Read and distance distribution based genome De novo sequence splicing method
A sequence splicing and genome technology, applied in the field of bioinformatics, can solve the problems of not considering the sequencing depth, considering the sequencing depth, and unbalanced sequencing depth, so as to solve the problem of unbalanced sequencing depth and complex repetitive regions, and eliminate repetitive regions Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
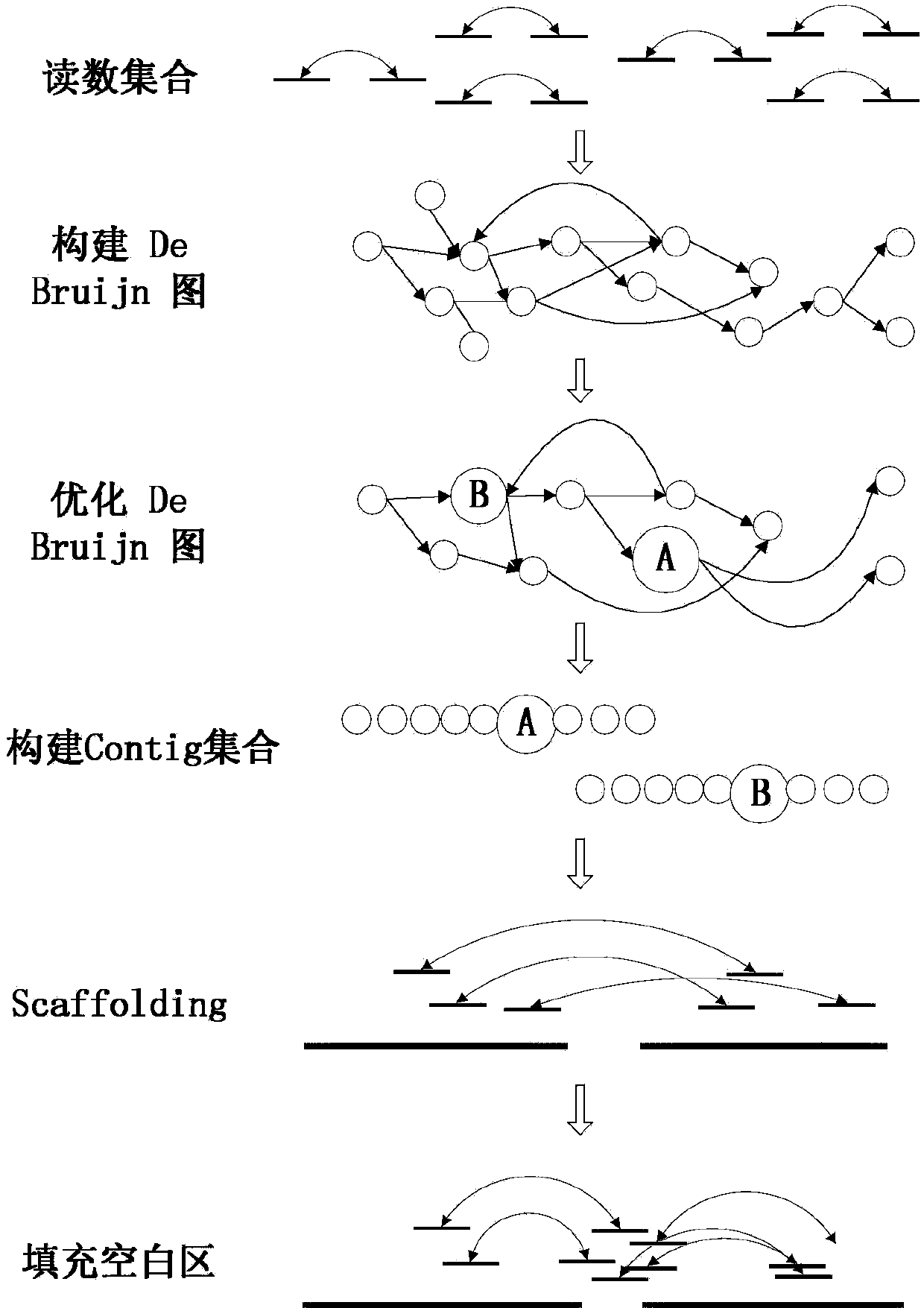
[0036] Such as figure 1 Shown, the concrete realization process of the present invention is as follows:
[0037] 1. Construction of De Bruijn diagram
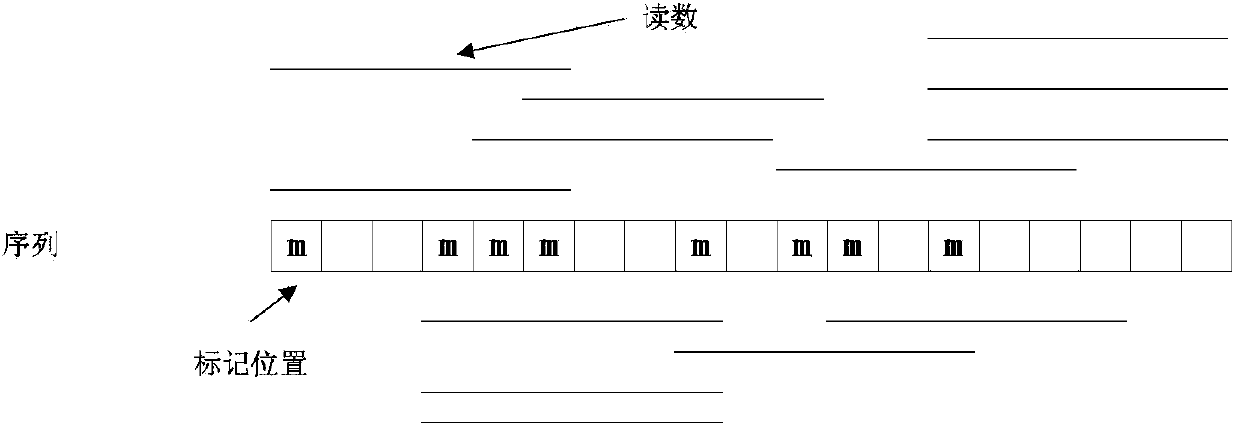
[0038] A read library in fasta format is read in, each read in the read library is the same length, and the left and right reads of the paired-end reads appear sequentially in the library and correspond to the forward and reverse strands, respectively. Only four bases {A, T, G, C} are present in all libraries. Each reading is a string of a certain length. Each k-mer is a string of length k. There are r-k+1 k-mers in total for reads of length r. Each node in the initial De Bruijn graph corresponds to a kmer.
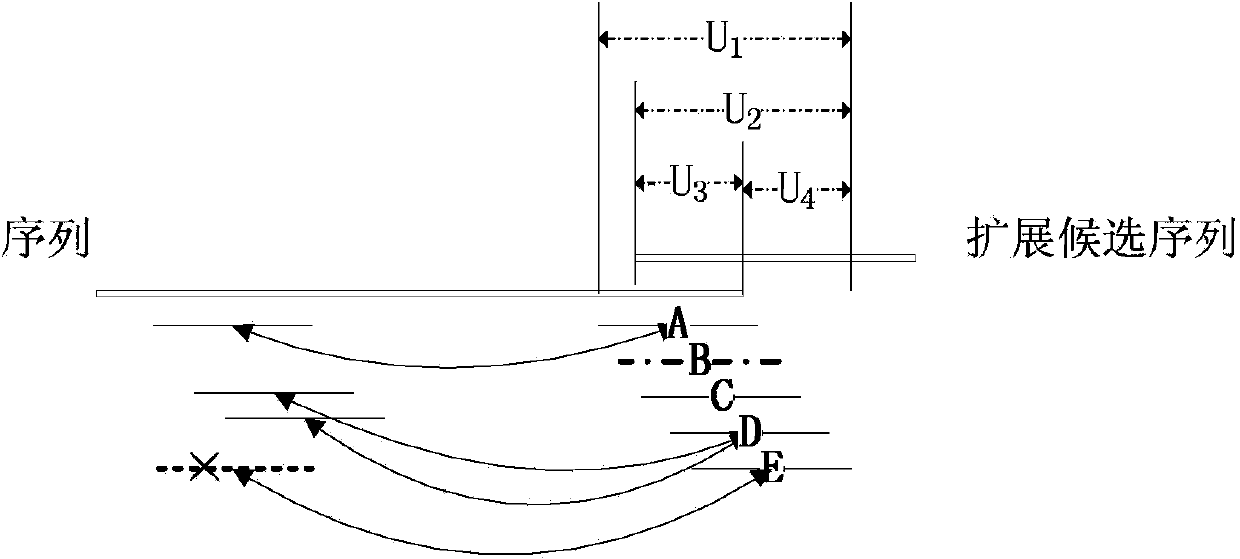
[0039] Read each reading in turn, and find the position of the k-mer in the De Bruijn diagram for the r-k+1 k-mers of each reading. If the k-mer does not exist, add it to the De Bruijn diagram the node. Every two k-mers that are adjacent in this read, that is, the last k-1 bases of one k-mer are the same as the firs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com