Patents
Literature
72 results about "Critical factors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cryopreservation of Adipose Tissue for the Isolation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
The present invention relates to a method and composition for the cryopreservation of adipose tissue with the intention to use this tissue in the culturing of stem and / or progenitor cells. The method uses a specific cryoprotection medium to prevent damage of the original tissue during the cryopreservation while still maintaining a high viability of the stem and / or progenitor cells obtained from the cryopreserved adipose tissue. Furthermore the cryoprotection medium of the present invention does not contain any kind of xenogeneic sera, a critical factor since it is the intention of that the cryopreserved tissue is used for obtaining stem and / or progenitor cells that can be used in medicine. The cryoprotection medium is characterized in that it is a solution of physiological water comprising glycerol and sucrose and / or trehalose and optionally serum albumin.
Owner:CRYO SAVE
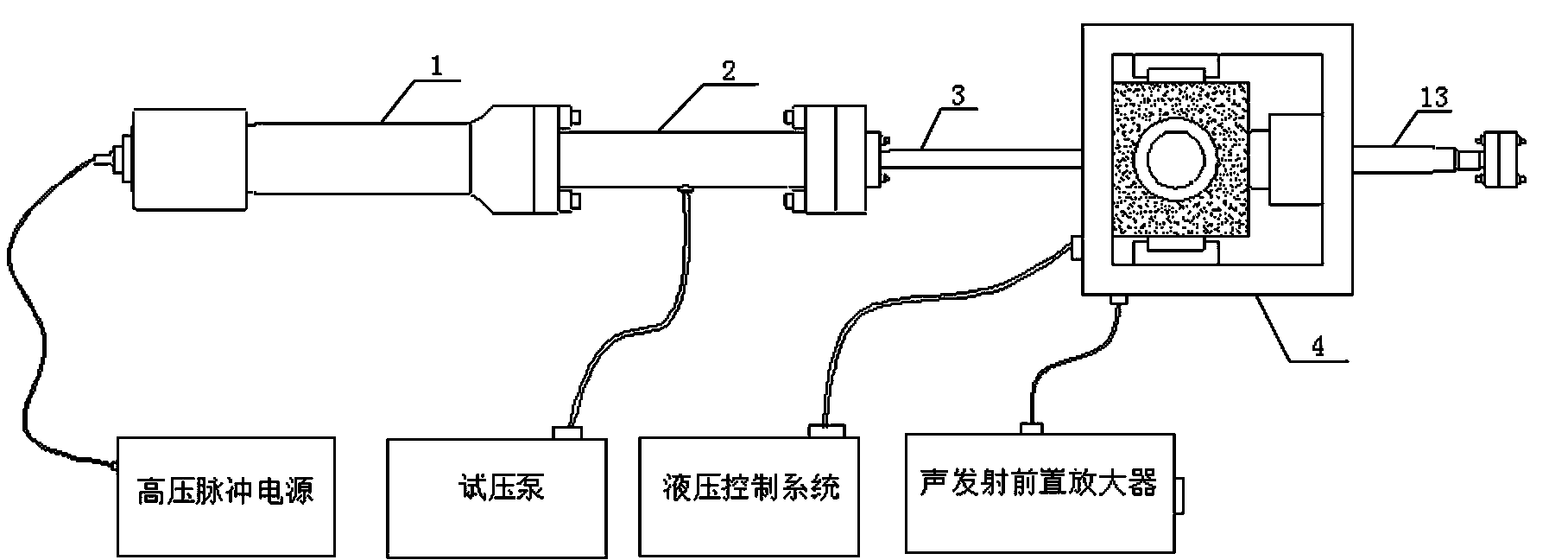
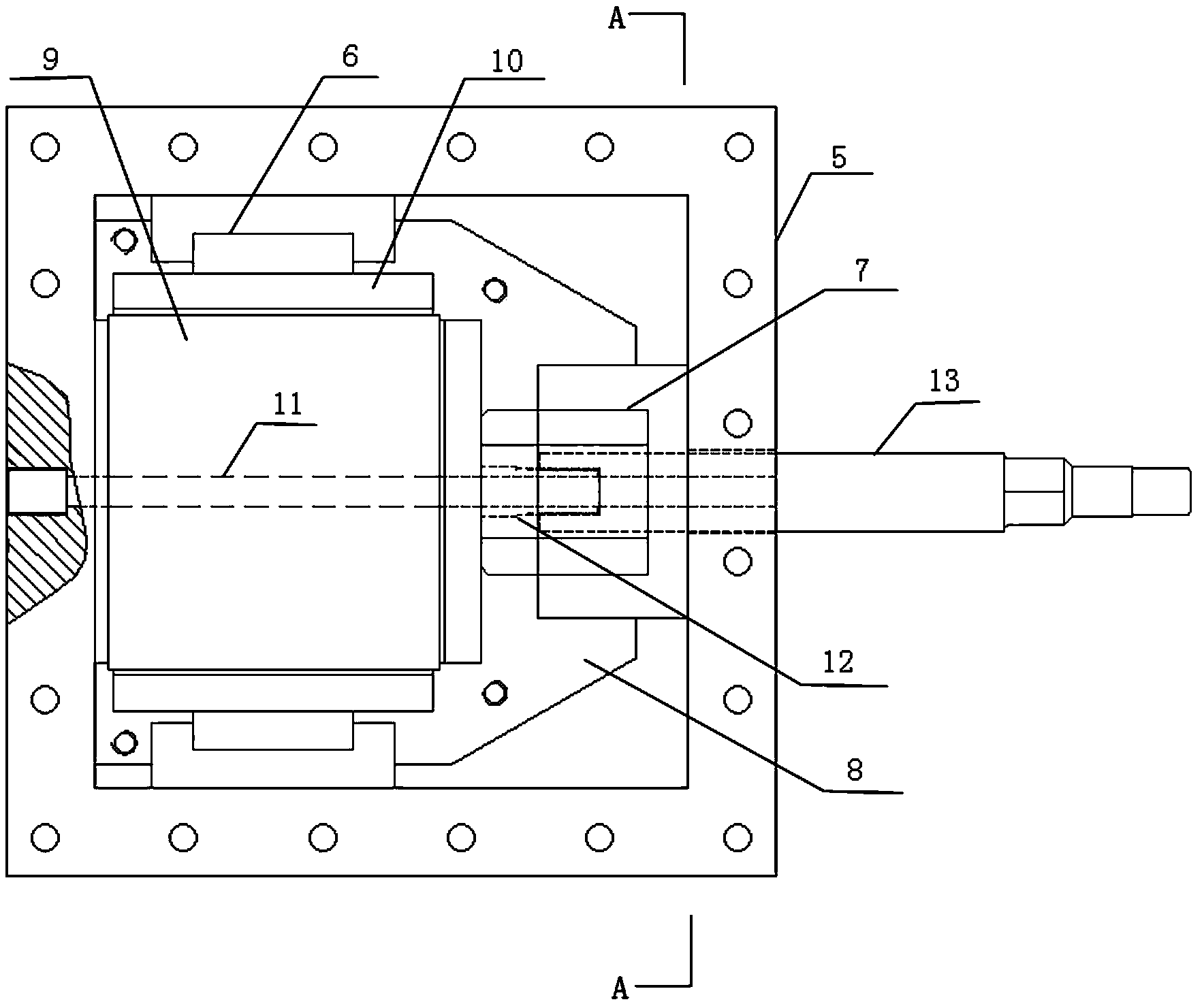
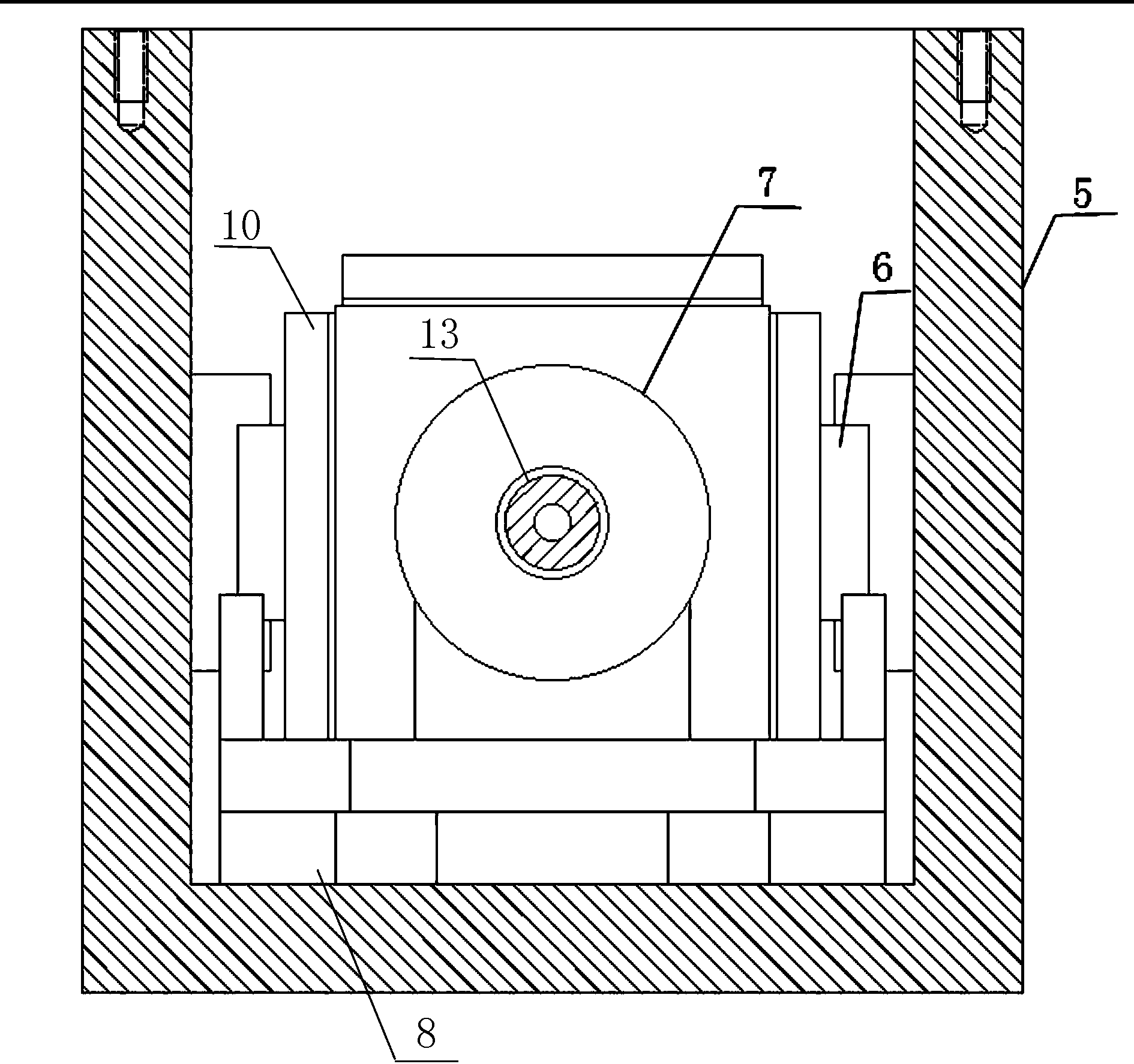
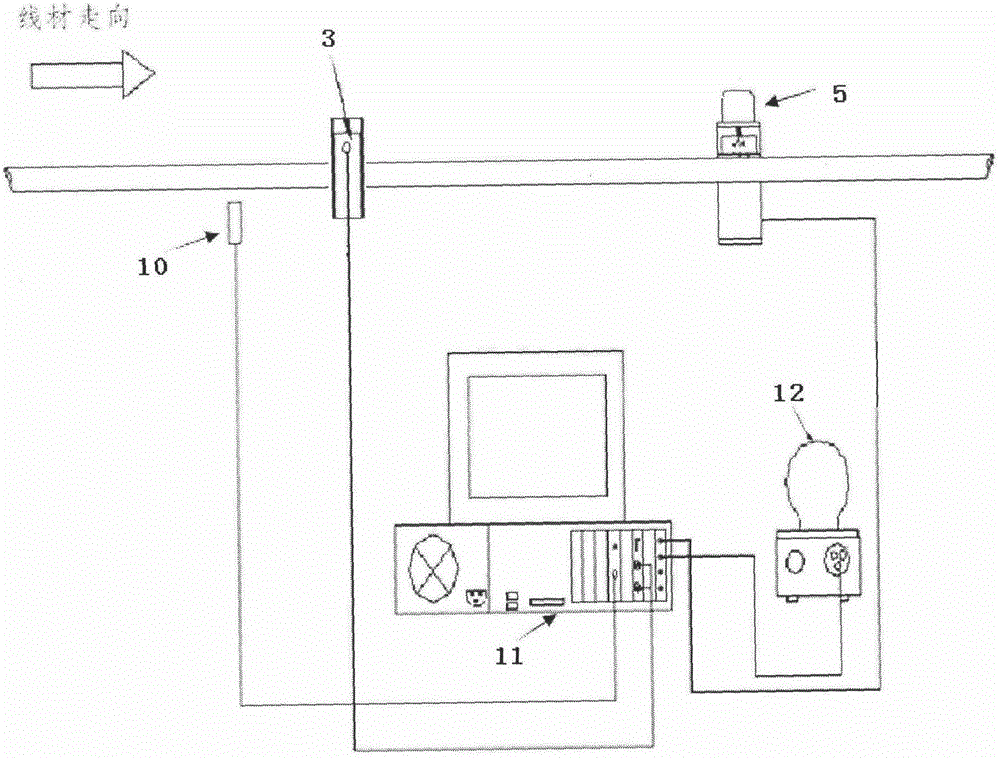
Coal seam anti-reflection experiment device based on high-voltage electric pulse
InactiveCN104061014ADetermine the impactDetermine the scopeFluid removalGas removalElectrical impulseEngineering
The invention relates to a device for performing experiments by combining high-voltage pulse discharging and the traditional coal seam anti-reflection technology, in particular to a coal seam anti-reflection experiment device based on high-voltage electric pulse. The coal seam anti-reflection experiment device based on high-voltage electric pulse comprises a high-voltage pulse power supply, a first tube body, a second tube body, a third tube body, a rigid triaxial pressure chamber, a pressure testing pump, a hydraulic control system and a sound reflection preamplifier, wherein the first tube body, the second tube body and the third tube body are connected in sequence. The traditional hydraulic fracturing technology is simulated in the rigid triaxial pressure chamber, the high-voltage pulse power supply supplies power to a discharging electrode, therefore, the positions around a through hole of a coal sample fracture, a fracturing positions and an expanding process of the fractures in the coal sample are monitored all the time, critical factors affecting fracture development of the coal sample and state transformation of gas, an actuating range and effect laws of pulse discharging on fracture development can be obtained through the later CT scanning and electron microscopy observation results, and a theoretical foundation is provided for practical application of high-voltage pulse discharging into underground coal seam anti-reflection.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
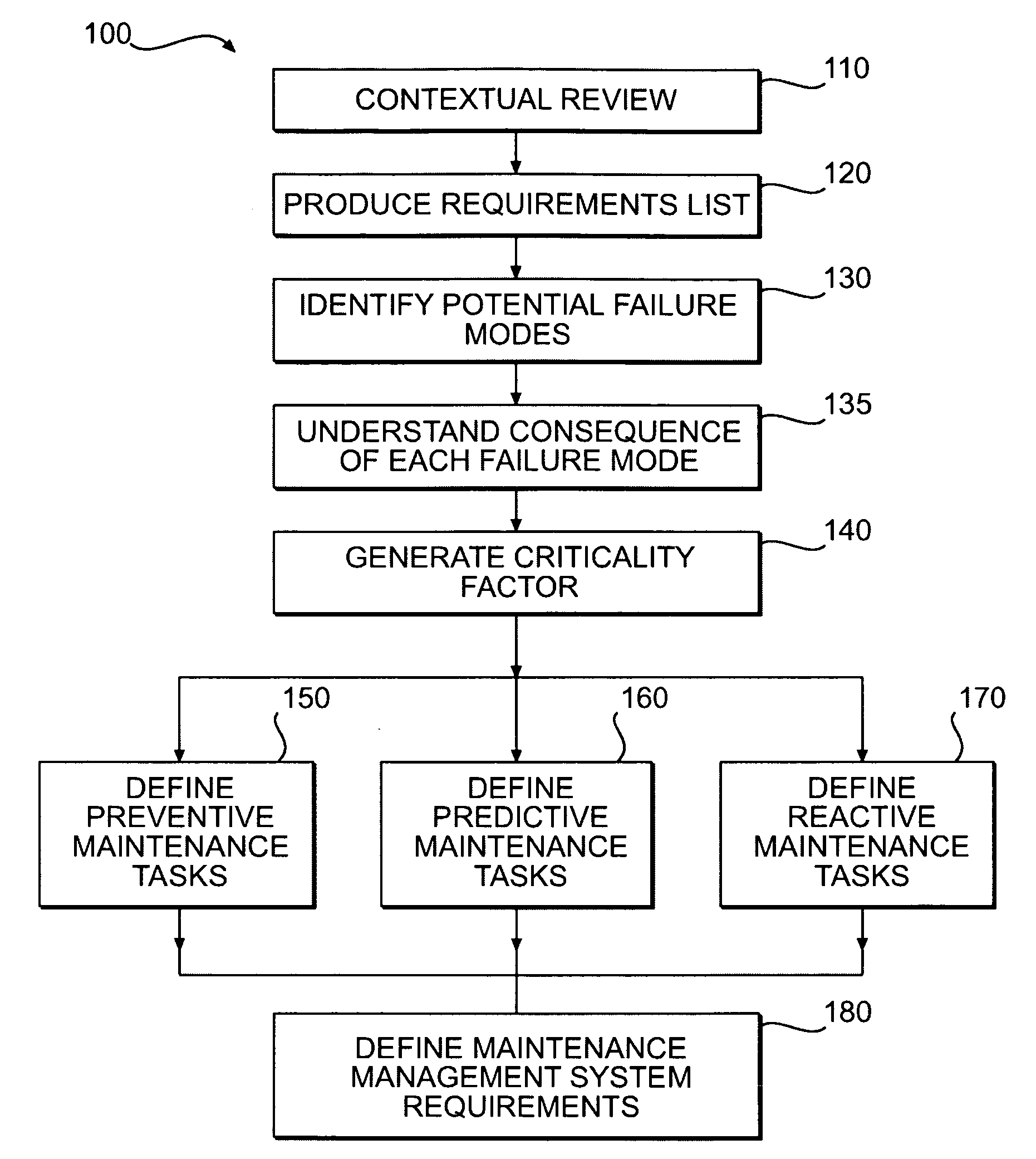
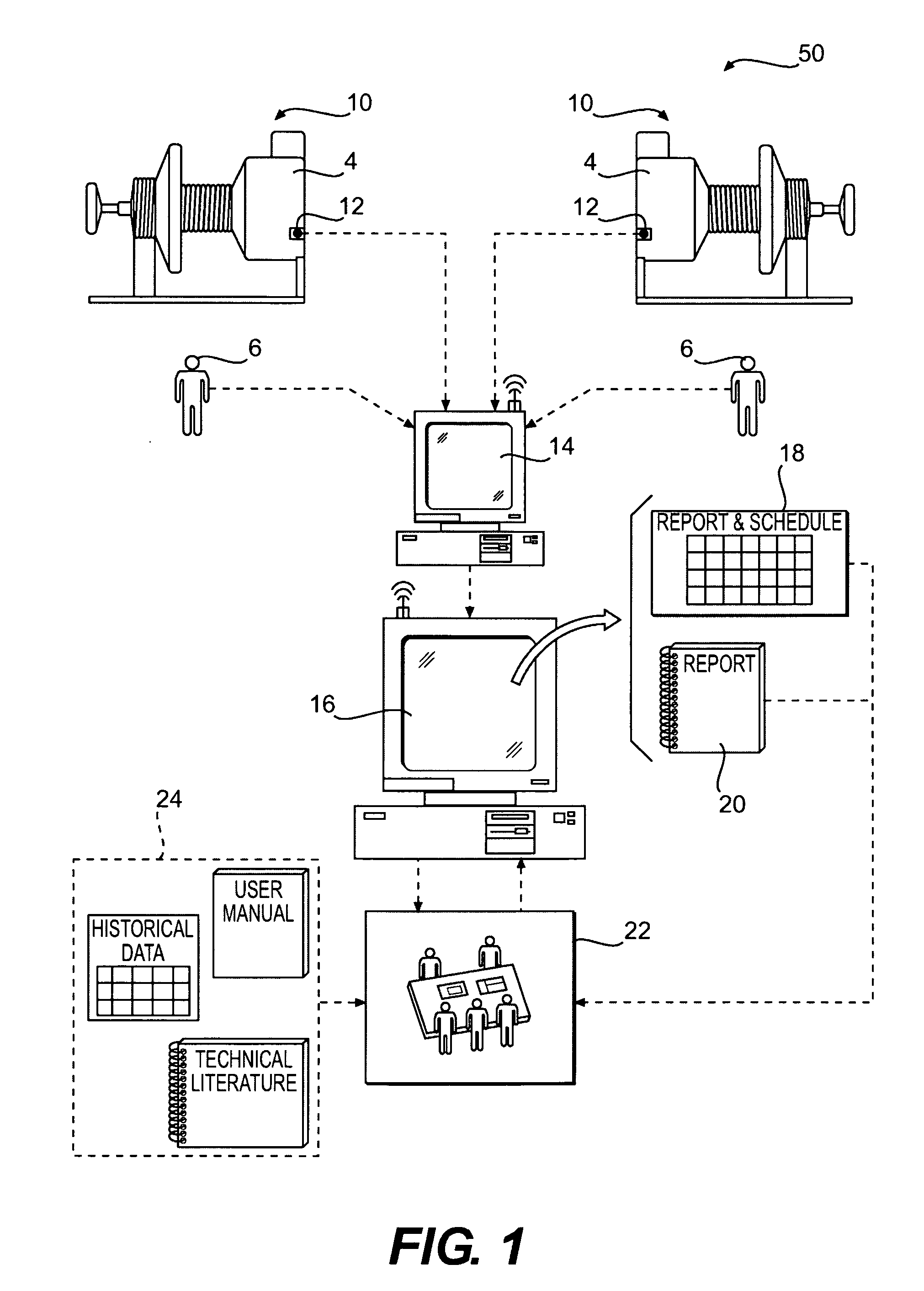
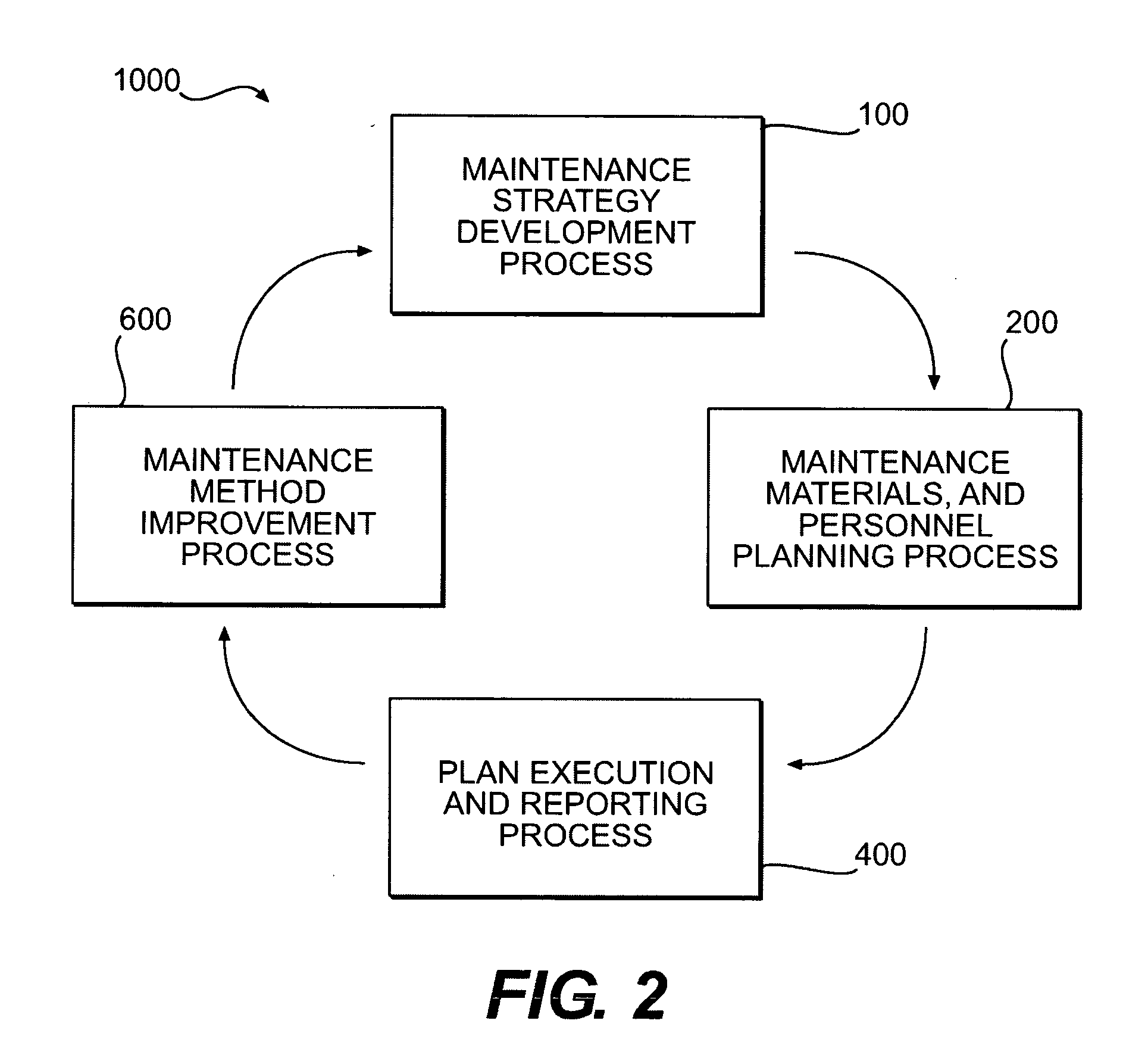
Maintenance management of a machine
ActiveUS20080133178A1Programme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsCritical factorsMaintenance management
Methods of providing maintenance management of a machine are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method involves identifying a machine component failure that, if not repaired, will result in a functional failure of the machine. A criticality factor is assigned to the machine component failure based on at least a probability of occurrence of the functional failure and a consequence of the functional failure to a machine user. A maintenance task is generated to repair the machine component failure, and a triggering condition that activates the maintenance task is defined. The method further involves conducting a machine repair in response to a detection of the triggering condition, and maintaining a record that includes information relating to the conducted machine repair. The method of providing maintenance management is also modified based on at least the record.
Owner:SOLAR TURBINES
MCrAlY-coating
A gas turbine component consists of a superalloy base material with a single crystal structure and a protective MCrAlY-coating (6). The MCrAlY-coating (6) has a g / g′ single crystal structure, which is epitaxial with the base material. It has be determined the critical factors for the successful epitaxial and crack-free growth of the MCrAlY-coating (6).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
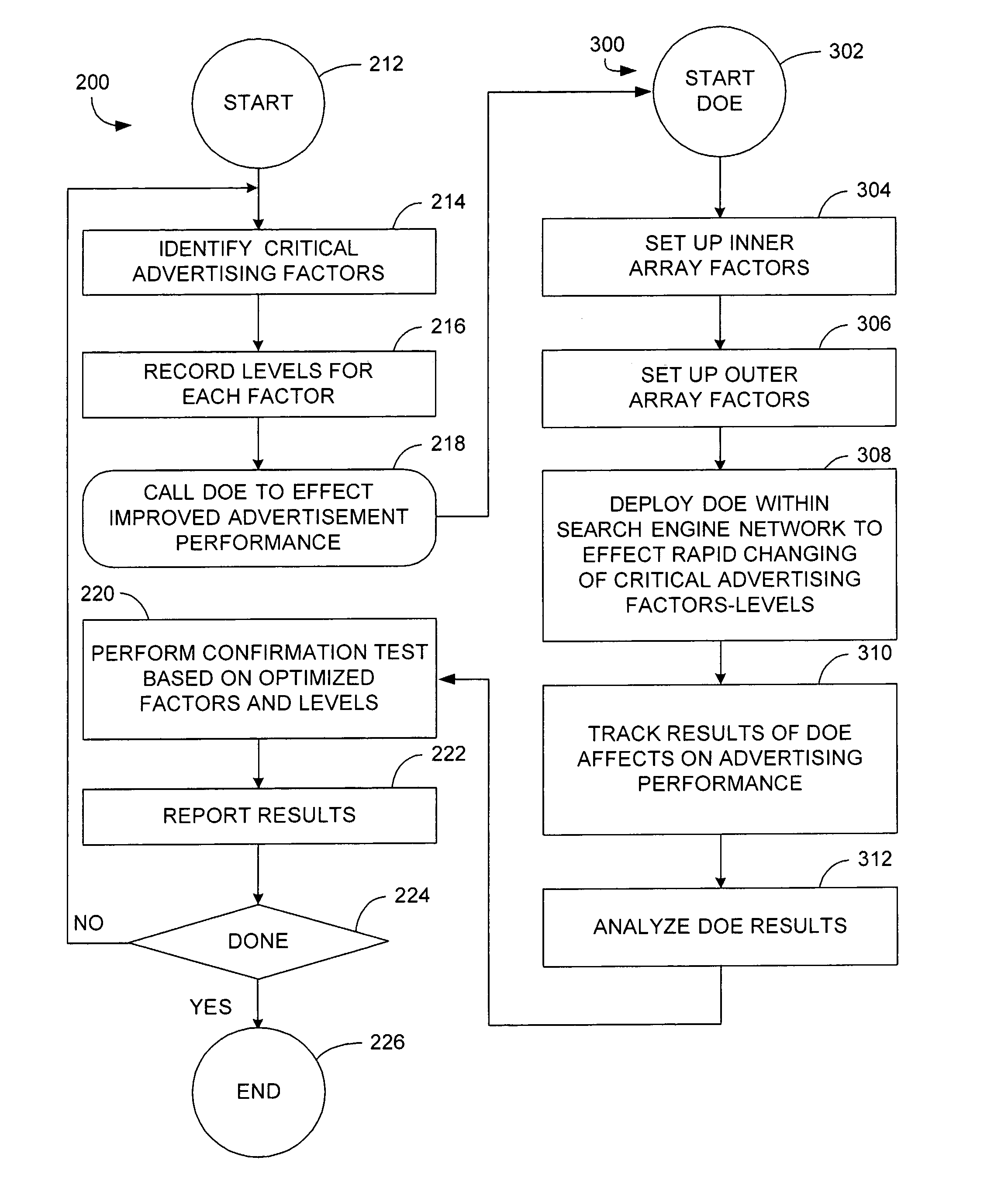
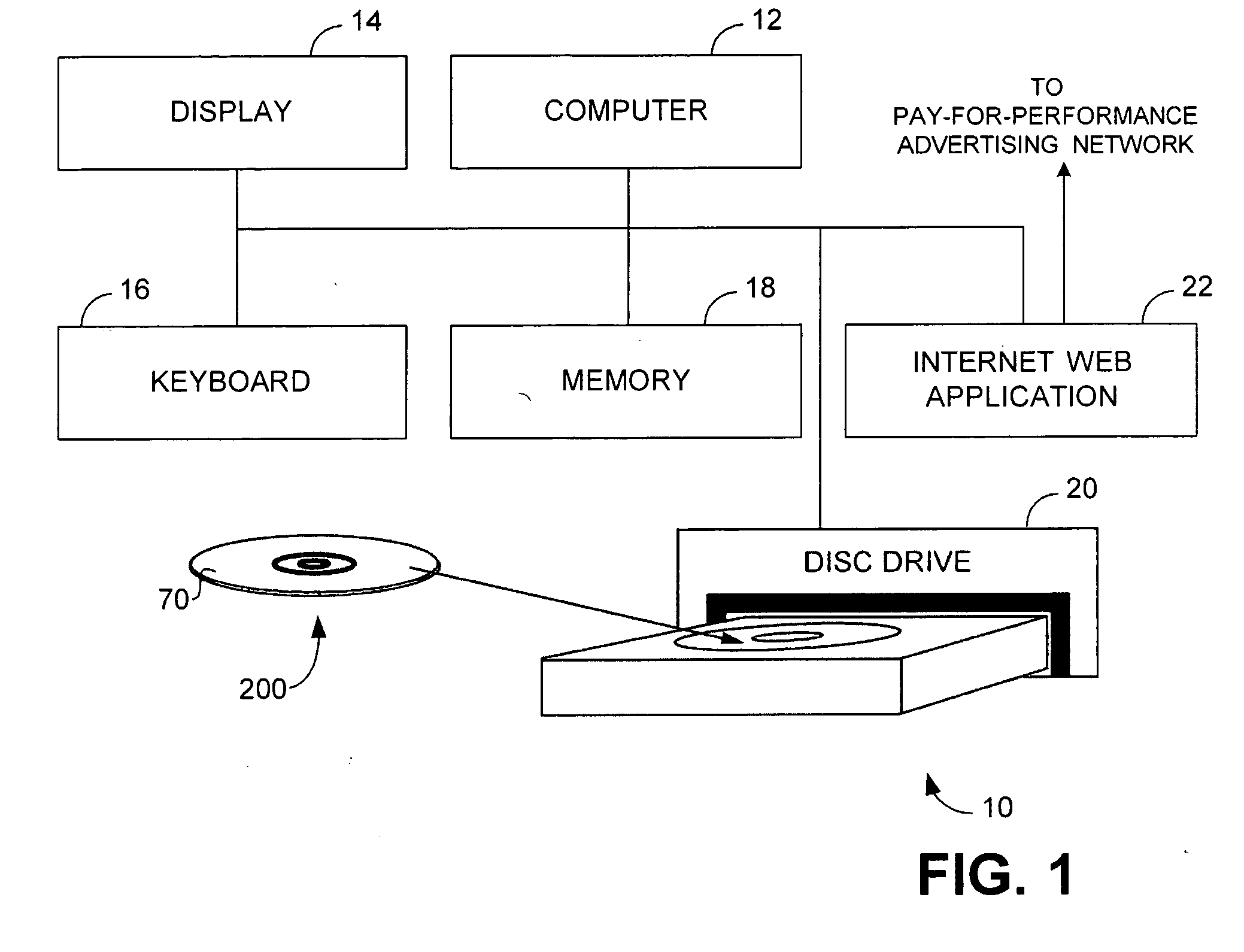
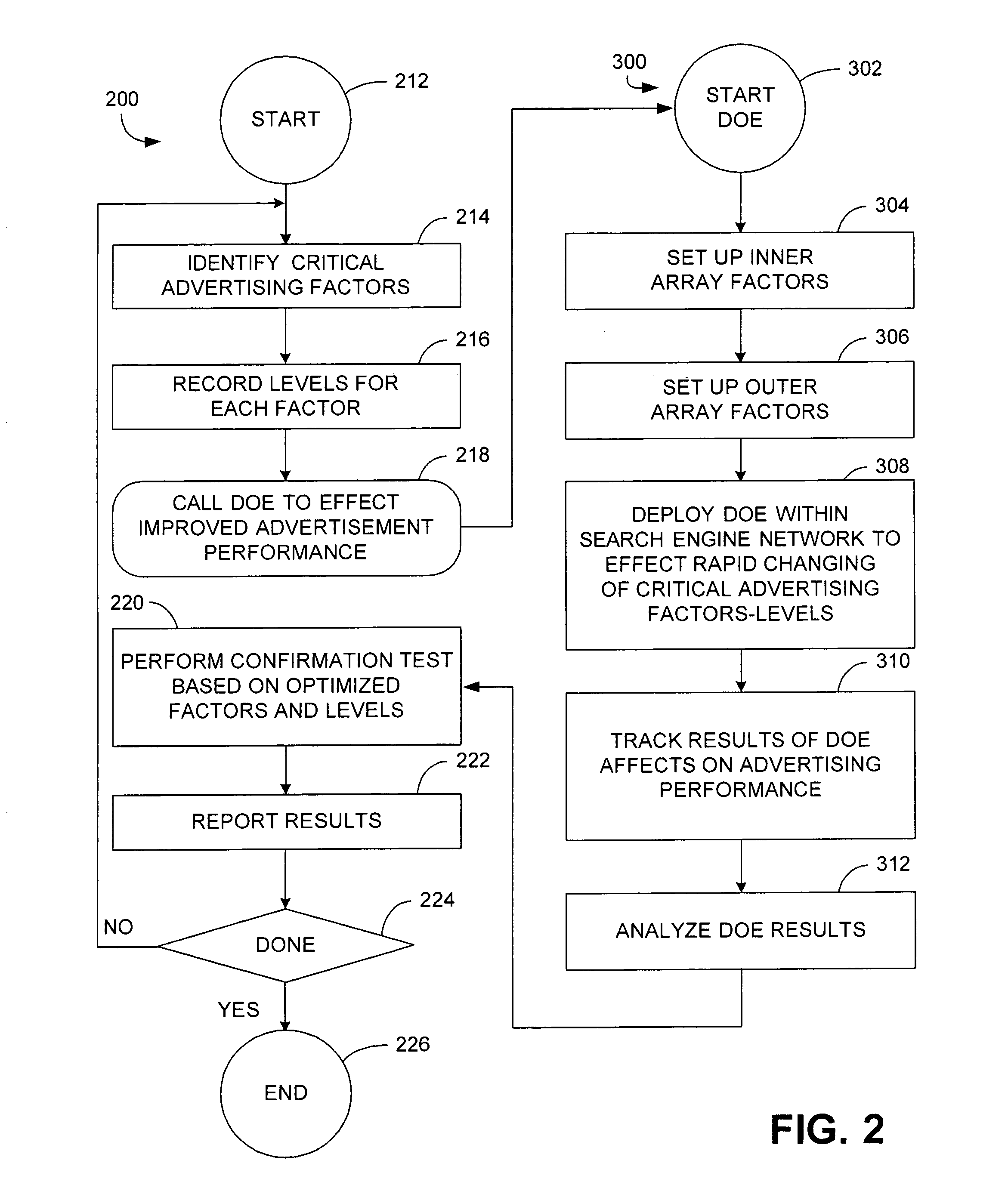
Apparatus and method of identifying critical factors in a pay-for-performance advertising network
InactiveUS20070094072A1Facilitate improved web page performanceImprove performanceMarketingApplication programming interfaceFractional factorial design
An apparatus and method for improving the performance of an Internet website includes a performance processor that identifies a plurality of critical performance factors that facilitate improved website performance and then tests in real time, by utilization of an application programming interface, the influence of individual ones of said plurality of performance factors by application of a fractional factorial design.
Owner:ETICA ENTERTAINMENT
Precise digitized seedling system
InactiveCN104737896AShorten the production cycleIncrease productionClimate change adaptationAgriculture gas emission reductionOxygenCritical factors
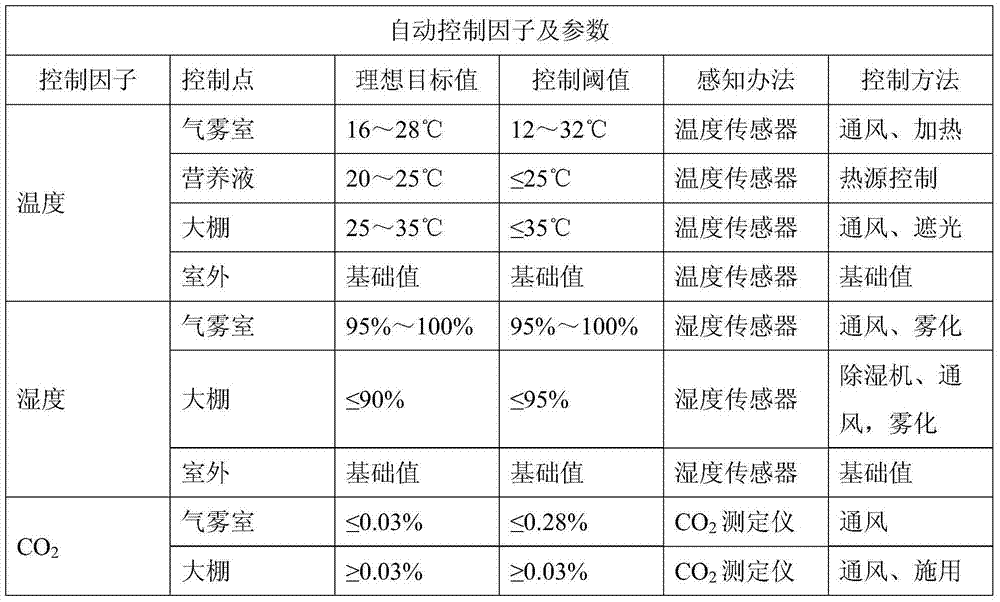
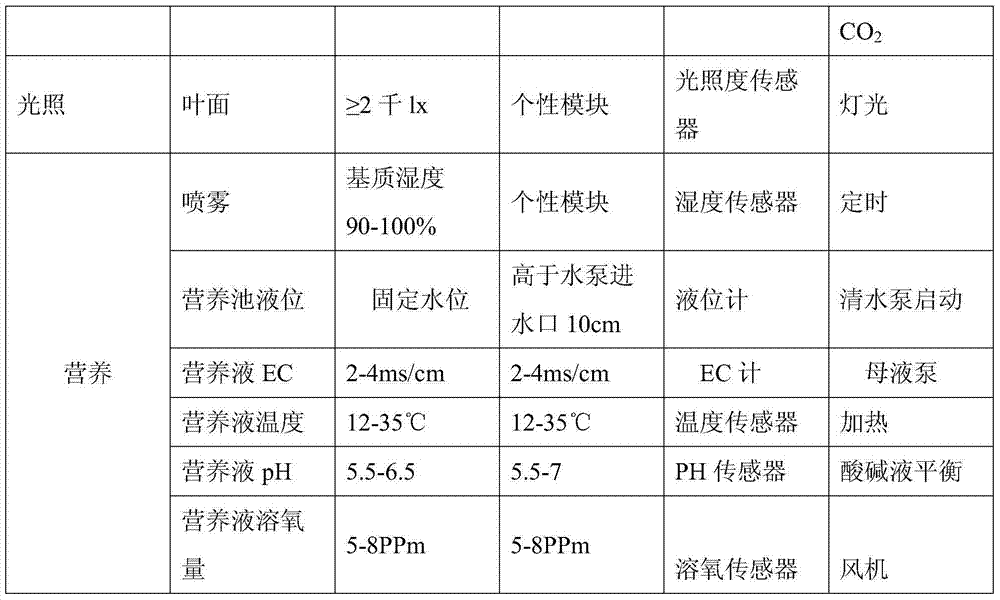
The invention discloses a precise digitized seedling system. Temperature, humidity, water (atomizing periods), gas (oxygen and CO2), fertilizers (inorganic slat and PH value), lights (leaf surface illumination intensity) and critical factors all which impact on plant seedling and growth and are involved in plant atomizing seedling are comprehensively and automatically regulated and controlled by the precise digitized seedling system. When seedlings of tobaccos, flowers and other plants are grown by the precise digitized seedling system, the seedling periods can be shortened, more robust seedlings can be cultivated, and the seedling space is saved; besides the precise digitized seedling system is efficient, reduced in cost, green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:HUNAN NICEWAY CNC TECH
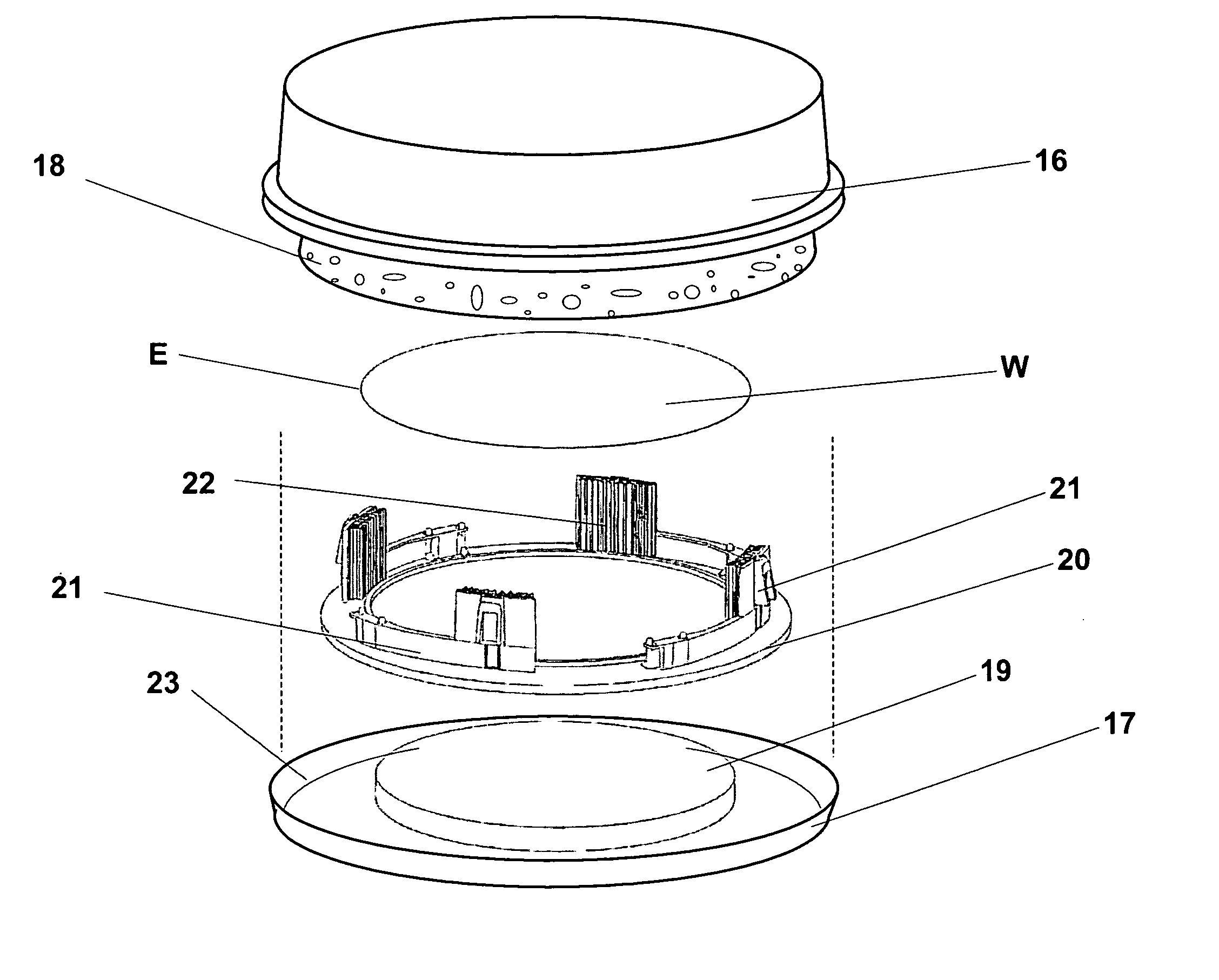
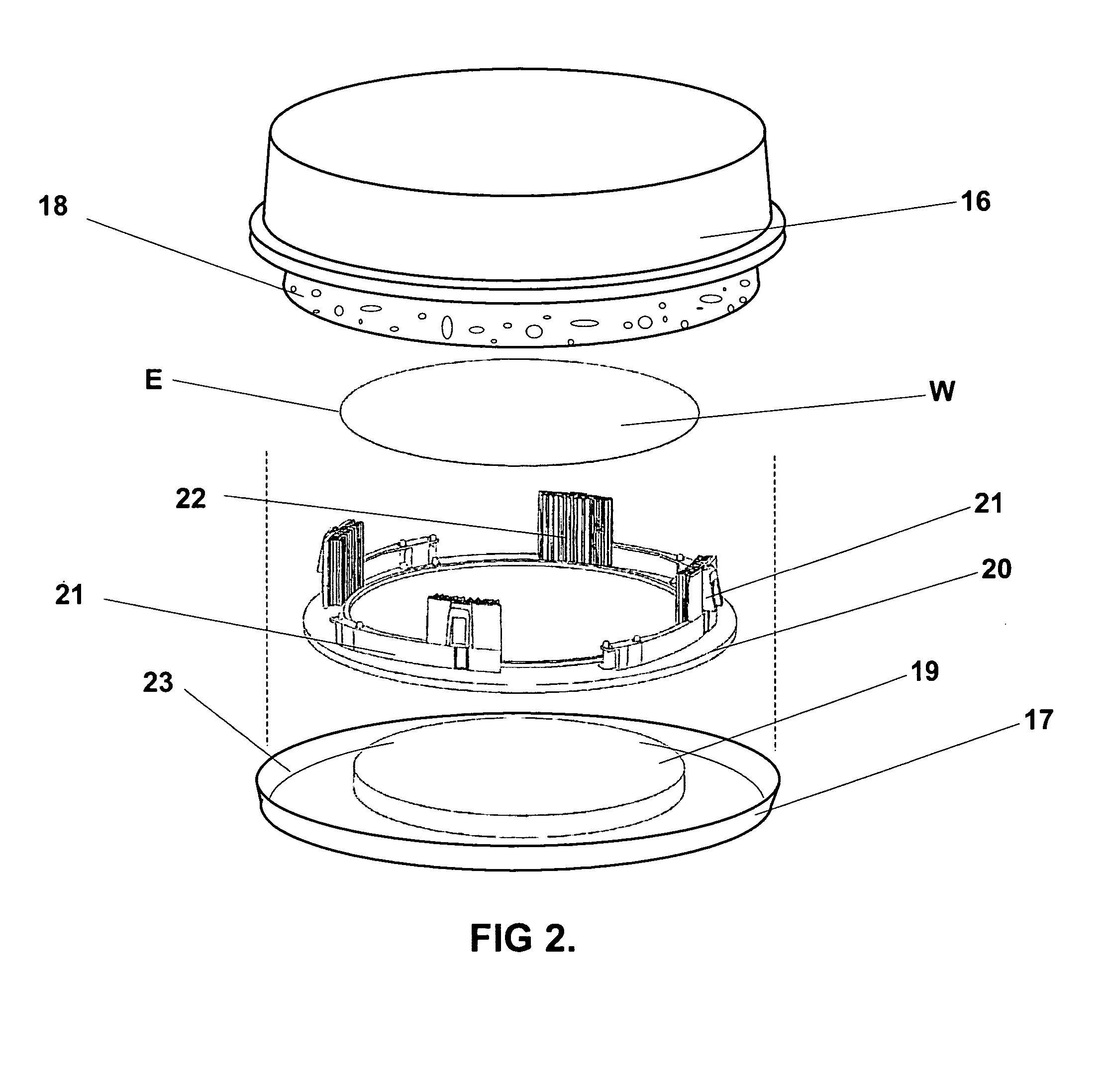
Integrated circuit wafer packaging system and method
InactiveUS7578392B2Reduce yieldReduce scratchesInternal framesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuality assuranceMulti method
A packaging system, hereinafter referred to as the Critical Packaging System, relates to critical issues that associate with sensitive articles such as IC wafers before, during and after shipment phases. The system employs a choice of two or more specialty designed containers, and any one selected design having choices of two or more methods by which to avoid, reduce and / or eliminate wafer damage from breakage, scratches and / or corrosion during shipment phases. For the purpose of maximizing product yield during packaging phases a special apparatus is used to insert wafers within containers without scratch damage. The following programs are used in packaging: (1) Quality Assurance / Certification, (2) Critical Factor Monitoring, and (3) a Recycle and Refurbish Program. These programs are specifically designed to achieve new levels of product yields, reduce product cost, and landfill impact.
Owner:CONVEY INC
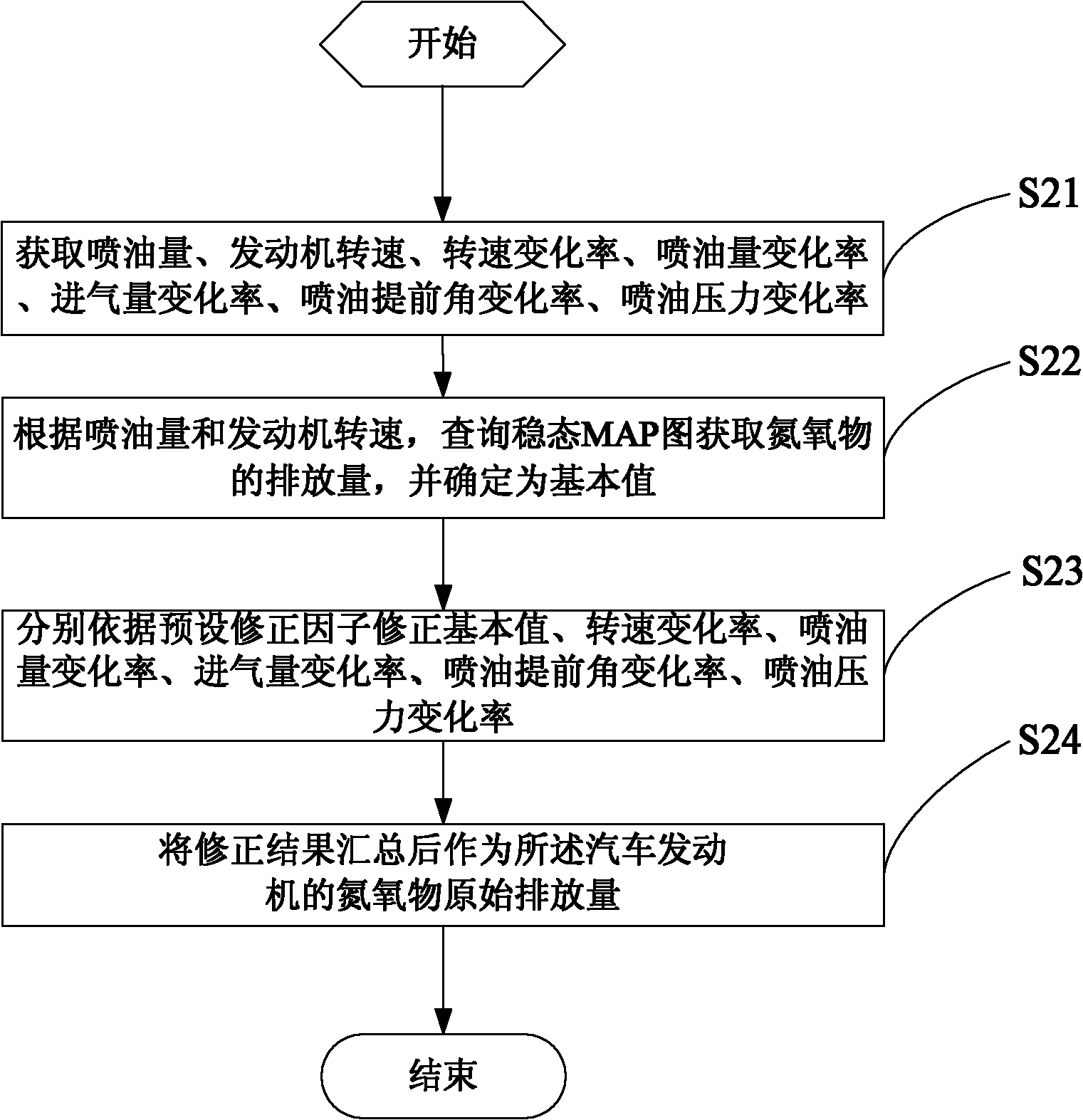
Transient compensation method and system for nitrogen oxide discharging of automobile engine
ActiveCN102102566AReduce mistakesHigh precisionInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust treatment electric controlInjection pressureNitrogen oxides
Owner:WEICHAI POWER CO LTD
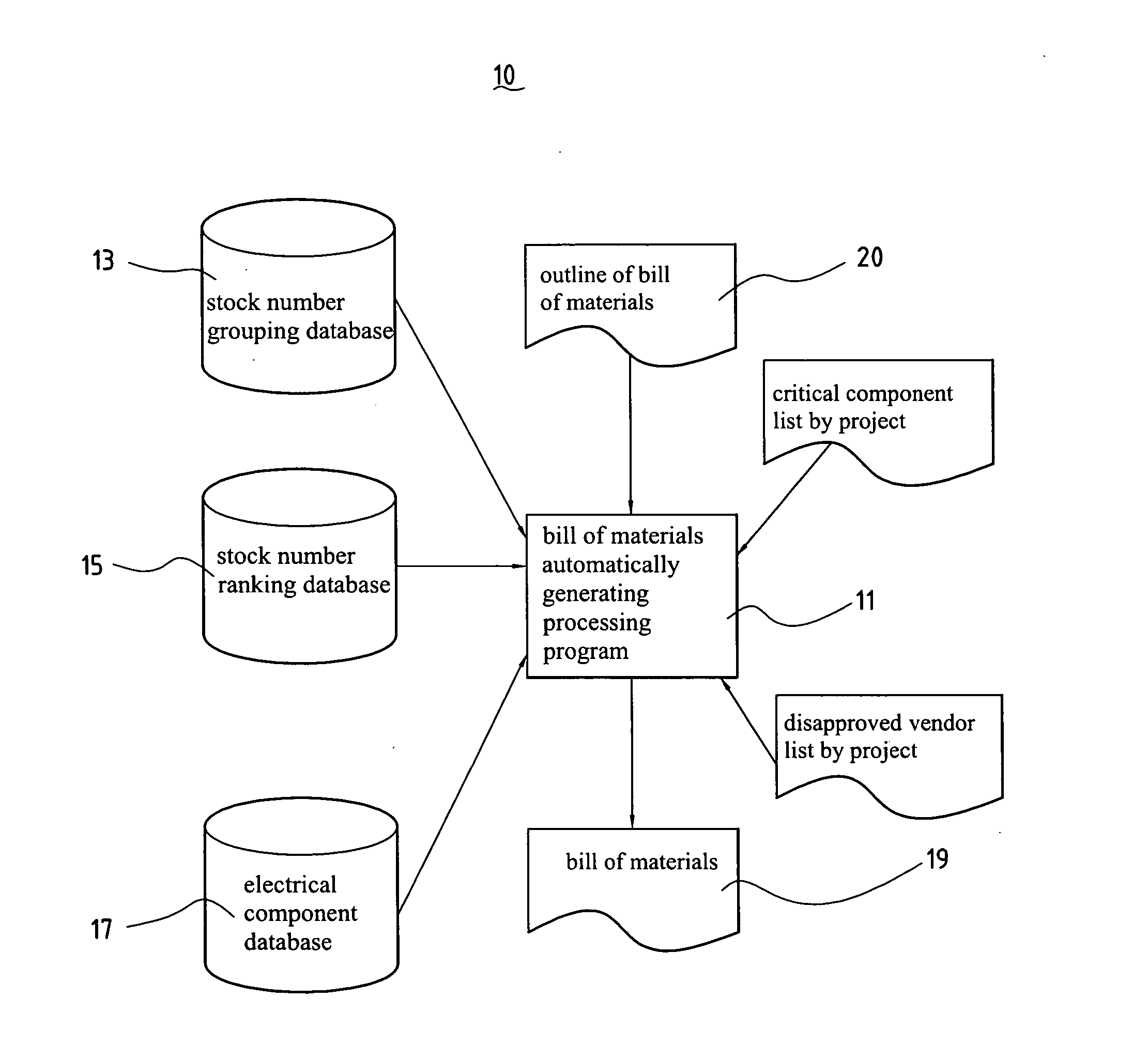
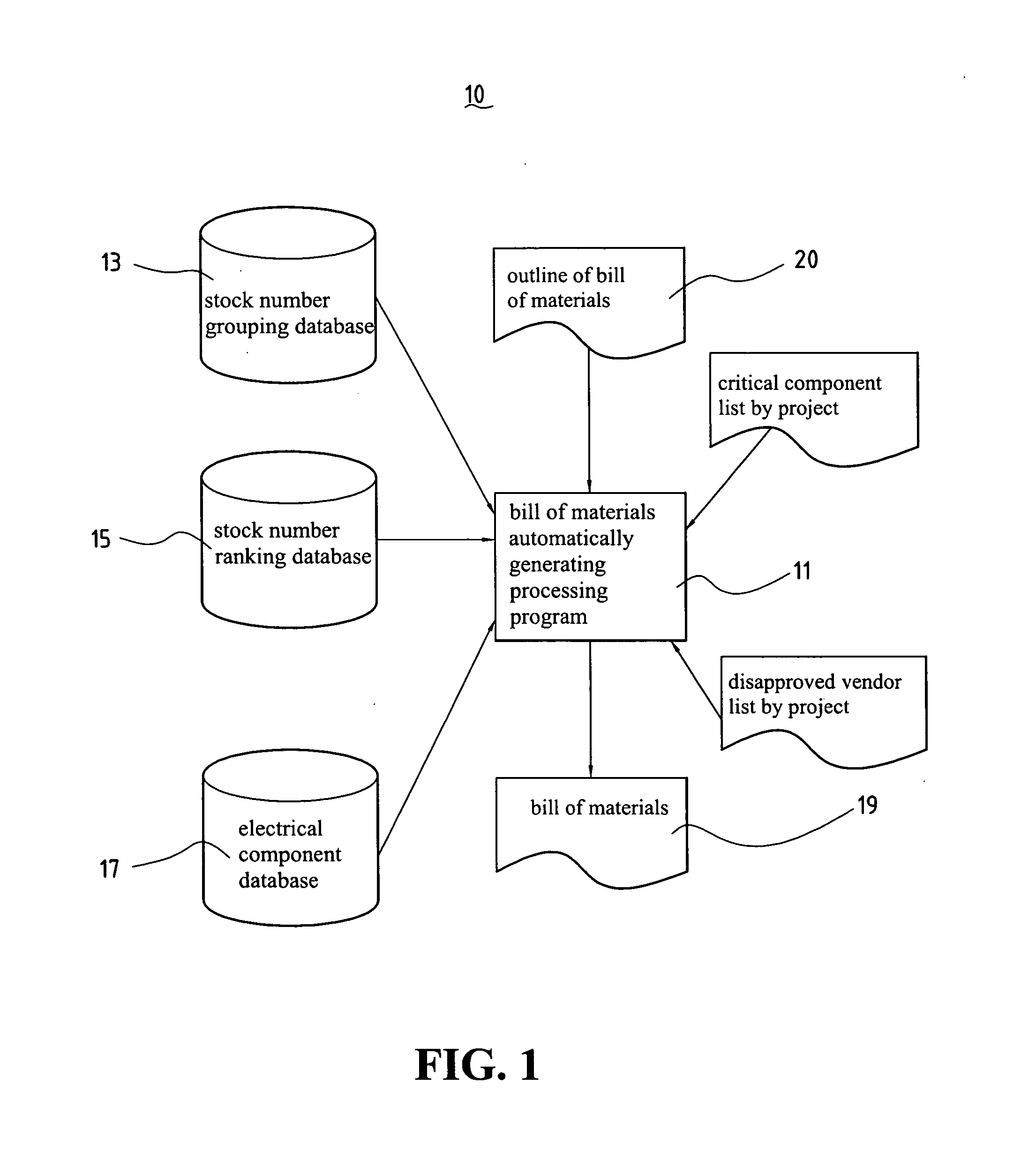
Generating system for automatically generating the bill of materials for electrical products
InactiveUS20060106685A1Animal feeding devicesSpecial data processing applicationsBill of materialsRanking
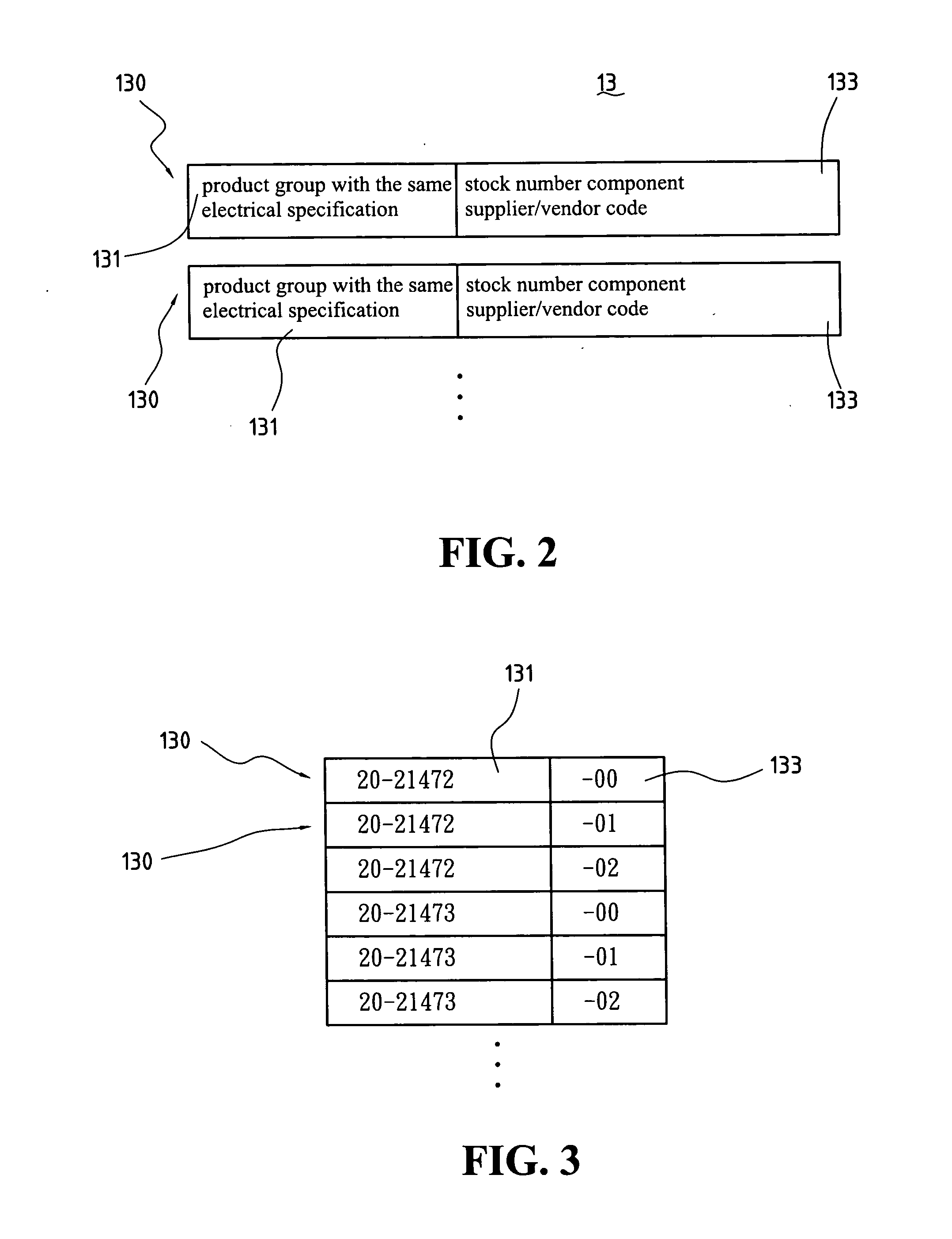
A generating system of automatically generating electrical type product bill of materials of the present invention comprises a stock number grouping database, a stock number ranking database, and a bill of materials automatically generating processing program. The stock number grouping database comprises at least one material group records comprising at least a product group with the same electrical specification and at least one stock number group component supplier / vendor code. The stock number ranking database comprises at least one stock number ranking record, each stock number ranking record corresponds to one of the stock number group records and is used to record an evaluating rate after evaluating with the stock number group records according to a ranking critical factor. The bill of materials automatically generating processing program is used to generate a bill of materials of the corresponding electrical circuit design according to the bill of materials outline of the input electrical circuit design diagram, stock number grouping database, stock number ranking database, and a material choosing critical factor.
Owner:FIRST INTERNATIONAL COMPUTER
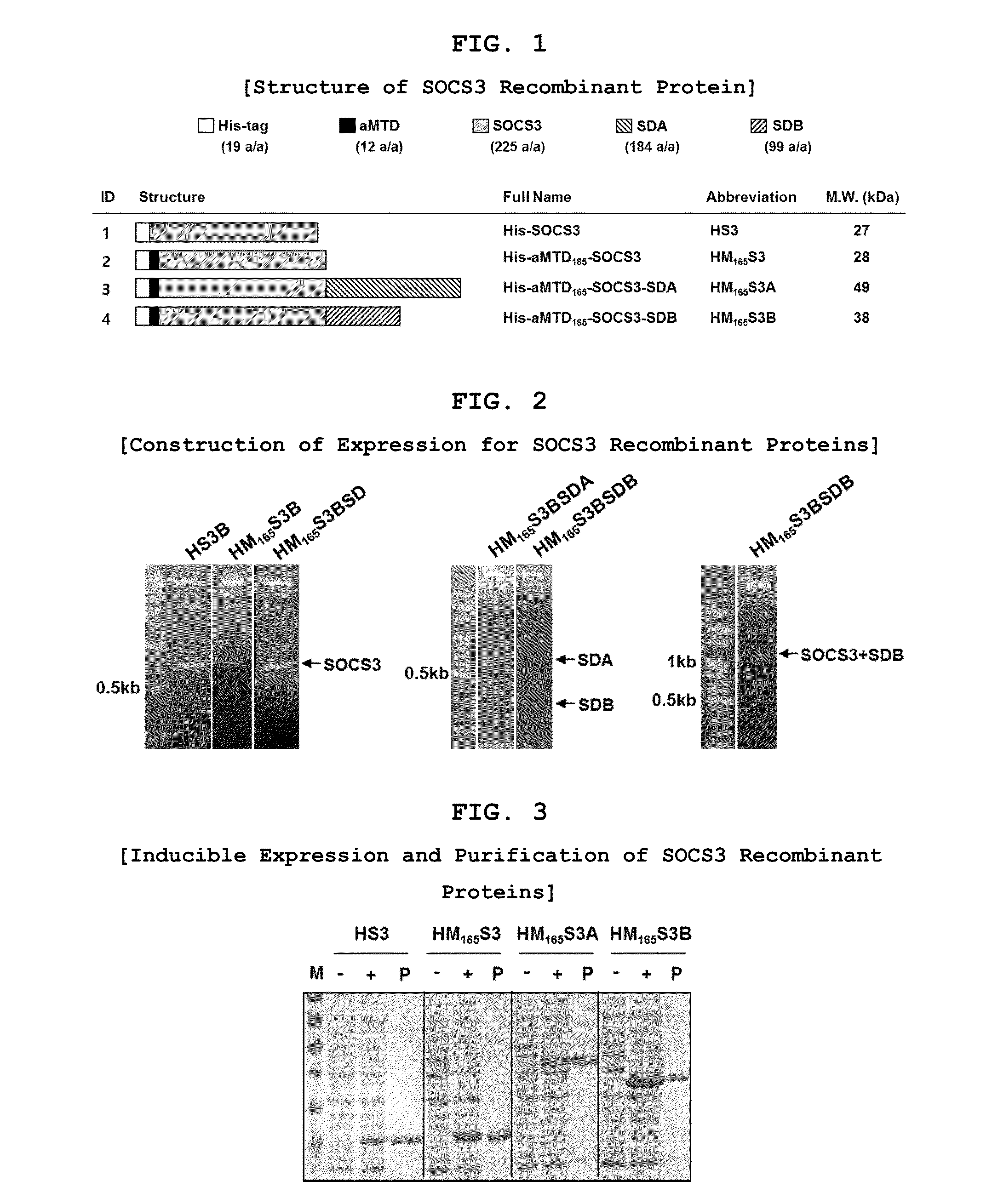
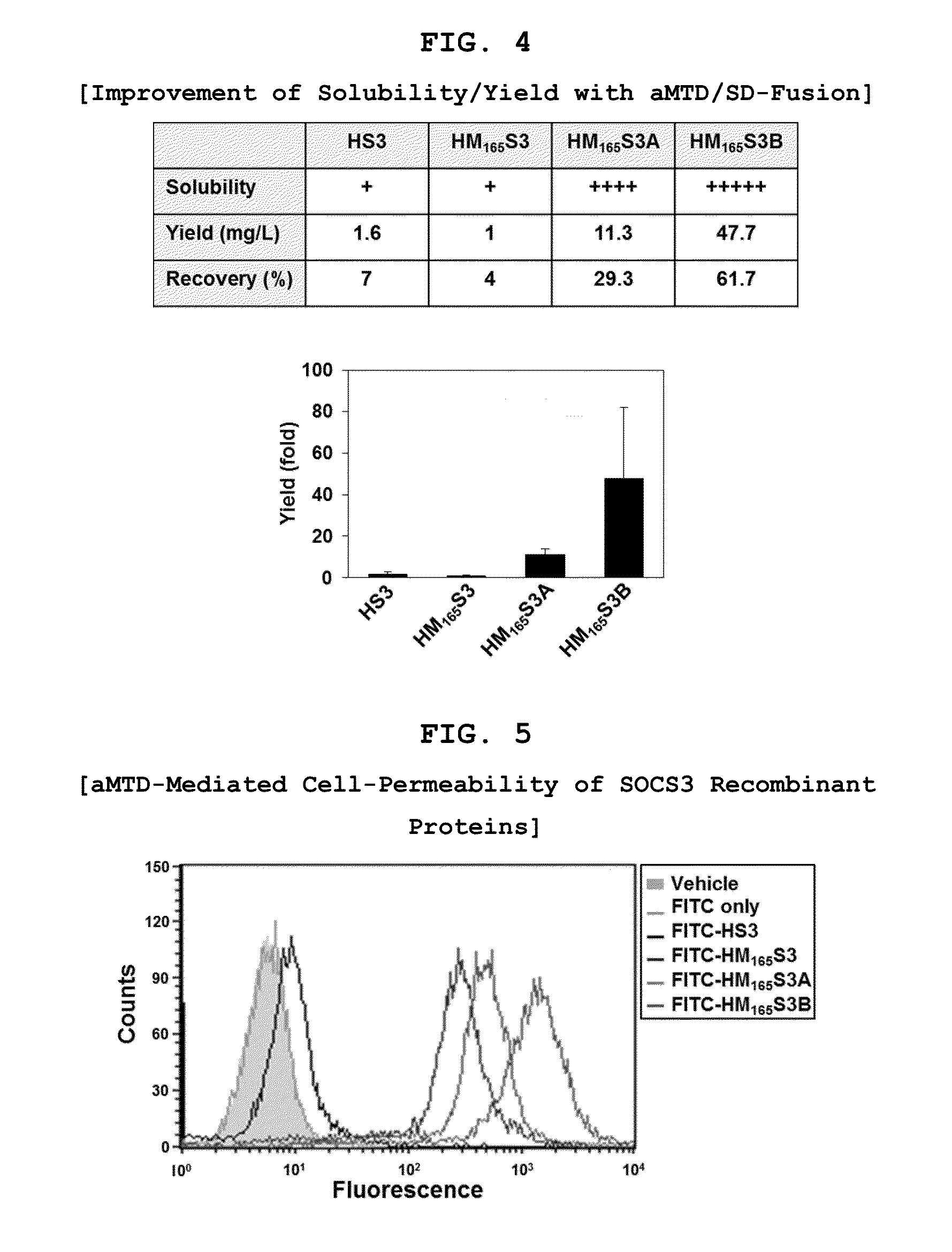
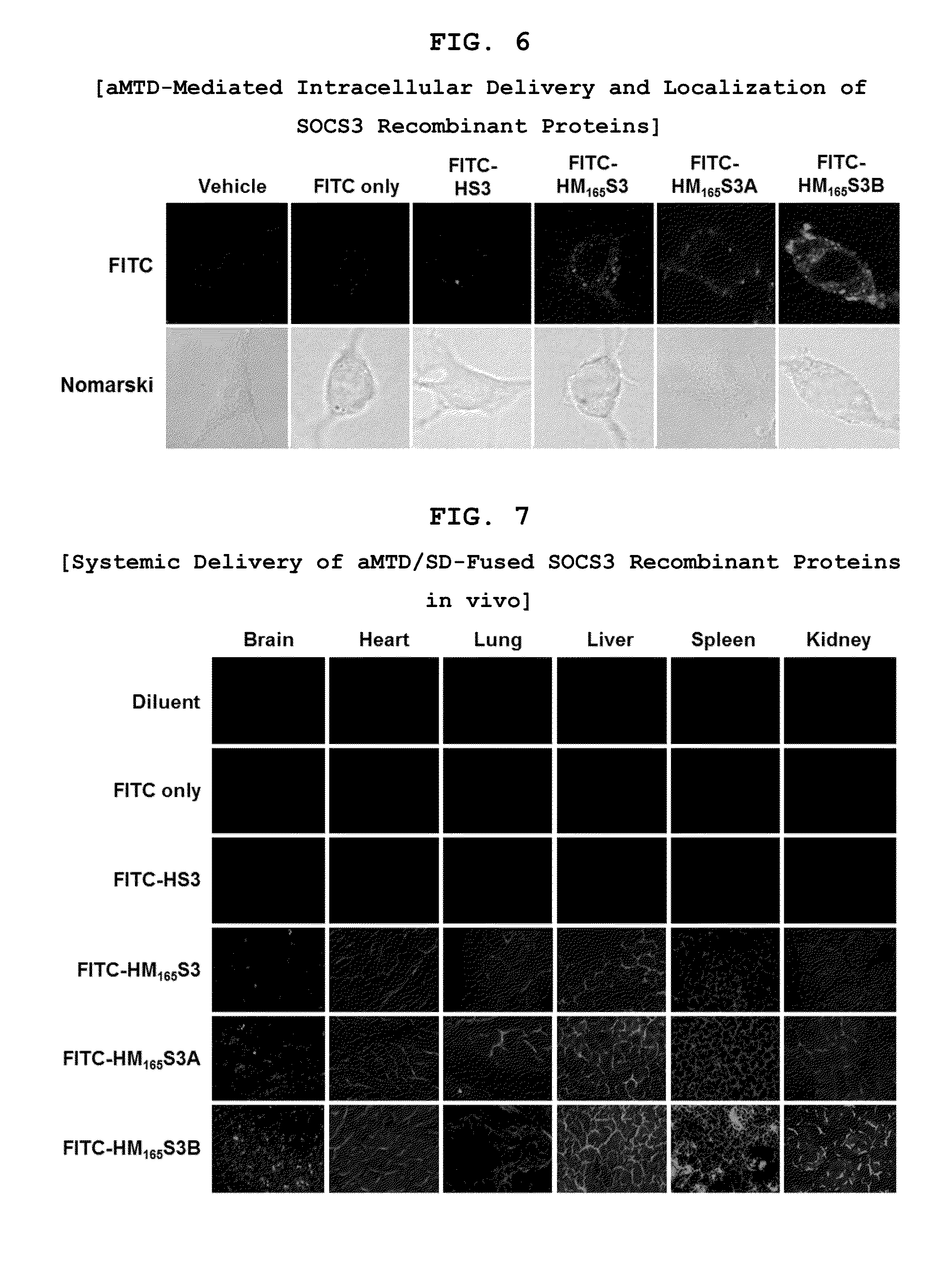
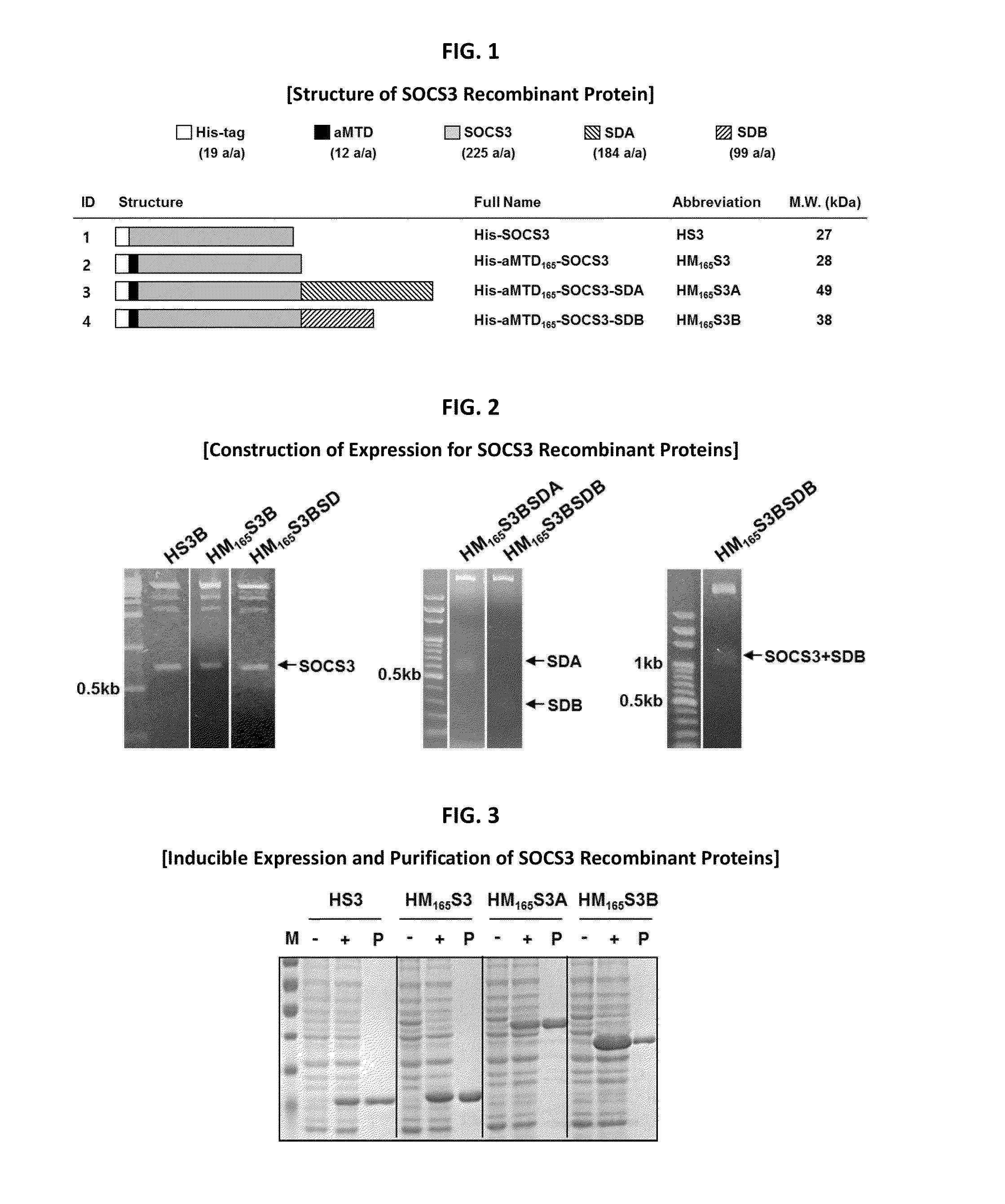
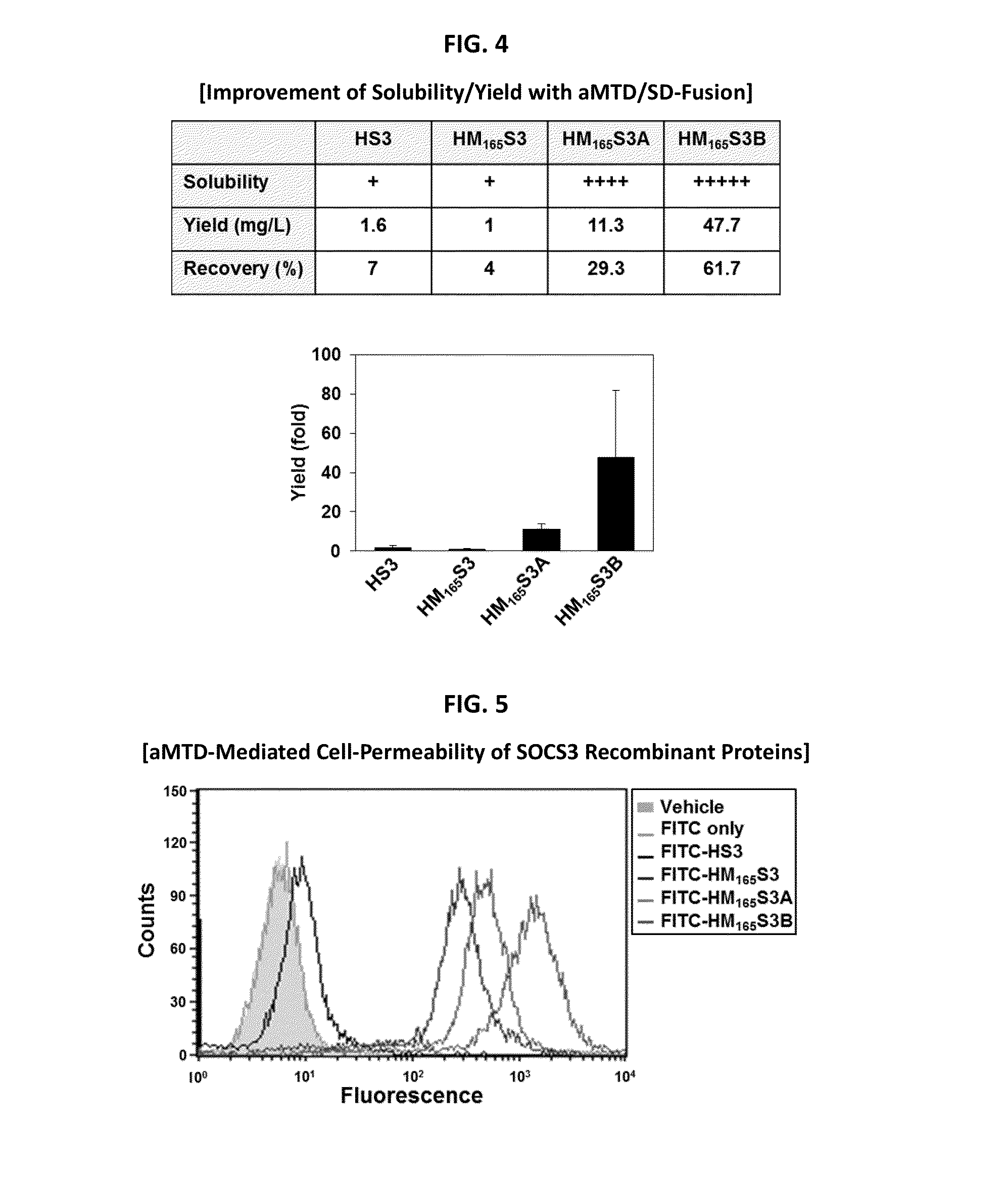
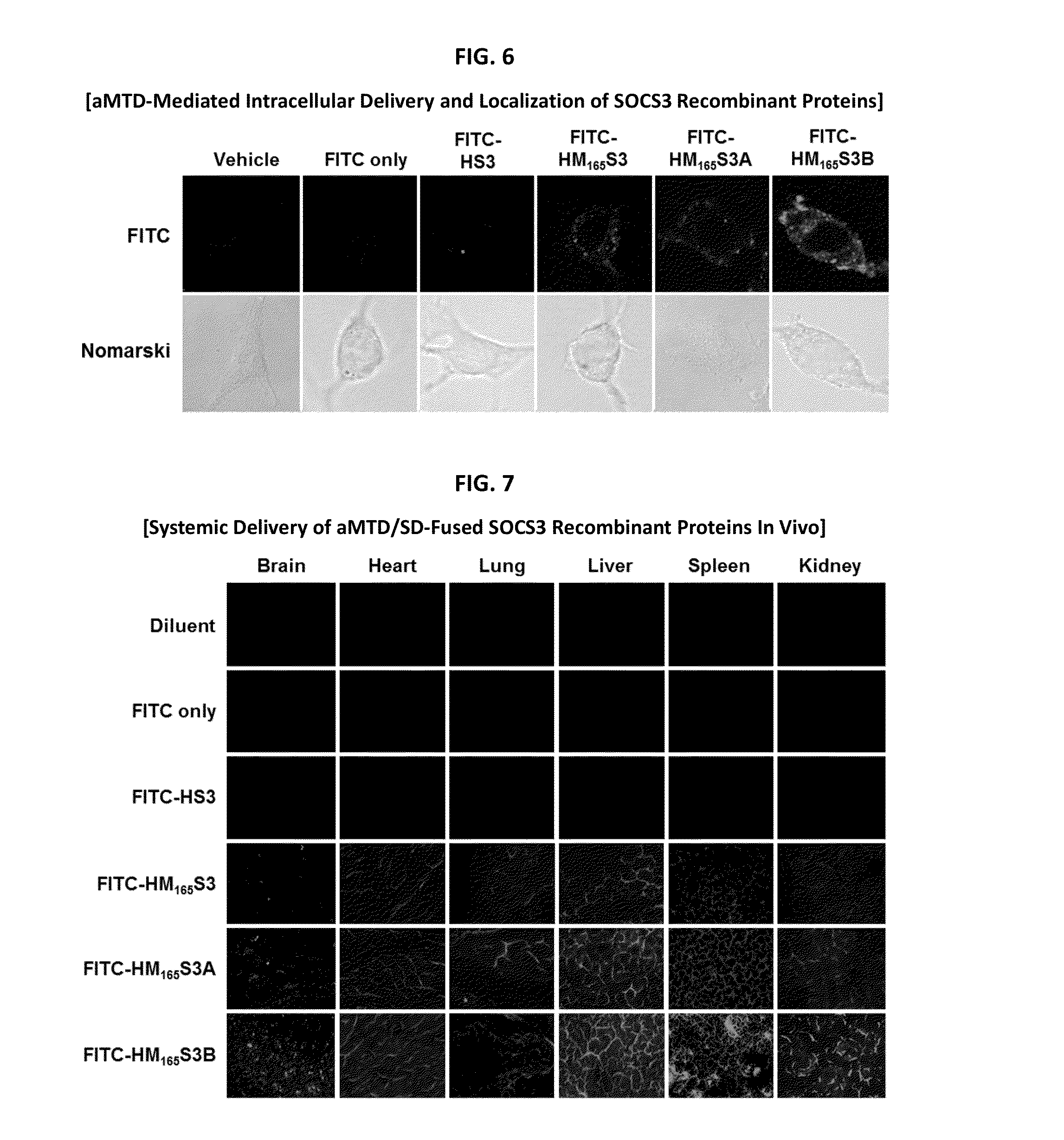
Development of Protein-Based Biotherapeutics That Penetrates Cell-Membrane and Induces Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effect - Improved Cell-Permeable Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling (iCP-SOCS3) Proteins, Polynucleotides Encoding the Same, and Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Compositions Comprising the Same
InactiveUS20160060310A1Good effectImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityHepatocellular carcinoma
Protein transduction exploits the ability of some cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) sequences to enhance the uptake of proteins and other macromolecules by mammalian cells. Previously developed hydrophobic CPPs, named membrane translocating sequence (MTS), membrane translocating motif (MTM) and macromolecule transduction domain (MTD), are able to deliver biologically active proteins into a variety of cells and tissues. Various cargo proteins fused to these CPPs have been used to test the functional and / or therapeutic efficacy of protein transduction. For example, recombinant proteins consisting of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 protein (CP-SOCS3) fused to the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 4-derived MTM were developed to inhibit inflammation and apoptosis. However, CP-SOCS3 fusion proteins expressed in bacteria were hard to purify in soluble form. To address these critical limitations, CPP sequences called advanced MTDs (aMTD) have been developed in this art. This is accomplished by (i) analyzing previous developed hydrophobic CPP sequences to identify specific critical factors (CFs) that affect intracellular delivery potential and (ii) constructing artificial aMTD sequences satisfied for each critical factor. In addition, solubilization domains (SDs) have been incorporated into the aMTD-fused SOCS3 recombinant proteins to enhance solubility with corresponding increases in protein yield and cell- / tissue-permeability. These recombinant SOCS3 proteins fused to aMTD / SD having much higher solubility / yield and cell- / tissue-permeability have been named as improved cell-permeable SOCS3 (iCP-SOCS3) proteins. Previously developed CP-SOCS3 proteins fused to MTM were only tested or used as anti-inflammatory agents to treat acute liver injury. In the present art, iCP-SOCS3 proteins have been tested for use as anti-cancer agents in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Since SOCS3 is frequently deleted in and loss of SOCS3 in hepatocytes promotes resistance to apoptosis and proliferation, we reasoned that iCP-SOCS3 could be used as a protein-based intracellular replacement therapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. The results support this reasoning: treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma cells with iCP-SOCS3 results in reduced cancer cell viability, enhanced apoptosis and loss of cell migration / invasion potential. Furthermore, iCP-SOCS3 inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in a subcutaneous xenografts model. In the present invention with iCP-SOCS3 fused to an empirically determined combination of newly developed aMTD and customized SD, macromolecule intracellular transduction technology (MITT) enabled by the advanced MTD may provide novel protein therapy against hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:CELLIVERY THERAPEUTICS
Development of Protein-Based Biotherapeutics That Penetrates Cell-Membrane and Induces Anti-Angiogenic Effect - Improved Cell-Permeable Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling (iCP-SOCS3) Proteins, Polynucleotides Encoding the Same, and Anti-Angiogenic Compositions Comprising the Same
InactiveUS20160060313A1Good effectImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSolubilityApoptosis
In principle, protein-based biotherapeutics offers a way to control biochemical processes in living cells under non-steady state conditions and with fewer off-target effects than conventional small molecule therapeutics. However, systemic protein delivery in vivo has been proven difficult due to poor tissue penetration and rapid clearance. Protein transduction exploits the ability of some cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) sequences to enhance the uptake of proteins and other macromolecules by mammalian cells. Previously developed hydrophobic CPPs—named membrane translocating sequence (MTS), membrane translocating motif (MTM) and macromolecule transduction domain (MTD)—are able to deliver biologically active proteins into a variety of cells and tissues. Various cargo proteins fused to these CPPs have been used to test the functional and / or therapeutic efficacy of protein transduction. Previously, recombinant proteins consisting of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOSC3) fused to the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 4-derived MTM were developed to inhibit inflammation and apoptosis. However, this SOCS3 fusion proteins expressed in bacteria cells were hard to be purified in soluble form. To address these critical limitations, CPP sequences called advanced MTDs (aMTDs) have been developed in this art. The development of this art has been accomplished by (i) analyzing previous developed hydrophobic CPP sequences to identify specific critical factors (CFs) that affect intracellular delivery potential and (ii) constructing artificial aMTD sequences that satisfy each critical factor. Furthermore, solubilization domains (SDs) have been incorporated into the aMTD-fused SOCS3 recombinant proteins to enhance solubility with corresponding increases in protein yield and cell- / tissue-permeability. These recombinant SOCS3 proteins fused to aMTD / SD having much higher solubility / yield and cell- / tissue-permeability have been named as improved cell-permeable SOCS3 (iCP-SOCS3) proteins. Previously developed SOCS3 recombinant proteins fused to MTM were only tested or used as anti-inflammatory agents to treat acute liver injury. In the present art, iCP-SOCS3 proteins have been tested for use as anti-angiogenic agents. Since SOCS3 is known to be an endogenous inhibitor of pathological angiogenesis, we reasoned that iCP-SOCS3 could be used as a protein-based intracellular replacement therapy for inhibiting angiogenesis in tumor cells. The results demonstrated in this art support this following reasoning: Cancer treatment with iCP-SOCS3 results in reduced endothelial cell viability, loss of cell migration potential and suppressed vascular sprouting potentials. In the present invention with iCP-SOCS3, where SOCS3 is fused to an empirically determined combination of newly developed aMTD and customized SD, macromolecule intracellular transduction technology (MITT) enabled by the advanced MTDs may provide novel protein therapy against cancer cell-mediated angiogenesis.
Owner:CELLIVERY THERAPEUTICS
Single daily dosage form for prevention and treatment of metabolic syndrome
InactiveUS9056134B2Effective treatmentImprove complianceBiocideSalicyclic acid active ingredientsCvd riskCritical factors
The present invention is in the fields of medicine, pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, endocrinology and cardiology. The invention provides compositions comprising a statin, an inhibitor of the angiotensin converting enzyme, an antiplatelet compound and an anti-hyperglycemic compound for use in the treatment and / or prevention of cardiometabolic risk factors of Metabolic Syndrome and treatment and / or prevention of Metabolic Syndrome. The present invention provides for the use of such compositions in the manufacture of products for treatment and / or prevention of Metabolic Syndrome. The biguanide metformin of the composition could be present in extended release form allowing its use together with the other drugs in a single dosage form at low dose. This combination of drugs in a single daily dosage greatly improves compliance and adherence to treatment which is a critical factor for treating patients with Metabolic Syndrome.
Owner:NUCITEC DE C V
Maintenance management of a machine
ActiveUS7496475B2Programme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsMaintenance managementCritical factors
Methods of providing maintenance management of a machine are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method involves identifying a machine component failure that, if not repaired, will result in a functional failure of the machine. A criticality factor is assigned to the machine component failure based on at least a probability of occurrence of the functional failure and a consequence of the functional failure to a machine user. A maintenance task is generated to repair the machine component failure, and a triggering condition that activates the maintenance task is defined. The method further involves conducting a machine repair in response to a detection of the triggering condition, and maintaining a record that includes information relating to the conducted machine repair. The method of providing maintenance management is also modified based on at least the record.
Owner:SOLAR TURBINES
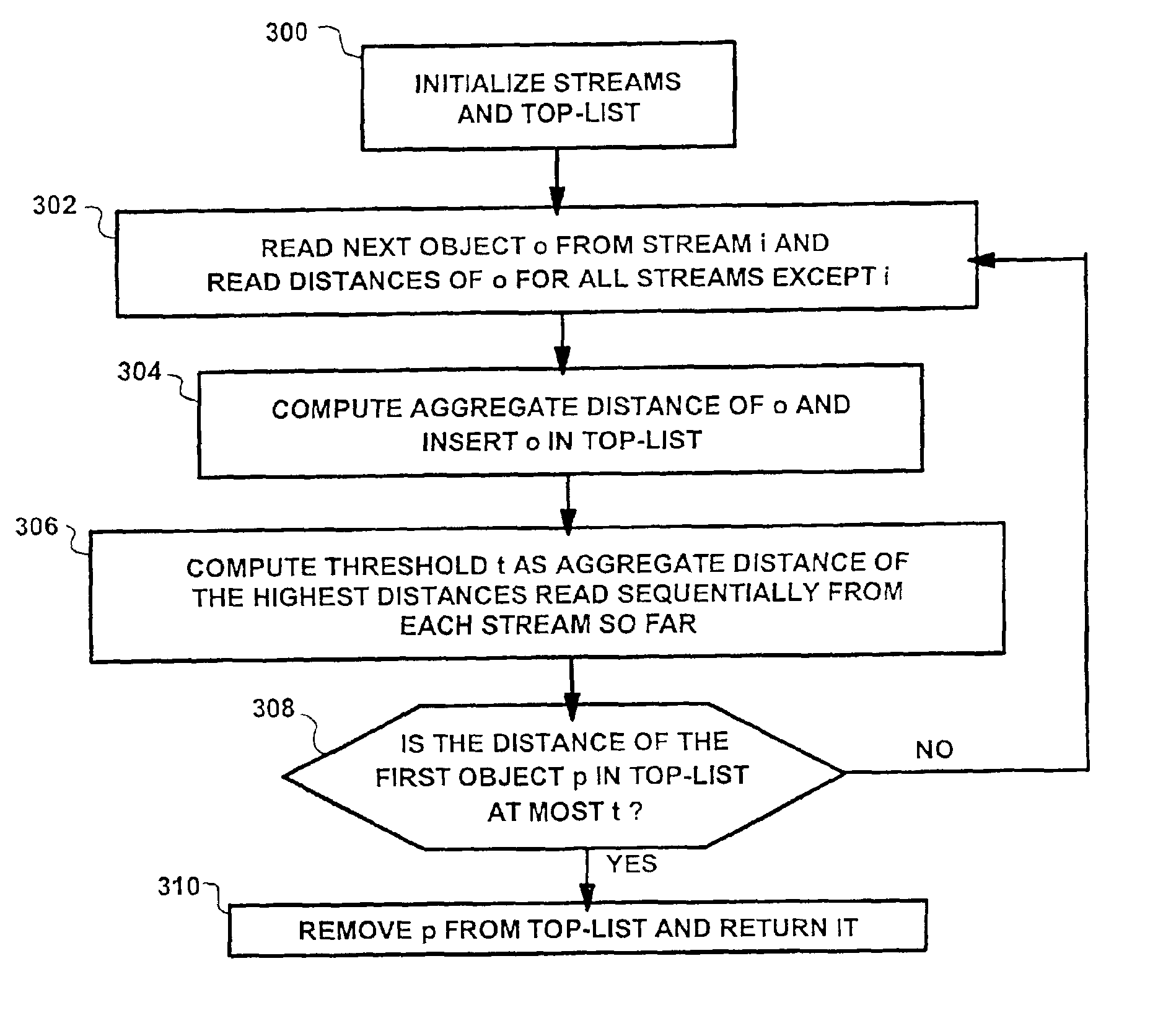
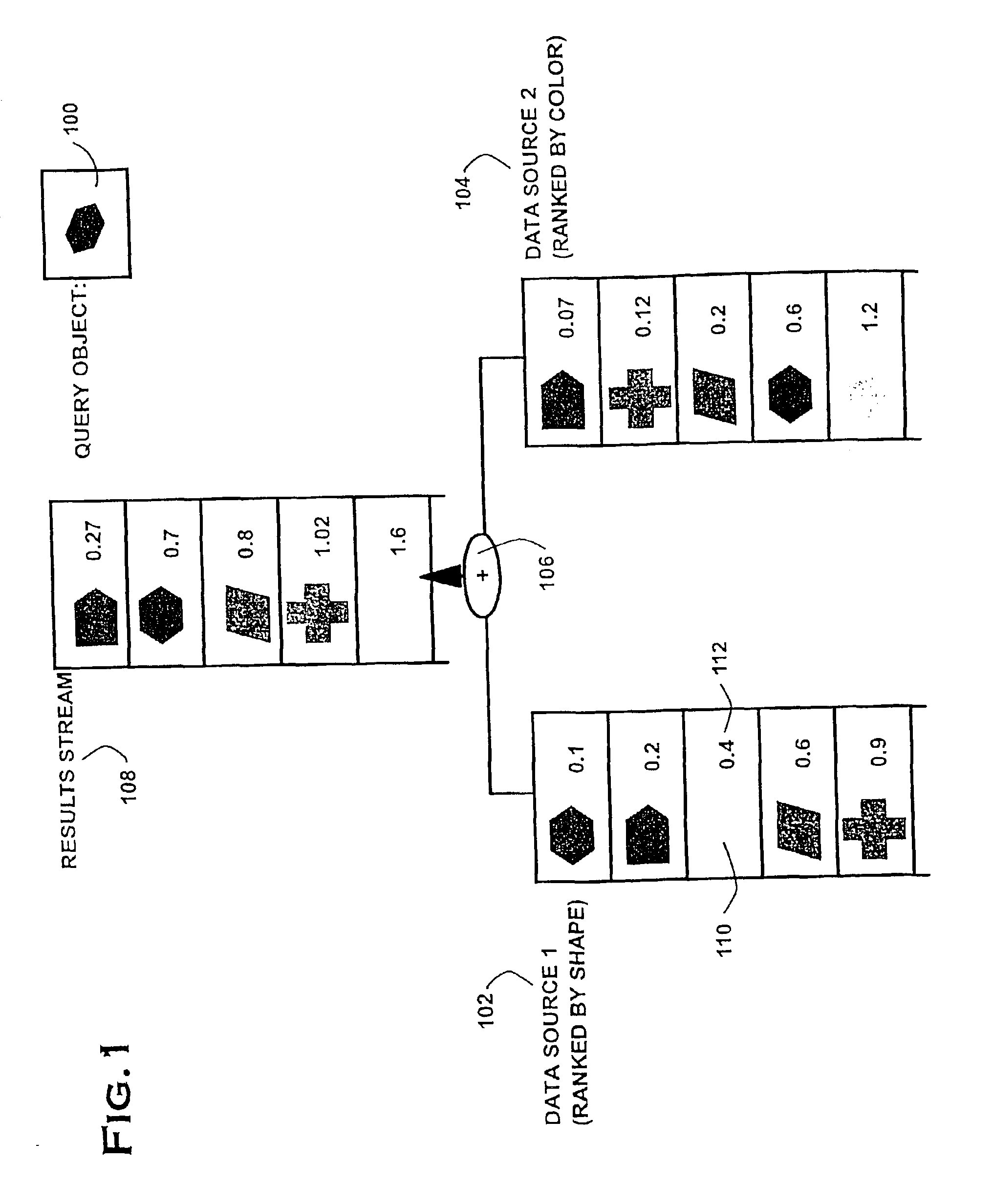
Dynamic optimization of multi-feature queries
InactiveUS6917932B2Minimize query response timeReduce query costData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalCost evaluationDynamical optimization
The present invention provides an elegant solution for processing multi-feature queries, which considers the differing access costs associated with each feature. Access cost is a critical factor in determining how individual features should be processed in terms of retrieving through sorted or random access, and, hence, in minimizing the overall query response time. The present invention operates dynamically during query processing and seeks to minimize the total query cost in terms of number of features retrieved and cost for access. It works by evaluating different combinations of feature access plans (sorted and random access) according to the number of retrieved features and forward access costs, and it selects the lowest cost plan. Experimental results on practical data show a significant speed-up in multi-features queries using the proposed solution.
Owner:SINOEAST CONCEPT
Ion thruster operation life evaluation method based on grid corrosion
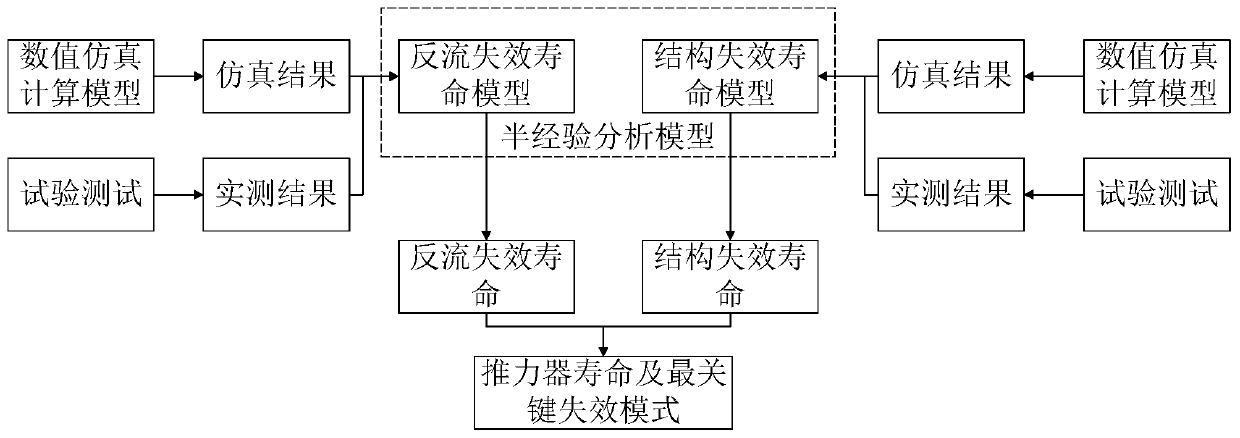
ActiveCN111199099AQuickly determine the most critical factors affecting lifeReduce processing stepsSustainable transportationStructural/machines measurementTest measurementProcess engineering
The invention discloses an ion thruster operation life evaluation method based on grid corrosion. The method comprises the following steps of substituting a test measurement result and a numerical simulation calculation result into a semi-empirical analysis model; calculating to obtain the operation life of the ion thruster; evaluating the operation life of the ion thruster by using limited test data. Therefore, the most critical factors of the influence of the service life of the ion thruster can be quickly determined, the links of machining, manufacturing, assembling, testing, testing and the like of the thruster after failure are effectively reduced, the production cost of products is reduced, and the application range and the application value of the ion thruster can be predicted in advance.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
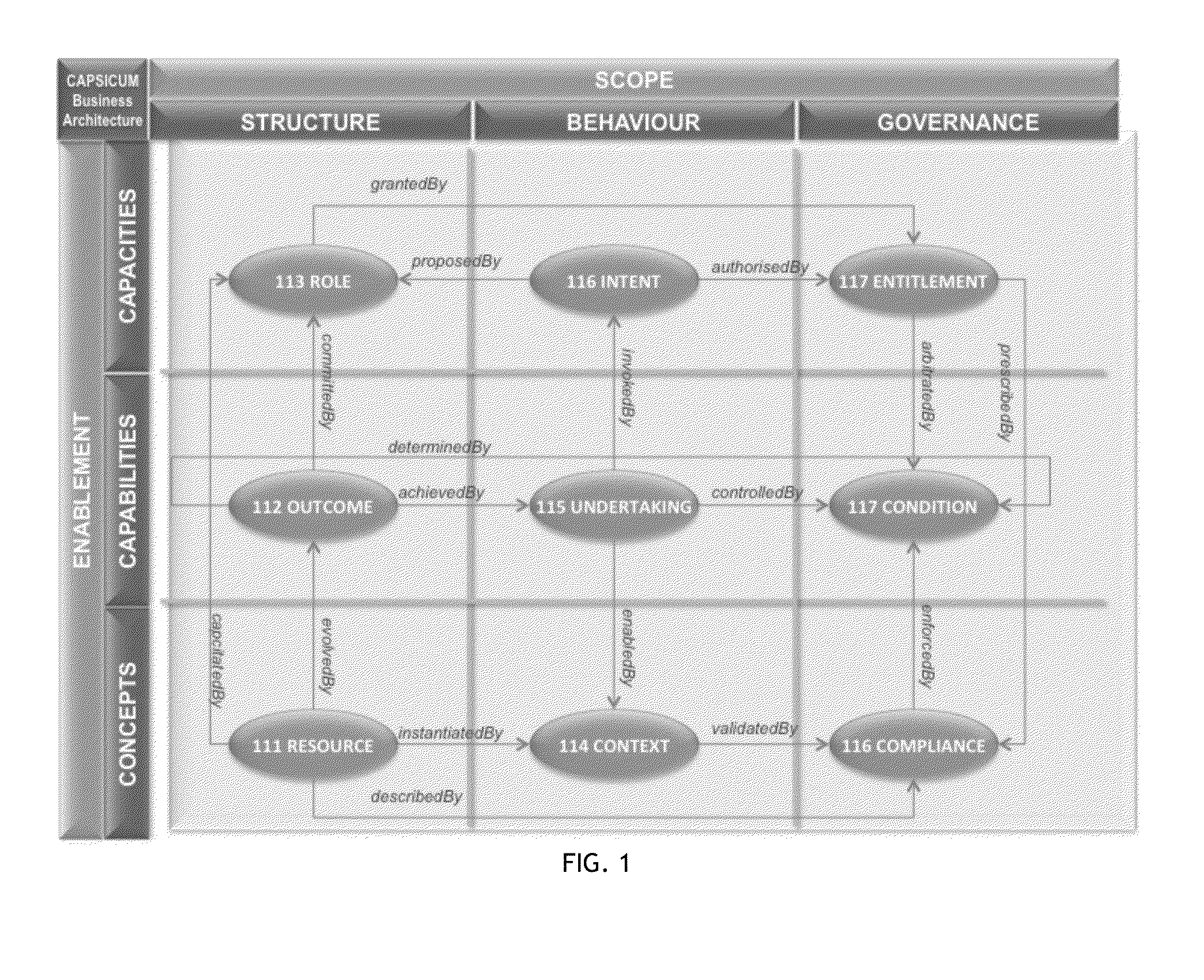
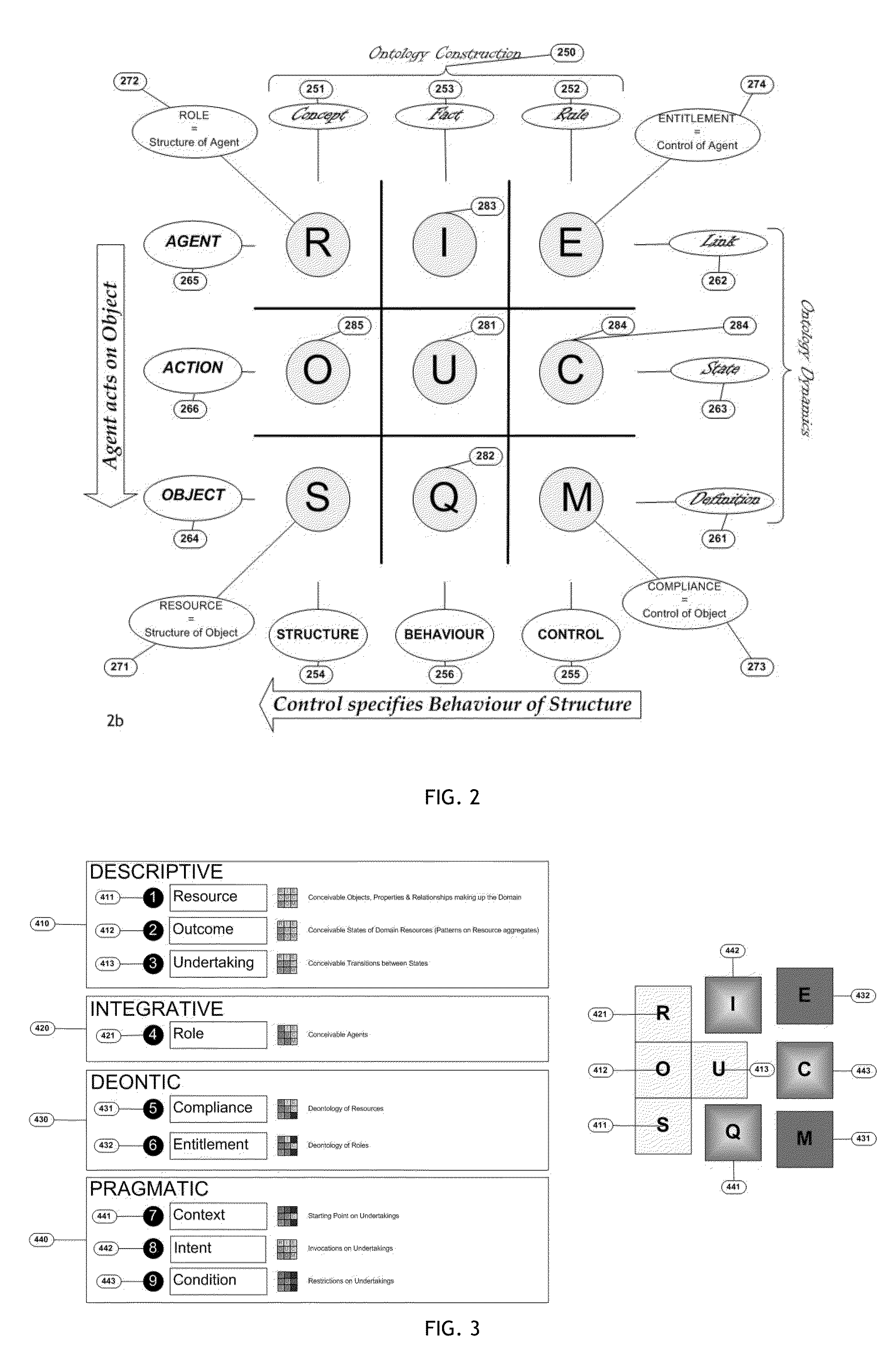
Method and system for the discovery and description of business endeavours
A key ingredient in the design and development of enterprise software systems is a precise description of the business endeavour. In practice the engineering designs for corporate systems are surprisingly poorly articulated due to the difficulty organisations face in clearly defining their business needs in a structured and unambiguous manner. One problem is that the notations used in business process specifications are technical in nature, notoriously complex and not particularly intelligible to business stakeholders. Further, since the business environment is highly dynamic, static documentation is quickly out-of-date and rarely reusable beyond the lifespan of any particular project. There is a constant disconnect between the fluid, evolving nature of business strategies and the brittle, rigid nature of process automation. As a consequence, business stakeholders have little direct control over the structure, behaviour and governance of information systems, which is a major contributing factor in the pervasive issue of system inflexibility and adaptability. This invention provides a method and corresponding system design for addressing these limitations by articulating a business endeavour in a comprehensive, structured conceptual model that is independent of underlying technology and responsive to the dynamics of business strategy.
Owner:ROACH TERENCE MALCOLM
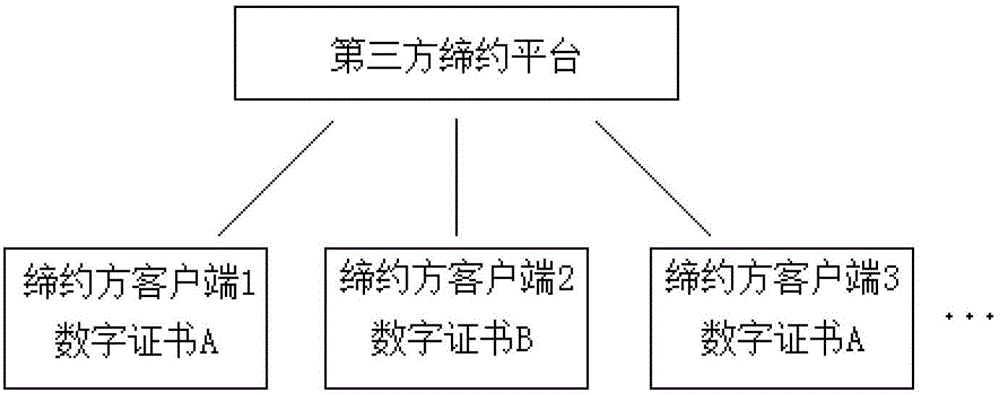
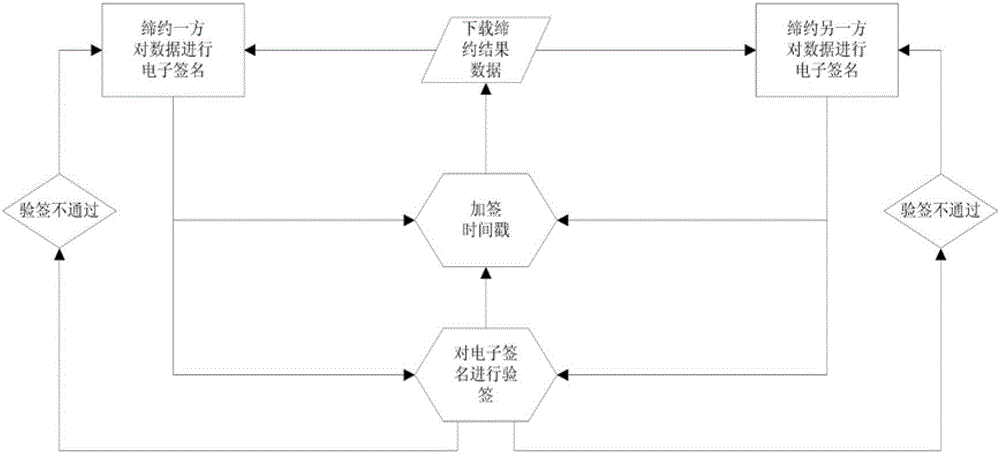
Third-party platform electronic contracting system based on electronic signature technology
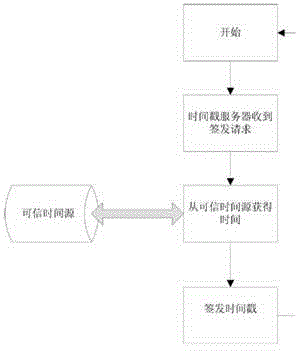
ActiveCN102724042AGuaranteed complete and authentic certificationEnsure safetyUser identity/authority verificationThird partyTimestamp
A third-party platform electronic contracting system based on the electronic signature technology comprises contracting party client sides and a third-party contracting platform. Contracting parties hold the same or different digital certificates, and the third-party contracting platform is used for electronic contracting, can provide integrated verification and timestamps for different certificate chains, certificate states and certificate validity periods and guarantees accuracy and validity of mutual electronic contracting of the contracting parties held the same or different digital certificates issued by the CA (certification authority). The third-party platform electronic contracting system uses the electronic signature technology for decomposition, simulation, reconstruction, recombination and solidification of critical steps, critical factors and critical processes, so that technological holes of existing electronic contracting are made up, and accuracy and validity of electronic contracting are guaranteed.
Owner:江苏买卖网电子商务有限公司
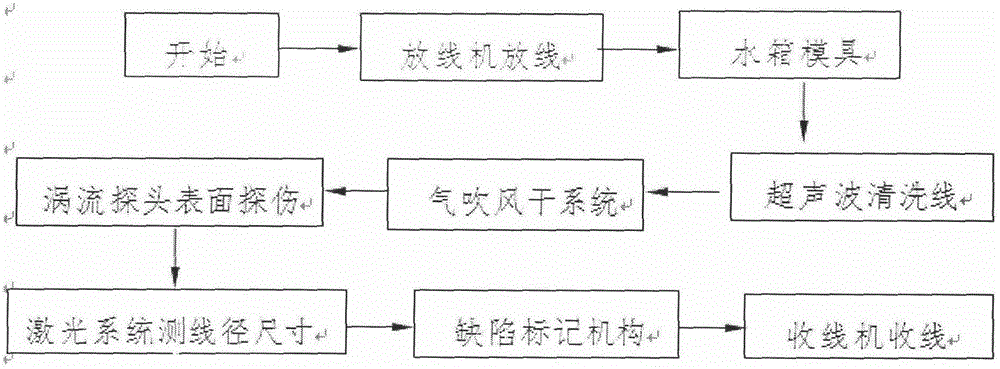
An online detecting method for metal wire surface detects and a detecting device
InactiveCN105548348AImprove detection efficiencyImprove detection accuracyMaterial magnetic variablesEddy-current testingCritical factors
An online detecting method for metal wire surface detects is provided. Surface defects are critical factors influencing quality in cold drawing processes of metal wires. The wire surface defects can be detected in real time in production and processing processes through the method. The method is based on an eddy current testing technique, utilizes an electromagnetic induction principle that eddy current is generated in a conductor through an exciting coil, and measures an eddy current change by means of an exploring coil, thus acquiring metal surface defect related information, and implementing the method. A detecting process is free of contact with an object to be detected and free of a coupling medium. The method is high in detection speed and precision and can meet online detection requirements.
Owner:NO 52 INST OF CHINA NORTH IND GRP CORP
Methods for accelerating the production and maturation of distilled, uniquely flavored spirits
InactiveUS20050084597A1Great tasteEnsure accessibilityAlcoholic beverage preparationMalt preparationChemistryCritical factors
Factors that are critical to the preparation of wood products and useful for flavoring aqueous food products are disclosed. As a result of identifying these critical factors, the herein described process produces a wood product that transfers the desired flavor profile to the aqueous food product efficiently and economically. The resultant wood squares produce excellent flavor in ten percent, or less, of the time it takes for traditional aging.
Owner:COPPER FOX DISTILLERY ENTERPRISES
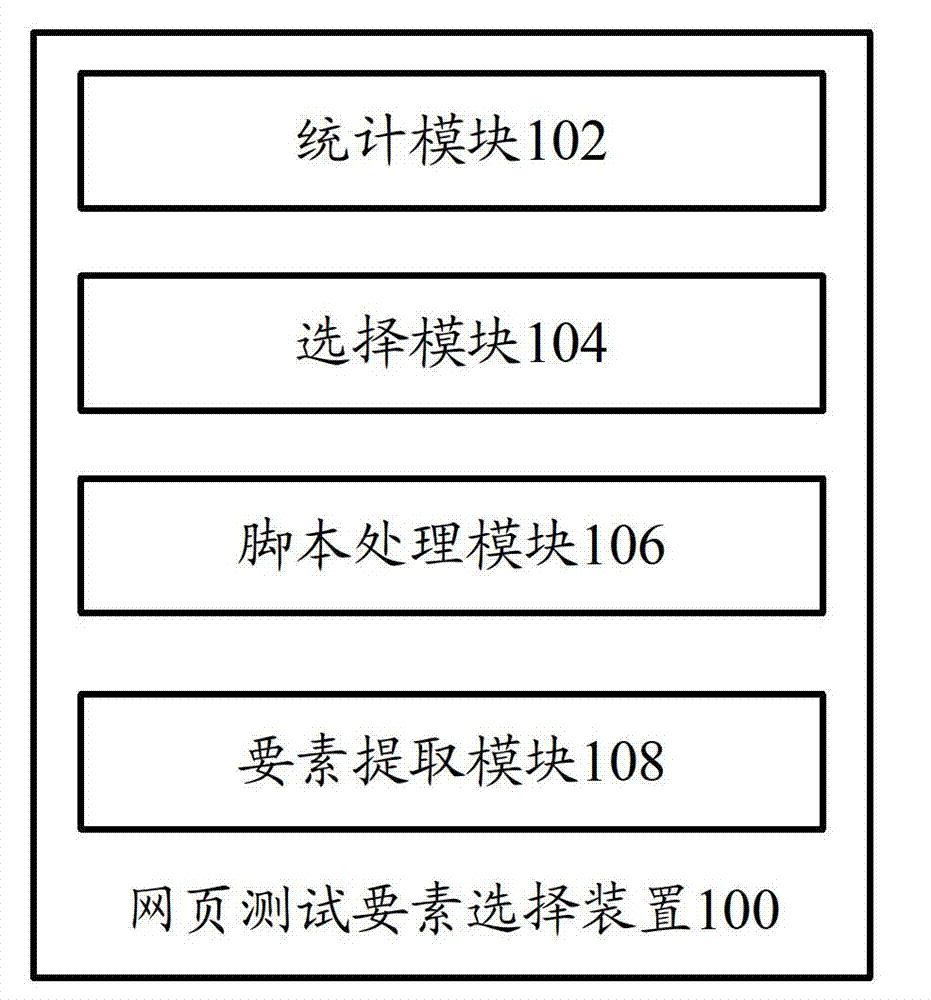
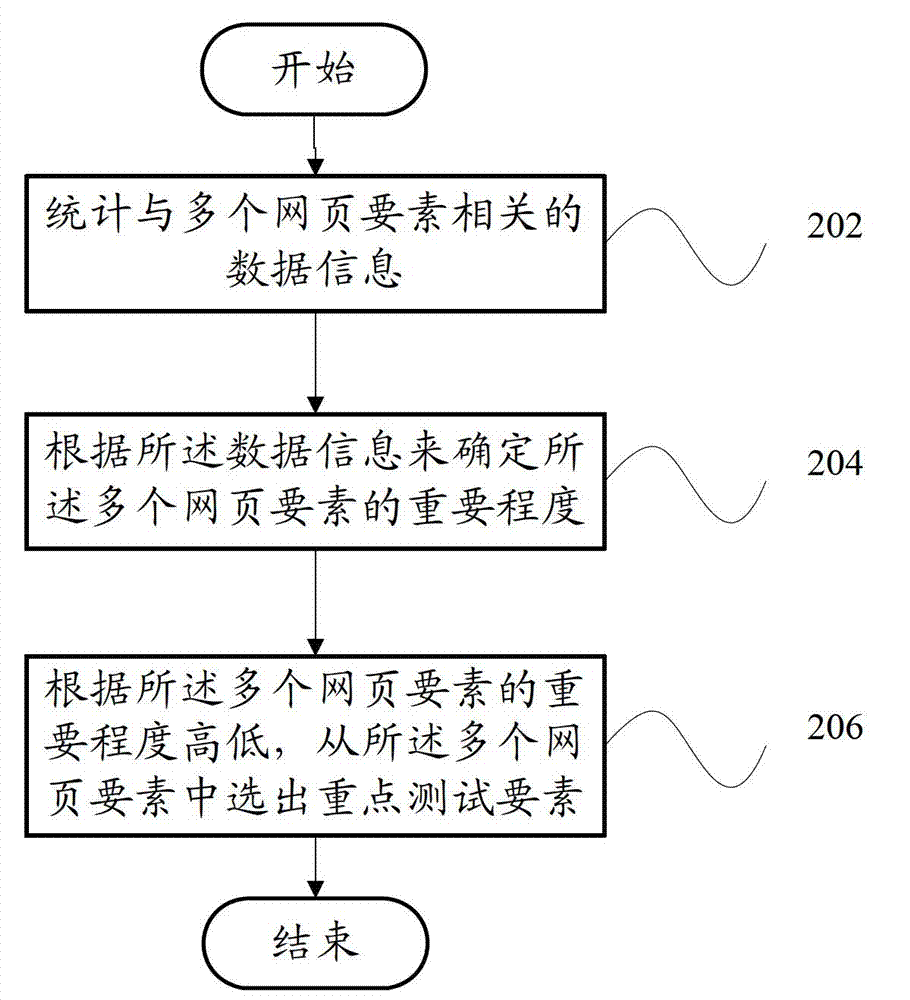
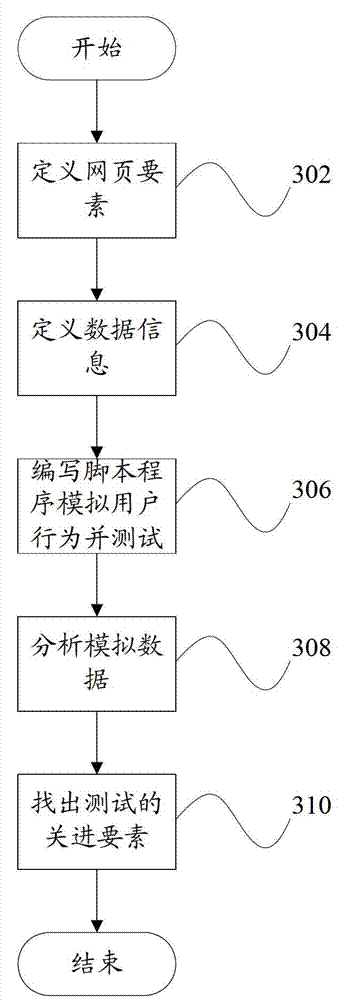
Webpage testing factor selecting device and webpage testing factor selecting method
The invention provides a webpage testing factor selecting device which comprises a statistic module and a selecting module. The statistic module counts data information relevant to a plurality of webpage factors; and the selecting module judges important degrees of the webpage factors according to the data information, and selects the key testing factor from the webpage factors according to the important degrees of the webpage factors. Correspondingly, the invention further provides a webpage testing factor selecting method. According to the technical scheme, a critical factor in testing of a webpage system can be found out, so that webpage testing personnel can efficiently finish system testing and guarantee quality as much as possible.
Owner:ZICT TECH CO LTD
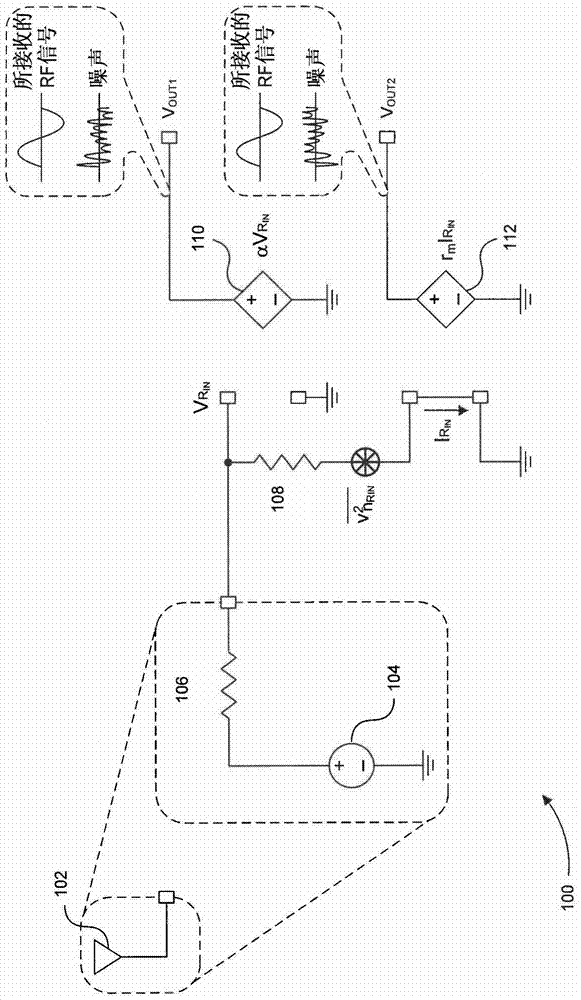
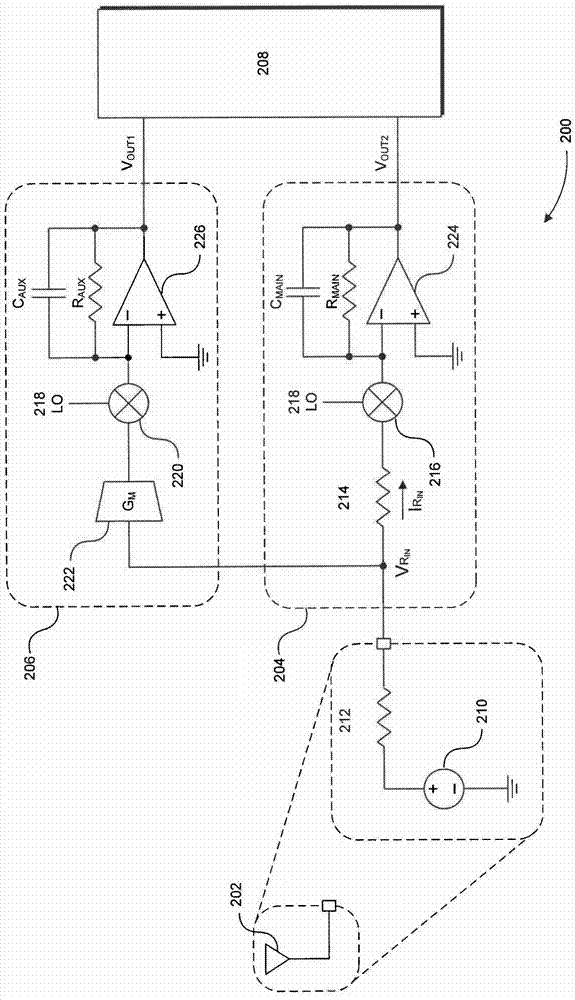
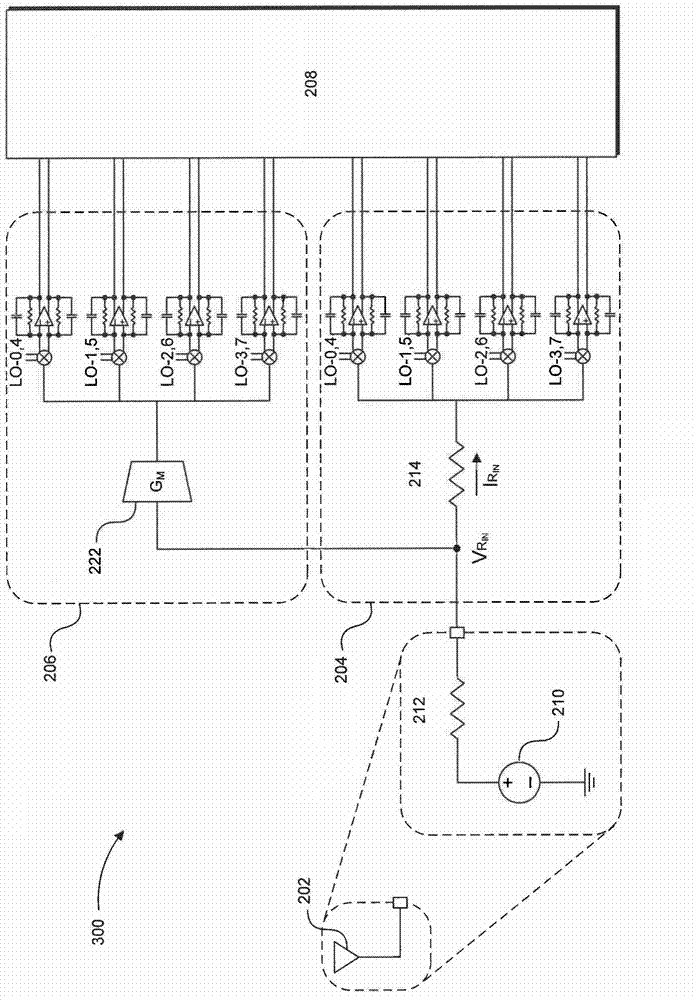
Blocker-tolerant wideband noise-canceling receiver
Because of associated disadvantages of narrow-band off-chip radio-frequency (RF) filtering, a mixer-first receiver front-end designed to tolerate blockers with minimal gain compression and noise factor degradation is disclosed. The mixer-first receiver front-end includes two separate downconversion paths that help to minimize added noise and voltage gain prior to baseband filtering, which are critical factors in eliminating narrow-band off-chip RF filtering.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
Data Processing System And Method
InactiveUS20080250421A1Error detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsData processing systemCritical factors
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
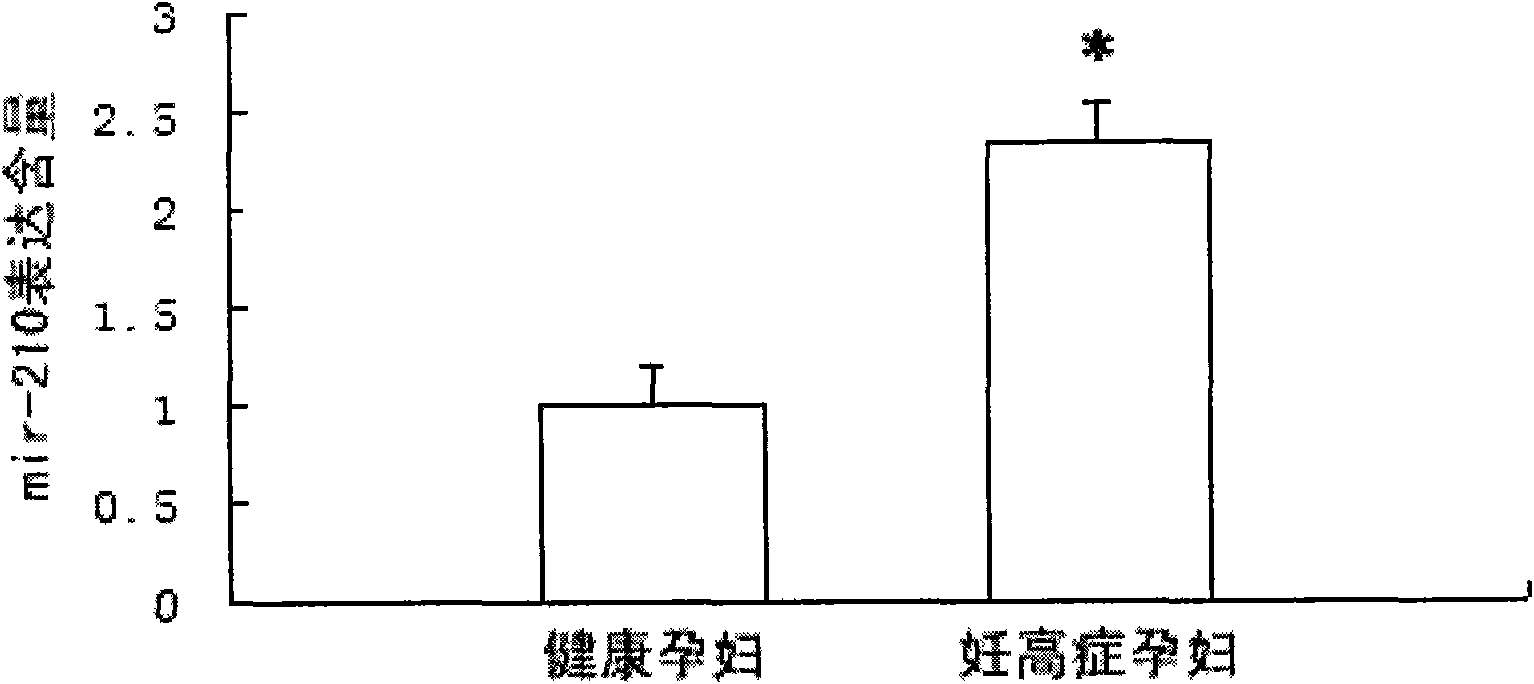
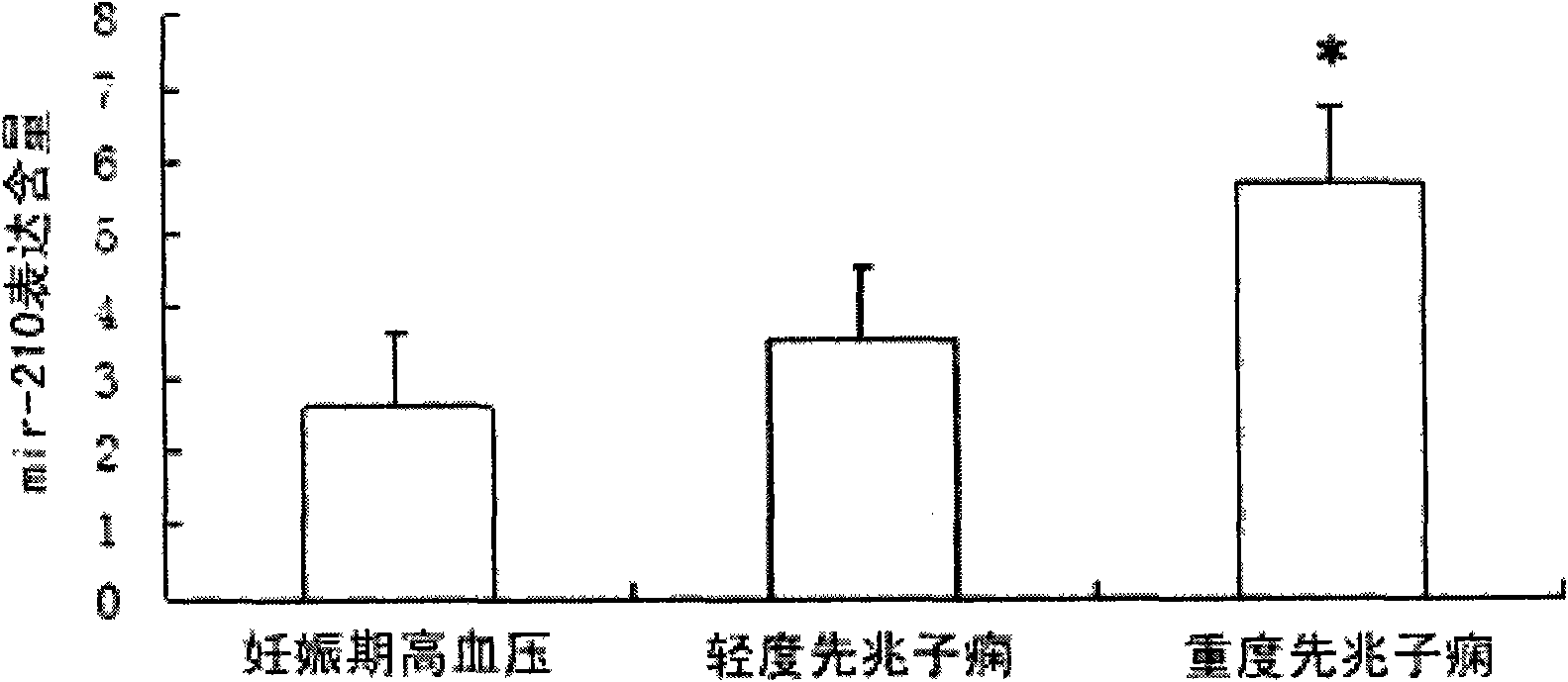
Hsa-mir-210 kit for detecting pregnancy-hypertension syndrome and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN101643785AEffective early detectionReduce pregnancy induced hypertensionMicrobiological testing/measurementCritical factorsPediatrics
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical detection. Pregnancy-hypertension syndrome is one of the critical factors resulting in death for gravida, puerpera, etus and infant. The current detection method is carried out mainly relying on the symptom existing clinically as well as based on some biochemical indicators; in fact, pregnancy-hypertension syndrome exists in early pregnantstage, while early detection landmark is lack in clinical practice for early detection and prevention of the disease. The invention aims at providing a hsa-mir-210 kit for detecting pregnancy-hypertension syndrome and a detection method thereof. By detecting variation of the hsa-mir-210 content in plasma or serum, the invention can more effectively carry out early detection on patients with pregnancy-hypertension syndrome and discover high-risk people with pregnancy-hypertension syndrome so as to prevent the disease effectively in time, and decrease occurrence of pregnancy-hypertension syndrome as well as related complication.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
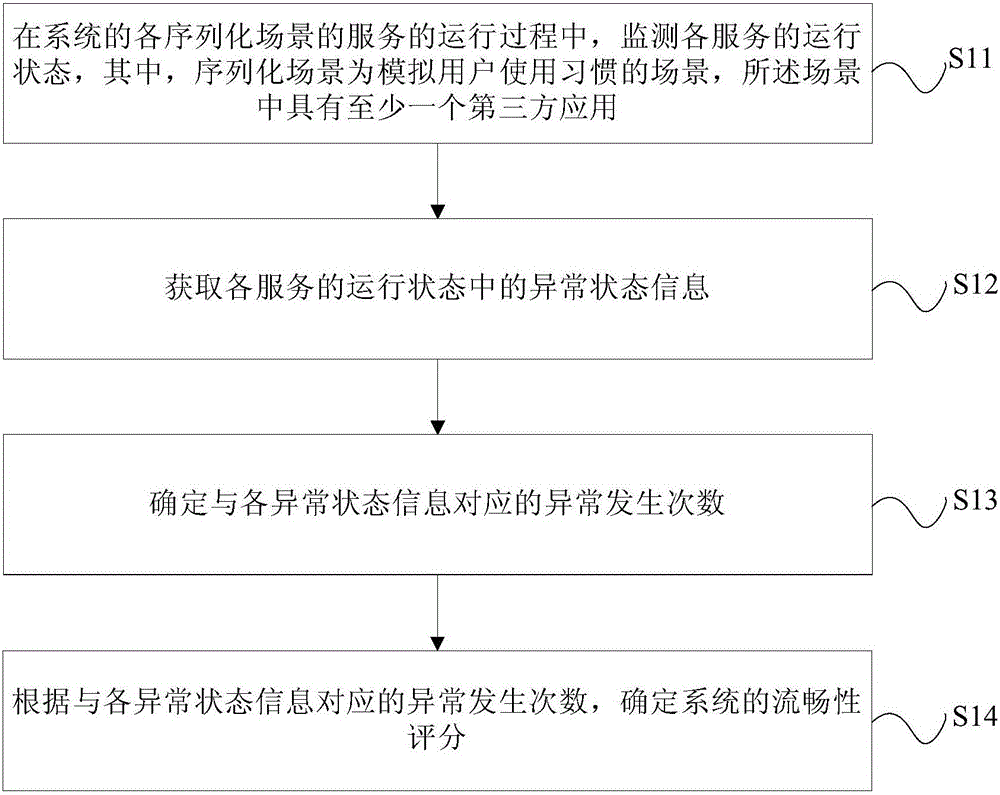
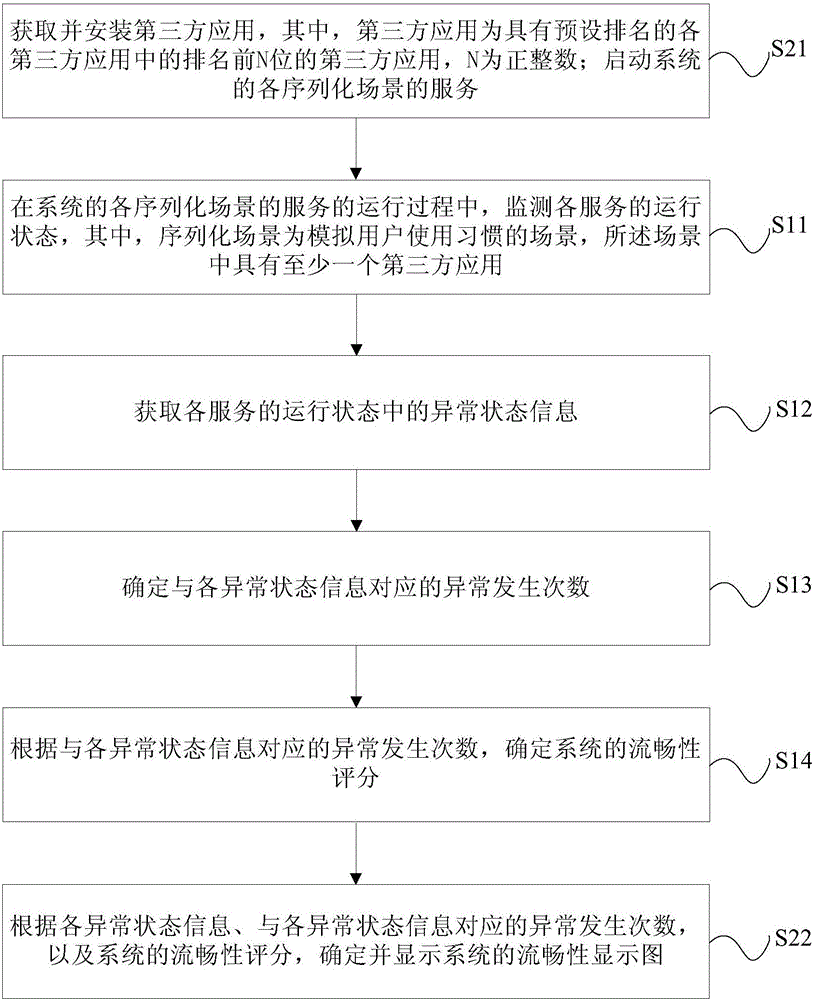
Performance evaluation method and device for system smoothness and terminal
ActiveCN106528389ADetermine true abilityDetermine persistenceHardware monitoringThird partyCritical factors
The invention relates to a performance evaluation method and device for system smoothness and a terminal. The method comprises the following steps: monitoring a running state of each service in a running process of a service of each serialized scene of a system, wherein the serialized scene is a scene in which a use habit of a user is simulated, and at least one third-party application is provided in the scene; acquiring abnormal state information in the running state of each service; determining exception occurring times corresponding to each piece of abnormal state information; and determining a smoothness score of the system according to the exception occurring times corresponding to each piece of abnormal state information. Through adoption of the performance evaluation method and device, each scene is monitored from the aspect of the user to obtain a measurement quantization value, and an evaluation index is obtained specific to most critical factors influencing each scene to give a smoothness score of the terminal under a certain configuration and a certain version, so that the actual capability and sustainability of the system smoothness can be determined according to the smoothness score; the user can be assisted in selecting equipment; and the defects of a software version and a hardware version are overcome.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
Single Daily Dosage Form for Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome
ActiveUS20120021049A1Improve complianceEffective treatmentSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideCritical factorsCvd risk
The present invention is in the fields of medicine, pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, endocrinology and cardiology. The invention provides compositions comprising a statin, an inhibitor of the angiotensin converting enzyme, an antiplatelet compound and an anti-hyperglycemic compound for use in the treatment and / or prevention of cardiometabolic risk factors of Metabolic Syndrome and treatment and / or prevention of Metabolic Syndrome. The present invention provides for the use of such compositions in the manufacture of products for treatment and / or prevention of Metabolic Syndrome. The biguanide metformin of the composition could be present in extended release form allowing its use together with the other drugs in a single dosage form at low dose. This combination of drugs in a single daily dosage greatly improves compliance and adherence to treatment which is a critical factor for treating patients with Metabolic Syndrome.
Owner:NUCITEC DE C V
Method and system for informed decision making to locate a workforce
InactiveUS20110276355A1Facilitates and support decisionDigital data processing detailsOffice automationUser needsCritical factors
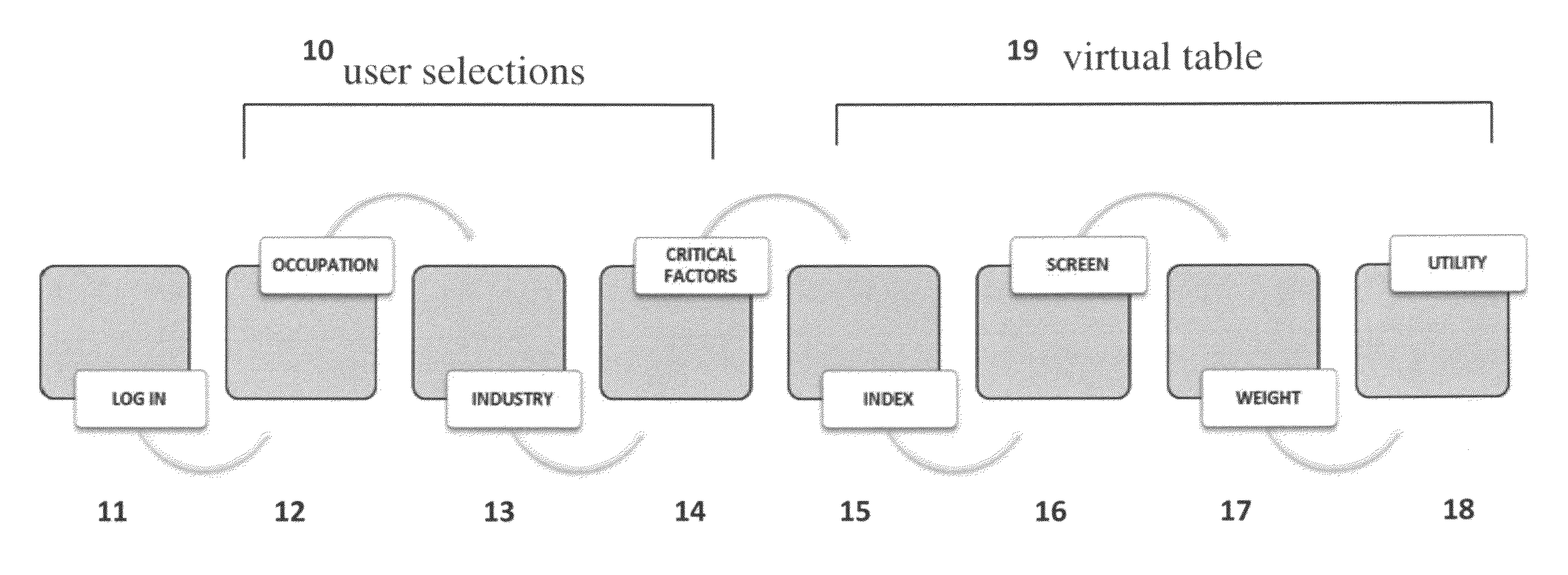
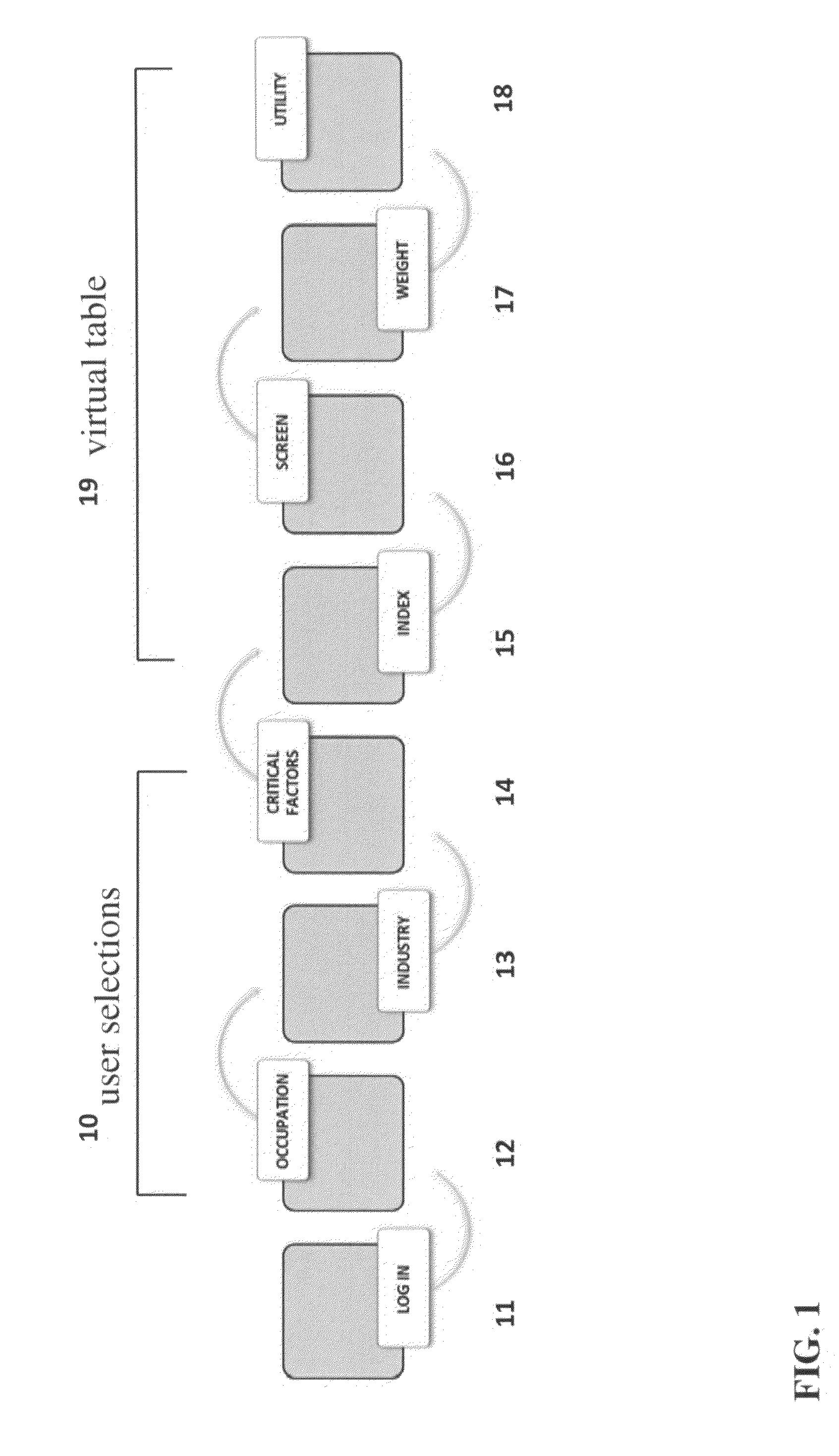
The present invention generally relates to a computer-implemented method and system for informed decision making when a user decides between and amongst geographic areas having a suitable workforce. More specifically, the present invention applies user selections that send SQL statements that extract and index data on workforce demographics for a range of areas over a Network. Data is returned to the user's computer as a virtual table and is a mixture of critical or informational factors representing all areas returning data. Areas are ranked according to the value of an area's lowest returned index number, and data is displayed where each critical factor's lowest index value and its corresponding low value are extracted and used as ranking factors for all area's returning data. Areas are screened by acceptable values for critical factors. Area utilities are created by weighting critical factors based on user needs when selecting a workforce.
Owner:BRUCE MICHAEL +1
System configuring a human machine interface on multiple displays
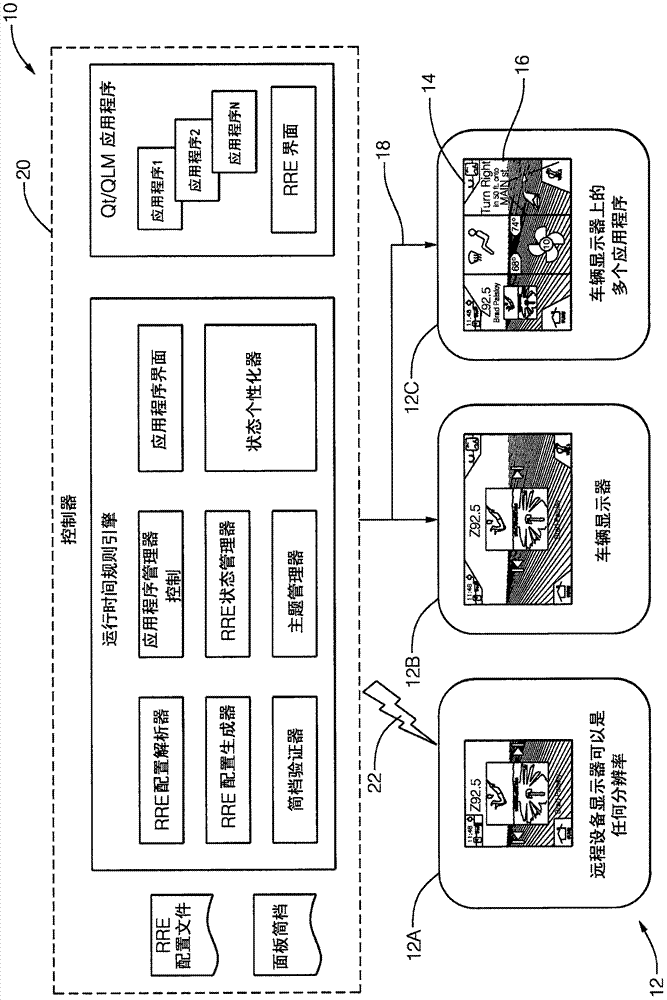
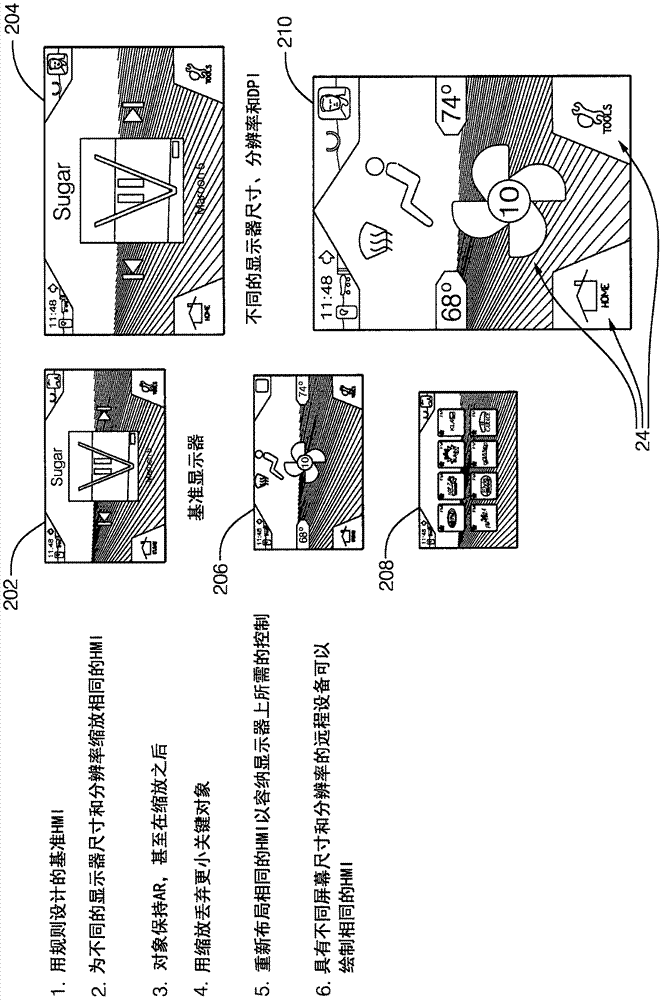
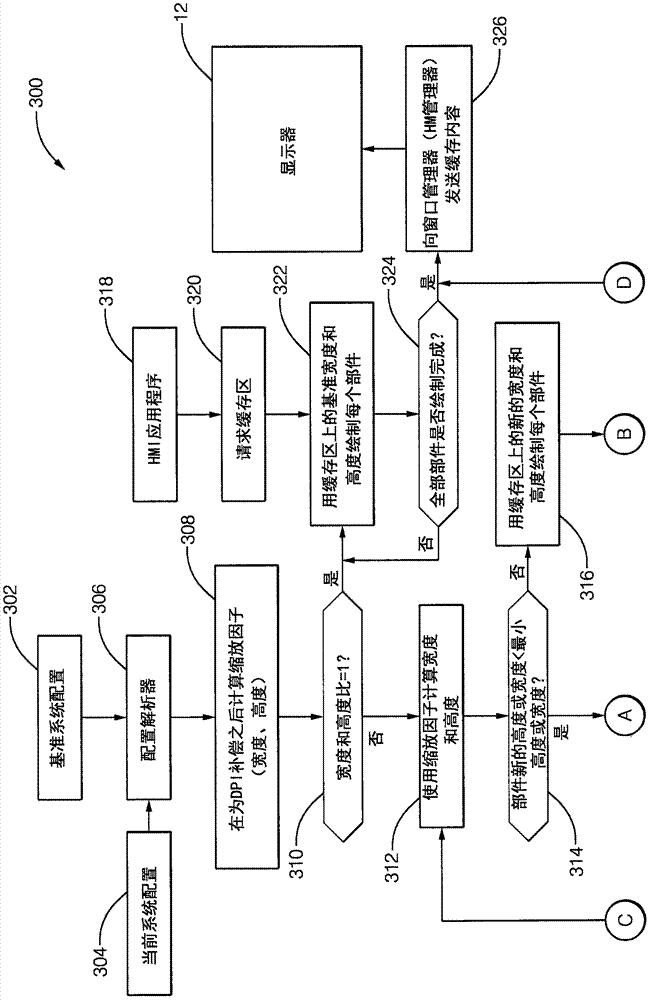
InactiveCN106896978AExecution for user interfacesInput/output processes for data processingHuman–machine interfaceImage resolution
A system (10) for operating a display (12) as a human-machine interface suitable for use in an automated vehicle includes a display (12) and a controller (20). The display (12) is located in the vehicle so as to be viewable by an occupant of the vehicle, the display (12) being characterized by a display resolution (14) and a display size (16). The controller (20) communicates with the display (12). The controller (20) is configured to: determine how many components (24) can be shown on the display (12) based on the display size (16), determine a list of selected components (24) from the list of possible components (24), wherein each of the possible components (24) is characterized by a critical factor, and selected components (24) have a critical factor greater than a critical threshold, the configuration of each selected component is determined based on the display resolution (14), wherein the The configuration includes an aspect ratio as well as manipulating the display (12) to show the occupant selected components (24).
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Process method for removing fluid inclusions in quartz sand by combining microwaves with acid leaching
The invention discloses a process method for removing fluid inclusions in quartz sand by combining microwaves with acid leaching. According to the process method disclosed by the invention, microwave power is the most critical factor which affects the removal effect of the fluid inclusions in quartz sand, and a scientific and accurate treatment process is put forward. The process comprises the steps of: performing irradiation treatment on high-purity quartz sand by microwaves, wherein the microwave power is 1800-2400w; and then performing acid leaching by using monomer acid with a mass fraction of 5-15% for 6-24 hours, wherein the monomer acid is hydrochloric acid, nitric acid or hydrofluoric acid. A plenty of experiments verify that the light transmissivity of quartz sand materials treated by the process is stabilized to be not less than 90.0%, and reaches up to 99.2%, and the purity of SiO2 reaches 99.988%. The process method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, stable and reliable and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Integrated circuit wafer packaging system and method
InactiveUS20080185315A9Increase productionOptimize the desired level of wafer protection during shipmentInternal framesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuality assuranceMulti method
A packaging system, hereinafter referred to as the Critical Packaging System, relates to critical issues that associate with sensitive articles such as IC wafers before, during and after shipment phases. The system employs a choice of two or more specialty designed containers, and any one selected design having choices of two or more methods by which to avoid, reduce and / or eliminate wafer damage from breakage, scratches and / or corrosion during shipment phases. For the purpose of maximizing product yield during packaging phases a special apparatus is used to insert wafers within containers without scratch damage. The following programs are used in packaging: (1) Quality Assurance / Certification, (2) Critical Factor Monitoring, and (3) a Recycle and Refurbish Program. These programs are specifically designed to achieve new levels of product yields, reduce product cost, and landfill impact.
Owner:CONVEY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com