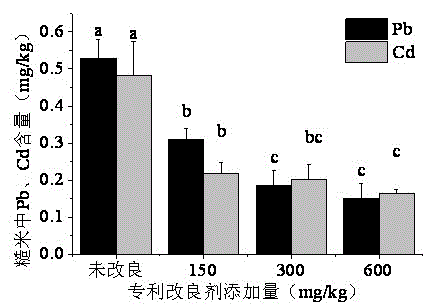
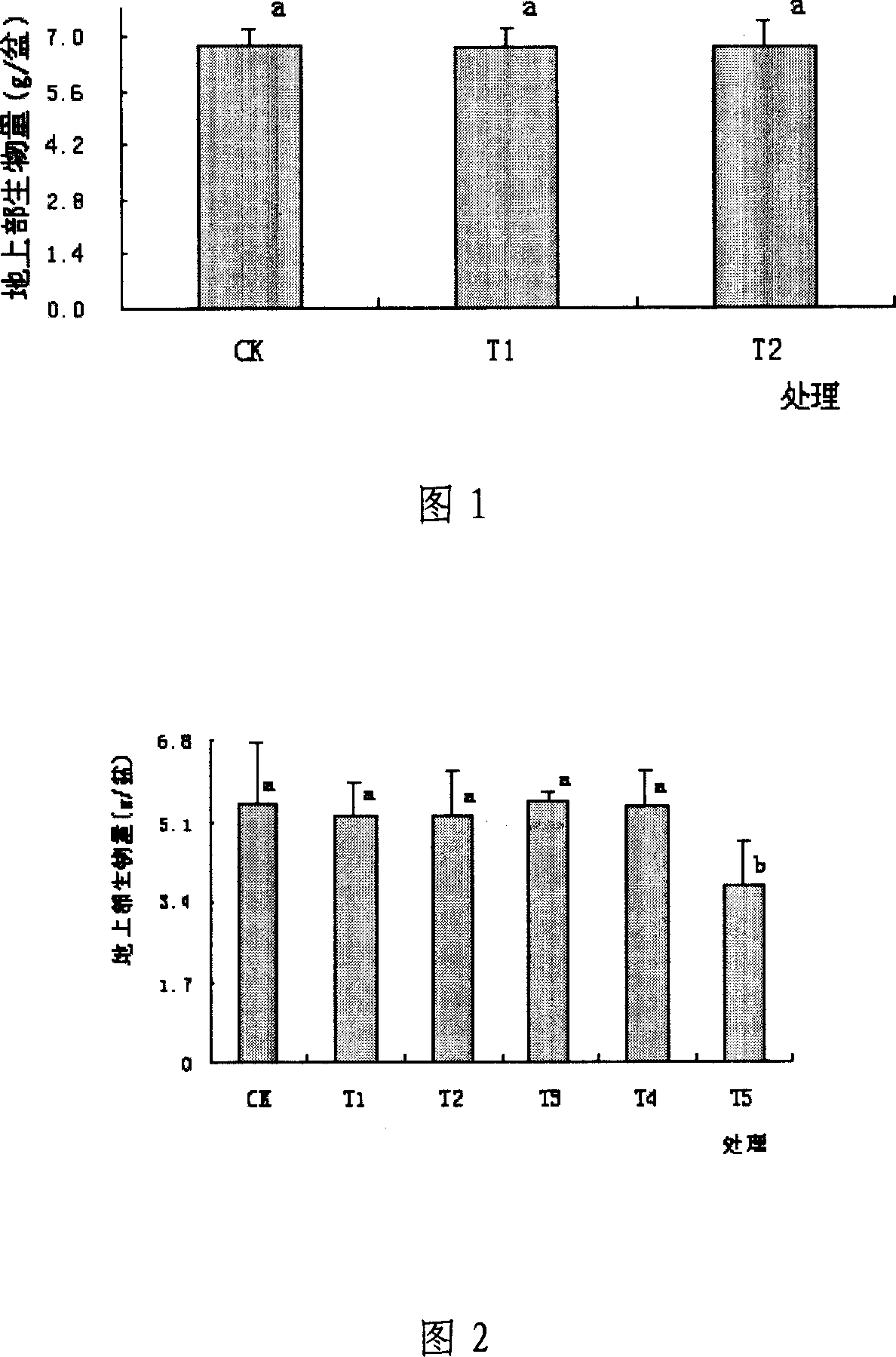
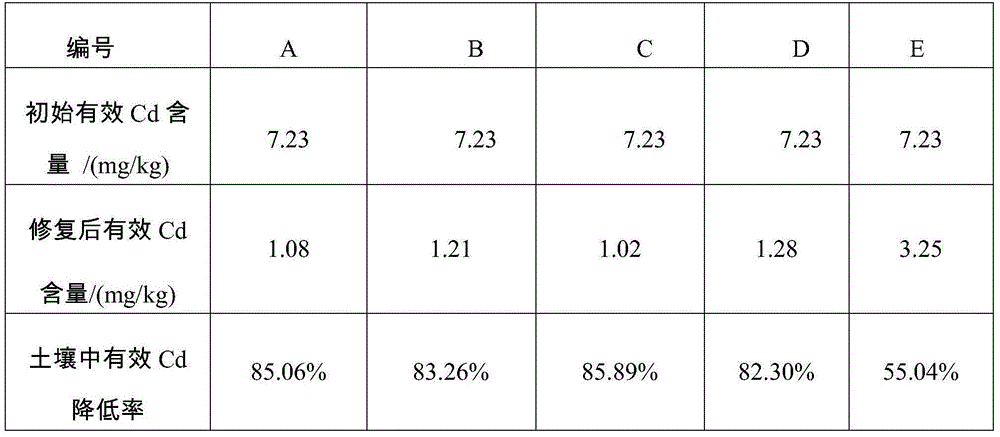
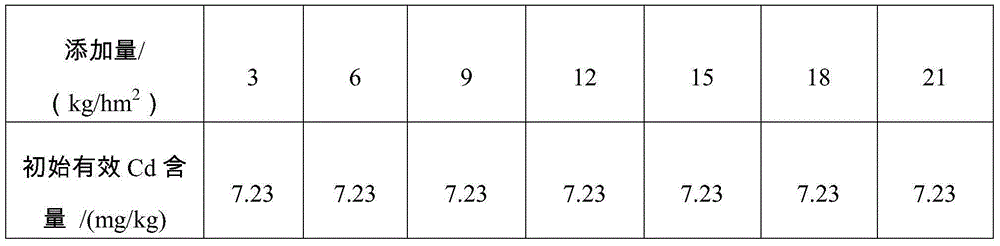
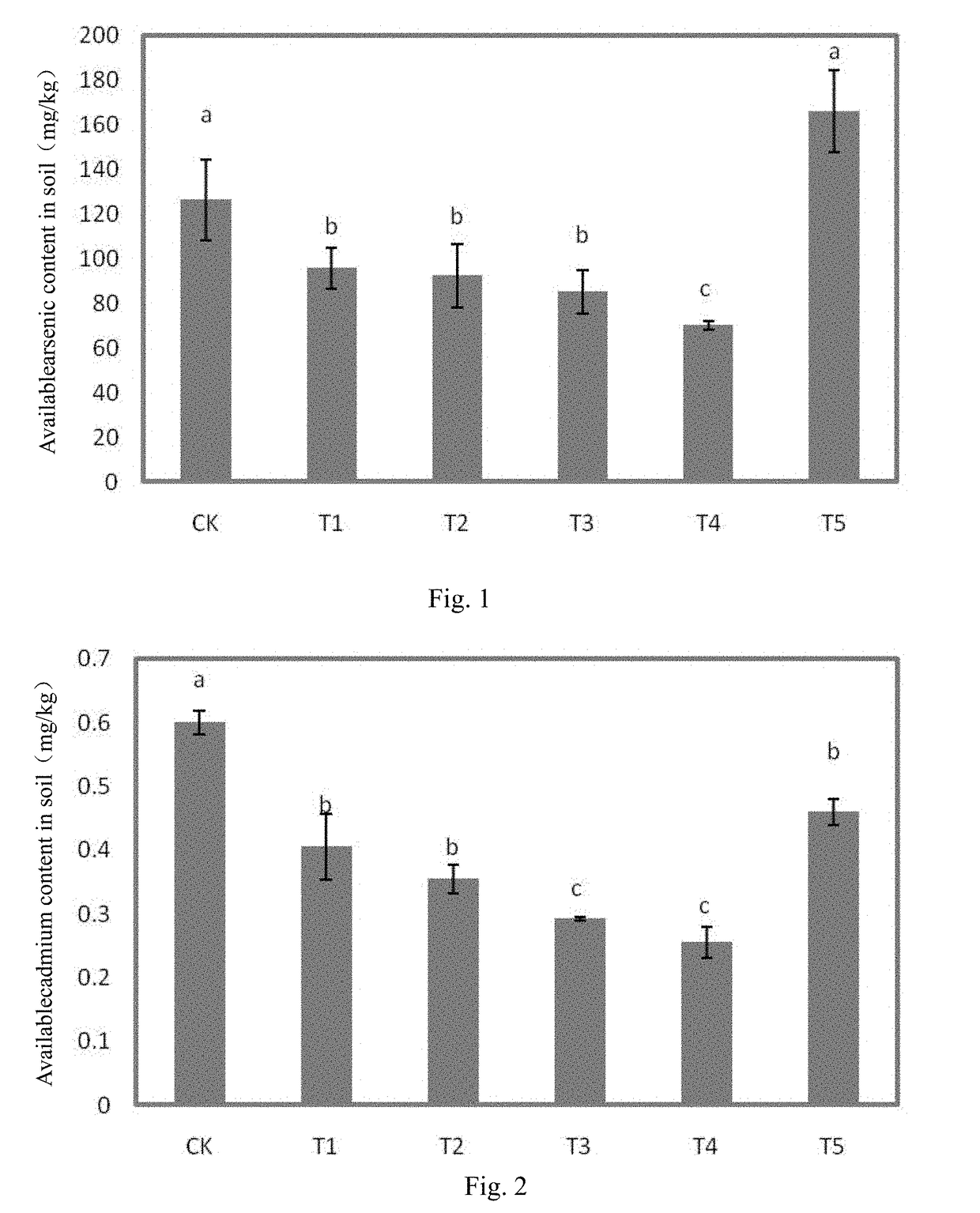
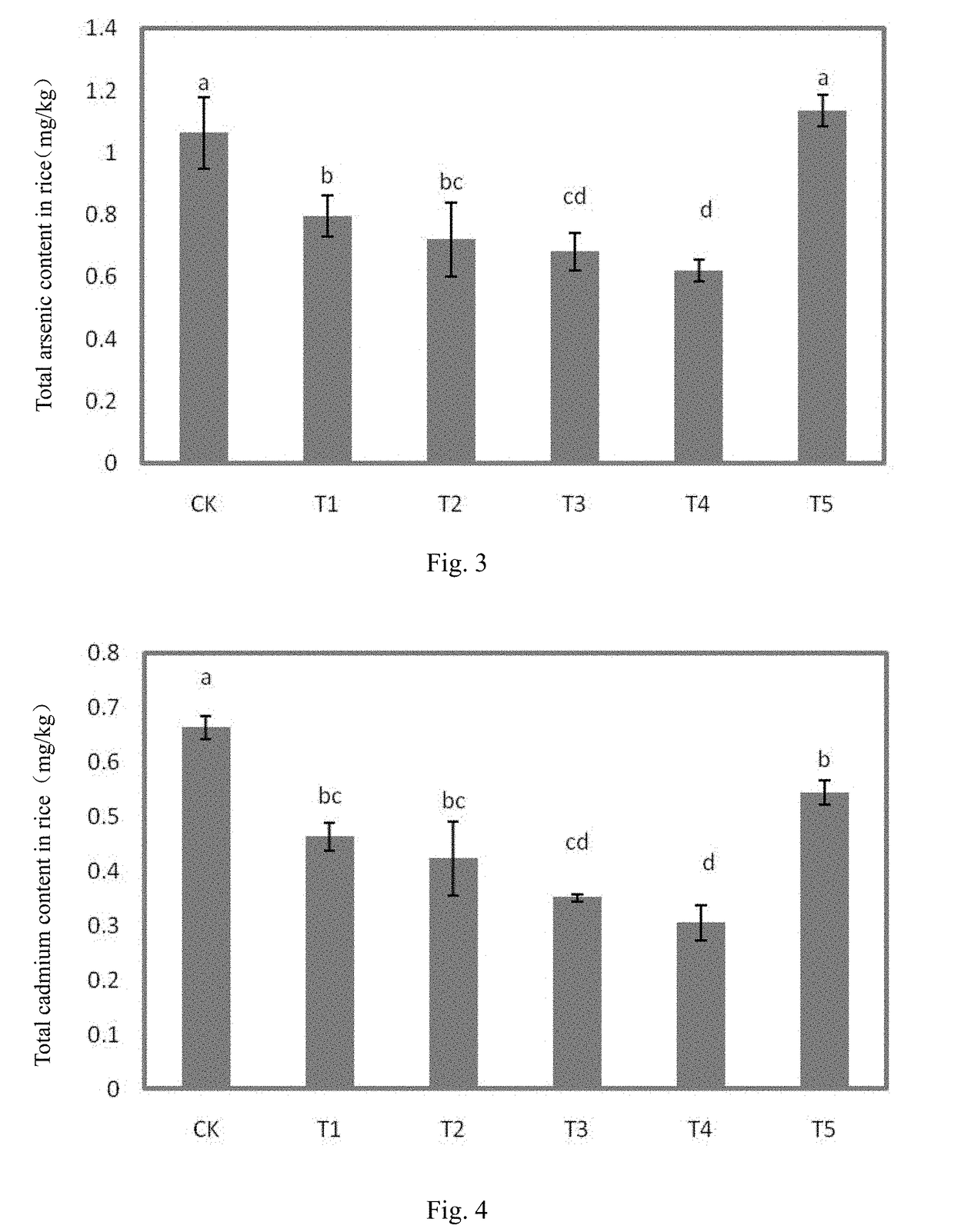
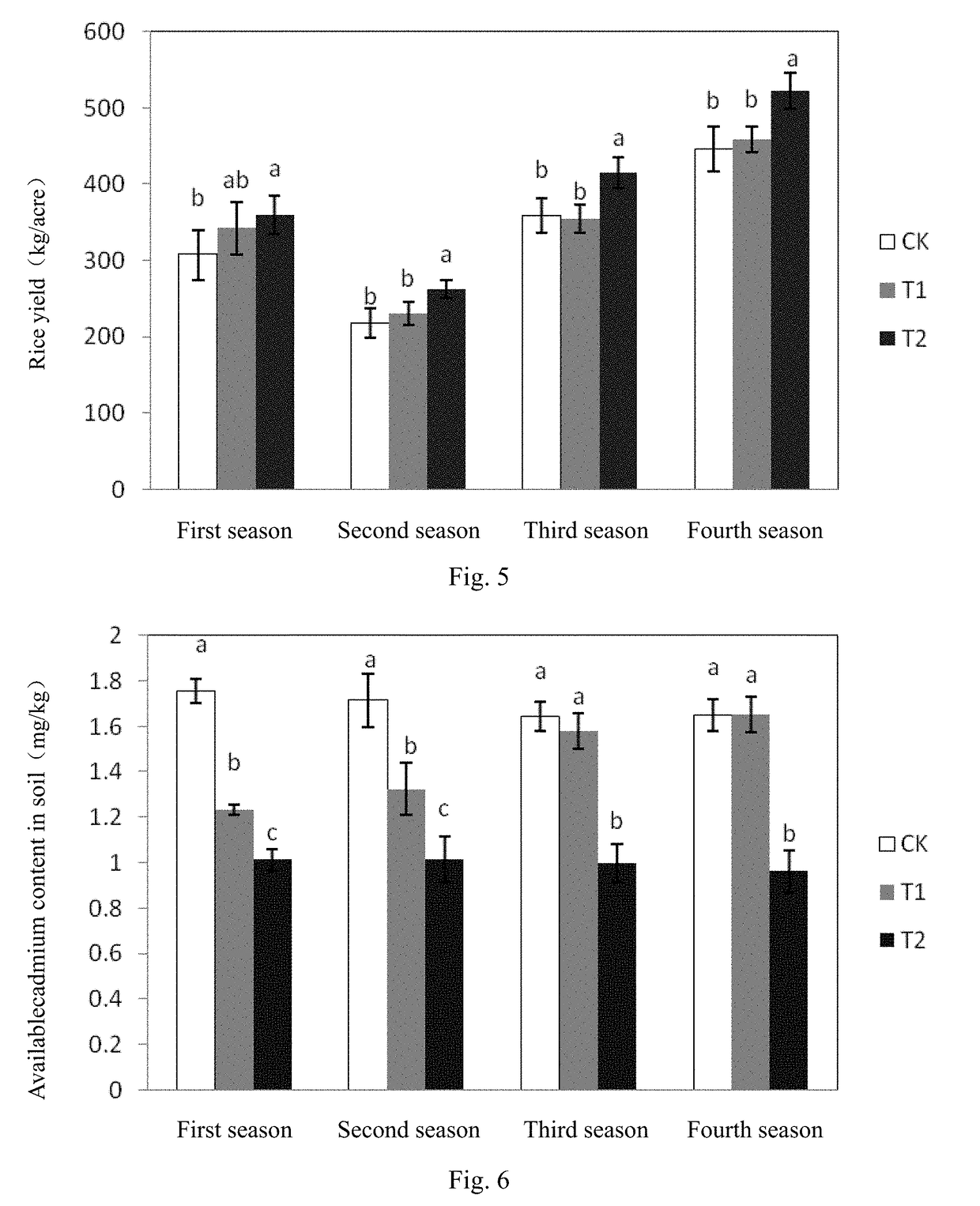
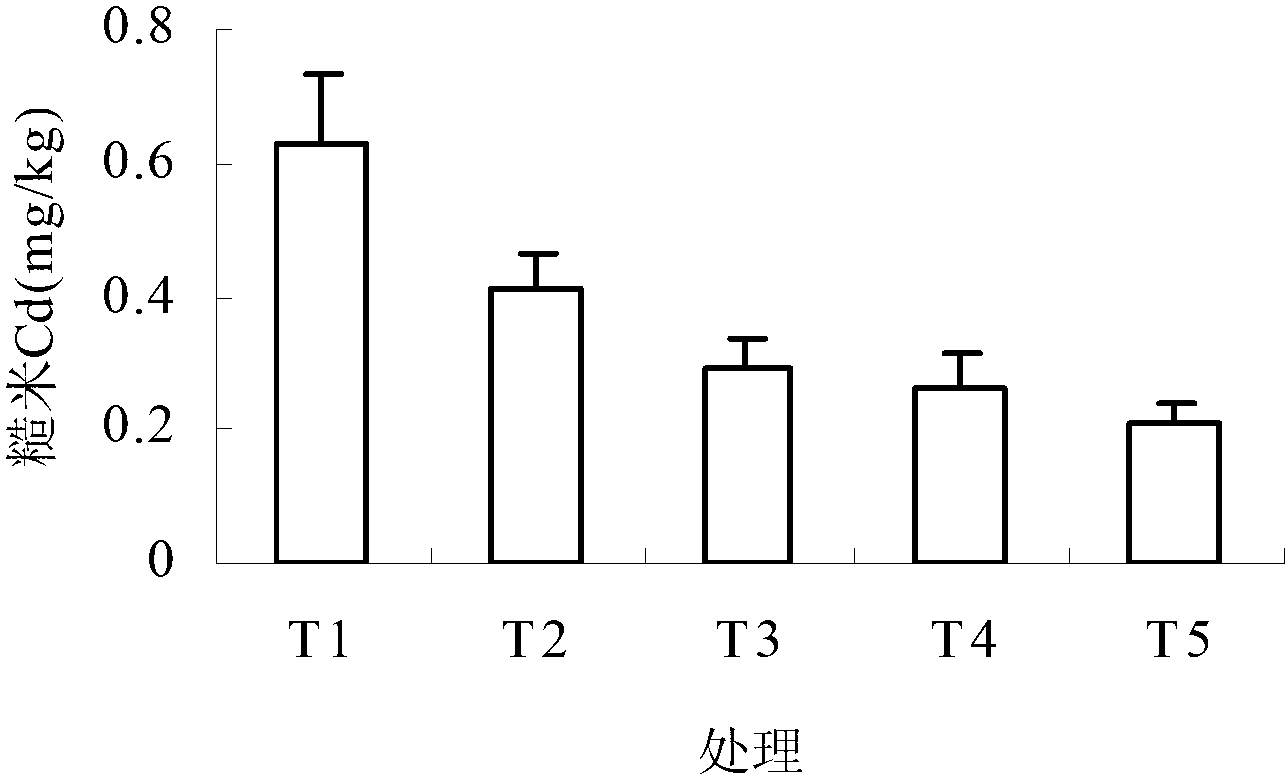
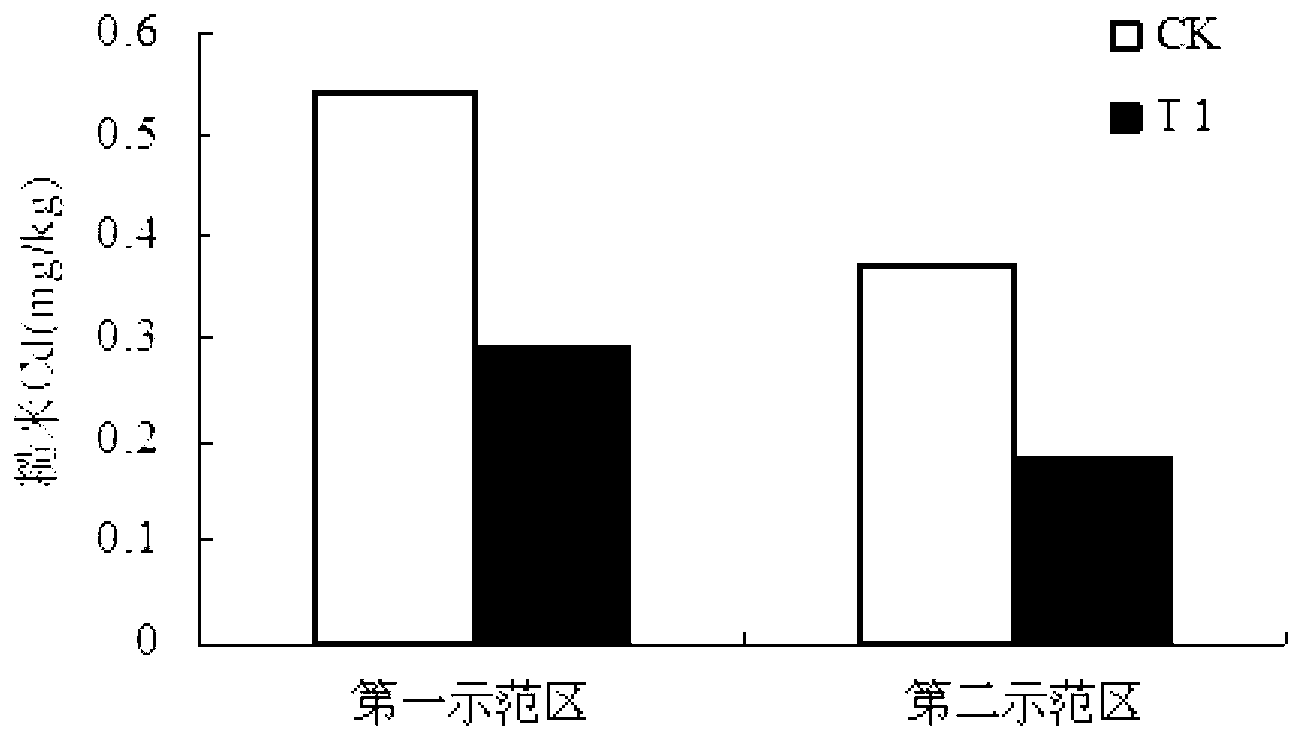
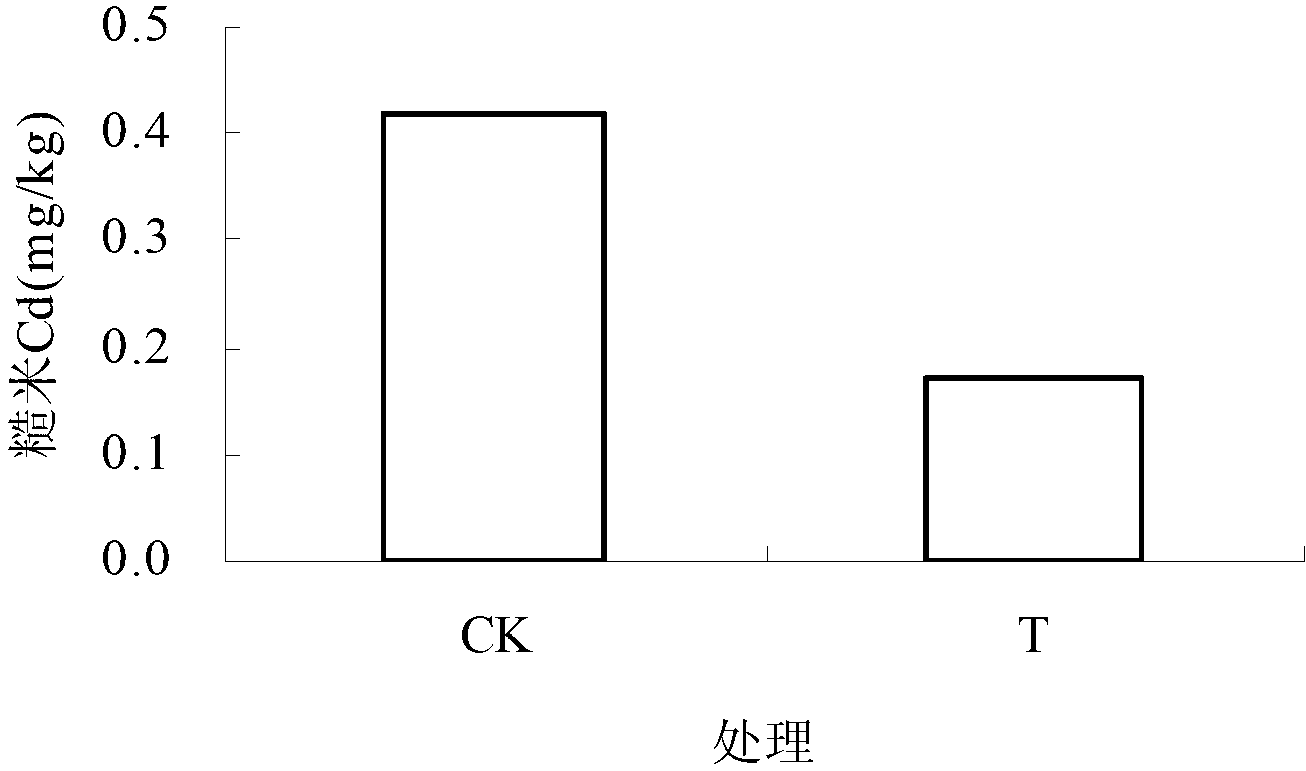
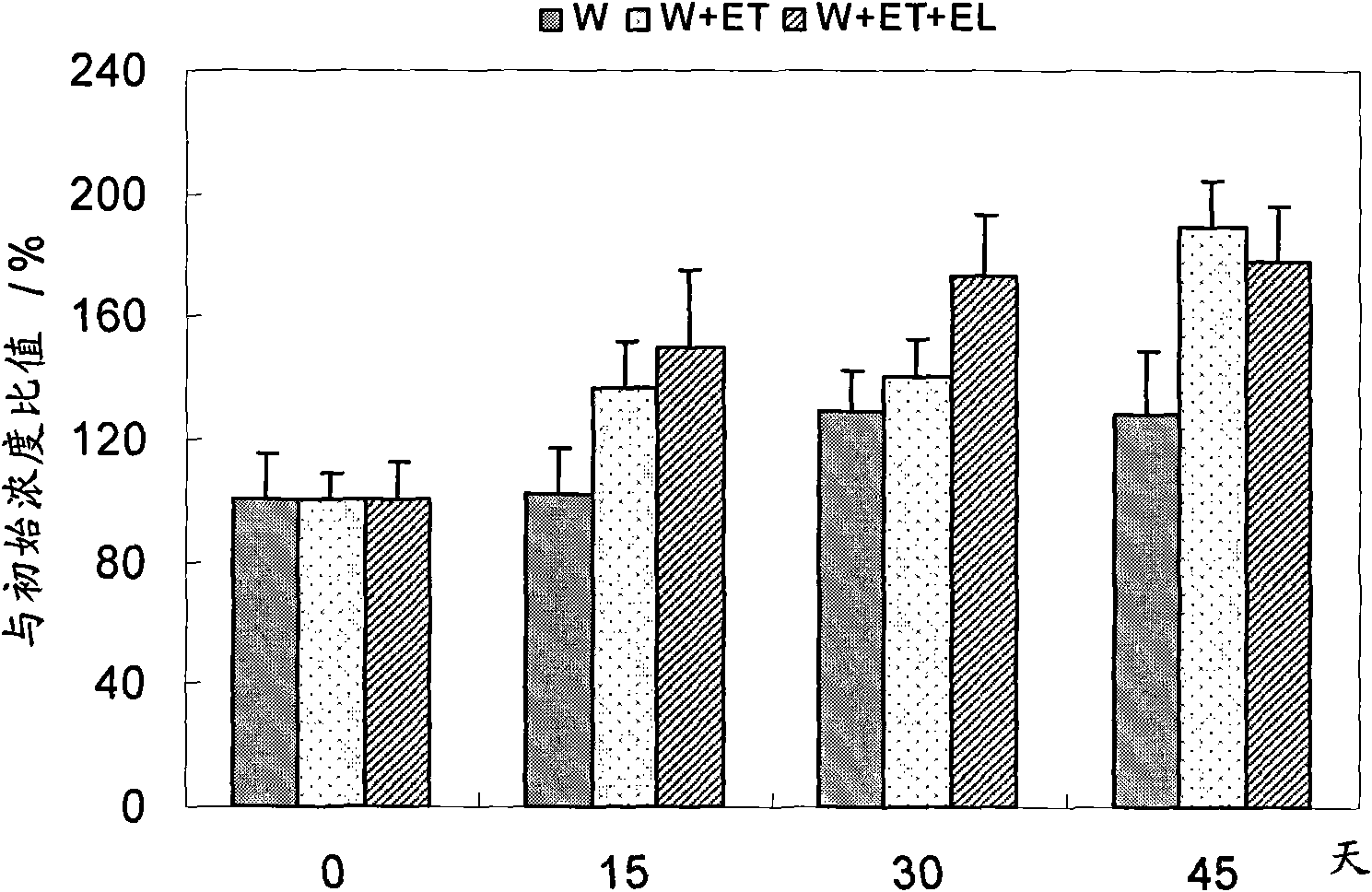
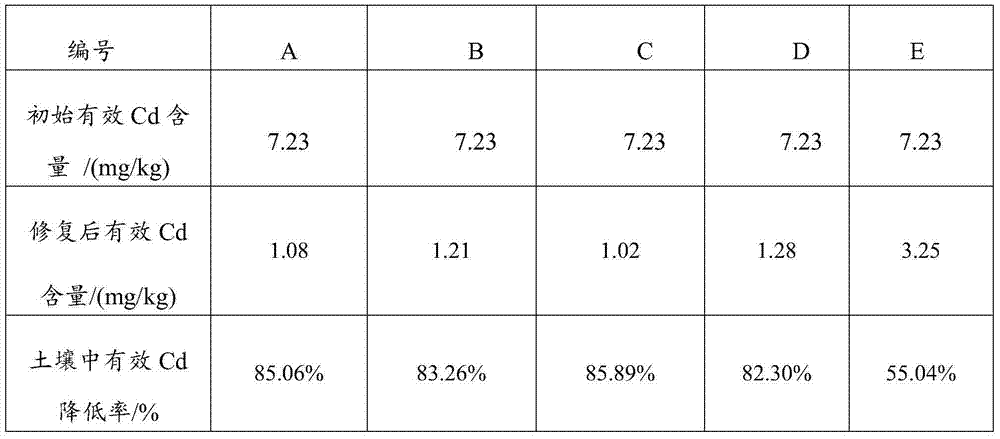
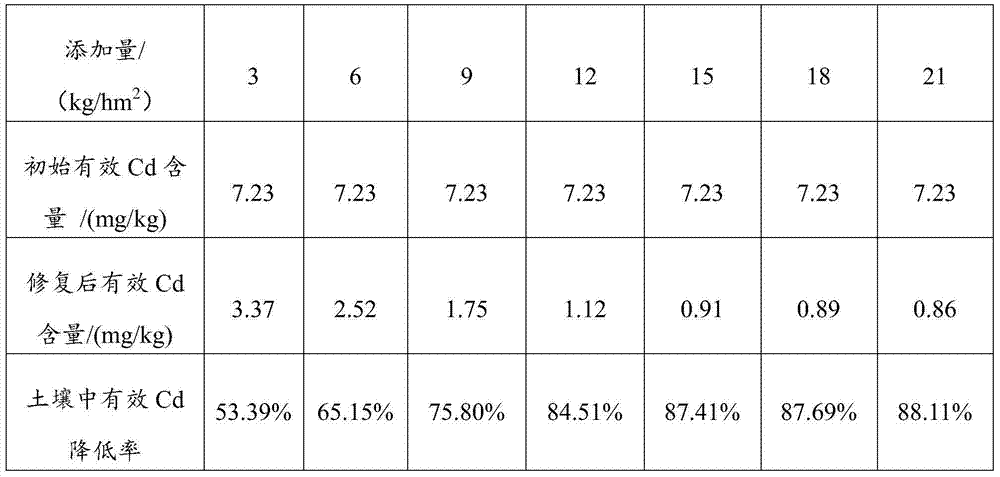
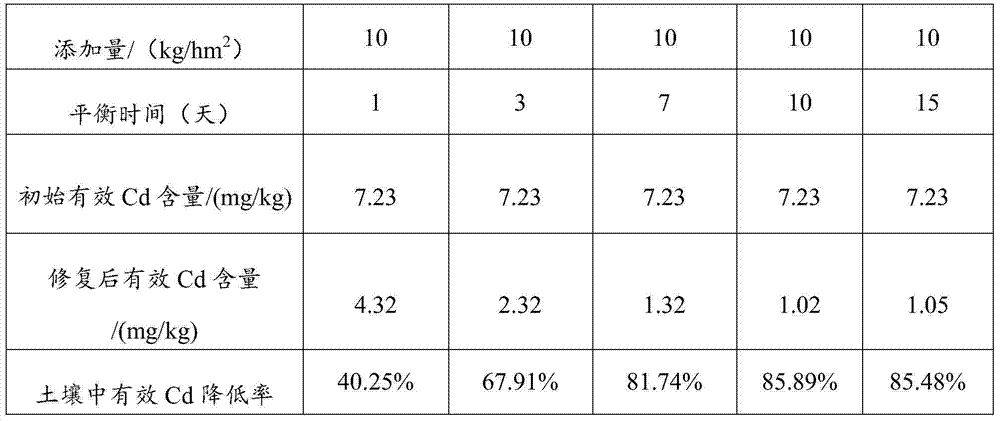
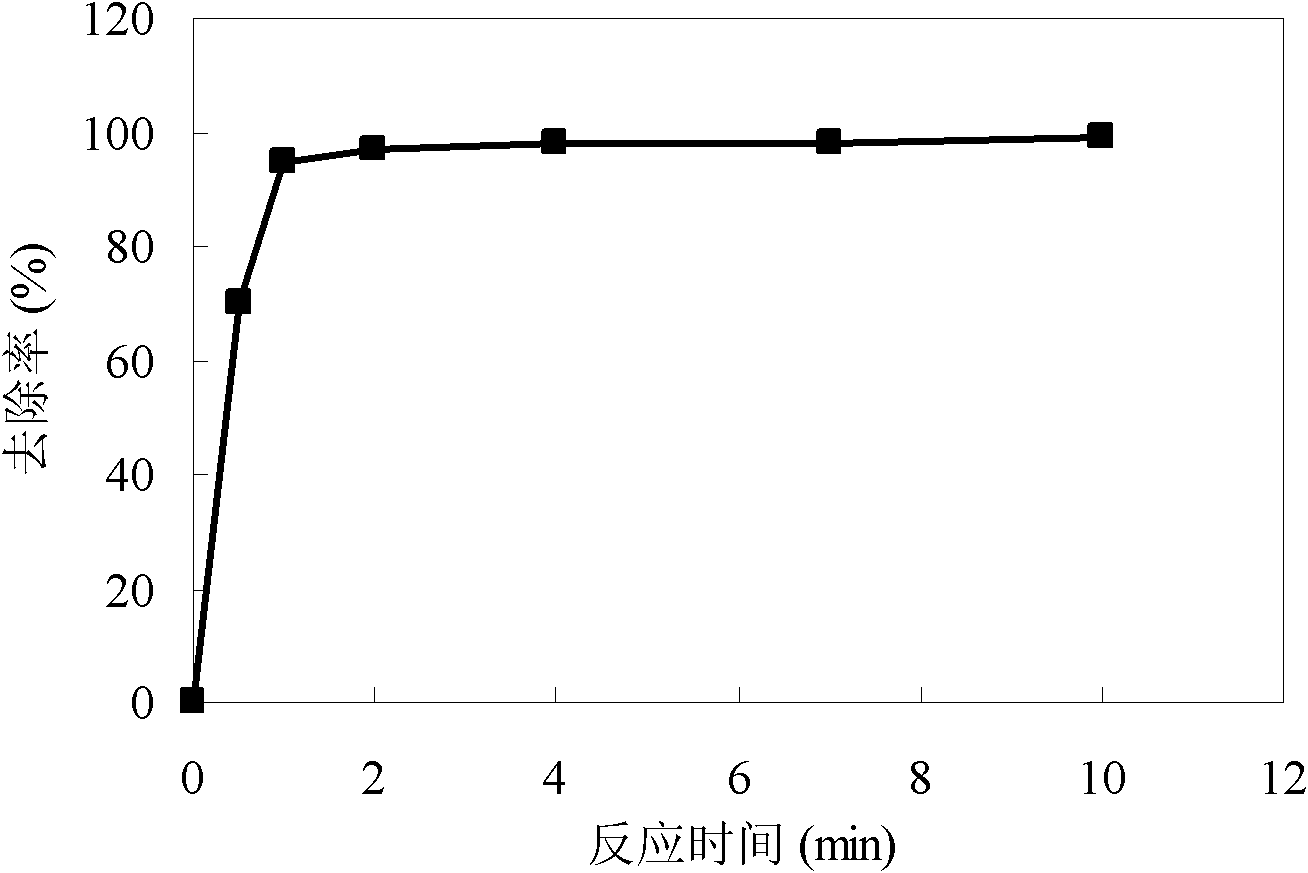
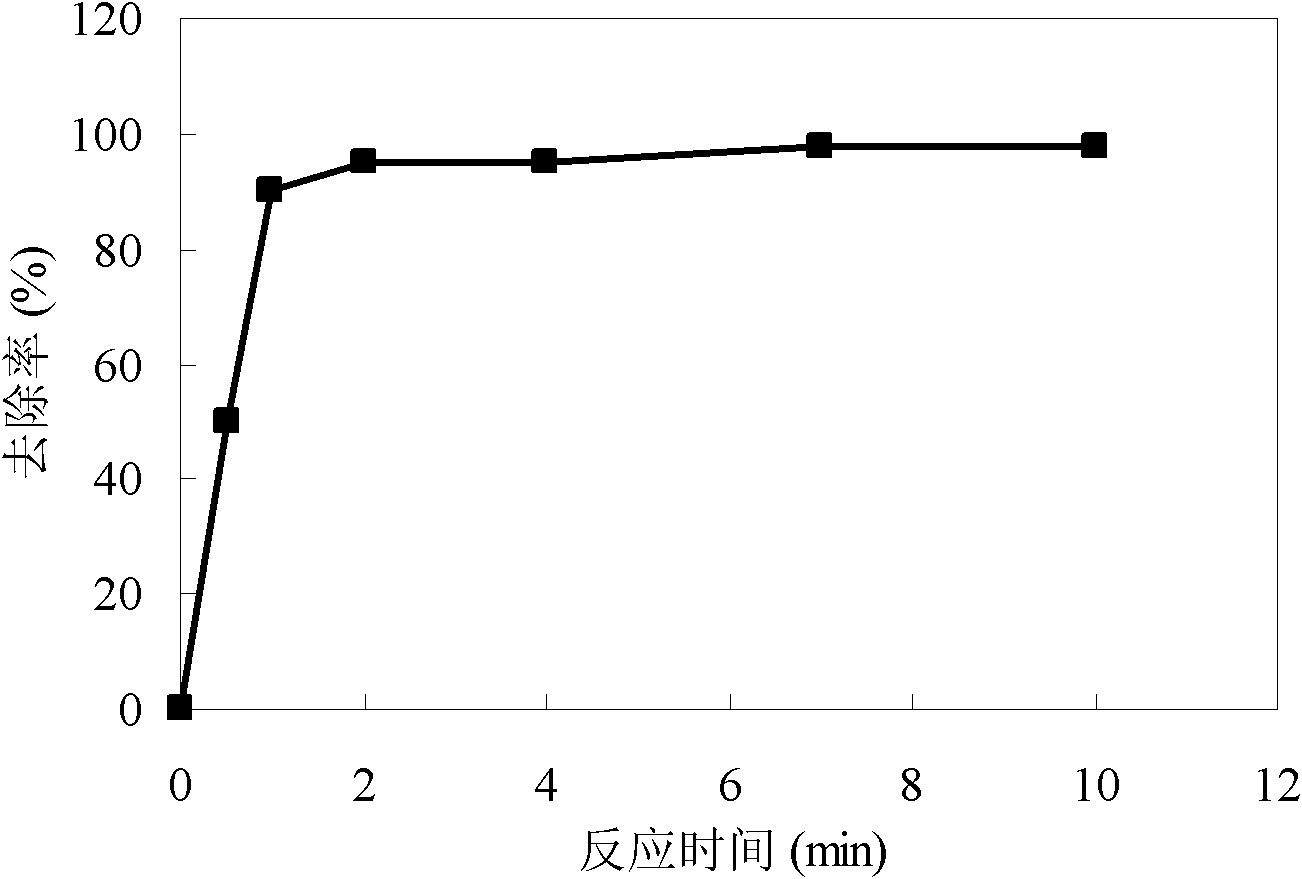
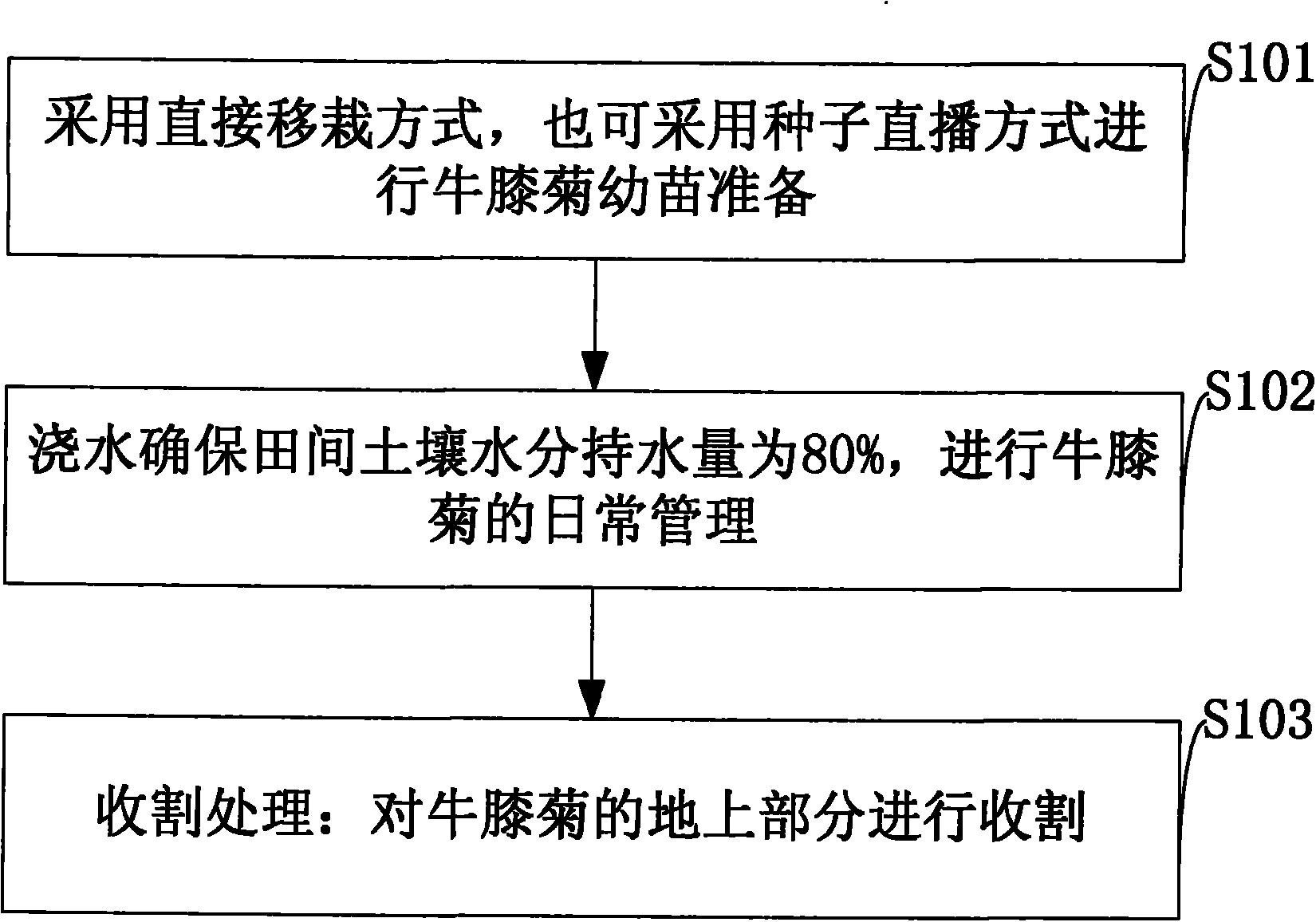
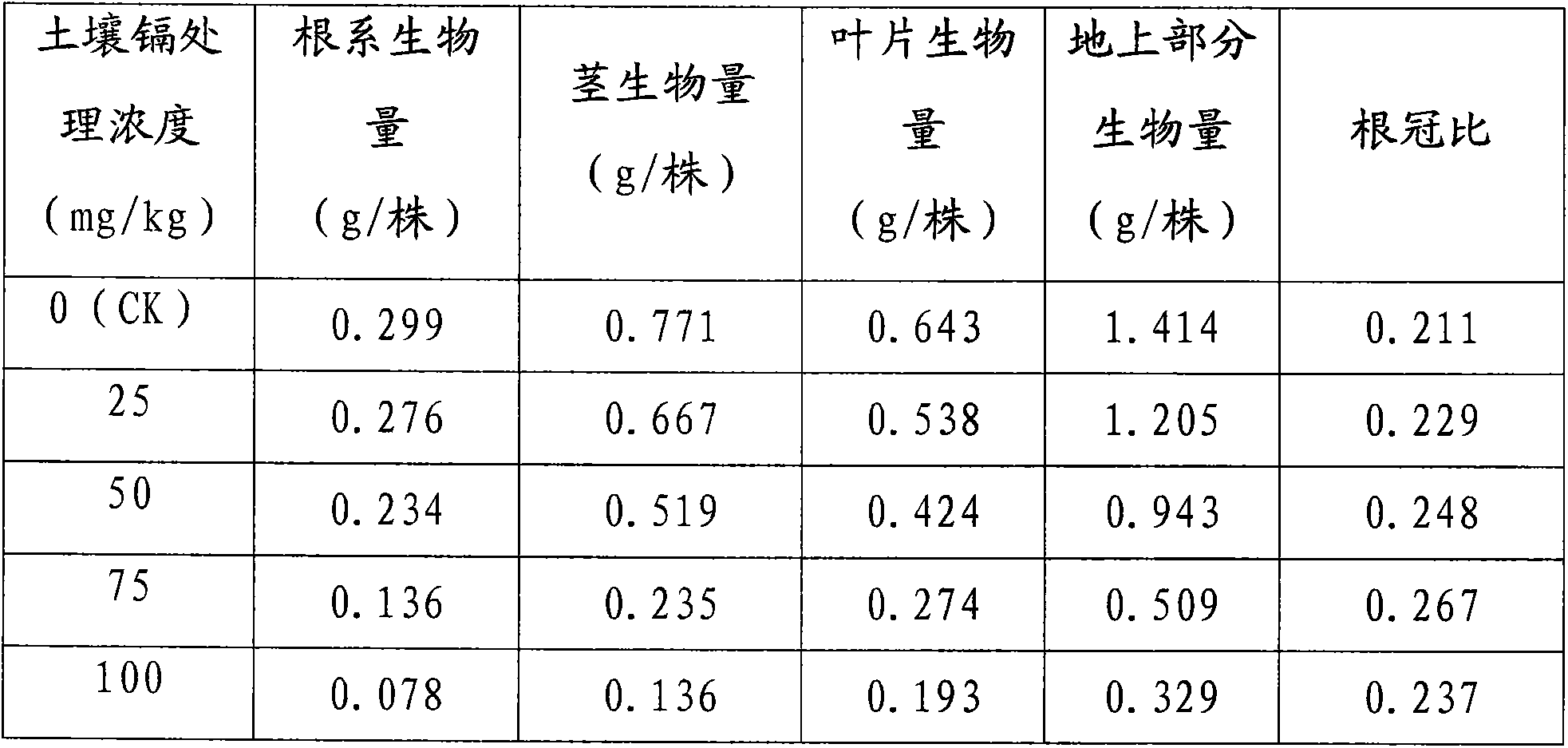
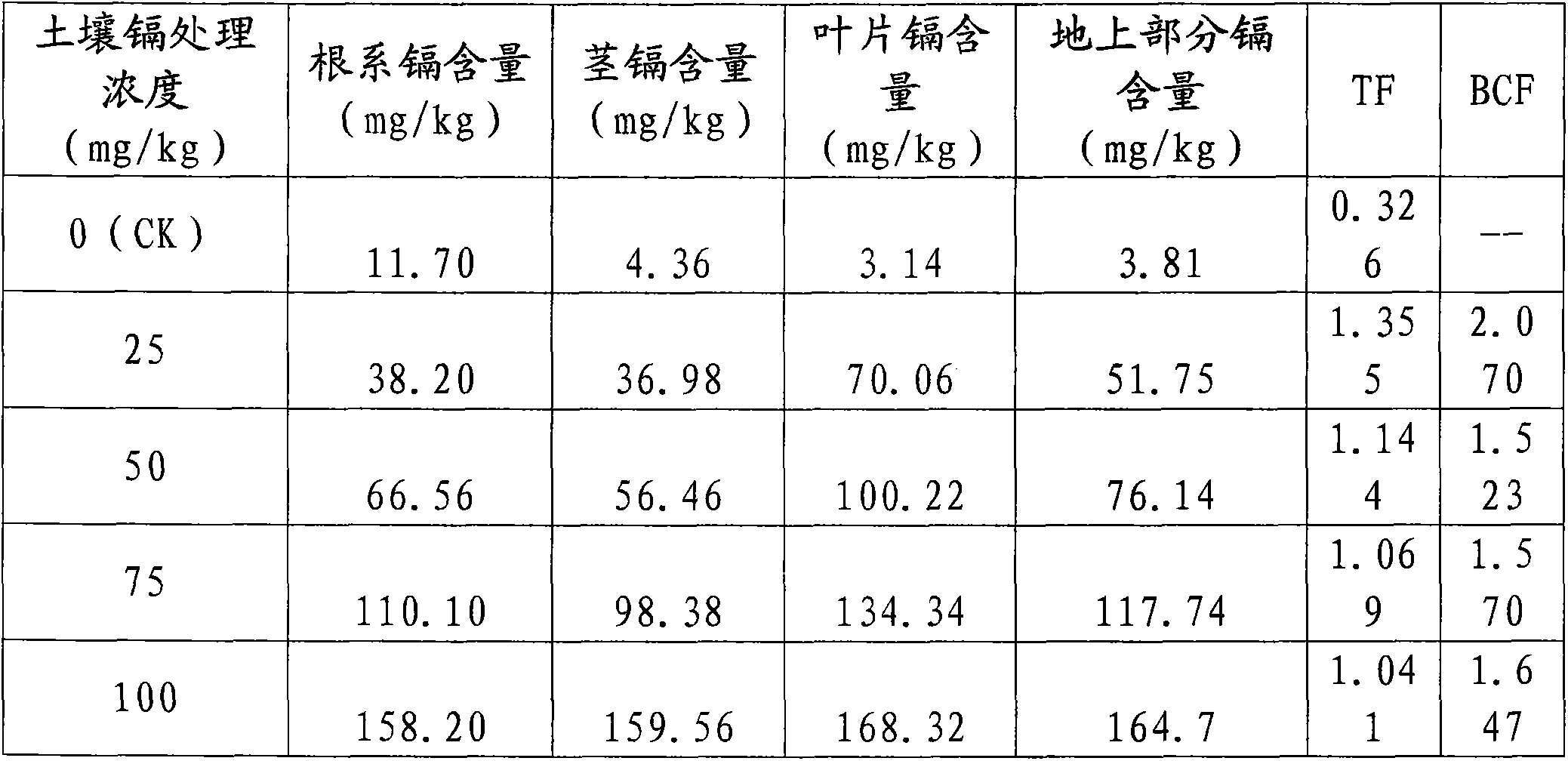
Patents
Literature
701 results about "Cadmium pollution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Restoration agent for lowering cadmium/lead effective state content in soil, and use method and application thereof
ActiveCN104650921AReduce the effective contentReduce available lead contentContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSoil scienceSulfate
The invention discloses a restoration agent for lowering cadmium / lead effective state content in soil, which is composed of quicklime, calcium sulfate, wood charcoal, iron chloride and water, wherein the weight ratio of the quicklime, calcium sulfate, wood charcoal and iron chloride is (1-2):(1-2):(1-2):(0.5-1), and the water accounts for 30-45 wt% of the soil. The restoration agent can be used for treating heavily polluted soil; and common chemical passivators can only restore lightly polluted soil, and do not have obvious effect on heavy pollution. The restoration agent can be used for treating both acidic soil and neutral soil. The restoration agent has high remediation efficiency for cadmium polluted soil; the reaction mechanisms relate to chemical precipitation and physical adsorption; and when one action fails due to change of the outside conditions, the other action can perform the guarantee function. The restoration agent has certain control actions on the lead effective state content in the polluted soil.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST FOR NONFERROUS METALS
Preparation method and application of magnesium oxide-rice husk biological carbon composite material
ActiveCN106669603AReduced bioavailabilityImprove the phenomenon of low pollution adsorption effectOther chemical processesContaminated soil reclamationCarbon compositesMixed materials
The invention belongs to the technical field of water and soil pollution restoration, and discloses a magnesium oxide-rice husk biological carbon composite material as well as a preparation method and application of the magnesium oxide-rice husk biological carbon composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: cleaning rice husks, drying the rice husks under a temperature of 80 to 90 DEG C for 10 to 16 hours, carrying out smashing and screening, heating to a temperature of 300 to 400 DEG C under a condition of feeding nitrogen and isolating oxygen at the rate of 3 to 8 DEG C per minute, carrying out thermal cracking for 2 to 4 hours, naturally cooling to a room temperature, cleaning the smashed rice husks, and drying the smashed rice husks to constant weight, so as to obtain rice husk biological carbon; adding the rice husk biological carbon into a magnesium oxide suspension with the mass percentage of 0.6 to 3 percent to obtain a mixed material; carrying out uniform stirring and mixing and then ultrasonic reaction for 1 to 2 hours, putting the mixed material under a condition of 85 to 105 DEG C for 20 to 24 hours, and carrying out thermal treatment at 300 to 400 DEG C for 20 to 60 minutes under a condition of feeding N2 to obtain the magnesium oxide-rice husk biological carbon composite material. The composite material can be applied to adsorbing and removing cadmium from cadmium polluted wastewater or cadmium polluted soil.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Sulfate reducing bacteria-phosphate solubilizing bacteria and application thereof in combined remediation of cadmium contaminated soil
ActiveCN104450552AIncrease productionImprove securityBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationSulfate-reducing bacteriaPhosphate
The invention discloses a bacterial strain b capable of resisting the growth of heavy metal Cd and reducing sulfate, and a bacterial strain capable of resisting the growth of the heavy metal Cd and solubilizing phosphate. The classification and name of the bacterial strain b and the bacterial strain are respectively enterbacter ludwigii SRB-2-5U-2 and pseudochrobactrum saccharolyticum LB-4-4-1c, which are already preserved in the Common Microbe Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms. The bacterial strains disclosed by the invention can be used for simultaneously remediating the surface soil, deep soil and rhizosphere soil of a plant, reducing the pollution of Cd to surface water and underground water, and also improving the activity and fertility of the soil.
Owner:西安金博瑞生态科技有限公司
Composite passivator applicable to rice field soil cadmium pollution and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105586044ASlow water absorptionHigh water absorptionAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersSodium BentoniteSoil biology
The invention provides a composite passivator applicable to rice field soil cadmium pollution. The composite passivator is mainly prepared from chitosan, sodium bentonite, bone meal, lime, charcoal, ZnO and nanometer FeO. The invention further provides a preparation method and application of the composite passivator. By means of the composite passivator, the available cadmium content in rice and the cadmium content in rice can be remarkably reduced, the soil pH value can be improved, vast rice soil polluted by heavy metal cadmium can be treated, the organic matter content is greatly improved, and the soil biology-chemical characteristic is improved.
Owner:山东地宝土壤修复科技有限公司
A kind of pseudomonas and its use and method for removing cadmium pollution in environment
ActiveCN102286405ASolve pollutionAdaptableBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates pseudomonas, use thereof and a method for removing cadmium pollution to the environment. The pseudomonas class is named pseudomonas putidaHN103 and the collection number in a collection center is CCTCCNo.M2011184; and the shape and characteristics of the pseudomonas putidaHN103 comprise: 1) on a culture medium, a bacterial colony which used to be colorless and transparent turns white, smooth and convex-like with irregular edges; and 2) according to the result of bacterial microscopic examination, pseudomonas belongs to brevibacterium and is gram negative. The use of the bacteria is the use of the bacteria as a biological repair material for removing cadmium pollution. The method for removing cadmium pollution to the environment comprises the following steps: 1) regulating the cadmium ion concentration in sewage to a range in which pseudomonas can grow normally; 2) placing pseudomonas; 3) keeping the pseudomonas in the sewage for a certain time period; and 4) removing bacterial absorbing cadmium ions. The pseudomonas requires small investment, is low in cost, high in adaptability and capable of effectively removing cadmium, can quickly and obviously lower the concentration of cadmium ions in the environment and is suitable for biological remediation environments polluted by cadmium.
Owner:武汉华中农大资产经营有限公司
Phytoremediation method for soil with cadmium pollution
ActiveCN103521508APromote absorption and enrichmentImprove repair rateContaminated soil reclamationBiological activationPhytoremediation
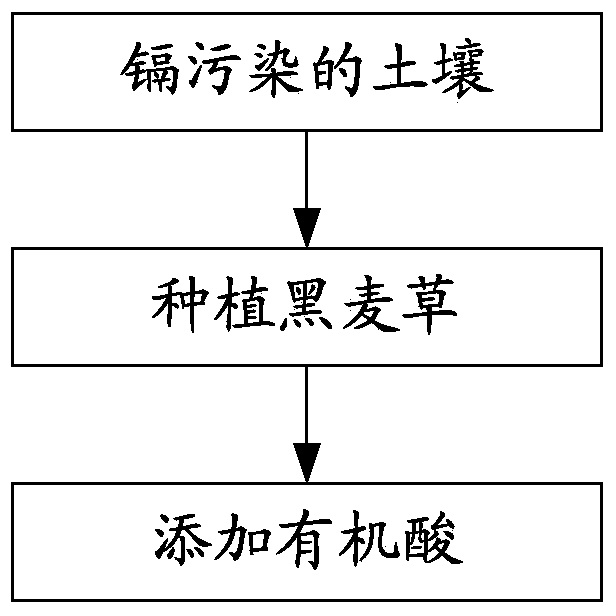
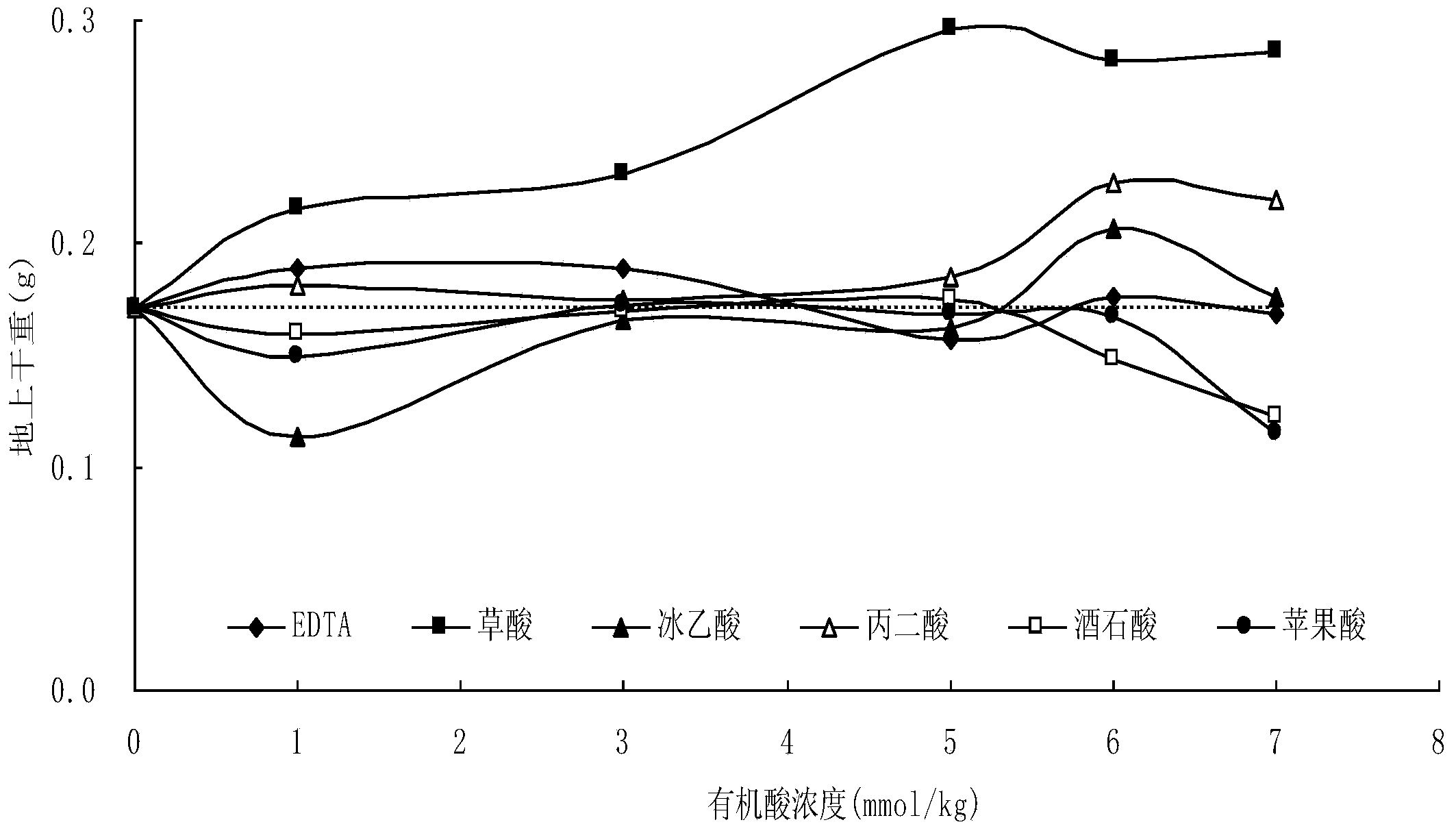
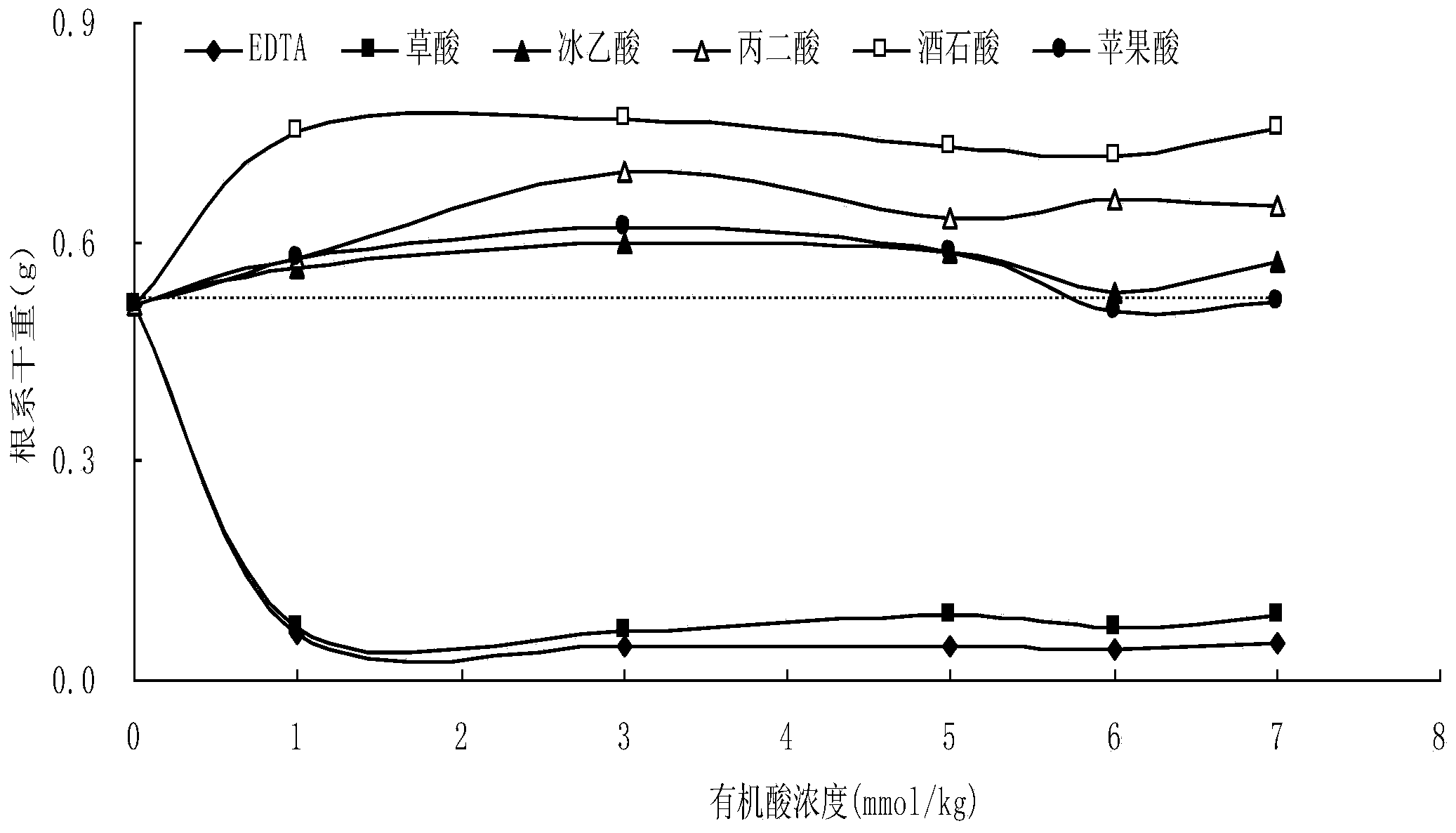
The invention discloses a phytoremediation method for soil with cadmium pollution. The method comprises the following steps: ryegrass is planted in soil with cadmium pollution; organic acid is added before harvest, and the organic acid is one selected from ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, oxalic acid, glacial acetic acid, propane diacid, tartaric acid or malic acid. In the method, based on ryegrass as a biomass raw material, when the ryegrass is used to restore the soil with cadmium pollution, through activation and induction actions of the organic acid, the bio-availability of heavy metal cadmium is raised, absorption and enrichment of cadmium of plants are promoted, and therefore the phytoremediation speed of soil with heavy metal pollution is raised. In addition, the organic acid can promote increase of amount of dry matter of overground parts and root systems of ryegrass to some extent, and finally, long-term goals of harmony of soil productivity restoration and local landscapes, ecological balance and sustainable development are achieved.
Owner:FARMLAND IRRIGATION RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Remediation method for cadmium-contaminated soil
InactiveCN104874594AClose the loopNo secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationPollution soilSoil remediation
Owner:南京宇行环保科技有限公司
Cadmium pollution bioremediation agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103361072AReasonable mix of typesReduced mobilityAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersHigh absorptionBacillus cereus
The invention provides a cadmium pollution bioremediation agent which is composed of the following ingredients in parts by weight: 10-20 parts of core rhzomorph, 10-20 parts of a nutritional ingredient, 2-6 parts of an enzyme activity substance and 54-78 parts of an rhzomorph carrier. The invention further provides an application of the cadmium pollution bioremediation agent. The cadmium pollution bioremediation agent is reasonable in microorganism specie collocation and high in comprehensive function. Microorganisms in the core rhzomorph can be planted and grow in soil rapidly to form strong bacterial colonies, and heavy metal ions, namely, cadmium Cd<+1> can be directly absorbed to microbial cell walls or into cells to be cured and passivated. Besides, bacillus cereus and beer yeast in the composition have high absorption and passivation function on heavy metal ions, namely, cadmium Cd<+1>, chromium Cr<+1> and lead Pb<+1>, due to the high comprehensive function, the mobility of the heavy metal ions, namely, cadmium Cd<+1>, is reduced, and the purpose of reducing absorption of crops on the heavy metal ions is achieved.
Owner:HUNAN TAIGU BIOTECH
Method for restoring cadmium pollution of soil in passivation mode
ActiveCN101745524ADoes not affect productionImprove repair effectContaminated soil reclamationLand productivitySoil organic matter
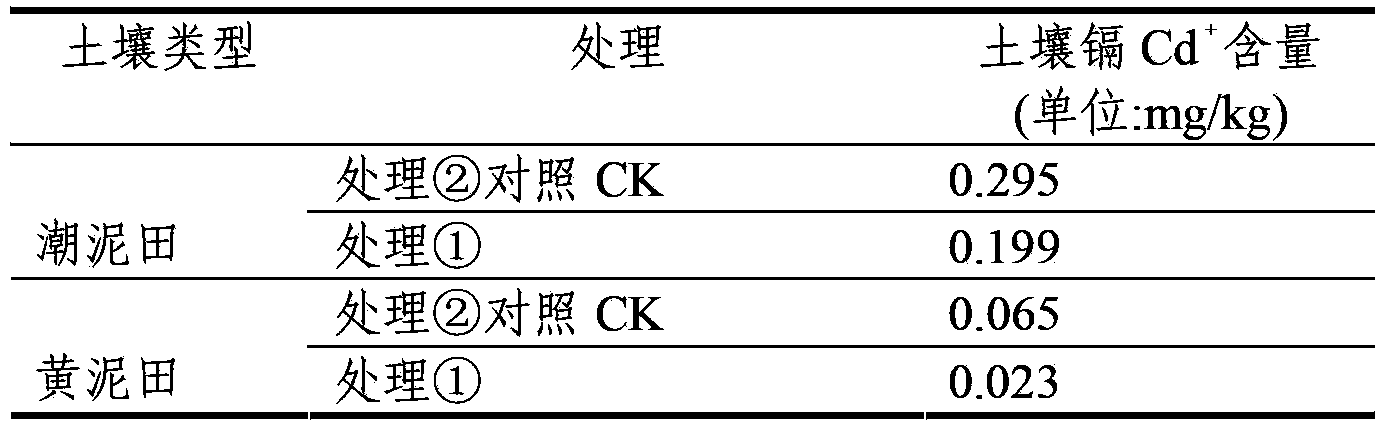
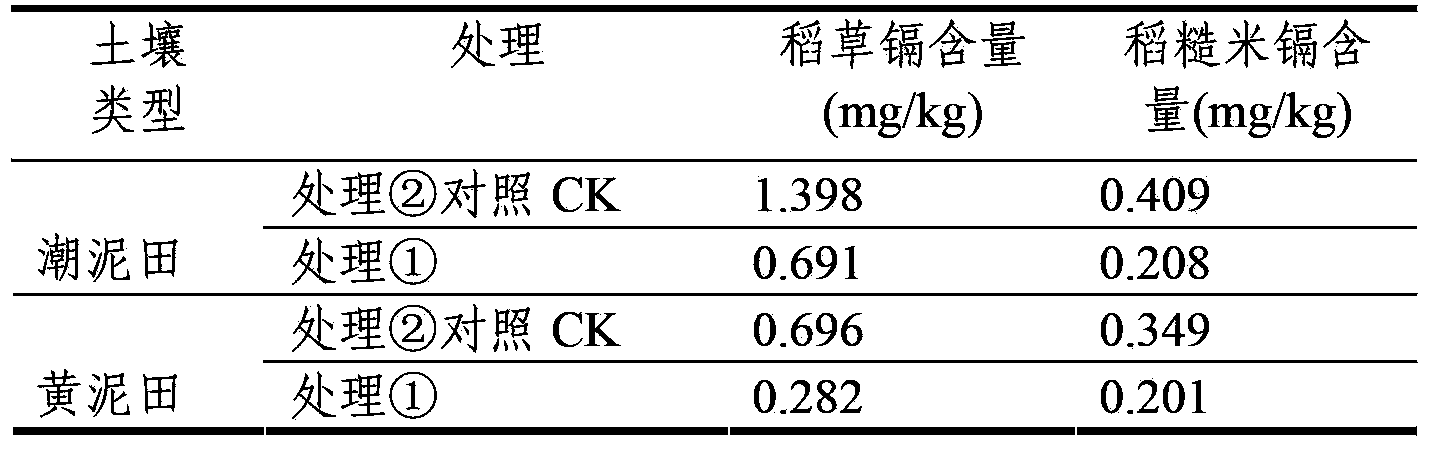
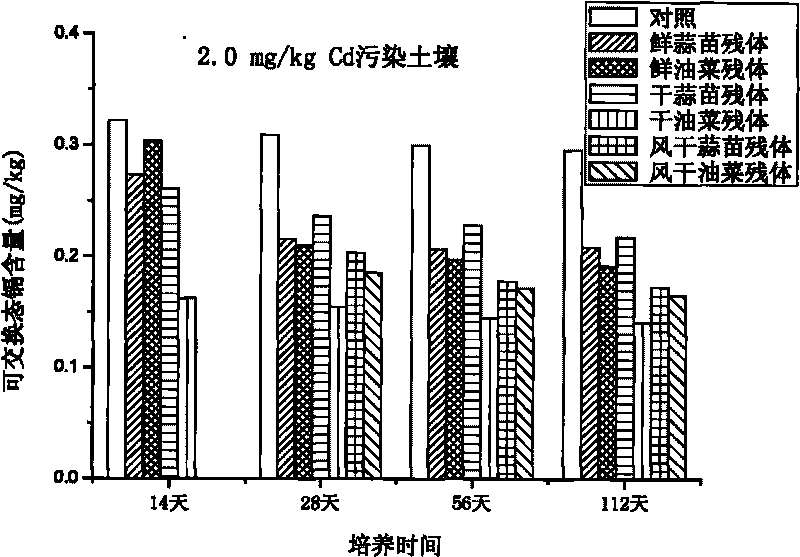
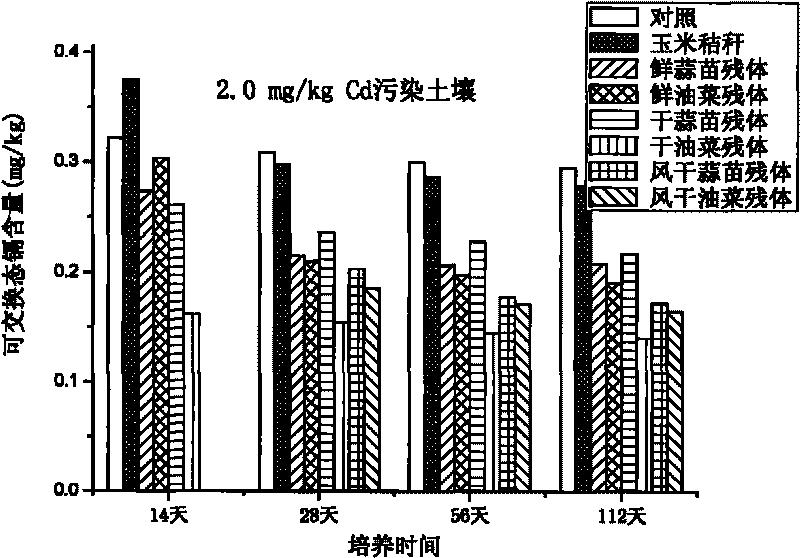
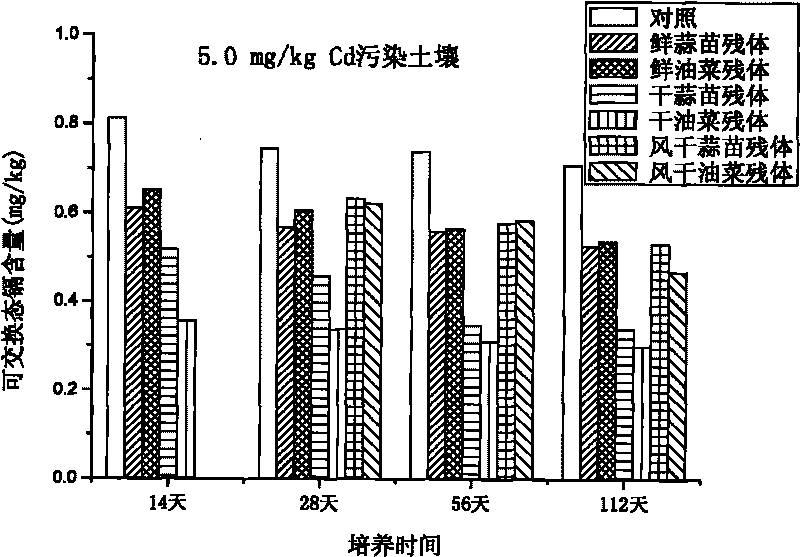
The invention relates to a method for improving soil, in particular to a method for restoring cadmium pollution of soil in a passivation mode. The method is to add plant residue rich in sulfydryl in the soil and mainly comprises the following steps of: 1, grinding the plant residue rich in the sulfydryl to ensure that the length of the residue is less than 10cm; 2, adding the plant residue obtained in the step 1 into the soil to be restored and mixing the residue and the soil, wherein the weight part ratio of the soil to be restored to the plant residue of fresh plant is 1:0.001; and 3, ensuring that the moisture content of the soil added with the plant residue is maintained over 50 percent of the maximum field moisture capacity within 20 to 40 days, wherein the plant residue rich in the sulfydryl is cruciferae plant residue or liliaceae plant residue. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of environmental friendliness, low restoring cost, no influence on farmland production, and improvement on soil fertility, content of soil organic matter and land productivity.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Water treatment method for removing Tl<+> and/or Cd2<+> by producing nanometer iron and manganese oxides in situ
ActiveCN102145947AHigh electronegativityLarge specific surface areaWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentFerric hydroxideWater source
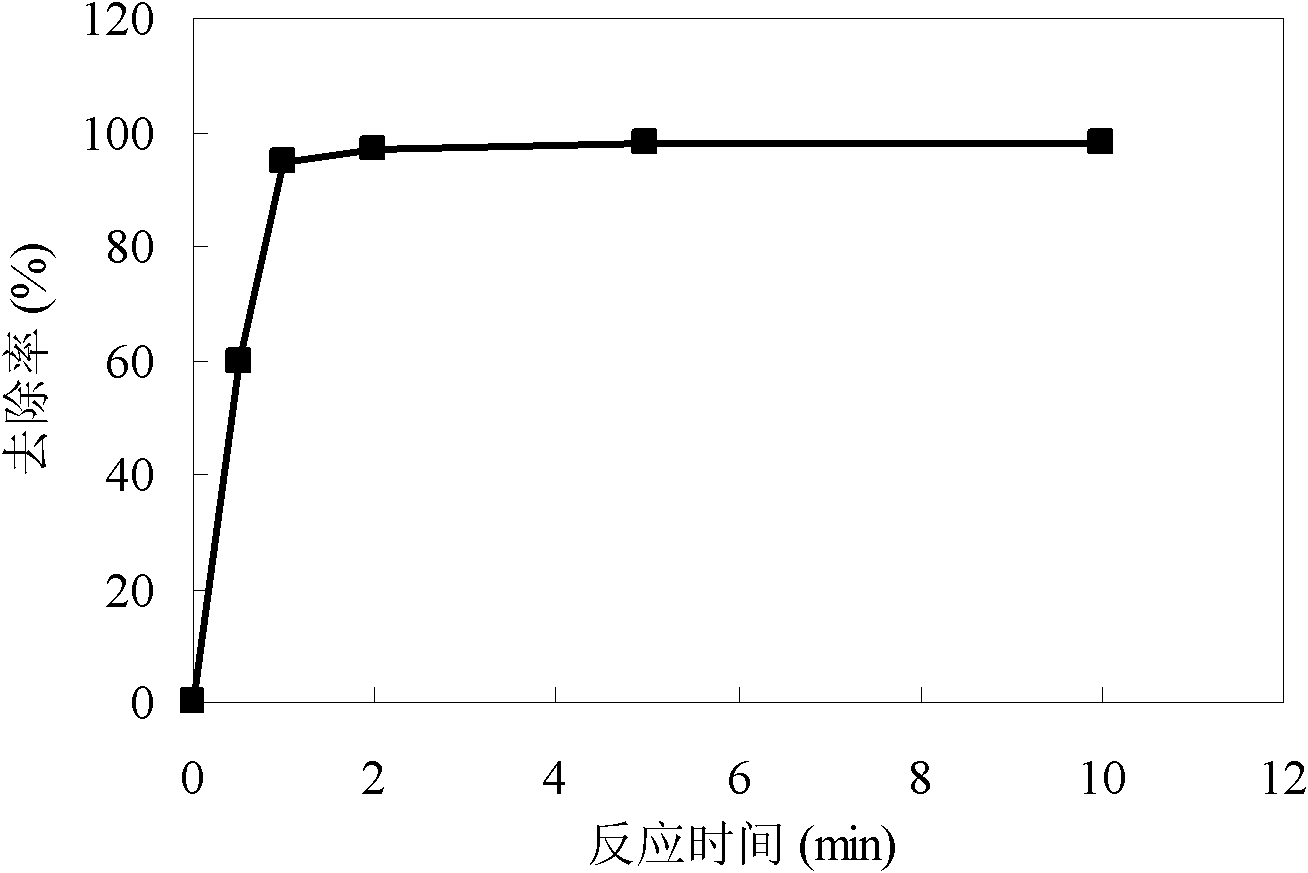
The invention discloses a water treatment method for removing Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+> by producing nanometer iron and manganese oxides in situ, relating to a water treatment method of thallium and / or cadmium-containing source water and solving the problems of complex process, high running cost and low removing efficiency of thallium and / or cadmium existing in the conventional water treatment technology specific to thallium and / or cadmium-polluted source water. The method comprises the following steps of: adding permanganate and ferrous salt into Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+>-containing water; stirring to obtain a mixed solution; adding a coagulant; and performing conventional water treatment. A nanometer ferric hydroxide-manganese dioxide oxide composite adsorbent which has a large specific surface area and high electronegativity and is easy for precipitation separation is produced in situ by making permanganate react with the ferrous salt, so that Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+> can be removed effectively andspecifications in the national Sanitary Standard for Drinking Water are met. The method has the advantages of high removing efficiency, simple process, flexibility and convenience for operation, no change of the original treatment process of a water plant, low running cost and the like, and can be applied to emergency treatment of a water pollution event.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Lead-cadmium compound conditioner for rice field soil as well as preparation and application methods thereof
ActiveCN103143557AReduce absorptionControl activityContaminated soil reclamationCadmium CationSepiolite
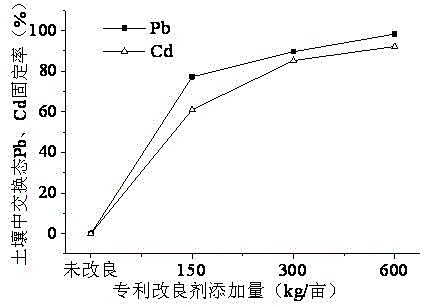
The invention discloses a lead-cadmium compound conditioner for rice field soil as well as preparation and application methods of the lead-cadmium compound conditioner. The conditioner is composed of the raw materials in mass fractions: 30-50% of calcium carbonate, 5-10% of hydroxyapatite, 20-30% of sepiolite and 20-30% of zeolite; the preparation of the conditioner comprises the following steps of: weighing various raw materials according to the mass fractions of the components of the lead-cadmium compound conditioner; continuously stirring the various raw materials in a stirring device for at least 30 min, and thoroughly stirring and evenly mixing all the materials; and the method of application of the conditioner comprises the following steps of: (1) analyzing the total quantity of lead and cadmium in the rice field and the content of lead and cadmium in exchange state; (2) determining the pollution level of the rice field soil by using an evaluation model; (3) applying the lead-cadmium compound conditioner according to the lead-cadmium pollution level in the rice field, and applying the lead-cadmium compound conditioner to the slightly polluted rice field at 100-150 kg / mu, to the mildly polluted rice field by 150-300 kg / mu and to medium-polluted rice field at 300-600 kg / mu, and balancing and stabilizing for 10-15 days; and (4) analyzing and measuring the content of lead and cadmium in exchange state in the rice field, and if the fixed rate is lower than 90%, additionally applying the conditioner at 100-150 kg / mu.
Owner:廖柏寒 +1
Method for repairing cadmium pollution soil using with asteraeae plant
InactiveCN101147914ADoes not destroy physical and chemical propertiesNo secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationPollution soilCadmium Cation
The present invention relates to a method for repairing soil contaminated by cadmium. It is characterized by that said invention utilizes plantation of bidens tripartite in the soil contaminated by cadmium so as to attain the goal of repairing said soil. Said invention also provides the plantation method of bidens tripartite and its field management method.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Composite improvement agent, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105131961AReduced activityImprove fertilityContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersNitrateFood safety
The invention provides an improvement agent used in cadmium-polluted soil, which includes following components, in proper ratio: agricultural rare earth nitrates, waste catalyst, medical stone, humic acid mineral powder, sepiolite, plant ash, kaolin and zeolite. When the improvement agent is applied in heavy metal-polluted soil, heavy metal in soil is effectively passivated and immobilized under a synergistic effect of the components above, and meanwhile, the polluted soil is effectively repaired, so that activity of the heavy metal in soil is significantly reduced and adsorption of crops to the heavy metal is effectively reduced, thereby reducing heavy metal content in crops significantly. The improvement agent is excellent in stability and environment-friendly property, is free of secondary pollution, is low in cost and is easy to popularize in large scale. When the fertilizer is applied in heavy metal-polluted soil, the use quantity is only 10-200 kg / hm<2>. The composite fertilizer can significantly reduce the heavy metal content in crops, so that the heavy metal content in crops reaches national food safety standard.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Preparation for reducing accumulation of cadmium in crops and application method thereof
InactiveCN103980030AEasy to prepareSimple and fast operationPlant growth regulatorsBiocideSide effectSulfate
The invention belongs to the fields of soil heavy-metal pollution treatment in environment protection and agricultural product safety, and relates to a preparation for reducing accumulation of cadmium in crops and an application method thereof. The preparation for reducing accumulation of cadmium in crops comprises the compositions with the following concentration: 50-80 g / L of reduced glutathione, 15-30 mg / L of sodium selenite and 2.0-3.0*10<3> mg / L of zinc sulfate. The crops mean paddy rice or barley. The preparation has the advantages of preparing simpliness, usage convenience, no toxic and side effects, low cost and the like. The preparation is used by spraying on leaf surfaces, the operation is similar to operation of spraying pesticides, the application method is simple and easy to operate, and the preparation is also capable of improving the content of zinc, selenium and other nutritional elements in the crops. The preparation is applicable to paddy rice, barley and other crops for producing low-cadmium products, and is suitable for popularization application in moderate / mild cadmium-pollution regions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Preparation and use of slow-release iron-based biochar soil heavy metal passivator
ActiveUS20180119008A1Broaden applicationSave materialAgriculture tools and machinesContaminated soil reclamationSoil heavy metalsGrowing season
The invention discloses a method for the preparation and use of a slow-release iron-based biochar soil heavy metal passivator. The slow-release iron-based biochar soil heavy metal passivator of the present invention is prepared by an one-step method, wherein iron-based biochar, kaolin and a biological starch are mixed into a core material in a specific ratio; an acidic silica sol and a chitosan solution are prepared, under the effects of an alkaline catalyst and an emulsifier, as a chitosan and silica-sol composite material as a coating, and the iron-based biochar is coated with the alkaline coating material, with the core material and the coating material being controlled at a certain volume ratio. The passivator has a wide raw material source, a simple and convenient preparation process, easy industrialized production, and can passivate the heavy metal arsenic and cadmium efficiently and inhibit the absorption and accumulation of arsenic and cadmium. The passivator prepared by the present invention can last for 4 growing seasons and has a higher passivation efficiency and a longer action time than common iron-based biochar passivators. The passivator can be widely used in the control of arsenic and cadmium pollution farmland.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Combined prevention and control method for cadmium exceeding of rice in medium-light cadmium-polluted soil
InactiveCN103004439ALower redox potentialReduced bioavailabilityHorticultureSoil-working methodsBiologyHeavy metals
The invention discloses a combined prevention and control method for cadmium exceeding of rice in medium-light cadmium-polluted soil. The method comprises the following steps of: uniformly spreading a soil passivant onto the surface of medium-light cadmium-polluted soil before ploughing and fertilizing the medium-light cadmium-polluted soil; uniformly stirring; balancing for over three days, and applying a basic fertilizer; transplanting low-cadmium-absorption paddy rice onto soil to which the basic fertilizer is applied; and adopting a flooding irrigation management measure at the infertility period of the low-cadmium-absorption paddy rice to complete combined prevention and control of cadmium exceeding of rice. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low cost, environment friendliness, saving in resources, easiness in operating, and the like, the biological effectiveness of cadmium in acid heavy metal-polluted soil can be effectively lowered, and cadmium accumulation of rice is reduced.
Owner:湖南宇丰农科生态工程有限公司
Agricultural method for recovering cadmium pollution farmland soil
The invention relates to an agricultural method for recovering cadmium pollution farmland soil, comprising the following steps of: 1. recovering the cadmium pollution soil by nightshades; 2. recovering the cadmium pollution soil by Beta vulgaris var.cicla L, wherein the asarum exact of the invention has the advantages of high efficiency and low residual and is harmonious with the environment and other living beings; and 3. testing the total cadmium removal amount of the nightshade plants and Beta vulgaris var.cicla L plants. The invention not only can continuously remove heavy metals in the soil for a long time but also can ensure that the biomass is not reduced and prevents plant diseases and insect pests from increasing.
Owner:SHENYANG UNIV
Immobilized Bacillus having phosphate dissolving and heavy metal passivation functions and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106591277AIncrease resilience to adverse environmentsRepair repair works wellContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganism based processesPhosphateBacillus cereus
The invention discloses an immobilized Bacillus having phosphate dissolving and heavy metal passivation functions and a preparation method and an application thereof, which belong to the technical field of cadmium pollution soil biological restoration. The immobilized Bacillus comprises biological carbon and Bacillus cereus B19, can be used for restoring the soil with severe cadmium pollution, and has better restoration effect. The composite microbe fertilizer contains the immobilized Bacillus, an organic fertilizer and an inorganic nutrient having the phosphate dissolving and heavy metal passivation functions. The composite microbe fertilizer has the advantages that cost is low, soil available nutrient content is increased, yield increase is achieved, the soil with cadmium pollution is effectively repaired, introduction of heavy metal cadmium in human body with crops can be effectively controlled, agricultural product safety is guaranteed; in addition, the composite microbe fertilizer cannot change a farmland utilization mode without secondary pollution, is conveniently used, and is economic and feasible.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Passivating agent for reducing cadmium activity of acidic vegetable soil and use method thereof
ActiveCN103143556AReduce cadmium activityReduce heavy metal contentContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceSoil cadmium
The invention discloses a passivating agent for reducing the cadmium activity of acidic vegetable soil and a use method thereof. The passivating agent contains the following components by weight: 31.3-46.2% of lime, 26.7-39.0% of potassium humate, and 25.0-37.8% of rice husk carbon. The use method consists of: subjecting the passivating agent to basal application totally according to a dose of 150-450kg per 667 square meters, then conducting plowing and uniform raking to make the passivating agent and contaminated soil mixed uniformly, spraying water, performing balancing for 1-3 days, and then carrying out sowing or transplanting. Through the synergistic effect of various components, the passivating agent involved in the invention can reduce the cadmium activity of the soil and the heavy metal content of vegetables, and improve the crop yield and quality, thus being able to be widely applied to remediation of acidic vegetable soil suffering moderate and mild cadmium pollution or severe pollution.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Chemical fixing agent for heavy metal contaminated soil remediation and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN103275725AEasy to fixWide variety of sourcesContaminated soil reclamationChemical inhibitorsPhosphateSoil remediation
The invention provides a chemical fixing agent for heavy metal contaminated soil remediation and a preparation and an application thereof. the preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) using titanium dioxide waste residue as a raw material, stirring while adding phosphate and an alkaline substance into a solution successively, and adjusting pH to alkaline; and 2) adding an oxidizing agent into a mixed liquor, fully stirring, reacting for 60-120min, filtering, drying the residue at 50-80 DEG C, grinding and sieving through a 20-mesh sieve so as to obtain a heavy metal fixing agent. The heavy metal fixing agent is added into lead-cadmium contaminated soil according to the mass ratio of 5%. Effective state cadmium and lead fixed rates reach 34-43% and 41-48% respectively. According to the heavy metal fixing agent provided by the invention, industrial solid wastes are fully utilized, and the preparation process is simple and requires low cost. In addition, the fixing agent prepared by the preparation method has a good effect of fixing heavy metal and can be used for lead-cadmium contaminated soil remediation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Plant repairing method for soil polluted by heavy metal cadmium
InactiveCN101486041AReduce environmental risksReduce usageContaminated soil reclamationVolumetric Mass DensityCadmium Cation
The invention discloses a method for recovering plants in soil subjected to heavy metal cadmium pollution, and belongs to the field of soil pollution control in environmental protection. The method comprises the following steps: (A) periodically measuring the content of cadmium in the soil, and grafting willow; and (B) after the willow is grafted for two months, adding chemical enhancer consisting of ethyl lactate and ethylene diamine tetraacetic aid into the soil. In the step A, the willow is selected from Jiangsu willow clone J1011, and the planting density of the willow is between 4 and 6 strains every square meter when the content of the cadmium in the soil is 6 milligrams in every kilogram of soil. The method can overcome the defects of short and small strains, low growth rate, small amount of ground biology, and the like during recovery of the plants polluted by the heavy metal cadmium, improve recovery efficiency by singly using organic ligand as a chelate extracting agent to recover the heavy metals, has lower recovery cost, and reduces the use level of synthetic chelating agent such as EDTA by using the ethyl lactate so as to reduce environmental risk for recovering the heavy metal cadmium in the soil by extracting the plants.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Chemical enhanced phytoremediation method of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-cadmium pollution soil
InactiveCN101642769AReduce usageReduce environmental risksContaminated soil reclamationVolumetric Mass DensityCadmium Cation
The invention relates to a chemical enhanced phytoremediation method of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-cadmium pollution soil, belonging to the field of soil pollution regulation; the method comprises the following steps: (A) the content of cadmium, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, phenanthrene and pyrene in the soil is measured, and willow sowing is carried out; (B) chemical enhancer constitutedby ethyl lactate and ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid is added after the willow is sewed for four months. The willow is golden silk willow J1022, and the planting density of the willow is respectively 4-6 per square meter in the soil which has 5mg phenanthrene, 50mg pyrene and 6mg cadmium in one kilogram. The method avoids the disadvantages of short and small plant, slow growing speed, and low living weight at the upper part of the soil in the phytoremediation, reduces the environment risk of heavy metal cadmium in the plant extraction soil remediation; the adding of the chemical enhancer improves the remediation efficiency that an organic ligand is singly used as chelating solvent extraction agent to remediate the heavy metal, and the remediation effect of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon of organic pollutants in the soil is enhanced at the same time, and the remediation of cadmium and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon combined pollution in the soil is realized at the same time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Phytoremediation method for cadmium polluted farmland
InactiveCN102114490ALarge biomassMake the most of planting timeContaminated soil reclamationPotassiumPhytoremediation
The invention relates to a phytoremediation method for a cadmium polluted farmland, comprising the following steps of: in a cadmium polluted farmland containing cadmium of below 8mg / kg, planting grain amaranth and red leaf amaranth in a crop rotation mode, applying potassium fertilizer, harvesting for many times, and concentrating all plant materials for landfill. According to the phytoremediation method for a cadmium polluted farmland, planting is performed thrice per year, wherein the grain amaranth is planted twice, and the red leaf amaranth with a short crop rotation period is planted between double planting of the grain amaranth, thus optimizing the arrangement of crop rotation; and on management, the grain amaranth planted for the first time is cut twice to fully utilize the favorable growing conditions in summer and accumulate more biomass, and the grain amaranth planted finally is not cut but grows to be ripe, thus optimizing the accumulation of biomass and the work efficiency. Such a crop rotation mode fully utilizes the planting time in a year, and is conductive to the growth of the grain amaranth planted thirdly. The invention has the advantages of high efficiency, easiness in operate, no secondary pollution and low cost.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Compound fertilizer for repairing cadmium contaminated soil as well as preparation method and application of compound fertilizer
InactiveCN104844375AHelp reduce absorptionReduce cadmium contentFertilizer mixturesPotassiumRare earth
The invention provides a compound fertilizer for repairing cadmium contaminated soil. The compound fertilizer comprises nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrition components and appropriate proportions of agricultural nitric acid rare earth, waste catalyst agent, humic acid mineral powder, meerschaum, plant ash, kaolin and zeolite components. When the compound fertilizer is applied to the cadmium contaminated soil, under the synergistic action of the components, the cadmium in the soil is effectively passivated and fixed, and meanwhile the contaminated soil is effectively repaired, so that the activity of the cadmium in the soil is significantly reduced, the compound fertilizer is beneficial for reducing the absorption of cadmium by crops, and then the cadmium content in the crops is significantly reduced. The compound modifier provided by the invention is relatively good in stability and environment-friendliness, does not generate secondary pollution, and is low in cost and easy to popularize in a large area, and when applied to the cadmium contaminated soil, the applied amount is only 10-200kg / hm<2>, and the cadmium content in the crops can be significantly reduced to reach a national edible safety standard.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Method for treating soil and aquatic lead, zinc, cadmium pollution by cone south mustard
InactiveCN1623933ALow costImprove repair efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationBiological water/sewage treatmentZincBiology
A process for eliminating the pollution of Pb, Zn and Cd to said and water by use of arabis paniculata features that the Arabis paniculata is planted in the polluted sol or water for absorbing Pb, Zn and Cd. When their concentrations in the plant reach a certain value, the plant on the ground is cut out and its root is retained for growing the plant no the ground and further cutting it out.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Water treatment method for adsorbing and removing Tl<+> and/or Cd2<+> by producing nanometer manganese dioxide in situ
InactiveCN102145948AHigh electronegativityLarge specific surface areaWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentPermanganate saltEmergency treatment
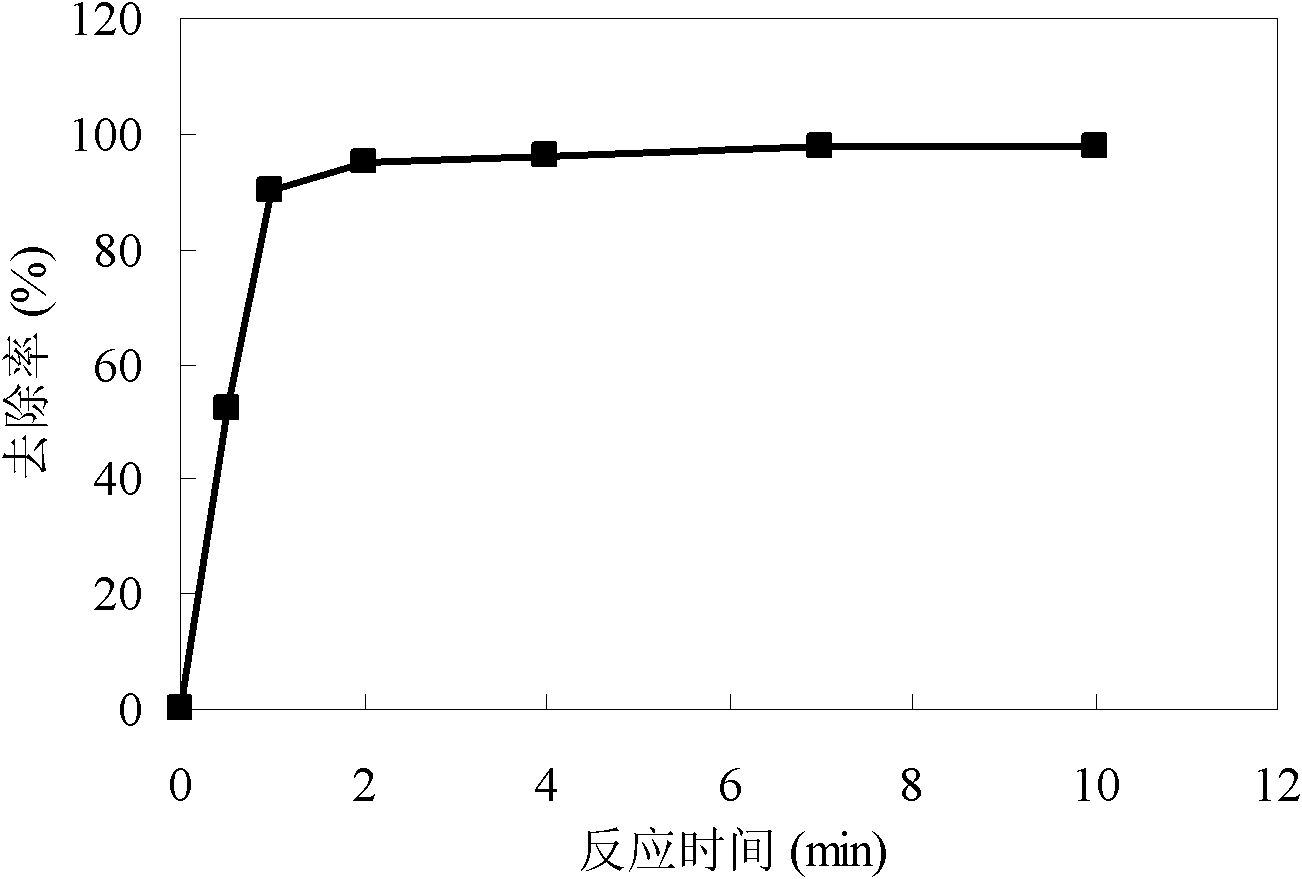
The invention discloses a water treatment method for adsorbing and removing Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+> by producing nanometer manganese dioxide in situ, relating to a water treatment method of thallium and / or cadmium-containing source water and solving the problems of complex process, high running cost and low removing efficiency of thallium and / or cadmium existing in the conventional water treatment technology specific to thallium and / or cadmium-polluted source water. The method comprises the following steps of: adding permanganate and sodium thiosulfate into Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+>-containing water; stirring to obtain a mixed solution; adding a coagulant; and performing conventional water treatment. Nanometer manganese dioxide which has a large specific surface area and high electronegativity and is easy for precipitation separation is produced in situ by making permanganate react with sodium thiosulfate, so that low-concentration Tl<+> and / or Cd2<+> in water can be removed effectively and specifications in the national Sanitary Standard for Drinking Water are met. The method has the advantages of high removing efficiency, simple process, flexibility and convenience for operation, no change of the original treatment process of a water plant, low running cost and the like, and can be applied to emergency treatment of a water pollution event.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Remediation method for heavy metal cadmium pollution of orchard soil based on galinsoga parviflora
InactiveCN103447290AReduce contentHave patienceContaminated soil reclamationGermplasmSoil heavy metals
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
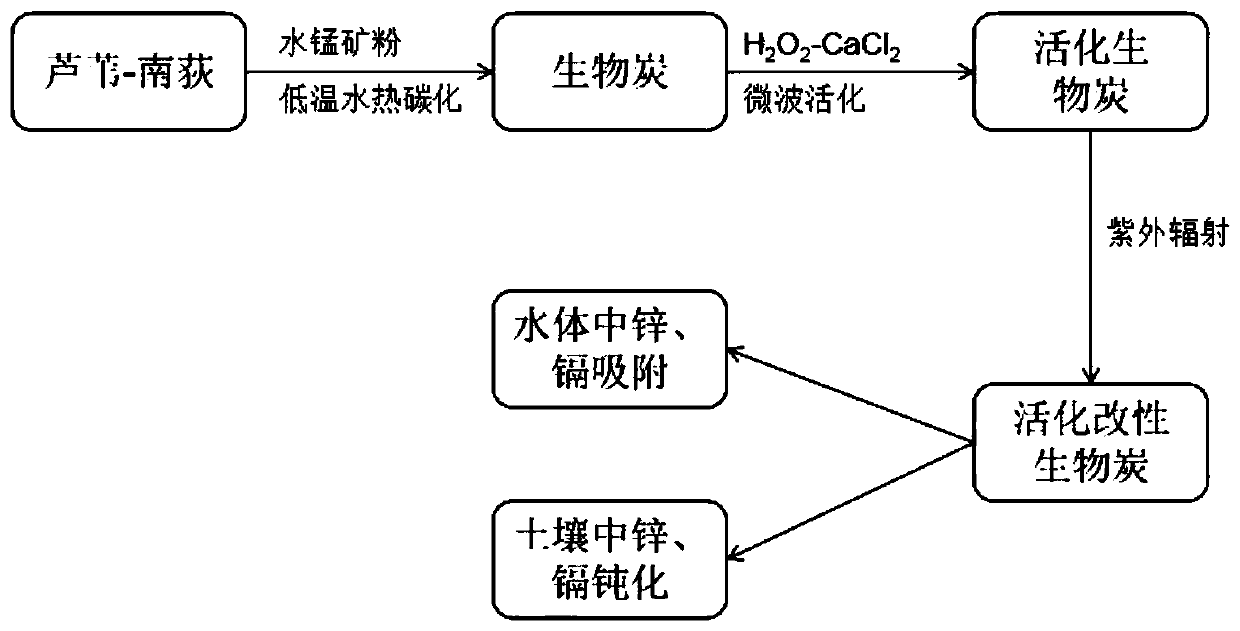
Preparation method and application of multi-site activated and modified reed-lutarioriparius biochar
ActiveCN110327882AImprove stabilityHigh pHOther chemical processesWater contaminantsMulti siteSoil heavy metals
The invention relates to the field of treatment to heavy metal pollution in water and soil, in particular to a preparation method of multi-site activated and modified reed-lutarioriparius biochar andapplication thereof to removal of heavy metals zinc and cadmium. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly washing, drying and crushing reed-lutarioriparius biomass, ultrasonicallystirring in an aqueous manganese ore powder solution thoroughly, then performing low-temperature hydrothermal carbonization to produce unactivated and unmodified biochar, then soaking the biochar ina calcium chloride-hydrogen peroxide mixed solution, activating a biochar-calcium chloride-hydrogen peroxide mixed solution by using microwave, and then modifying the dried biochar through ultravioletradiation to obtain activated and modified biochar, wherein the obtained biochar is applied to the removal of the heavy metals zinc and cadmium in the water and the soil. An application method comprises the following steps: adding the activated and modified biochar into heavy metal zinc and cadmium wastewater for an adsorption reaction; or directly adding into heavy metal zinc and cadmium contaminated soil, thoroughly mixing uniformly, and aging for a period of time to complete bioremediation of heavy metal zinc and cadmium pollution in the soil.
Owner:JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
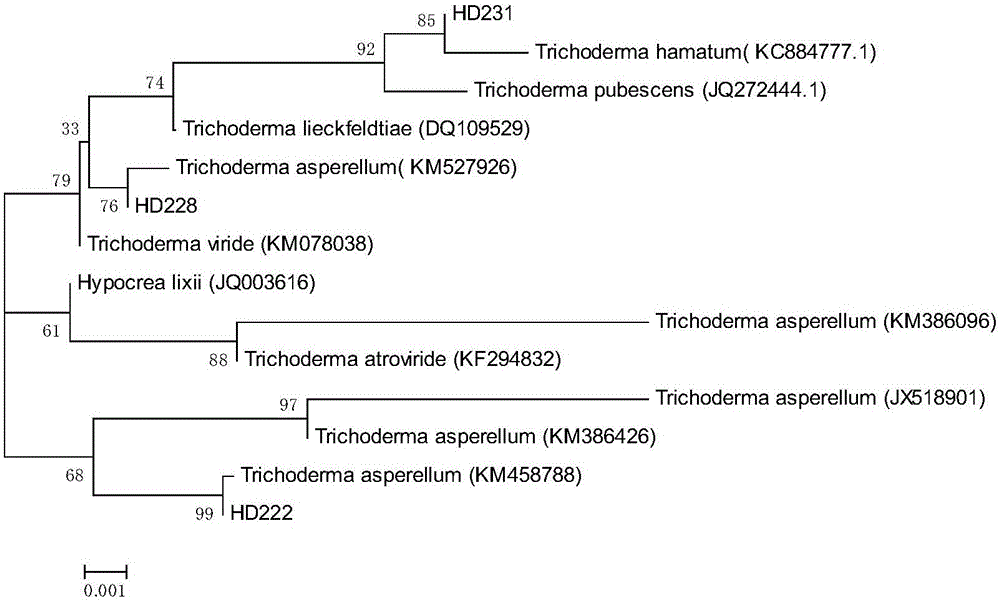
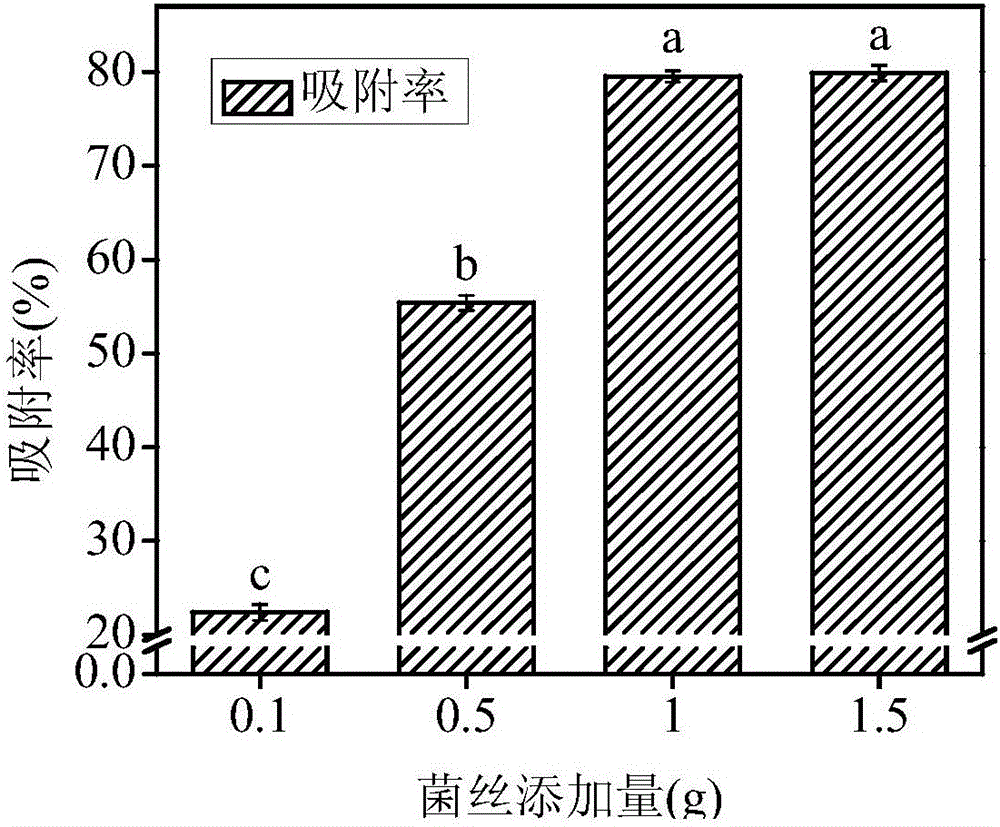
Trichoderma asperellum and application thereof in remediation for heavy metal pollution
InactiveCN106434374AHas a growth-promoting effectHas a detoxifying effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismBiotechnology
The invention relates to trichoderma asperellum and an application thereof in remediation for heavy metal pollution. The trichoderma asperellum HD228 is separated from cadmium-containing soil in Hengdong County, Hunan, and the preservation number of the trichoderma asperellum HD228 is CGMCC No.12870. The strain (the trichoderma asperellum HD228) has a high cadmium adsorbing capacity, and meanwhile, the strain has a growth promoting effect on rice and has a detoxifying effect on cadmium-stressed rice. Therefore, the trichoderma asperellum HD228 has a potential of developing double functions in a process of conducting soil remediation on cadmium-contaminated rice fields, and a good strain is provided for cadmium-contaminated soil microbial remediation engineering. The application provided by the invention has theoretical and realistic significance for the remediation of cadmium pollution of the cadmium-contaminated rice fields.
Owner:HUNAN AGRI BIOTECH RES CENT
Method for comprehensively controlling cadmium pollution of rice by utilizing modifier and agricultural technology
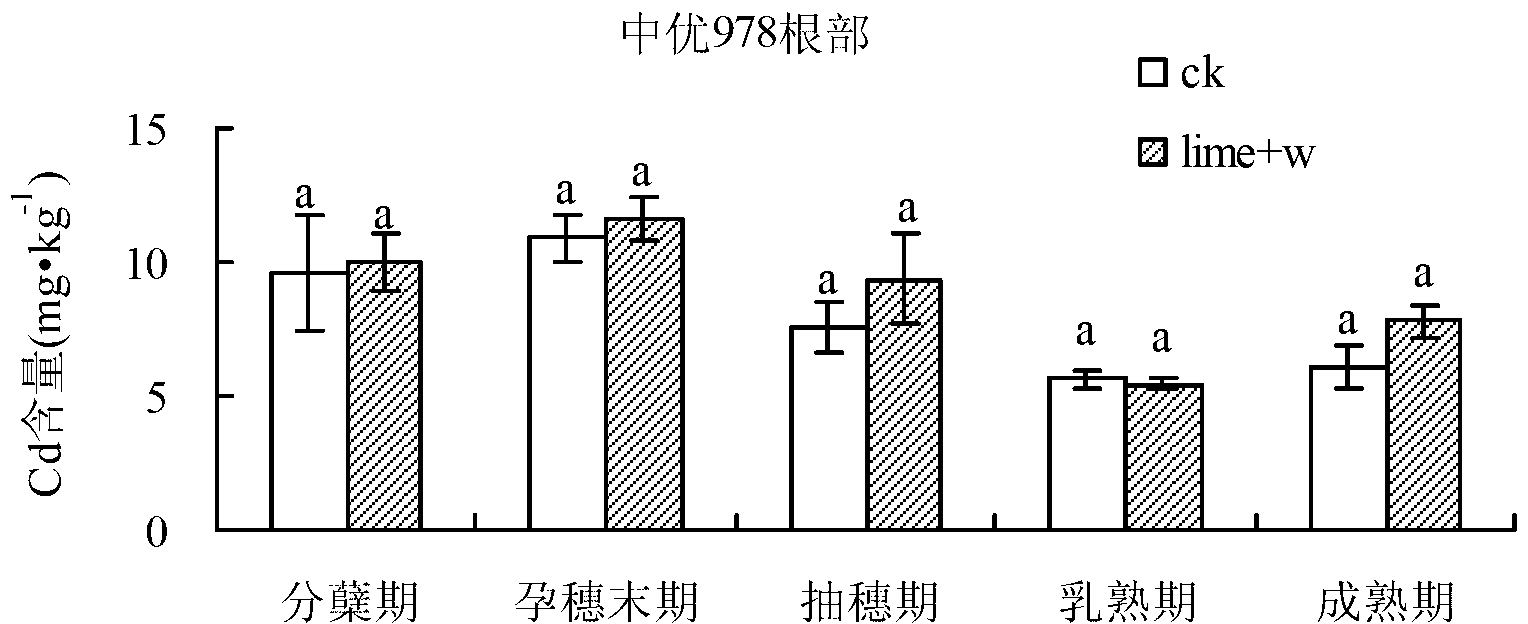
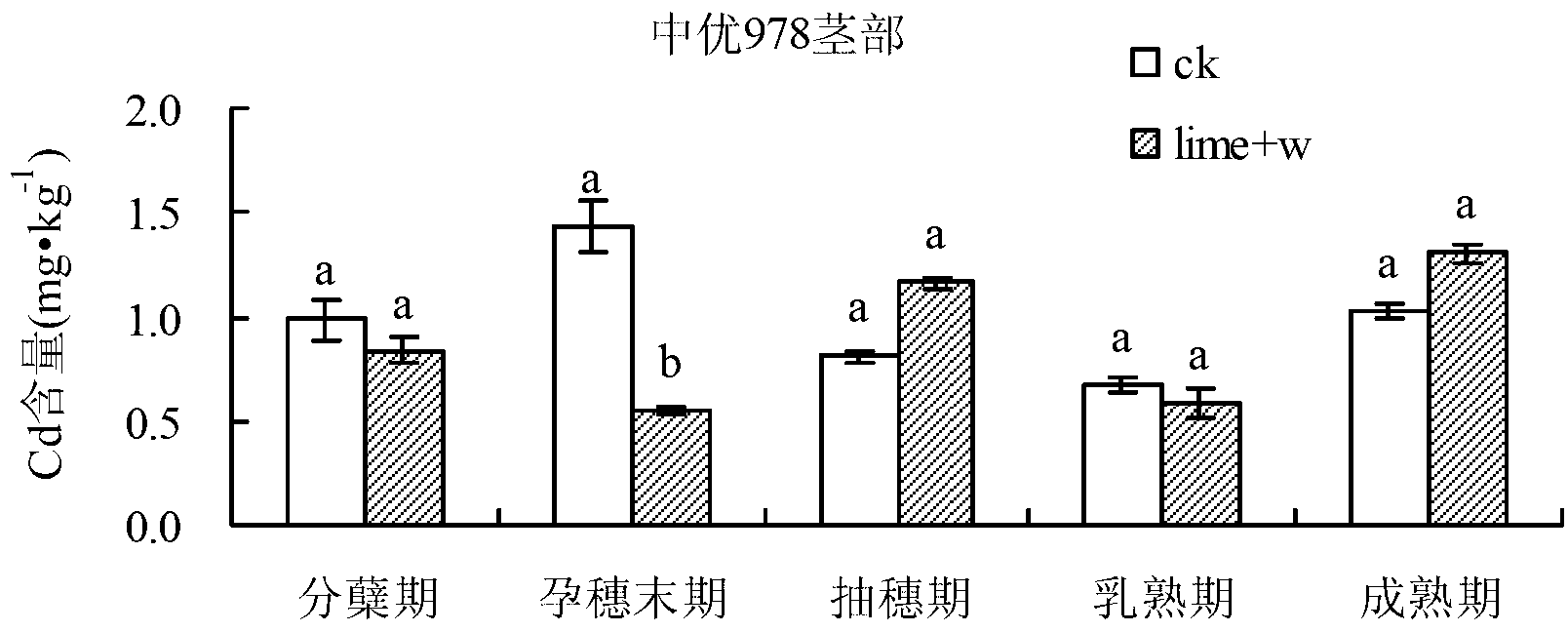
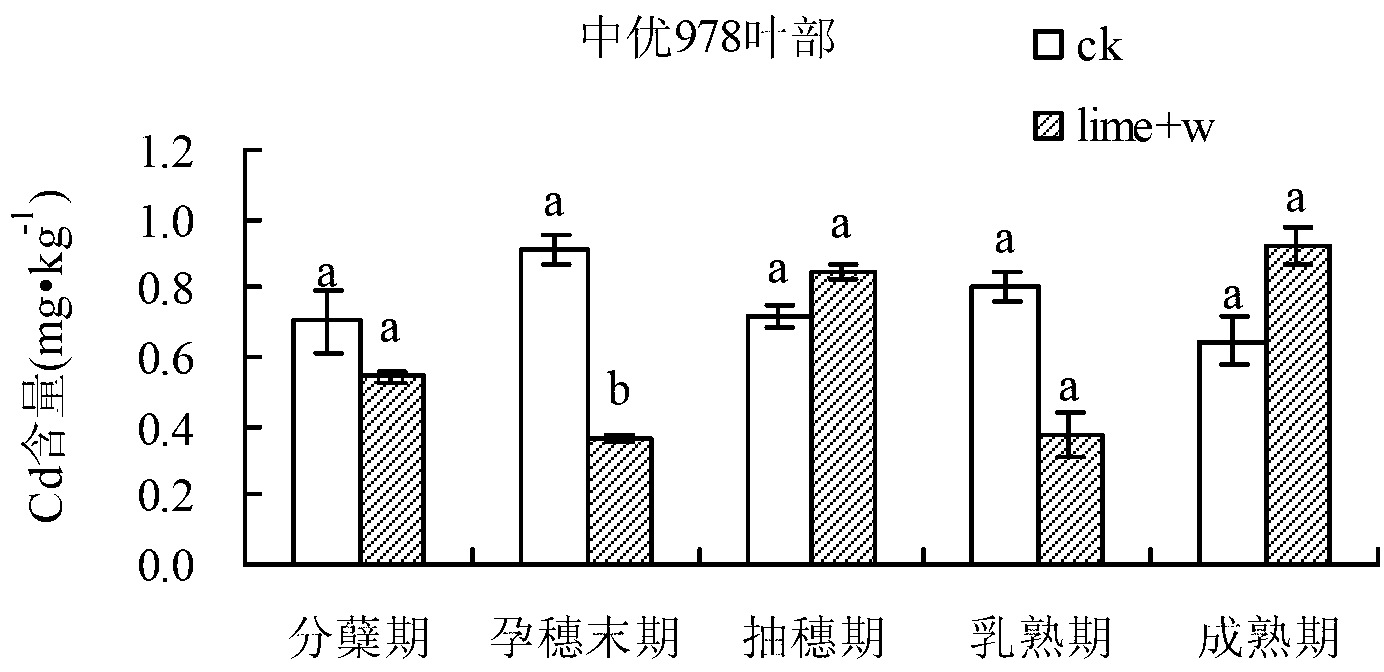
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively controlling cadmium pollution of rice by utilizing a modifier and an agricultural technology. The method comprises the steps of irrigating a rice field at the final booting phase of the rice, keeping a water layer of 2-3 cm on a field surface, broadcasting 60 Kg quicklime per mu into water uniformly, and keeping a waterflooding state of the field till the field is dried or drained by nature transpiration and evaporation 5 days before harvesting. With the adoption of the method, Cd elements in soil are gathered at inedible parts of the rice, such as a root, a stem and a leaf, so that the Cd accumulation amount at a grain part is reduced significantly; the Cd elements are effectively prevented and controlled from migrating to the rice; and the Cd content in the rice is reduced.
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com