Pathogenic microorganism detection method and kit based on metagenomics
A pathogenic microorganism and metagenomics technology, which is applied in the field of pathogenic microorganism detection methods and kits based on metagenomics to achieve the effects of reducing the proportion of small fragments, reducing the loss of DNA and improving the construction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
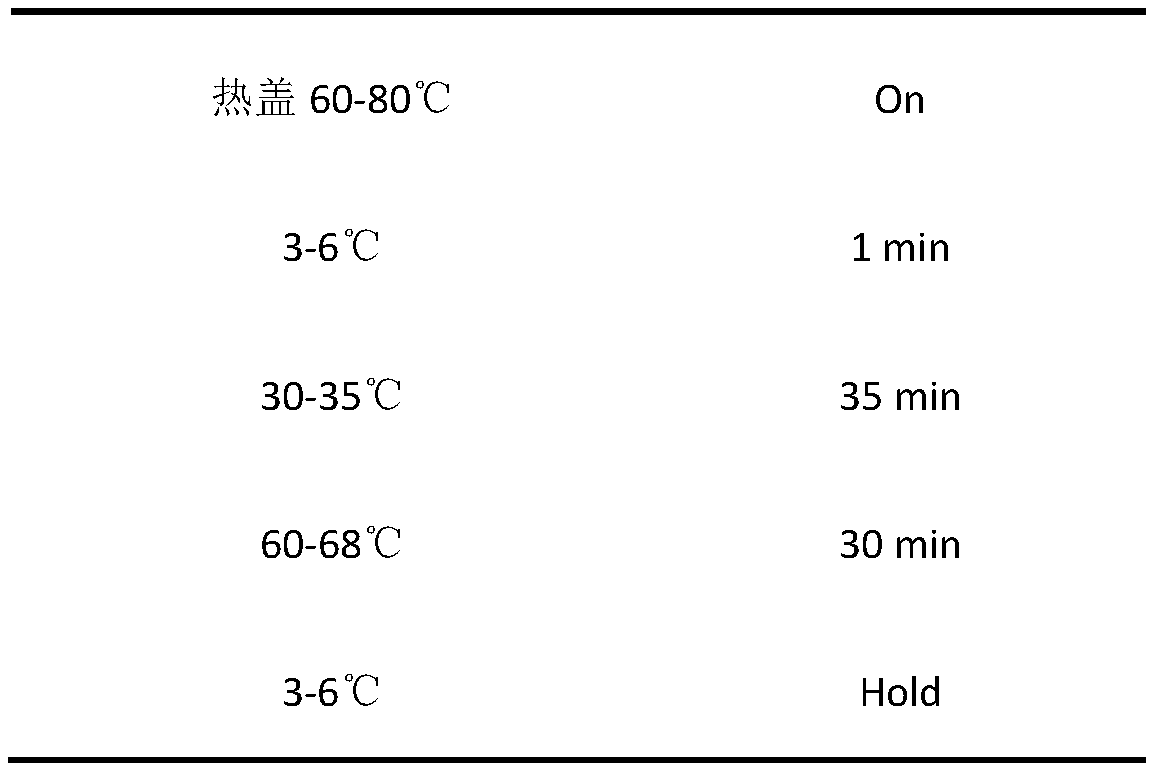
Examples
experiment example 1
[0096] In this example, an experiment is carried out on the reaction system of fragmentation enzyme, and the fragmentation enzyme is commercially available DNA Frafmentation Ligase.
[0097] plan a
[0098] DNA sample 1 μl, fragmentation buffer 1 μl, fragmentation enzyme 2 μl, Enhance 0.5 μl, Buffer EB to make up the system to 15 μl,
[0099]
[0100] Option b
[0101] DNA sample 1 μl, fragmentation buffer 2 μl, fragmentation enzyme 4 μl, Enhance 1 μl, Buffer EB to make up the system to 15 μl, and the reaction conditions refer to scheme a.
[0102] plan c
[0103] 1 μl of DNA sample, 1.5 μl of fragmentation buffer, 3 μl of fragmentation enzyme, 0.75 μl of Enhance, and Buffer EB to make up the system to 15 μl, and the reaction conditions refer to scheme a.
[0104] plan d
[0105] 1 μl of DNA sample, 1.5 μl of fragmentation buffer, 5 μl of fragmentation enzyme, 1 μl of Enhance, Buffer EB to make up the system to 15 μl, and the reaction conditions refer to scheme a.
[0...
experiment example 2
[0128] Since polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 (PVP-K30) has a certain cross-linking property at a certain content as an excipient of pharmaceutical preparations, the applicant believes that this cross-linking property may have a positive effect on the homogeneity of the fragmentation reaction.
[0129] Therefore, based on the scheme b in Experimental Example 1, 0.02 mg of PVP-K30 was added to the system to carry out the fragmentation reaction experiment. The results are shown in Table 4:
[0130] Table 4
[0131]
[0132]
[0133] However, compared with the results in Table 2, the results in Table 4 show that the homogeneity after the fragmentation reaction is not improved, but slightly decreased.
[0134] In subsequent experiments, the applicant continued to use scheme b as the basis, adding 0.2 μl polyethylene glycol 2000 and 0.02 mg of PVP-K30 to the system, and carried out the fragmentation reaction experiment. The results are shown in Table 5:
[0135] table 5
[0136] ...
experiment example 3
[0139] In this example, experiments were carried out on the scheme of magnetic bead purification.
[0140] Sample 1: Take the product of Scheme b in Example 1 as Sample 1.
[0141] Sample 2: Based on scheme b in Example 1, 0.2 μl of polyethylene glycol 2000 was added to the system, and the reaction product was sample 2.
[0142] Scenario A, A':
[0143] S1, pipette 10 μL EBBuffer and 30 μL DNA Clean Beads into 20 μL sample, and mix well;
[0144] S2, incubate at room temperature for 1 min;
[0145] S3, after centrifugation, separate the magnetic beads and the liquid under the action of an external magnetic field, and remove the supernatant after the solution is clarified;
[0146] S4, continue to add 100 μL of 70% ethanol solution to rinse the magnetic beads under the action of an external magnetic field, incubate at room temperature for 10 seconds, and remove the supernatant;
[0147] S5, exposing the magnetic beads to air for 5 minutes to dry,
[0148] S6, add 10 μL of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com