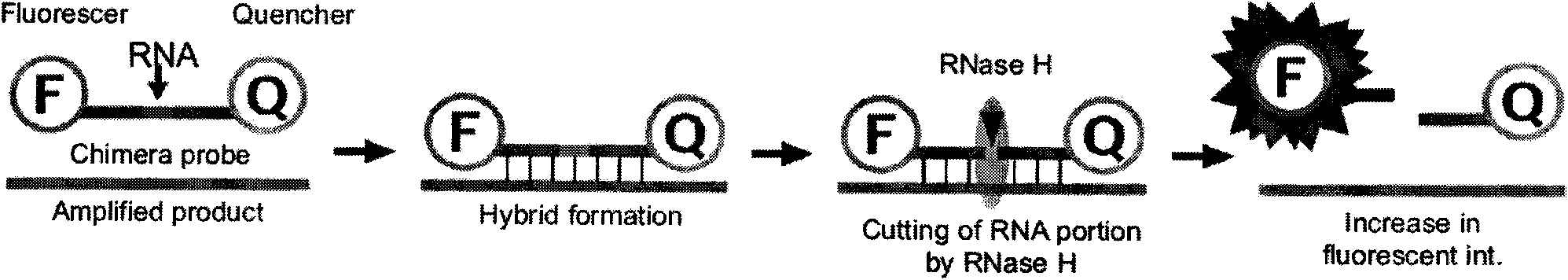
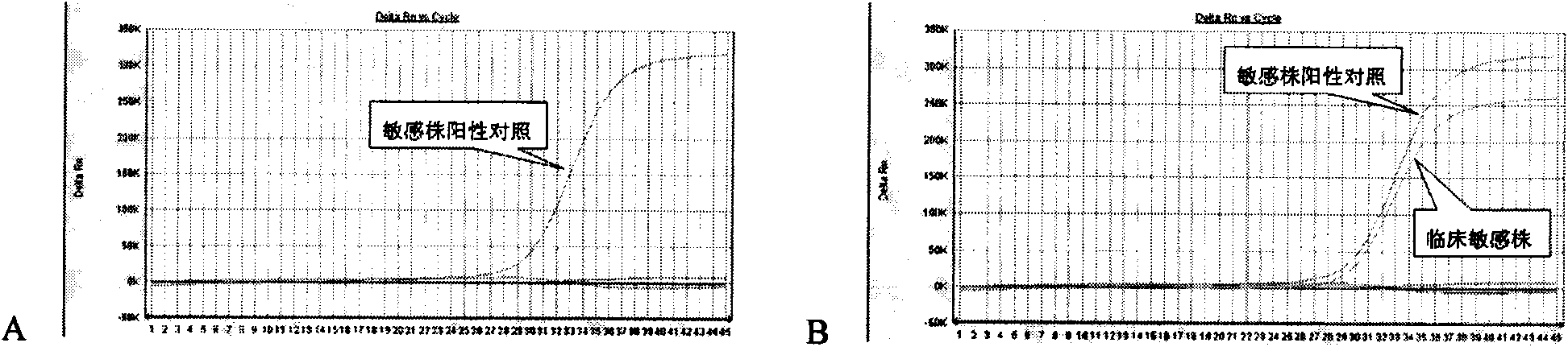
Method for detecting resistant mutant of mycoplasma pneumoniae
A technology of mycoplasma pneumoniae and drug-resistant mutations, applied in the fields of biology and medicine, can solve the problems of children with abnormal cartilage development, and achieve the effect of high specificity and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: the specificity analysis of PCR primer of the present invention
[0031] Use Tiangen Bacteria Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (product number: DP302-02) to extract Mycoplasma pneumoniae standard strain (ATCC15531), Mycoplasma pneumoniae standard strain (ATCC29342), Escherichia coli (ATCC25922), Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC700603) , Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC25923), Streptococcus pneumoniae (ATCC49619), Mycoplasma pneumoniae macrolide-sensitive clinical strains, Mycoplasma pneumoniae 2063 mutation-resistant clinical strains, Mycoplasma pneumoniae 2064 mutation-resistant clinical strains of genomic DNA It is the amplification template (extraction time is about 25 minutes). The amplification system was prepared according to the instructions with specific upstream and downstream primers for Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Takara PCR amplification reagent (product number: DR100A). The amplification conditions were: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 5 minutes; denaturation at ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: Mycoplasma pneumoniae clinical isolate of the present invention
[0033] The PCR amplification products of the Mycoplasma pneumoniae standard strain (ATCC15531, a macrolide-sensitive strain), the 2063 mutant strain and the 2064 mutant strain were gel-cut and purified, inserted into the PCR product cloning vector, confirmed by sequencing, purified, and read Calculate the plasmid copy number after the OD value, and dilute this vector to 10 5 Copy / ml Take 1 microliter for each PCR (about 10 2 copy) was used as a positive control, and the negative control was Escherichia coli genomic DNA at the same concentration. The above, downstream primers, non-mutation-sensitive strain detection probe, 2063 mutation-resistant strain probe, 2064 mutation-resistant strain probe and Takara's CycleavePCR TM The Core Kit (product number: DCY501) was used to prepare the PCR reaction system according to the instructions. The concentrations of the three probes were optimized t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com