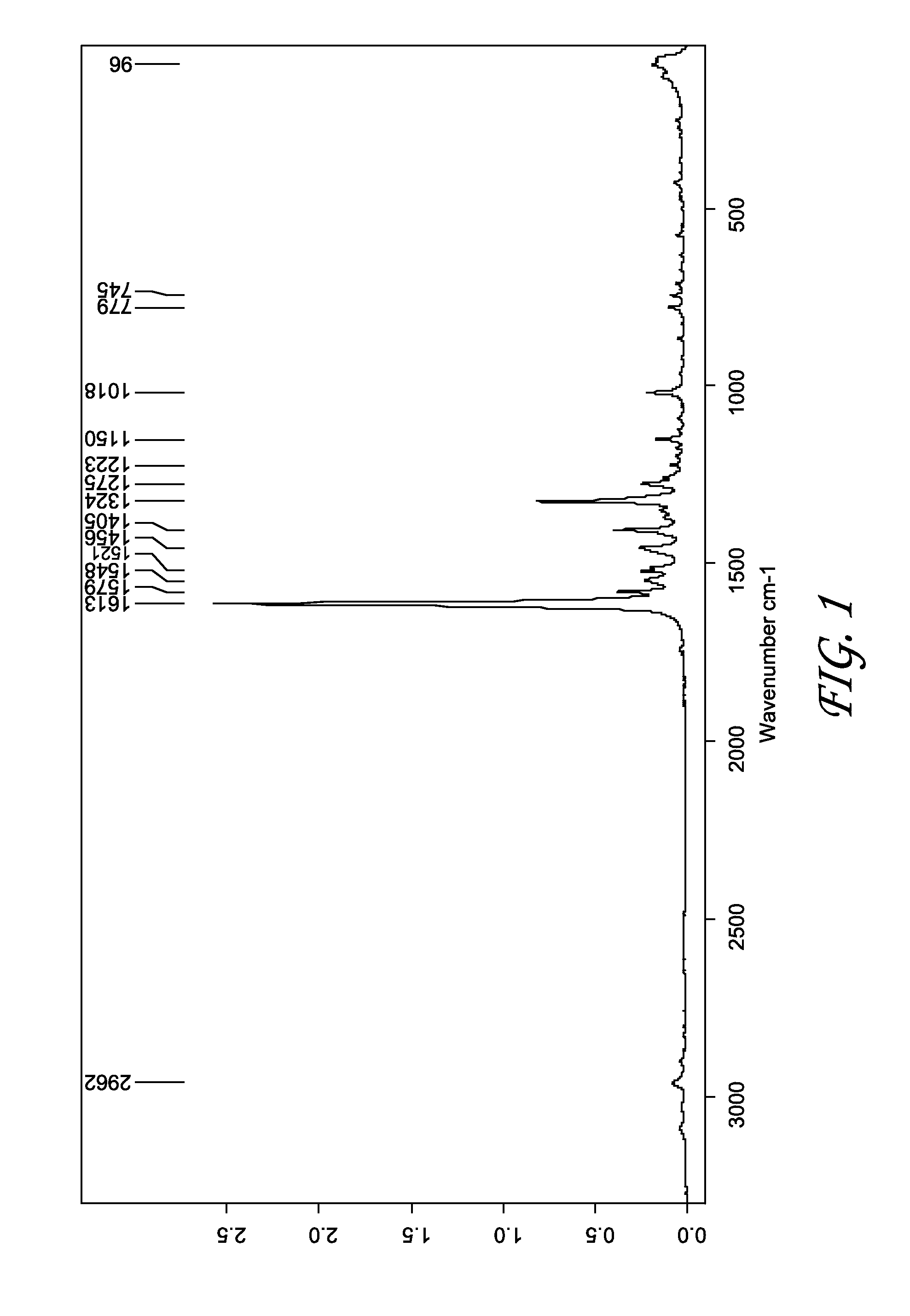
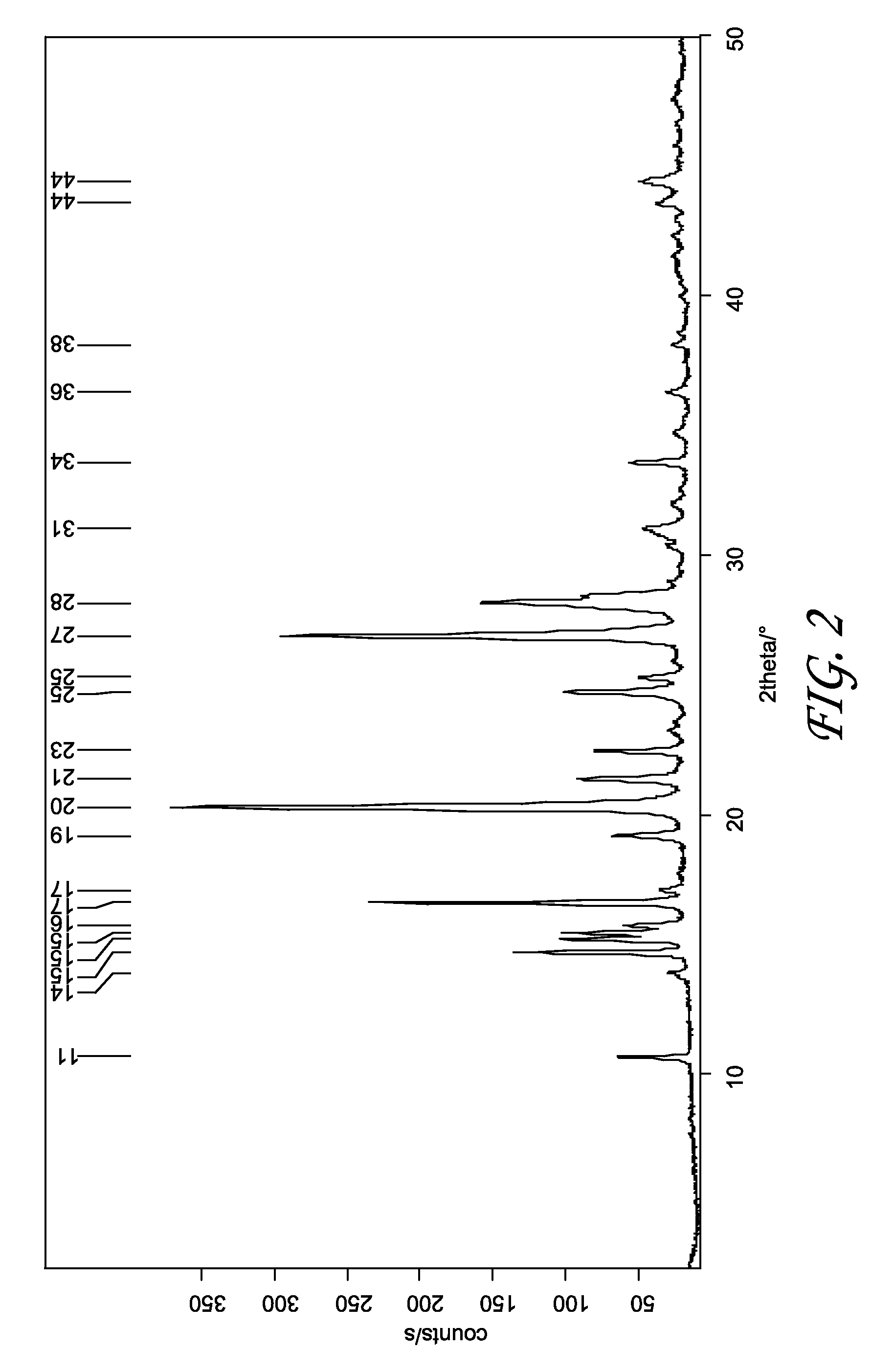
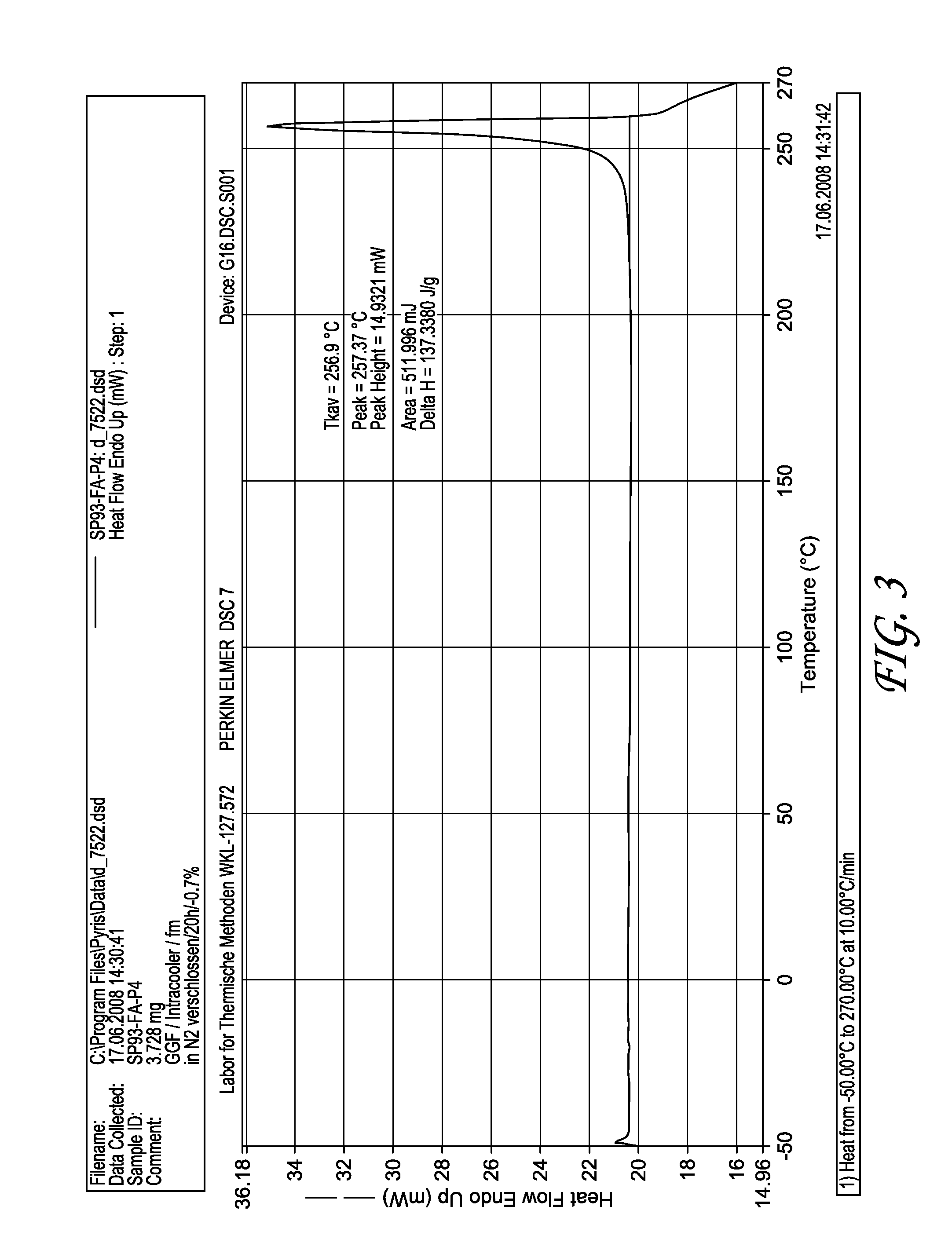
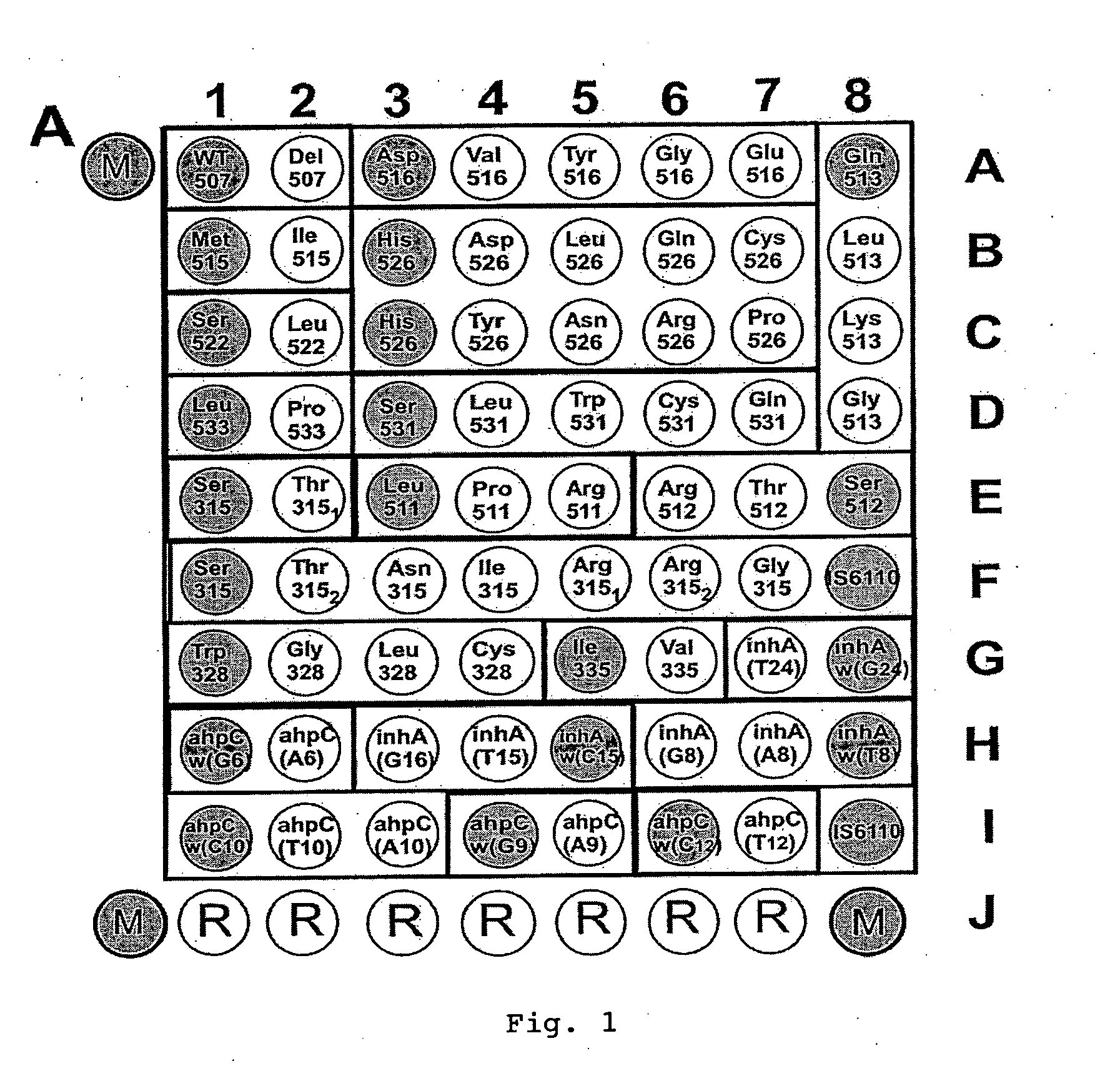
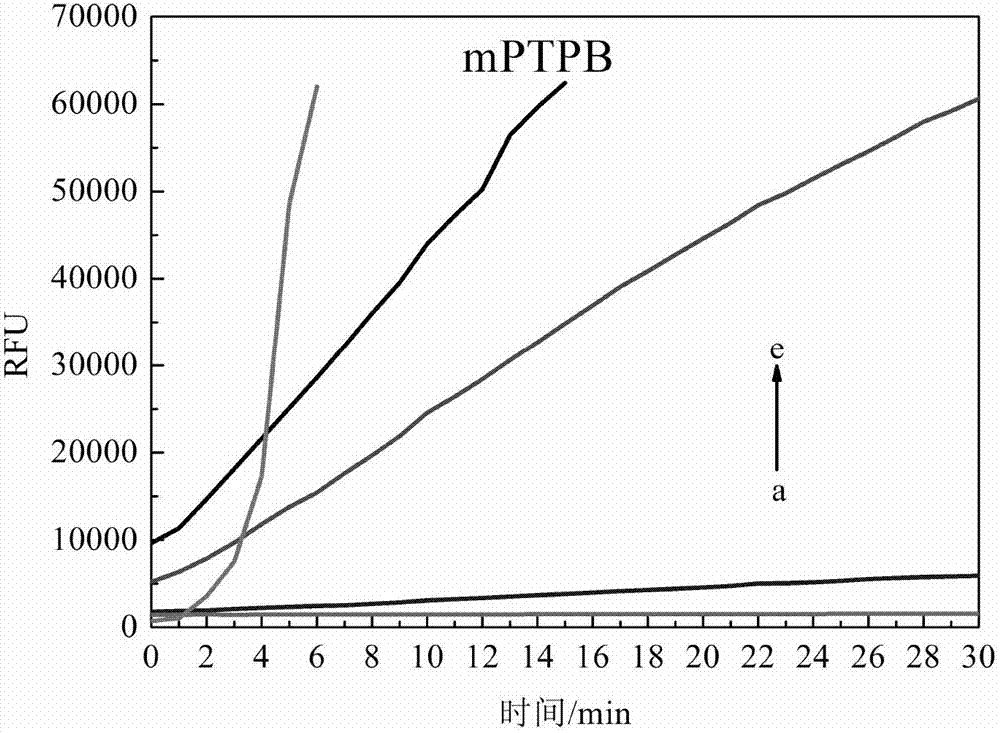
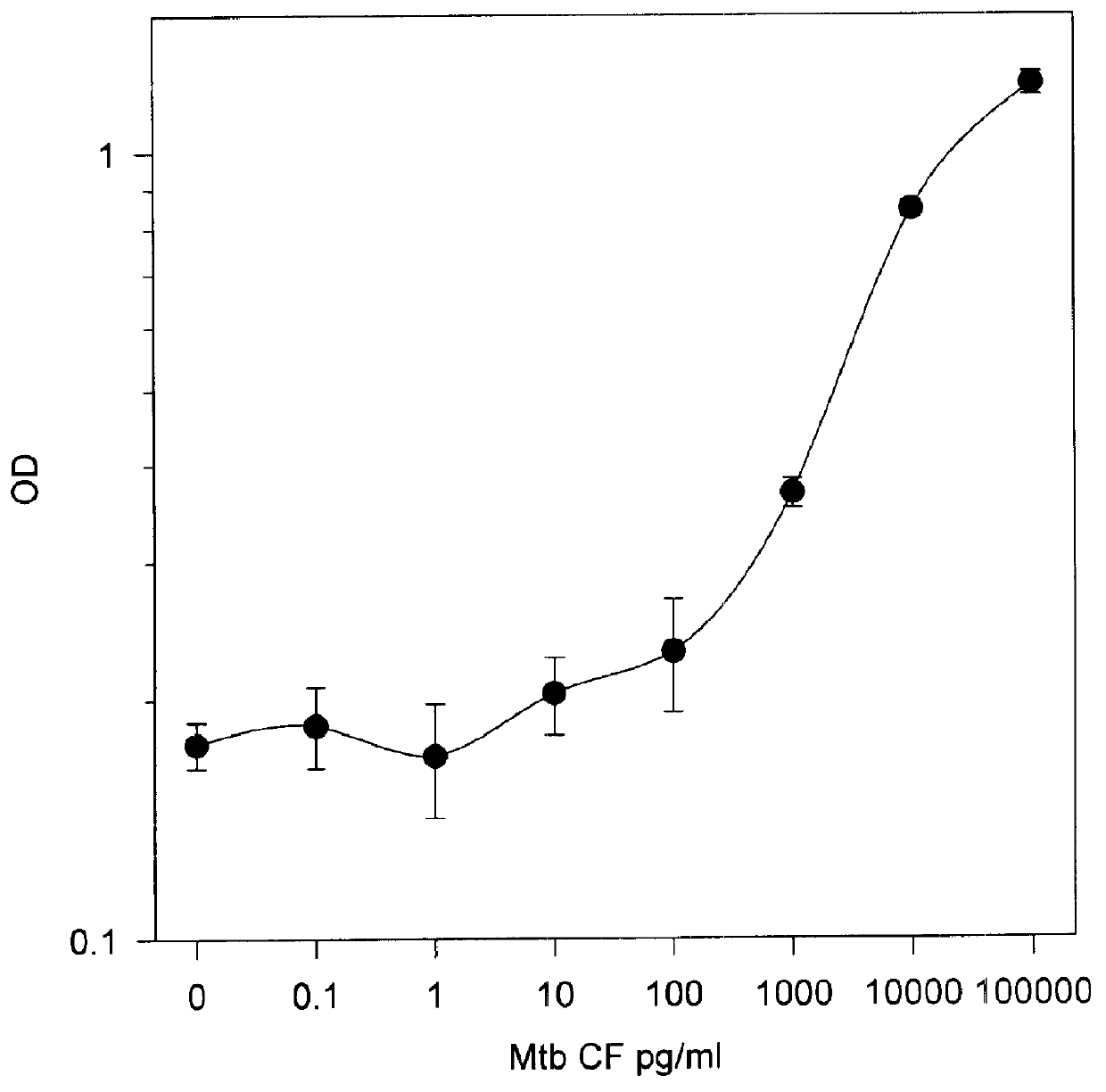
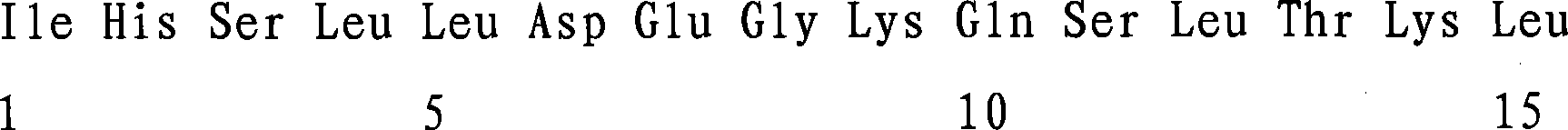Patents
Literature
657 results about "Tuberculosis mycobacterium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
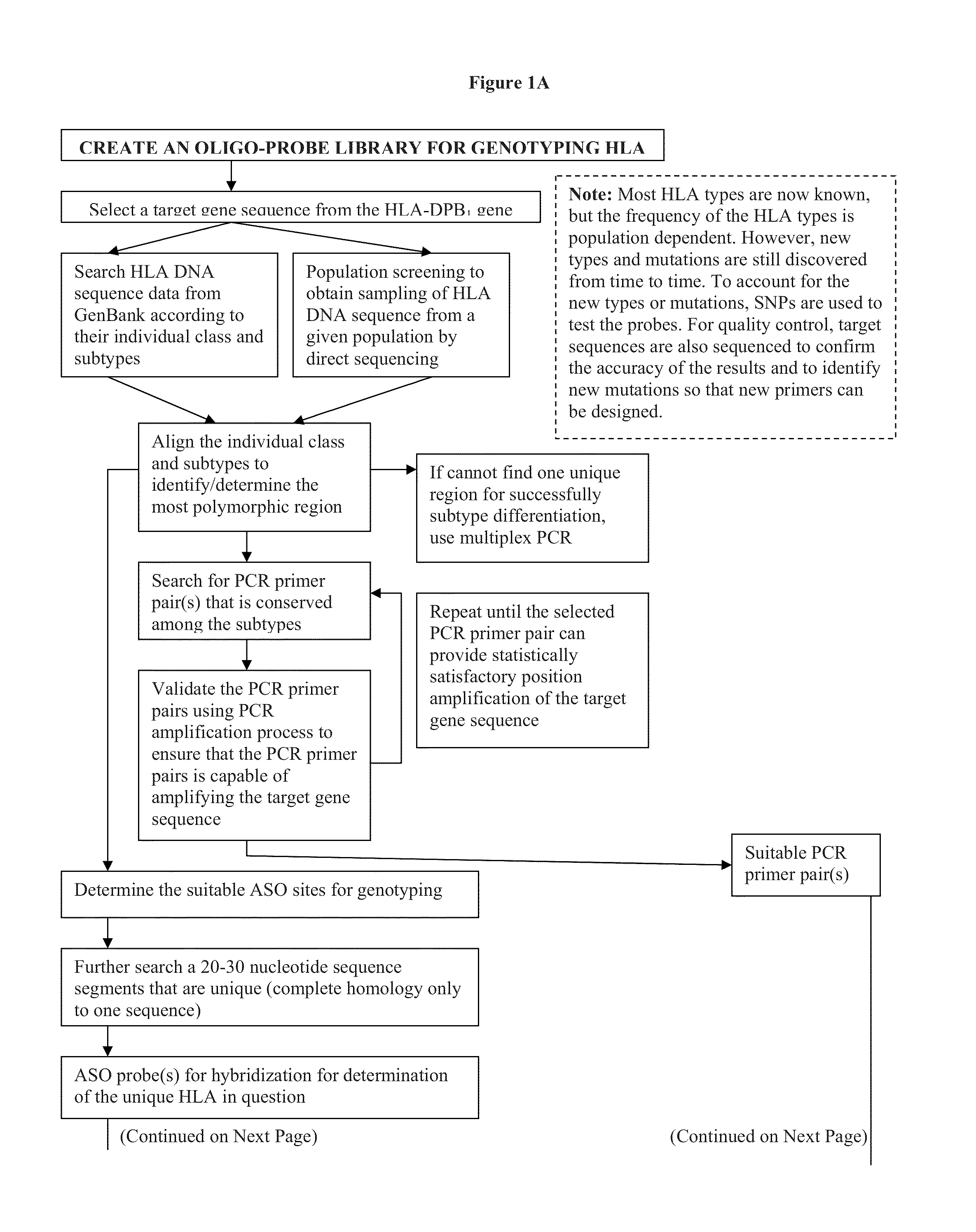
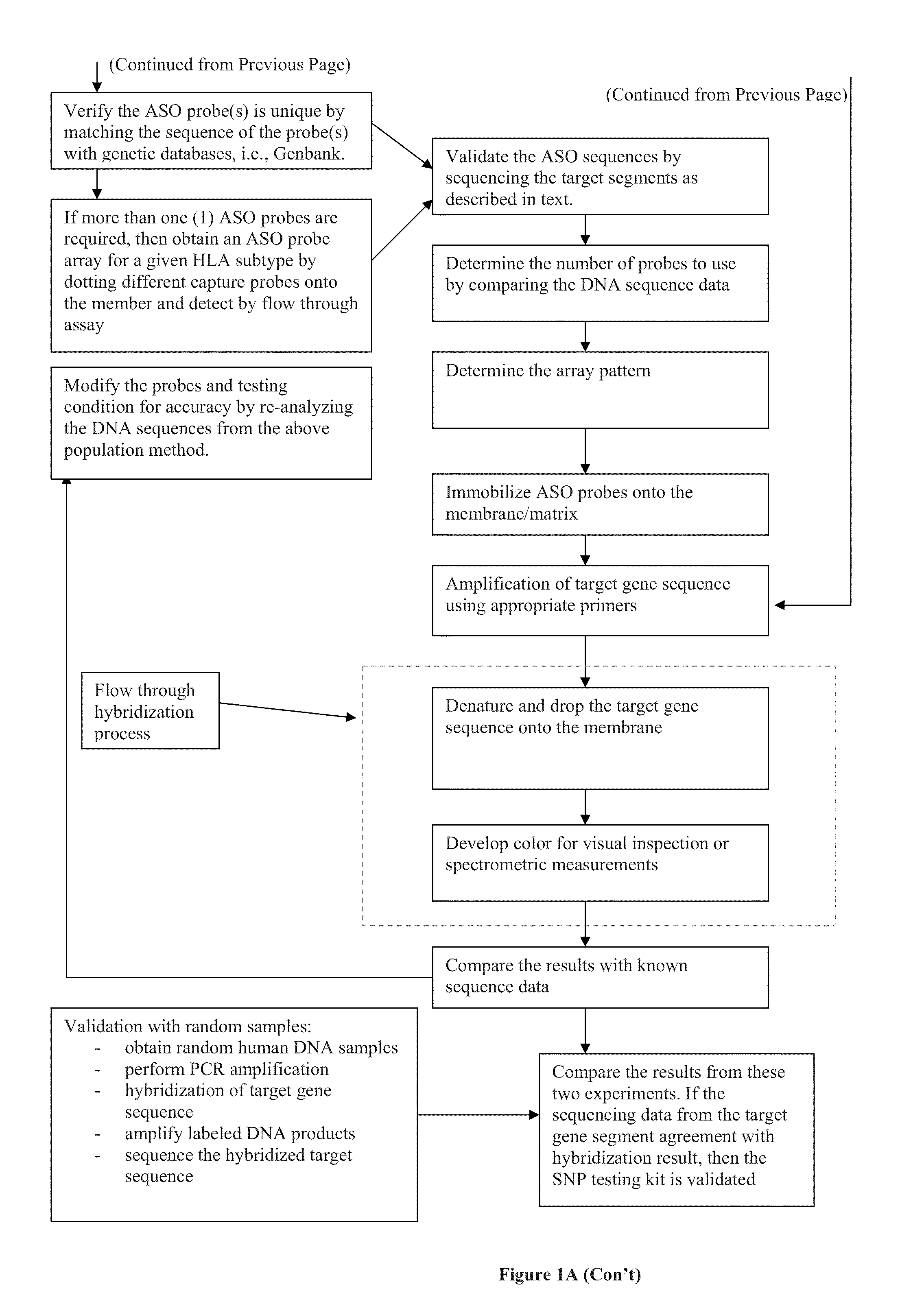
Compositions and methods for detecting, identifying and quantitating mycobacterial-specific nucleic acids
ActiveUS20110281754A1Inherent limitationAuxiliary diagnosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyTuberculosis mycobacterium
Disclosed are compositions and methods for isolating, detecting, amplifying, and quantitating Mycobacterium-specific nucleic acids in a sample. Also disclosed are compositions and diagnostic kits comprising Mycobacterium IS6110-specific oligonucleotide amplification primers and labeled oligonucleotide detection probes that specifically bind to the amplification products obtained therefrom. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for the isolation and characterization of nucleic acids that are specific to one or more tubercular pathogens, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, in particular, from a wide variety of samples including those of biological, environmental, clinical and / or veterinary origin.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
M. tuberculosis antigens
InactiveUS6991797B2High expressionEnhance immune responseBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenTuberculosis mycobacterium
The present invention is based on the identification and characterization of a number of novel M. tuberculosis derived proteins and protein fragments. The invention is directed to the polypeptides and immunologically active fragments thereof, the genes encoding them, immunological compositions such as vaccines and skin test reagents containing the polypeptides.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
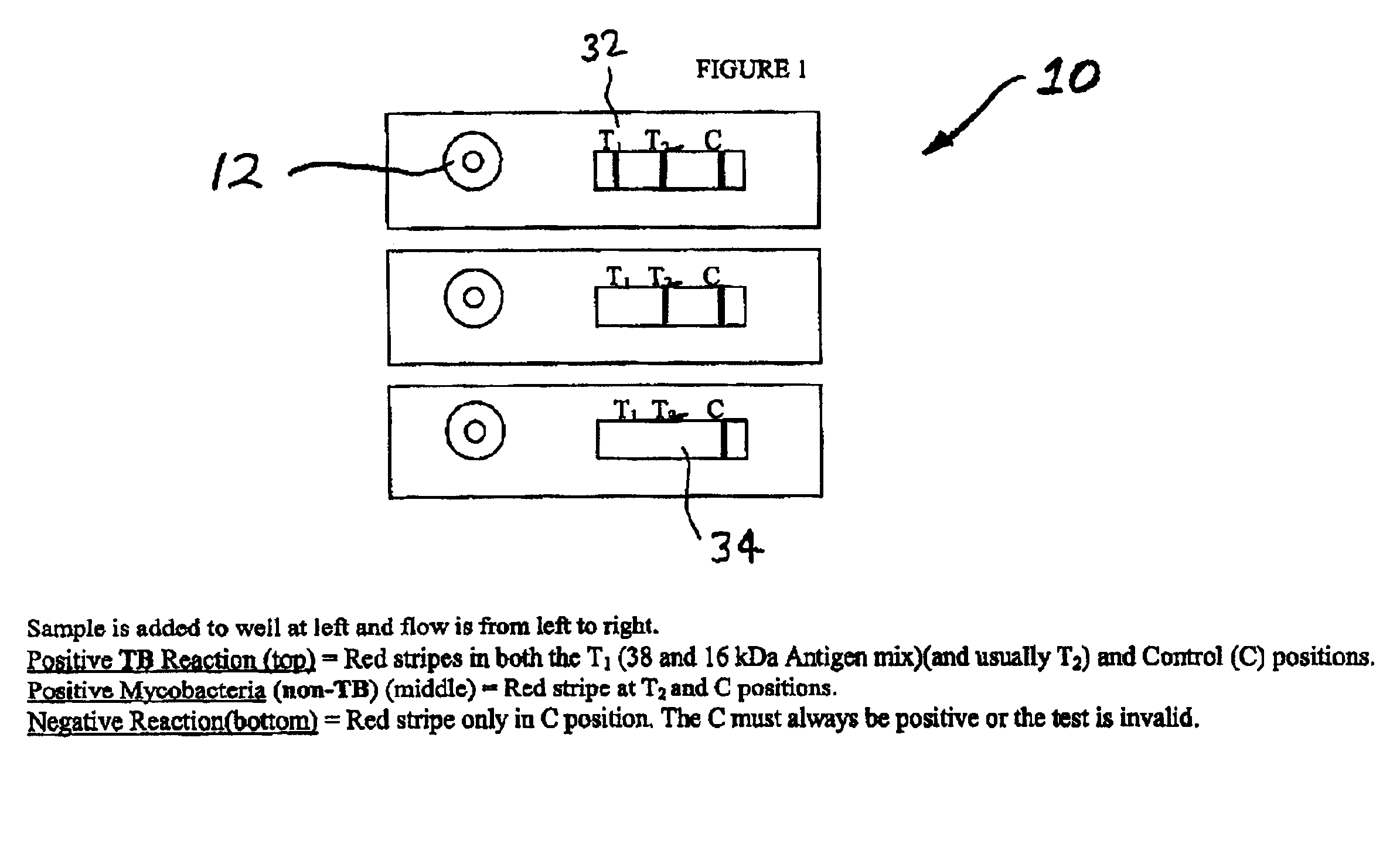
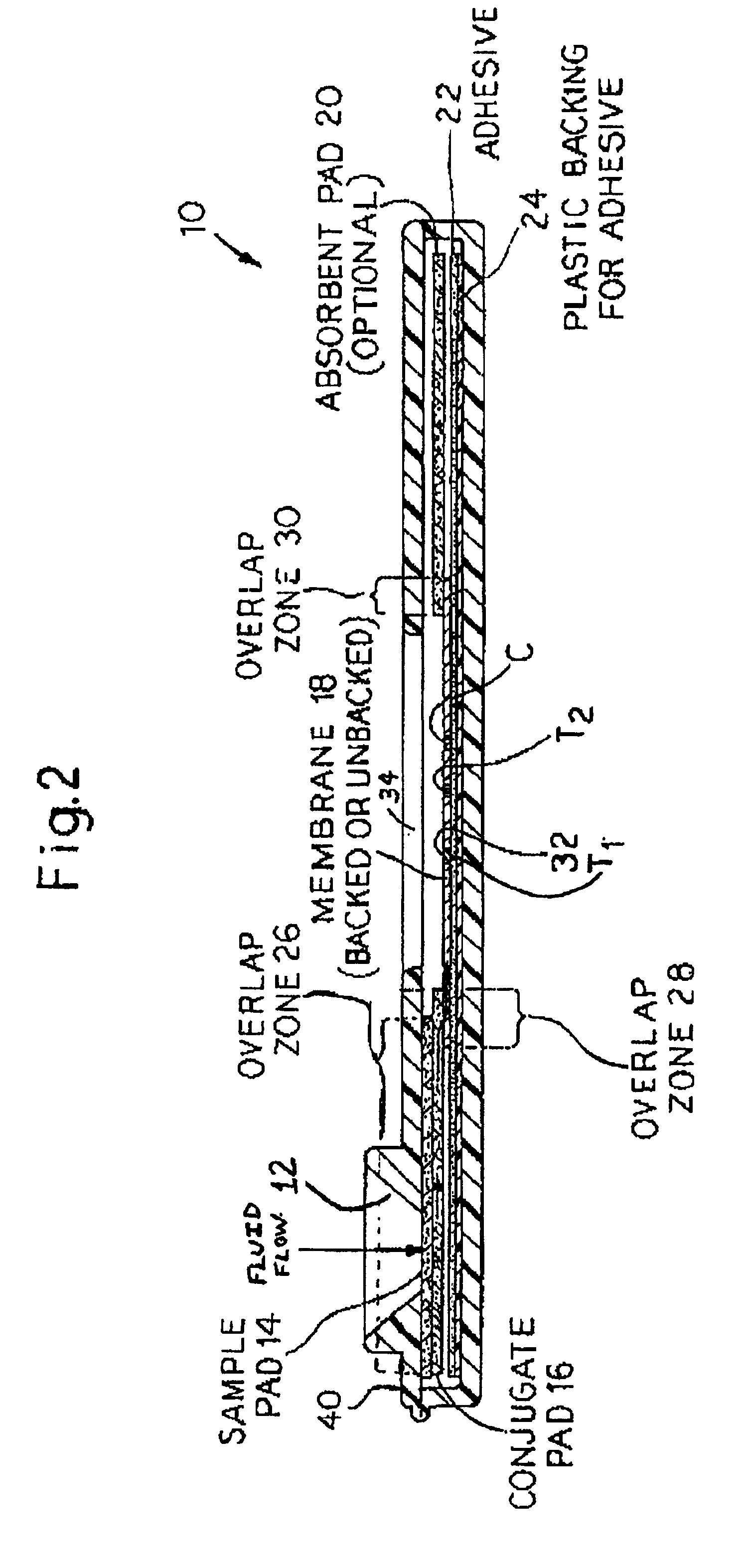
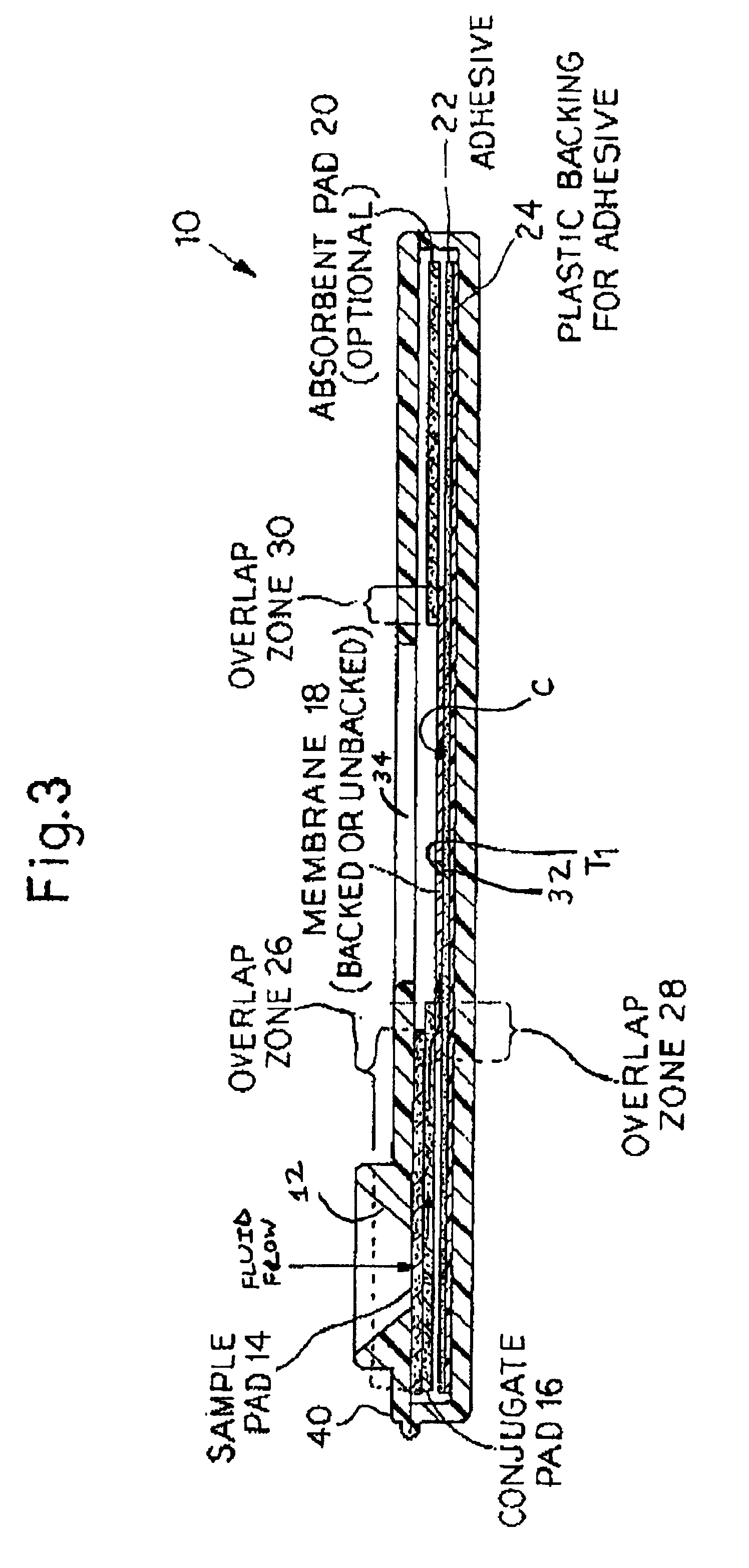
Rapid lateral flow assay for determining exposure to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacteria
InactiveUS6841159B2Auxiliary diagnosisAuxiliary judgmentBacterial antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMycobacterial antigenImmunization status
An assay method and kit is disclosed for detecting the presence of at least one predesignated, target antibody to a mycobacterium in a sample selected from one or more patient bodily fluids. The method comprises the following steps: (a) contacting the sample of one or more patient bodily fluids with at least one mycobacterium antigen on a lateral-flow assay membrane to bind to the target antibody in the sample; (b) previously, simultaneously or subsequently to step (a), binding the at least one mycobacterium antigen with a conjugated label producing a detectable signal; and (c) detecting the signal whereby the presence of the target antibody is determined in the sample by the intensity or presence of the signal. The method can further comprise the step of evaluating immunization status of the patient from whom the sample came by comparing the signal or lack thereof with immunizations previously received by the patient and in comparison to a known standard control. In a preferred embodiment, the mycobacterium antigen specifically binds to Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific antibodies. Preferably, the immunoassay of the present invention comprises a lateral-flow assay comprising a membrane, a conjugated label pad, and at least one mycobacterium antigen bound to the membrane. In a preferred embodiment, the at least one mycobacterium antigen is selected from the group consisting of 38 kDa and 16 kDa antigens.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
Fusion proteins of mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveUS7311922B1Good antigenicityHigh sensitivityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenSerum ige
The present invention relates to fusion proteins containing at least two Mycobacterium species antigens. In particular, it relates to nucleic acids encoding fusion proteins that include two or more individual M. tuberculosis antigens, which increase serological sensitivity of sera from individuals infected with tuberculosis, and methods for their use in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tuberculosis infection.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
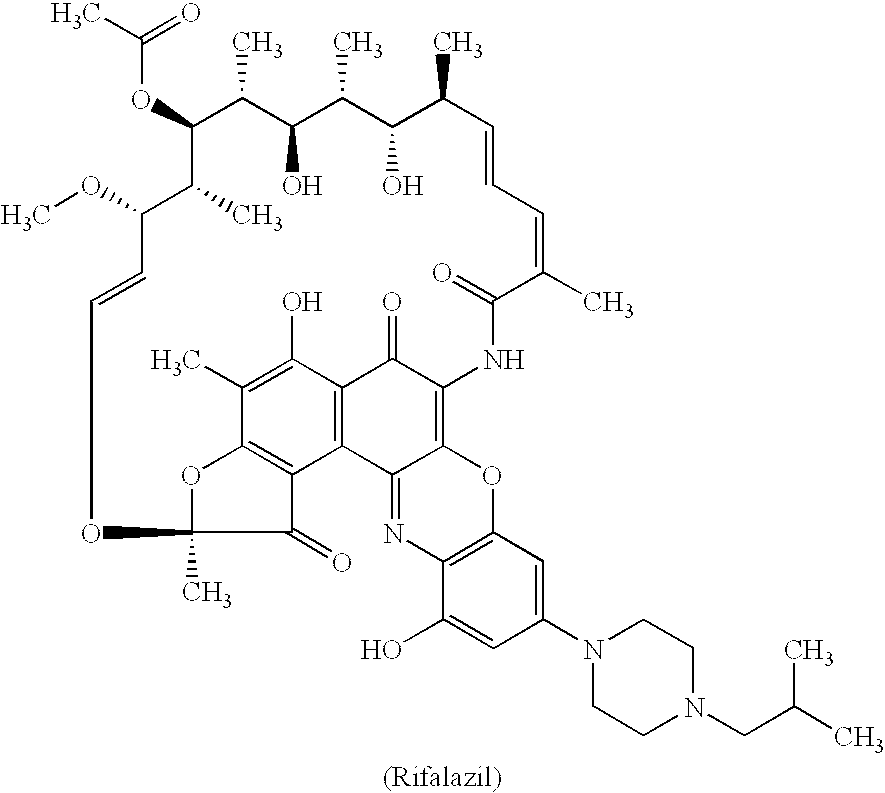
Method for treatment of bacterial infections with once or twice-weekly administered rifalazil
A method for treatment of bacterial infections with rifalazil administered once-weekly or twice-weekly. A method for treatment of tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, infections caused by Mycobacterium avium complex, infections caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae and infections caused by Helicobacter pylori by administering to a patient suffering from the bacterial infection 1-100 mg of rifalazil once or twice a week. In this dose regimen, the treatment is fast, efficacious and eliminates undesirable secondary symptoms observed with daily doses of 1-50 mg of rifalazil.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method to detect bacteria
InactiveUS6461833B1Reduce populationReduce needMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDrugBacilli
The present invention relates to a method for enhancing the time of response of an assay for a first bacterium, wherein: a) the first bacterium is exposed to infection by phage particles to which the first bacterium is permissive; b) the infected bacterium is treated to inactivate exogenous phage particles; c) the treated bacterium is cultivated in the presence of a second bacterium which is permissive to infection by the phage or its replicand and which has a doubling rate greater than the effective doubling rate of the first bacterium; and d) assessing the extent of plaque formation and / or of second bacterium growth in the cultivated second bacterium cells. The method can be used to assess the presence of first bacterium in a sample, notably where the first bacterium is a slow growing bacterium, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, where the method enables an operator to detect the presence of low amounts of the bacterium in sample within days instead of weeks as required by conventional cultivation techniques. The invention can also be used to assess the effect of a drug or other treatment on a bacterium or on a virus. The invention also provides a diagnostic kit for use in the method of the invention.
Owner:BIOTEC LAB
Fusion proteins of mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveUS20080269151A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntigenTuberculosis mycobacterium
The present invention relates to fusion proteins containing at least two Mycobacterium species antigens. In particular, it relates to nucleic acids encoding fusion proteins that include two or more individual M. tuberculosis antigens, which increase serological sensitivity of sera from individuals infected with tuberculosis, and methods for their use in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tuberculosis infection.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
Crystalline form of r)-3-(4-(2-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)pyridin- 5-yl)-3-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxymethyl oxazolidin-2-one dihydrogen phosphate
ActiveUS20100227839A1Reduce filter timeImprove usabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphateAntibacterial activity
A crystalline form of crystalline (R)-3-(4-(2-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-5-yl)-3-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxymethyl oxazolidin-2-one dihydrogen phosphate, methods of making the crystalline form and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the crystalline form are useful antibiotics. Further, the derivatives of the present invention may exert potent antibacterial activity versus various human and animal pathogens, including Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococi, Enterococci and Streptococi, anaerobic microorganisms such as Bacteroides and Clostridia, and acid-resistant microorganisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium. Accordingly, the compositions comprising the crystalline form may be used in antibiotics.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Method for simultaneous detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and identification of mutations in mycobacterial DNA resulting in the resistance of microorganisms to rifampicin and isoniazid on biological microarrays, set of primers, biochip, and set of oligonucleotide probes used in the method
InactiveUS20100261163A1Low costShort timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIsoniazidNucleotide
The present invention relates to molecular biology, microbiology, and medicine and provides the method for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex with simultaneous evaluation of sensitivity of the strains to rifampicin and isoniazid in clinical sample on differentiating biochip. The method is based on two-stage multiplex PCR to obtain fluorescent DNA fragments followed by hybridization of these fragments on microarray containing the set of specific discriminating oligonucleotides. The determination of the resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to rifampicin and isoniazid is carried out by evaluation of point nucleotide substitutions in DNA of microorganism. The present invention allows conduct analysis directly in clinical sample, to evaluate a number of mutations simultaneously, to decrease the cost price of analysis, and to reduce the time of its conducting. The present invention also relates to set of primers, biochip, and set of oligonucleotide probes used in realization of the method.
Owner:UCHREZHDENIE ROSSIISKOI AKADI NAUK INST MOLEKULYARNOI BLOLOGII IM V A ENGELGARDTA RAN IMB RAN
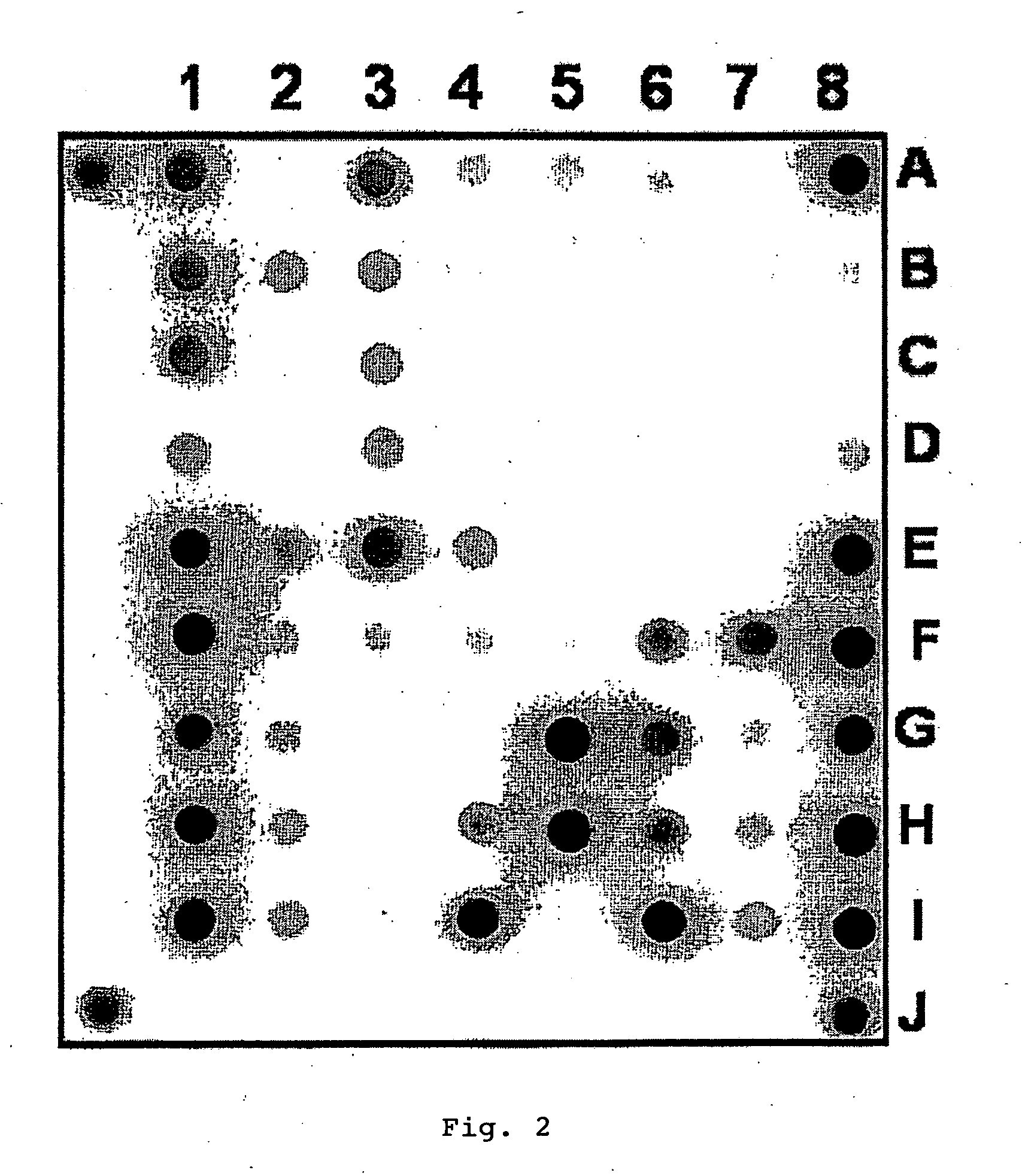
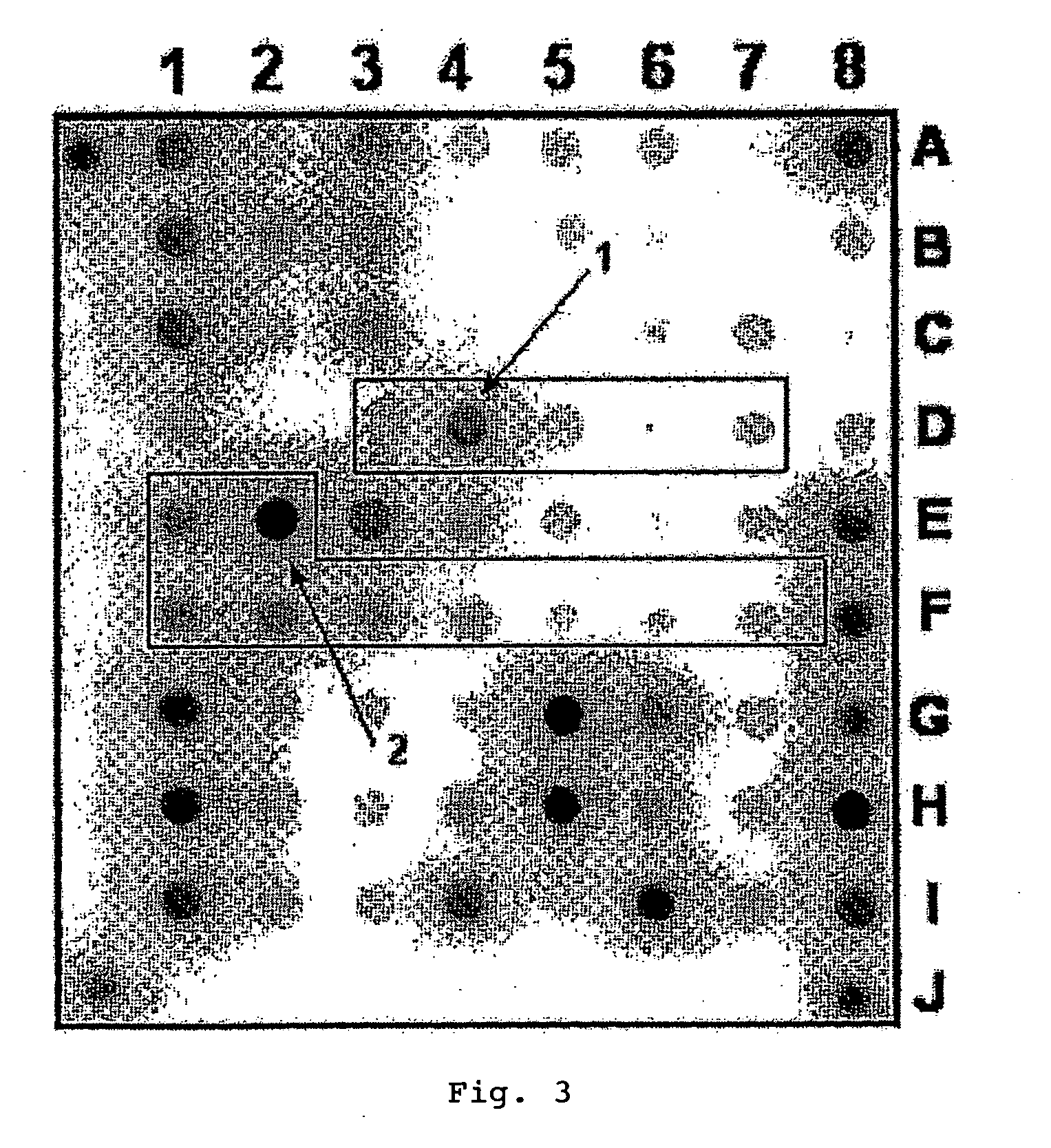
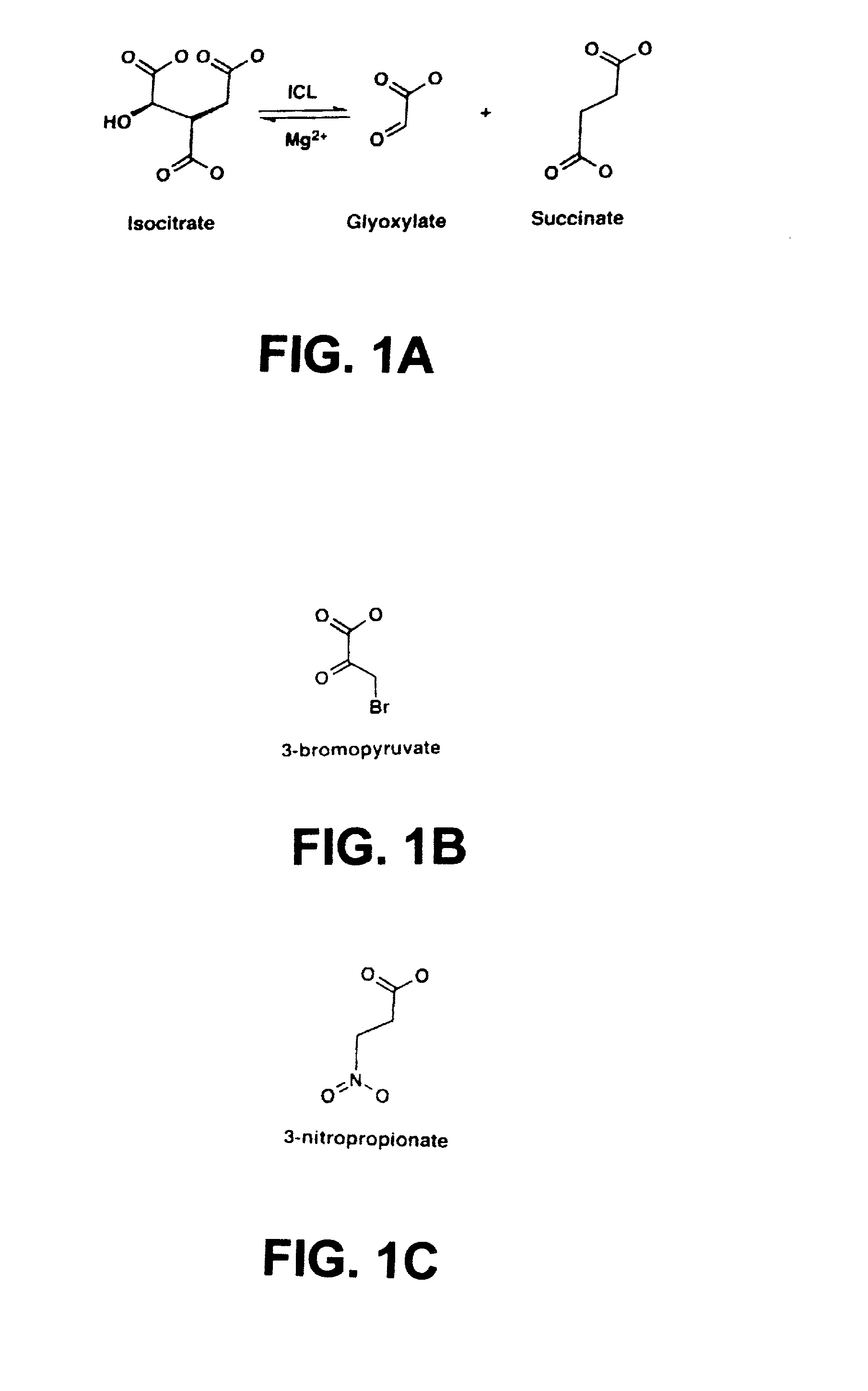
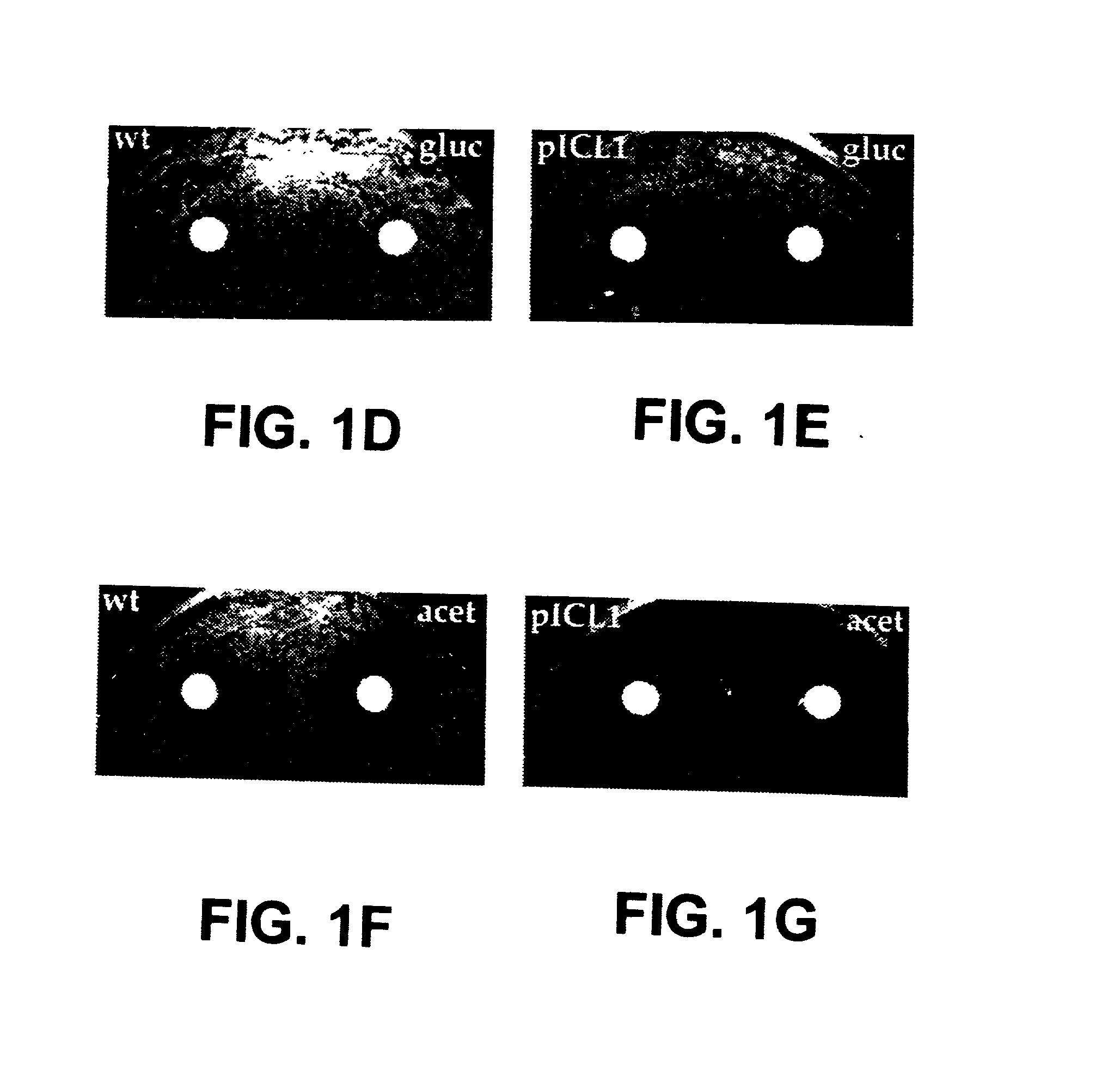
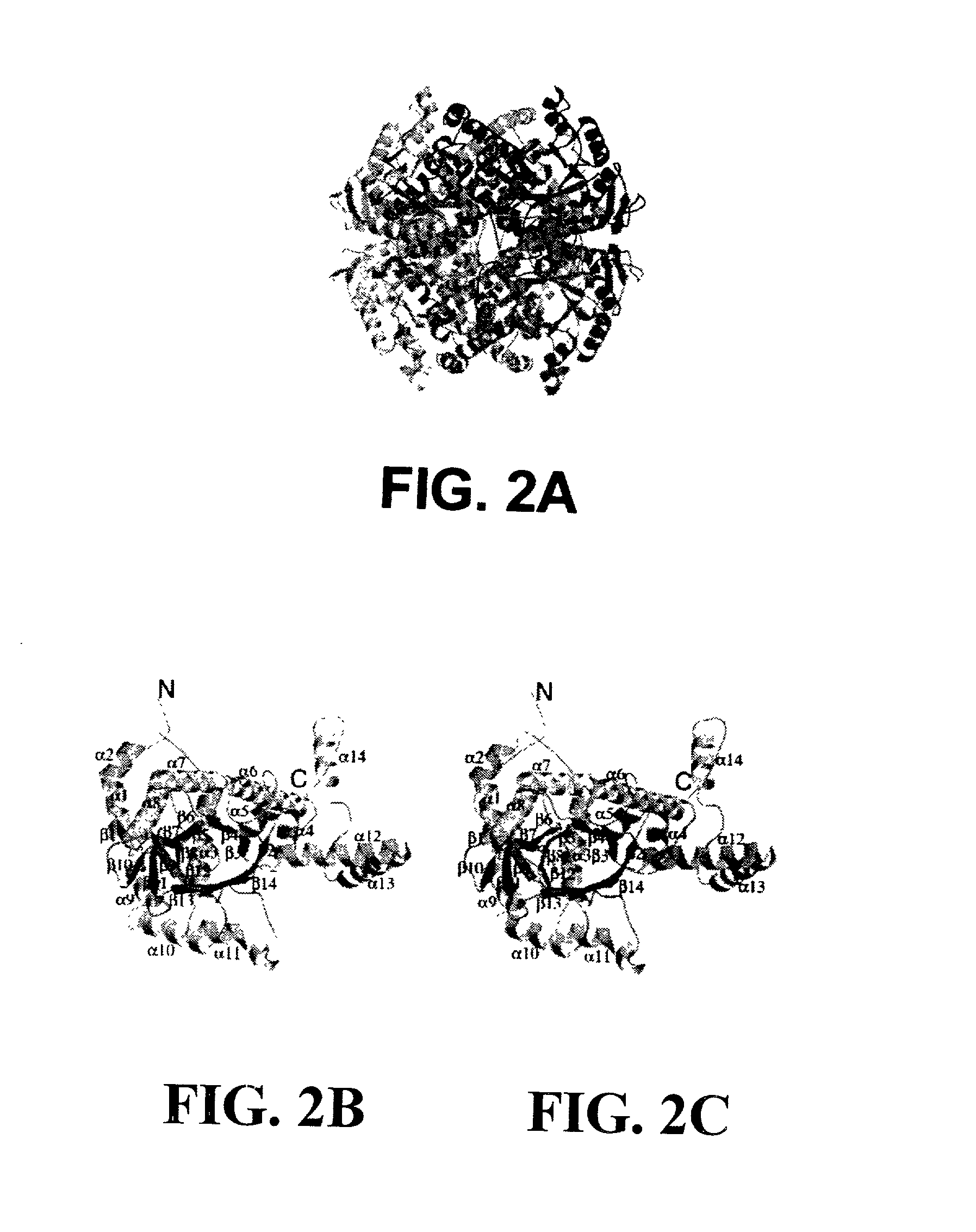
Structure of isocitrate lyase enzyme from mycobacterium tuberculosis and inhibitory agents to combat persistent infection
InactiveUS20030018166A1Reduce usagePromote recombinationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMalate synthaseMicroorganism
The invention provides methods and compositions for use in identifying inhibitors of biochemical pathways important for persistent infection, allowing the identification and / or design of improved therapeutics for treating persistent infections by pathogenic microbes. Particularly disclosed is the importance of the glyoxylate shunt to the persistent phase of various infectious agents, including Mycobacteria, such as M. tuberculosis, and the identification of preferred targets for drug development, including the enzymes isocitrate lyase (ICL) and malate synthase. Crystals and three-dimensional structures of M. tuberculosis ICL, without ligand and in complex with two inhibitors are also disclosed, for exemplary use in the design of inhibitors and therapeutic agents.
Owner:BIOCHAIN INST
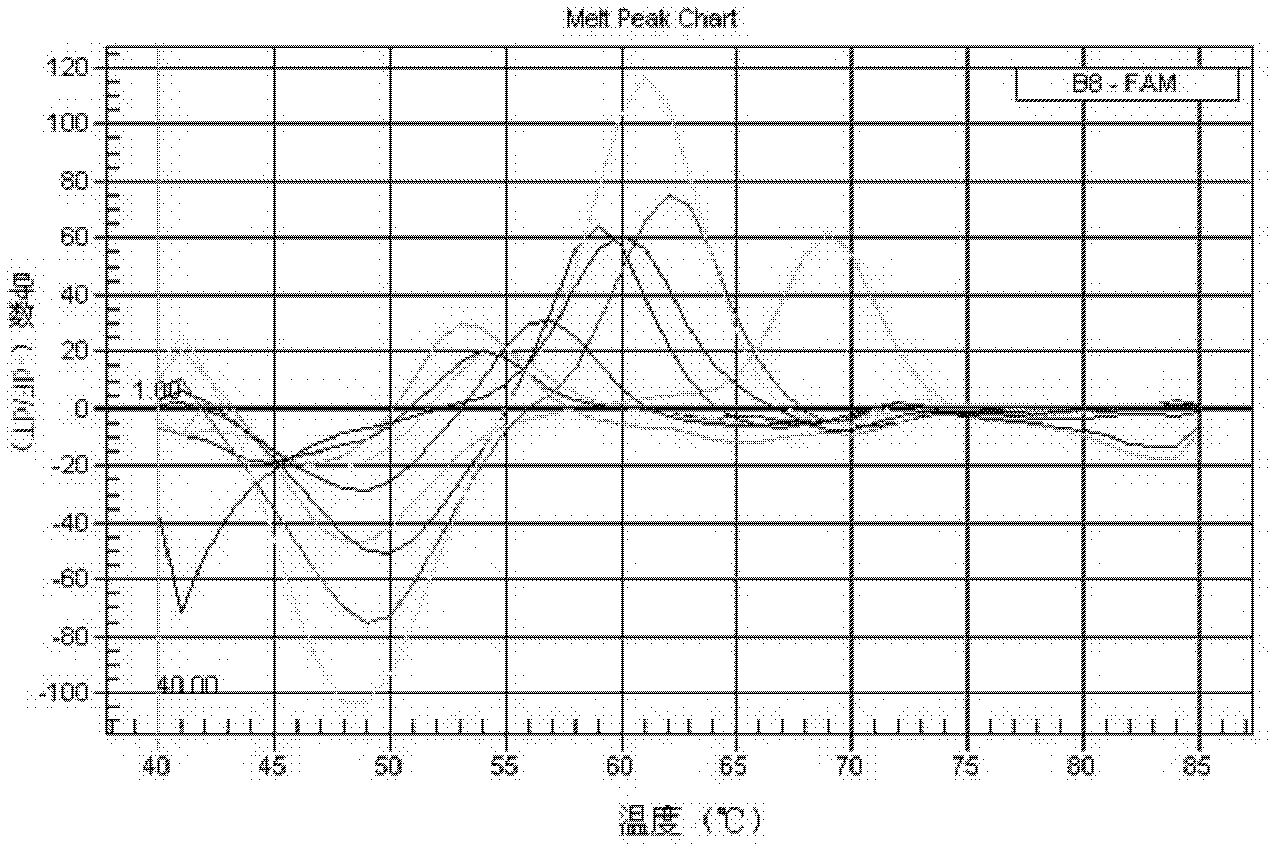
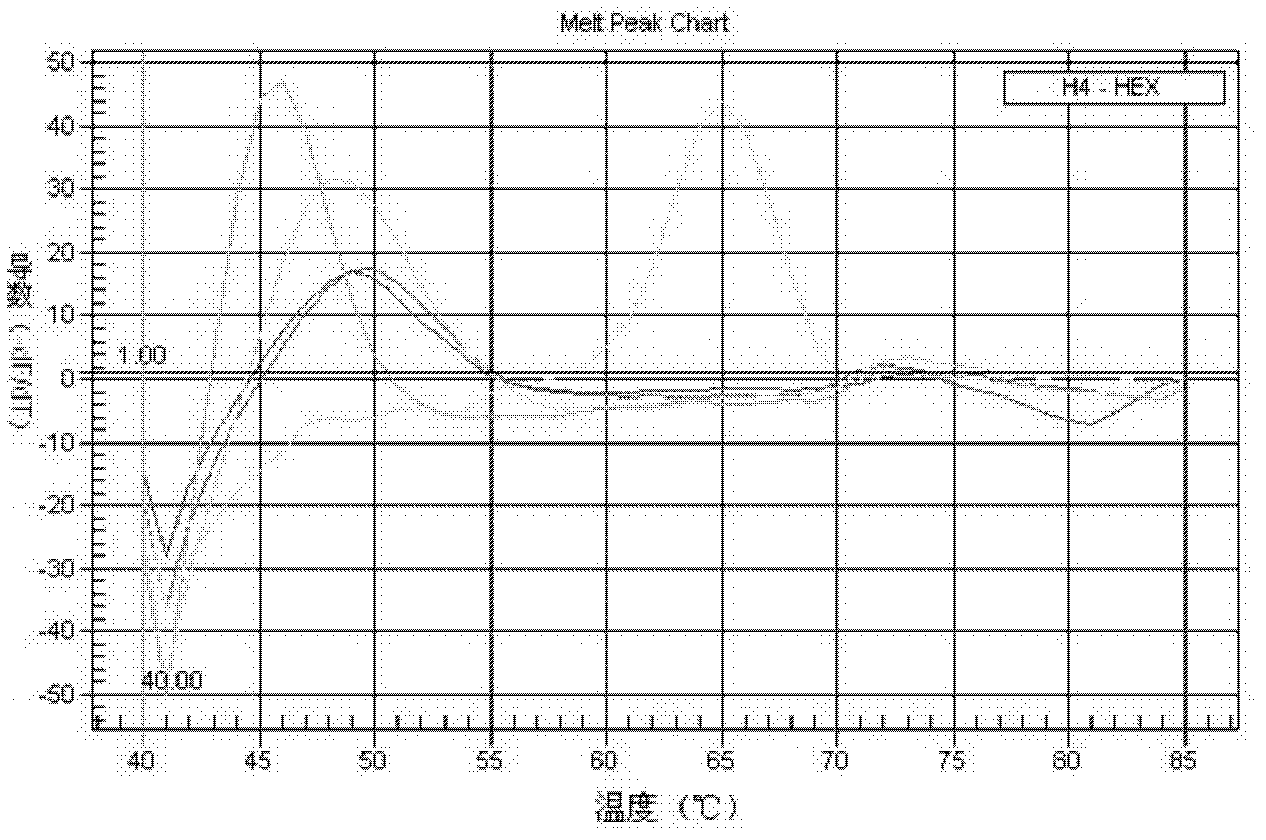
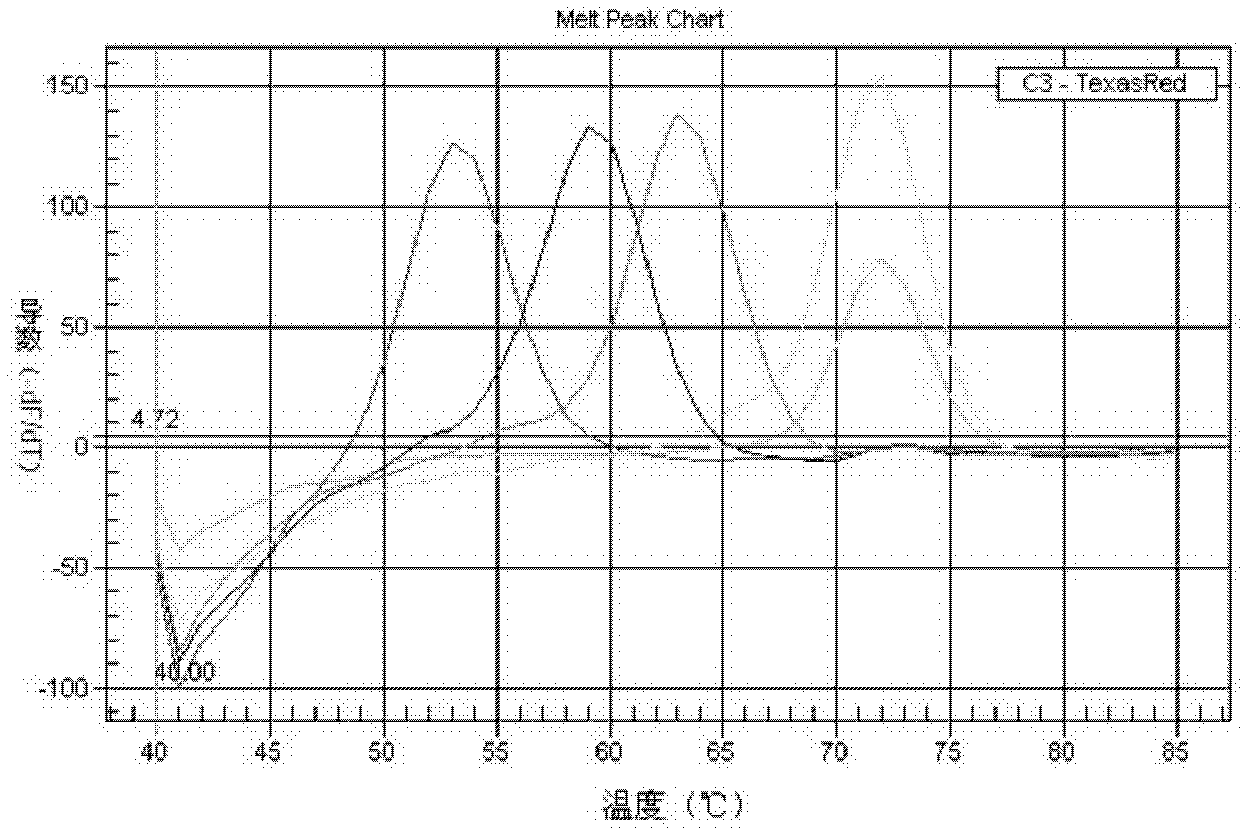
Rapid identification method and kit of novel mycobacterium strain
ActiveCN102634575AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceRapid identificationNuclease
The invention relates to a double-marking probe detecting and melting curve analyzing method used for identifying mycobacterium strains and a kit using the method to identify various mycobacterium strains at the same time. The kit provided by the invention comprises a primer capable of designing mycobacterium 16S rRNA, a double-marking oligonucleotide probe capable of identifying mycobacterium strains, and a thermostable DNA polymerase without 5' nuclease activity. The detecting method and the kit, which are provided by the invention, can detect and / or identify 24 kinds of common mycobacteria. The method and the kit can judge the results according to melting peaks of different Tm values produced by the sequence hybridization of the probe and the different strains, meanwhile rapidly and accurately detect the mycobacteria, and identify the mycobacteria, non-mycobacteria, mycobacterium tuberculosis compounding groups and nontuberculosis mycobacteria, and the result of identifying the mycobacteria can be reported after 3-4 hours, thus the method and the kid can assist the clinical diagnosis, and guide efficient clinical chemotherapy at the early stage.
Owner:THE 309TH HOSPITAL OF CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY +1
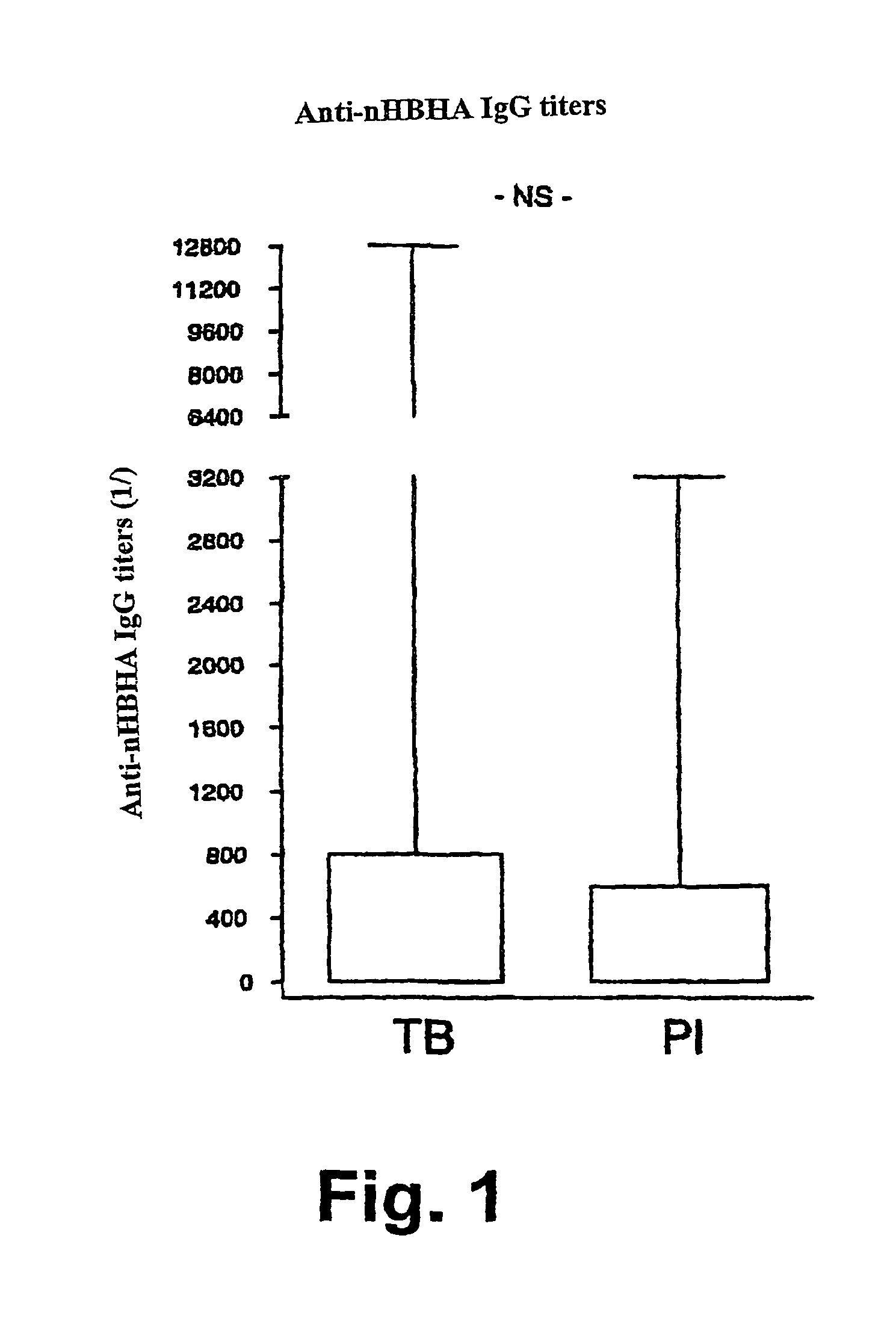
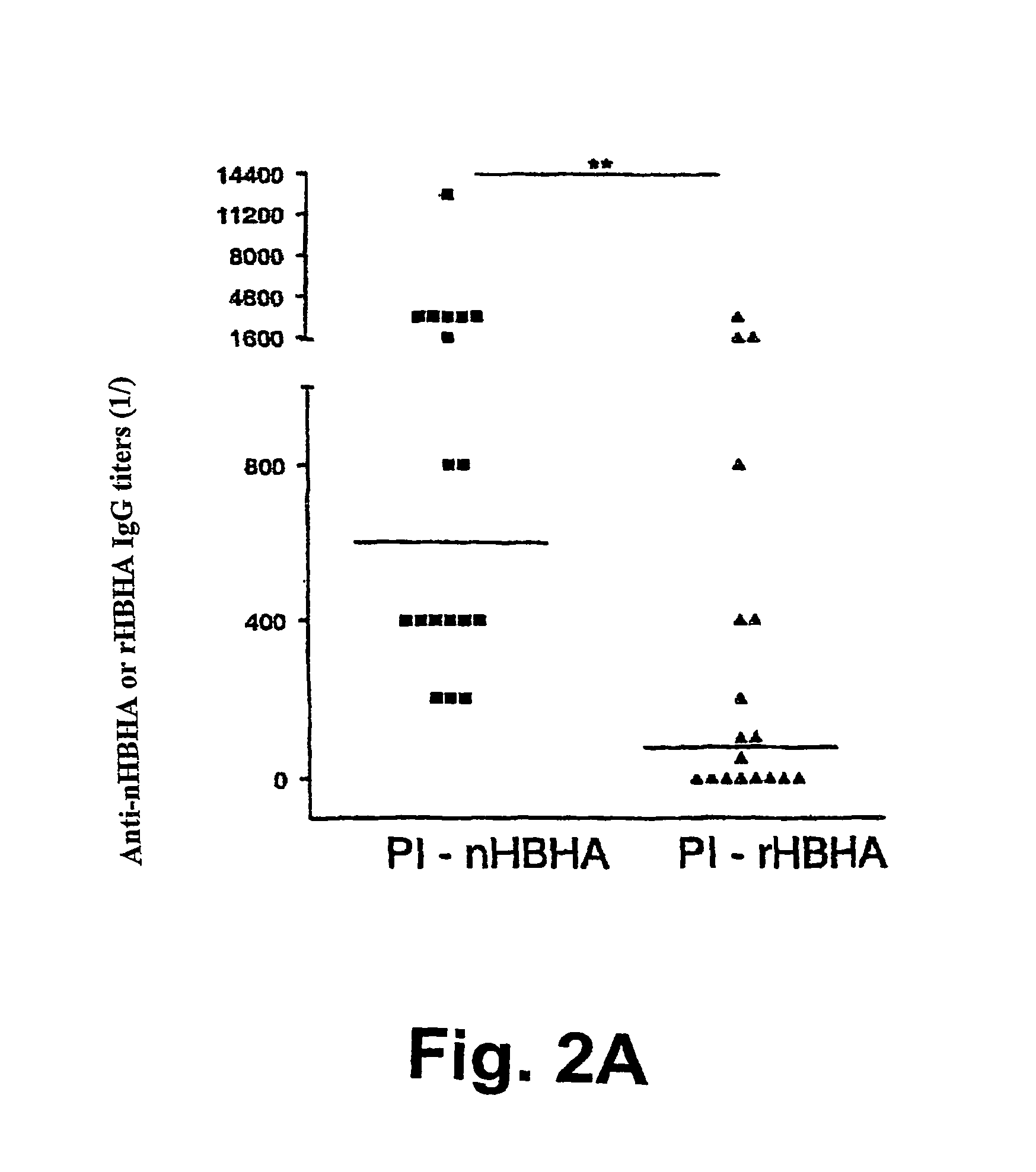
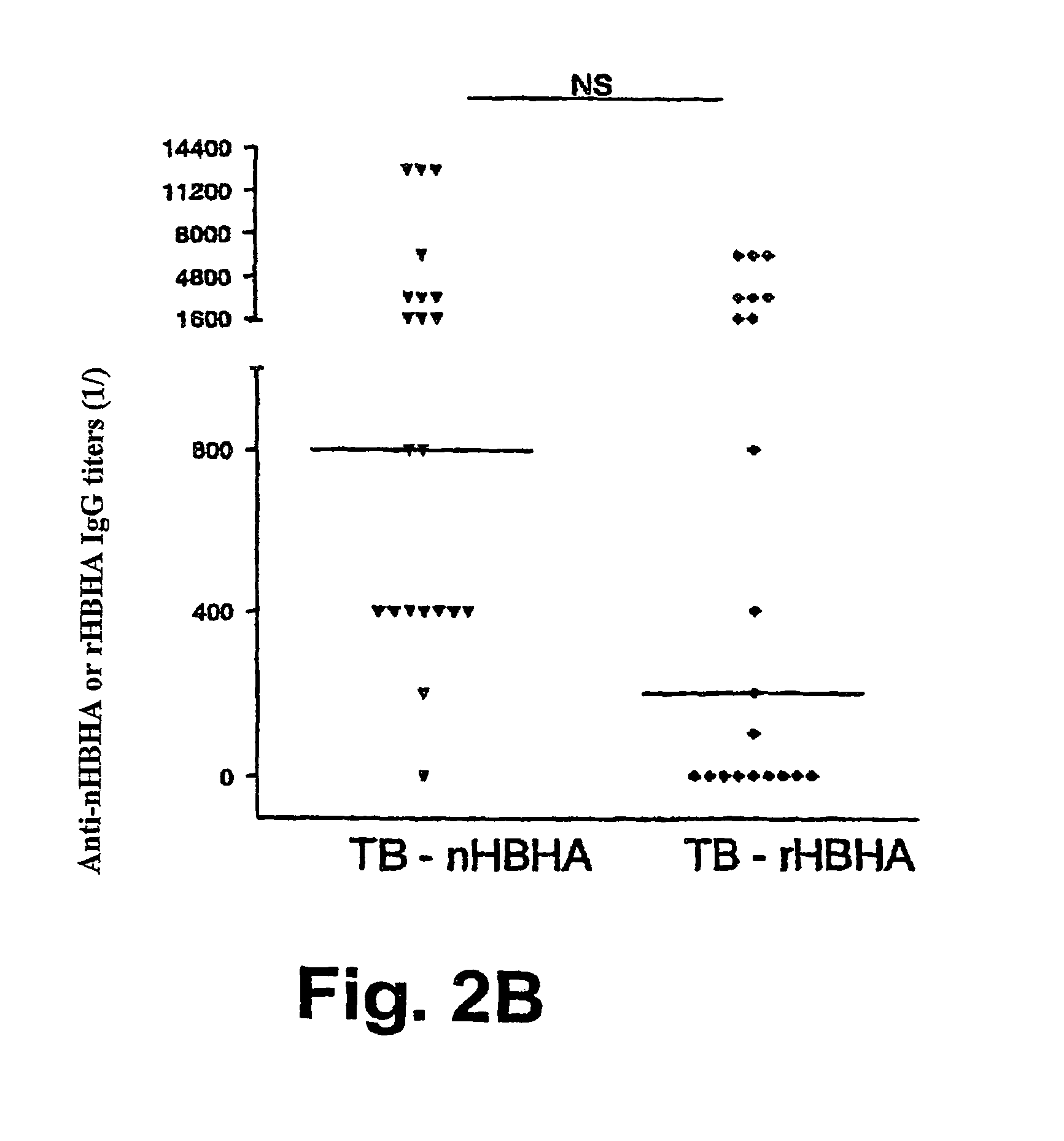
Detection of tuberculosis and infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis using HBHA
The present invention concerns methods for in vitro detection of an infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mammals, and methods for in vitro distinction between mammals infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in which the disease is declared (active form) and mammals which are infected but asymptomatic for tuberculosis (latent form), and a method for in vitro distinction between mammals presenting an active form of tuberculosis and mammals not infected by M. tuberculosis or presenting a latent form of tuberculosis. The present invention also pertains to kits for detection and distinction between infected mammals presenting tuberculosis symptoms and infected mammals with no disease development, and a kit for distinguishing between mammals presenting an active form of tuberculosis and mammals not infected by M. tuberculosis or presenting a latent form of tuberculosis.
Owner:INSTITUT PASTEUR DE LILLE +3
Rapid genotyping analysis and devices thereof
InactiveUS20130244887A1Accurate measurementNot require expensiveMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationDiseaseGenotyping
The present invention discloses methods, primer, probes, and kits for genotyping various mutations or disease-causing agent. In one embodiment, the present invention is applied to detecting the presence of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis, HBV, beta-globin mutations, mutations related to thrombophilia, or the presence of sexually transmitted diseases in a subject.
Owner:DIAGCOR LIFE SCI LTD
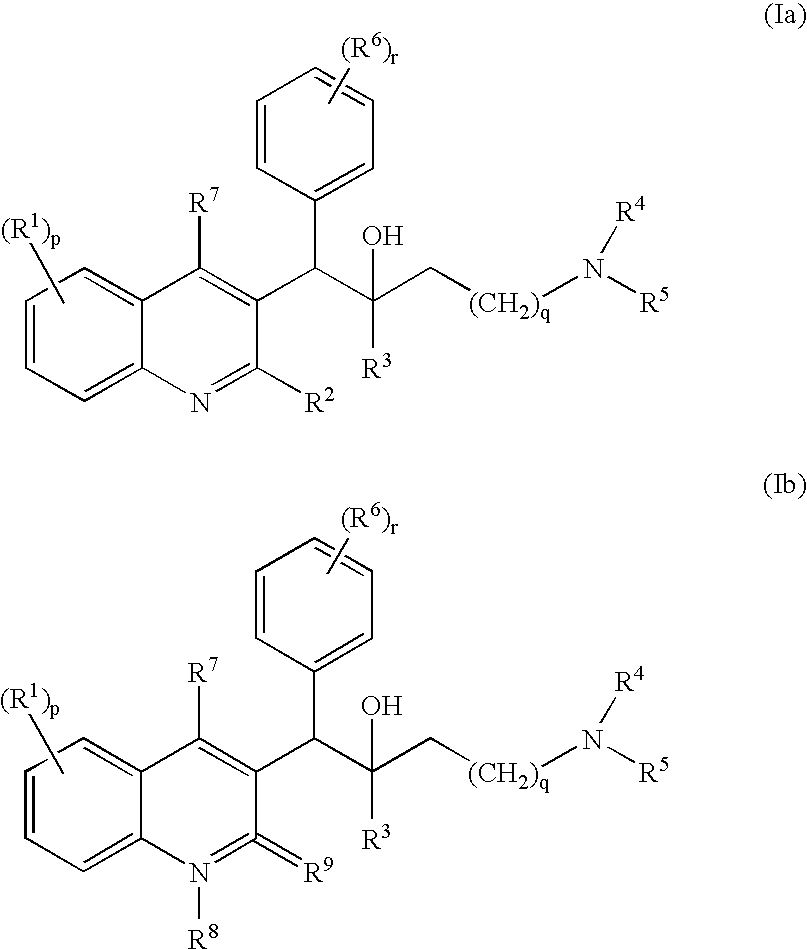
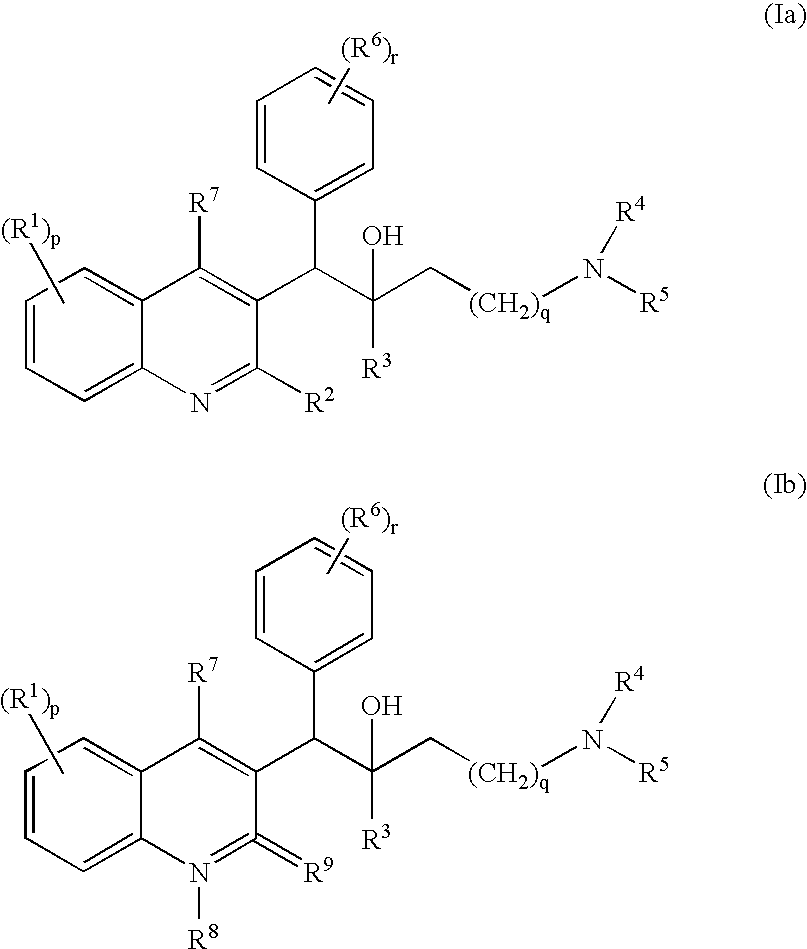
Mycobacterial inhibitors
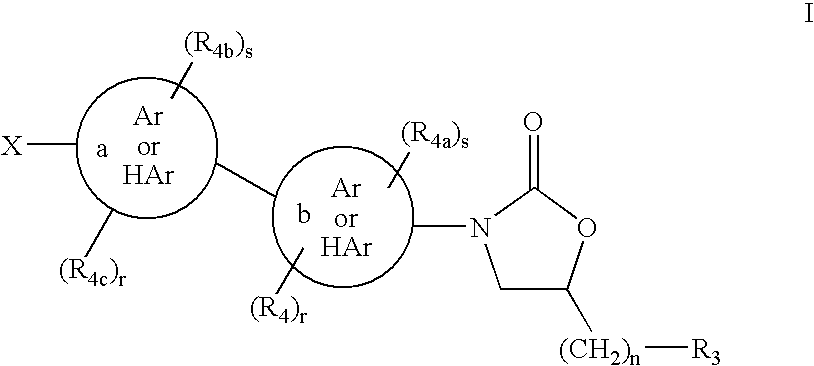
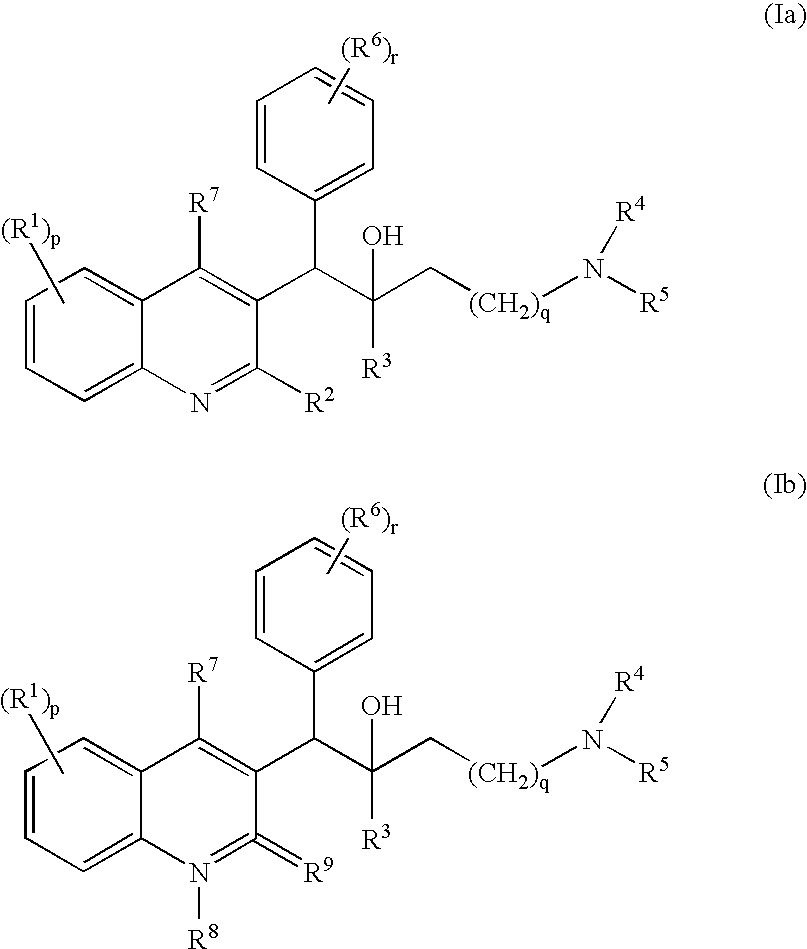
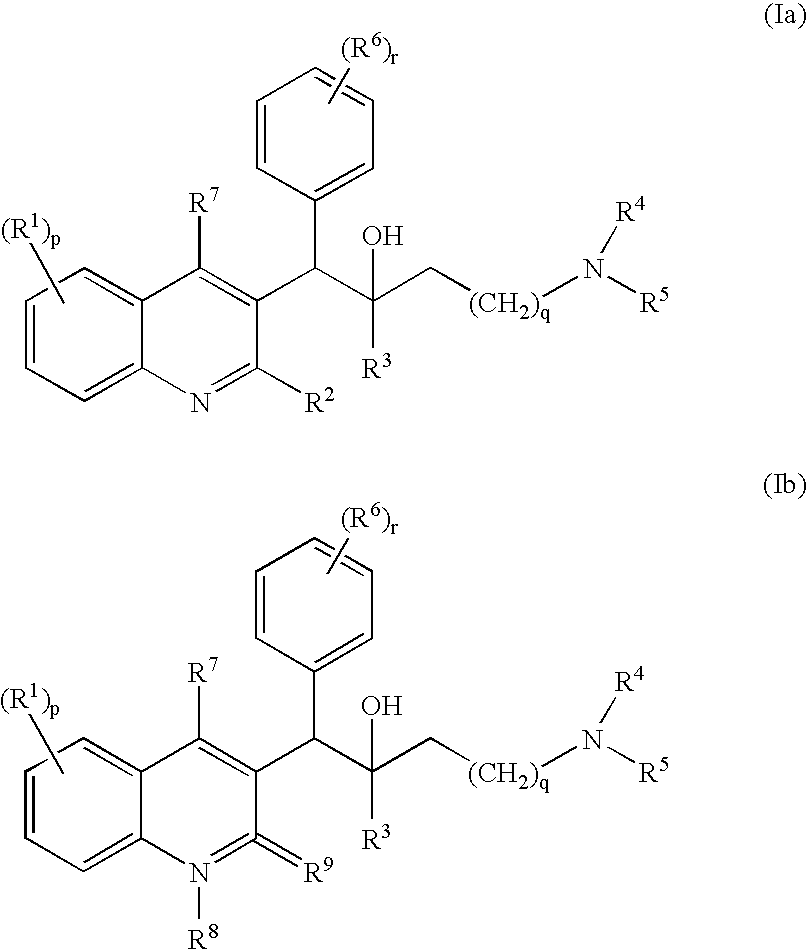
The present invention relates to novel substituted quinoline derivatives according to the general Formula (Ia) or the general Formula (Ib)the pharmaceutically acceptable acid or base addition salts thereof, the stereochemically isomeric forms thereof, the tautomeric forms thereof and the N-oxide forms thereof. The claimed compounds are useful for the treatment of mycobacterial diseases, particularly those diseases caused by pathogenic mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. avium and M. marinum. In particular, compounds are claimed in which, independently from each other, R1 is bromo, p=1, R2 is alkyloxy, R3 is optionally substituted naphthyl or phenyl, q=1, R4 and R5 each independently are hydrogen, methyl or ethyl, R6 is hydrogen, r is equal to 0 or 1 and R7 is hydrogen. Also claimed is a composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and, as active ingredient, a therapeutically effective amount of the claimed compounds, the use of the claimed compounds or compositions for the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of mycobacterial diseases and a process for preparing the claimed compounds.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Nucleic acid fragments and polypeptide fragments derived from M. tuberculosis
InactiveUS20020094336A1Bacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSkin testADAMTS Proteins
The present invention is based on the identification and characterization of a number of M. tuberculosis derived novel proteins and protein fragments (SEQ ID NOs: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 17-23, 42, 48, 50, 52, 54, 56, 58, 60, 62, 64, 66, 68, 70, 72-86, 88, 90, 92, 94, 141, 143, 145, 147, 149, 151, 153, and 168-171). The invention is directed to the polypeptides and immunologically active fragments thereof, the genes encoding them, immunological compositions such as vaccines and skin test reagents containing the polypeptides. Another part of the invention is based on the surprising discovery that fusions between ESAT-6 and MPT59 are superior immunogens compared to each of the unfused proteins, respectively.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Cyclopropyl group substituted oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof
This invention relates to new oxazolidinones having a cyclopropyl moiety, which are effective against aerobic and anerobic pathogens such as multi-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci, Bacteroides spp., Clostridia spp. species, as well as acid-fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species. The compounds are represented by structural formula I: its enantiomer, diastereomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Novel mycobacterial inhibitors
The present invention relates to novel substituted quinoline derivatives according to the general Formula (Ia) or the general Formula (Ib) the pharmaceutically acceptable acid or base addition salts thereof, the stereochemically isomeric forms thereof, the tautomeric forms thereof and the N-oxide forms thereof. The claimed compounds are useful for the treatment of mycobacterial diseases, particularly those diseases caused by pathogenic mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. avium and M. marinum. In particular, compounds are claimed in which, independently from each other, R1 is bromo, p=1, R2 is alkyloxy, R3 is optionally substituted naphthyl or phenyl, q=1, R4 and R5 each independently are hydrogen, methyl or ethyl, R6 is hydrogen, r is equal to 0 or 1 and R7 is hydrogen. Also claimed is a composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier and, as active ingredient, a therapeutically effective amount of the claimed compounds, the use of the claimed compounds or compositions for the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of mycobacterial diseases and a process for preparing the claimed compounds.
Owner:JANSSEN PHARMA NV
Compound for inhibiting mycobacterium tuberculosis, screening method and uses thereof
InactiveCN102732474AInhibitory activityReduce workloadAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseTyrosine
The present invention discloses a screening method of a compound for inhibiting mycobacterium tuberculosis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a screening model adopting tyrosine phosphatase as a target point: adopting genome DNA of tubercle bacillus H37 Rv as a template, adopting a PCR technology to clone tyrosine phosphatase gene, transforming host cells, culturing the transformant to obtain recombinant tyrosine phosphatase from the culture, carrying out enzyme activity analysis, and establishing the screening model adopting tyrosine phosphatase as the target point; and (2) adopting the screening model established in the step (1) to screen a compound providing inhibition activity for the tyrosine phosphatase. With the method of the present invention, the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor with anti-mycobacterium tuberculosis effect can be rapidly and efficiently screened. In addition, the present invention further discloses a compound screened by using the screening method, and uses of the compound in preparations of drugs for treatments of diseases, wherein the inducement or one of the inducements of the diseases is the tyrosine phosphatase.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bacterial strain eliminating aquatic product Gram-positive pathogenic bacterium and application thereof
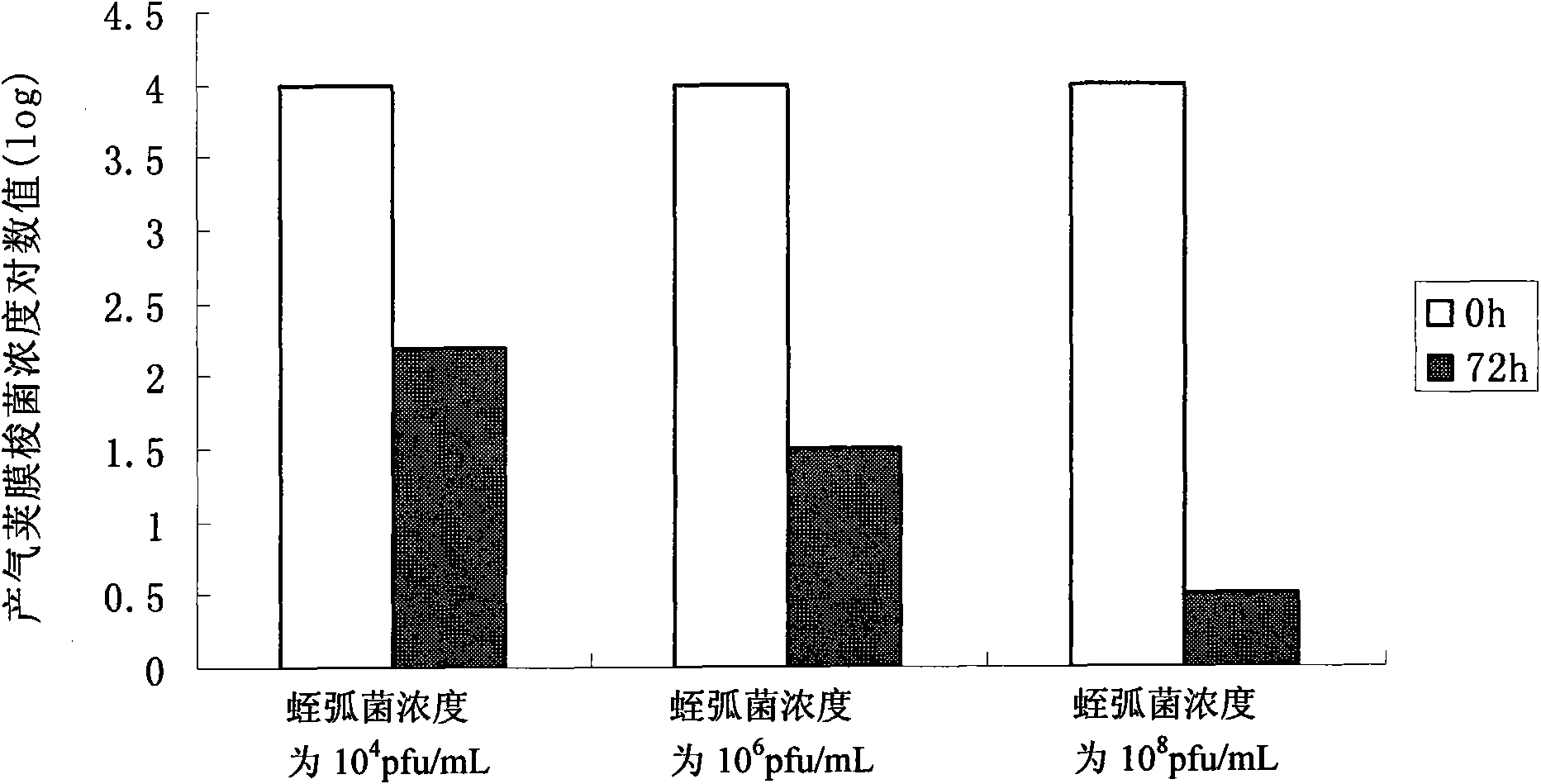
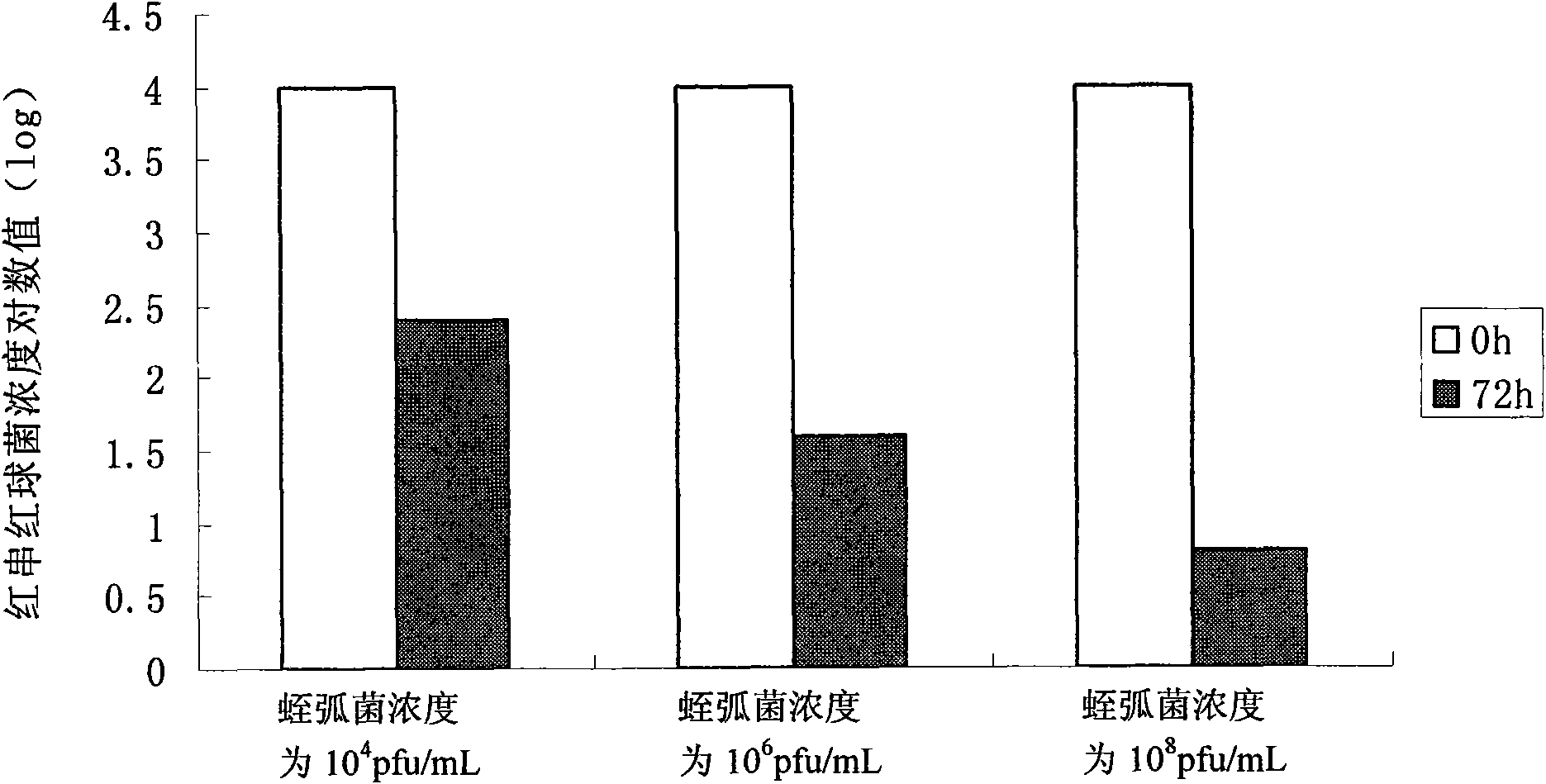
The invention discloses a bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bacterial strain eliminating aquatic product Gram-positive pathogenic bacterium and an application thereof. The invention separates to obtain bdellovibrio bacteriovorus BDS02 the length of flagellum of which is at least 1.8mu m. The bdellovibrio bacteriovorus with flagellum on the end is cambered single cell the size of which is 0.65*0.2 mu m when observed by an electron microscope. The two layer plating method is used for cultivating the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bacterial strain at the temperature of 28 DEG C for four days to form transparent round negativecolony the diameter of which is 1-2mm. Before the microorganism preparation prepared by the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus BDS02 is eaten by aquatic products, common Gram-positive pathogenic bacteria comprising Mycobacterium tuberculosis, star-shaped nocardia asteroids, rhodococcus erythropolis, streptococcus faecalis, staphylococcus epidermidis, clostridium perfringens and corynebacterium glutamicum in the transportation process and cultivation process can be eliminated, which improves the safe factor of raw aquatic products for consumers, protects the health of the consumers and provides guarantee for greenly processing and producing the aquatic products.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
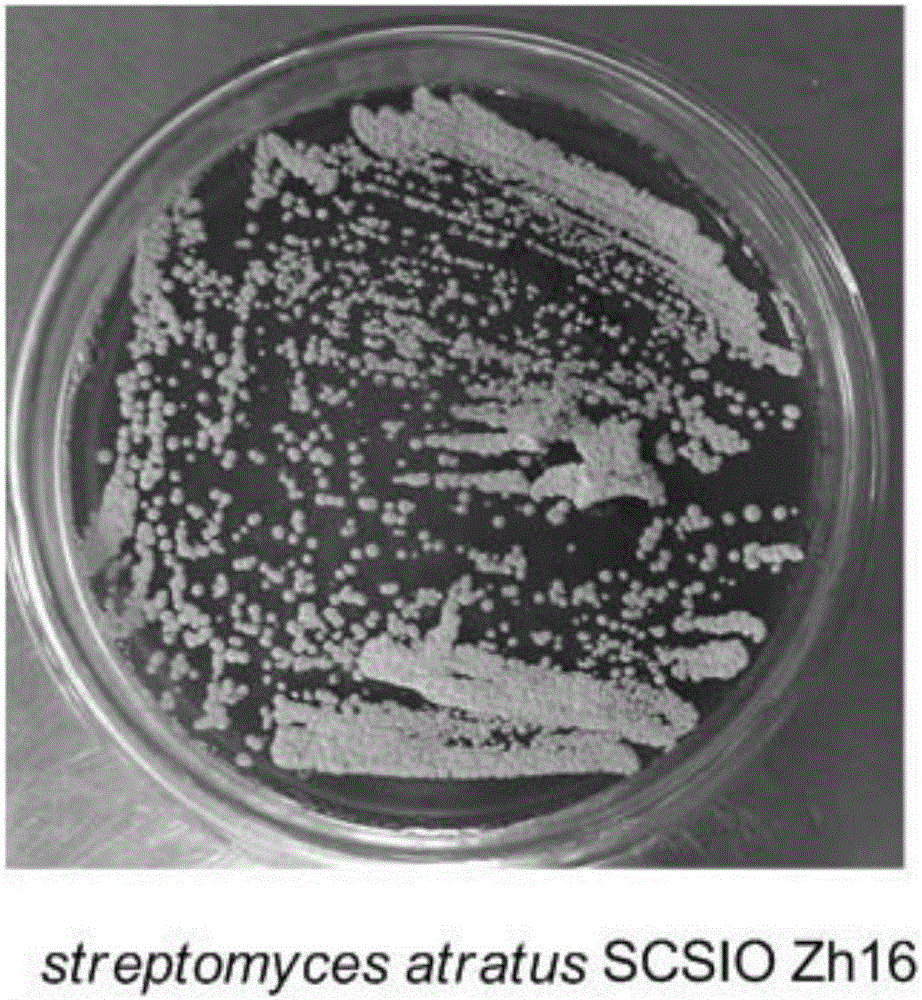
Streptomyces atratus and application of cyclic peptide compounds with same to preparing mycobacterium tuberculosis resistant medicines
ActiveCN106279370AGood inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsBacteriaCyclic peptideAntituberculous drugs
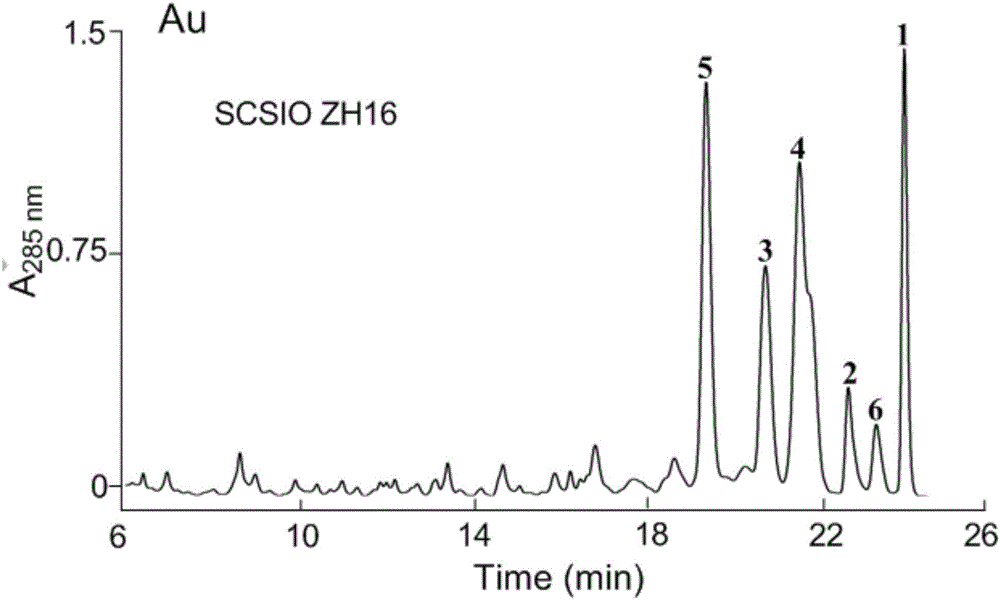
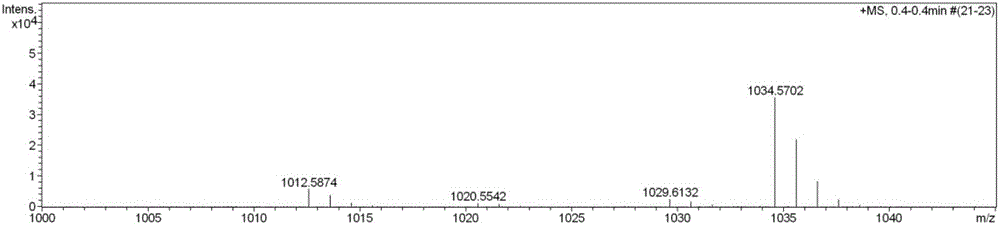
The invention discloses streptomyces atratus and application of cyclic peptide compounds with the same to preparing mycobacterium tuberculosis resistant medicines. A structural formula of the cyclic peptide compounds is shown. A preservation number of the streptomyces atratus SCSIO Zh16 is CGMCC No.12198. The streptomyces atratus and the application have the advantages that the six cyclic peptide compounds are obtained from fermentation cultivation substances of the streptomyces atratus SCSIO Zh16 by means of separation, the cyclic peptide compound 6 is high in mycobacterium tuberculosis resistant activity, obvious effects of inhibiting mycobacterium tuberculosis can be realized by the cyclic peptide compound, accordingly, the cyclic peptide compounds can be used for preparing anti-tuberculosis medicines and can be used for treating tuberculosis, alternative compounds can be provided for developing novel anti-tuberculosis medicines, and the streptomyces atratus and the application have important significance on developing marine medicinal materials in China.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
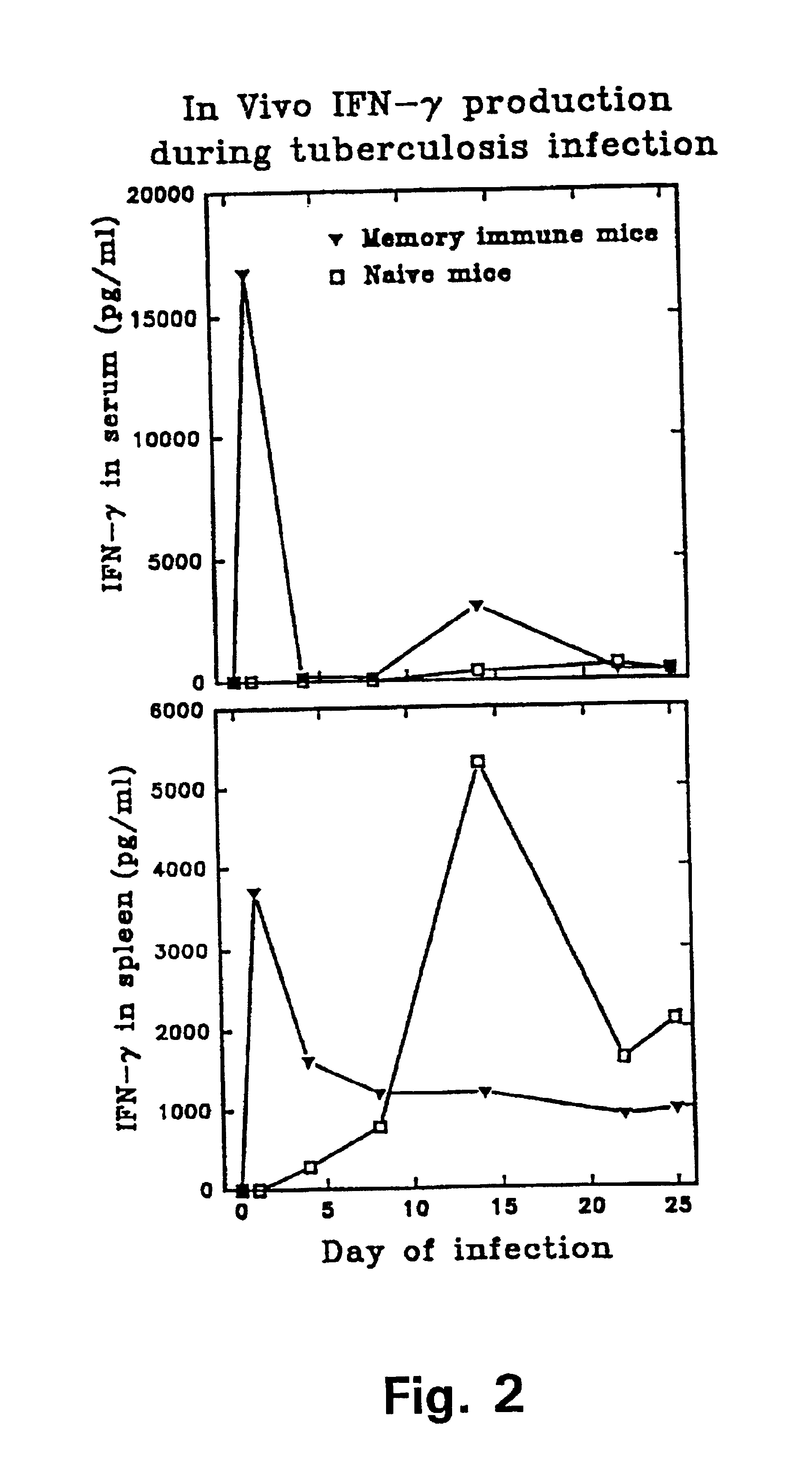
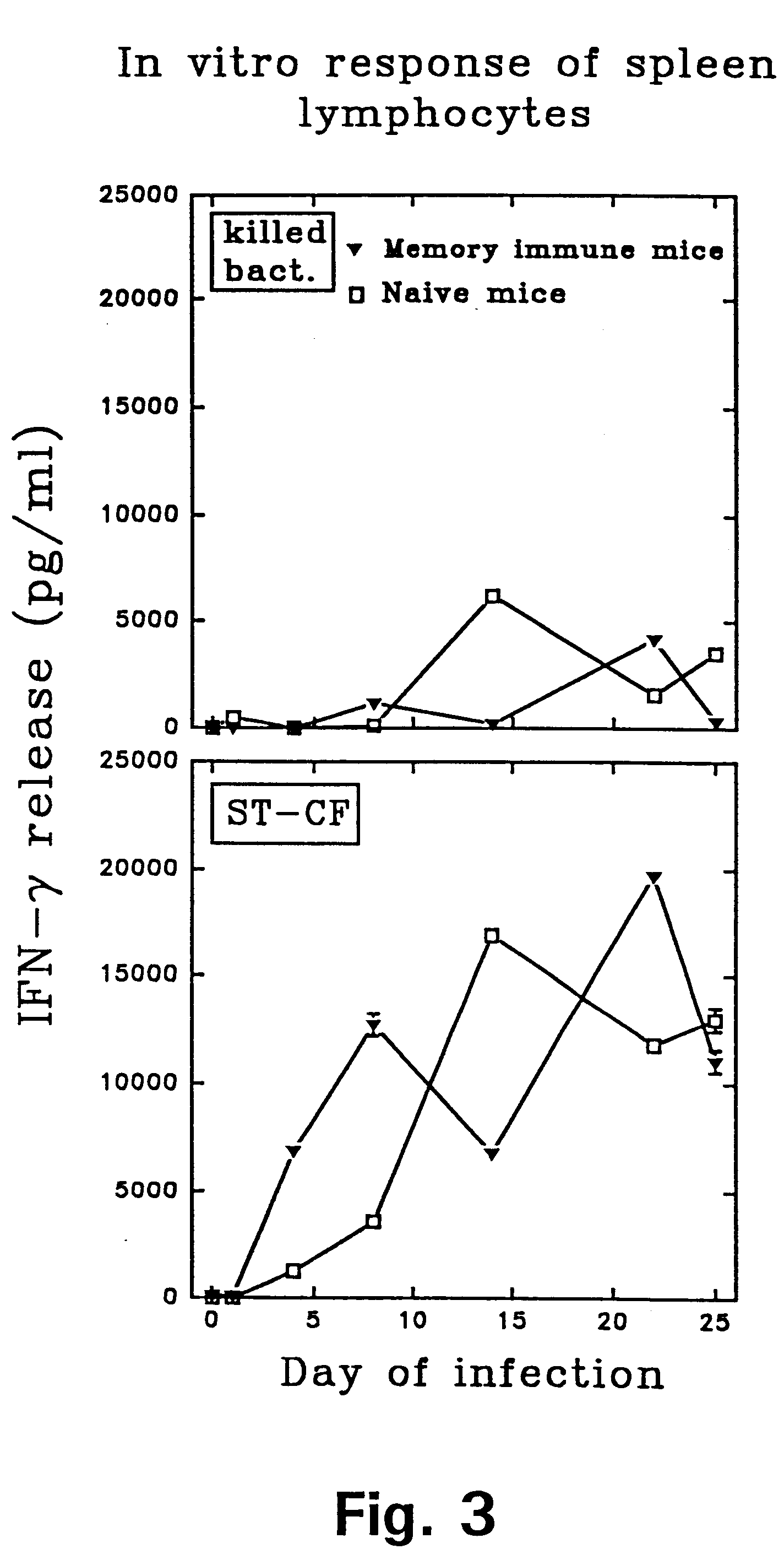
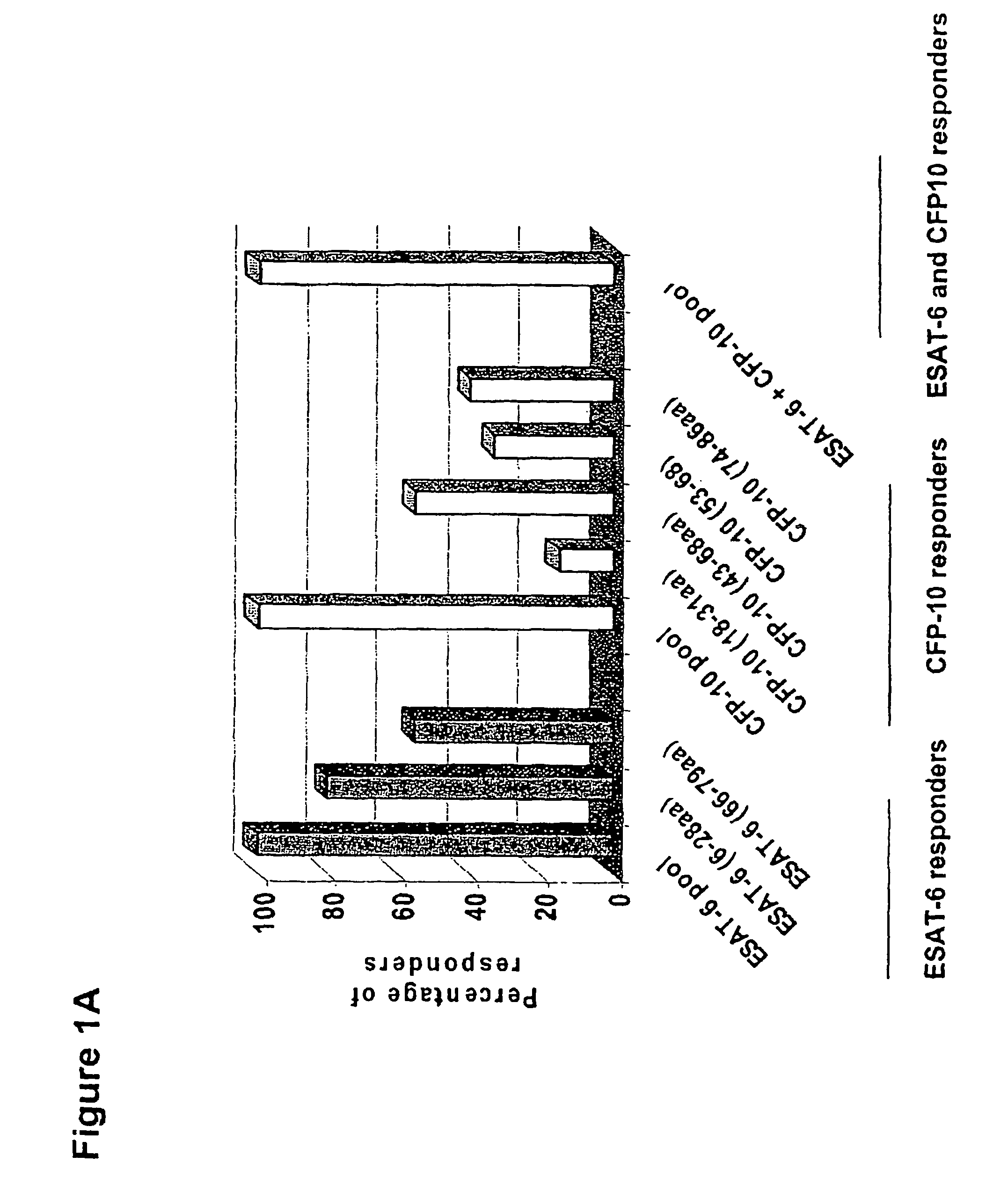
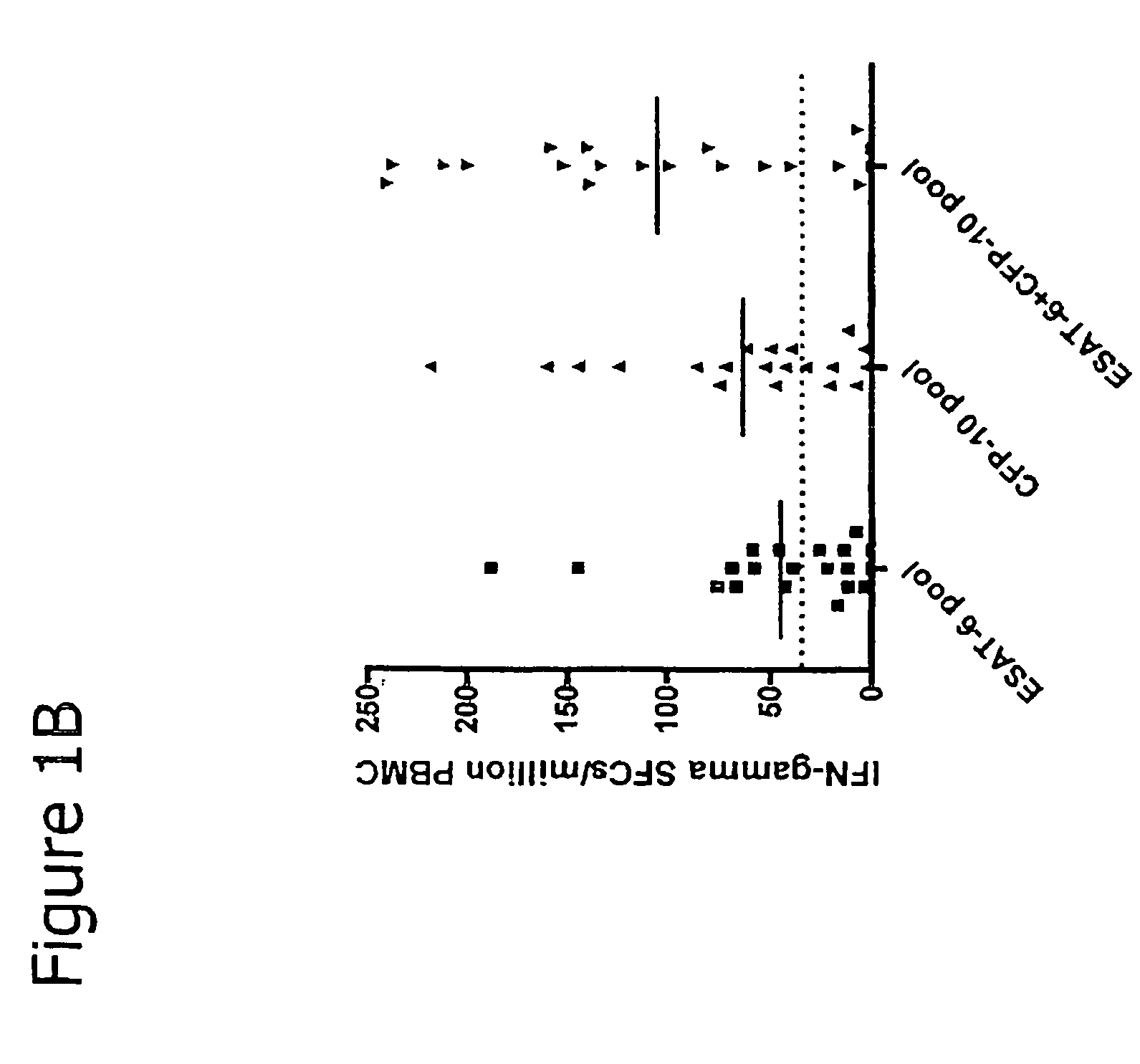
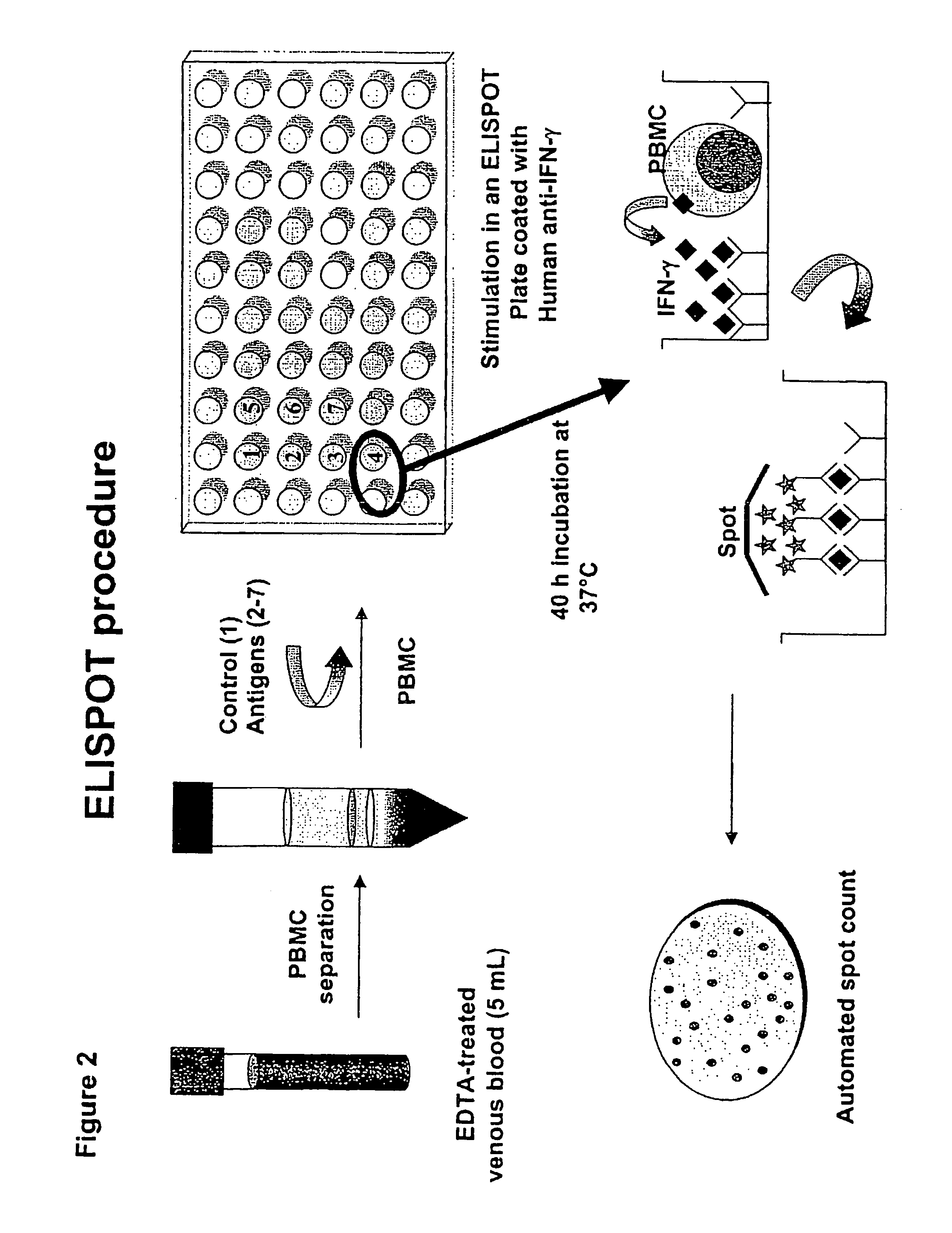
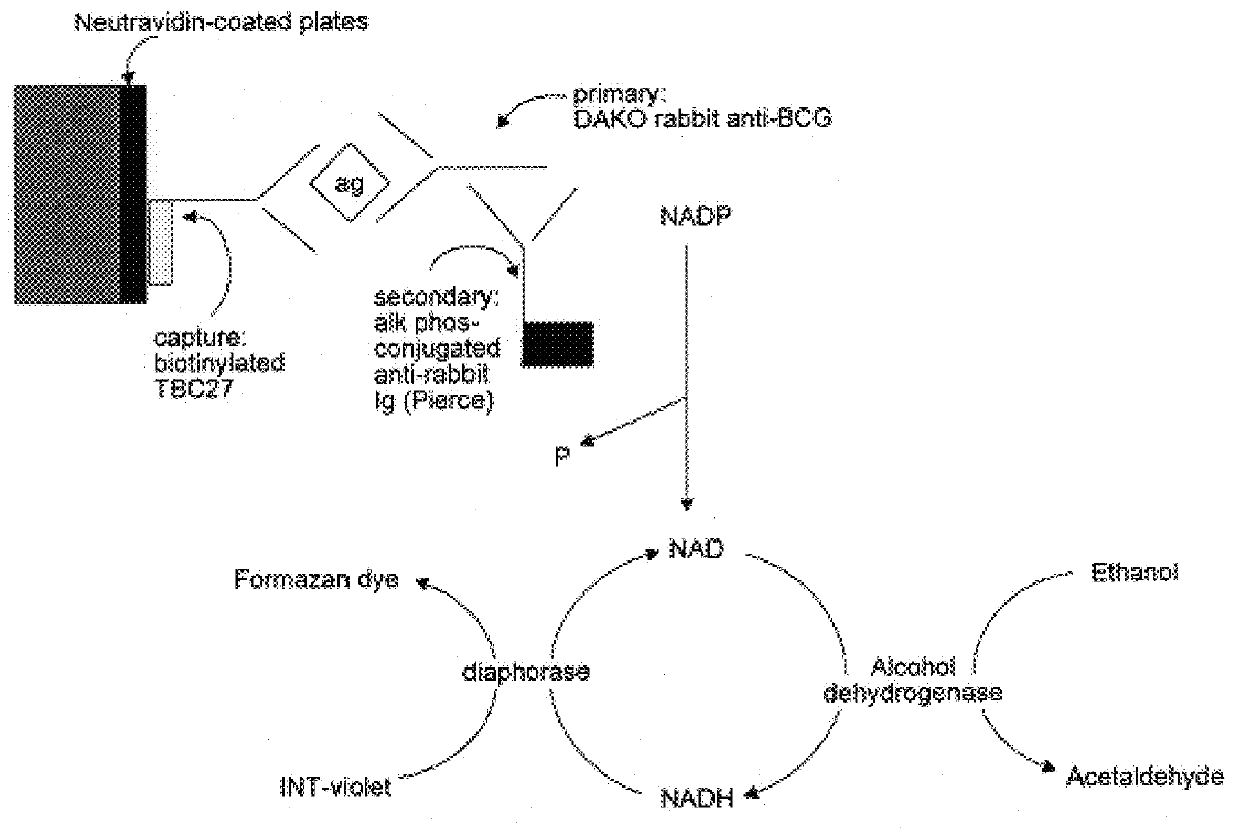
Immune diagnostic assay to diagnose and monitor tuberculosis infection
InactiveUS7785607B2High detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseT lymphocyte
The present invention relates to a method of diagnosing and monitoring various distinct presentations of tuberculosis: active tuberculosis disease, latent tuberculosis infection and recent tuberculosis infection. The rapid immune assay is based on the evaluation of the frequency of Interferon (IFN) gamma-producing antigen-specific T lymphocytes responding to selected peptide sequences from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, selected for their immunogenicity. The invention concerns also immunogenic and vaccine compositions based on these specific peptide sequences.
Owner:INST NAT PER LE MALATTIE INFETTIVE LAZZARO SPALLANZANI IRCCS
Nucleic acid fragments and polypeptide fragments derived from M. tuberculosis
InactiveUS20040013685A1High expressionReduce bacterial loadBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTuberculosis mycobacteriumSkin test
The present invention is based on the identification and characterization of a number of novel M. tuberculosis derived proteins and protein fragments. The invention is directed to the polypeptides and immunologically active fragments thereof, the genes encoding them, immunological compositions such as vaccines and skin test reagents containing the polypeptide.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Reagent for detecting tubercle bacillus infection in vitro and method thereof
ActiveCN101446585AValid in vitro assayOvercome the disadvantages of unsatisfactory effectImmunoglobulins against bacteriaBiological testingBCG vaccineT cell
The invention discloses a reagent for detecting tubercle bacillus infection in vitro and a method thereof. The reagent comprises M233 polypeptide represented by SEQ ID No.1; and cytokine released from T cells is detected by contacting the M233 polypeptide or an analog thereof with the T cells of a tubercle bacillus host to determine whether the T cells identify the M233 polypeptide or the analog thereof. The reagent has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, being free from interference of BCG vaccine and non-tuberculosis mycobacteria vaccine, being capable of detecting active pulmonary tuberculosis patients, the patients with dormant infection and healthy persons who contact with mycobacterium nontuberculosis. The reagent and the method are especially applicable to detecting tuberculosis and / or dormant infection thereof for Chinese people.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RHFAY BIOTECH CO LTD
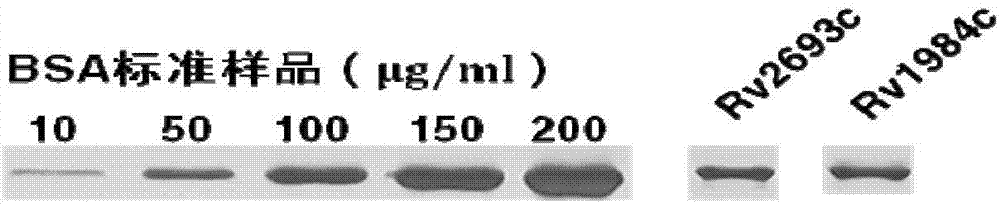
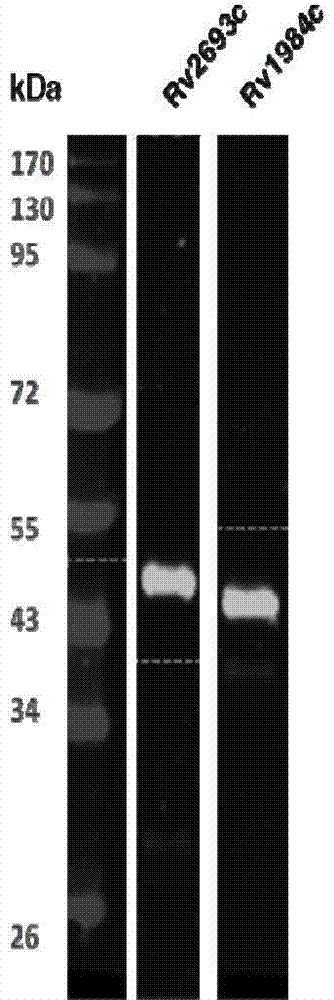
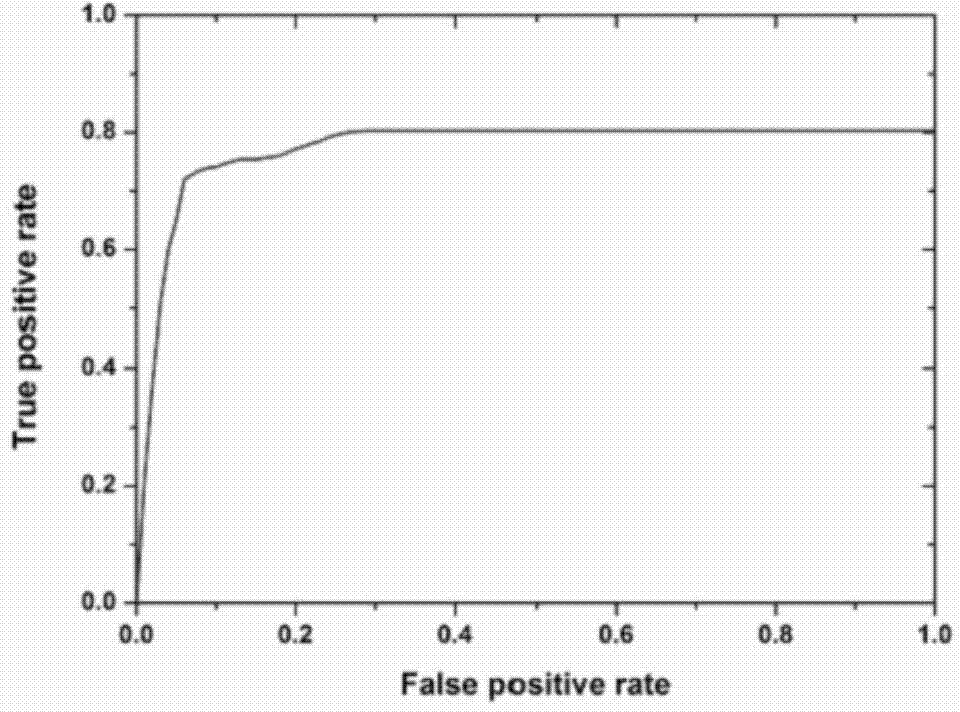
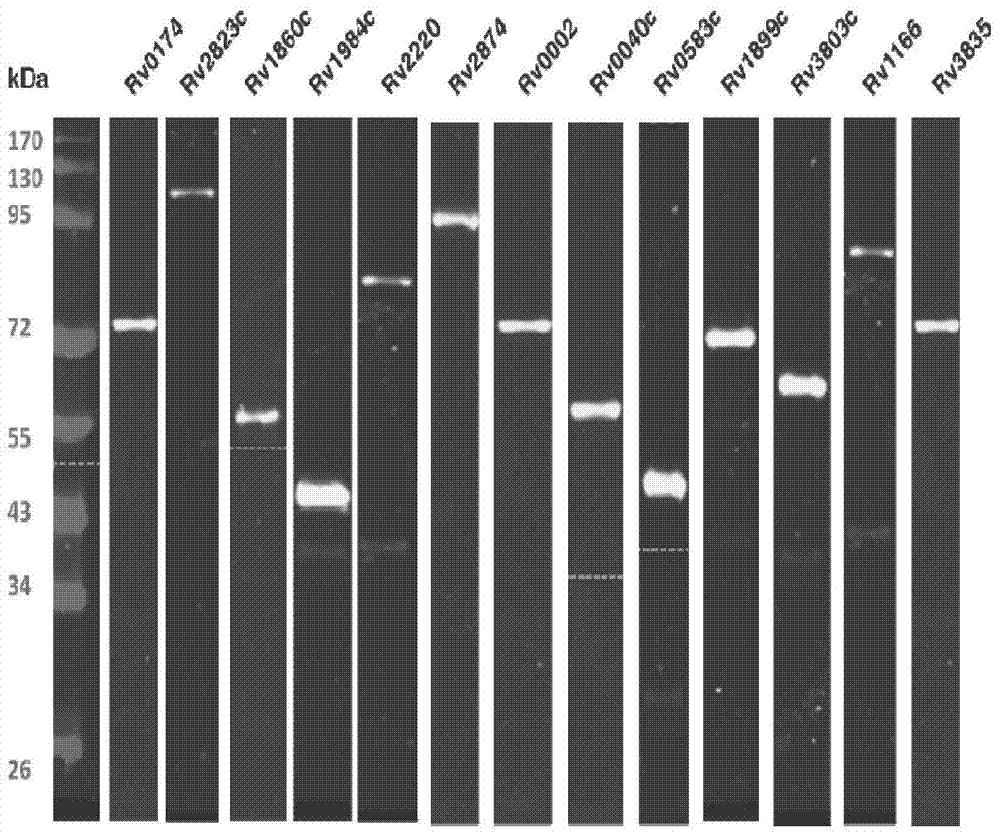
Application of mycobacterium tuberculosis protein in preparation of products used for diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection
The invention provides mycobacterium tuberculosis protein Rv2693c and / or Rv1984c in development and / or designing of products capable of discrimination, diagnosis, auxiliary diagnosis, screening and / or auxiliary screening of latent tuberculosis infection. The invention further provides protein chips prepared from the two mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins. The protein chips prepared in the invention are used for detecting the levels of IgM antibodies respectively corresponding to the twp proteins in serum of a patient with latent tuberculosis infection and of a normal person, and detection results of the antibodies respectively corresponding to the three protein are analyzed together so as to determine whether an examined person suffers from latent tuberculosis infection; detection results show that optimal operating points of the protein chips provided by the invention in auxiliary diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection have specificity of 80.3% and sensitivity of 75.6%, both higher than indexes of diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in the prior art.
Owner:TB HEALTHCARE BIOTECHNOLOGY (GUANGDONG) CO LTD
Detection of mycobacteria
InactiveUS6383763B1Rapid assessmentLess sensitiveAntibody ingredientsBiological testingMicrobiologyGenus
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the detection of infection and disease due to members of the genus Mycobacterium. In particular, the present invention is well-suited to the detection and identification of patients with disease or infection due to M. tuberculosis or MAC.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Method for detecting multi-drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
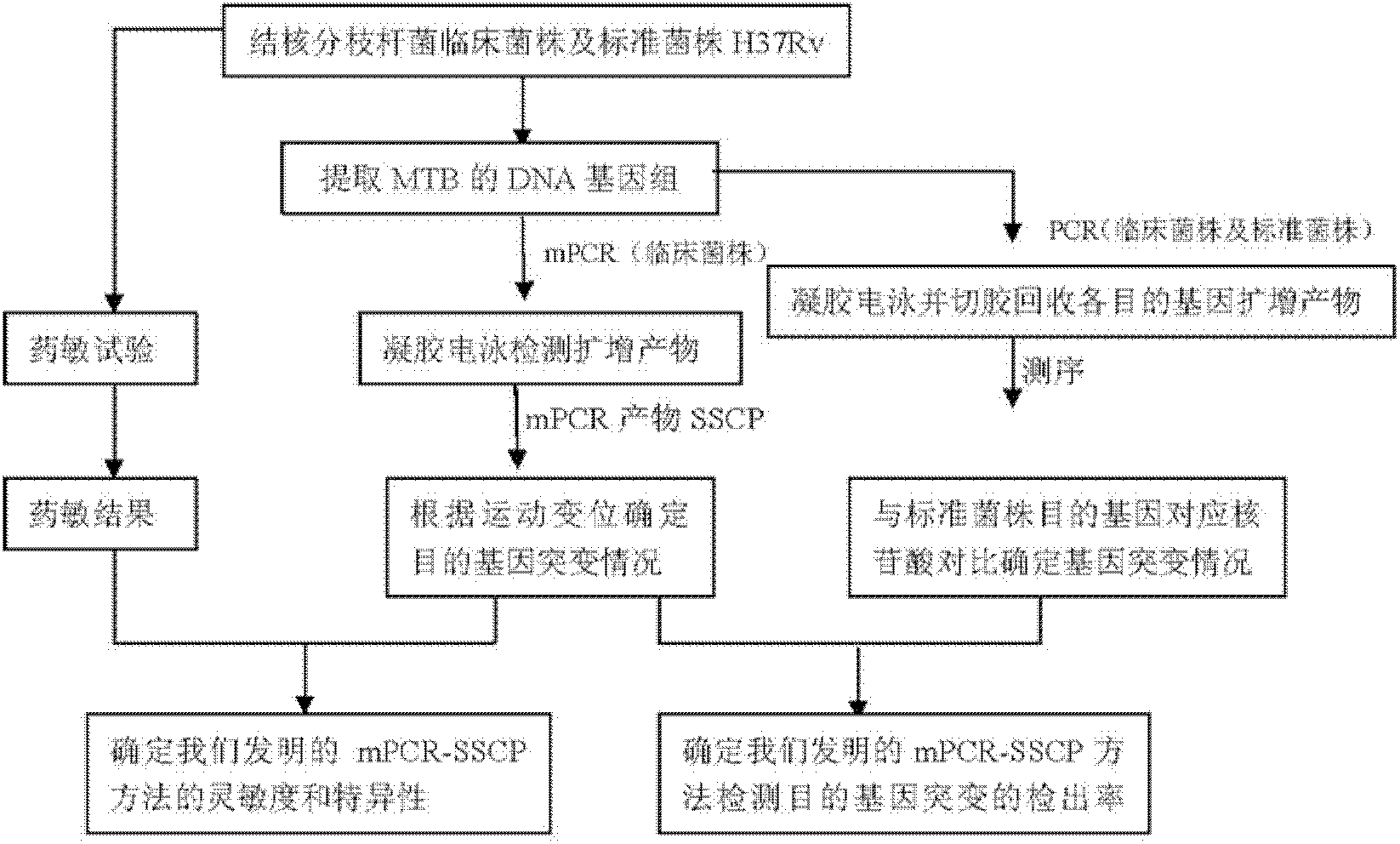
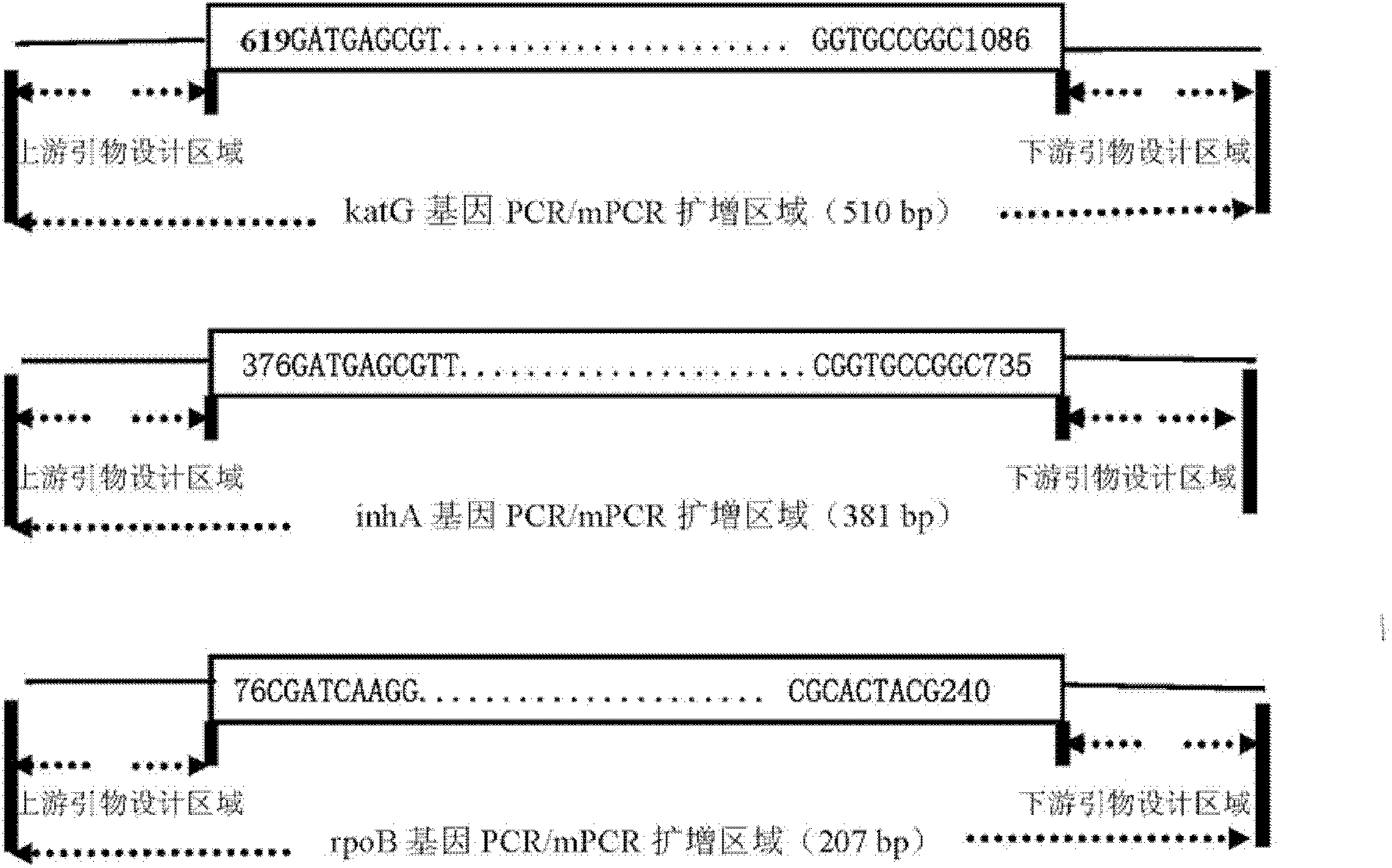
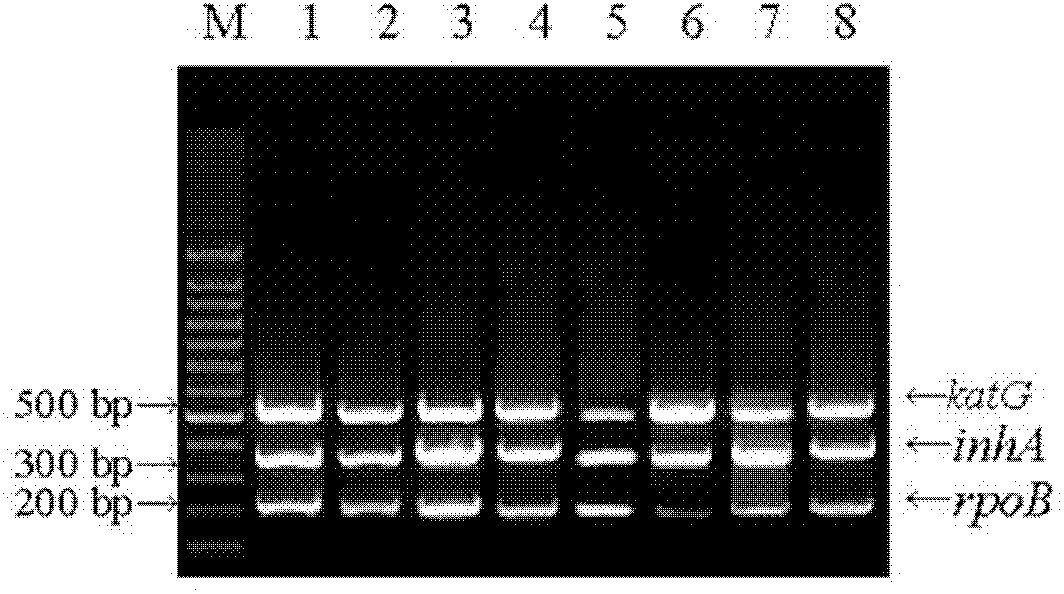
InactiveCN102559916AVerify reliabilityExperiment operation is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSingle-strand conformation polymorphismIsoniazid resistance
The invention relates to a method for detecting multi-drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which aims at detecting the resistance of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis to isoniazid and rifampicin at the same time and has the characteristics of high specificity and sensitivity, quickness in detection, and easiness and convenience in operation. The technical scheme is as follows: the method comprises the following steps: A, establishing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) templates of an MTB clinical strain and a standard strain H37Rv; B, designing three pairs of primers of katG, inhA and rpoB gene fragments which are closely related to the isoniazid resistance and the rifampin resistance, performing mPCR amplification on katG, inhA and rpoB genes of the clinical strain, and performing PCR amplification on katG, inhA and rpoB genes of the clinical strain and the standard strain H37Rv; and C, detecting the mutation conditions of related INH-resistant and RFP-resistant 3 genes of the clinical strain at the same time by a single-strand conformation polymorphism detection method.
Owner:孙爱华 +2
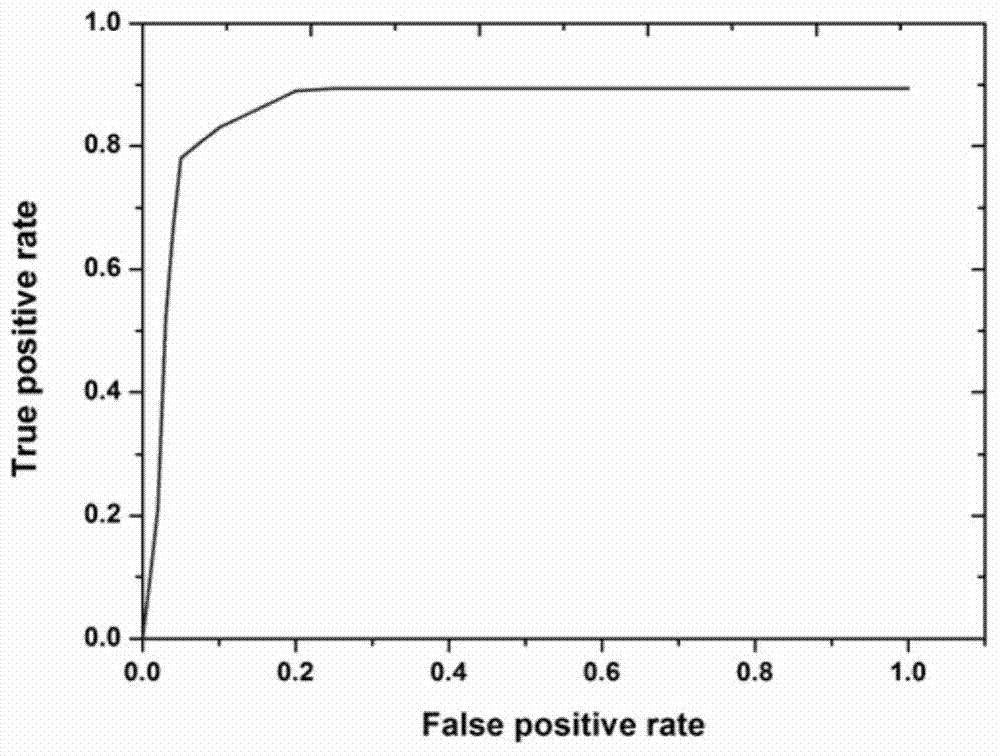
Application of mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins in preparation of products used for diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection
The invention provides 13 mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins in development and / or designing of products capable of discrimination, diagnosis, auxiliary diagnosis, screening and / or auxiliary screening of latent tuberculosis infection. The invention further provides protein chips prepared from 13 mycobacterium tuberculosis protein antigens. The protein chips prepared in the invention are used for detecting the levels of IgG antibodies respectively corresponding to the 13 protein antigens in serum of a patient with latent tuberculosis infection and of a normal person, and detection results of the antibodies respectively corresponding to the three protein are analyzed together so as to determine whether an examined person suffers from latent tuberculosis infection; detection results show that optimal operating points of the protein chips provided by the invention in auxiliary diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection have specificity of 89.4% and sensitivity of 80.6%, both higher than indexes of diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in the prior art.
Owner:广东希格生物科技有限公司
Bicyclic nitroimidazoles covalently linked to substituted phenyl oxazolidinones
The current invention provides a series of bicyclic nitroimidazole- substituted phenyl oxazolidinones in which a bicyclic nitroimidazole pharmacophore is covalently bonded to a phenyl oxazolidinone, their pharmaceutical compositions, and the method of use of the compositions for prevention and treatment of bacterial infections. The bicyclic nitroimidazole-substituted phenyl oxazolidinones possess surprising antibacterial activity against wild- type and resistant strains of pathogens, and are therefore useful for the prevention, control and treatment of a number of human and veterinary bacterial infections caused by these pathogens, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Owner:TENNOR THERAPEUTICS (SUZHOU) LTD
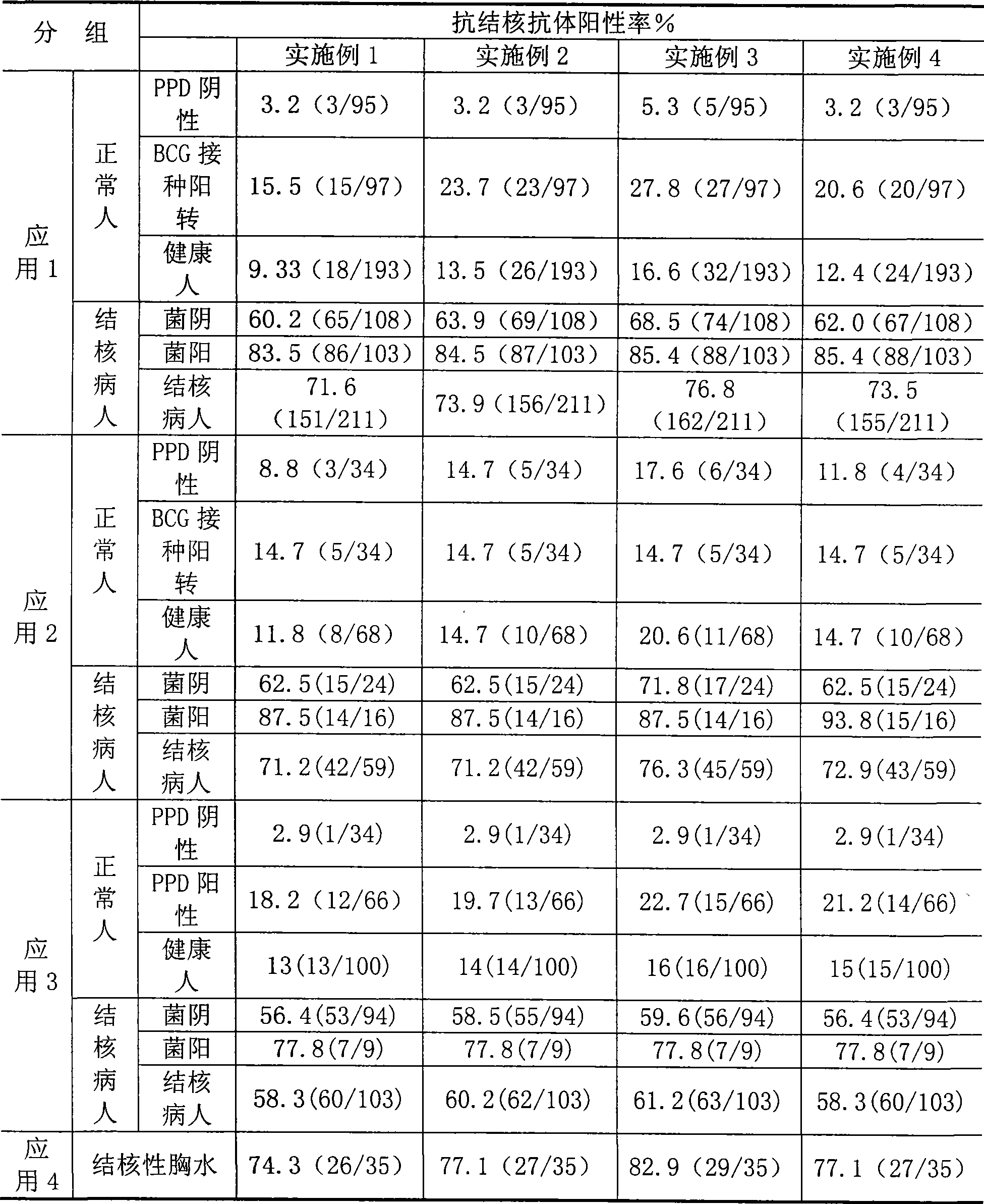
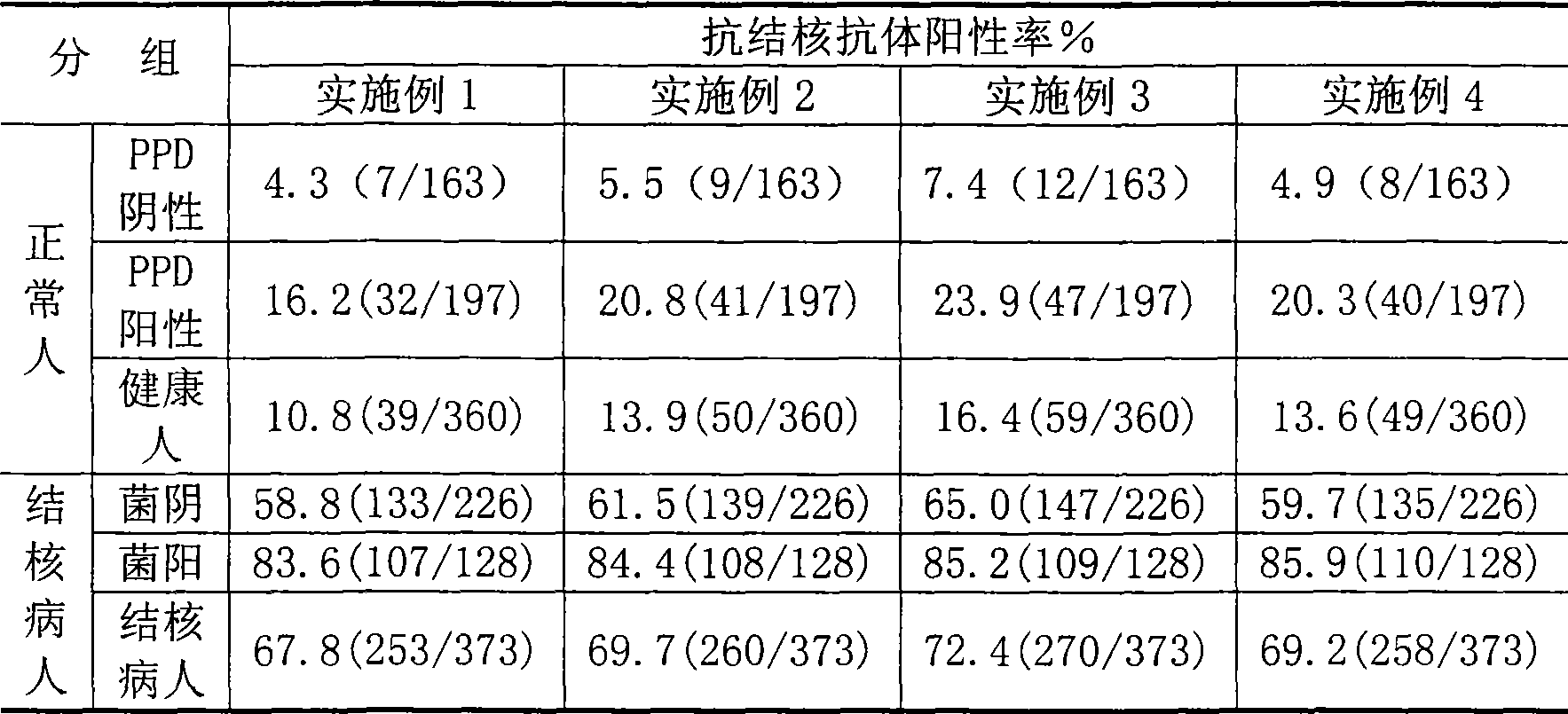
Tuberculosis antibody multi-antigen ELISA detecting kit and making method
The invention relates to a tuberculosis antibody multiple antigen ELISA detection kit and a preparation method thereof, which pertains to the field of tuberculosis medical immunology diagnostic techniques and mainly uses detection antigen, enzyme-linked antihuman IgG antibodies, substrates, positive control serum of tuberculosis patients, control serum of normal person, calf serum and polystyrene microplates to form the kit, wherein, the detection antigen adopts the mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains of lipid Arabian mannose (LAM), 38kD and 16kD to be combined with arbitrary one or more than one mycobacterium tuberculosis recombinant proteins in the recombinant proteins of MPT63, MTB48 and CFP10-ESAT6. The mycobacterium tuberculosis has high sensitivity, strong specificity and complementarity, can be used for detecting specific antitubercular antibodies in such body fluid samples as serum, hydrothorax and the like, and assisting the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Owner:中国人民解放军总医院第二附属医院
Tuberculosis antigen specific whole blood IFN-gamma diagnosis kit, method for producing the same and method for using same
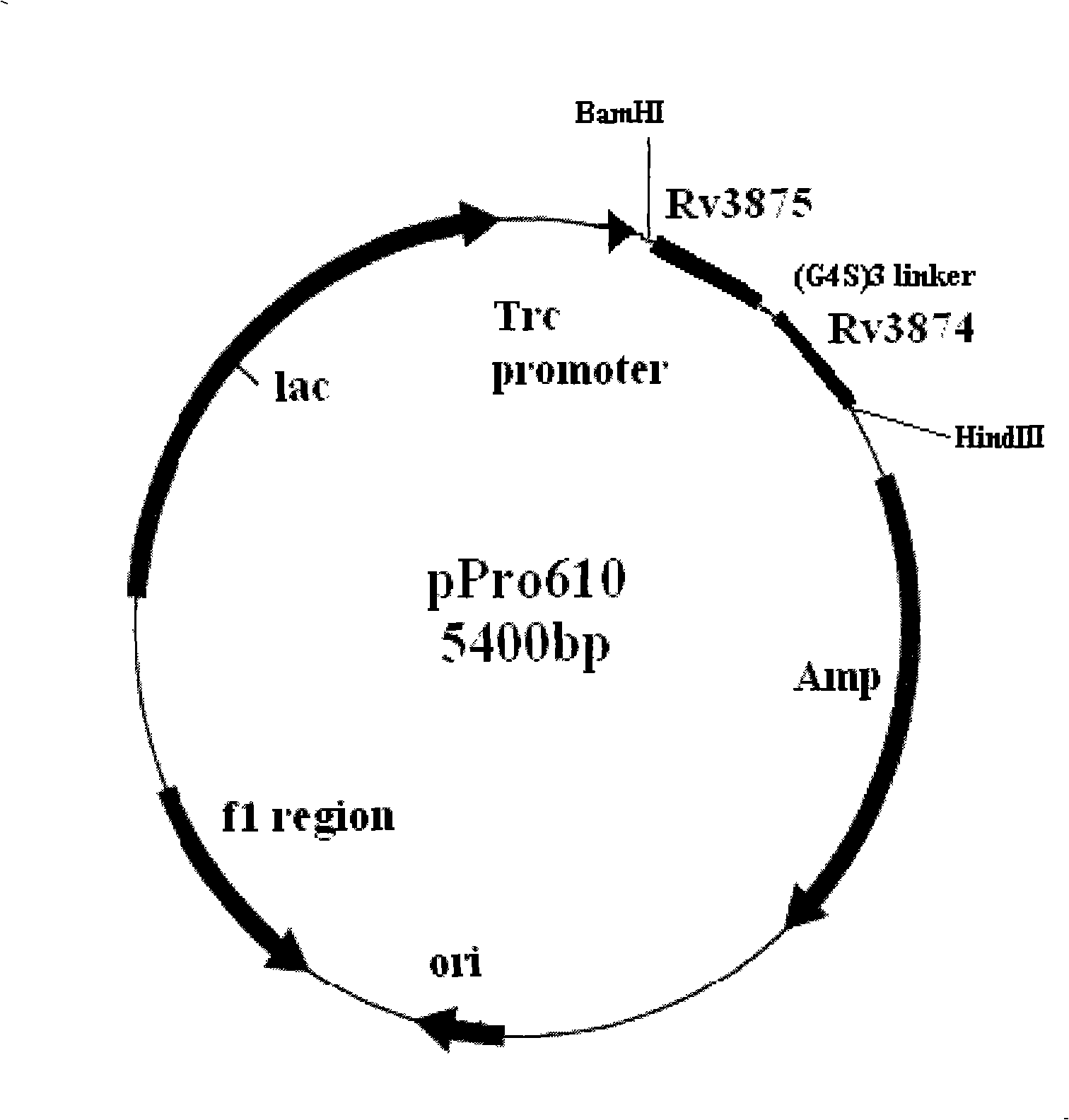
InactiveCN101493454ADiagnostic advantageShorten the timeBiological testingEscherichia coliEnzyme linked immunoassay
The invention relates to a diagnostic kit for tuberculosis and mycobacterium tuberculosis infectors, a preparation method and an application method thereof. By using the linker for encoding 15 amino acid (G4S1) 3, the encoding genes (SEQ.ID.NO.6) of a mycobacterium tuberculosis specific antigen Rv3875 and Rv3874 are connected in series, and then inserted into an E. coli expression vector, and the high-efficiency expression and purification for the fusion protein of Rv3875 and Rv3874 in the E. coli are achieved. The recombinant protein at least comprises 8 T cell epipositions which can be used for cell immunity diagnosis, and a diagnostic kit and diagnostic method for a whole blood IFN-Gamma release analysis method are established by taking the protein as the basis and combining the human IFN-Gamma enzyme-linked immunoassay technology, and can be used for the early, specific diagnosis and screening of tuberculosis and mycobacterium tuberculosis infectors.
Owner:范雄林
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com