Epitope analogs
a technology of epitopes and analogs, applied in the field of epitope analogs, can solve the problems of cells that do not respond to free or soluble antigens, and achieve the effect of similar or improving immunological properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
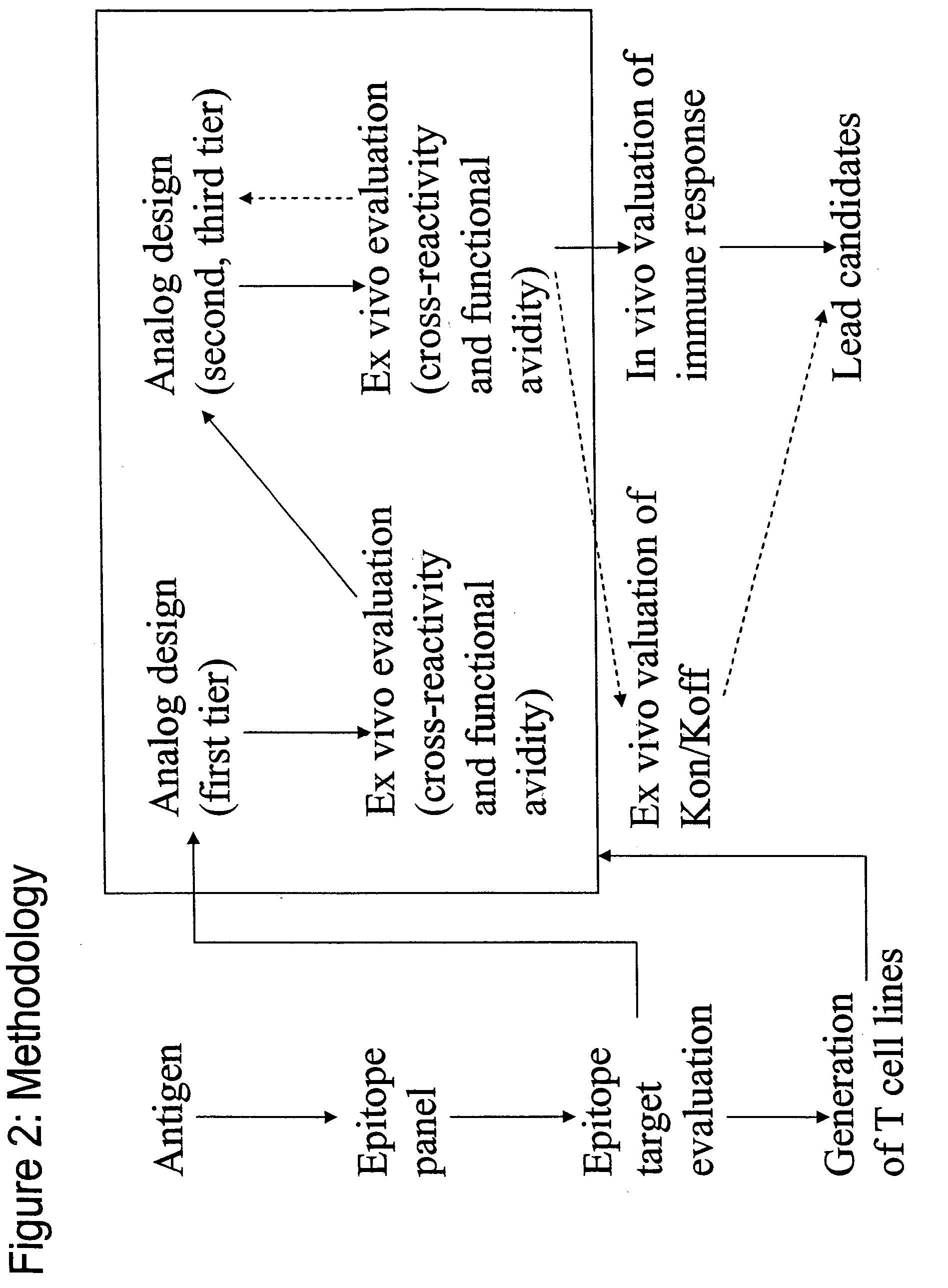
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Peptide Synthesis, Purification and Characterization
[0361] Peptides were synthesized on either a Symphony multiple peptide synthesizer (PTI technologies, MA) or an ABI 433A peptide synthesizer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, Calif.) at 0.05-0.1 mmole scale using standard Fmoc solid phase chemistry. C-terminal free acid peptides were synthesized using pre-load PEG-PS resins (on Symphony) or Wang resin (on ABI). C-terminal amidated peptides were synthesized on Fmoc-PAL-PEG-PS resin. All resins were purchased from Applied Biosystems (Foster City, Calif.). The Fmoc-amino acids used in peptide syntheses were purchased from Novabiochem (San Diego, Calif.) and AnaSpec (San Jose, Calif.). Post-synthesis cleavage was carried on by the standard protocol.
[0362] Peptide purification was carried out on either semi-preparative HPLC columns or SPE cartridges (Phenomenex, Torrance, Calif.). The purity of all peptides was ≧90%. The identity of each peptide was verified by Maldi-TOF MS (Voyager D...
example 2
De Novo Designed SSX-241-49 Analogs
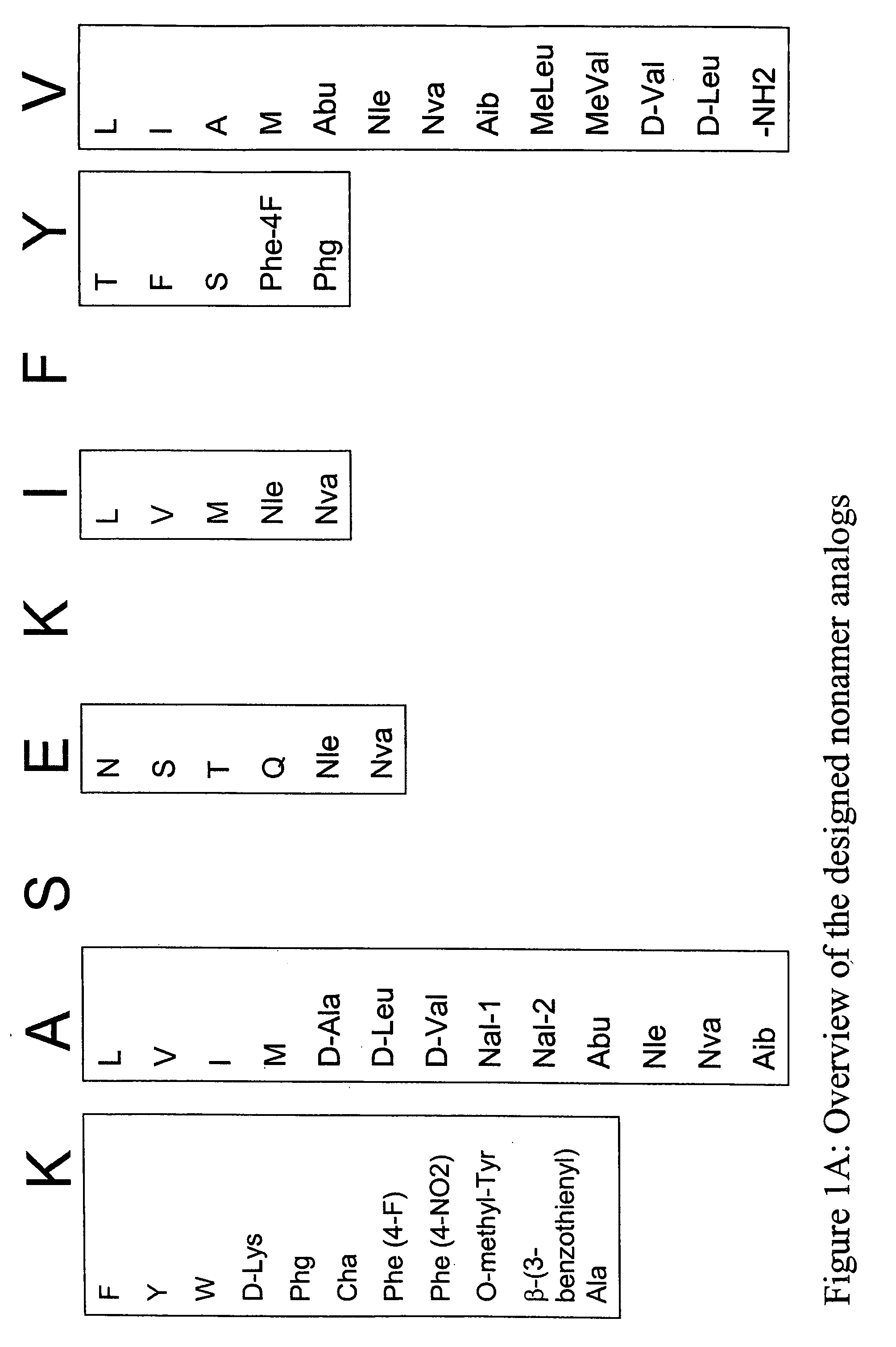
[0363] Structural modification of a moderately antigenic peptide can considerably improve peptide-MHC binding, CTL recognition, and / or immunogenicity. General guidelines regarding how to modify a wild-type epitope in order to achieve a peptide analog with enhanced potency are known in the art. An appreciated strategy is to optimize the residues at the so-called anchor positions for binding to the particular MHC molecule at issue. In the case of HLA-A2 a marked preference for hydrophobic residues at the P2 and PΩ positions has been observed, particularly L, and M at P2, and V at PΩ. (PΩ denotes the C-terminal residue of the epitope. For HLA-A2 that is P9 or P10 depending on the length of the peptide.) Replacing the P1 position with aromatic residues, such as F, Y and W can also be advantageous.
TABLE 7Coefficients used by the BIMAS algorithm(Algorithm available by hypertext transfer protocol: / / bimas.cit.nih.gov / molbio / hla_bind / )9-mer Coefficient T...
example 3
[0366] The following analogs were produced using the predictions in Example 1.
TABLE 9SEQ IDCatergoryNumberPeptide nameSequencewild-type1SSX-2 41-49KASEKIFYVN-terminal Primary Anchor2SSX-2 41-49 (A42L)KLSEKIFYV3SSX-2 41-49 (A42V)KVSEKIFYV4SSX-2 41-49 (A42I)KISEKIFYV5SSX-2 41-49 (A42M)KMSEKIFYV6SSX-2 41-49 (A42(D-Ala))K(D-Ala)SEKIFYV7SSX-2 41-49 (A42(D-Leu))K(D-Leu)SEKIFYV8SSX-2 41-49 (A42(D-Val))K(D-Val)SEKIFYV9SSX-2 41-49 (A42(Nal-1))KNal-1SEKIFYV10SSX-2 41-49 (A42(Nal-2))KNal-2SEKIFYV11SSX-2 41-49 (A42(Abu))KAbuSEKIFYV12SSX-2 41-49 (A42(Nle))KNleSEKIFYV13SSX-2 41-49 (A42(Nva))KNvaSEKIFYV14SSX-2 41-49 (A42(Aib))KAibSEKIFYVN-terminal Secondary15SSX-2 41-49 (K41F)FASEKIFYVAnchor16SSX-2 41-49 (K41W)WASEKIFYV17SSX-2 41-49 (K41Y)YASEKIFYV18SSX-2 41-49 (K41(D-Lys))(D-Lys)ASEKIFYV19SSX-2 41-49 (K41(Phg))PhgASEKIFYV20SSX-2 41-49 (K41(Cha))ChaASEKIFYV21SSX-2 41-49 (K41(Phe-4F))Phe(4-F)ASEKIFYV22SSX-2 41-49 (K41(Phe-4NO2))Phe(4-NO2)ASEKIFYV23SSX-2 41-49 (K41(O-methyl Tyr))O-methyl-TyrASEKIF...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com