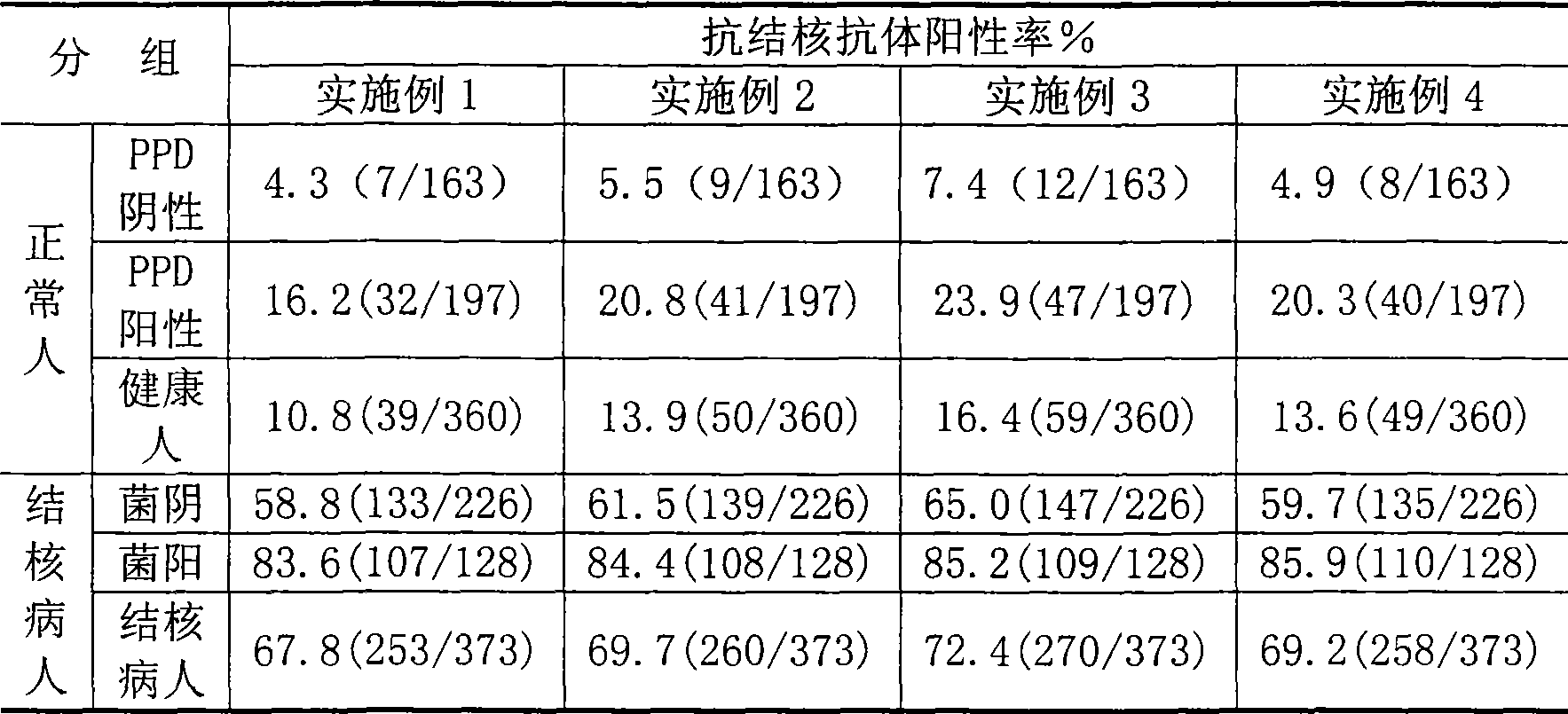
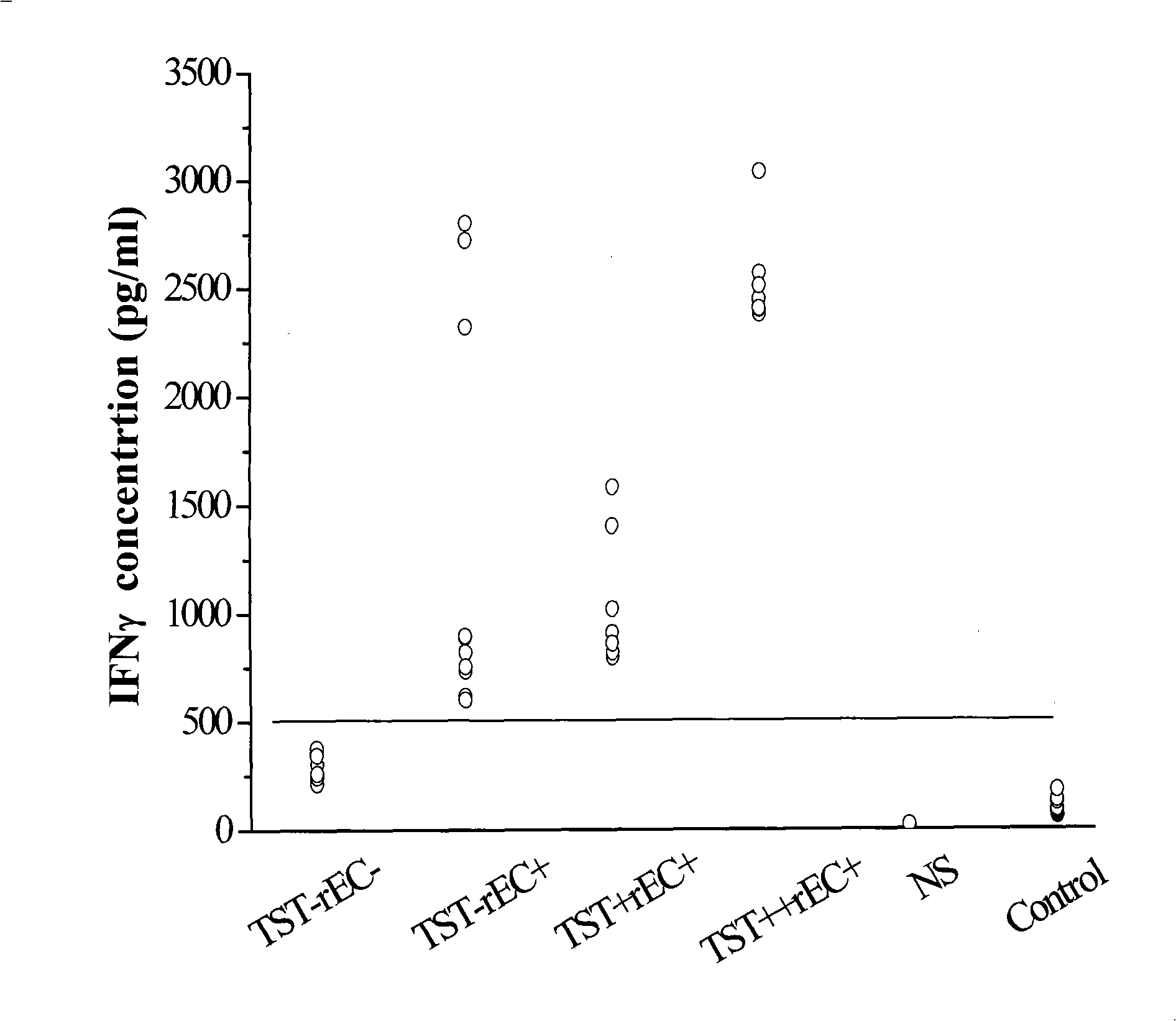
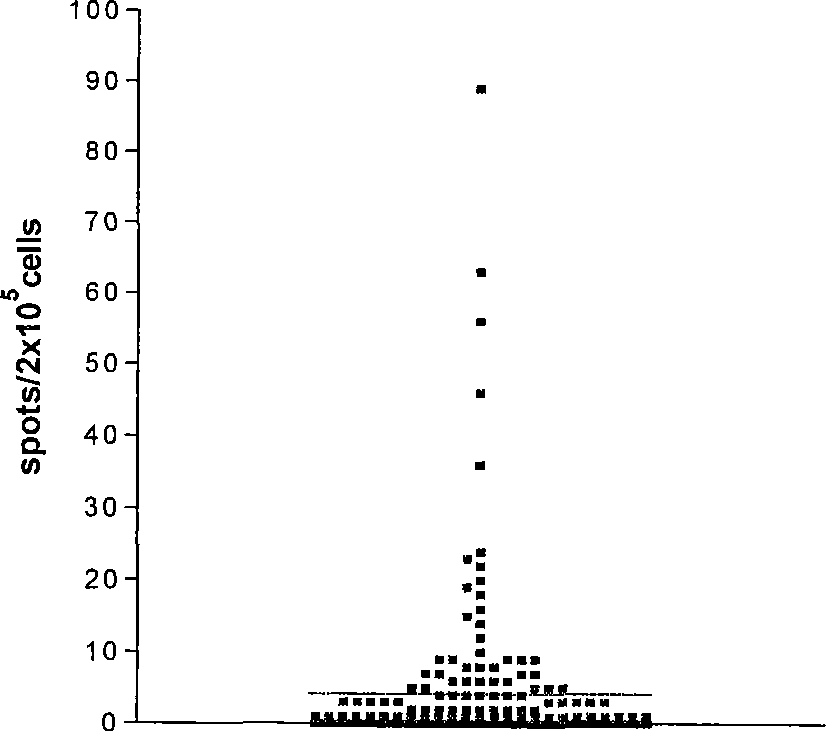
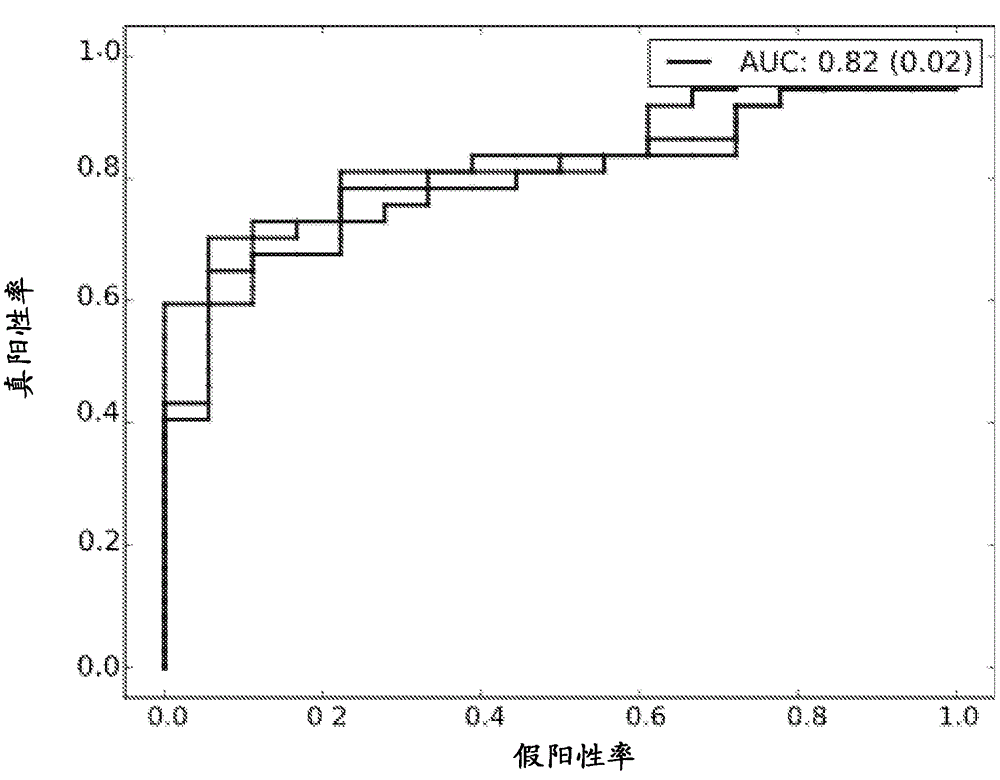
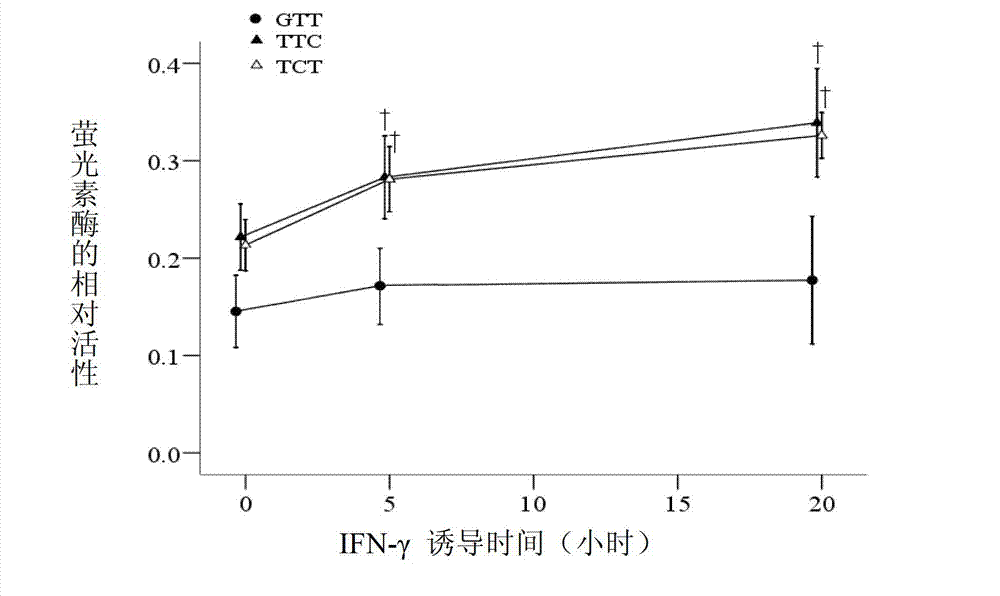
Patents
Literature
524 results about "Tuberculosis Disease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
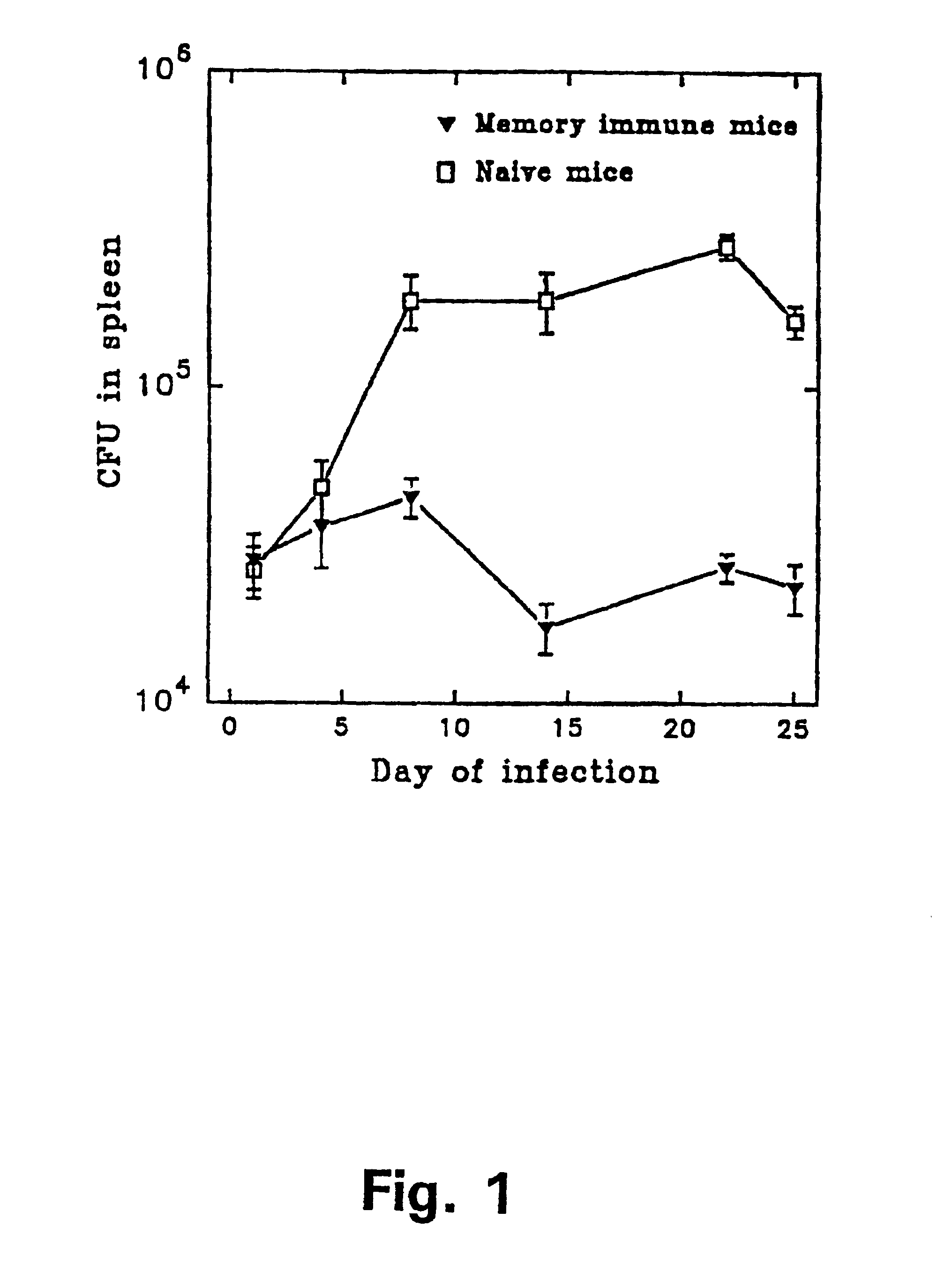
Tuberculosis is a disease caused by infection with the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis can damage a person's lungs or other parts of the body and cause serious illness. The disease can be treated with antibiotics.
Compositions and methods for detecting, identifying and quantitating mycobacterial-specific nucleic acids
ActiveUS20110281754A1Inherent limitationAuxiliary diagnosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyTuberculosis mycobacterium
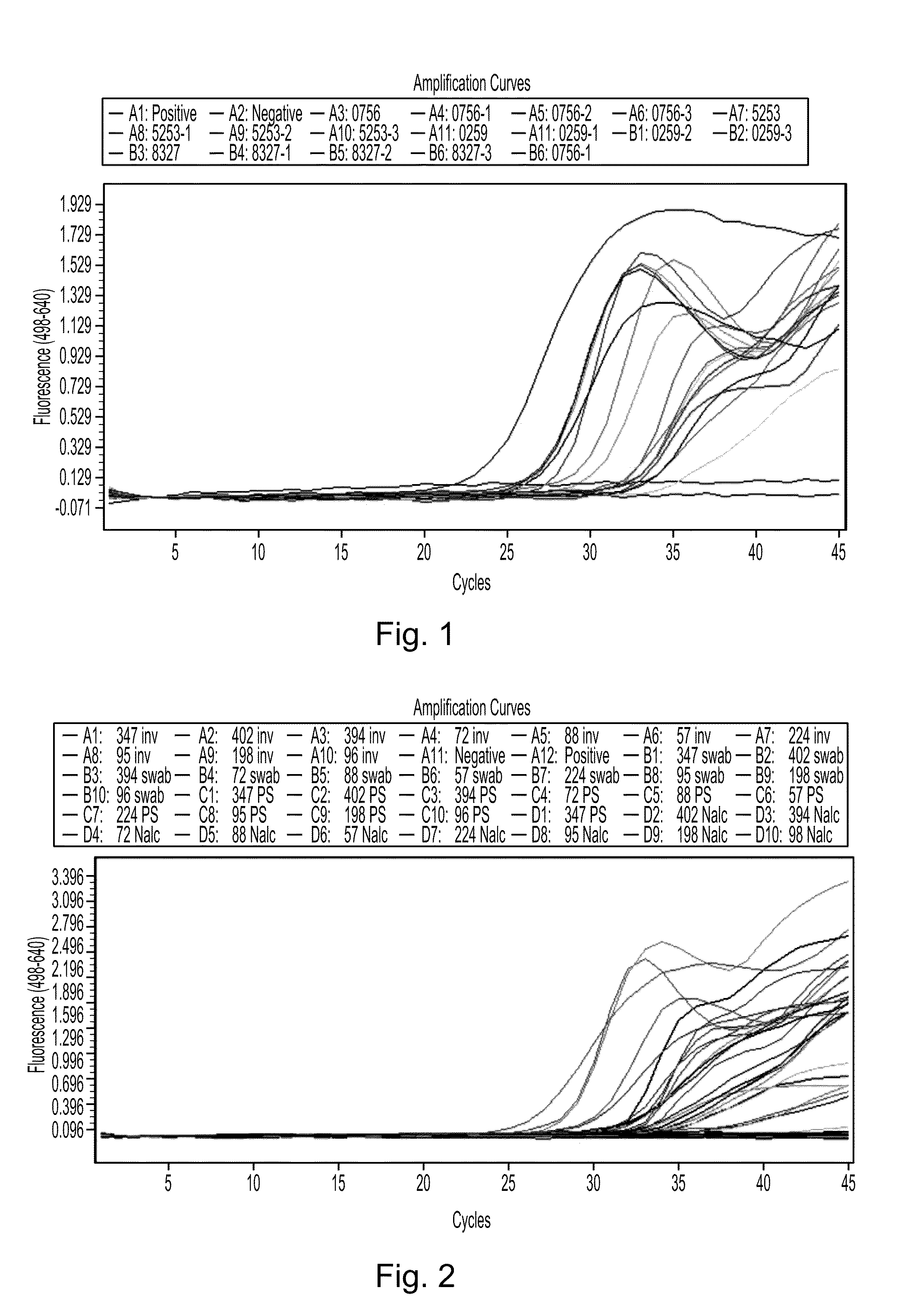
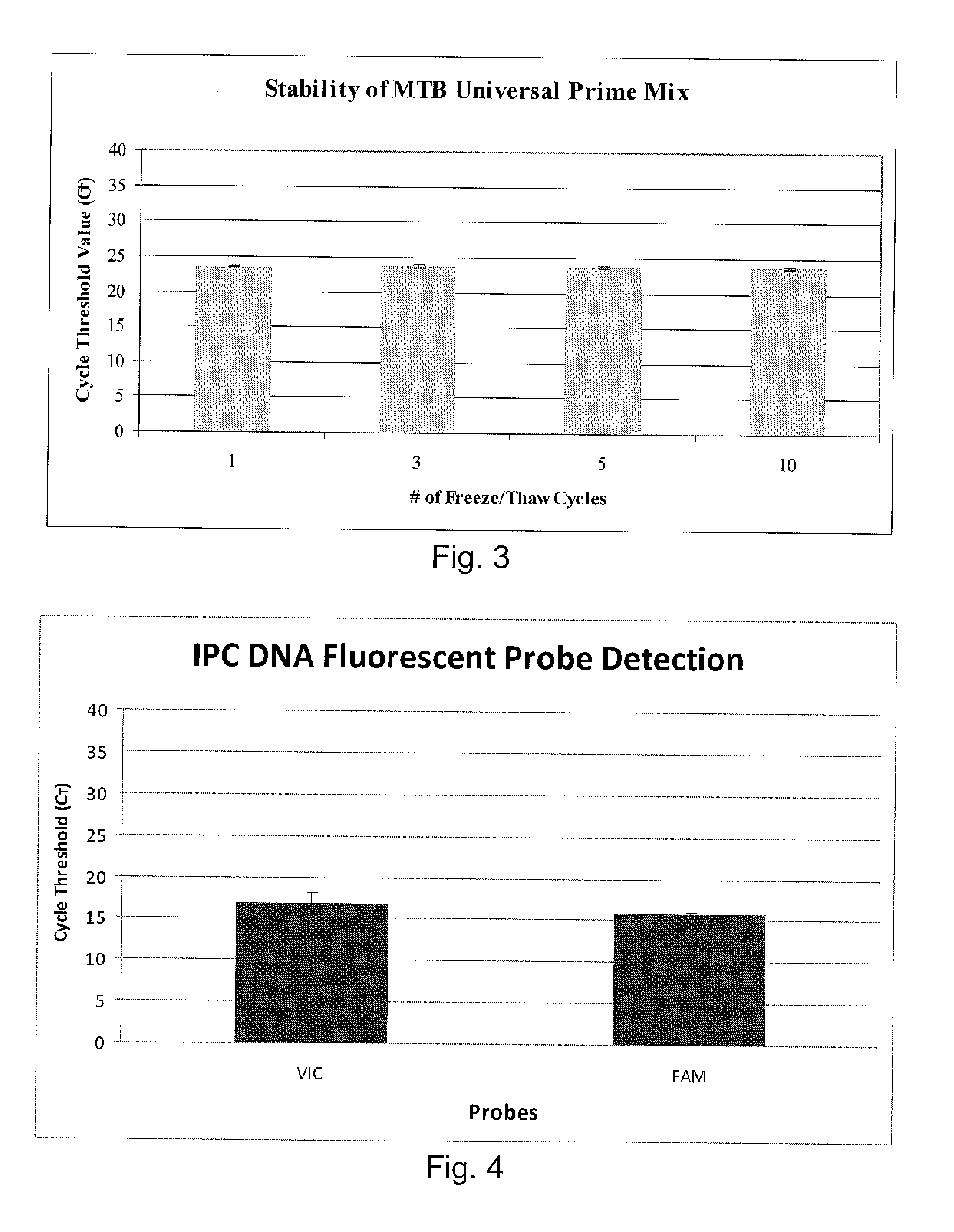
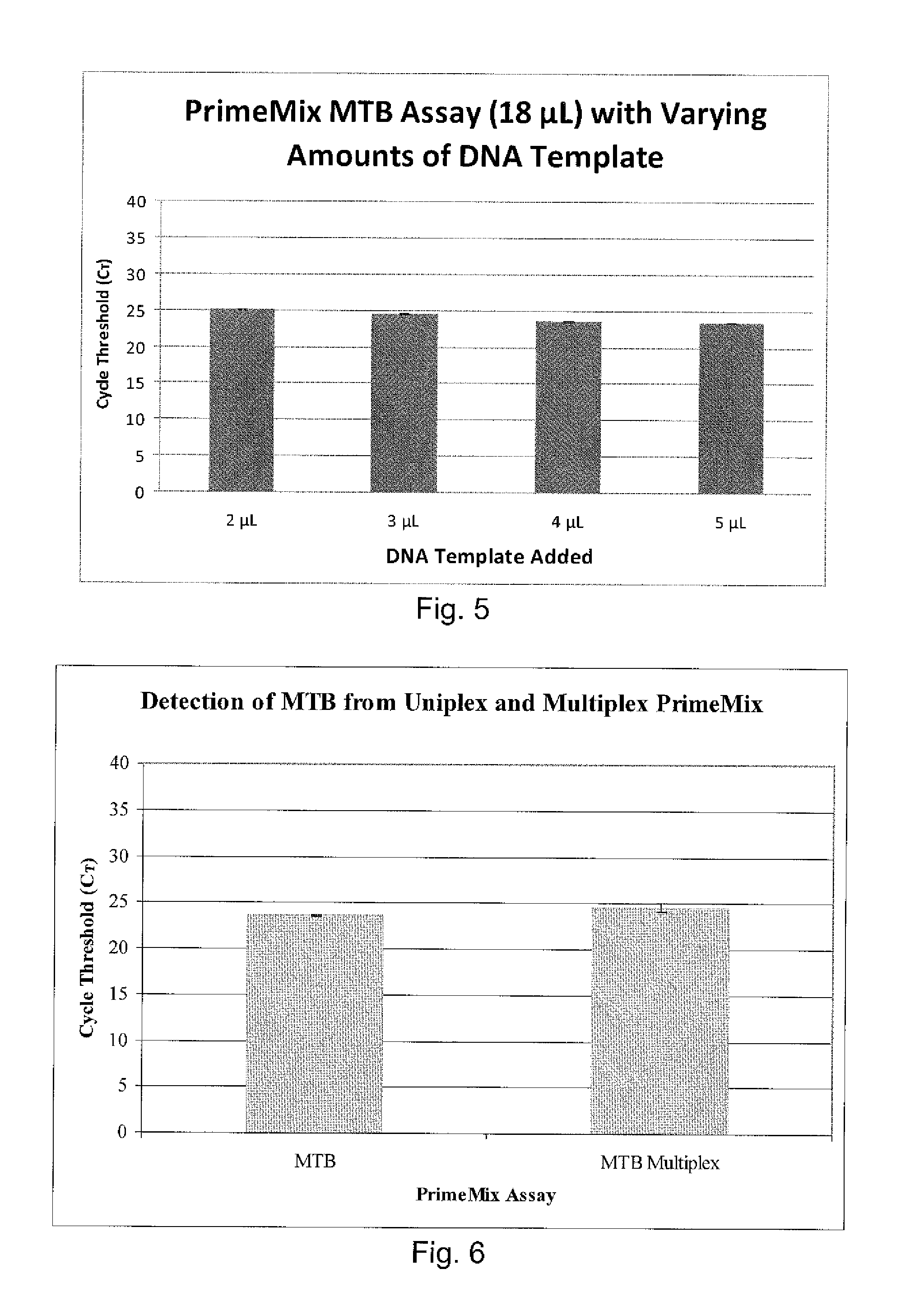
Disclosed are compositions and methods for isolating, detecting, amplifying, and quantitating Mycobacterium-specific nucleic acids in a sample. Also disclosed are compositions and diagnostic kits comprising Mycobacterium IS6110-specific oligonucleotide amplification primers and labeled oligonucleotide detection probes that specifically bind to the amplification products obtained therefrom. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for the isolation and characterization of nucleic acids that are specific to one or more tubercular pathogens, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, in particular, from a wide variety of samples including those of biological, environmental, clinical and / or veterinary origin.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
M. tuberculosis antigens
InactiveUS6991797B2High expressionEnhance immune responseBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenTuberculosis mycobacterium
The present invention is based on the identification and characterization of a number of novel M. tuberculosis derived proteins and protein fragments. The invention is directed to the polypeptides and immunologically active fragments thereof, the genes encoding them, immunological compositions such as vaccines and skin test reagents containing the polypeptides.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
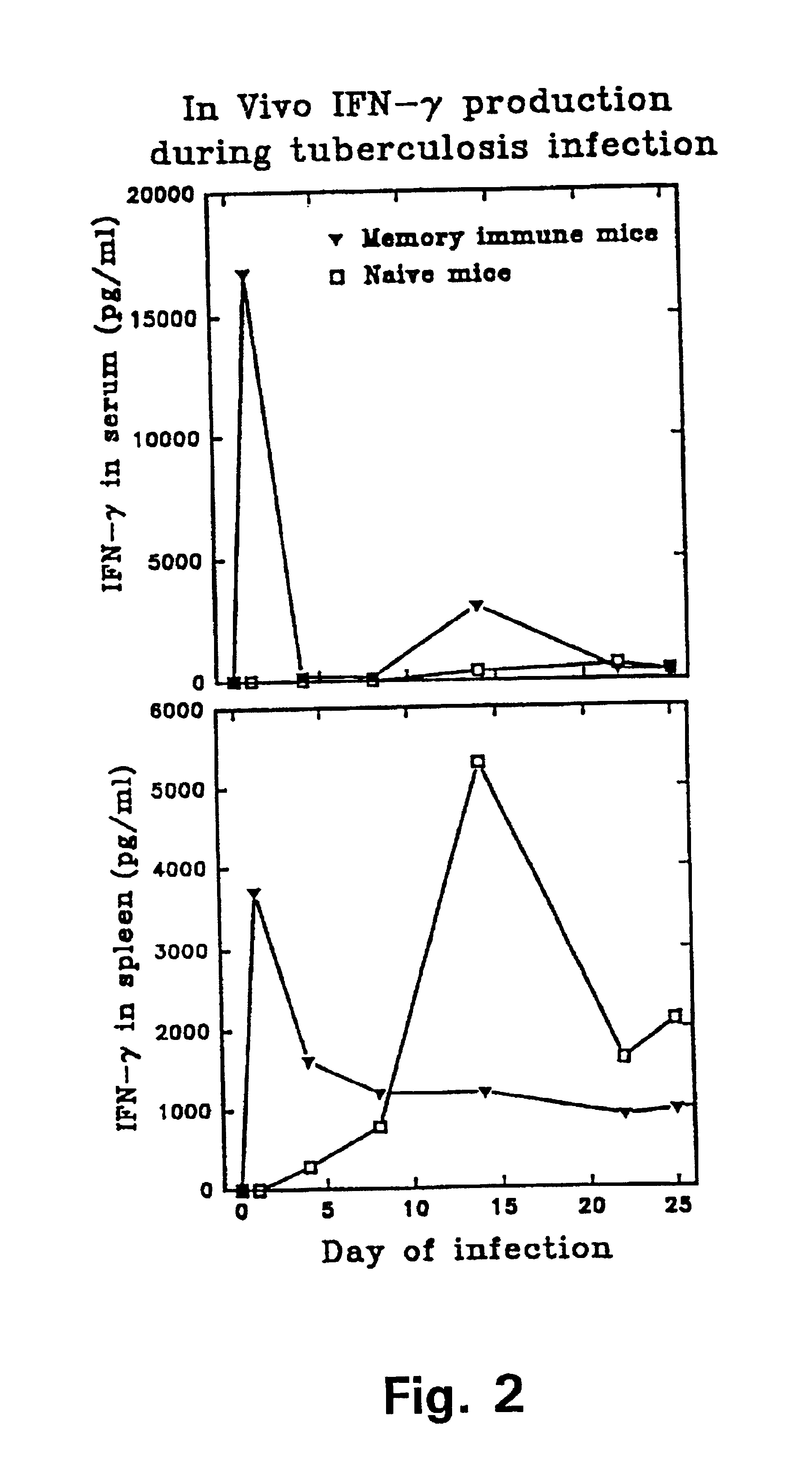
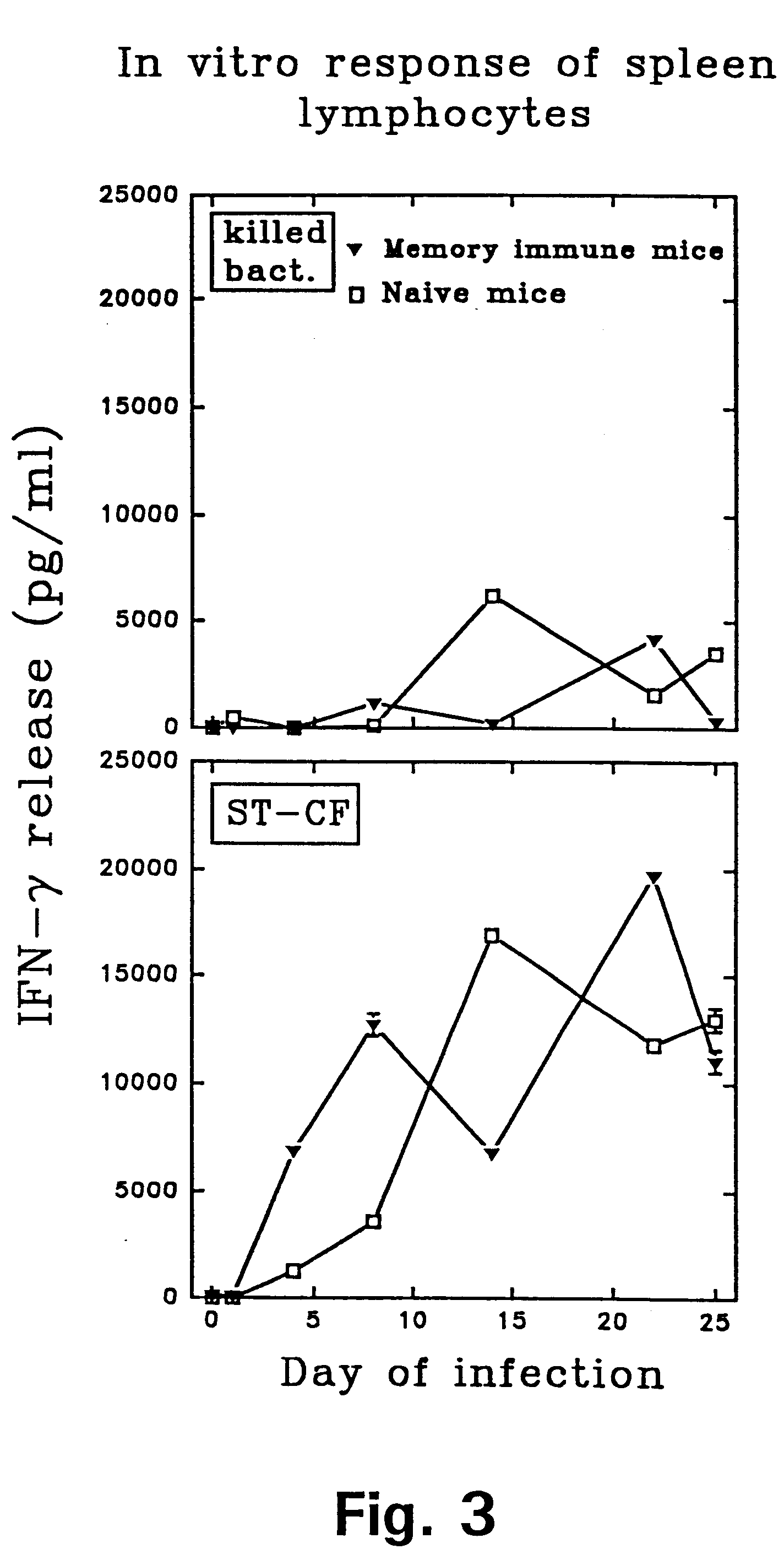
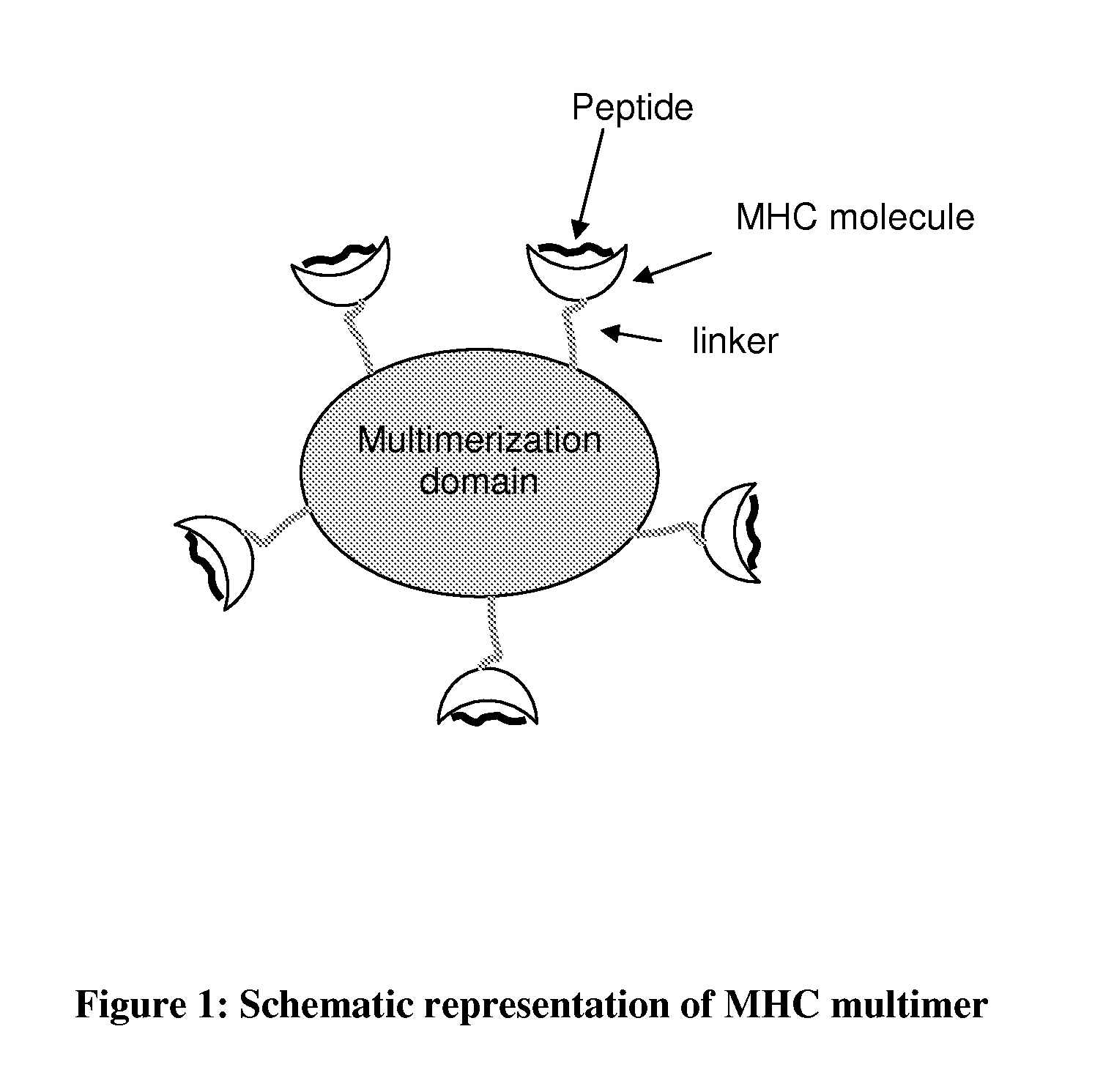
MHC Multimers in Tuberculosis Diagnostics, Vaccine and Therapeutics
The present invention relates to MHC-peptide complexes and uses thereof in the diagnosis of, treatment of or vaccination against a disease in an individual. More specifically the invention discloses MHC complexes comprising Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigenic peptides and uses there of.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
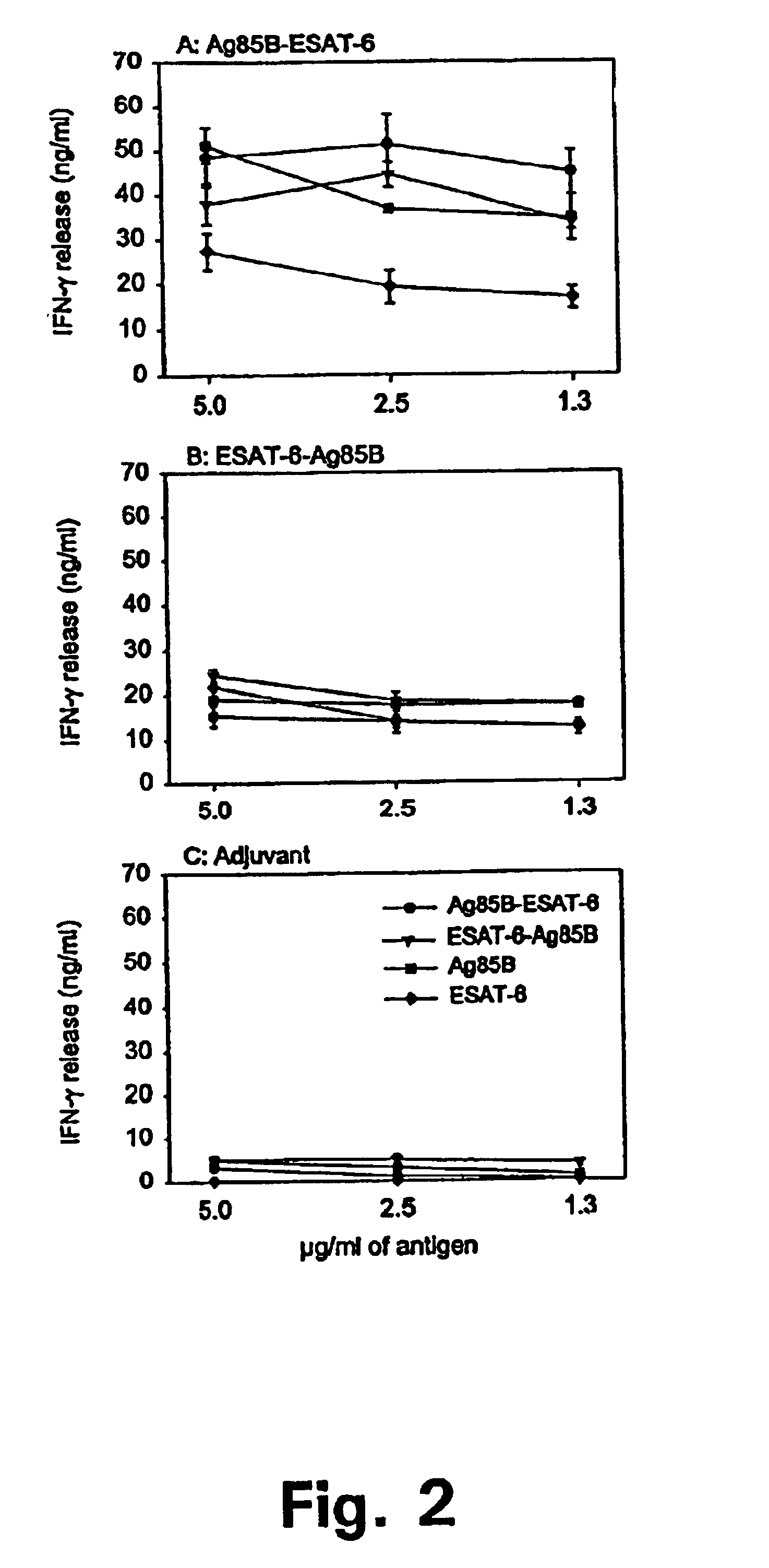
Hybrids of M. tuberculosis antigens
InactiveUS7037510B2Improving immunogenicityImprove propertiesBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunological memoryImmunodominant Antigens
The present invention discloses fusion proteins of the immunodominant antigens ESAT-6 and Ag85B from Mycobacterium tuberculosis or homologues thereof, and a tuberculosis vaccine based on the fusion proteins, which vaccine induces efficient immunological memory.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Fusion proteins of mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveUS7311922B1Good antigenicityHigh sensitivityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenSerum ige
The present invention relates to fusion proteins containing at least two Mycobacterium species antigens. In particular, it relates to nucleic acids encoding fusion proteins that include two or more individual M. tuberculosis antigens, which increase serological sensitivity of sera from individuals infected with tuberculosis, and methods for their use in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tuberculosis infection.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
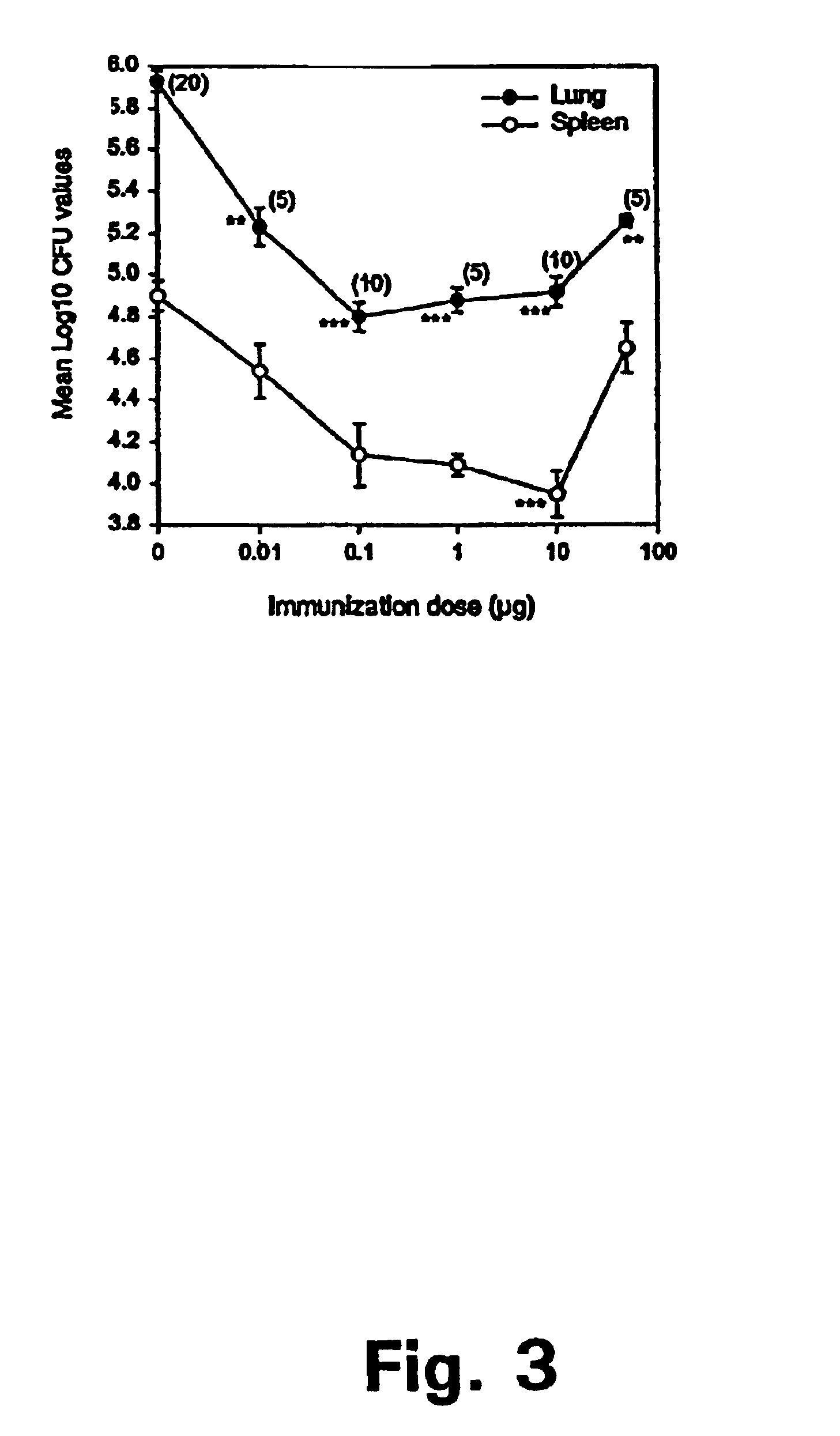
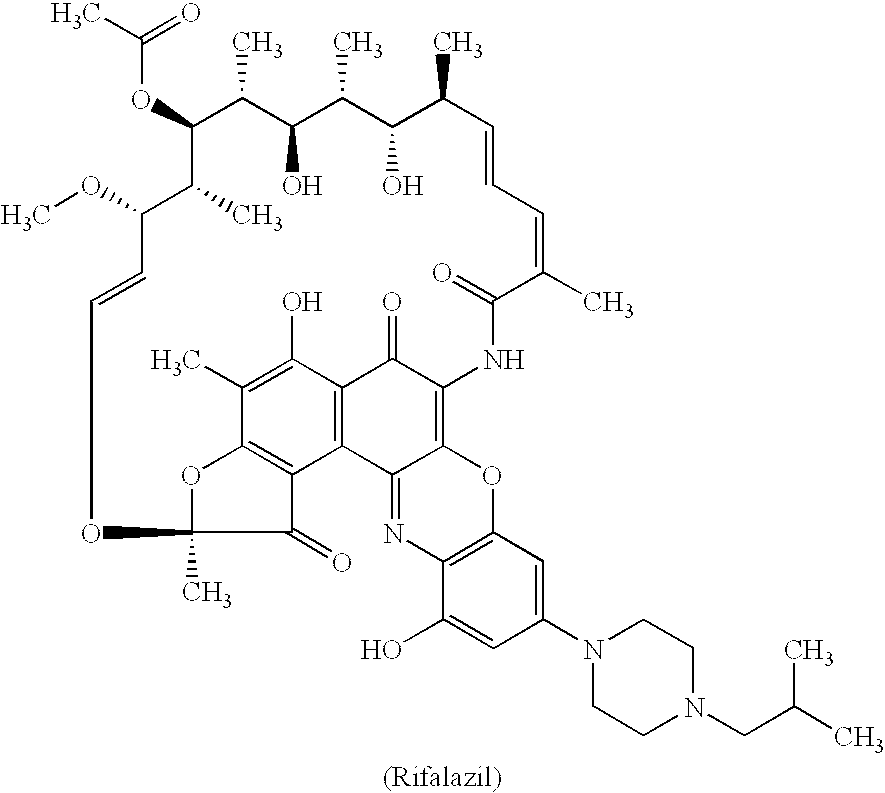
Method for treatment of bacterial infections with once or twice-weekly administered rifalazil
A method for treatment of bacterial infections with rifalazil administered once-weekly or twice-weekly. A method for treatment of tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, infections caused by Mycobacterium avium complex, infections caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae and infections caused by Helicobacter pylori by administering to a patient suffering from the bacterial infection 1-100 mg of rifalazil once or twice a week. In this dose regimen, the treatment is fast, efficacious and eliminates undesirable secondary symptoms observed with daily doses of 1-50 mg of rifalazil.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
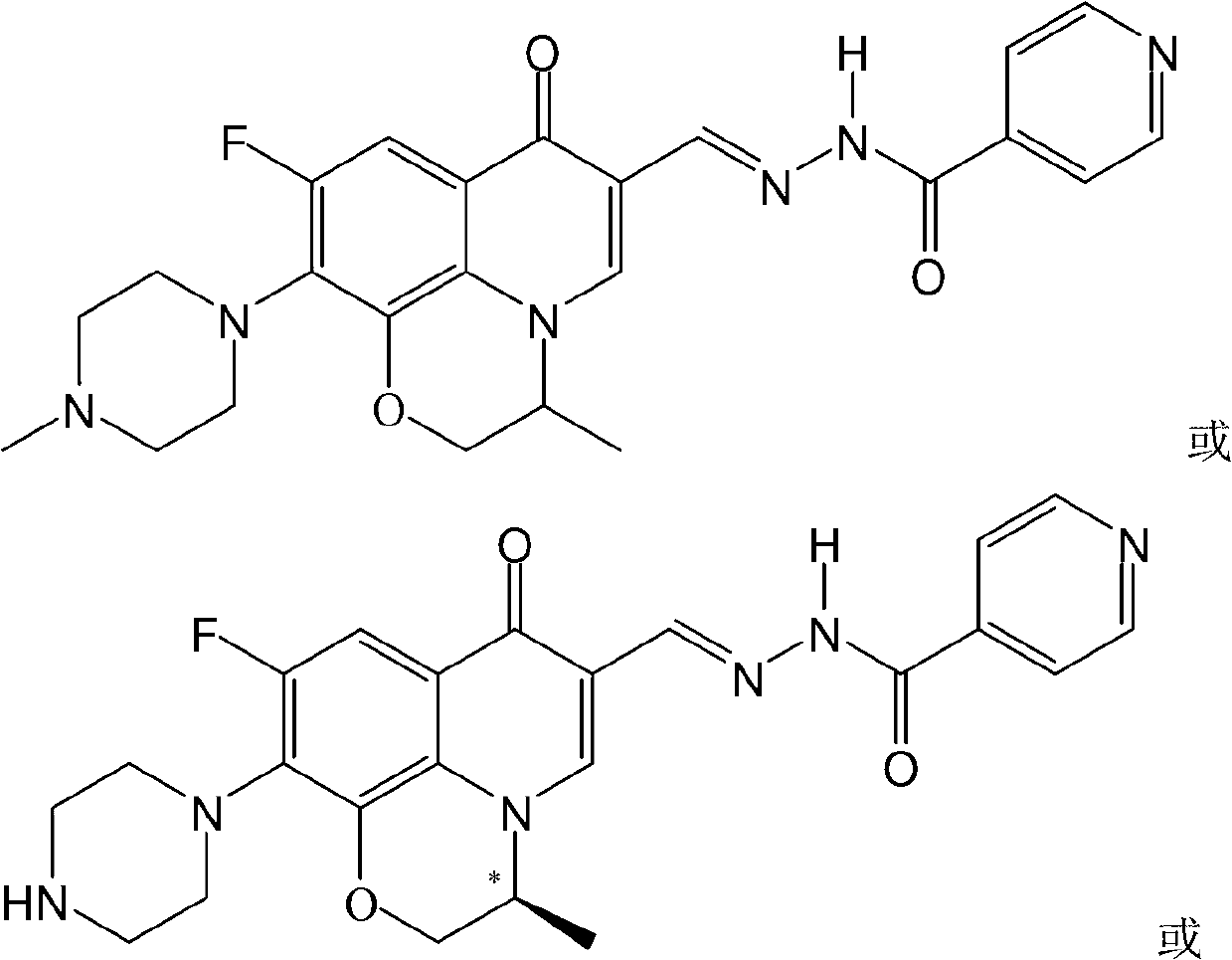
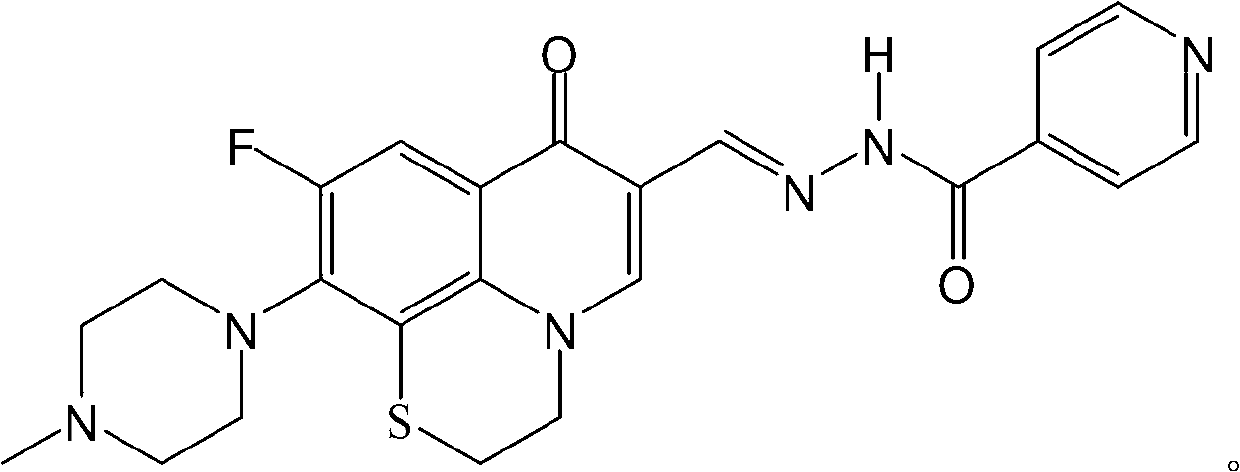
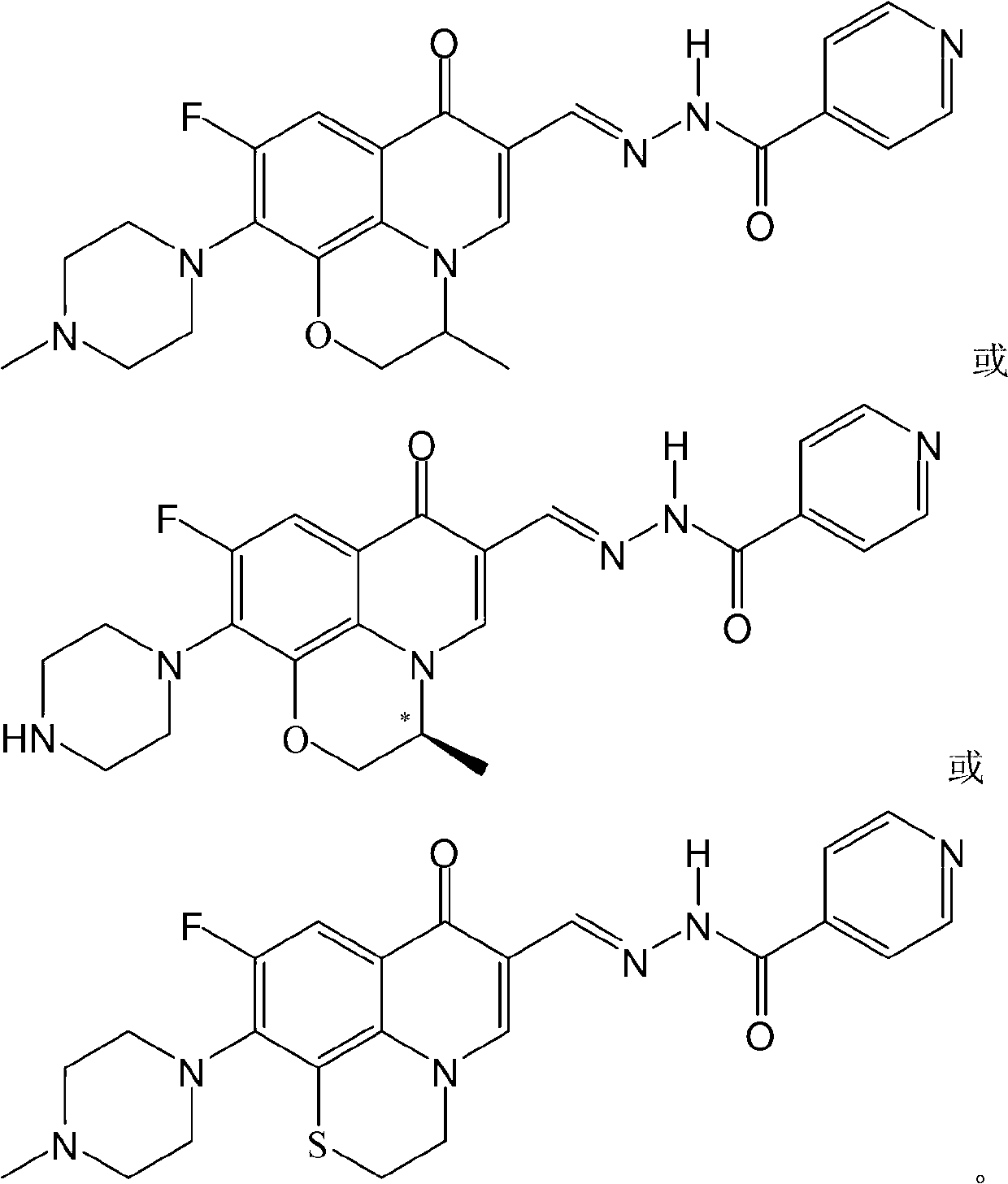
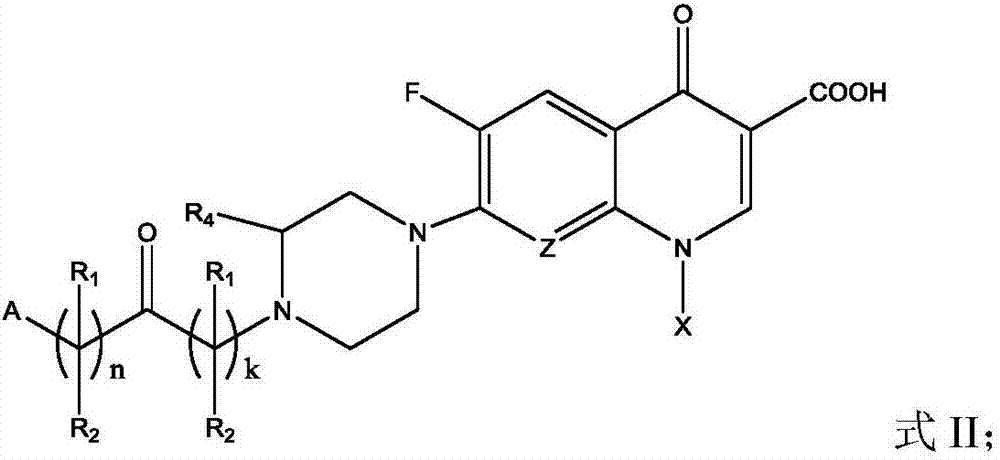
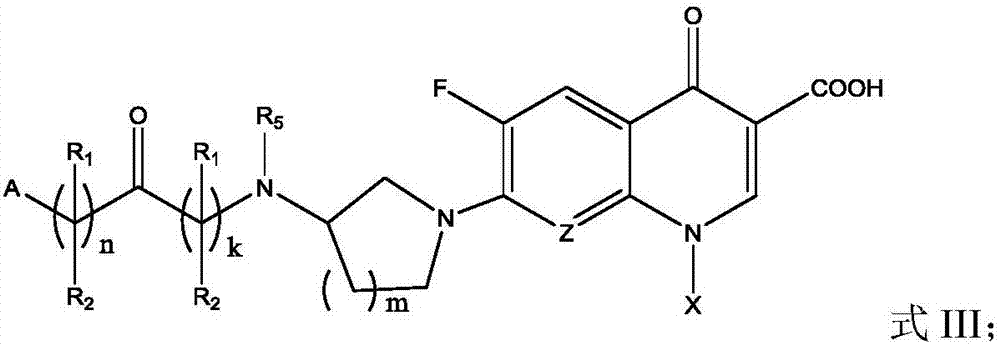
Fluoroquinolone acetal isoniazone, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102827187ASmall side effectsReduce the chance of developing drug resistanceAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsOxygen atomSide effect
The invention discloses a fluoroquinolone acetal isoniazone, of which the chemical structure general formula is disclosed as Formula I shown in the description, wherein R1 is hydrogen atom or methyl group; R2 is hydrogen atom or amino group; R3 is hydrogen atom, methyl group, ethyl group, formacyl group, acetyl group, aroyl group or sulfonyl group; R4 is hydrogen atom or methyl group; and X is oxygen atom or sulfur atom. The fluoroquinolone isoniazone disclosed by the invention implements complementarity between the two anti-tuberculosis medicines fluoroquinolone and the isoniazide, lowers the toxic and side effect of the fluoroquinolone and the isoniazide, reduces the generation probability of drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for the double-effect antimicrobial agent, and can be used as an anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis medicine for brand-new structure development of medicinal active substances.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Fusion proteins of mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveUS20080269151A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntigenTuberculosis mycobacterium
The present invention relates to fusion proteins containing at least two Mycobacterium species antigens. In particular, it relates to nucleic acids encoding fusion proteins that include two or more individual M. tuberculosis antigens, which increase serological sensitivity of sera from individuals infected with tuberculosis, and methods for their use in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tuberculosis infection.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
Compounds and methods for diagnosis and immunotherapy of tuberculosis
Compounds and methods for diagnosing tuberculosis or for inducing protective immunity against tuberculosis are disclosed. The compounds provided include polypeptides that contain at least one immunogenic portion of one or more Mycobacterium proteins and DNA molecules encoding such polypeptides. Diagnostic kits containing such polypeptides or DNA sequences and a suitable detection reagent may be used for the detection of Mycobacterium infection in patients and biological samples. Antibodies directed against such polypeptides are also provided. In addition, such compounds may be formulated into vaccines and / or pharmaceutical compositions for immunization against Mycobacterium infection.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
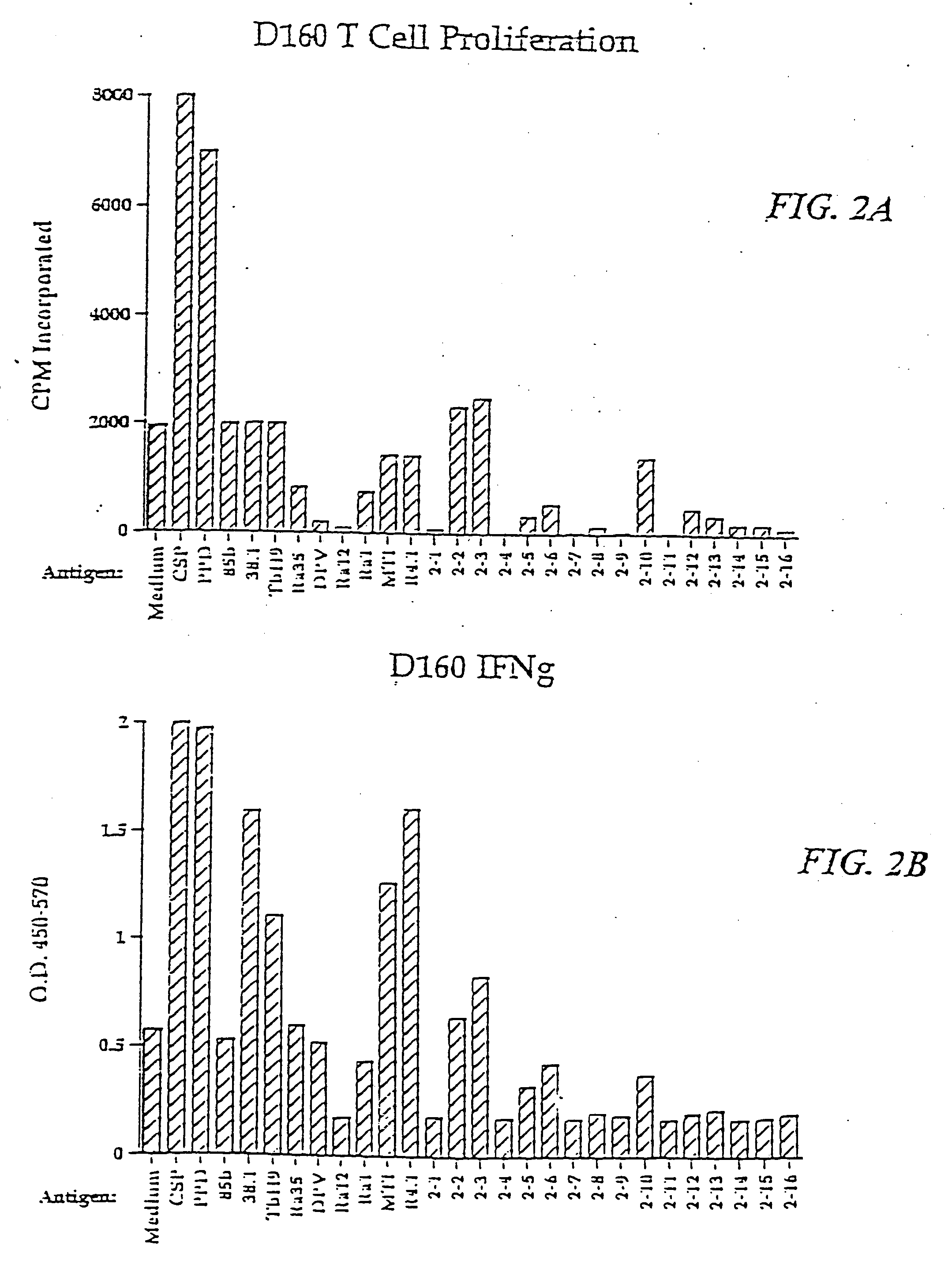
Reagent and method for detecting active tuberculosis and tuberculosis dormant infection
The invention belongs to the biomedical detection field, in particular relates to a reagent and method used for detecting activity tuberculosis and latent tuberculosis infection; based on the genomic principle, the invention discloses a novel detection reagent for mycobacterium tuberculosis, containing protein or polypeptide which is represented by SEQ ID1-2, 4-5, 8-28; the method uses one or a plurality of SEQ ID 1-28 protein or polypeptide to contact T cells of a mycobacterium tuberculosis host, and detects cytokine released from the T cells; the method can detect the tuberculosis and latent infection effectively and is not interfered by BCG vaccine at the same time; the invention also discloses a diagnostic reagent kit and other application based on the protein or polypeptide and the method; compared with the T-SPOT of the prior art, the invention can improve detectable rate obviously under the condition that the specificity is not reduced; the reagent kit has cheap price, and the cost is 1 / 5 to 1 / 10 of that of the T-SPOT reagent, thus being beneficial to being popularized in the developing countries and poor areas.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV +1
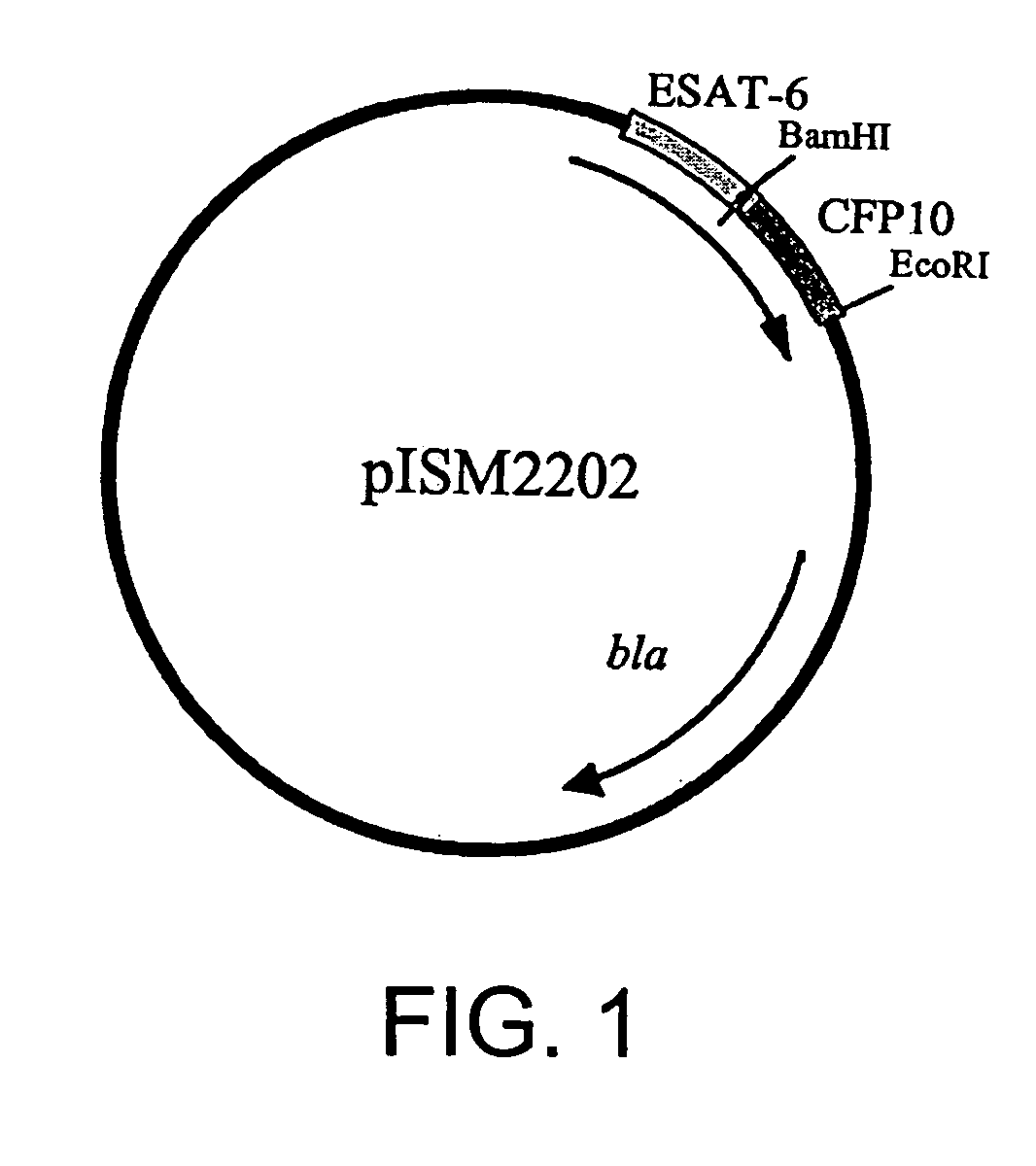
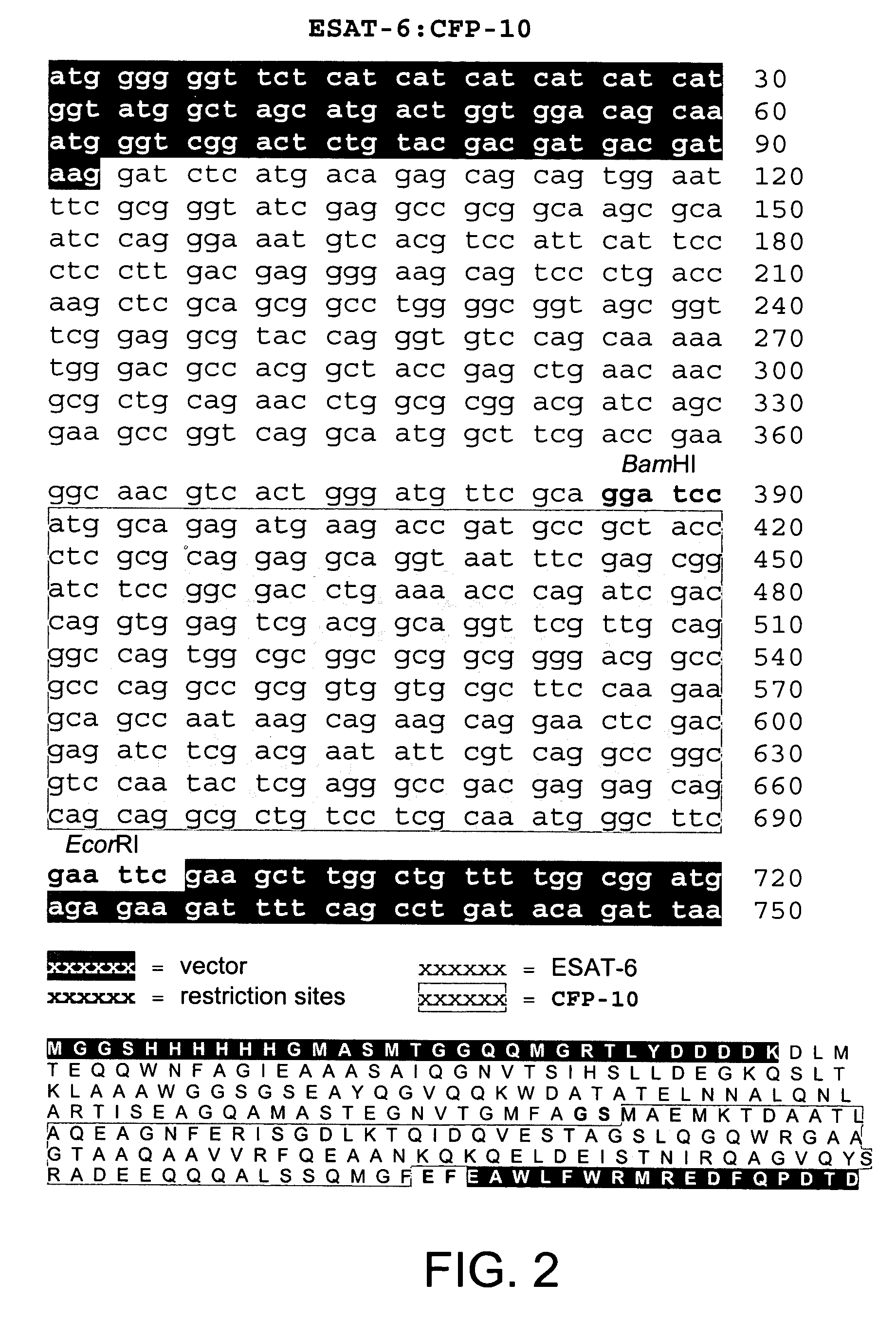
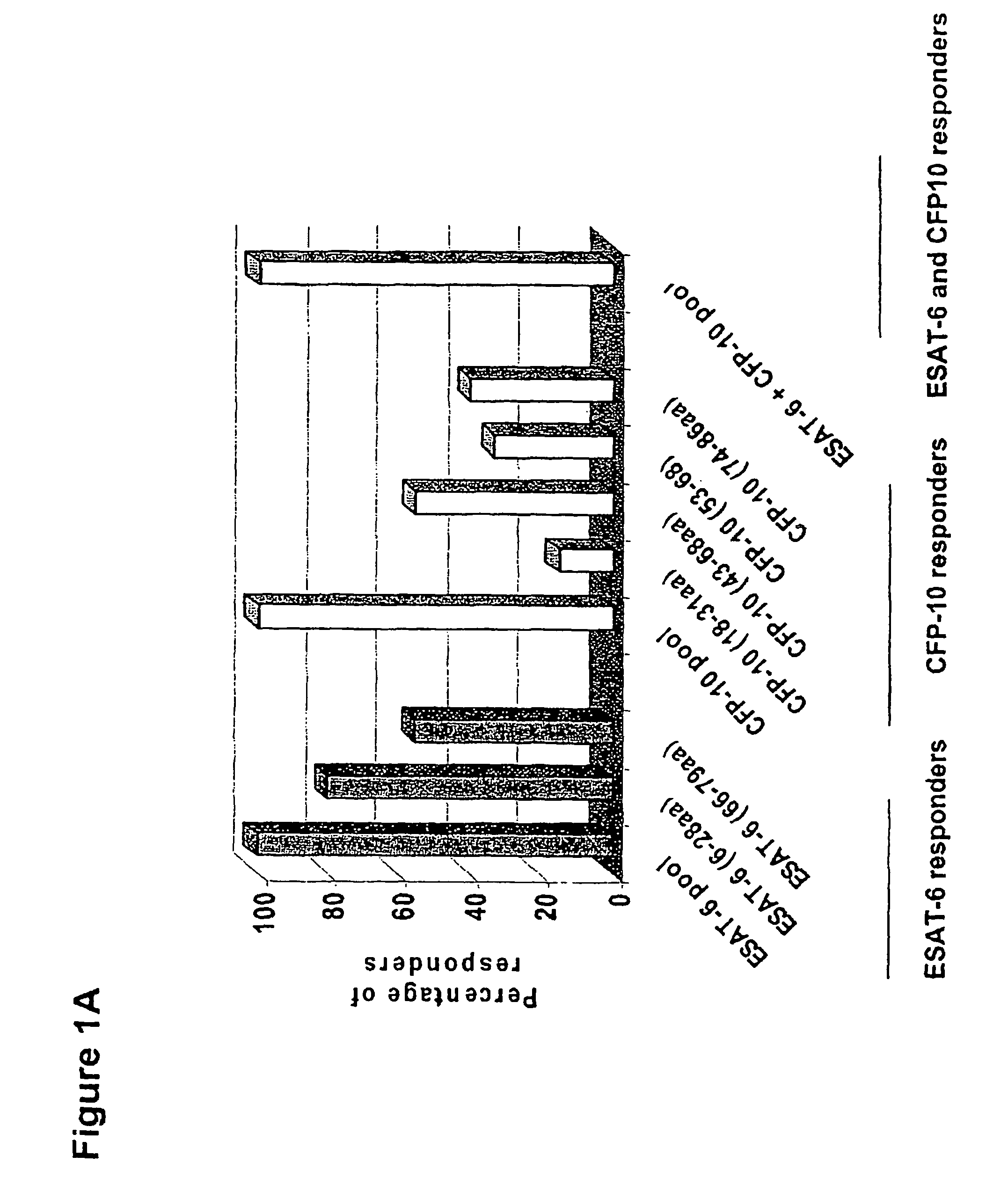
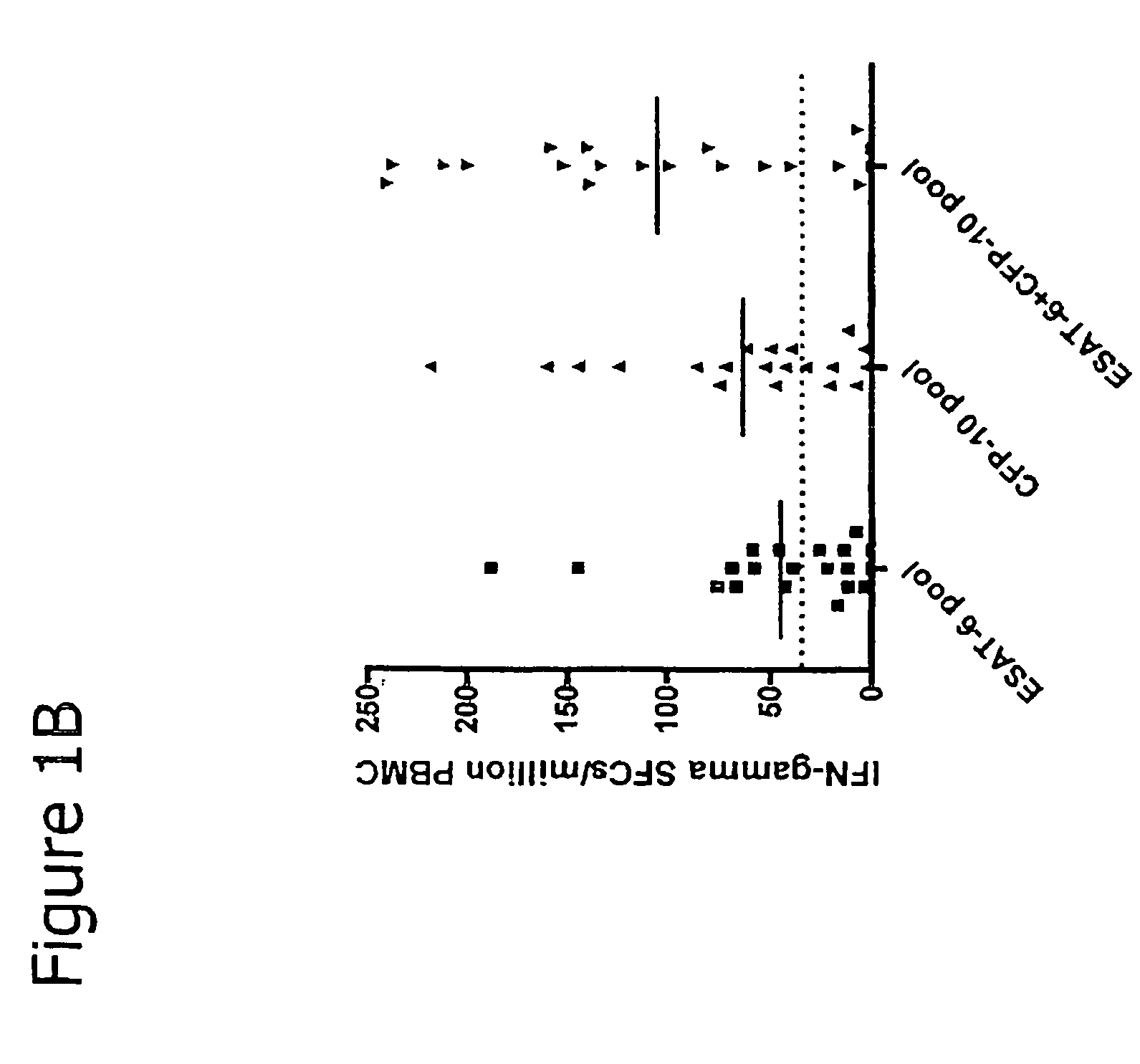
Recombinant ESAT-6:CFP-10 fusion protein useful for specific diagnosis of tuberculosis
InactiveUS20060024332A1Avoid unnecessary slaughterEasy to testBacterial antigen ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseNitric oxide
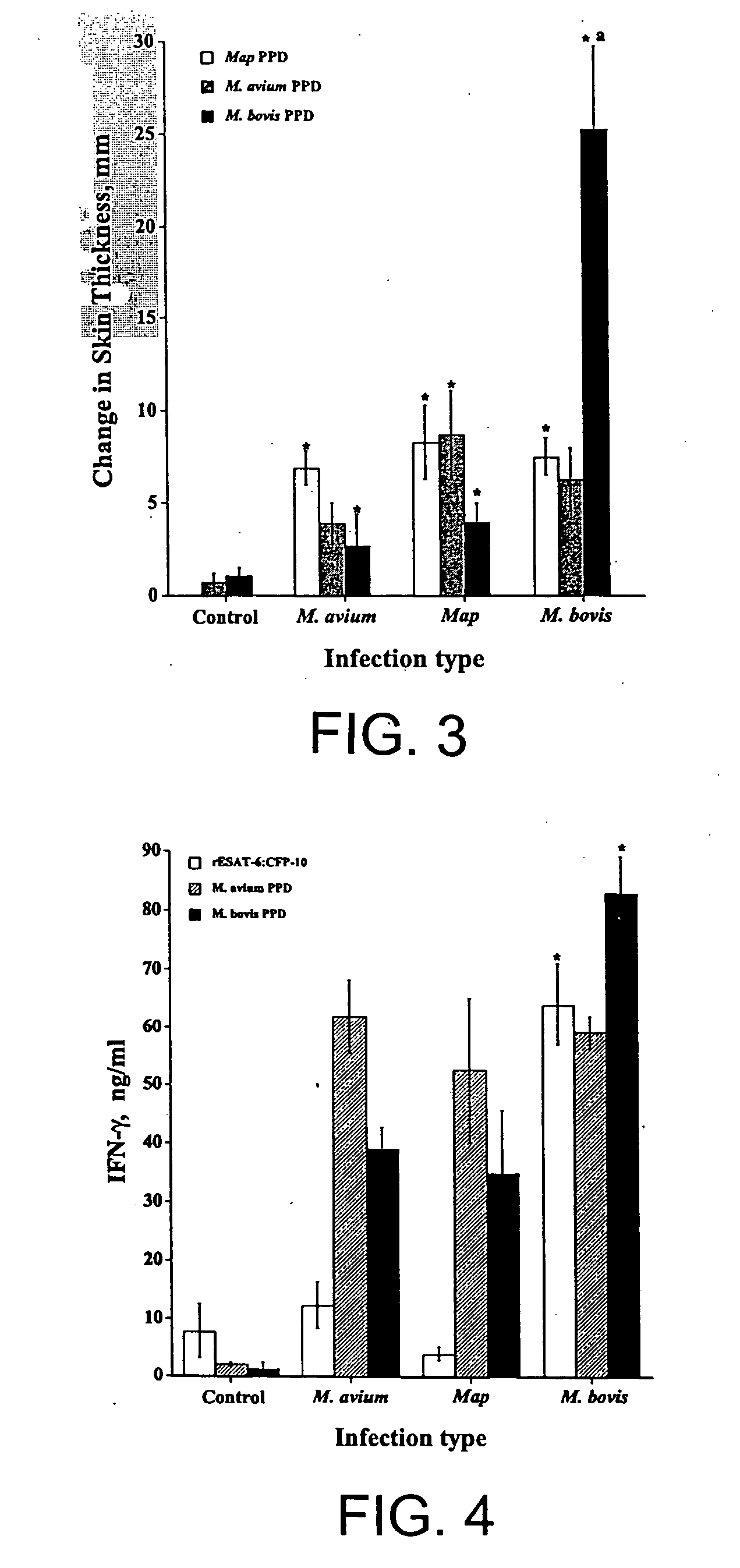
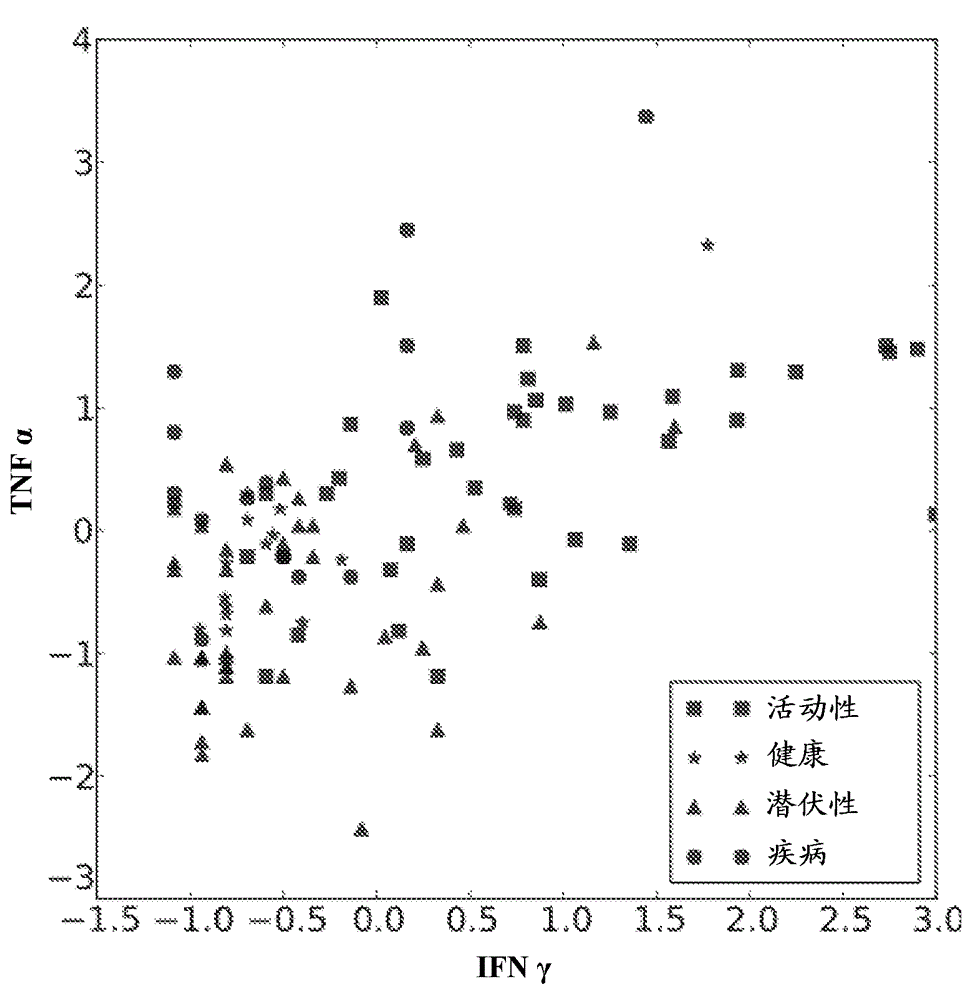
The fusion protein rESAT-6:CFP-10 is useful for differentiating infection of an animal with Mycobacterium bovis from exposure of the animal to other species of Mycobacteria, especially M. avium and M. avium subspecies paratuberculosis (Map). Cells stimulated with the fusion protein are capable of eliciting a variety of in vivo and in vitro responses (e.g. hypersensitivity skin response, IFN-γ, nitric oxide, and TNF-α) indicative of M. bovis infection. This invention will facilitate diagnosis of tuberculosis in cattle, reindeer and other susceptible animal species, thereby preventing unnecessary slaughter of uninfected animals suspected of having of the disease.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
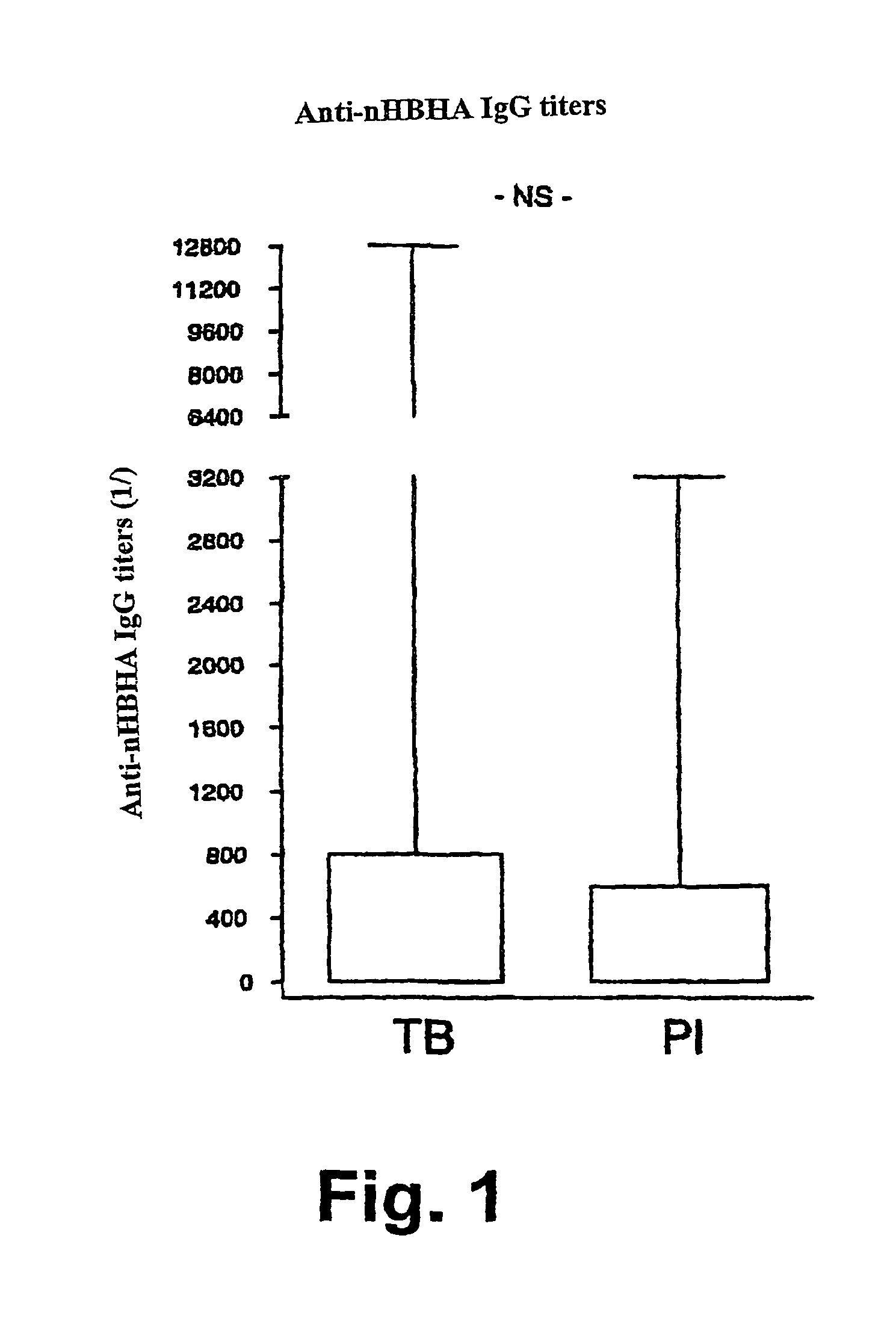
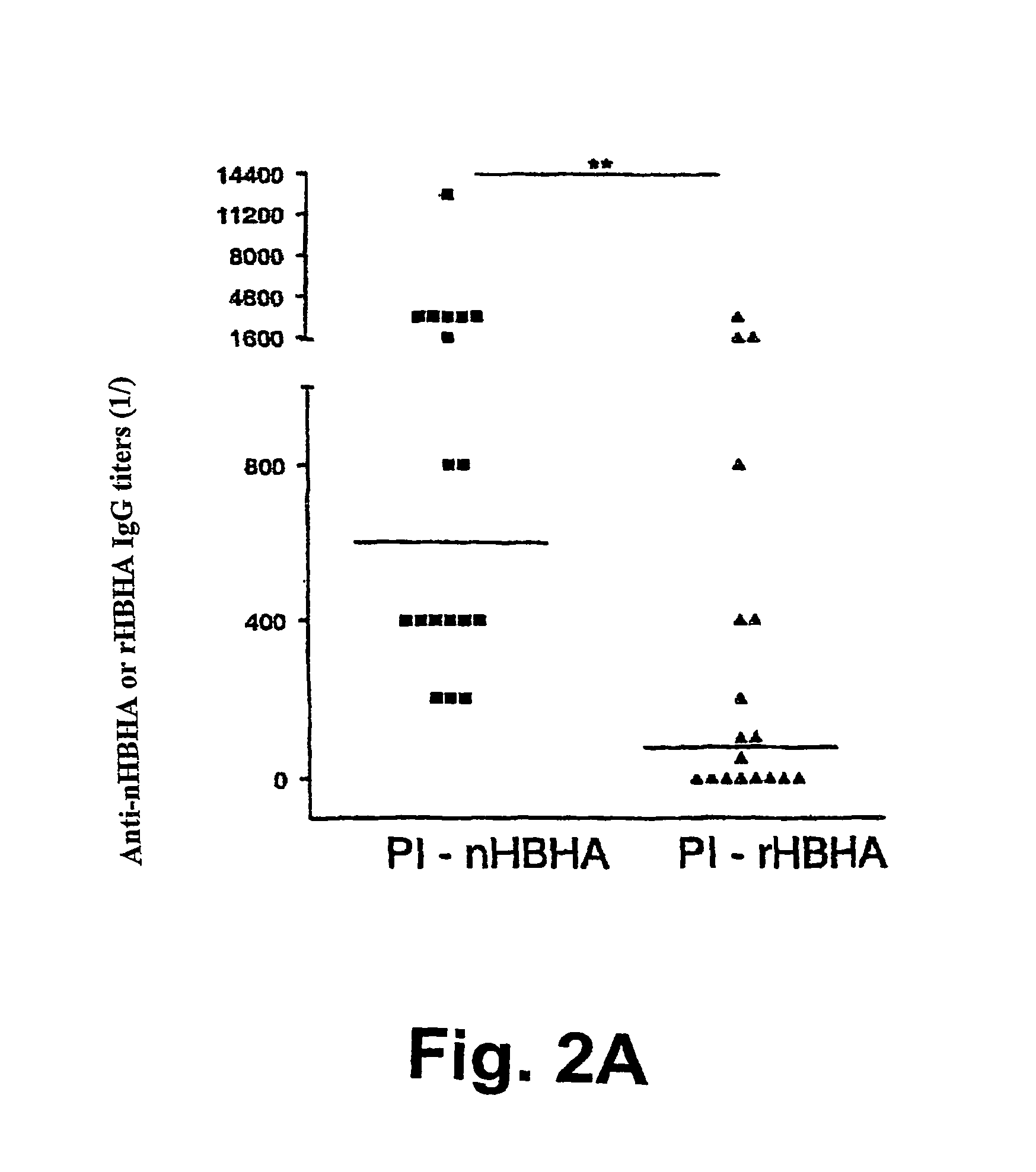
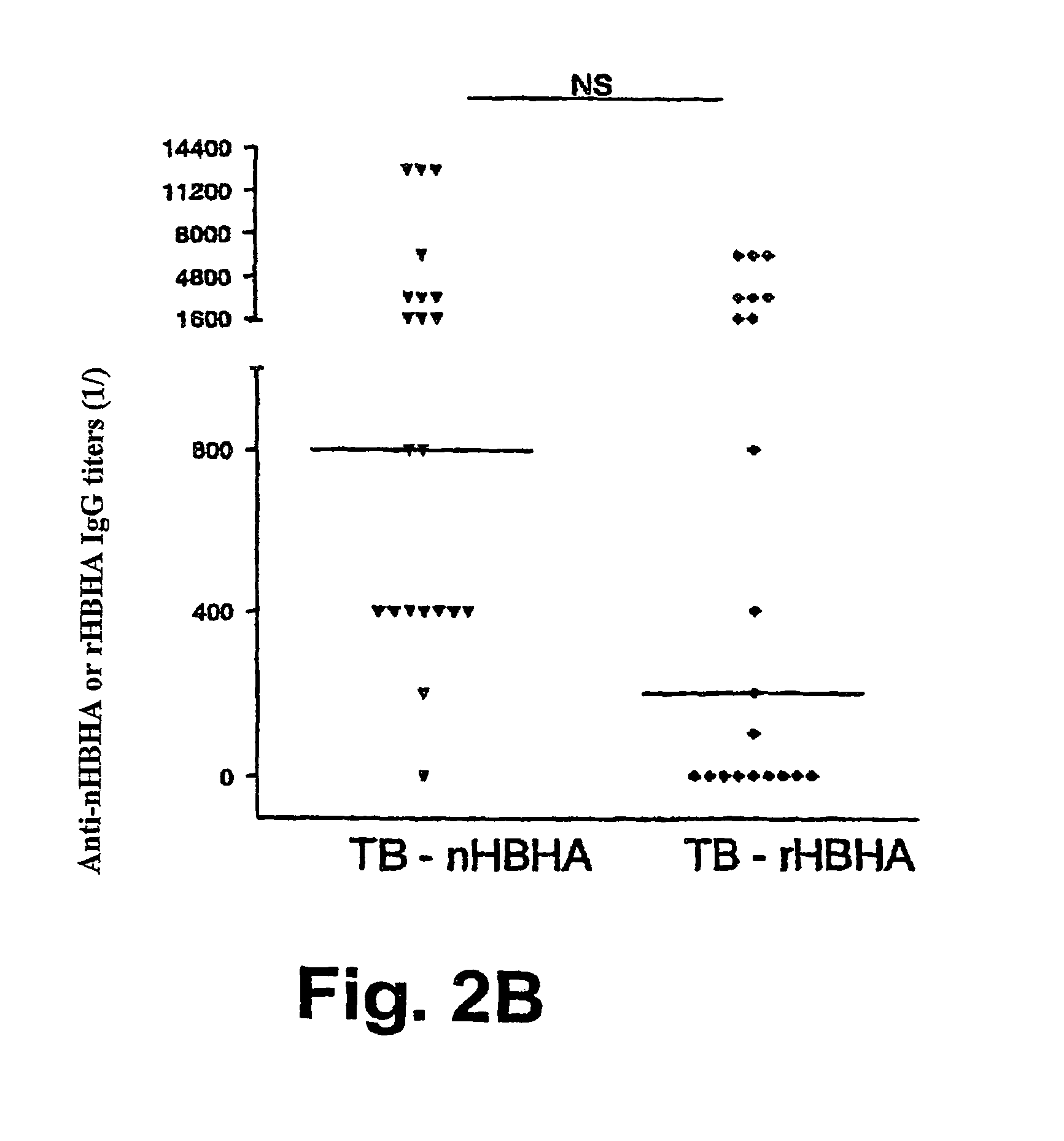
Detection of tuberculosis and infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis using HBHA
The present invention concerns methods for in vitro detection of an infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mammals, and methods for in vitro distinction between mammals infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in which the disease is declared (active form) and mammals which are infected but asymptomatic for tuberculosis (latent form), and a method for in vitro distinction between mammals presenting an active form of tuberculosis and mammals not infected by M. tuberculosis or presenting a latent form of tuberculosis. The present invention also pertains to kits for detection and distinction between infected mammals presenting tuberculosis symptoms and infected mammals with no disease development, and a kit for distinguishing between mammals presenting an active form of tuberculosis and mammals not infected by M. tuberculosis or presenting a latent form of tuberculosis.
Owner:INSTITUT PASTEUR DE LILLE +3
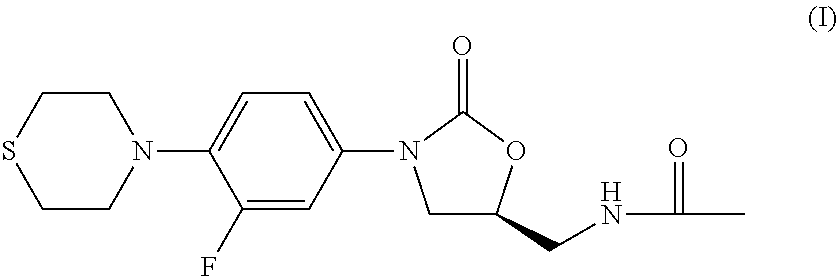
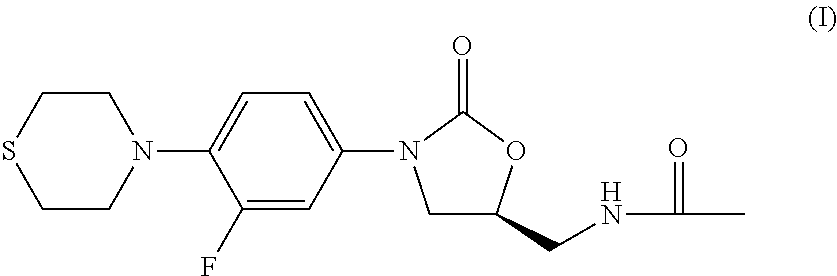
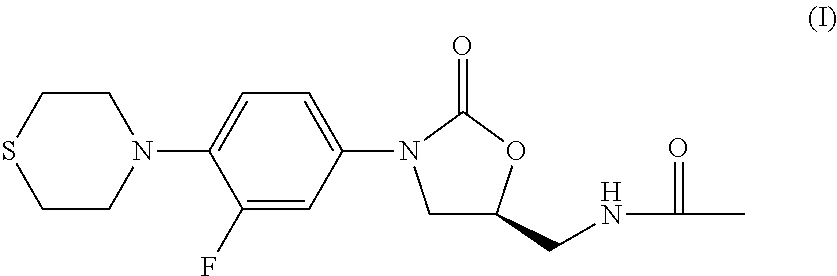
Combination Therapy for Tuberculosis
The present invention relates to methods of treating tuberculosis, including multi-drug resistant varieties and latent tuberculosis. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of treating tuberculosis in a mammal comprising administering to said mammal in need thereof an effective amount of a compound of formula (I), (S)—N-[[3-[3-fluoro-4-(4-thiomorpholinyl)phenyl]-2-oxo-5-oxazolidinyl]methyl]acetamide, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in combination with at least two agents useful in the treatment of tuberculosis. The present invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, (ii) a therapeutically effective amount of at least one agent useful in the treatment of tuberculosis and (iii) one or more pharmaceutically acceptable carriers or vehicles.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
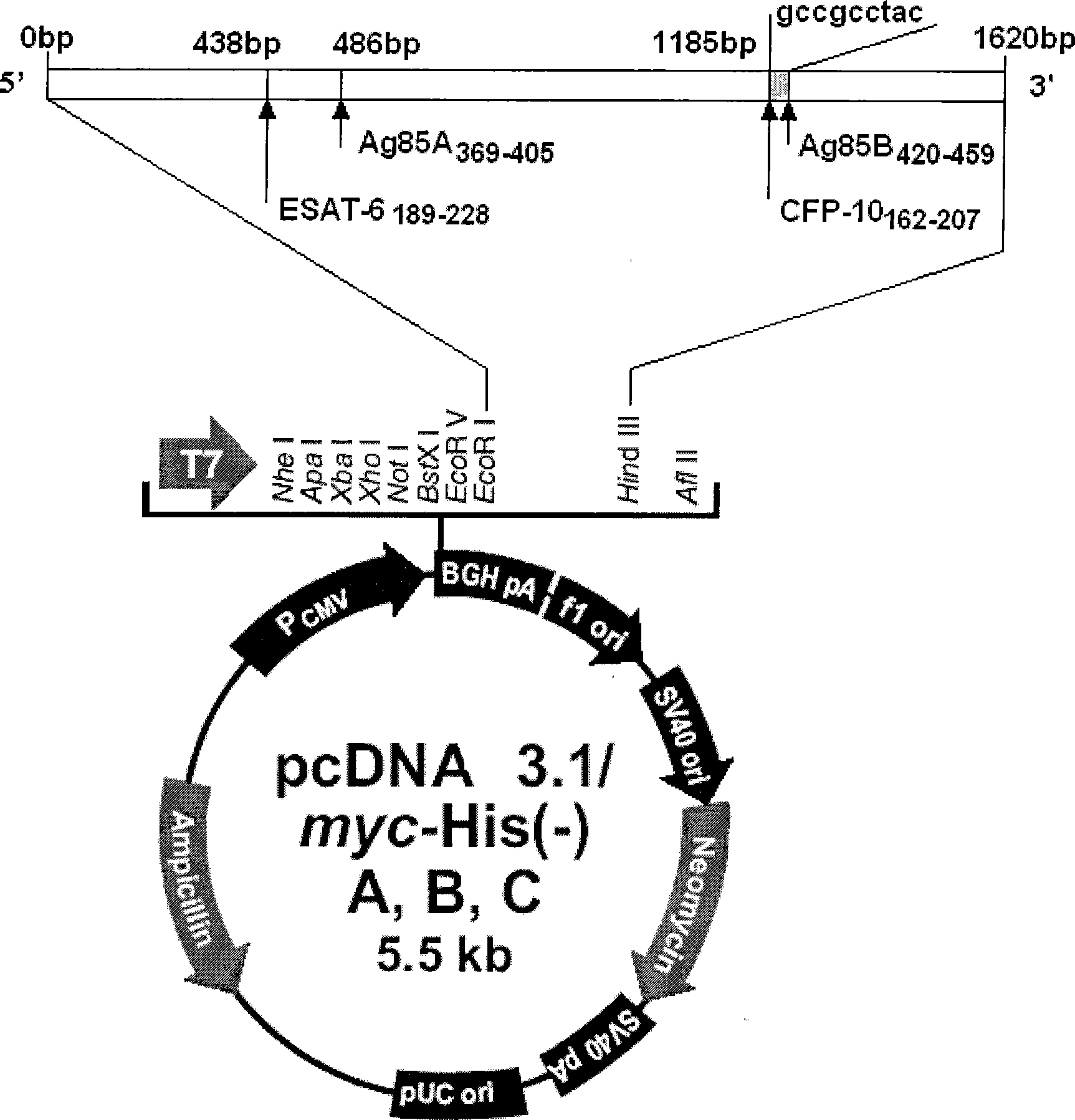
Tuberculosis gene vaccine based on T cell epitope as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101451145AActivate immune responseDoes not affect the spatial structureAntibacterial agentsGenetic material ingredientsIntramuscular injectionTreating tuberculosis
The invention discloses a tuberculosis gene vaccine based on T cell epitopes, wherein a full-length gene, embedded with four T cell epitope polypeptide genes which come from mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen, of mycobacterium tuberculosis heat shock protein is inserted into a vector. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the vaccine, which comprises the following steps: four T cell epitope genes, namely EAST-6189-228, Ag85A369-405, CFP10162-207 and Ag85B420-459 which come from the mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen are inserted into an HSP65 full-length gene. The invention also discloses application of an ECANS tuberculosis gene vaccine. Through the intramuscular injection of the gene vaccine into an immune mouse, the experiment proves that the vaccine can induce a specific antibody which aims at a plurality of tuberculosis antigens to response, can induce stronger tuberculosis specific killing response, can induce Th1 immune response at the same time, secrete high-level IFN gamma, and is a good vaccine for preventing and treating tuberculosis.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
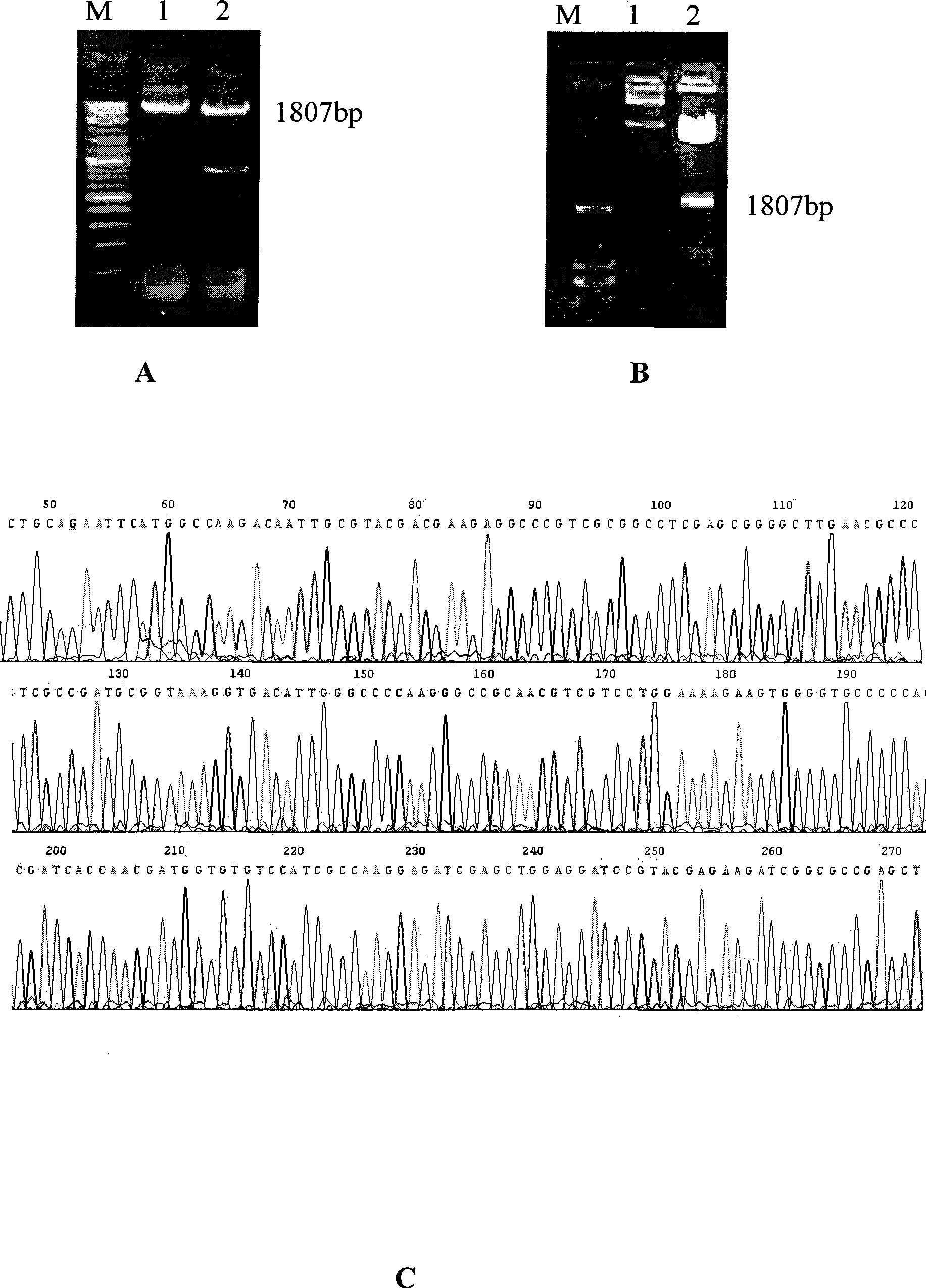
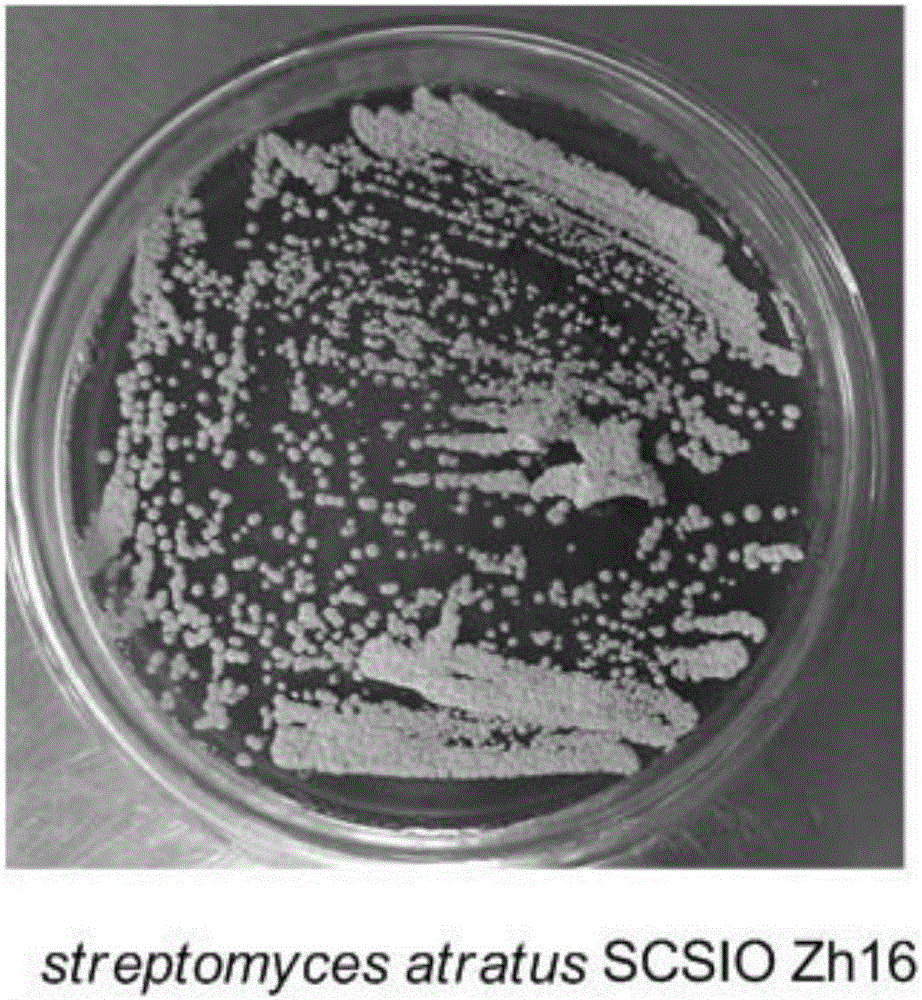
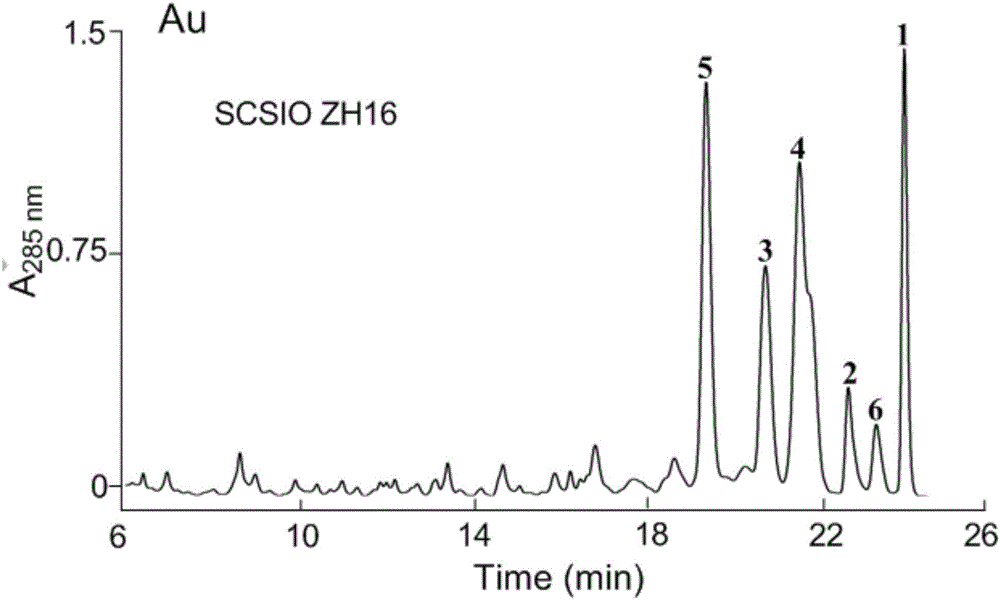
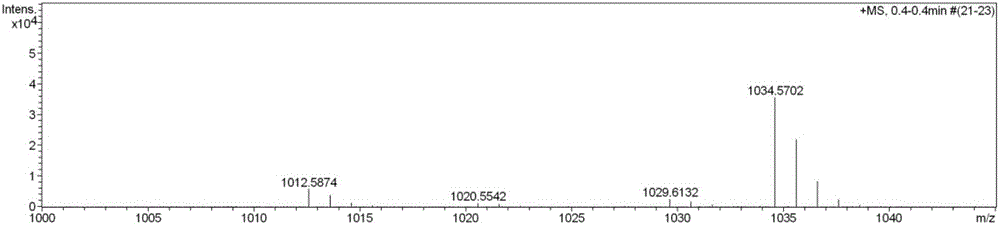
Streptomyces atratus and application of cyclic peptide compounds with same to preparing mycobacterium tuberculosis resistant medicines
ActiveCN106279370AGood inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsBacteriaCyclic peptideAntituberculous drugs
The invention discloses streptomyces atratus and application of cyclic peptide compounds with the same to preparing mycobacterium tuberculosis resistant medicines. A structural formula of the cyclic peptide compounds is shown. A preservation number of the streptomyces atratus SCSIO Zh16 is CGMCC No.12198. The streptomyces atratus and the application have the advantages that the six cyclic peptide compounds are obtained from fermentation cultivation substances of the streptomyces atratus SCSIO Zh16 by means of separation, the cyclic peptide compound 6 is high in mycobacterium tuberculosis resistant activity, obvious effects of inhibiting mycobacterium tuberculosis can be realized by the cyclic peptide compound, accordingly, the cyclic peptide compounds can be used for preparing anti-tuberculosis medicines and can be used for treating tuberculosis, alternative compounds can be provided for developing novel anti-tuberculosis medicines, and the streptomyces atratus and the application have important significance on developing marine medicinal materials in China.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
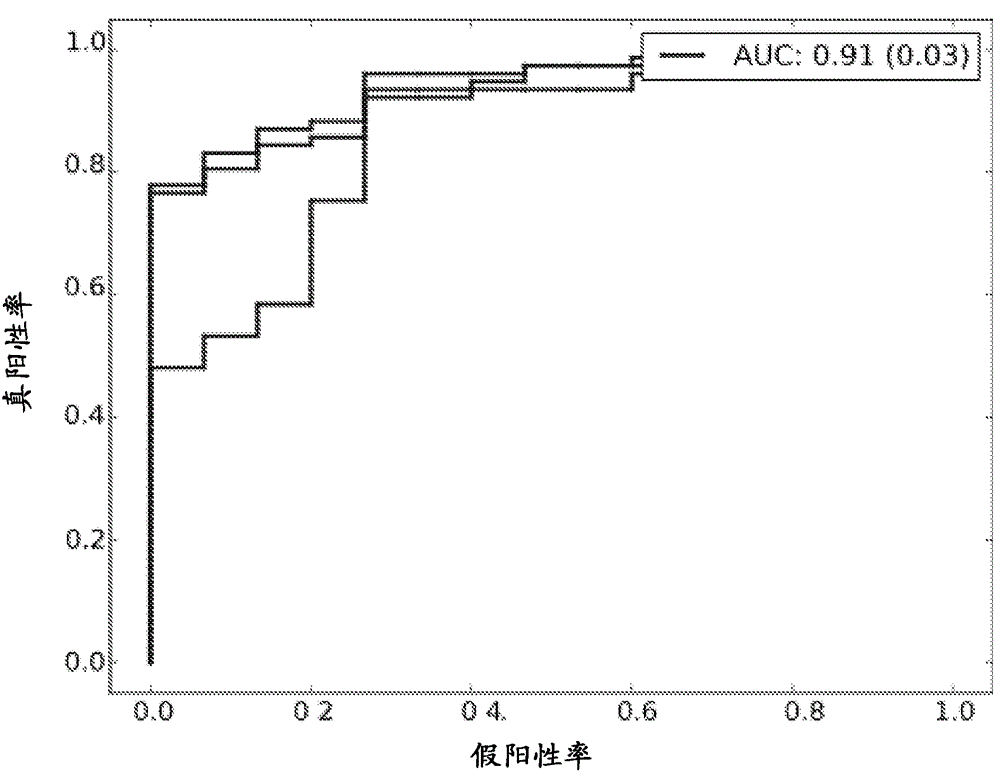
Immune diagnostic assay to diagnose and monitor tuberculosis infection
InactiveUS7785607B2High detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseT lymphocyte
The present invention relates to a method of diagnosing and monitoring various distinct presentations of tuberculosis: active tuberculosis disease, latent tuberculosis infection and recent tuberculosis infection. The rapid immune assay is based on the evaluation of the frequency of Interferon (IFN) gamma-producing antigen-specific T lymphocytes responding to selected peptide sequences from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, selected for their immunogenicity. The invention concerns also immunogenic and vaccine compositions based on these specific peptide sequences.
Owner:INST NAT PER LE MALATTIE INFETTIVE LAZZARO SPALLANZANI IRCCS
Reagent for detecting tubercle bacillus infection in vitro and method thereof
ActiveCN101446585AValid in vitro assayOvercome the disadvantages of unsatisfactory effectImmunoglobulins against bacteriaBiological testingBCG vaccineT cell
The invention discloses a reagent for detecting tubercle bacillus infection in vitro and a method thereof. The reagent comprises M233 polypeptide represented by SEQ ID No.1; and cytokine released from T cells is detected by contacting the M233 polypeptide or an analog thereof with the T cells of a tubercle bacillus host to determine whether the T cells identify the M233 polypeptide or the analog thereof. The reagent has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, being free from interference of BCG vaccine and non-tuberculosis mycobacteria vaccine, being capable of detecting active pulmonary tuberculosis patients, the patients with dormant infection and healthy persons who contact with mycobacterium nontuberculosis. The reagent and the method are especially applicable to detecting tuberculosis and / or dormant infection thereof for Chinese people.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RHFAY BIOTECH CO LTD
Method of Diagnosis of Infection by Mycobacteria and Reagents Therefor
InactiveUS20120165246A1Improve diagnostic accuracyReduce in quantityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSpecific detectionMycobacterium Infections
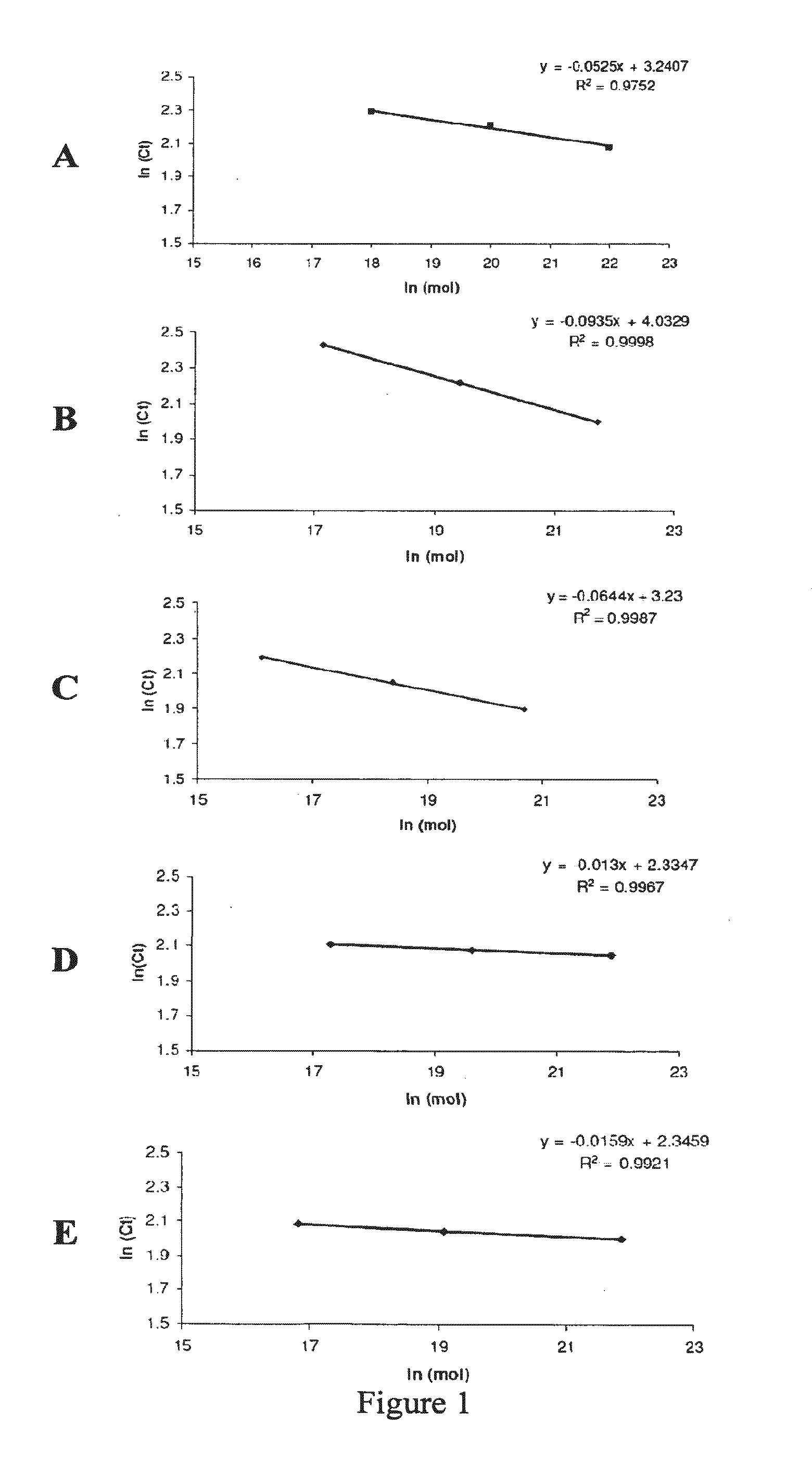
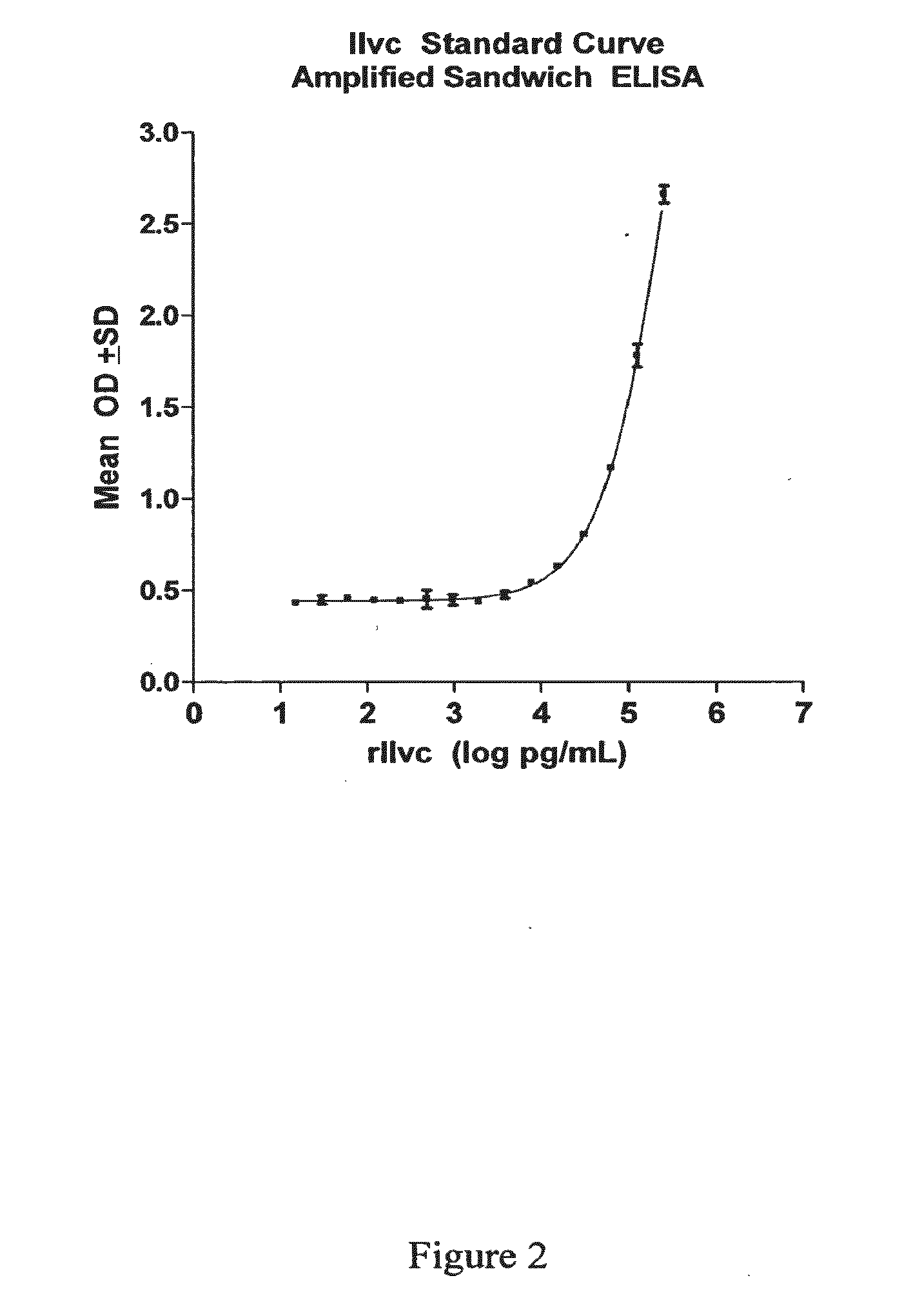
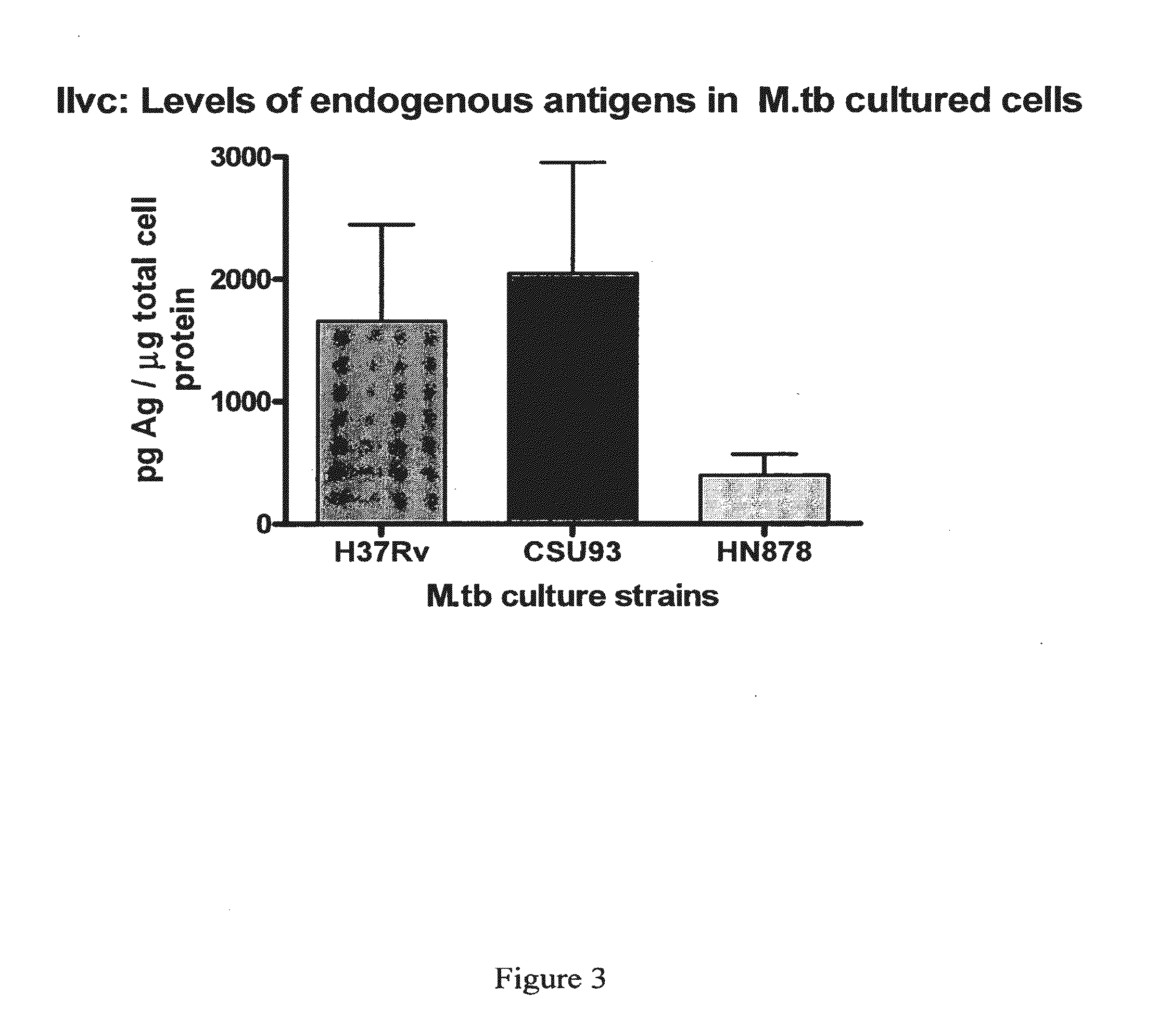
The present invention provides a method of specifically detecting the presence of one or more Mycobacteria of the M. tuberculosis complex, said method comprising detecting ilvC nucleic acid of one or more Mycobacteria of the M. tuberculosis complex in a sample under conditions that do not detect ilvC nucleic acid of the M. avium complex. The invention also provides methods of diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis in a subject employing the specific detection ilvC nucleic acid of one or more Mycobacteria of the M. tuberculosis complex.
Owner:TYRIAN DIAGNOSTICS LTD
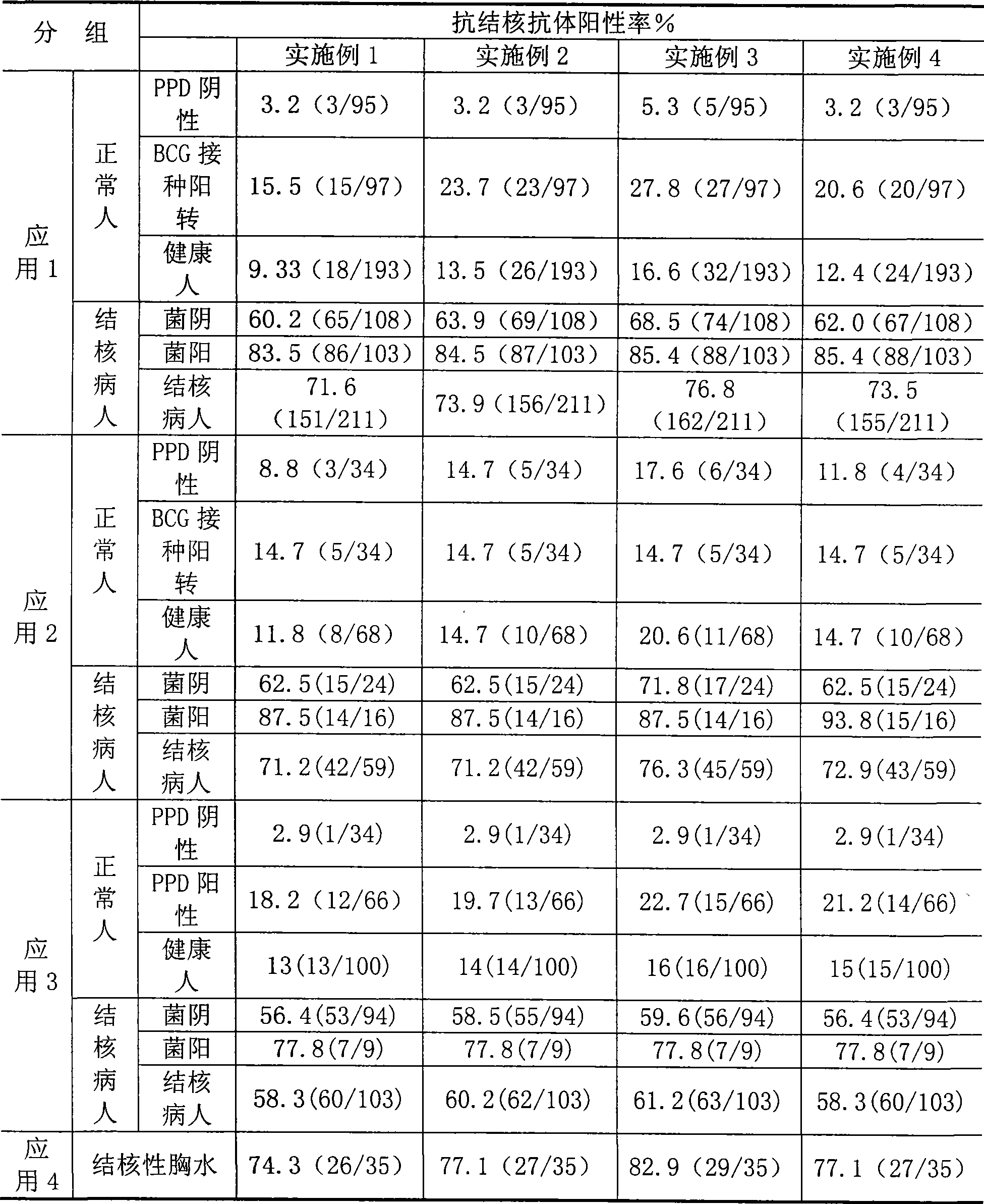
Tuberculosis antibody multi-antigen ELISA detecting kit and making method
The invention relates to a tuberculosis antibody multiple antigen ELISA detection kit and a preparation method thereof, which pertains to the field of tuberculosis medical immunology diagnostic techniques and mainly uses detection antigen, enzyme-linked antihuman IgG antibodies, substrates, positive control serum of tuberculosis patients, control serum of normal person, calf serum and polystyrene microplates to form the kit, wherein, the detection antigen adopts the mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains of lipid Arabian mannose (LAM), 38kD and 16kD to be combined with arbitrary one or more than one mycobacterium tuberculosis recombinant proteins in the recombinant proteins of MPT63, MTB48 and CFP10-ESAT6. The mycobacterium tuberculosis has high sensitivity, strong specificity and complementarity, can be used for detecting specific antitubercular antibodies in such body fluid samples as serum, hydrothorax and the like, and assisting the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Owner:中国人民解放军总医院第二附属医院
Tuberculosis antigen specific whole blood IFN-gamma diagnosis kit, method for producing the same and method for using same
InactiveCN101493454ADiagnostic advantageShorten the timeBiological testingEscherichia coliEnzyme linked immunoassay
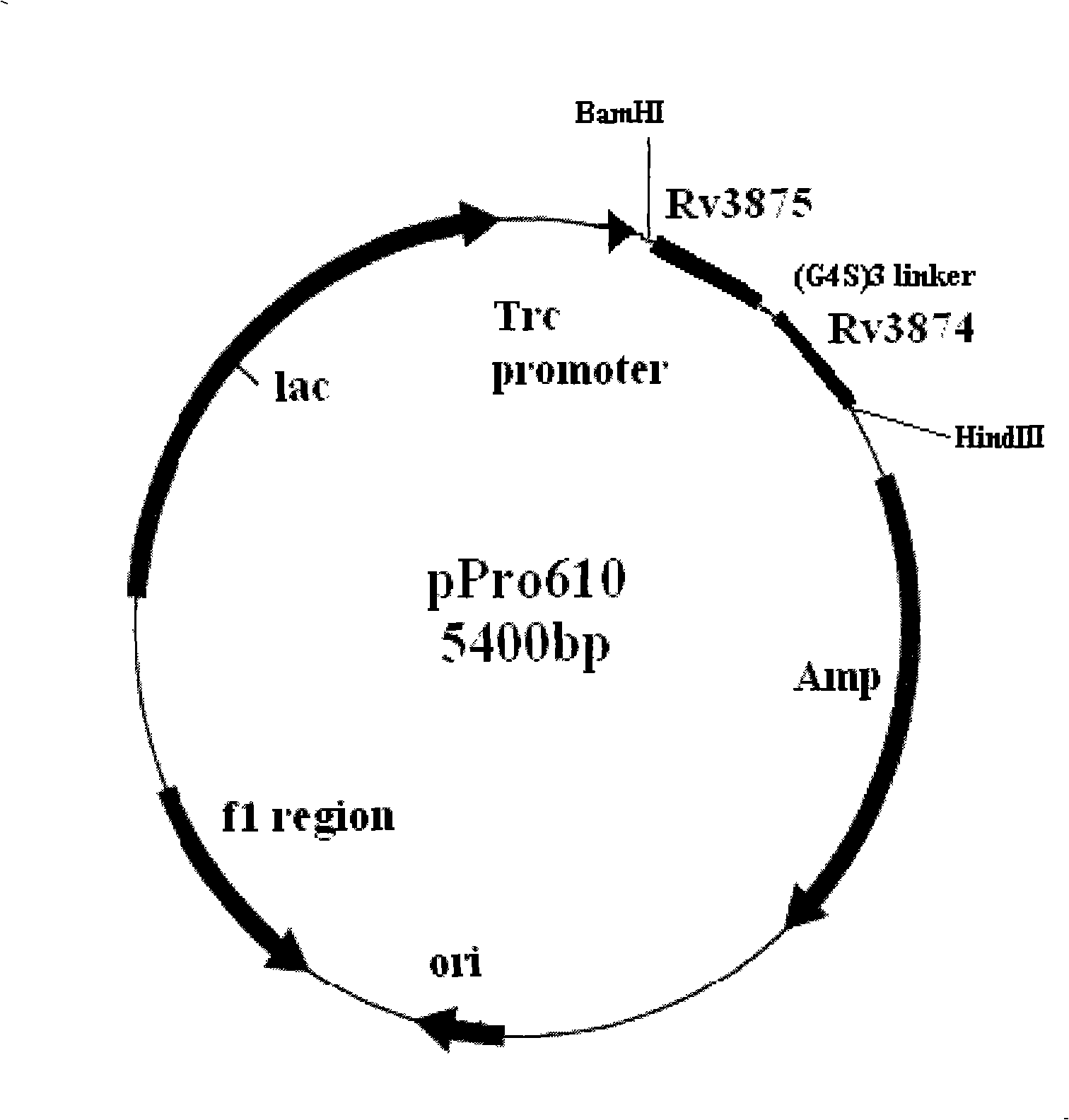
The invention relates to a diagnostic kit for tuberculosis and mycobacterium tuberculosis infectors, a preparation method and an application method thereof. By using the linker for encoding 15 amino acid (G4S1) 3, the encoding genes (SEQ.ID.NO.6) of a mycobacterium tuberculosis specific antigen Rv3875 and Rv3874 are connected in series, and then inserted into an E. coli expression vector, and the high-efficiency expression and purification for the fusion protein of Rv3875 and Rv3874 in the E. coli are achieved. The recombinant protein at least comprises 8 T cell epipositions which can be used for cell immunity diagnosis, and a diagnostic kit and diagnostic method for a whole blood IFN-Gamma release analysis method are established by taking the protein as the basis and combining the human IFN-Gamma enzyme-linked immunoassay technology, and can be used for the early, specific diagnosis and screening of tuberculosis and mycobacterium tuberculosis infectors.
Owner:范雄林
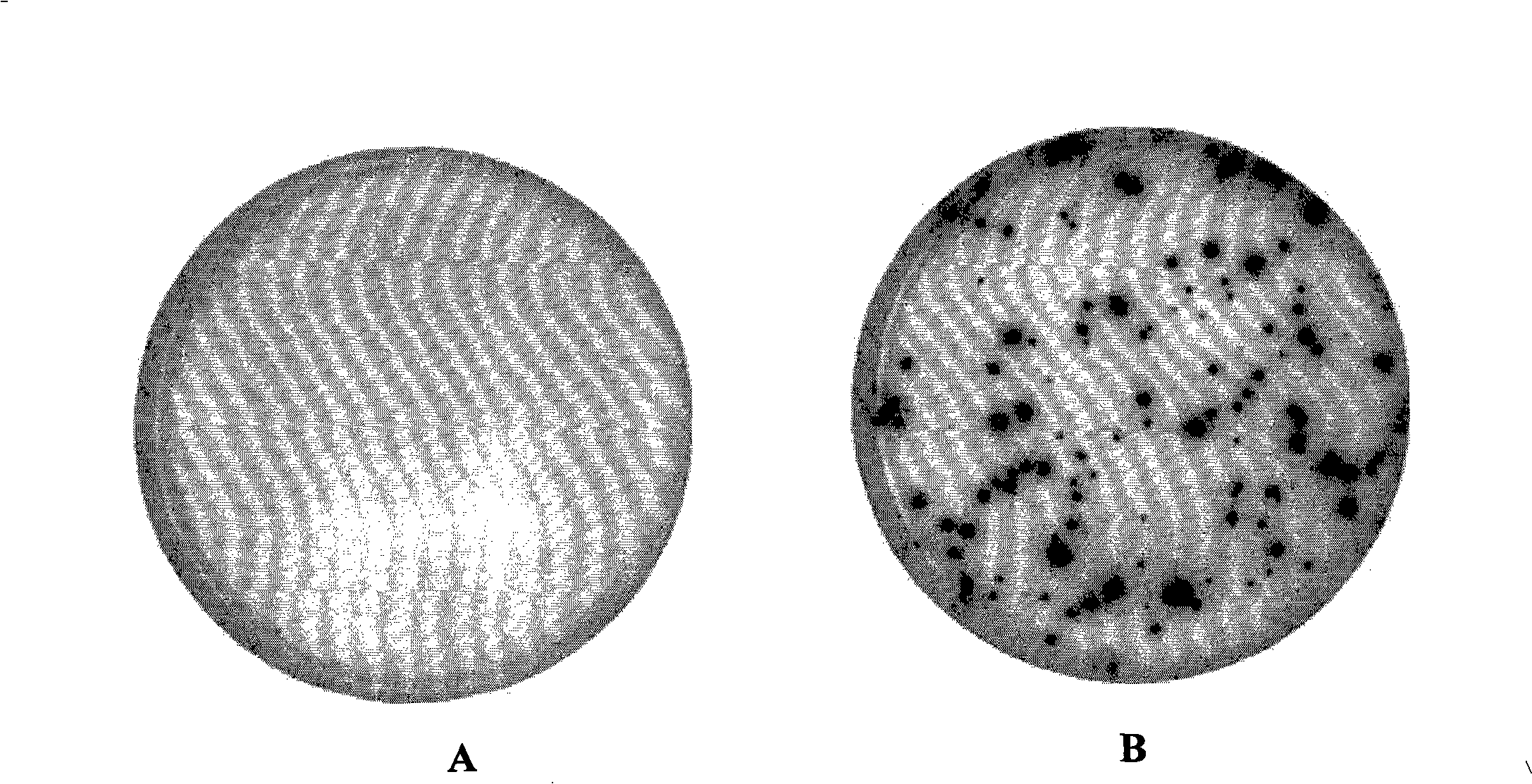
ELISA fleck diagnosis kit for tubercle bacillus infect and method for preparing specific antigen
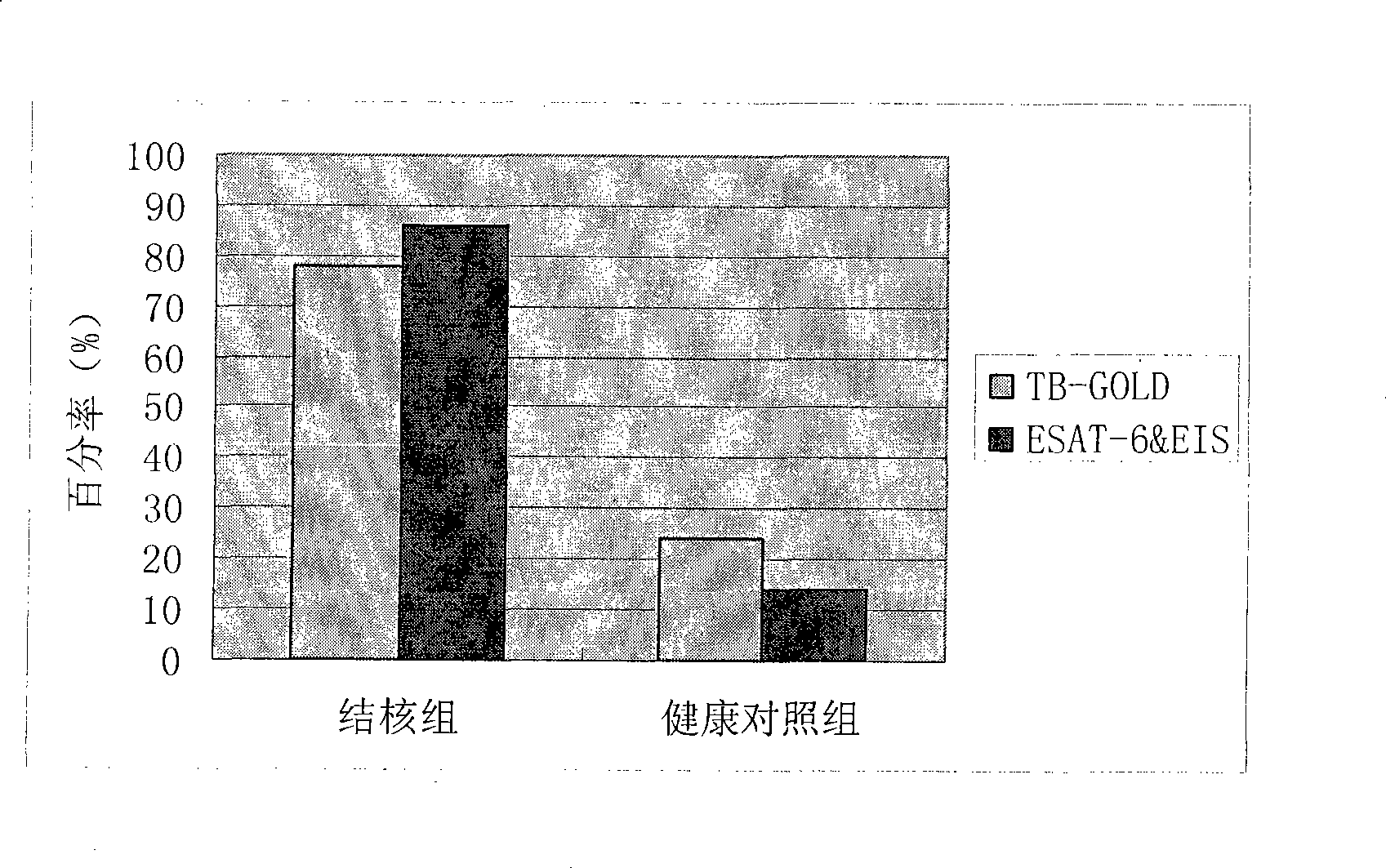
The invention relates to a reagent kit for diagnosing enzyme linked immune spots infected by tubercle bacillus and a method for preparing a specific antigen. The reagent kit comprises a reagent kit body and a detection reagent arranged in the kit body; the detection reagent comprises a positive standard solution, a chromogenic agent, a concentrated detergent and a diluent; the detection reagent also comprises a specific antigen of mycobacterium tuberculosis, a coated INF-gamma resistant antibody and an enzyme label secondary antibody of a vector protein conjugate; the specific antigen of mycobacterium tuberculosis is fusion protein expressed by an ESAT-6 gene and an EIS gene of the mycobacterium tuberculosis; and the INF-gamma resistant antibody is a murine IgG antibody. The method for preparing the specific antigen comprises the following steps: proper tubercle bacillus special antigen ESAT-6 and EIS are combined; and the prepared recombining fusion protein contains main antigenic determinants of two antigens. The recombining fusion protein definitely contains a T cell epitope suitable for the limitation of different HLA, and does not influence results by different groups and different HLA distribution. Clinical tests on tuberculosis patients and healthy people of different groups show that the reagent kit has more excellent specificity and sensitivity than a current similar product.
Owner:THE THIRD PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
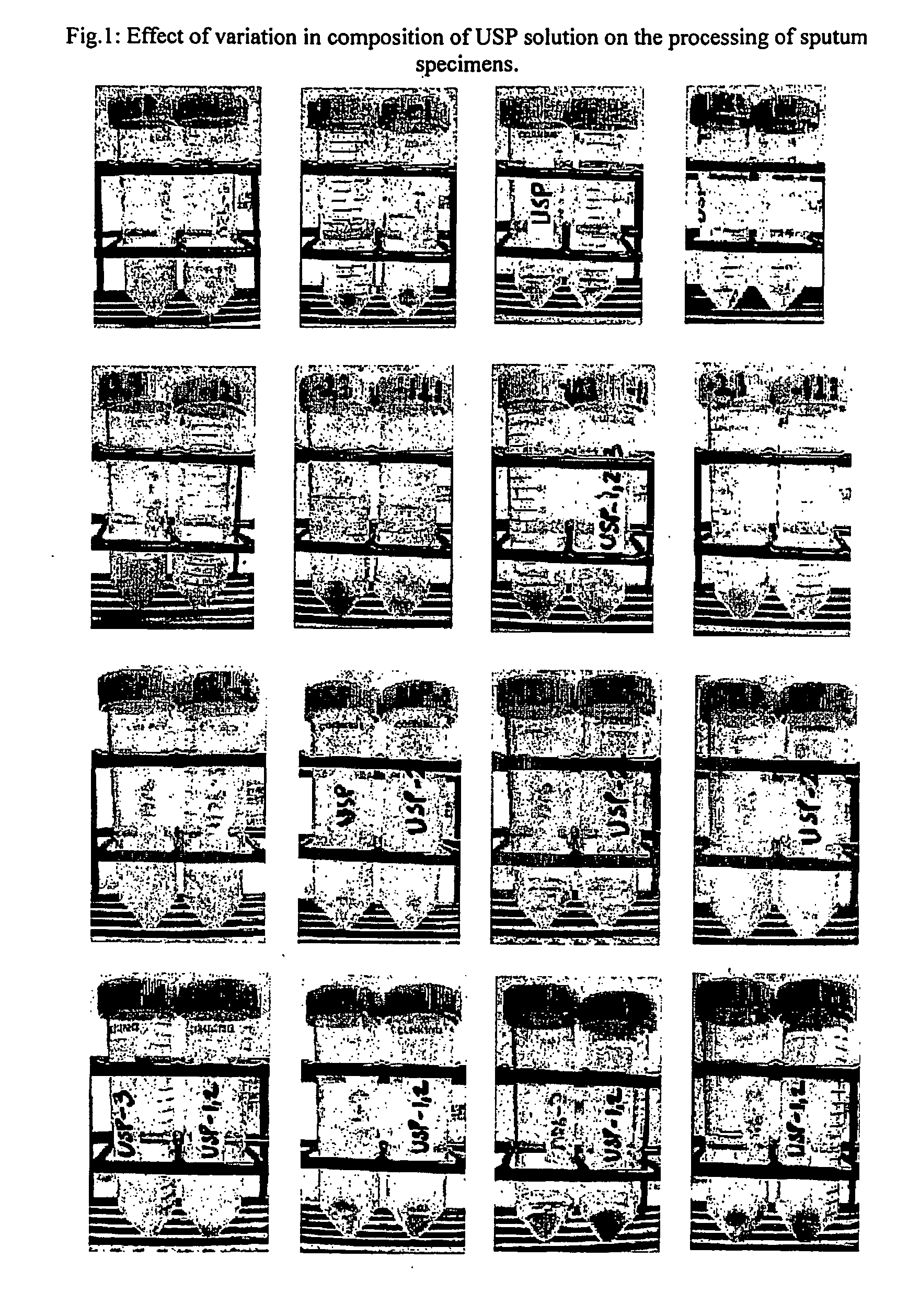
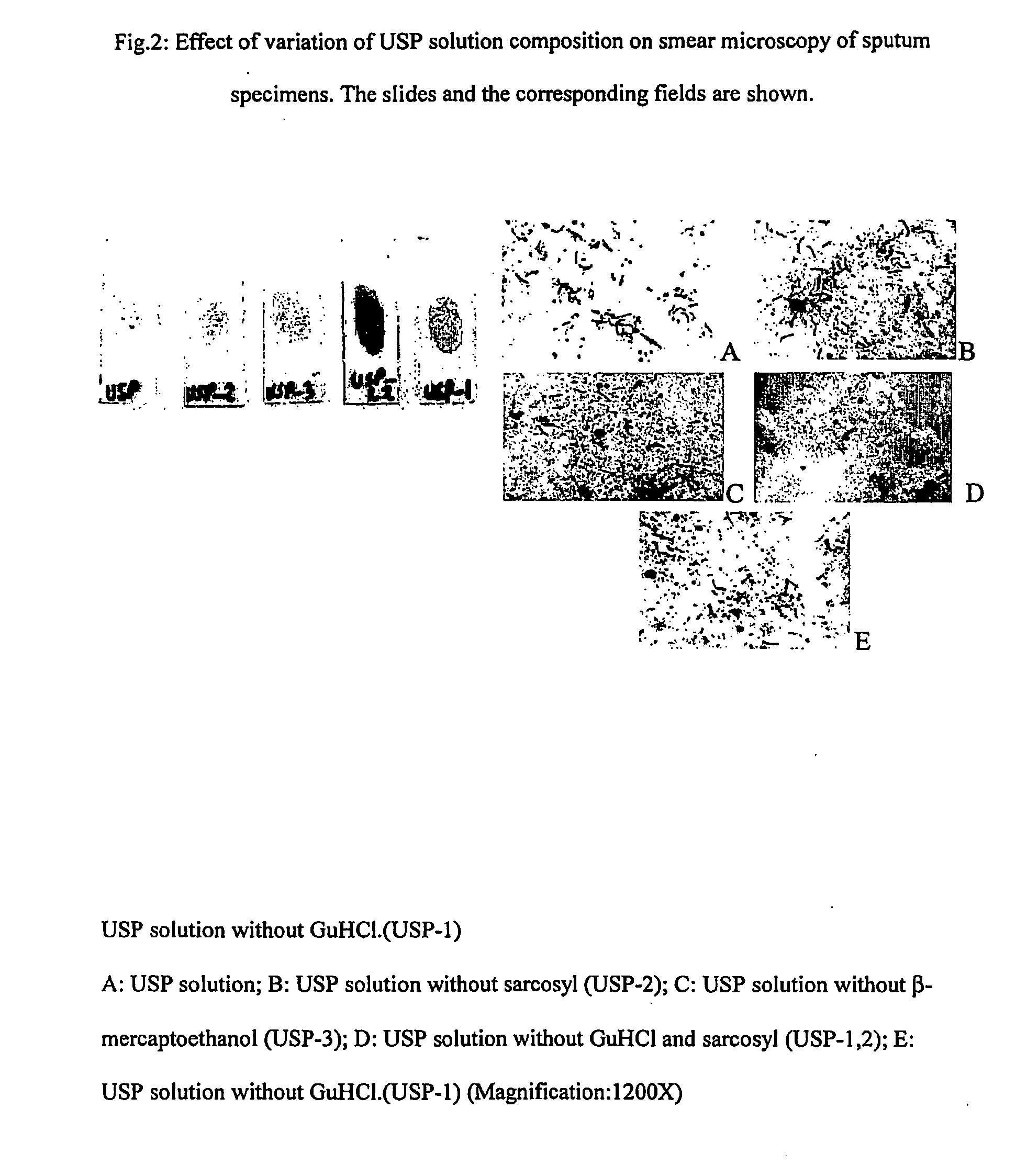
Method for diagnosis of tuberculosis by smear microscopy, culture and polymerase chain reaction using processed clinical samples and kit thereof
InactiveUS20070111206A1Effective and economicalSimple and rapid and safe and sensitive and accurate diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionSmear microscopyMycobacterium
The present invention relates to a method of processing clinical samples for diagnosing bacterial infections by smear microscopy, culture or PCR as well as a kit for performing the said method. This invention also pertains to two sets of primers specific for the DevR gene of M. tuberculosis as well as to a method of using said primers for screening patients for tuberculosis by PCR.
Owner:DEPT OF BIOTECHNOLOGY MINIST OF SCI & TECH GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
Method of detecting surrogate markers in a serum sample
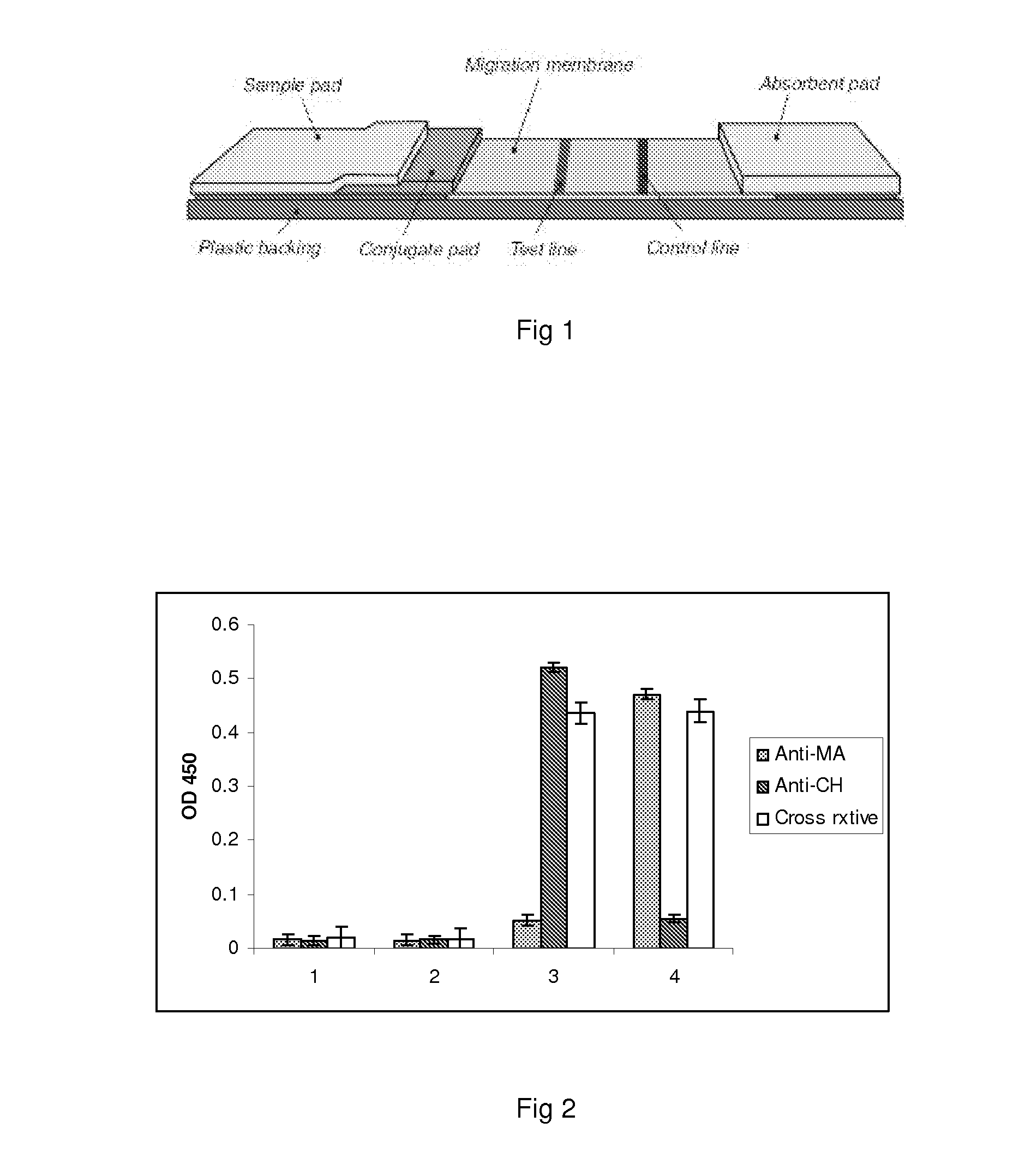
ActiveUS20130137598A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCompetitive bindingCholesterol
The invention provides a method of detecting surrogate markers for active tuberculosis in a serum sample. The surrogate markers are selected from serum mycolic acid antigen, serum anti-mycolic acid antibodies or both. The method includes the steps of combining the serum sample with a labelled monoclonal immunoglobulin antibody or fragment thereof to mycolic acids to produce a combined serum sample, the antibody or fragment thereof not substantially cross-reacting with cholesterol and the label being selected so that binding of the labelled antibody to immobilized mycolic acid antigen of mycobacterial origin produces a detectable signal and combining a blank sample with the labelled monoclonal immunoglobulin antibody or fragment thereof to mycolic acid to produce a combined blank sample. The method includes exposing both samples to immobilised mycolic acid antigen of mycobacterial origin or a synthetic analogue or analogues thereof so that the labelled immunoglobulin antibodies or fragments thereof in each sample bind to the immobilised antigen to produce detectable signals. If the surrogate markers are present, the signal produced by the blank sample will be stronger than that produced by the serum sample because of inhibition of binding of the labelled antibody in the serum sample arising from prior binding of the labelled antibody with the mycolic acid antigen in the serum sample or by competitive binding of serum anti-mycolic acid antibodies in the serum sample to the immobilised mycolic acid antigen or both.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PRETORIA
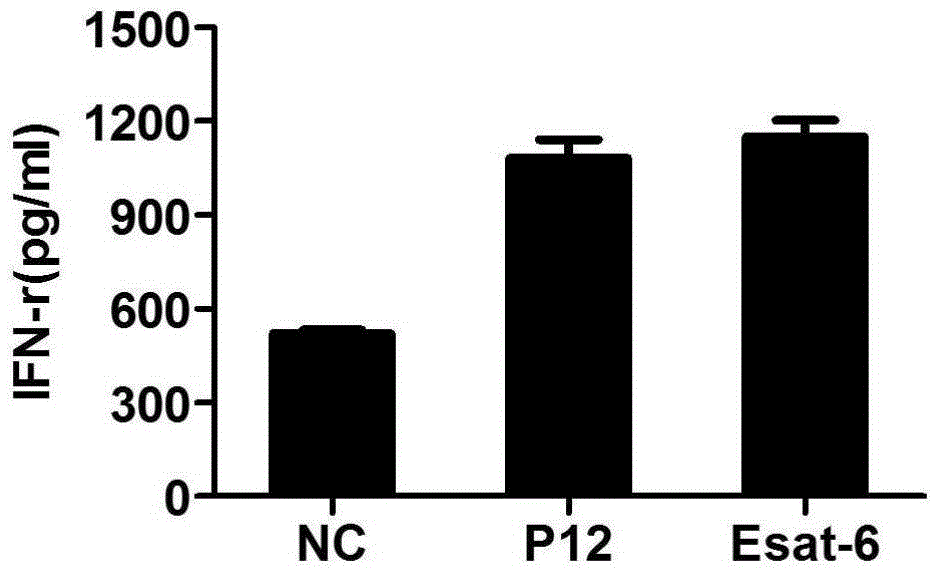
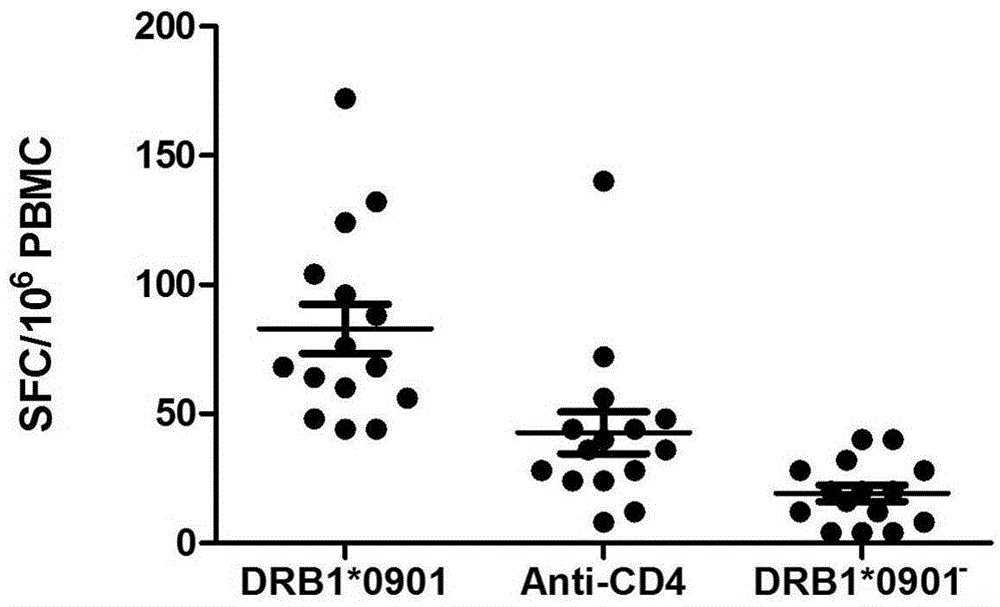
Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific CD4+T cell epitope peptide P12 and application thereof
InactiveCN105481947AHigh affinityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsGenotypeTGE VACCINE
The present invention discloses a Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific CD4+T cell epitope peptide P12 and application thereof. The present invention comprehensively utilizes bioinformatics and immunoinformatics technologies, screens epitope peptide with anti-TB activity by using the antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis; the screened epitope peptide P12 and HLA-DRB1*09: 01 molecules have high affinity; and the epitope peptide can be widely identified by CD4+T cells of patients with TB. Since HLA-DRB1*09:01 genotype is widely carried by Chinese people, the Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific HLA-DRB1*09:01 restricted Th1 epitope peptide is not found currently. The determination of epitope peptide P12 provides a theoretical basis and a novel solution for the development of TB vaccines, diagnostic reagents and therapeutic drugs, and is of great significance for the prevention and treatment of tuberculosis.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
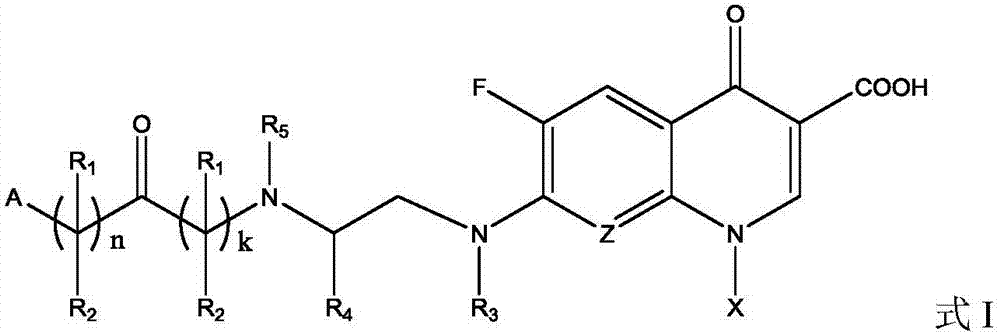
Fluoroquinolone amino derivatives and application thereof
ActiveCN107880023AHigh antibacterial activitySmall toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSolubilityDisease
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry, and in particular relates to fluoroquinolone derivatives and an application thereof. The compounds shown in a formula (I) are obtained by structural modification of fluoroquinolone medicines. The compounds provided by the invention can not only treat the infection caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis and common bacteria, but also can has activity inhibition effects on bacterial persister, citrus pathogenic bacteria, nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) and interleukin IL-17 PPI; and the compounds have a simple and easy preparation process and mild conditions, a plurality of the compounds with enhanced antibacterial activity, improved water solubility and reduced toxic and side effects are obtained, and the compounds are expectedto reduce the dosage, shorten the treatment cycle and improve patient compliance, thereby providing novel molecular types and research ideas for medicines of tuberculosis and other diseases.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Biomarkers for diagnosing and/or monitoring tuberculosis
InactiveCN104823052APromote or inhibit the production ofDisease diagnosisAntimycobacterialCausative organism
The invention relates to biomarkers for diagnosing and / or monitoring tuberculosisin both immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals, monitoring the responses of individuals to anti-mycobacterial chemotherapy, monitoring the progression of latent tuberculosis to active tuberculosis, differentiating active tuberculosis from latent tuberculosis, and from other clinical conditions that mimic tuberculosis (TB). The invention also relates to methods for diagnosing, treating and monitoring tuberculosis using said biomarkers. The above pertain in all aspects both to pulmonary and extrapulmonary Mycobacterium.tuberculosis infections, with Mycobacterium.tuberculosis being the causative organism in tuberculosis.
Owner:PROTEINLOGIC
Mycobacterium tuberculosis medicament sensitive phenotype detection method and application of method
InactiveCN102146430AWon't spreadReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyResazurin
The invention discloses a mycobacterium tuberculosis medicament sensitive phenotype detection method, which comprises the following steps of: 1) adding 2.5 to 6mul of 0.2 percent of resazurin dissolved by using methanol with mass percentage concentration into the inner side of a tube cover of a sterile centrifuge tube, and sterilizing the centrifuge tube after the methanol is volatilized; 2) inoculating 5 to 50mg of mycobacterium tuberculosis to be detected into a 7H9-S culture medium, regulating the concentration of the bacteria solution by adopting turbidimetry, regulating the concentration of the bacteria solution to the concentration of a Mcburney turbidimetric 1 tube by using sterile water or 0.9-percent physiological saline, and diluting the bacteria solution by 20 times by using the 7H9-S culture medium; 3) inoculating 50 to 150mu of diluted bacteria solution into the centrifuge tube of the step 1); 4) adding 100mul of anti-tubercular medicament solution diluted by 7H9-S and to be detected into the centrifuge tube of the step 3), wherein the concentration of the medicament to be detected is 0.01mug / ml to 2.5mg / ml; 5) after the centrifuge tube of the step 4) is covered closely, culturing the solution for 6 to 7 days at the temperature of 37 DEG C; and 6) inverting and oscillating the centrifuge tube of the step 5), and culturing the solution for 12 to 48 hours at the temperature of 37 DEG C after the solution becomes blue. Proved by experiments, in the mycobacterium tuberculosis medicament sensitive phenotype detection method and application of the mycobacterium tuberculosis medicament sensitive phenotype detection method in anti-tubercular medicament screening, the method has low workload and short detection time; compared with a traditional L-J medium medicament sensitive detection method, the accuracy reaches 90 to 99 percent; and the method has good biological safety, does not cause laboratory propagation of tuberculosis, is suitable for large-scale.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
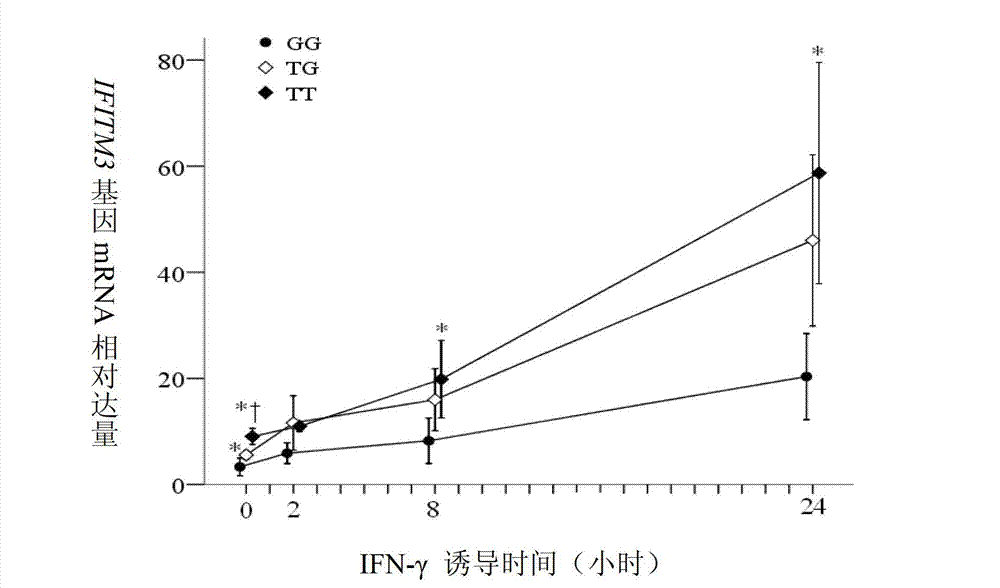
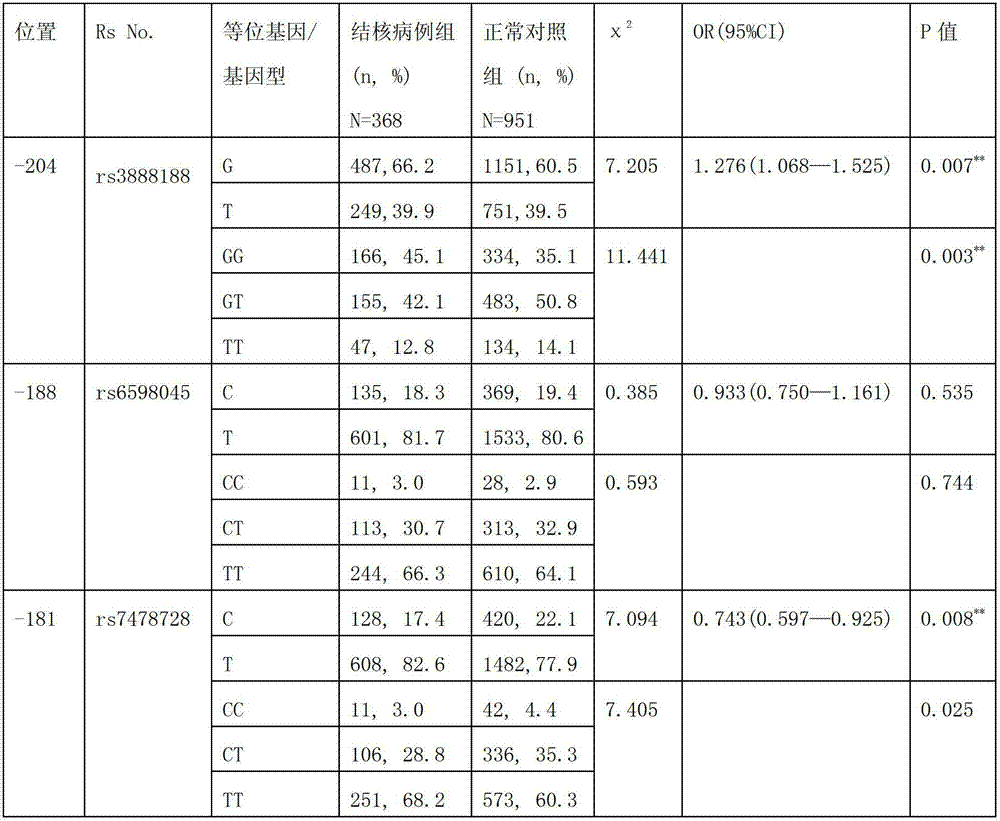
Application of single nucleotide polymorphism rs3888188 to detection of tuberculosis susceptibility
InactiveCN102808030AMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscription initiation siteTranslation initiation sites
The invention discloses an application of single nucleotide polymorphism rs3888188 to detection of tuberculosis susceptibility. The SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) is the rs3888188 and is positioned in a human IFITM3 (interferon induced transmembrane protein) gene core promoter region (namely the upstream 103bp of a transcription initiation site / the upstream 204bp of a translation initiation site ATG), the rs3888188G is a risk factor of tuberculosis susceptibility, and the polymorphism of the rs3888188 is highly related with tuberculosis. When the genotype of the site is GG, the tuberculosis susceptibility or tuberculosis causing risk of an individual to be detected is increased. The application is of significant meaning and value in the aspects of diagnosing and treating the tuberculosis to reasonably prevent the tuberculosis.
Owner:BEIJING CHILDRENS HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
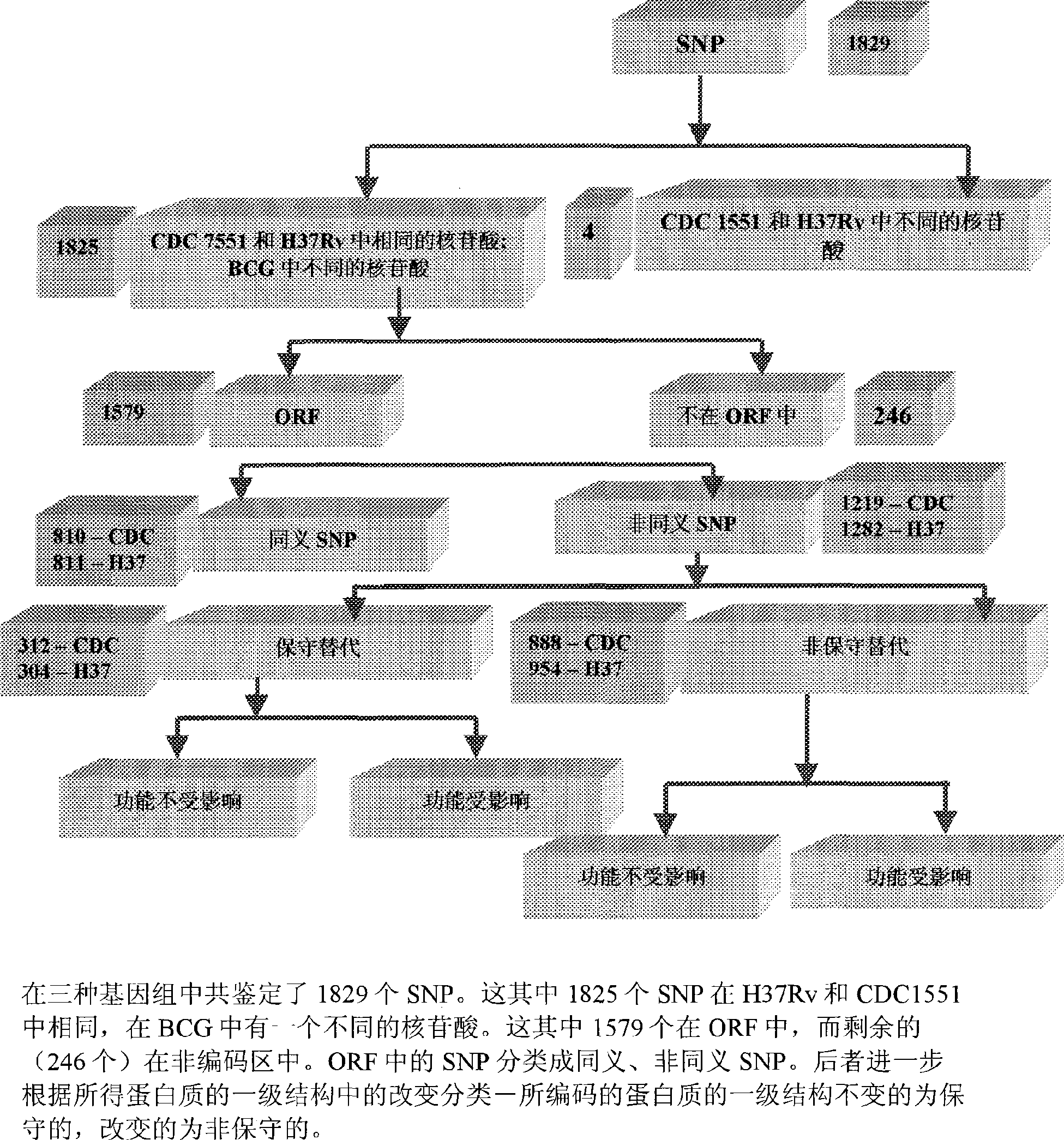
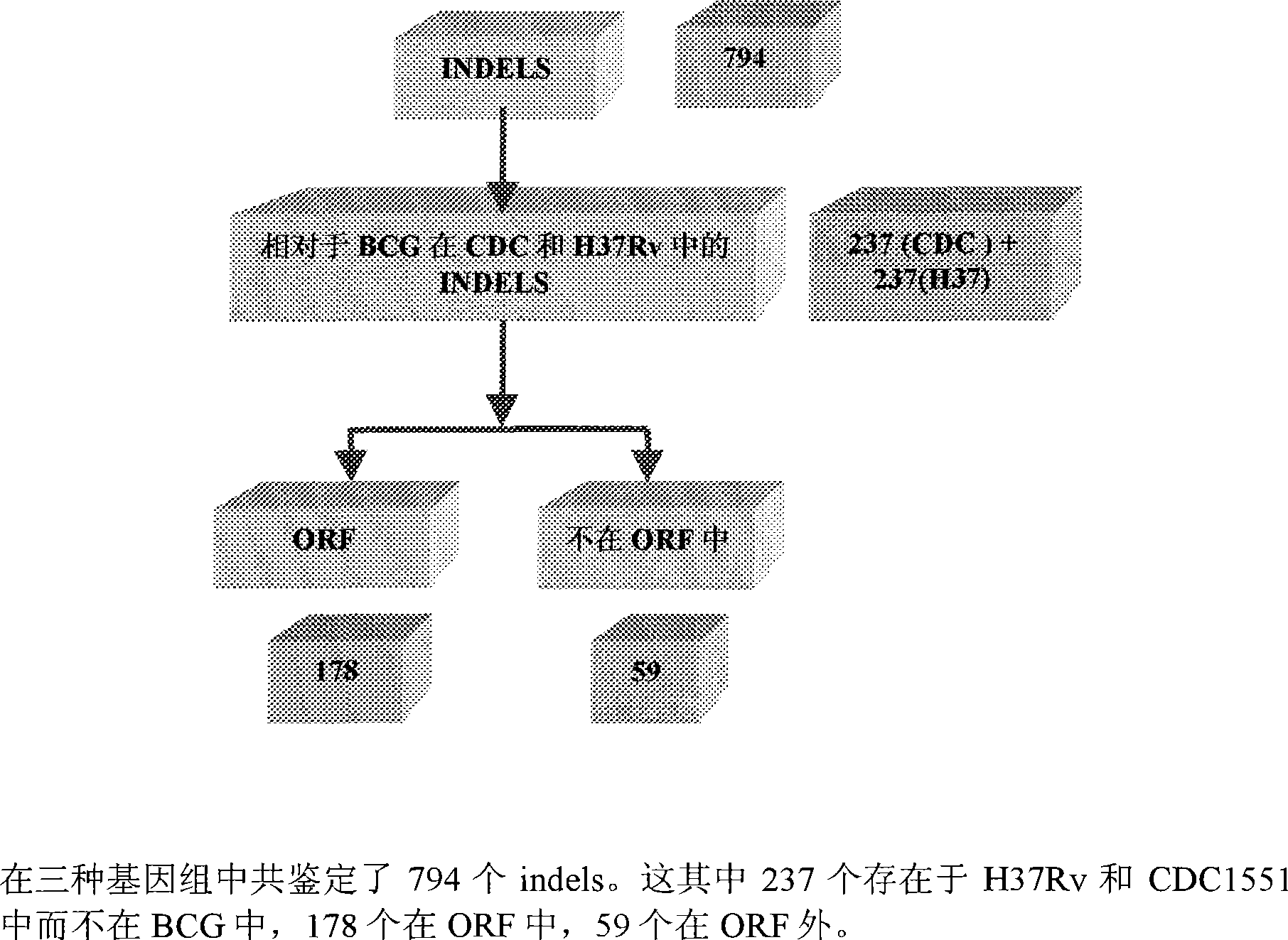
Construction of a comparative database and identification of virulence factors through comparison of polymorphic regions in clinical isolates of infectious organisms
InactiveCN101421415AReduce new targetsImprove protectionMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsVirulent characteristicsDrug target
The present invention is directed to novel nucleotide sequences to be used for diagnosis, identification of the strain, typing of the strain and giving orientation to its potential degree of virulence, infectivity and / or latency for all infectious diseases more particularly tuberculosis. The present invention also includes method for the identification and selection of polymorphisms associated with the virulence' and / or infectivity in infectious diseases more particularly in tuberculosis by a comparative genomic analysis of the sequences of different clinical isolates / strains of infectious organisms. The regions of polymorphisms, can also act as potential drug targets and vaccine targets.; More particularly, the invention also relates to identifying virulence factors of M. tuberculosis strains and other infectious organisms to be included in a diagnostic DNA chip allowing identification of the strain, typing of the strain and finally giving orientation to its potential degree of virulence. Although the present invention has been illustrated with specific reference to the polymorphic region in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the said invention is not to be understood and construed as being limited to Tuberculosis but is applicable to all infectious diseases.
Owner:阿维斯塔金格兰技术有限公司 +1
TB diagnostic based on antigens from M. tuberculosis
The present invention is based on the identification and characterization of a number of novel M. tuberculosis derived proteins and protein fragments. The invention is directed to the polypeptides and immunologically active fragments thereof, the genes encoding them, immunological compositions such as diagnostic reagents containing the polypeptides.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com