Biomarkers for diagnosing and/or monitoring tuberculosis
A biomarker, tuberculosis technology, applied in disease diagnosis, biomaterial analysis, measurement devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0175] Example 1: Validity of IFN-γ and TNF-α as TB Biomarkers
[0176] The use of IFN-[gamma], TNF-[alpha] and additional CD for the effectiveness of discriminating different sample types (healthy, latent TB, active TB, disease) was evaluated.
[0177] 1. The combination of IFN-γ and TNF-α consistently produces better discriminative signals than these antigens alone.
[0178] 2. Additional CDs were identified, which further improved predictive characteristics for certain predictive tasks.
[0179] The study was performed on n = 92 human samples to identify potential markers capable of distinguishing TB-disease subjects from TB-free control subjects.
[0180] The demographics of each patient are summarized in Table 1:
[0181] Table 1: Demographic and patient data for each sample analyzed
[0182] group grouping Diagnostic classification BCG history? TB position age gender comorbidity A 4C yes N / A 52 male psoriasis A ...
Embodiment 2
[0235] Example 2: Effectiveness of Additional Biomarkers in Combination with IFN-γ and TNF-α
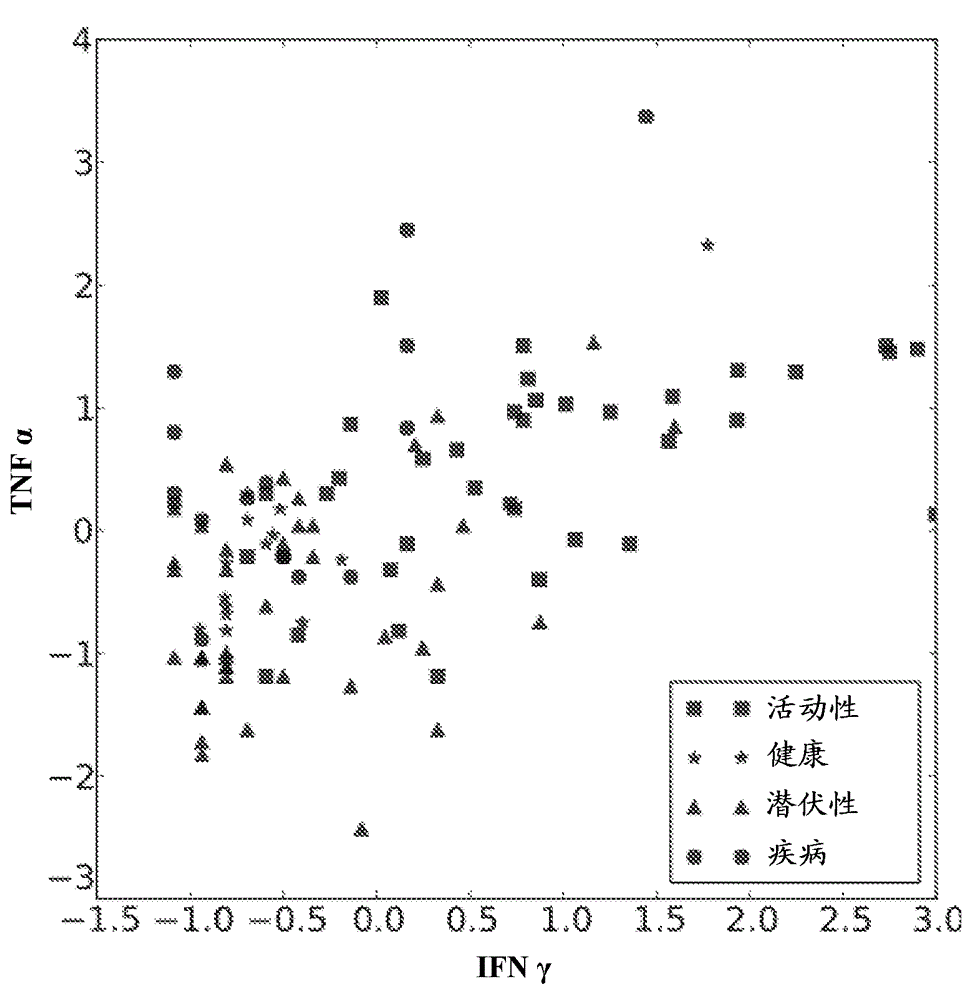
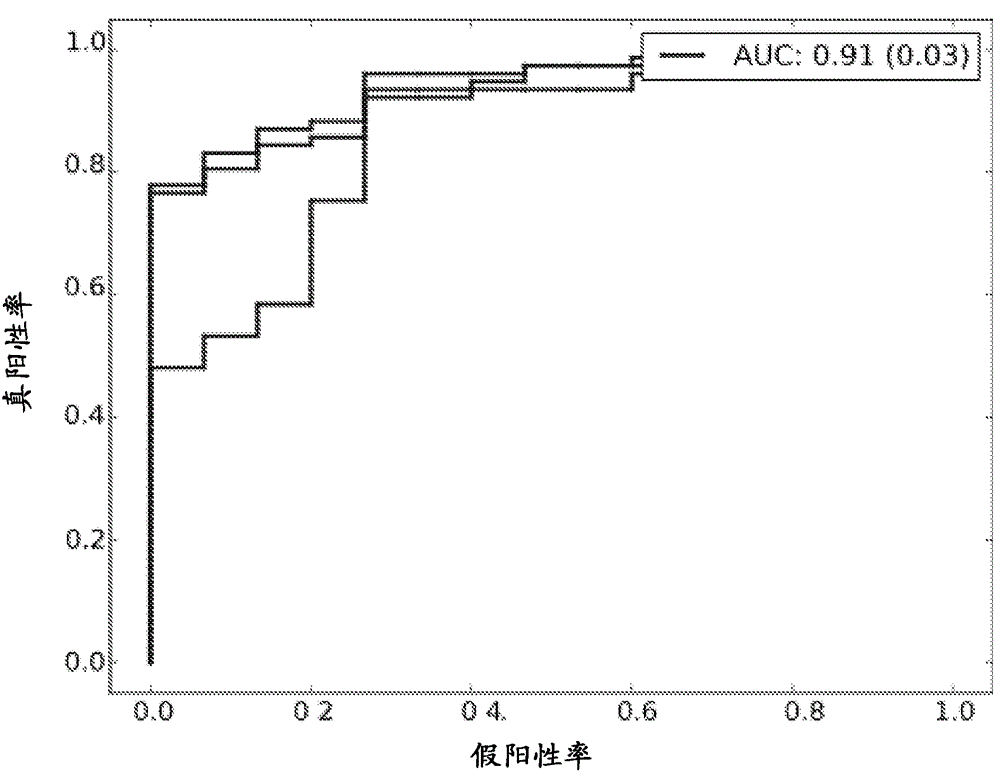
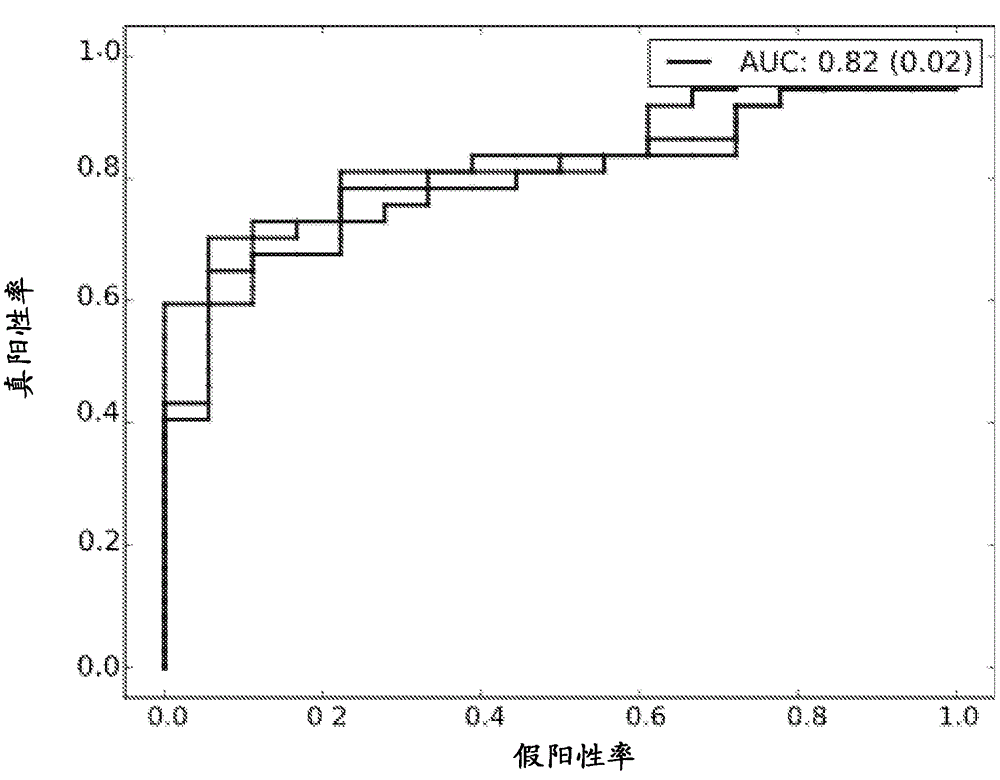
[0236] Additional antigens were identified that may complement the pattern of discrimination observed for IFN-γ and TNF-α. first, Figure 1-3 Scatterplots are shown for all antigens that were significantly differentially expressed (pv=0.05) between at least two considered sample types (healthy, active, latent, disease). Several sCDs appear to add an additional axis of discrimination between sample types, complementing IFN-γ and TNF-α. Table 3 summarizes the predicted performance of these CDs when combined with TNF-α and IFN-γ. This "joint" predictor performed at least as well as IFN-γ and TNF-α and generally improved the results obtained with the two antigen models for the prediction tasks Health / TB and Health / Latency.
[0237] Table 3: Predictive performance of different combinations of antigens for the alternative classification task
[0238]
[0239]Table 3 shows the area...
Embodiment 3
[0241] Example 3: Replication of the Activity / Latency Model Using Increasing Patient Sample Sizes
[0242] The purpose of this experiment was to validate the activity / latency predictive features identified in the initial screen and providing the results described in Example 1 and Example 2. For this purpose, unrelated samples were obtained from Imperial College London. These include the following numbers of active and latent TB cases:
[0243] Active TB: 94 samples (51: IGRA positive)
[0244] Latent TB: 89 samples (45: IGRA positive)
[0245] Table 4: Demographic and patient data for each sample analyzed
[0246] gender age BCG? IGRA diagnosis Diagnostic classification group Female 56 Y QFT+ Lung + uveitis TB 2 ATB Female 51 N QFT- LTBI 4B LTBI Female 21 Y NT lymph node TB 1 ATB male 21 Y QFT- LTBI 4A LTBI Female 49 Y QFT+ Skin TB 2 ATB Female 33 Y QFT+ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com