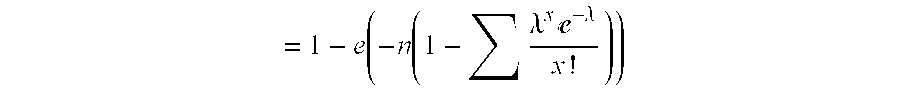Patents
Literature
66 results about "Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Pseudomonas exotoxin (or exotoxin A) is an exotoxin produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It inhibits elongation factor-2. It does so by ADP-ribosylation of EF2. This then causes the elongation of polypeptides to cease. (The mechanism of the toxin is similar to that of Diphtheria toxin.)
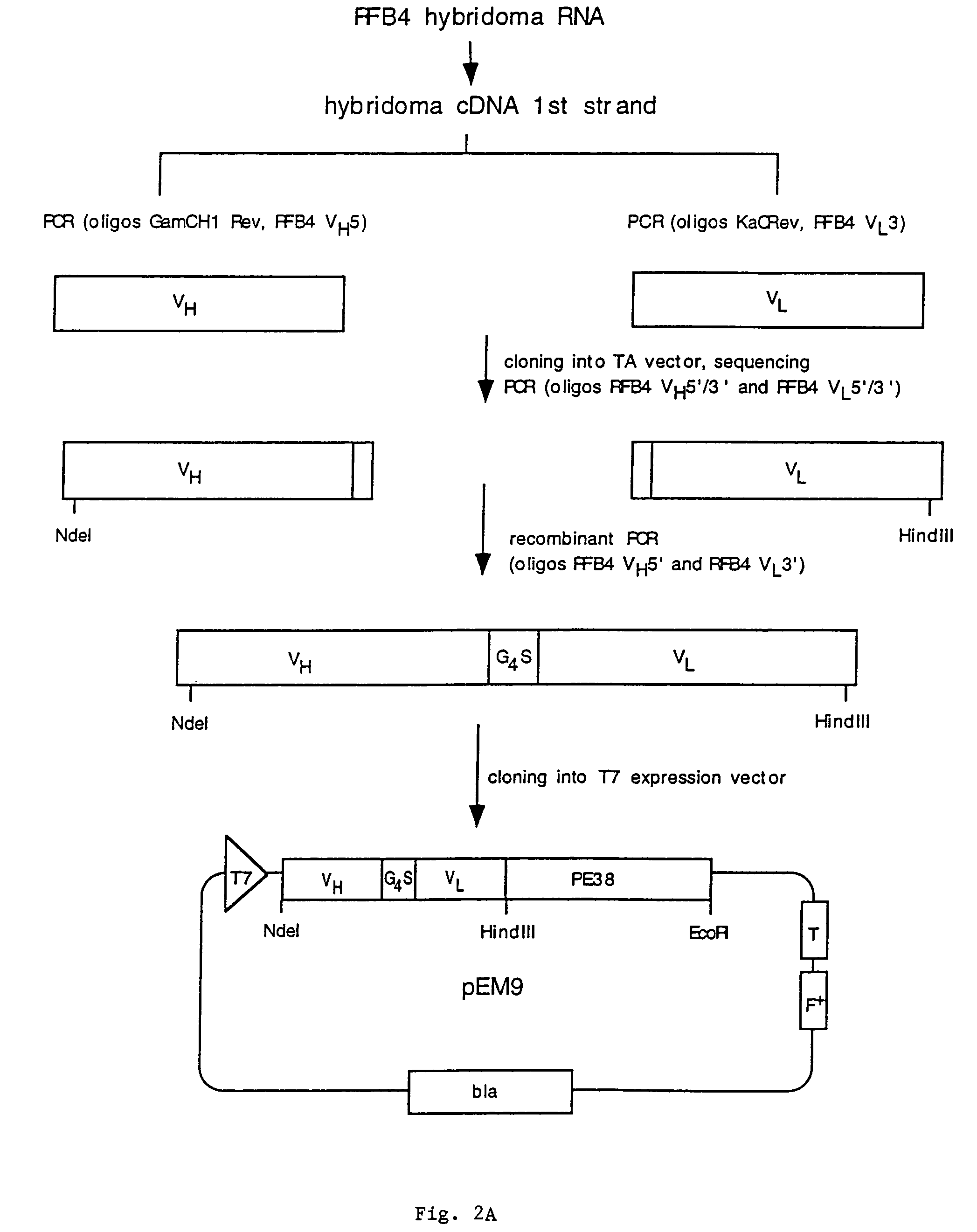
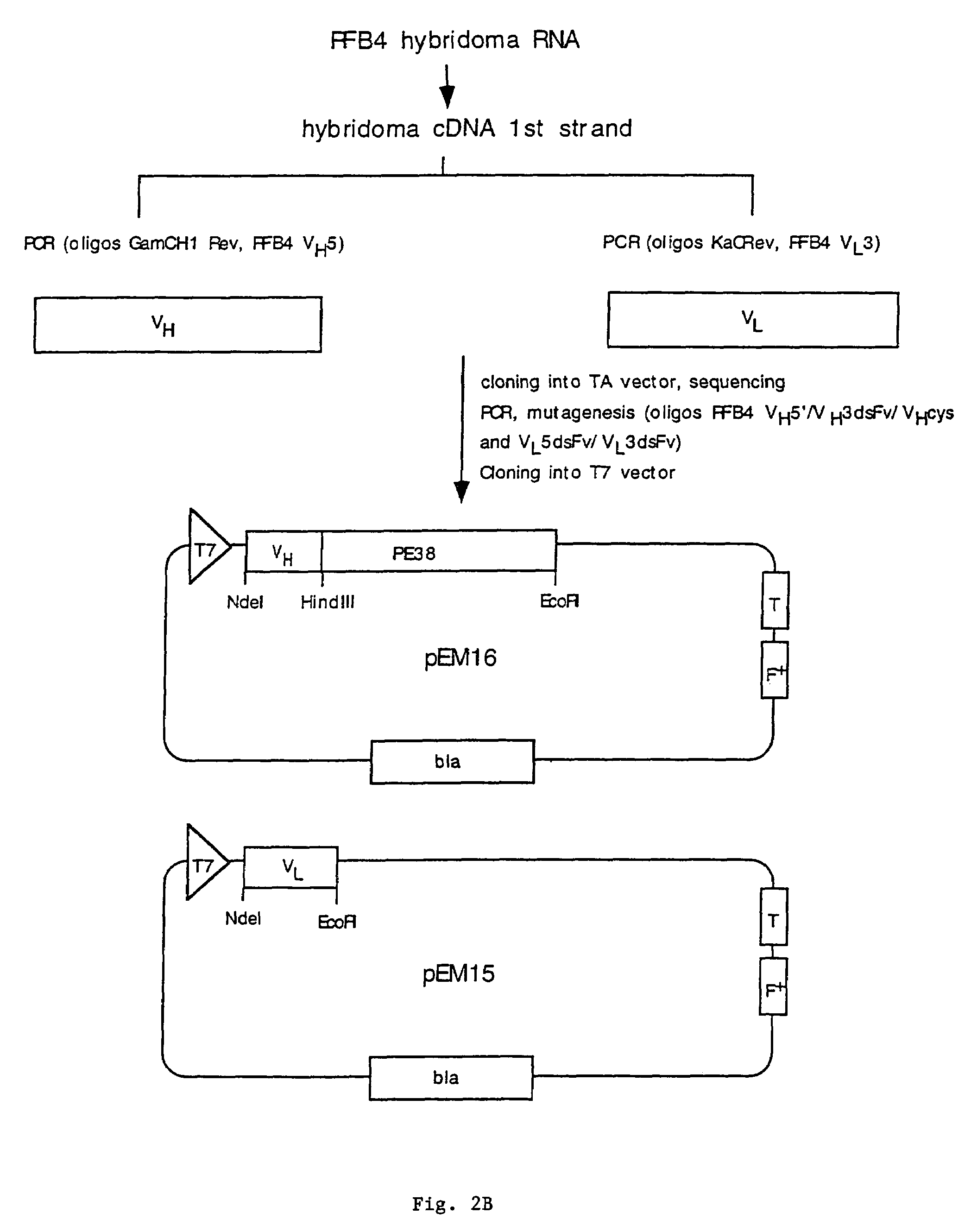
Recombinant antibodies and immunoconjugates targeted to CD-22 bearing cells and tumors
InactiveUS7541034B1Growth inhibitionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APseudomonas
Methods and compositions relating to recombinant anti-CD22 antibodies with high binding affinity, and immunoconjugates comprising the anti-CD22 antibody linked to a therapeutic agent such as a Pseudomonas exotoxin or a detectable label. The invention provides diagnostic methods, and means to inhibit the growth of malignant B cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICAN AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Modified pseudomonas exotoxin a
ActiveUS20150099707A1Increased serum half-lifeOptimize treatment planOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APseudomonas
The invention provides a Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising an amino acid sequence having a substitution of one or more B-cell and / or T-cell epitopes. The invention further provides related chimeric molecules, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions. Methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal, methods of inhibiting the growth of a target cell, methods of producing the PE, and methods of producing the chimeric molecule are further provided by the invention.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Mutated pseudomonas exotoxins with reduced antigenicity
ActiveUS20090142341A1Peptide/protein ingredientsBacteria peptidesPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AEpitope
The invention provides mutated Pseudomonas exotoxins (PE) that have reduced immunogenicity compared to PEs containing the native sequence. The PEs of the invention have one or more individual mutations of positions of the native sequence of PE that reduce antibody binding to one or more PE epitopes. Nucleic acids encoding the mutated PEs, chimeric molecules comprising them, compositions comprising the chimeric molecules and methods of using them, are also provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Compositions and methods for targeting a polypeptide to the central nervous system
InactiveUS20050100986A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AInsulin-like growth factor
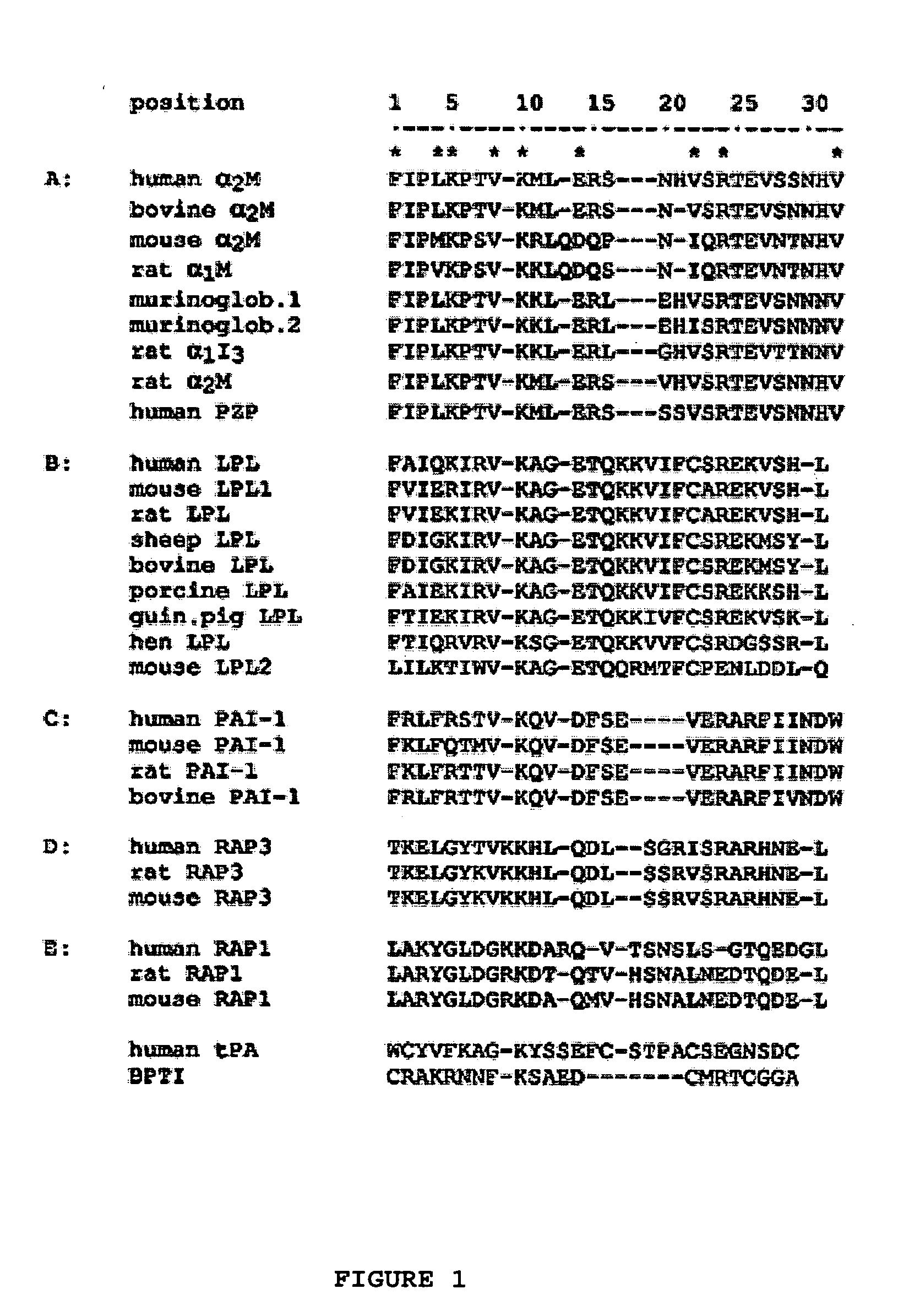
The invention provides a chimeric CNS targeting polypeptide having a BBB-receptor binding domain and a payload polypeptide domain. The chimeric CNS targeting polypeptide can have a BBB-receptor binding domain consisting of a receptor binding domain from ApoB, ApoE, aprotinin, lipoprotein lipase, PAI-1, pseudomonas exotoxin A, transferrin, α2-macroglobulin, insulin-like growth factor, insulin, or a functional fragment thereof. Nucleic acids encoding a chimeric CNS targeting polypeptide are also provided. Further provided is a method of delivering a polypeptide to the CNS of an individual. The method consists of administering to the individual an effective amount of a chimeric CNS targeting polypeptide, said chimeric CNS targeting polypeptide comprising a BBB-receptor binding domain and a payload polypeptide domain. The method also can deliver a polypeptide to the lysosomes of CNS cells.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Deletions in domain II of pseudomonas exotoxin a that remove immunogenic epitopes
ActiveUS8871906B2Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AEpitope
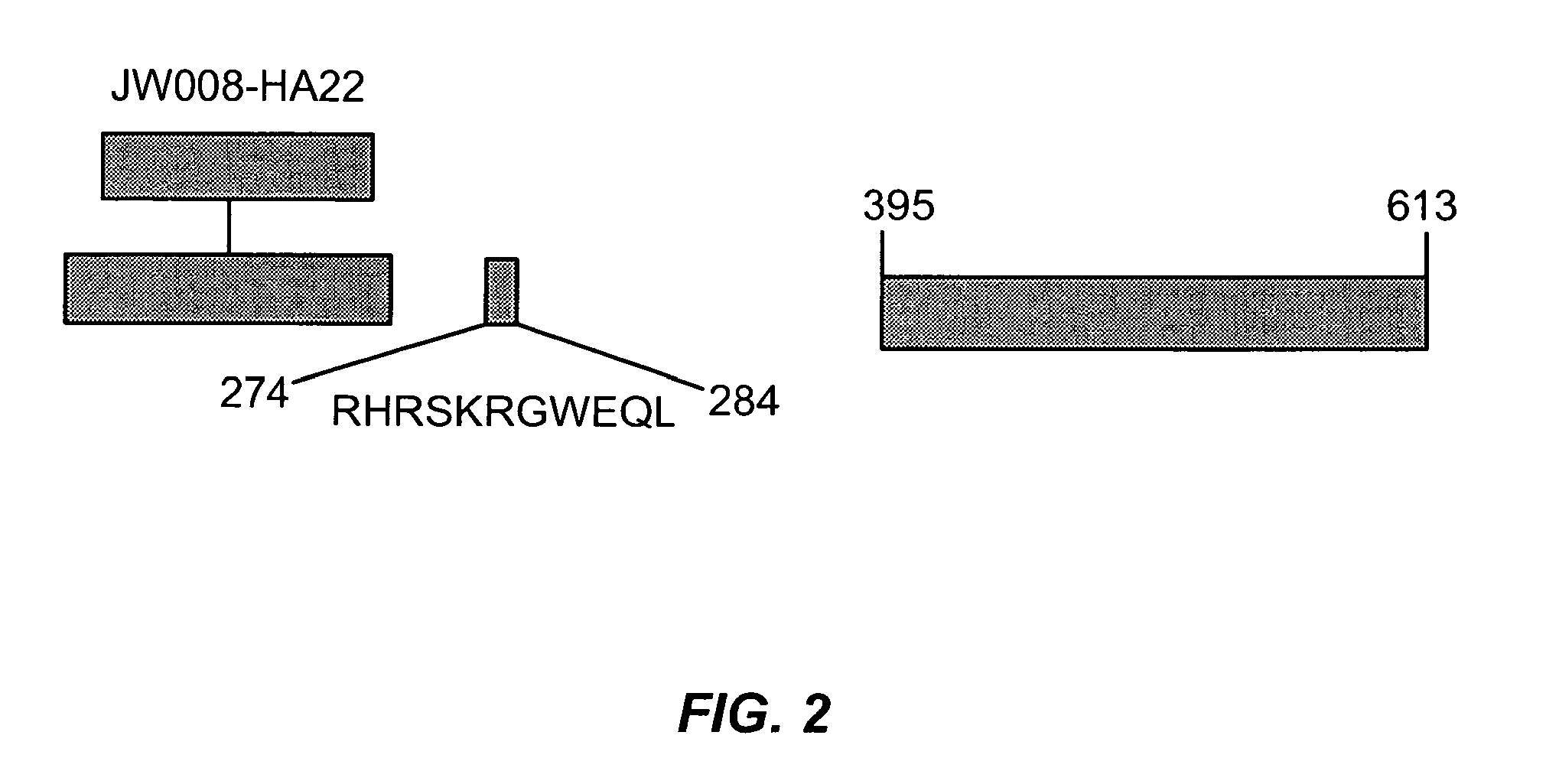
The invention provides mutated, cytotoxic forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising a furin cleavage sequence conjugated or fused directly to residues 395-613 of PE or variants of that sequence. These minimal forms of PE are smaller than previous cytotoxic forms of PE, reduce non-specific toxicity, and reduce immunogenicity due to domain II or domain Ib of PE. The invention further provides nucleic acids encoding said PEs, chimeric molecules containing them, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Recombinant antibodies and immunoconjugates targeted to cd-22 bearing cells and tumors
InactiveUS20090305411A1BacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APseudomonas
Methods and compositions relating to anti-CD22 antibodies with high binding affinity, and immunoconjugates comprising the anti-CD22 antibody linked to a therapeutic agent such as a Pseudomonas exotoxin or a detectable label. The invention provides diagnostic methods, and means to inhibit the growth of malignant B cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Deletions in domain ii of pseudomonas exotoxin a that remove immunogenic epitopes
ActiveUS20100215656A1Maintain immunogenicitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AEpitope
The invention provides mutated, cytotoxic forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising a furin cleavage sequence conjugated or fused directly to residues 395-613 of PE or variants of that sequence. These minimal forms of PE are smaller than previous cytotoxic forms of PE, reduce non-specific toxicity, and reduce immunogenicity due to domain II or domain Ib of PE. The invention further provides nucleic acids encoding said PEs, chimeric molecules containing them, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
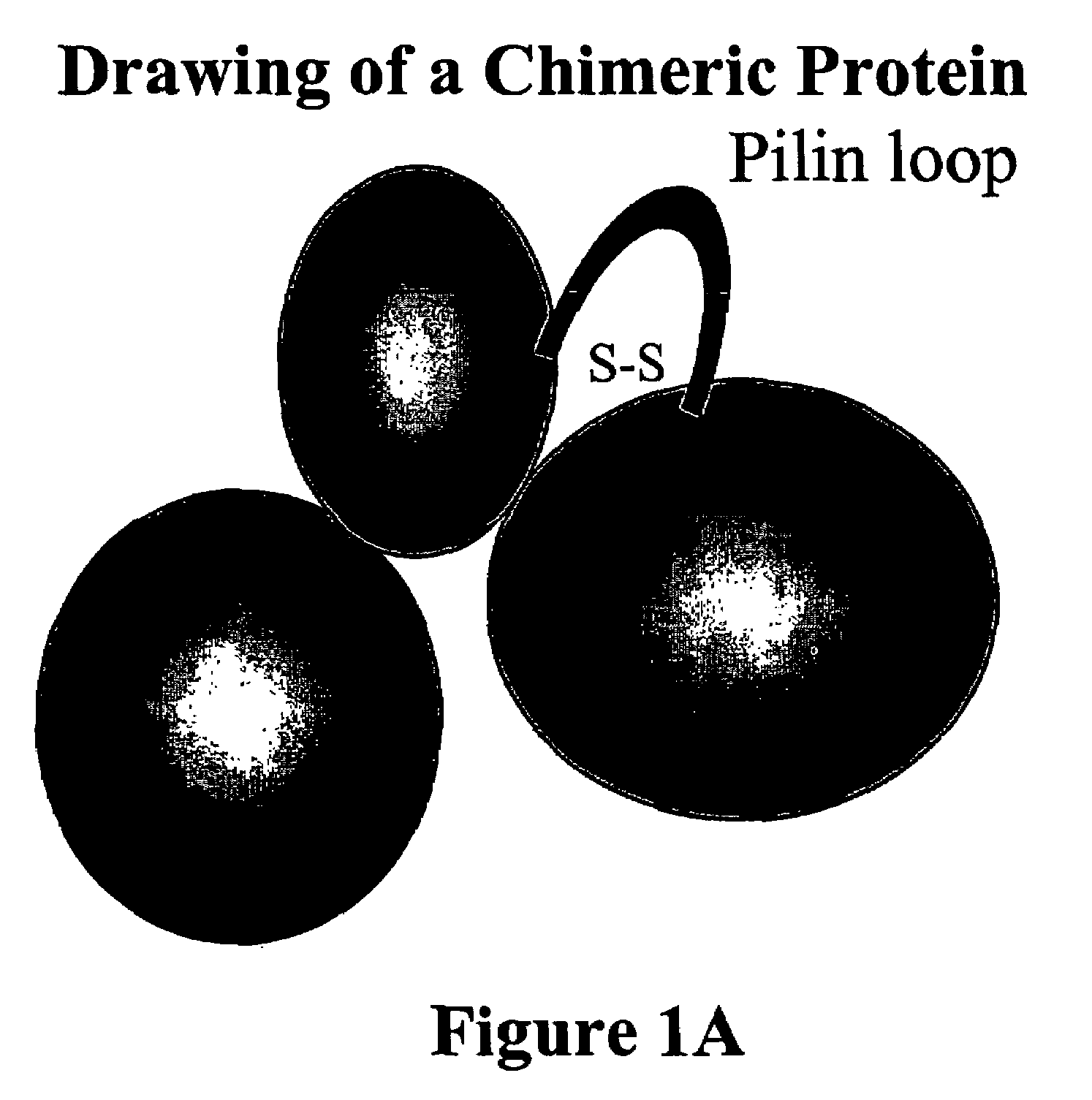
Chimeric protein comprising non-toxic pseudomonas exotoxin and type IV pilin sequences
InactiveUS20070003578A1Reduce adhesionAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin ABacterial exotoxin
The invention provides chimeric proteins comprising a non-toxic Pseudomonas exotoxin A sequence and a Type IV pilin loop sequence, wherein the Type IV loop sequence is inserted within the non-toxic Pseudomonas exotoxin A. The invention also provides polynucleotides encoding the chimeric proteins, and compositions comprising the polynucleotides or the chimeric proteins. The invention also provides methods for using the chimeric proteins, polynucleotides and compositions of the invention.
Owner:THE GOV OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEP OF HEALTH & HUAMN SERVICES
Compositions and methods for targeting a polypeptide to the central nervous system
InactiveUS20060198833A1Nervous disorderSugar derivativesPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AInsulin-like growth factor
The invention provides a chimeric CNS targeting polypeptide having a BBB-receptor binding domain and a payload polypeptide domain. The chimeric CNS targeting polypeptide can have a BBB-receptor binding domain consisting of a receptor binding domain from ApoB, ApoE, aprotinin, lipoprotein lipase, PAI-1, pseudomonas exotoxin A, transferrin, α2-macroglobulin, insulin-like growth factor, insulin, or a functional fragment thereof. Nucleic acids encoding a chimeric CNS targeting polypeptide are also provided. Further provided is a method of delivering a polypeptide to the CNS of an individual. The method consists of administering to the individual an effective amount of a chimeric CNS targeting polypeptide, said chimeric CNS targeting polypeptide comprising a BBB-receptor binding domain and a payload polypeptide domain. The method also can deliver a polypeptide to the lysosomes of CNS cells.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Polymer-Linked Pseudomonas Exotoxin Immunotoxin
InactiveUS20080125363A1Antibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APolymer science
Owner:ENZON PHARM INC
Chimeric HIV fusion proteins as vaccines
InactiveUS20120213811A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AReticulum cell
A method for treating HIV infection is disclosed. The method comprises administering to a patient in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of a fusion protein comprising: a) a Pseudomonas Exotoxin A (PE) peptide comprising a binding domain and a PE translocation domain, the PE peptide being devoid of cytotoxic domain III; b) optionally gag24, being fused to the PE peptide; c) a fragment of gp120 C1 domain, being fused to the PE peptide or fused to the gag24 if the gag24 is present; d) a fragment of gp 120 C5 domain, being fused to the fragment of gp120 C1 domain; e) a fragment of gp41 amino acid sequence, being fused to the fragment of gp 120 C5 domain, and f) optionally an endoplasmic reticulum retention sequence, being fused to the C-terminus of the fragment of gp41.
Owner:THEVAX GENETICS VACCINE
Fusion protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus as PRRS vaccine
ActiveUS20080008722A1SsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AAllergy
The present invention provides a PRRSV subunit vaccine comprising a fusion protein having neutralization titers evoked, PE-PQGAB-K3, which comprises a chimeric polypeptide containing N-terminal portions of PRRSV ORF5 and ORF6 structure proteins; a portion of Pseudomonas exotoxin A binding and translocation domain; and a carboxyl terminal domain containing KDEL-KDEL-KDEL(K3) sequence. Less inflammation of PE-PQGAB-K3 vaccine group in their lungs post being PRRSV-challenged indicates that PQGAB without an antigen-specific allergy effect. Importantly, PE-PQGAB-K3 vaccine presents a good protection against PRRSV infection than control groups in pig challenged experiment.
Owner:AGRI TECH RES INST
Pseudomonas Exotoxin A Cd4+T-Cell Epitopes
InactiveUS20080193976A1Improve concentrationIncrease concentrationAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AWild type
The present invention provides PE CD4+T-cell epitopes, as well as novel variants that exhibit reduced immunogenic responses, as compared to the parental PE. The present invention further provides DNA molecules that encode novel PE variants, host cells comprising DNA encoding novel PE variants, as well as methods for making PEs less immunogenic. In addition, the present invention provides various compositions that comprise these PE variants that are less immunogenic than wild-type PEs.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
FcεPE chimeric protein for targeted treatment of allergy responses, a method for its production and pharmaceutical compositions containing the same
InactiveUS6919079B1Efficient killingGeneral immunosupressive effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliDisease
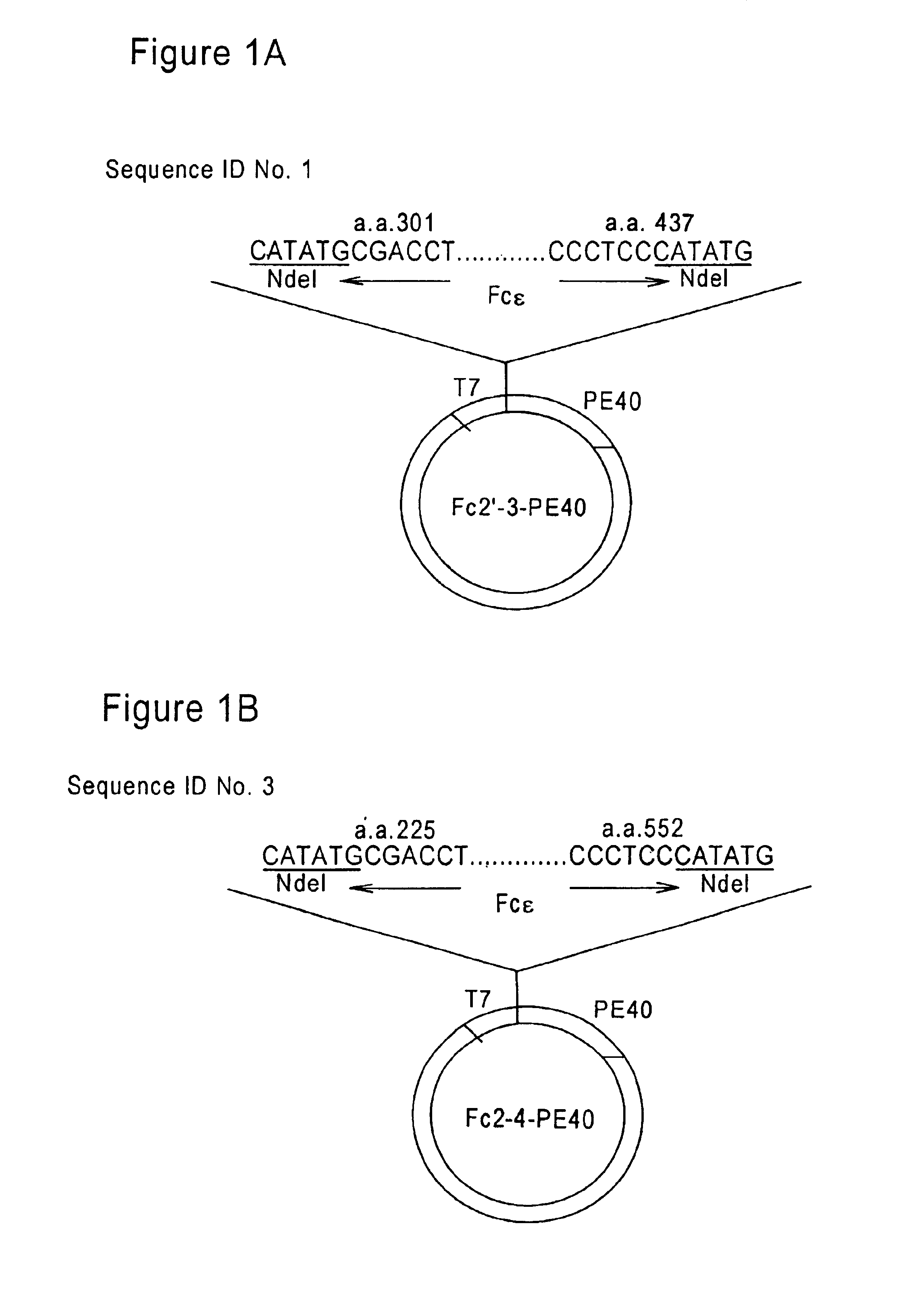
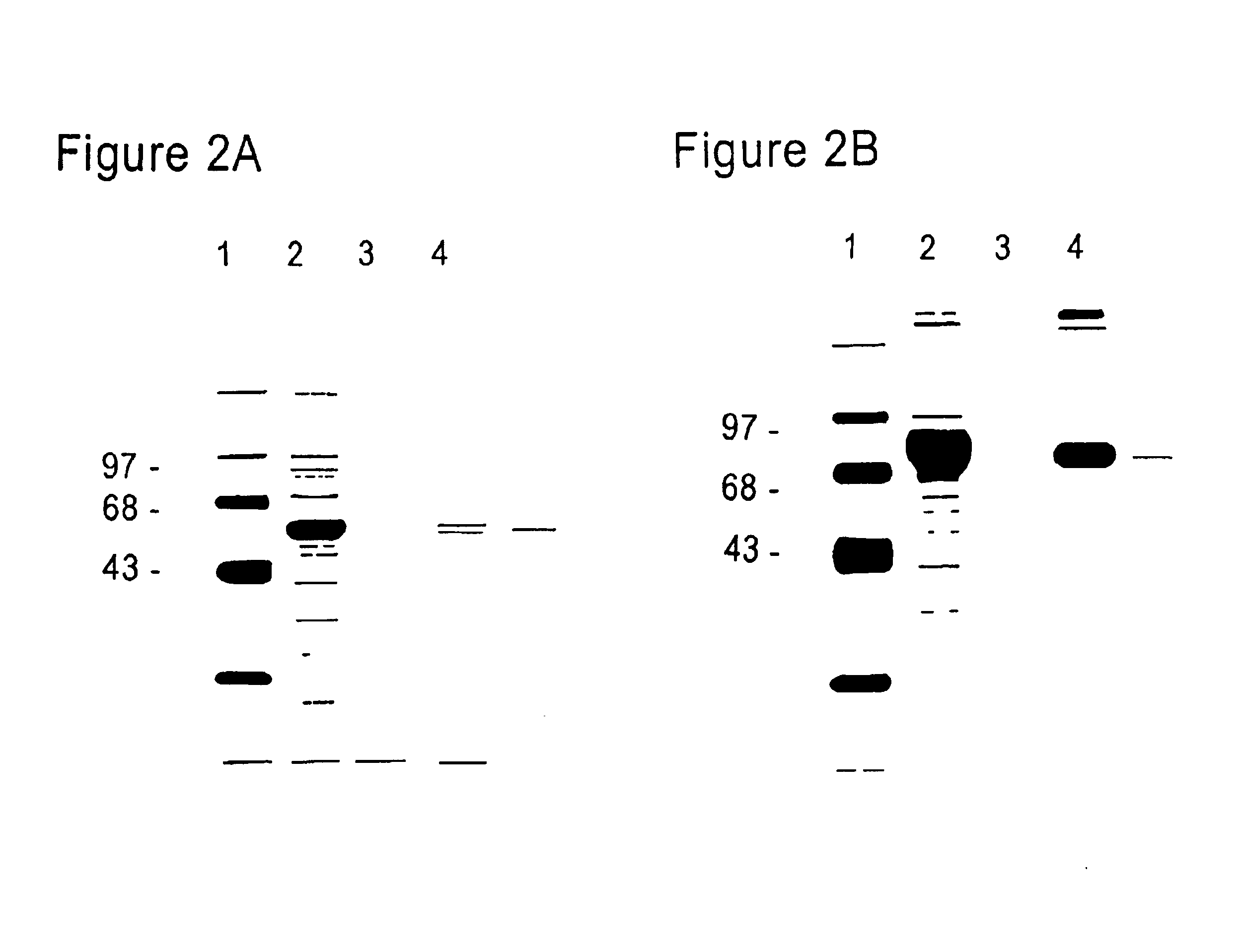
The present invention generally relates to a new approach for the therapy of allergic responses, based on targeted elimination of cells expressing the FcεRI receptor by a chimeric cytotoxin Fc2′-3-PE40. A sequence encoding amino acids 301-437 of the Fc region of the mouse IgE molecule was genetically fused to PE40—a truncated form of PE lacking the cell binding domain. The chimeric protein, produced in E. coli, specifically and efficiently kills mouse mast cell lines expressing the FcεRI receptor, as well as primary mast cells derived from bone marrow. The present invention provides a chimeric protein for targeted elimination of FcεRI expressing cells especially useful for the therapy of allergic responses. The said chimeric protein is comprised of a cell targeting moiety for FcεRI expressing cells and a cell killing moiety. The preferred killing moiety is the bacterial toxin Pseudomonas exotoxin (PE). This Pseudomonas exotoxin is a product of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The present invention also relates to a method for the preparation of said protein. This chimeric protein is prepared by genetically fusing the Fc region of the mouse IgE molecule to PE40, a truncated form of PE lacking the cell binding domain. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions, for the treatment of allergic diseases and for the treatment of hyperplasias and malignancies, comprising as an active ingredient the above mentioned chimeric protein and a conventional adjuvant product.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Immunotoxin derived from a recombinant human autoantibody and method of using thereof
ActiveUS20060013809A1Preventing Myasthenia GravisInduce immune toleranceHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin ACDNA library
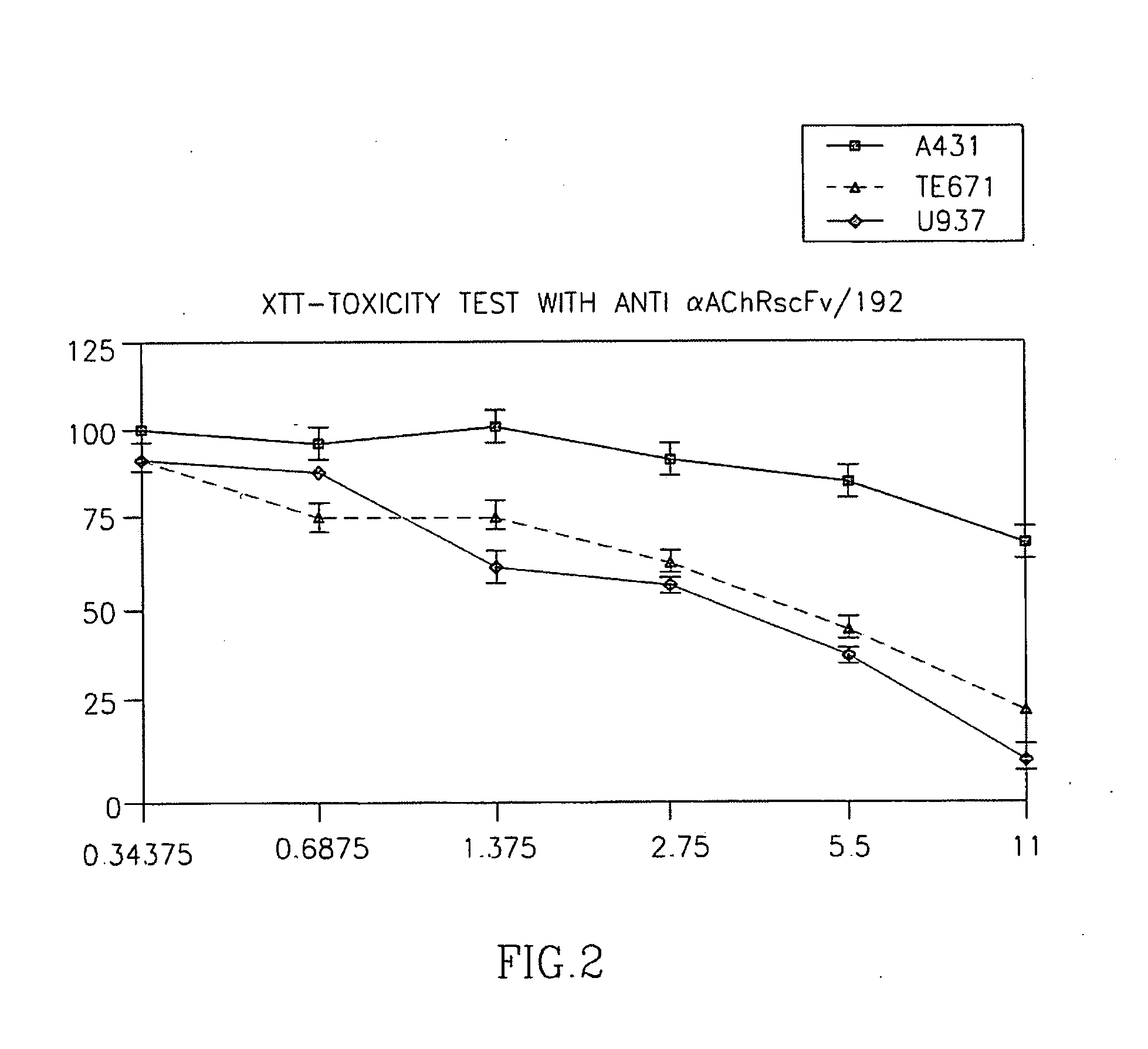
The invention is directed to an immunotoxin directed at fetal AchR, wherein the immunotoxin may comprises a human Fab fragment based on a human autoantibody or human combinatorial cDNA library and may be a pseudomonas exotoxin A-based single chain Fv IT (35-scFV-ETA). The invention is further directed to method of treating a patient with soft tissue tumour comprising the step of exposing the patient to the immunotoxin of the invention.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Target-specificity dual-mutant amalgamation protein
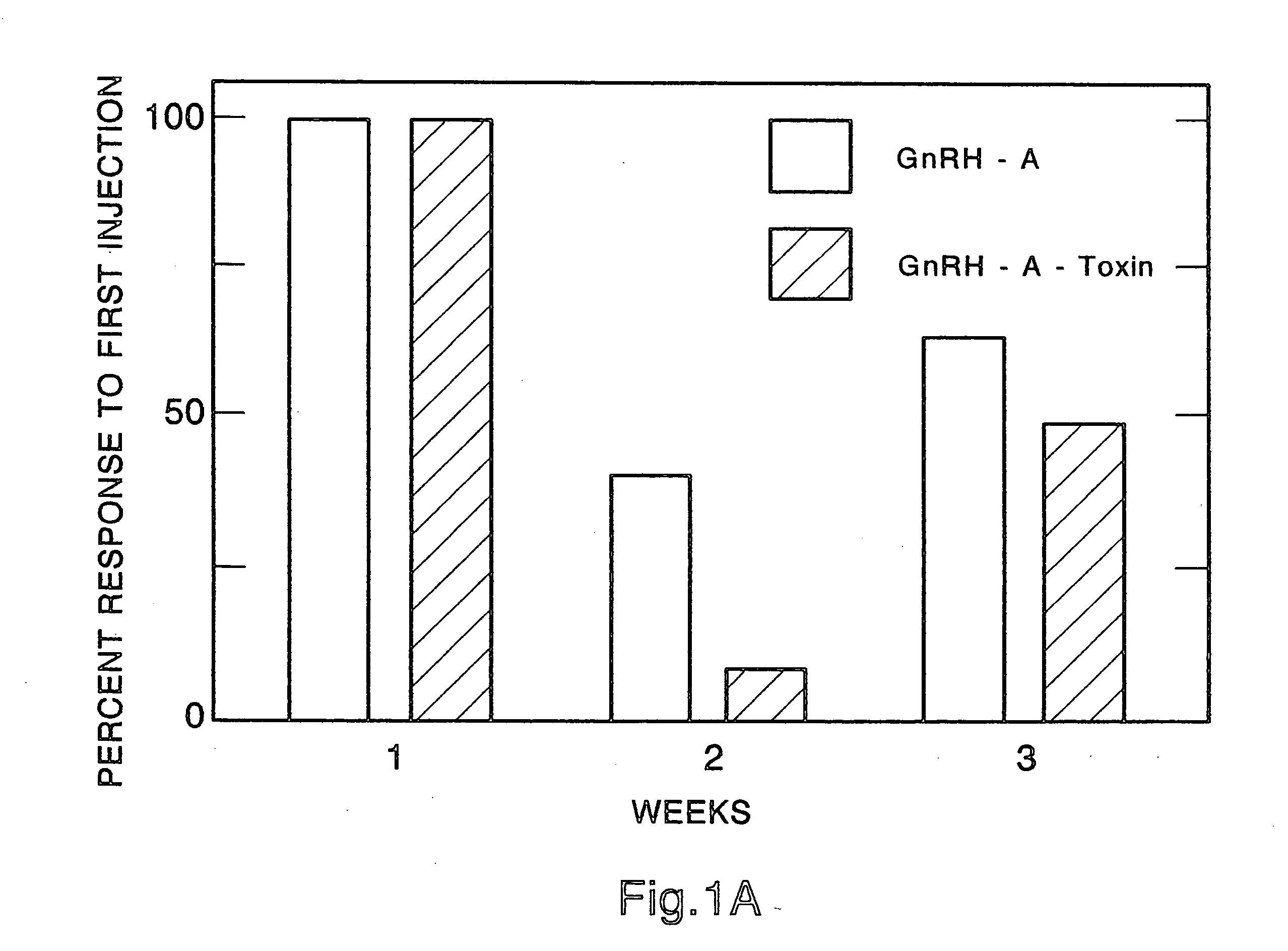
ActiveCN101343328ANo lethal effectLow costPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin ACytotoxicity
The invention discloses target specific double mutant fusion protein, which is established by human gonadotropin releasing hormone mutant (mGnRH) and recombinant pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A mutant (PE38m4a) fusion protein. The mGnRH-PE38m4a protein provided by the invention has obvious specific binding activity and cytotoxicity to the tumor cell lines which comprise colon cancer HT-29 cells, oophoroma OVCAR3 cells, cervical adenocarcinoma HeLa cells or liver cancer HepG-2 cells, and the like; the normal cells basically have no lethal function; the activity of the fusion protein is enhanced by approximate nine to ten times compared with the activity of natural PEA; the cost is low, the method is simple, therefore the target specific double mutant fusion protein is more suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:SHANGHAI SILINGE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Pseudomonas exotoxin a with reduced immunogenicity
ActiveUS20120263674A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin ACytotoxicity
The present invention provides improved Pseudomonas Exotoxin A (PE) molecules with high cytotoxicity and reduced immunogenicity, compositions containing the improved (PE), and methods of use.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH OFFICE OF TECH TRANSFER
Chimeric protein comprising non-toxic Pseudomonas exotoxin A and Type IV pilin sequences
InactiveUS7314625B2Antibacterial agentsSenses disorderPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APseudomonas tolaasii
The invention provides chimeric proteins comprising a non-toxic Pseudomonas exotoxin A sequence and a Type IV pilin loop sequence, wherein the Type IV loop sequence is inserted within the non-toxic Pseudomonas exotoxin A. The invention also provides polynucleotides encoding the chimeric proteins, and compositions comprising the polynucleotides or the chimeric proteins. The invention also provides methods for using the chimeric proteins, polynucleotides and compositions of the invention.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Preparation method and application of fusion protein and vaccine composition containing same
ActiveCN104277115AShort timeEase of mass productionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AMycoplasmal pneumonia
The invention provides a fusion protein, a fusion protein-containing vaccine composition for mycoplasmal pneumonia of swine (MPS) and an application of the vaccine composition. The fusion protein comprises pseudomonas exotoxin A structural domains I and II, an antigenic protein for MPS and a carboxyl terminal part, wherein the antigenic protein for MPS comprises any one of an NrdF protein, a P102 protein, a P97R1 protein, a P97R2 protein, a P97R1-NrdF protein and a P97R2-NrdF protein. The invention also discloses the vaccine composition containing immune dosage of fusion protein and the application of the vaccine composition to preparation of drugs for preventing and / or treating MPS. The vaccine composition has the advantages that recombinant expression can be carried out on the components of the vaccine composition in quantity by means of genetic engineering, thus not only consuming short time but also facilitating large-scale production; the vaccine composition can generate humoral immunity and cellular immunity and can gain better immune effects.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Fusion protein and encoding gene thereof as well as application of fusion protein
InactiveCN102134279AAntiviralsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin APolyclonal antibodies
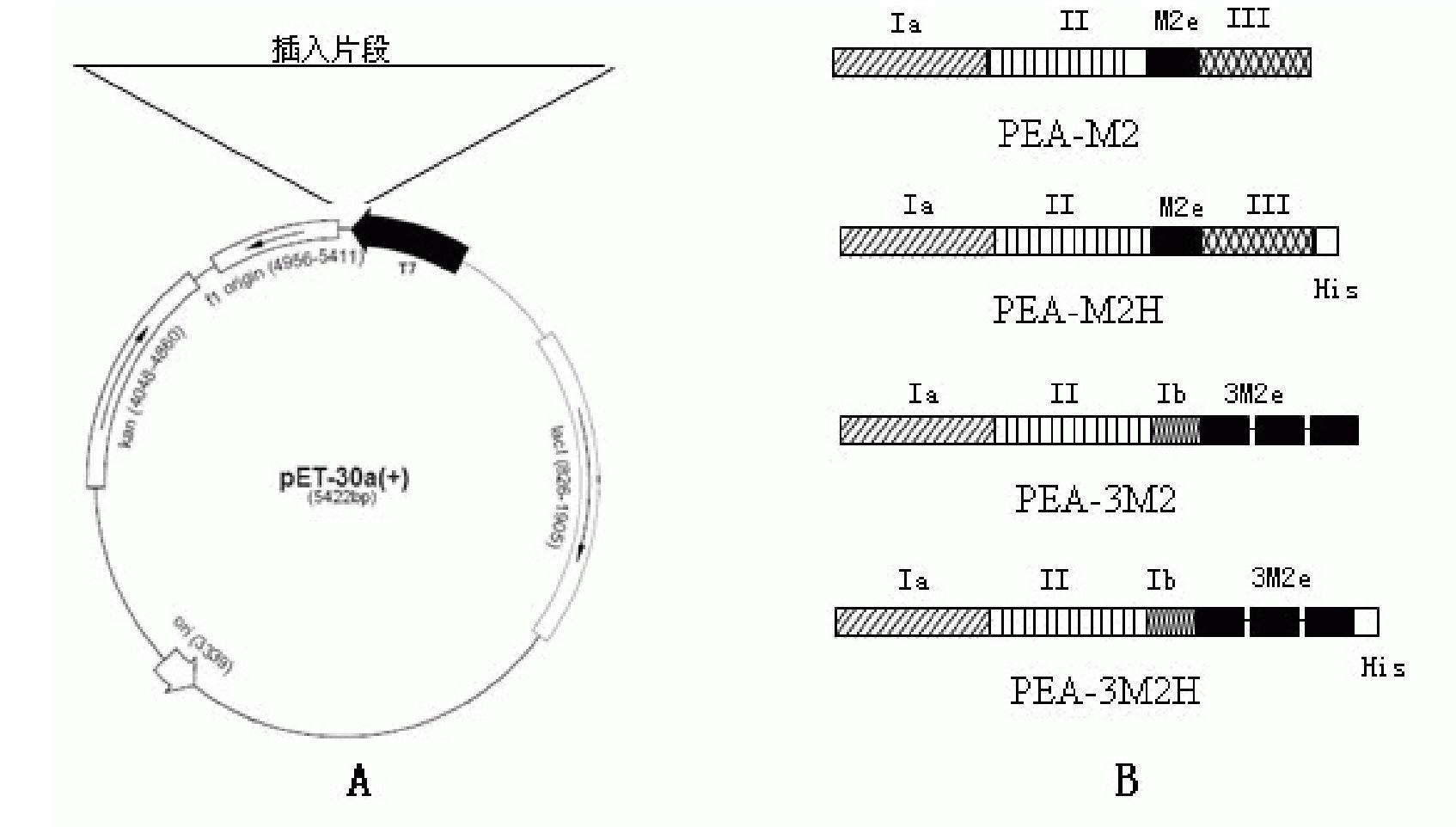
The invention relates to a fusion protein and an encoding gene thereof as well as an application of the fusion protein. The fusion protein is obtained by fusing an unnecessary domain or carboxyl terminal of pseudomonas exotoxin A with 1-3 extracellular domains of a copied influenza A virus M2 protein, wherein the amino acid sequence of the pseudomonas exotoxin A is a part selected from the 1st-392nd positions and the 407th-657th positions from an amino terminal of a sequence 15 in a sequence table. The invention also discloses a gene for encoding the fusion protein. The fusion protein can be used for preparing influenza A virus vaccines. The fusion protein can stimulate an organism to generate M2 polyclonal antibodies and can stimulate the organism to generate cell immune responses aimingat M2e.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Method for inactivating gonadotrophs
InactiveUS20050277582A1Easy to transportImprove solubilityPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesGeloninPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A
Certain toxic compounds (T) such as, for example, compounds based upon diphtheria toxin, ricin toxin, pseudomonas exotoxin, .alpha.-amanitin, pokeweed antiviral protein (PAP), ribosome inhibiting proteins, especially the ribosome inhibiting proteins of barley, wheat, corn, rye, gelonin and abrin, as well as certain cytotoxic chemicals such as, for example, melphalan and daunomycin can be conjugated to certain analogs of gonadotropin-releasing hormone to form a class of compounds which, when injected into an animal, destroy the gonadotrophs of the animal's anterior pituitary gland. Hence such compounds may be used to sterilize such animals and / or to treat certain sex hormone related diseases.
Owner:NETT TORRANCE +3
Fusion protein, preparation method and application thereof, expression system and vaccine
InactiveCN109134667AGood antigenicityImprove solubilityViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AEpitope
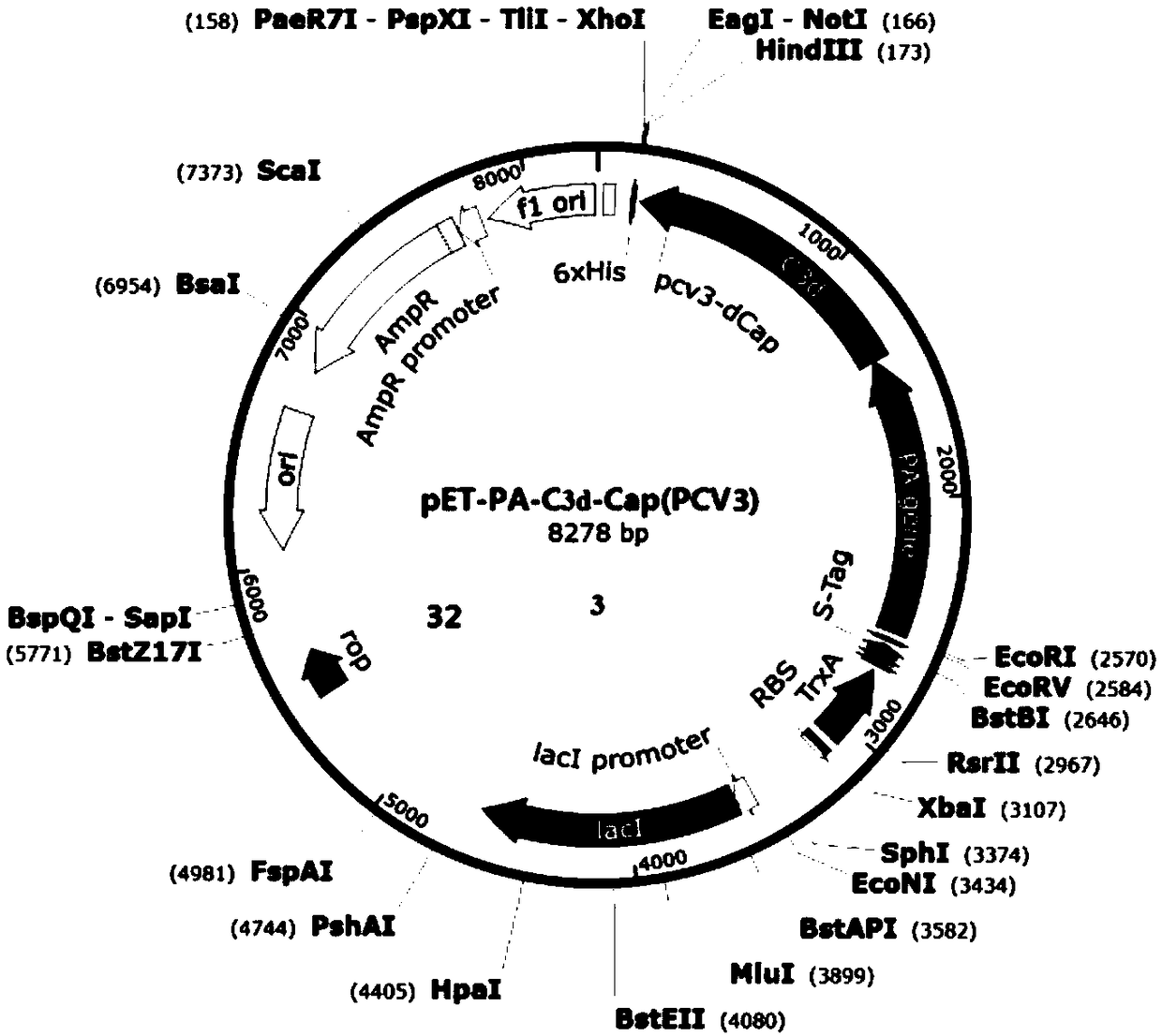
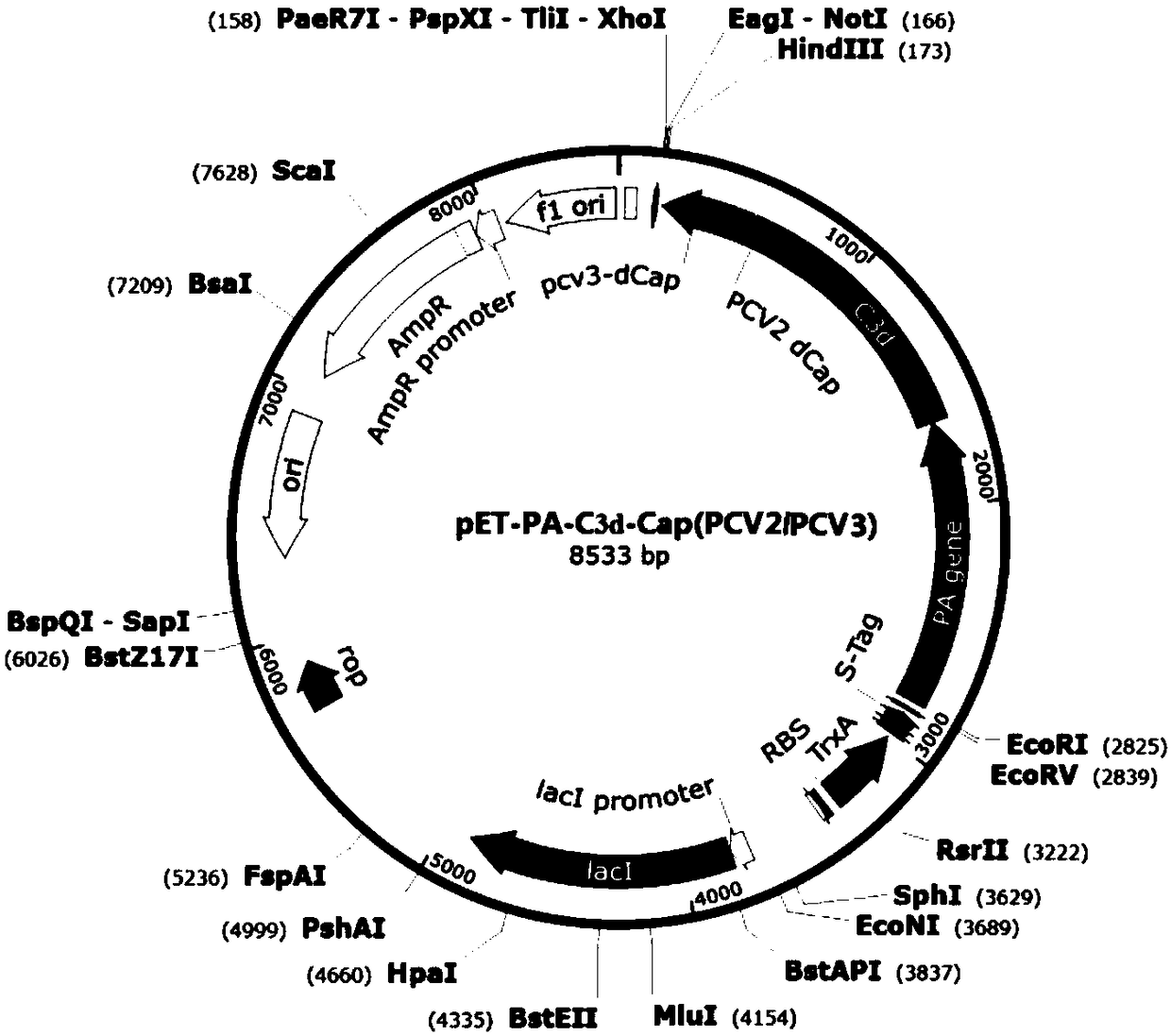
The invention provides a fusion protein and a preparation method and application thereof, an expression system and a vaccine, and relates to the technical field of biology. The fusion protein providedherein includes Pseudomonas exotoxin A domain section, porcine circovirus type 2 Cap protein dominant epitope section, porcine circovirus type 3 Cap protein dominant epitope section and carboxy terminus. The epitopes of PCV2 (porcine circovirus type 2) and PCV3 Cap proteins are screened out; the epitopes have good antigenicity and are easy to highly express; the epitopes are fused to partial functional fragments of PEA (Pseudomonas exotoxin A); carboxy terminal sequence and enhanced immunogenicity are imparted to C end of the fusion protein; therefore, the fusion protein is more soluble. Thefusion protein herein has the advantages of targeted positioning, good antigenicity, and high expression quantity. The fusion protein is advantageous in good safety, stable titer, zero toxic and sideeffects and cellular immune response activation when applied as an antigen to prepare vaccines.
Owner:TECON BIOLOGY CO LTD
Optimized nucleic acid sequences for the expression of VB4-845
ActiveUS8318472B2Animal cellsHybrid immunoglobulinsEscherichia coliPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A
An optimized nucleic acid sequence encoding the immunoconjugate VB4-845 is disclosed. Modifications to the original VB4-845 nucleic acid sequence include optimization of the sequences encoding the VH region, VL region, linkers and pseudomonas exotoxin A. The modifications improved the yield of VB4-845 in an Escherichia coli expression system.
Owner:VIVENTIA BIO
Targeted anti-tumor recombinant protein and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102153655ASmall steric hindranceHigh affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEscherichia coliPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A
The invention relates to a targeted tumor-resistant recombinant protein and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to a targeted tumor-resistant recombinant protein medicament. A truncated cell factor hIL6 is connected to a derivative PE38KDEL of pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A through a joint, and an amino acid mutation derivative of hIL6 serving as a guide vector comprises 1-28 amino acidsof truncated hIL6 amino ends. The invention further relates to application of the recombinant targeted protein to tumor resistance. The targeted tumor-resistant recombinant protein hIL6 (T23)-PE38KDEL is constructed by gene modification and codon optimization, the vacant site resistance between two ligands is reduced, and the activity is improved; and efficient soluble expression is realized in escherichia coli, the bottleneck of low expression of natural genes is broken, and large-scale preparation of the recombinant toxin becomes possible.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Pseudomonas exotoxin a cd4+ t-cell epitopes
The present invention provides PE CD4+ T-cell epitopes, as well as novel variants that exhibit reduced immunogenic responses, as compared to the parental PE. The present invention further provides DNA molecules that encode novel PE variants, host cells comprising DNA encoding novel PE variants, as well as methods for making PEs less immunogenic. In addition, the present invention provides various compositions that comprise these PE variants that are less immunogenic than wild-type PEs.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LTD
Preparation method and application of fusion protein and vaccine composition containing same
ActiveCN104277116AShort timeEase of mass productionViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AHighly pathogenic
The invention provides a fusion protein, a highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (HP-PRRS) vaccine composition containing the fusion protein and an application of the vaccine composition. The fusion protein comprises pseudomonas exotoxin A structural domains I and II, an HP-PRRS antigenic protein and a carboxyl terminal part, wherein the HP-PRRS antigenic protein comprises an Nsp9 protein and an Nsp10 protein. The invention also discloses the vaccine composition containing immune dosage of fusion protein and the application of the vaccine composition to preparation of drugs for preventing and / or treating HP-PRRSs. The vaccine composition has the advantages that recombinant expression can be carried out on the components of the vaccine composition in quantity by means of genetic engineering, thus not only consuming short time but also facilitating large-scale production.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Recombinant S1 protein of novel mutant strain of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and subunit vaccine of recombinant S1 protein
ActiveCN104046637AGood reactogenicityAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin ASeroconversion
The invention discloses a recombinant S1 protein of a novel mutant strain of a porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and a subunit vaccine of the recombinant S1 protein. The protein is obtained by the steps of cloning a fusion gene fragment PE(delta III)-S1(m)-KDEL3 containing a KDEL3 gene sequence, a gene sequence of III-region-deleted pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A and an S1(m) gene sequence to a baculovirus vector to obtain a recombinant vector; carrying out recombinant vector site specificity transposition on a seroconversion DH10Bac competent cell of the recombinant vector to obtain a recombinant bacmid; transfecting the recombinant bacmid to an Sf9 cell under the mediation of a liposome to obtain a recombinant Sf9 cell; expressing by using the recombinant Sf9 cell. According to the invention, a PE(delta III)-S1(m)-KDEL3 fusion protein is firstly expressed by using a baculovirus expression system on the basis of optimizing the predilection of a codon of mammalian with S1 genes, so that the recombinant baculovirus for efficiently and accurately expressing the fusion protein is obtained. Proved by IFA and Western blot, the recombinant baculovirus can be used for accurately expressing the fusion protein, and the fusion protein has favorable reactionogenicity.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Gastric cancer targeted recombinant toxin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103087199APeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AProkaryotic expression
The invention relates to a gastric cancer targeted recombinant toxin and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to a targeted recombinant toxin and a preparation method thereof. The gastric cancer targeted recombinant toxin is formed by connecting human gastrin G17 with recombinant toxin PE38KDEL derived from pseudomonas exotoxin A, and particularly the recombinant toxin is prepared by using G17 expressed by a prokaryotic expression system and translated reversely as a guiding unit through gene engineering expression; and a unique fermentation condition for producing a soluble protein in a large scale is established, and the recombinant toxin targeting gastric cancer and having high selective killing activity is provided.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Pseudomonas exotoxin a with less immunogenic b cell epitopes
ActiveUS20140213529A1Treat and prevent cancerBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin AImmunogenicity
The invention provides a Pseudomonas exotoxin A (PE) comprising an amino acid sequence having a substitution of one or more of amino acid residues E420, D463, Y481, L516, R563, D581, D589, and K606, wherein the amino acid residues are defined by reference to SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention further provides related chimeric molecules, as well as related nucleic acids, recombinant expression vectors, host cells, populations of cells, and pharmaceutical compositions. Methods of treating or preventing cancer in a mammal, methods of inhibiting the growth of a target cell, methods of producing the PE, and methods of producing the chimeric molecule are further provided by the invention.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Modified Forms of Pseudomonas Exotoxin A
InactiveUS20130121983A1Reduce and prevent PE38-induced immunogenicityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousPseudomonas exotoxin
Pseudomonas exotoxin A or “PE” is a 66 kD, highly potent, cytotoxic protein secreted by the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Various forms of PE have been coupled to other proteins, such as antibodies, to generate therapeutically useful cytotoxin conjugates that selectively target cells of a desired phenotype (such as tumor cells). In the present invention, peptides spanning the sequence of an approximately 38 kD form of Pseudomonas exotoxin A protein were analyzed for the presence of immunogenic CD4+ T cell epitopes. Six immunogenic T cell epitopes were identified. Residues were identified within each epitope for introduction of targeted amino acid substitutions to reduce or prevent immunogenic T-cell responses in PE molecules which may be administered to a heterologous host.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com