Remote protein homology detection and fold recognition method based on Top-n-gram
A top-n-gram and recognition method technology, which is applied in the field of protein remote homology detection and folding recognition, can solve the problems of inability to distinguish the difference in the frequency of amino acid occurrence, binary spectrum can not find the optimal threshold, etc., to improve the prediction effect , the effect of removing noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
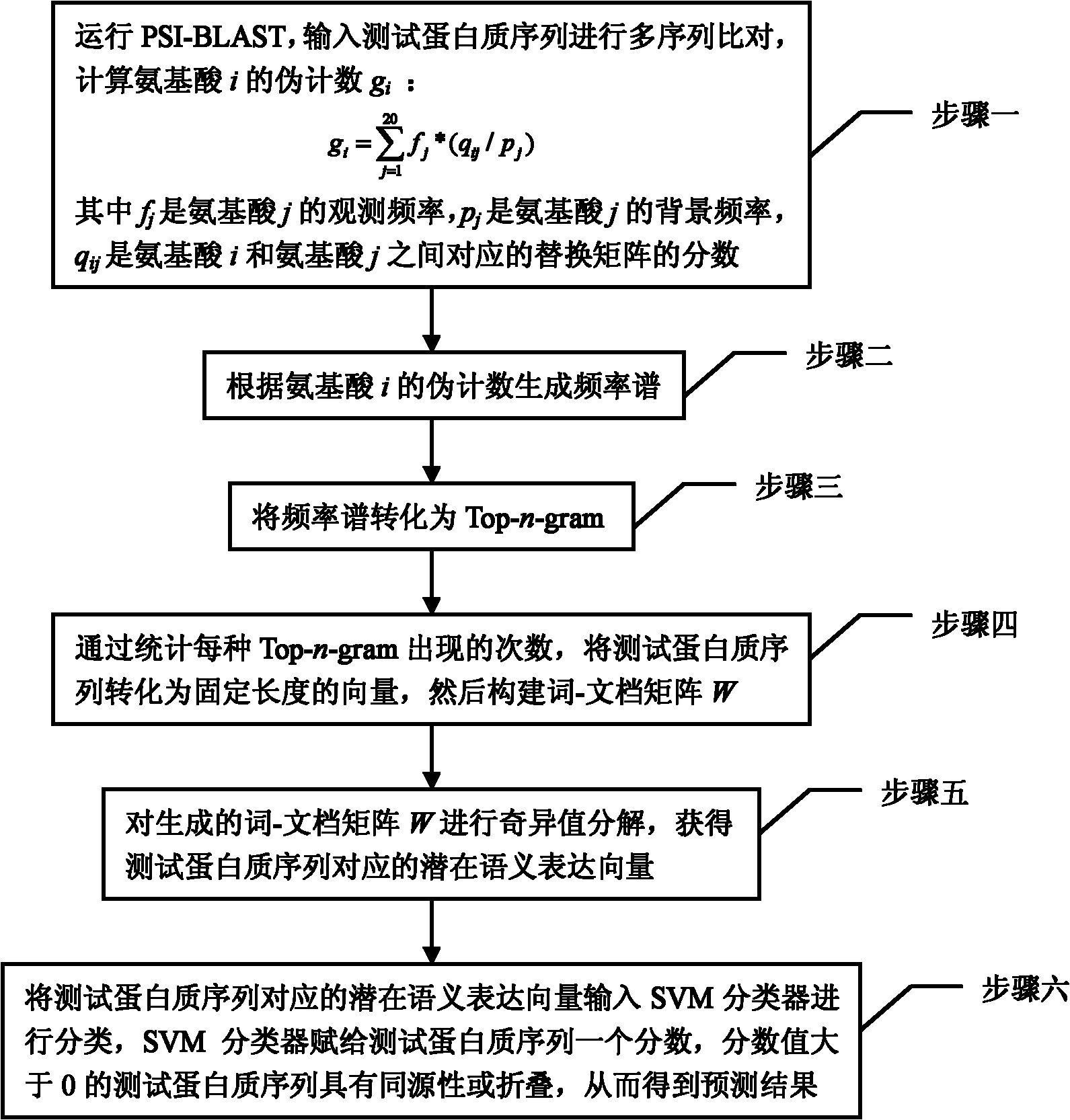
[0044] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, a Top-n-gram-based protein remote homology detection and folding recognition method, the specific steps are:
[0045] Step 1: Run PSI-BLAST, input the test protein sequence for multiple sequence alignment, and calculate the pseudo count g of amino acid i i :
[0046] g i = Σ j = 1 20 f j * ( q ij / p j )
[0047] where f j is the observed frequency of amino acid j, p j is the background frequency of amino acid j, q ij is the fraction of the substitution matrix corresponding between amino acid i and amino acid j;
[0048] Step 2: generate a frequency spectrum according to the pseudo-count of amino acid...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0059] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of step 2 in the Top-n-gram-based protein remote homology detection and folding recognition method described in specific embodiment 1. The method to generate the frequency spectrum is:
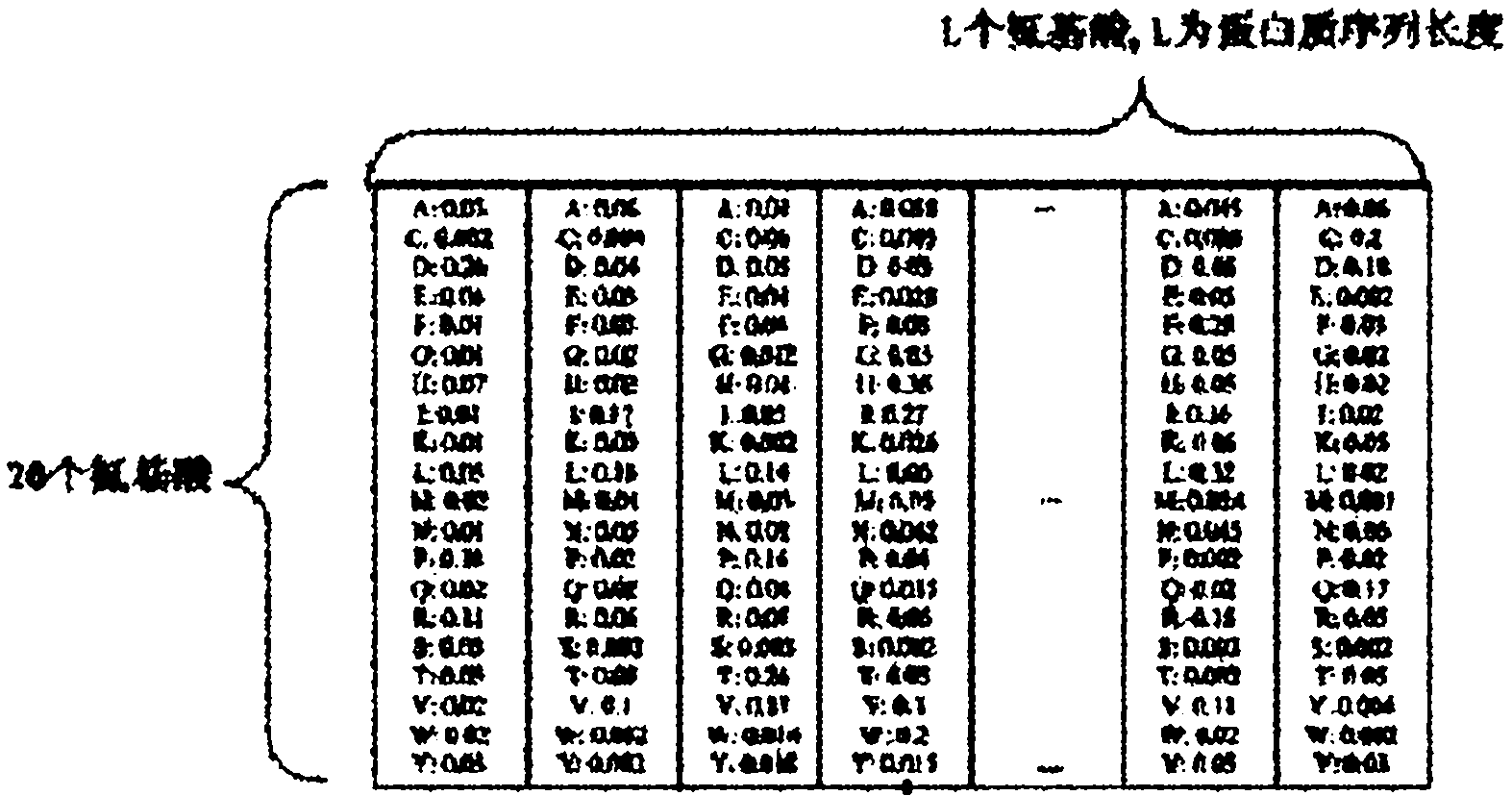
[0060] Calculate the target frequency Q of 20 standard amino acids at each amino acid position in the test protein sequence i :
[0061] Q i =(αf i +βg i ) / (α+β)
[0062] Among them, β is a free parameter, which is the default value of 10 in PSI-BLAST, and α is all the amino acid species appearing in a column in the multiple sequence alignment minus 1;
[0063] Express the frequency spectrum as a matrix M, whose dimension is L×N, where L is the length of the protein sequence, N is a constant 20, that is, the number of standard amino acids, and the elements in M are the target spectral rate Q i .
[0064] target frequency Q i Indicates the occurrence frequency of a certain amino acid at a specific position in a pro...
specific Embodiment approach 3
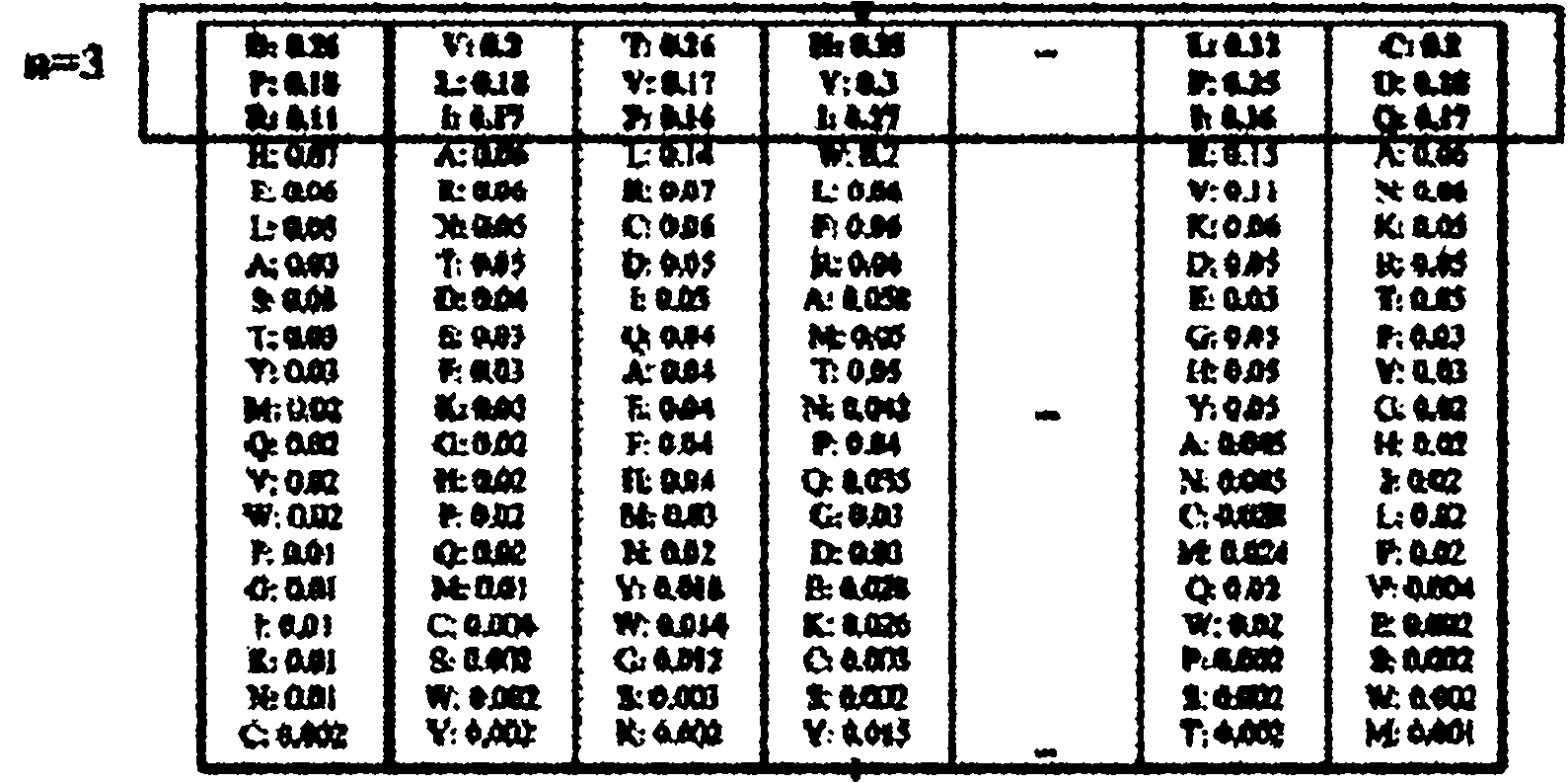
[0065] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is a further description of step three in the method for remote homology detection and folding recognition of proteins based on Top-n-gram described in specific embodiment one. The method of converting the frequency spectrum into Top-n-gram is:
[0066] Arrange the 20 standard amino acids in each row of the frequency spectrum in descending order according to their target frequencies, and then combine the top n amino acids with the highest target frequencies into a Top-n-gram according to their frequencies, and each Top-n-gram is passed through amino acids in Different positions in the Top-n-gram distinguish their different frequencies, and a total of L Top-n-grams are obtained, where n is an integer greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 5.
[0067] The value of n can be an integer greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 20, but in practice, an integer of greater than or equal to 1 and less than or eq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com