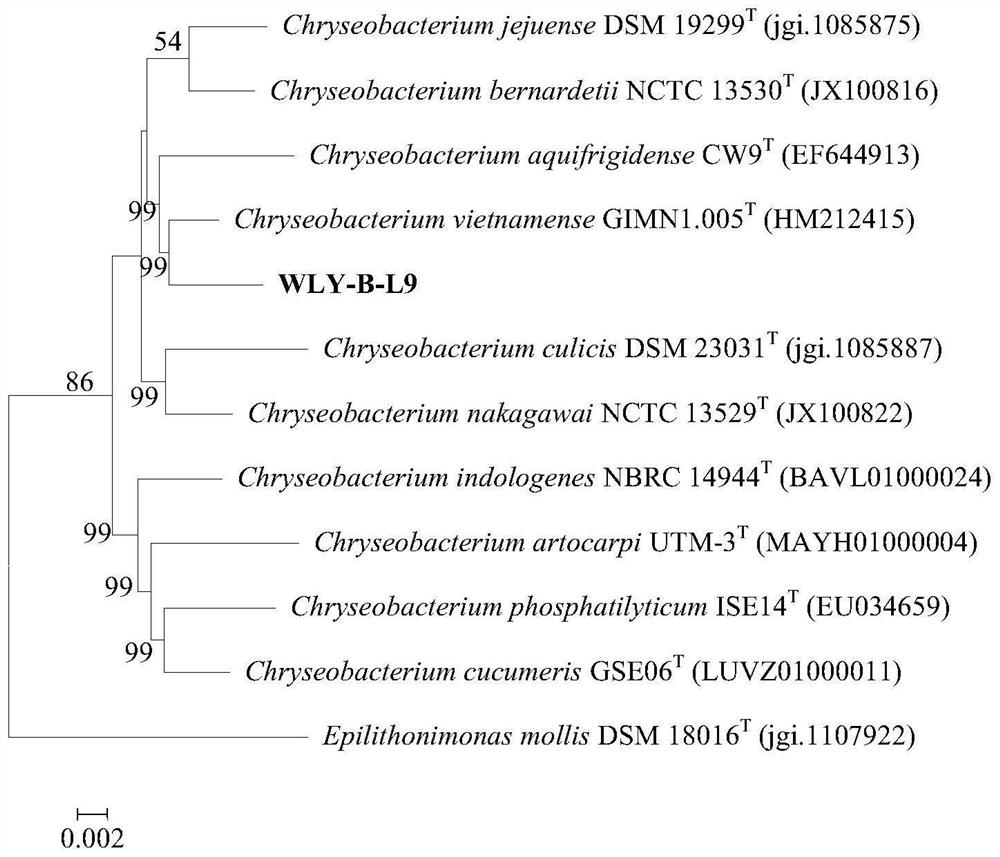
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Chryseobacterium sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
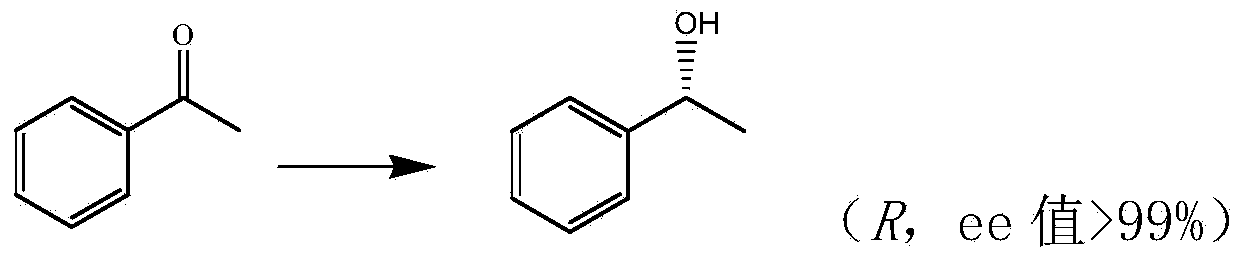
Application of Chryseobacterium sp. and carbonyl reductase thereof in production of aprepitant chiral intermediate
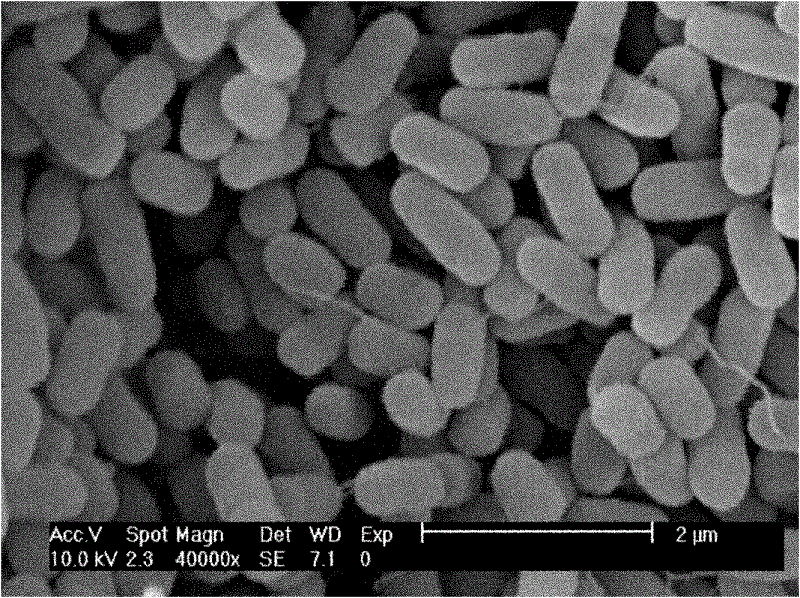
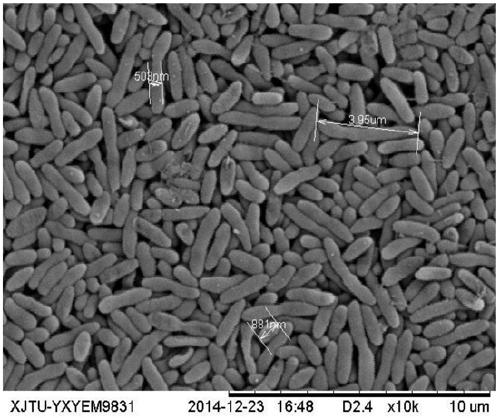
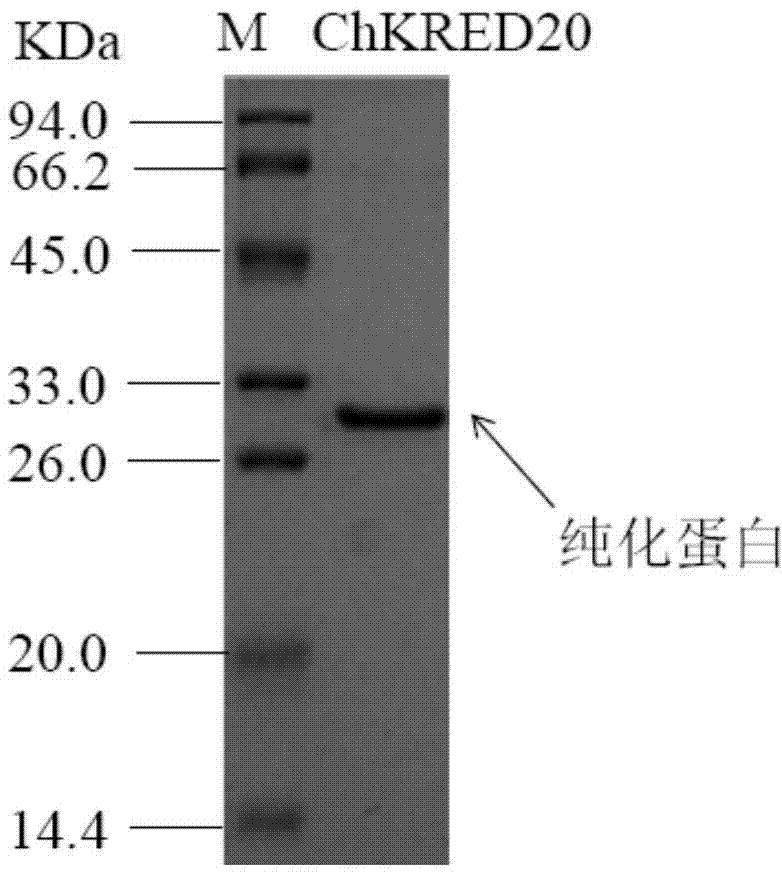
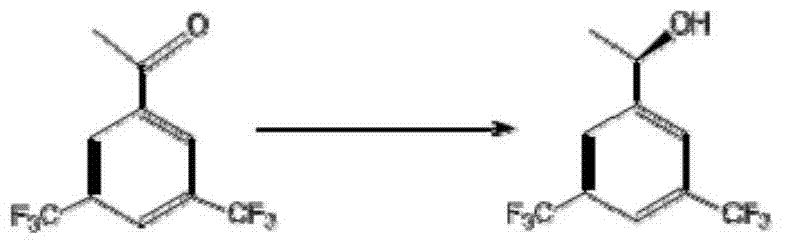
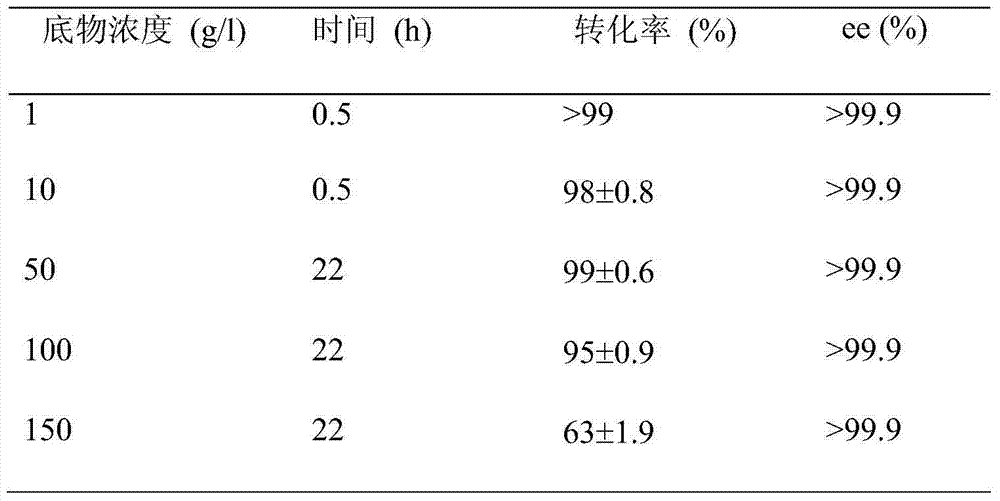
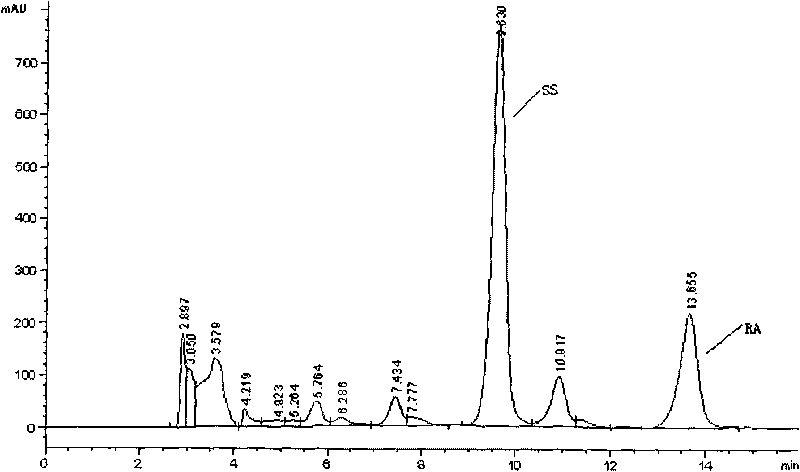
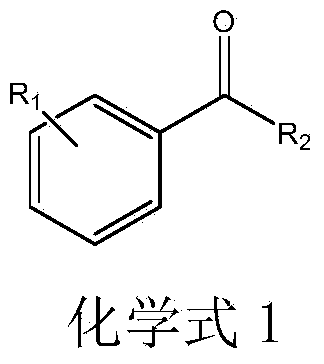
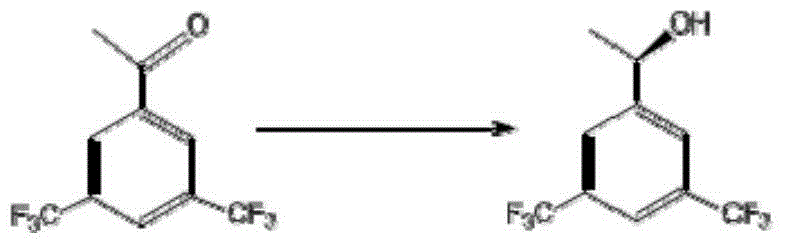
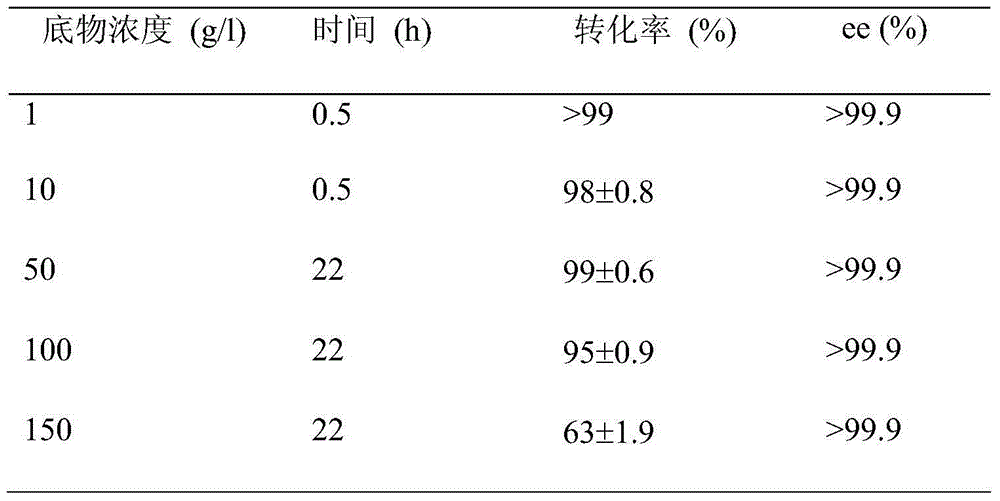
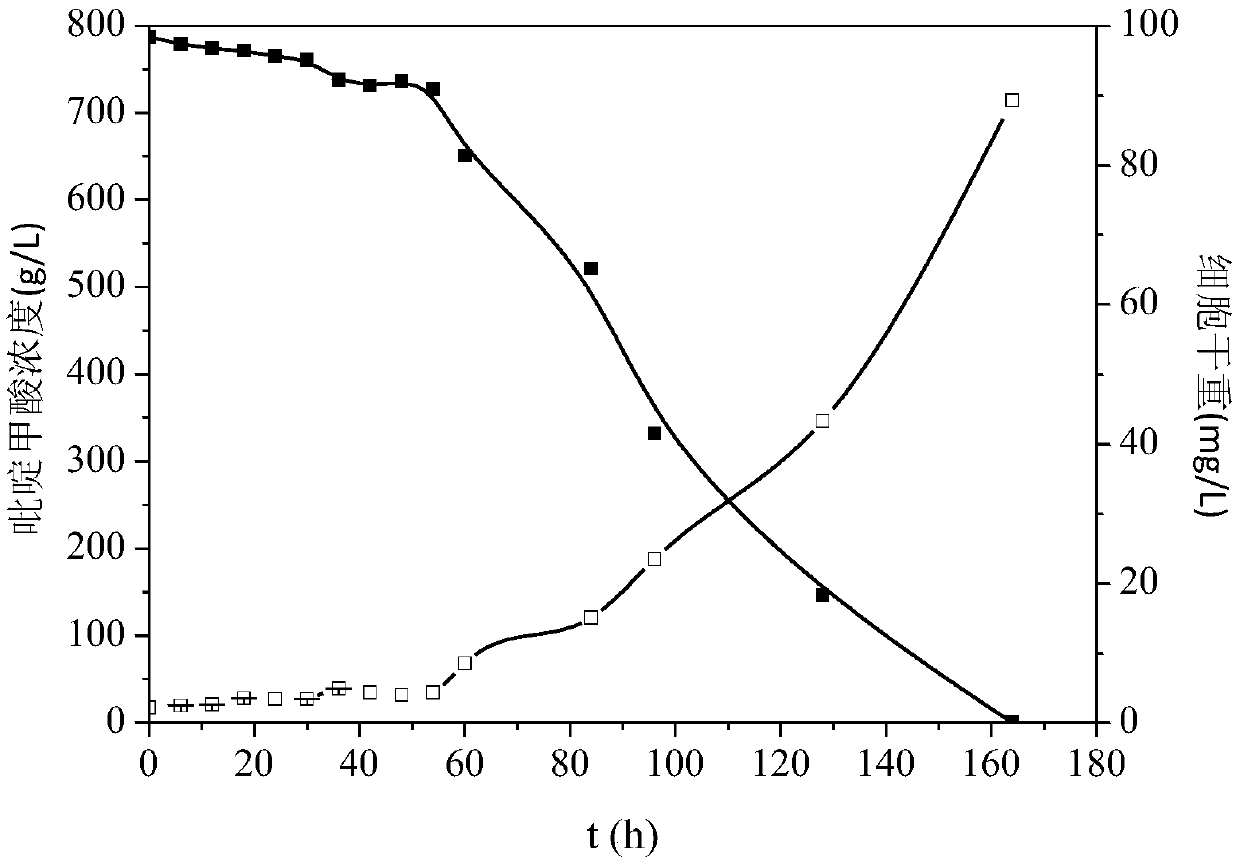
The invention discloses a strain of Chryseobacterium sp. CA49 (with an accession number of CCTCC M2012484), carbonyl reductase ChKRED20 coded by the genome of the strain and preparation of an aprepitant chiral intermediate (R)-1-[3,5-di(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol by using the original strain of Chryseobacterium sp. or the carbonyl reductase as a biocatalyst. The enantiomeric excess value of the produced intermediate is greater than 99.9%. Crude ChKRED20 enzyme powder can catalyze up to 200 g / L of a substrate and enables a conversion rate of more than 99% to be obtained in 24 h; a coenzyme circulating system is simple and cheap, the produced intermediate is easy to separate and purify, and a high recovery rate and good industrial application prospects are obtained.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
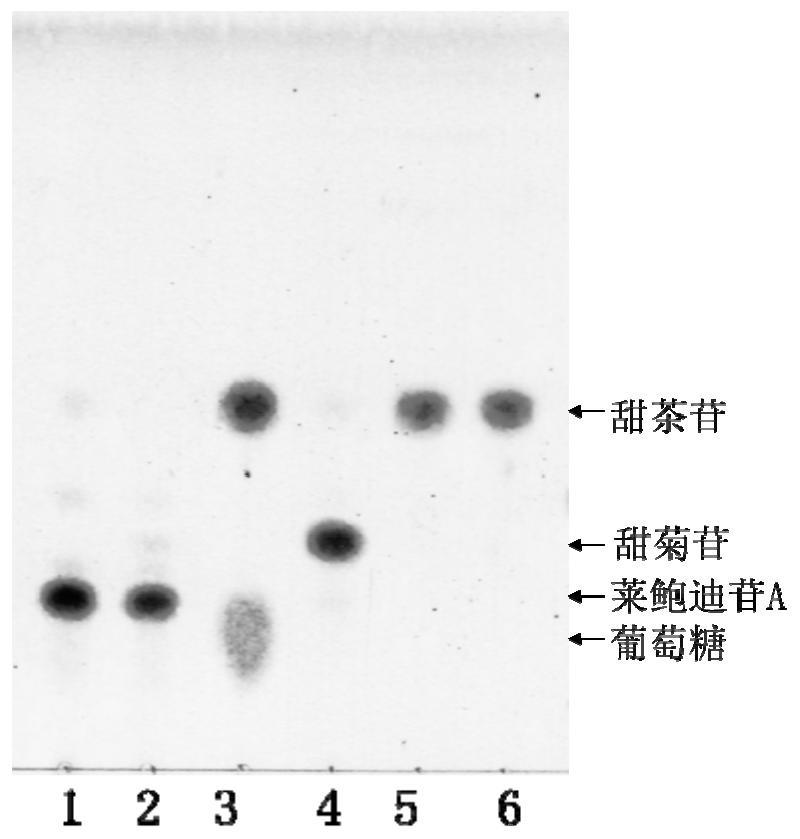
Method for preparing rubusoside by stevioside
InactiveCN101701238AHigh purityLimited sources of solutionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationFood additiveAlglucerase
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Microorganism for promoting black nightshade to remove trace cadmium pollution in water and method for removing cadmium pollution
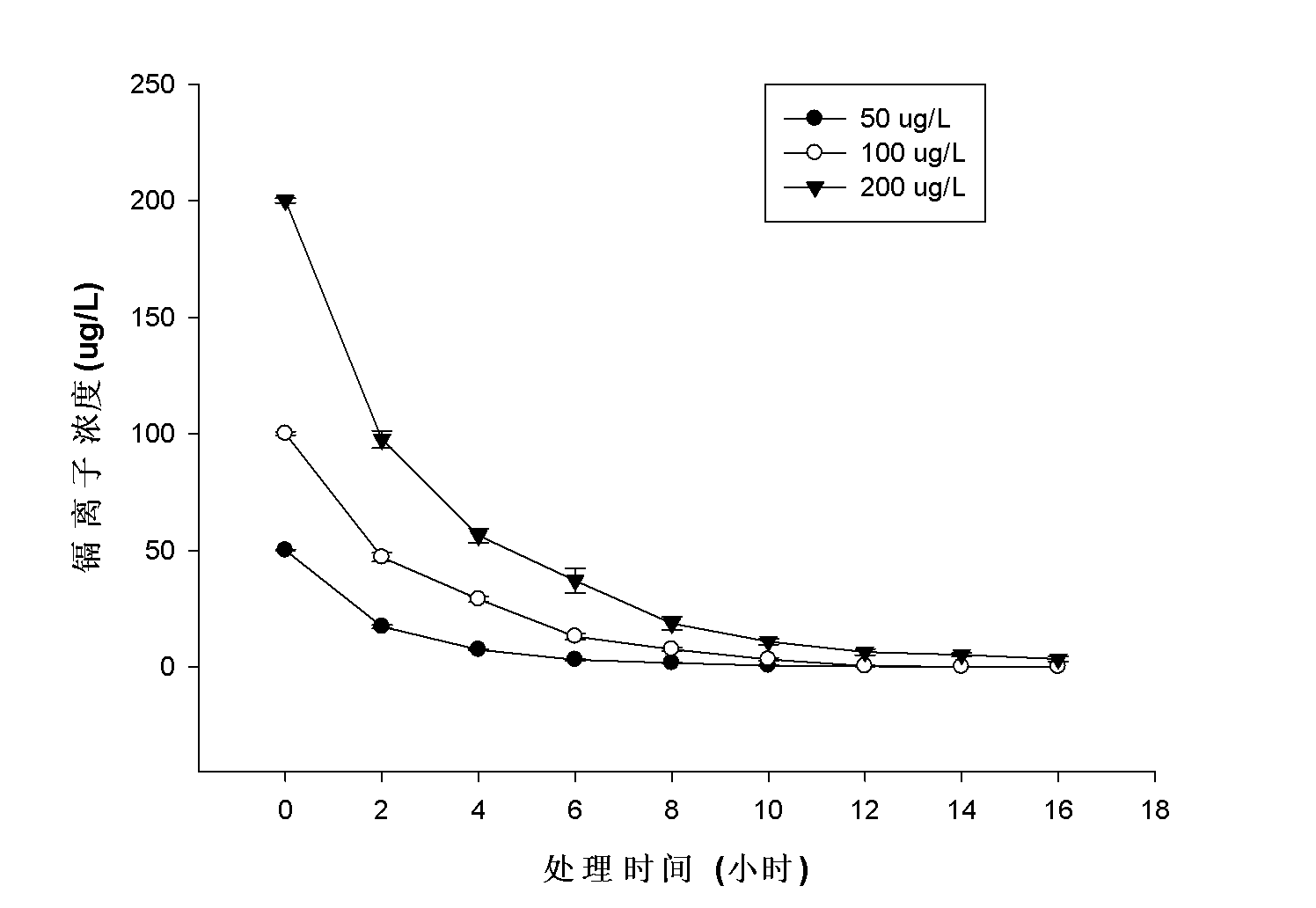
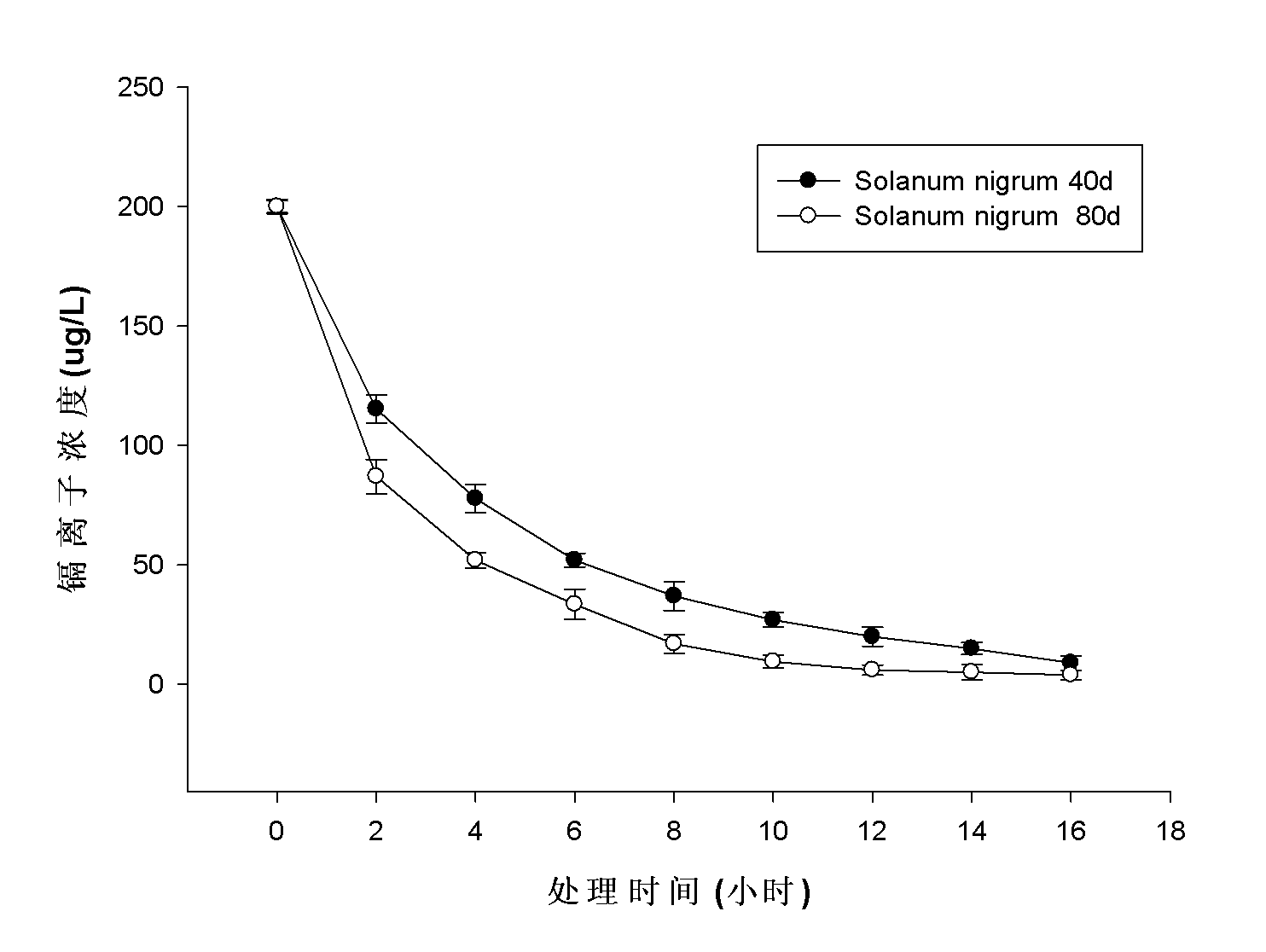
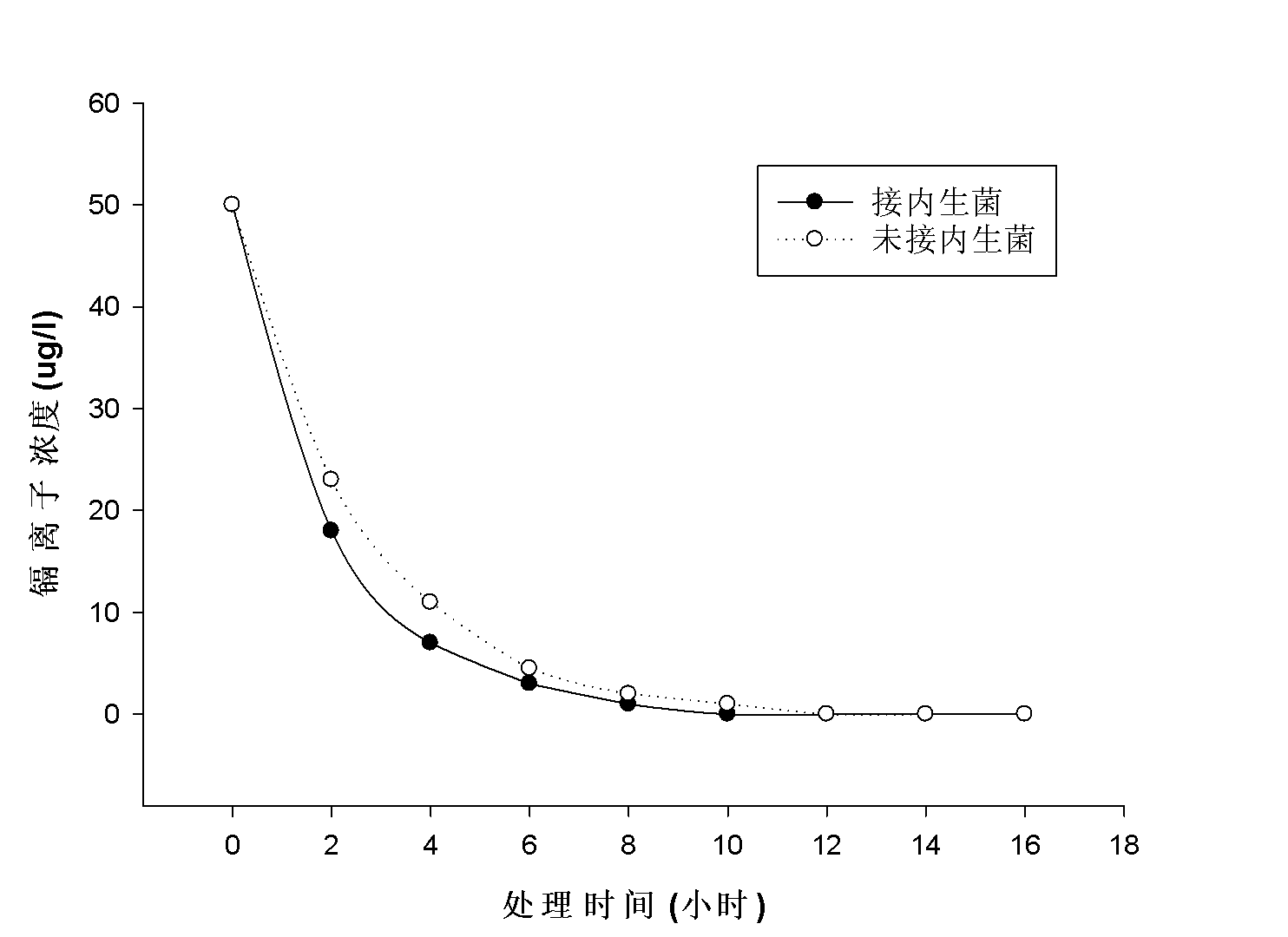
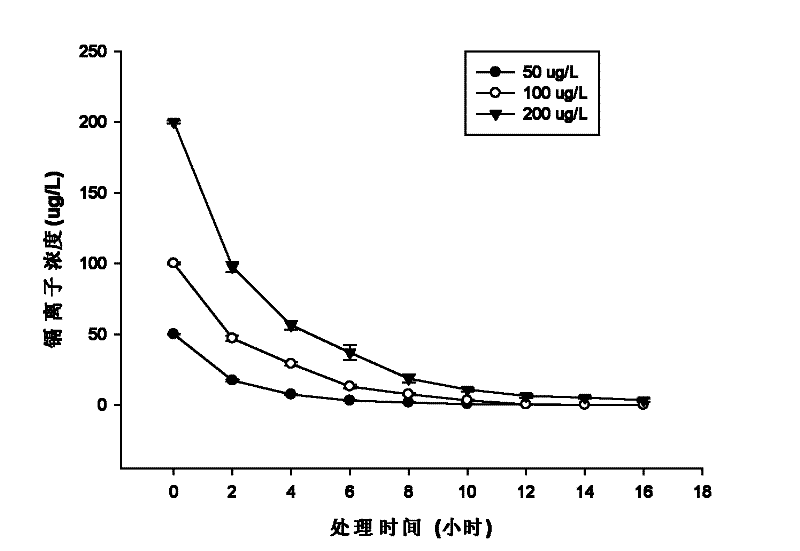
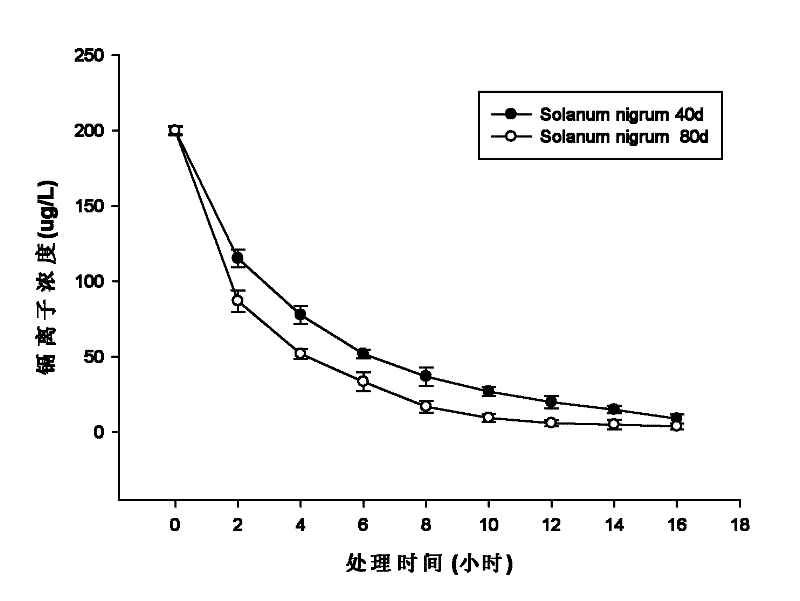
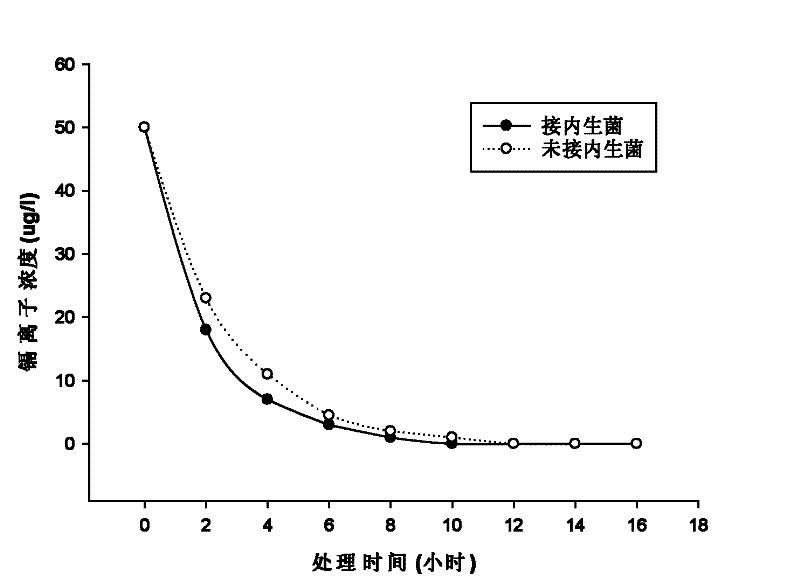
The invention provides a microorganism for promoting black nightshade to remove trace cadmium pollution in water and a method for removing cadmium pollution, aiming to purify drinking water subjected to cadmium pollution by virtue of the high-efficiency absorption characteristic of super-accumulated plants, namely black nightshade, to cadmium. In the method, the black nightshade is cultured in an aquaculture manner, and Chryseobacterium sp. LKS03 is inoculated to the black nightshade to promote the roots of the black nightshade to grow; and during purification of drinking water, the roots of black nightshade plants are immersed into the drinking water subjected to cadmium pollution, and each black nightshade plant correspondingly purifies about 1-1.2L of the drinking water in a purification cycle, wherein the purification time is for 2-12h according to the cadmium ion concentration (not higher than 200mug / L) in a water sample, and the capability of the black nightshade plants for purifying the water sample is optimum in the 45th-80th day in the culture cycle of the black nightshade. The method is specific to the cadmium pollution in the drinking water and has the advantages of good removal effect, simplicity and convenience for operation, wide applicable range, and great application potential in the aspect of drinking water purification.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
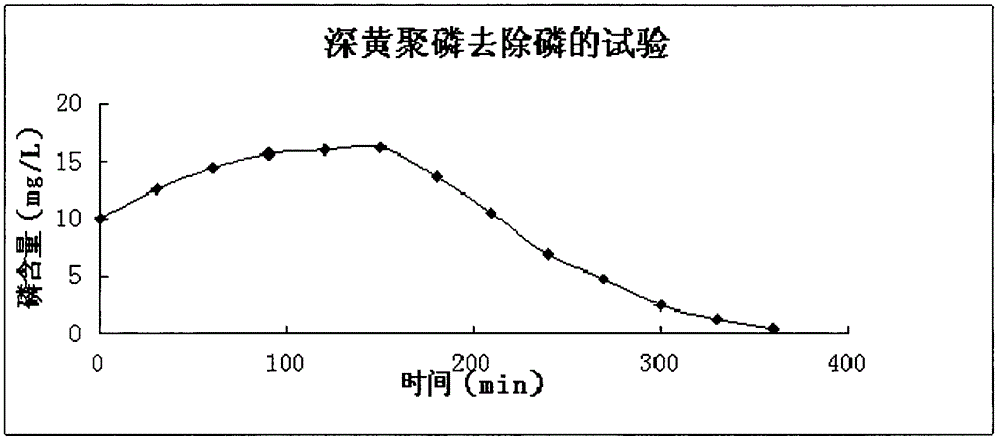
Chryseobacterium sp. for removing phosphorus in sewage at low temperature and separation culture method
ActiveCN102433277AHigh removal rateBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesPhysical chemistrySewage
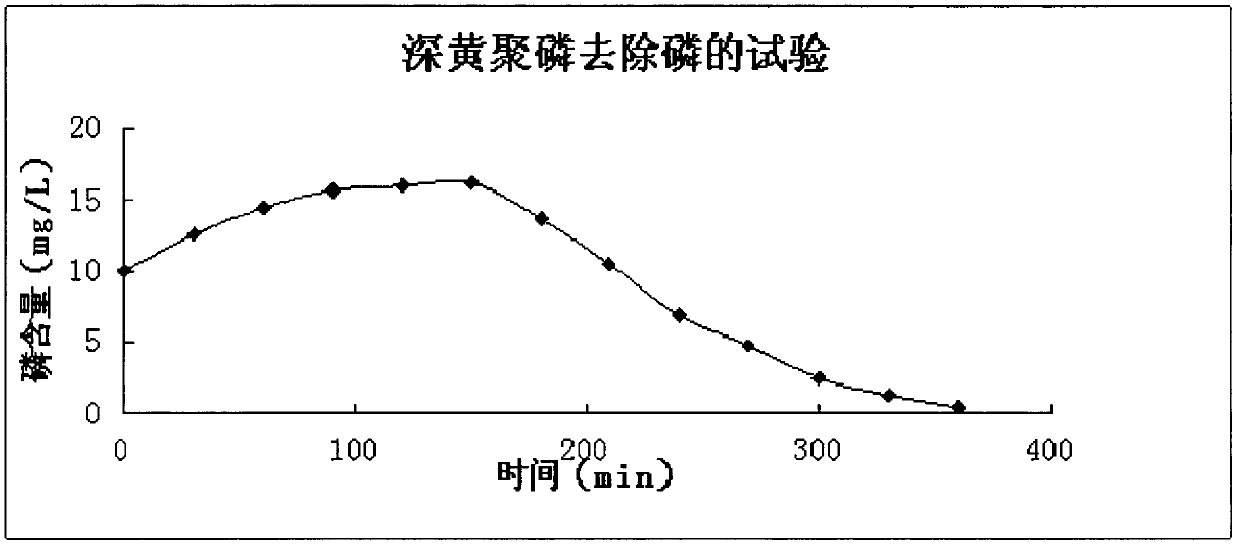
The invention discloses Chryseobacterium sp. for removing phosphorus in sewage at low temperature and a separation culture method. The Chryseobacterium sp. deep yellow polyphosphorus CGMCC No.5282 for removing the phosphorus in the sewage at low temperature has the ability of removing the phosphorus in the sewage at low temperature under aerobic conditions. The experimental result shows that: in spite of obvious inhibition of a low-temperature environment, the Chryseobacterium sp. deep yellow polyphosphorus CGMCC No.5282 for removing the phosphorus in the sewage at low temperature has a remarkable effect of strengthening the removal of the phosphorus at low temperature, especially at the temperature of between 8 and 12 DEG C, and the removal rate of the phosphorus is improved by 10 percent; and the effluent standard is superior to the first-grade A effluent standard (water temperature is less than or equal to 12 DEG C, and the control index of the first-grade A standard is 0.5mg / L).
Owner:GUOZHONG AIHUA TIANJIN MUNICIPAL ENCIRONMENT ENG
Biological deferrization demanganization functional bacterium
InactiveCN101230326AStrong biochemical abilityGood manganese removal effectBacteriaWater/sewage treatmentManganeseFlora
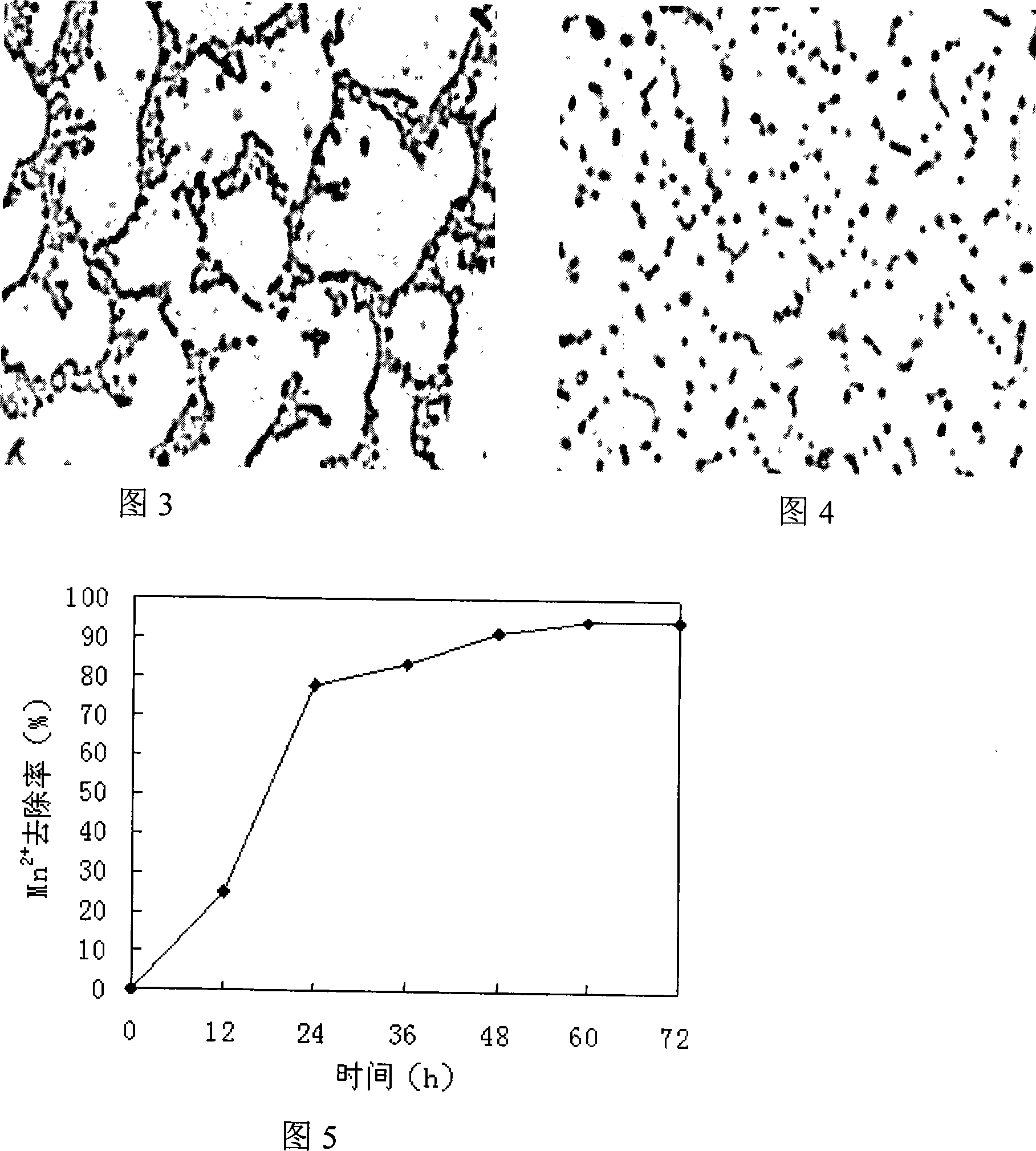
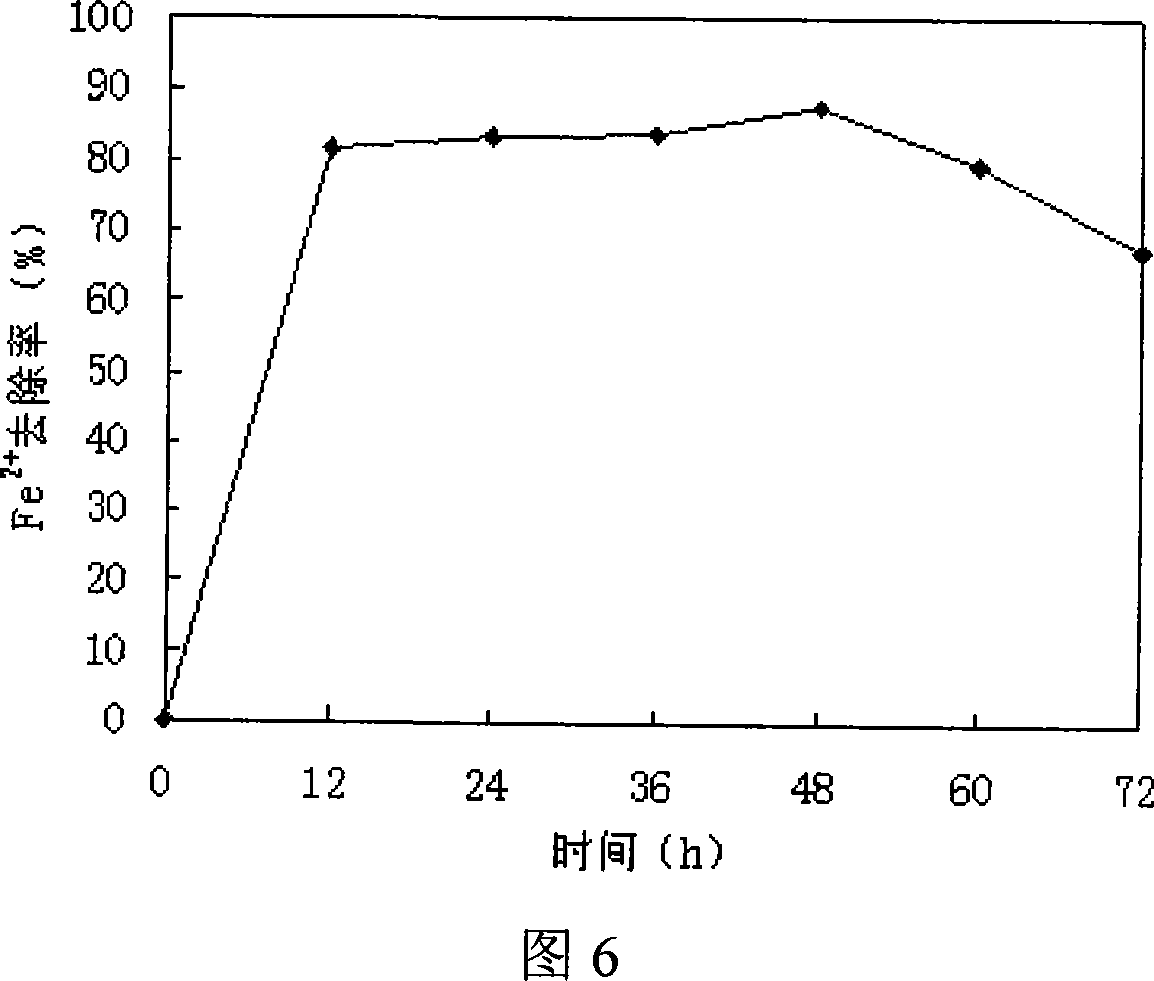
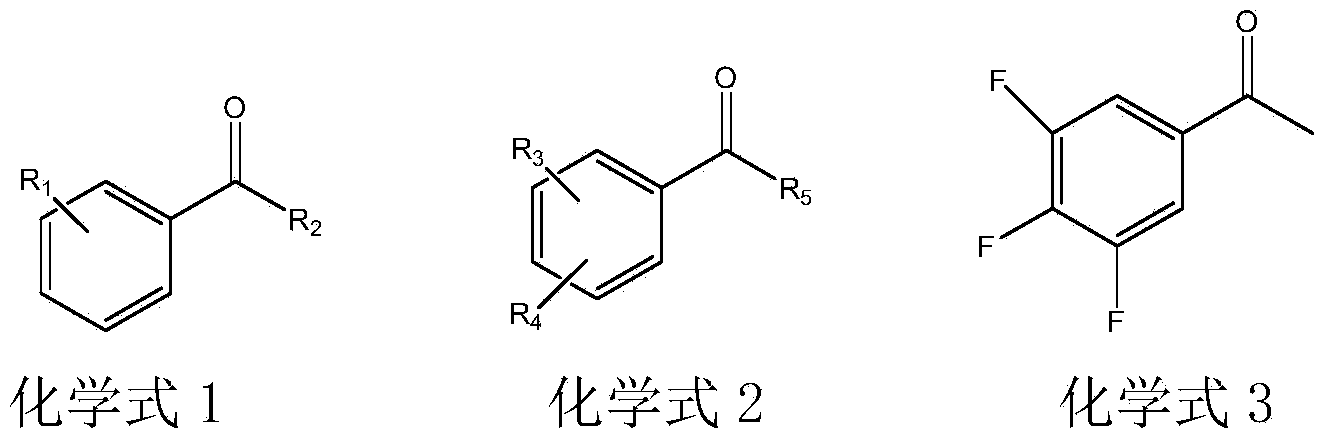
The invention provides a biological iron-removing manganese-removing functional bacterium, which relates to a microorganism. The invention solves the problems that the present biological oxidation manganese removing engineering flora is established by natural selection, the biochemical capability is weak, the manganese removing effect is poor; the establishment of the water treatment removing manganese biologic filter pond needs a long time for cultivation, domestication and startup, and the restoring period after the engineering flora is damaged is long. The biological iron-removing manganese-removing functional bacterium MSB-4(Chryseobacterium sp.) belongs to flavobacterium, is preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Commission of Culture Collection Management, the storage date is 30 Octomber 2007, the storage number is CGMCC No.2239; strain MSB-4 is aerobic strain, the length is 1.5-2 micrometers, the width is 0.8-1.1 micrometers, the strain is short rod-shaped cell with two blunt ends; brown yellow colony is formed on the substrate, the colony is non-transparent and round; the strain MSB-4 has metachromatic granules and lipoid granules, has no brood cell; N, N, N<1>, N<1>-tetramethyl-para-phenylene diamine stain is positive. The biological iron-removing manganese-removing functional bacterium MSB-4 of the invention has the capability for removing the Mn<2+>, <Fe2+> in the water, Mn<2+> removing rate can reach up to 94.44 percent, and the Fe<2+> removing rate can reach up to 90.13 percent.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Application of carbonyl reductase ChKRED20 in catalyzing carbonyl substrate
The invention provides application of carbonyl reductase ChKRED20 serving as a biocatalyst in asymmetric catalysis of multiple prochiral carbonyl substrates to generate corresponding chiral alcohols. The carbonyl reductase ChKRED20 comes from Chryseobacterium sp. CA49 and has high activity and enantioselectivity.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Application of Chryseobacterium sp. and carbonyl reductase thereof in production of aprepitant chiral intermediate
ActiveCN103497911BHigh recovery rateEasy to separate and purifyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGenomeEthanol
The invention discloses a strain of Chryseobacterium sp. CA49 (with an accession number of CCTCC M2012484), carbonyl reductase ChKRED20 coded by the genome of the strain and preparation of an aprepitant chiral intermediate (R)-1-[3,5-di(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethanol by using the original strain of Chryseobacterium sp. or the carbonyl reductase as a biocatalyst. The enantiomeric excess value of the produced intermediate is greater than 99.9%. Crude ChKRED20 enzyme powder can catalyze up to 200 g / L of a substrate and enables a conversion rate of more than 99% to be obtained in 24 h; a coenzyme circulating system is simple and cheap, the produced intermediate is easy to separate and purify, and a high recovery rate and good industrial application prospects are obtained.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Strain of chryseobacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN109943498AStrong targetingGood dissociation effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPotassiumExchangeable calcium
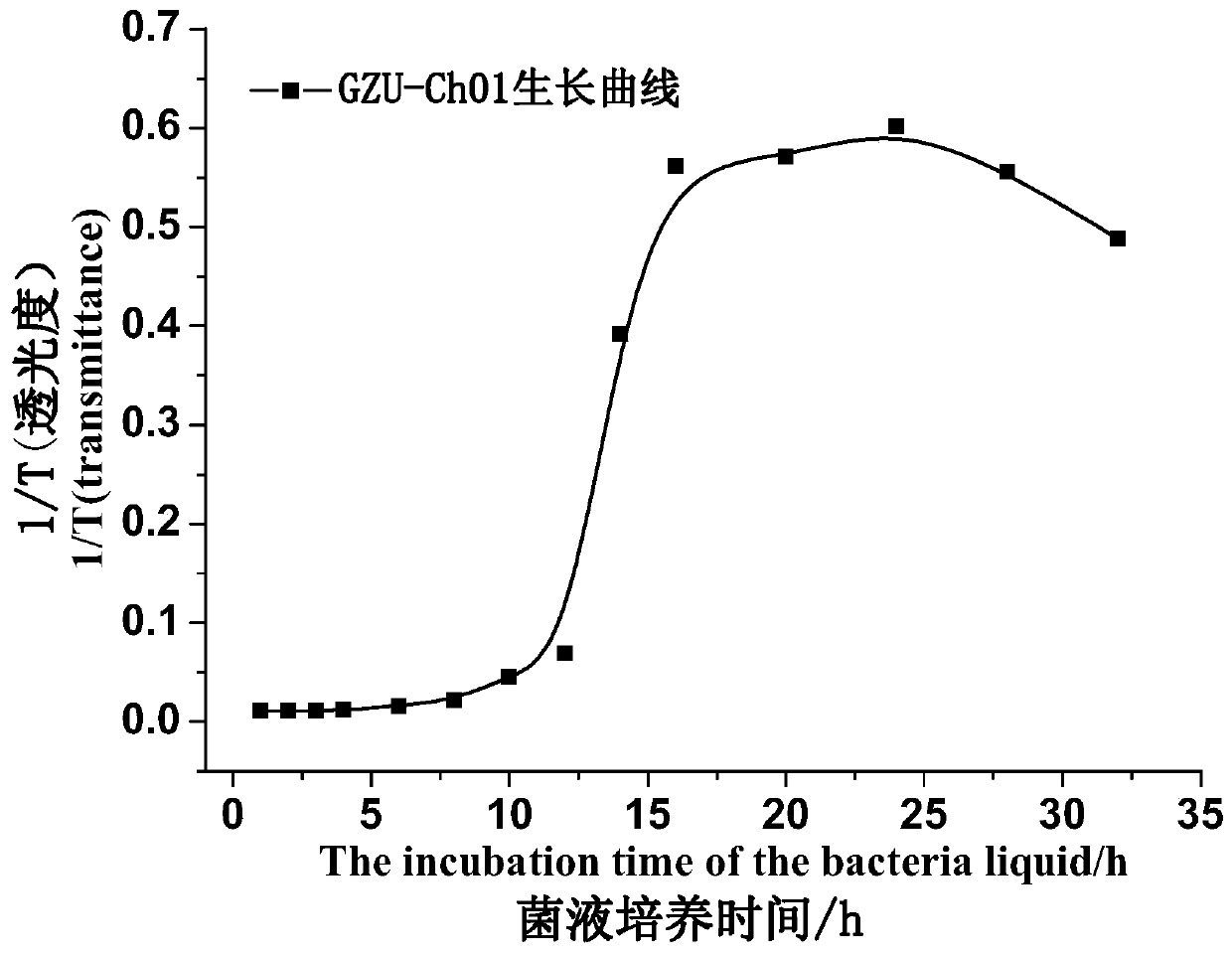
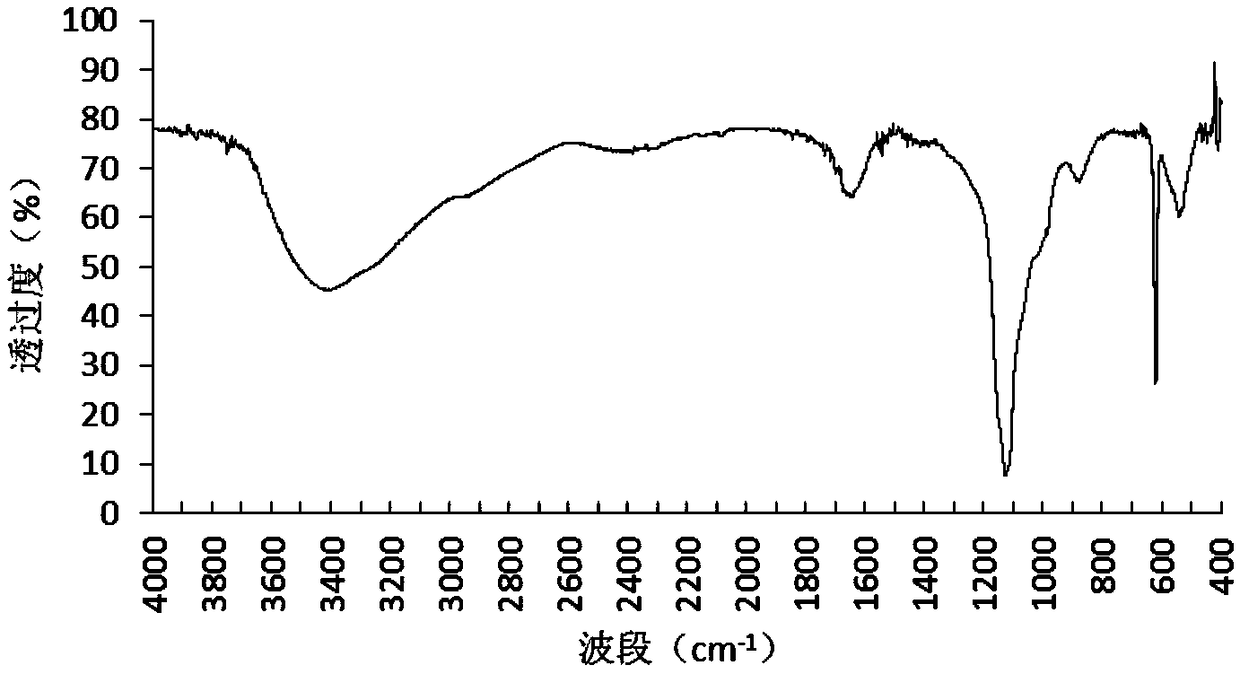
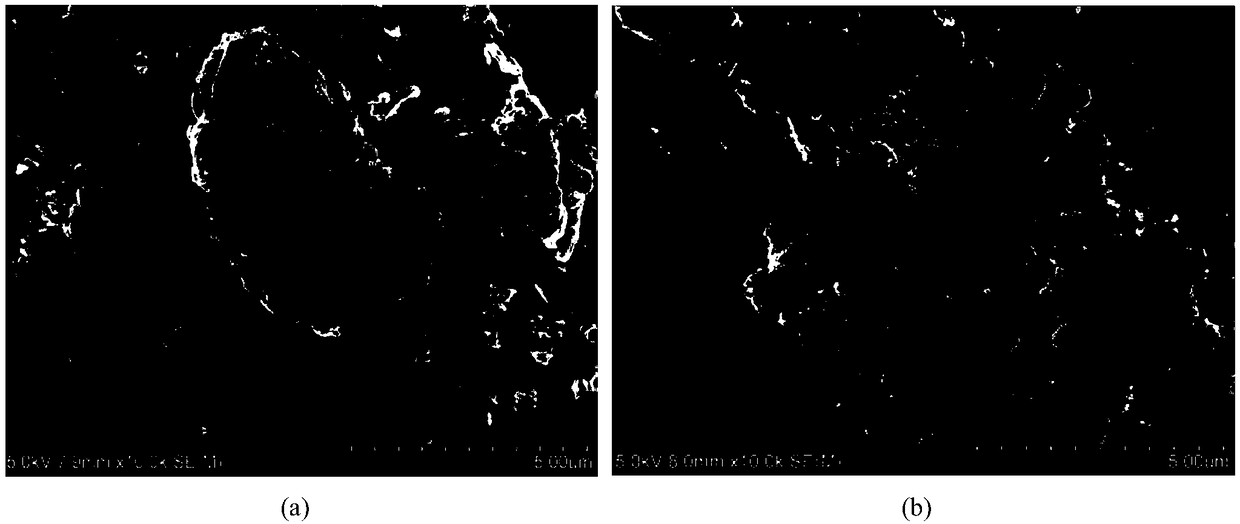
The invention discloses a strain of chryseobacterium and application thereof. The strain is the chryseobacterium; the strain is named as Chryseobacterium sp GZU-Ch01, and is preserved in typical culture Storage Center in China on December 19, 2017, and the deposit number is CCTCCNO: M2017810. The Chryseobacterium sp. GZU-Ch01 can effectively decompose insoluble potassium, phosphorus, silicon, calcium, sulfur and other components in coal gangue into quick-acting potassium, effective phosphorus, effective silicon, exchangeable calcium, effective sulfur and the like absorbed by plants as nutrients. In particular, the GZU-Ch01 can effectively dissociate the insoluble potassium from the coal gangue into the quick-acting potassium, provide a valuable source of potassium resources, has a good dissociation effect on other potassium-containing minerals, add other potassium-containing minerals such as potassium feldspar to the coal gangue, and can further enhance the potassium content of a mineral microbial compound fertilizer using the coal gangue as a base material.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
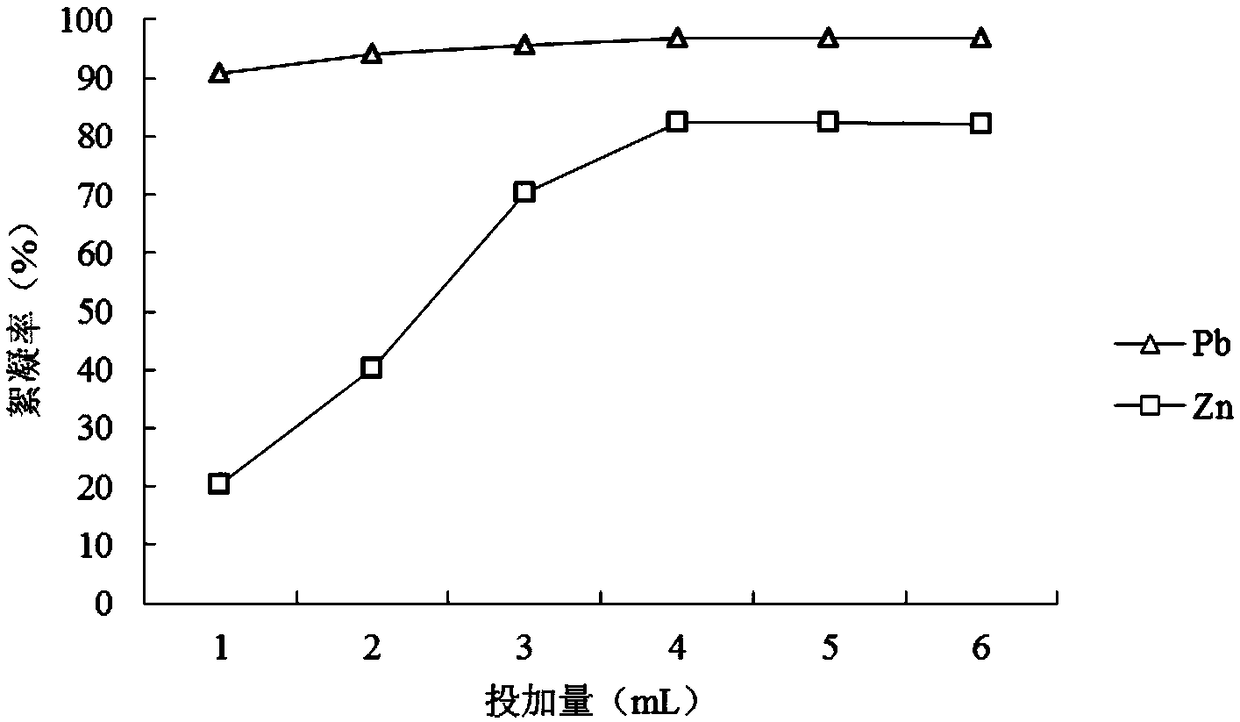
Preparation method of microbial flocculating agent for treating lead-zinc waste water
InactiveCN108658245AEasy to handleSimple processMicroorganismsWater contaminantsCulture fluidWastewater
The invention discloses a preparation method of a microbial flocculating agent for treating lead-zinc waste water. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) separating out a strain Chryseobacterium sp with flocculating ability from soil polluted by lead and zinc; (2) inoculating a single strain in a seed medium to obtain a seed culture solution; (3) inoculating the seed culture solution obtained from step (2) in a fermenting medium, and culturing to obtain a fermentation culture solution; and (4) centrifuging the fermentation culture solution obtained from step (3) to obtain supernateor a supernate extractor which is the microbial flocculating agent. The preparation method is simple in process and low in cost, and the prepared flocculating agent has good effect of treating the lead-zinc waste water, and does not cause secondary pollution.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
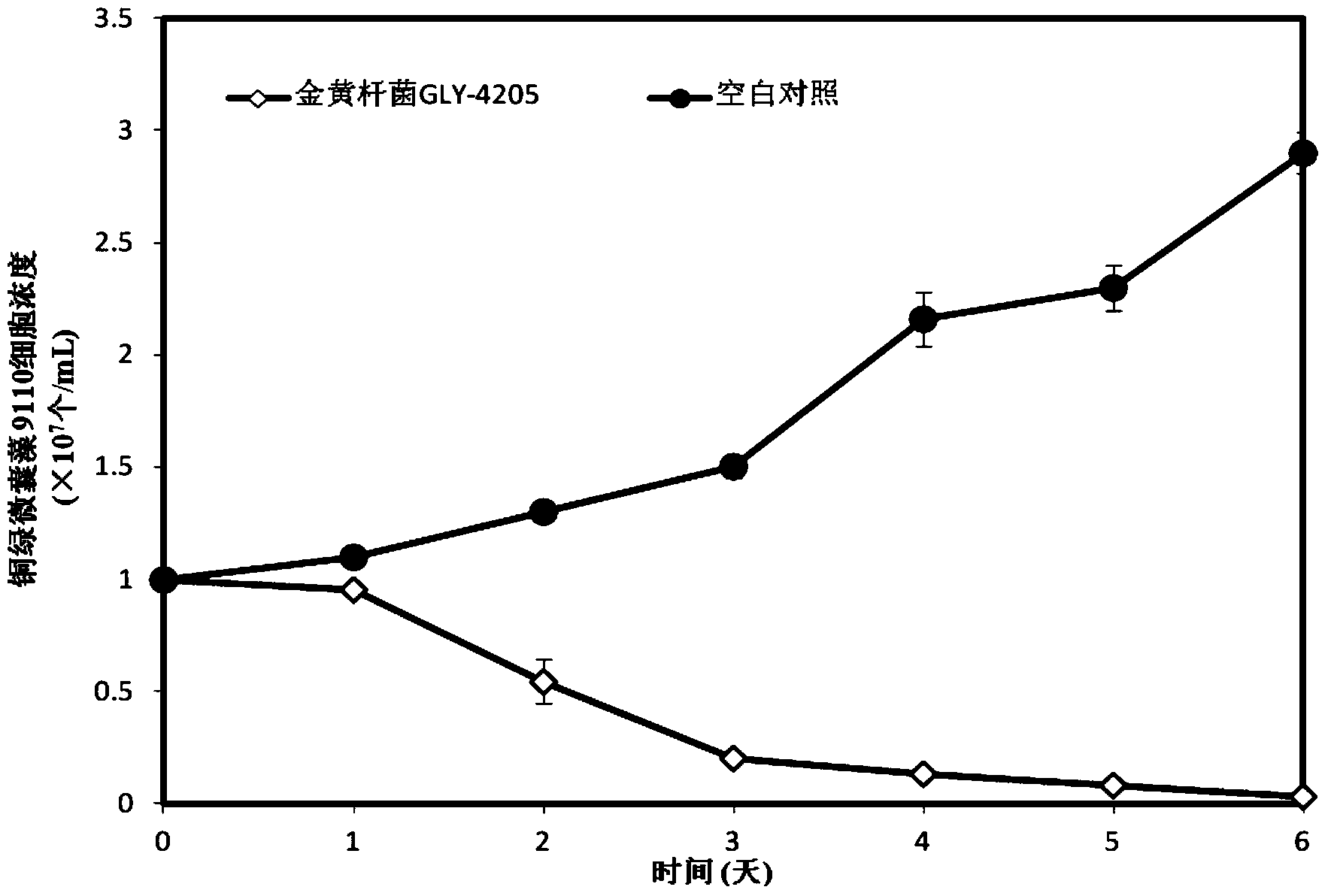
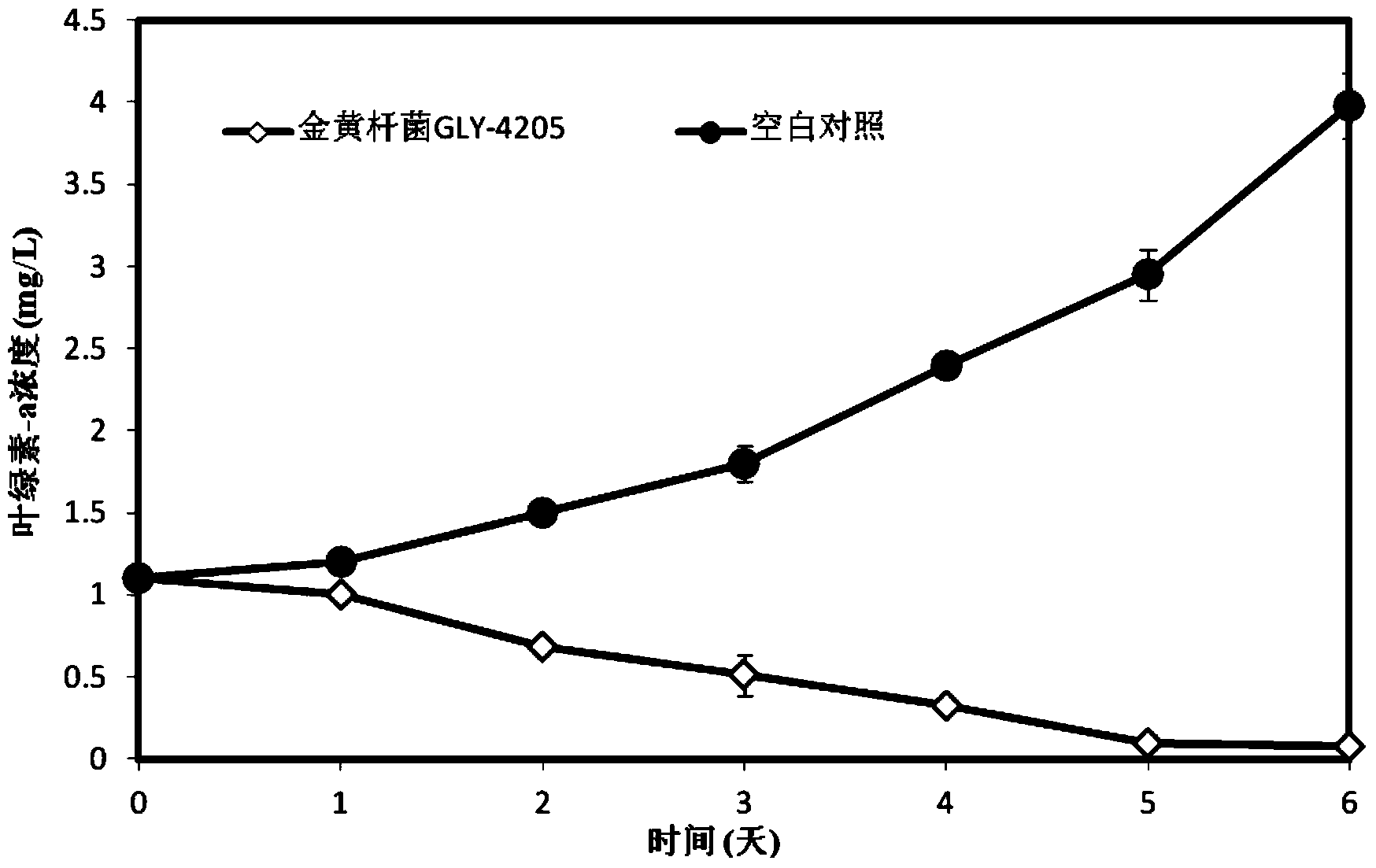
Algicidal Chryseobacterium sp. and its application in cyanobacterial bloom control
The invention discloses an algicidal Chryseobacterium sp. and its application in cyanobacterial bloom control. Highly algicidal Chryseobacterium sp. GLY-4205 is separated from water in Taihu Lake, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.8283, and an identification result of effective algicidal components separated and purified from a fermentation product of the highly algicidal Chryseobacterium sp. GLY-4205 show that the effective algicidal components comprise 3-isopropyl-hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, 7-hydroxy-3-isobutyl-hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro-3-(2-methylpropyl)-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione and hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione. The half lethal doses LD50 of the above four algicidal substances on Microcystis aeruginosa 9110 are 3.9[mu]g / mL, 0.95[mu]g / mL, 2.82[mu]g / mL, and 5.7[mu]g / mL respectively. Hexahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione has no lethal effect on synechococcus BN60, and the half lethal doses LD50 of the residual three algicidal substances on the half lethal doses are 17.19[mu]g / mL, 1.31[mu]g / mL and 3.84[mu]g / mL respectively. The algicidal Chryseobacterium sp. can be used for developing and producing novel biological algicides in order to be finally applied in the cyanobacterial bloom control of lakes.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
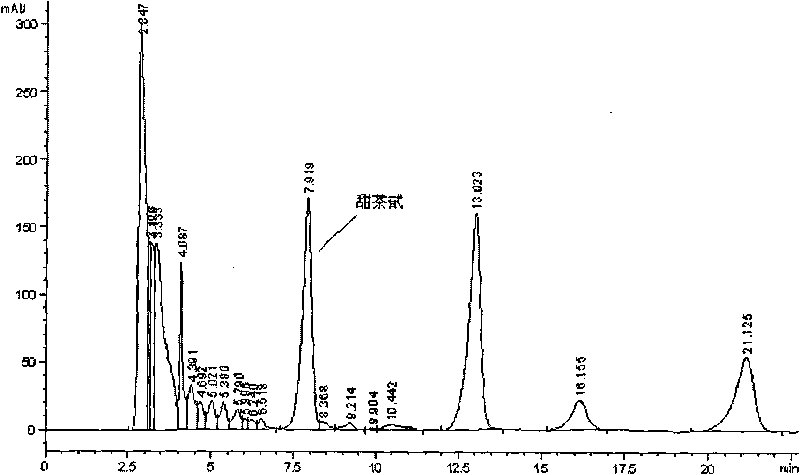
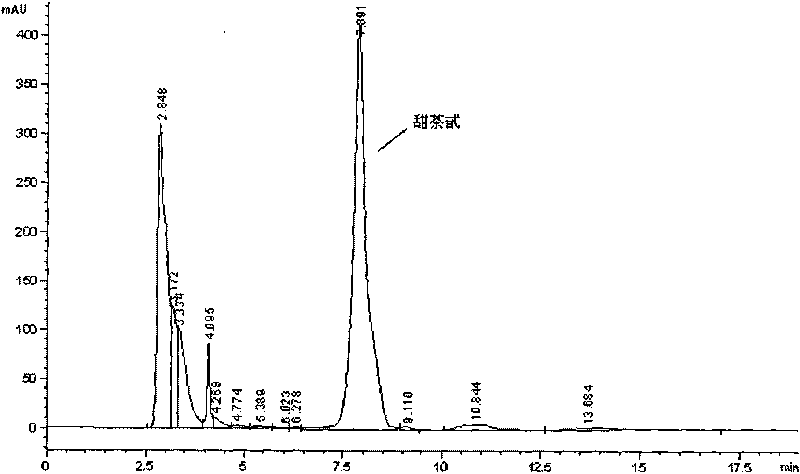
Strain for efficiently converting stevioside into rubusoside and culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN111944724AImprove stabilityImprove temperature stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHydrolysis
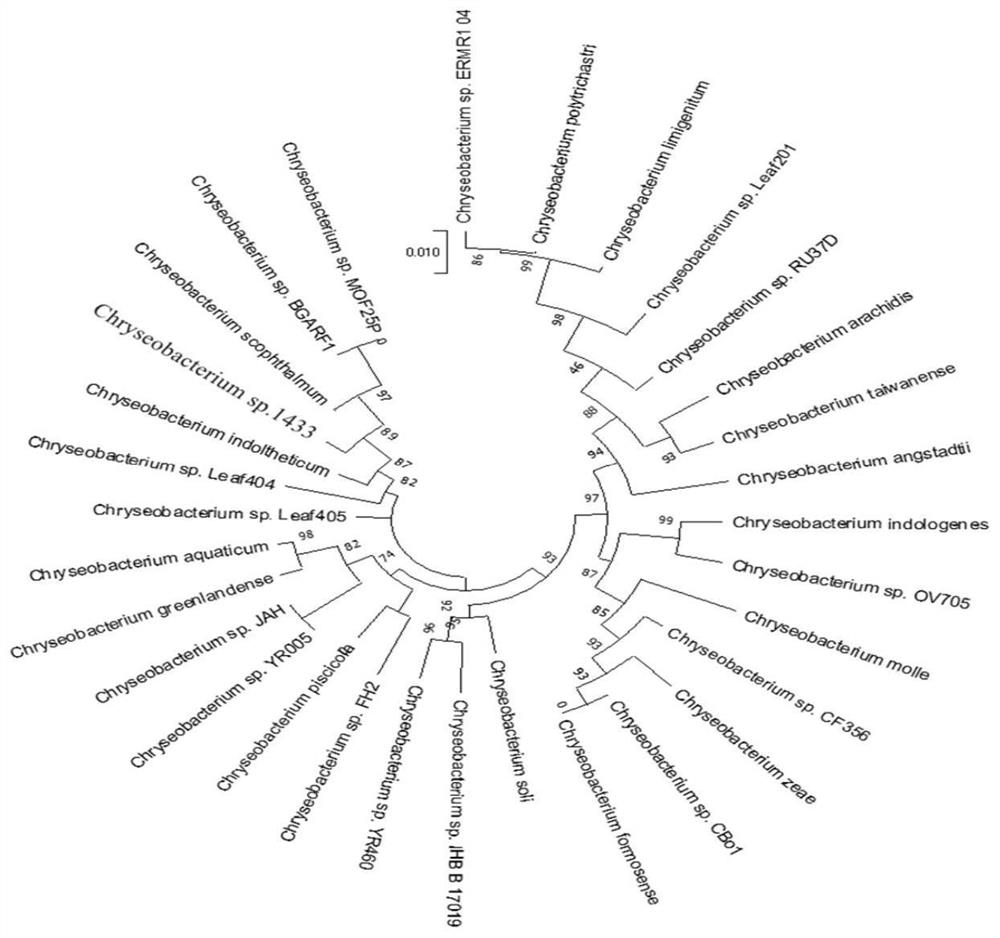
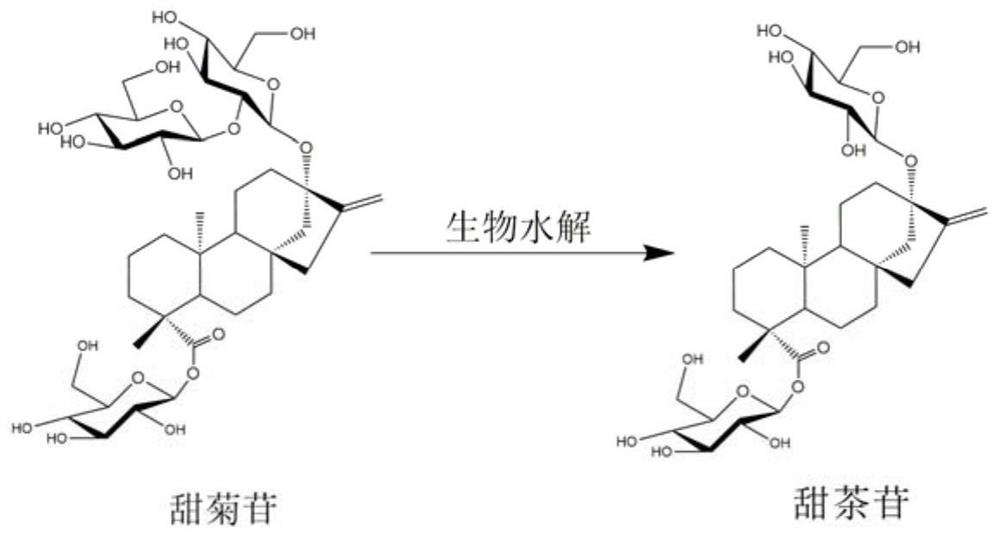
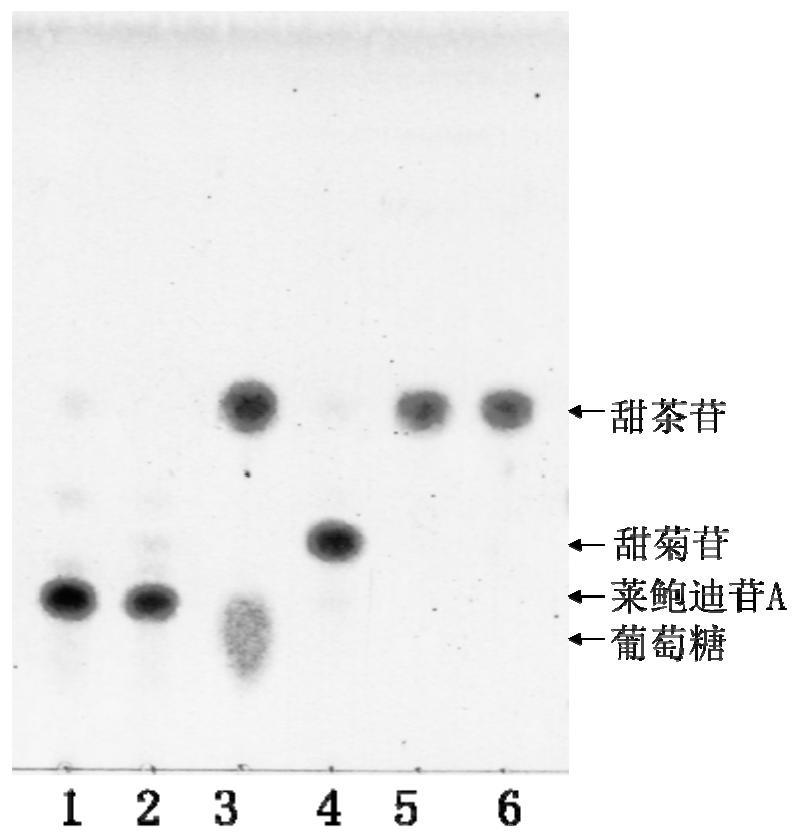
The invention relates to a strain for efficiently converting stevioside into rubusoside and a culture method and application thereof. A strain of (Chryseobacterium sp.) 1433 is preserved in the ChinaGeneral Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 6, 2020, the preservation number is CGMCC No.20188 and the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 3, No. 1 Yard, West Beichen road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The invention also relates to the culture method of the strain and the application of the strain in preparing the rubusoside. The (Chryseobacterium sp.1433) screened and separated by the invention can hydrolyze sophorose of the stevioside into glucosyl to generate the rubusoside and cannot further hydrolyze the rubusoside, so that the conversion rate of the biological strain to the stevioside reaches 100 percent, the yield of the rubusoside reaches 100 percent and the strain is completely superior to the reported related strains.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Chryseobacterium for efficient degradation of picolinic acid, and applications thereof
The invention provides a strain of Chryseobacterium for efficient degradation of picolinic acid, and applications thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. According to the present invention, a strain of picolinic acid degradation bacterial Chryseobacterium is separated and screened, wherein the strain is classified and named Chryseobacterium sp, is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and has the preservation number of CGMCC NO.10699; and the Chryseobacterium sp can effectively degrade picolinic acid in a wide pH value range or wide temperature range or in a wide pH value range and wide temperature range, can be adopted as a biological strengthening preparation so as to be used in aerobic biological treatment of picolinic acid wastewater within a weak alkali to weak acidity range and a wide temperature range, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for preparing rubusoside by stevioside
InactiveCN101701238BHigh purityLimited sources of solutionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationFood additiveAlglucerase
The present invention relates to a preparation raw material and a preparation method of rubusoside, which belongs to the field of food additives. Stevioside is transformed into rubusoside by the catalysis of chryseobacterium JH (Chryseobacterium sp.JH) CCTCC NO: M209202 or beta-glucosidase produced by the same. Concretely, the stevioside is prepared into bacterium culture liquid or enzyme transformation liquid and is transformed into rubusoside under the conditions of proper liquid loading quantity, proper transformation temperature, proper pH, proper time and the like after a right amount of bacteria or enzymes are added, and the rubusoside with high purity is obtained after the transformed rough transformation liquid is further separated and purified. The invention provides a novel raw material for preparing the rubusoside, which expands the source of raw materials and has stronger practical value.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Chryseobacterium sp. L31 and application thereof
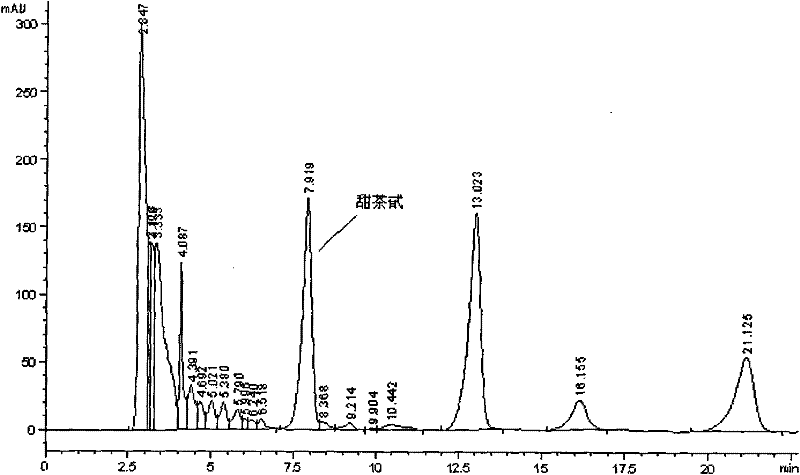
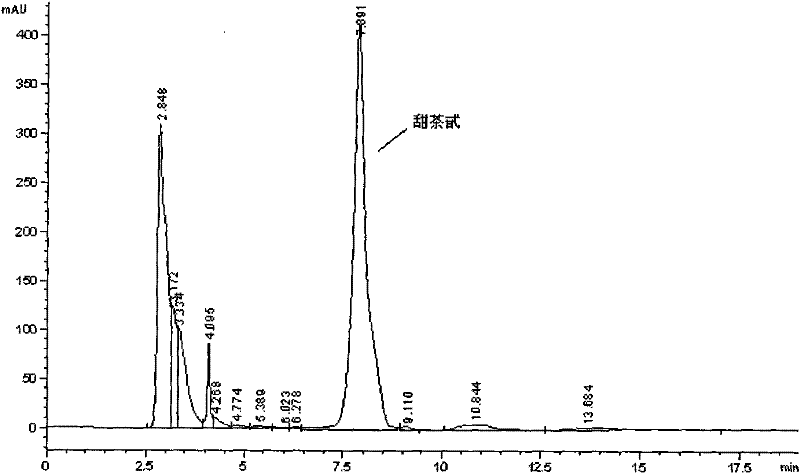
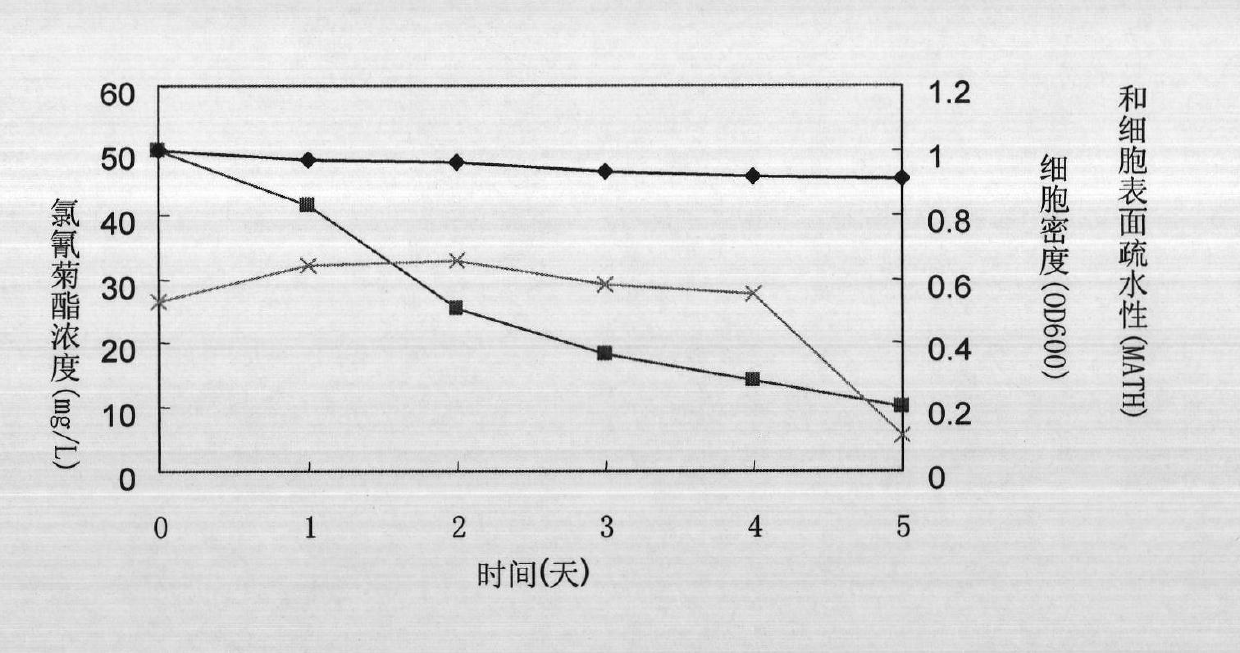
InactiveCN101948789AImprove degradation rateHigh cell surface hydrophobicityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCypermethrinMicrobiology
The invention provides a Chryseobacterium sp. L31 strain of which the preservation number is CGMCC No. 4137, which is separated and obtained from a sewage treatment aeration tank of Shandong Huayang pesticide factory by an acclimating method. The strain can degrade cypermethrin pesticide of 50mg / L by about 71% in 3 days, and can maintain stable degradation ability. In addition, the cell surface of the strain has very high hydrophobicity, and the hydrophobicity of the cell surface can be adjusted for finishing adsorption degradation of the hydrophobic pesticide.
Owner:中国农业科学院研究生院
Indole-producing Chryseobacterium sp. And application thereof
ActiveCN114703078AEnhanced inhibitory effectSuppress dysplasiaBiocideCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyMetabolite
The invention provides a Chryseobacterium indologenes producing strain, a culture of the strain, an application of the strain in resisting nematodes, and a use method of the strain and the culture. The culture (including fermentation broth, metabolite and extract) of the Chryseobacterium indole and the compound separated from the culture can inhibit the development of various nematodes, especially has a remarkable inhibition effect on pine wood nematodes, can be used for preparing corresponding products capable of being practically applied, and has wide application prospects. The application potential in the fields of medicines, pesticides and cleaning products is huge.
Owner:沈阳恩柽研究院有限公司
Chryseobacterium sp., fungicide containing Chryseobacterium sp., application of Chryseobacterium sp. And fungicide and method for degrading plastic
ActiveCN114540260AWith research and developmentWith engineering applicationBacteriaPlastic recyclingBiotechnologyPolyethylene glycol
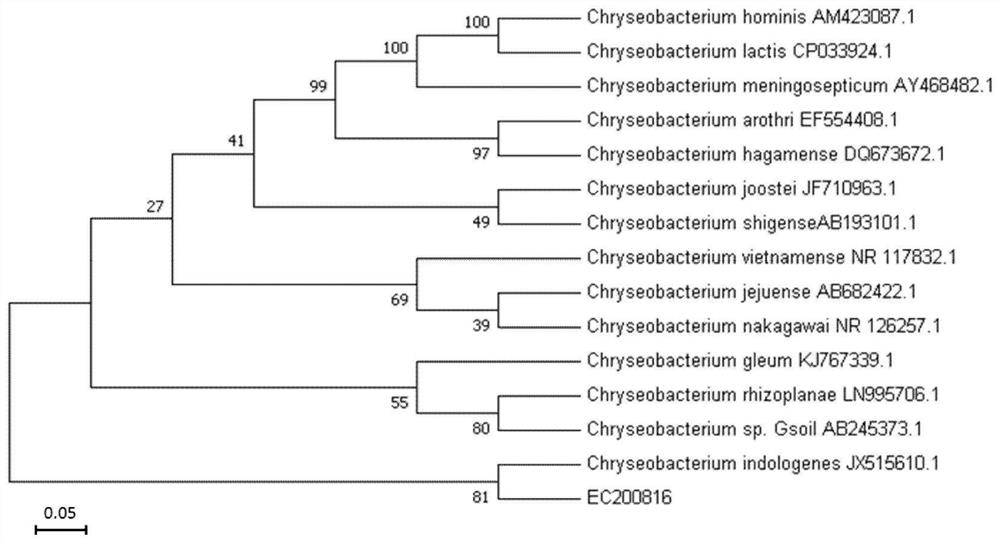
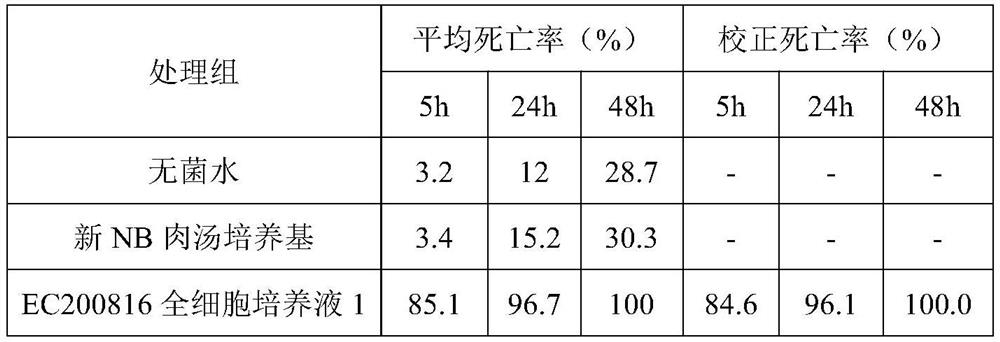
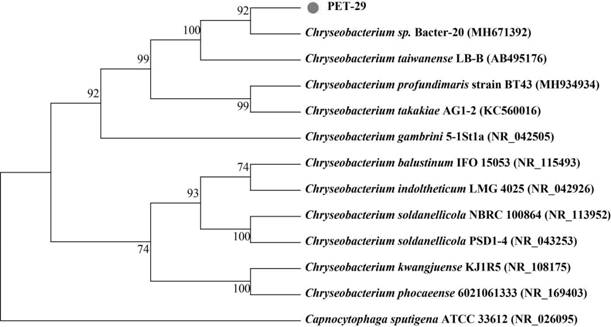
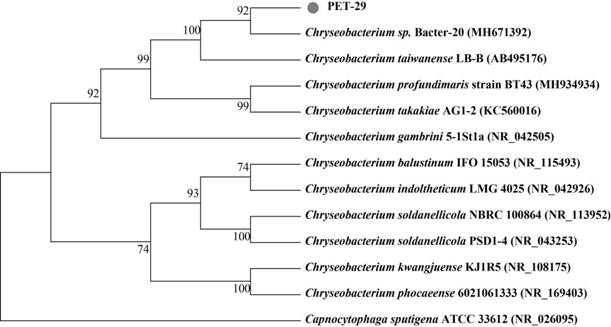
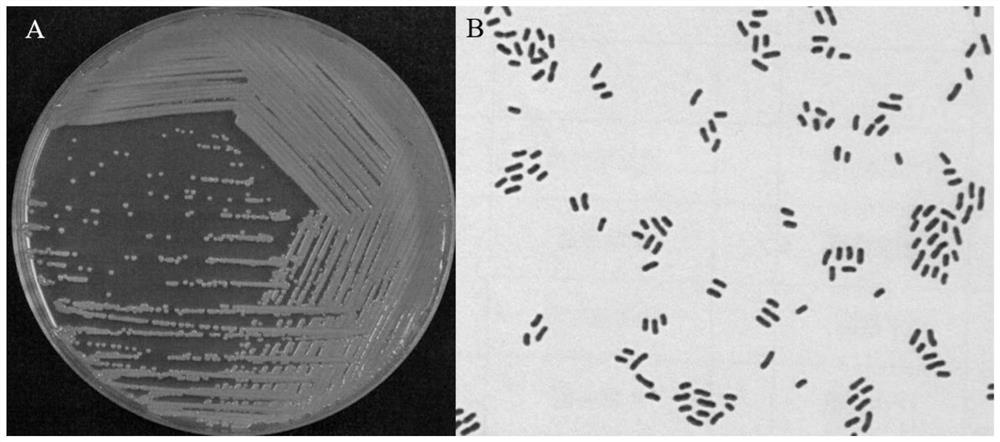
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses Chryseobacterium sp., a fungicide containing the Chryseobacterium sp., application of the Chryseobacterium sp. And a method for degrading plastics. The strain name of the Chryseobacterium sp. PET-29 is Chryseobacterium sp. PET-29, and the preservation number of the Chryseobacterium sp. PET-29 is CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) NO: M 2022311. The bacterial agent provided by the invention contains the Chryseobacterium sp. The invention also provides the application of the Chryseobacterium sp. And the microbial inoculum in plastic degradation. The method for degrading the plastic comprises the step of contacting the Chryseobacterium sp. And / or the fungicide with the plastic. The Chryseobacterium sp. Strain or the bacterial agent containing the strain can be used for biodegrading polyethylene glycol terephthalate plastics, and has further research and development and engineering application prospects in the fields of novel plastic degrading enzyme mining and modification, waste plastic recycling, environmental plastic pollution bioremediation and the like.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of Chryseobacterium bacterial strain and application thereof
ActiveCN109943498BStrong targetingGood dissociation effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPotassiumBiology
The invention discloses a strain of the genus Chryseobacterium and an application thereof. The strain is Chryseobacterium sp; National Object Collection Center, the collection number is CCTCCNO: M2017810. Chryseobacterium sp GZU-Ch01 of the present invention can effectively decompose insoluble potassium, phosphorus, silicon, calcium, sulfur and other components in coal gangue to become available potassium, available phosphorus, available silicon, exchangeable calcium, effective Sulfur, etc. are used as nutrients absorbed by plants. In particular, GZU‑Ch01 can effectively dissociate insoluble potassium in coal gangue, making it into available potassium, which provides a valuable source of potassium resources. The gangue is mixed with other potassium-containing minerals such as potassium feldspar, which can further increase the potassium content in the mineral and microbial compound fertilizer based on coal gangue.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Chryseobacterium sp. capable of using methane and application thereof
InactiveCN102071161BImprove oxidation activityStrong toleranceBacteriaDispersed particle separationMicrobiologyPaddy field
The invention discloses chryseobacterium sp. JT03 capable of using methane. The preservation number of a strain is CCTCC No.M2010100. The chryseobacterium sp. can be used for preparing a methane biological absorbent, a garbage treating agent and a biological catalyst. The chryseobacterium sp. overcomes the application defects of low bacteria density of methane-oxidizing bacteria, difficulty in amplification culture of bacteria and the like, and has high affinity to methane. The chryseobacterium sp. is particularly suitable for methane artificial sources such as household garbage landfill sites, paddy fields and the like, and can be widely popularized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
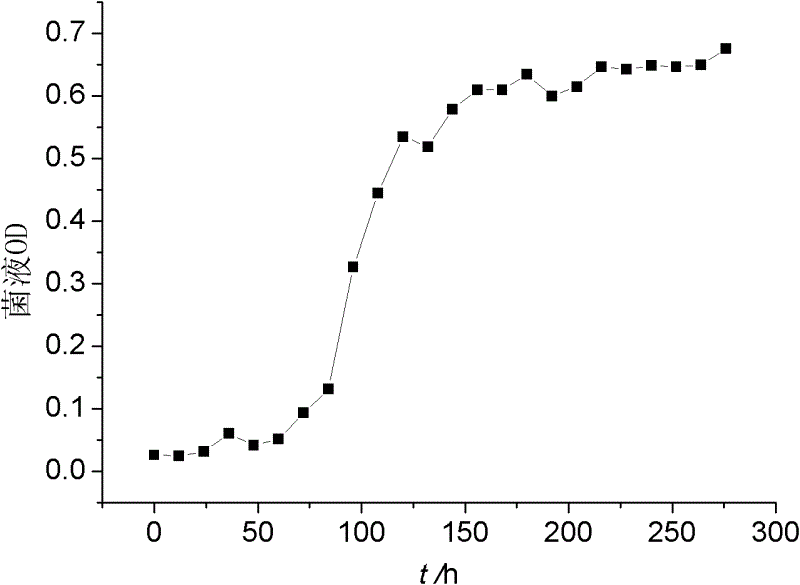
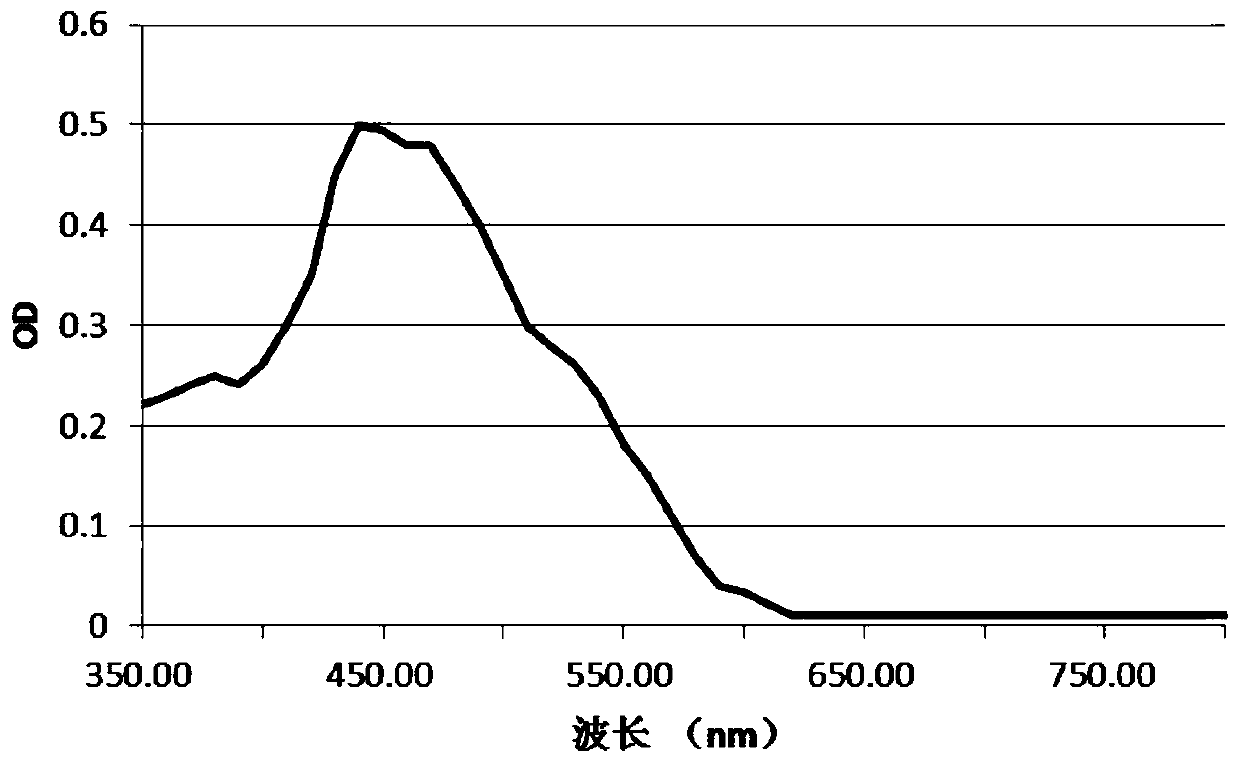
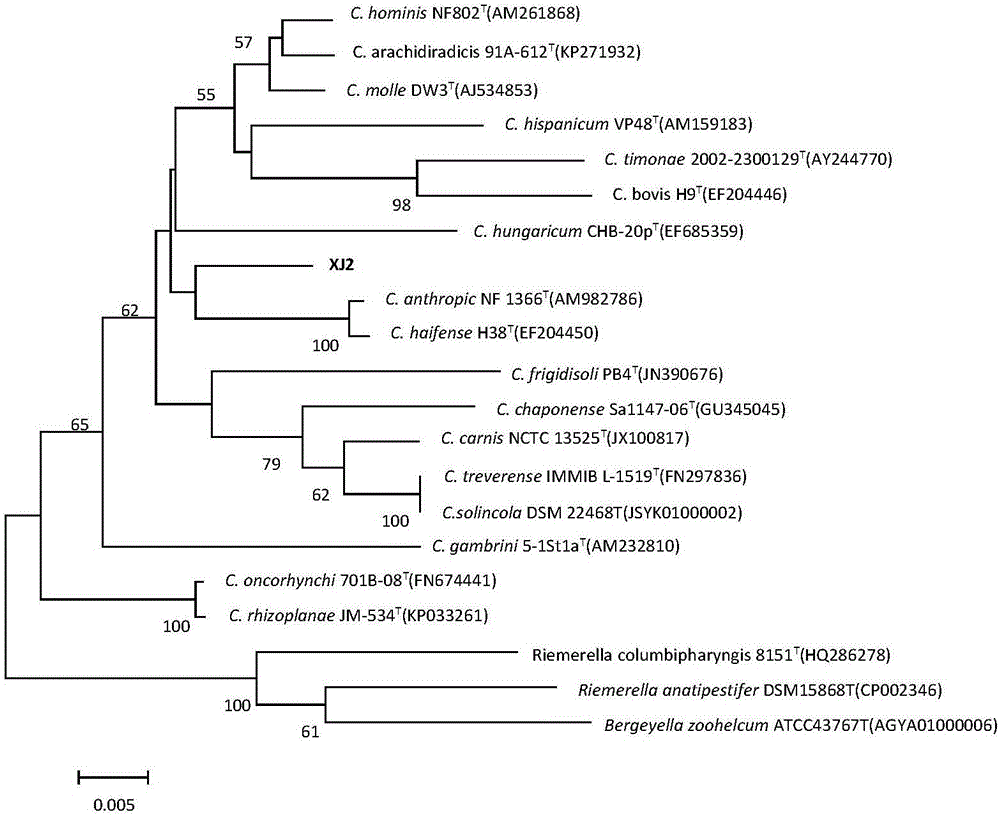
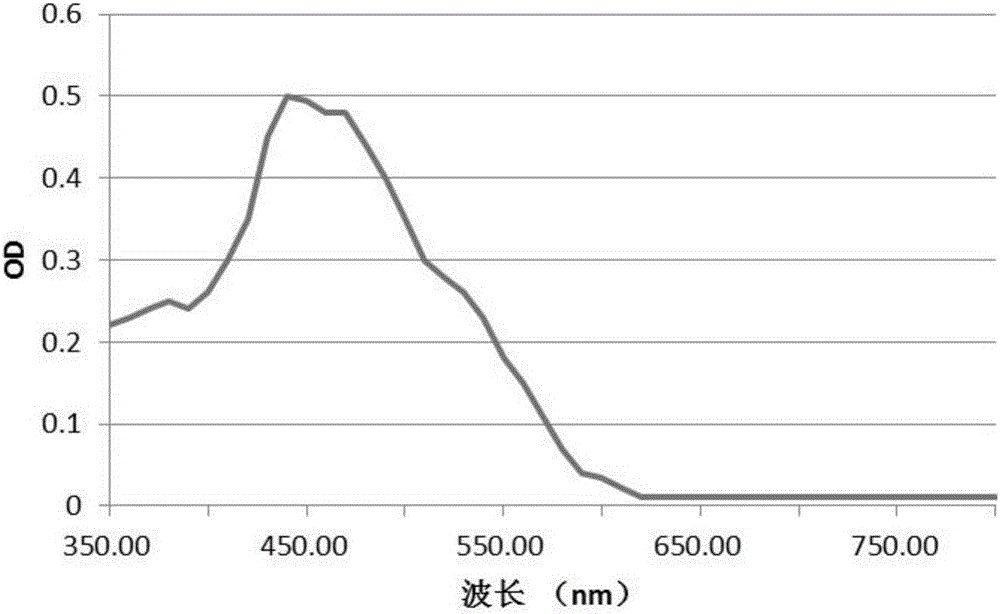
A new strain of natural yellow pigment producing bacteria xj2 and its preparation and application
ActiveCN106701640BFast growthLow requirements for cultivation conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhoto stability
The invention discloses a new strain of natural yellow pigment producing bacteria XJ2 and its pigment preparation. Chryseobacterium sp. ) The identification of XJ2 CGMCC No.13157 shows that it belongs to a typical new strain. It produces natural yellow pigment through activation, proliferation and extraction. The natural yellow pigment produced is soluble in water, methanol and ethanol, and easily soluble in acetone and acetic acid. Low polar solvents such as ethyl ester and n-butanol, the ethanol solution of the extract has a maximum absorption peak at 438nm; it has anti-oxidation function; it is stable in the range of pH2.0~9.0; it has good thermal stability and certain light Stability has great practical significance for the production of natural yellow pigment.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
New strain of producing strain XJ2 of natural yellow pigment and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN106701640AFast growthLow requirements for cultivation conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesN-ButanolEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a new strain of a producing strain XJ2 of a natural yellow pigment and preparation of pigment. It is indicated that the new strain is a typical new strain by identifying Chryseobacterium sp.XJ2 CGMCC No.13157, the natural yellow pigment is produced through activation, proliferation and extraction, the produced natural yellow pigment can be dissolved in water, methanol and ethanol and is easily dissolved in acetone, ethyl acetate, n-butanol and other ultralow-polarity solvents, the extract ethanol solution has a maximum absorption peak at the position of 438 nm, and the new strain has an anti-oxidation function, is stable in the pH range of 2.0-9.0, has good thermal stability and certain light stability, and has great practical significance for the production of the natural yellow pigment.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Chryseobacterium sp. for removing phosphorus in sewage at low temperature and separation culture method
ActiveCN102433277BHigh removal rateBacteriaTreatment using aerobic processesPhysical chemistrySewage
The invention discloses Chryseobacterium sp. for removing phosphorus in sewage at low temperature and a separation culture method. The Chryseobacterium sp. deep yellow polyphosphorus CGMCC No.5282 for removing the phosphorus in the sewage at low temperature has the ability of removing the phosphorus in the sewage at low temperature under aerobic conditions. The experimental result shows that: in spite of obvious inhibition of a low-temperature environment, the Chryseobacterium sp. deep yellow polyphosphorus CGMCC No.5282 for removing the phosphorus in the sewage at low temperature has a remarkable effect of strengthening the removal of the phosphorus at low temperature, especially at the temperature of between 8 and 12 DEG C, and the removal rate of the phosphorus is improved by 10 percent; and the effluent standard is superior to the first-grade A effluent standard (water temperature is less than or equal to 12 DEG C, and the control index of the first-grade A standard is 0.5mg / L).
Owner:GUOZHONG AIHUA TIANJIN MUNICIPAL ENCIRONMENT ENG
Biological deferrization demanganization functional bacterium
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A novel high-efficiency β-glucosidase csbgl and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN111893109BImprove efficiencyEfficient hydrolysis abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideHydrolysis
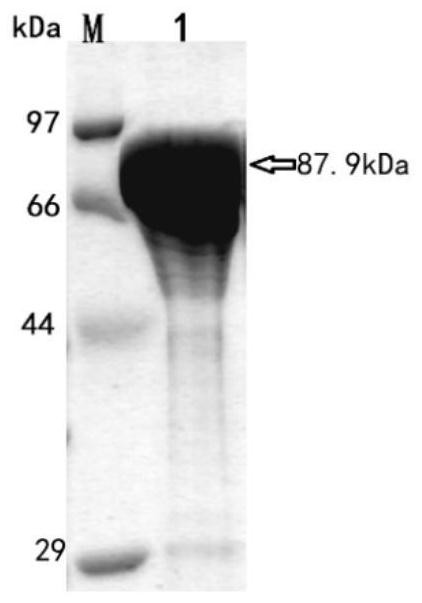
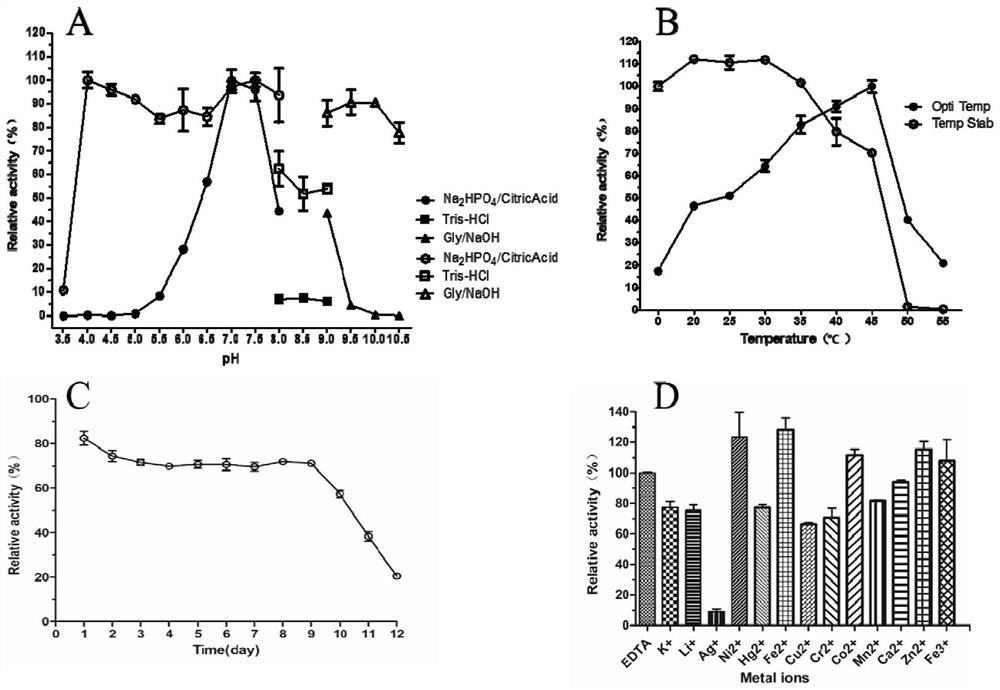
The invention relates to a novel high-efficiency β-glucosidase CsBGL and its coding gene and application. A β-glucosidase CsBGL, the amino acid sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The nucleotide sequence of the coding gene of the β-glucosidase CsBGL is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The β-glucosidase CsBGL is derived from Chryseobacterium sp. 1433, and the Chryseobacterium sp. 1433 was preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on July 6, 2020. Collection number CGMCC No.20188, address: Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 3, Yard 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The invention provides a novel and efficient β-glucosidase CsBGL, which can hydrolyze the sophoryl group of stevioside into glucose group, generate rubusoside, and will not further hydrolyze rubusoside, so that the conversion rate of stevioside reaches 100%, sweet tea The yield of glycosides reaches 100%.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for preparing bio-organic fertilizer from kitchen garbage
InactiveCN112939700AAccelerate the degree of humificationHigh activityBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bio-organic fertilizer from kitchen garbage. The method comprises the following steps: adding feathers into kitchen garbage, degrading the feathers into amino acids by using a bacterial agent prepared from a feather degrading bacterium, namely Chryseobacterium sp., and supplementing nutrients in the composting process of the kitchen garbage by using the amino acids, so that the activity of microorganisms is improved and humification degree of the kitchen garbage is accelerated. Besides, keratin waste and kitchen garbage waste are organically combined, a large amount of amino acids in feather is obtained through efficient feather degrading bacteria, the effect of replacing rapeseed meal compost in the prior art can be achieved, the cost is greatly reduced, and the final bio-organic fertilizer is high in activity, can effectively improve crop growth, and especially has a salt stress relieving effect on salinized soil in facility agriculture.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Bacillus aureus, inoculants containing the same, applications thereof, and methods for degrading plastics
ActiveCN114540260BMild conditionsLow costBacteriaPlastic recyclingBiotechnologyPolyethylene terephthalate glycol
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses a strain of aureus aureus, a bacterial agent containing the bacteria, applications thereof and a method for degrading plastics. The bacterial strain of the aureobacter aureus is named as the aureus PET-29 ( Chryseobacterium sp. PET‑29), the deposit number is CCTCC NO:M 2022311. The microbial inoculum provided by the present invention contains the aforementioned Bacillus aureus. The present invention also provides the application of the above-mentioned Bacillus aureus and the above-mentioned bacterial agent in degrading plastics. The method for degrading plastic comprises: contacting the above-mentioned aureobacteria and / or the above-mentioned bacterial agent with plastic. The Bacillus aureus strain provided by the invention or the bacterial agent containing the strain can be used for biodegrading polyethylene terephthalate plastics, in the discovery and transformation of new plastic degrading enzymes, the recycling of waste plastics, the bioremediation of environmental plastic pollution, etc. The field has the prospect of further research and development and engineering application.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
New strain of Chryseobacterium sp. And application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of wine brewing microorganisms, and particularly relates to a novel Chryseobacterium strain and application thereof. The invention provides a novel strain of Chryseobacterium aiming at the problem that the variety of functional microorganisms capable of improving aroma in the fermentation process of Baijiu in the existing report is less. The preservation number of the novel strain of the Chryseobacterium is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) The new strain provided by the invention can simultaneously produce 2, 5-dimethylpyrazine, 2, 3-butanedione, 4-octanone, ethyl phenylacetate, indole, phenylacetaldehyde, dibutyl adipate and the like, provides a new strain for aroma production in white spirit brewing, enriches the resources of brewing microorganisms, and has a very good application value.
Owner:WULIANGYE +1
Oral flora microorganisms for children autism assessment
ActiveCN111455076AIncrease abundanceReduce abundanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacteroides
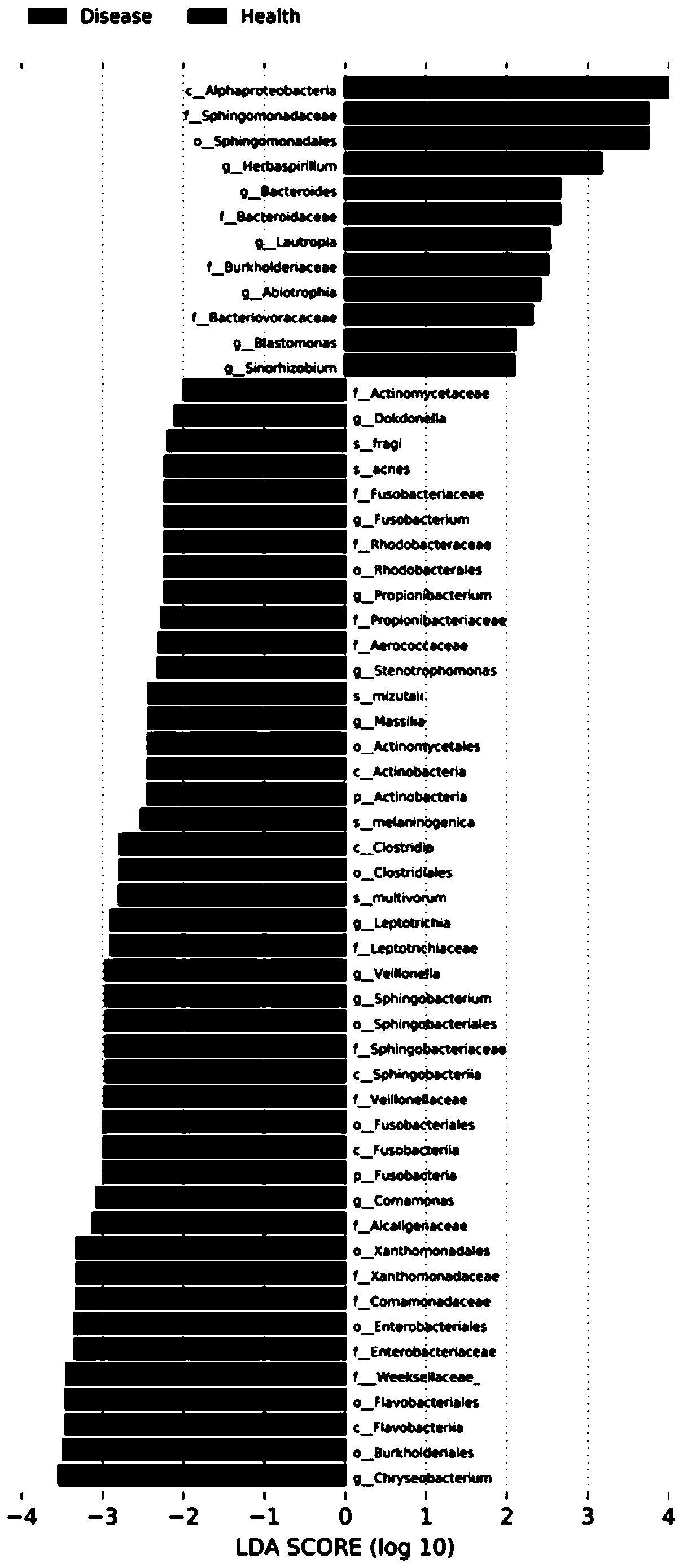
The invention provides an oral flora microorganism for evaluating autism of children, which is characterized in that oral swabs are adopted to respectively sample oral flora of children with autism and healthy children, genomic DNA is extracted, and high-throughput sequencing is performed through an Illumina Hiseq platform; the obtained data is analyzed through QIIME software, a molecular marker of bacteria is found through LEfSe analysis, and the molecular marker is applied to molecular diagnosis of autism; the data after noise reduction optimization is compared with oral flora data of healthy children; the obtained Chryseobacterium, comamonas, veillonella, sphingobacterium, Leptotrichia, Massilia, stenotrophomonas, propionibacterium, fusobacterium, Herbaspirillum, bacteroides, Lautropia,auxotrophic bacteria, Gemmatimonas and Sinorhizobium fredii have relatively high specificity and sensitivity; the microorganisms can be used as characteristic bacterial genus to evaluate children autism.
Owner:QILU CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG UNIV
A strain of Chryseobacterium efficiently degrading picolinic acid and its application
The invention provides a strain of Chryseobacterium that efficiently degrades picolinic acid and its application, belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. The present invention isolates and screens a picolinic acid-degrading bacterium, Chryseobacterium sp., which is classified as Chryseobacterium sp. and is preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Committee for the Collection of Microorganisms, with the preservation number CGMCC NO.10699. The advantage of the present invention is that this Chryseobacterium can effectively degrade picolinic acid under the condition that the pH value range is wider or the temperature range is wider, and the pH value range is wider and the temperature range is wider; The aerobic biological treatment of picolinic acid wastewater in a wide temperature range from weak base to weak acid has broad application prospects.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Microorganism for promoting black nightshade to remove trace cadmium pollution in water and method for removing cadmium pollution
The invention provides a microorganism for promoting black nightshade to remove trace cadmium pollution in water and a method for removing cadmium pollution, aiming to purify drinking water subjected to cadmium pollution by virtue of the high-efficiency absorption characteristic of super-accumulated plants, namely black nightshade, to cadmium. In the method, the black nightshade is cultured in anaquaculture manner, and Chryseobacterium sp. LKS03 is inoculated to the black nightshade to promote the roots of the black nightshade to grow; and during purification of drinking water, the roots of black nightshade plants are immersed into the drinking water subjected to cadmium pollution, and each black nightshade plant correspondingly purifies about 1-1.2L of the drinking water in a purification cycle, wherein the purification time is for 2-12h according to the cadmium ion concentration (not higher than 200mug / L) in a water sample, and the capability of the black nightshade plants for purifying the water sample is optimum in the 45th-80th day in the culture cycle of the black nightshade. The method is specific to the cadmium pollution in the drinking water and has the advantages of good removal effect, simplicity and convenience for operation, wide applicable range, and great application potential in the aspect of drinking water purification.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Novel efficient beta-glucosidase CsBGL as well as encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN111893109AImprove efficiencyEfficient hydrolysis abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideBacterosira
The invention relates to a novel efficient beta-glucosidase CsBGL as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the beta-glucosidase CsBGL is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. The nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene of the beta-glucosidase CsBGL is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. The beta-glucosidase CsBGL is derived from Chryseobacterium sp. 1433, the Chryseobacterium sp. 1433was preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 6, 2020, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 20188, and the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academyof Sciences, No. 3, No. 1 Yard, Beichenxi Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing City. The novel efficient beta-glucosidase CsBGL provided by the invention can hydrolyze sophorose of stevioside into glucosyl to generate rubusoside, the rubusoside cannot be further hydrolyzed, so that the conversion rate of the rubusoside reaches 100%, and the yield of the rubusoside reaches 100%.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com