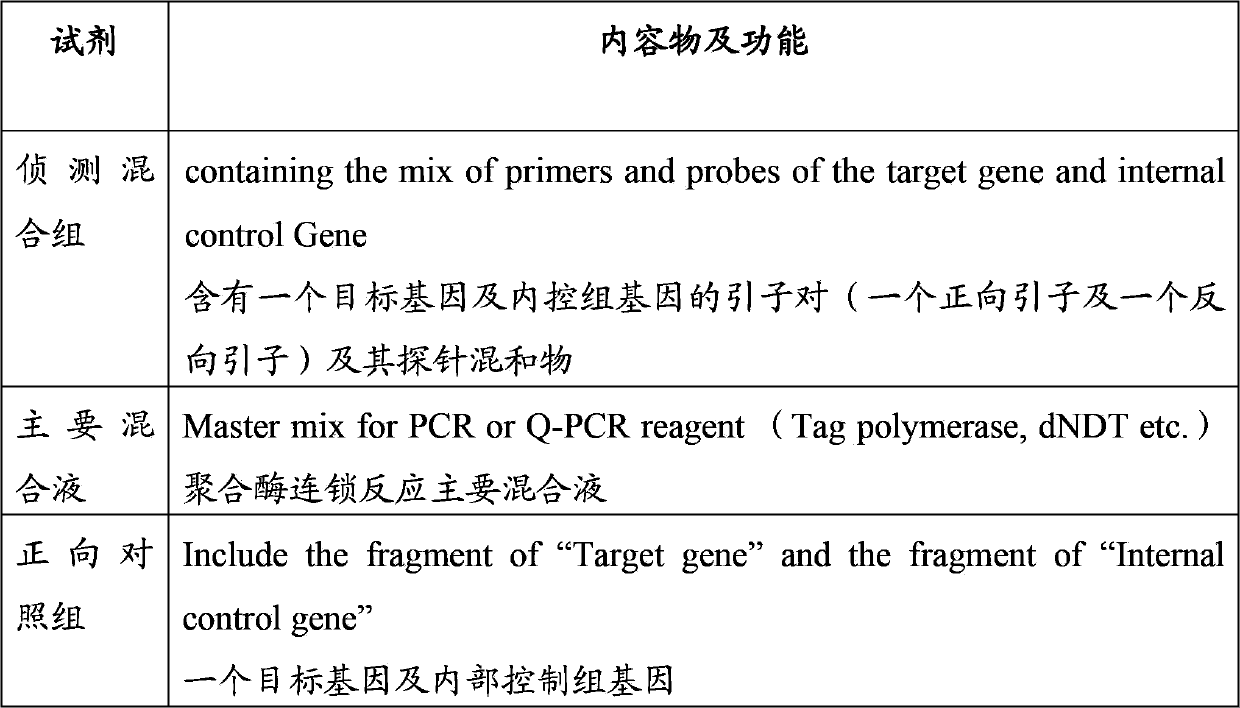
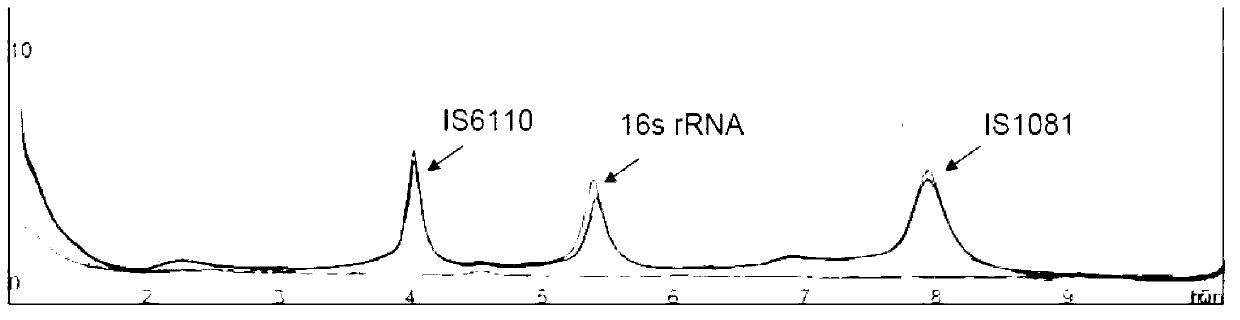
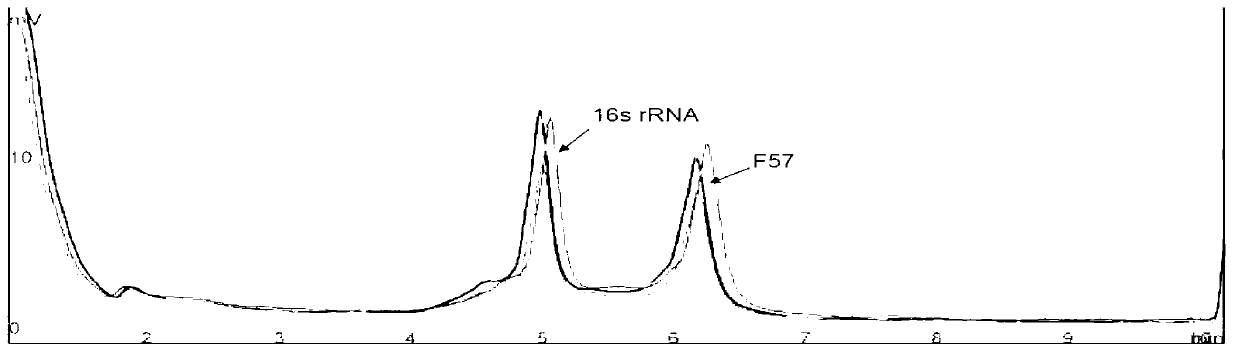
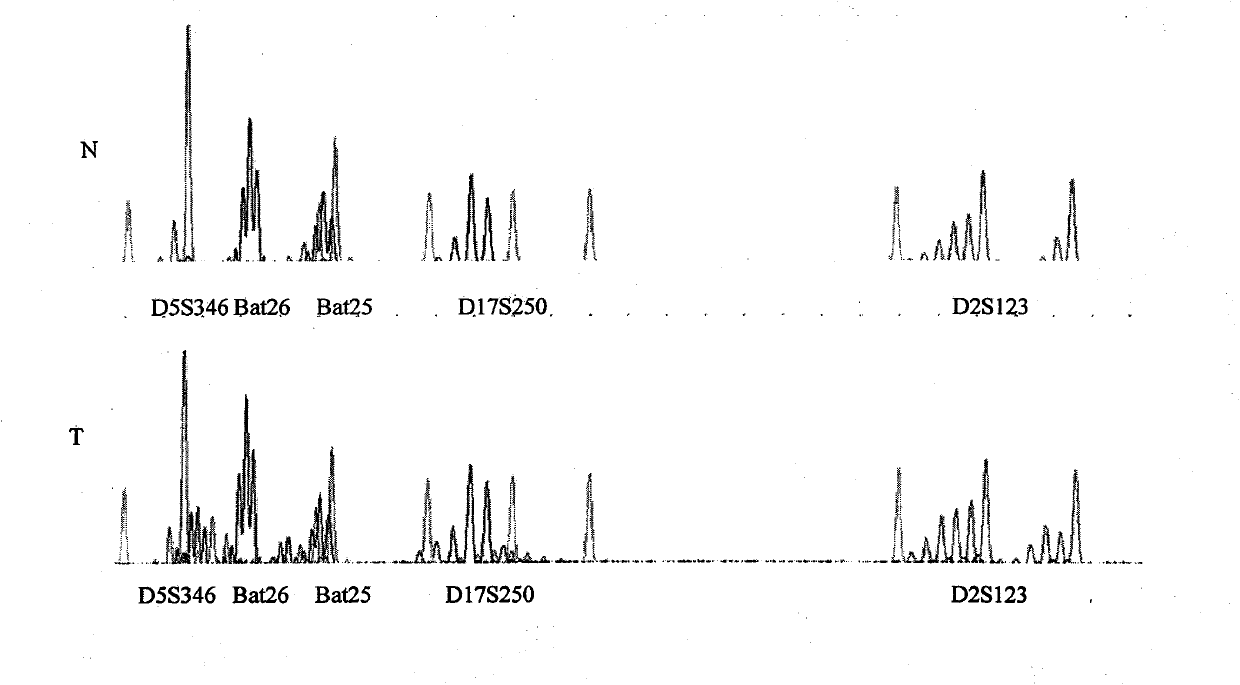
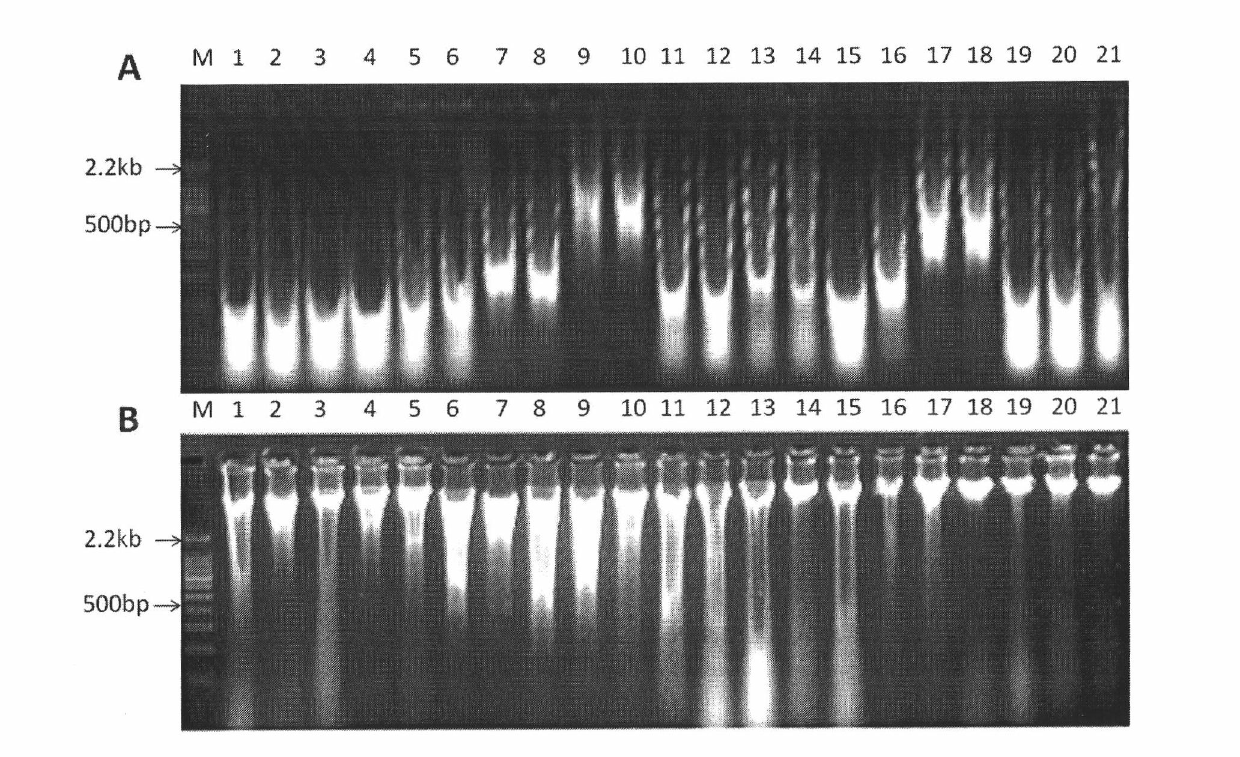
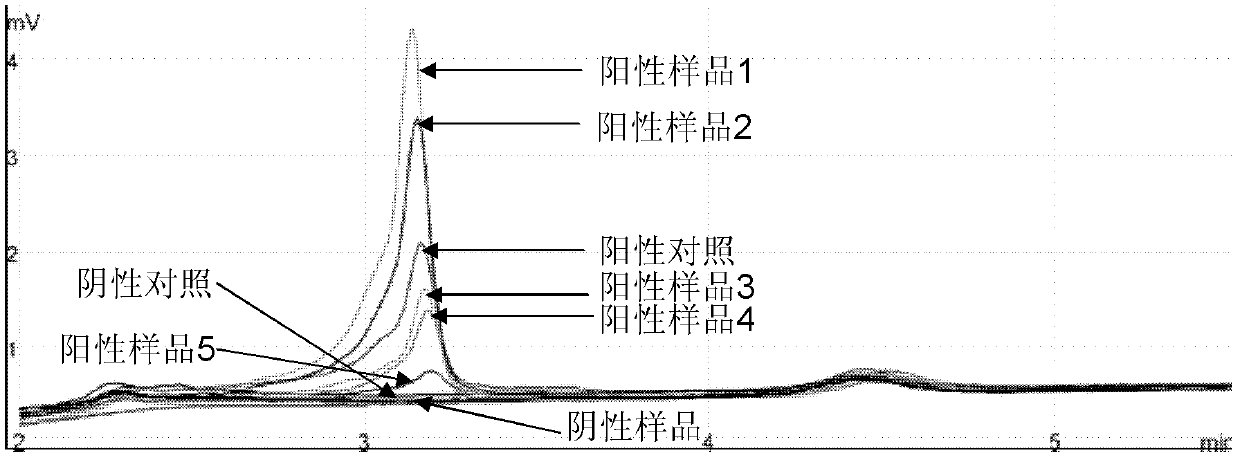
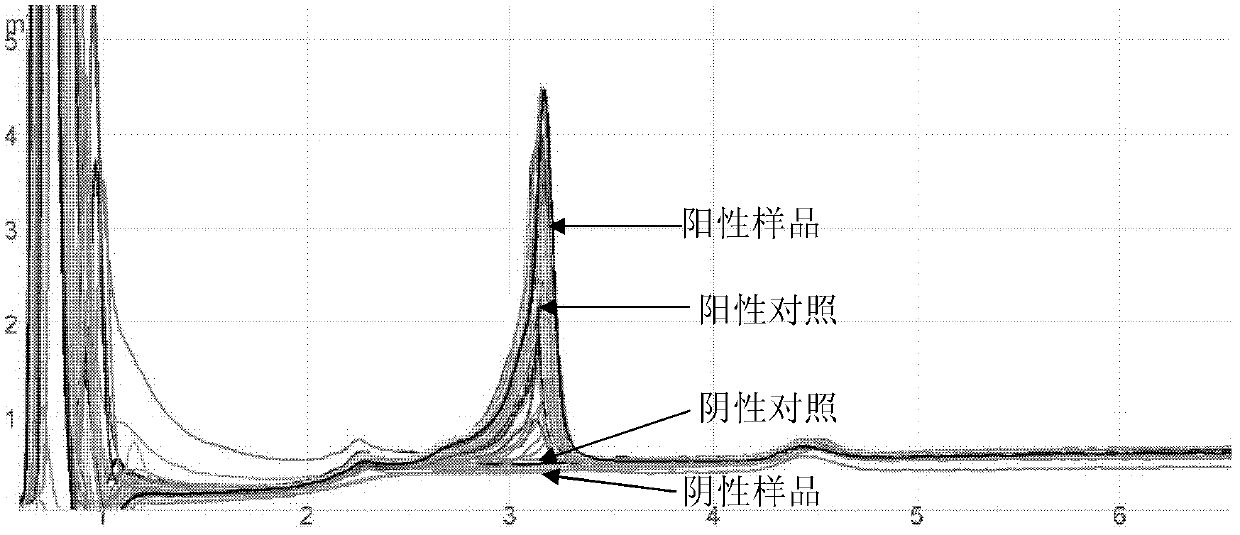
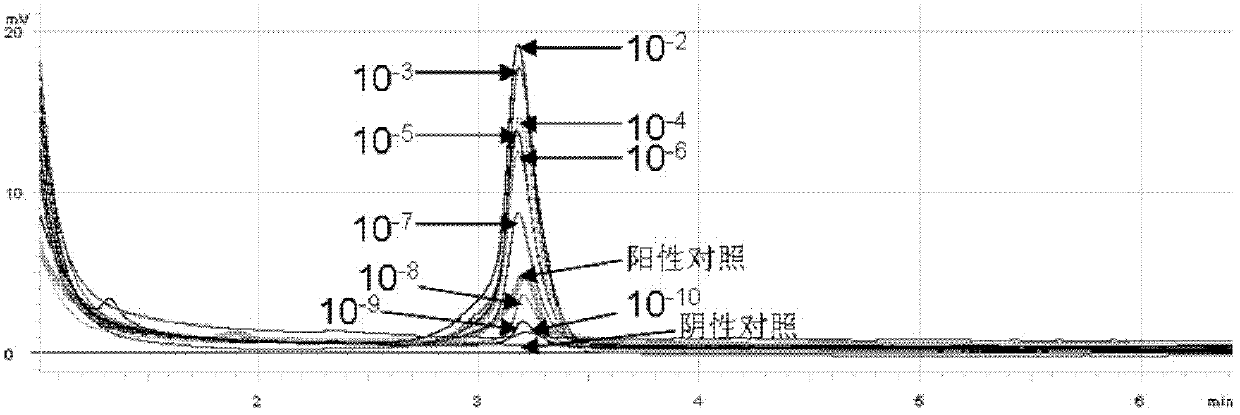
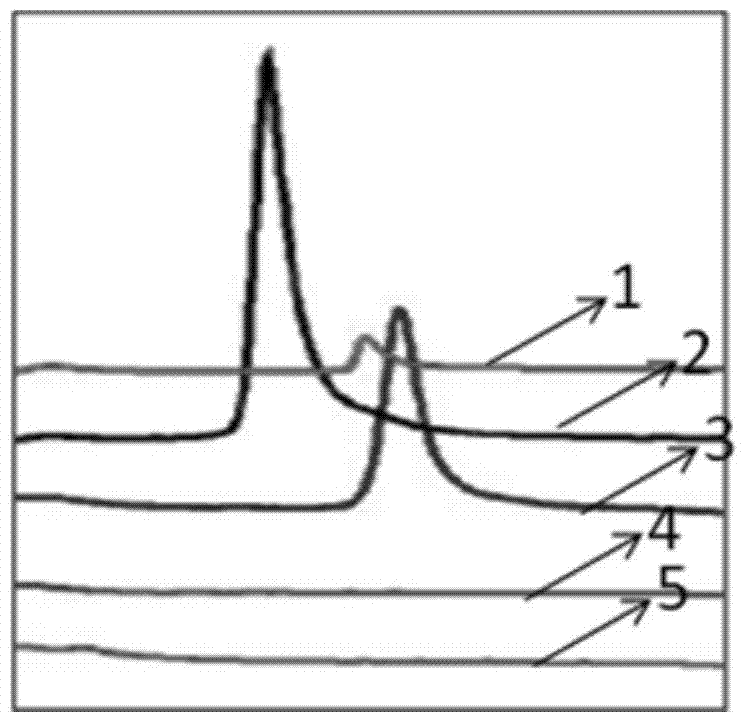
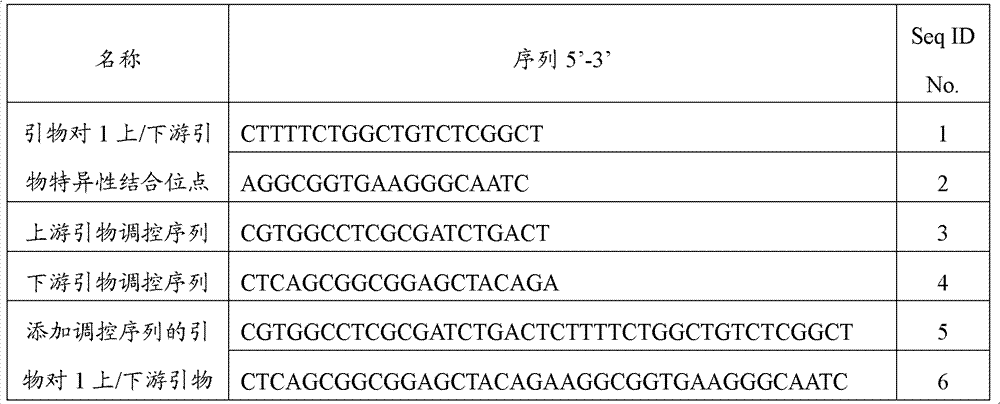
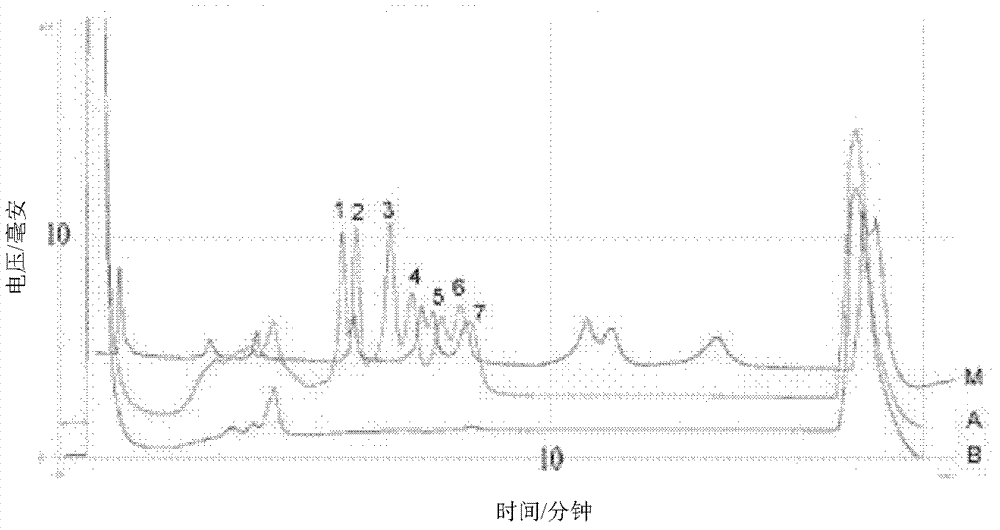
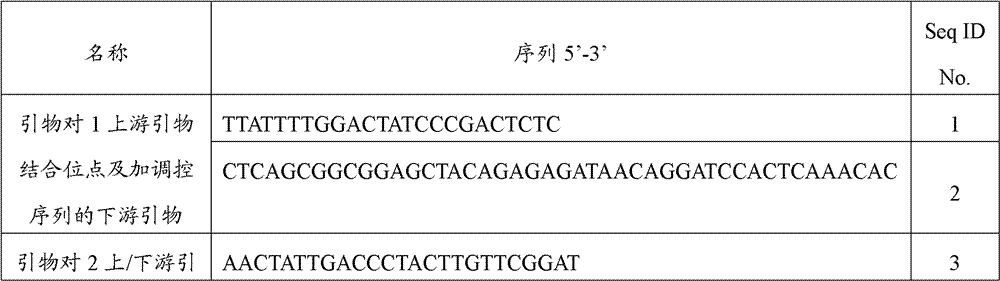
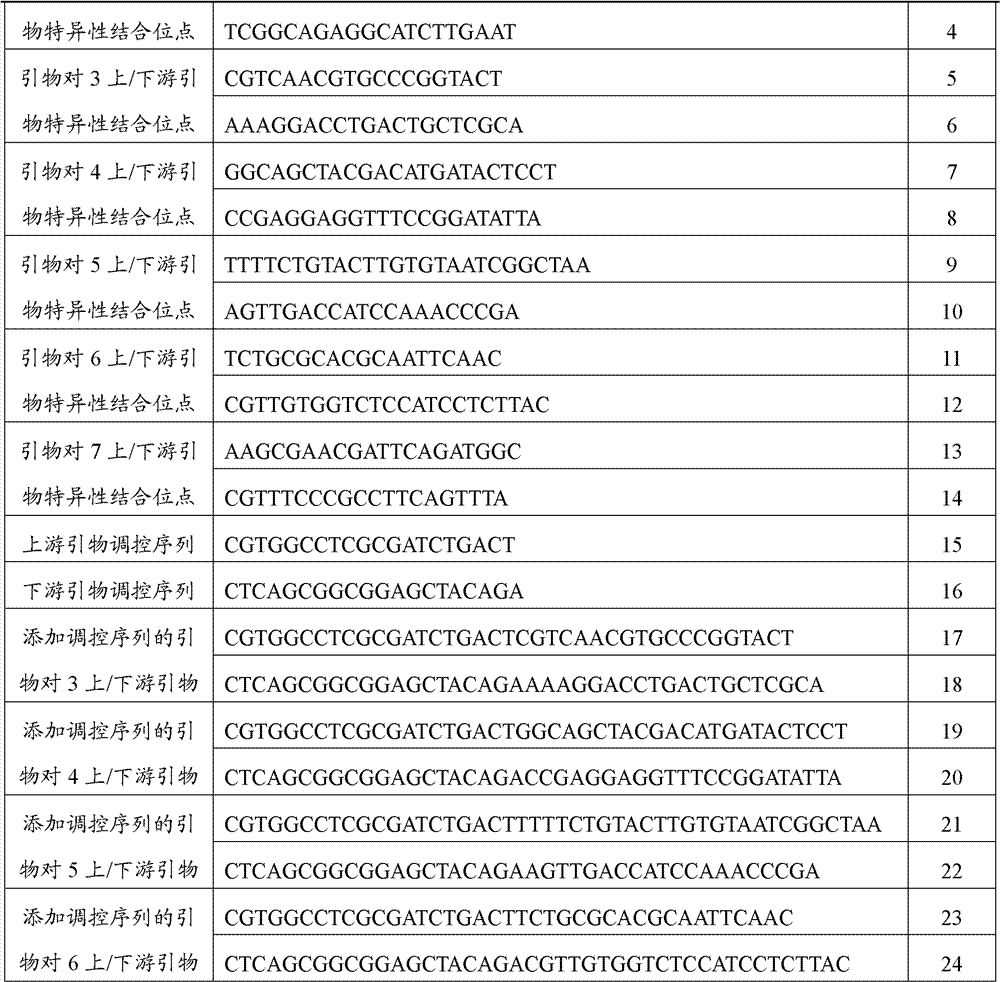
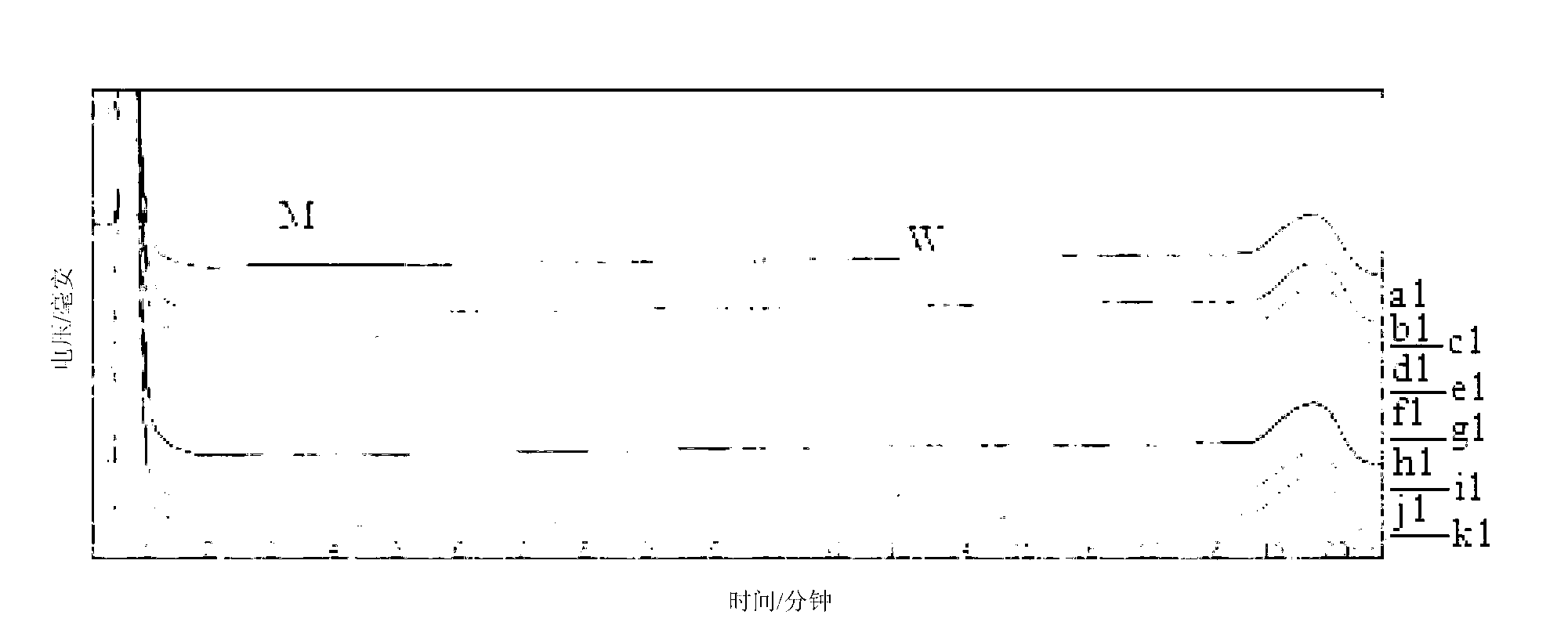
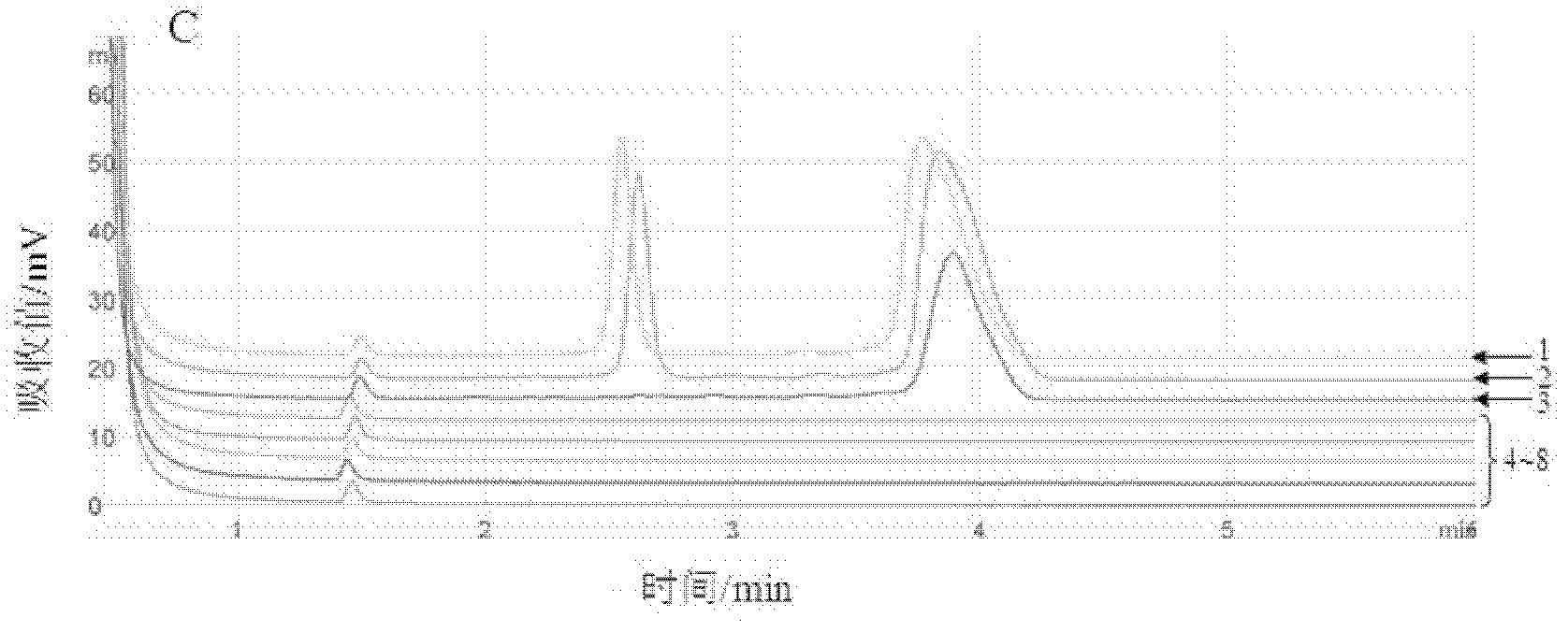
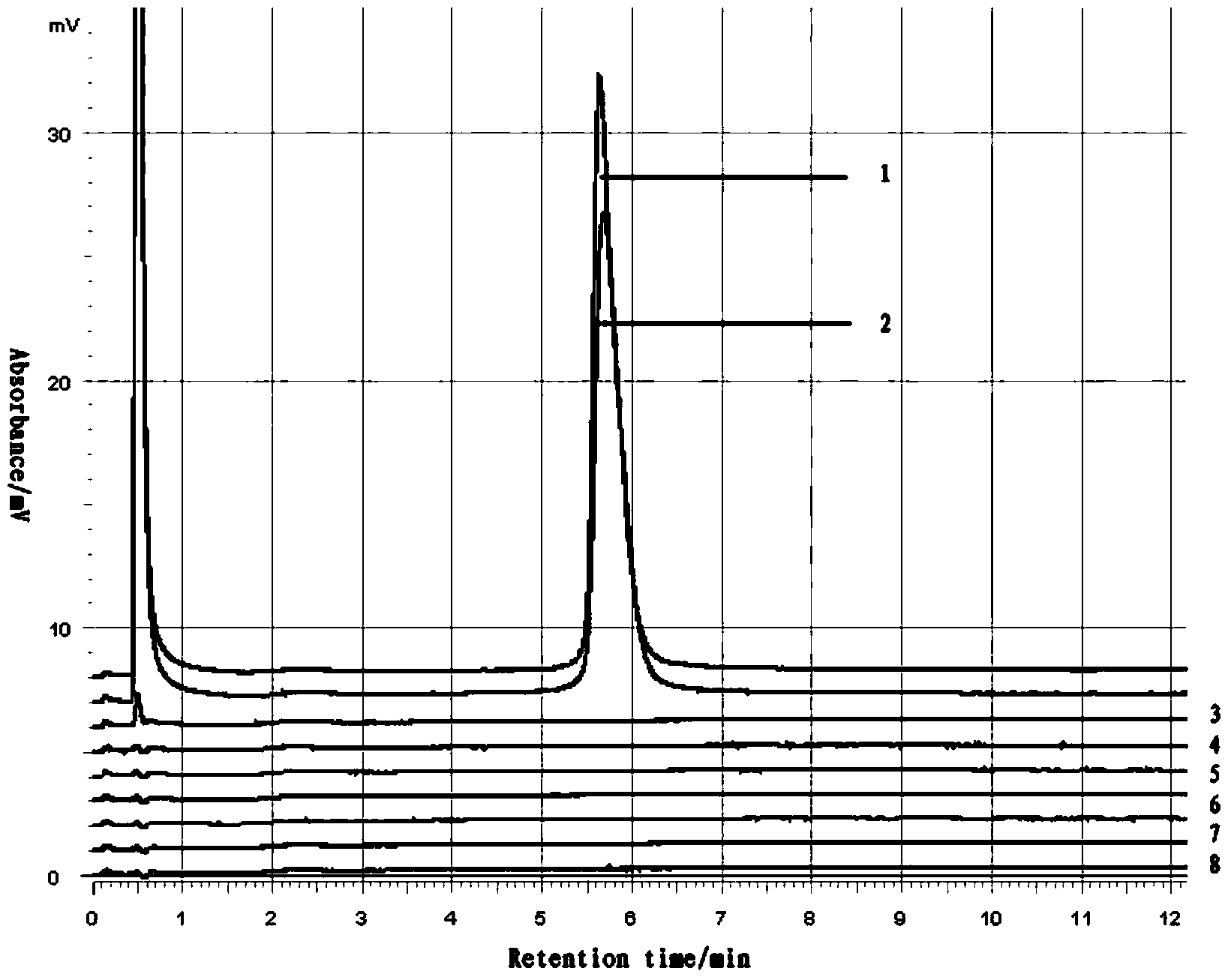
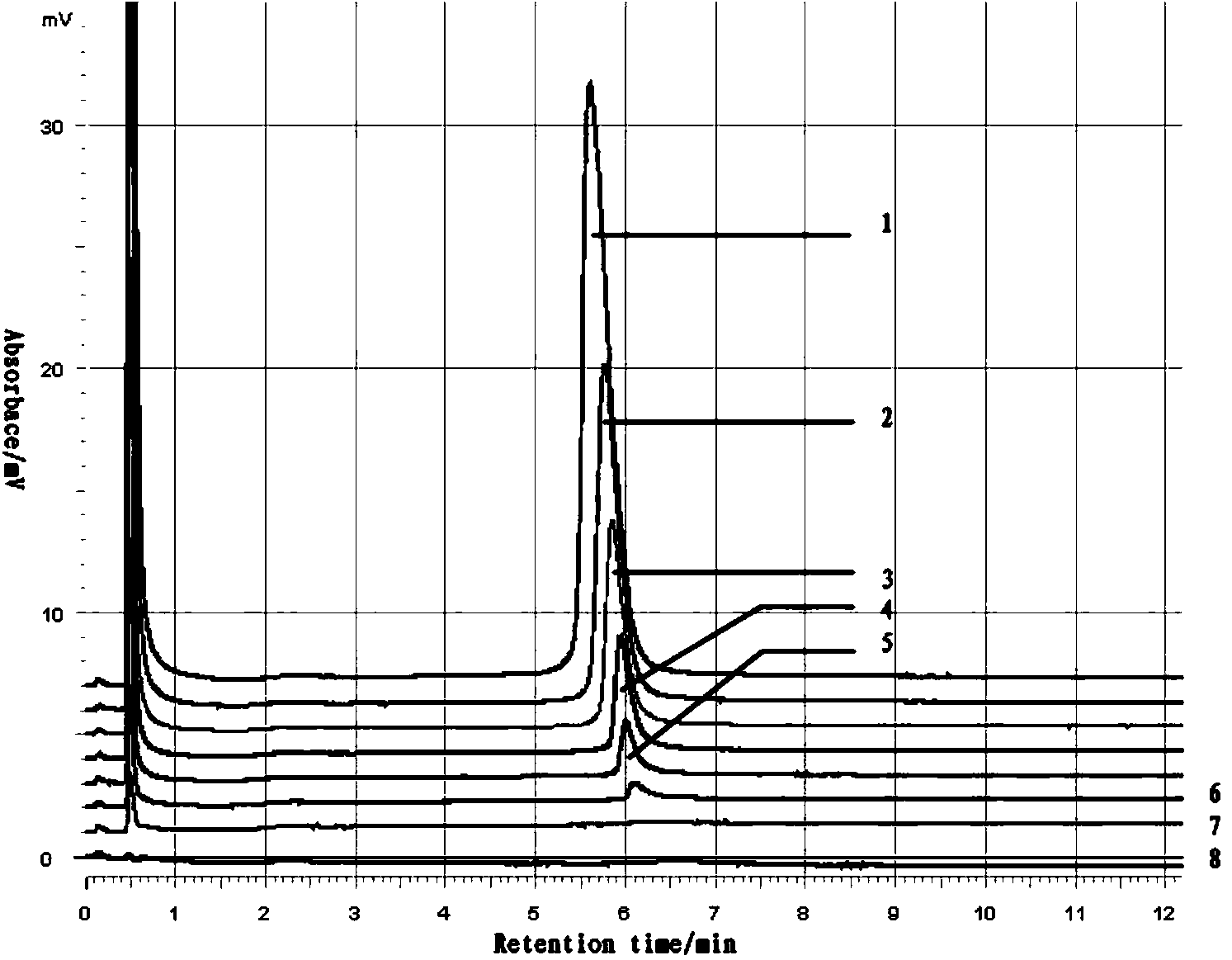
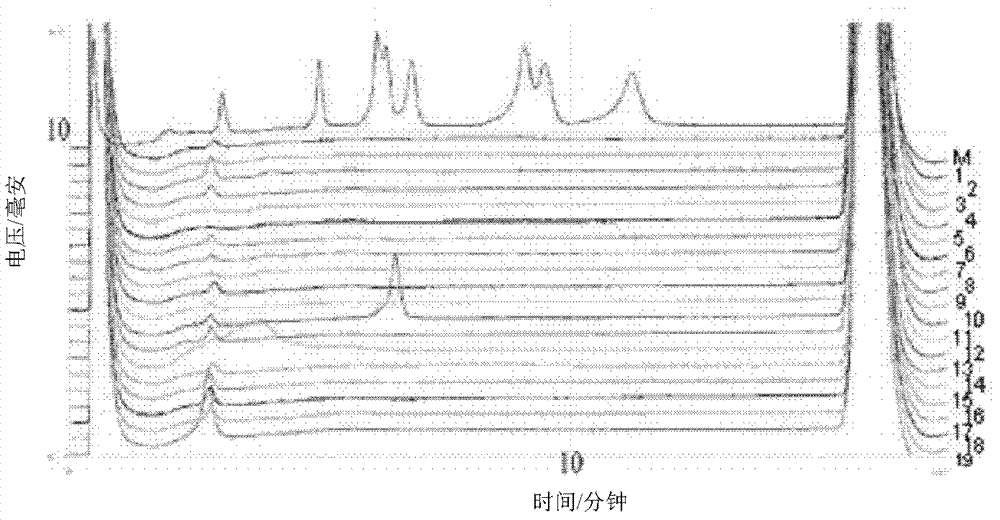
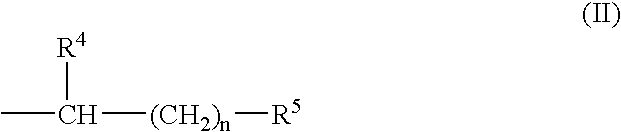Patents
Literature
54 results about "Denaturing high performance liquid chromatography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
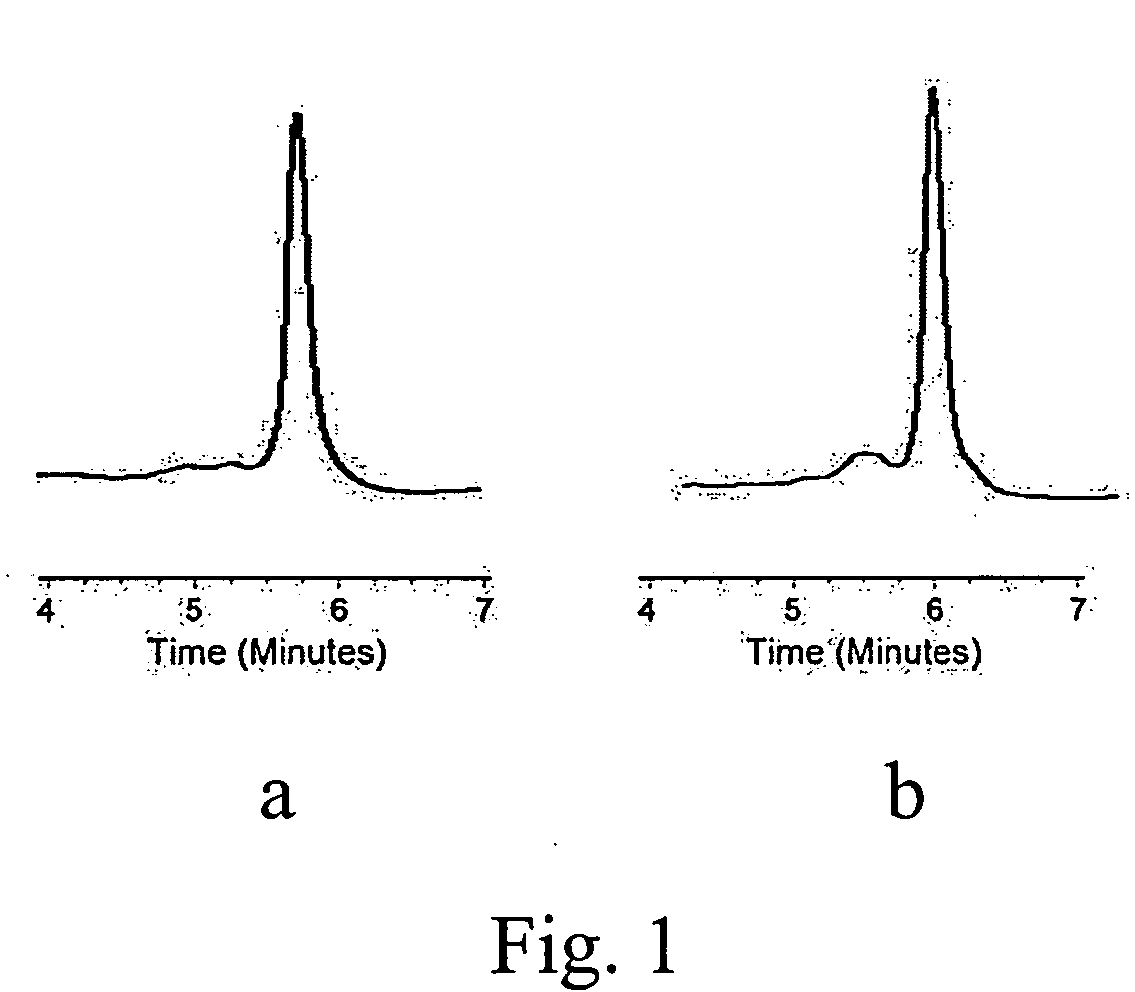
Denaturing High Performance Liquid Chromatography (DHPLC) is a method of chromatography for the detection of base substitutions, small deletions or insertions at the DNA . Thanks to its speed and high resolution, this method is particularly useful for finding polymorphisms in DNA.
Cancer screening method
InactiveUS20080311570A1Accurate screening resultEasy diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationScreening cancerScreening method
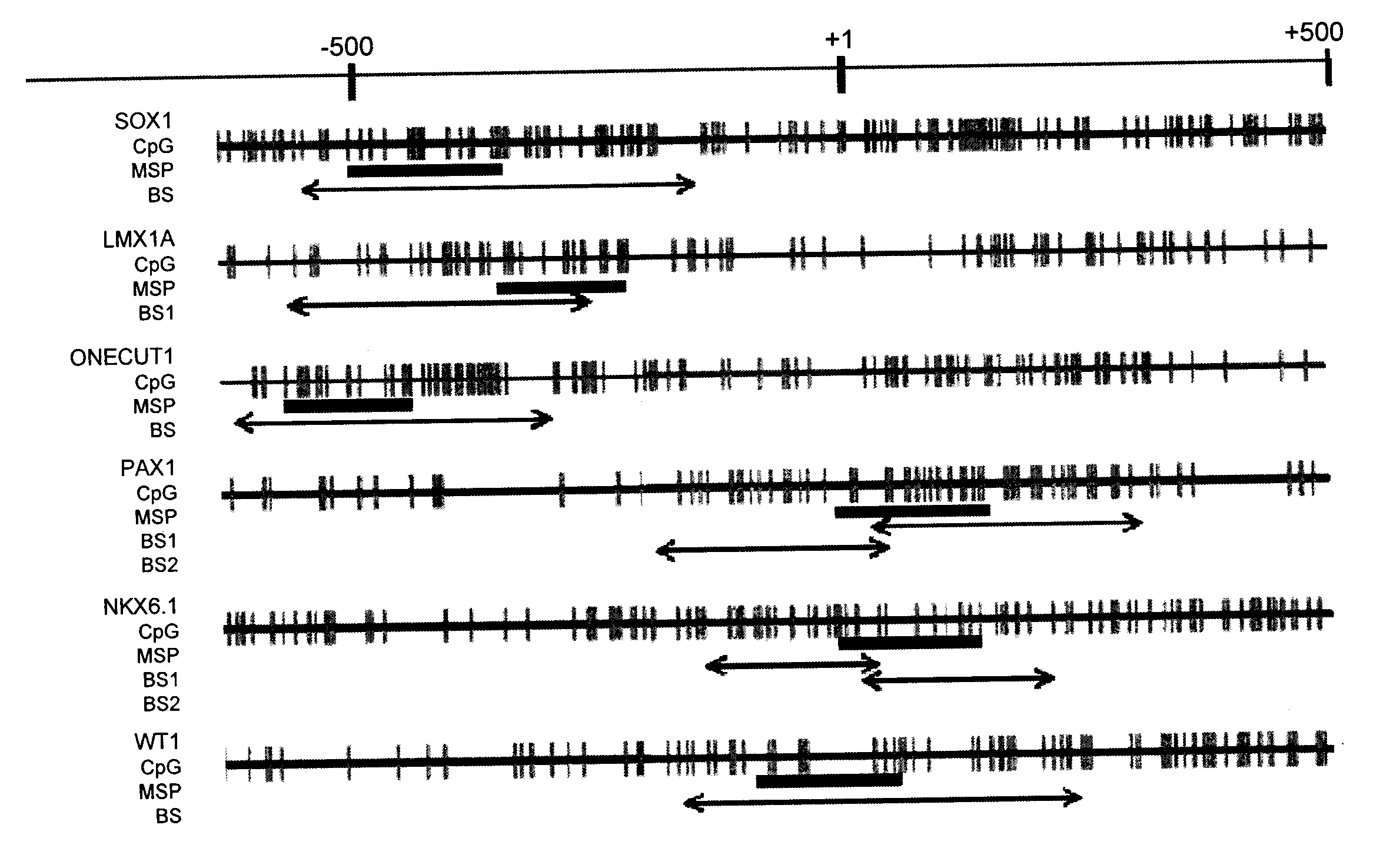
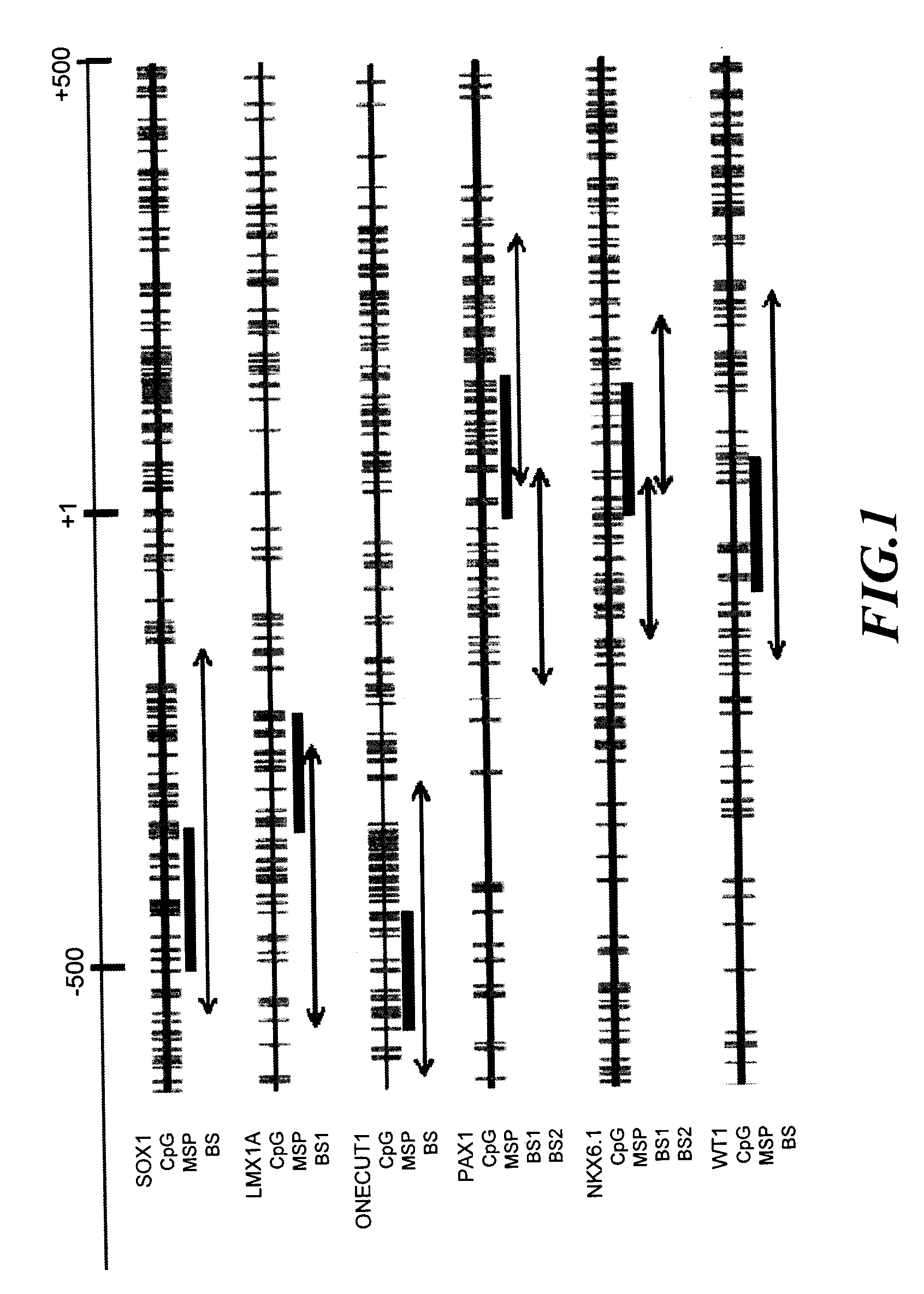
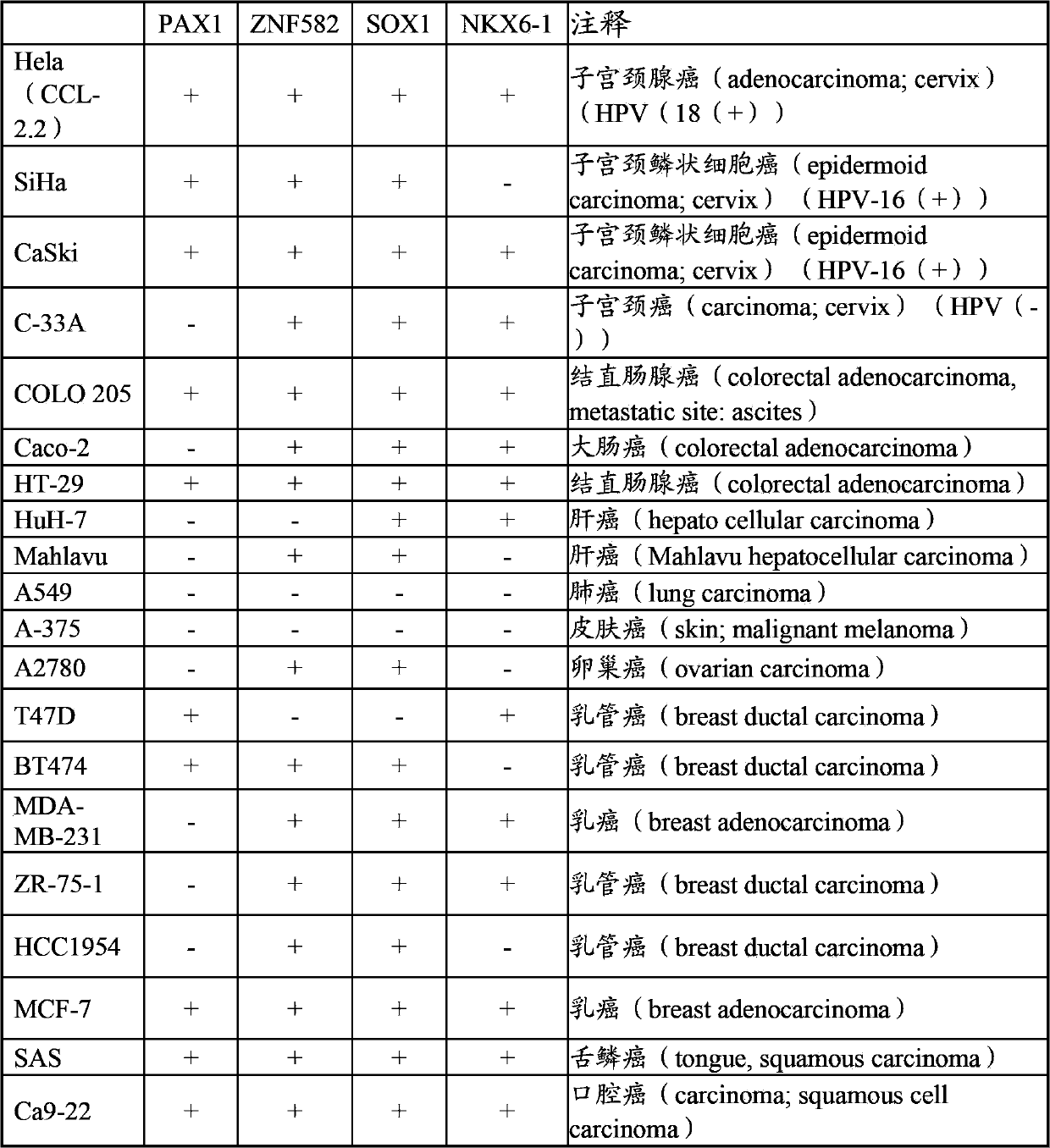
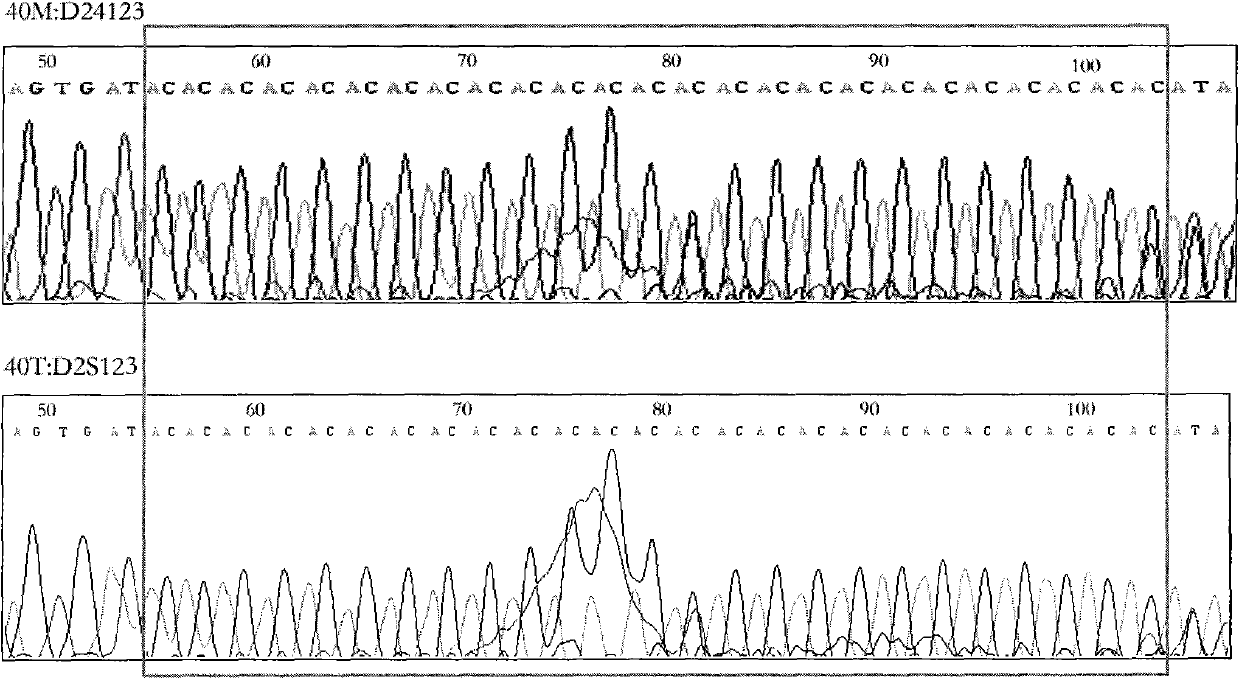
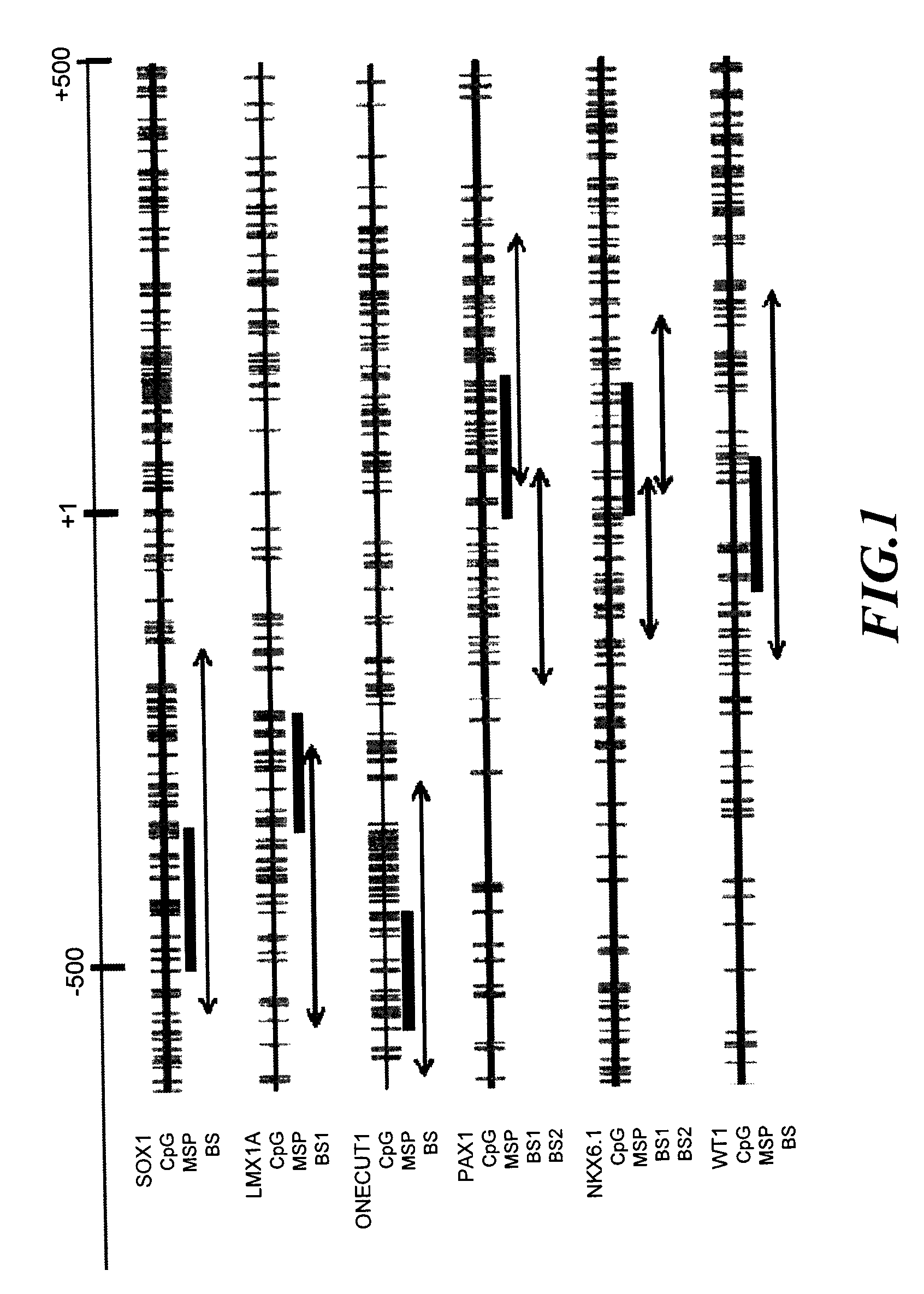
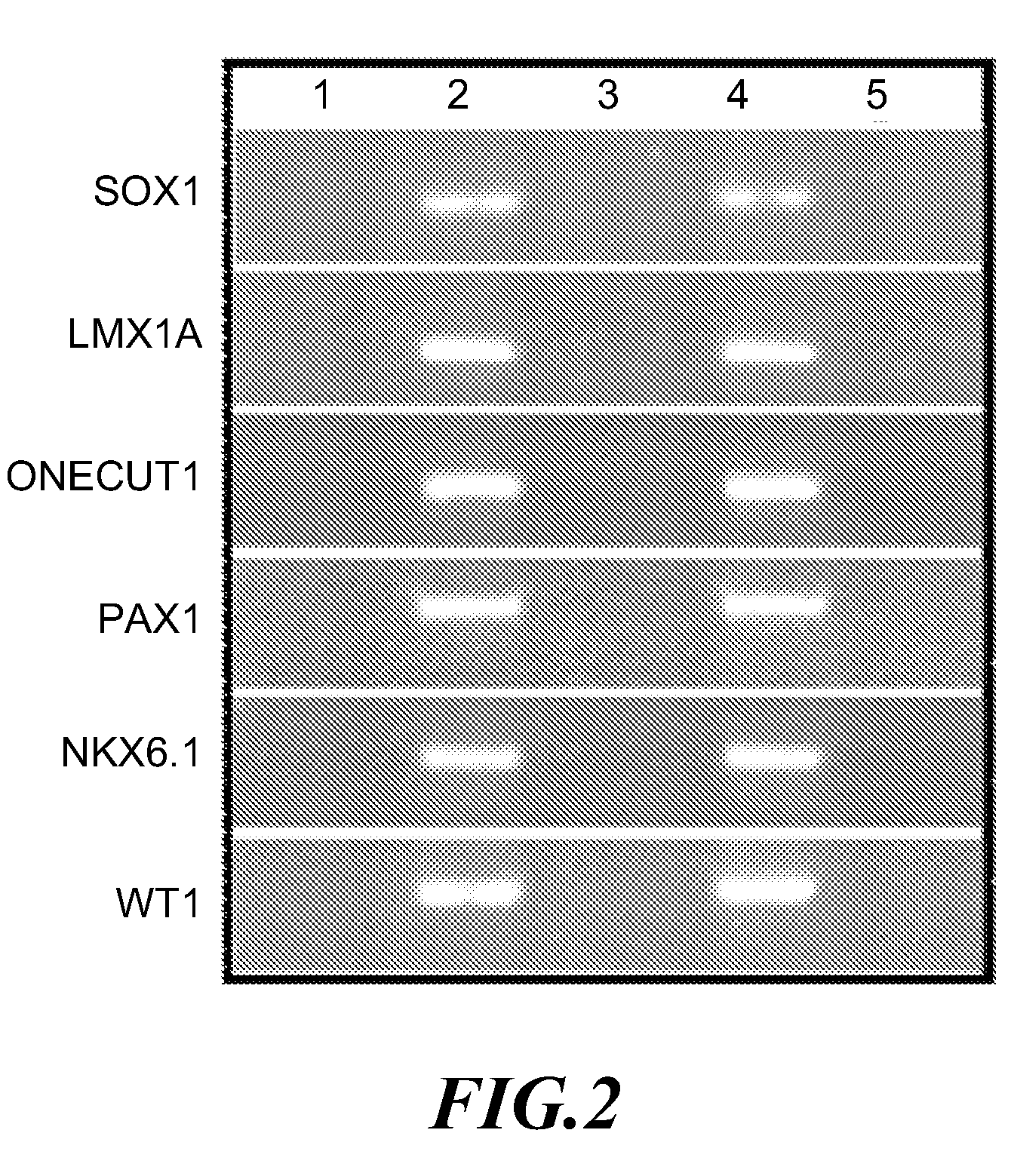
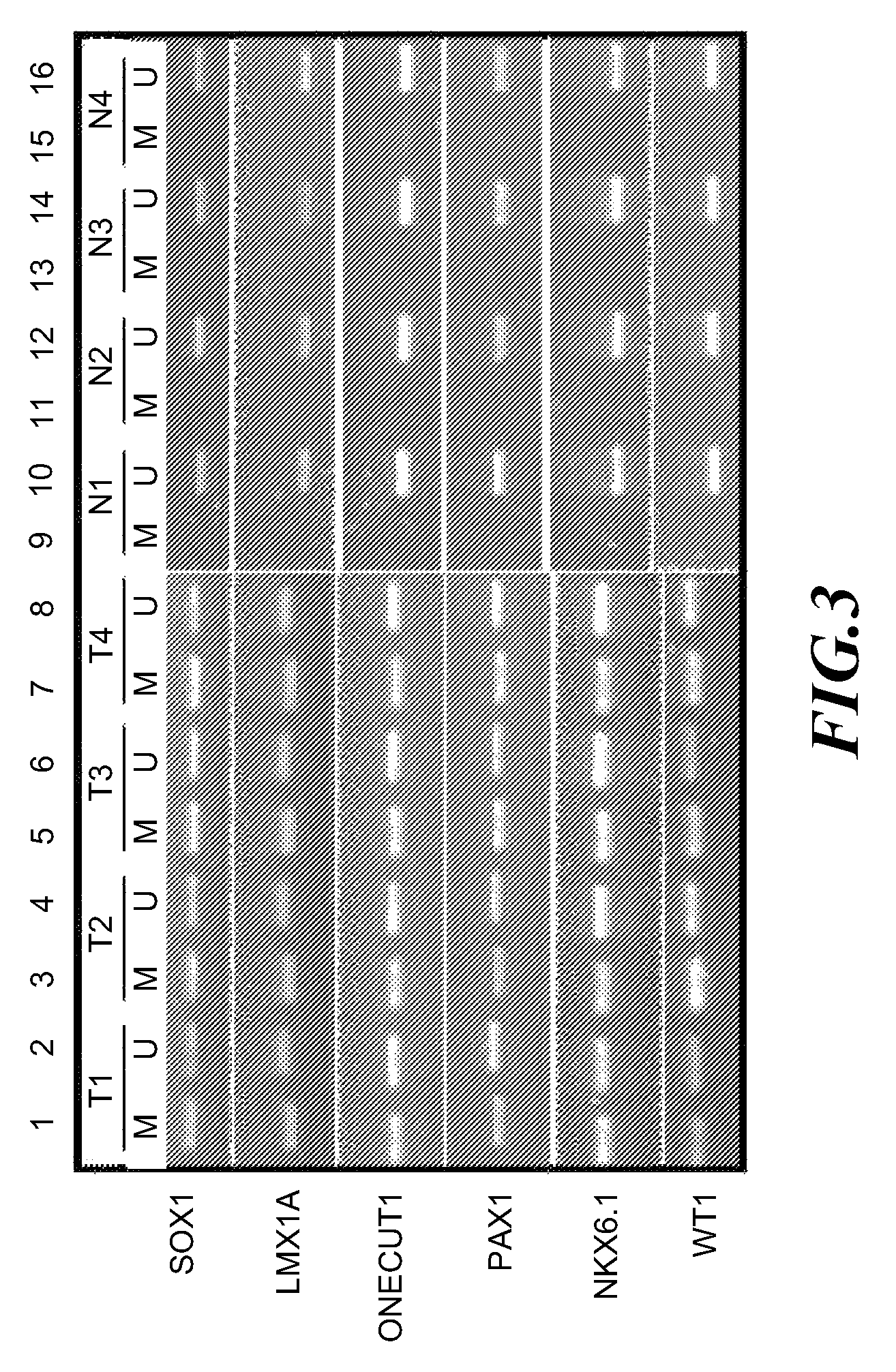
A method for screening cancer comprises the following steps: (1) providing a test specimen; (2) detecting the methylation state of the CpG sequence in at least one target gene within the genomic DNA of the test specimen, wherein the target genes is consisted of SOX1, PAX1, LMX1A, NKX6-1, WT1 and ONECUT1; and (3) determining whether there is cancer or cancerous pathological change in the specimen based on the presence or absence of the methylation state in the target gene; wherein method for detecting methylation state is methylation-specific PCR (MSP), quantitative methylation-specific PCR (QMSP), bisulfite sequencing (BS), microarrays, mass spectrometer, denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC), and pyrosequencing.
Owner:NAT DEFENSE MEDICAL CENT
Primer and kit for detecting microdeletion of chromosome Y and use method of primer
ActiveCN103571957AImprove throughputSimplify testing proceduresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrobiologyRepeatability
The invention discloses a primer and a kit for detecting microdeletion of a chromosome Y and a use method of the primer. The primer disclosed by the invention is a specific primer aiming at six STSs (Sequence Tagged Sites) and reference genes, and the kit containing the primer can be used for rapidly and accurately detecting the microdeletion of the chromosome Y through the combination of multiplex PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and DHPLC (Denaturing High Performance Liquid Chromatography) detection, so that detection program is simple and the detection sensitivity, the result repeatability and the sample flux are high.
Owner:SHANGHAI SIMPLEGENE CLINICAL LAB CO LTD
Cancer screening test kit
The present invention relates to a cancer biomarker molecule, a screening test kit and a detection method thereof. According to the present invention, analysis of methylating areas of specimen target genes PAX1, ZNF582, SOX1 and NKX6-1 are adopted, plural of segments of target gene-specific oligonucleotide primers or probes are designed, and the oligonucleotide probes are adopted to detect presence or absence of methylation of the target genes so as to further determine possibility of cancer occurrence; and the methylation state detection method comprises methylation-specific PCR (MSP), quantitative methylation-specific PCR (QMSP), bisulfite sequencing (BS), microarrays, mass spectrometer, denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC), pyrosequencing or Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and the like.
Owner:湖南宏雅基因技术有限公司
Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (mPCR)-denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) primers and method for detecting and identifying mycobacterium
InactiveCN102808031ARapid identificationStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPositive controlMycobacterium Infections
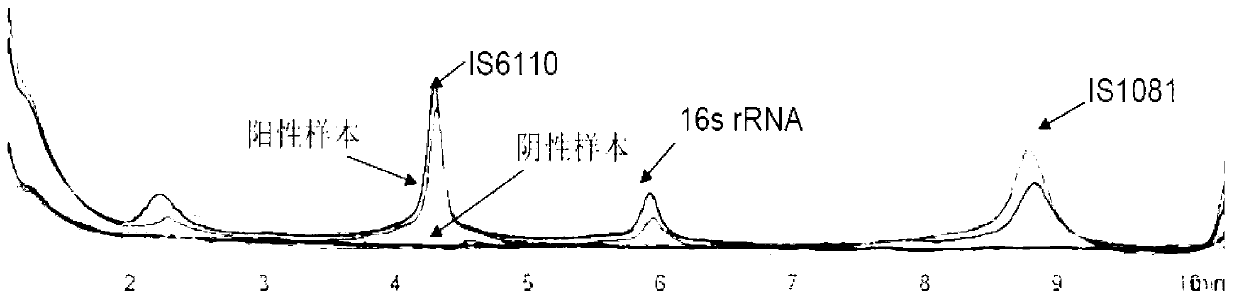
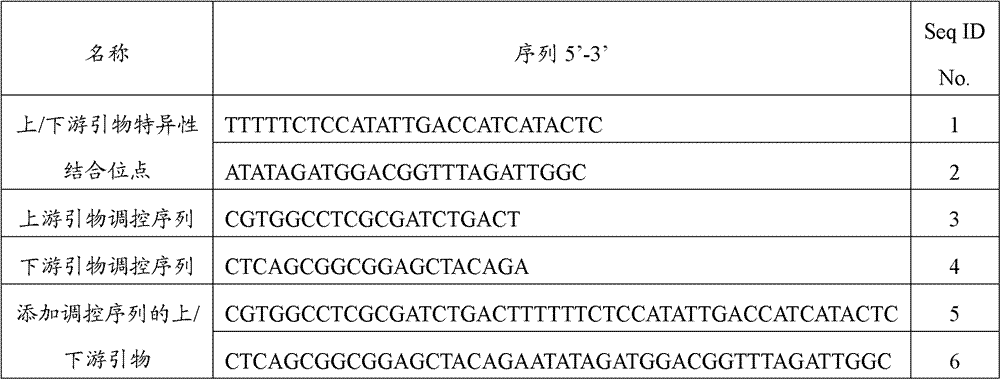
The invention provides a group of nucleic acids used in a quintuple multiplex polymerase chain reaction (mPCR)-denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) method for detecting mycobacterium and identifying pathogenic mycobacterium. The nucleic acids comprise five pairs of primers of which the nucleic acid sequences are shown as SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2, SEQ ID No.4 and SEQ ID No.5, SEQ ID No.7 and SEQ ID No.8, SEQ ID No.10 and SEQ ID No.11, and SEQ ID No.13 and SEQ ID No.14, and PCR amplification products which are used as positive control and of which the nucleic acid sequences are shown as SEQ ID No.3, SEQ ID No.5, SEQ ID No.9, SEQ ID No.12 and SEQ ID No.15. The invention also provides a kit using the nucleic acids and a detection method; the method is high in specificity and flexibility and easy to operate, and high flux can be achieved; and the method has important practical significance to clinical identification on the mycobacterium infection and infectious agents of the mycobacterium infection.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF GUANGDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU +1
Method for extracting DNA from old formalin-fixed tissues
InactiveCN101787364AQuality improvementHigh puritySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationLarge fragmentA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for extracting DNA from old formalin-fixed tissues. The basic principle of the method is to utilize the microwave thermal effect for fast removing formalin in the fixed tissues via water molecules, and eliminate the DNA-protein crosslinking caused by aldehyde groups of the formalin, thereby completely or partially recovering a DNA structure and further obtaining the DNA with better quality. The invention relates to the simple and high-efficient method for extracting the DNA from the old formalin-fixed tissues, which is based on microwave thermal remediation and can obtain the DNA with higher quality (large fragments and high purity), so that the method can be used for multiplex fluorescent PCR-capillary electrophoresis (FM-CE), denaturing high performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) analysis, direct DNA sequencing and other molecular biological method analyses.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cancer screening method
InactiveUS7820386B2Accurate screening resultEasy diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationScreening cancerScreening method
A method for screening cancer comprises the following steps: (1) providing a test specimen; (2) detecting the methylation state of the CpG sequence in at least one target gene within the genomic DNA of the test specimen, wherein the target genes is consisted of SOX1, PAX1, LMX1A, NKX6-1, WT1 and ONECUT1; and (3) determining whether there is cancer or cancerous pathological change in the specimen based on the presence or absence of the methylation state in the target gene; wherein method for detecting methylation state is methylation-specific PCR (MSP), quantitative methylation-specific PCR (QMSP), bisulfite sequencing (BS), microarrays, mass spectrometer, denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC), and pyrosequencing.
Owner:NAT DEFENSE MEDICAL CENT
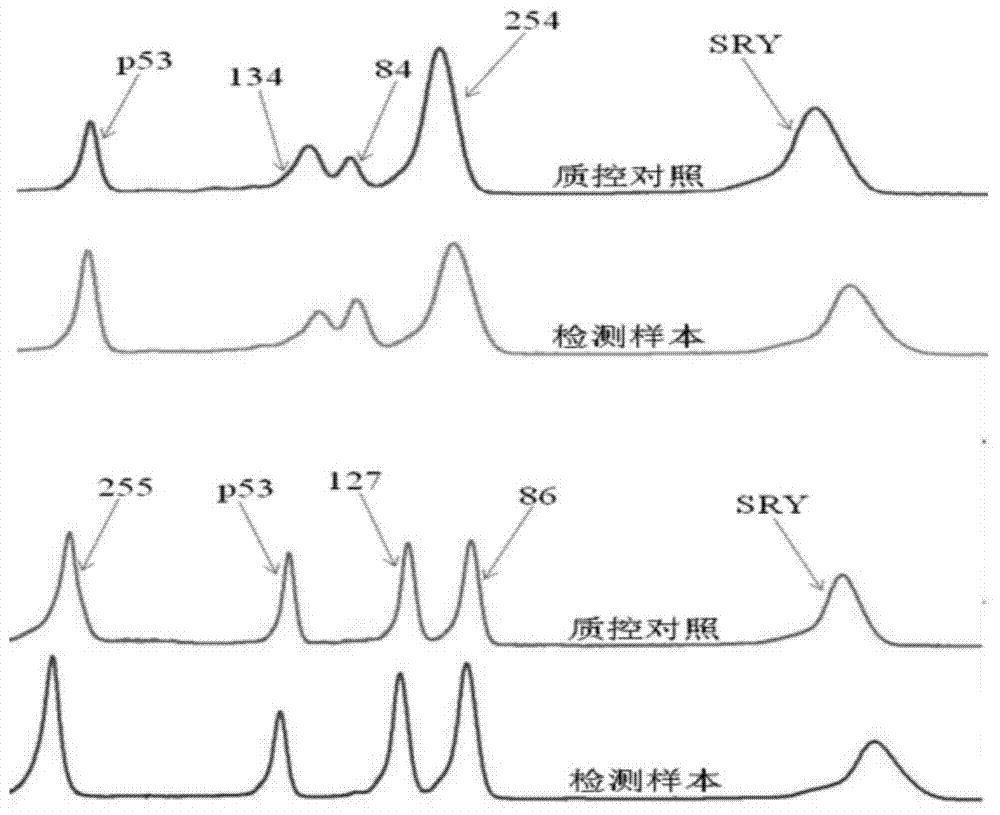
Ratio electrochemical DNA sensor-modified electrode for detecting gene P53 and preparation method of modified electrode
ActiveCN106434903ASimple methodSimple reaction conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorSingle strand dna
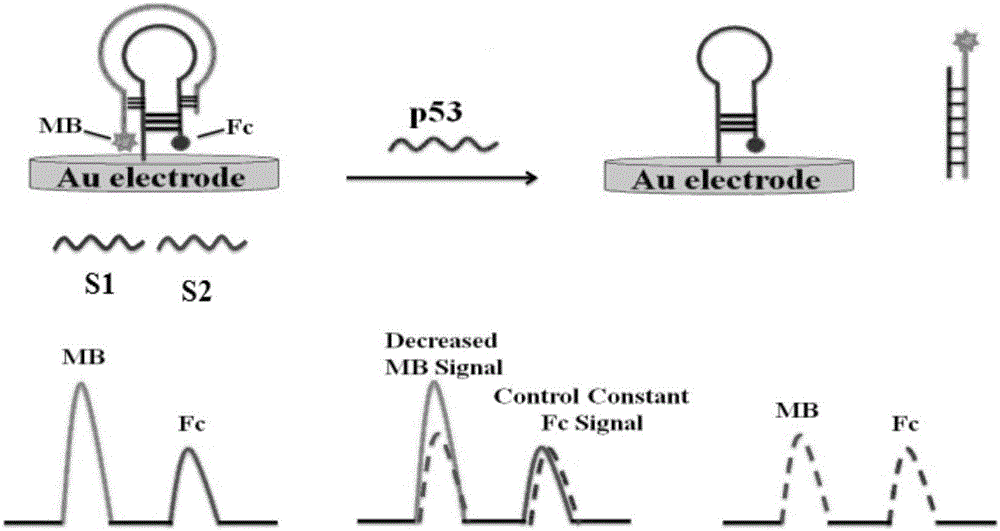
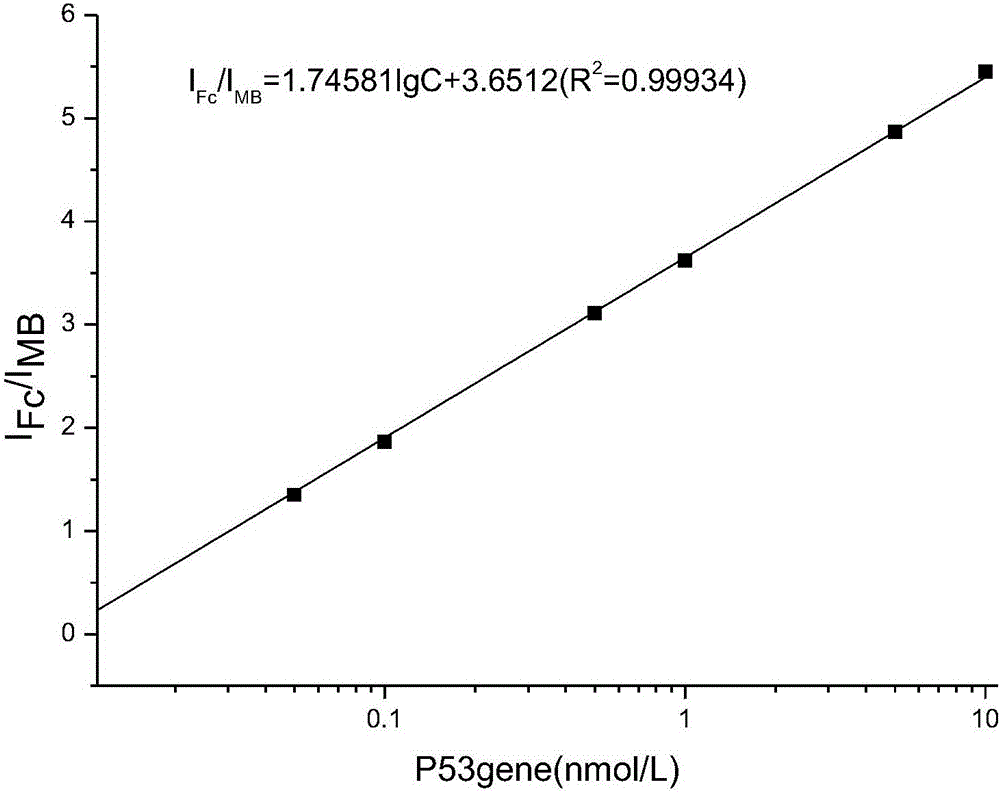
The invention relates to the technical field of electrochemical detection, and particularly discloses a modified electrode for detecting a tumor suppressor gene P53 and a preparation method of the modified electrode. A probe for detecting the gene P53 is composed of a single-stranded DNA auxiliary probe S1 and a single-stranded DNA capturing probe S2, wherein the DNA strand sequence of the S1 is 5'-Fc-CTC TCA GTG ATT TTT TTA GTG AGA GAG-(CH2)6-SH-3', and the DNA strand sequence of the S2 is 5'-MB-TCA CTG AGT CTT CCA GTG TGA TGA TCA CT-3'. According to the method, preparation is easy, control is convenient, the use cost is low, and compared with the methods such as capillary electrophoresis, denaturing high performance liquid chromatography, denaturing gel gradient electrophoresis and a yeast-separated allele function analysis technique, the electrochemical biosensor mode has the advantages that samples do not need to be pretreated, control is easy, the reaction conditions are simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Food foodborne pathogenic bacteria rapidly identifying method
InactiveCN108410968ALess consumablesShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStaphylococcus aureusPathogenic bacteria
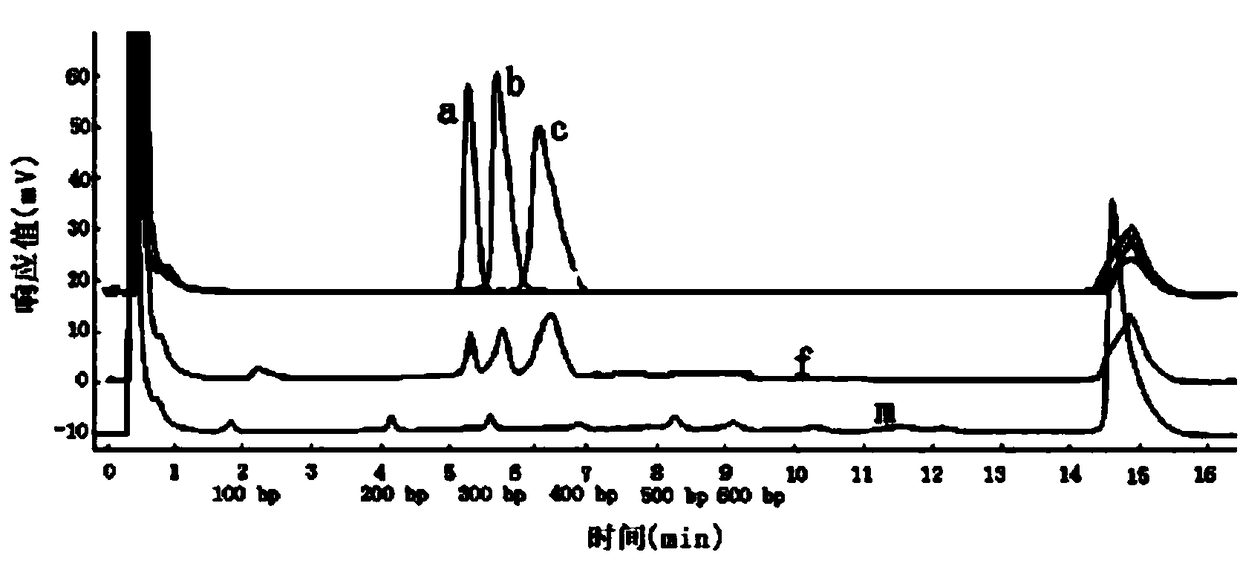
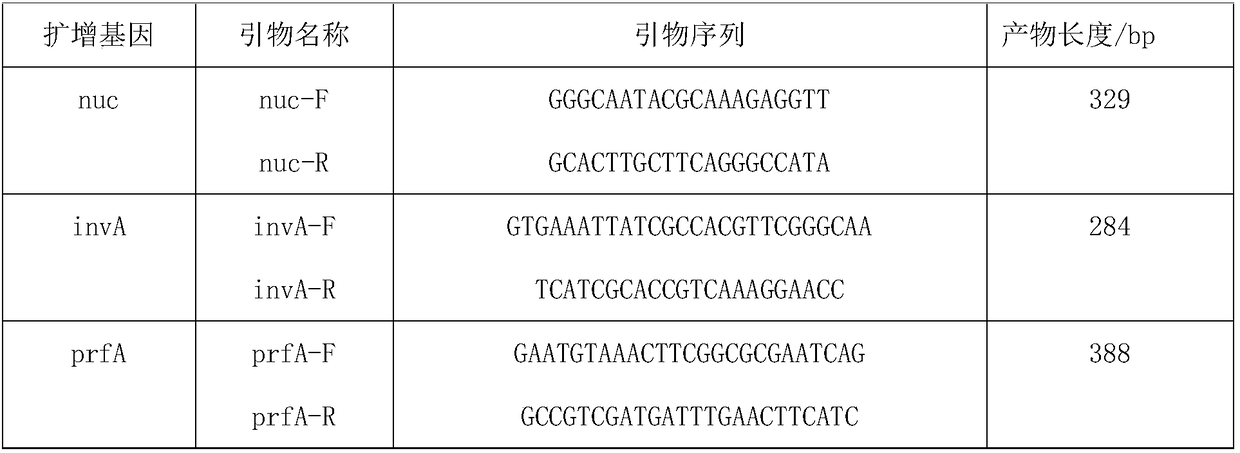
The invention discloses a food foodborne pathogenic bacteria rapidly identifying method. The food foodborne pathogenic bacteria rapidly identifying method comprises the steps of 1) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) template extraction, 2) primer screening and reaction system optimization including selecting the specific genes of nuc, invA and prfA of staphylococcus aureus, salmonellas and listeria monocytogenes to separately design primer pairs, 3) PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, 4) PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection of strain DNA, during which only strains coinciding with target amplification can be detected with amplification absorption peaks while other non-targeted amplification bacteria detected to be negative. The food foodborne pathogenic bacteria rapidly identifying method can detect three foodborne pathogenic bacteria in food when applied every single time, thereby saving time and consumable agent, simplifying operation, avoiding excessive artificial errors and achieving high sensitivity.
Owner:芜湖市食品药品检验中心
PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) assay primer and assay method for transgenic rapeseed RF2 strain
InactiveCN103173548AStrong specificitySimple and fast operationComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationA-DNA
The invention discloses a PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) assay primer and assay method for transgenic rapeseed RF2 strain. The primer is strong in specificity, and can be used in PCR and used for specifically amplifying a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment of the transgenic rapeseed RF2 strain, and the amplified product can be applied to subsequent DHPLC analysis. The assay method provides an assay method for the transgenic rapeseed RF2 strain, which is convenient to operate, good in extension performance and strong in specificity. The PCR amplified product is analyzed by utilizing the DHPLC, the resolution of the fragment of the PCR amplified can be a plurality of basic groups, and the resolution rate is high. The primer and assay method provided by the invention provide a simple, convenient, effective and reliable assay method to assay of the transgenic rapeseed RF2 strain, and are particularly applicable to port inspection and quarantine and other departments.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Primer and polymerase chain reaction-denatured high performance liquid chromatography (PCR-DHPLC) kit for detecting mycobacteria
InactiveCN102433384AStrong specificityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlNucleotide
The invention relates to a primer for detecting mycobacteria. Nucleotide sequences of an upstream primer and a downstream primer are shown as sequence tables, namely SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2 respectively. A polymerase chain reaction-denatured high performance liquid chromatography (PCR-DHPLC) kit for detecting the mycobacteria comprises a PCR buffer solution, a primer pair for detecting the mycobacteria, deoxy-ribonucleoside triphosphate (dNTP), MgCl2, thermus aquaticus deoxyribonucleic acid (Taq DNA) polymerase, double distilled water, negative control (sterile physiological saline) and positive control (plasma DNA with an amplification product), wherein a nucleotide sequence of the amplification product is shown as SEQ ID No.3. The invention provides a kit for rapidly detecting the infection of the mycobacteria and a PCR-DHPLC detection method applying the kit. The kit and the detection method have high specificity, sensitivity and throughput, are easy to operate, and have a great practical significance for clinically distinguishing the infection of the mycobacteria and other pathogens.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF GUANGDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU +1
Primer and kit for detecting methylation of MGMT (O<6>-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase) genes and use method of primer
InactiveCN103571958AReduce work intensityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrobiologyMGMT gene methylation
The invention discloses a primer and a kit for detecting methylation of MGMT (O<6>-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase) genes, a use method of the primer and application of the primer and the kit. The primer disclosed by the invention is a specific primer designed according to sequences of promoter regions of the human MGMT genes, and the kit containing the primer can be used for rapidly and accurately detecting the methylation of the MGMT gene with high sensitivity through the combination of nest-shaped PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification and DHPLC (Denaturing High Performance Liquid Chromatography) detection.
Owner:北京海思特医学检验实验室有限公司
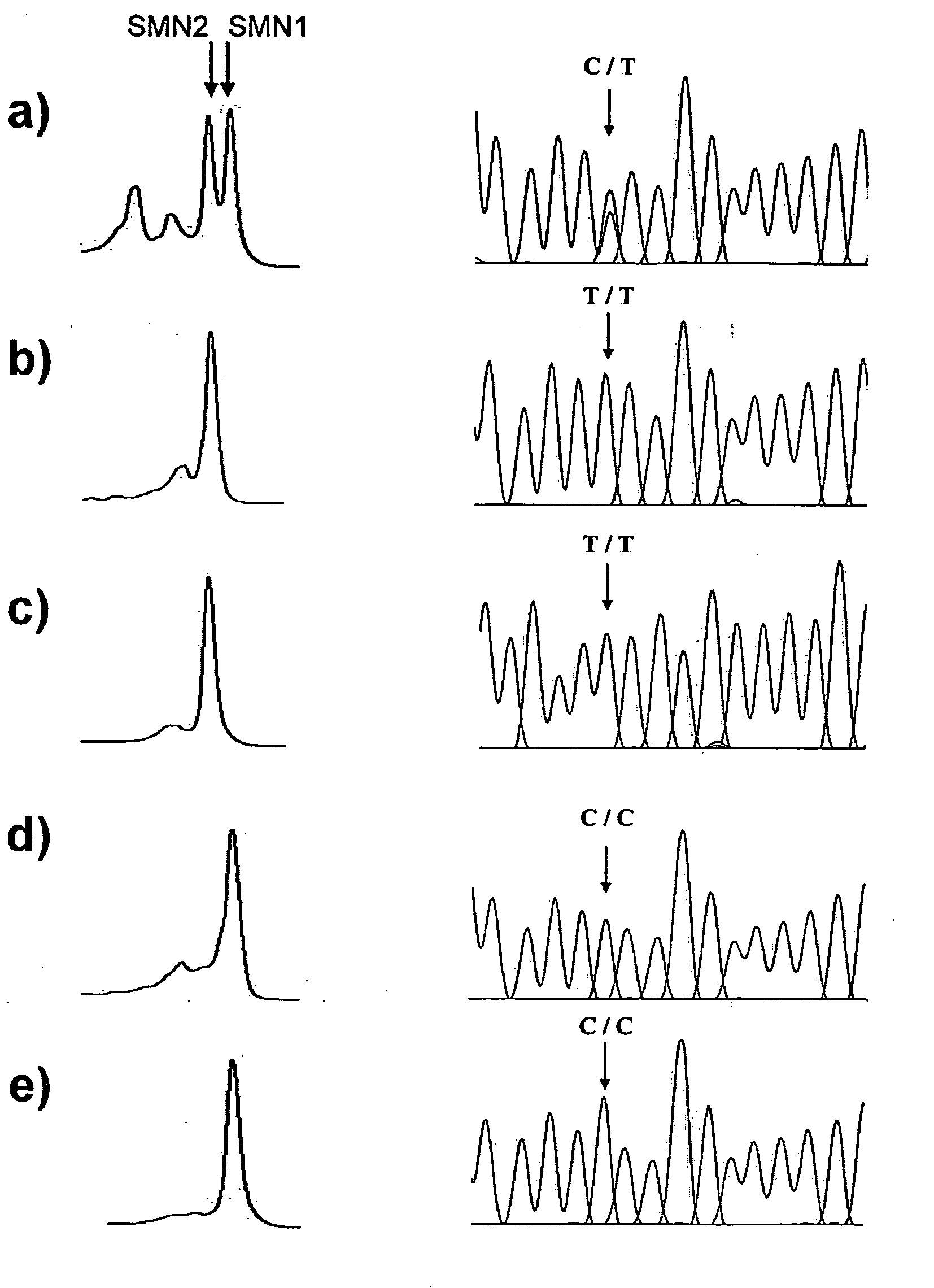
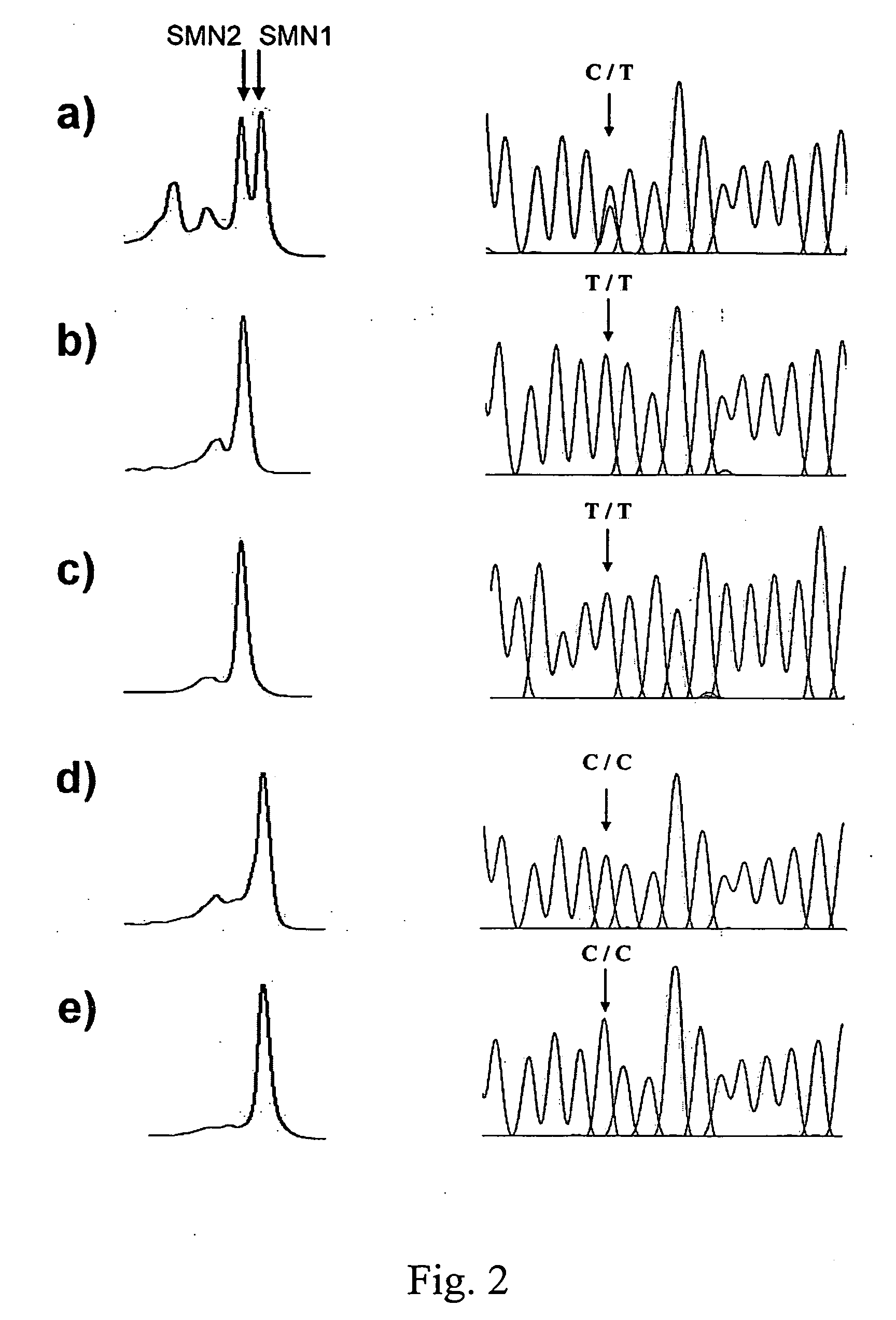
Methods for SMN genes and spinal muscular atrophy carriers screening
A method for SMN genes identifying is disclosed, as well as a method for spinal muscular atrophy carriers screening. The method comprises steps of following: (a) providing a genomic DNA; (b) amplifying the genomic DNA with a pair of primers; and (c) injecting the amplified product into DHPLC (Denaturing High Performance Liquid Chromatography). The method of the present invention can identify SMA patients, and also the carriers of SMA.
Owner:YI NING SU
Methods and compositions for mutation analysis of polynucleotides by liquid chromatography
Methods, compositions, and kits for separating heteroduplex and homoduplex DNA molecules in a test mixture by temperature-compression denaturing high performance liquid chromatography (tcDHPLC). The method includes use of nitrogen-containing additives in the mobile phase that allow detection of diverse heteroduplex molecules to be performed at the same pre-selected temperature. An example of a preferred additive is betaine. Standard mixtures of DNA fragments, such as mutation standards containing known heteroduplex and homoduplex molecules, can be used to select the concentration of additive and temperature. Compositions and kits including the mobile phase, mutation standards, PCR primers, separation media, and DNA polymerase are also provided.
Owner:TRANSGENOMIC
Multiplex PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and detection method for genetically modified cotton
InactiveCN102952863AHigh sensitivityHigh resolutionComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementFragment sizeQuarantine
The invention discloses a multiplex PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and a detection method for genetically modified cotton. The primer has strong specificity and can be used for PCR amplification and DHPLC analysis. The detection method is simple and convenient to operate, good in expansion performance and high in sensitivity, and multi-target detection of genetically modified cotton is realized. The DHPLC is used to analyze PCR amplified products, fragment size resolution can reach multiple bases, and resolution ratio is high. The multiplex PCR-DHPLC detection primer and the detection method for genetically modified cotton have the advantages that the detection method is simple, convenient, effective, reliable, high in throughput and especially suitable for departments of port inspection and quarantine, agricultural production, plant protection and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and detection method for genetically modified rice strain KMD
InactiveCN102952858AStrong specificityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetically modified riceFragment size
The invention discloses a PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and a detection method for genetically modified rice strain KMD. The primer has strong specificity and can be used for PCR amplification and DHPLC analysis. The detection method is simple and convenient to operate, good in expansion performance and high in sensitivity. The DHPLC is used to analyze PCR amplified products, fragment size resolution can reach multiple bases, and resolution ratio is high. The PCR-DHPLC detection primer and the detection method for genetically modified rice strain KMD have the advantages that the detection method is simple, convenient, effective, reliable and especially suitable for departments of port inspection and quarantine and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Multiplex PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and detection method for genetically modified maize
InactiveCN102952861AHigh sensitivityHigh resolutionComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementFragment sizeQuarantine
The invention discloses a multiplex PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and a detection method for genetically modified maize. The primer has strong specificity and can be used for PCR amplification and DHPLC analysis. The detection method is simple and convenient to operate, good in expansion performance and high in sensitivity, and multi-target detection of the genetically modified maize is realized. The DHPLC is used to analyze PCR amplified products, fragment size resolution can reach multiple bases, and resolution ratio is high. The multiplex PCR-DHPLC detection primer and the detection method for genetically modified maize have the advantages that the detection method is simple, convenient, effective, reliable, high in throughput and especially suitable for departments of port inspection and quarantine and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) assay primer and assay method for transgenic rapeseed RT73 strain
InactiveCN103173550AStrong specificitySimple and fast operationComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationRapeseed
The invention discloses a PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) assay primer and assay method of transgenic rapeseed RT73 strain. The primer is strong in specificity, and can be used in PCR and used for specifically amplifying a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment of the transgenic rapeseed RT73 strain, and the amplified product can be applied to subsequent DHPLC analysis. The assay method provides an assay method for the transgenic rapeseed RF2 strain, which is convenient to operate, good in extension performance and strong in specificity. The PCR amplified product is analyzed by utilizing the DHPLC, the resolution of the fragment of the PCR amplified can be a plurality of basic groups, and the resolution rate is high. The primer and assay method provided by the invention provide a simple, convenient, effective and reliable assay method to assay of the transgenic rapeseed RT73 strain, and are particularly applicable to port inspection and quarantine and other departments.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Dual polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography (PCR-DHPLC) detection method for staphylococcus aureus in aquatic products
ActiveCN102399897AImprove throughputHighly automated detectionComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementDuplex pcrStaphylococcus cohnii
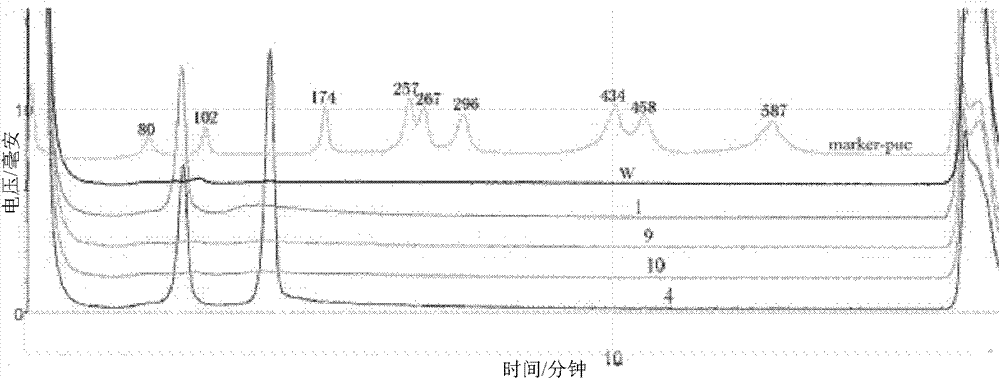
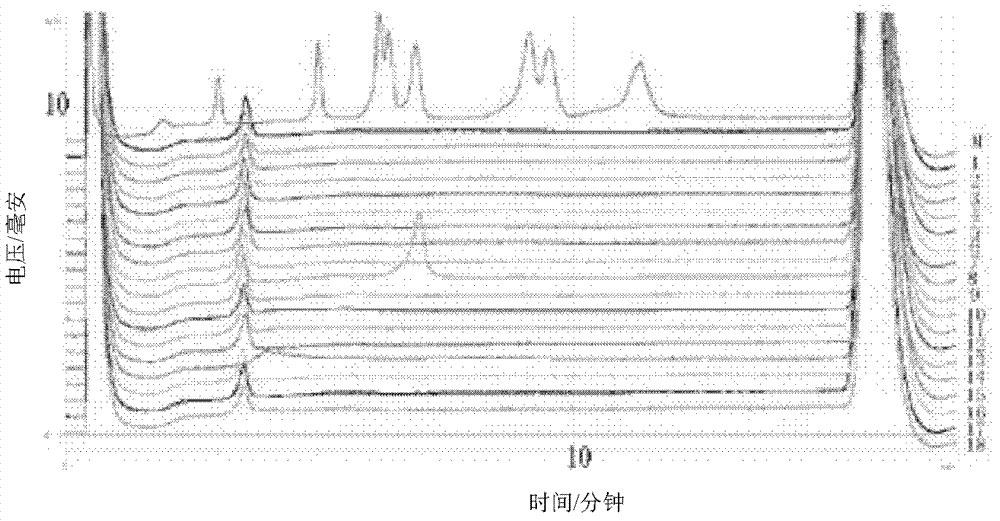
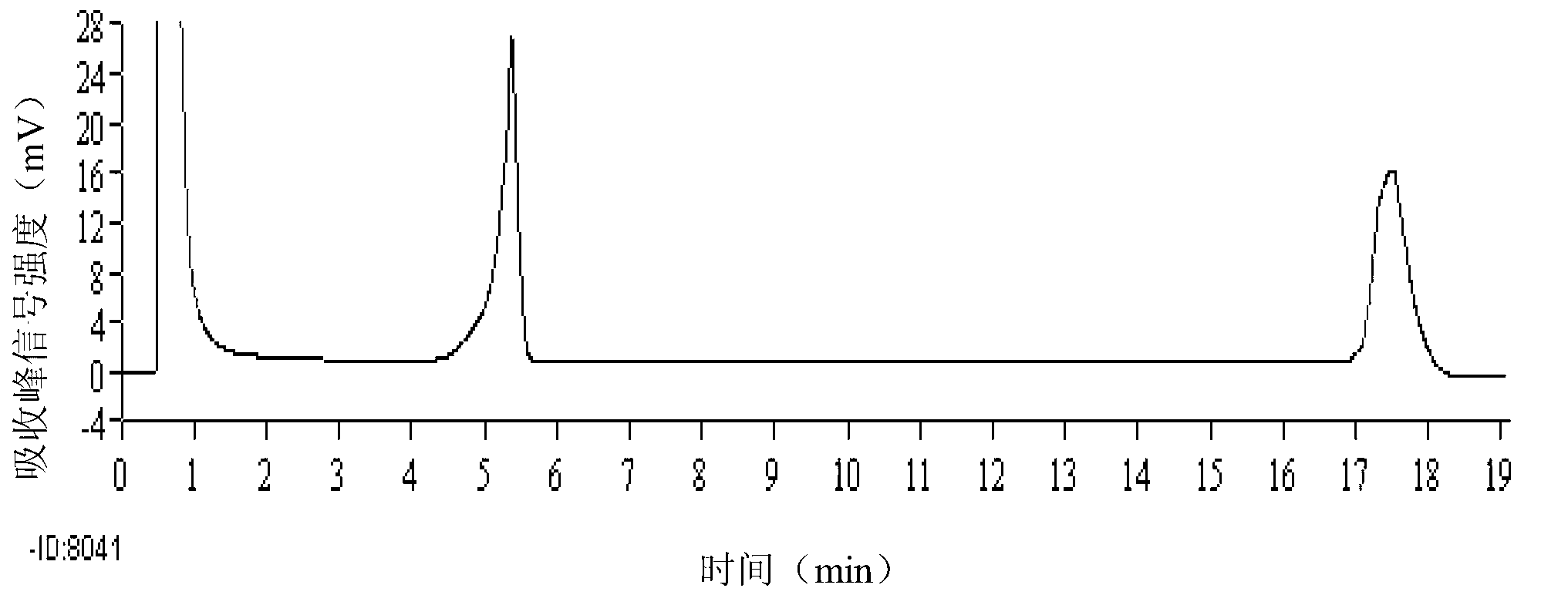
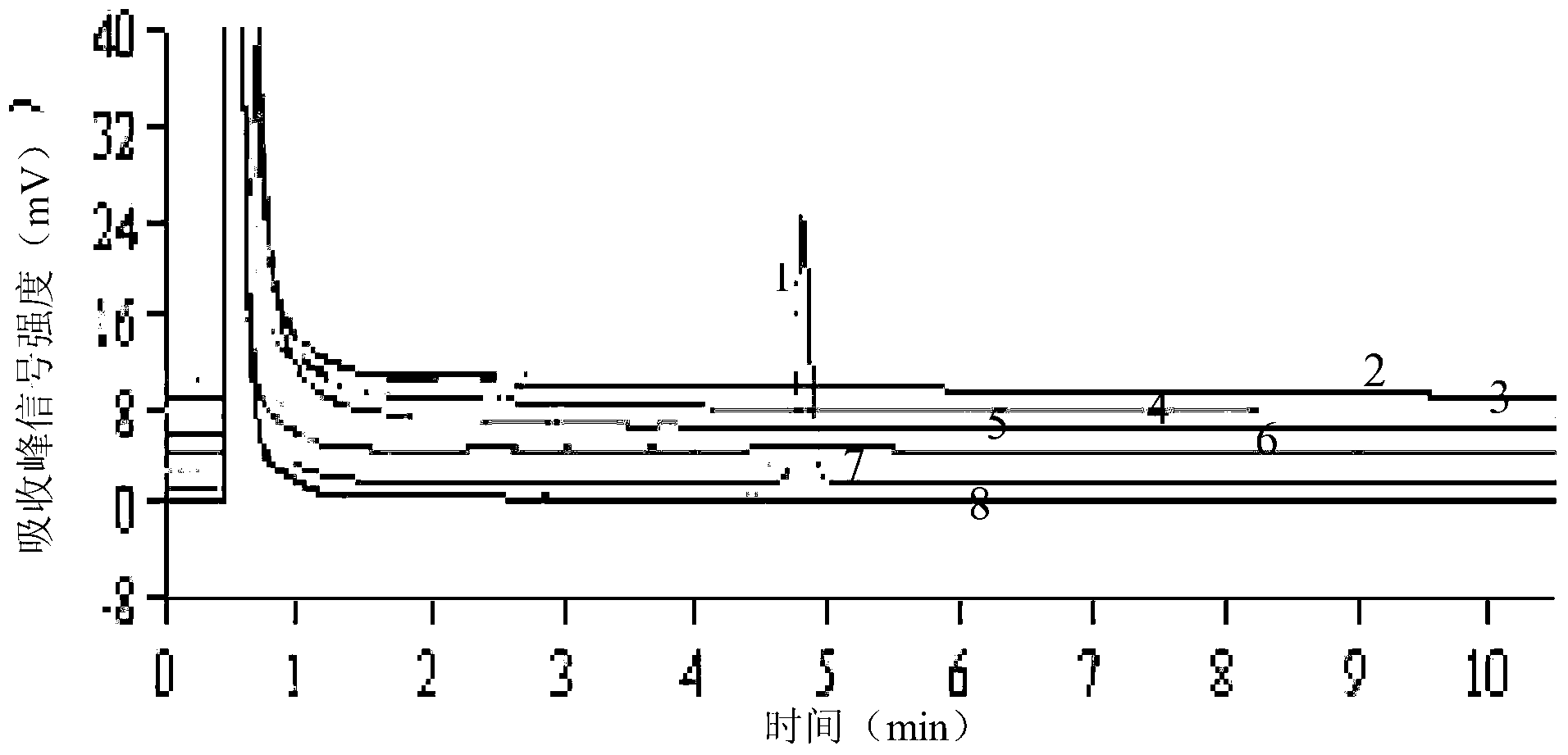
The invention relates to a dual polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography (PCR-DHPLC) detection method for staphylococcus aureus in aquatic products, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, staphylococcus aureus culture: aquatic product samples to be tested are mixed with enrichment liquid for culture; 2, staphylococcus aureus genome deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extraction; 3, primer design; 4, dual PCR amplification by using the staphylococcus aureus genome DNA as templates; and 5, DHPLC peak type map obtaining through PCR product DHPLC detection for analysis and identification. The integral detection method has the advantages that the reaction condition is simplified, the detection sensitivity is improved, in addition, the operation is simpler and more convenient, and the goal of high flux is reached.
Owner:中华人民共和国舟山出入境检验检疫局
Specific primers for detecting swine infuenza virus subtype H5 by using DHPLC (denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) and application thereof
InactiveCN104178587AQuick screeningAutomated screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesOutbreakDenaturing high performance liquid chromatography
The invention relates to specific primers for detecting swine infuenza virus subtype H5 by using DHPLC (denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) and application thereof. The specific primers are nucleotide sequences disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. By adopting the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification-nondenatured DHPLC combined analysis mode, the invention establishes a new method for quickly screening swine infuenza viruses. The method can quickly and automatically screen swine infuenza viruses at high flux, greatly enhances the detection efficiency, shortens the detection time, and has important clinical meanings for preventing and controlling outbreak of swine infuenza subtype H5.
Owner:徐超
PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and detection method for genetically modified maize strain CBH351
InactiveCN102952859AStrong specificitySimple and fast operationComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementFragment sizeQuarantine
The invention discloses a PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and a detection method for genetically modified maize strain CBH351. The primer has strong specificity and can be used for PCR amplification and DHPLC analysis. The detection method is simple and convenient to operate, good in expansion performance and high in sensitivity. The DHPLC is used to analyze PCR amplified products, fragment size resolution can reach multiple bases, and resolution ratio is high. The PCR-DHPLC detection primer and the detection method for genetically modified maize strain CBH351 have the advantages that the detection method is simple, convenient, effective, reliable and especially suitable for departments of port inspection and quarantine and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Fasciolopsis PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primers, kit and detection method
InactiveCN103266177AImprove detection efficiencyHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFasciolopsisPolymerase L
The invention discloses fasciolopsis PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primers, a kit and a detection method. Primers SEQ ID NO.1-2 are designed according to the gene sequence of fasciolopsis, and a PCR-DHPLC method is utilized to carry out qualitative detection on the fasciolopsis in food or aquatic plants. The kit comprises a 5U / mu L Taq DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, 2.5 mM of PCR reaction solution, 2.5 mM of dNTP (deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate), 10 mu M of SEQ ID NO.1 and 10 mu M of SEQ ID NO.2. The method can detect the fasciolopsis to the precision of 1 fasciolopsis / gram sample. The invention has the advantages of short time consumption and simple operation, can save abundant human resources and material resources, and is suitable for the requirements of quick detection.
Owner:郑秋月
Assay primer and assay method of PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) of transgenic rice KF8 strain
InactiveCN103333957AStrong specificitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAssayAgricultural science
The invention discloses an assay primer and assay method of PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) of transgenic rice KF8 strain. The primer is strong in specificity, and can be used in PCR and used for specifically amplifying a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment of the transgenic rice KF8 strain, and the amplified product can be applied to subsequent DHPLC analysis. The assay method for the transgenic rice KF strain is convenient to operate, good in extension performance and strong in specificity. The PCR amplified product is analyzed by utilizing the DHPLC, the resolution of the fragment of the PCR amplified product can reach a plurality of basic groups, and the resolution rate is high. According to the primer and assay method provided by the invention, a simple, convenient, effective and reliable assay method is provided to assay of the transgenic rice KF strain and is particularly applicable to port inspection and quarantine and other departments.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Soil microbial diversity analysis method
InactiveCN104830974AHigh sensitivityReduce pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAToxic material
The invention relates to a soil microbial diversity analysis method, belonging to the technical field of soil microbial analysis. In order to solve the problems of heavy pollution and long time consumption, the soil microbial diversity analysis method is provided. The soil microbial diversity analysis method includes microbial genome DNA extraction of acquired soil to obtain a genome DNA extract; detection of the genome DNA extract to determine the soil genomic DNA concentration and purity; PCR amplification of DNA extracted from the soil to obtain a PCR amplification product; and microbial diversity analysis of the PCR amplification product by use of denaturing high Performance liquid chromatography. According to the method, primer marking is not needed, glue leaking using toxic substance formamide and acrylamide is not needed, the radioactive pollution is reduced, and the soil microbial diversity analysis method has the effects of less pollution, high degree of automation, short detection time, high sensitivity, and good detection strip separation effect.
Owner:TAIZHOU UNIV +1
PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and detection method for genetically modified maize strain MON89034
InactiveCN102952862AStrong specificitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationQuarantineGenetically modified maize
The invention discloses a PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and a detection method for genetically modified maize strain MON89034. The primer has strong specificity and can be used for PCR amplification and DHPLC analysis. The detection method is simple and convenient to operate, good in expansion performance and high in sensitivity, and multi-target detection of genetically modified maize strain MON89034 is realized. The DHPLC is used to analyze PCR amplified products, fragment size resolution can reach multiple bases, and resolution ratio is high. The PCR-DHPLC detection primer and the detection method for genetically modified maize strain MON89034 have the advantages that the detection method is simple, convenient, effective, reliable and especially suitable for departments of port inspection and quarantine and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Detection kit and detection method for Campylobacter jejuni in pork
InactiveCN104278087AEfficient detectionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPhosphoric acidPolymerase L
The invention relates to a detection kit for Campylobacter jejuni in pork. The detection kit comprises a culture medium and a detection solution, wherein the culture medium is broth. The detection solution is composed of 3-5 mu l of 10 PCR (polymerase chain reaction) buffer solution, 0.2-0.4 mu l of Taq DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, 3-5 mu l of dNTP (deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate), 0.1-0.6 mu l of 100bp DNA Ladder Marker, 1-2 mu l of PCR primer, 5-10 ml of Tris.cl, 1-2.2mg of sodium chloride, 1-2.2mg of magnesium chloride, 0.2-0.5mg of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate and 3-5mg of enrichment broth. The detection kit is an improvement on the basis of the conventional PCR technology, and can be used for qualitative detection of Campylobacter jejuni. By integrating the advantages of PCR, DHPLC (denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) and other techniques, the detection kit has the advantages of high specificity of detection results and high sensitivity, and ensures the effective detection of Campylobacter jejuni in food.
Owner:中山鼎晟生物科技有限公司
Trichina PCR-DHPLC (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Denaturing High Performance Liquid Chromatography) detection primer as well as kit and detection method
InactiveCN103255226AImprove accuracyIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMaterial resourcesBiology
The invention discloses a trichina PCR-DHPLC (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Denaturing High Performance Liquid Chromatography) detection primer as well as a kit and a detection method. In allusion to a gene sequence of the trichina, detection primers SEQ ID NO.1-2 are designed and a PCR-DHPLC method is used for the qualitative detection of the trichina in detected animal derived food. The kit comprises Taq DNA polymerase with concentration of 5U / microlitre, 2.5mM of PCR reaction liquid, 2.5mM of dNTP (Diethyl-Nitrophenyl Thiophosphate), 10 microns of SEQ ID NO.1 and 10 microns of SEQ ID NO.2. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for precisely detecting the polypide sample of one trichina, and has the advantages of being short in detection time and simple to operate, saving lots of manpower and material resources and being suitable for rapid detection.
Owner:郑秋月 +3
PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and detection method for genetically modified maize strain BT11
InactiveCN102952860AStrong specificitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFragment sizeQuarantine
The invention discloses a PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) detection primer and a detection method for genetically modified maize strain BT11. The primer has strong specificity and can be used for PCR amplification and DHPLC analysis. The detection method is simple and convenient to operate, good in expansion performance and high in sensitivity. The DHPLC is used to analyze PCR amplified products, fragment size resolution can reach multiple bases, and resolution ratio is high. The PCR-DHPLC detection primer and the detection method for genetically modified maize strain BT11 have the advantages that the detection method is simple, convenient, effective, reliable and especially suitable for departments of port inspection and quarantine and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Methylation gene for liver cancer screening
ActiveCN106811523ASensitive detectionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideCervical cancer screening
The invention discloses a methylation gene for liver cancer screening. The gene is STAP1, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene is as shown in SEQ ID No: 1 and at least contains a methylation locus. According to the methylation gene for liver cancer screening, methylation sequencing can be performed by the aid of methods such as a methylation specific polymerase chain reaction method, a bisulfite sequencing method, a micro-array method, a mass-spectrographic analysis method, a denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography method and a pyrosequencing method, and the methylation gene is high in sensitivity, reliable in result and high in practicability and can sensitively detect early-phase liver cancer and earlier-phase liver cancer.
Owner:BEIJING YOUAN HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Primer and method for PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography) detection for endogenous genes of wheat
InactiveCN102952857AStrong specificitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationExtensibilityQuarantine
The invention discloses a primer and a method for PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography) detection for endogenous genes of wheat. The primer is high in specificity and can be used for PCR amplification and DHPLC analysis. The method for detection for the endogenous genes of the wheat is simple in operation, good in extensibility and high in sensitivity. PCR amplification products are analyzed by means of DHPLC, the segment size resolution of the PCR amplification products can reach multiple basic groups, and the resolution ratio is high. The primer and the method have the advantages that the method is a simple, convenient, effective and reliable method for detection for the endogenous genes of the wheat, and the primer and the method are particularly suitable for port inspection and quarantine departments and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) assay primer and assay method for transgenic rapeseed MS1 strain
InactiveCN103173551AStrong specificitySimple and fast operationComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementImage resolutionDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a PCR-DHPLC (polymerase chain reaction-denaturing high performance liquid chromatography) assay primer and assay method for transgenic rapeseed MS1 strain. The primer is strong in specificity, and can be used in PCR and used for specifically amplifying a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment of the transgenic rapeseed MS1 strain, and the amplified product can be applied to subsequent DHPLC analysis. The assay method provides an assay method for the transgenic rapeseed MS1 strain, which is convenient to operate, good in extension performance and strong in specificity. The PCR amplified product is analyzed by utilizing the DHPLC, the resolution of the fragment of the PCR amplified can be a plurality of basic groups, and the resolution rate is high. The primer and assay method provided by the invention provide a simple, convenient, effective and reliable assay method to assay of the transgenic rapeseed MS1 strain, and are particularly applicable to port inspection and quarantine and other departments.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com