Development of Protein-Based Biotherapeutics That Penetrates Cell-Membrane and Induces Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effect - Improved Cell-Permeable Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling (iCP-SOCS3) Proteins, Polynucleotides Encoding the Same, and Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Compositions Comprising the Same
a technology of protein-based biotherapeutics and cell-membrane, which is applied in the field of protein-based biotherapeutics that, can solve the problems of poor yield and relatively low cell- and tissue-permeability, low solubility of socs3 proteins fused to fgf4-derived mtm, and inability to further clinically develop as therapeutic agents. improve the solubility/yield and cell-/tissue-permeability, and the effect of anti-
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
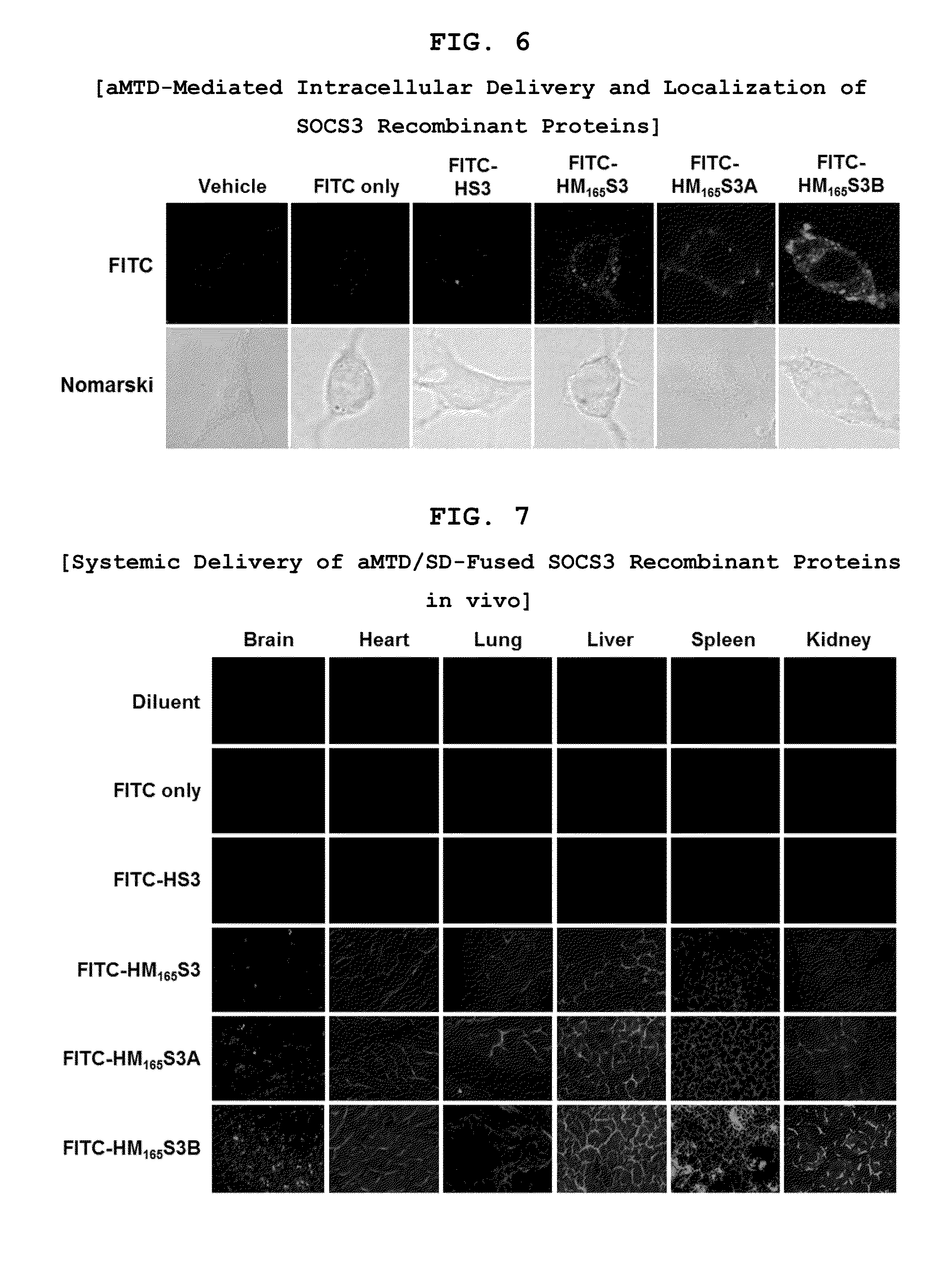
Development of Novel Advanced Macromolecule Transduction Domain (aMTD)
[0091]H-regions of signal sequences (HRSP)-derived CPPs (MTM, MTS and MTD) do not have a common sequence, a sequence motif, and / or a common structural homologous feature. In this invention, the aim is to develop improved hydrophobic CPPs formatted in the common sequence and structural motif that satisfy newly determined ‘critical factors’ to have a ‘common function’, to facilitate protein translocation across the membrane with similar mechanism to the analyzed CPPs. 6 critical factors have been selected to artificially develop novel hydrophobic CPP, namely advanced macromolecule transduction domain (aMTD). These 6 critical factors include the followings: amino acid length of the peptides (ranging from 9 to 13 amino acids), bending potentials (dependent with the presence and location of proline in the middle of sequence (at 5′, 6′, 7′ or 8′ amino acid) and at the end of peptide (at 12′)), instability index (II) for...
example 2
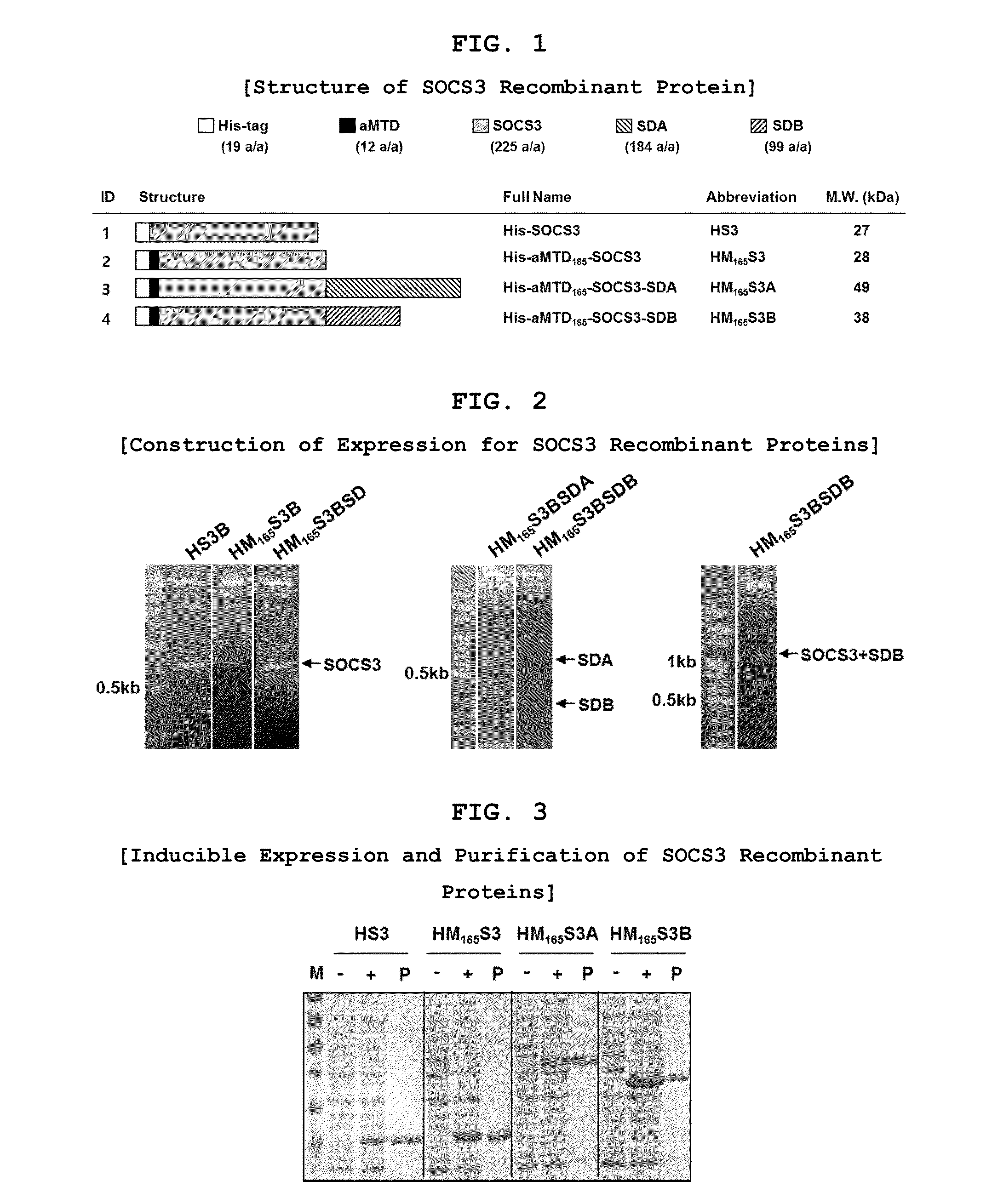
Construction of Expression Vectors for Recombinant SOCS3 Proteins
[0092]Histidine-tagged human SOCS3 proteins were constructed by amplifying the SOCS3 cDNA (225 amino acids) for aMTD fused to SOCS3 cargo. The PCR reactions (100 ng genomic DNA, 10 μmol each primer, each 0.2 mM dNTP mixture, lx reaction buffer and 2.5 U Pfu(+) DNA polymerase (Doctor protein, Korea)) were digested on the restriction enzyme site between Nde I (5′) and Sal I (3′) involving 35 cycles of denaturing (95° C.), annealing (62° C.), and extending (72° C.) for 45 sec each. For the last extension cycle, the PCR reactions remained for 10 min at 72° C. The PCR products were subcloned into 6×His expression vector, pET-28a(+) (Novagen). Coding sequence for SDA or SDB fused to C terminus of his-tagged aMTD-SOCS3 was cloned at BamHI (5′) and SalI (3′) in pET-28a(+) from PCR-amplified DNA segments and confirmed by DNA sequence analysis of the resulting plasmids.
example 3
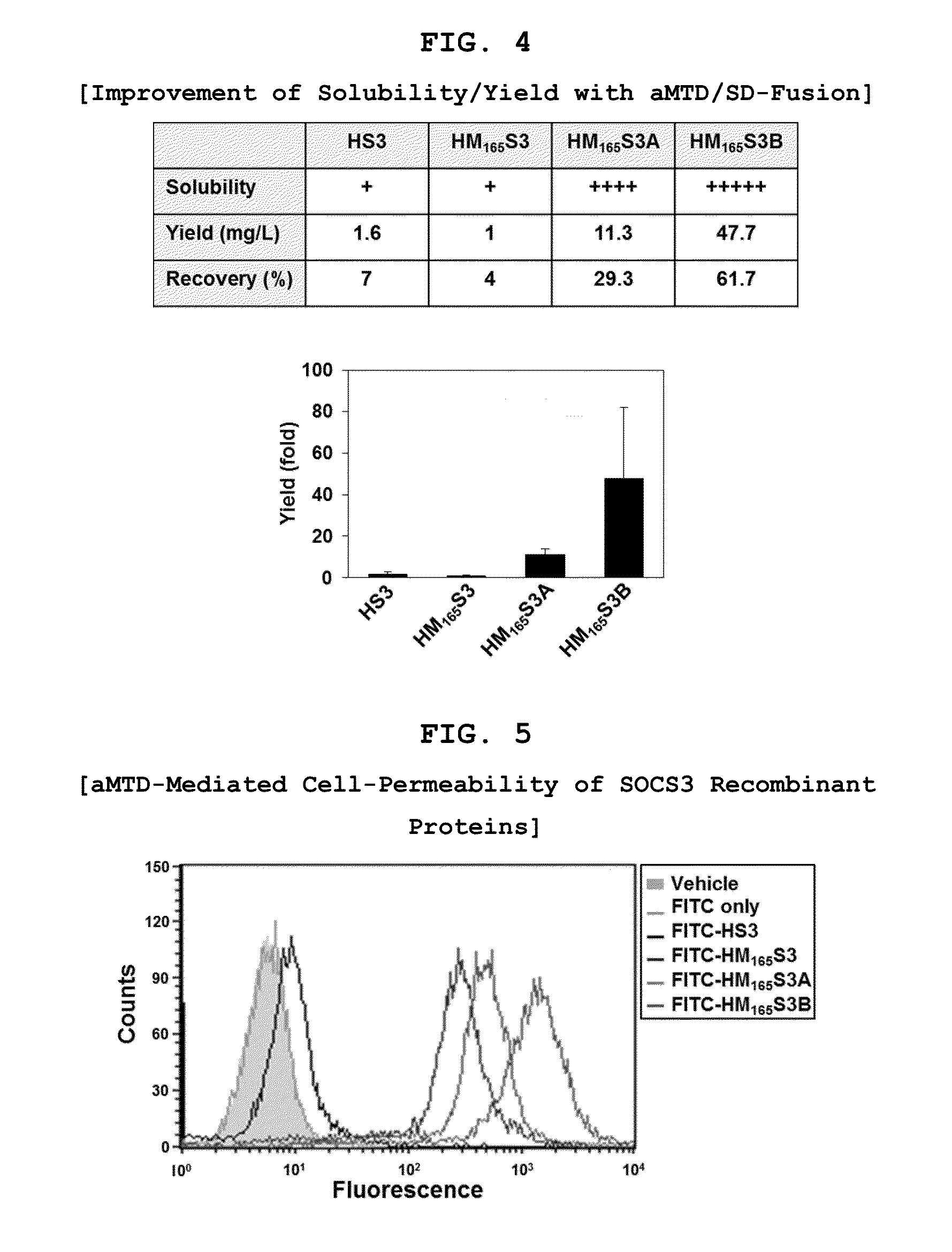
Inducible Expression, Purification, and Preparation of Recombinant Proteins
[0093]The recombinant proteins were purified from E. coli BL21-CodonPlus (DE3) cells grown to an A600 of 0.6 and induced for 3 hrs with 0.6 mM IPTG. Denatured recombinant proteins were purified by Ni2+ affinity chromatography as directed by the supplier (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). After purification, they were dialyzed against a refolding buffer (0.55 M guanidine HCl, 0.44 M L-arginine, 50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 100 mM NDSB, 2 mM reduced glutathione, and 0.2 mM oxidized glutathione) and changed to a physiological buffer such as DMEM medium.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Solubility (mass) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Permeability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com