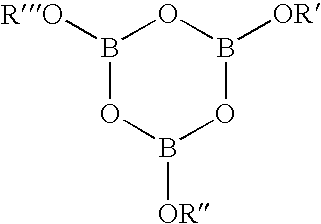
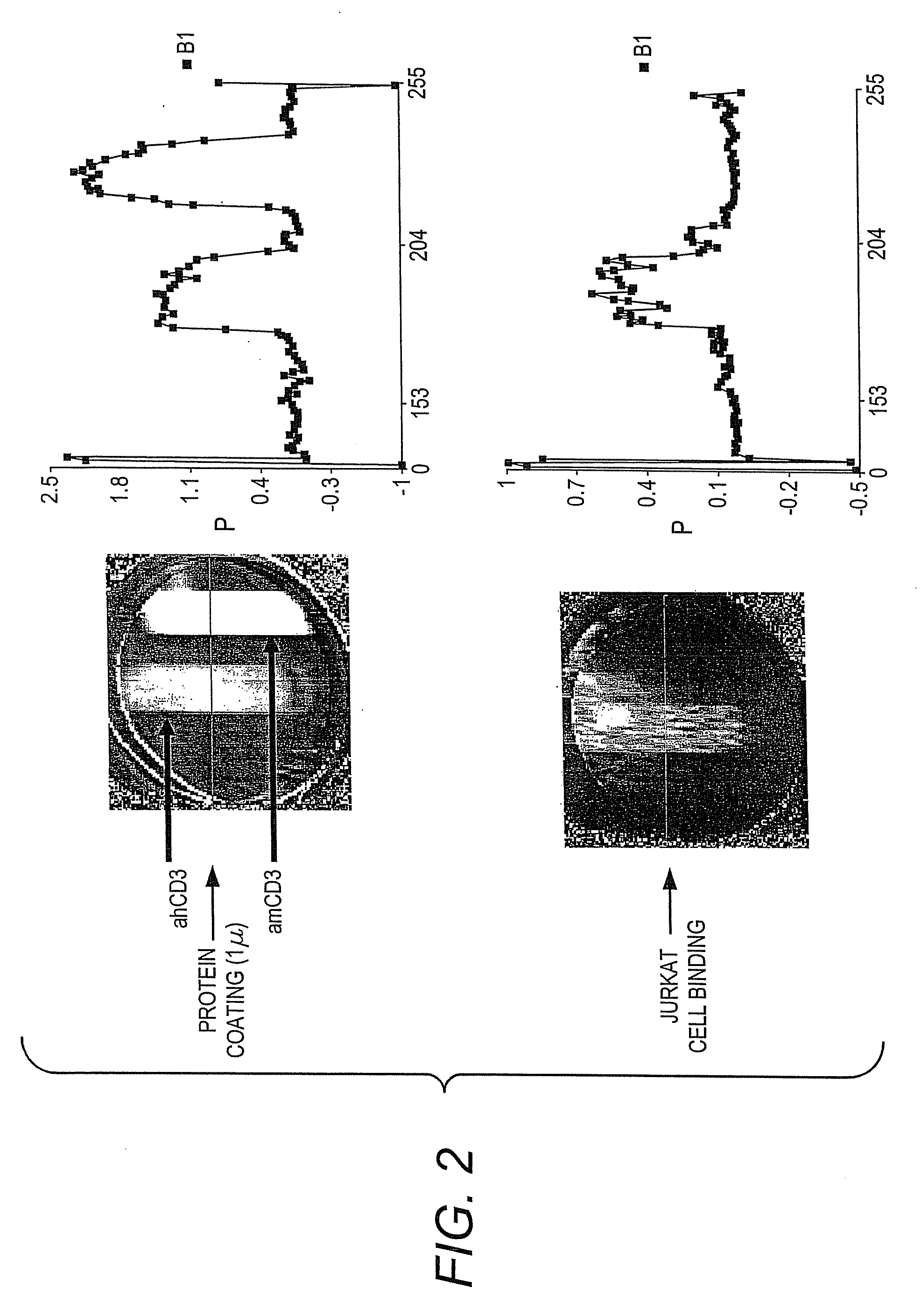
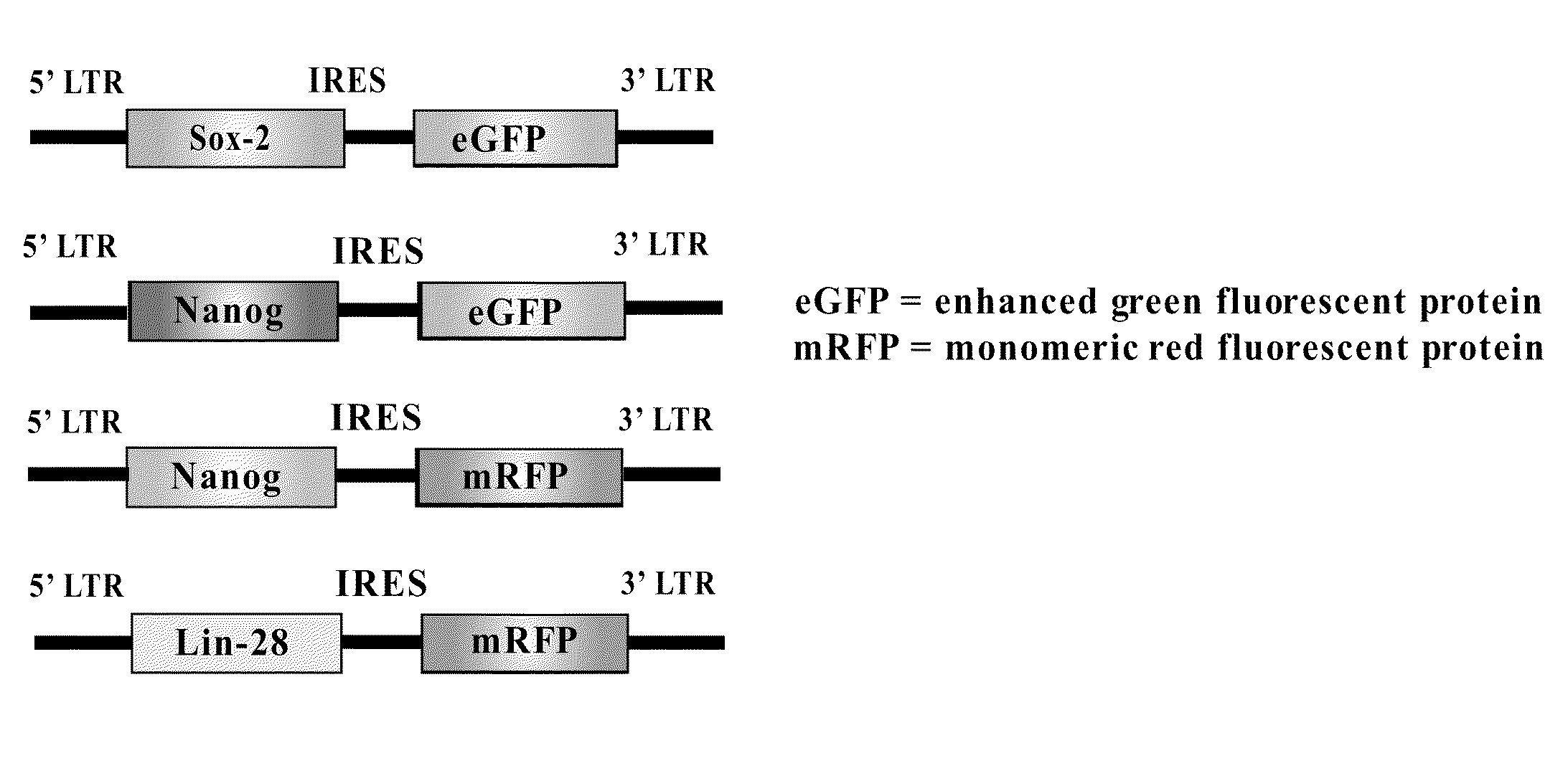
Patents
Literature
326 results about "Cell method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
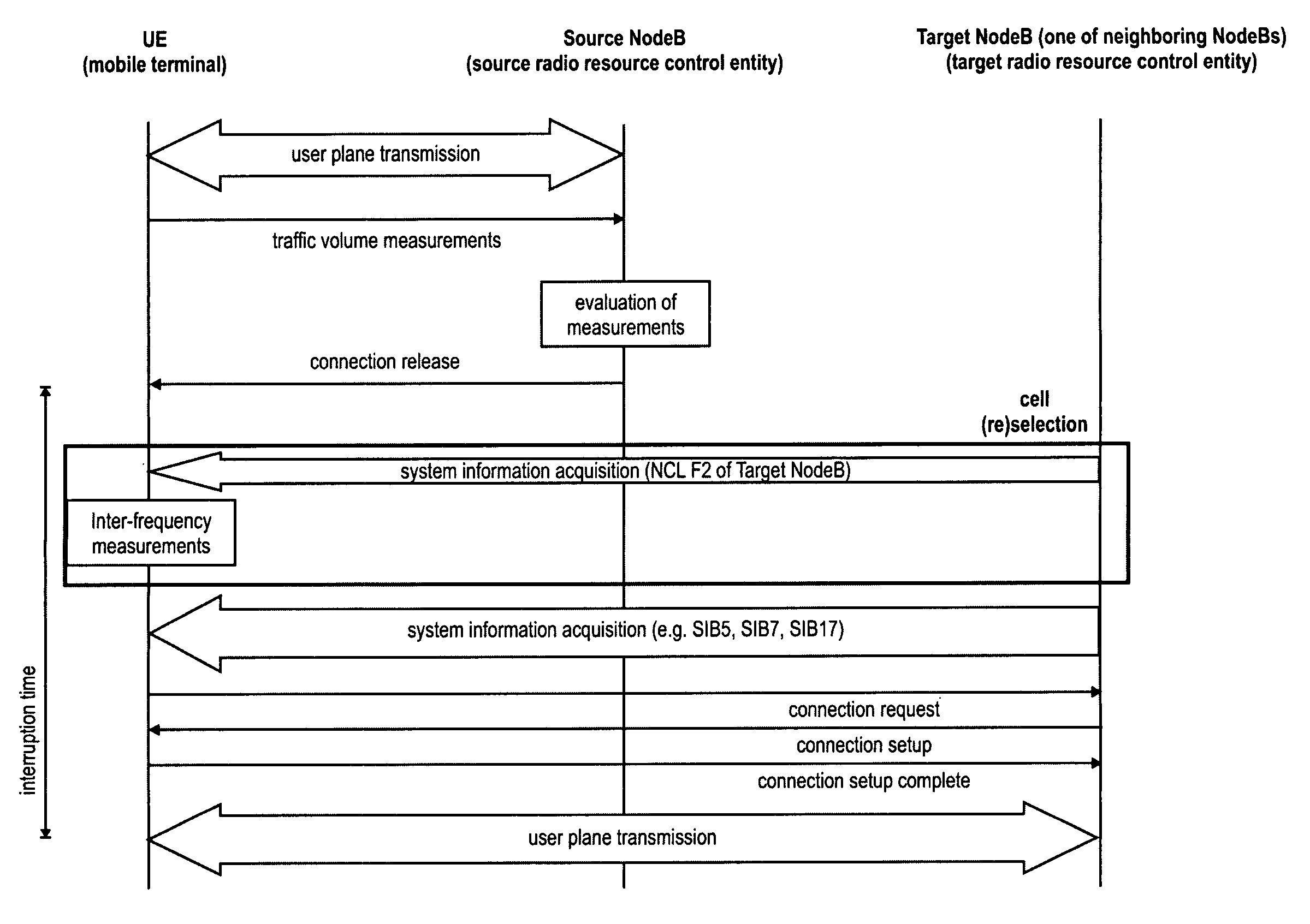
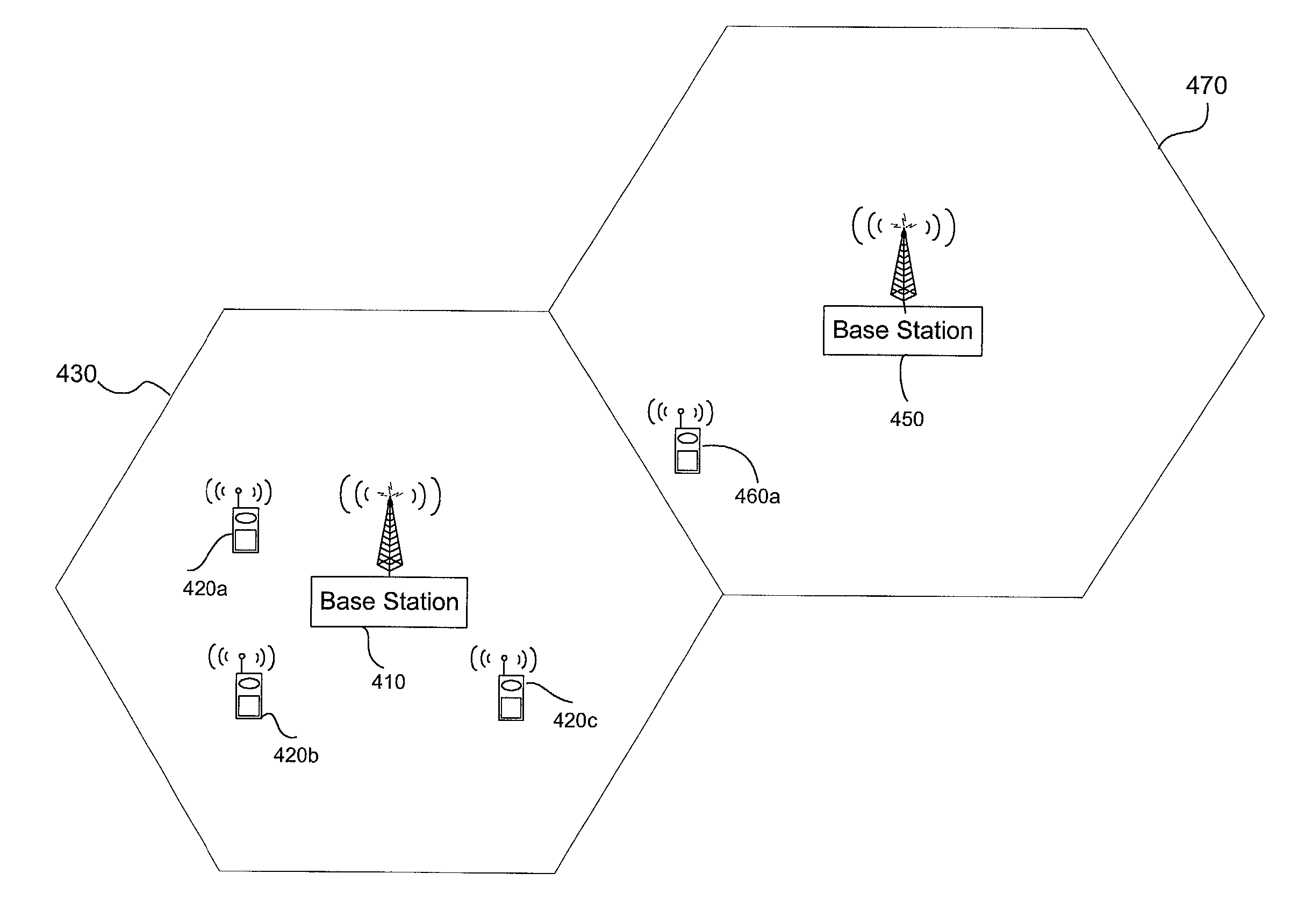
Improved acquisition of system information of another cell
InactiveUS20090274086A1Reduce the necessary timeSave resourcesAssess restrictionBroadcast transmission systemsAcquisition timeComputer science
Method for informing a mobile terminal (MN), which is located in a first cell, on system information of a second cell. In particular, pointers to the system information are transmitted from the base station of the first cell to the mobile node, while the mobile node is located in the first cell. The MN processes said pointer, comprising e.g. information on the transmission format and timing of system information in the second cell. Using an acquisition gap assigned by the network, the MN changes the frequency to the second frequency so as to acquire the system information based on the previously received scheduling information. Thus, the acquisition time for important system information may be reduced, as no Master Information Block on the second frequency has to be processed first, in order to acquire the system information.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
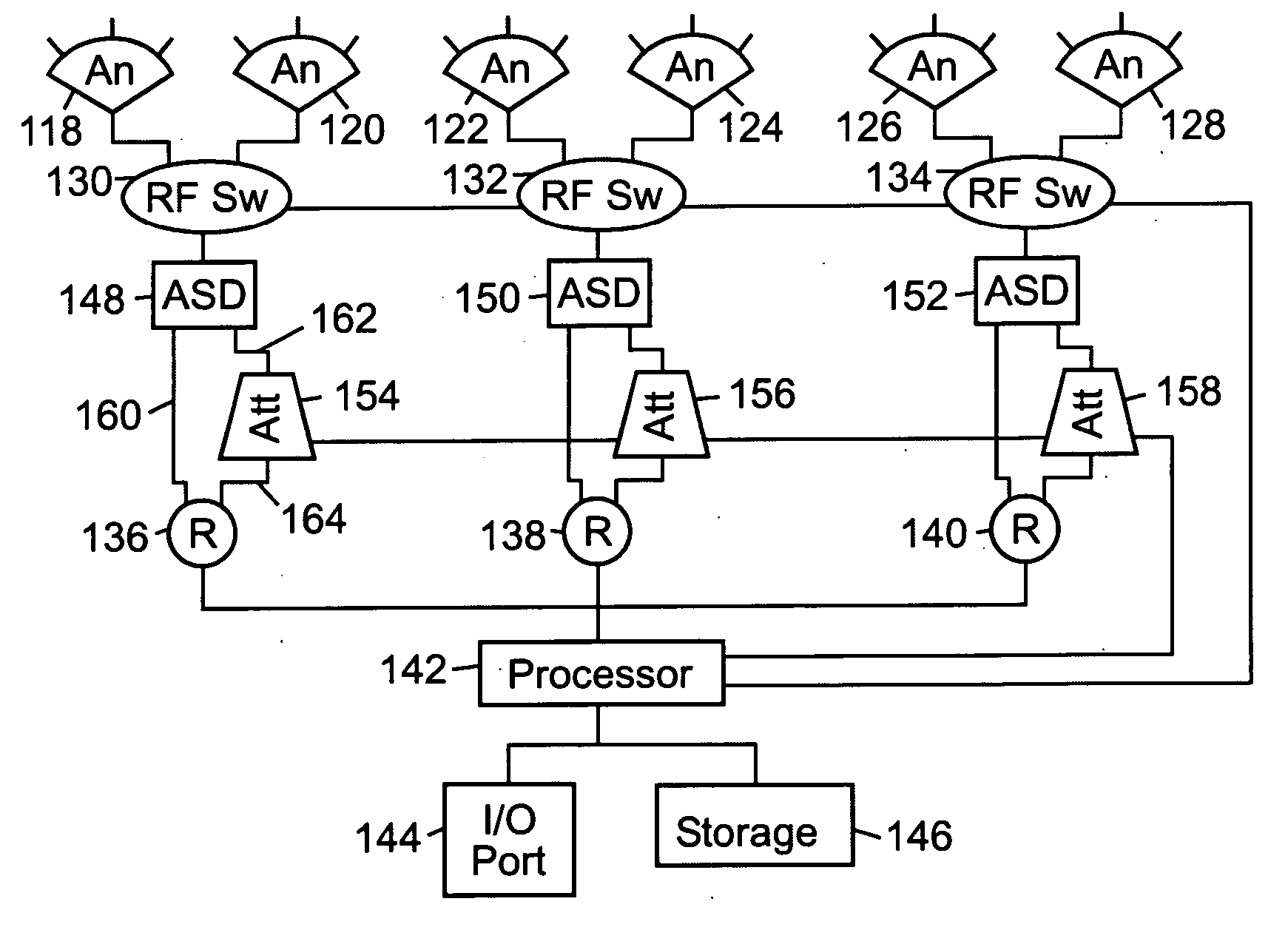
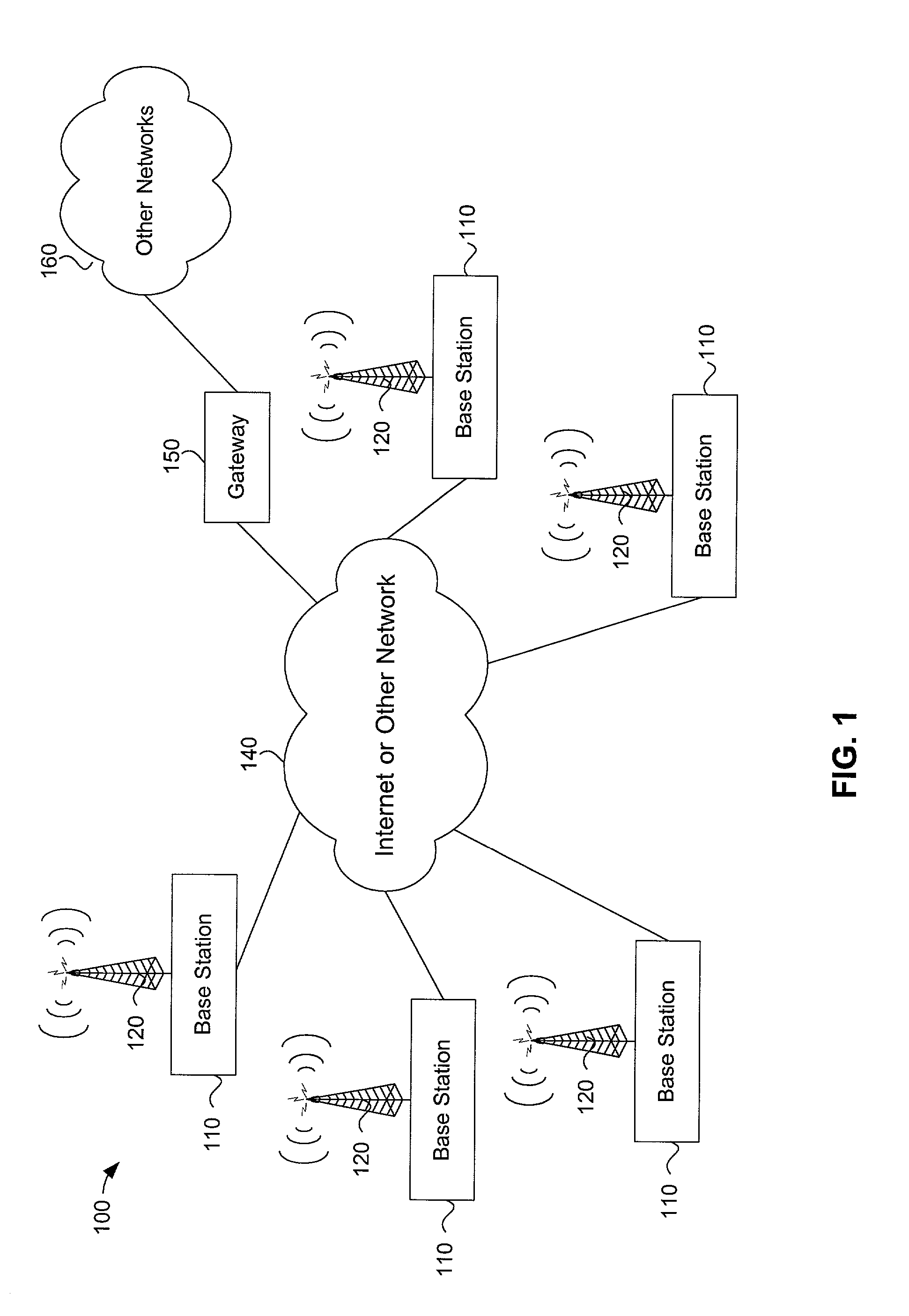
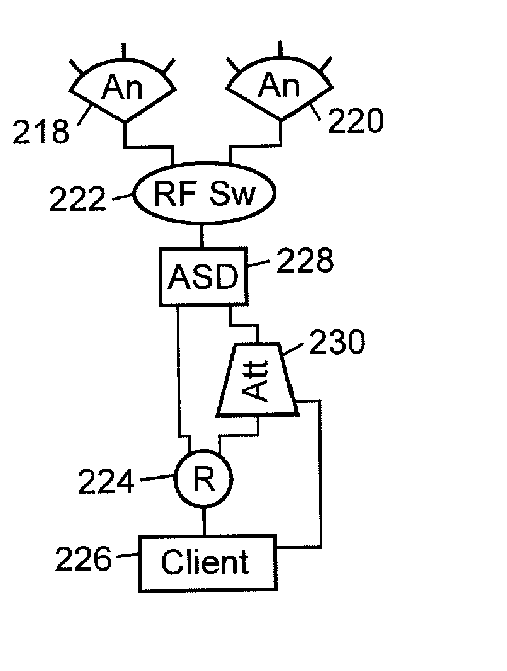
Method and apparatus for high throughput multiple radio sectorized wireless cell
InactiveUS20050003865A1Minimize interferenceImprove throughputSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityDirectional antennaLoad management
Methods and apparatus for high throughput wireless cells, capable of functioning as access points, are described. The wireless cells may be equipped with multiple radios to increase the amount of throughput available through a single wireless cell. Multiple antennas attached to the radios through RF switches may enable the wireless cell to service multiple clients simultaneously. The physical sectors of the antennas may overlapped to form virtual sectors that provide greater flexibility in client load management and in simultaneously servicing multiple clients. Attenuators may reduce interference from foreign wireless cells or clients. Systems and methods for assigning minimally interfering channels to either physical sectors or to radios to reduce interference between adjacent sectors and overlapping sectors are also disclosed. An antenna horn may also allow any antenna to be used as a directional antenna and may enable the antenna's angle of coverage to be adjusted. The use of multiple antennas on a client to reduce interferences is also described.
Owner:ROTANI
Photochromic compounds
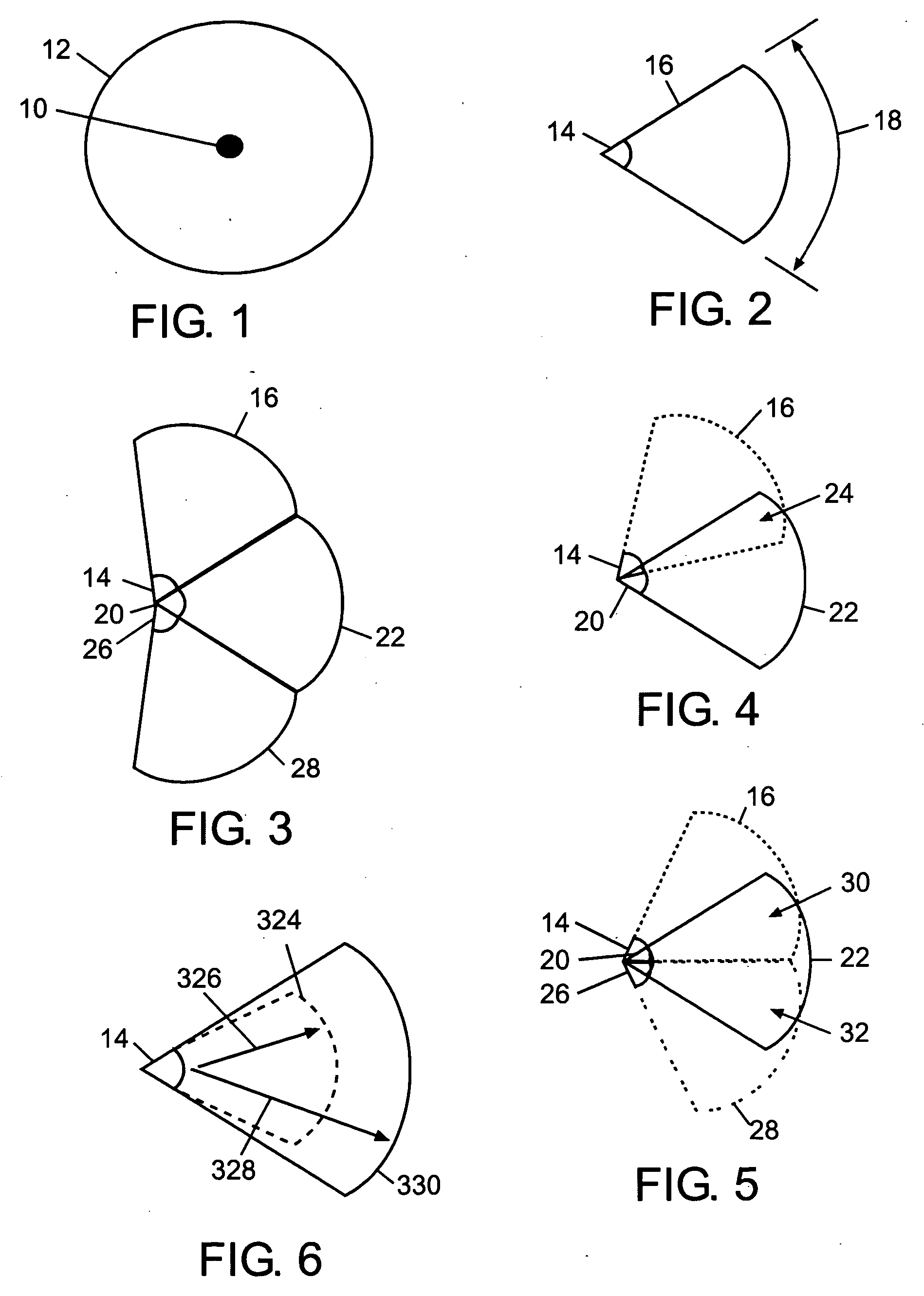
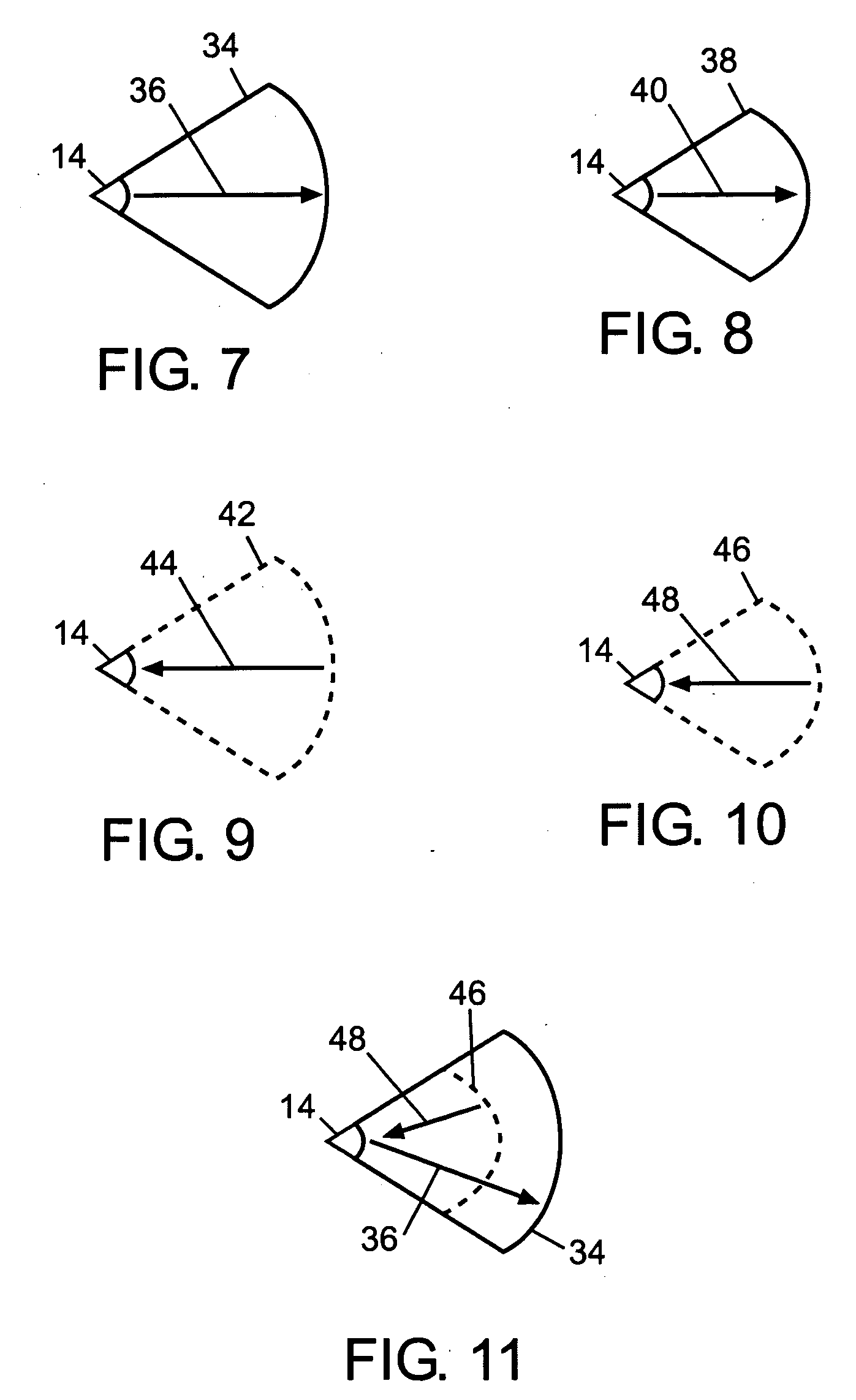
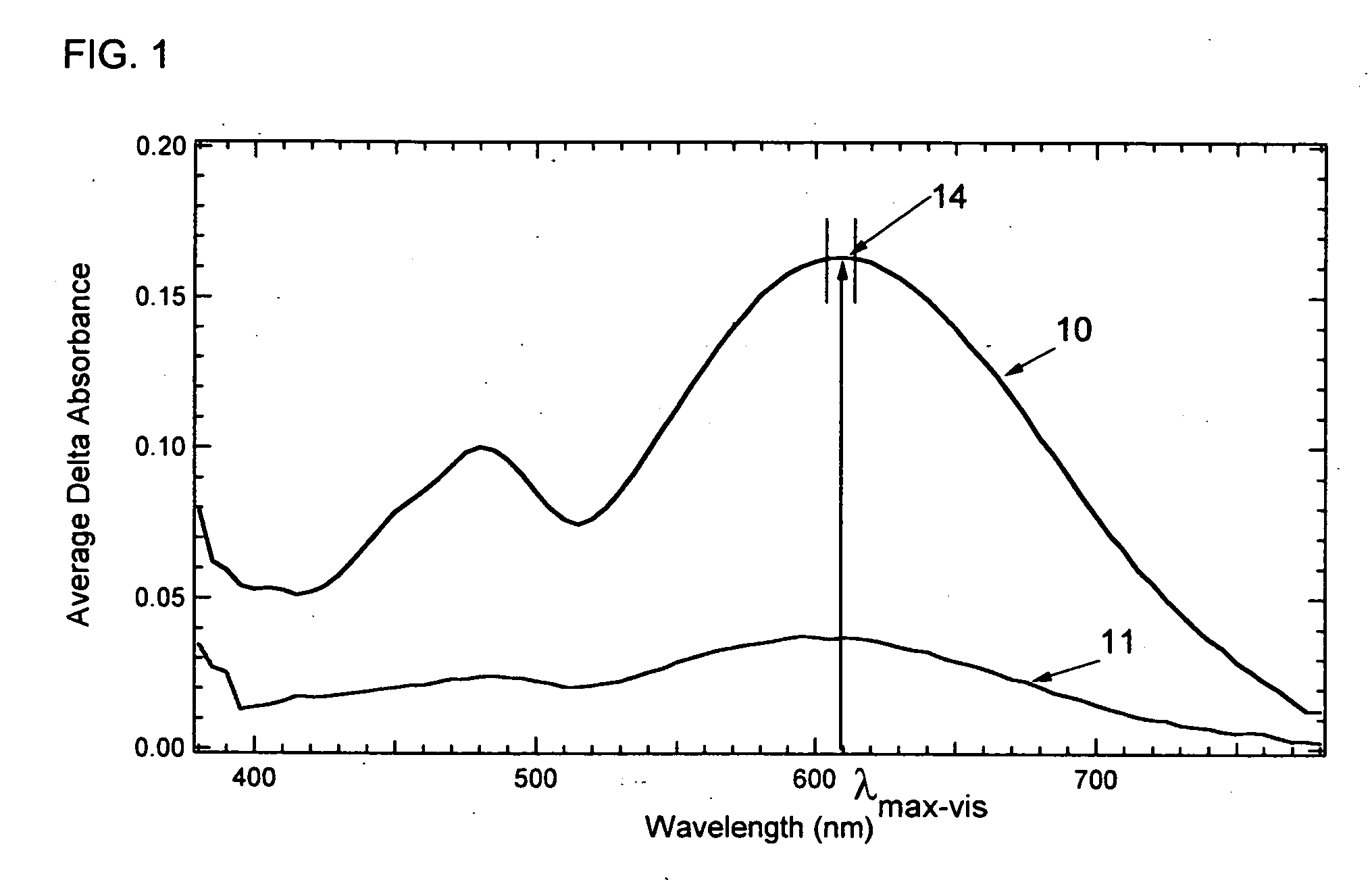
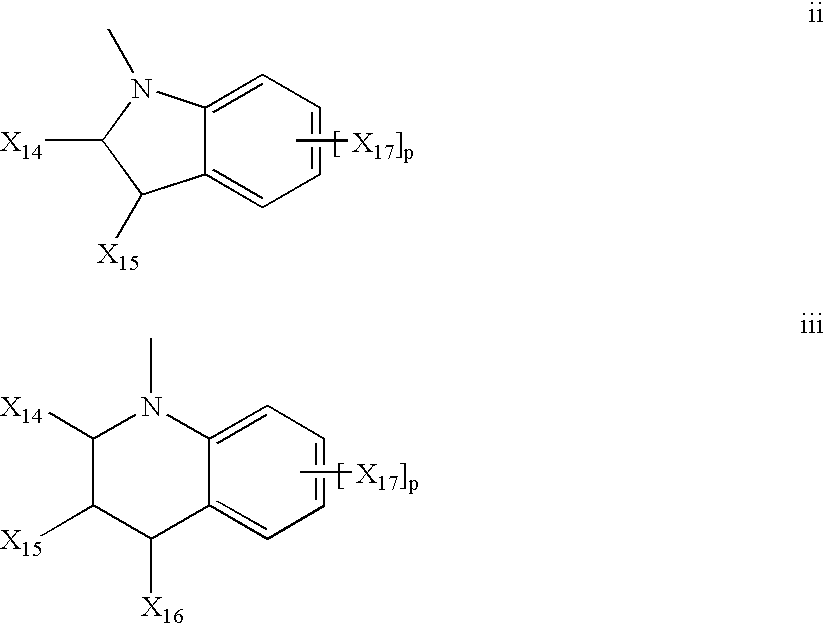
Various non-limiting embodiments disclosed herein relate generally to photochromic compounds, which may be thermally reversible or non-thermally reversible, and articles made therefrom. Other non-limiting embodiments relate to photochromic-dichroic compounds, which may be thermally reversible or non-thermally reversible, and articles made therefrom. For example, one non-limiting embodiment provides a thermally reversible, photochromic compound adapted to have at least a first state and a second state, wherein the thermally reversible, photochromic compound has an average absorption ratio greater than 2.3 in at least one state as determined according to CELL METHOD. Another non-limiting embodiment provides a photochromic compound comprising: (a) at least one photochromic group chosen from a pyran, an oxazine, and a fulgide; and (b) at least one lengthening agent L attached to the at least one photochromic group and represented by the formula —[S1]c-[Q1-[S2]d]d′-[Q2-[S3]e]e′-[Q3-[S4]f]f′—S5—P, which is described herein.
Owner:TRANSITIONS OPTICAL INC
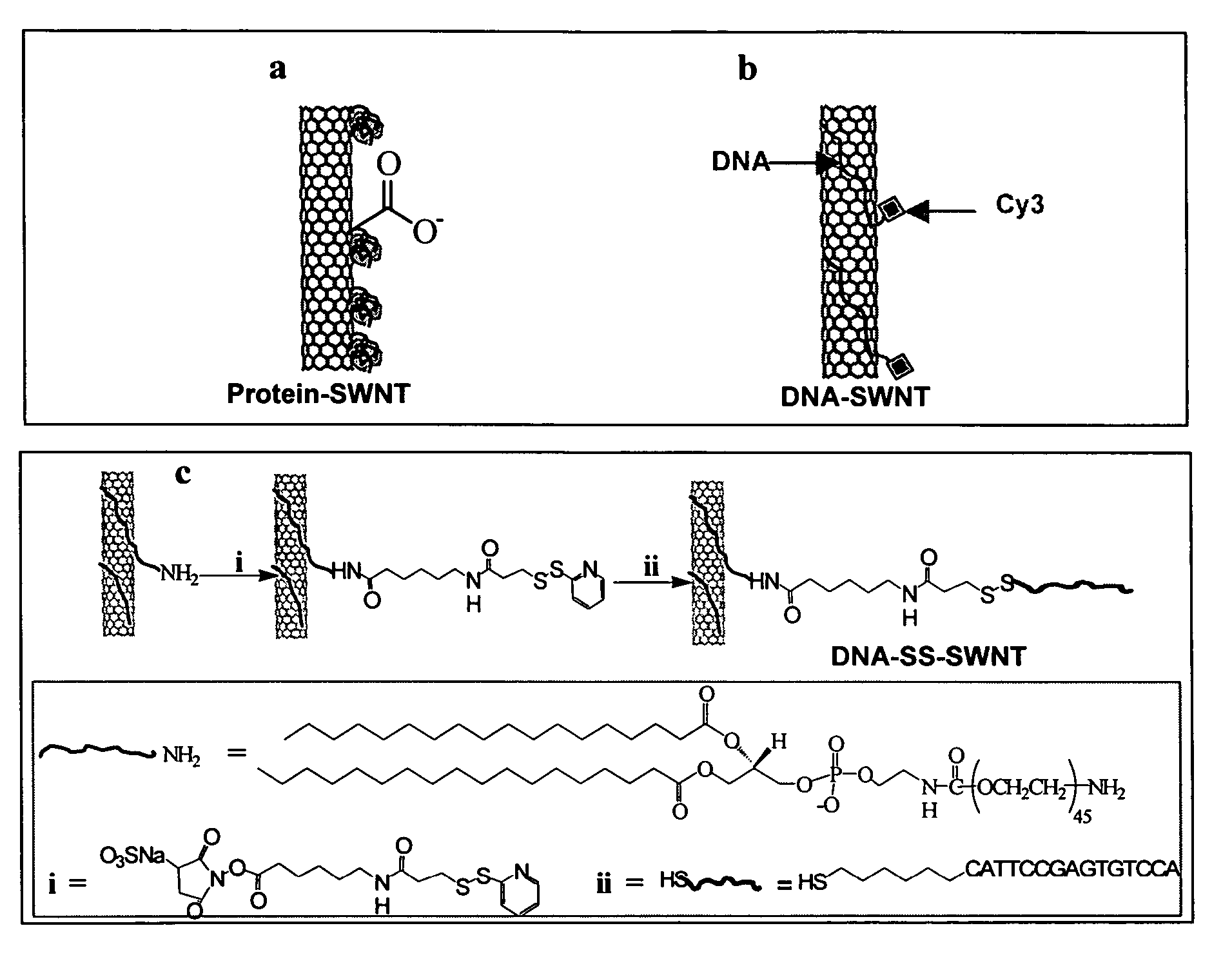
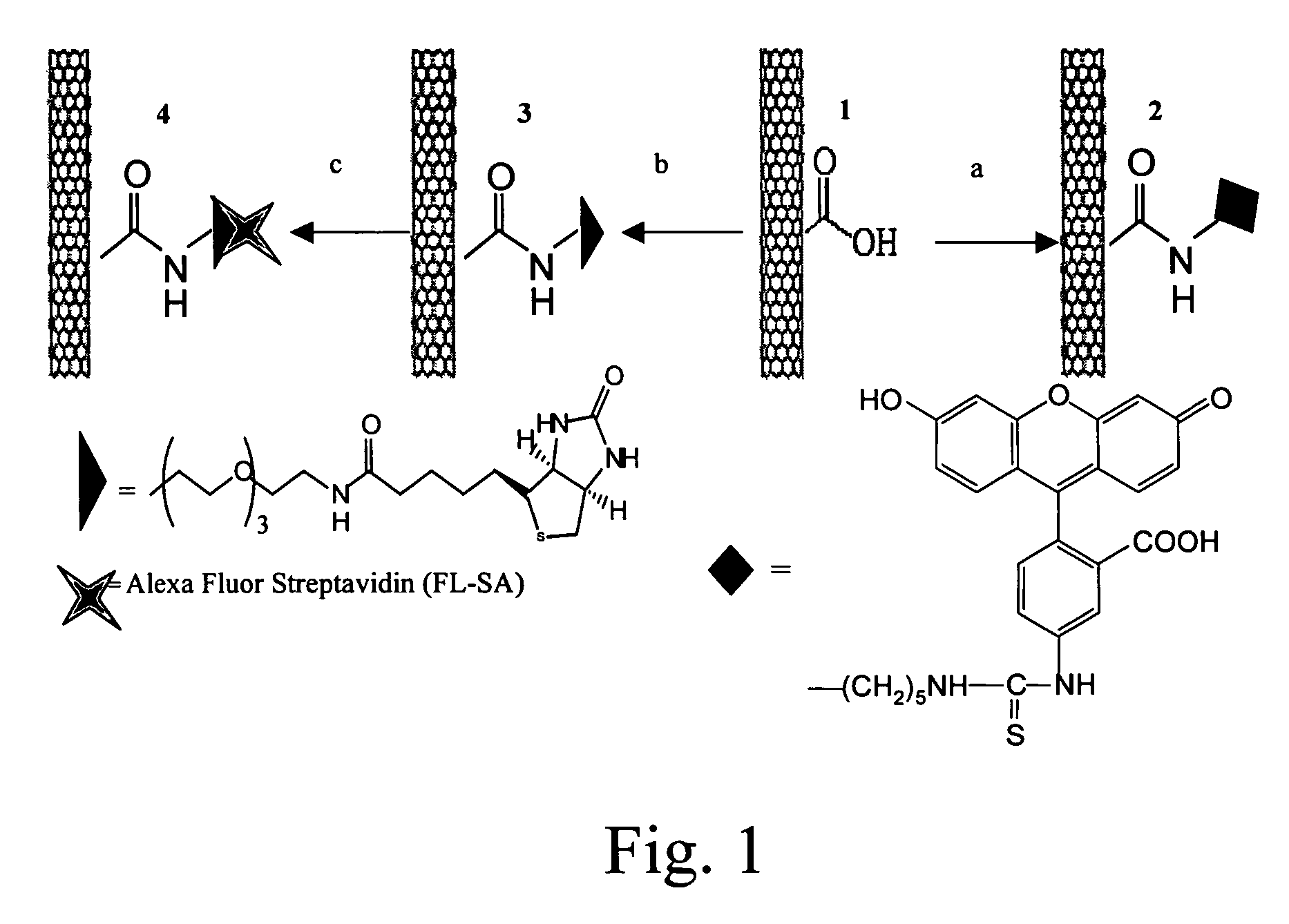
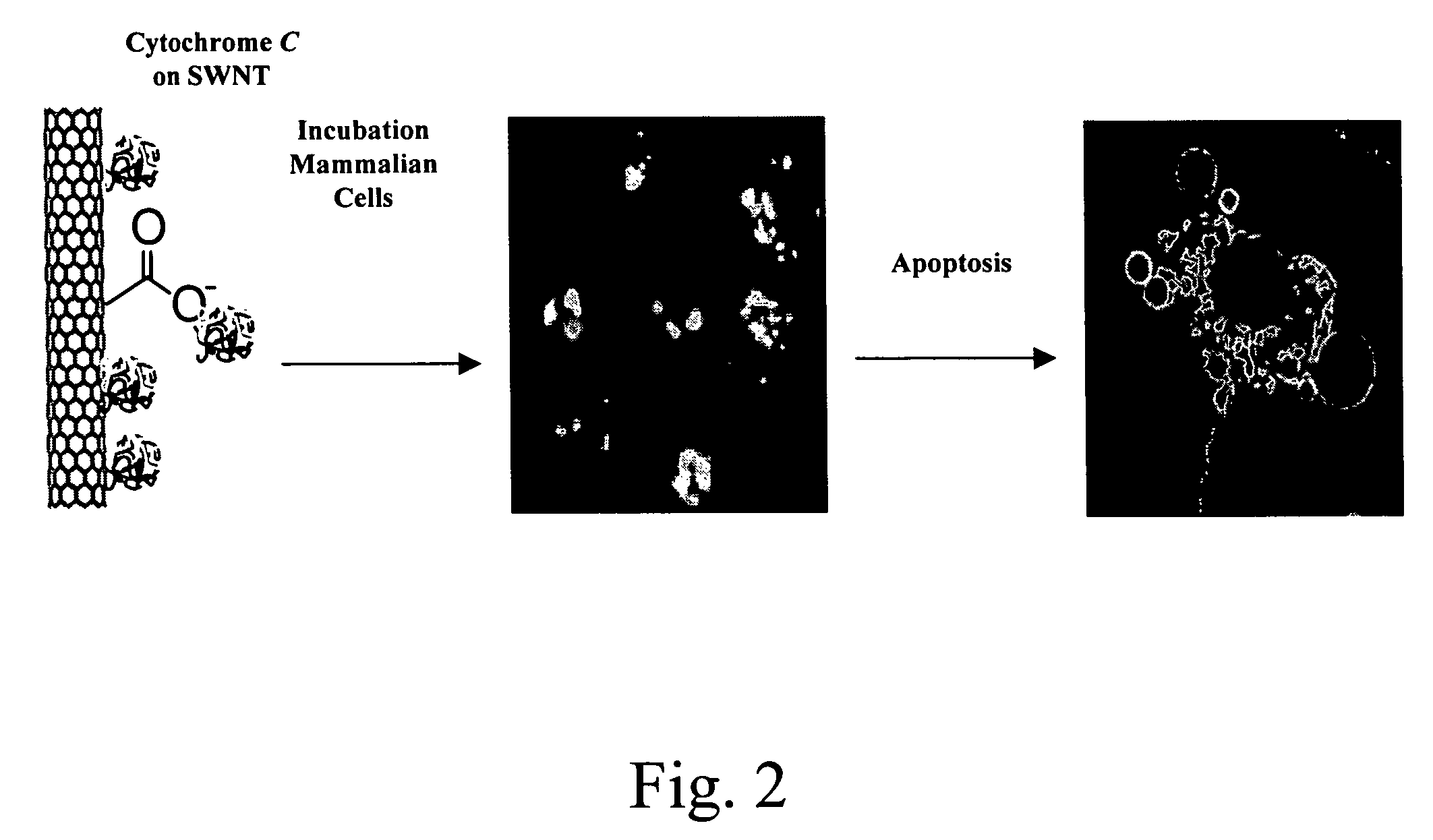
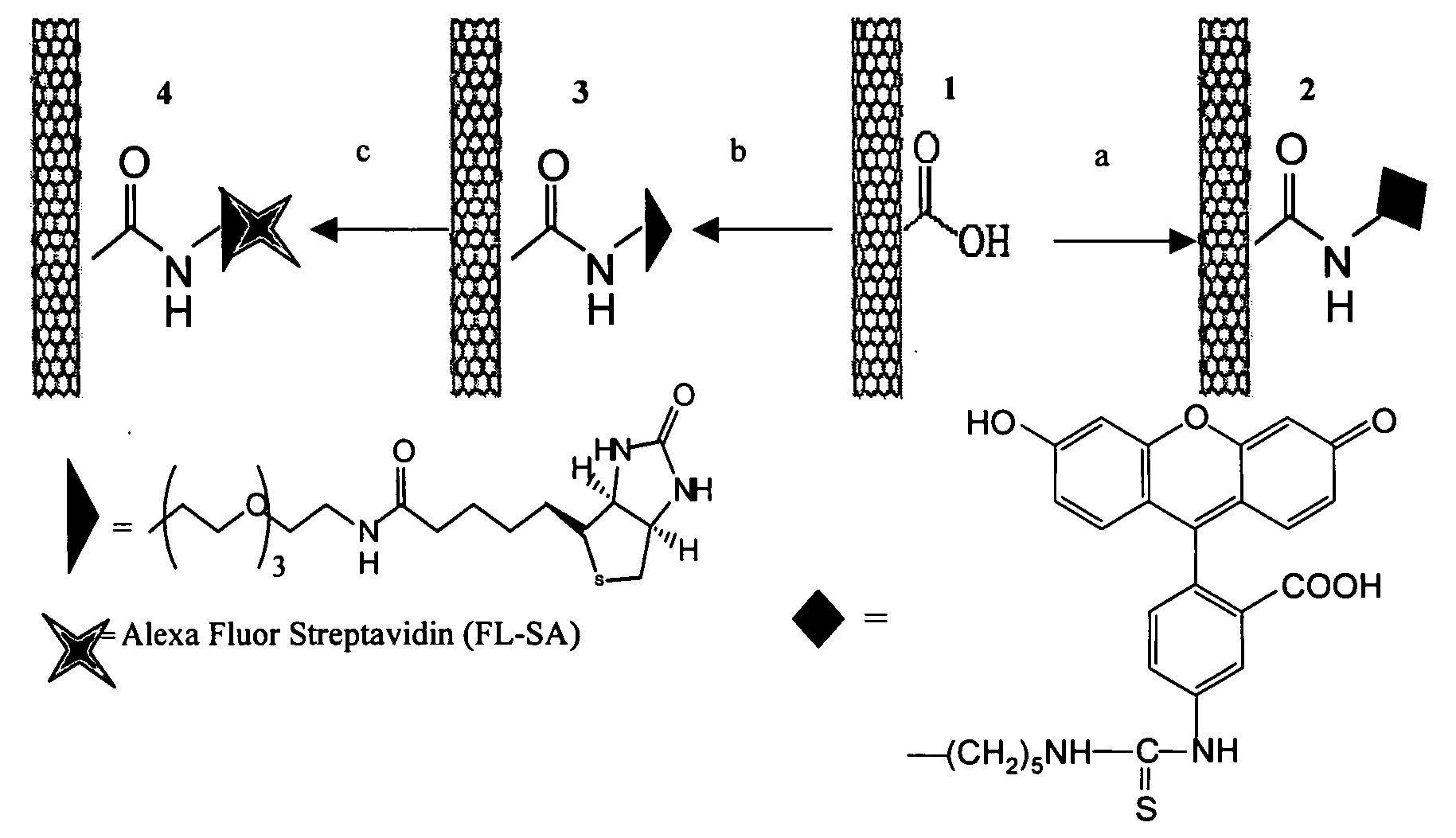
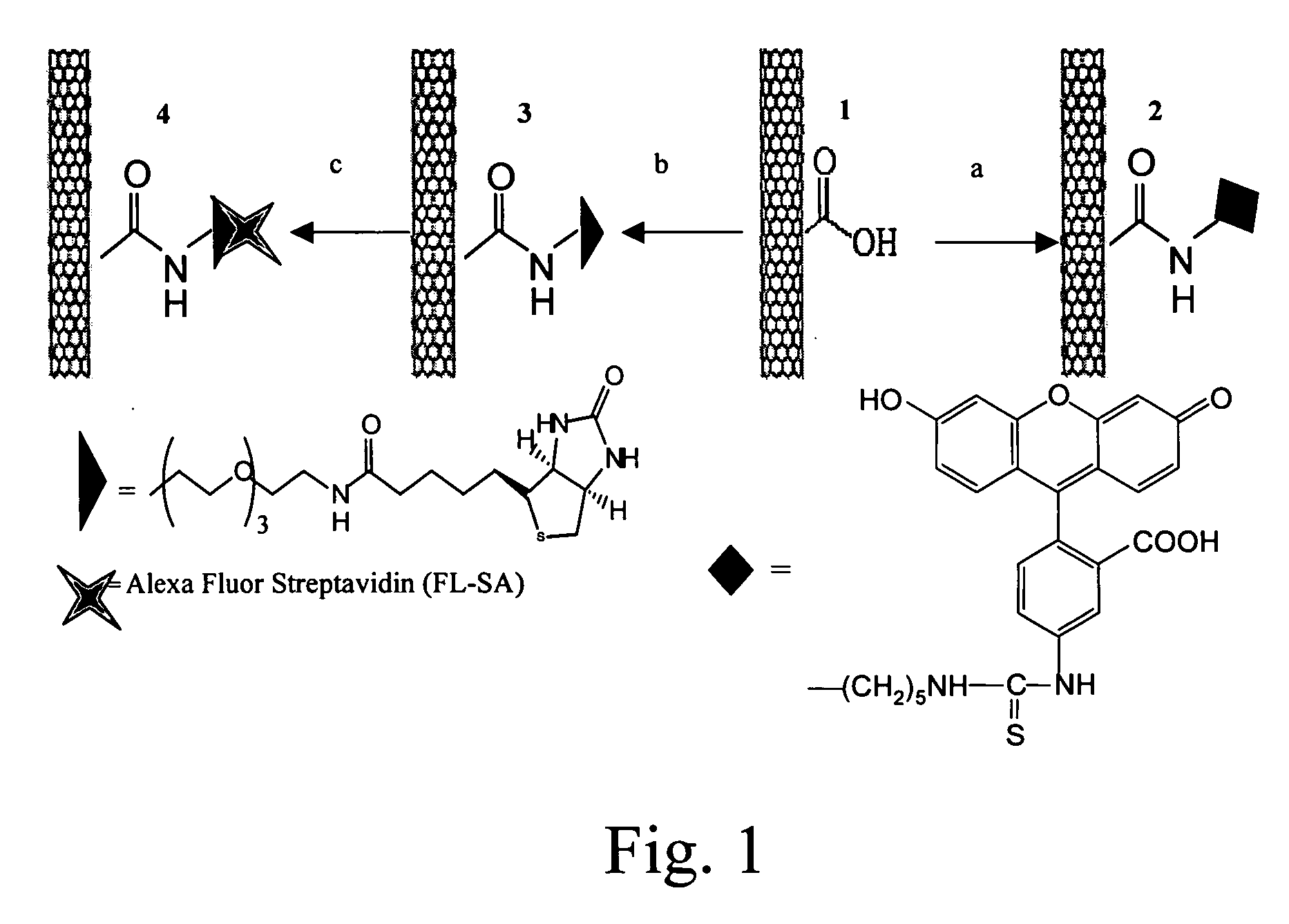
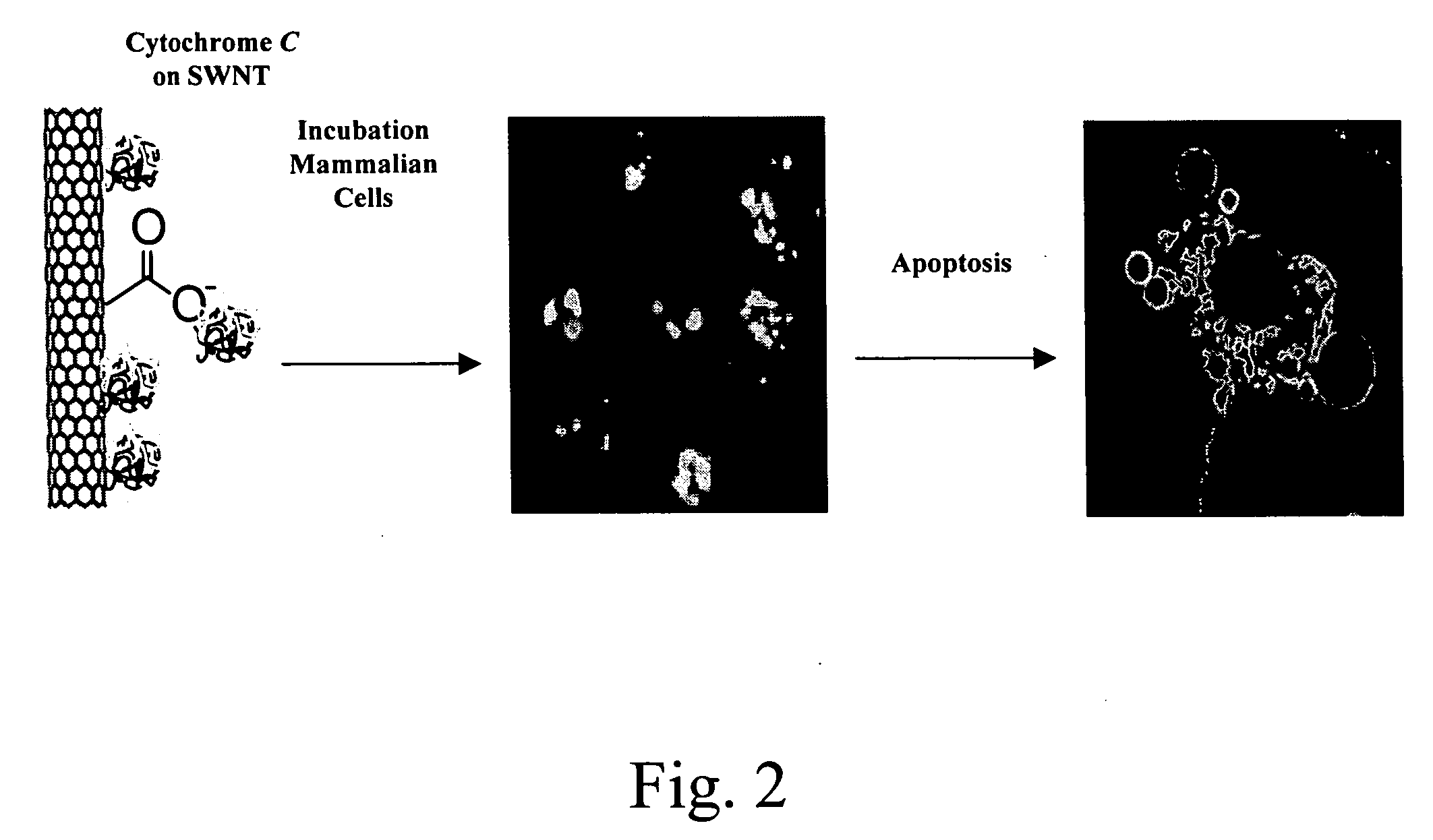
Hydrophobic nanotubes and nanoparticles as transporters for the delivery of drugs into cells
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Hydrophobic nanotubes and nanoparticles as transporters for the delivery of drugs into cells
InactiveUS20060275371A1Poor cellular uptakeReduced bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideEndosomal membraneNanoparticle
Methods and materials for delivering biologically active molecules to cells in vitro or in vivo are provided. The methods and materials use carbon nanotubes or other hydrophobic particles, tubes and wires, functionalized with a linking group that is covalently bound to the nanotubes, or, alternatively, to the biologically active molecule, such as a protein. The biologically active molecule is preferably released from the nanotube when the complex has been taken up in an endosome.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
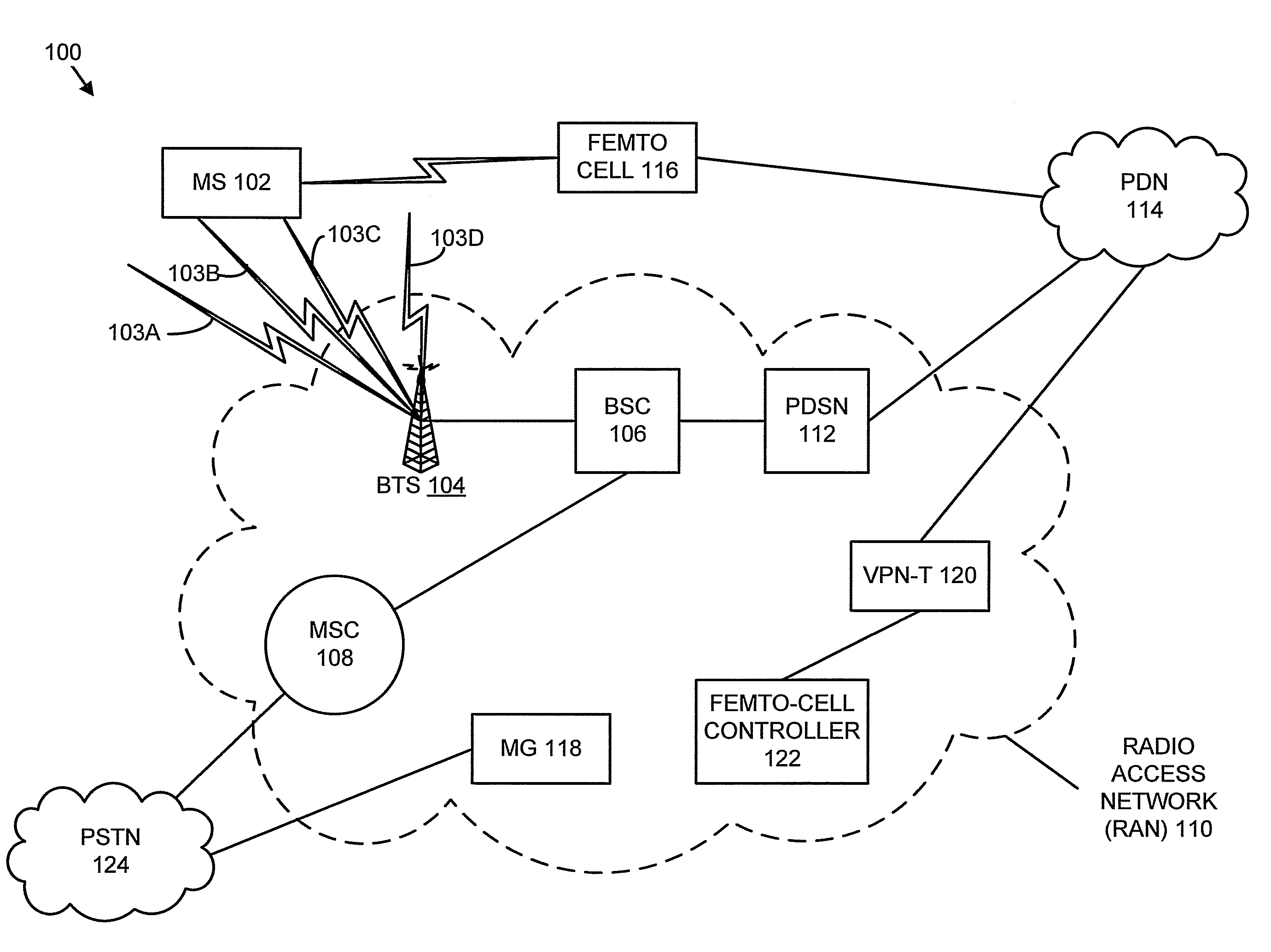
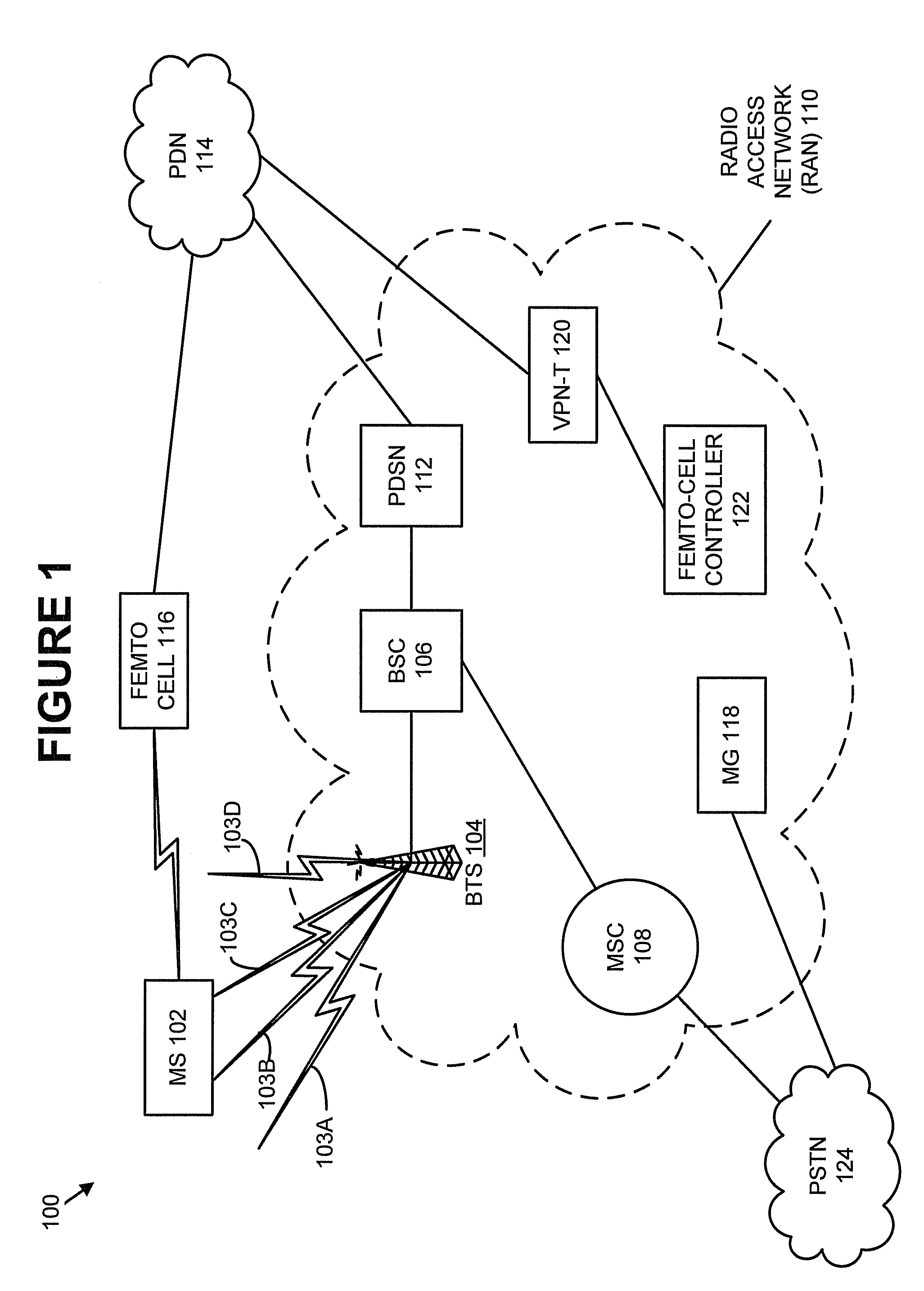
Methods and systems for temporarily modifying a macro-network neighbor list to enable a mobile station to hand off from a macro network to a femto cell
ActiveUS7929970B1Improve network efficiencyWaste of resourceNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsMobile station
Methods and systems are disclosed for temporarily modifying a macro-network neighbor list to enable a mobile station to hand off from a macro network to a femto cell. A method includes receiving a signal indicating that the mobile station detected coverage of a femto cell; after receiving the signal, adding the femto cell to the neighbor list, thereby enabling the mobile station to handoff to the femto cell; detecting that the mobile station completed handoff to the femto cell; and in response to detecting that the mobile station completed handoff to the femto cell, removing the femto cell from the neighbor list.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
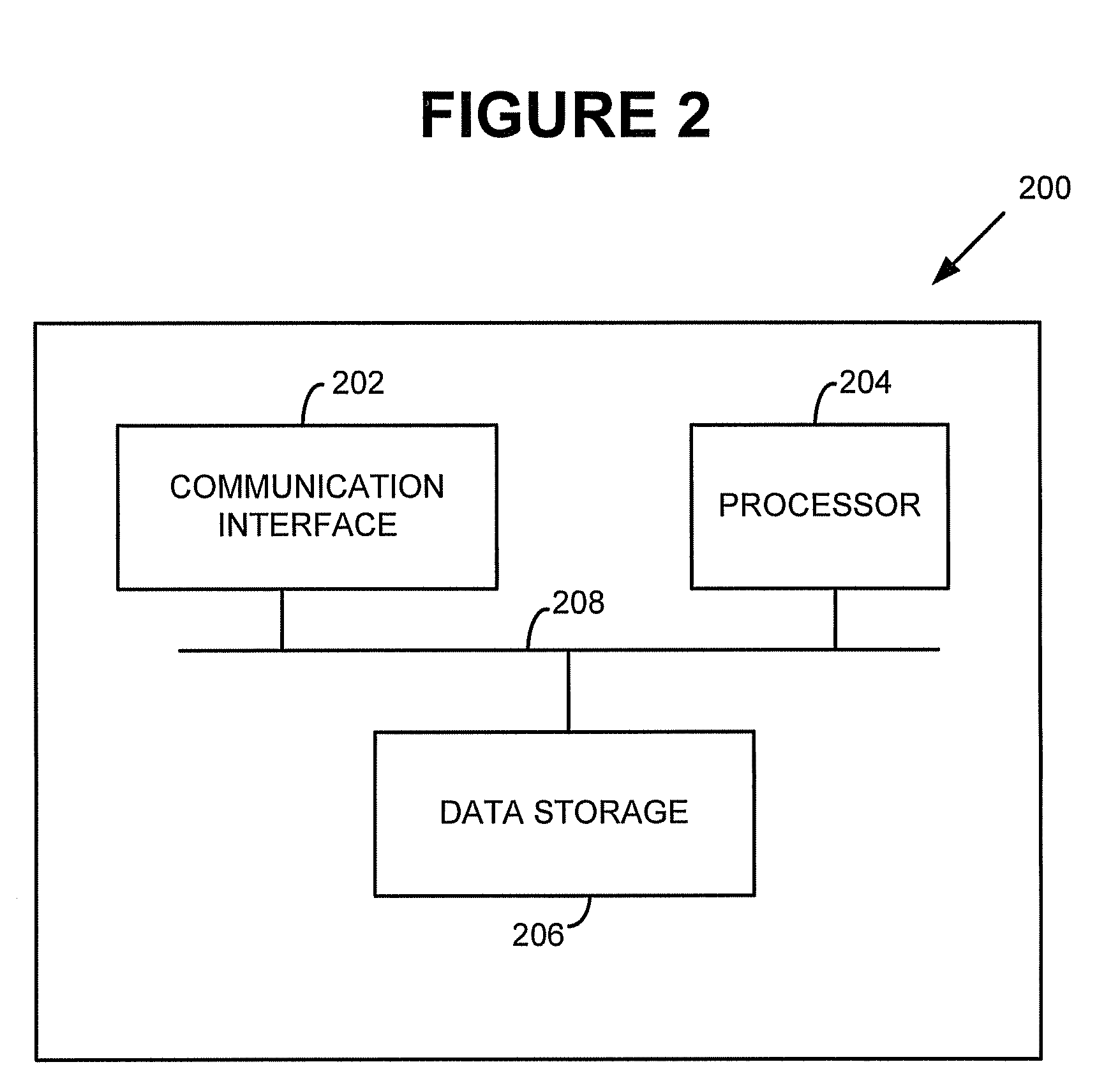
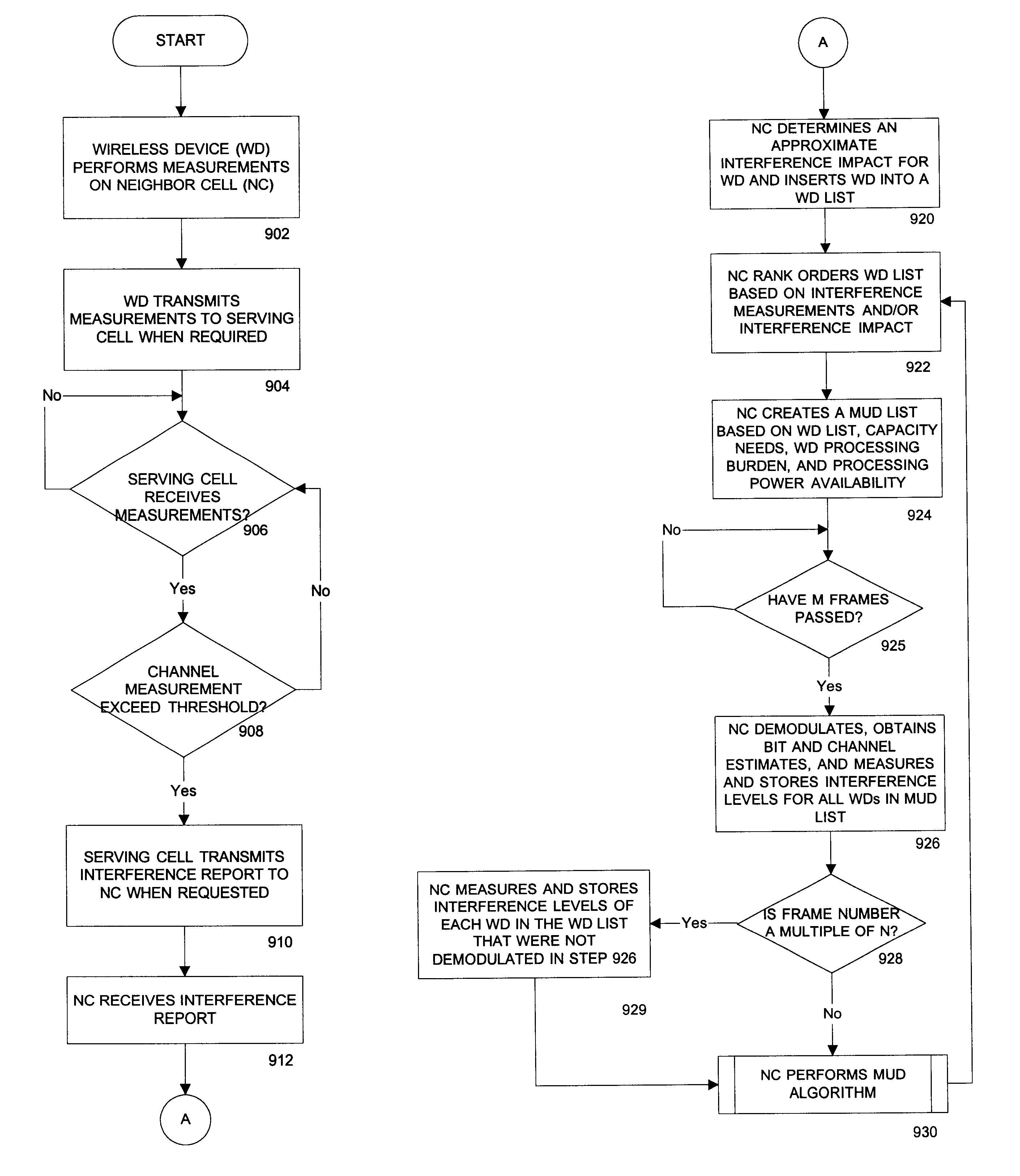
Methods and systems for reducing interference across coverage cells
InactiveUS6771934B2Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionMulti user detectionDevice Monitor
Methods and systems are provided for reducing interference across coverage cells using base stations interconnected by a packet network. A wireless device monitors the channel signal strength of its serving cell and its neighboring cell. The serving cell collects measurements from the wireless devices within its cell and informs its neighboring cell when one of the wireless device may be causing significant interference to the neighboring cell. The neighboring cell collects this information and executes a multi-user detection and cancellation algorithm on a subset of these interfering wireless devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and systems for reducing interference across coverage cells
InactiveUS20030003906A1Reduce distractionsError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionMulti user detectionDevice Monitor
Methods and systems are provided for reducing interference across coverage cells using base stations interconnected by a packet network. A wireless device monitors the channel signal strength of its serving cell and its neighboring cell. The serving cell collects measurements from the wireless devices within its cell and informs its neighboring cell when one of the wireless device may be causing significant interference to the neighboring cell. The neighboring cell collects this information and executes a multi-user detection and cancellation algorithm on a subset of these interfering wireless devices.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
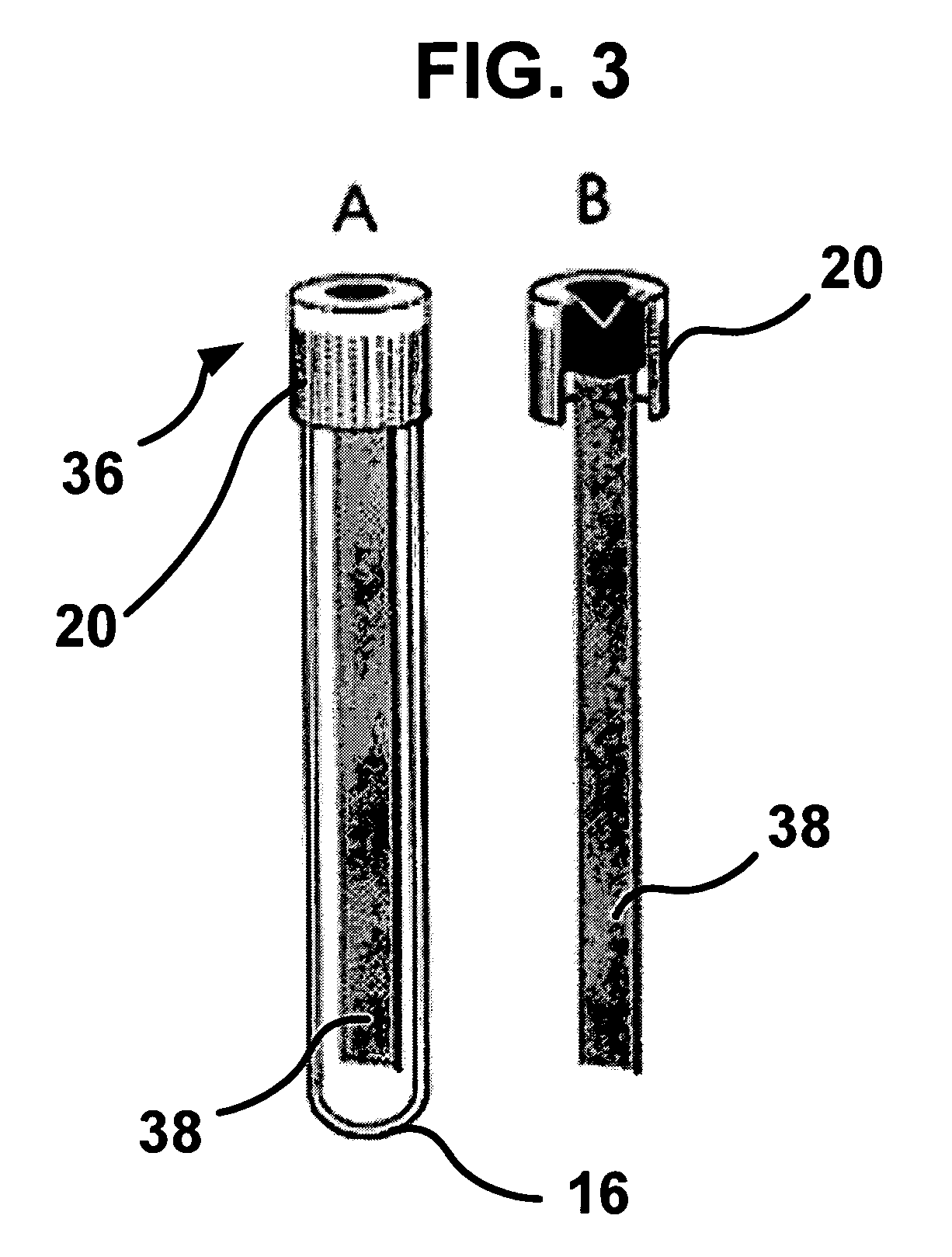
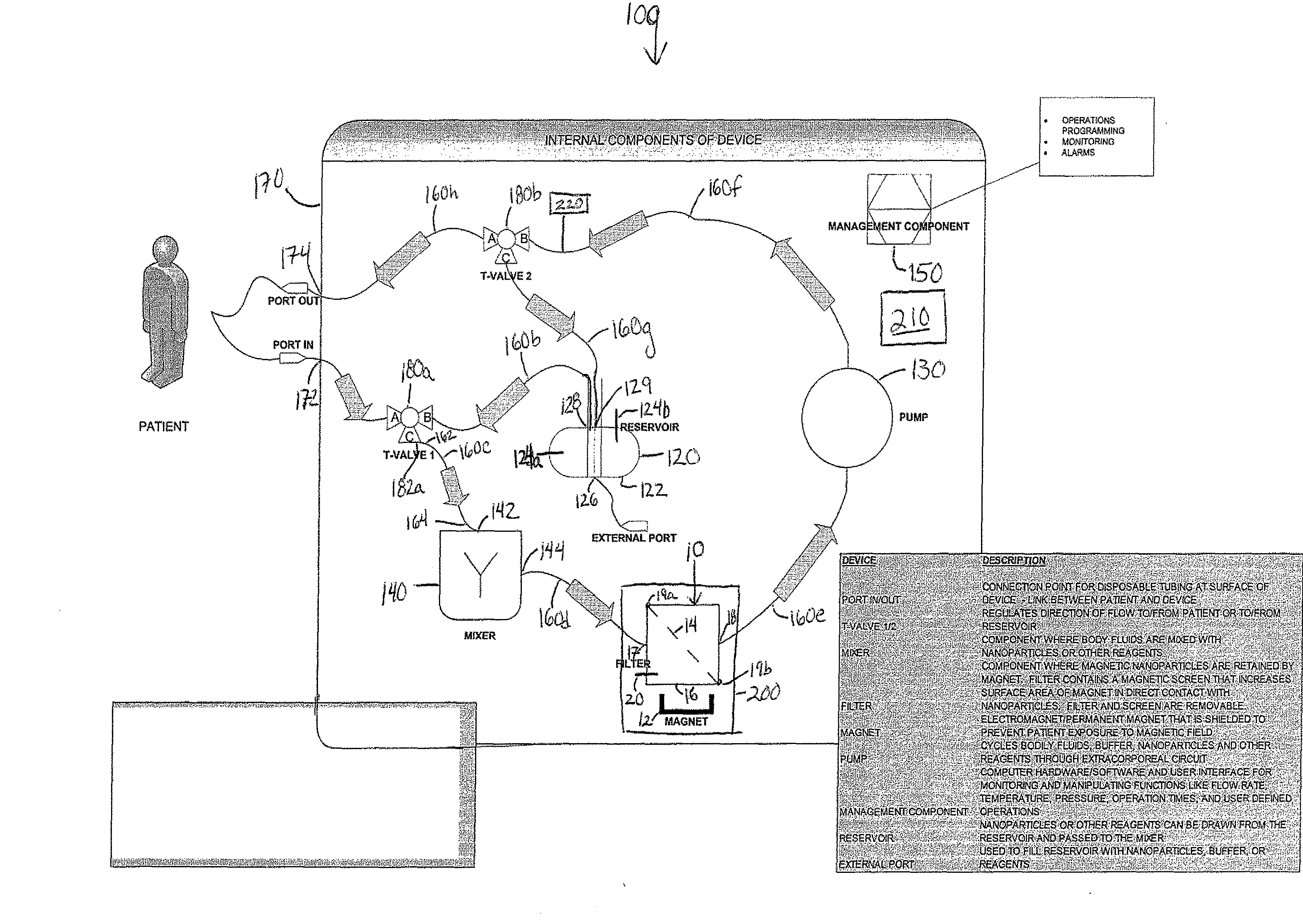
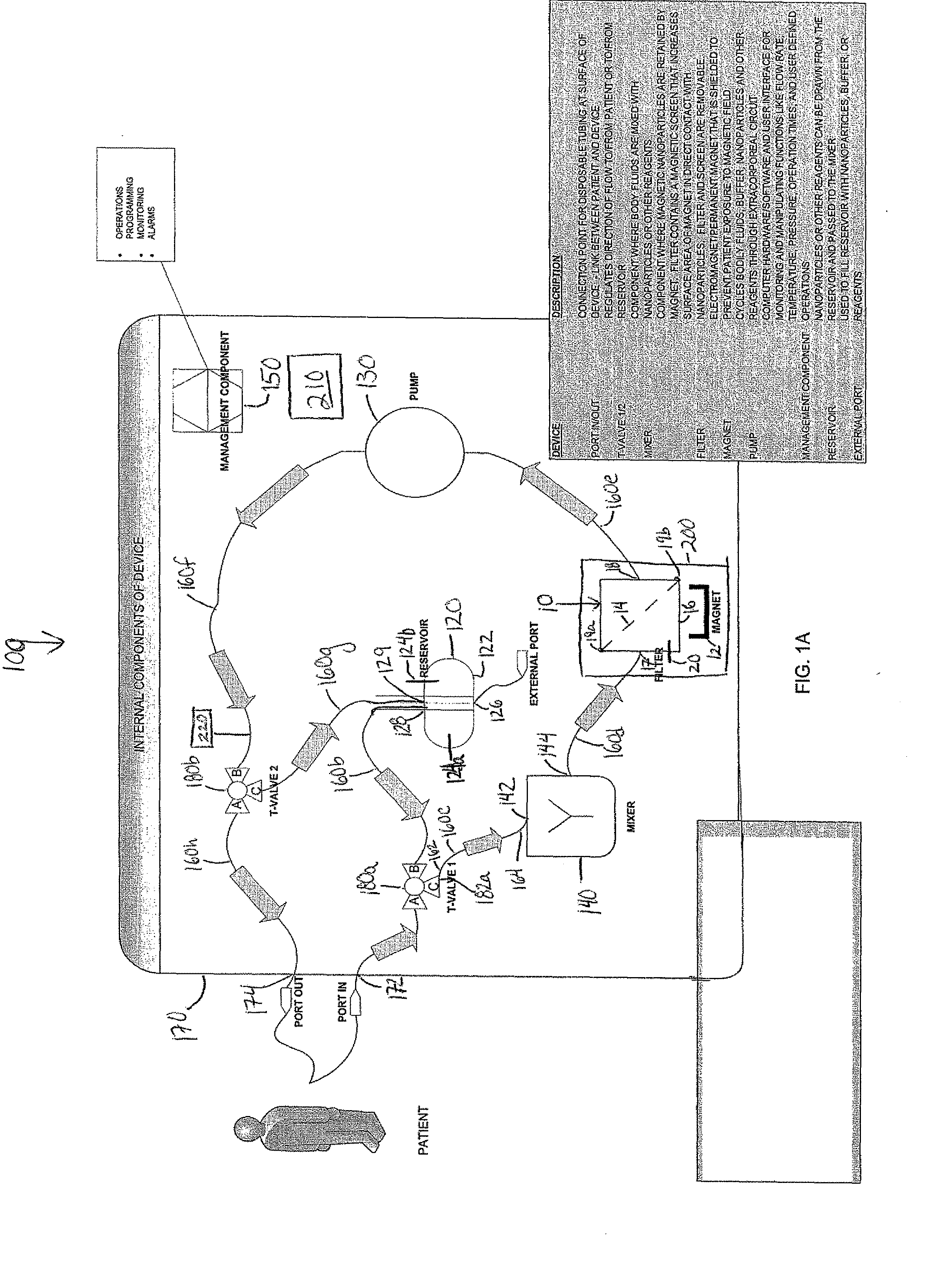
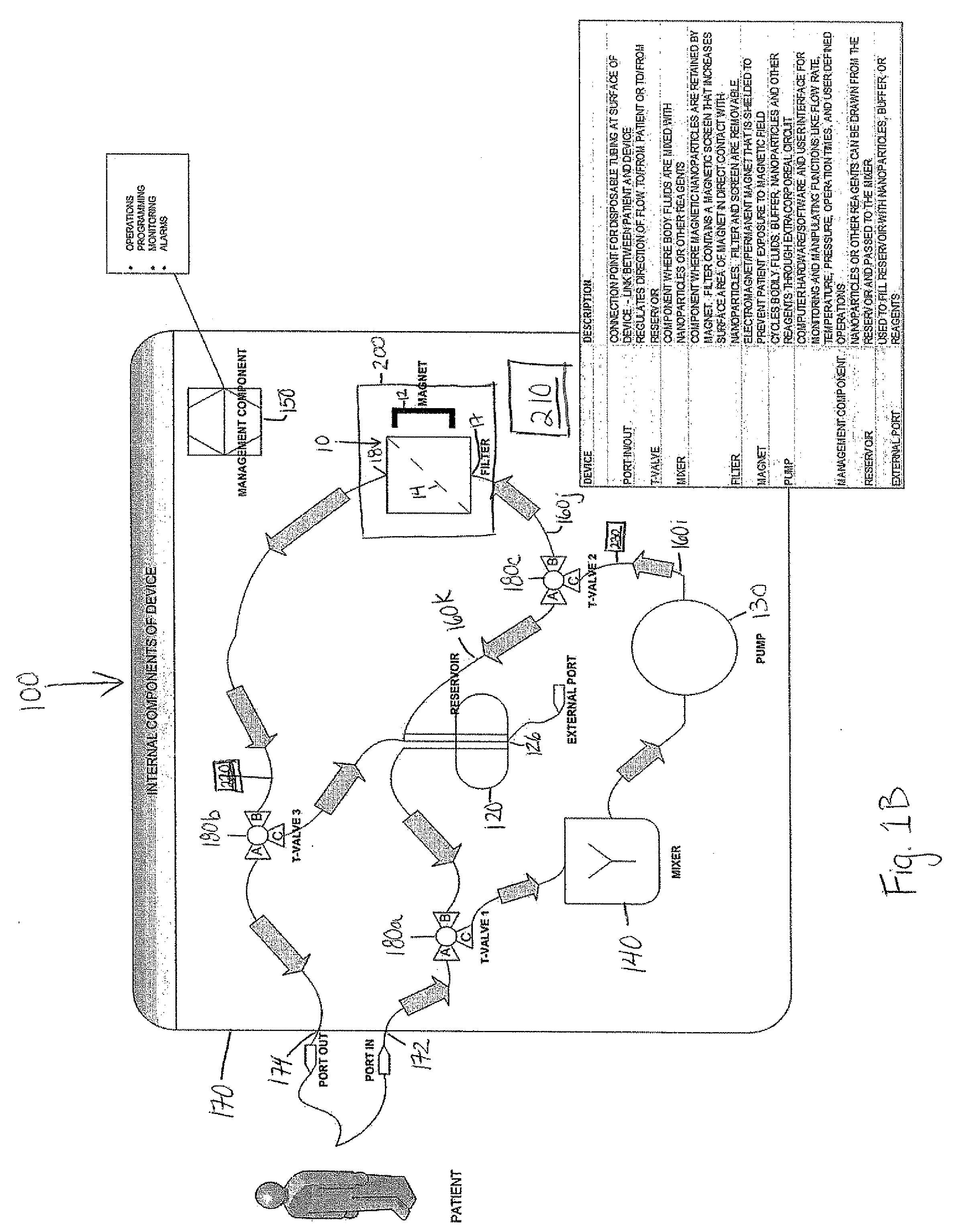
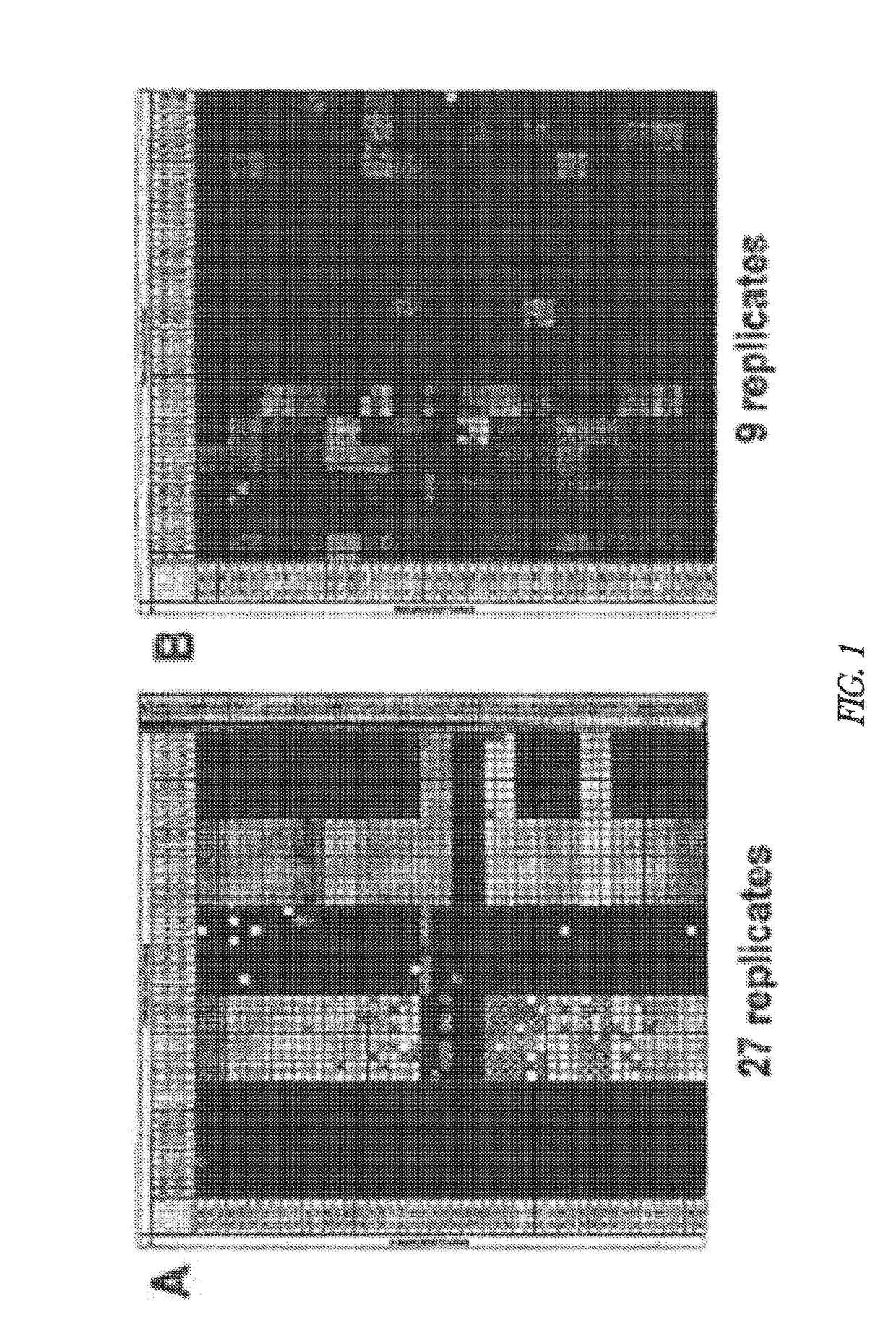
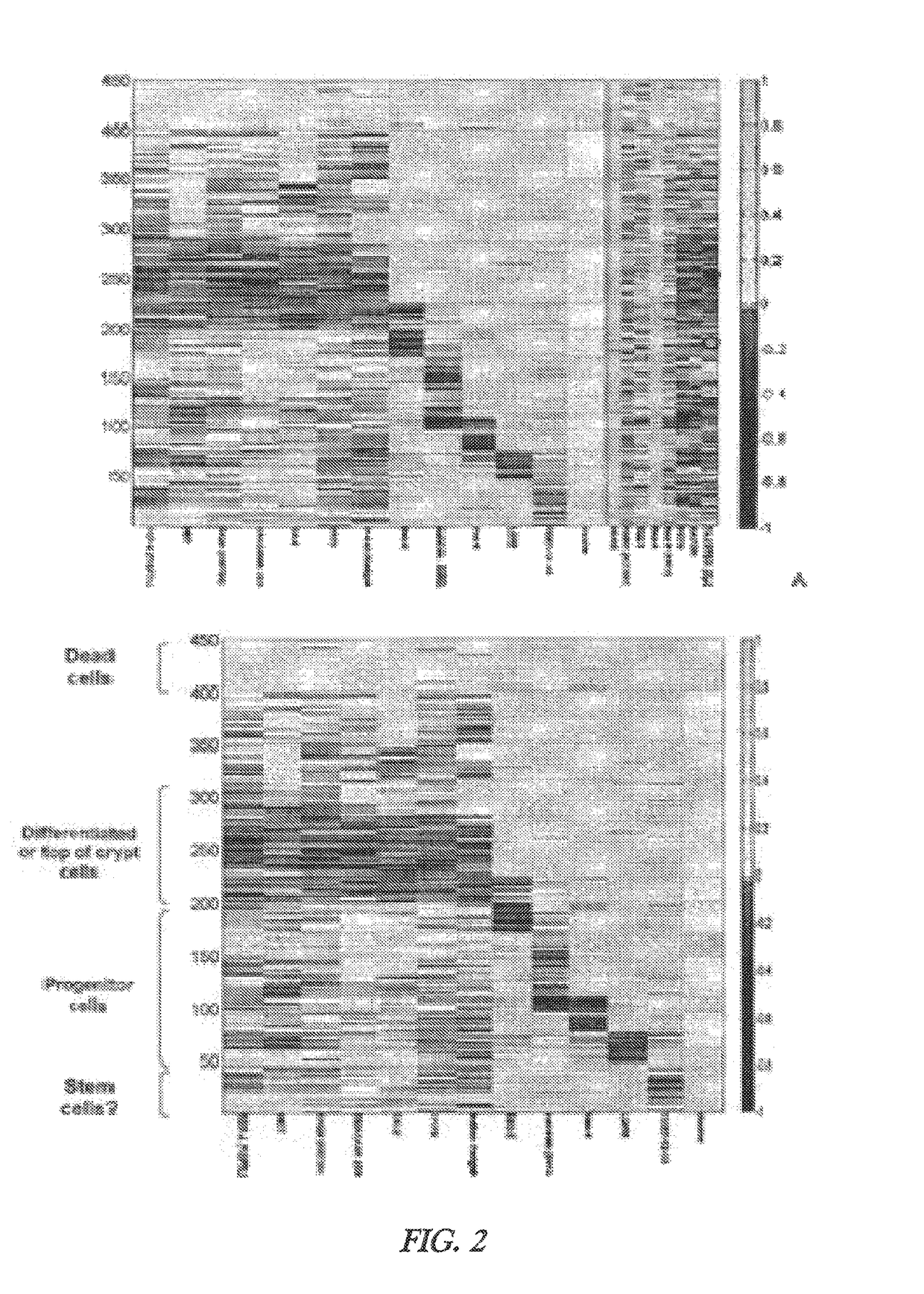
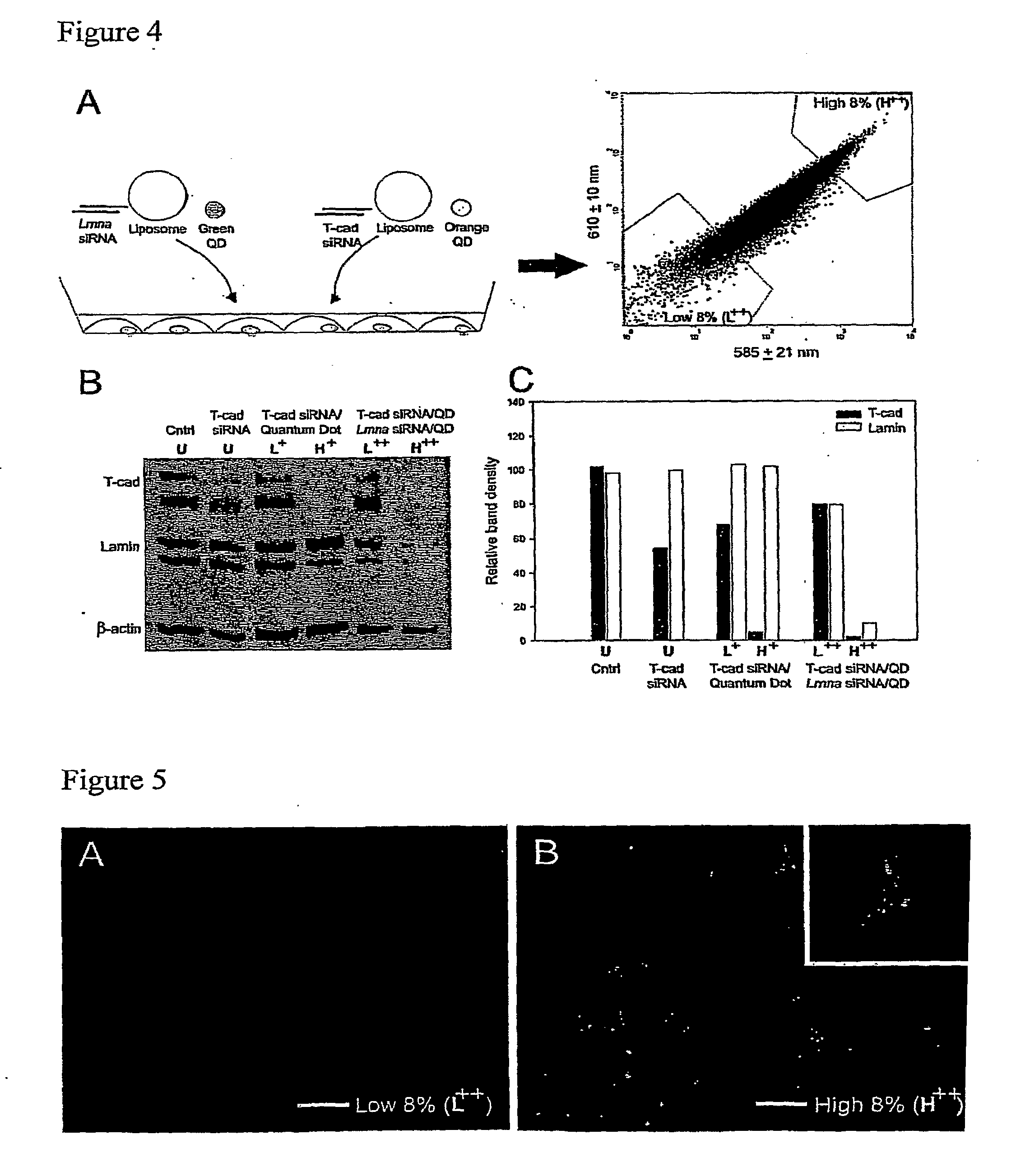
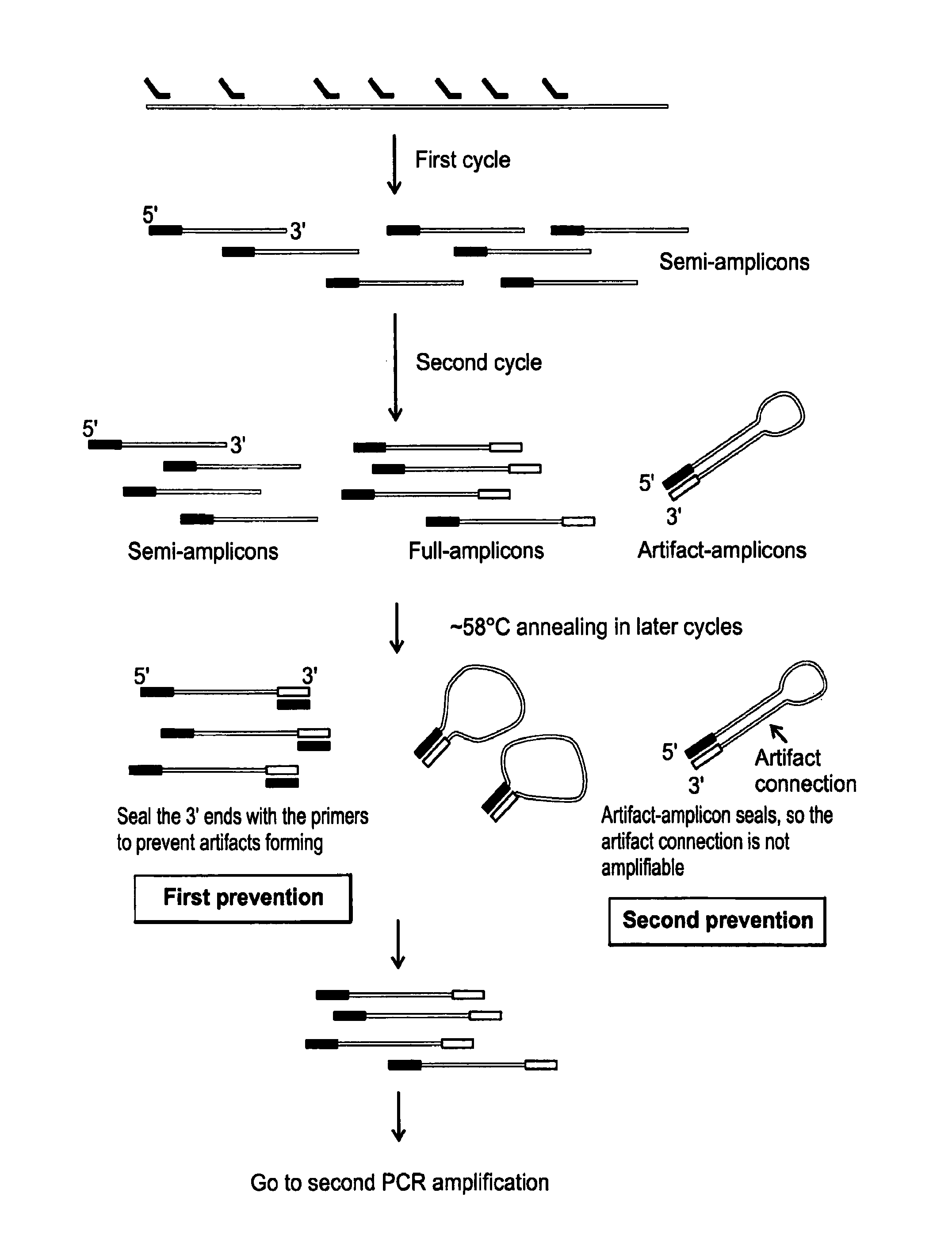
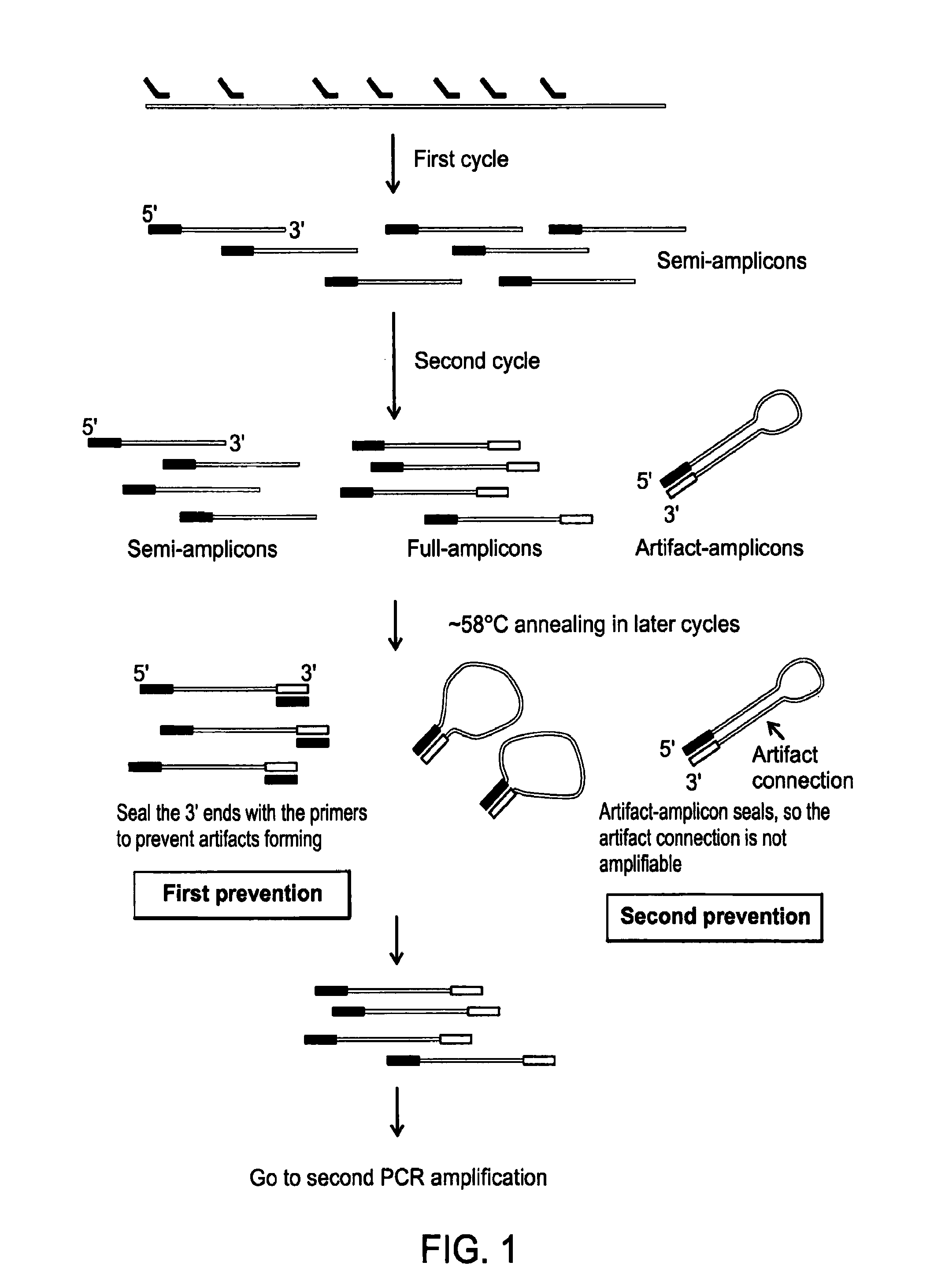
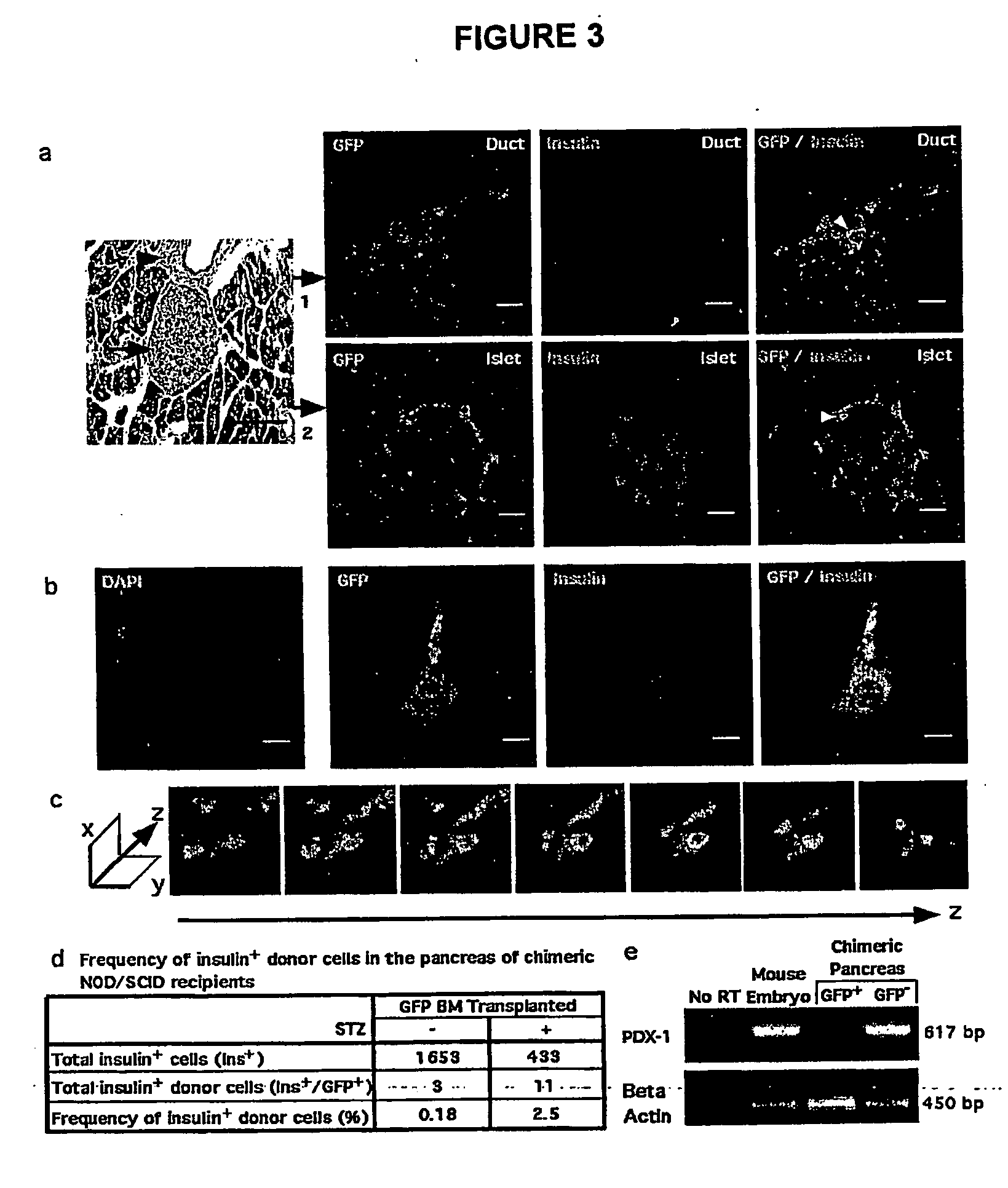
Cell and sub-cell methods for imaging and therapy
InactiveUS20070243137A1Reduce in quantityLow costPowder deliverySnake antigen ingredientsImaging agentLoad cell
Methods are disclosed to rapidly form and load cells and cell-derived vesicles. Loaded materials can include imaging agents, drugs and magnetic particles. Methods are also presented to additionally target the loaded cells or vesicles, leading to new forms of imaging, treatment, diagnosis, and detection by a large number of techniques. The preparation and use of reduced sized cells that retain subset characteristics of the parent cell are also described.
Owner:NANOPROBES
Methods for Rapid Distinction between Debris and Growing Cells
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods of ex vivo progenitor and stem cell expansion by co-culture with mesenchymal cells
Methods of ex-vivo expansion and at the same time inhibiting differentiation of stem cells by co-culture with mesenchymal cells, transplantable populations of renewable progenitor and stem cells expanded thereby, and their uses in therapeutic applications.
Owner:GAMIDA CELL
Blood test prototypes and methods for the detection of circulating tumor and endothelial cells
InactiveUS20050244843A1Enhance anti-tumor immune responseDramatic utilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAbnormal tissue growthProgenitor
Methods and devices for isolating and diagnosing disease with a cell adhesion matrix system, mimicking a metastatic, cardiovascular or placental environment, are disclosed. The cell adhesion matrix facilitates the enrichment of target cells such as metastatic tumor cells, fetal cells and endothelial progenitor cells from a fluid sample such as blood for diagnostic and therapeutic applications in treating patients afflicted with disease, such as cancerous, cardiovascular and fetal diseases, as well as for research applications in molecular analysis of metastatic, and cardiovascular and fetal diseases. Blood test prototypes and methods for the cell enrichment and detection of circulating tumor and endothelial cells using multiplex molecular analysis are described herein. In addition, methods and compositions for determining host immunity to tumor in subjects with risk of cancer progression and methods for isolating an enriched fraction of fetal cells from pregnant females for prenatal diagnosis are also described herein.
Owner:CHEN WEN TIEN +2
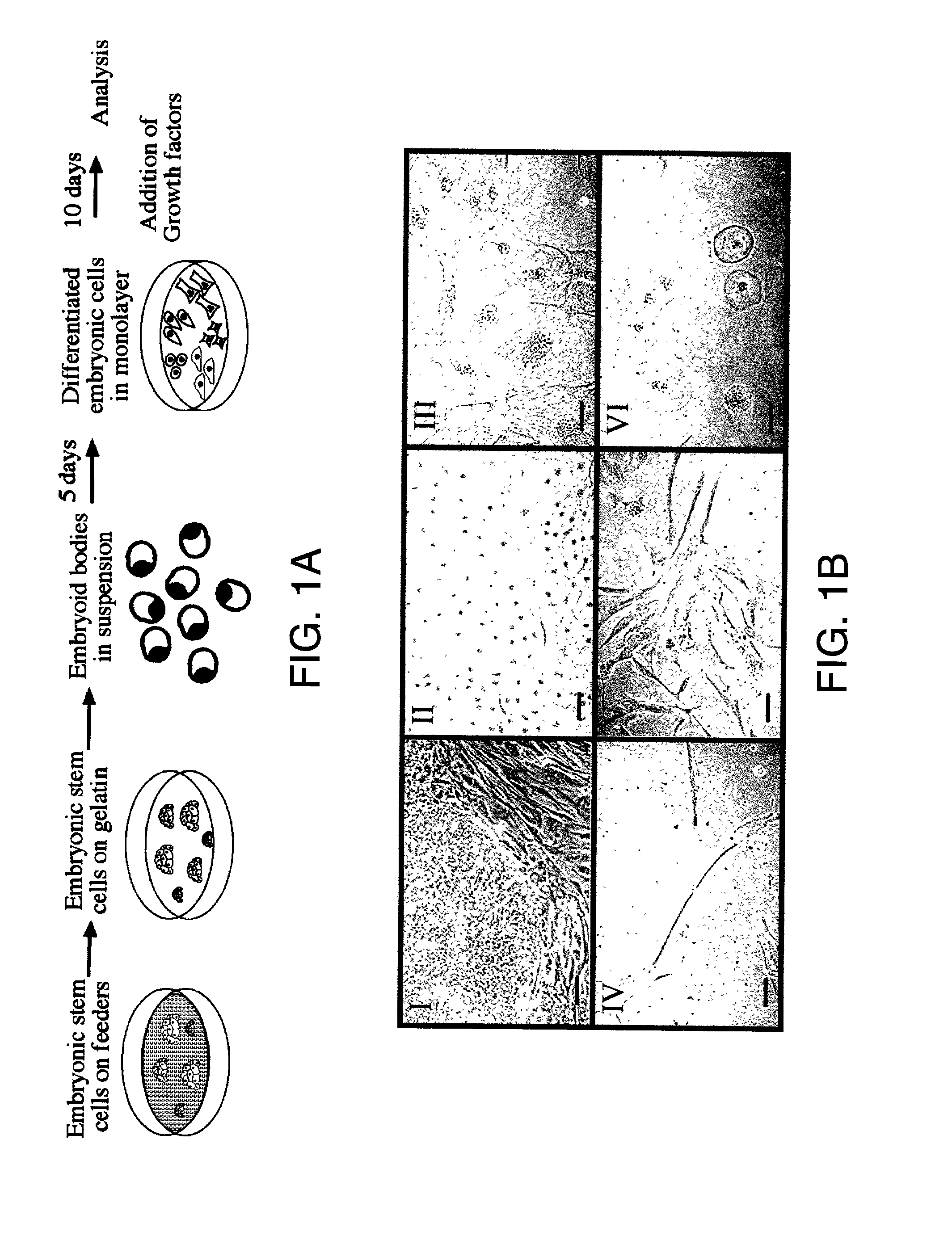
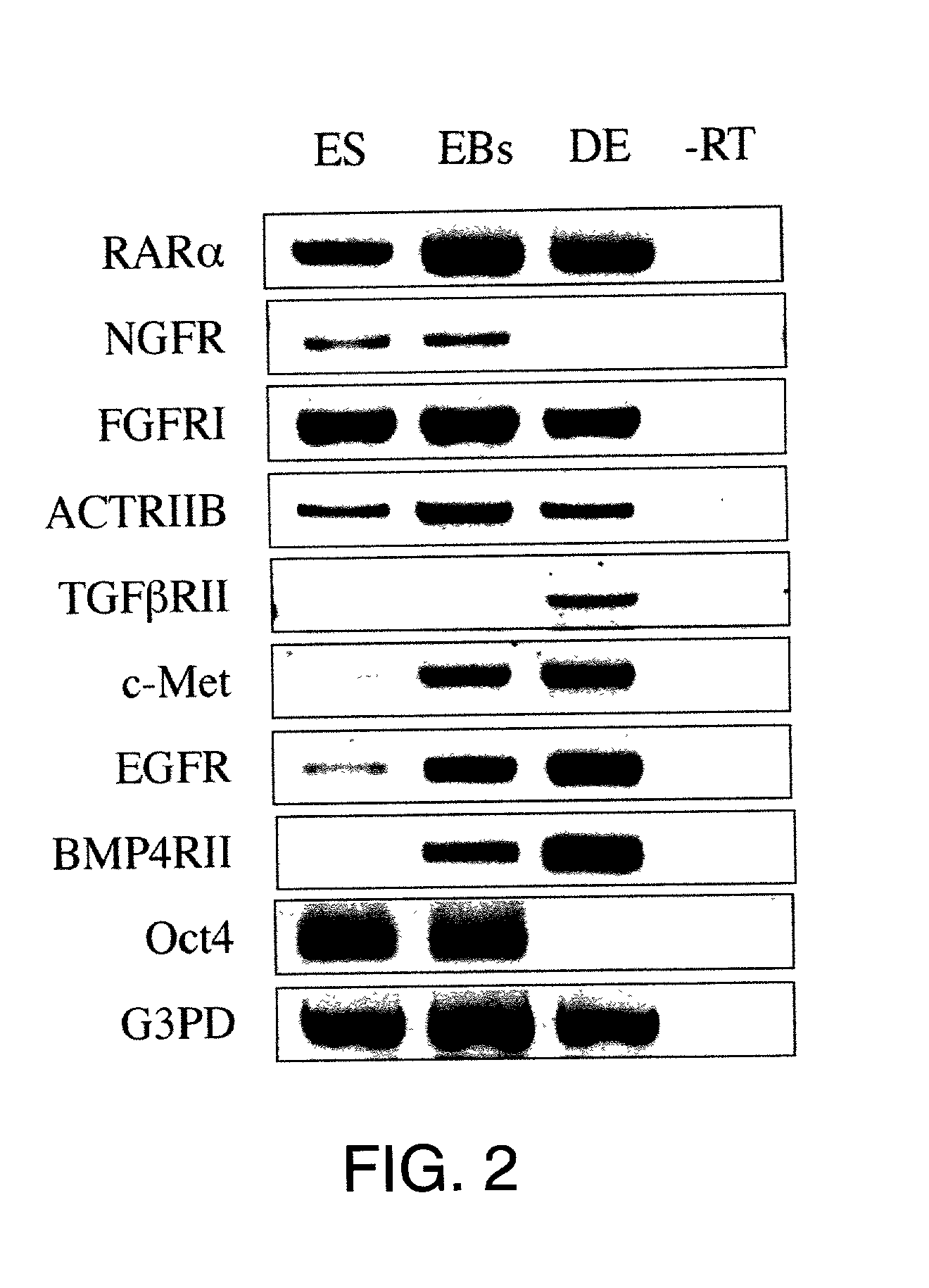
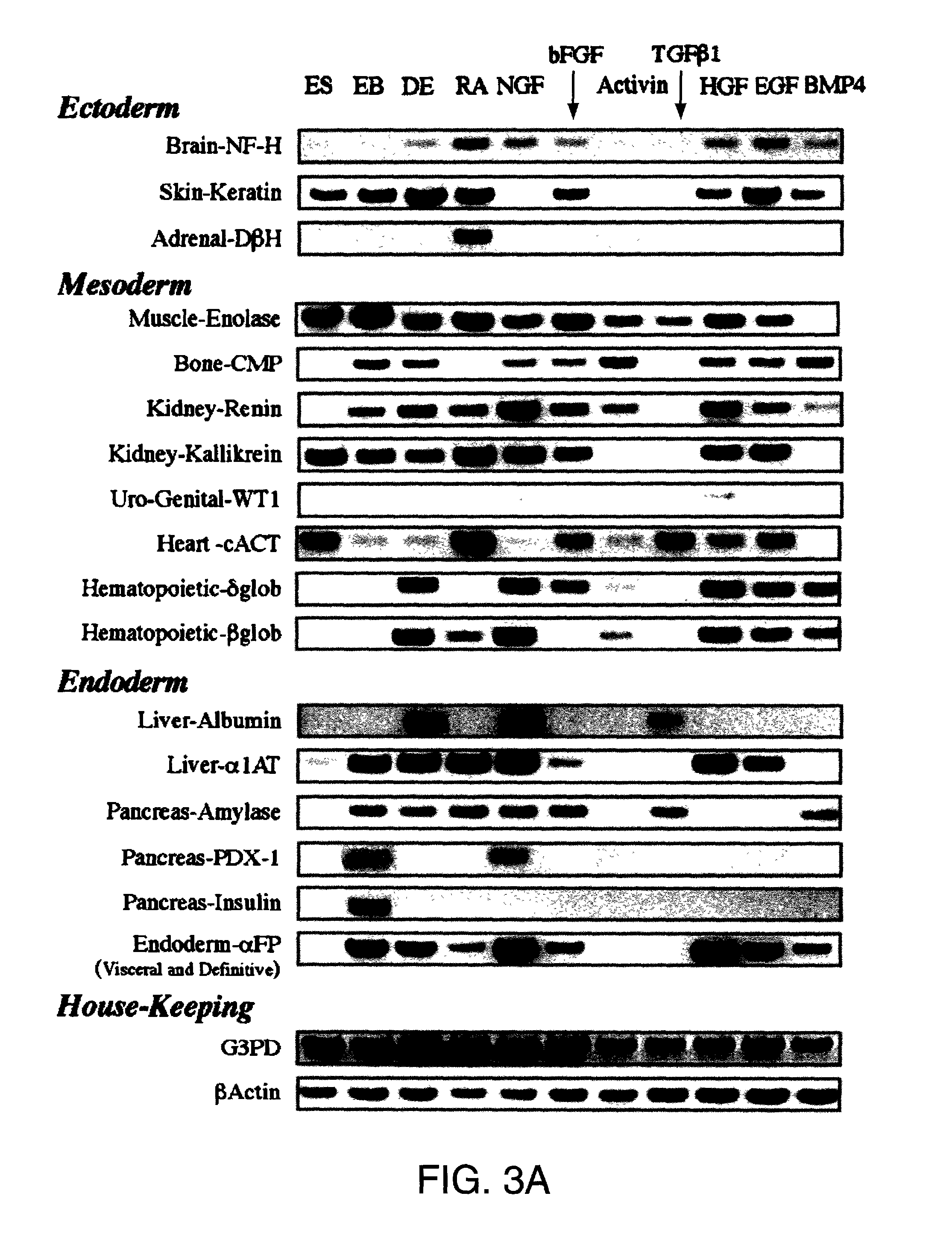
Directed differentiation of embryonic cells
Methods are described for mapping a pathway of differentiation of a population of embryonic cells which includes exposing the cells to an exogenous factor and measuring gene expression products that are characteristic of a particular cell type or lineage. Directing differentiation of human embryonic cells relies on dissociated embryoid bodies which are then exposed to one or more exogenous factors to enrich a culture for a particular cell type. The differentiated cells may be used for treating a medical condition in a human. Kits for determining differentiation pathways and screening exogenous factors for their utility in differentiation are provided.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Device and method of using superparamagnetic nanoparticles in treatment and removal of cells
InactiveUS20110098623A1Simple methodAntibacterial agentsOther blood circulation devicesCancer cellFunctionalized nanoparticles
Methods and devices for selectively removing from a subject a target cell, pathogen, or virus expressing a binding partner on its surface are presented. In one embodiment, the device contains an excorporeal circuit, which includes, at least, a magnetic filter comprising a magnet and a removable, magnetizable substrate capable of capturing magnetic nanomaterials; and a pump in fluid communication with the magnetic filter, wherein the pump moves fluid through the excorporeal circuit. The magnet is capable of generating a magnetic field sufficient to capture magnetic nanomaterials in the magnetic field. In a preferred embodiment, the target cells are cancer cells and / or cells infected with pathogenic agents. The devices may be designed for extracorporeal or in vivo uses. Functionalized superparamagnetic nanoparticles are either mixed ex vivo with a biological fluid from the patient or injected into the patient. Then the biological fluid, which includes the nanoparticles is transported to the magnetic filter to remove any nanoparticles that are complexed to the target cells, pathogens, or virus, and any free nanoparticles. Optionally, the functionalized nanoparticles contain and deliver a therapeutic agent. In one embodiment, the therapeutic agent is released when the nanoparticle binds to the target cells, pathogens, or virus.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Recording and mapping lineage information and molecular events in individual cells
InactiveUS20150225801A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular pathwaysFluorescent imaging
Methods and systems for recording and mapping lineage information and molecular events in individual cells are provided. Molecular changes, which may result from random or specific molecular events, are introduced to defined regions in cells over multiple cell cycle generations. Techniques such as fluorescent imaging are applied to track and identify the molecular changes before such information is used for lineage analysis or for identifying key processes and key players in cellular pathways.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
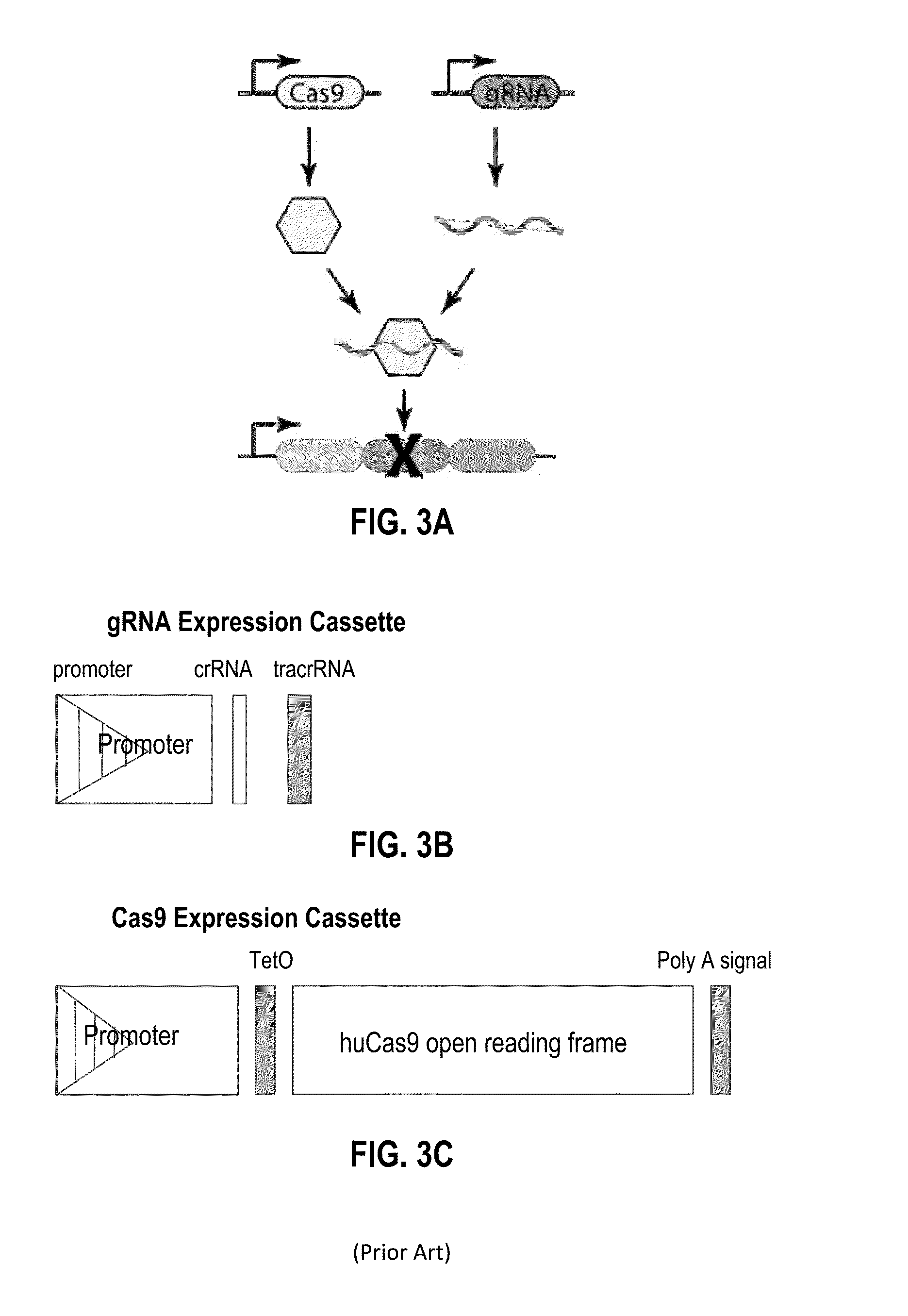
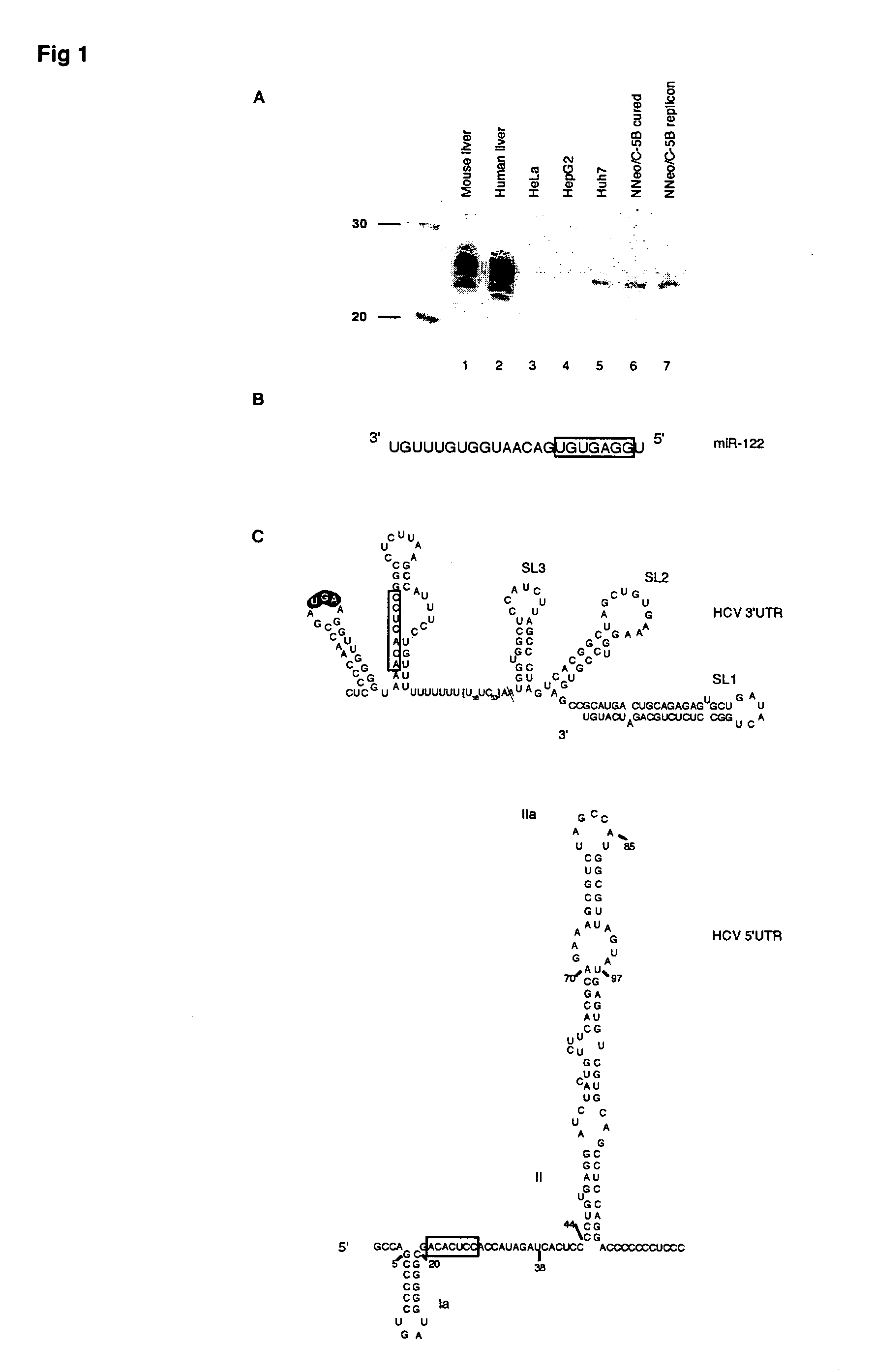
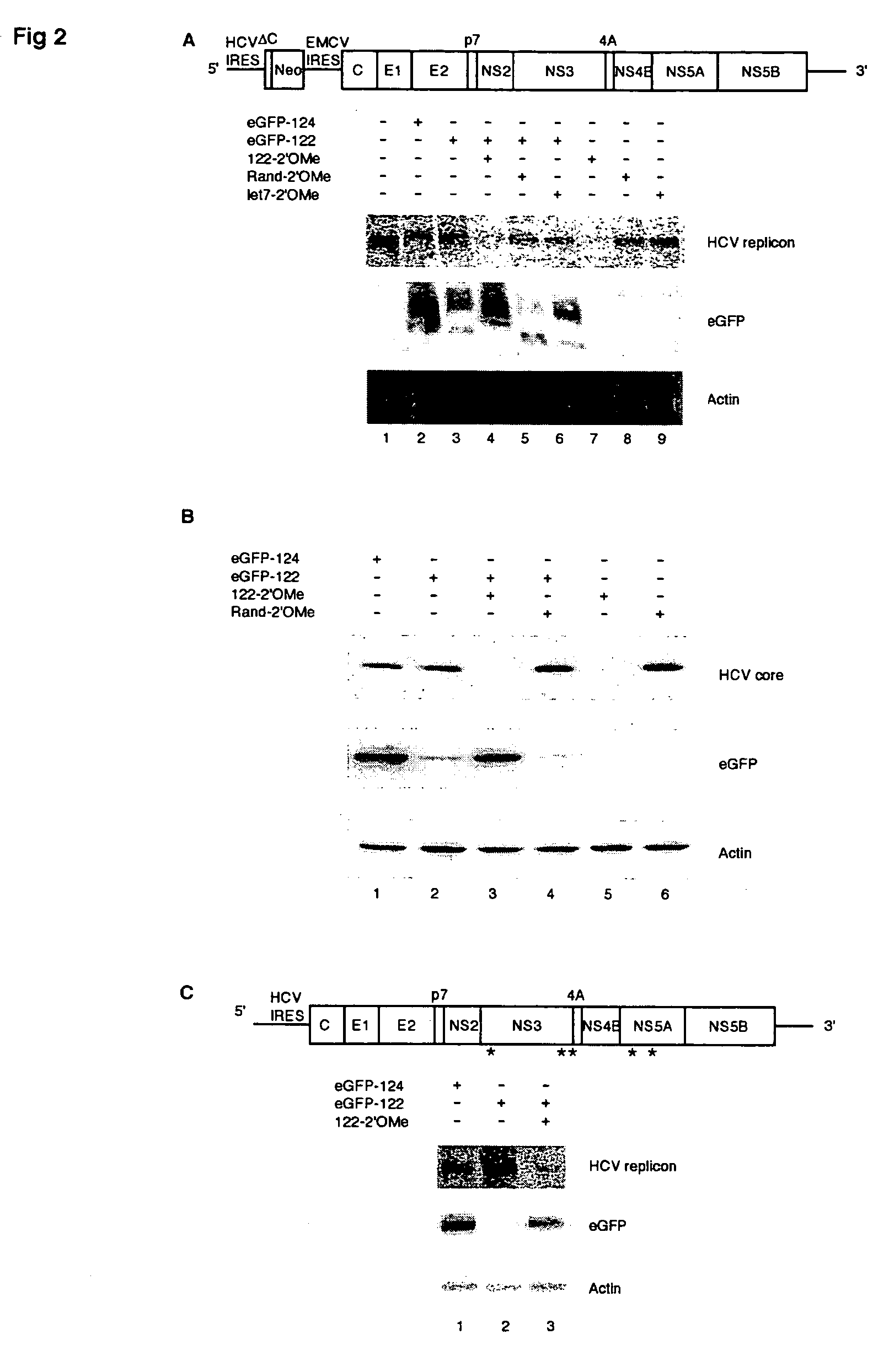
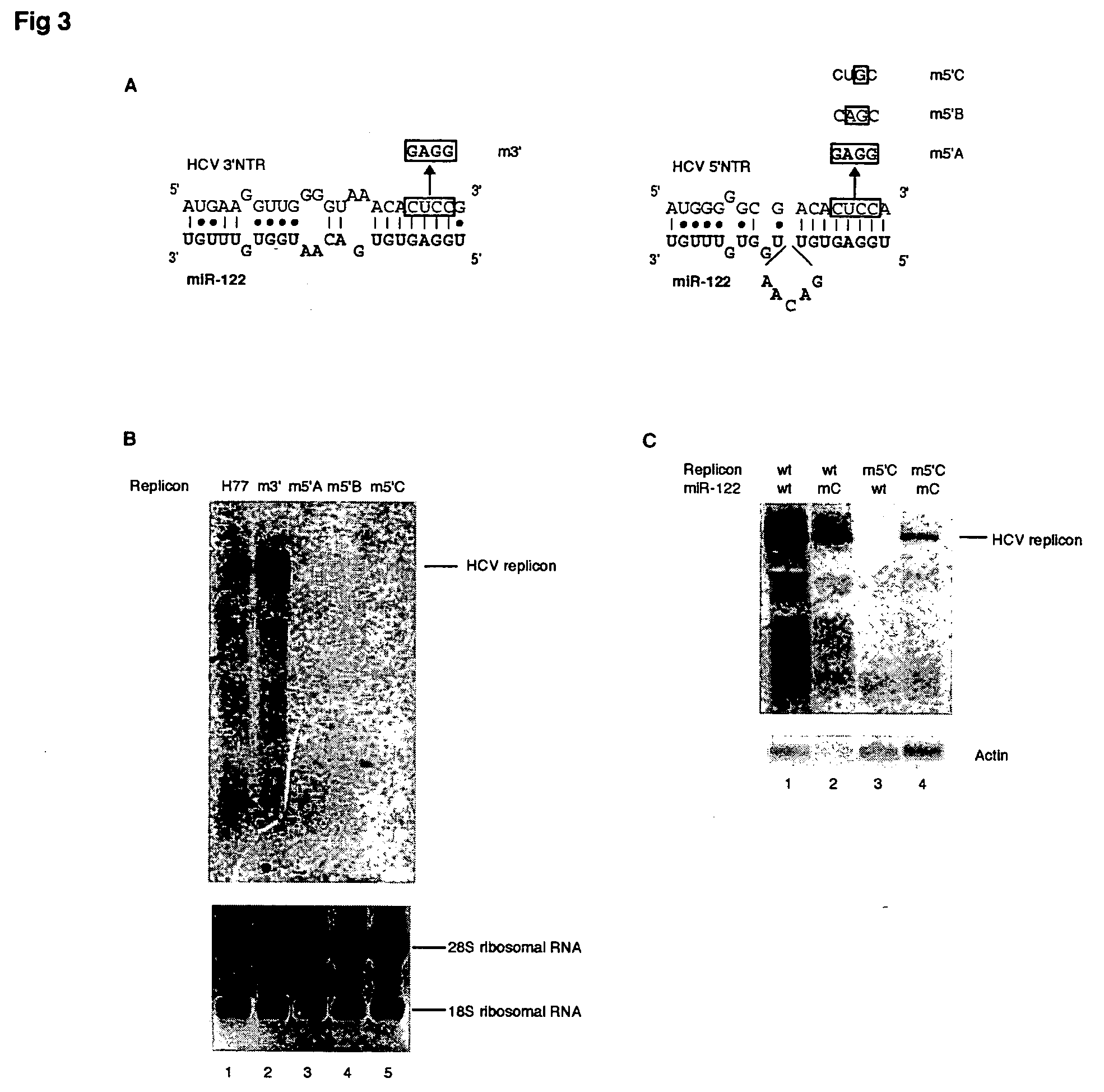
Methods and compositions for reducing viral genome amounts in a target cell
Methods and compositions for reducing viral genome amounts in a target cell are provided. In the subject methods, the activity of a miRNA is inhibited in a manner sufficient to reduce the amount of viral genome in the target cell, e.g., by introducing a miRNA inhibitory agent in the target cell. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, kits and systems for use in practicing the subject methods. The subject invention finds use in a variety of applications, including the treatment of subjects suffering from a viral mediated disease condition, e.g., an HCV mediated disease condition.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods for closed chromatin mapping and DNA methylation analysis for single cells
ActiveUS20150368694A1Reduce and minimize and prevent chanceLess efficiently ligatedMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDNA methylationGenomic DNA
Methods of identifying DNase I Hyper-Resistant Sites (DHRS), or in board sense, highly compact chromatin and characterizing the DNA methylation status of DMRs such as CpG islands and CpG island shores are provided. The methods are particularly useful for analysis of genomic DNA from low quantities of cells, for example, less than 1,000 cells, less than 100 cells, less than 10 cells, or even one cell, and can be used to generate chromatin and methylation profiles. The downstream analyses include in parallel massive sequencing, microarray, PCR and Sanger sequencing, hybridization and other platforms. These methods can be used to generate chromatin and DNA methylation profiles in drug development, diagnostics, and therapeutic applications are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Methods and systems for analysis of single cells
Methods are provided for diagnosis and prognosis of disease by analyzing expression of a set of genes obtained from single cell analysis. Classification allows optimization of treatment, and determination of whether on whether to proceed with a specific therapy, and how to optimize dose, choice of treatment, and the like. Single cell analysis also provides for the identification and development of therapies which target mutations and / or pathways in disease-state cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
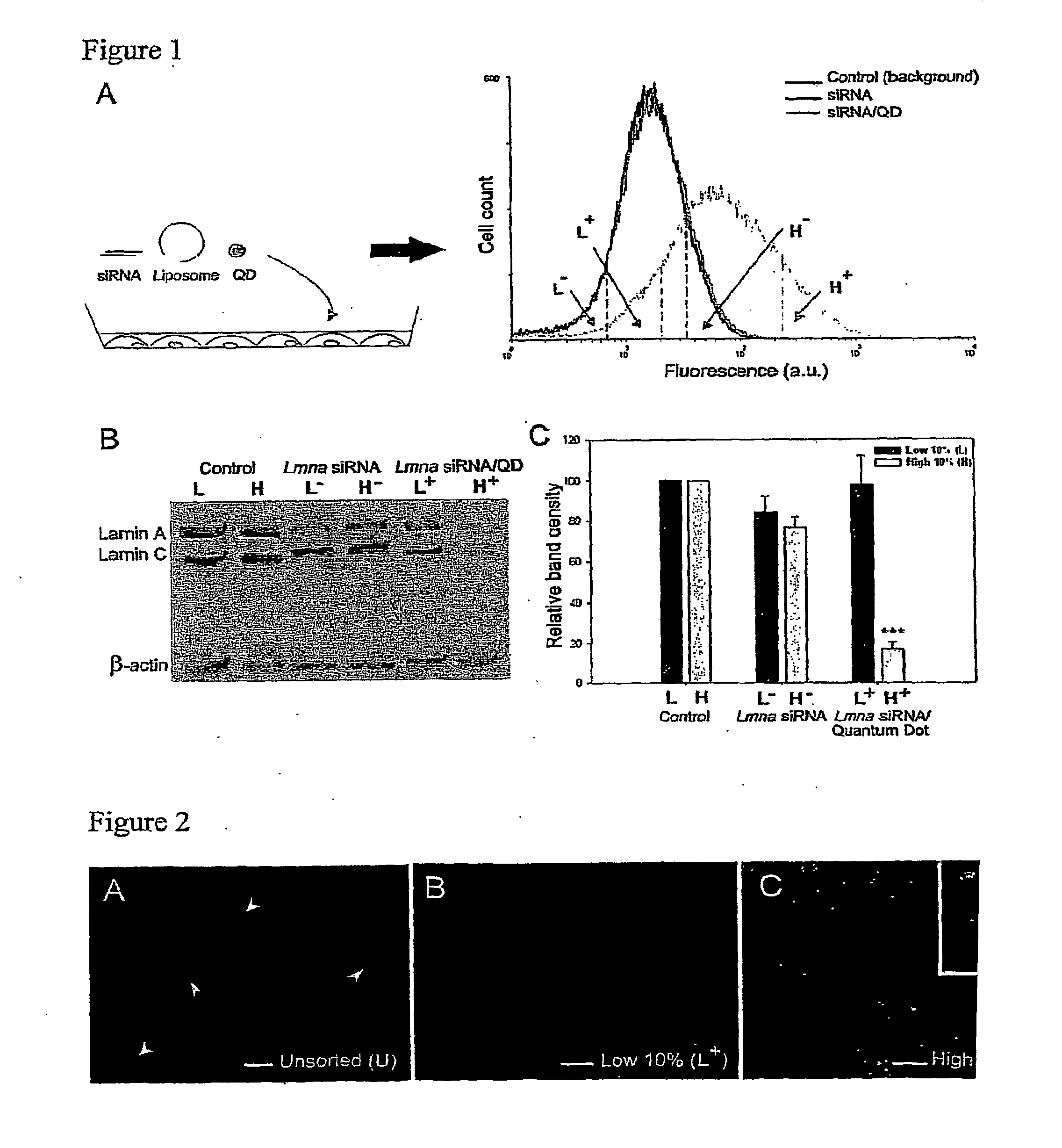
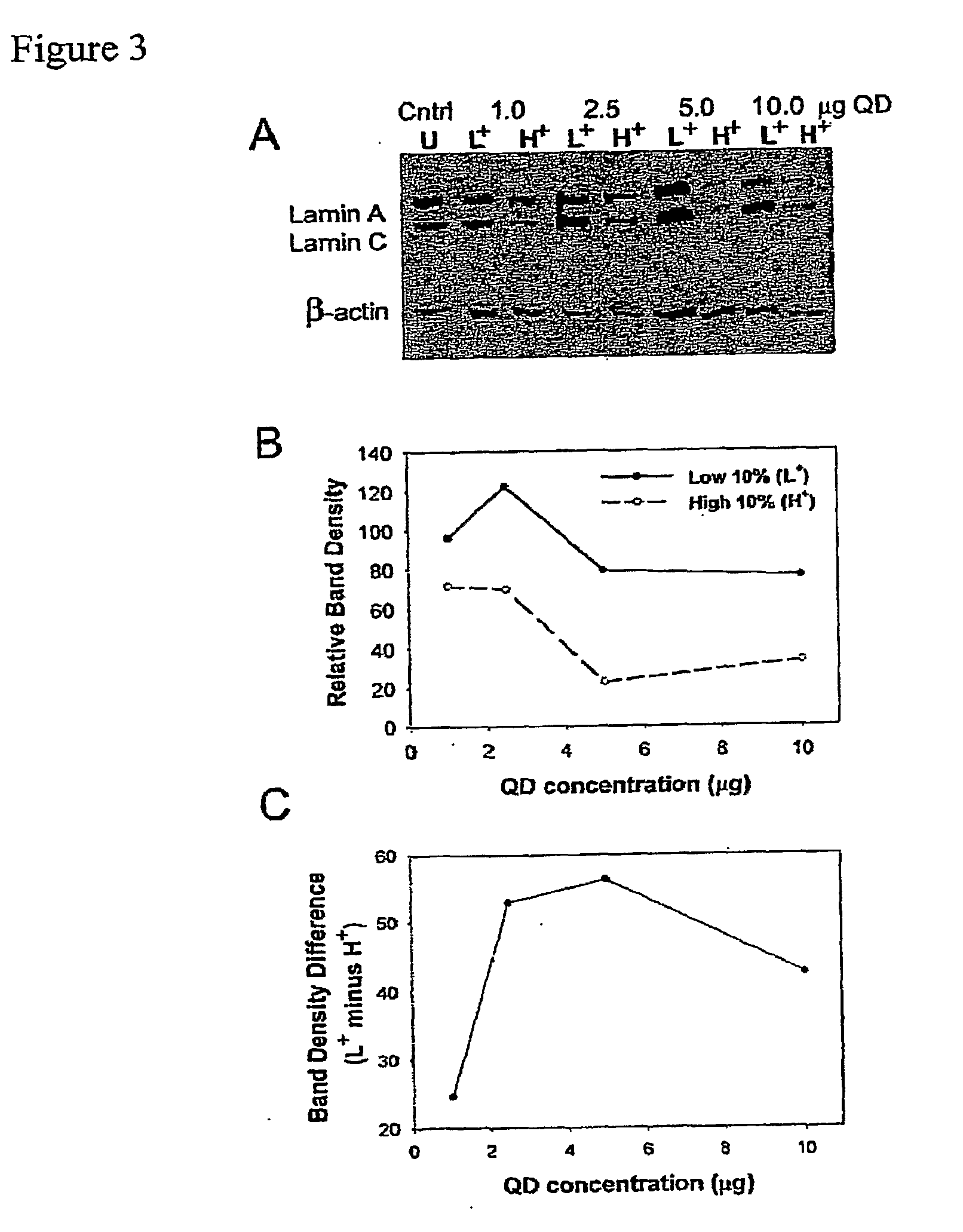
Compositions and Methods to Monitor RNA Delivery to Cells
InactiveUS20090317802A1Microbiological testing/measurementGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsNanoparticleQuantum dot
Methods and compositions for tracking or monitoring uptake of siRNA by mammalian cells are provided. The methods and compositions may be used to monitoring the silencing activity of the internalized siRNA. The compositions contain an siRNA, an optically or magnetically detectable nanoparticle such as a quantum dot and, optionally, a transfection reagent. Cells are contacted with an siRNA and an optically or magnetically detectable nanoparticle, optionally in the presence of a transfection reagent. Detection of internalized nanoparticles is indicative of siRNA uptake. The invention allows analysis, identification, processing, etc., of cells that have efficiently taken up siRNA. In one embodiment, cells are sorted into at least two populations based on the amount of siRNA taken up.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
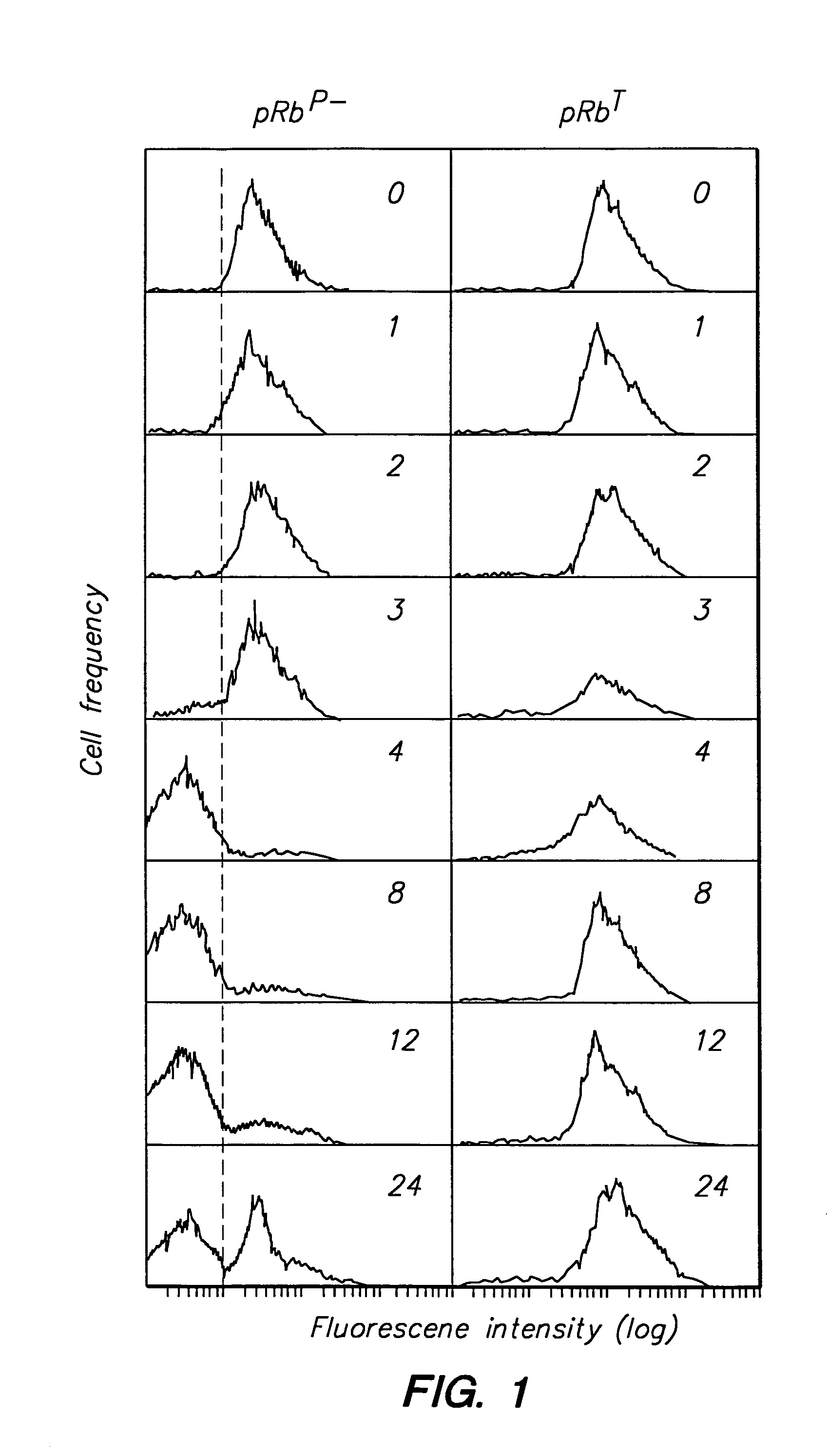
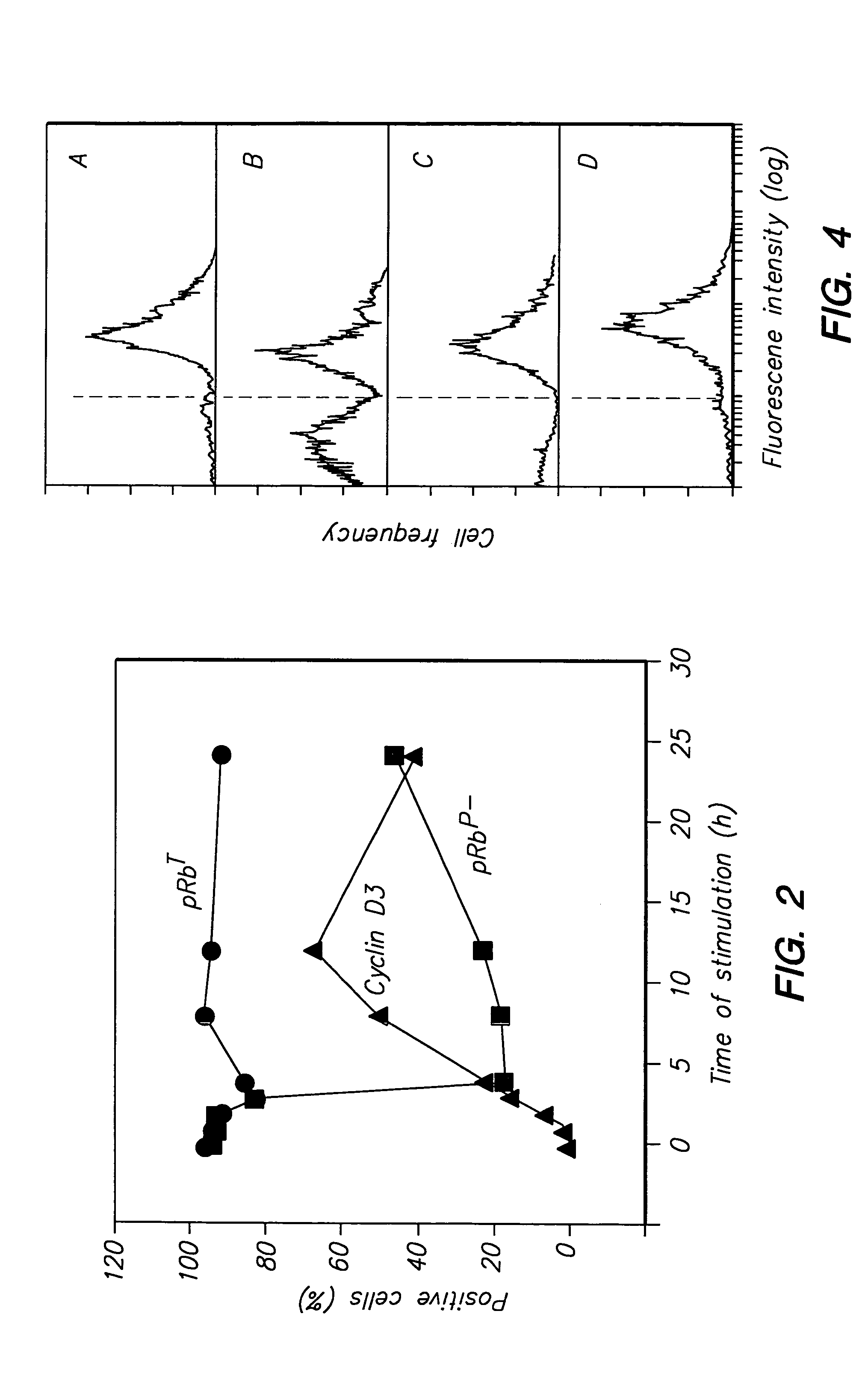
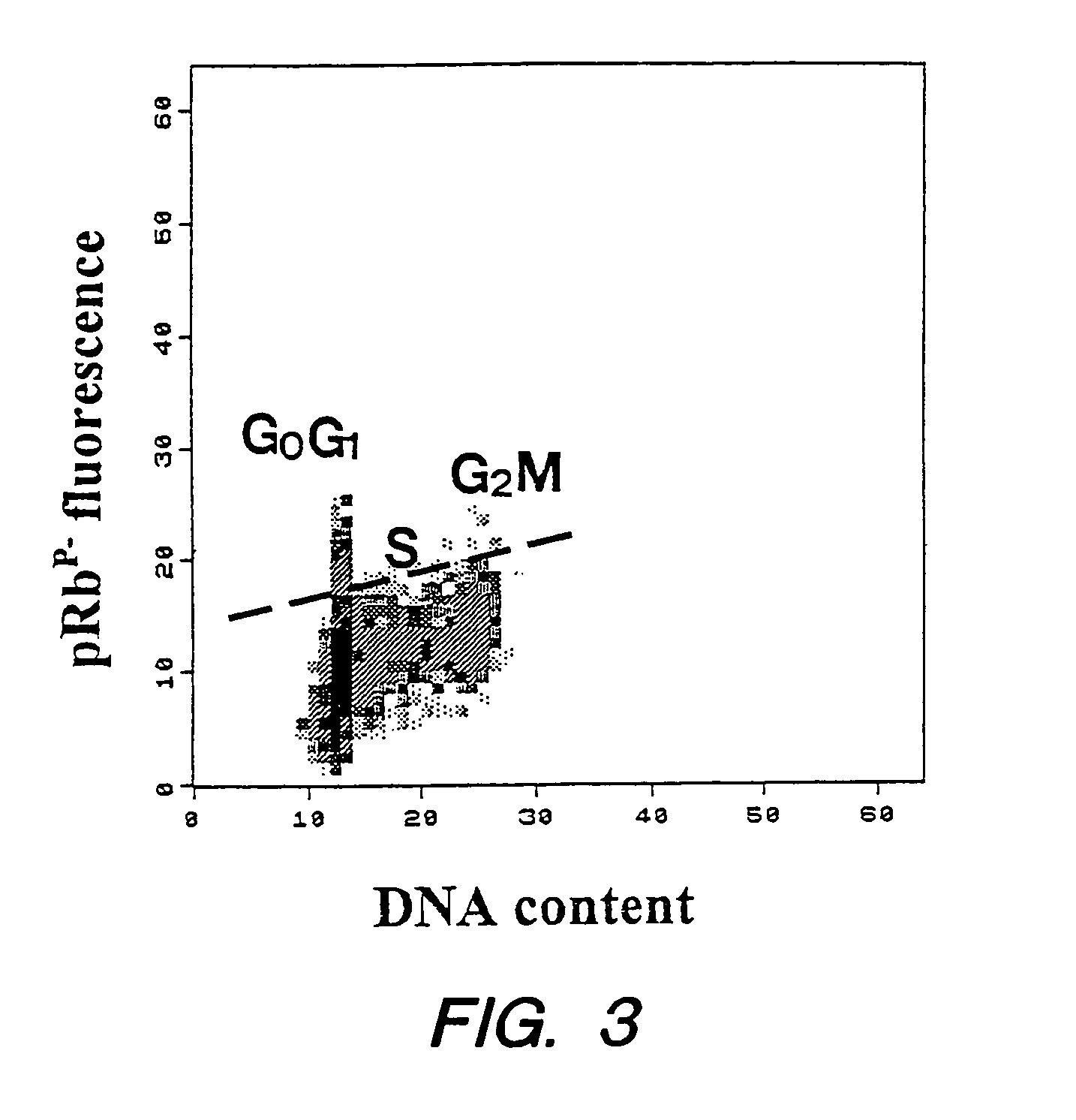
Detection of protein conformations in single cells
InactiveUS7070943B2Avoid missing signalMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyPhosphorylationChemical compound
Methods, reagents, and kits are provided that permit flow cytometric determination of the phosphorylation status of retinoblastoma susceptibility gene protein (pRB) in individual cells. Methods are described that permit the hypophosphorylated, active, form of pRB to be measured either as an absolute quantity or as a proportion of total cellular pRB. Further described are methods that permit pRB phosphorylation status to be correlated with cell cycle phase and with protein components of the cell cycle. Screening of chemical compounds for antiproliferative and antineoplastic activity using the flow cytometric assays is demonstrated. Reagent kits that facilitate the subject methods are also provided.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Methods of Amplifying Whole Genome of a Single Cell
ActiveUS20140200146A1Large coverageImprove fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGeneticsGenome
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
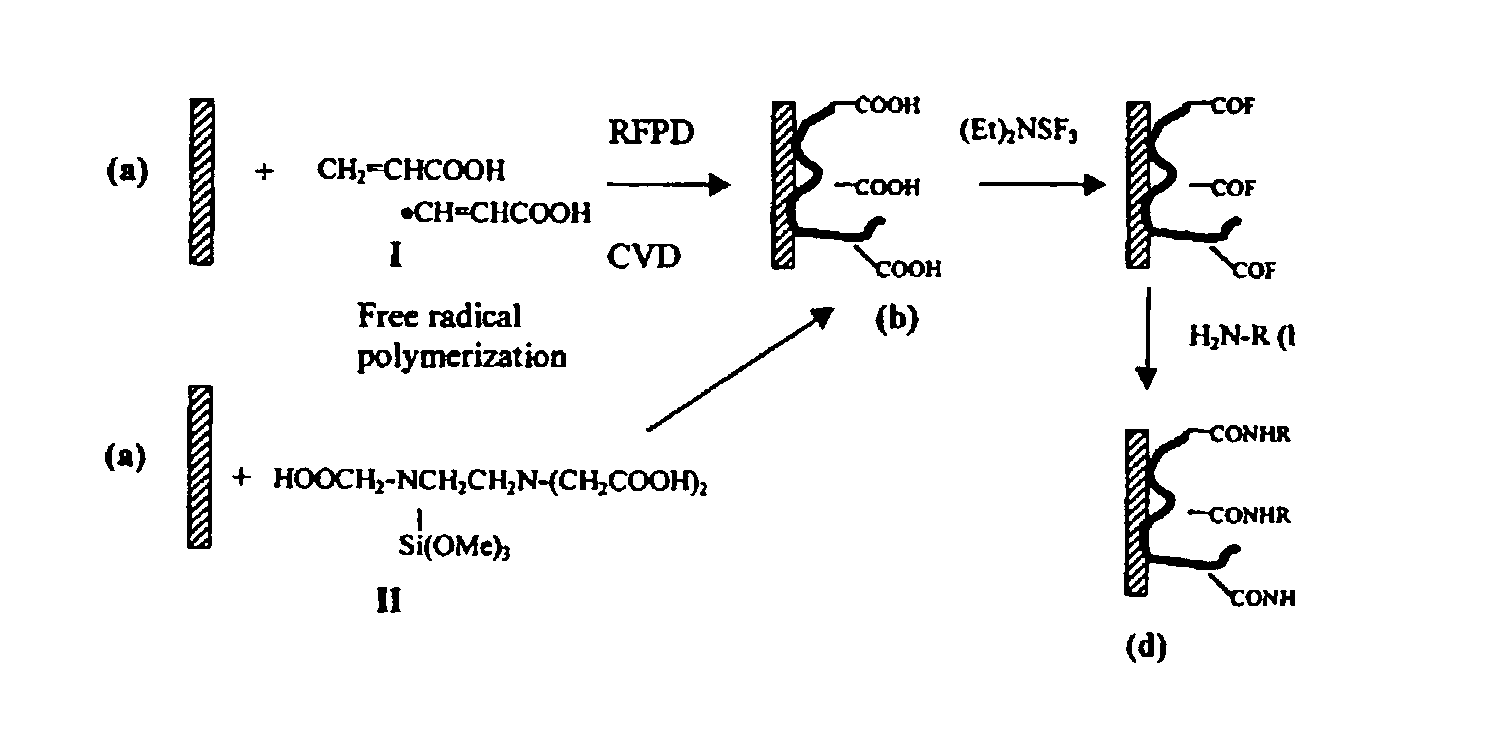
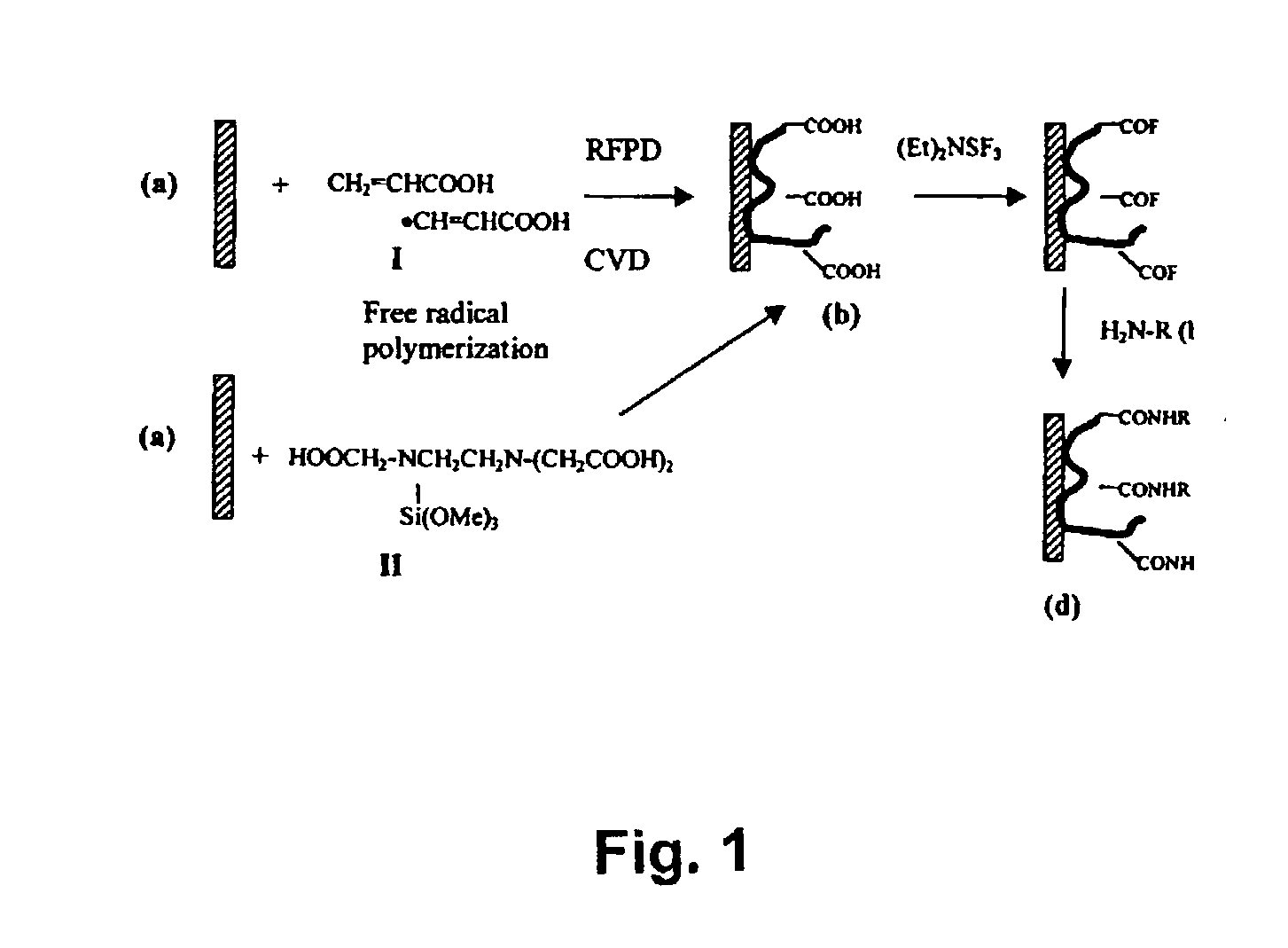
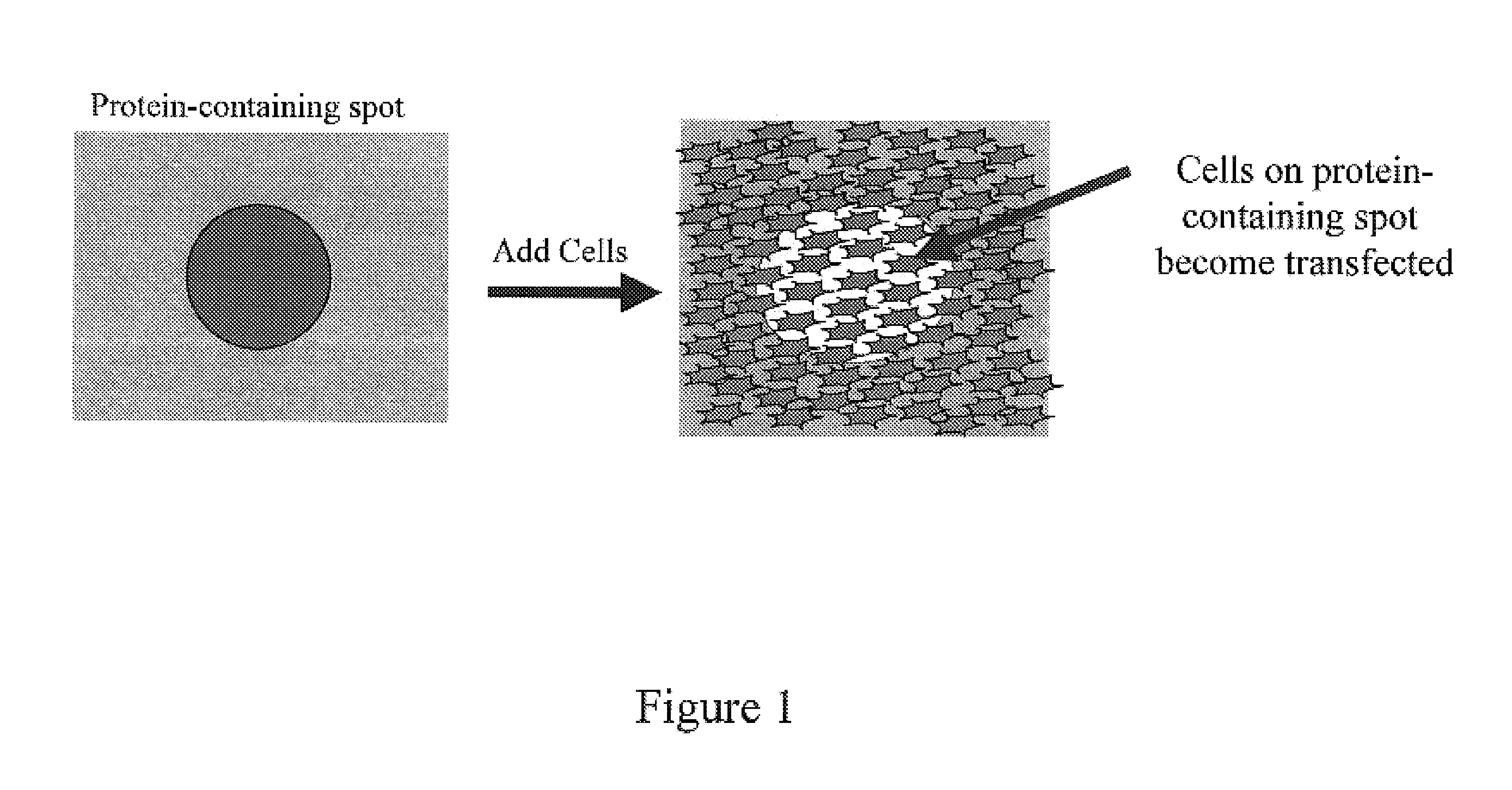
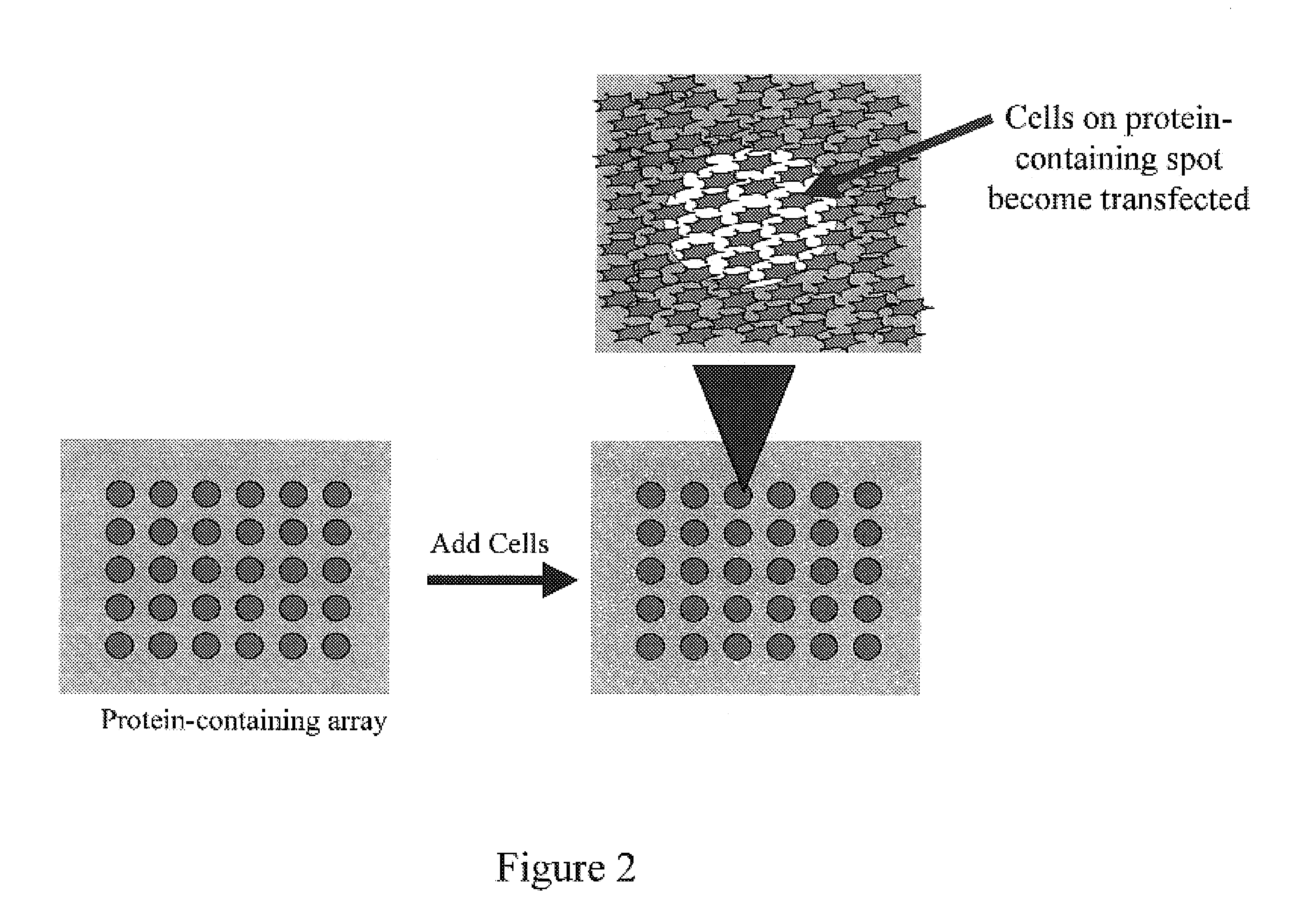
Polymer-coated substrates for immobilization of biomolecules and cells
ActiveUS20030198968A1Rapid and uniform introductionVersatile and cost-effective processBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsSide chainPendant group
Methods for preparing a substrate for the arraying and immobilizing of biomolecules or cells are described. The methods include providing a solid support and depositing by a chemical plasma-mediated polymerization process a polymeric coating on the surface. The polymeric coating comprises at least one pendant functional group capable of attaching a biomolecule or a cell. A material of the polymeric coating is preferably selected in such a way that its surface properties enhance binding between the pendant group and the biomolecule or cell. A substrate for the immobilization of biomolecules and cells is also provided. The substrate comprises a solid support made of a polymeric material. The solid support has at least one first pendant functional group suitable for attaching a first biomolecule or a first cell on its surface. The substrate further comprises a polymeric coating deposited on the surface of the substrate. The polymeric coating increases the attachment of the first biomolecule or the first cell to the first functional group.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
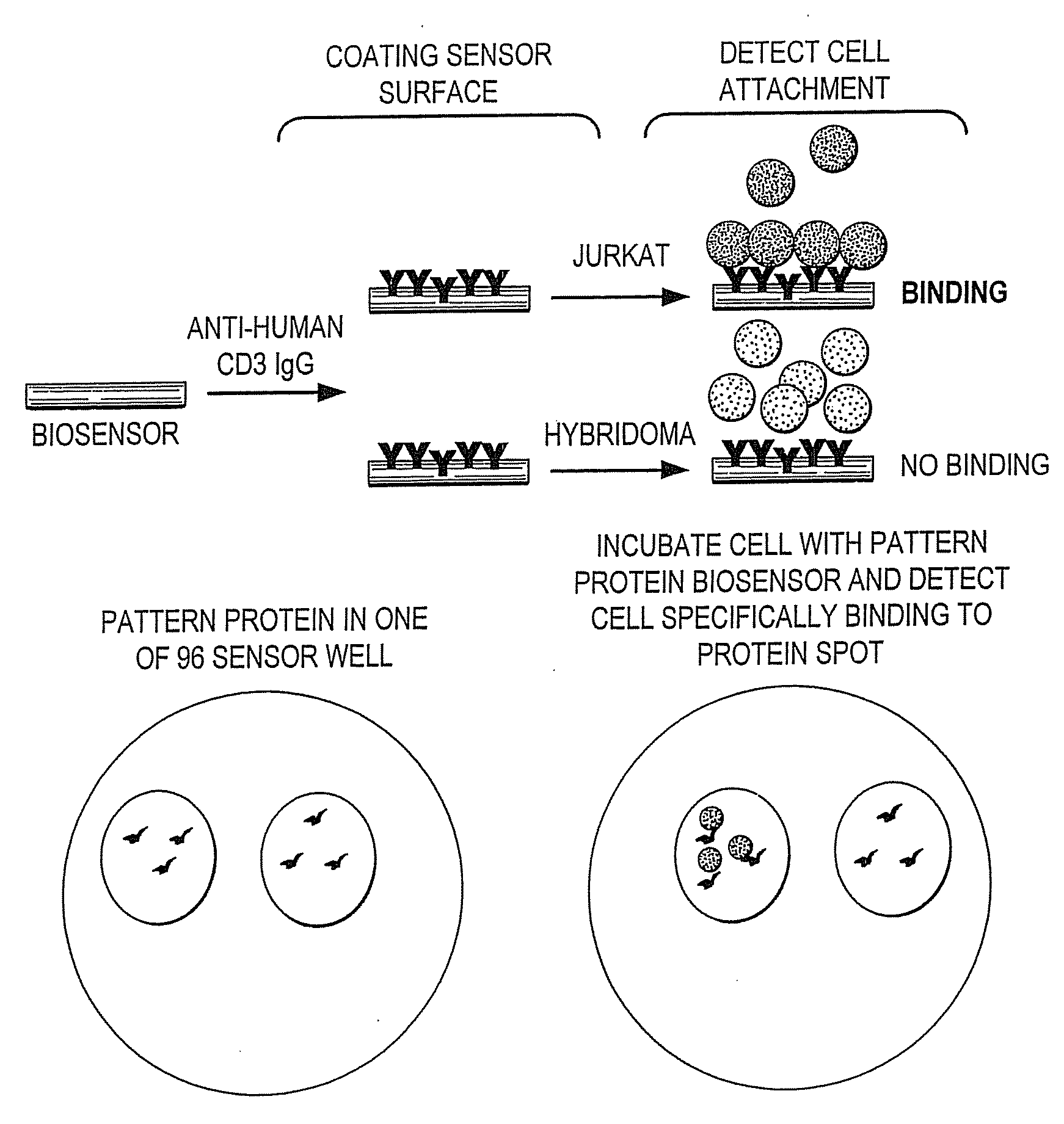
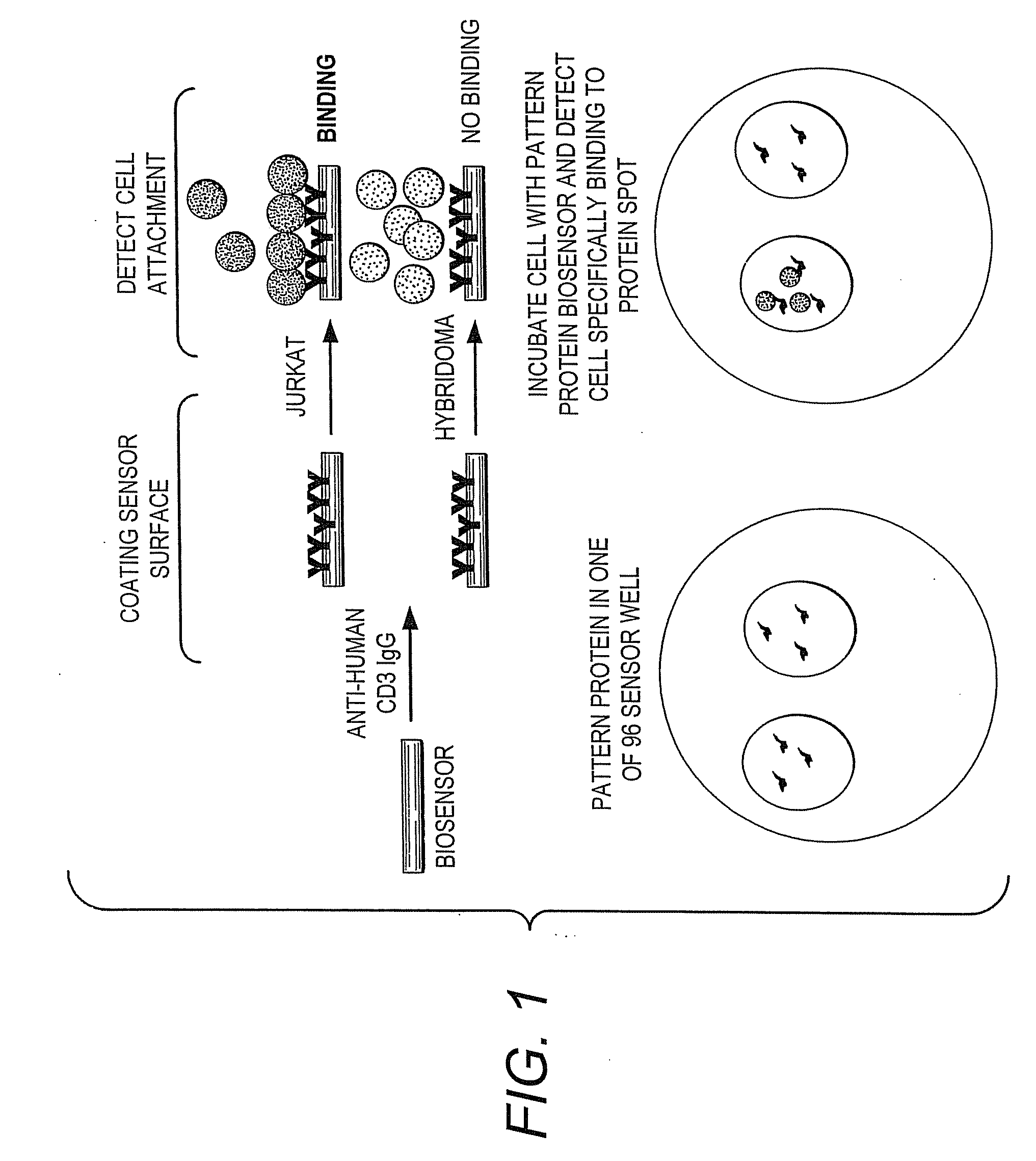
Methods of Detection of Changes in Cells
ActiveUS20090130703A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyCell method
Owner:X BODY
Methods and systems for harvesting cells
ActiveUS20140030805A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyCell method
Owner:PLURI BIOTECH LTD
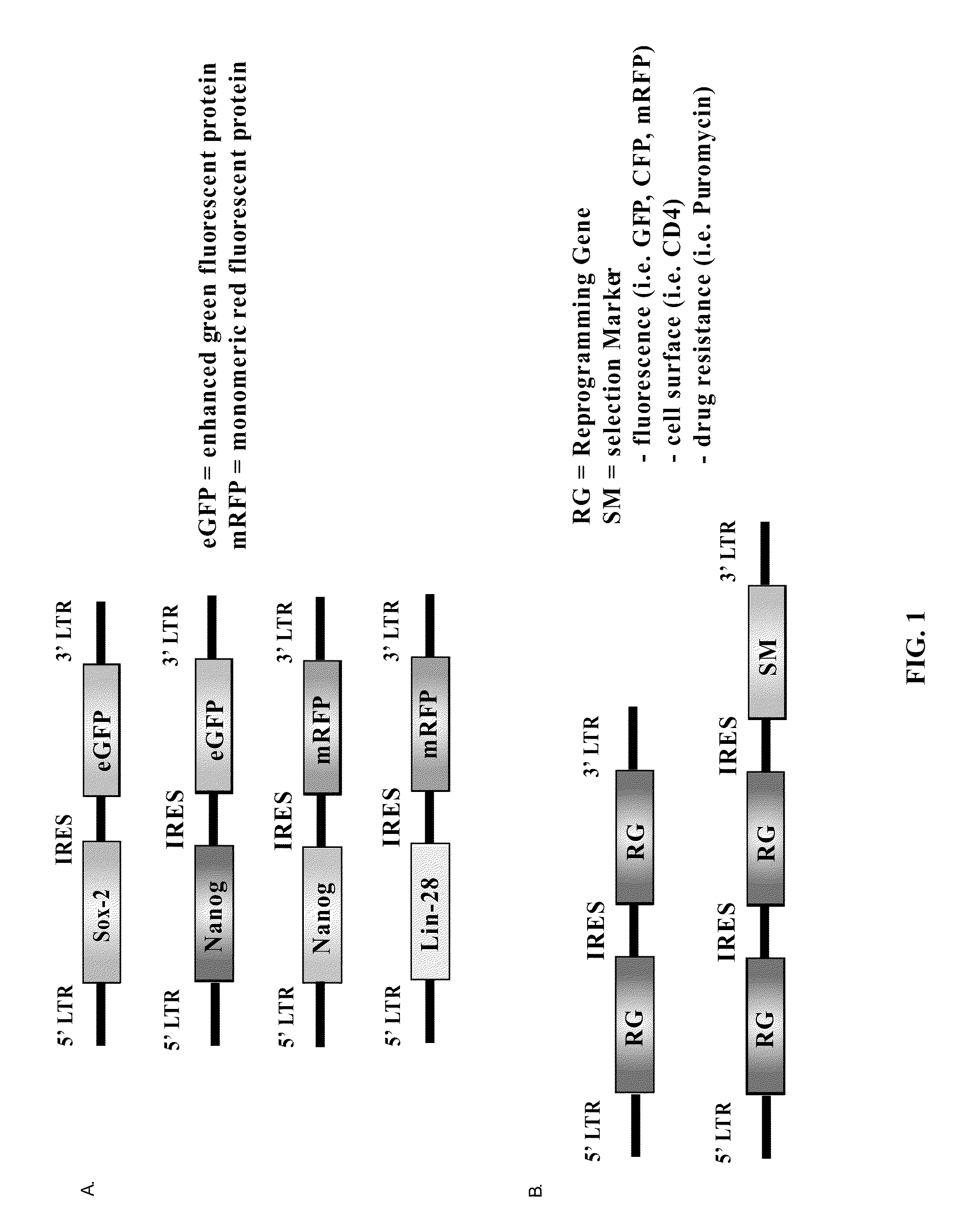
Methods for the production of ips cells
ActiveUS20100041054A1Improving transfectionReduce chanceVirusesGenetically modified cellsGeneHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Methods and composition of induction of pluripotent stem cells are disclosed. For example, in certain aspects methods for generating induced pluripotent stem cells using reporter genes are described. Furthermore, the invention provides novel reprogramming vectors employing reporter genes.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Method and device for protein delivery into cells
InactiveUS7105347B2Reduce deliveryImprove delivery efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVolumetric Mass DensityCell cluster
Owner:CORNING INC
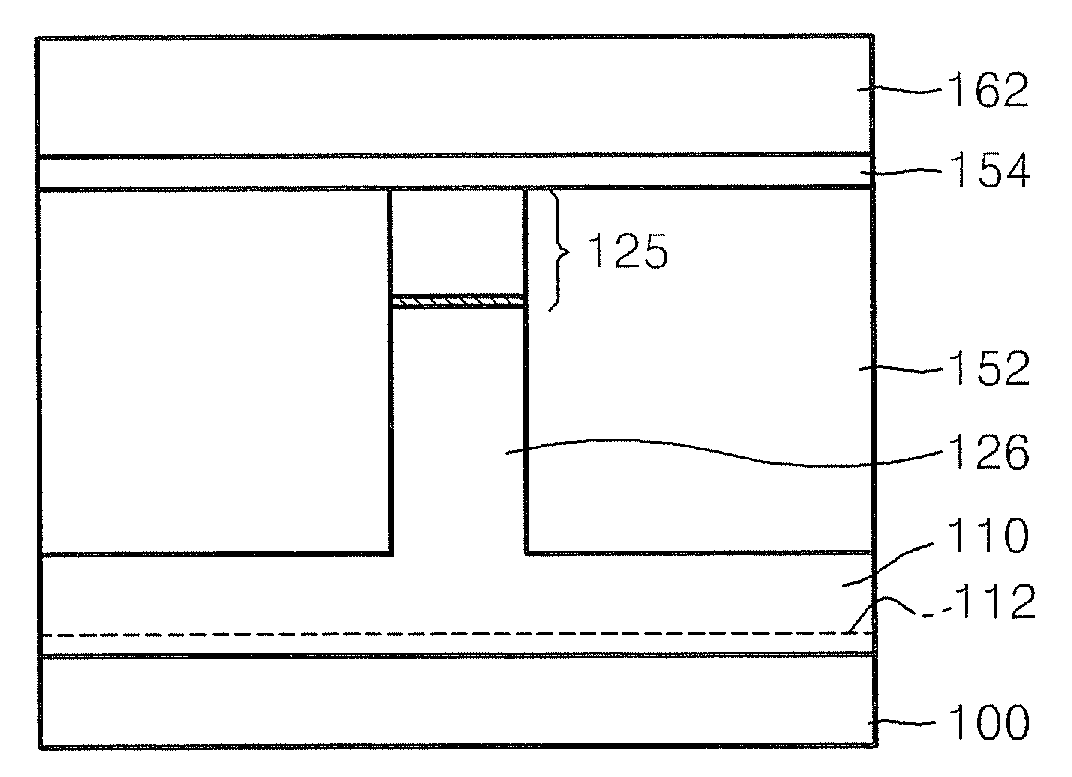
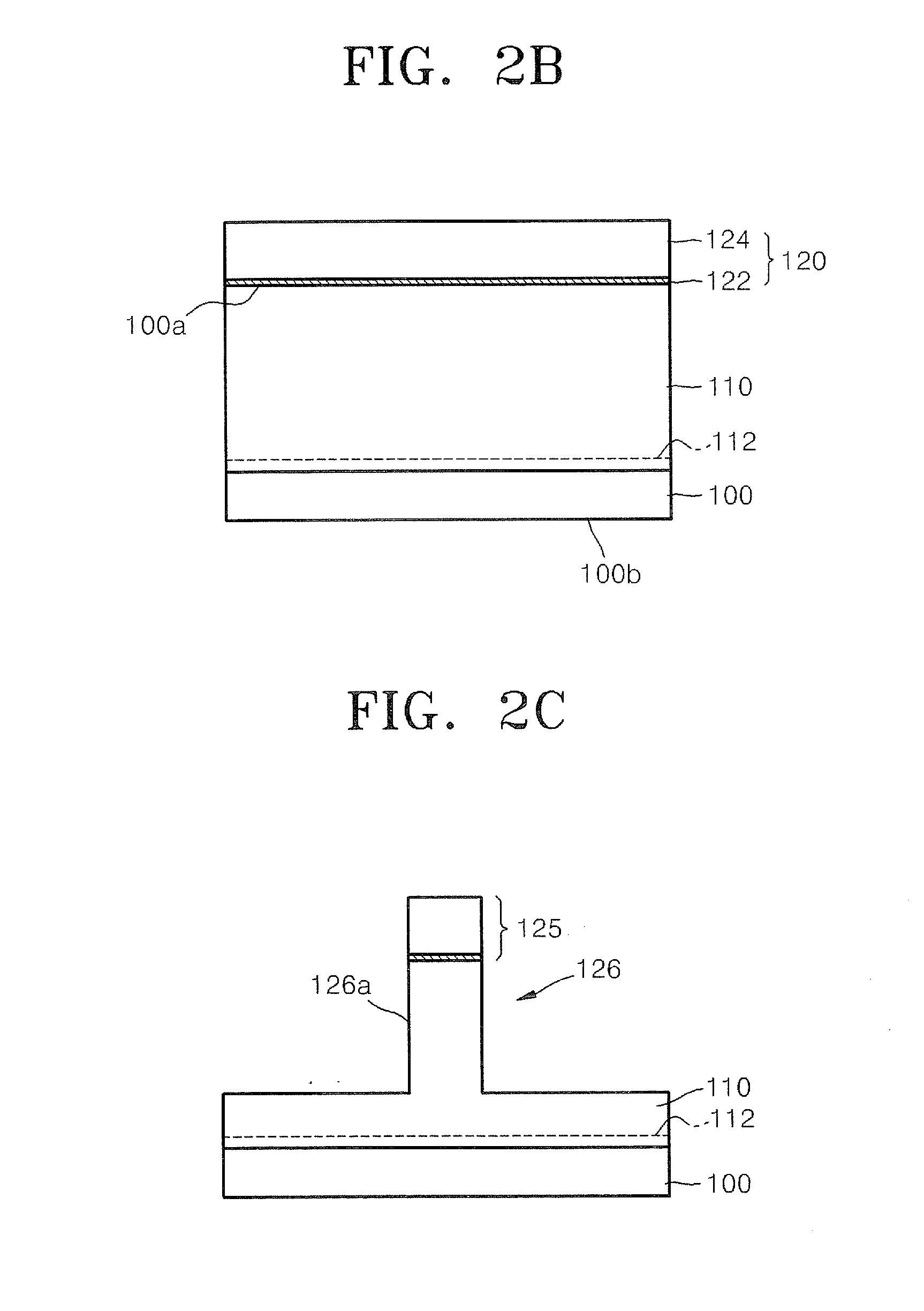
Methods of Forming Field Effect Transistors and Capacitor-Free Dynamic Random Access Memory Cells
Methods of forming capacitor-free DRAM cells include forming a field effect transistor by forming a first semiconductor wafer having a channel region protrusion extending therefrom and surrounding the channel region protrusion by an electrical isolation region. A portion of a backside of the first semiconductor wafer is then removed to define a semiconductor layer having a primary surface extending opposite the channel region protrusion and the electrical isolation region. A gate electrode is formed on the primary surface. The gate electrode extends opposite the channel region protrusion. The source and drain regions are formed in the semiconductor layer, on opposite sides of the gate electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Regeneration initiating cells
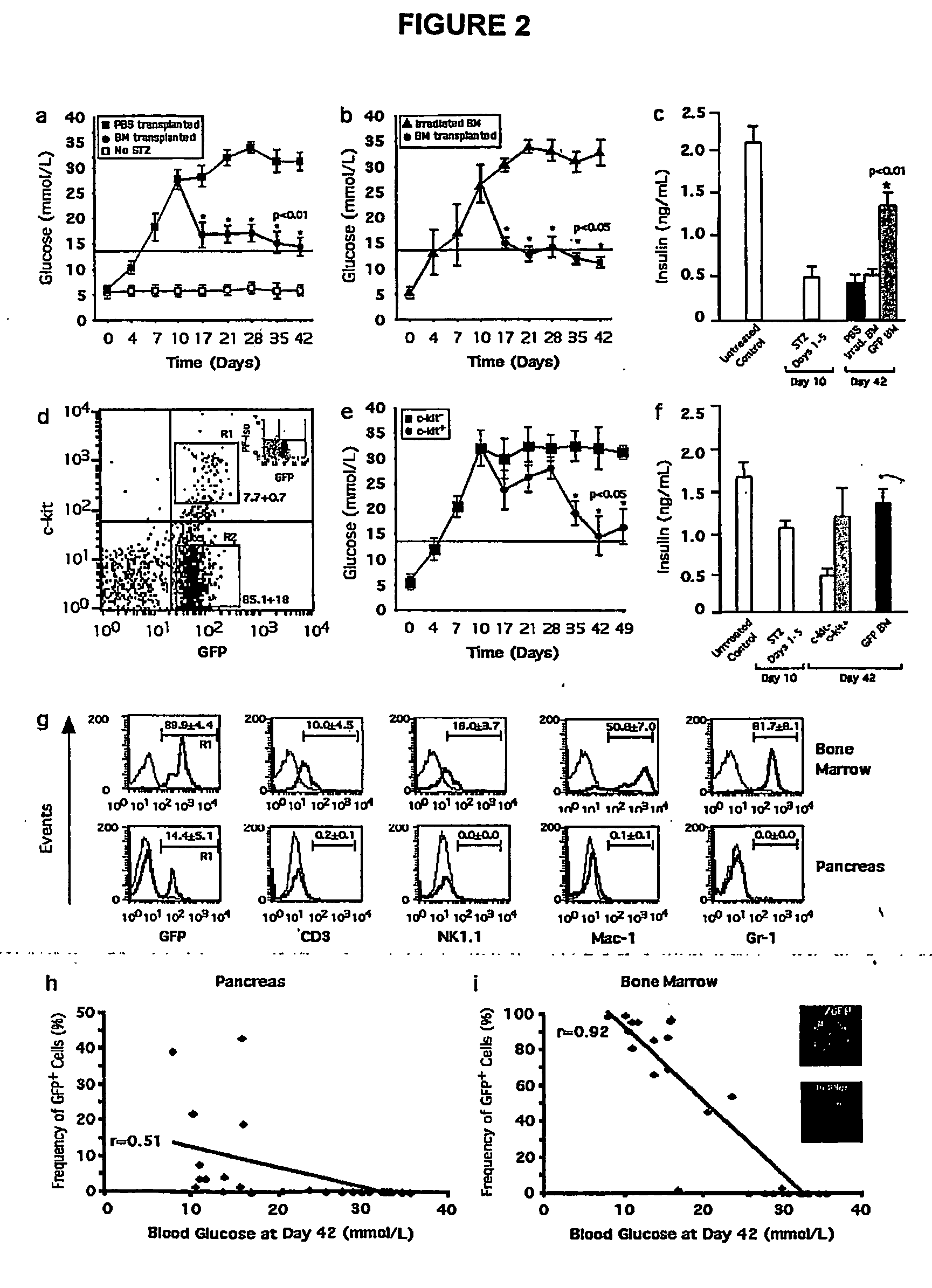
InactiveUS20060140913A1Rescue hyperglycemiaSpeed up the repair processBiocideArtificial cell constructsAcute hyperglycaemiaMedicine
Methods and compositions for treating hyperglycemia and pancreatic damage as well as stimulating the repair or regeneration of islet cells are disclosed.
Owner:THE JOHN P ROBARTS RES INST
Method and apparatus for high throughput multiple radio sectorized wireless cell
InactiveUS20050250453A1Minimize interferenceImprove throughputSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityDirectional antennaLoad management
Methods and apparatus for high throughput wireless cells, capable of functioning as access points, are described. The wireless cells may be equipped with multiple radios to increase the amount of throughput available through a single wireless cell. Multiple antennas attached to the radios through RF switches may enable the wireless cell to service multiple clients simultaneously. The physical sectors of the antennas may overlapped to form virtual sectors that provide greater flexibility in client load management and in simultaneously servicing multiple clients. Attenuators may reduce interference from foreign wireless cells or clients. Systems and methods for assigning minimally interfering channels to either physical sectors or to radios to reduce interference between adjacent sectors and overlapping sectors are also disclosed. An antenna horn may also allow any antenna to be used as a directional antenna and may enable the antenna's angle of coverage to be adjusted. The use of multiple antennas on a client to reduce interferences is also described.
Owner:ROTANI
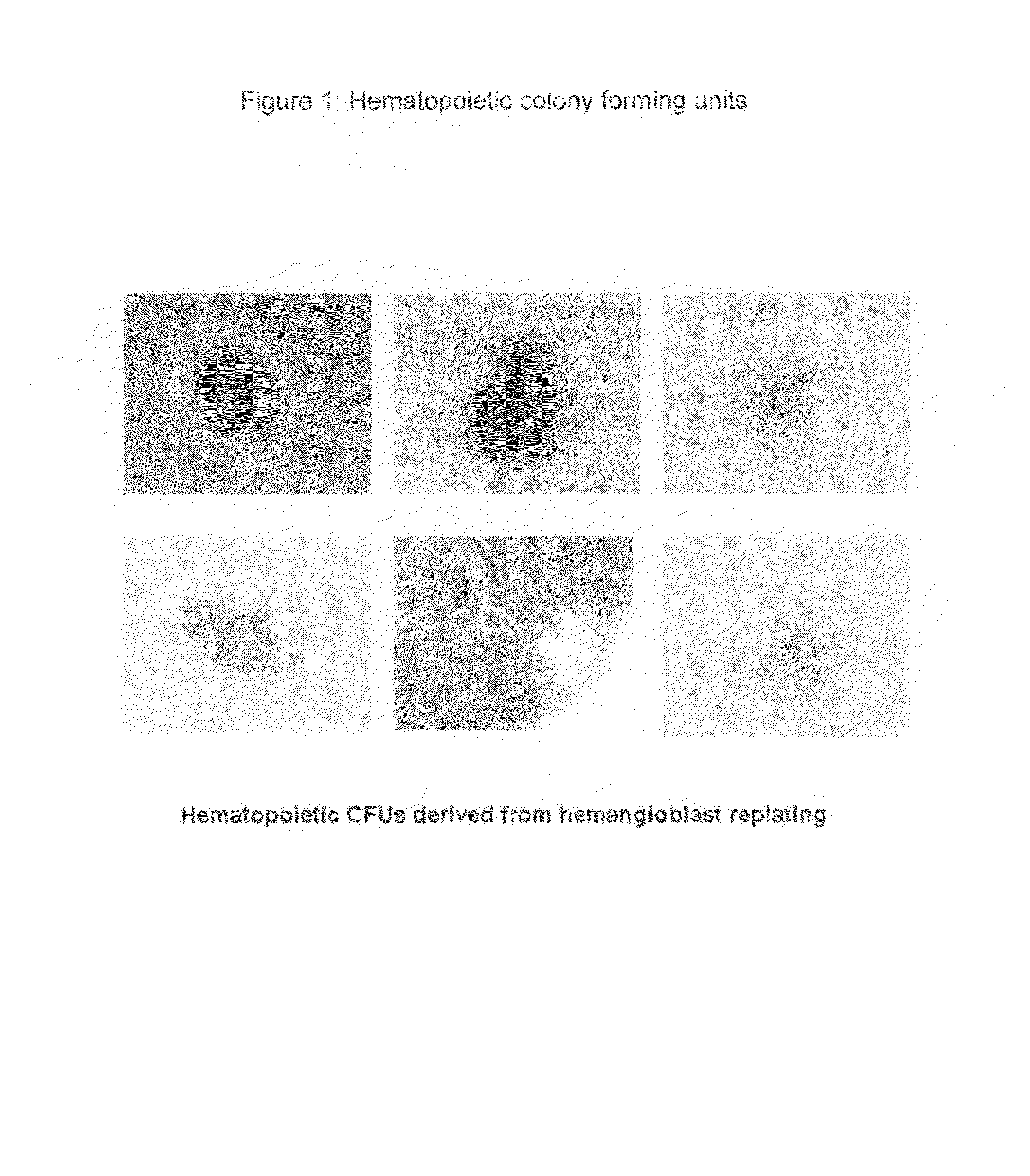
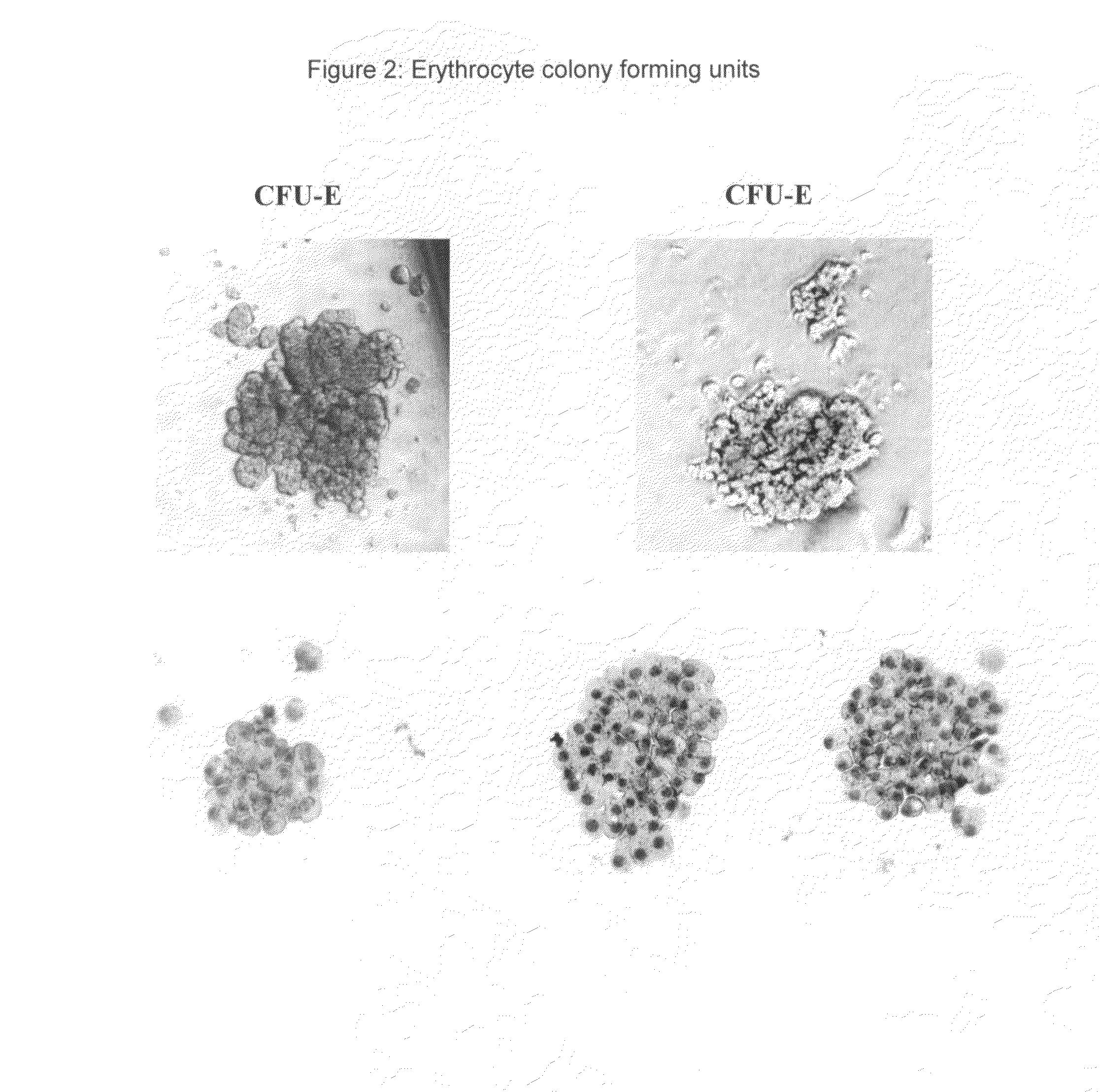
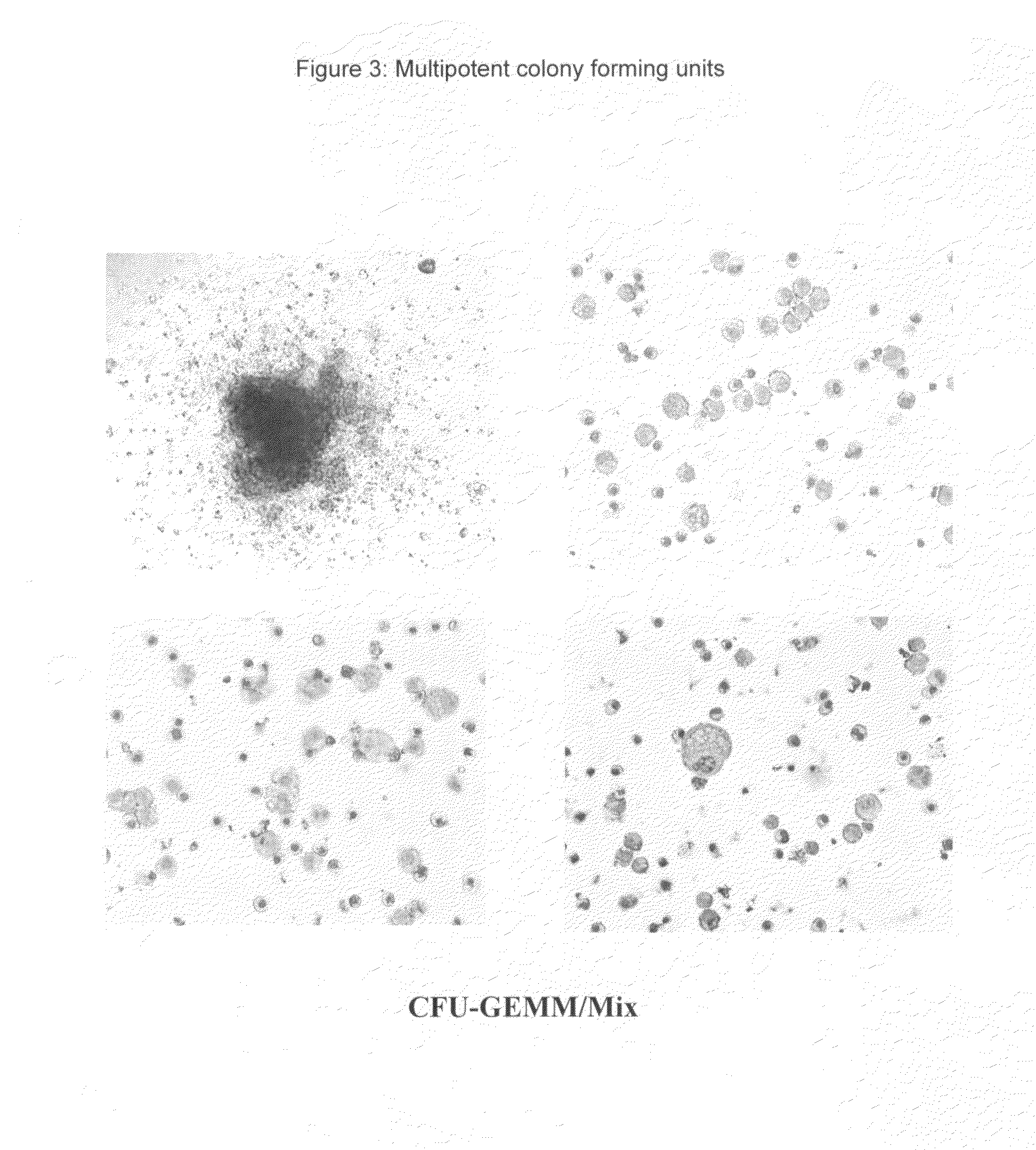
Hemangio-colony forming cells
ActiveUS8017393B2Reduce riskInduce toleranceCulture processArtificial cell constructsHematopoietic cellCell biology
Methods of generating and expanding human hemangio-colony forming cells in vitro and methods of expanding and using such cells are disclosed. The methods permit the production of large numbers of hemangio-colony forming cells as well as derivative cells, such as hematopoietic and endothelial cells. The cells obtained by the methods disclosed may be used for a variety of research, clinical, and therapeutic applications.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com