A kind of strain producing surfactant-resistant lipase and preparation method of surfactant-resistant lipase
A surfactant and lipase technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, detergent compounding agents, etc., can solve the problem of no lipase produced by bacteria of the genus Chryseobacterium, no lipase preparation method, and the impact Problems such as the enzymatic properties of Chrysobacterium aureus lipase achieve the effect of enhancing the reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Embodiment 1, strain screening and identification
[0075] The bacterial strain Chryseobacterium WBRD1.11121501 provided by the present invention is isolated from the soil in Shanghai, China. A bacterial strain that can produce extracellular lipase was obtained by screening the newly collected soil samples on rhodamine B plates through enrichment culture or dilution coating. The strain was identified as Chryseobacterium sp. WBRD1.11121501 by 16SrRNA identification.
[0076] The strain has been deposited in the General Microorganism Center (CGMCC) of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms. The address of the depository unit is the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 3, Courtyard No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, zip code 100101. The preservation date of the bacterial strain is June 21, 2012, the preservation number is CGMCC No.6261, and the classification name is: Chryseobacterium sp.
[0077] The screening...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Embodiment 2, preparation of surfactant-resistant lipase
[0084] Get a freshly cultivated Chryseobacterium aureus WBRD1.11121501 slant (LB culture medium 30 ℃ and cultivate 48h, connect a ring to the seed shake flask that contains 30ml seed culture medium, 30 ℃, 150rpm cultivate 24h. Then with 1% inoculum size Inoculate into the fermentation medium and culture on a shaker at 30°C and 150rpm for 48 hours. The culture solution is centrifuged or micro-filtered to remove bacteria, and the supernatant is concentrated by ultrafiltration using a 10kDa membrane. Then the concentrated solution is subjected to segmented ammonium sulfate salting out and collected 20-70% saturation of the salted-out precipitate. Then use the Hitrap phenyl HP chromatographic column (GE HealthCare, product number: 17-5195-01) to carry out hydrophobic chromatography purification on the salted-out protein sample, first use the starting buffer and The elution buffer carries out gradient elution, then e...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Embodiment 3, partial enzymatic property of lipase produced by Chryseobacterium WBRD1.11121501
[0090]The lipase prepared by the present invention has the following properties. Unless otherwise specified, the detection of lipase activity adopts the pNPP method (see the "Specific Embodiments" section).
[0091] Impact on Stability
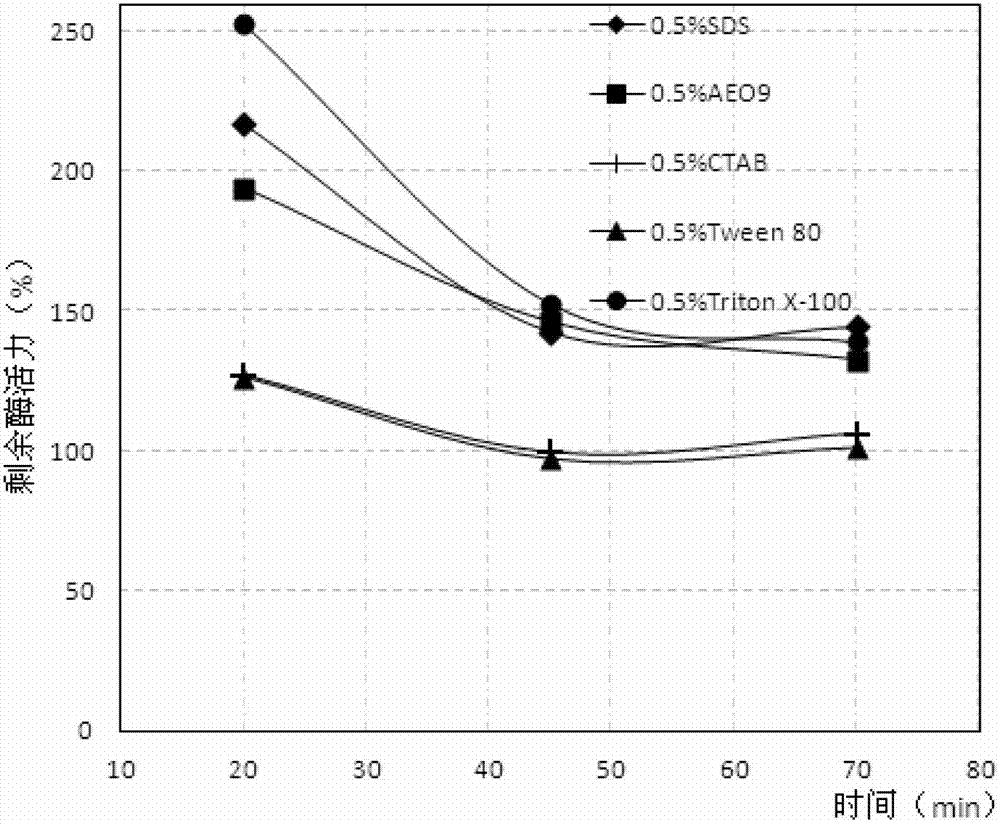
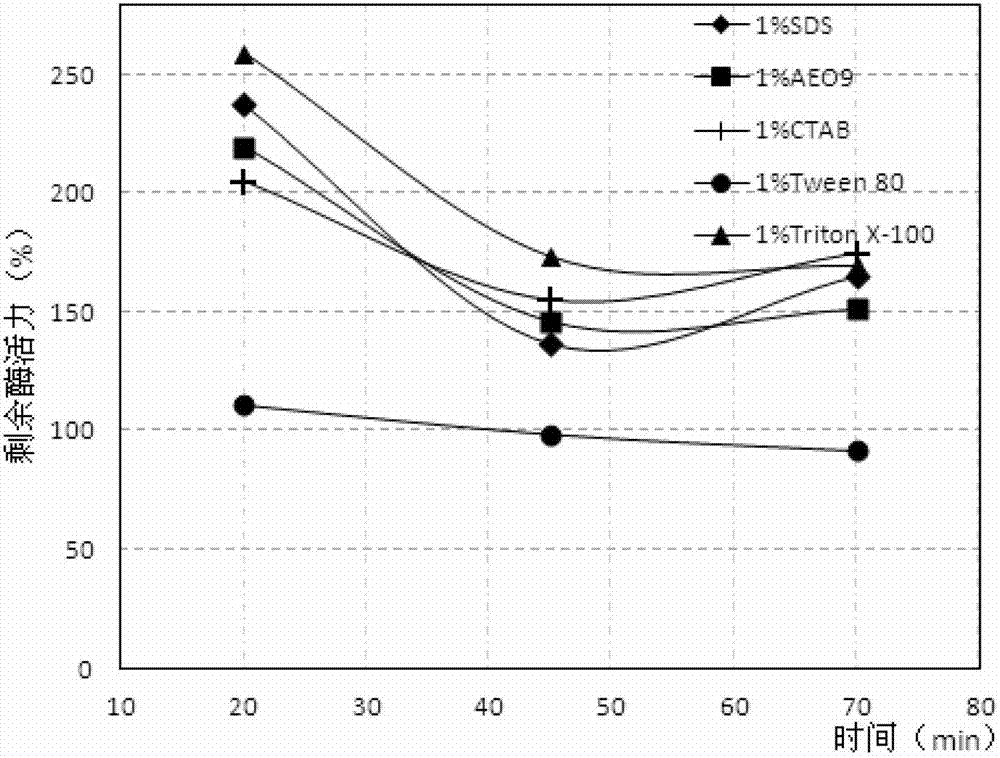
[0092] The detection method that surfactant affects the stability of Chryseobacterium lipase is to get 2ml of the enzyme solution to be tested with an activity of about 0.3 units / ml, and add the surfactant to be detected until the surfactant concentration is 0.5% or 1.0 %(v / v), put it at room temperature, take out 0.1ml samples of some samples at the 20th, 45th and 70th minutes respectively for detection of lipase activity. The control enzyme activity is 100%, and the relative enzyme activity of the experimental sample is calculated.
[0093] The effect of surfactant on the stability of Chryseobacterium lipase is shown in figure 2 and ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com