Patents
Literature
94 results about "Dna sensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cytosolic DNA Sensors (CDSs): a STING in the tail. The innate immune system provides the first line of defense against infectious pathogens and serves to limit their early proliferation. It is also vital in priming and activating the adaptive immune system.
Nanoparticle tracer-based electrochemical DNA sensor for detection of pathogens-amplification by a universal nano-tracer (AUNT)
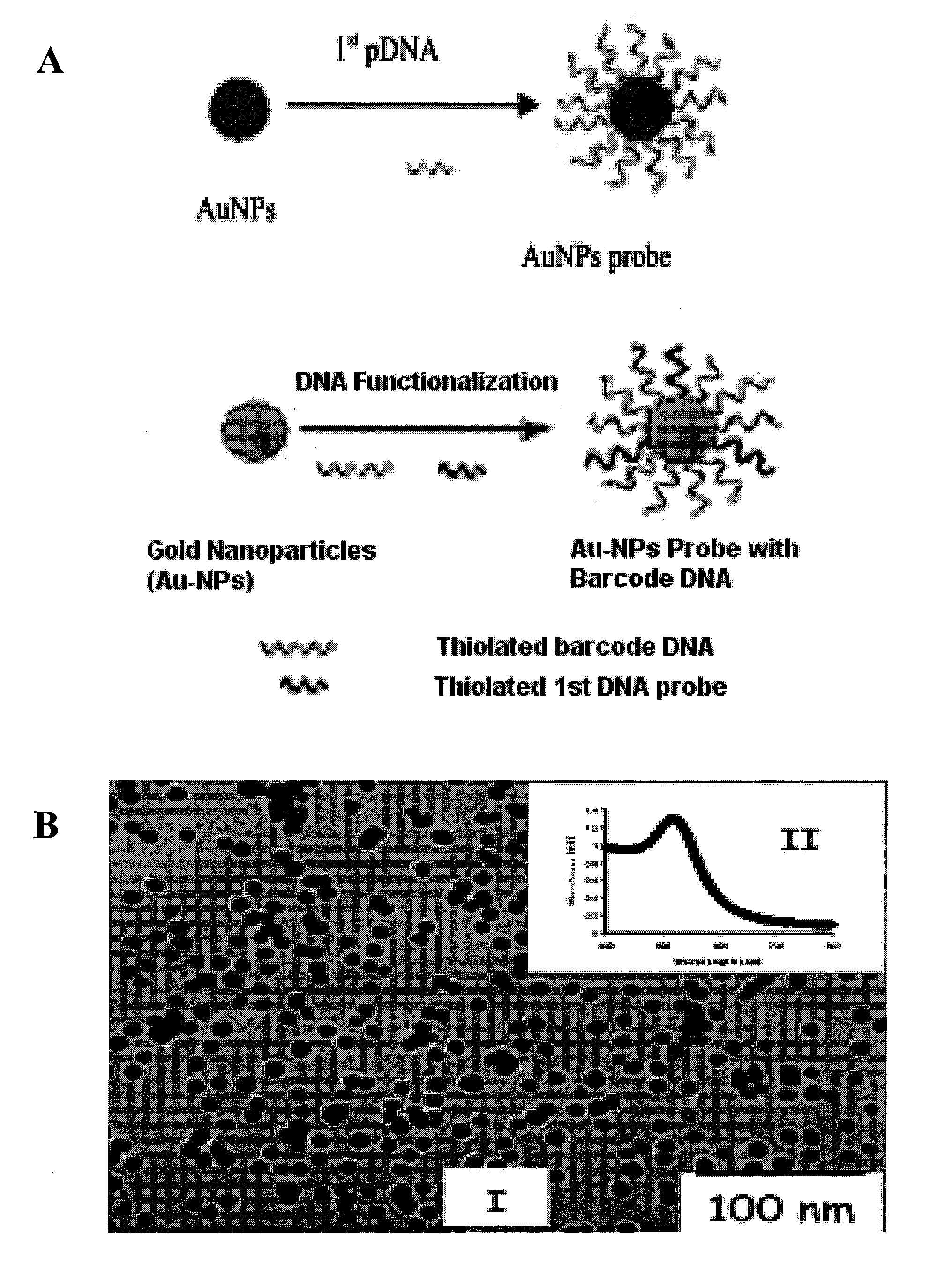
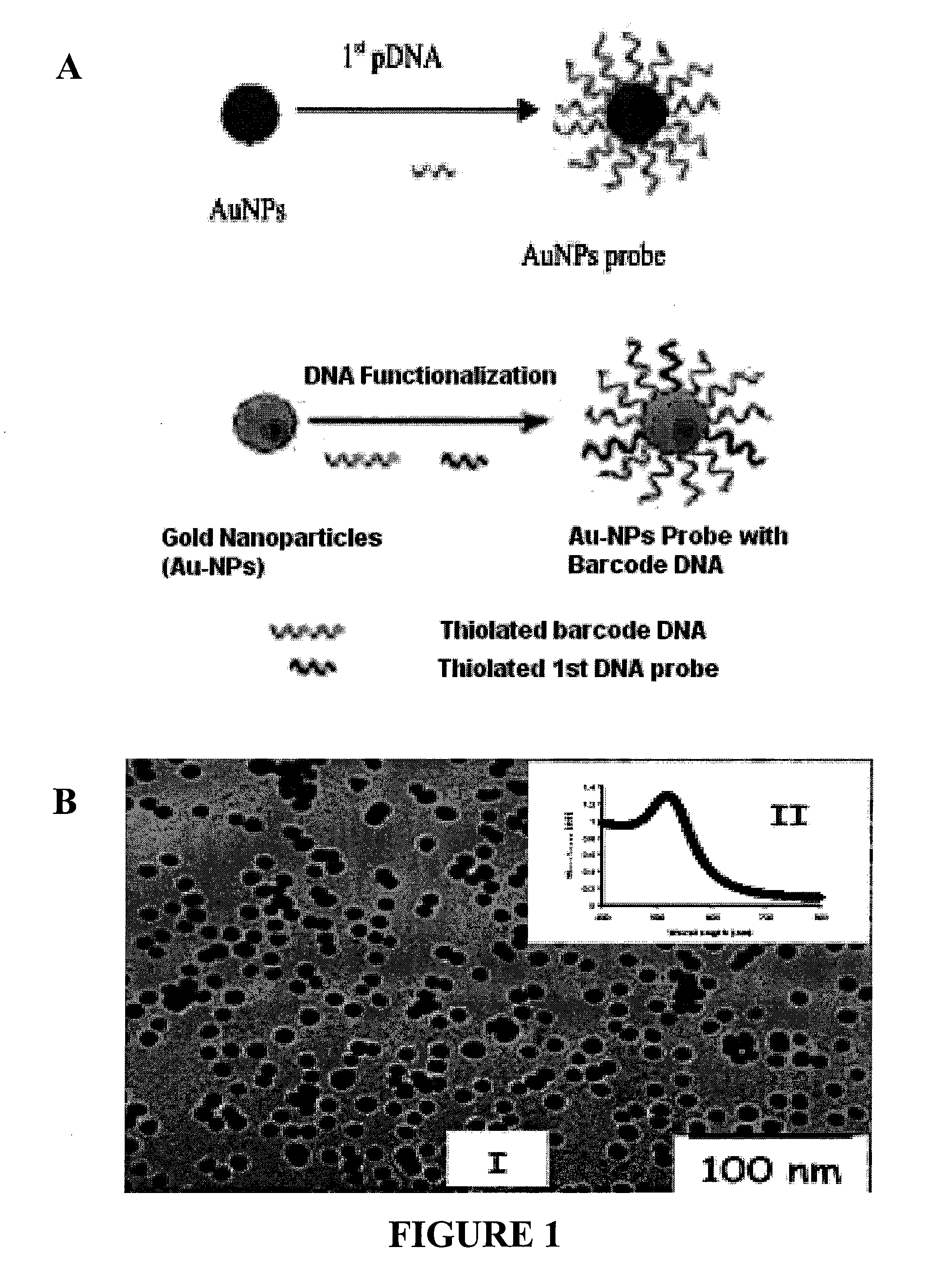
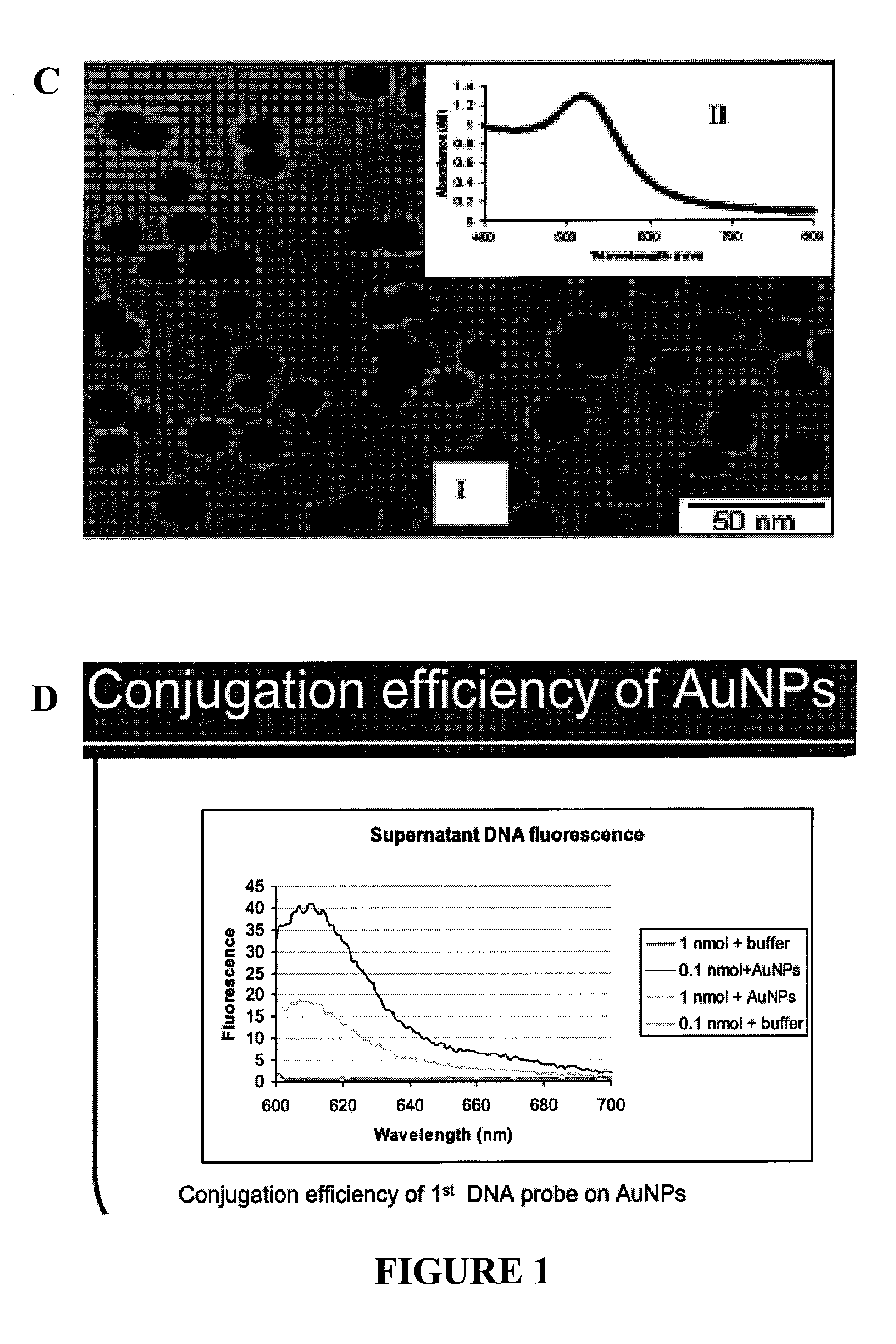
InactiveUS20110171749A1Rapid and sensitive detectionRapid and sensitive and valid identificationMaterial nanotechnologyNanomedicineSalmonella entericaEscherichia coli
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying a pathogen. The inventions provide an antibody-based biosensor probe comprising (AUNT) in combination with a polymer-coated magnetic nanoparticle. In particular, a nanoparticle-based biosensor was developed for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 bacterium in food products. Further described are biosensors for detecting pathogens at low concentrations in samples. Even further, a gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical biosensor detection and amplification method for identifying the insertion element gene of Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis is described. The present invention provides compositions and methods for providing a handheld potentiostat system for detecting pathogens outside of the laboratory. The AUNT biosensor system has applications detecting pathogens in food, water, beverages, clinical samples, and environmental samples.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
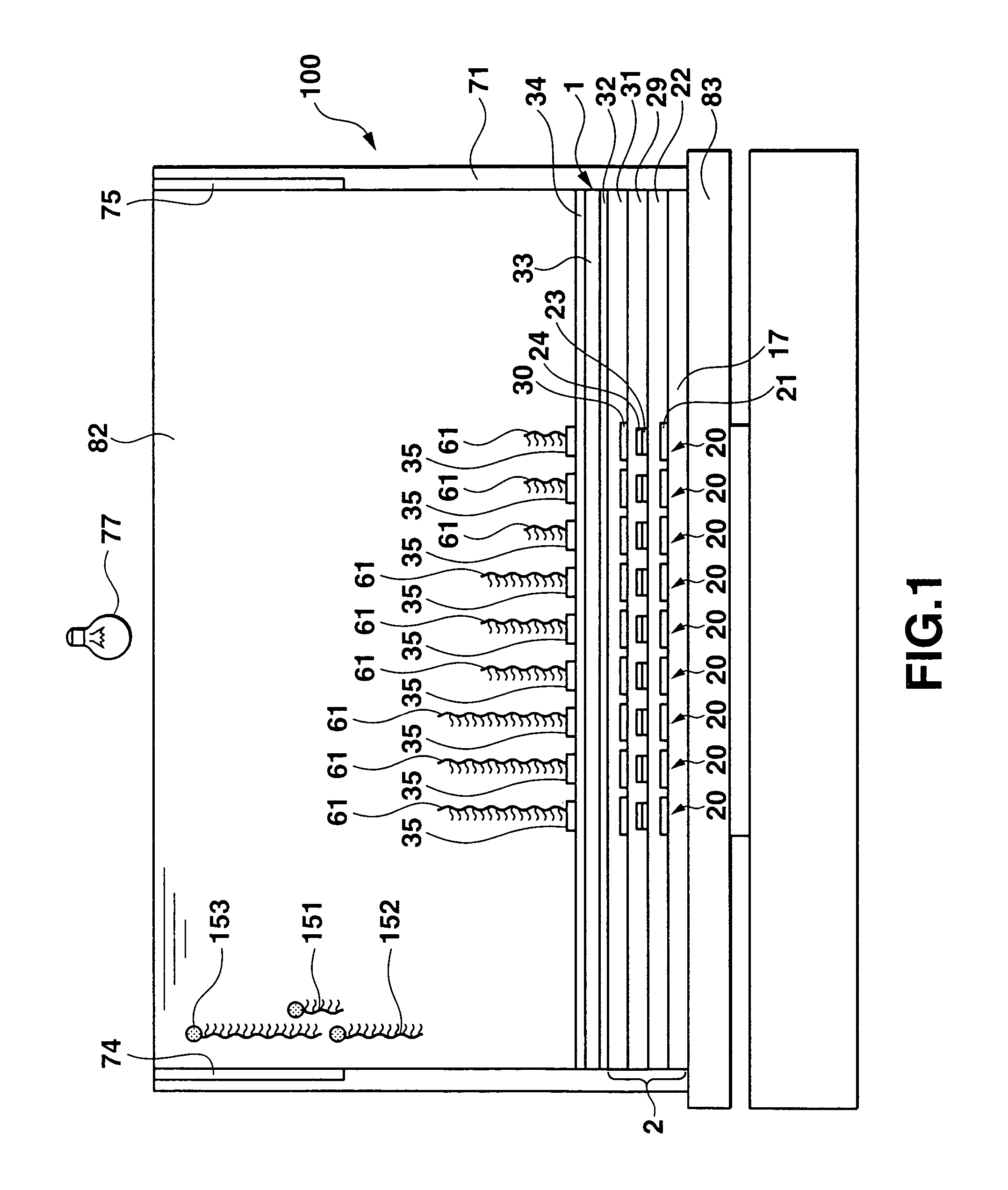
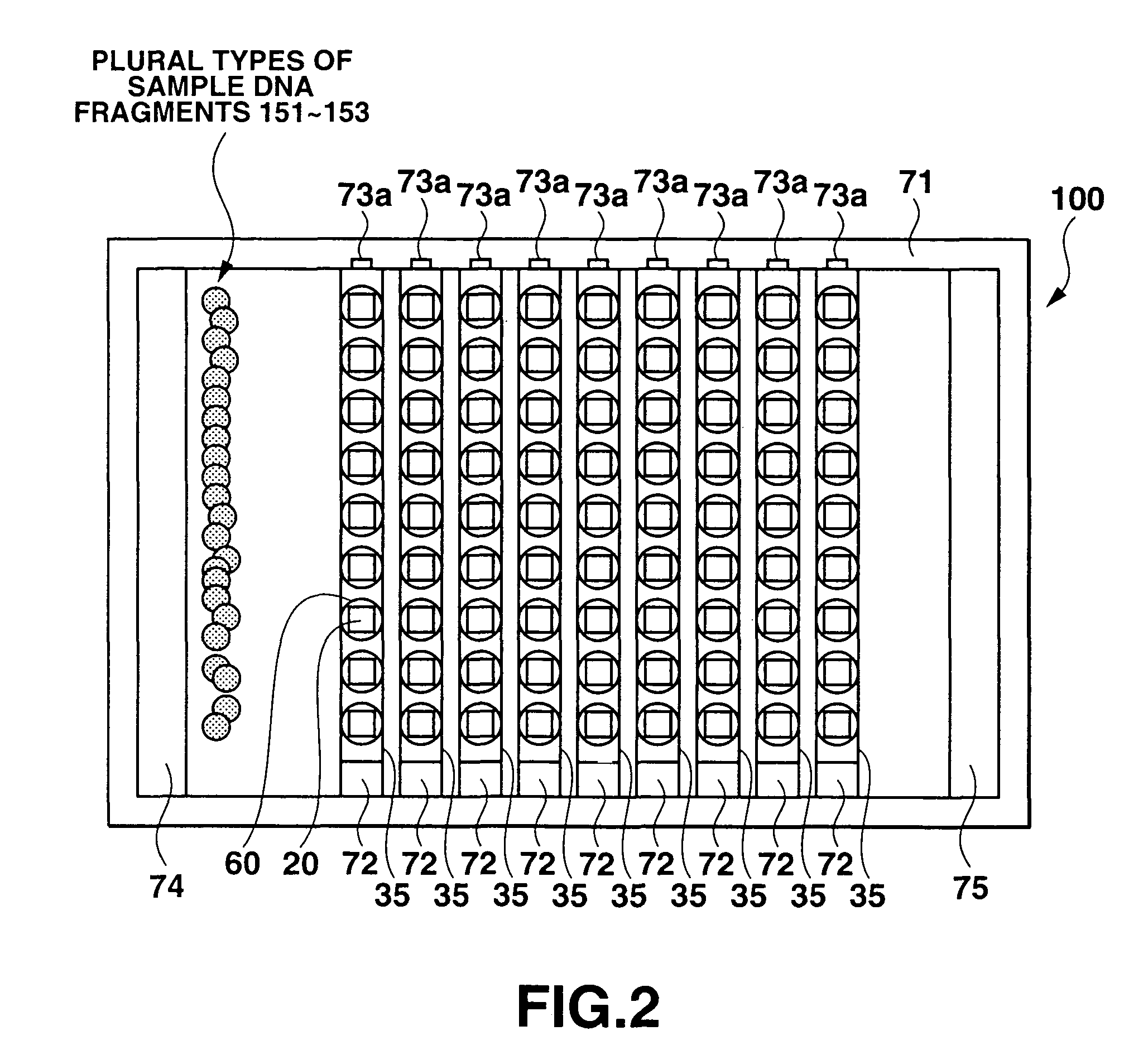
DNA analyzing apparatus, DNA sensor, and analyzing method
InactiveUS7824900B2EasilyFast hybridizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsElectrophoresisDNA fragmentation
A DNA analyzing apparatus includes a bath containing an electrophoresis medium. A plurality of probe electrodes are arranged in the bath. A plurality of spots each composed of probe DNA fragments having known base sequences are arranged on the respective probe electrodes. Temperature regulating elements are provided to adjust the temperatures of the plurality of spots via the corresponding probe electrode.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
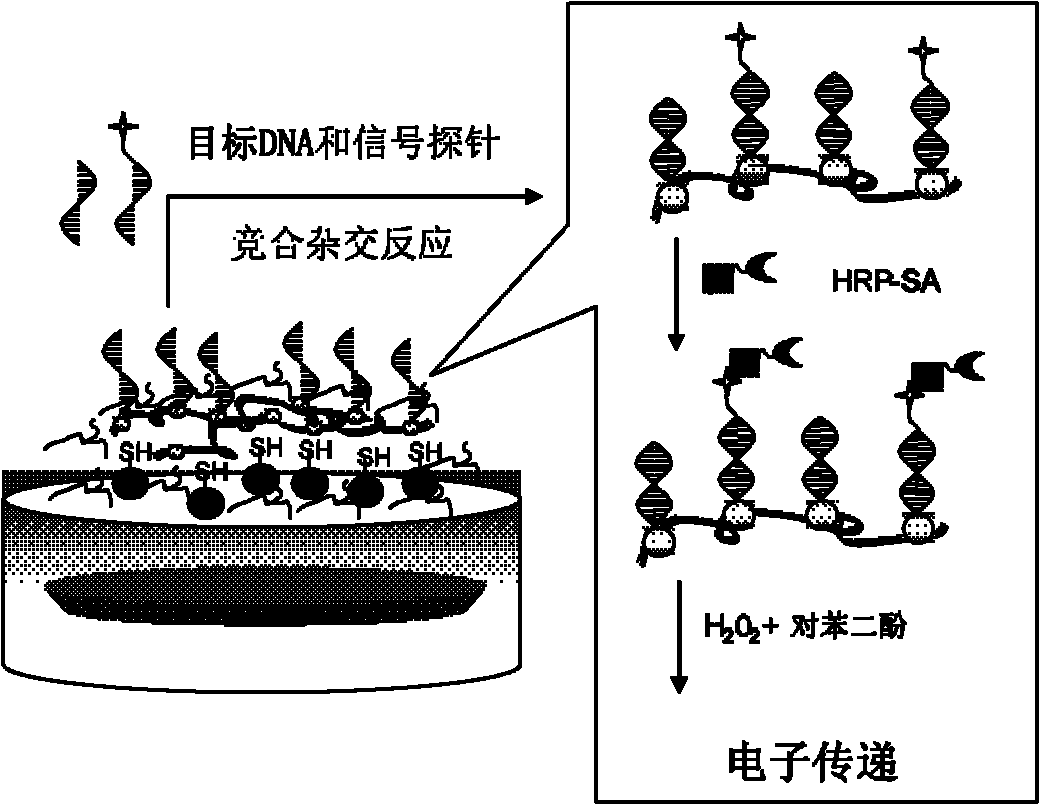
Preparation and application method of electrochemical reduction graphene oxide and nanogold modified electrode based DNA sensor
InactiveCN105758918AEasy to makeLow priceMaterial electrochemical variablesNanoparticleCarbon paste electrode
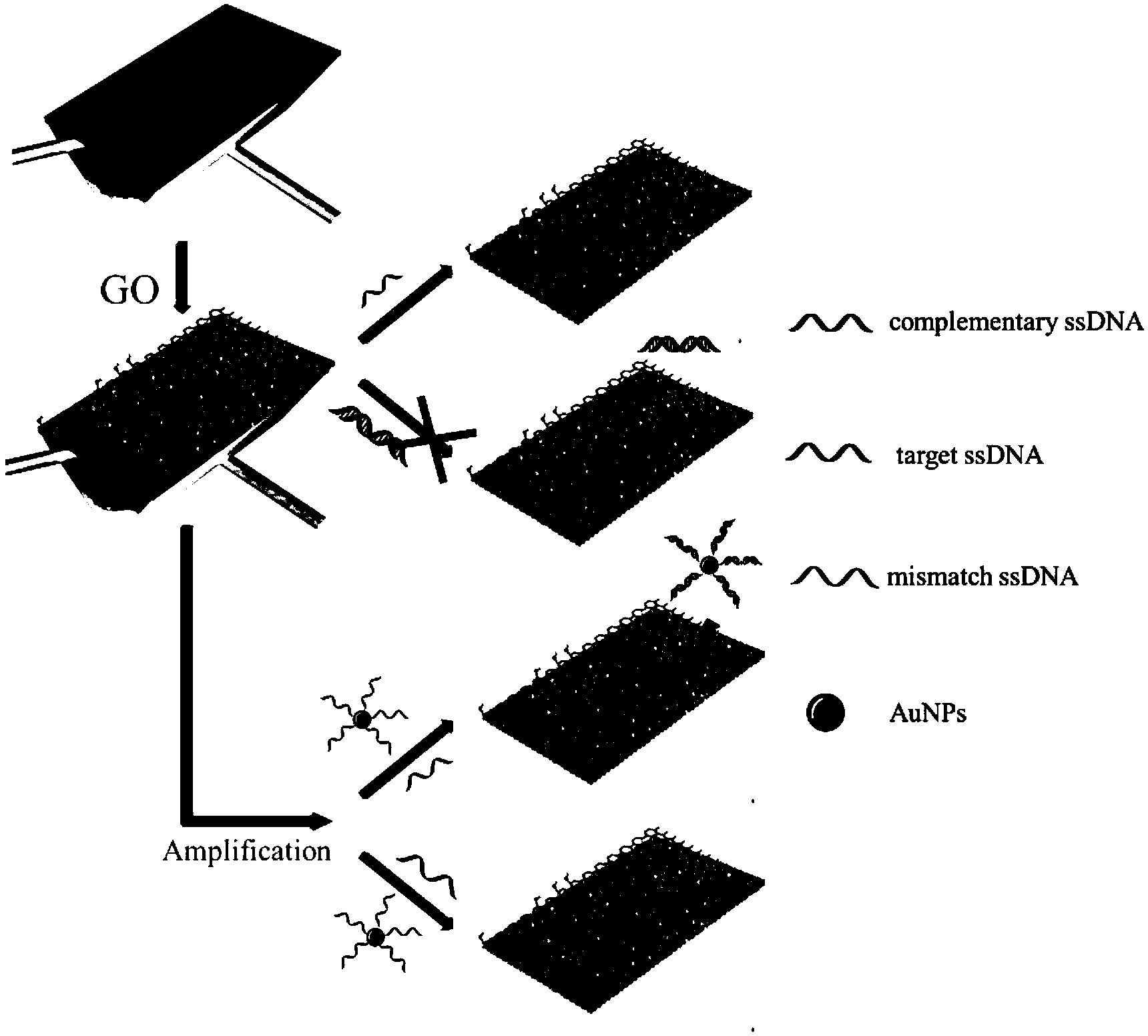
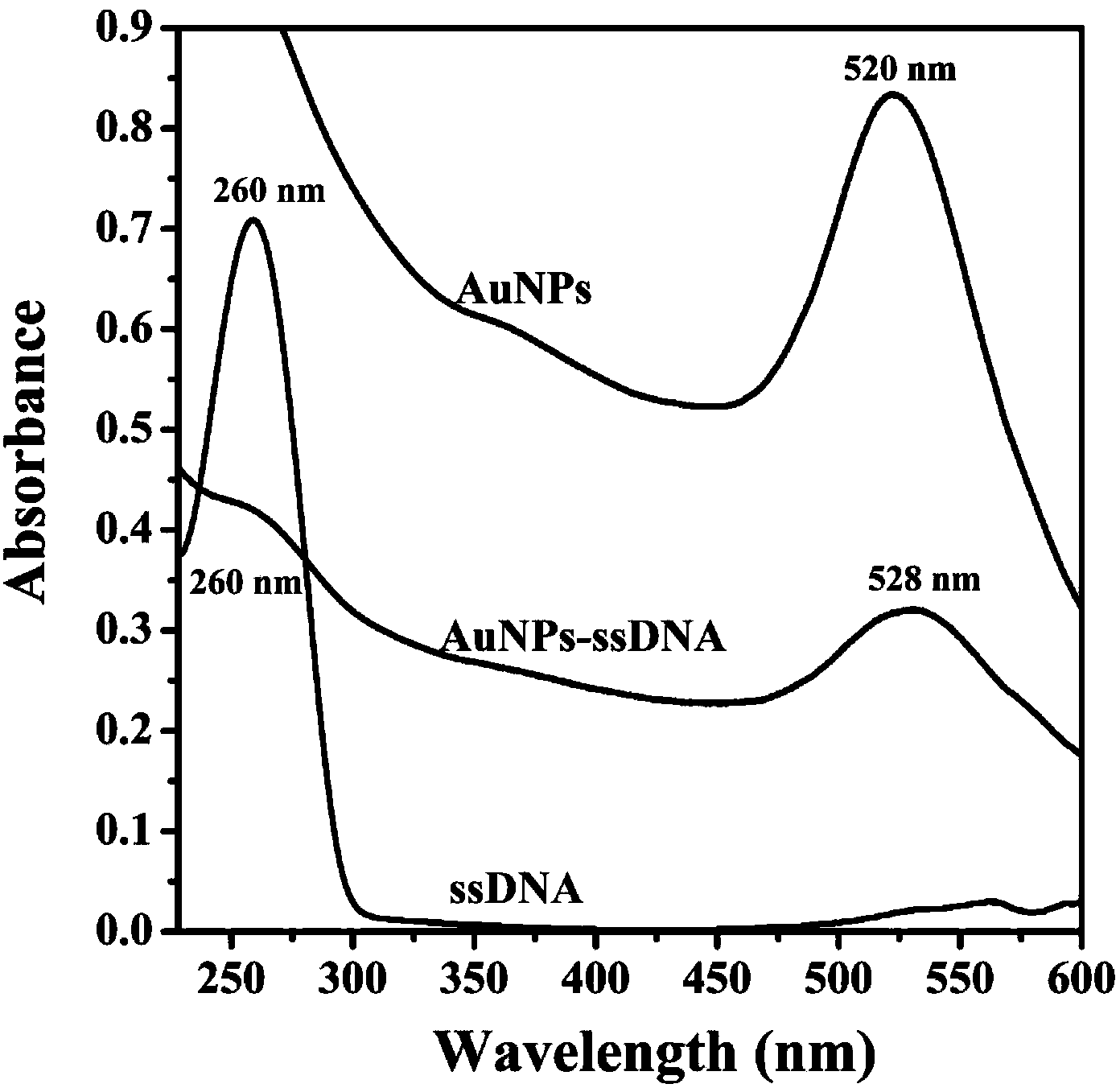
The invention discloses a novel electrochemical DNA sensor constructed by a nanogold and partially-reduced graphene oxide (p-RGO) modified ionic liquid carbon paste electrode (CILE) as a platform prepared by an electrochemical method, and a method of applying the CILE to detect the Listeria feature gene sequence. 1-hexylpyridiniumhexafluorophosphate as a modifier is used for preparing the substrate electrode CILE, gold nanoparticles are deposited on the surface of the substrate electrode CILE and then the p-RGO is prepared by controlling electrochemical reduction conditions; an amino-modified probe ssDNA is fixed on the surface of the electrode by an amido bond covalent bonding method through carboxyl groups remained on the surface of p-RGO to constitute ssDNA / p-RGO / AuNPs / CILE; methylene blue (MB) as an indicator is used for detecting the hybridization reaction after a target sequence is hybridized, and a differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) is used for detecting the Listeria feature gene segment.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Composite film modified DNA sensor and its preparation method and application in detection of lignin peroxidase (Lip) specific coding gene segment
InactiveCN102253092AImprove electronic conductivityLow Dynamic SituationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesComposite filmMagnetite Nanoparticles
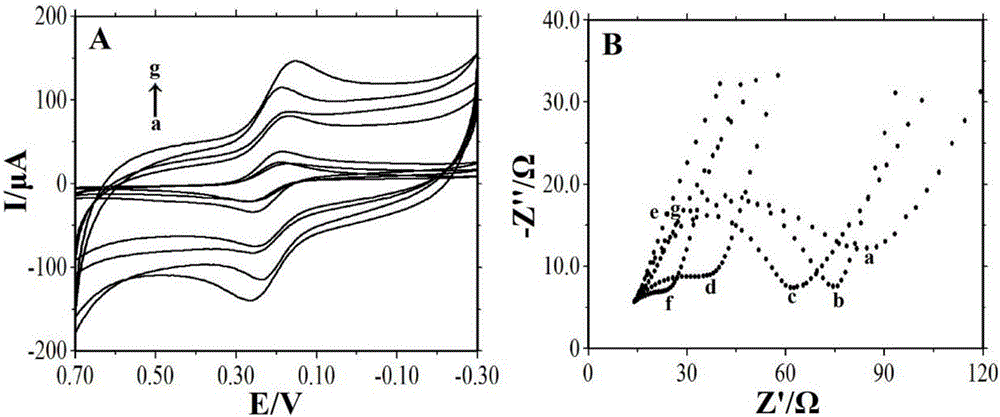
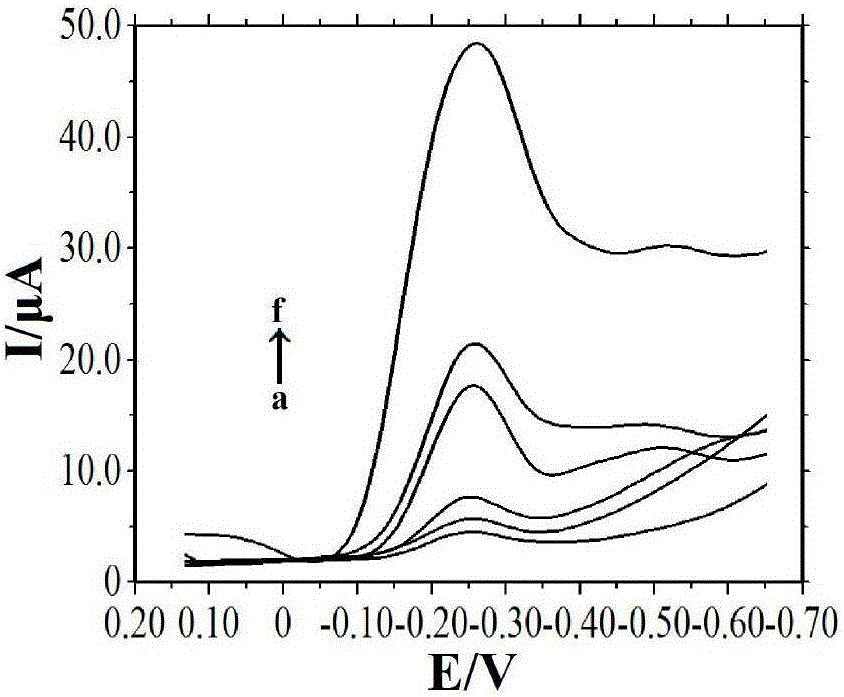
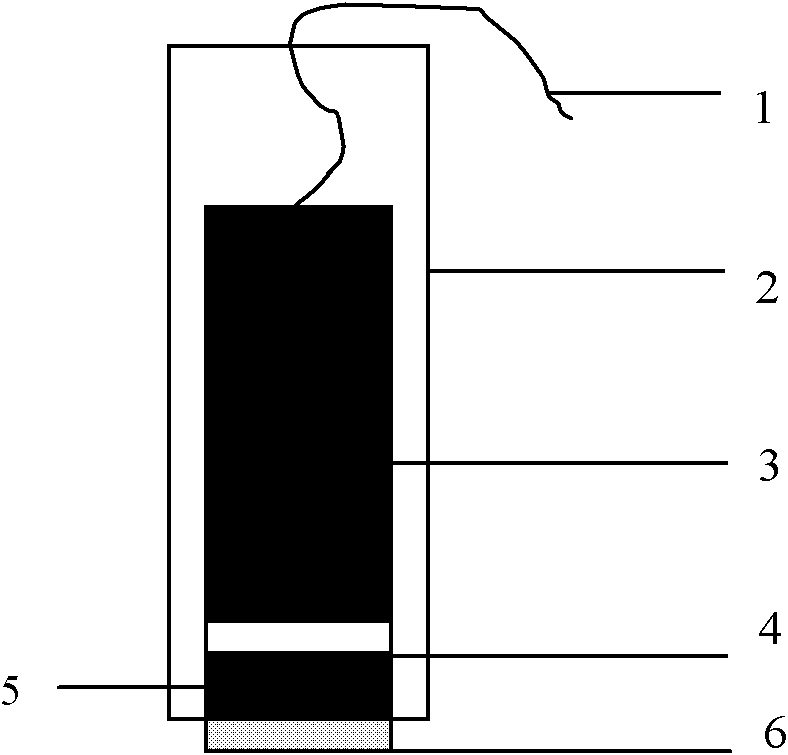
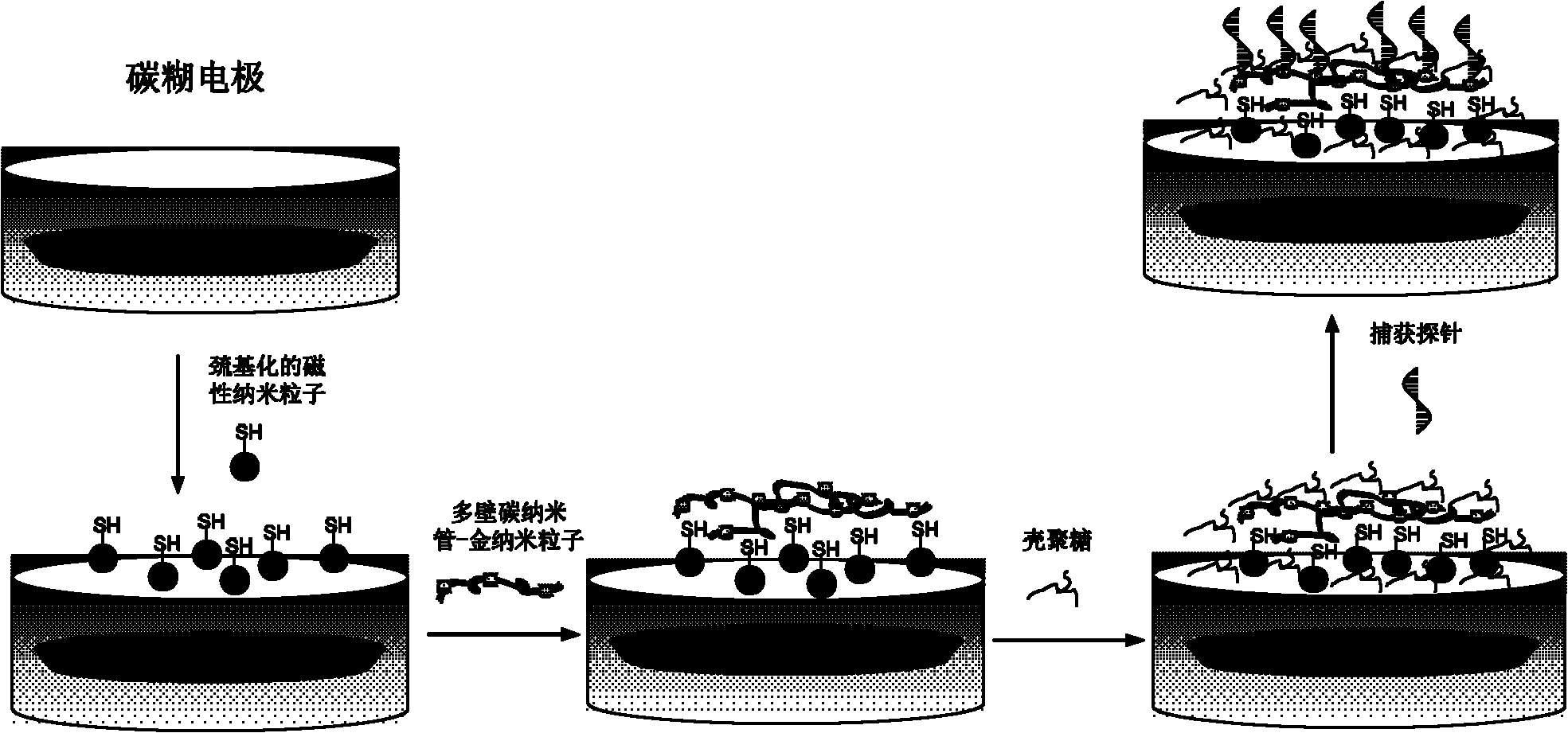
The invention discloses a composite film modified DNA sensor. The DNA sensor is characterized in that the sensor comprises a carbon paste electrode; the carbon paste electrode comprises a carbon rod, a Teflon tube, a magnet, and carbon paste; an induction end of the carbon paste electrode is coated with a sensitive substance; the sensitive substance comprises a composite film and a DNA capture probe; magnetic nanoparticles, multi-walled carbon nanoscale tube-gold nanoparticles and chitosan are utilized for modifying orderly the surface of the carbon paste electrode and compose the composite film; and the DNA capture probe is utilized for modifying the surface of the multi-walled carbon nanoscale tube-gold nanoparticles. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the DNA sensor. The preparation method comprises the processing steps of manufacturing a carbon paste electrode, modifying the surface of an induction end of the manufactured carbon paste electrode by a sensitive substance, and the like. The invention further discloses an application of the DNA sensor in detecting a lignin peroxidase (Lip) specific coding gene segment. Because a sensitive substance is utilized for modifying the surface of a carbon paste electrode of the DNA sensor, the DNA sensor has a strong capacity of electron conduction and a high accuracy of detection. The preparation method has the advantages of low cost and simple process.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Electrochemical DNA sensor based on graphene-precious metal composite and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103033544AOvercome the defect of low current densityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesSingle strand dnaCvd graphene
The invention relates to an electrochemical DNA sensor based on a graphene-precious metal composite and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing an aqueous dispersion of graphene oxide from graphite powder by utilizing a Hummer method; (2) preparing a nano-precious metal particle / graphene composite by a chemical reduction method; and (3) adhering the precious metal / graphene composite onto a glassy carbon electrode, modifying with single-stranded DNA, and hybridizing the modified electrode and a target gene so as to obtain the electrochemical DNA sensor. According to the electrochemical DNA sensor based on a graphene-precious metal composite, a detection limit of DNA can be greatly increased to 1.2*10<-10>mol / L.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
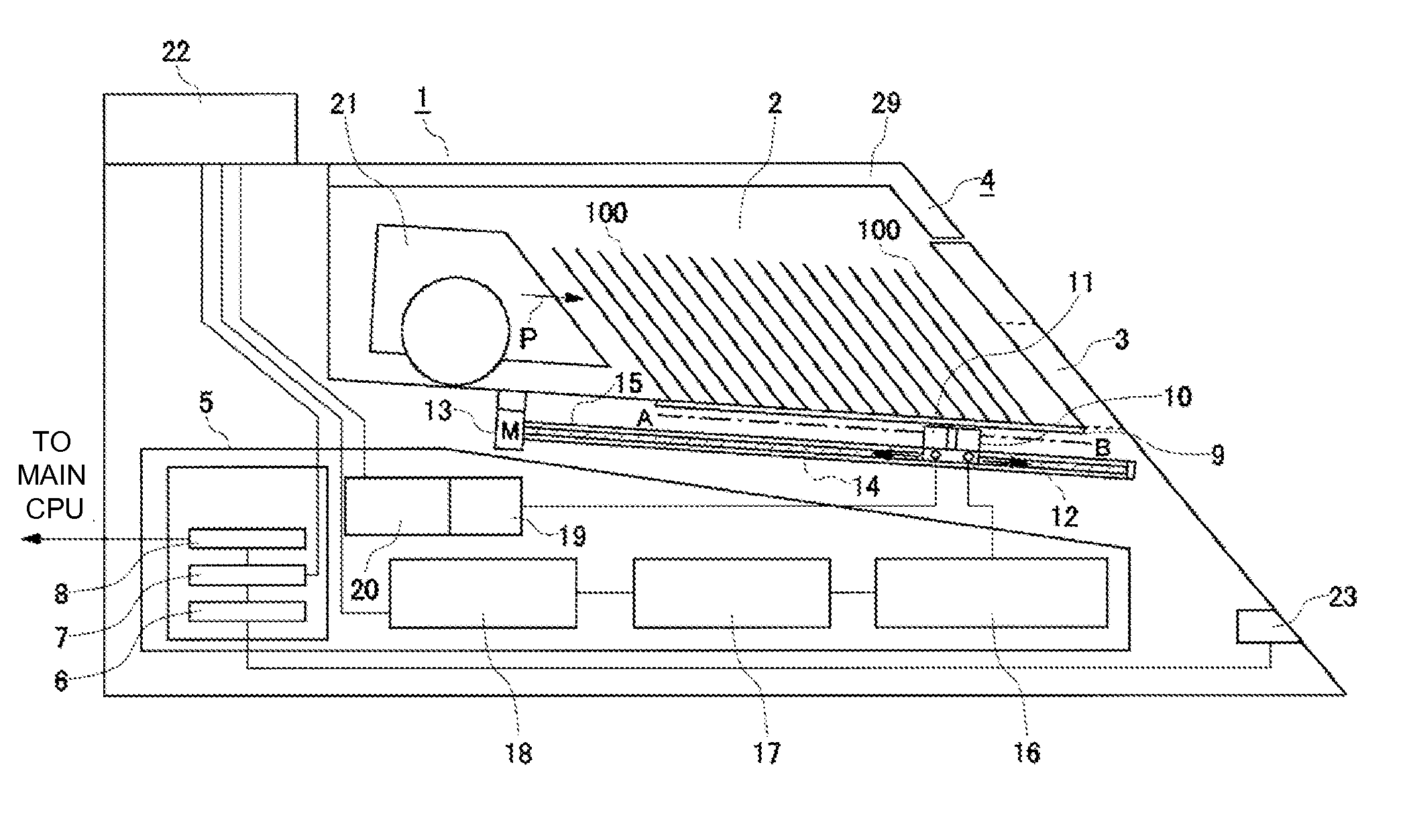
Card reading apparatus and table game system
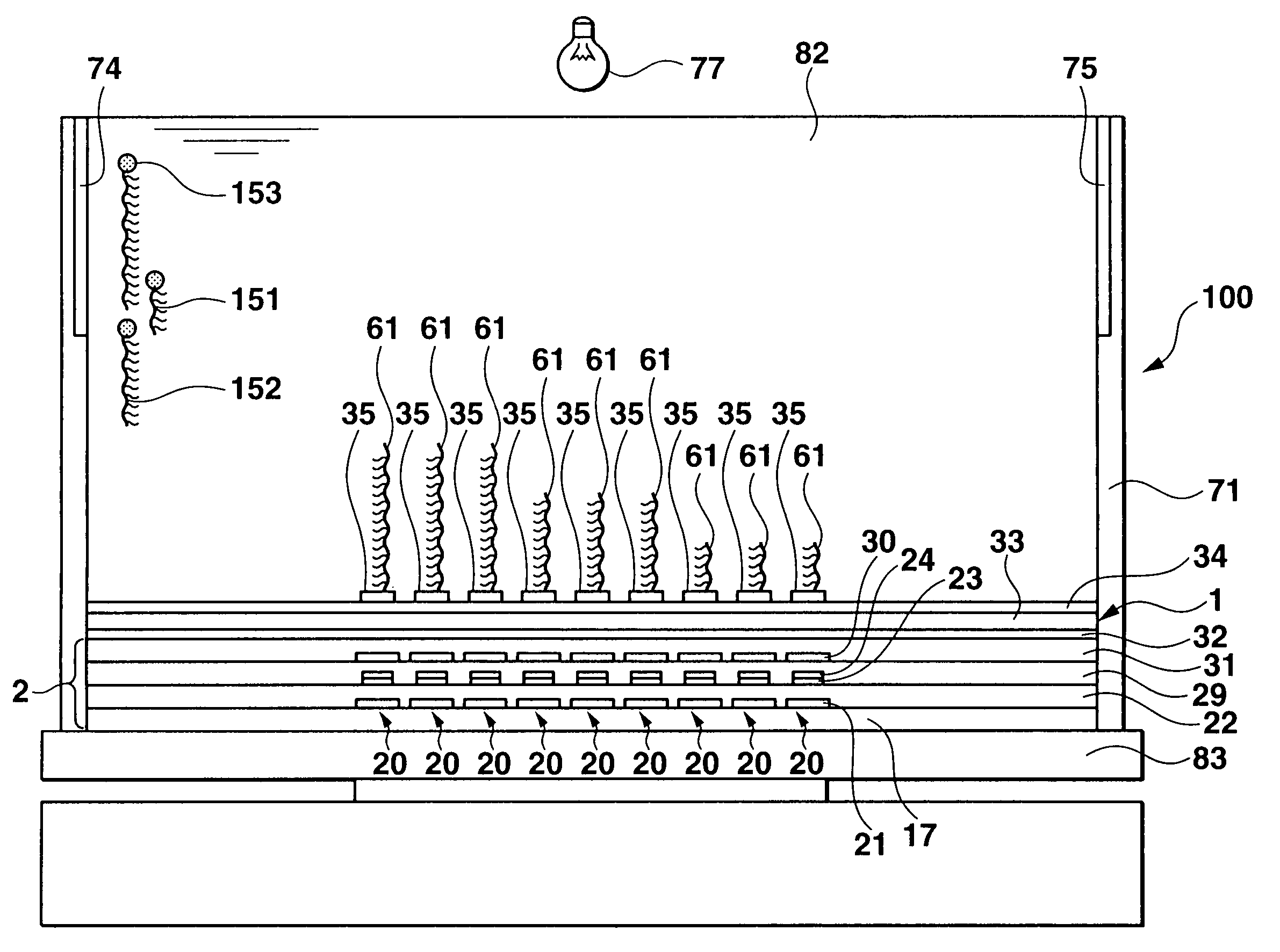
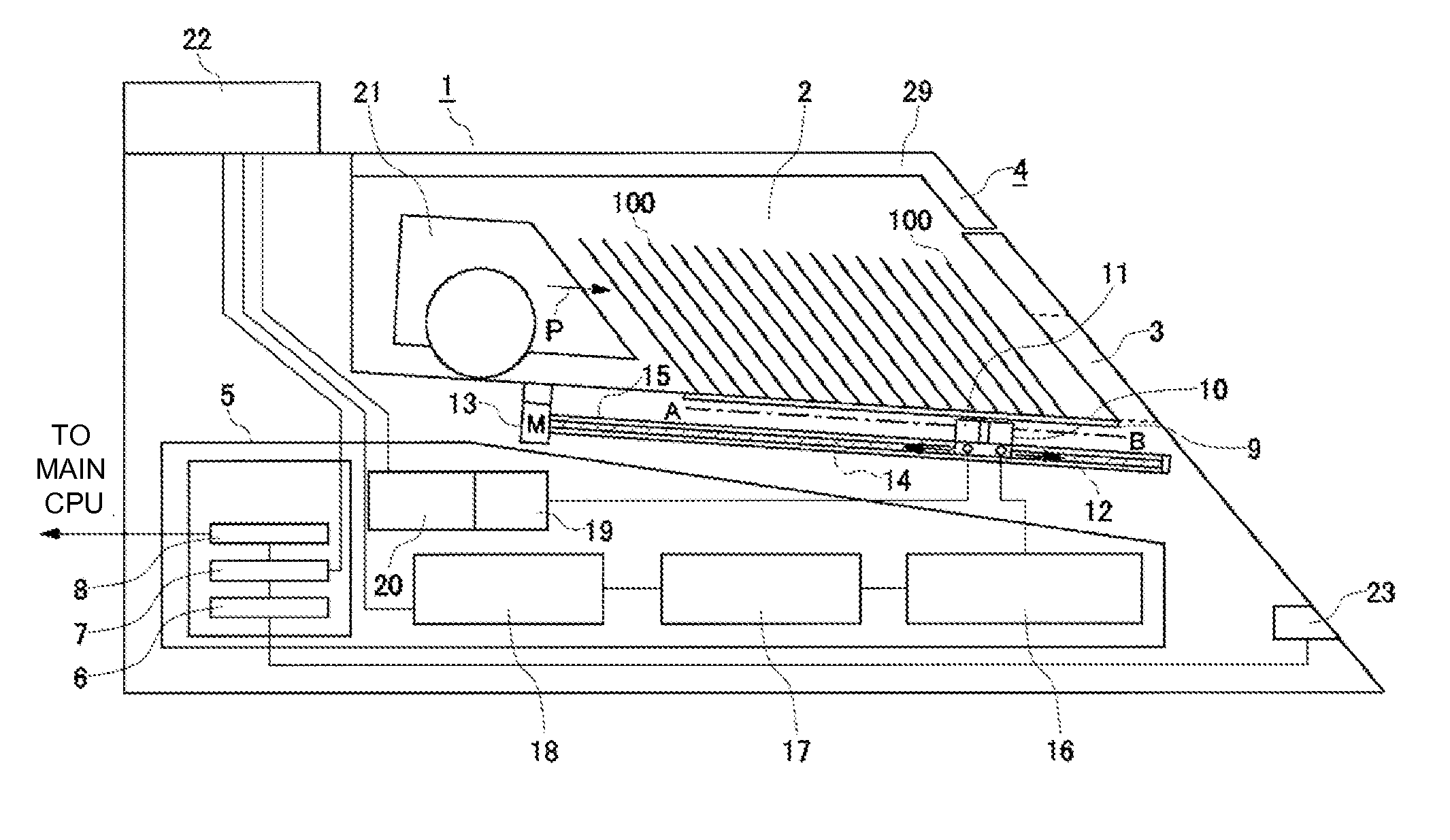
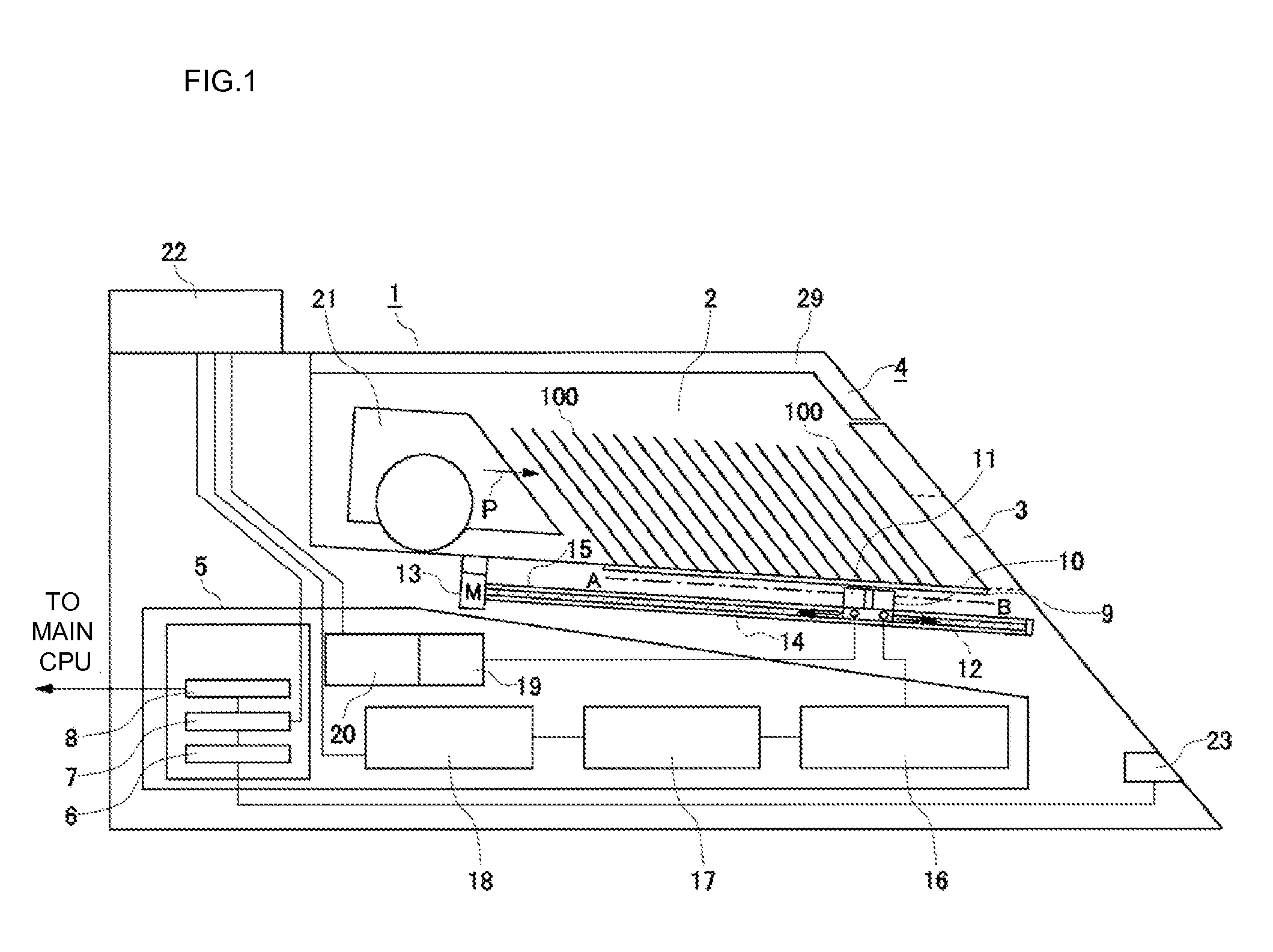
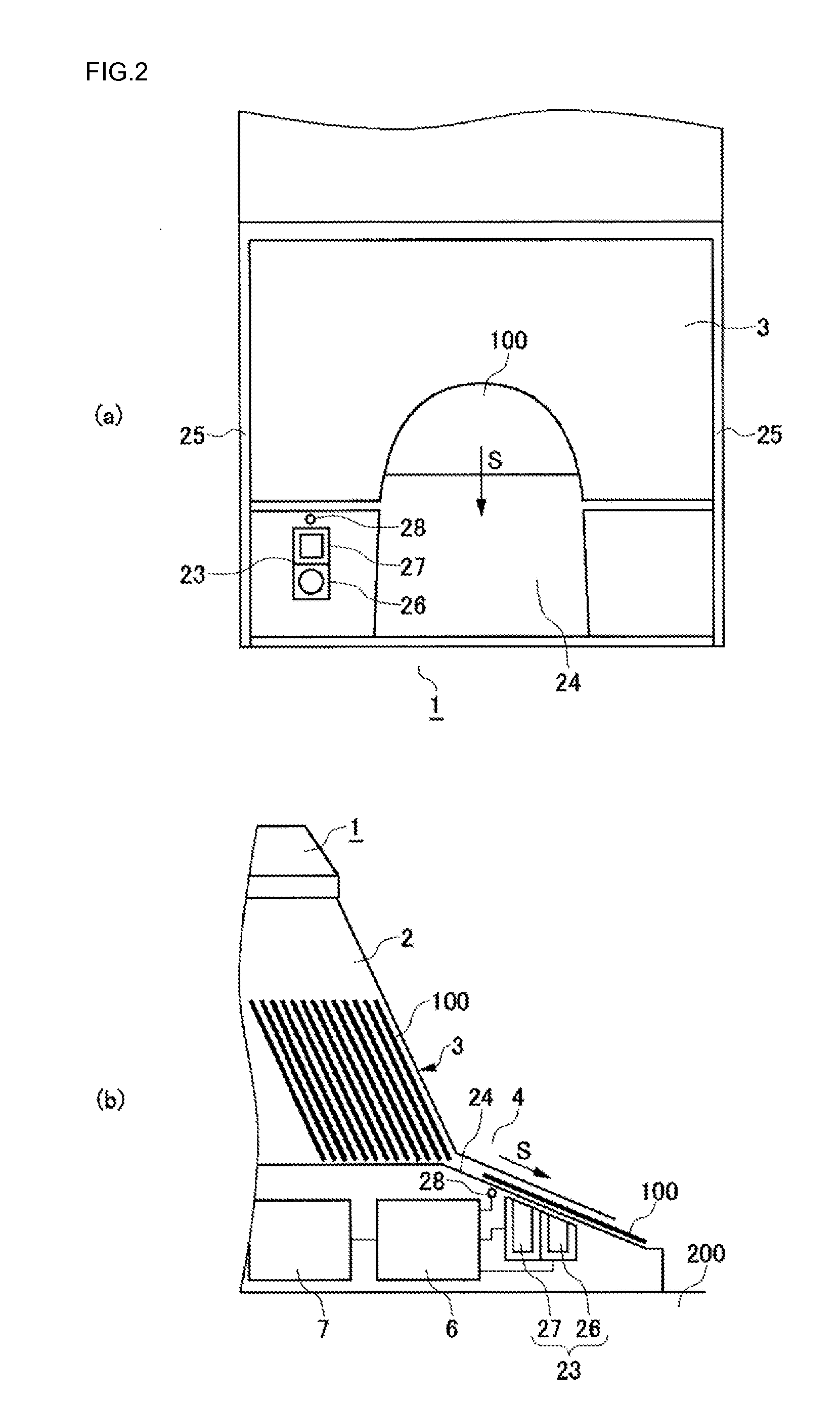
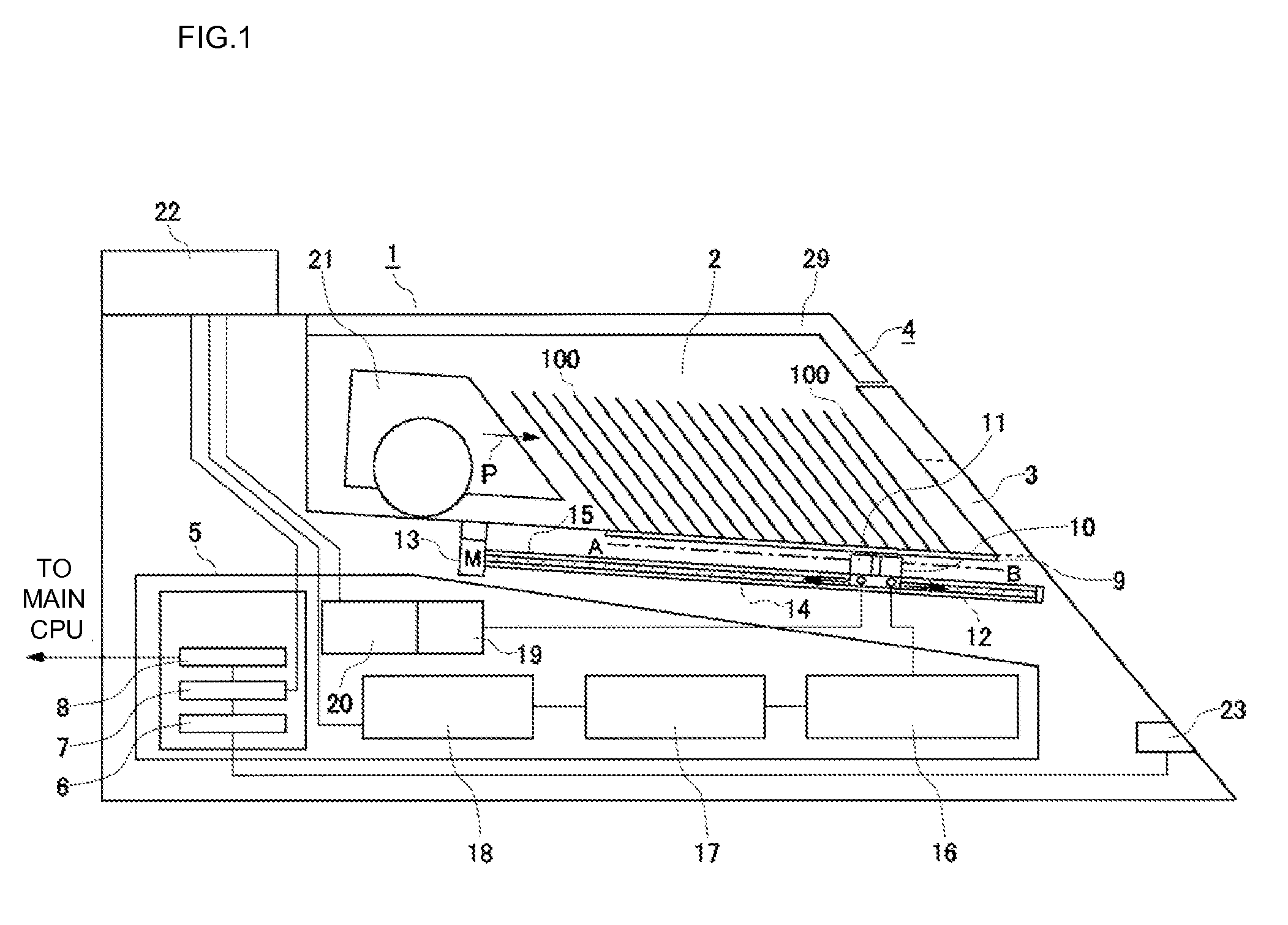
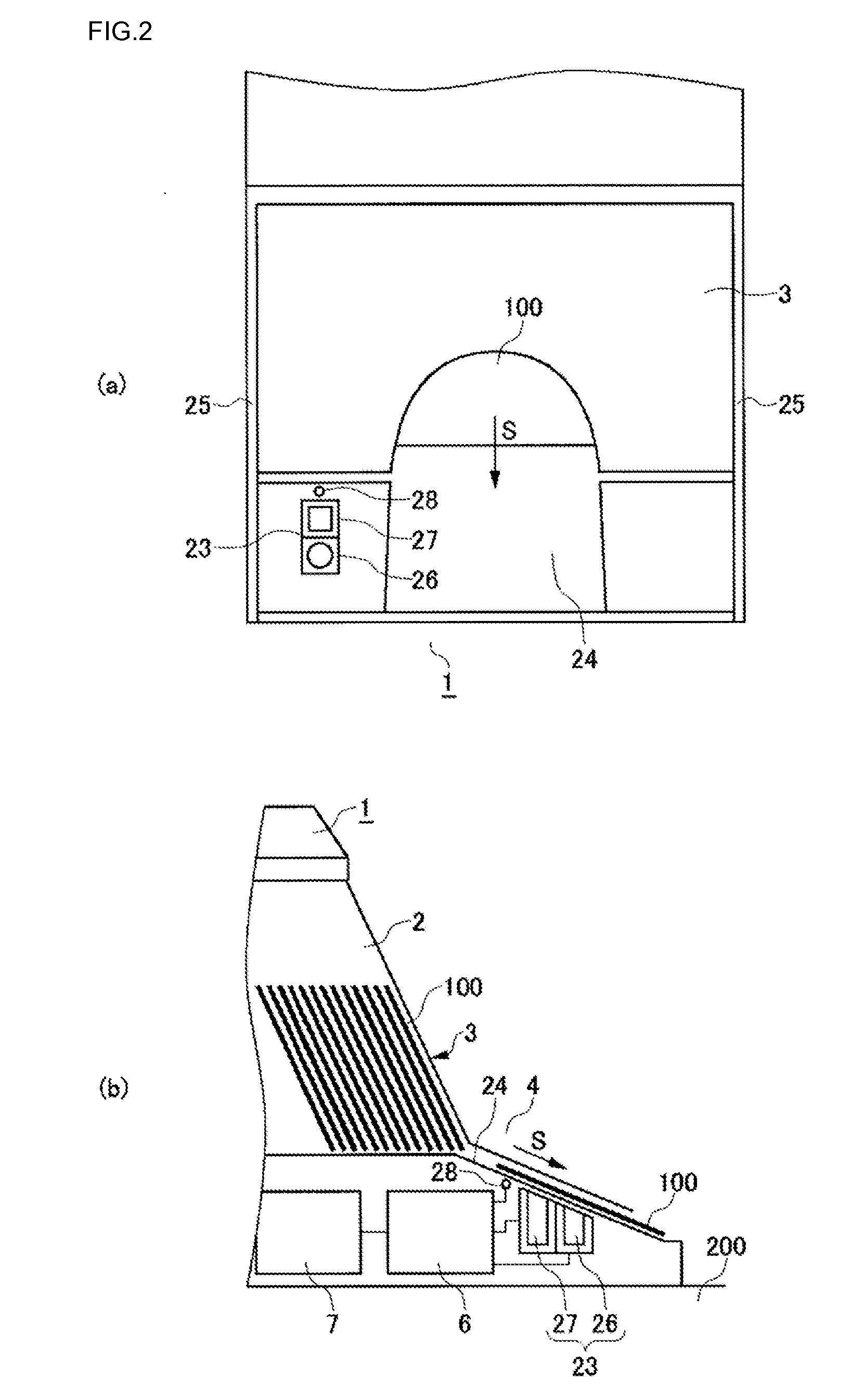
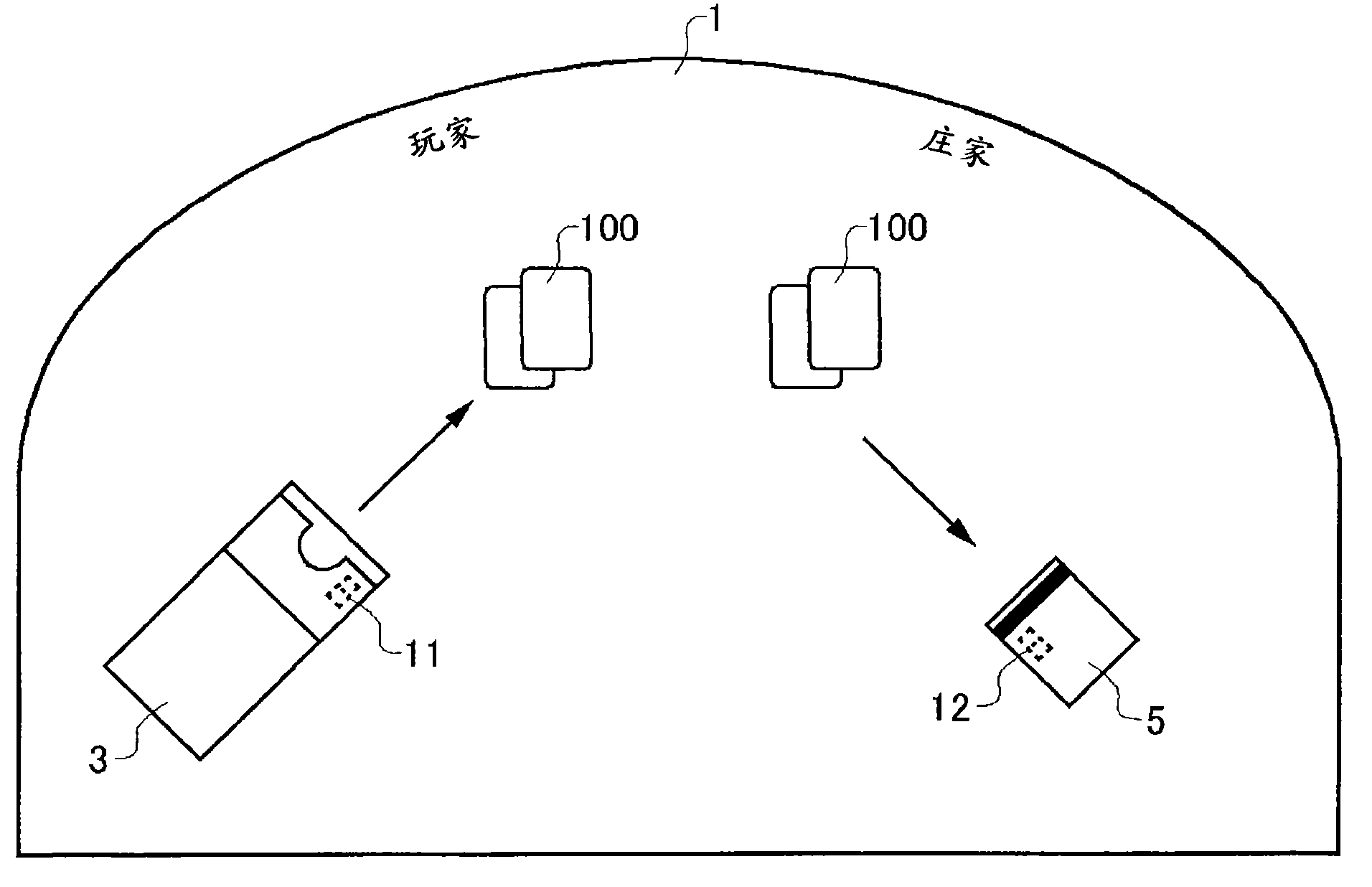
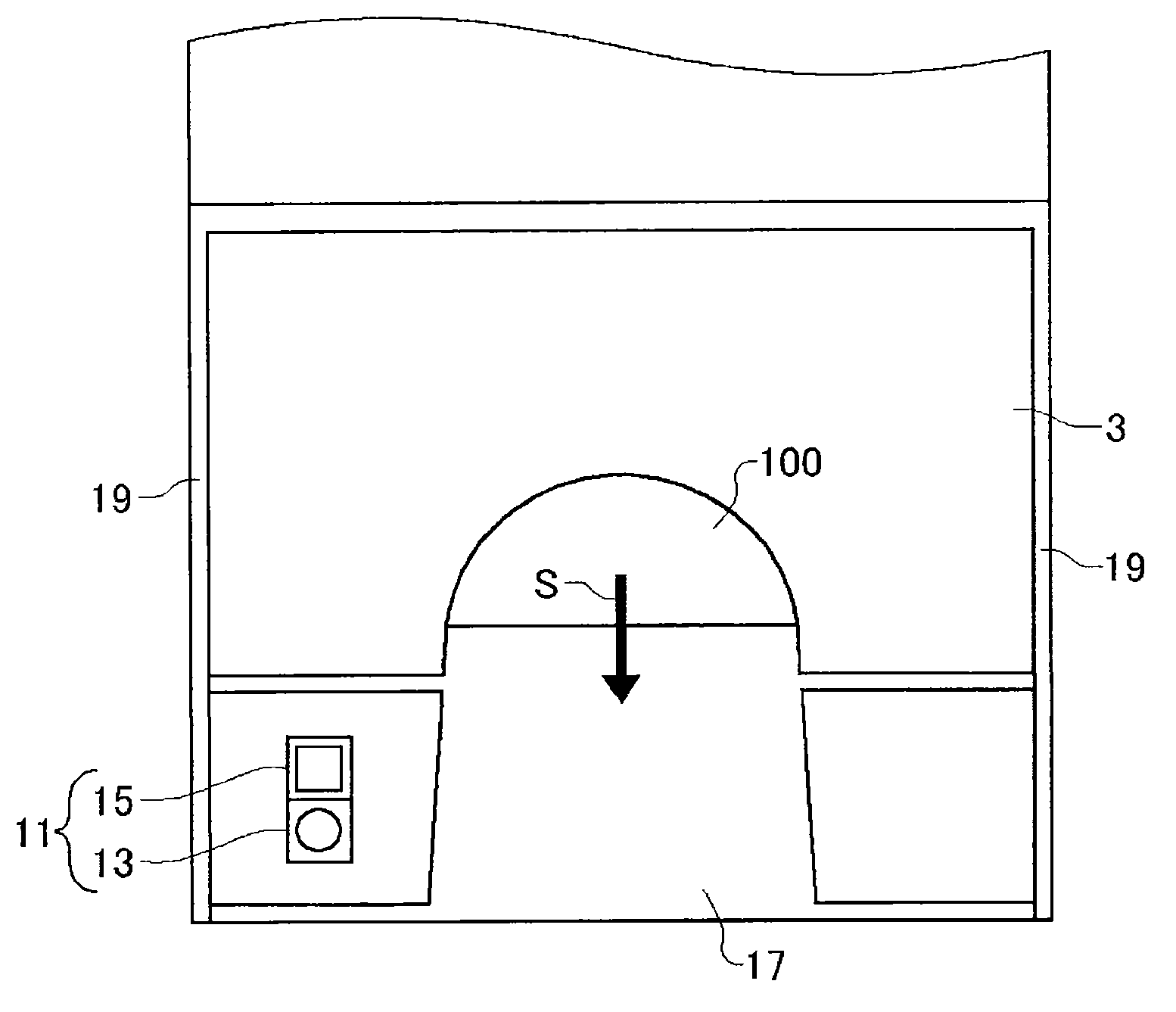
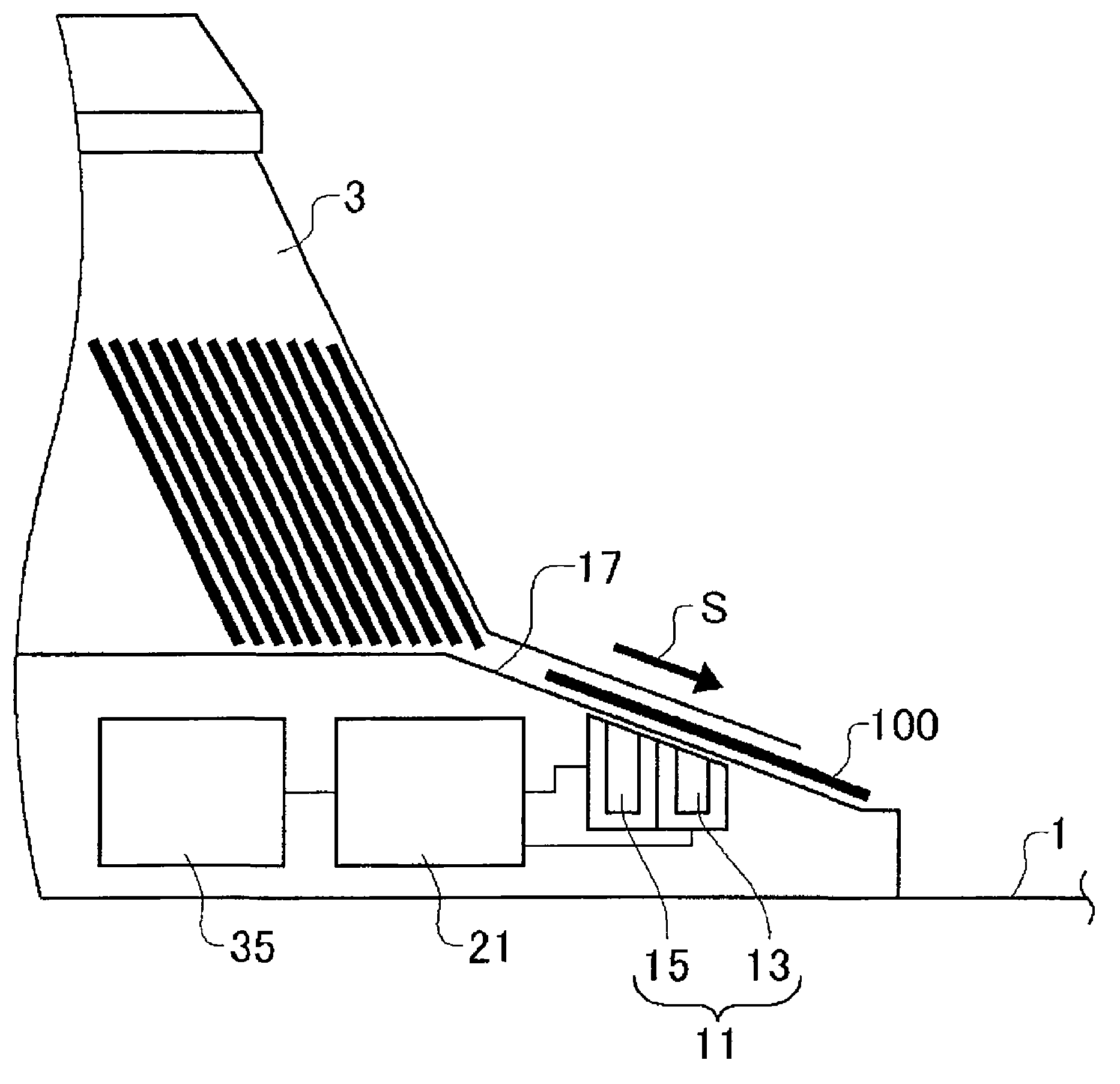
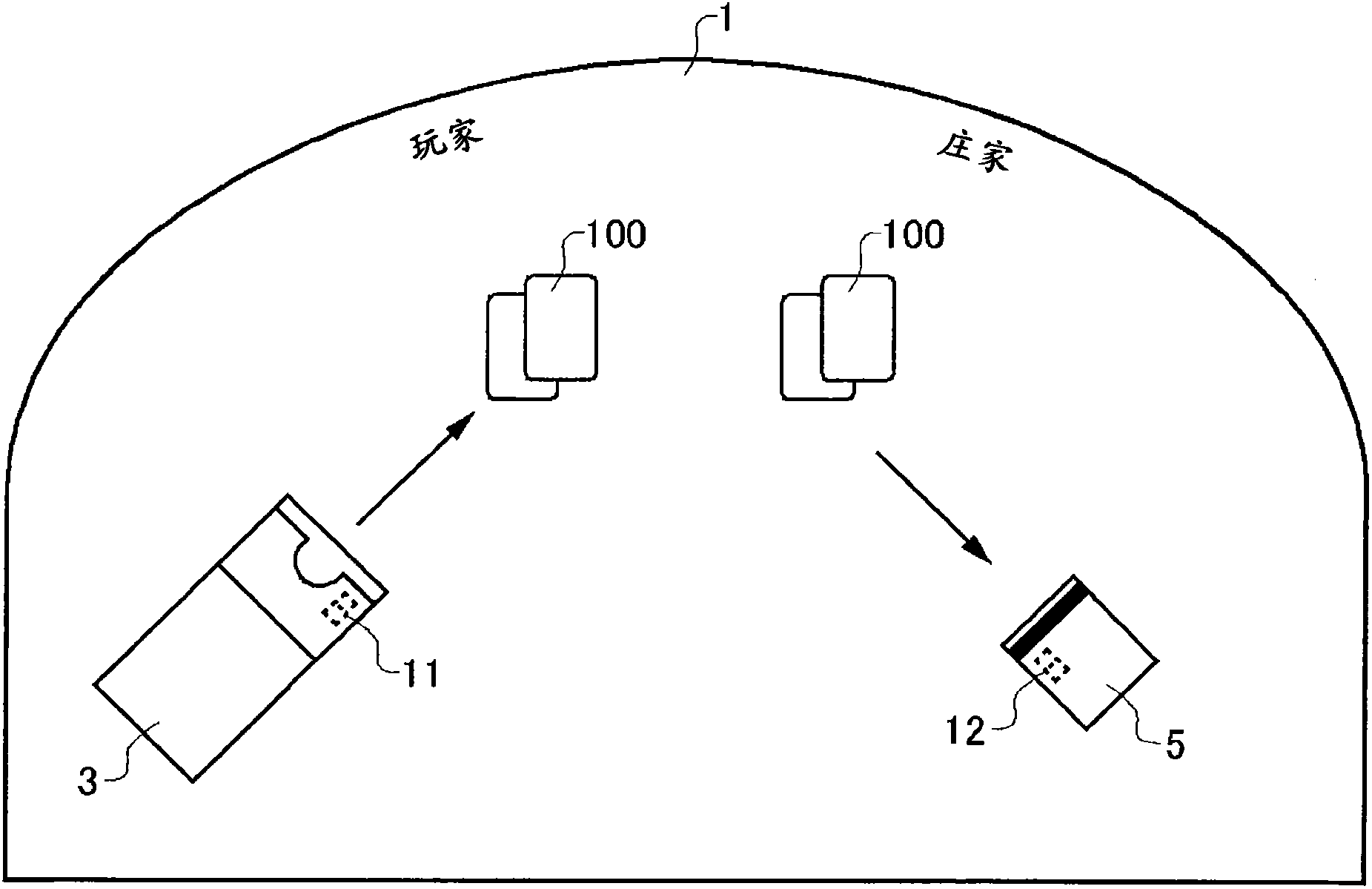
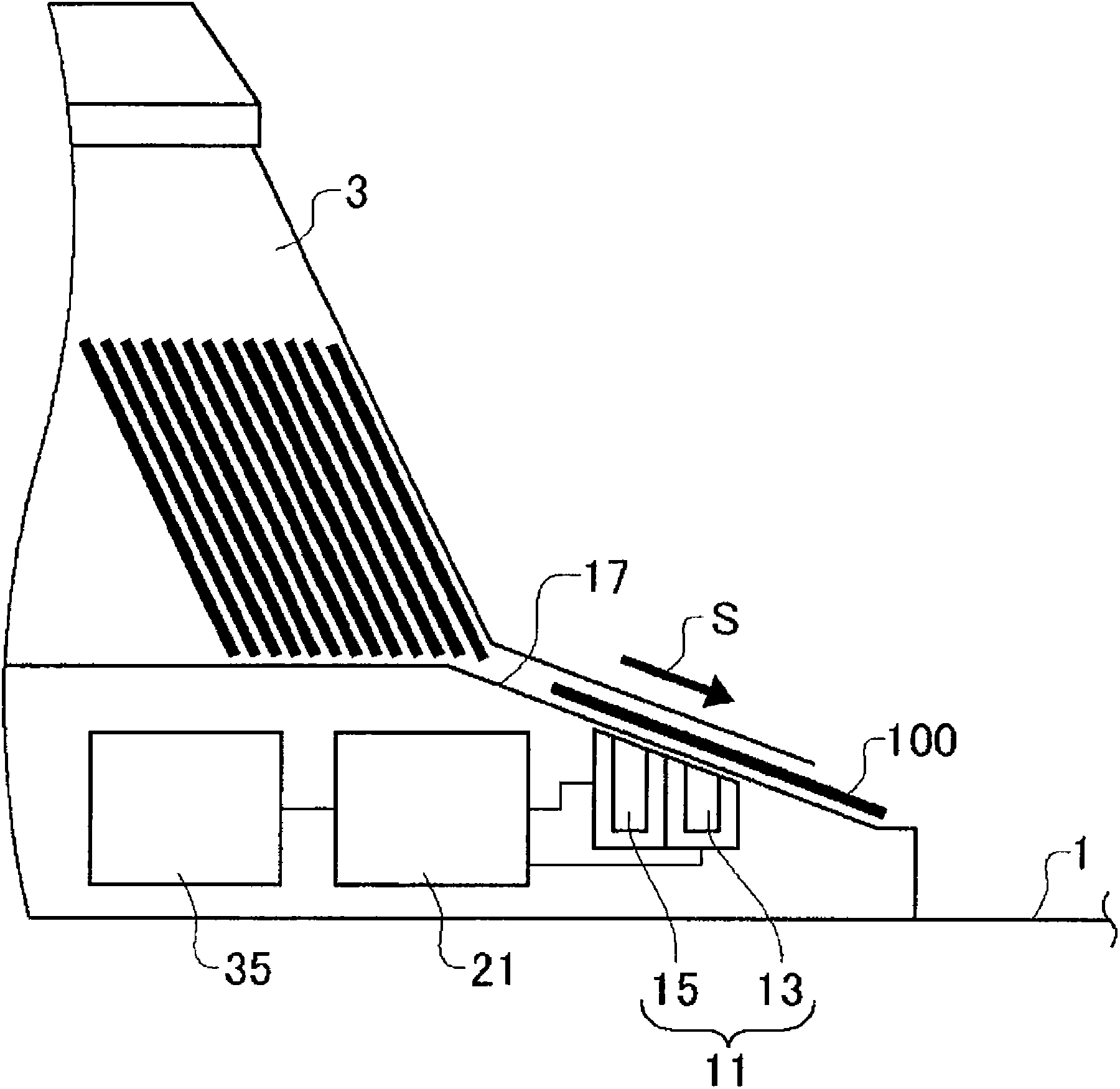
A card shooter apparatus (1) in a table game system a card shooter unit (4) including a card storage unit (2) that stores a plurality of cards (100) in a horizontal stack. A control device (5) constituted by a program storage unit, a computer device, or the like is placed in a lower part of the card shooter apparatus (1). A transparent bottom plate (9) is provided on a bottom of the card storage unit (2). An optical sensor (10) that receives reflected lights of lights applied to end surfaces of the plurality of cards (100) stored in the card storage unit (2), and a DNA sensor (11) that obtains DNA information from a DNA-containing coating applied to the cards (100) stored in the card storage unit 2 are placed below the bottom plate (9).
Owner:ANGEL GRP CO LTD
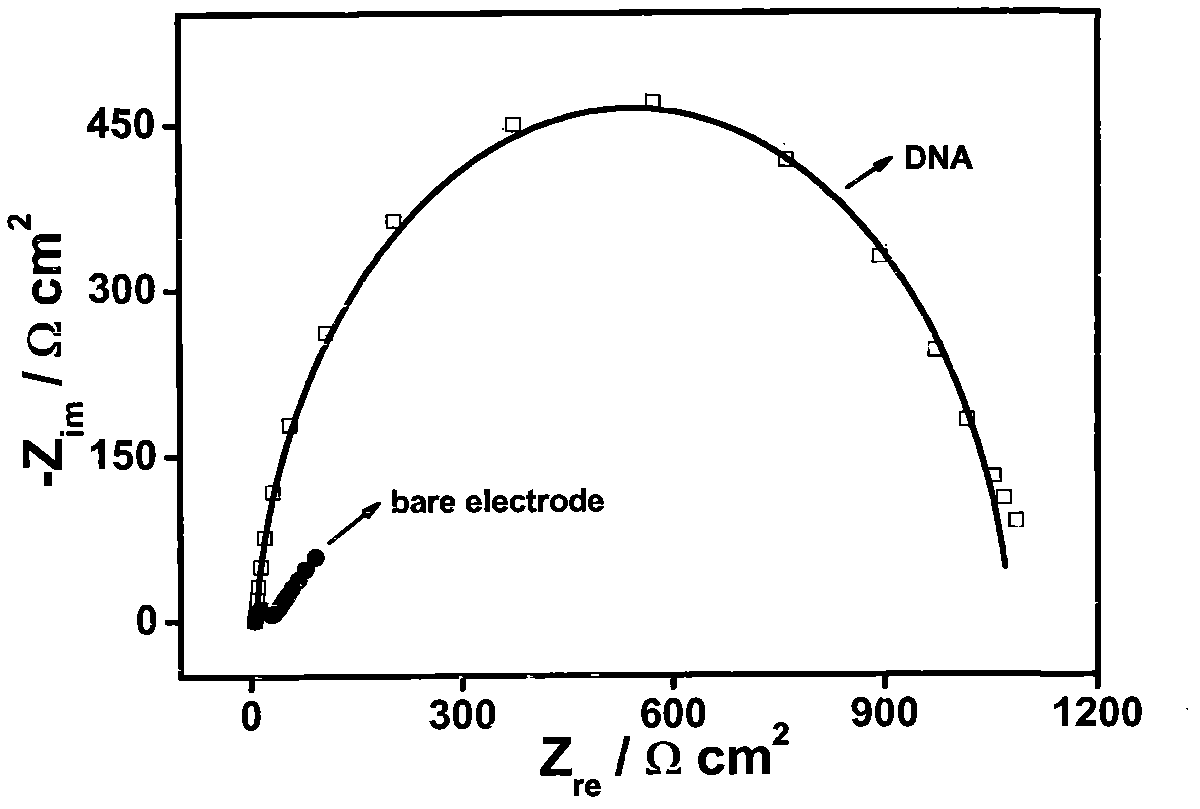
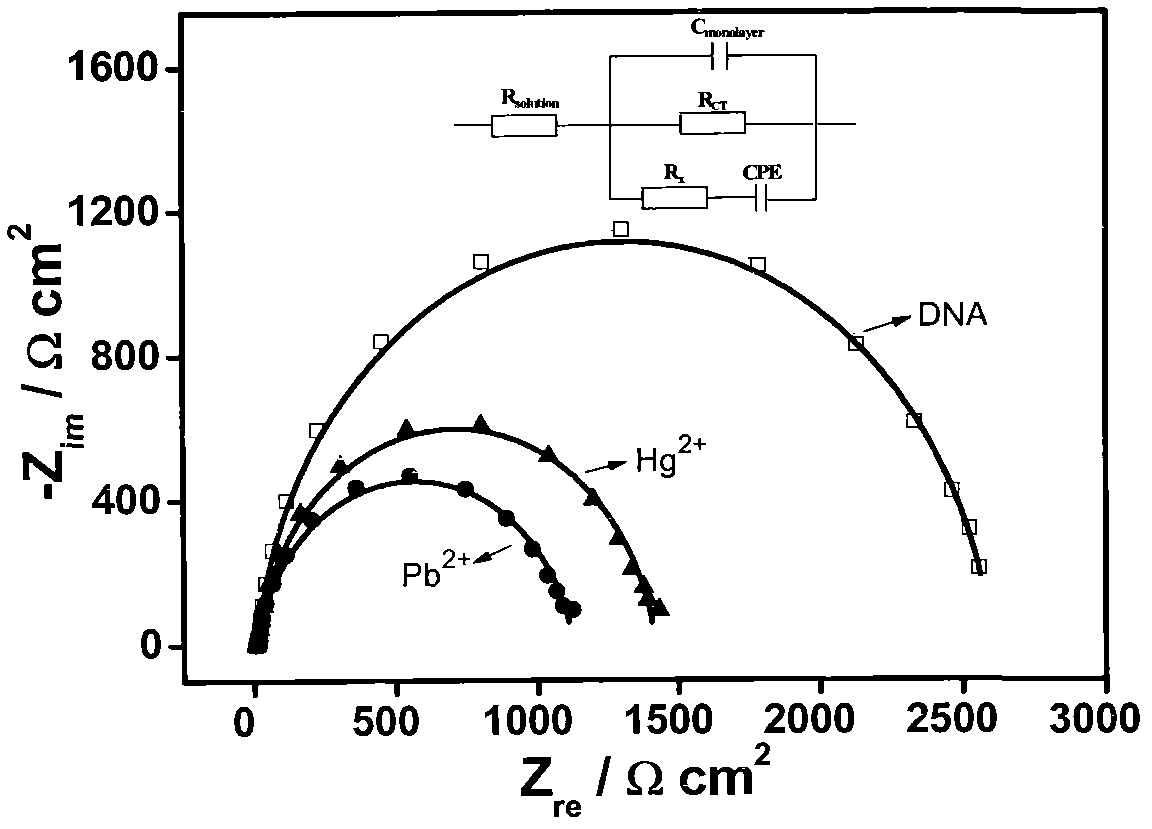
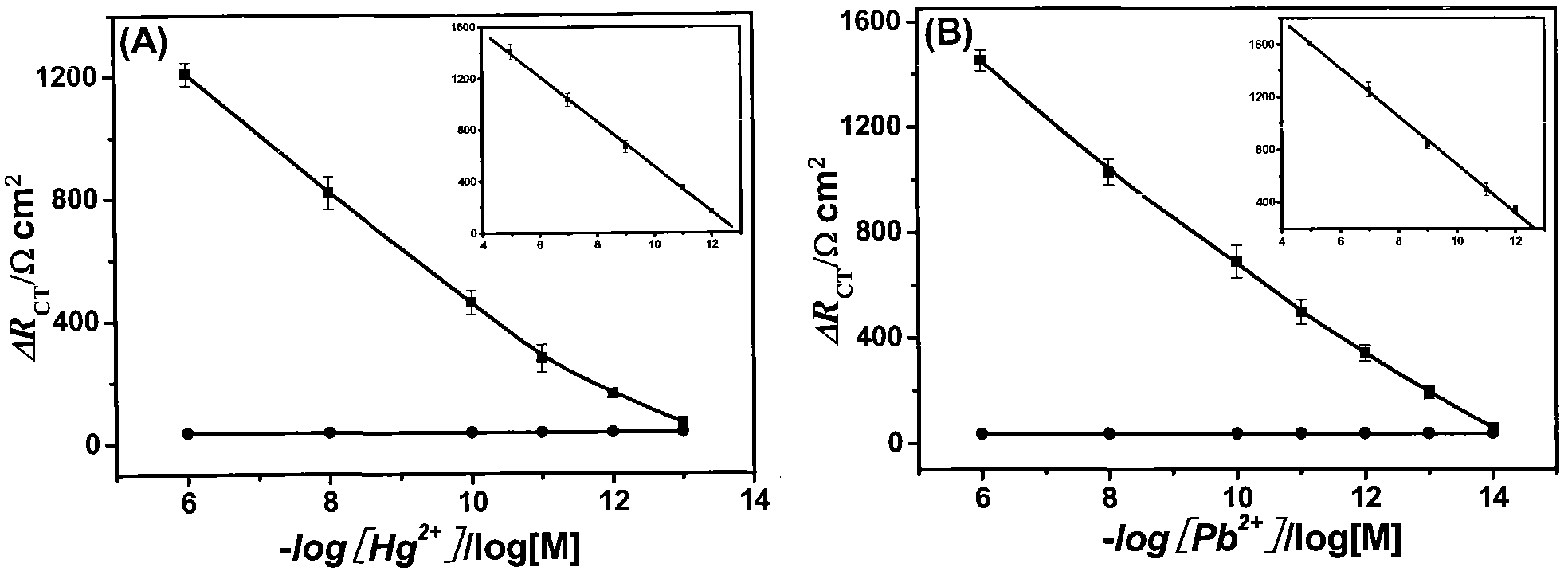
Method for simultaneously determining Pb<2+> and Hg<2+> based on electrochemical DNA biosensor
InactiveCN102721728AEliminate distractionsGood choiceMaterial impedanceMaterial electrochemical variablesMixed systemsMasking agent
The invention relates to a preparation method and a use of an electrochemical DNA biosensor based on Hg and Pb ion-induced DNA configuration change and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry and chemical sensors. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of 1, designing a functional zone composed of two parts of DNA sequences respectively used for specifically recognizing Hg ions and Pb ions and 2, assembling the functional zone on the surface of an Au electrode to obtain an electrochemical DNA biosensor. The electrochemical DNA biosensor obtained by the preparation method can be used for detecting a single Hg / Pb system of practical water and can also be used for separately detecting Hg and Pb ions of a mixed system through use of a masking agent. The preparation method of the electrochemical DNA biosensor allows mild conditions, is simple and convenient, and realizes good stability. The electrochemical DNA biosensor has high specificity, high sensitivity and high selectivity, can be operated simply and avoids labeling during detection.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Card reading apparatus and table game system
A card shooter apparatus (1) in a table game system includes a card shooter unit (4) including a card storage unit (2) that stores a plurality of cards (100) in a horizontal stack. A control device (5) constituted by a program storage unit, a computer device, or the like is placed in a lower part of the card shooter apparatus (1). A transparent bottom plate (9) is provided on a bottom of the card storage unit (2). An optical sensor (10) that receives reflected lights of lights applied to end surfaces of the plurality of cards (100) stored in the card storage unit (2), and a DNA sensor (11) that obtains DNA information from a DNA-containing coating applied to the cards (100) stored in the card storage unit 2 are placed below the bottom plate (9).
Owner:ANGEL GRP CO LTD
Preparation method for surface plasmon resonance DNA sensor based on graphene oxide
InactiveCN103411933ASensitive detectionSolving the difficult problem of lowering the detection limitAnalysis by material excitationResonance angleDna adsorption
The invention discloses a preparation method for a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) DNA sensor based on graphene oxide, and belongs to the technical field of nanometer material biology. The technical problem to be solved in the preparation method is that the distinctive effect of graphene oxide-DNA is utilized, the surface plasmon resonance technology and the signal amplification mechanism of the AuNPs are applied, based on the competitive inhibition method, the phenomenon that the single-stranded DNA with different concentrations is absorbed on the surface of a sensing chip to cause SPR spectral change, and the single-stranded DNA is detected through the linear change of the resonance angle. Through the adoption of the preparation method, the SPR technology is adopted, the GO (Graphene Oxide) is utilized to assemble the surface of the chip, the single-stranded DNA is sensitively detected through adopting the competitive inhibition method and the AuNPs signal amplification effect, the concentration of the single-stranded DNA is quantitatively detected through analyzing the change of the SPR peak, and the detection limit is ultra-low. The preparation method has the advantages as follows: the instrument and equipment are low in cost, the cost is low, the operation is simple, the efficiency is high, the precision is high, and the detection limit is ultra-low.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Game system, card, card shoe and card-shuffing device
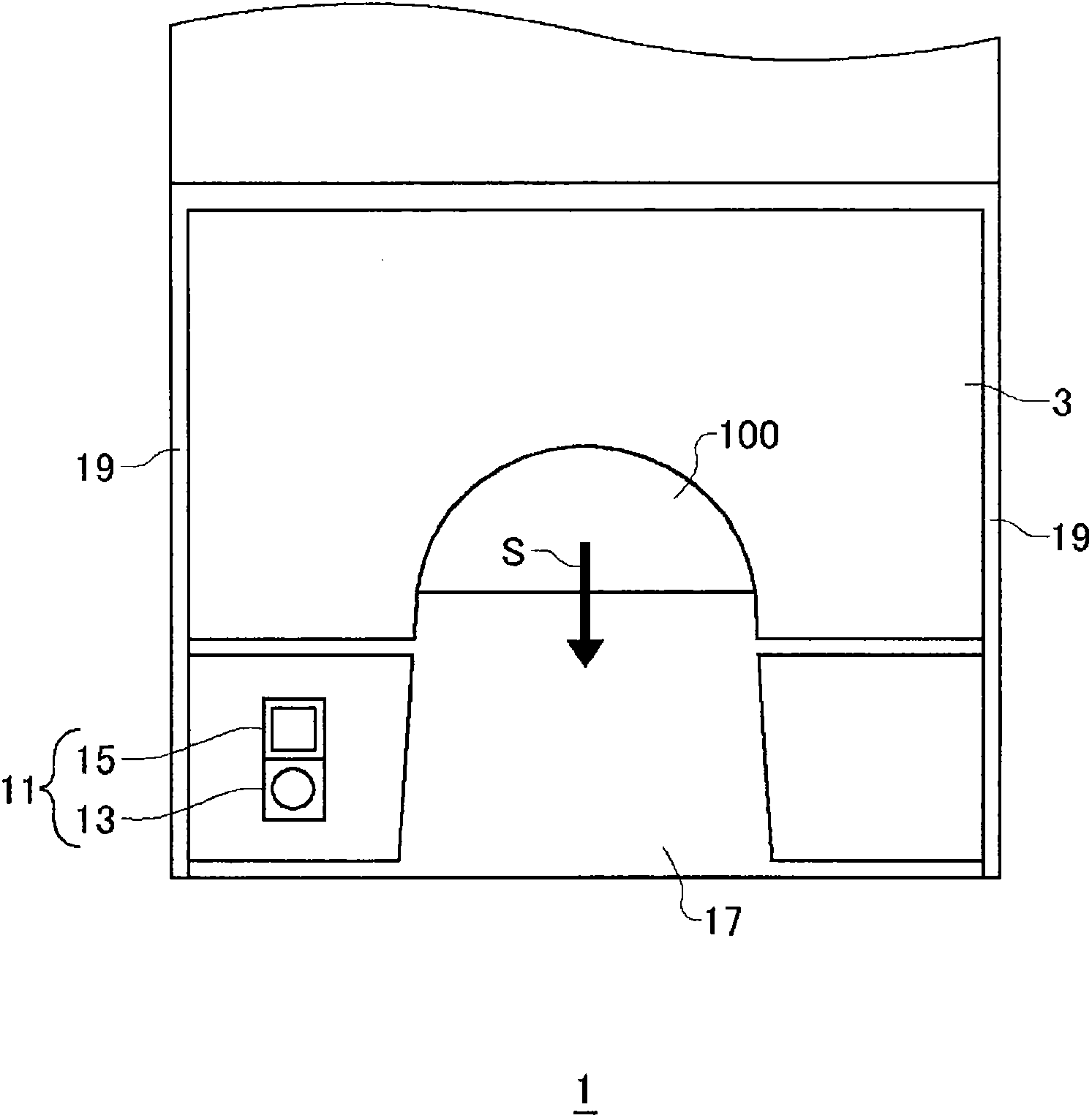
Deck information representing a deck of cards (100) is encoded by the DNA contained in the DNA ink (DNA-containing coating) with which the markings (101) representing card suit or rank are printed. The cards (100) are guided along rails (19) in a card shoe (3). A DNA sensor (13) is provided on the sliding surface (17) of the card shoe (3). When light from a light source of the DNA sensor (13) is shined on the DNA-containing coating of the marking (101) printed on the card (100), the light reflected from the DNA-containing coating (light of a prescribed frequency) is received by the DNA sensor (13). When the deck information is read from the DNA, the card (100) is verified using said deck information and the results of the verification are output, thereby allowing on-the-spot detection of cheating in card games as well as preventing those who have obtained cards (100) dishonestly from reproducing said cards (100).
Owner:ANGEL GRP CO LTD
Preparation and application of ZnO@CdTe-carboxylation C3N4 photoelectric DNA sensor
InactiveCN104297323AGood choiceHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingHousekeeping geneBiology
The invention relates to preparation and application of a ZnO@CdTe-carboxylation C3N4 photoelectric DNA sensor, and belongs to the technical field of biosensing detection. A ZnO@CdTe-carboxylation C3N4 compound is taken as a beacon material; qualitative and quantitative detection on the target DNA and the housekeeping gene of a physical tissue can be realized; the advantages of simple equipment, low cost and easiness in miniaturization are achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
DNA sensor for detecting staphylococcus aureus as well as preparation method and application of DNA sensor
ActiveCN104630869AInhibit aggregationGood dispersionElectrolytic coatingsMaterial electrochemical variablesStaphylococcus aureusA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA sensor for detecting staphylococcus aureus as well as preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of rapid pathogenic bacteria detection. A electrochemical carbon nano tube / gold nano particle composite membrane DNA sensor is prepared by utilizing the biological fixation effect and electrochemical electron transfer rate enhancing function of the gold nano particle, and is capable of effectively improving the detection sensitivity. According to the invention, a detection method, having high universality, high sensitivity and high accuracy, and detection conditions for staphylococcus aureus are preliminarily established through a detection technology in which specific staphylococcus aureus gene sequence is synthesized to be used as probe ssDNA so as to form a hybridization system with a complementation target ssNDA segment and methylene blue is used as a hybridization indicator.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Game system, card, card shoe and card-shuffing device
Deck information representing a deck of cards (100) is encoded by the DNA contained in the DNA ink (DNA-containing coating) with which the markings (101) representing card suit or rank are printed. The cards (100) are guided along rails (19) in a card shoe (3). A DNA sensor (13) is provided on the sliding surface (17) of the card shoe (3). When light from a light source of the DNA sensor (13) is shined on the DNA-containing coating of the marking (101) printed on the card (100), the light reflected from the DNA-containing coating (light of a prescribed frequency) is received by the DNA sensor (13). When the deck information is read from the DNA, the card (100) is verified using said deck information and the results of the verification are output, thereby allowing on-the-spot detection of cheating in card games as well as preventing those who have obtained cards (100) dishonestly from reproducing said cards (100).
Owner:ANGEL GRP CO LTD
Method for measuring 9-hydroxy fluorine based on electrochemistry hairpin DNA biosensor
InactiveCN102680549AHigh affinityHighly ordered structureMaterial electrochemical variablesSulfurImmobilized DNA
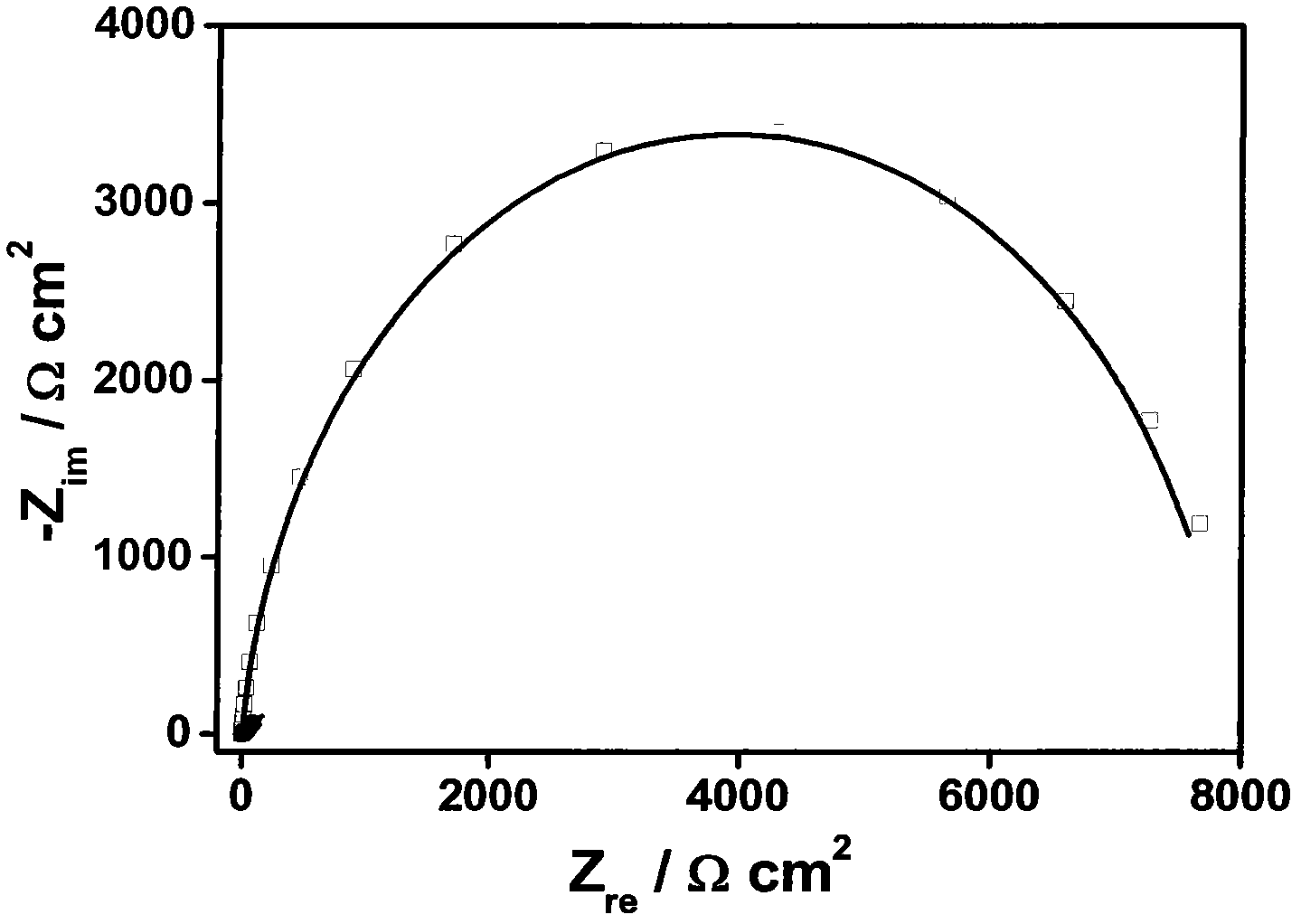
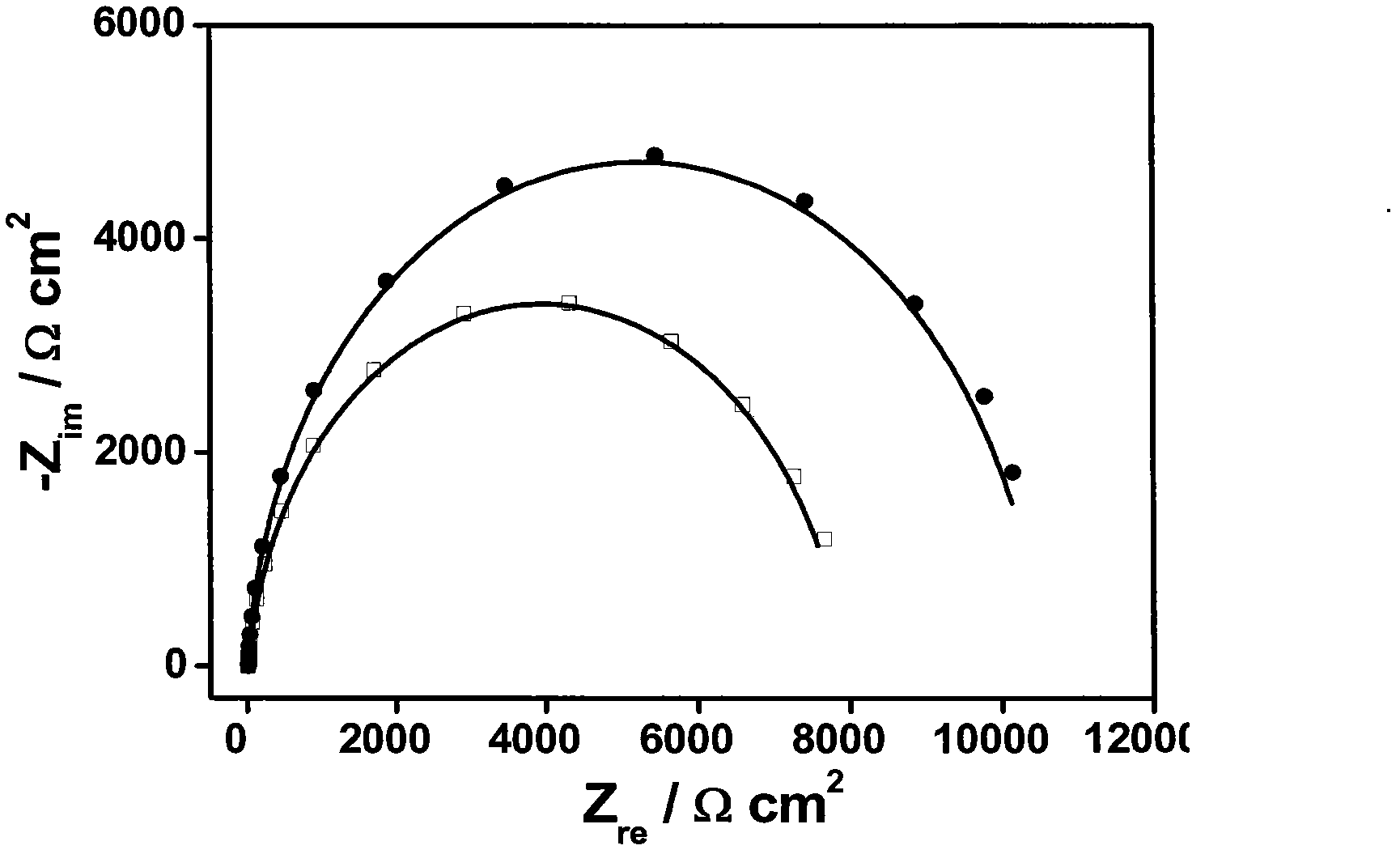
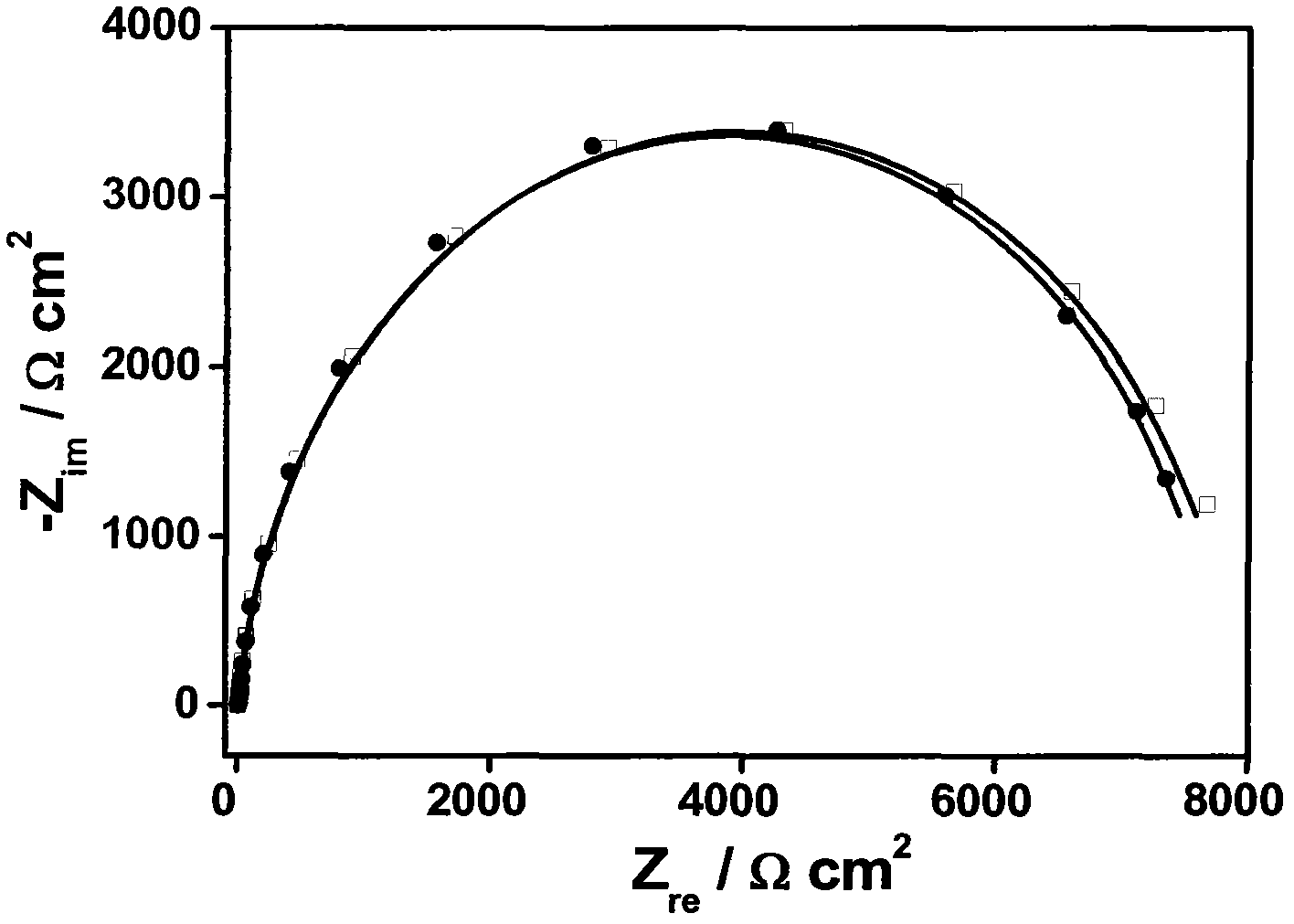
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrochemistry detection and chemical sensors for detecting 9-hydroxy fluorine based on a hairpin DNA modified gold electrode sensor, and relates to preparation of a hairpin DNA modified gold electrode capble of having electrochemical response to 9-hydroxy fluorine and detection on the 9-hydroxy fluorine with the electrode. Specifically, the synthetic sulfhydryl modified hairpin DNA is used as a raw material, the hairpin DNA is self-assembled to the surface of the gold electrode by the Au-S bond interaction to prepare the DNA modified electrode. The immobilized DNA electrode has high response to the 9-hydroxy fluorine, and the detection on the 9-hydroxy fluorine can be carried out according to the change of response of the electrochemistry to the impedance. The DNA sensor has the advantages of mild preparation condition, simplicity in operation, good stability and high sensitivity.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Arrangement and method for identifying people
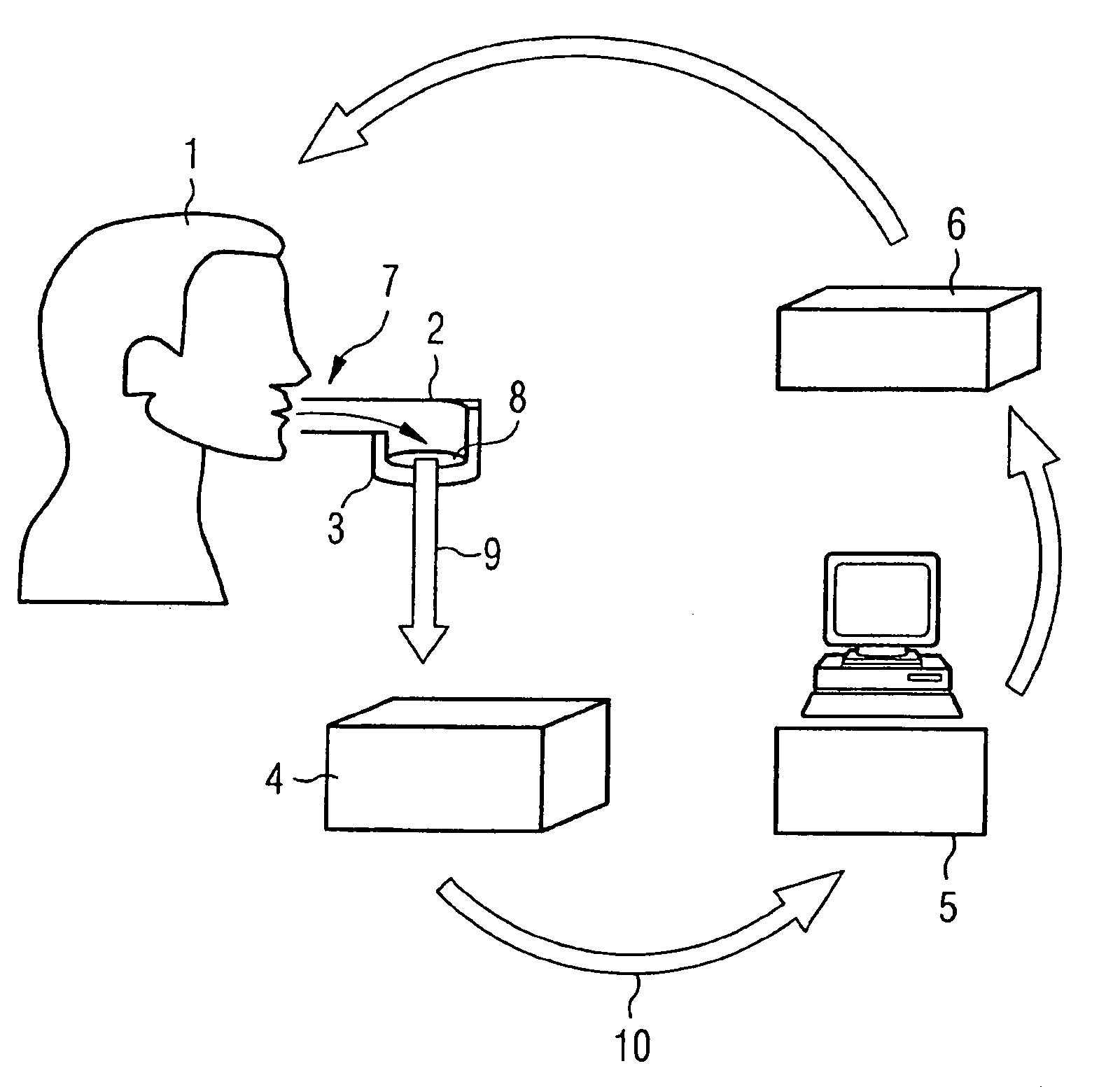
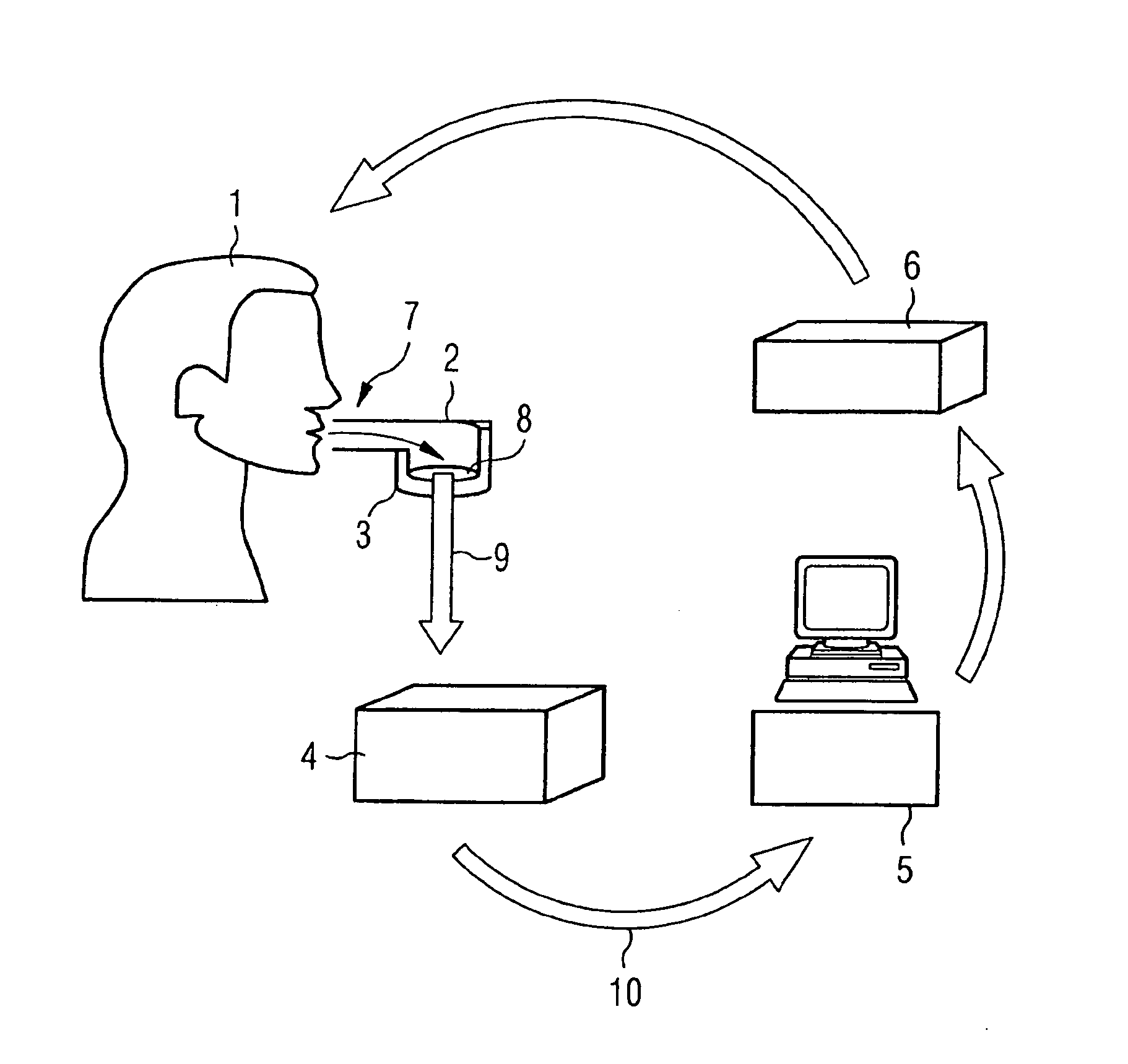
InactiveUS20090278659A1Easy to set upSimple designProgramme controlElectric signal transmission systemsComputer scienceDna sensor
A method for identifying people involves breathing respired air into a collector unit, trapping condensate from the respired air in the collector unit, introduction of the condensate by a same introduction to a DNA sensor unit, analysis of the condensate after a cell disruption, comparison of the result the data from a databank and output of the comparison result with analysis of the identity of a person.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
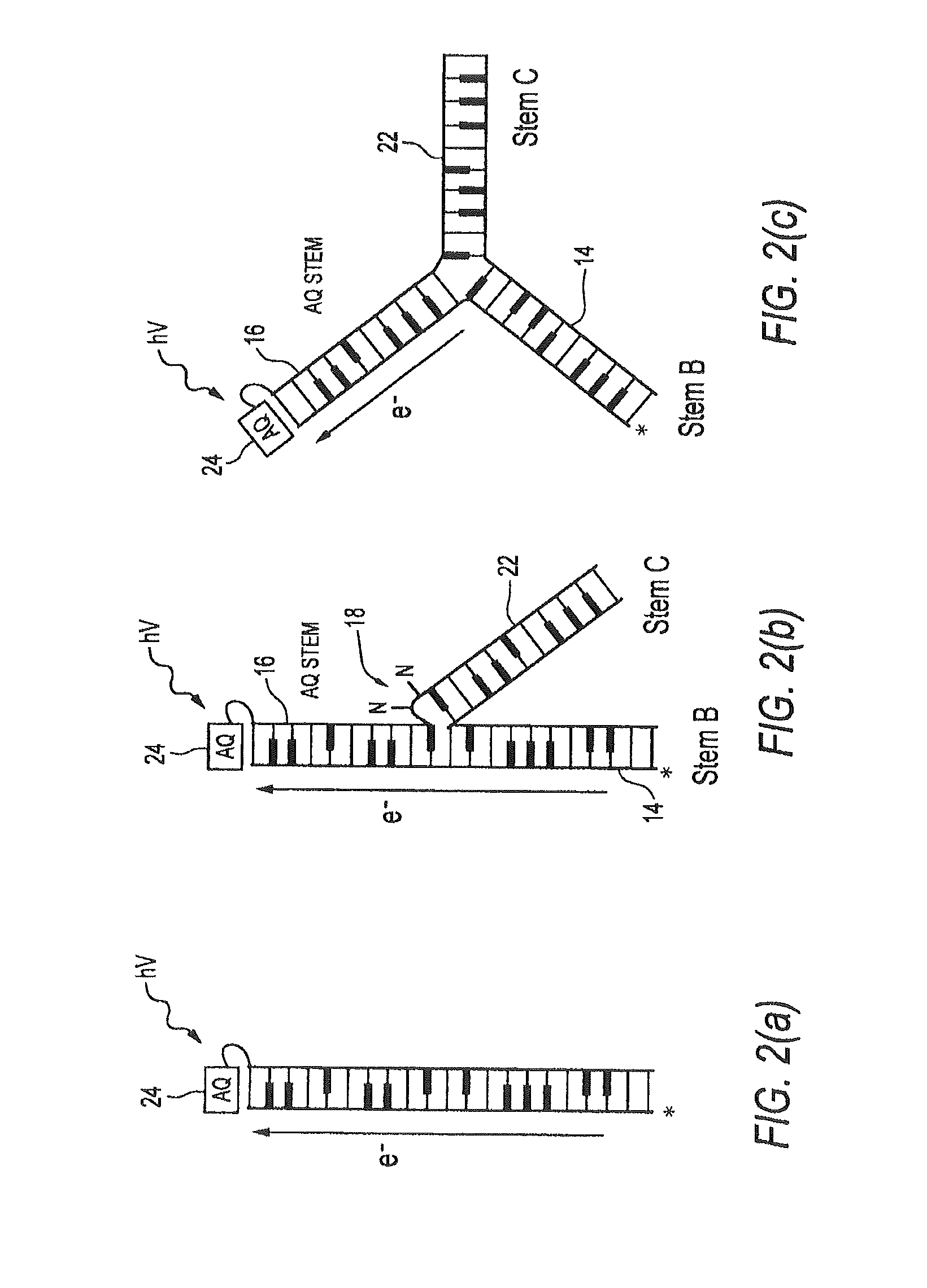
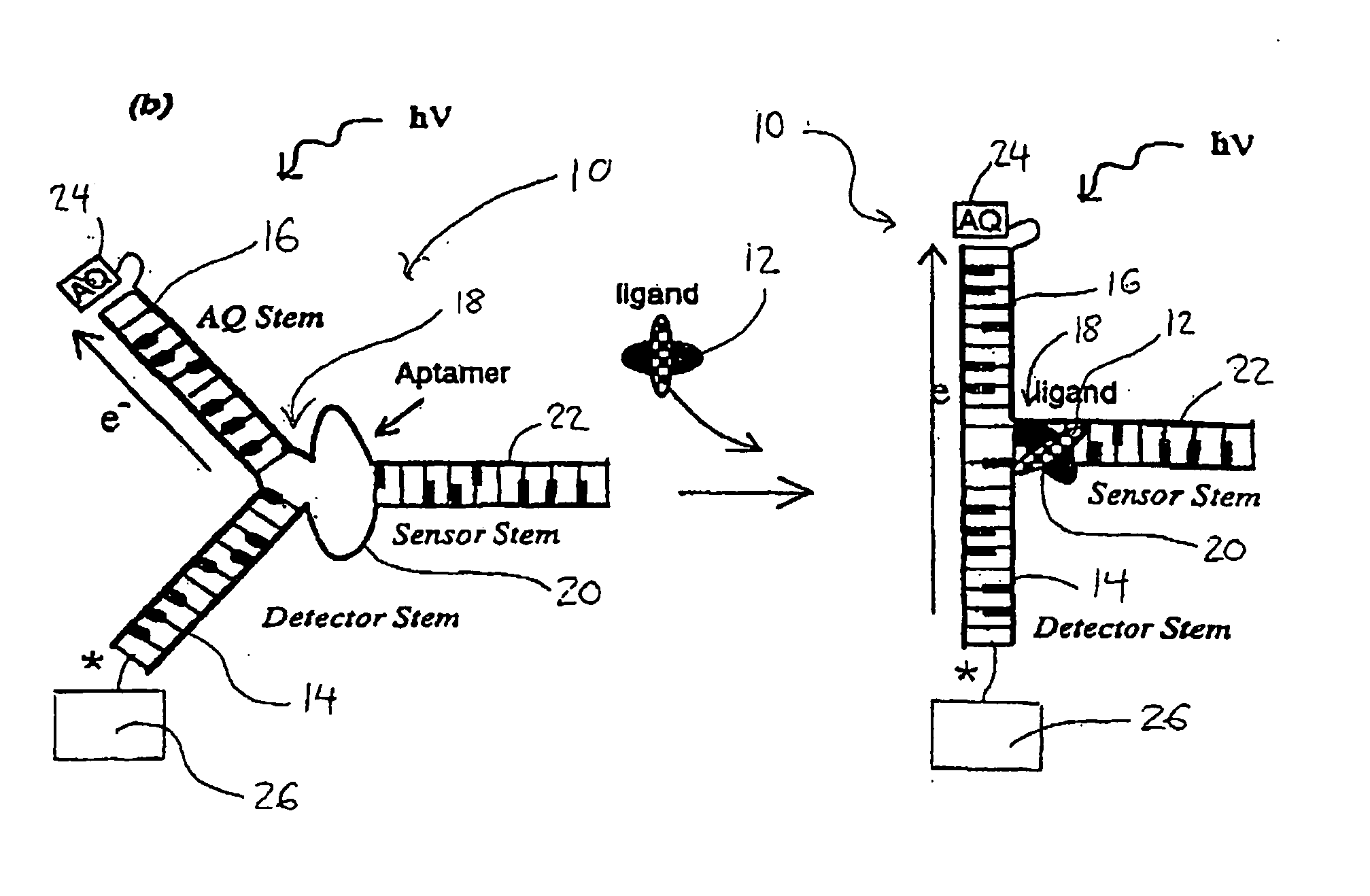
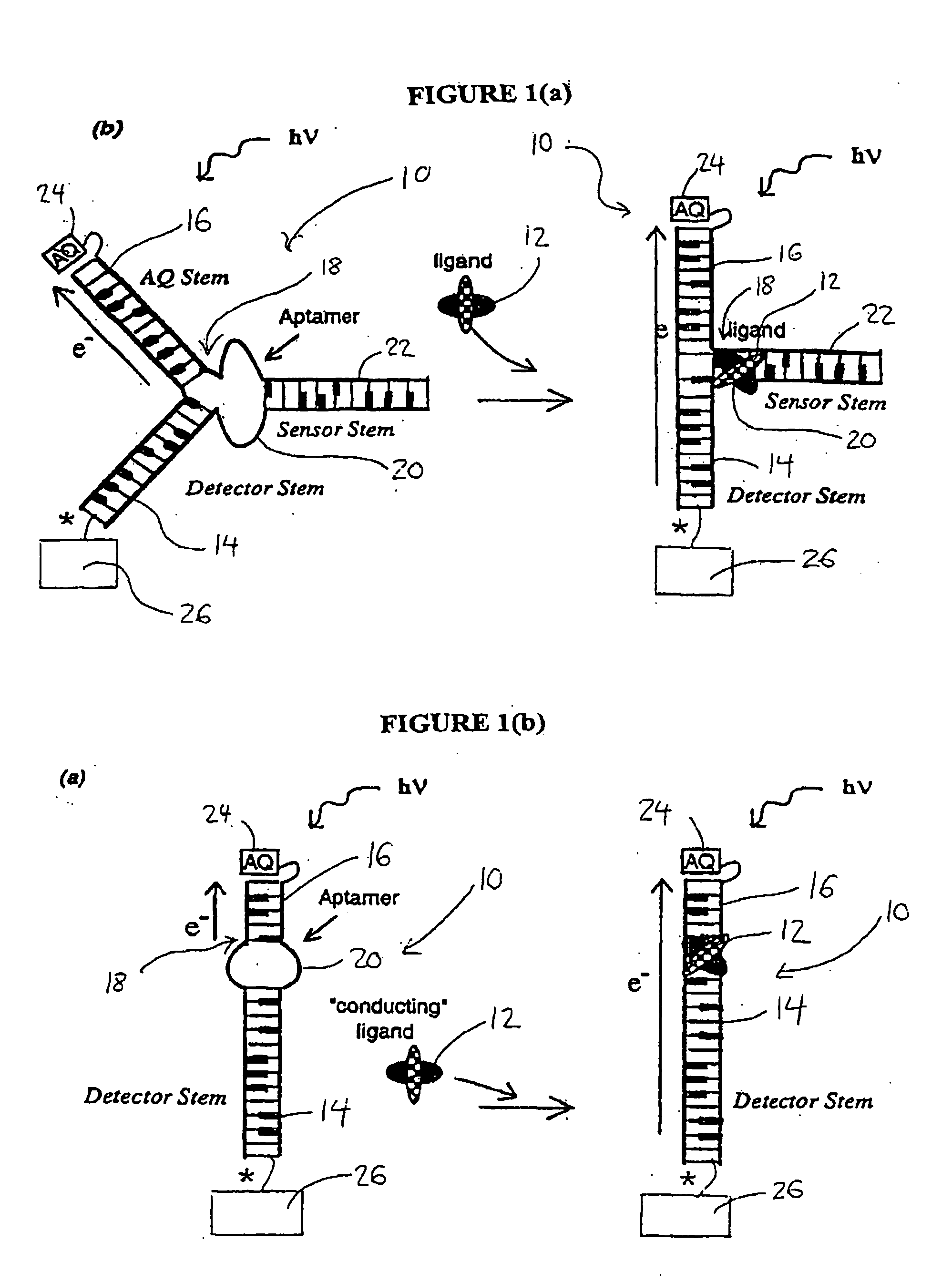
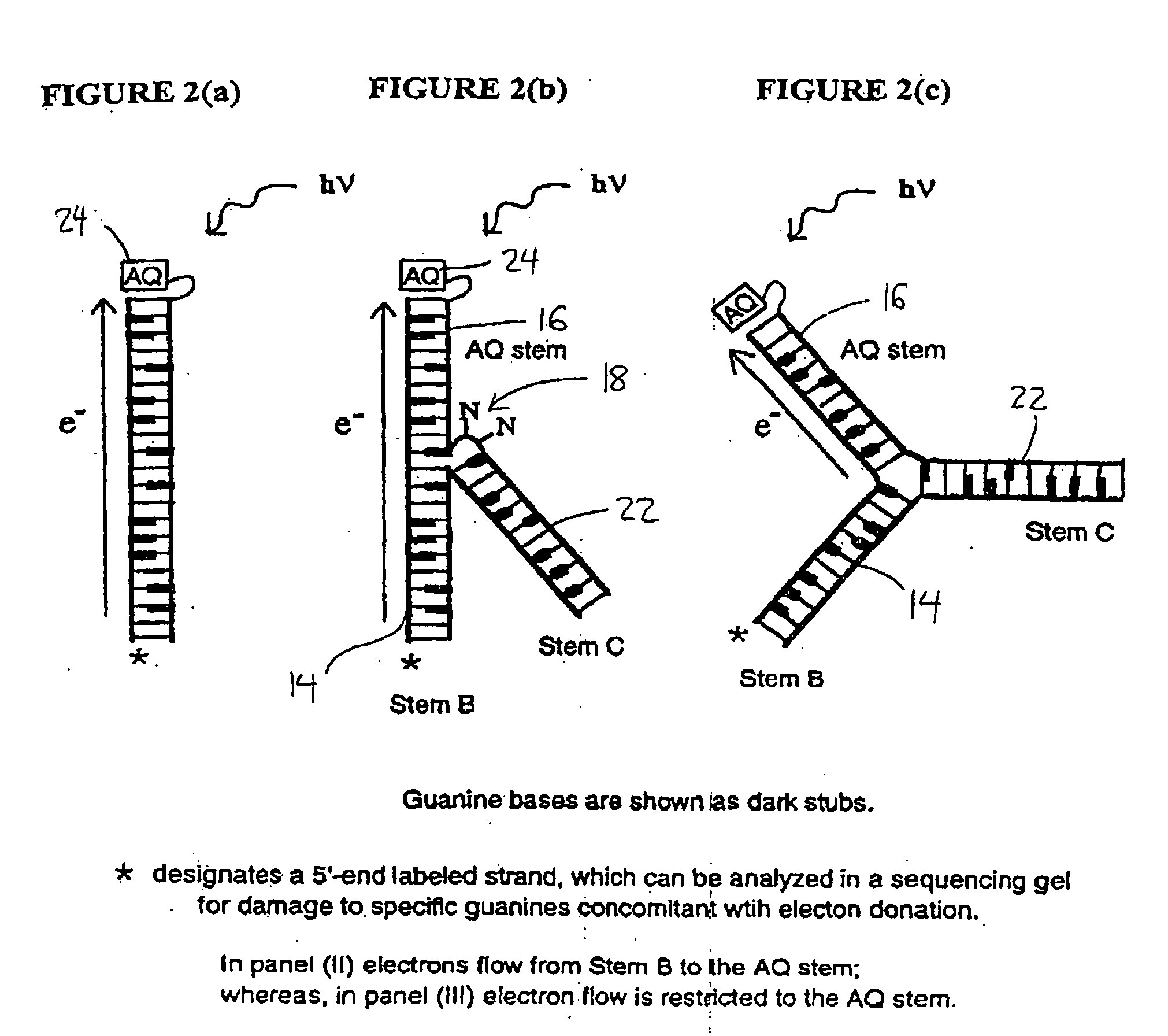
DNA and RNA conformational switches as sensitive electronic sensors of analytes
InactiveUS20080293160A1Removal and lessening of base pairing disruptionEnhanced charge transferSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAdenosineA-DNA
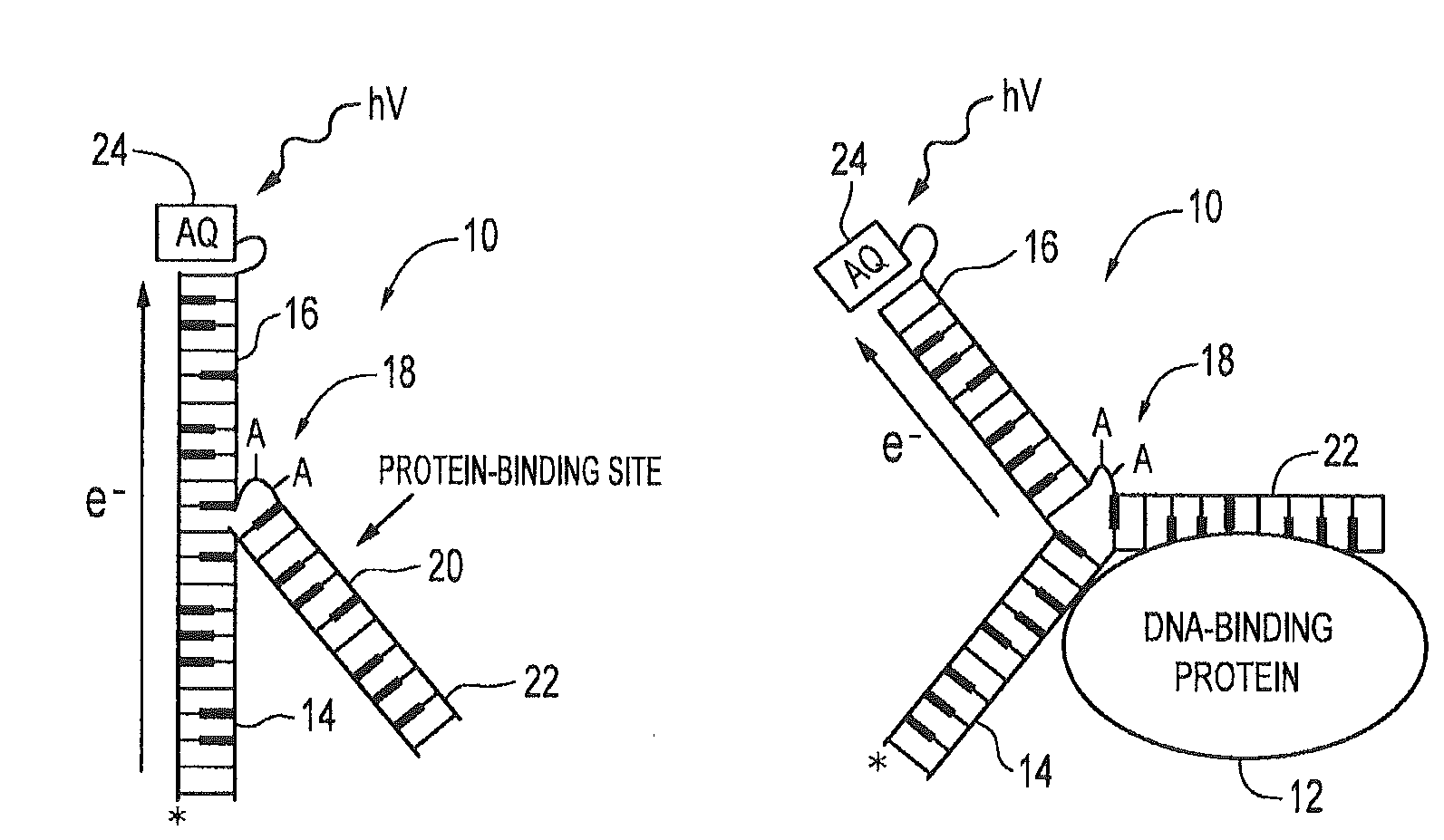
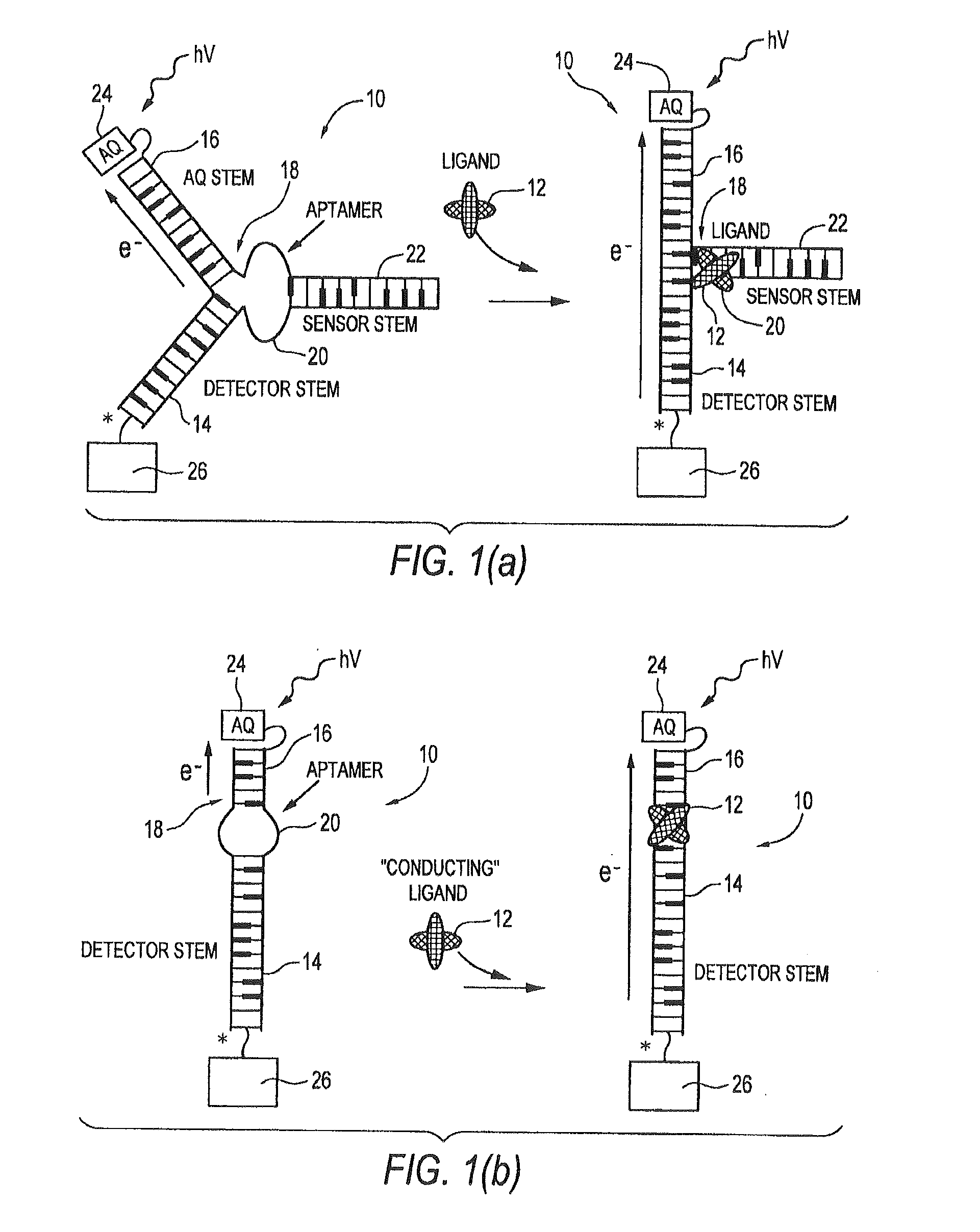
The electrical conductivity of DNA and other oligonucleotide constructs is dependent on its conformational state. Such a dependence may be harnessed for the electronic sensing of external analytes, for instance, adenosine or thrombin. Such a DNA sensor incorporates an analyte receptor, whose altered conformation in the presence of bound analyte switches the conformation, and hence, the conductive path between two oligonucleotide stems, such as double-helical DNA. Two distinct designs for such sensors are described that permit significant electrical conduction through a first or “detector” double-helical stem only in the presence of the bound analyte. In the first design, current flows through the analyte receptor itself whereas, in the second, current flows in a path adjacent to the receptor. The former design may be especially suitable for certain categories of analytes, including heterocycle-containing compounds such as adenosine, whereas the latter design should be generally applicable to the detection of any molecular analyte, large or small, such as the protein thrombin. Since analyte detection in these DNA sensors is electronic, the sensors may be used in rapid and automated chip-based detection of small molecules as well as of proteins and other macromolecules.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY
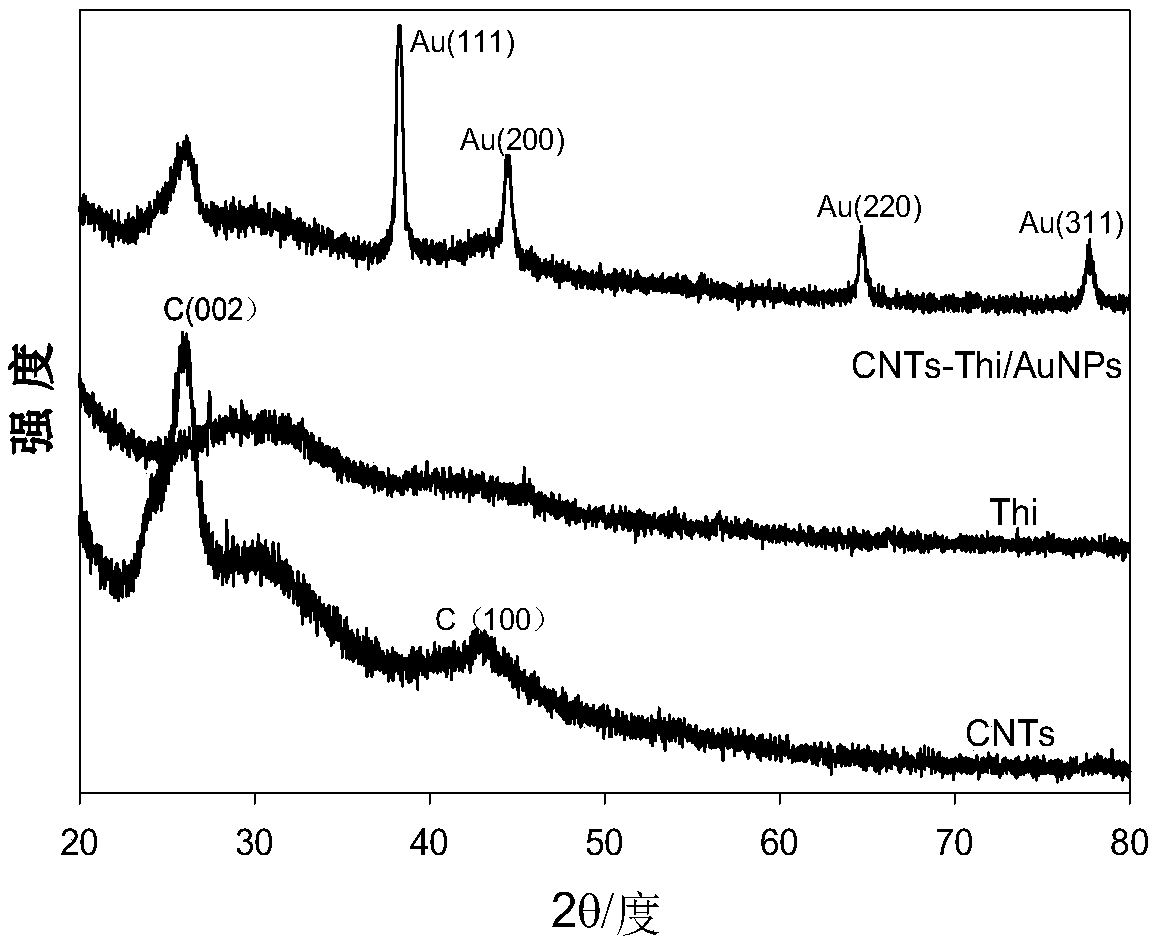
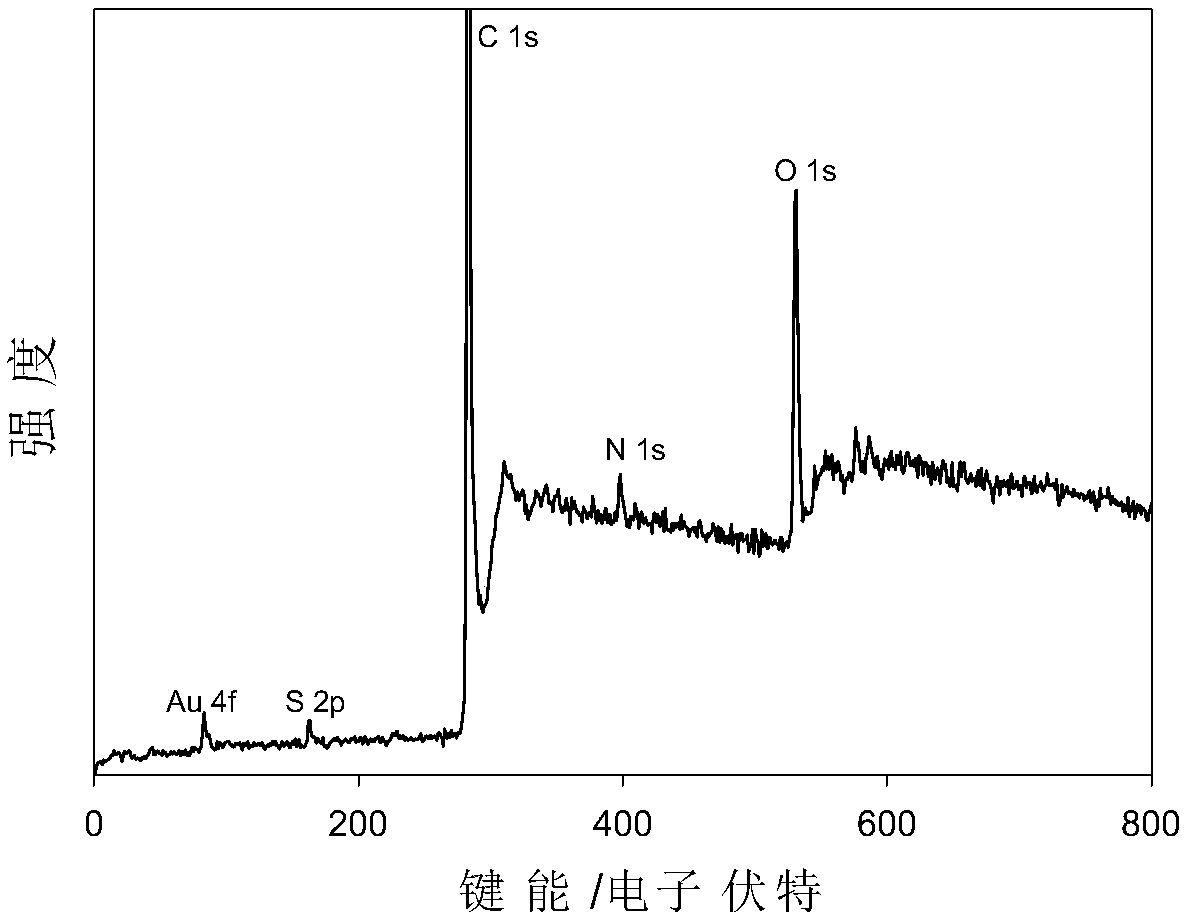
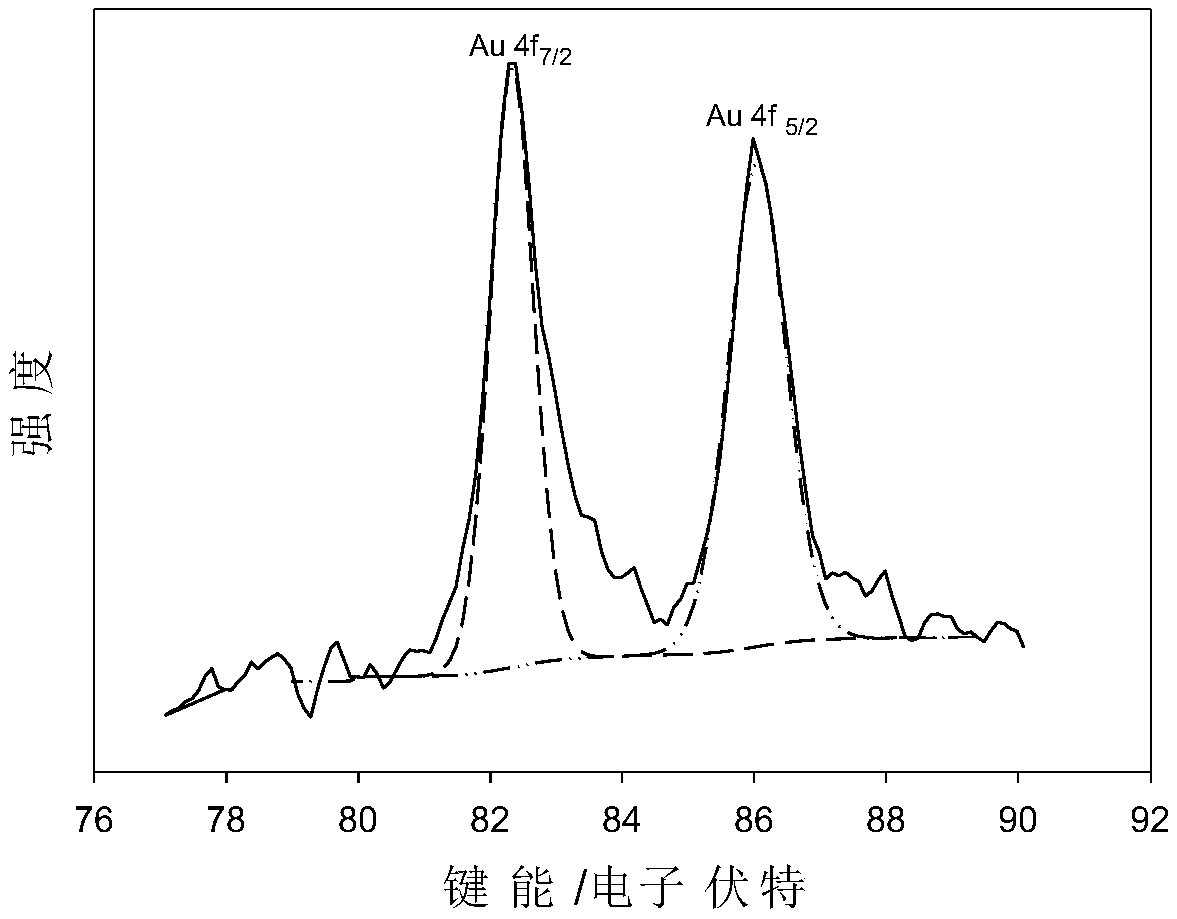
Carbon nanotube-thionine/gold nanoparticle composite material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109604629AImprove conductivityGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingNanoparticle ComplexSupport matrix
The invention discloses a carbon nanotube-thionine / gold nanoparticle composite material and a preparation method thereof. According to the carbon nanotube-thionine / gold nanoparticle composite material, acidified cut short carbon nanotubes and thionine are used as raw materials, and a carbon nanotube-thionine composite with high loading of thionine electrical signal molecules is prepared; and a ternary nanocomposite is prepared by using the carbon nanotube-thionine composite as a support matrix and micro-gold nanoparticles reduced by Au-N and Au-S bonding. The composite material has high conductivity, small gold particle size, uniform dispersion, large specific surface area and high adhesion ability on a substrate. The preparation method of the carbon nanotube-thionine / gold nanoparticle composite material is simple, convenient and easy to operate. The composite material can be used as sensitive electrical signal probes for immunosensors and DNA sensors.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Dna conformational switches as sensitive electronic sensors of analytes
InactiveUS20050205434A1Enhanced charge transferMisalignment and distortionImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteAdenosine
The electrical conductivity of DNA and other oligonucleotide constructs is dependent on its conformational state. Such a dependence may be harnessed for the electronic sensing of external analytes, for instance, adenosine. Such a DNA sensor incorporates an analyte receptor, whose altered conformation in the presence of bound analyte switches the conformation, and hence, the conductive path between two oligonucleotide stems, such as double-helical DNA. Two distinct designs for such sensors are described that permit significant electrical conduction through a first or “detector” double-helical stem only in the presence of the bound analyte. In the first design, current flows through the analyte receptor itself whereas, in the second, current flows in a path adjacent to the receptor. The former design may be especially suitable for certain categories of analytes, including heterocycle-containing compounds such as adenosine, whereas the latter design should be generally applicable to the detection of any molecular analyte, large or small. Since analyte detection in these DNA sensors is electronic, the potential exists for their application in rapid and automated chip-based detection of small molecules as well as of proteins and other macromolecules.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY
Aflatoxin B1 aptamer, DNA sensor, kit and application
ActiveCN105505940ARealize qualitative detectionEasy to carryMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideFluorescence
The invention provides an aflatoxin B1 aptamer, a DNA sensor, a kit and application. The aflatoxin B1 aptamer has the nucleotide sequence as follows: 5'-GTTmmmmmmmTGTTGTCTCTCT GTGTCTnnnnnnnTTCGCTAGGCCCACA-3', each m and n independently are A or T or C or G, and the m chain segment and the n chain segment achieve complementary pairing. According to the aflatoxin B1 aptamer, the DNA sensor, the kit and the application, no large instrument equipment is needed when the aflatoxin B1 is measured, and therefore the cost is low; a constant-temperature reaction is achieved, qualitative detection of naked eyes can be achieved, and quantitative detection can also be achieved; in addition, no fluorochrome is needed, and therefore the cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN KIVITA INNOVATIVE DRUG INST
Preparation method of graphene DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sensor
InactiveCN103630574AImprove conductivityIncreased sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanoparticleCvd graphene
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sensor. The preparation method comprises the steps of 1) growing graphene; 2) connecting gold nanoparticles with the surface of graphene obtained in the step 1); 3) preparing a graphene transistor device from the obtained graphene with the surface connected with the gold nanoparticles; 4) preparing the graphene DNA sensor by connecting the gold nanoparticles on the surface of graphene with DNA.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
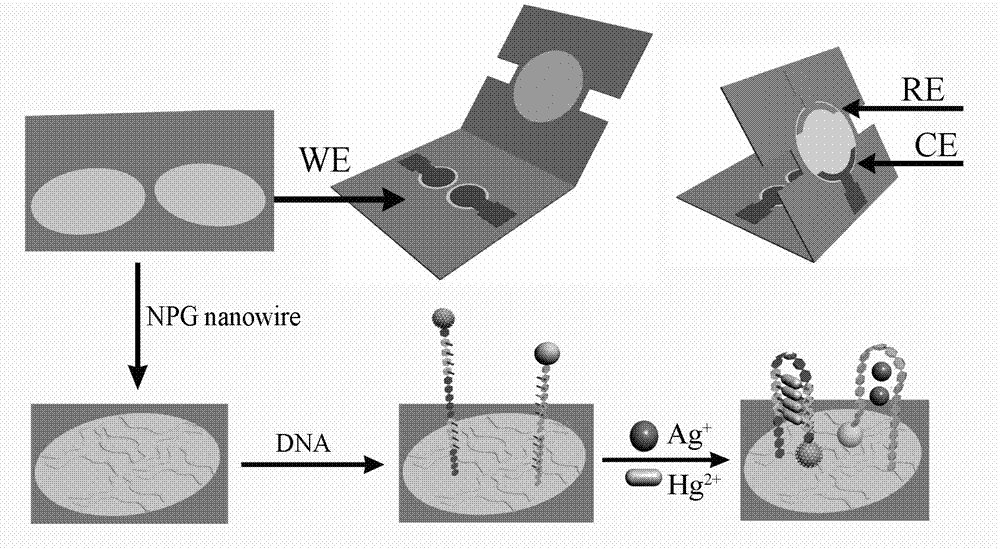
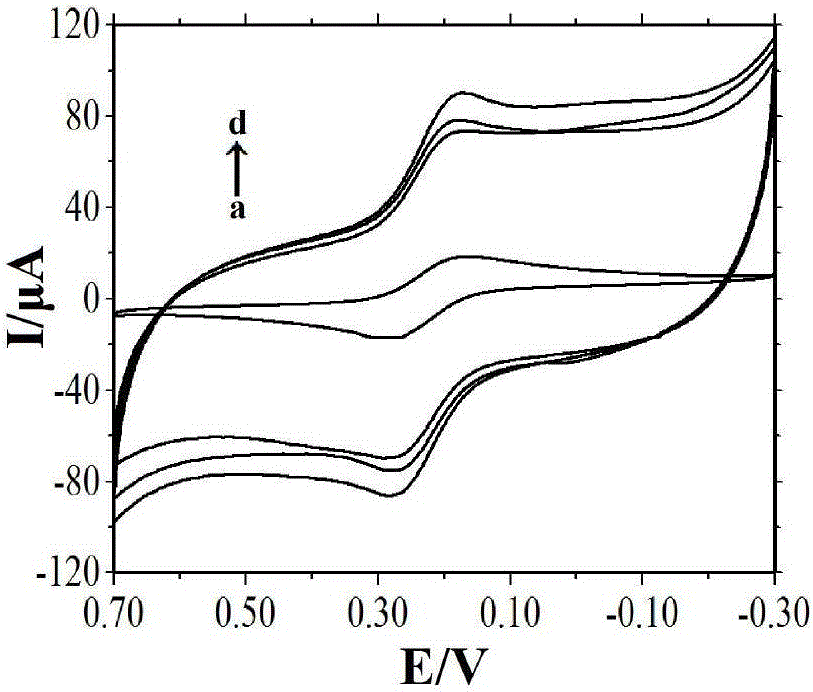
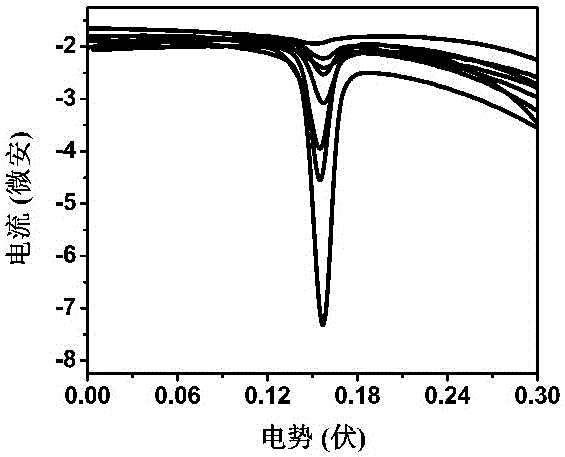
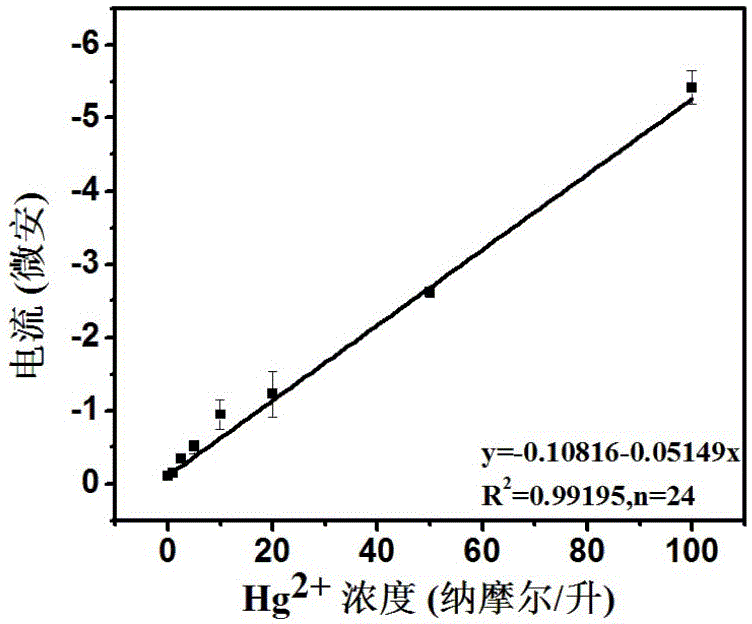
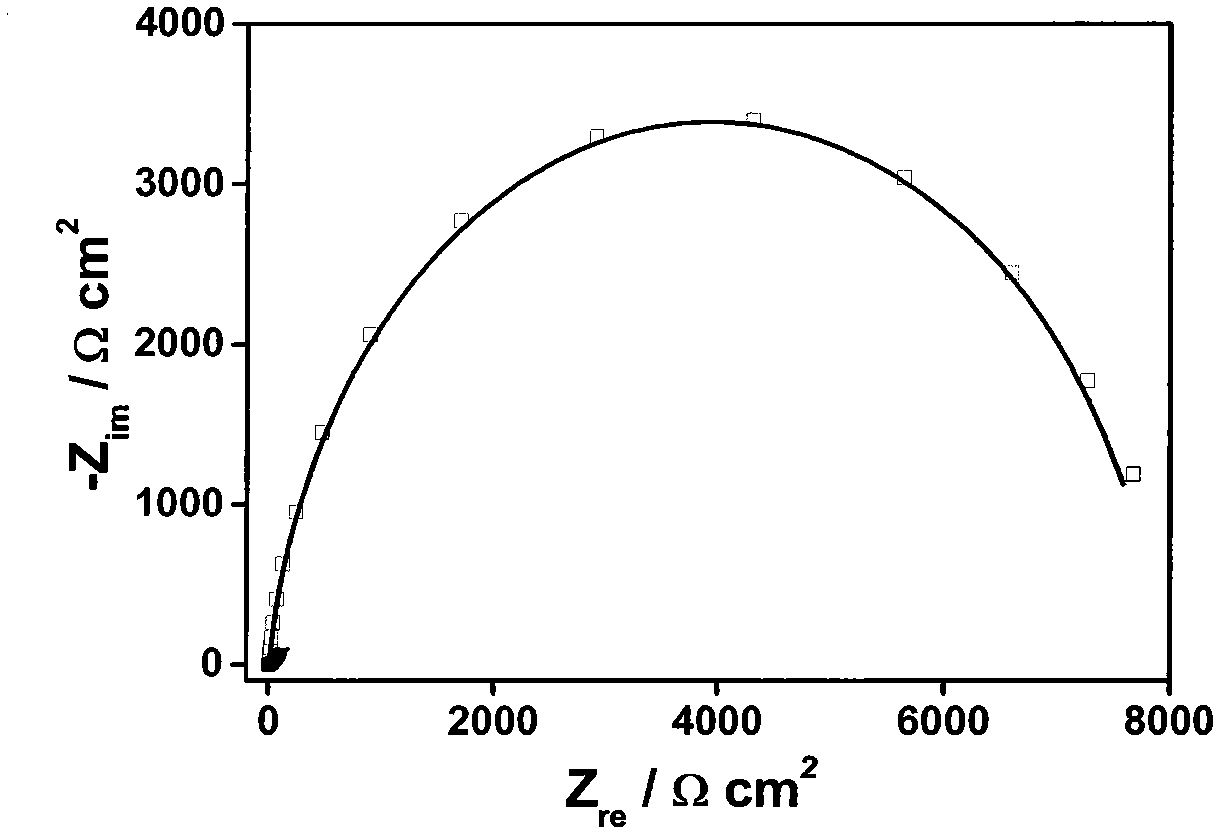
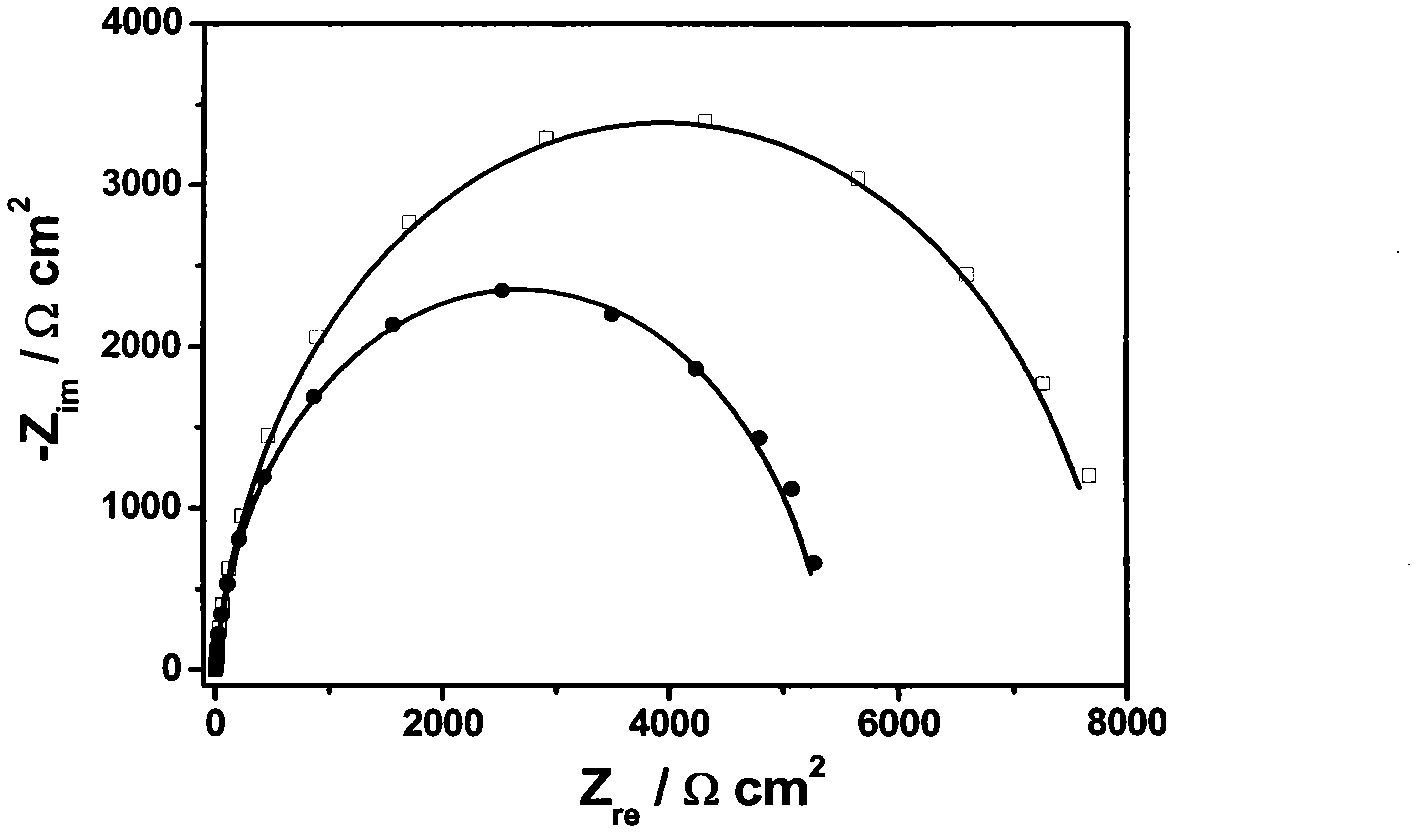
Method for preparing Ag@Au core-shell nano material and method for detecting mercury ions by Ag@Au core-shell nano material
InactiveCN105973971AHigh sensitivityThe detection process is fastMaterial electrochemical variablesNanoparticlePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to the field of detection of mercury ions in environments and particularly relates to preparation of an Ag@Au core-shell structure modified by desoxyribonuclease. The Ag@Au core-shell structure is applied to construction of an electrochemical DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sensor for detecting the mercury ions. According to a method for preparing a Ag@Au core-shell nano material and a method for detecting the mercury ions by the Ag@Au core-shell nano material, the Ag@Au core-shell structure is prepared and nano particles are modified by the desoxyribonuclease; the Ag@Au core-shell structure is used as a label for constructing the electrochemical DNA sensor for detecting heavy metal ions Hg<2+>. The preparation method of the nano material is simple and rapid and is low in cost; the DNA sensor taking the nano material as the label has relatively good selectivity, stability and repeatability.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
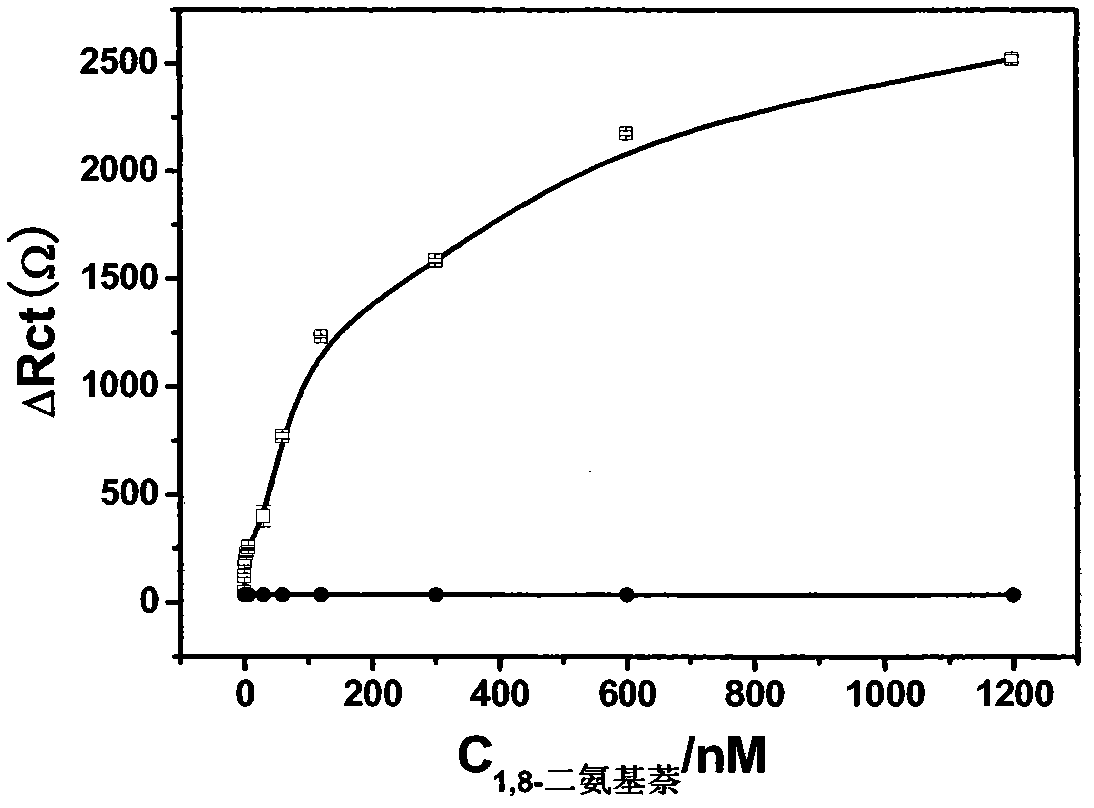
Method for detecting 1,8-diaminonaphthalene based on electrochemical DNA biosensor
InactiveCN102692435AIncreased sensitivityImprove stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical responseSulfur
Disclosed is a method for detecting 1,8-diaminonaphthalene based on an electrochemical DNA biosensor. The invention belongs to the technical field of electrochemical detection and chemical sensors for detecting 1,8-diaminonaphthalene based on a gold electrode modified by hairpin DNA, and relates to preparation of the gold electrode modified by hairpin DNA which has an electrochemical response to the 1,8-diaminonaphthalene and detection of the 1,8-diaminonaphthalene by adopting the electrode. Specifically, the preparation of the gold electrode comprises using hairpin DNA modified by dithio as a raw material, and self-assembling on the gold electrode surface through the action of gold-sulfur bonds to prepare the electrode modified by the hairpin DNA. Changes in impedance of a DNA film are caused by interaction between the electrode modified by the hairpin DNA and the 1,8-diaminonaphthalene, and detection of 1,8-diaminonaphthalene can be carried out according to responded changes in the impedance. A method for preparing the DNA biosensor of the invention has the advantages of mild conditions, simplicity and convenience, good stability, high sensitivity and simple operation.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
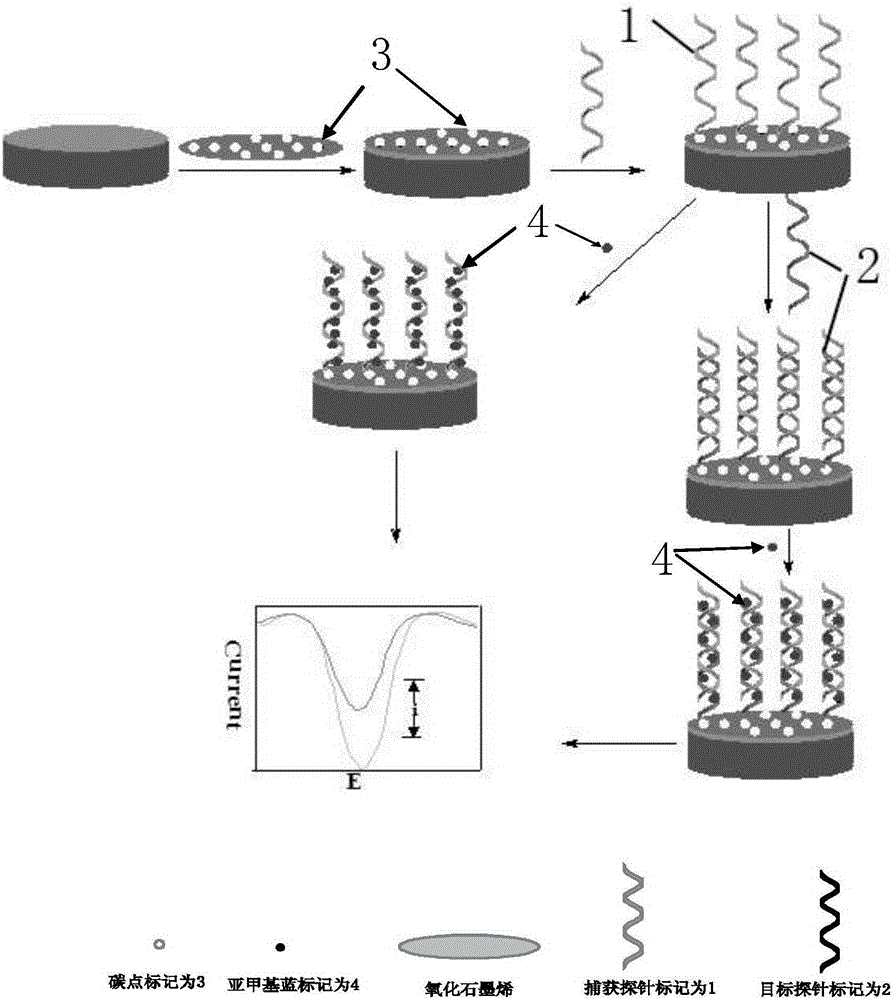
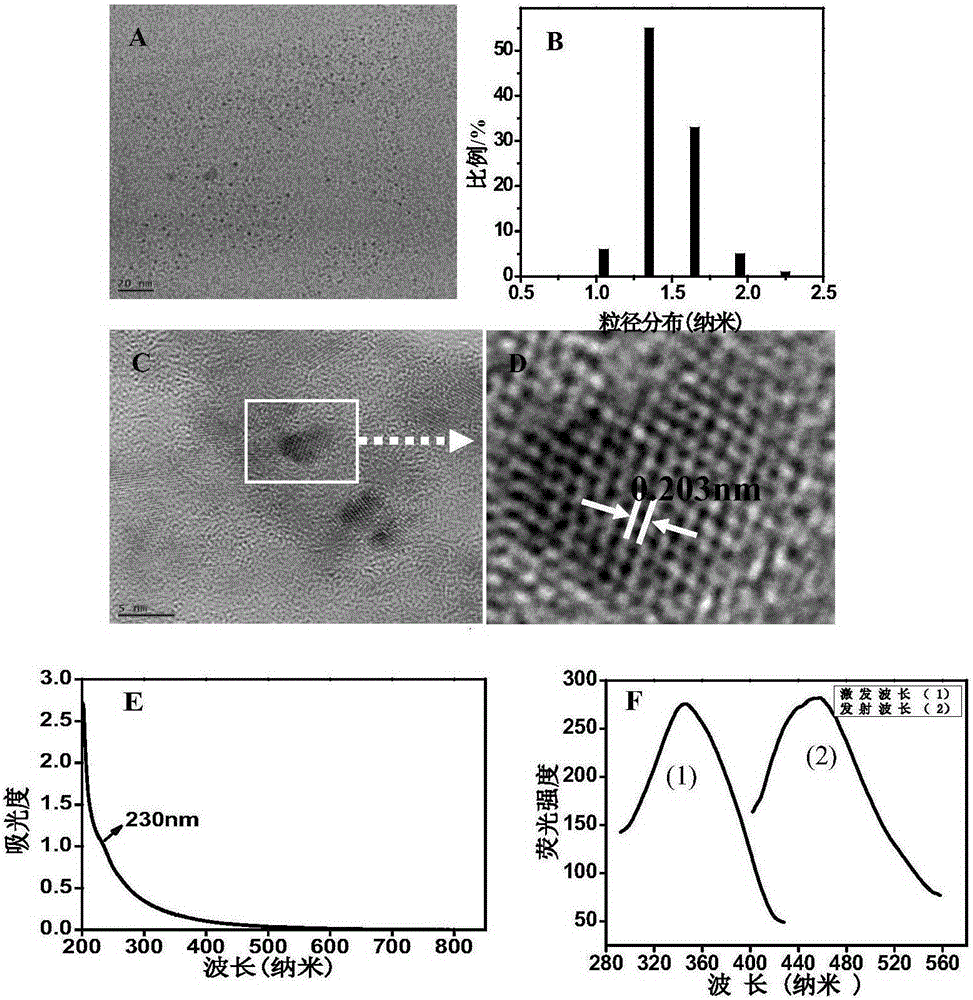
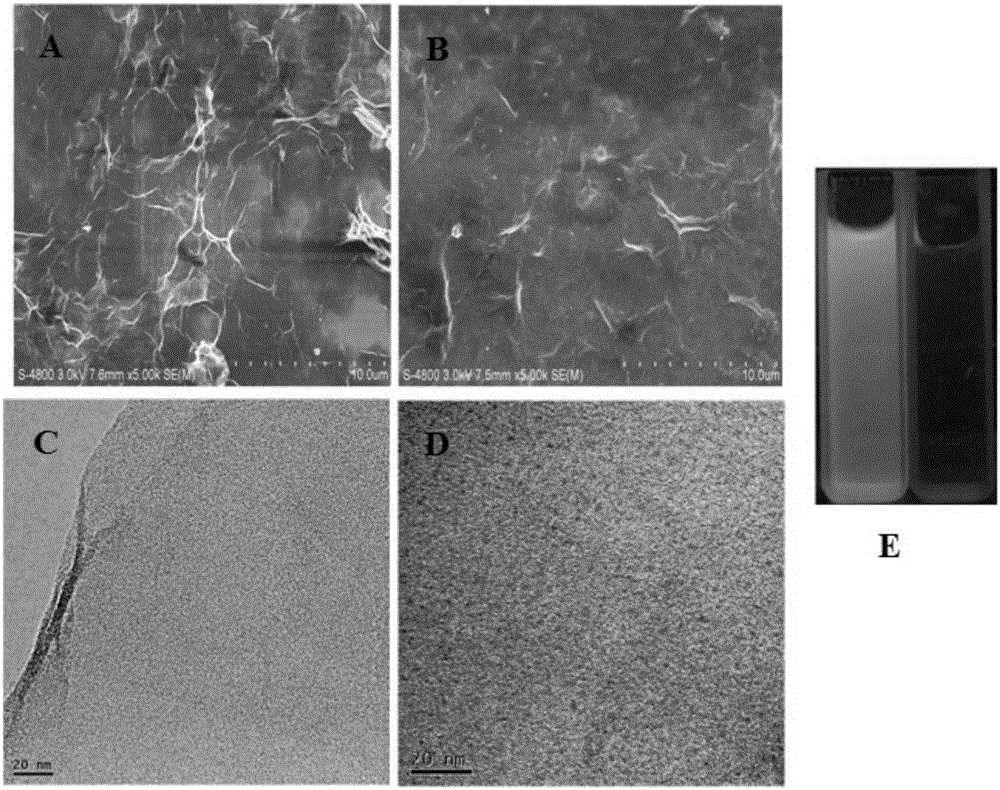
Method of testing PML/RAR alpha genes through electrochemical biosensor of carbon dot @ graphene oxide composite material
InactiveCN105334253AIncrease loadImprove transfer abilityMaterial electrochemical variablesSolution hybridizationElectrochemical biosensor
The invention discloses a method of testing PML / RAR alpha genes through an electrochemical biosensor of a carbon dot @ graphene oxide composite material. The method comprises the steps that (1) a specific probe is designed according to a gene segment to be tested, wherein the PML / RAR alpha fusion genes of acute promyelocytic leukemia are used as an example; (2) capture probes are self-assembled on the C-dots @ GO / GCE surface through amido bonds, and after hybridization of a DNA electrochemical sensor formed with methylene blue (MB) as the electrochemical hybridization indicator with a solution to be tested, whether the solution to be tested contains the PML / RAR alpha fusion genes or not is judged according to difference of electrical signals. The C-dots @ GO nanocomposite prepared through the method has good electrical conductivity, and abundant carboxyl on the GO surface can increase the number of the capture probes; the DNA sensor formed on such basis has the advantages of good selectivity and high sensitivity.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Vibrio DNA electrochemical sensor and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109142477AImproving Performance in Detection of Vibrio Characteristic DNAHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesHemolysisVibrio DNA
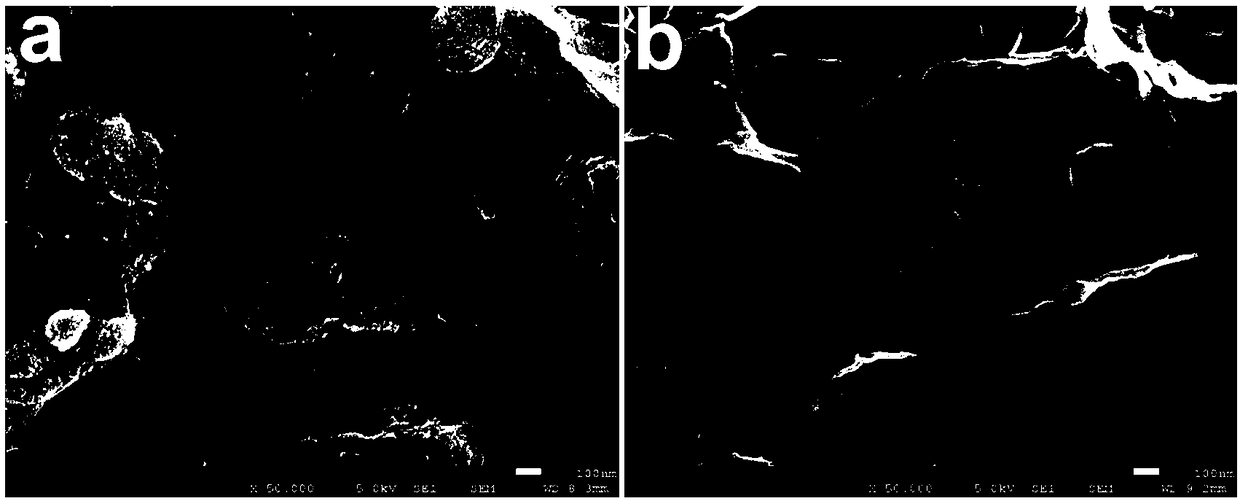
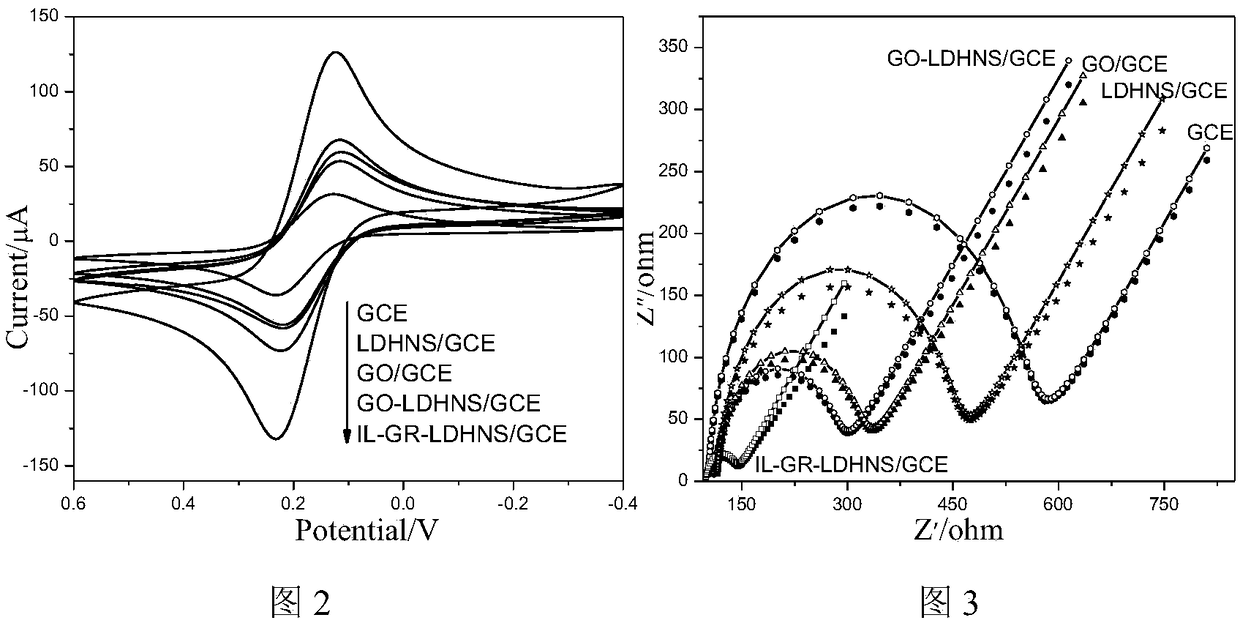
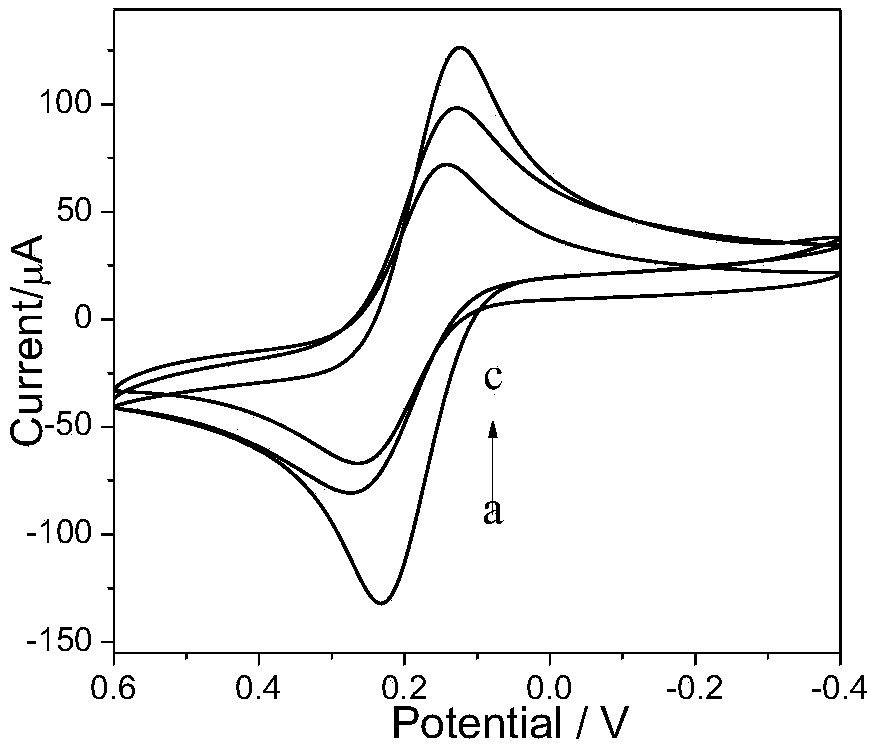
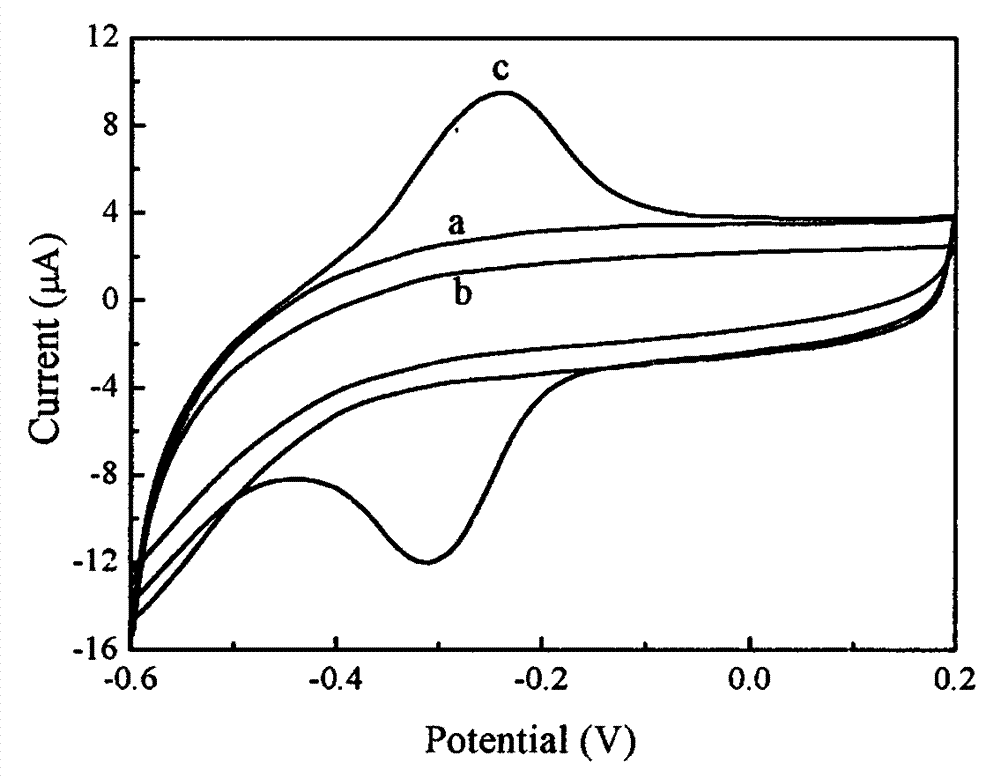
The invention discloses a vibrio DNA electrochemical sensor and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the steps that graphene oxide is stripped in a N,N-dimethyl formamidesolution containing amino ion liquid, and ion liquid functional graphene is prepared; then, hydrotalcite nano-sheets are prepared in the dispersion solution, an ion liquid functional graphene-like-hydrotalcite nano-sheets composite is prepared, a drip coating method is adopted for preparing a glass carbon electrode modified by the compound, a vibrio probe ssDNA is fixed to the surface of the modified electrode through a biologic connecting agent, and the vibrio DNA sensor is prepared. The DNA sensor has the good sensitivity and selectivity, the low detection limit and the side linear range. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing the modified electrode material, preparing the electrochemical auxiliary hemolysis vibrio DNA sensor, hybridizing the electrochemical auxiliary hemolysis vibrio DNA sensor with target DNA, and performing sensor electrochemical signal detection.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
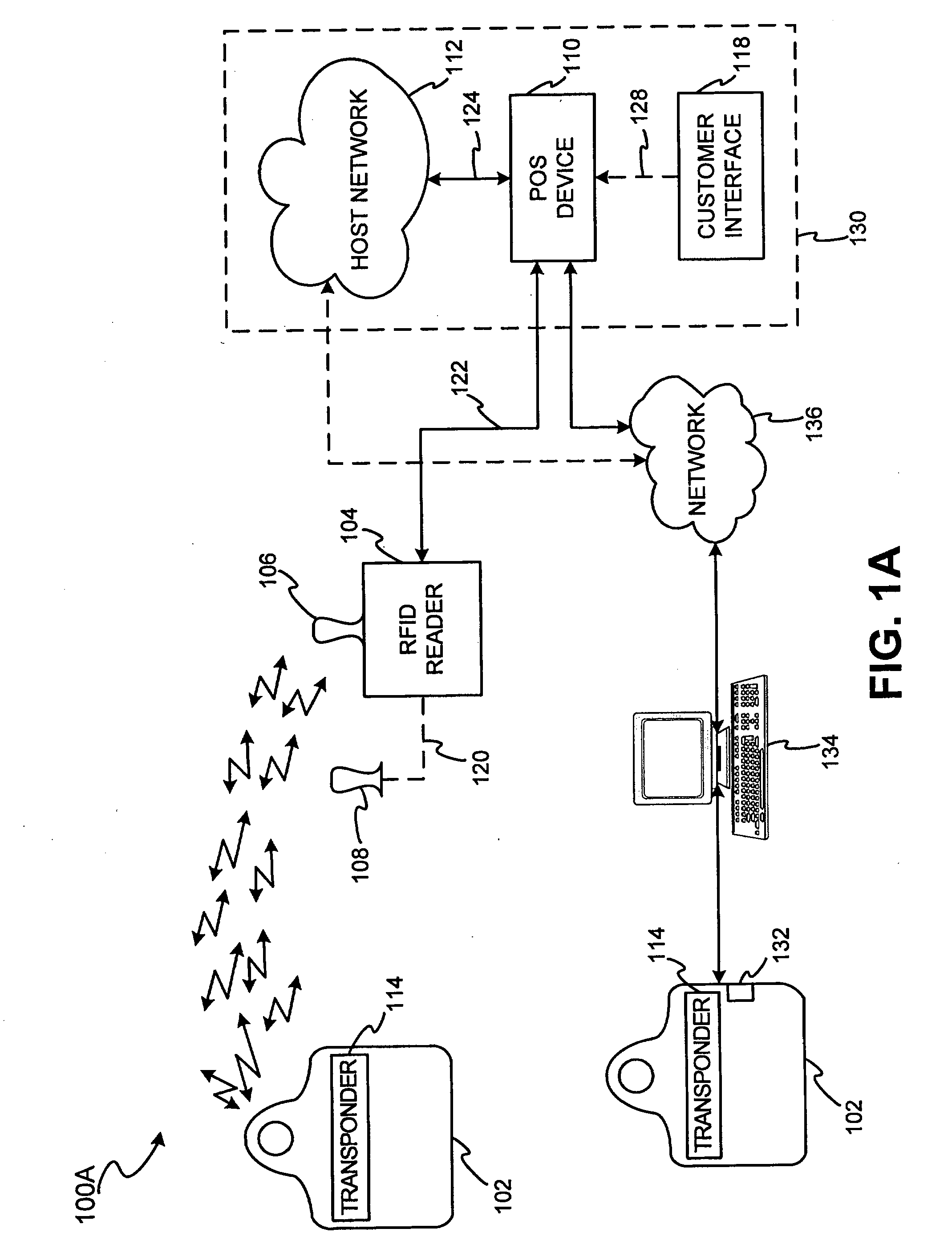
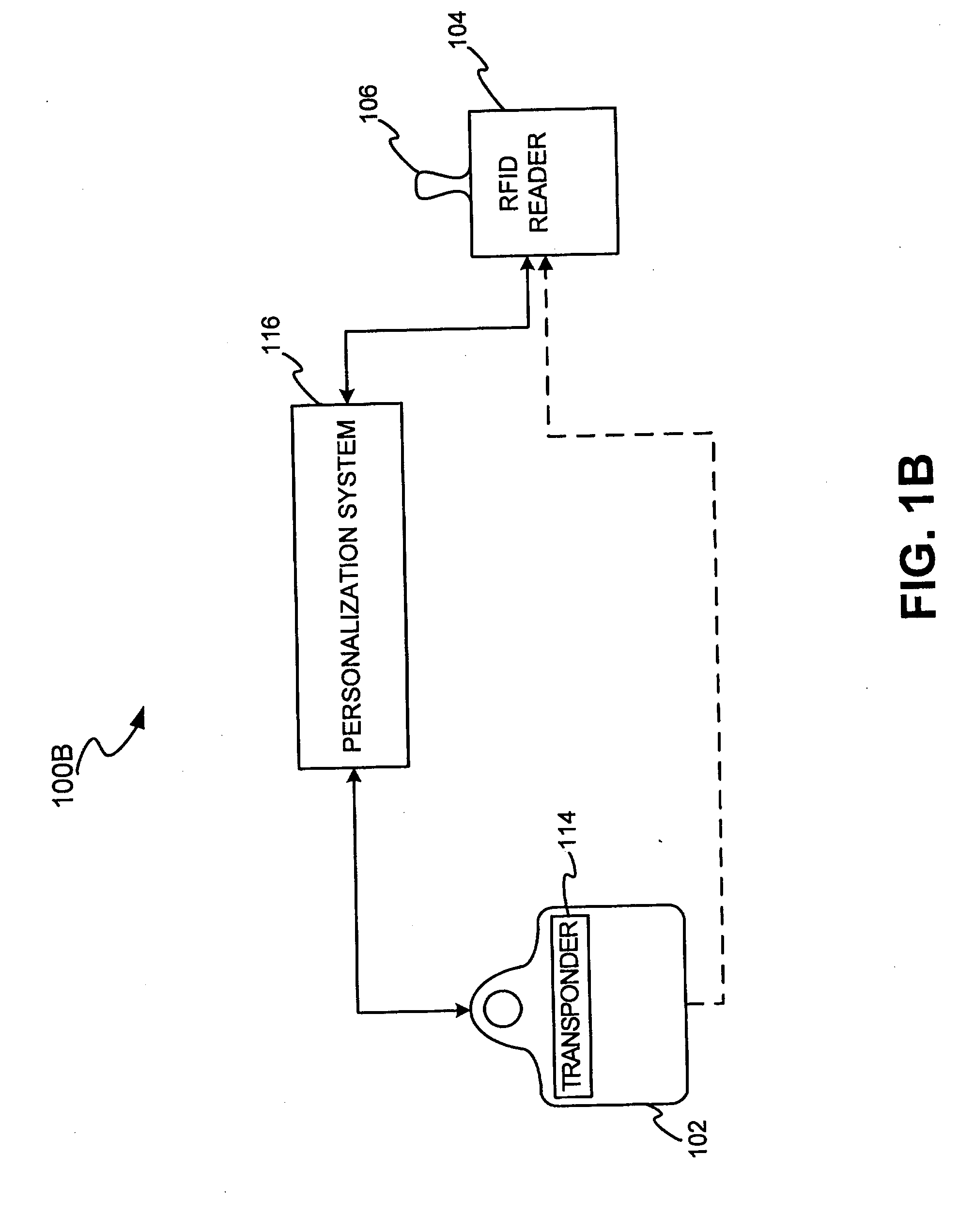
DNA sample data in a transponder transaction
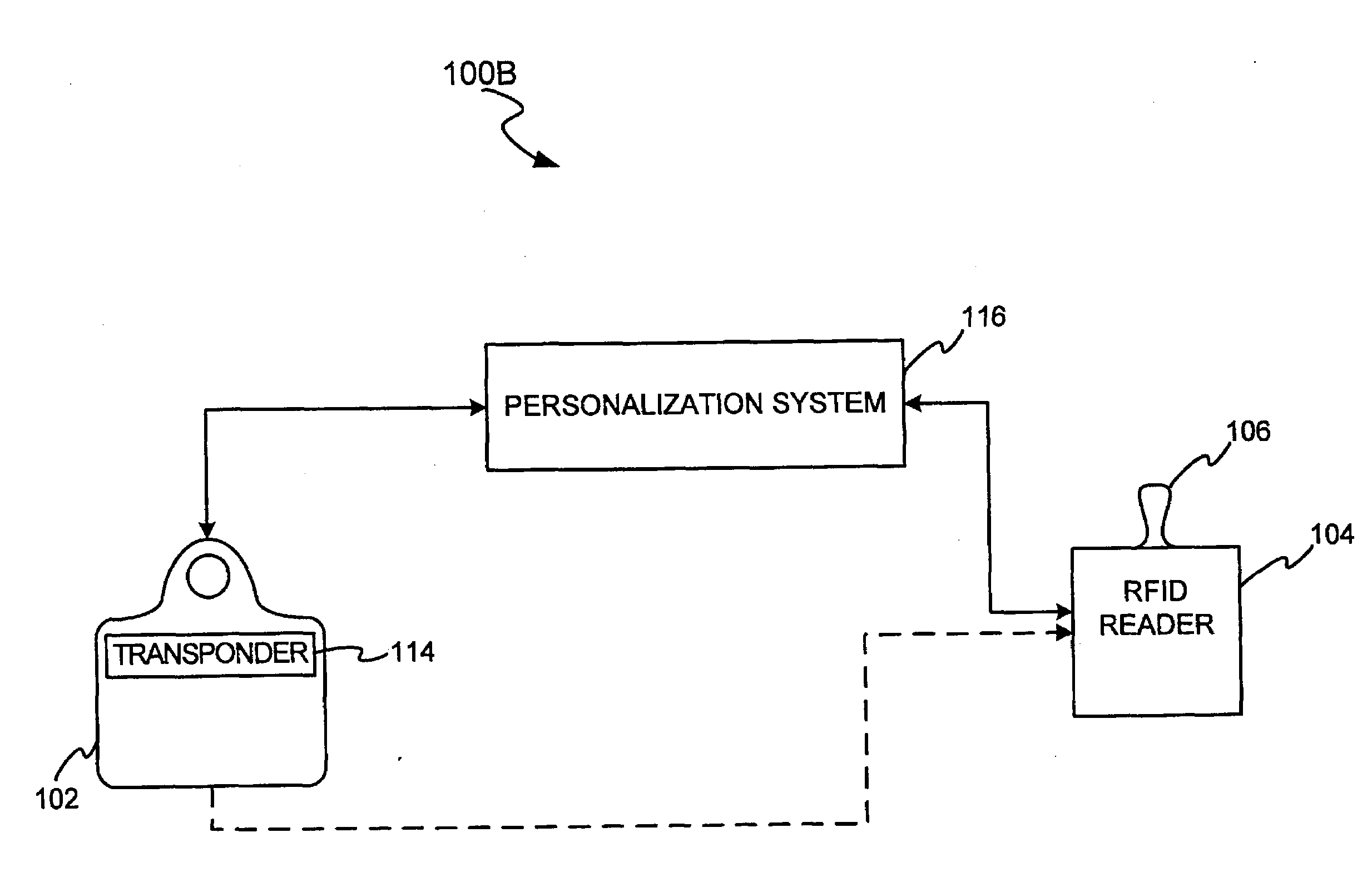
InactiveUS20090079546A1Easy to completeLimited accessCo-operative working arrangementsIndividual entry/exit registersAuthorizationDNA
The present disclosure relates to the use of DNA sample data as part of a biometric security system in a transponder transaction. The biometric security system also includes a DNA sensor that detects biometric samples, and a device for verifying biometric samples. In one embodiment, the biometric security system includes a transponder configured with a DNA sensor. In another embodiment, the system includes a reader configured with a DNA sensor. In yet another embodiment, the present invention discloses methods for proffering and processing DNA samples and DNA sample data to facilitate authorization of transactions.
Owner:LIBERTY PEAK VENTURES LLC
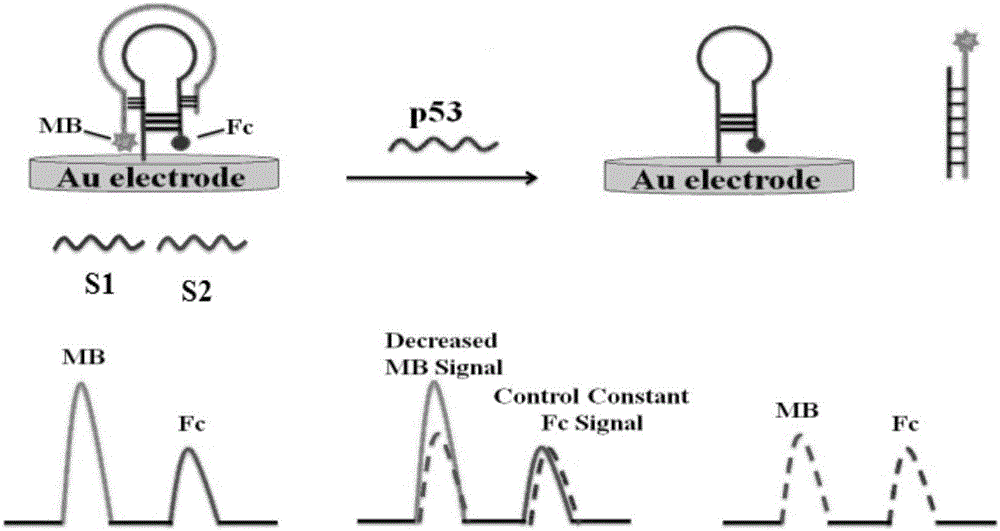
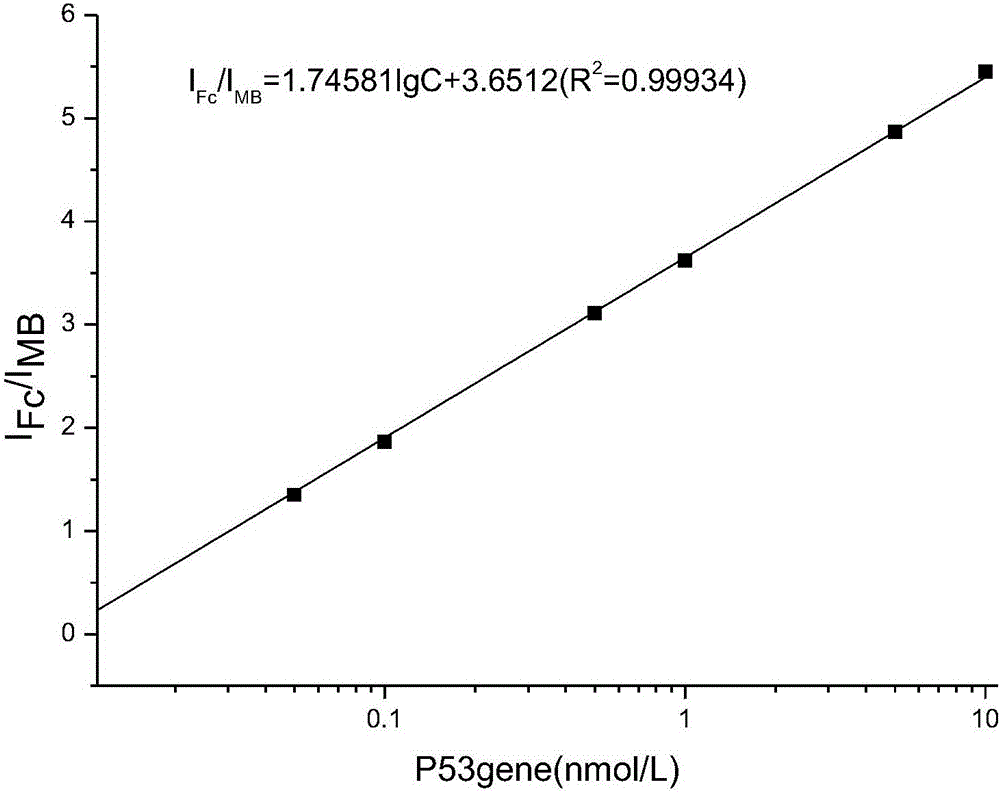
Ratio electrochemical DNA sensor-modified electrode for detecting gene P53 and preparation method of modified electrode
ActiveCN106434903ASimple methodSimple reaction conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorSingle strand dna
The invention relates to the technical field of electrochemical detection, and particularly discloses a modified electrode for detecting a tumor suppressor gene P53 and a preparation method of the modified electrode. A probe for detecting the gene P53 is composed of a single-stranded DNA auxiliary probe S1 and a single-stranded DNA capturing probe S2, wherein the DNA strand sequence of the S1 is 5'-Fc-CTC TCA GTG ATT TTT TTA GTG AGA GAG-(CH2)6-SH-3', and the DNA strand sequence of the S2 is 5'-MB-TCA CTG AGT CTT CCA GTG TGA TGA TCA CT-3'. According to the method, preparation is easy, control is convenient, the use cost is low, and compared with the methods such as capillary electrophoresis, denaturing high performance liquid chromatography, denaturing gel gradient electrophoresis and a yeast-separated allele function analysis technique, the electrochemical biosensor mode has the advantages that samples do not need to be pretreated, control is easy, the reaction conditions are simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Livestock and poultry housing spraying system
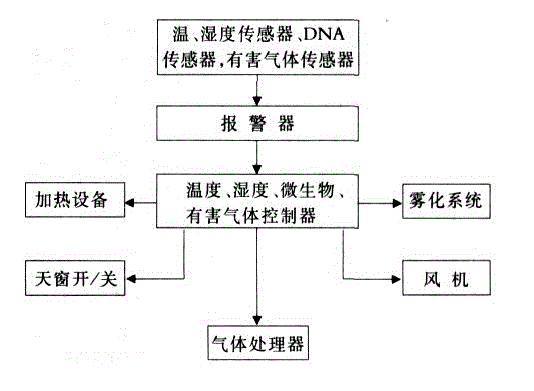
InactiveCN104642145APromote atomizationFacilitated DiffusionDispersed particle separationAnimal housingEngineeringMoisture sensor
The present invention discloses a spraying system, particularly a livestock and poultry housing spraying system. The spraying system comprises components as follows: temperature and humidity sensors, a DNA sensor, a harmful gas sensor, an alarm, temperature, humidity, microbes and harmful gas controllers, heating equipment, pulverization system, dormer window switch, fans and gas processors. The spraying system is operated in a full automatic mode. The spraying system can adjust the contents of various factors in livestock and poultry housing according to the feedback information from the sensors, start the pulverization device to perform cooling, disinfecting and immunizing, and start the ventilation device to realize ventilation.
Owner:GOLDENEST MACHINERY MFG QINGDAO
Ionic liquid functional graphene vibrio DNA electrochemical sensor and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109085222AGood choiceLow detection limitMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCovalent modificationIonic liquid
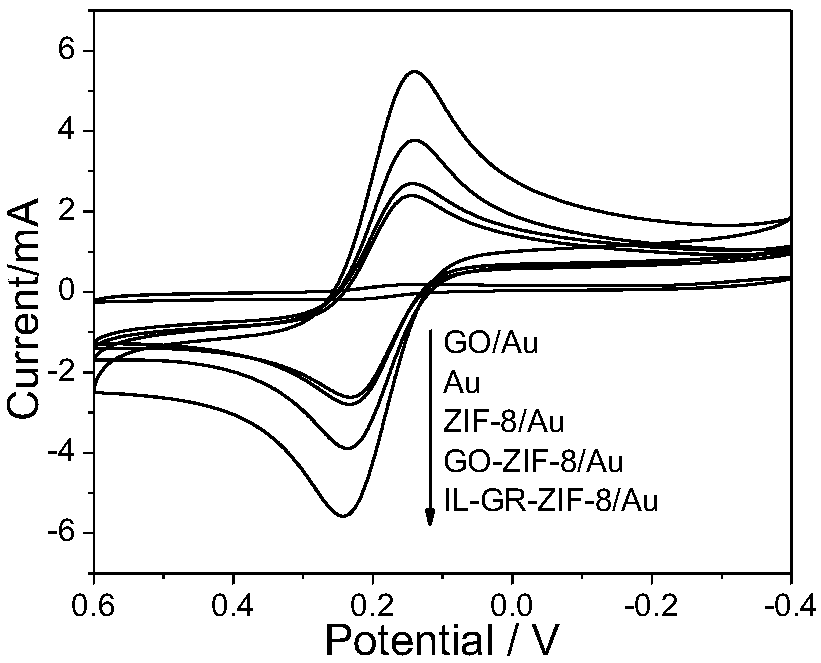
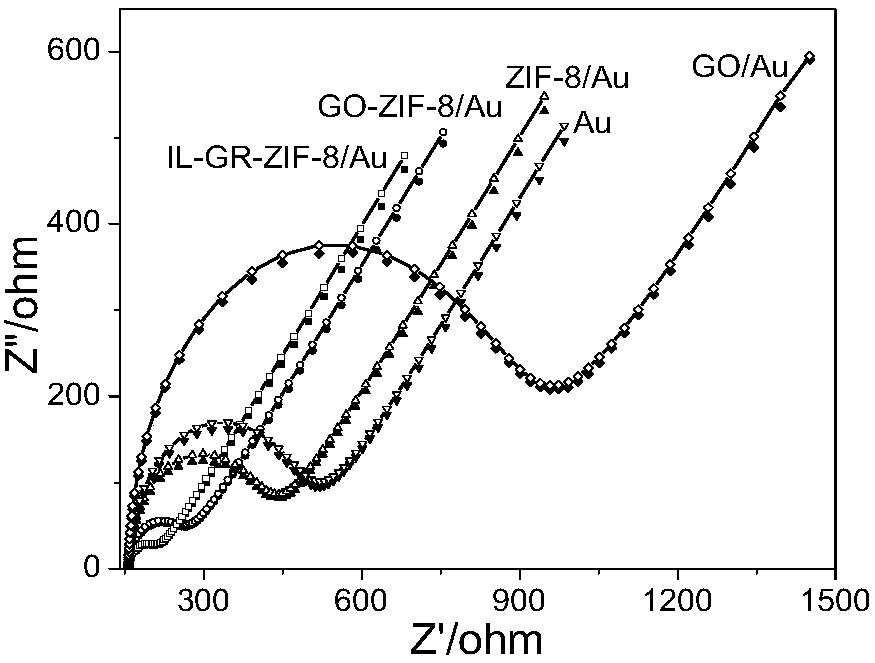
The invention discloses an ionic liquid functional graphene vibrio DNA electrochemical sensor and a preparation method and application thereof. Firstly, ZIF-8 is prepared in graphene oxide dispersion;then a graphene-ZIF-8 compound is subjected to covalent modification by amino functional ionic liquid to prepare an ionic liquid functional graphene-ZIF-8 compound; a gold electrode modified by the compound is prepared by a dispensing method; and then vibrio probe ssDNA is fixed on the surface of the modified electrode by a biological linker so as to prepare the vibrio DNA sensor. The DNA sensorhas excellent sensitivity and selectivity, a low detection limit and a wide linear range. The preparation method comprises: preparation of an electrode modification material; preparation of an electrochemical vibrio parahaemolyticus DNA sensor; hybridization of the electrochemical vibrio parahaemolyticus DNA sensor and target DNA; and sensor electrochemical signal detection. The sensor is simple in operation method and has potential application value.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of electrochemical bladder cancer DNA sensor
InactiveCN104297314AIncreased sensitivityGood choiceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBladder cancer cellN-Hydroxysuccinimide
According to the technical scheme of an electrochemical bladder cancer DNA sensor, carboxylation is carried out on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode by an electrochemical method, and a bladder cancer cell specific DNA probe is assembled on the glassy carbon electrode to prepare the bladder cancer DNA sensor. The glassy carbon electrode is a base electrode, and electrode carboxylation and probe single-stranded DNA assembling are successively carried out. By electrode carboxylation, the probe DNA is fixed. The probe DNA is an recognition element, and a biological bridging agent is 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl)carbodiimide and N-hydroxy succinimide. The preparation method is characterized in that the electrochemical bladder cancer DNA sensor with high sensitivity is obtained. The sensor has high sensitivity, high stability and good selectivity, and testing results of the sensor are better than those of a traditional DNA detection method. The preparation method comprises: 1, preparation of the electrochemical bladder cancer DNA sensor; 2, hybridization of the electrochemical bladder cancer DNA sensor and a target DNA; and 3, electrochemical signal detection of the sensor. The sensor has a simple operation method and is convenient for practical popularization and application.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com