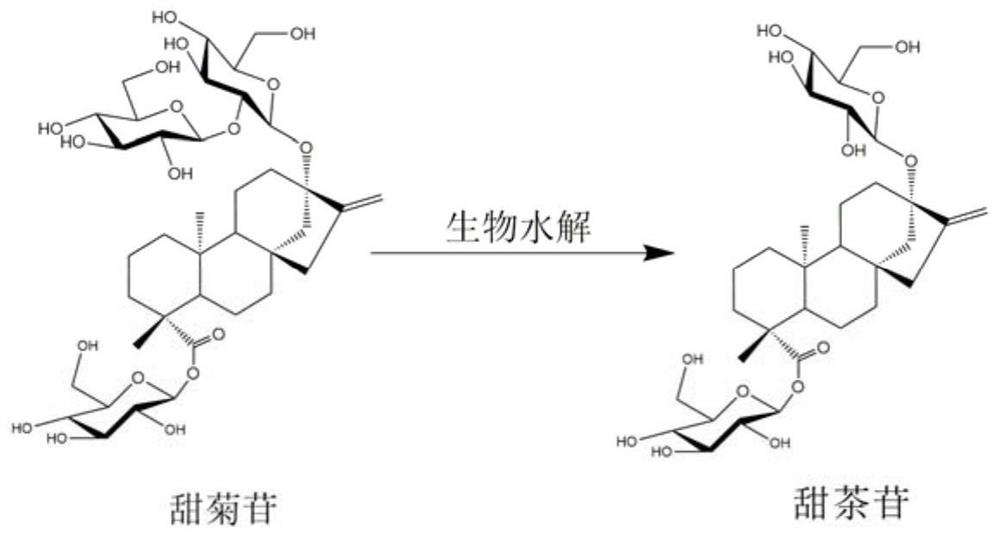
Strain for efficiently converting stevioside into rubusoside and culture method and application thereof
A cultivation method and rubusoside technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as low conversion rate, low catalytic efficiency, and poor specificity, and achieve the effects of easy operation, simple cultivation method, good pH stability and temperature stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Screening and isolation of embodiment 1 bacterial strain
[0040] The screening process of the above-mentioned Chryseobacterium sp. 1433 is as follows:
[0041] (1) Colony screening
[0042] Take 1000mL of offshore seawater outside the east gate of Qingdao Campus of Shandong University and filter it with a 0.22μm filter membrane, and paste the filtered filter membrane on the stevioside sole carbon source agar medium and culture it at 28-35°C for 3 days; Shandong University 5g each of the coastal sludge outside the east gate of the Qingdao campus and the humus of the seaside forest were diluted with 50mL of sterile water, and 200μL of each was inoculated on stevioside-only carbon source agar plates, and cultured at 28-35°C for 3 days; A total of 198 colonies were grown in the culture, and the growth of the strains was observed. 48 colonies with different shapes and appearances were selected and inoculated into the improved M9 liquid medium for re-screening. The liquid m...
Embodiment 2
[0048] The identification of embodiment 2 bacterial strains
[0049] (1) Characteristics of strains
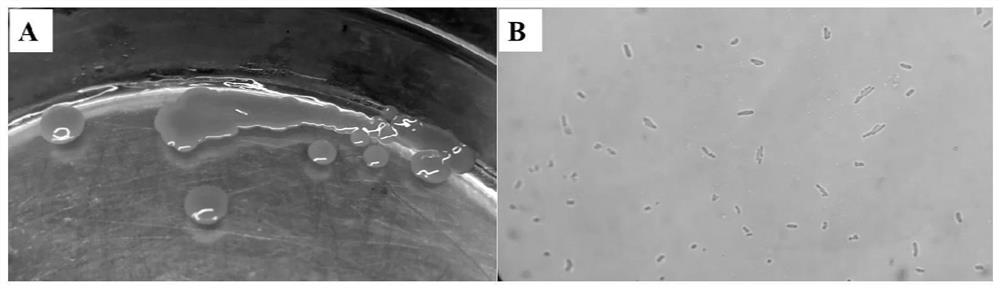
[0050] Biological characteristics of the strain: Gram-negative bacteria, aerobic, non-motile, non-flagellate, short rod-shaped, 0.40-0.46×1.0-1.27 μm in size, the colony is yellow, protruding, round and paste-like, YPD solid Grow on the culture medium at 30°C for 1 to 2 days, and form round colonies with a diameter of 0.5 to 2mm, such as figure 1 shown.
[0051] (2) Identification of strains
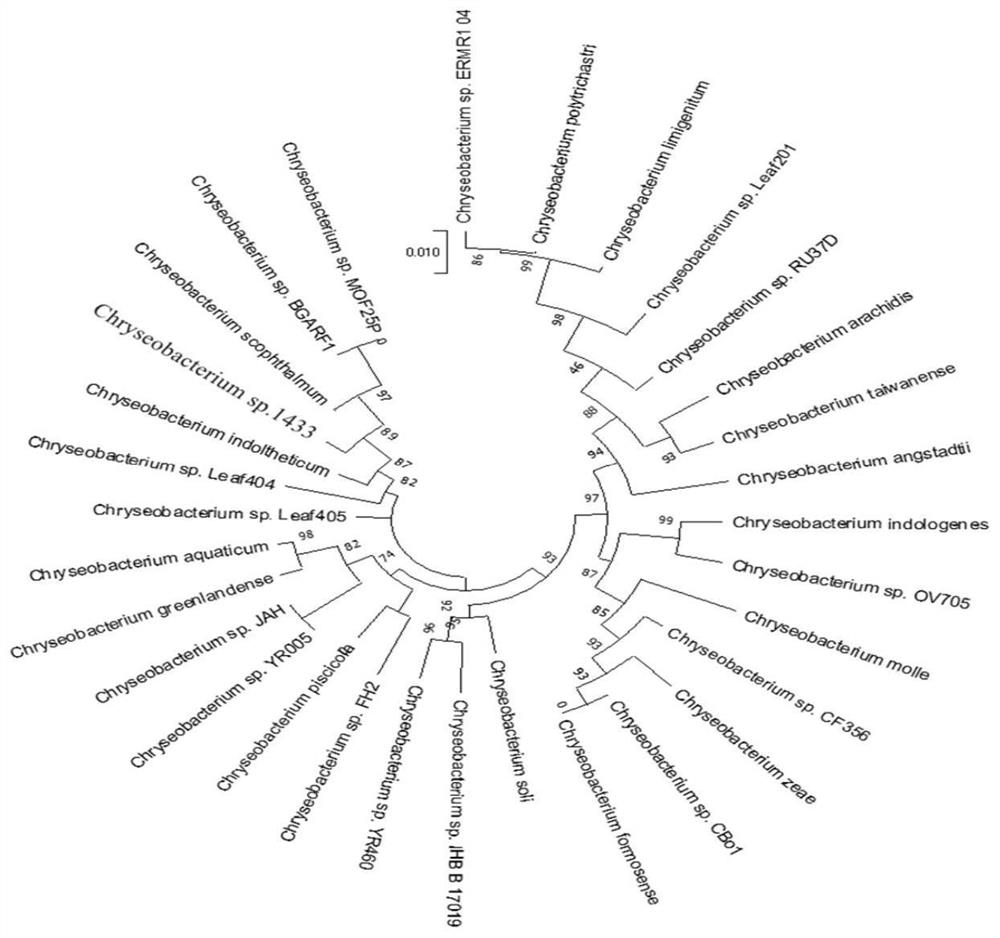
[0052] Obtain the 16SrDNA gene sequence of Chryseobacterium sp. 1433 through DNA extraction, PCR amplification and sequencing, as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, length is 1481bp, carry out BLAST alignment on GenBank and draw phylogenetic tree, phylogenetic tree is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0053] According to the results of 16S rDNA sequence alignment and the biological characteristics of the strain, the strain was identified as Chryseobacterium sp. and named Chryseobacterium sp. 1433.
Embodiment 3
[0054] The cultivation of embodiment 3 bacterial strains
[0055] The culture method of Chryseobacterium sp. (Chryseobacterium sp.) 1433 described in embodiment 1, comprises steps as follows:
[0056] Streak inoculation of Chryseobacterium sp. 1433 on the solid medium, culture at 30°C for 30h, and activate the strain; inoculate the activated strain into the liquid medium, and cultivate at 30°C and 300rpm 30h, prepare the seed liquid; inoculate the seed liquid into the liquid medium according to the volume ratio of 2%, and cultivate for 30h under the conditions of 30°C and 300rpm to obtain the bacterial liquid.
[0057] The solid medium is YPD solid medium; the composition of the YPD solid medium is: 1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 2% glucose, 2% agarose, all in mass percentage, pH 7.0.
[0058] The liquid medium is YPD liquid medium or LB liquid medium; the composition of the YPD liquid medium is: 1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 2% glucose, all in mass percentage, pH 7.0; LB liqu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com