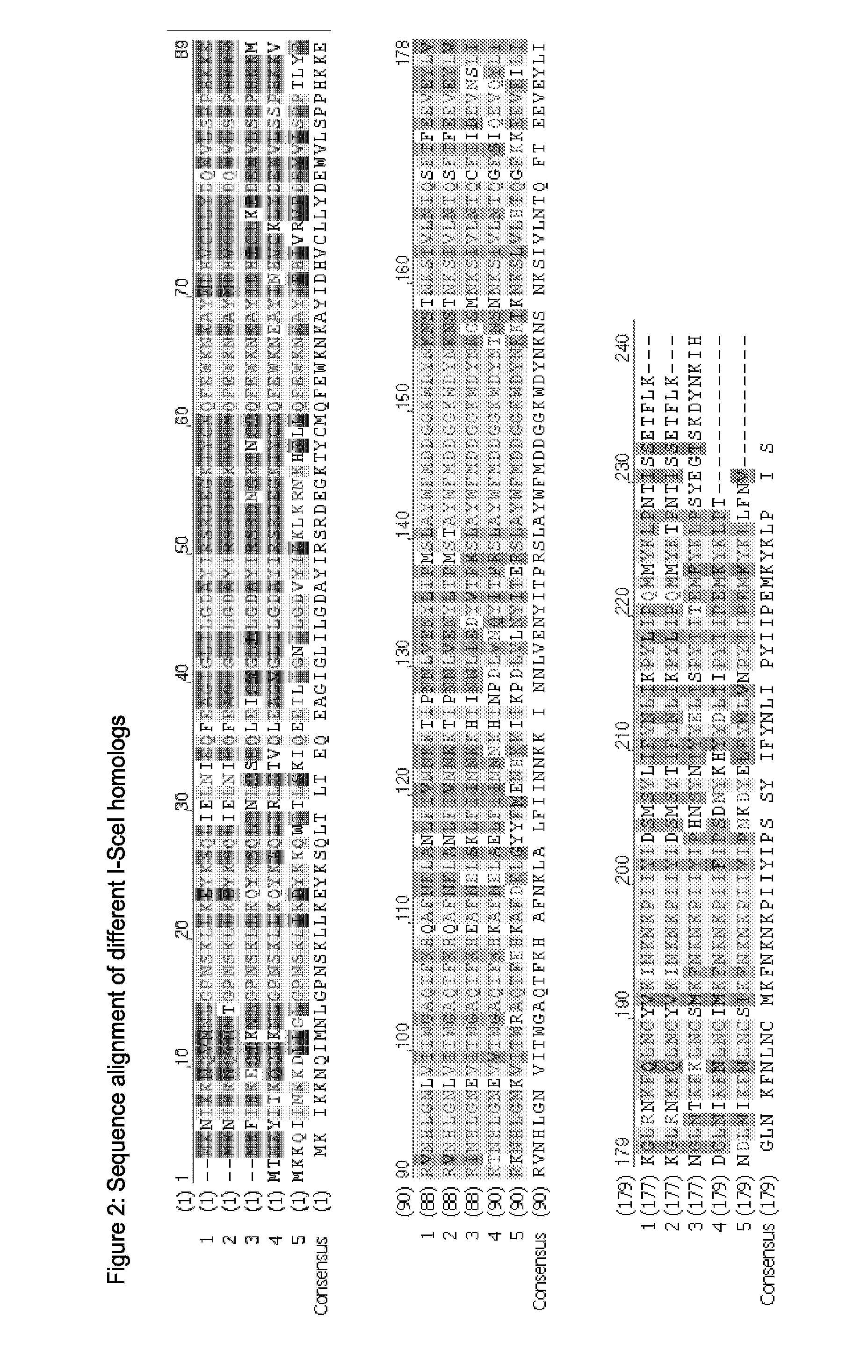
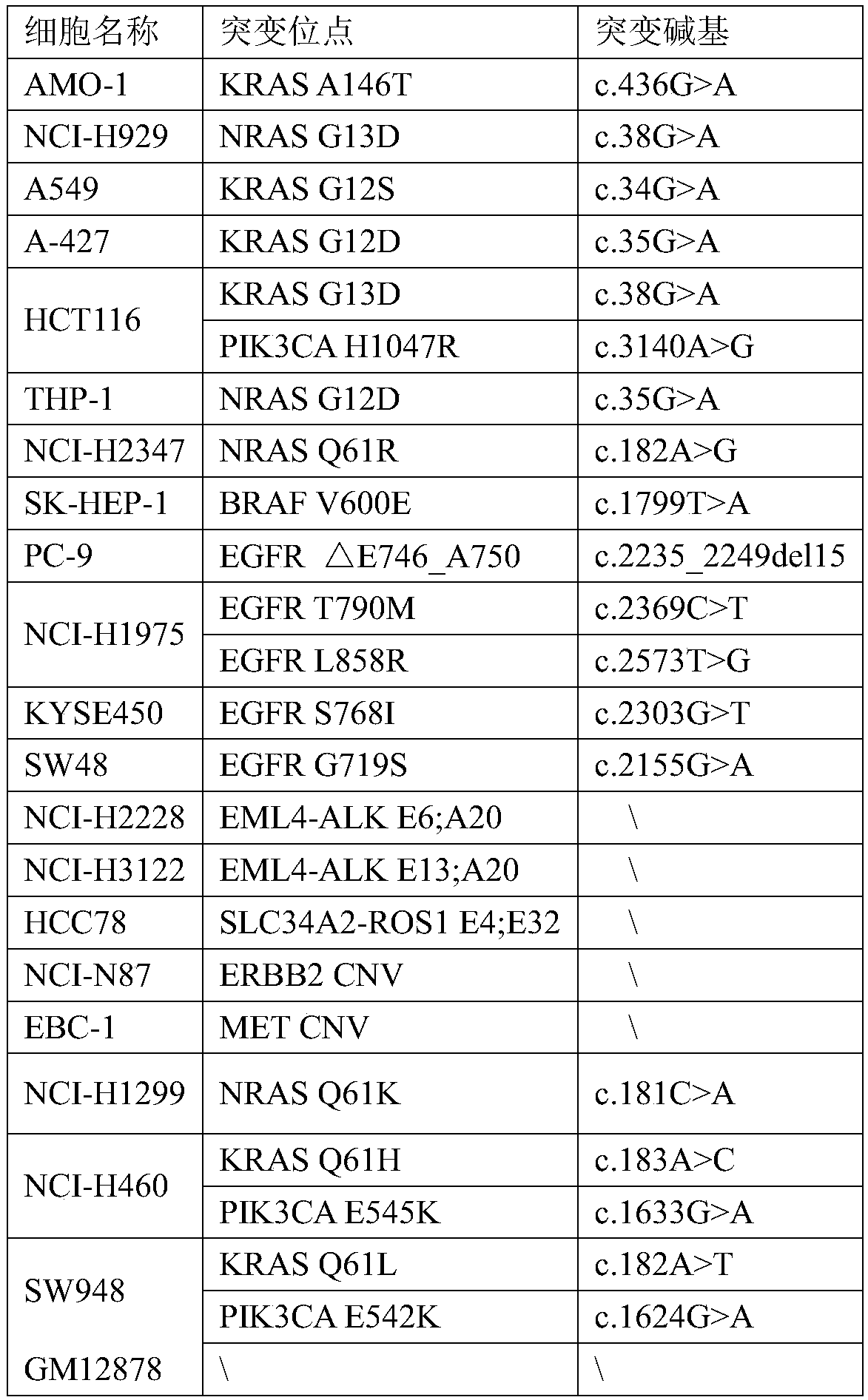
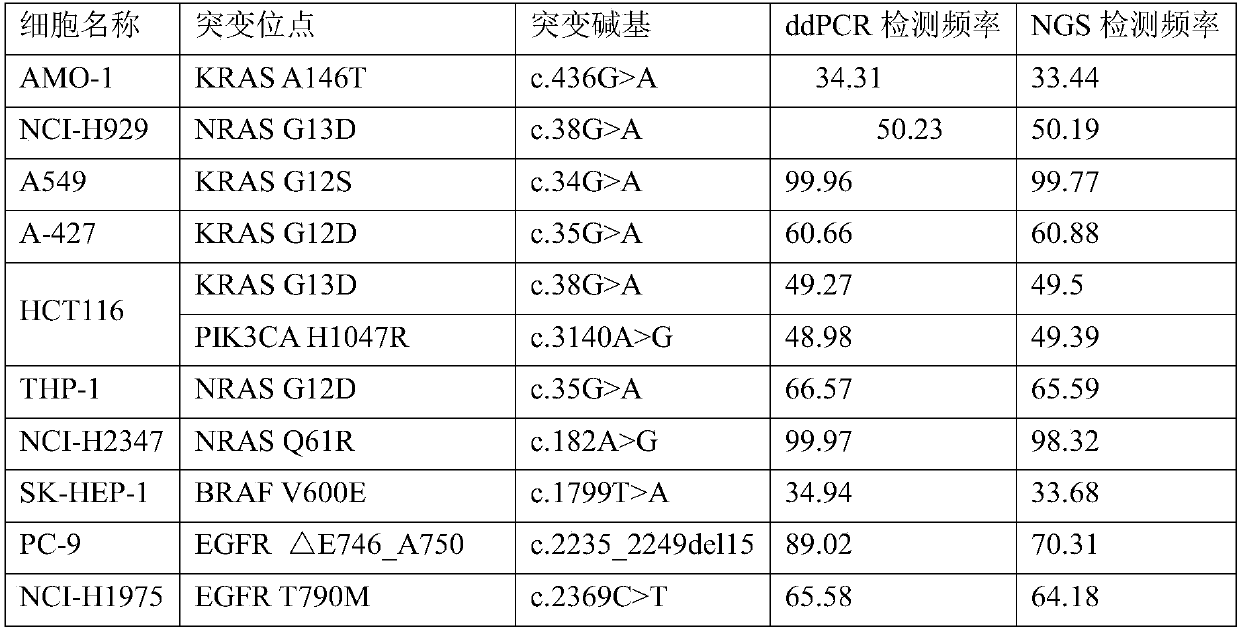
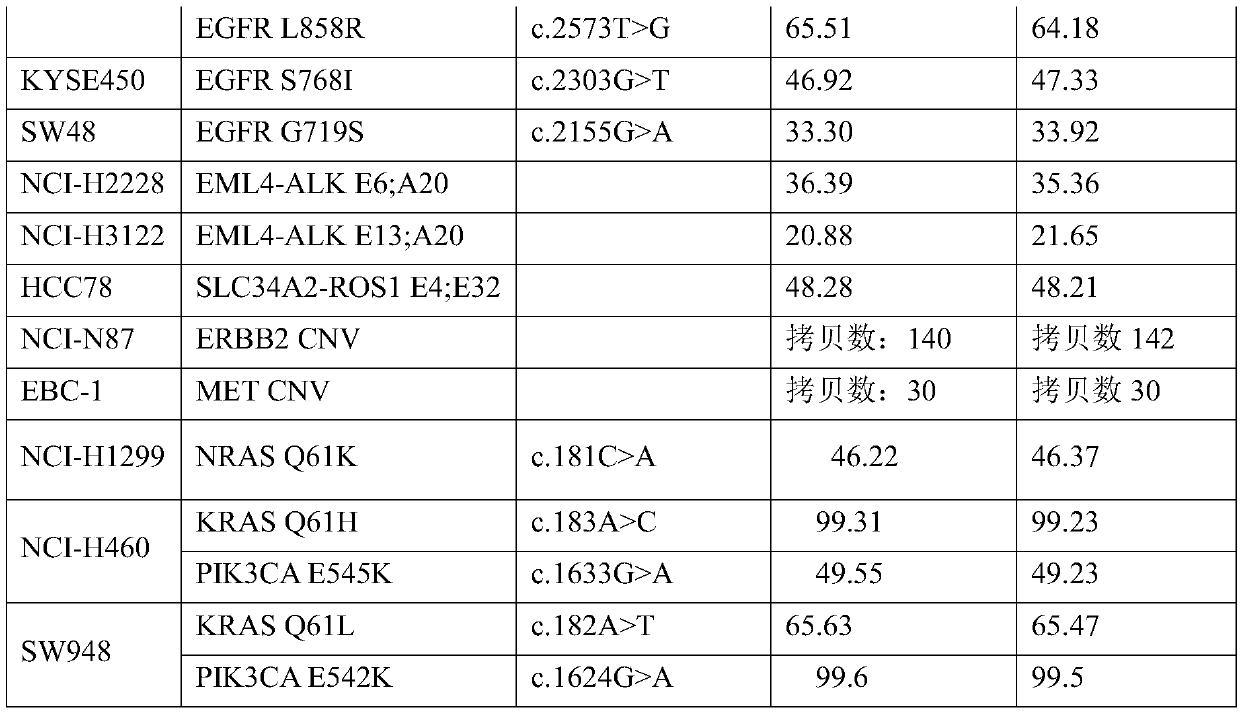
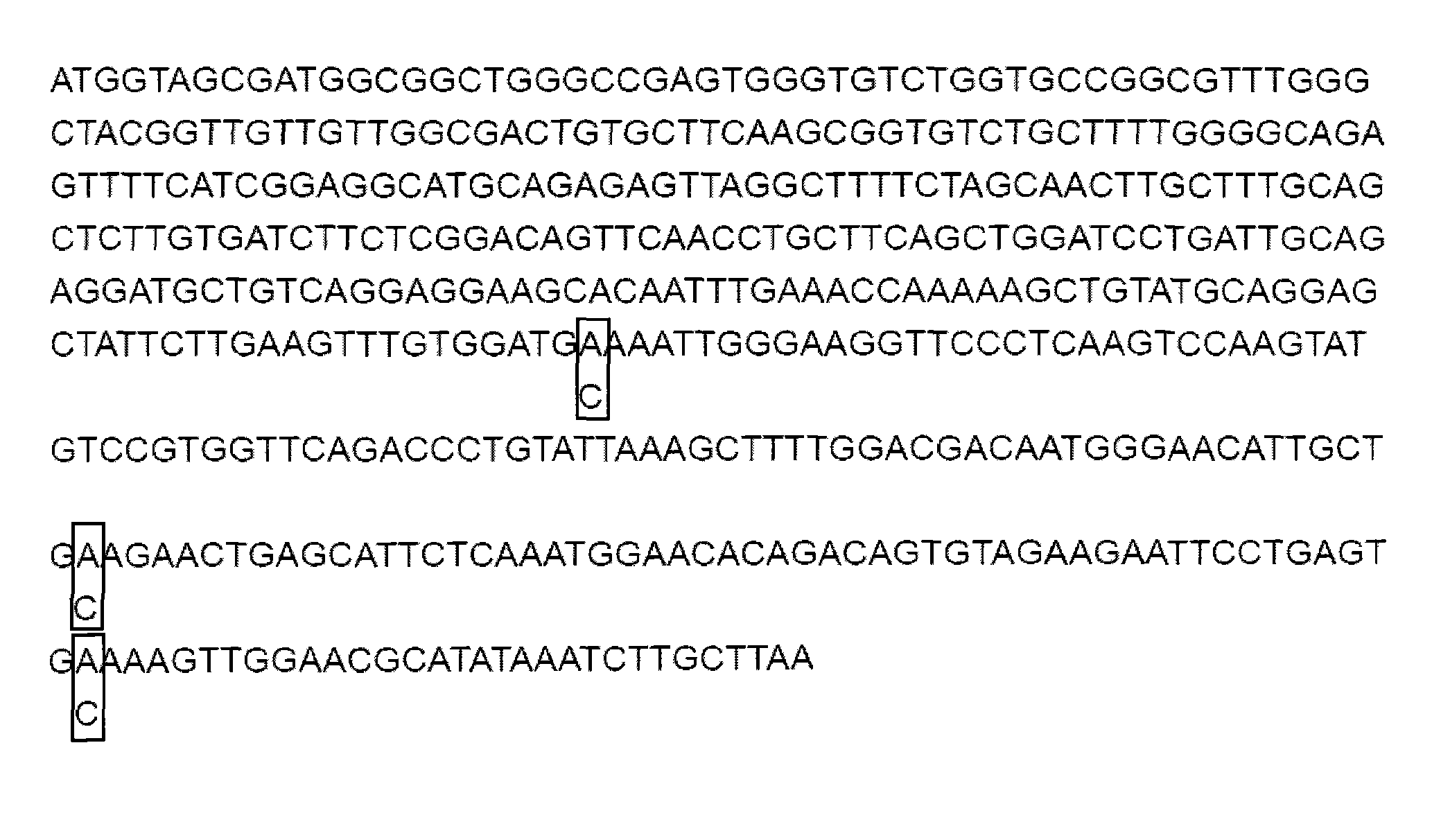Patents
Literature
91 results about "Targeted Mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A mutation created in a gene at a specific location. Targeted mutations are frequently generated in the laboratory to investigate the influence of inactivation of a particular gene product.
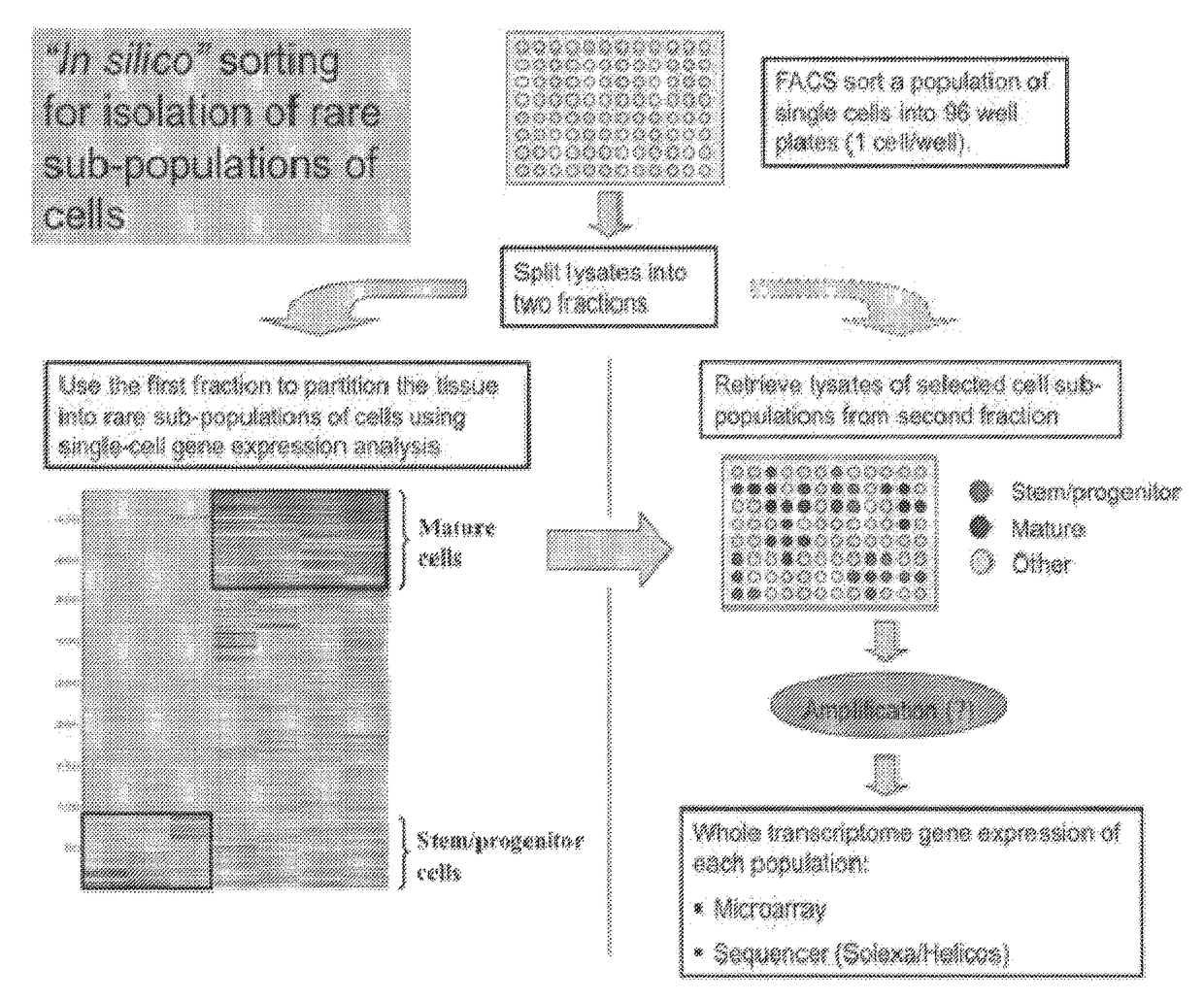
Single cell gene expression for diagnosis, prognosis and identification of drug targets
InactiveUS20100255471A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDrug targetDisease status
Methods are provided for diagnosis and prognosis of disease by analyzing expression of a set of genes obtained from single cell analysis. Classification allows optimization of treatment, and determination of whether on whether to proceed with a specific therapy, and how to optimize dose, choice of treatment, and the like. Single cell analysis also provides for the identification and development of therapies which target mutations and / or pathways in disease-state cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
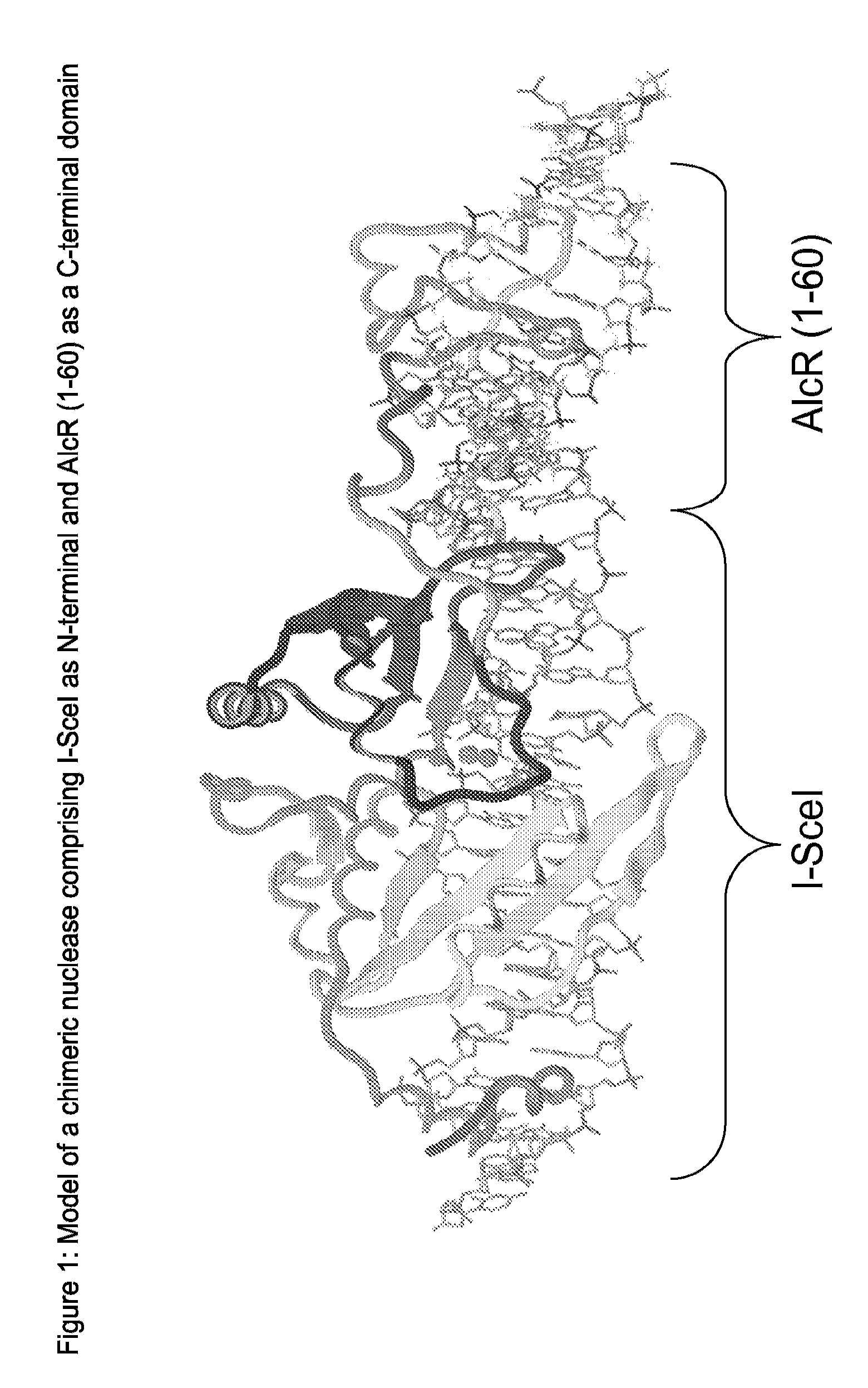
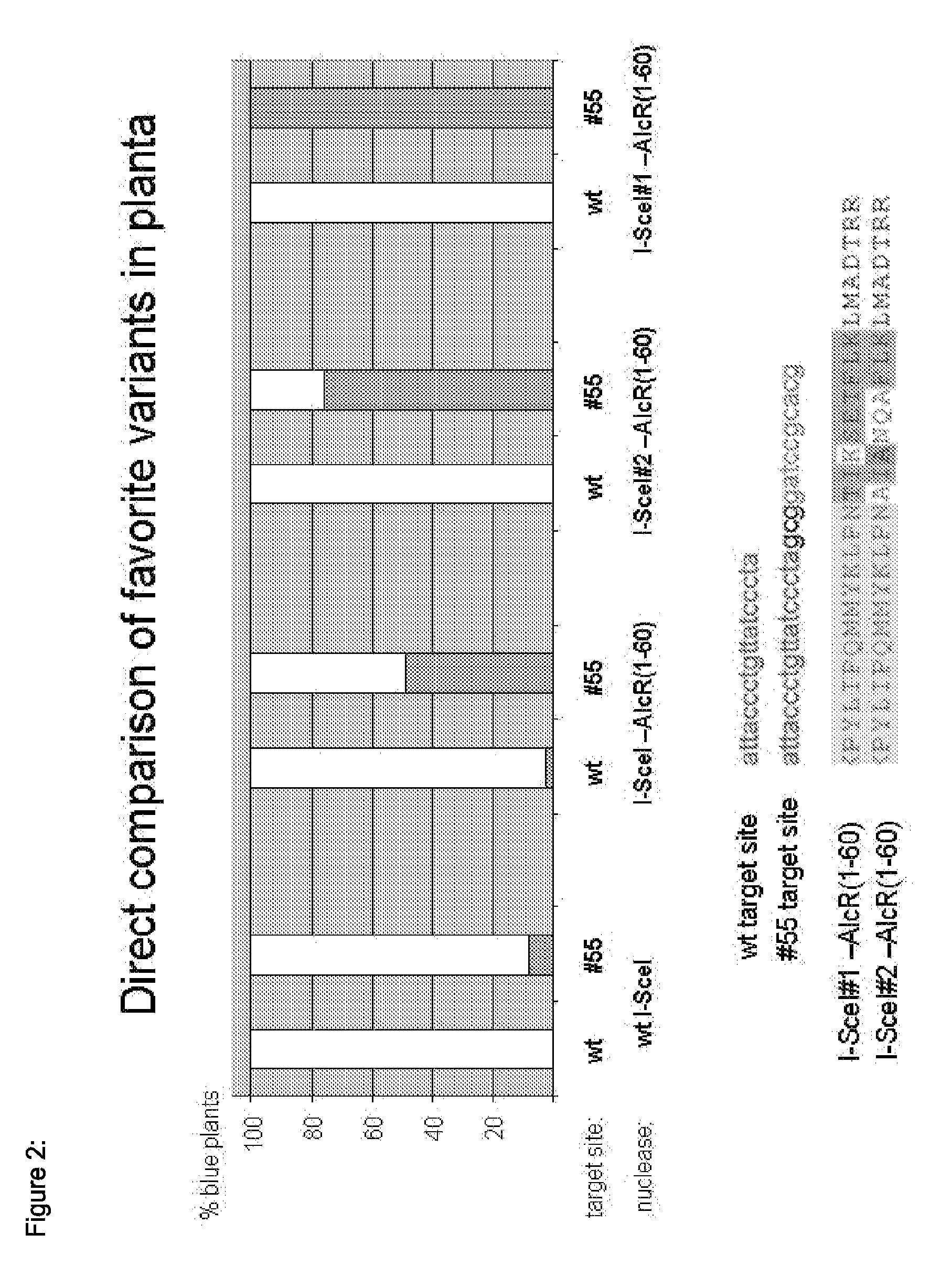
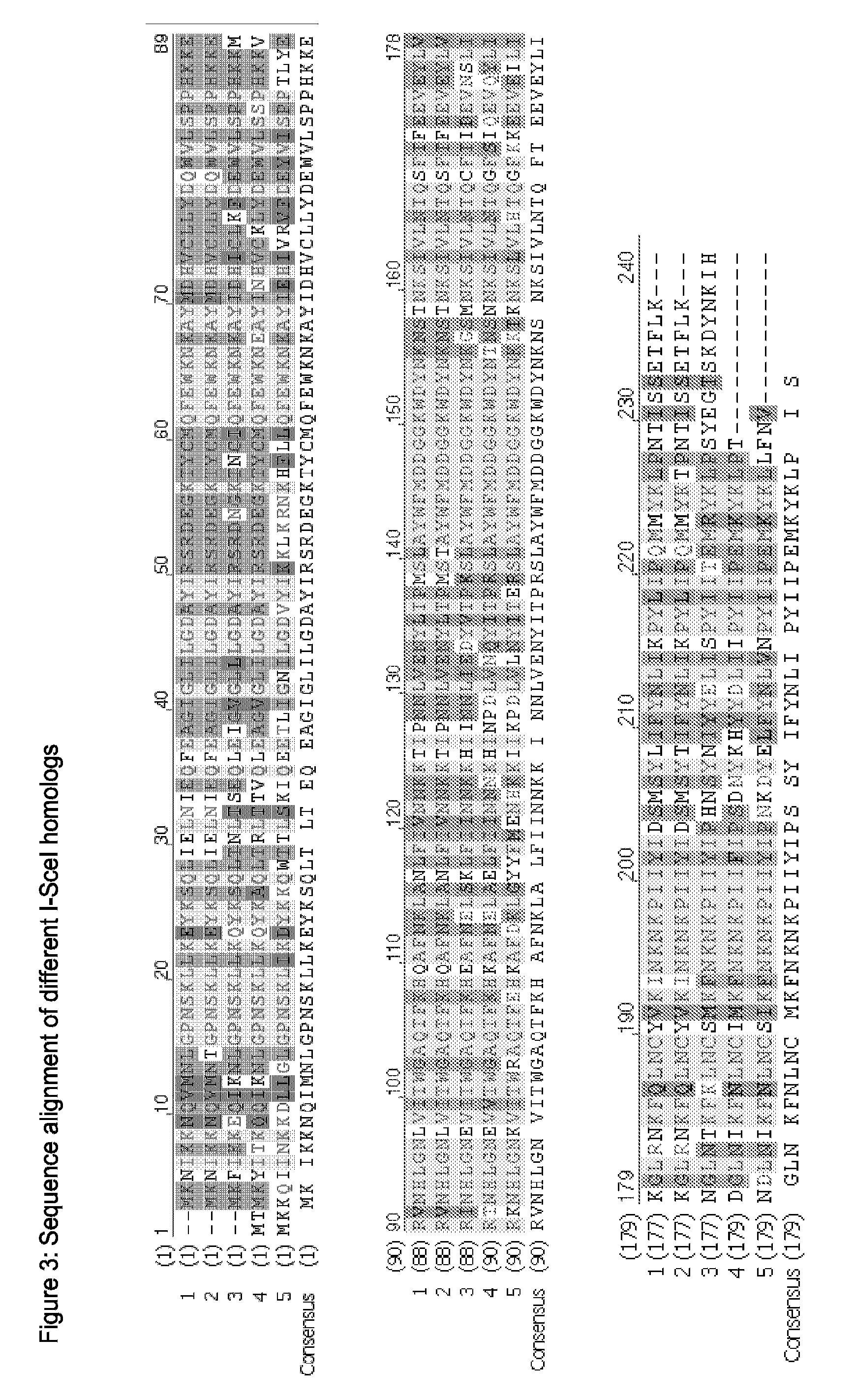
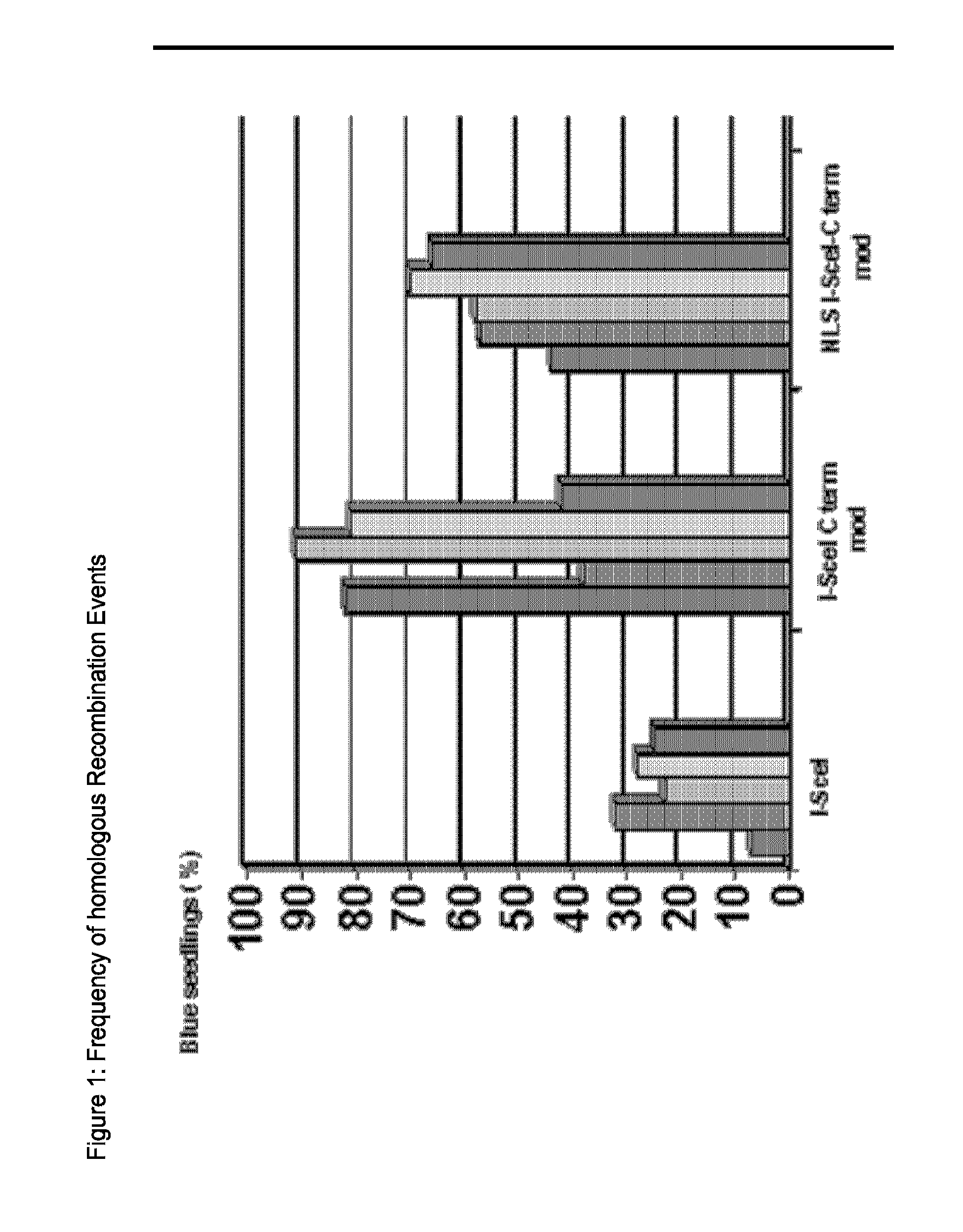
Chimeric Endonucleases and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20120324603A1Reduce contentFacilitate homologous recombinationFungiFusion with DNA-binding domainBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention relates to chimeric endonucleases, comprising an endonuclease and a heterologous DNA binding domain, as well as methods of targeted integration, targeted deletion or targeted mutation of polynucleotides using chimeric endonucleases.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Methods and systems for analysis of single cells
Methods are provided for diagnosis and prognosis of disease by analyzing expression of a set of genes obtained from single cell analysis. Classification allows optimization of treatment, and determination of whether on whether to proceed with a specific therapy, and how to optimize dose, choice of treatment, and the like. Single cell analysis also provides for the identification and development of therapies which target mutations and / or pathways in disease-state cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Single cell gene expression for diagnosis, prognosis and identification of drug targets
Methods are provided for diagnosis and prognosis of disease by analyzing expression of a set of genes obtained from single cell analysis. Classification allows optimization of treatment, and determination of whether on whether to proceed with a specific therapy, and how to optimize dose, choice of treatment, and the like. Single cell analysis also provides for the identification and development of therapies which target mutations and / or pathways in disease-state cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Molecular improvement method for lowering rice grain seed holding
ActiveCN106191107AReduce shatteringImprove work efficiencyPlant peptidesFermentationTransgenesisMolecular genetics
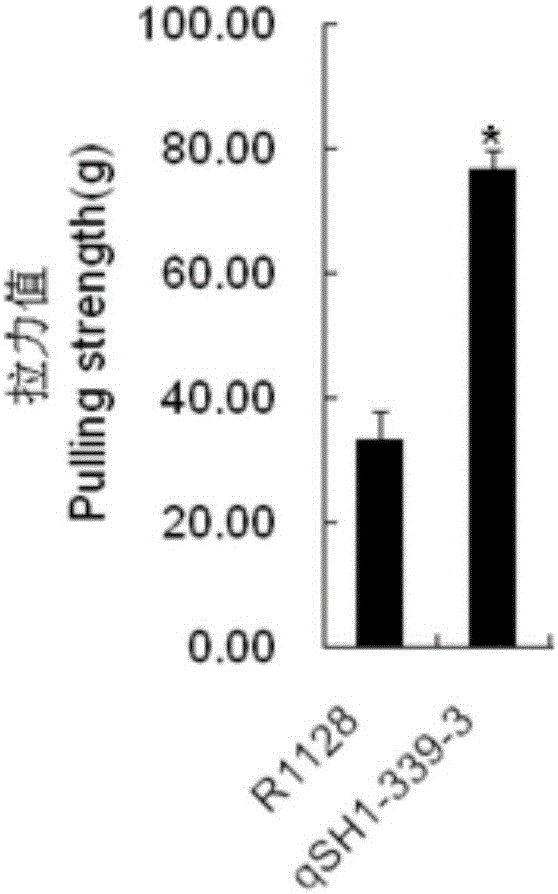
The invention discloses a molecular genetic improvement method for lowering rice seed holding by targeted modification on rice seed holding gene qSH1 by using a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) / Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: 1) selecting an appropriate target; 2) establishing a vector containing the target spot sequence; 3) establishing a recombinant vector containing the target spot sequence by utilizing the vector; 4) introducing the recombinant vector into receptor rice to obtain a transgenic positive plant; 5) obtaining a targeted-mutation mutant plant by utilizing the transgenic positive plant; 6) carrying out additive-generation growth on the mutant plant to obtain a transgenic-component-free homozygous mutant plant; and 7) carrying out seed holding investigation by using the homozygous mutant plant to obtain the plant with obviously lower seed holding as the seed-holding-improved plant. The method has the advantages of high directionality, small genetic background changes and the like, can avoid the risks caused by genetic transformation, and can culture the new species and new combination of transgenic-component-free rice with obviously lower seed holding.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
Chimeric Endonucleases and Uses Thereof
The invention relates to chimeric endonucleases, comprising a endonuclease and a heterologous DNA binding domain comprising one or more Zn2C6 zinc fmgers, as well as methods of targeted integration, targeted deletion or targeted mutation of polynucleotides using chimeric endonucleases.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Optimized Endonucleases and Uses Thereof
Provided are optimized endonucleases, as well as methods of targeted integration, targeted deletion or targeted mutation of [polynucleotides using optimized endonucleases.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
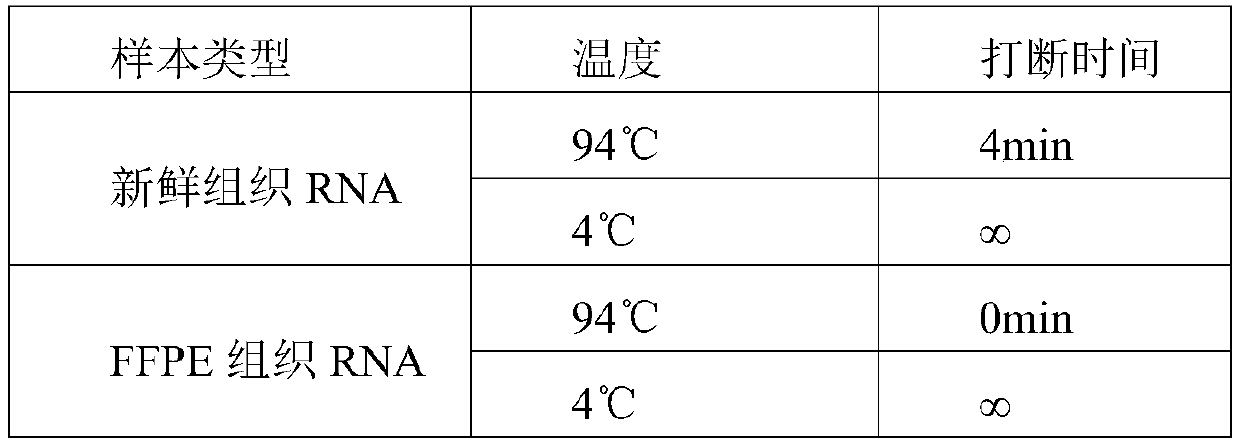
FFPE reference product for gene detection and preparation method and application of FFPE reference product
PendingCN109628595AHigh simulationAchieve accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMutation frequencyReference product
The invention discloses an FFPE reference product for gene detection and a preparation method and application of the FFPE reference product. The preparation method comprises the following steps that S1, cell culture is performed on a tumor cell line, and cell pellets are collected; S2, formalin fixation is performed on the cell pellets, then sepharose gel wraps the cell pellets to form cell aggregates, and the cell aggregate are prepared into cell paraffin blocks; S3, genomic DNA of the tumor cell line in the cell paraffin blocks is extracted, and genetic mutation frequency determination is performed on the genomic DNA of the tumor cell line; S4, the genomic DNA of the tumor cell line containing a target mutation site is mixed into a DNA mixture of a target mutation frequency, and the DNAmixture is the FFPE reference product for gene detection. According to the technical scheme, formalin fixation and paraffin wrapping are performed on the cells cultured by tumor cell line, so that thesituation of clinical samples can be better simulated.
Owner:ZHENYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY JIANGSU CO LTD
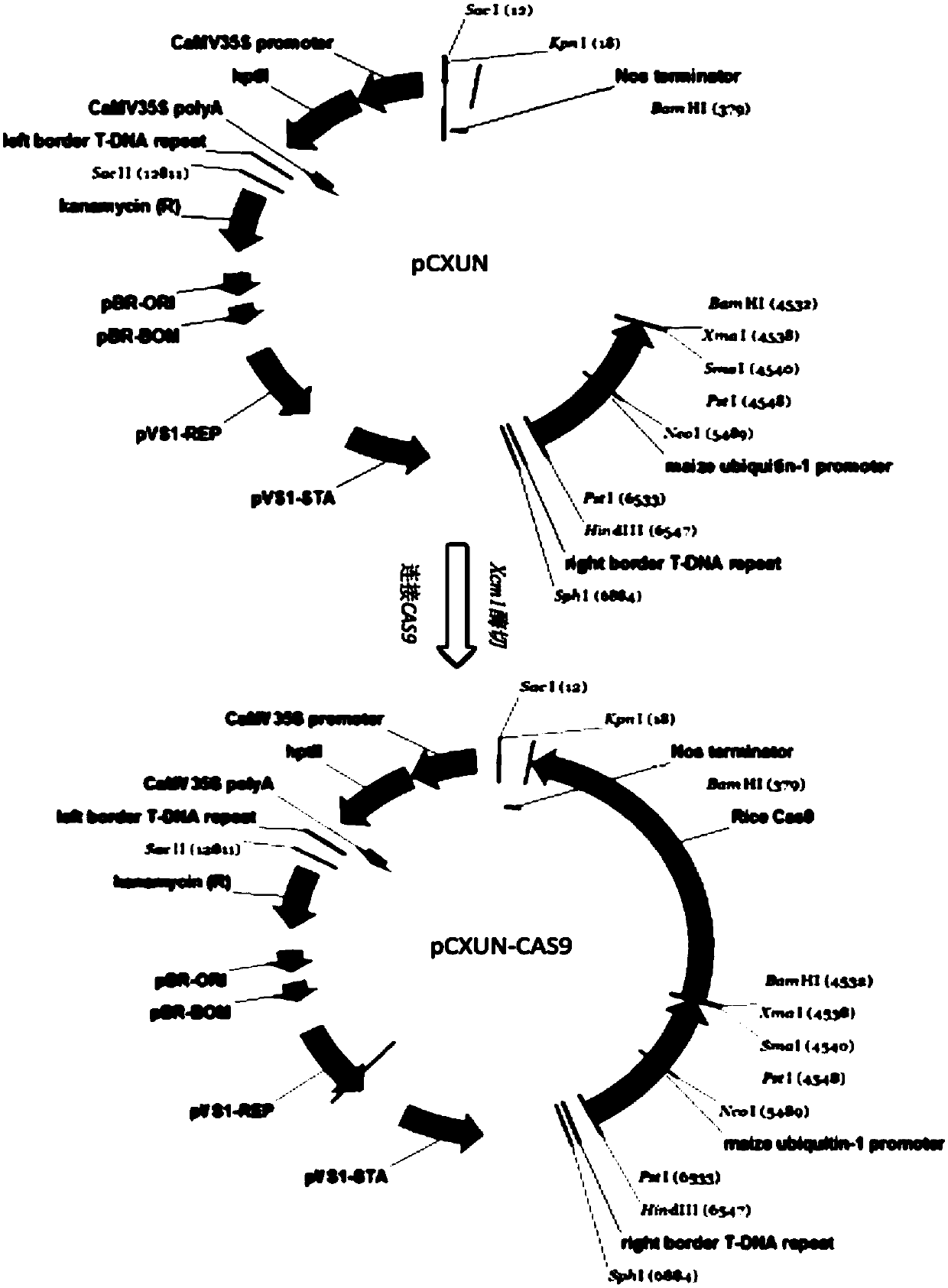
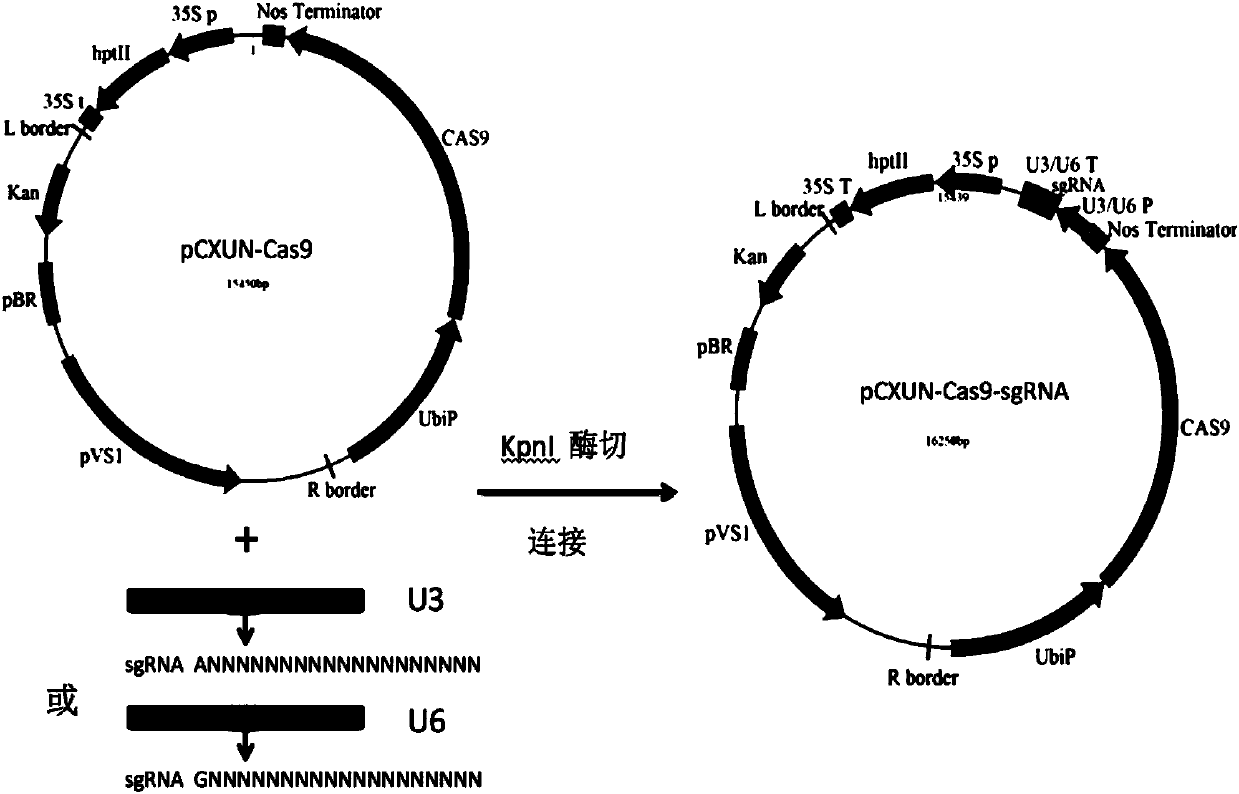
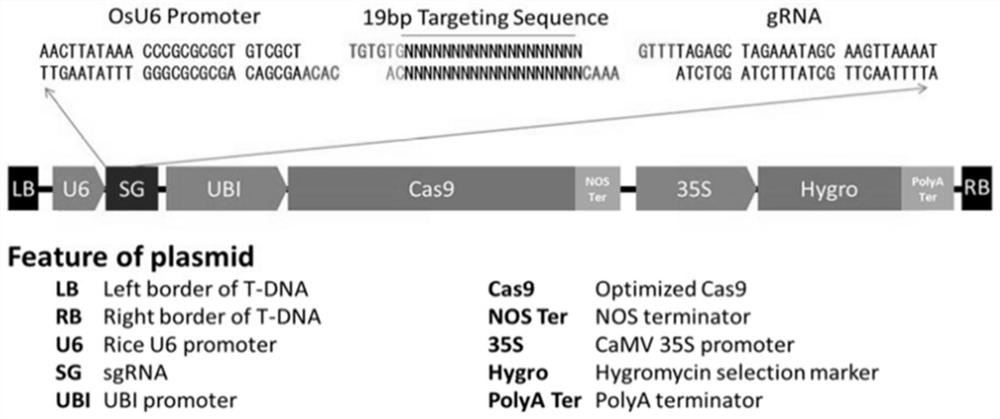
Rice efficient conversion vector pCXUN-Cas9-sgRNA and construction method thereof
InactiveCN107686845AEffective introductionEasy to transform hostVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and in particular relates to a rice high-efficiency transformation vector pCXUN-Cas9-sgRNA and a construction method thereof. The present invention uses CRISPR / CAS9 technology to efficiently transform rice knockout-related genes to obtain a vector, which is named pCXUN-CAS9-sgRNA. The vector contains the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence table. The present invention utilizes the sgRNA method to mutate the rice target gene to obtain a high-efficiency transformation carrier, which is a one-element carrier. The recombinant vector of the present invention can be used for directional mutation of the rice target gene, to study the functions and effects of related genes in rice, and can also be used to construct corresponding Gene mutants and large deletions. The carrier of the invention has high transformation efficiency and targeting mutation efficiency, and can be stably inherited and applied in rice.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
QRT-PCR (quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) method for identifying Indian variant of novel coronavirus
PendingCN113249525AReduce dependenceSave time for transshipmentMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMutation detectionVariant virus
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a qRT-PCR method for identifying Indian variant of novel coronavirus. According to the method, in order to improve the detection sensitivity and specificity, a TaqMan probe is introduced; in order to reduce the cost, two pairs of primers are changed into one pair and a half of primers, that is, two upstream primers respectively target a mutation site and an original non-mutation site, and one downstream primer is shared by the two upstream primers. in order to improve the sensitivity of mutation detection, mutation is introduced to the third site in the 5' direction of the mutation site of the upstream mutation primer, and by reducing the matching degree of the mutation primer and non-mutated virus nucleic acid and the matching degree of the non-mutated primer and the mutation virus nucleic acid in the reaction system, the amplification curve of the mutation virus nucleic acid amplified by mutation primer in the reaction system is earlier than the amplification curve of the non-mutation nucleic acid, and in the same way, the amplification curve of the non-mutation nucleic acid amplified by the non-mutation primer is earlier than the amplification curve of the mutated nucleic acid.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Gene site-directed multi-site mutation method
ActiveCN101580829ALow costShorten the timeRecombinant DNA-technologyFermentationForward primerMulti site
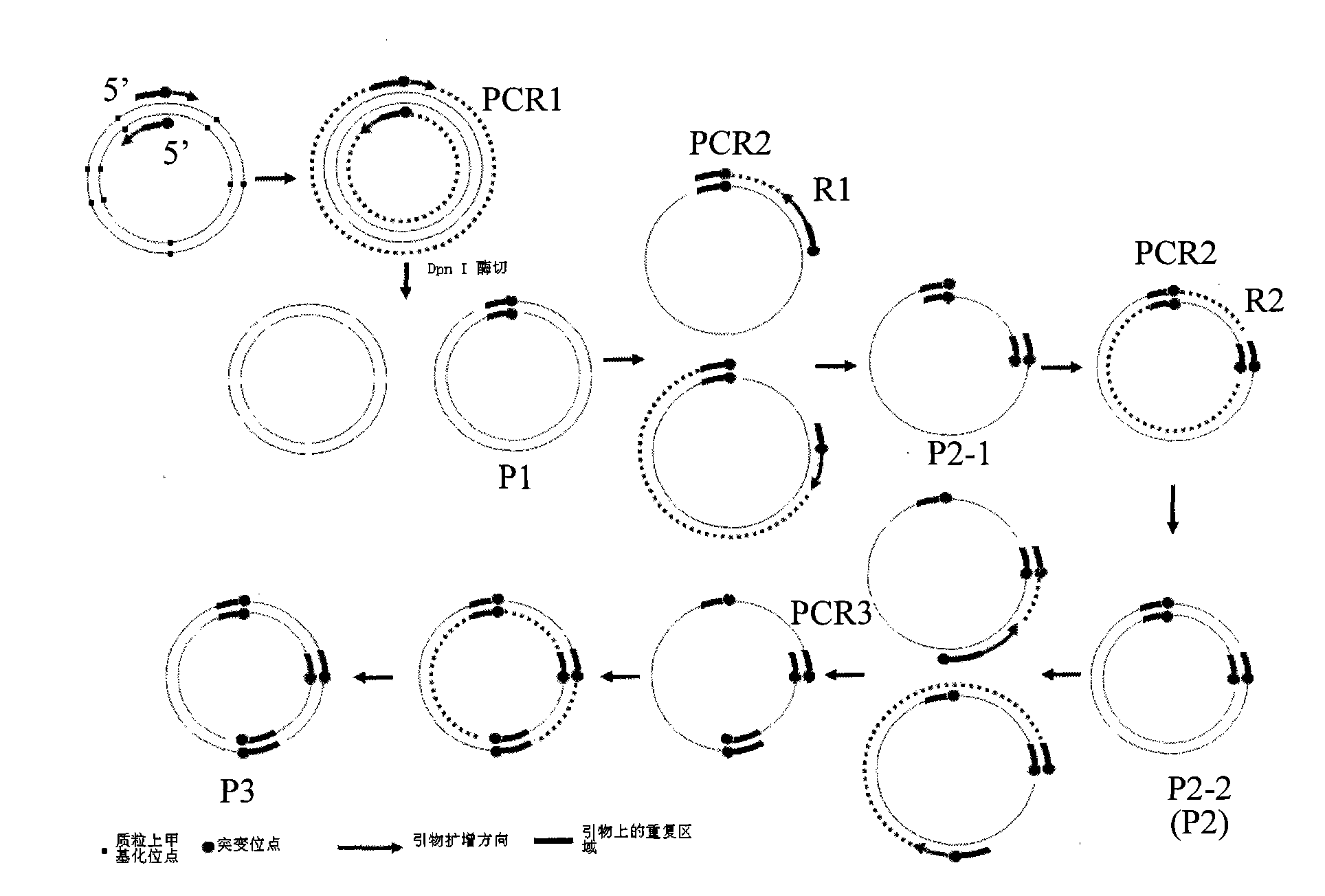
The invention relates to a gene site-directed multi-site mutation method, which comprises the following steps of: respectively designing a forward mutation primer and a reverse mutation primer according to sites of sequences where mutated bases are located, wherein the mutation sites are positioned in the middle of the forward primer and the position close to 5' end of the reverse primer; designing the same pairs of mutation primers according to the number of the mutation sites; taking a plasmid containing methylated sites as a template, carrying out the first round of PCR reaction on the first pair of primers with high fidelity polymerase for amplifying a gene fragment containing the first mutation base; adopting DpnI enzyme for carrying out the restriction enzyme digestion on the gene fragment, removing the template plasmid, obtaining a ring plasmid with a target mutation site and an opening; then taking the ring plasmid as the template and sequentially adding the residual mutation primers for PCR reaction for obtaining a ring plasmid with a plurality of mutation sites and an opening. The method utilizes a complementary region of the primers to complete the polymerase chain reaction of the ring plasmid template with the opening, thereby introducing the site-directed mutation with more than one site.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Compositions and methods of targeting mutant k-ras
ActiveUS20180201610A1Reduction of downstream signallingReduce signalingOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsTargeted MutationStereochemistry
Owner:NANTBIO INC
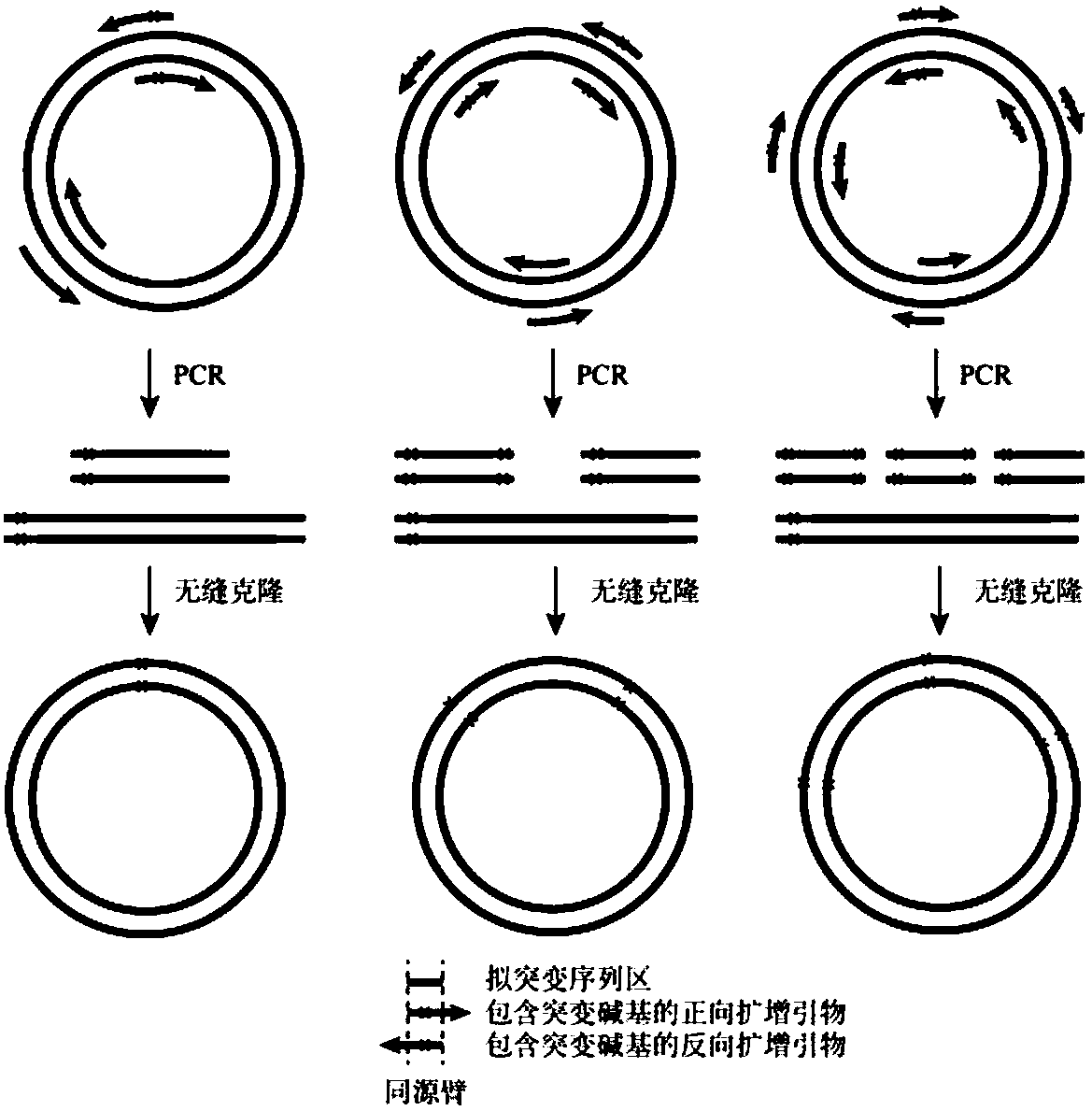
Gene site-directed mutation method based on seamless cloning, and applications thereof
PendingCN108486139AOvercoming success rateOvercoming the flaw of uncertain fidelityVector-based foreign material introductionReverse mutationRecombinase
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
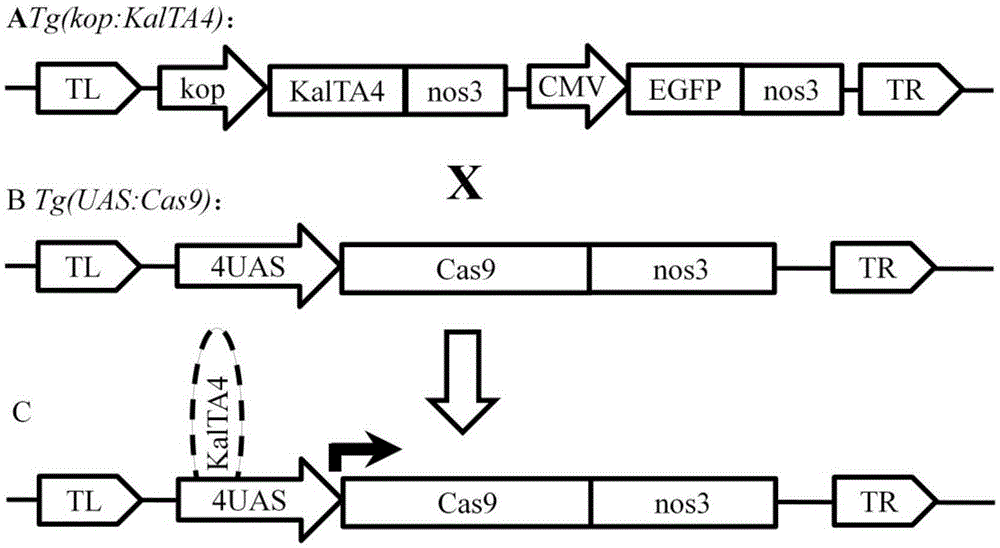
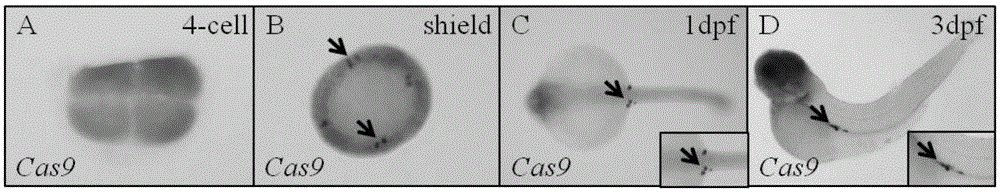
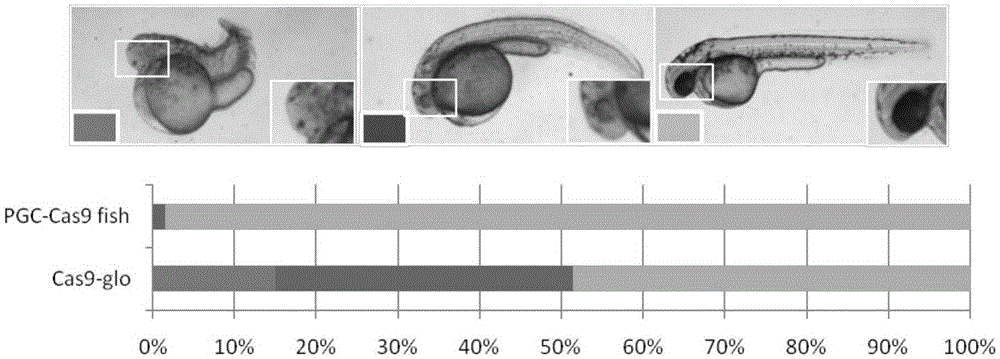
Transgenic vector for target mutation of primordial germ cells, method for preparing transgenic vector and application thereof
ActiveCN105274141AReduced phenotypic effects of mutationsImprove survival rateVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryPlant Germ CellsTargeted Mutation
The invention discloses a transgenic vector for target mutation of primordial germ cells, a method for preparing the transgenic vector and application thereof. The transgenic vector, the method and the application have the advantages that the vector pTol2 (UAS: Cas9) is introduced into zebrafish embryos at unicellular stages to obtain strains Tg (UAS: Cas9) and strains Tg (kop: KalTA4), and Cas9 genes can be efficiently, specifically and continuously expressed in the primordial germ cells of zebrafishes by hybrid embryos obtained after fishes of the strains Tg (UAS: Cas9) and female fishes of the strains Tg (kop: KalTA4) are hybridized; the hybrid embryos of the male fishes of the strains Tg (UAS: Cas9) and the female fishes of the strains (kop: KalTA4) are used as receptor embryos when mutation strains are about to be prepared, somatic mutation can be effectively reduced after gRNA [guide RNA (ribonucleic acid)] of target genes is directly injected, accordingly, the survival rate of the injected P0-generation embryos can be increased, P0-generation adult fishes can effectively pass on mutation, and accordingly the transgenic vector and the method have broad application prospects.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
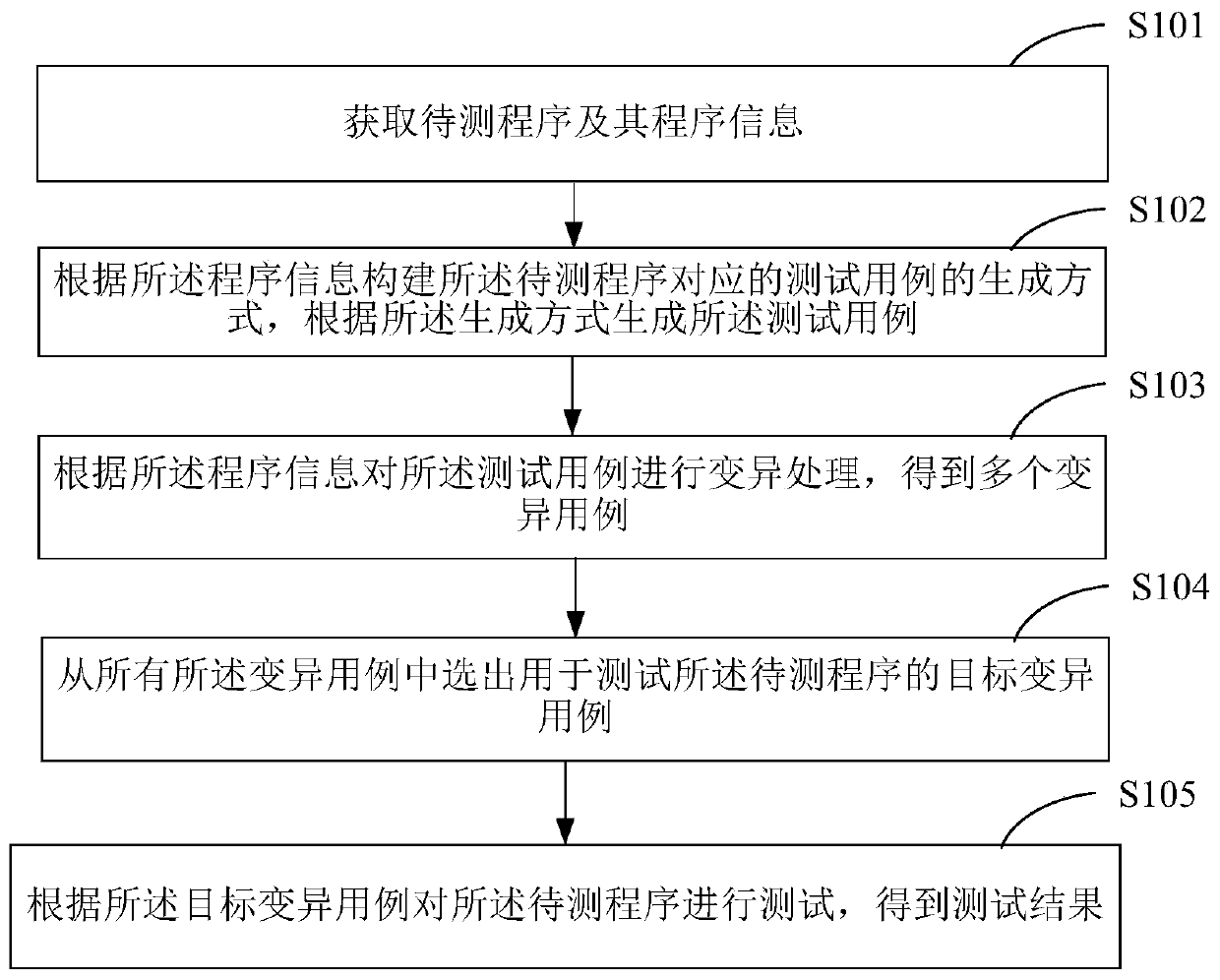
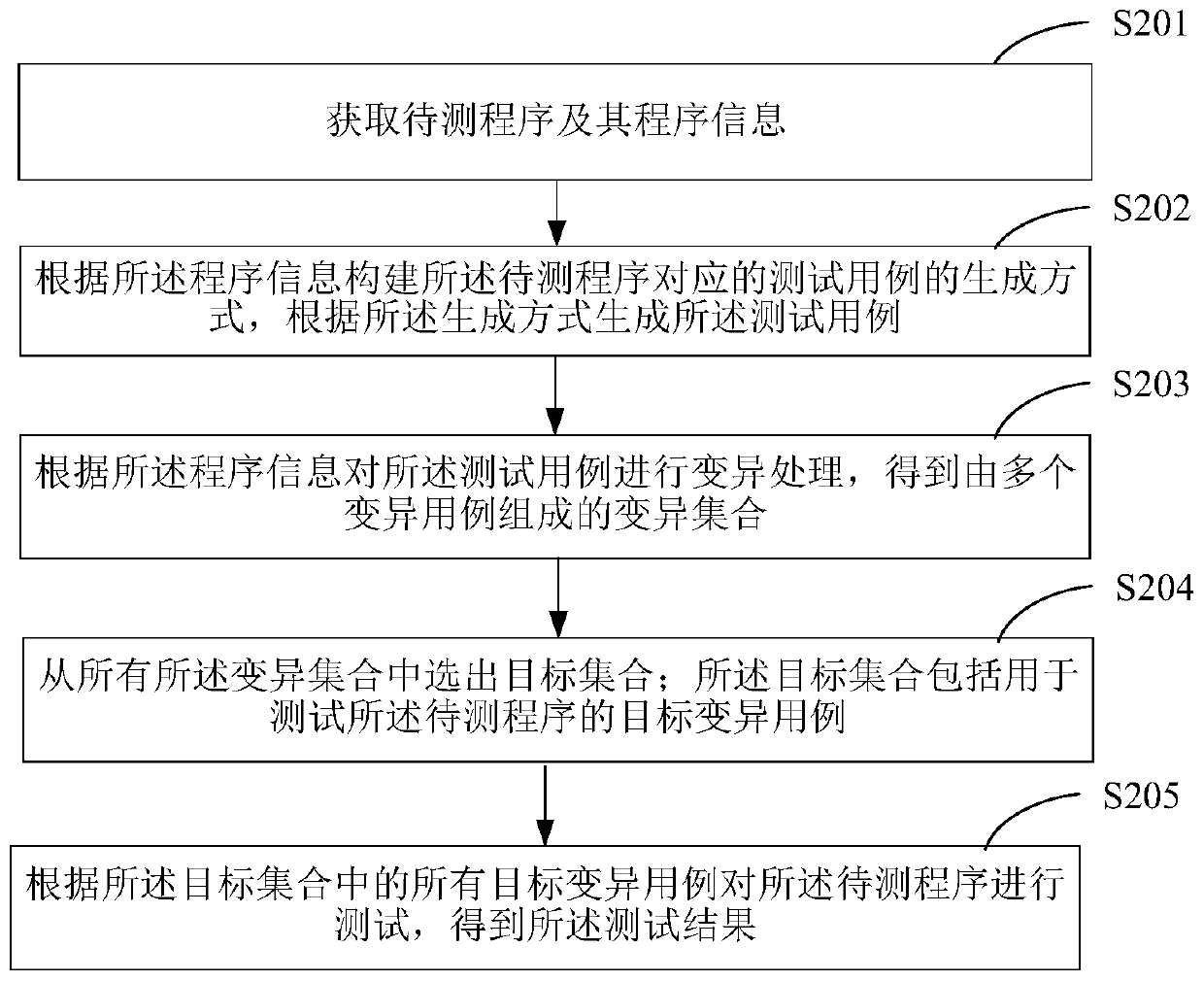
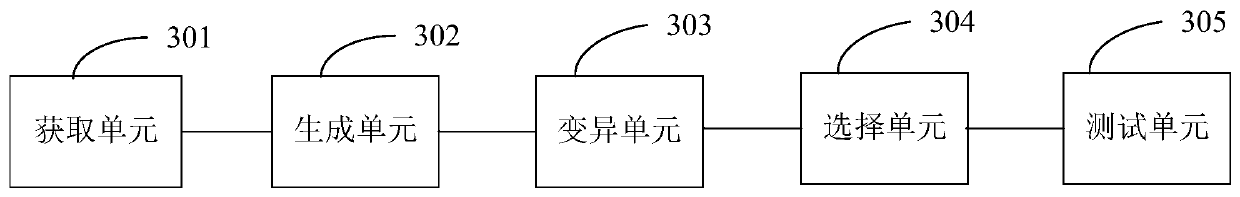
Program testing method and device
ActiveCN110765000AIncrease coverageEnsure comprehensivenessSoftware testing/debuggingAlgorithmCode coverage
The invention is suitable for the technical field of computer application, and provides a program testing method and device. The program testing method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-tested program and program information thereof; constructing a generation mode of a test case corresponding to the to-be-tested program according to the program information, and generating the test case according to the generation mode; performing variation processing on the test cases according to program information to obtain a plurality of variation cases; selecting a target variation case for testing the to-be-tested program from all variation cases; and testing the to-be-tested program according to the target variation case to obtain a test result. A test case corresponding to a to-be-tested program is generated according to program information of the to-be-tested program; the test cases are mutated to obtain the multiple mutation cases, and the mutation case with the highest case coverage rate is determined from the multiple mutation cases to serve as the target mutation case to test the to-be-tested program; and the code coverage rate when the to-be-tested program is tested is effectively increased, and the comprehensiveness of the test process and the test result is guaranteed.
Owner:SECZONE TECH CO LTD +1
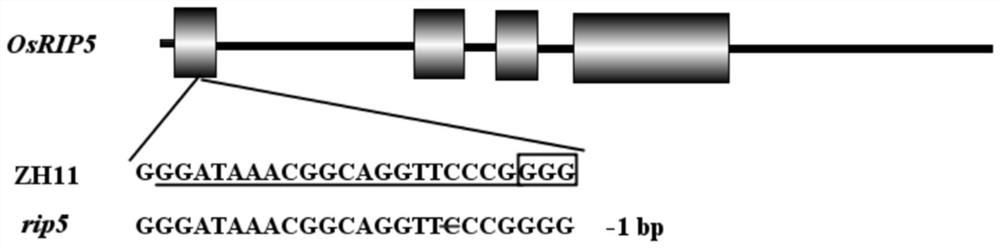
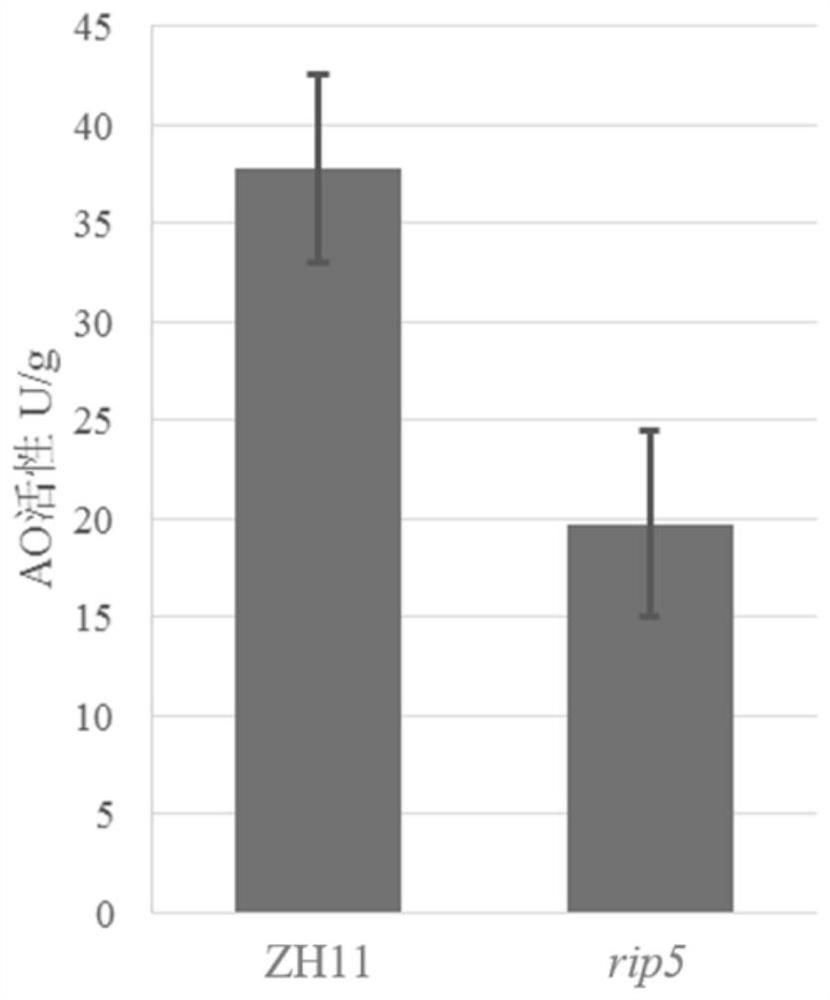
Application of ascorbic acid oxidase RIP5 to regulating and controlling of drought resistance of rice
InactiveCN111876394AImprove drought resistanceReduced activityOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyOxidative enzyme
The invention discloses an application of ascorbic acid oxidase RIP5 to regulating and controlling of drought resistance of rice. An RIP5 gene knockout mutant is constructed by targeted mutation of anRIP5 gene through a GRISPR / Cas9 system, and the inventor finds that the drought resistance of plants can be effectively improved by inhibiting the expression quantity and / or activity of the RIP5 protein, that is, the ascorbic acid oxidase gene RIP5 of rice can negatively regulate and control the drought resistance of the plants. The invention also provides a gRNA target sequence for editing the ascorbic acid oxidase gene RIP5 of the rice, and the gRNA target sequence cooperates with a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system to realize targeted mutation of the coding gene of the RIP5 protein, so thatthe drought resistance of the rice can be regulated and controlled. The research of the invention provides new gene targets and resources for drought resistance genetic breeding of the plants, and knockout mutant plants obtained by editing the gene have important application value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Molecular breeding method for thickening intermuscular thorns of erythroculter ilishaeformis and megalobrama amblycephala
PendingCN111560401AReduce in quantityIncreased area of intermuscular spursClimate change adaptationStable introduction of DNAFisheryMolecular breeding
The invention discloses a molecular breeding method for thickening intermuscular thorns of erythroculter ilishaeformis and megalobrama amblycephala, and belongs to the technical field of aquatic organism breeding. According to the molecular breeding method, based on a technical means of gene editing, the F0 generation of targeted mutation erythroculter ilishaeformis and megalobrama amblycephala mstn genes is obtained, and mutant individuals with mstn deletion and increased intermuscular bony area are obtained through passage. According to the invention, a parent method for obtaining erythroculter ilishaeformis and megalobrama amblycephala with increased intermuscular stabbing area by utilizing a gene editing technology is provided for the first time. The method is beneficial to large-scalecultivation of wild erythroculter ilishaeformis and megalobrama amblycephala which have thick intermuscular thorns and can be inherited in production. Being different from a transgenic method, the method can be applied to artificial breeding, overcomes the difficulty that intermuscular thorns are small and difficult to process in production, does not need to worry about the influence of transgenic food on people, is convenient for people to find the intermuscular thorns more easily when people eat erythroculter ilishaeformis and megalobrama amblycephala, and is easy to popularize in production.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Chimeric endonucleases and uses thereof
The invention relates to chimeric endonucleases, comprising an endonuclease and a heterologous DNA binding domain, as well as methods of targeted integration, targeted deletion or targeted mutation of polynucleotides using chimeric endonucleases.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Optimized endonucleases and uses thereof
Provided are optimized endonucleases, as well as methods of targeted integration, targeted deletion or targeted mutation of [polynucleotides using optimized endonucleases.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
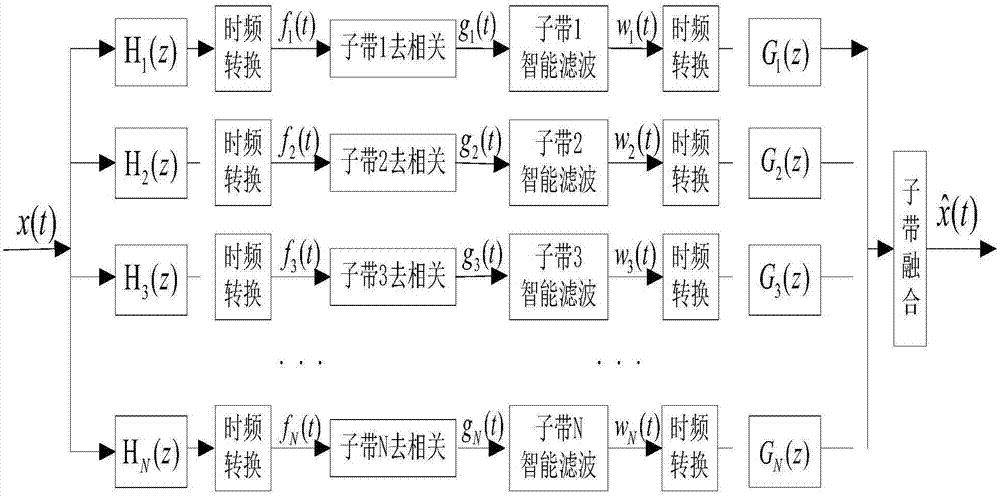
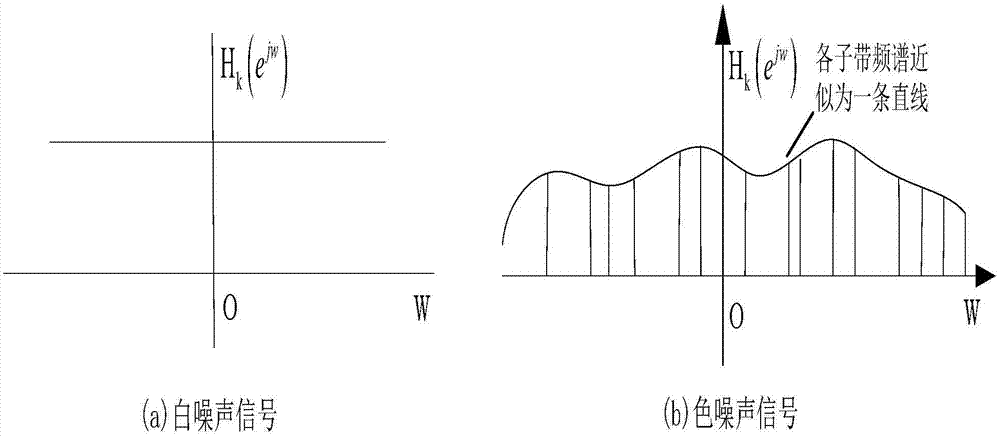
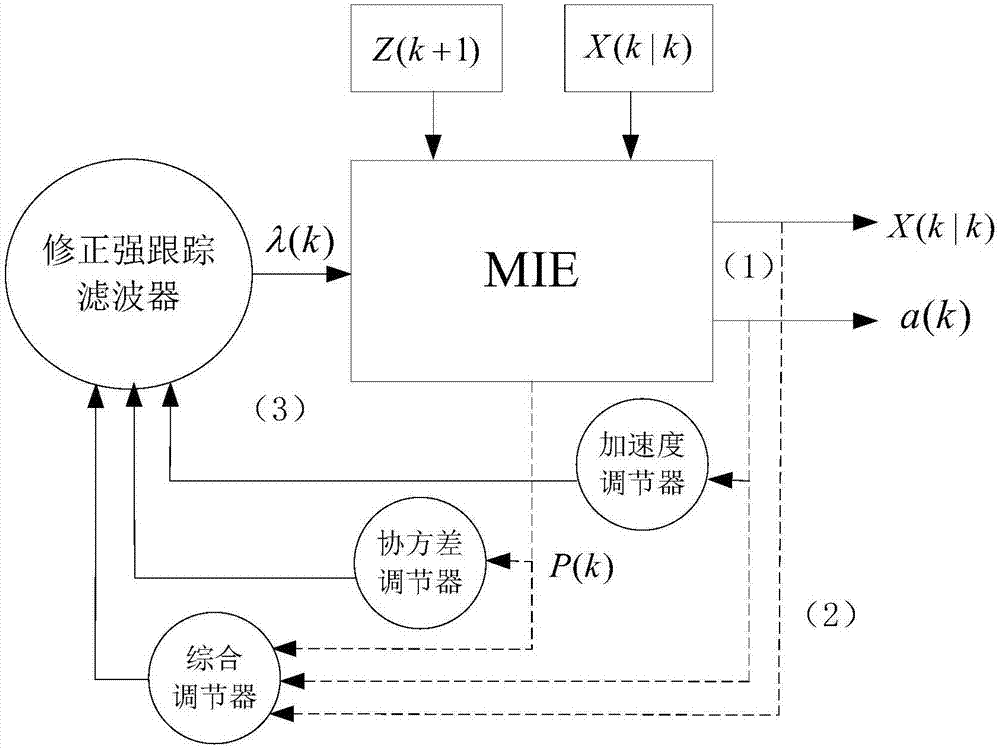
Three-dimensional space strong maneuvering target tracking method based on intelligent subband filtering
InactiveCN107315172AImprove tracking accuracyImprove reaction speedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPrior informationTarget signal
The invention discloses a three-dimensional space strong maneuvering target tracking method based on intelligent subband filtering, which belongs to the field of radar target tracking. The method uses an intelligently-adjusted subband filtering idea to effectively realize quick and accurate tracking on maneuvering of an unknown target in three-dimensional space. The method comprises steps: (1) subband decomposition for strong maneuvering target signals is carried out; (2) subband decorrelation for the strong maneuvering target signals is carried out; (3) intelligent subband filtering for the strong maneuvering target signals is carried out; (4) subband fusion for the strong maneuvering target signals is carried out; and (5) steps from the first to the fourth are iterated cyclically until all measuring plots are processed. On the basis of not requiring prior information of target maneuvering characteristics, the method has high tracking precision and reaction speed towards near space target mutation maneuvering, quick and precise tracking can be realized, and engineering realization is facilitated.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
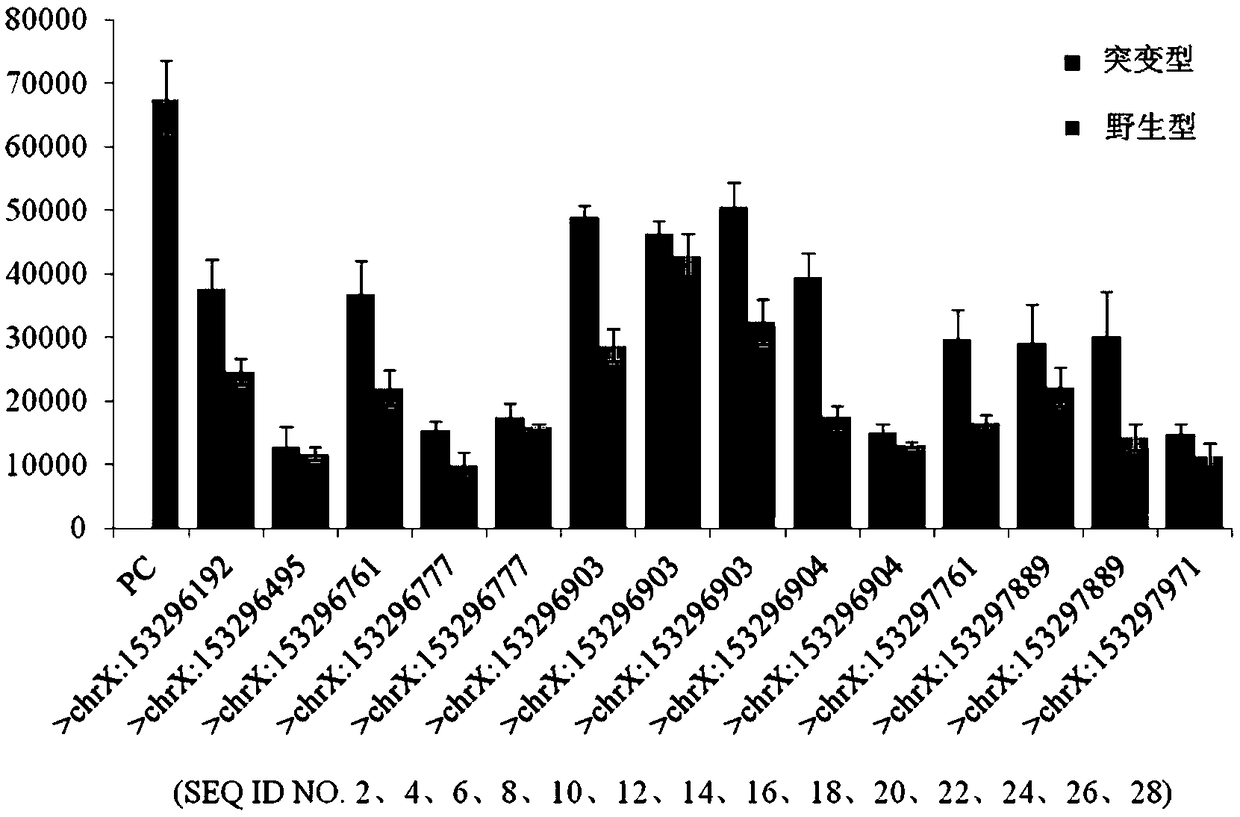
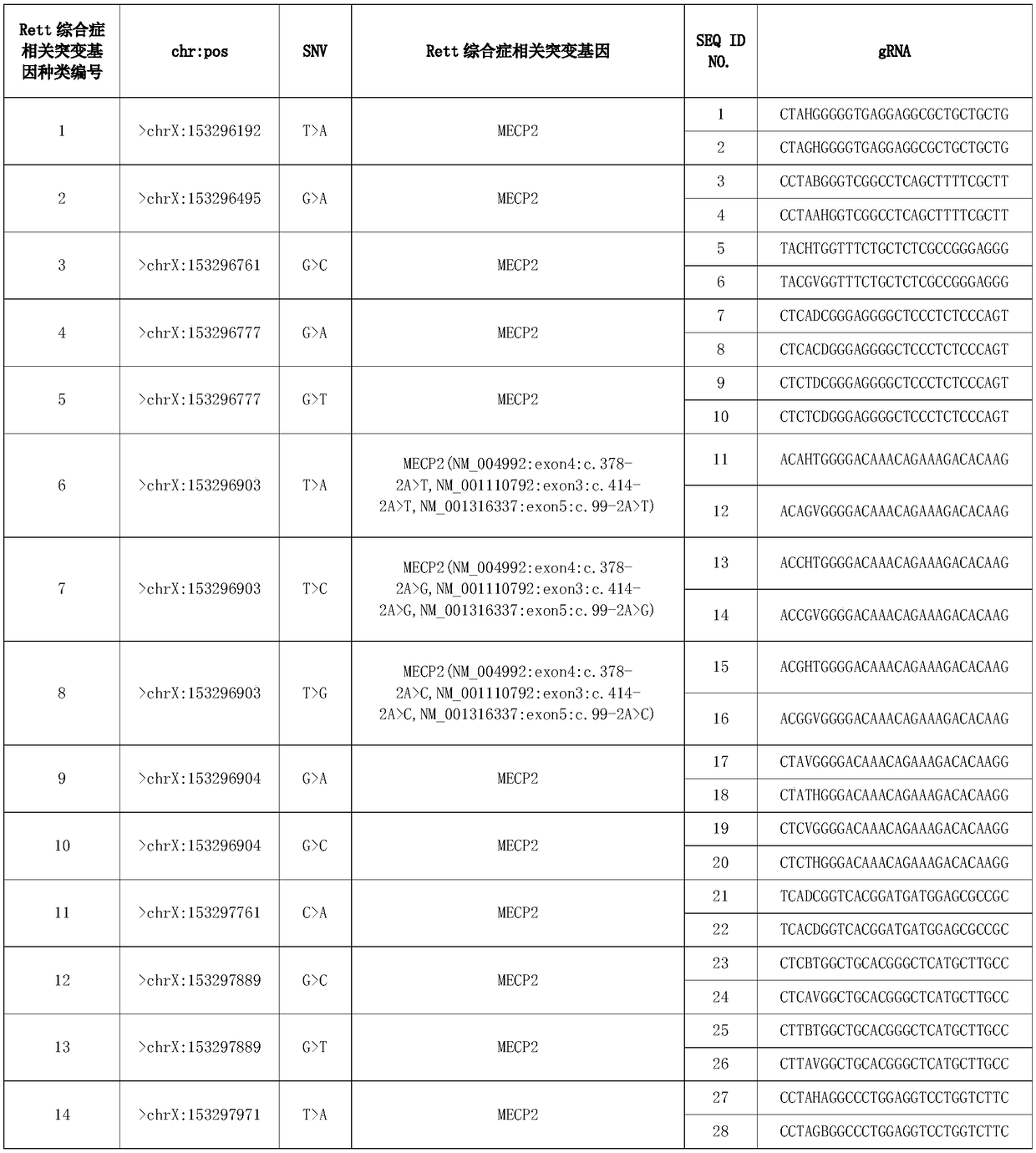
GRNA targeted to RNA of Rett mutation gene, and detection method and detection kit for the Rett mutation gene
The invention provides gRNA targeted to Rett syndrome-related mutation gene RNA and provides a detection method and a detection kit for human Rett syndrome-related mutation on the basis of a clusteredregularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-C2c2 system. In the detection method, by means of advantages of the gRNA targetedly-recognizing a transcription product RNA (target RNA sequence) of the Rett syndrome-related mutation gene, when the CRISPR-C2c2 composite detects the target RNA sequence, the composite can cut the report RNA having a detection label and release a detectable signal, so that when the CRISPR-C2c2 system is applied to detection for the Rett syndrome-related mutation gene, high sensitivity and accuracy are achieved. The detection method and the detection kit have huge commercial application potential value.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PLUSLIFE TECH CO LTD
Molecular breeding method for thickening intermuscular bones of silver carp and bighead carp
PendingCN111500581AReduce in quantityIncreased ossification areaClimate change adaptationMicroinjection basedMyostatinAnimal science
The invention belongs to the technical field of aquatic organism breeding, and discloses a molecular breeding method for thickening intermuscular bones of silver carp and bighead carp. The molecular breeding method provided by the invention is based on a technical means of gene editing, an F0 generation of targeted mutation silver carp and bighead carp mstn (myostatin) genes is obtained, and mutant individuals with deleted mstn and increased intermuscular ossification areas are obtained through passage. In the invention, a parent method for acquiring silver carp and bighead carp with increasedintermuscular ossification areas by utilizing a gene editing technology is put forward for the first time. According to the method, wild silver carp and bighead carp which have thick intermuscular bones and can be inherited can be cultivated on a large scale in production; different from a transgenic method, the method can be applied to artificial breeding, the difficulty that intermuscular bonesare fine and small and difficult to process in production is overcome, people do not need to worry about the influence of transgenic food on people, people can find intermuscular bones more easily when eating silver carp and bighead carp, and the method is easy to popularize in production.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
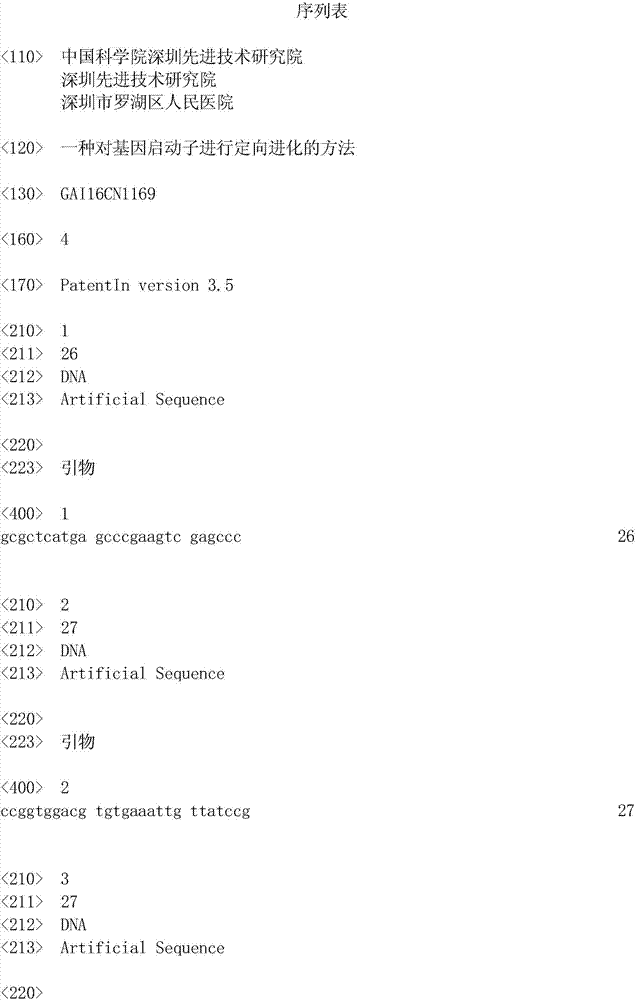
Method for carrying out directional evolution on gene promoter
ActiveCN107338241AImprove efficiencyIncrease productionDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationMutation frequencyA-DNA
The invention provides a method for carrying out directional evolution on a gene promoter. The method comprises the following steps: amplifying the promoter by adopting an error-prone PCR technology, thus obtaining a group of promoter sequences with high mutation frequency; removing harmful mutation by adopting a DNA shuffling technology, and collecting beneficial mutation, thus obtaining the promoter after shuffling; forming an expression cassette by adopting the recombinant promoter and a galactosidase gene, transforming host cells by adopting the expression cassette, and carrying out blue and white spot screening and enzyme activity determination, thus obtaining the target mutation promoter. With the method provided by the invention, the functional region of the gene promoter does not need to be analyzed, the cost is low, the operation is efficient, rapid, easy and convenient, the success rate is high, and the method is suitable for carrying out directional evolution on gene promoters of escherichia coli or other bacteria, fungi and mammalian cells.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Molecular breeding method for thickening intermuscular bones of grass carps and black carps
PendingCN111549031AReduce in quantityIncreased ossification areaHydrolasesClimate change adaptationMolecular breedingZoology
The invention discloses a molecular breeding method for thickening intermuscular bones of grass carps and black carps, and belongs to the technical field of aquatic organism breeding. The molecular breeding method provided by the invention is based on a technical means of gene editing, obtains an F0 generation of grass carp and black carp mstn genes subjected to targeted mutation, and obtains mutant individuals with mstn deletion and increased intermuscular bony area through passage. In the invention, a parent method for obtaining grass carp and black carp with increased intermuscular boning area by utilizing a gene editing technology is provided for the first time. According to the method, wild grass carps and black carps which have thick inherited intermuscular bones can be cultivated ona large scale in production, different from a transgenic method, the method can be applied to artificial breeding, overcomes the difficulty that intermuscular thorns are small and difficult to process in production, does not need to worry about the influence of transgenic food on people, is convenient for people to find the intermuscular thorns more easily when eating grass carps and black carps,and is easy to promote in production.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Methods and systems for analysis of single cells
Methods are provided for diagnosis and prognosis of disease by analyzing expression of a set of genes obtained from single cell analysis. Classification allows optimization of treatment, and determination of whether on whether to proceed with a specific therapy, and how to optimize dose, choice of treatment, and the like. Single cell analysis also provides for the identification and development of therapies which target mutations and / or pathways in disease-state cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for improving protein expression efficiency by employing model fitting and gene modification and application thereof
ActiveCN104878036AImprove expression efficiencyIncrease biological functionDepsipeptidesFermentationProtein targetRibosomal protein
The invention relates to a method for improving protein expression efficiency by employing model fitting and gene modification and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: fitting a secondary structure of an mRNA sequence of a target protein ribosomal protein L11 by employing M-fold software, inputting an about early 20-locus nucleotide sequence of an initiation codon and an about back 50-locous nucleotide sequence of the initiation codon and fitting. According to the fitted secondary structure, a hairpin structure behind the initiation codon is removed; targeted mutation is carried out on guanine, cytosine and the like in the hairpin structure; the content of the guanine and the cytosine is lowered; and the guanine and the cytosine are replaced with adenine and thymine; after site-directed mutation is carried out, mutants of the target protein with improved yield are screened by virtue of experiments; the biological functions of the mutants are further verified by virtue of biological function experiments; the mutants mutated by the method do not have a significant effect on the biological function when increasing expression of the ribosomal protein L11; and the method for improving recombinant ribosomal protein expression efficiency based on model fitting, site-directed mutation and experiment screening has relatively high universality and feasibility, and is also applicable to large-scale expression, industrial production and the like of other recombinant proteins.
Owner:江苏莱森生物科技研究院有限公司
Interleukin-2 mutation gene and its preparation
An interleukin-2 (IL-2) mutation gene with the base sequence shown by SEQ ID No.1 is prepared from natural IL-2 gene through overlapped PCR for targeted mutation to the base on the gene. Its advantages are less mutant site, high protein expression level, and no change to amino acid sequence of natural protein.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
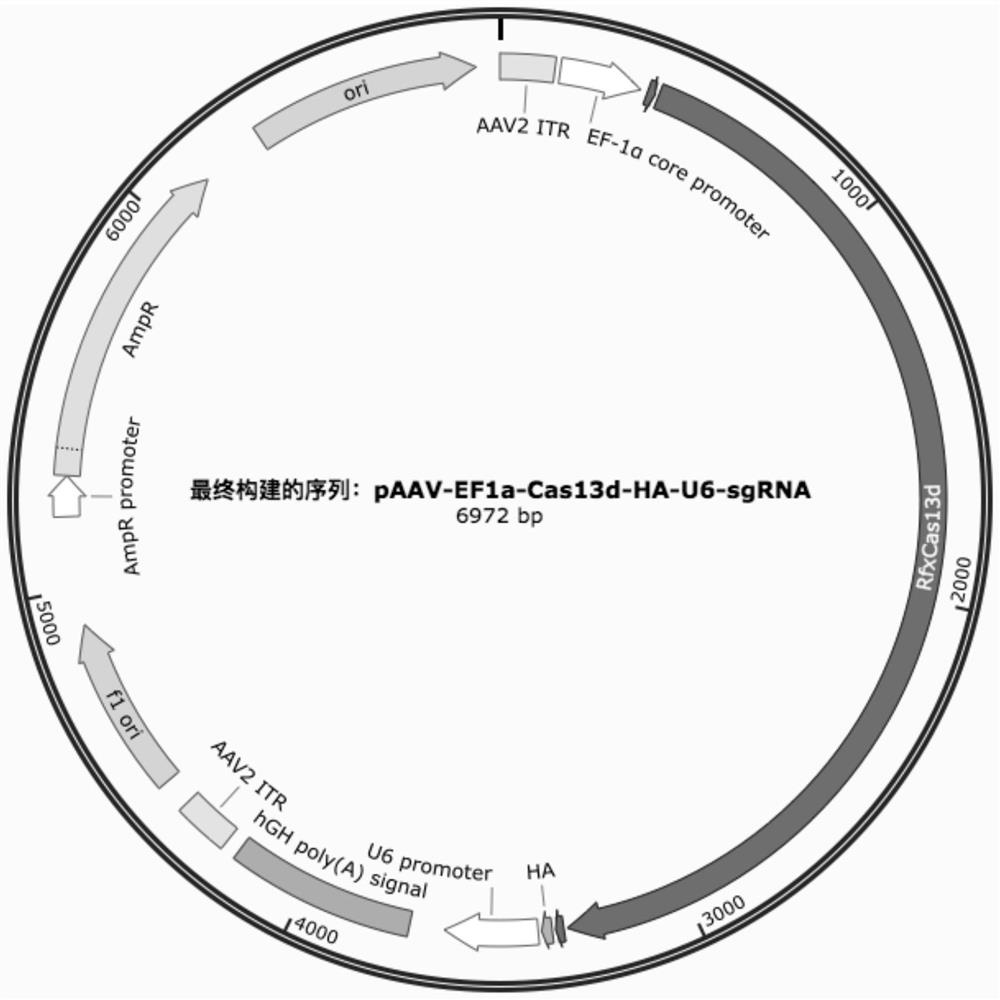
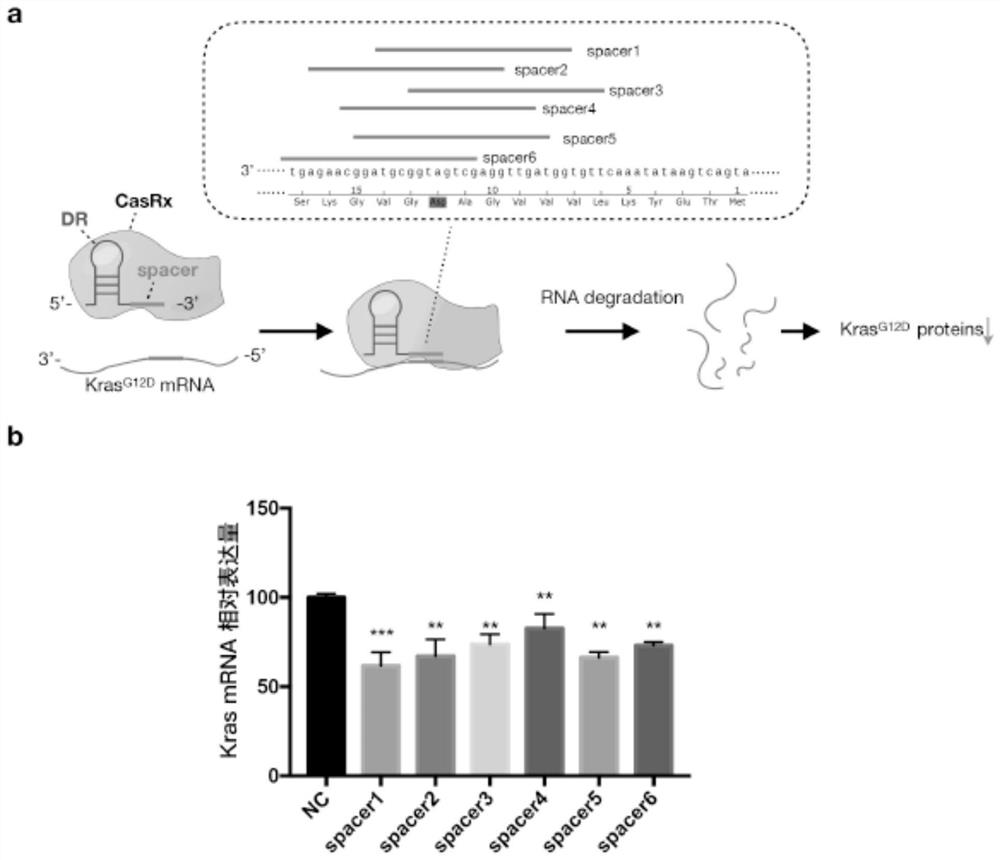
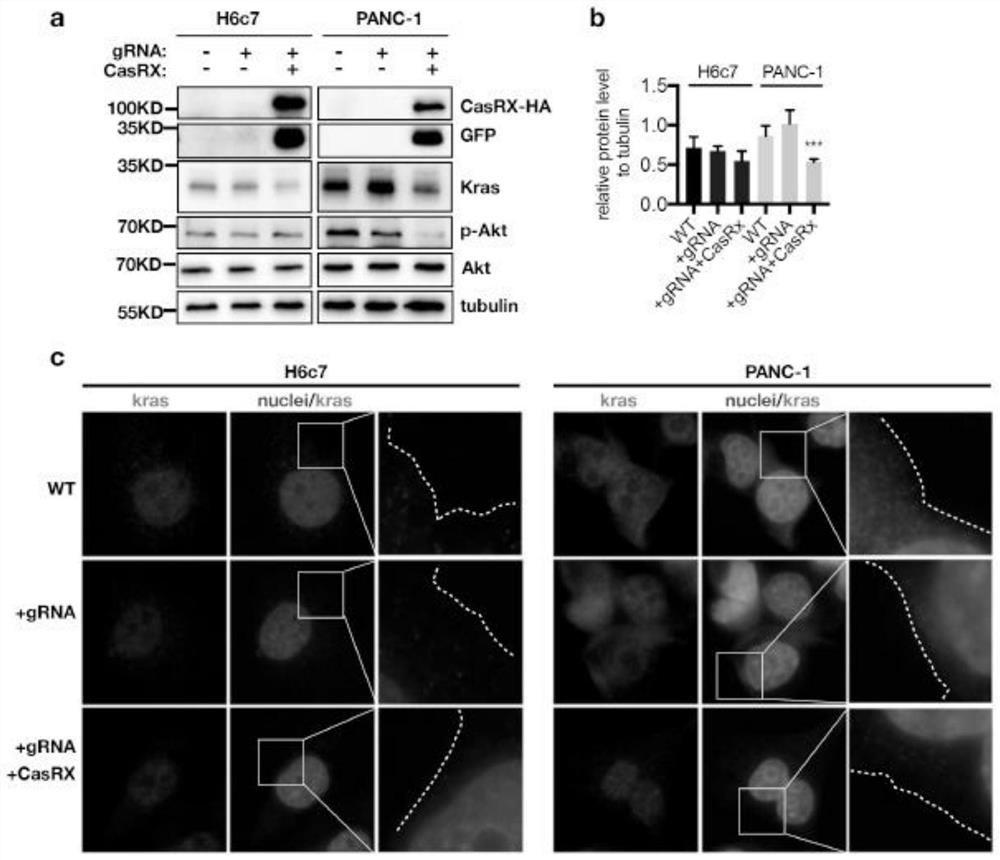
gRNA sequence of targeted KrasG12D mutant transcript, vector and application of vector
PendingCN111876421AImprove targetingImprove featuresOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsViral vectorBioinformatics
The invention relates to a gRNA sequence of a targeted KrasG12D mutant transcript. A gene sequence consists of gRNA-DR and a spacer sequence, wherein the gene sequence of the gRNA-DR is shown as SEQ ID NO.7, and the spacer sequence is shown as any one of SEQ ID NO.1-6. The invention further discloses an adenovirus vector which carries the gRNA sequence of a targeted KrasG12D mutant transcript. Theinvention further provides the adenovirus vector which carries the gRNA sequence of the targeted KrasG12D mutant transcript and a gene sequence for coding a CasRx protein. The invention further provides an application of the adenovirus vector to preparation of a medicine for treating cancer, by using KrasG12D as a target. Compared with targeting property and specificity of conventional shRNA, thetargeting property and the specificity of siRNA are both improved. Compared with a CRISPR-Cas9 technology, the vector has a lower off-target effect.
Owner:蒋望
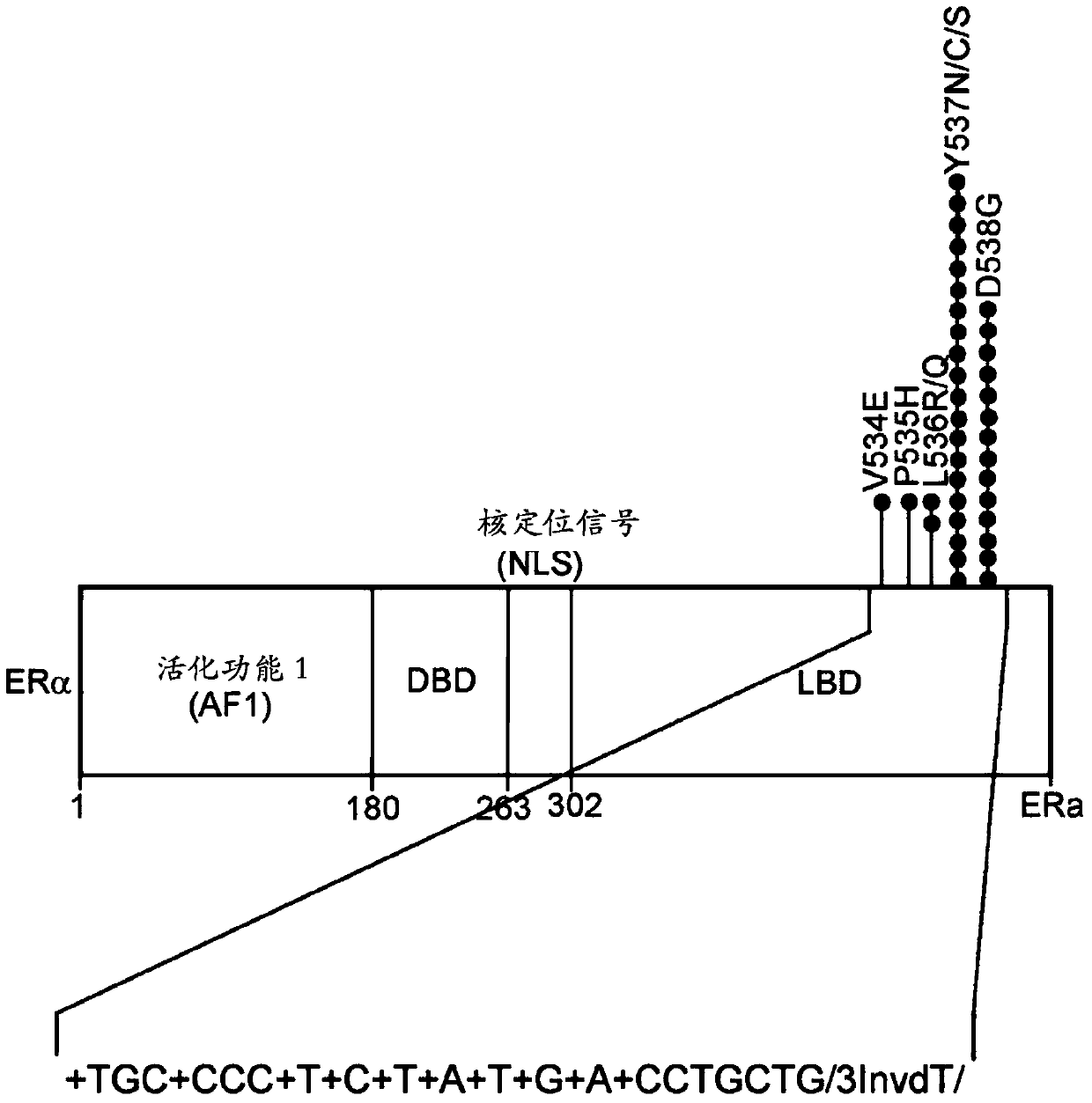
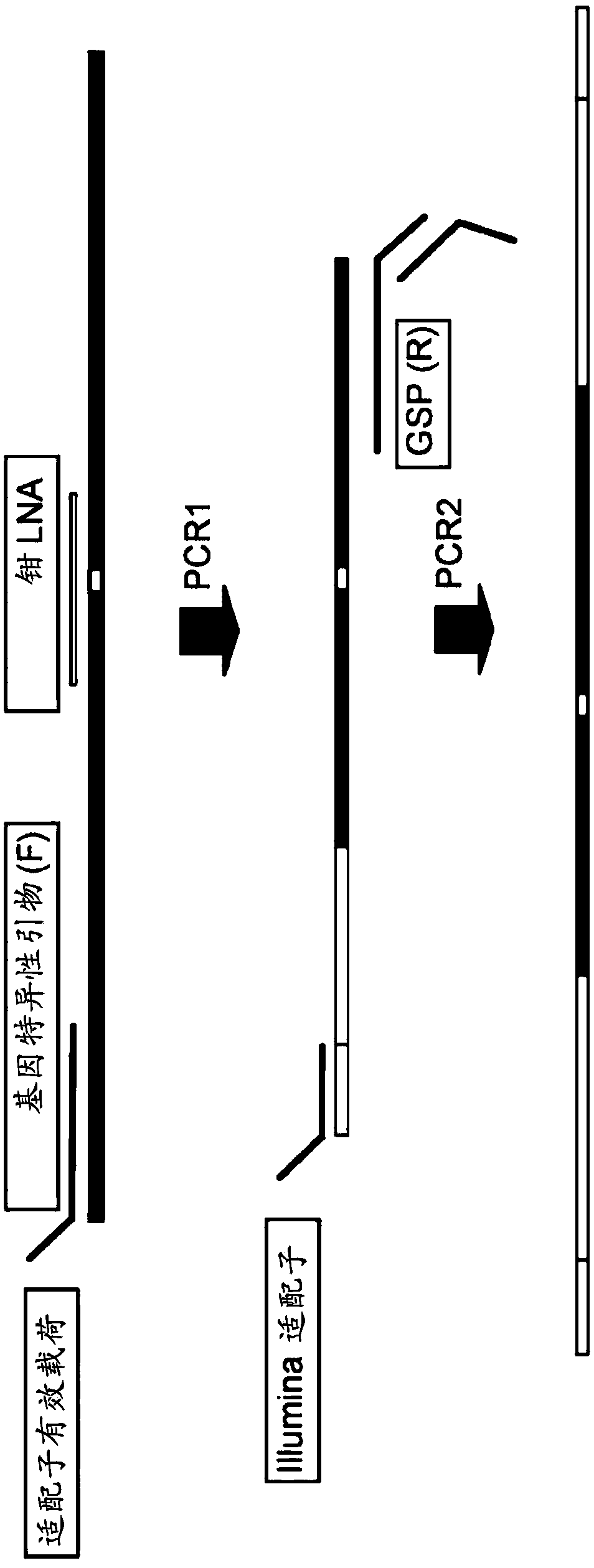
Lna-based mutant enrichment next-generation sequencing assays
Ultra-sensitive assays for the detection of mutations, e.g., from blood-based sources of tumor genetic material (circulating tumor cells or plasma), or other settings in which limiting amounts of DNA,e.g., tumor DNA, is available. The assay is exemplified in the estrogen receptor, but is broadly customizable to target mutations in other genes.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Probe pool for detecting NTRK-1-2-3 fusion gene variation based on NGS method and kit thereof
PendingCN110791552AStrong specificityHigh and uniform coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFresh TissueNucleic acid sequence
The invention discloses a probe pool for detecting NTRK-1-2-3 fusion gene variation based on an NGS method and a kit thereof. The probe pool is selected from at least one of probes with nucleic acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-74, and the kit is suitable for detecting the NTRK-1-2-3 fusion gene variation of FFPE and fresh tissues based on an NGS method. The capture probe is designed according to the highly related region of the NTRK-1-2-3 fusion gene variation, the coverage rate is high and uniform, and the specificity of fusion detection is improved. The library conversion rate is high, the RNA usage amount is low, and the sequencing cost is low. According to the present invention, the hot spot targeting mutant gene is covered, the probe capture specificity is high, and in addition, one product can meet the detection requirements of a variety of pan-cancer NTRK-1-2-3 fusion genes, can solve the clinical sample preparation problem, and can reduce the complex problem of repeatedwork of experimental workers.
Owner:基恩生物科技(大连)有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com