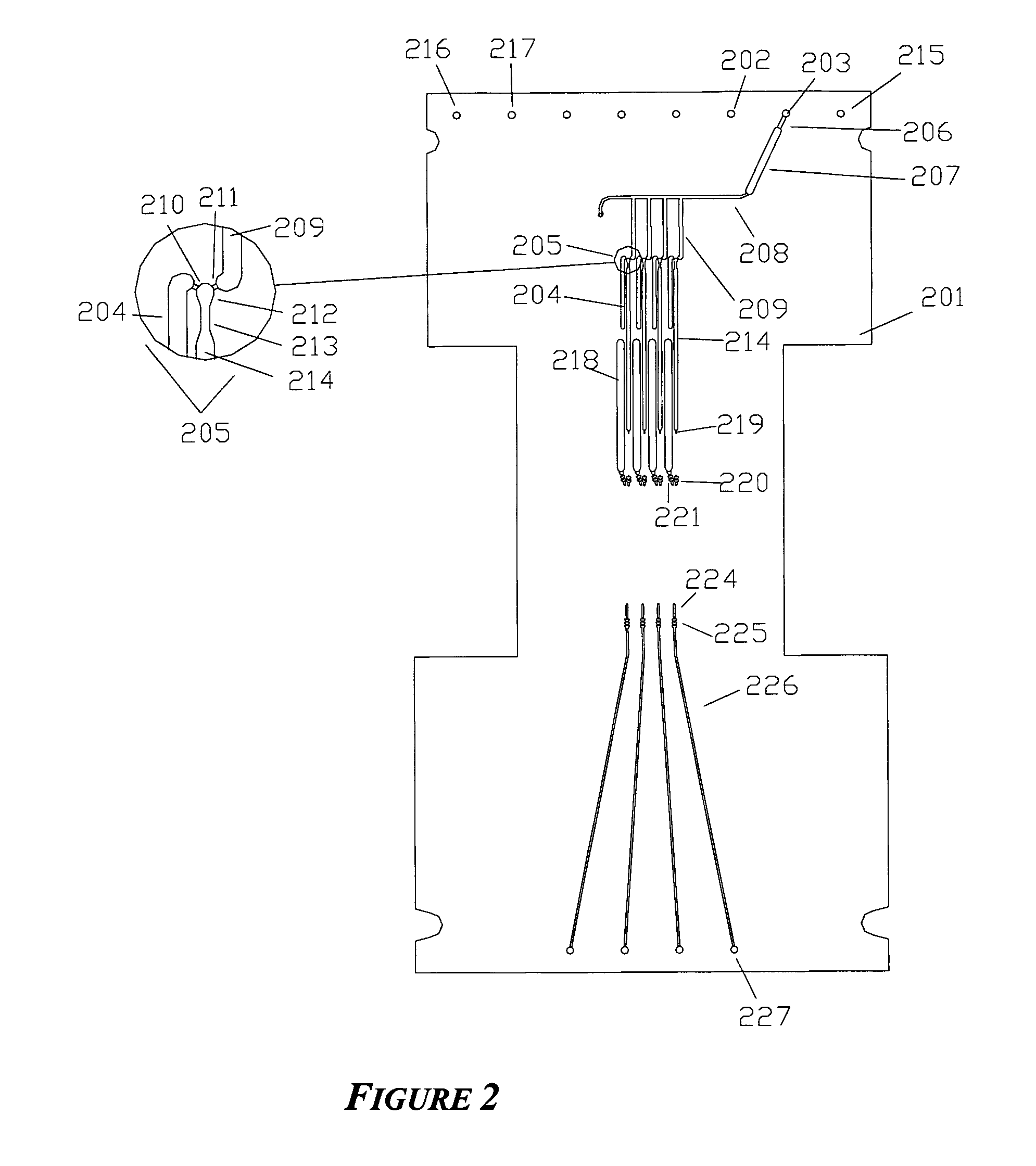
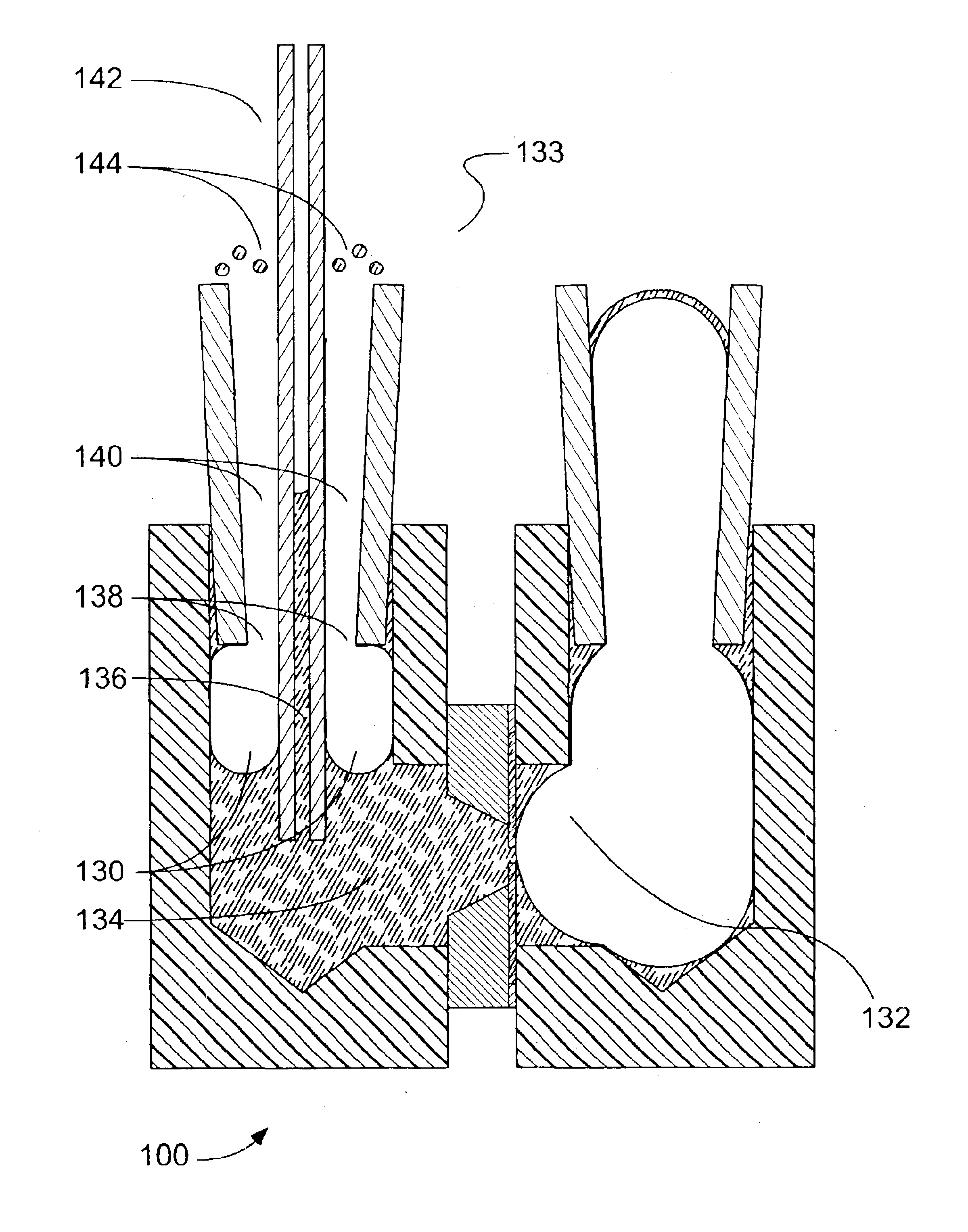
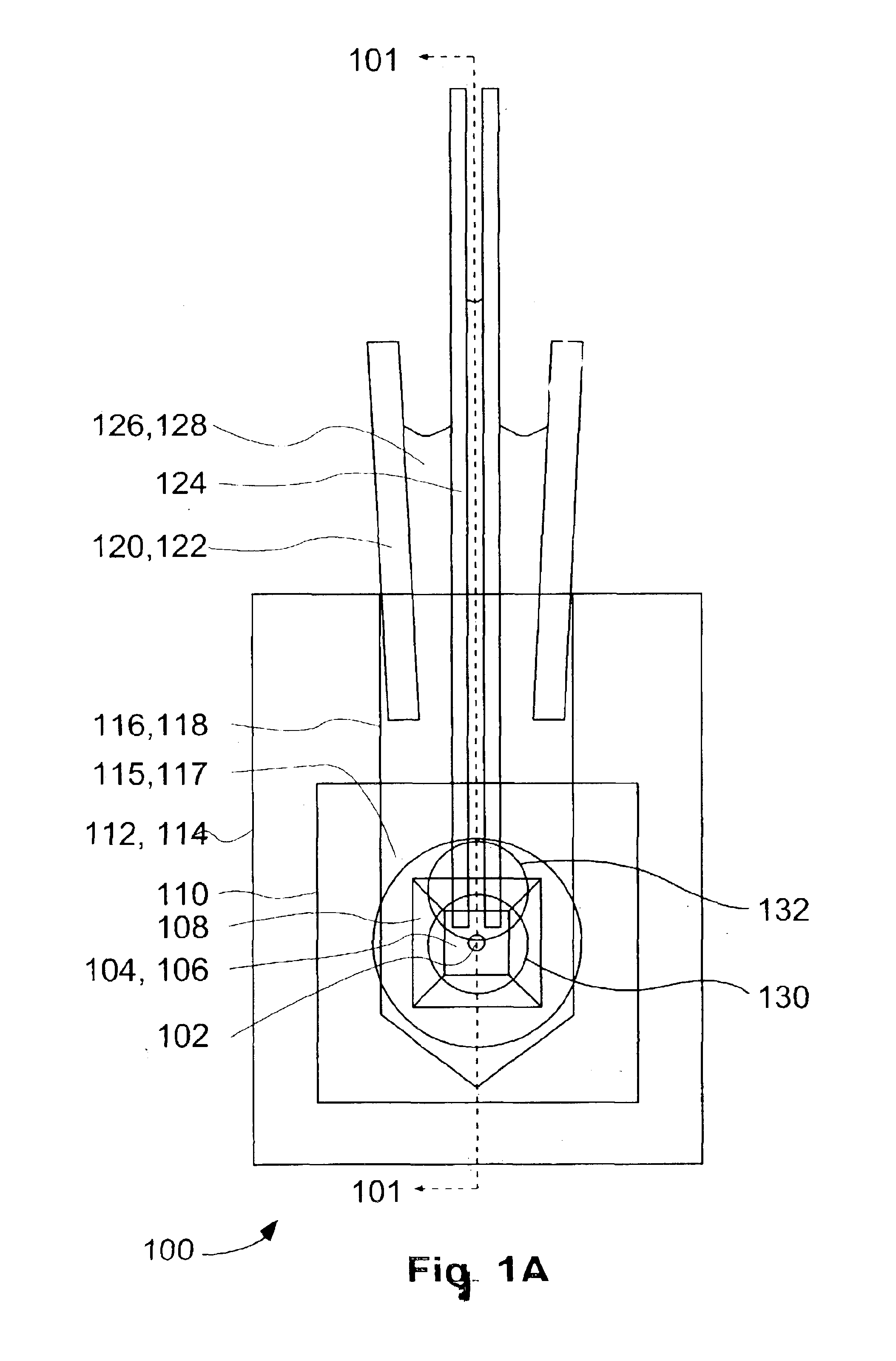
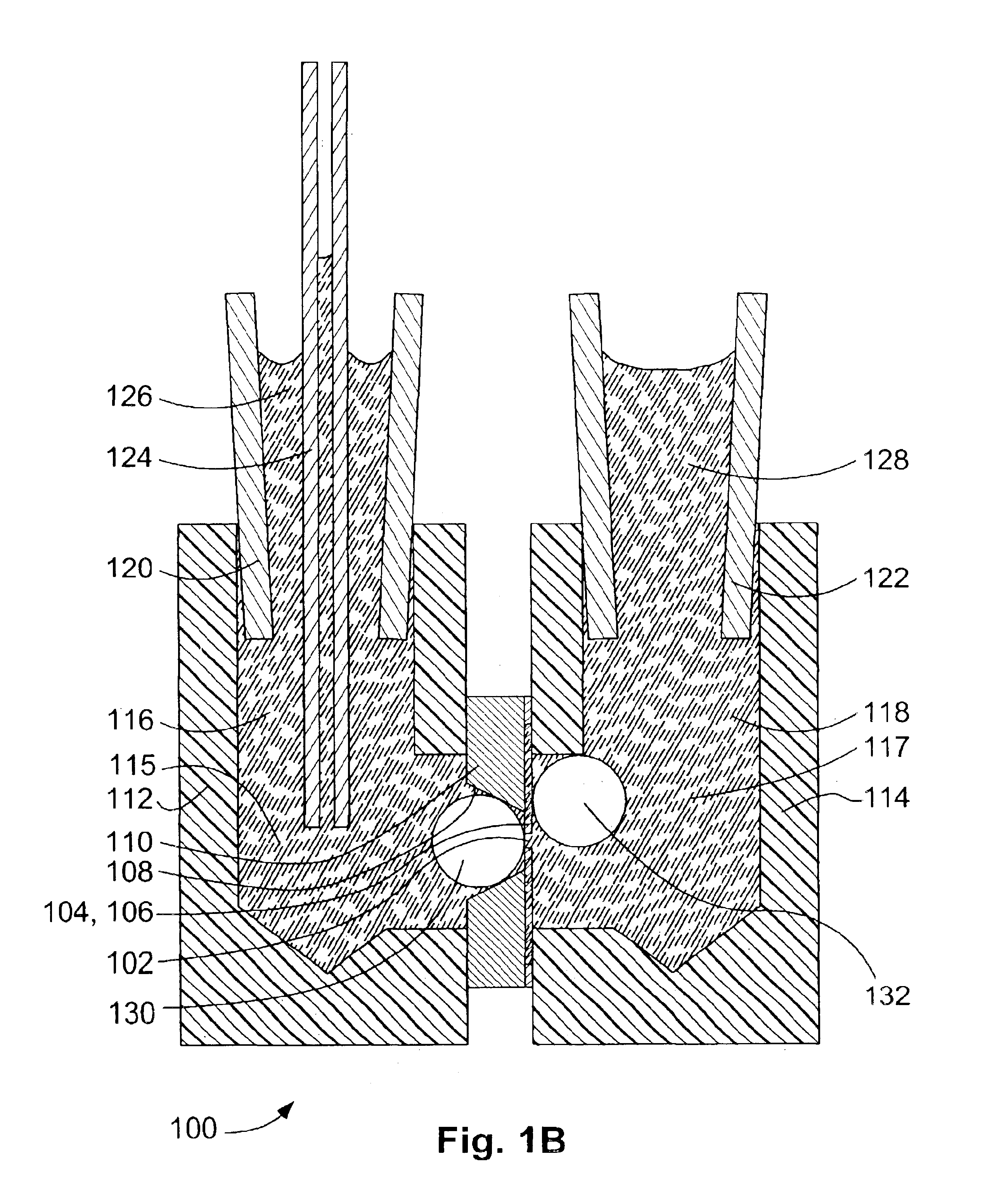
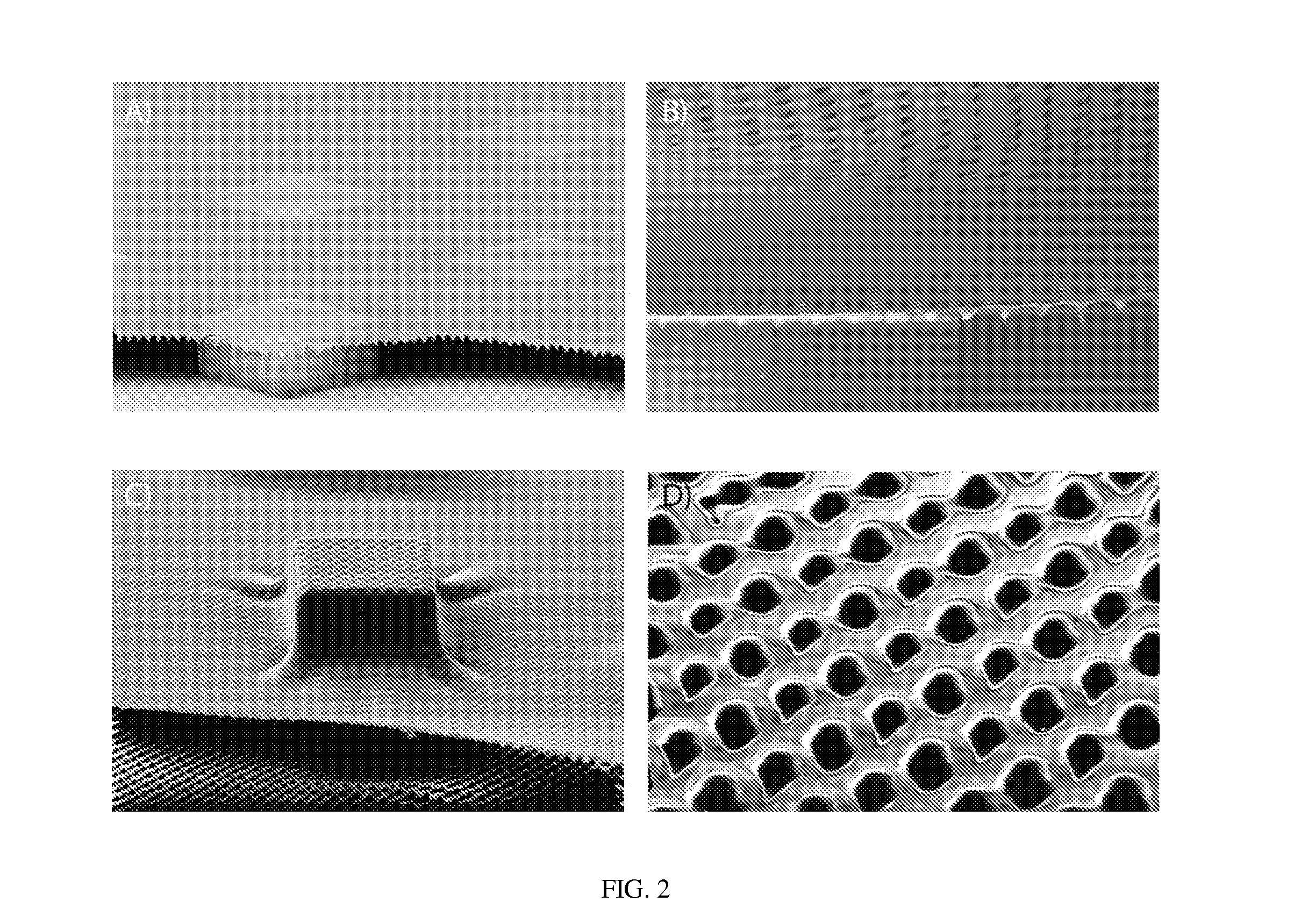
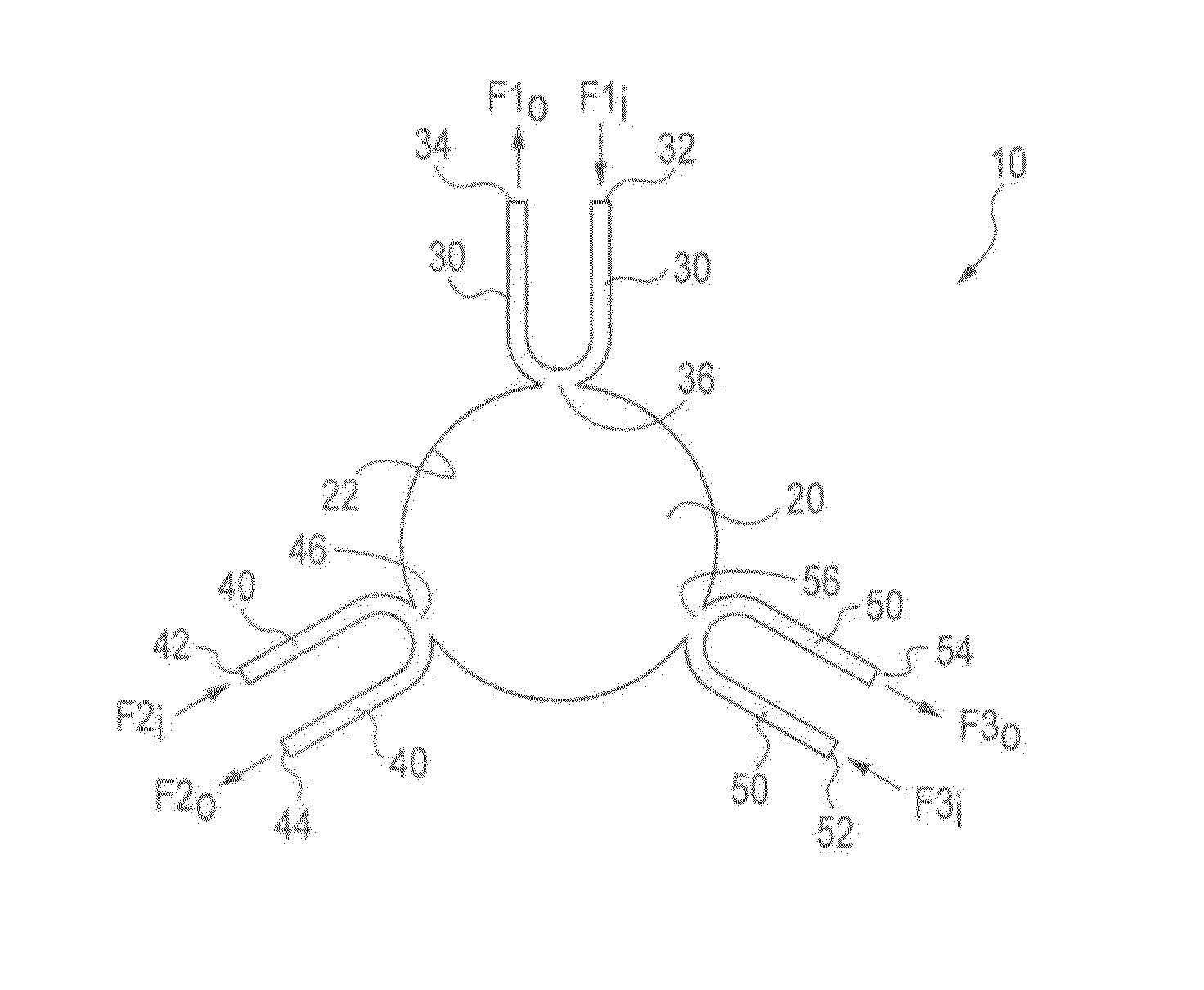
Patents
Literature
72 results about "Microfluidic chamber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microfluidic nucleic acid analysis
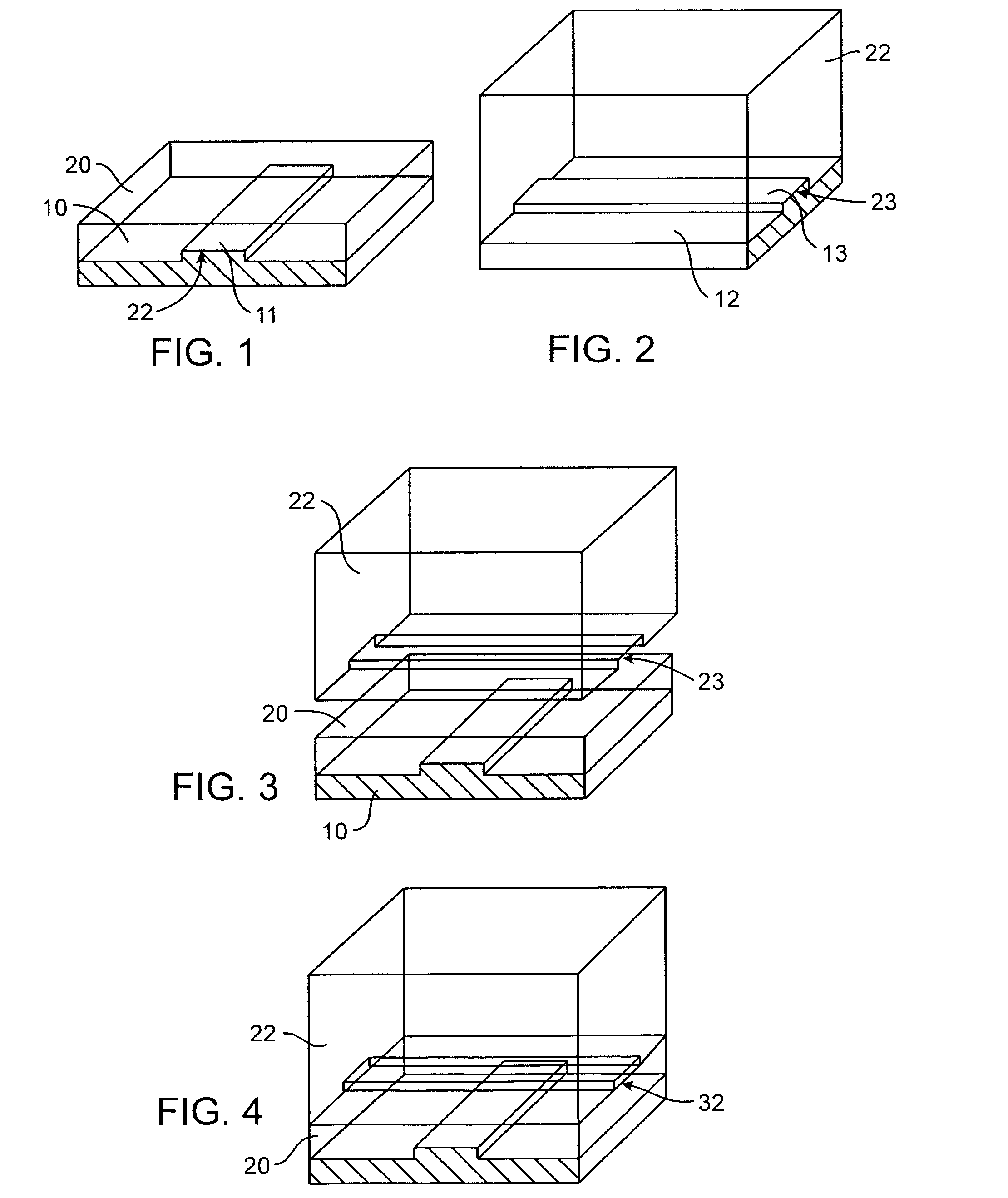
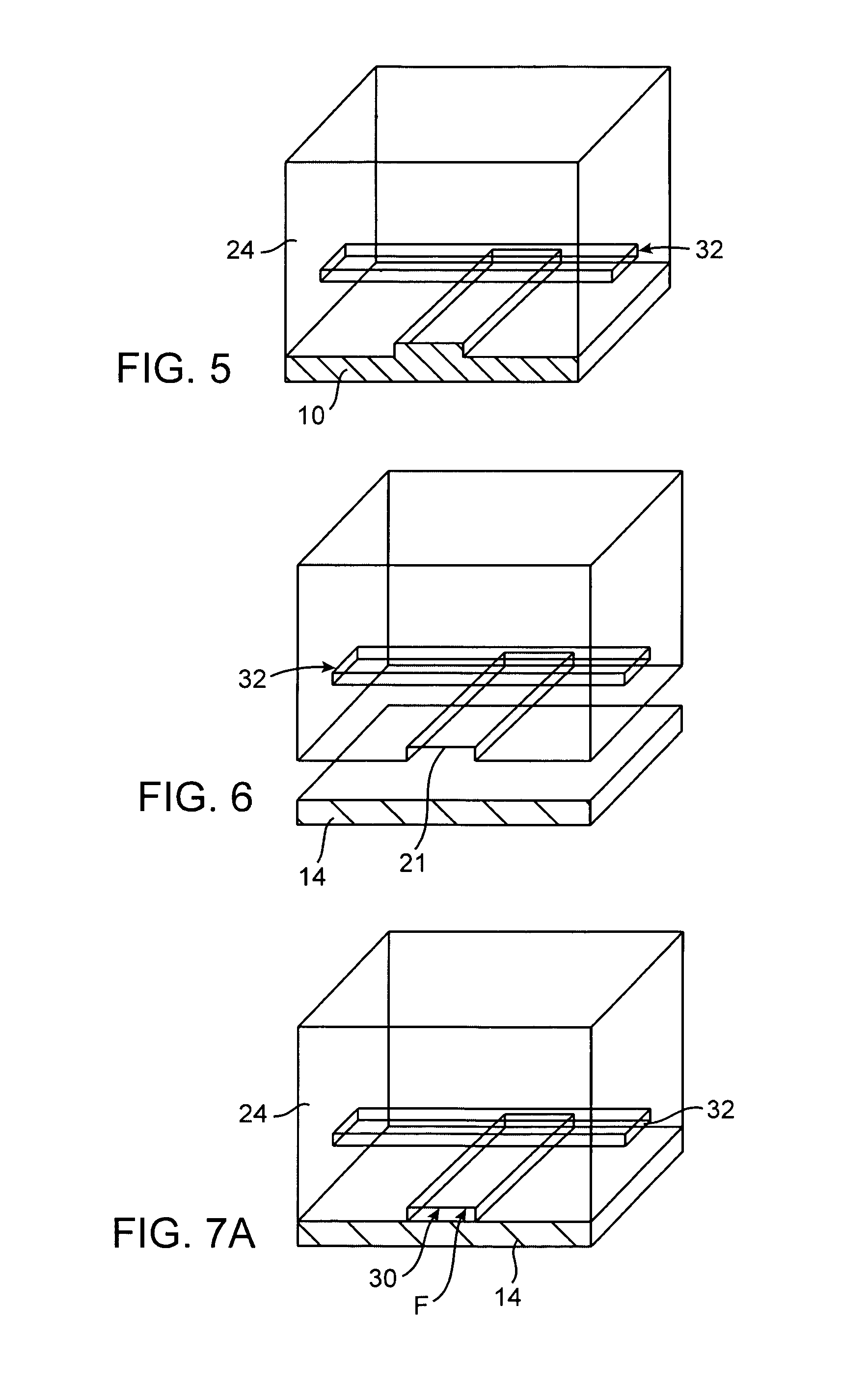
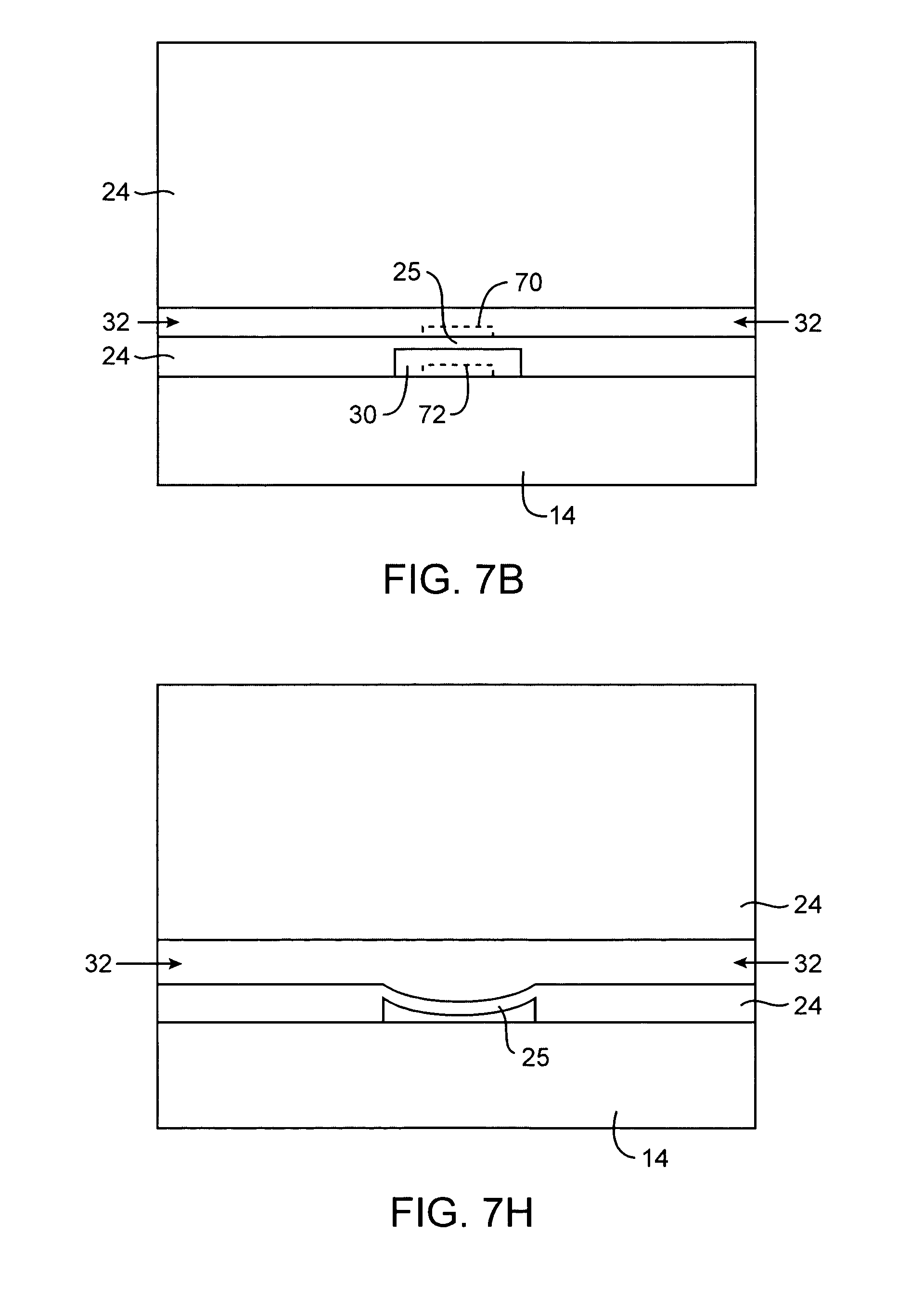
ActiveUS20050053952A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCDNA libraryCells isolation
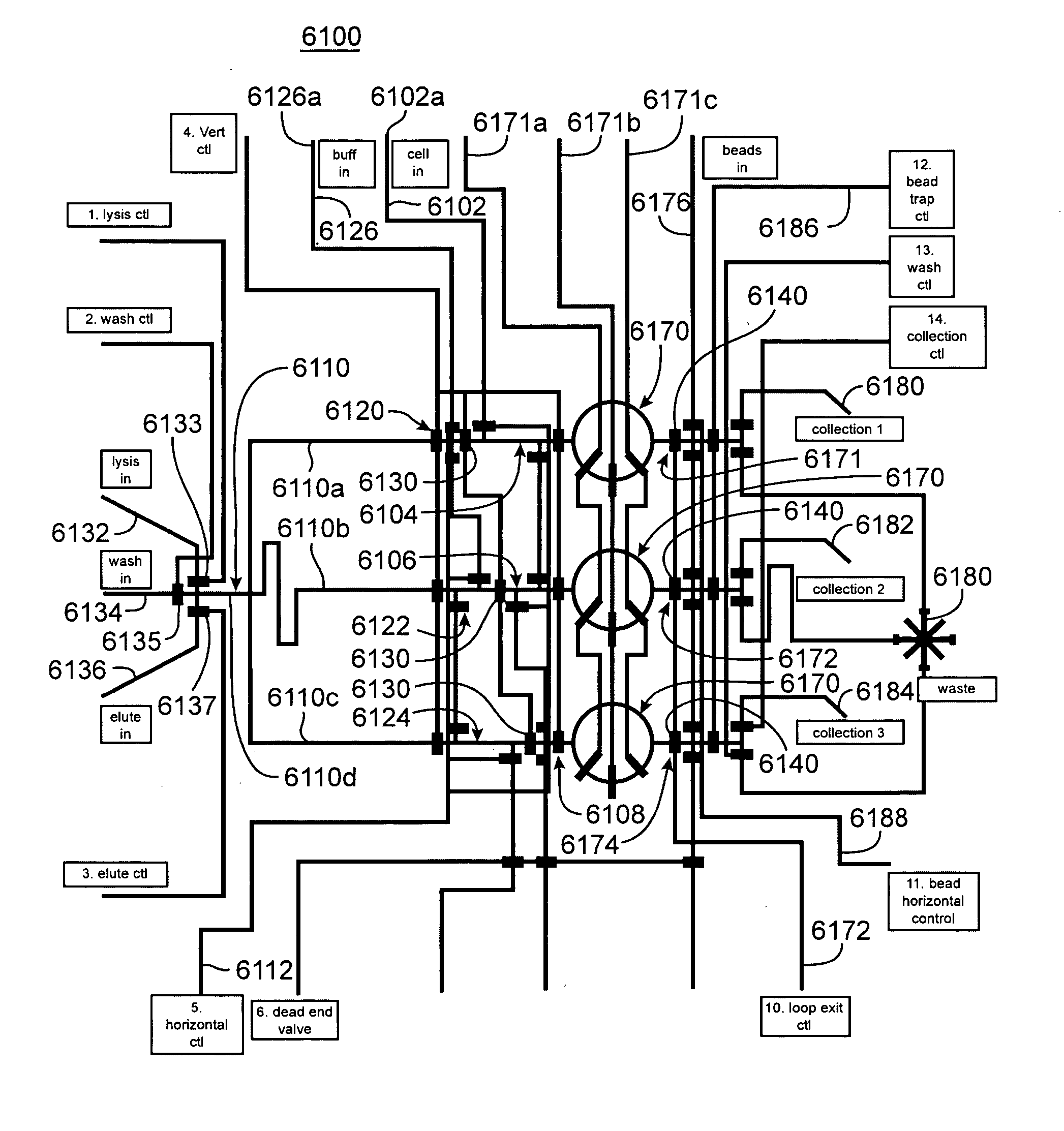
Nucleic acid from cells and viruses sampled from a variety of environments may purified and expressed utilizing microfluidic techniques. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, individual or small groups of cells or viruses may be isolated in microfluidic chambers by dilution, sorting, and / or segmentation. The isolated cells or viruses may be lysed directly in the microfluidic chamber, and the resulting nucleic acid purified by exposure to affinity beads. Subsequent elution of the purified nucleic acid may be followed by ligation and cell transformation, all within the same microfluidic chip. In one specific application, cell isolation, lysis, and nucleic acid purification may be performed utilizing a highly parallelized microfluidic architecture to construct gDNA and cDNA libraries.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Fluid mixing in low aspect ratio chambers
InactiveUS20050019898A1Suitable for useShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersFlow mixersEngineeringLow volume
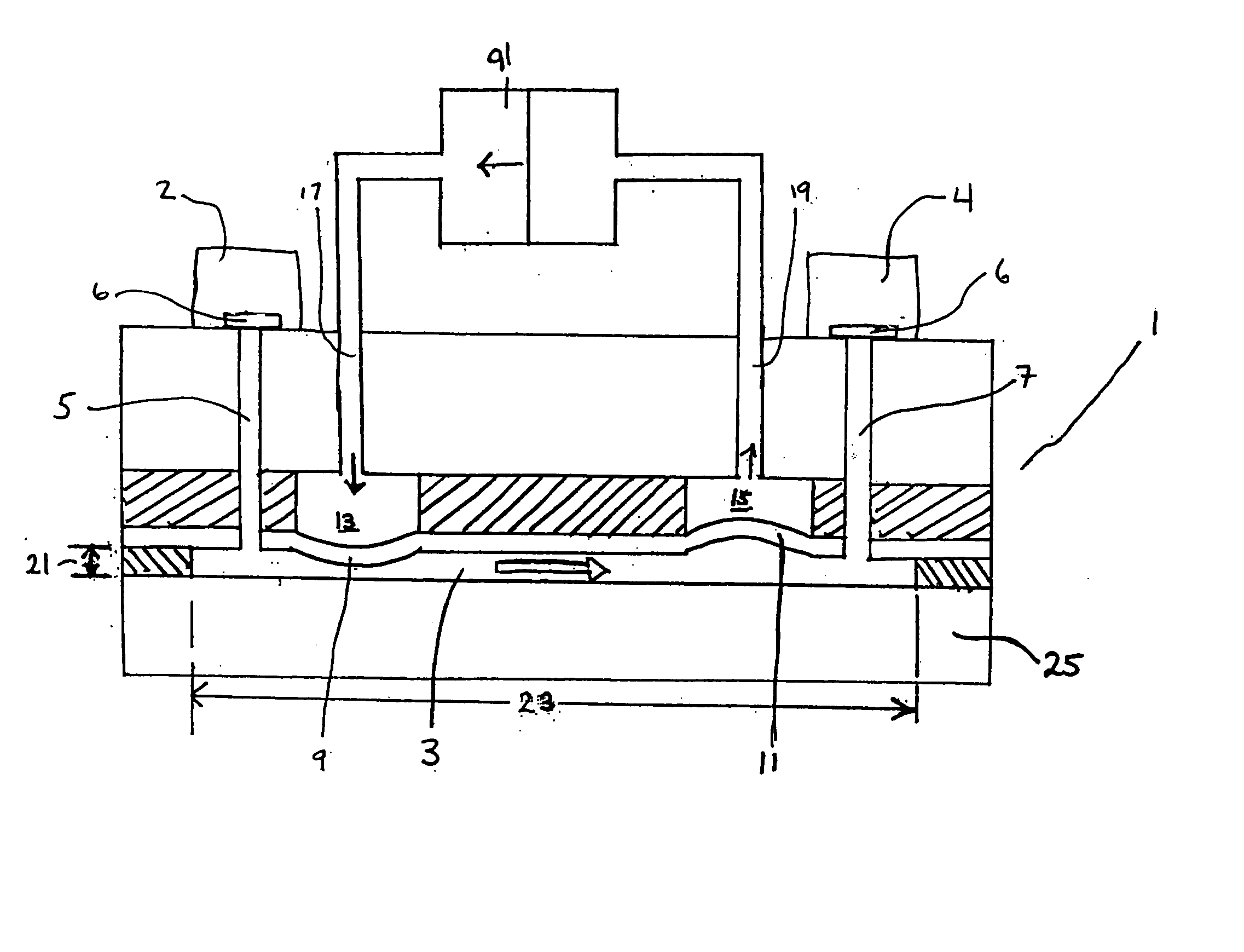
A method and system for performing mixing in a low volume, low aspect ratio microfluidic chamber (3) is described. Two or more mixing bladders (13,15) formed adjacent the microfluidic chamber are inflated and deflated in reciprocating fashion to cause inward and outward deflection of discrete regions of the chamber wall to mix fluid within the chamber. Mixing bladders are actuated by air or another gas, or by a liquid such as water, pumped in and out of the bladders with a pump which may be located remote from the microfluidic device including the microfluidic chamber. In an alternative embodiment, mixing is generated by applying alternating mechanical forces to a surface of a flexible chamber forming device. The microfluidic chamber may be a hybridization chamber formed on a microarray (25) slide with the use of a microarray interface device, or it may be a microfluidic chamber formed in various other types of microfluidic devices.
Owner:ADEY NILS +6
Methods and apparatus for introducing liquids into microfluidic chambers
InactiveUS20050022895A1High energyPotential energyLiquid degasificationCircuit elementsHigh energyEngineering
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
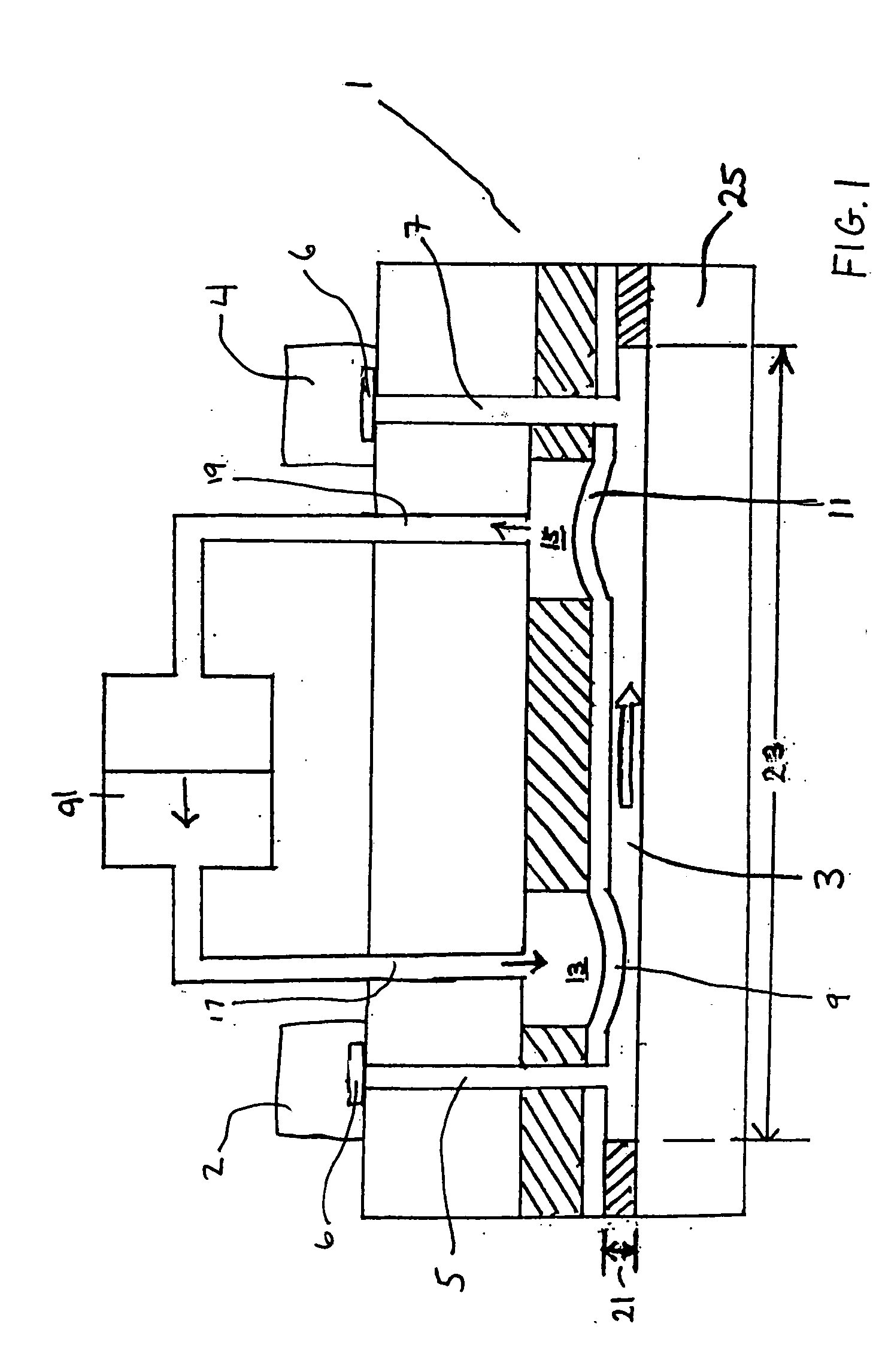
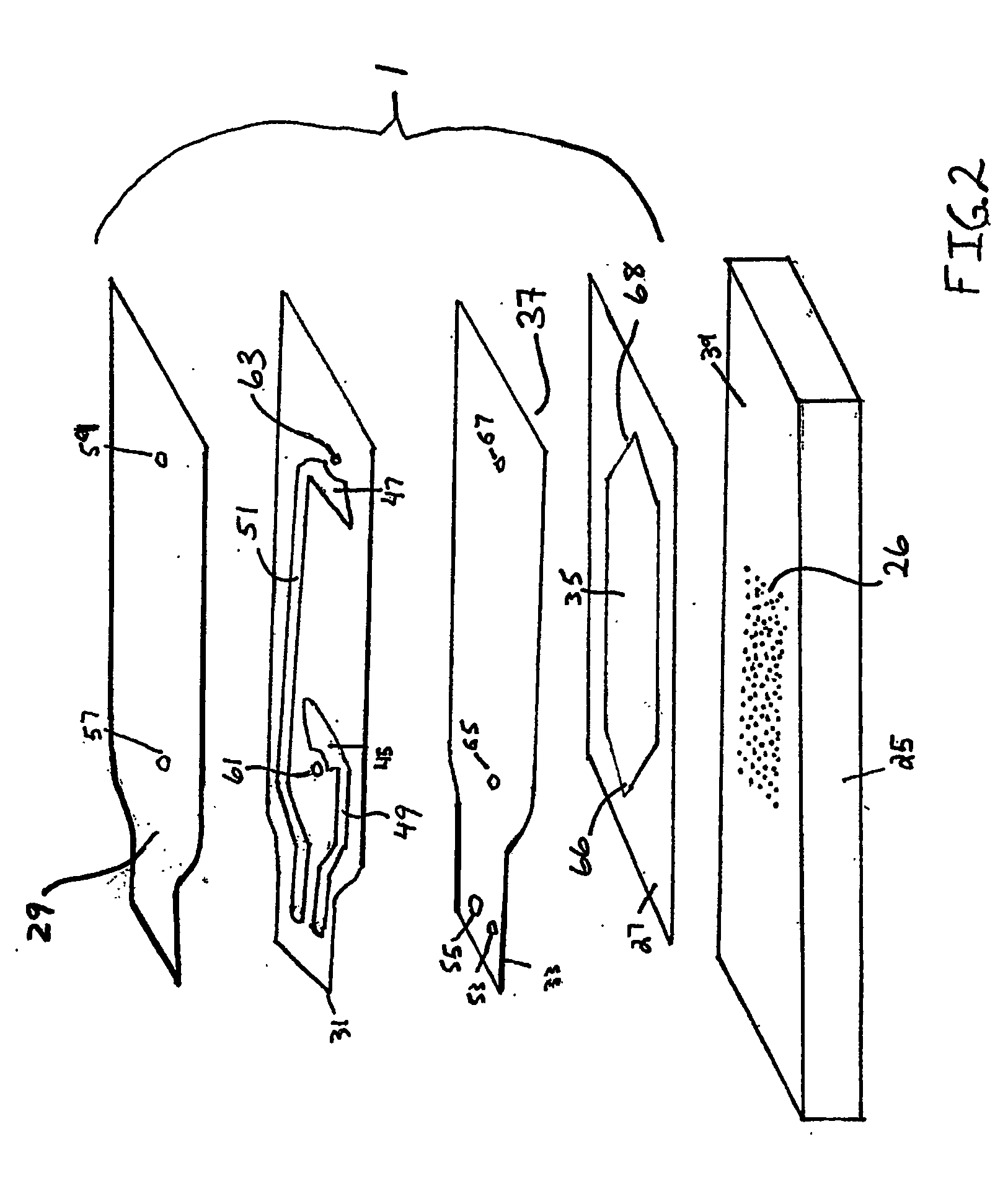
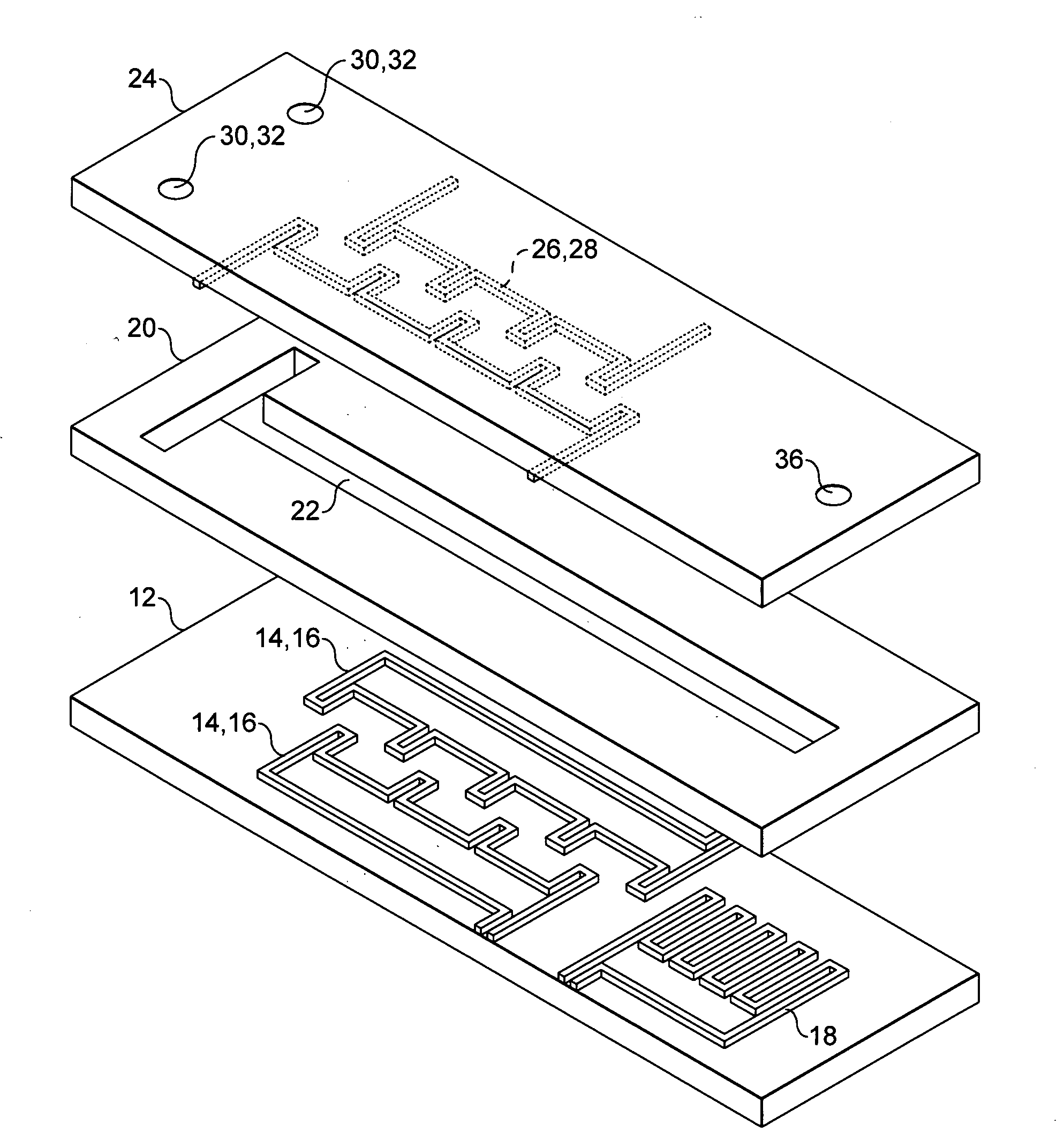
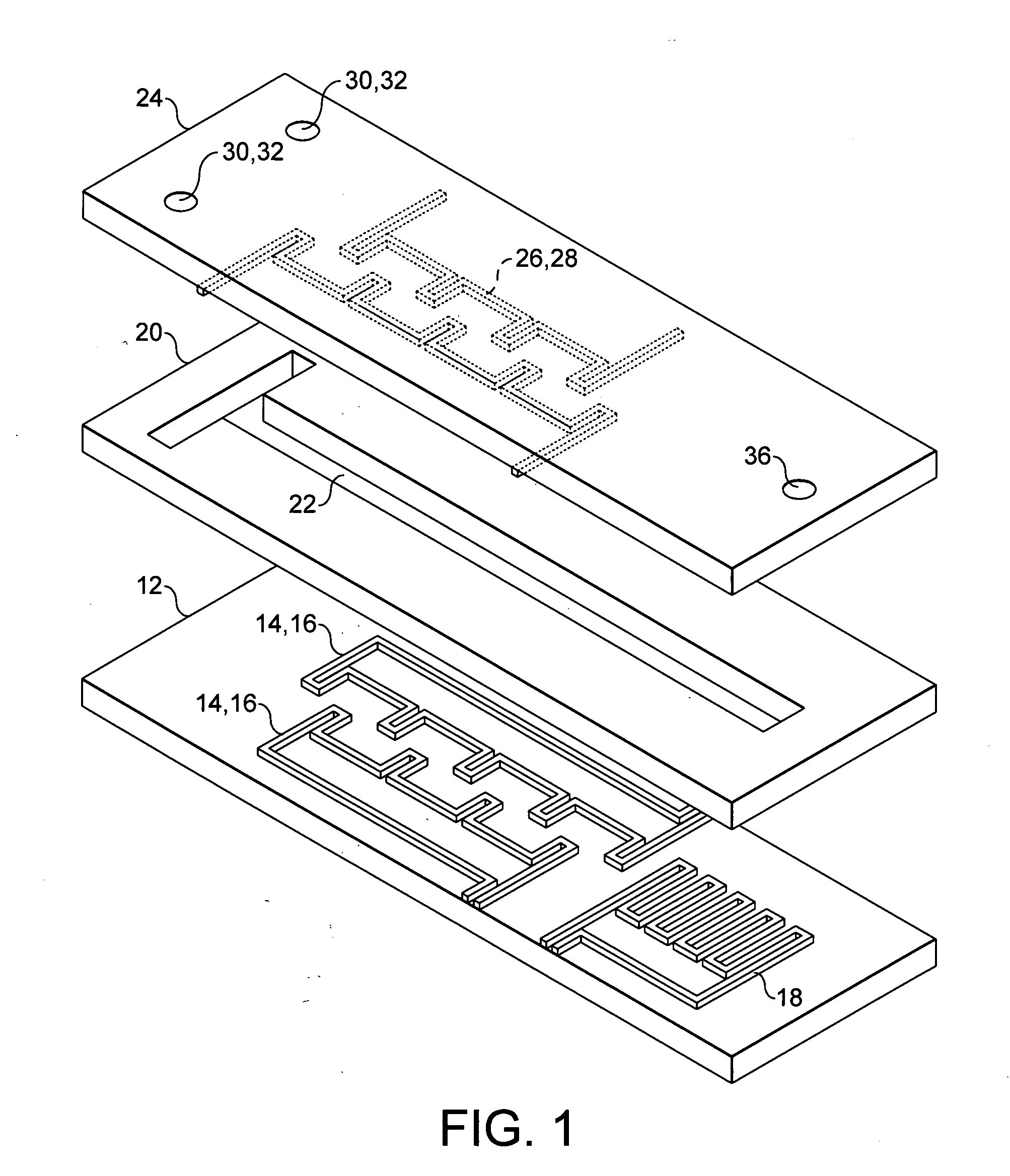
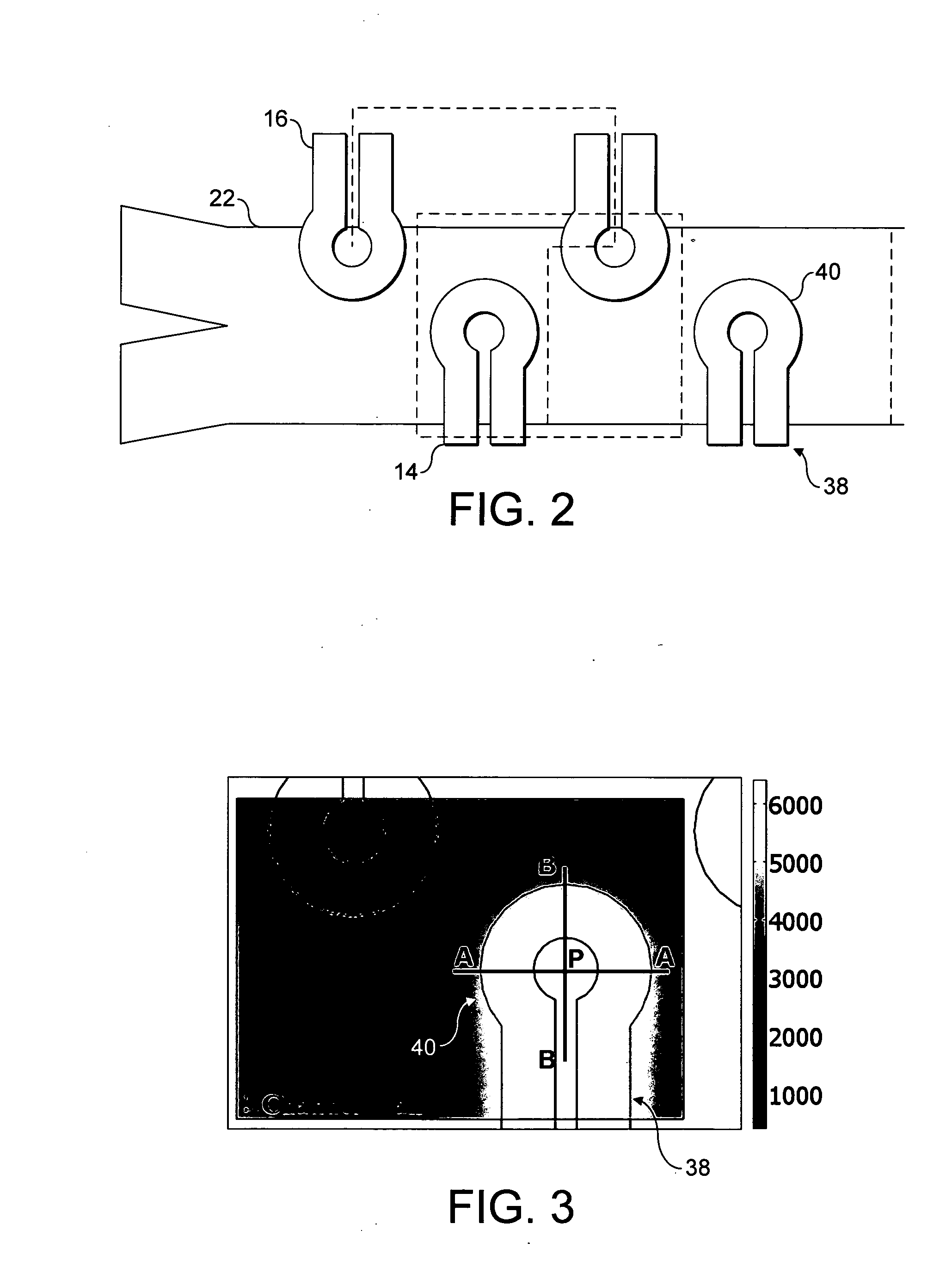
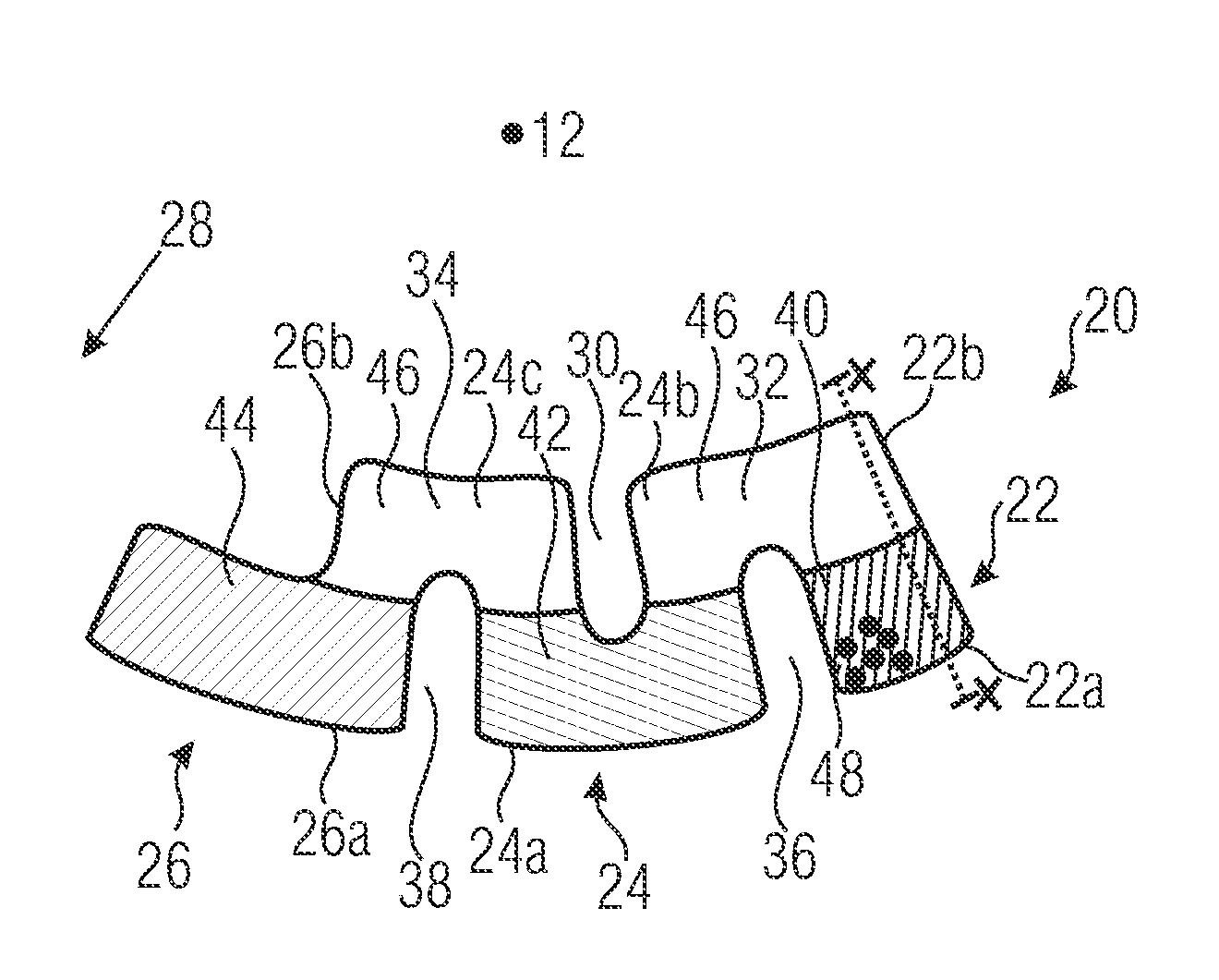
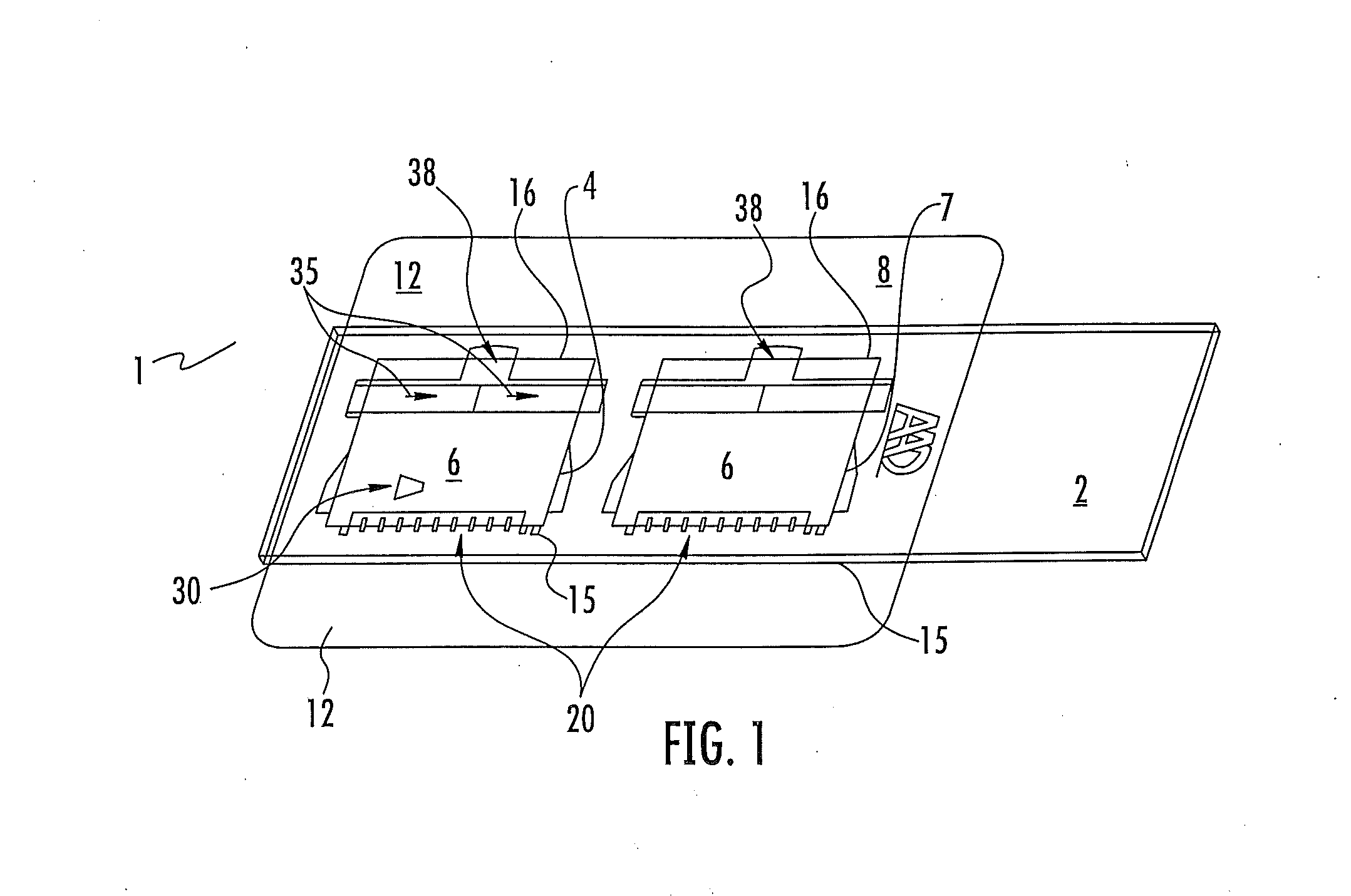
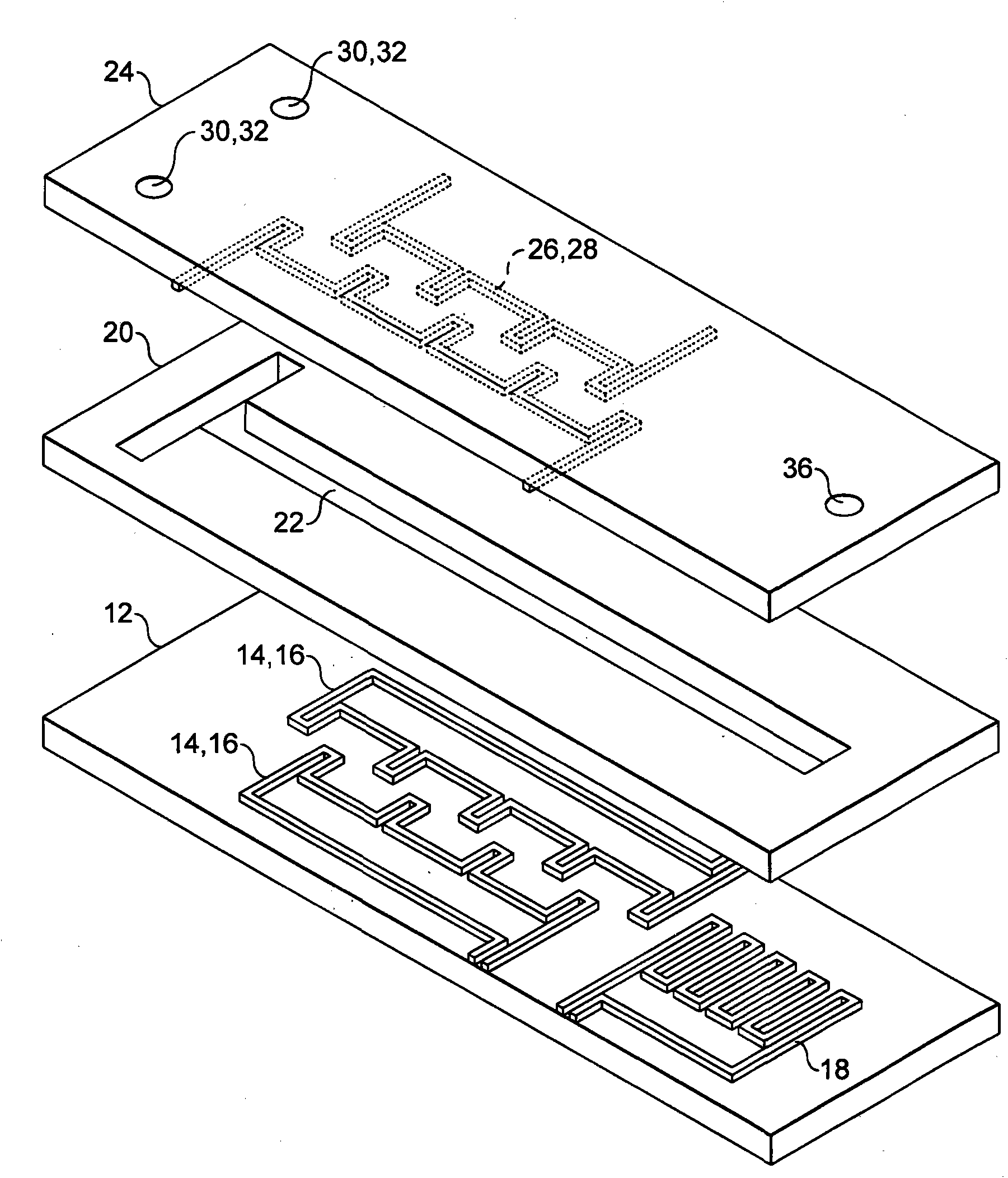
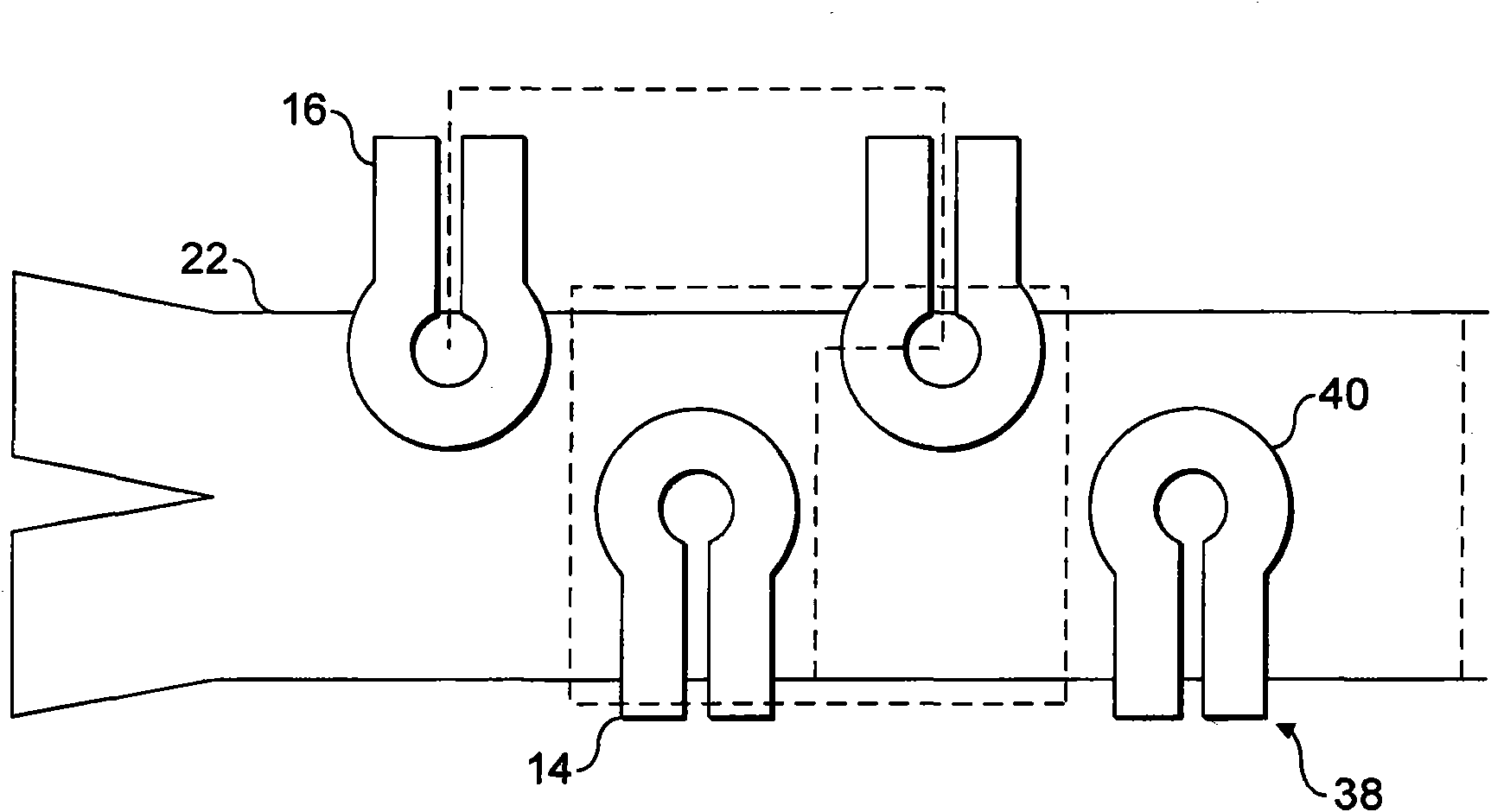
Microfluidic chamber assembly for mastitis assay
InactiveUS20090233329A1Easy to doSmall volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMammalWhite blood cell
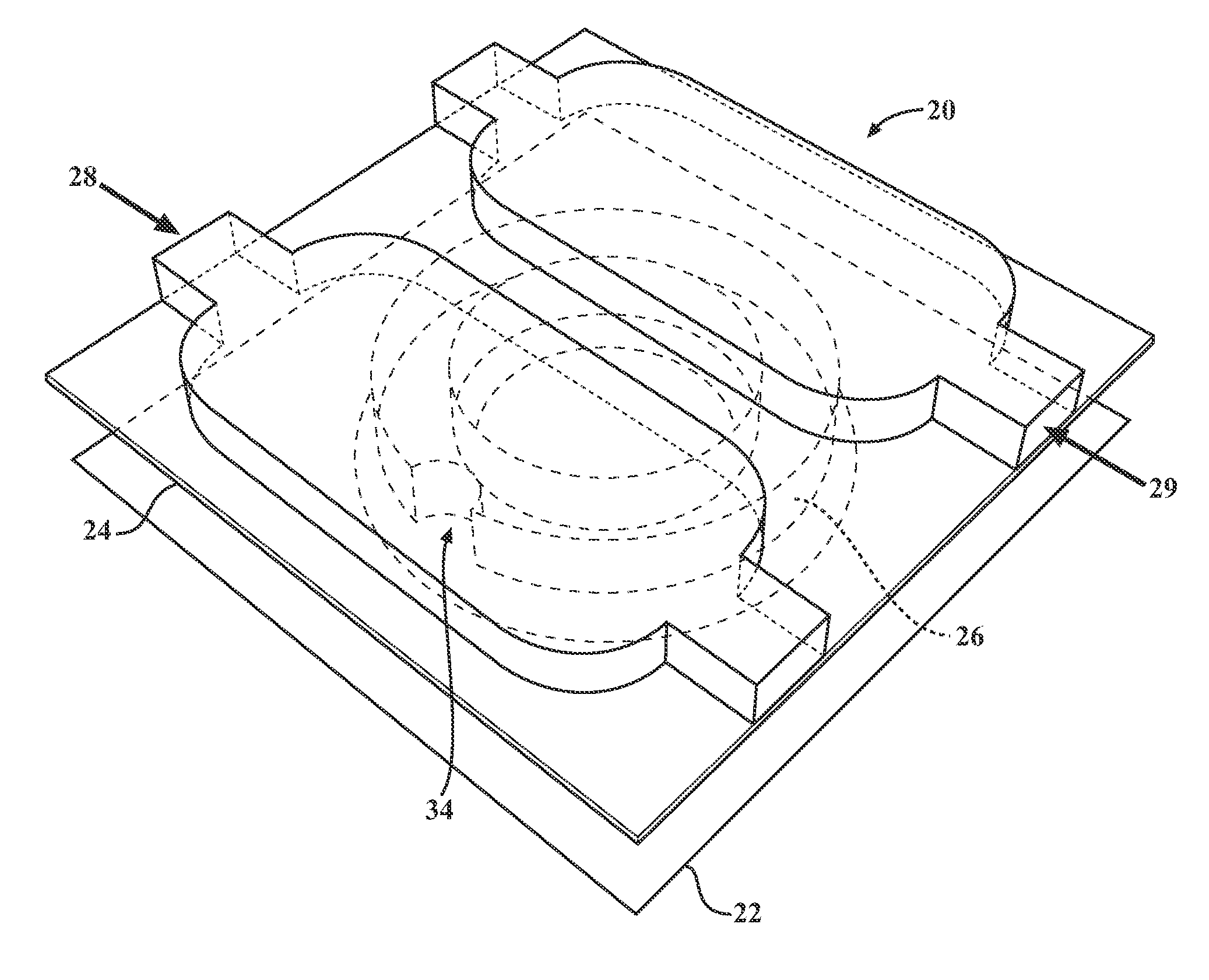
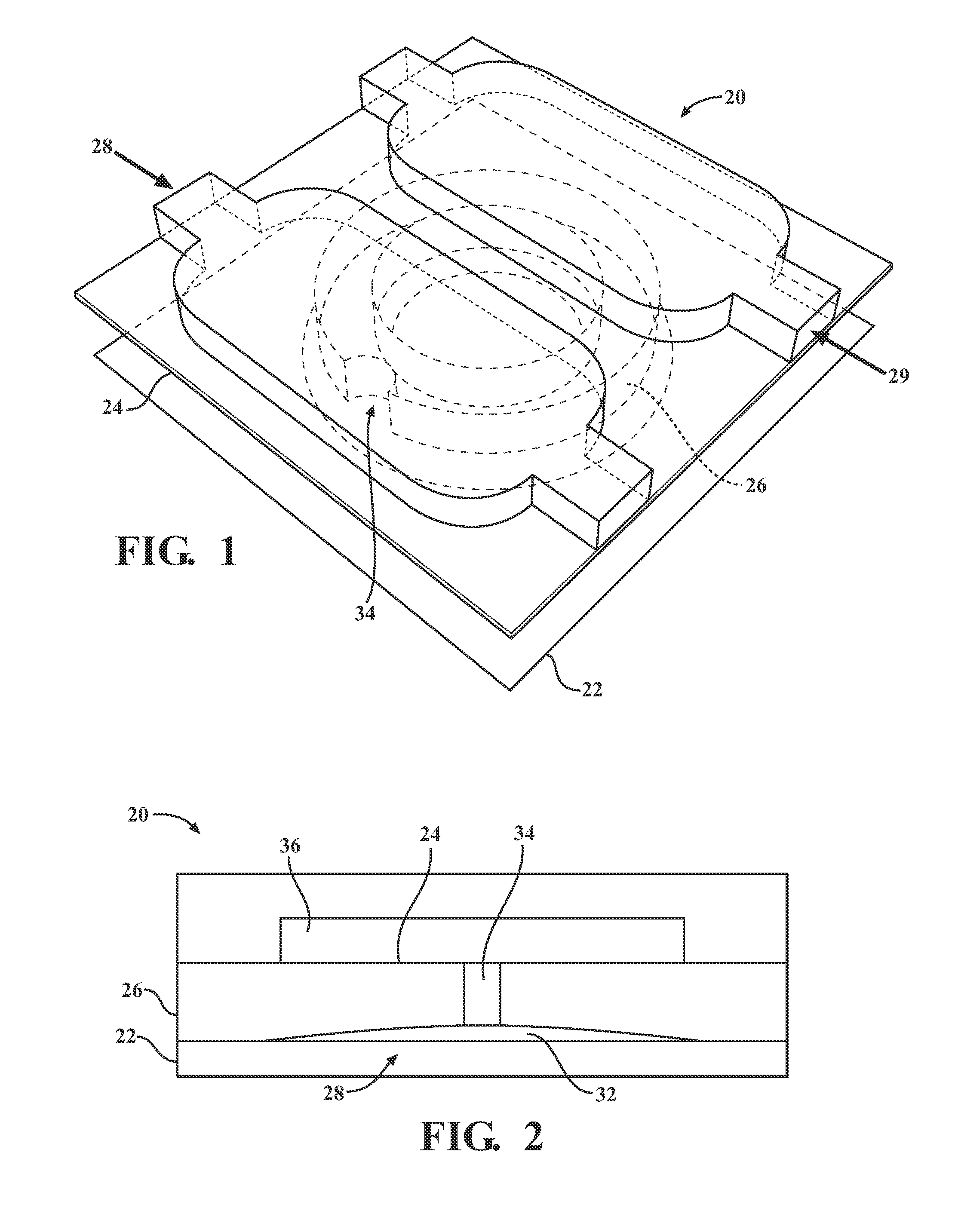
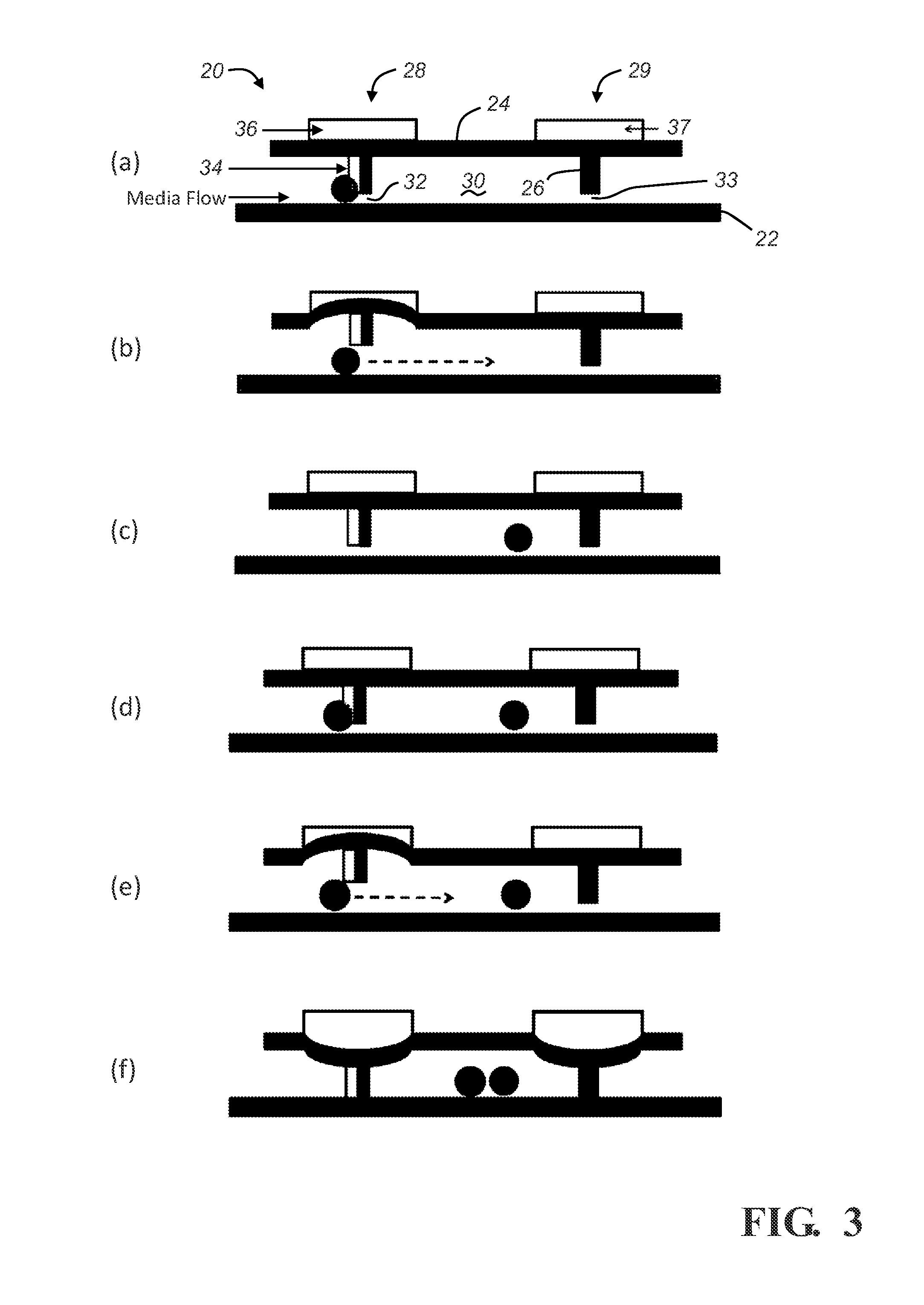
The present invention relates to a device and method for the detection of mastitis or other disease from a body fluid of a mammal for example from cow's milk. The device and method relates to a wedge microfluidic chamber for using a minimal amount of fluid and being able to use the device to observe leukocytes in a mono-layer for the purpose of disease detection, cell counts or the like.
Owner:ADVANCED ANIMAL DIAGNOSTICS
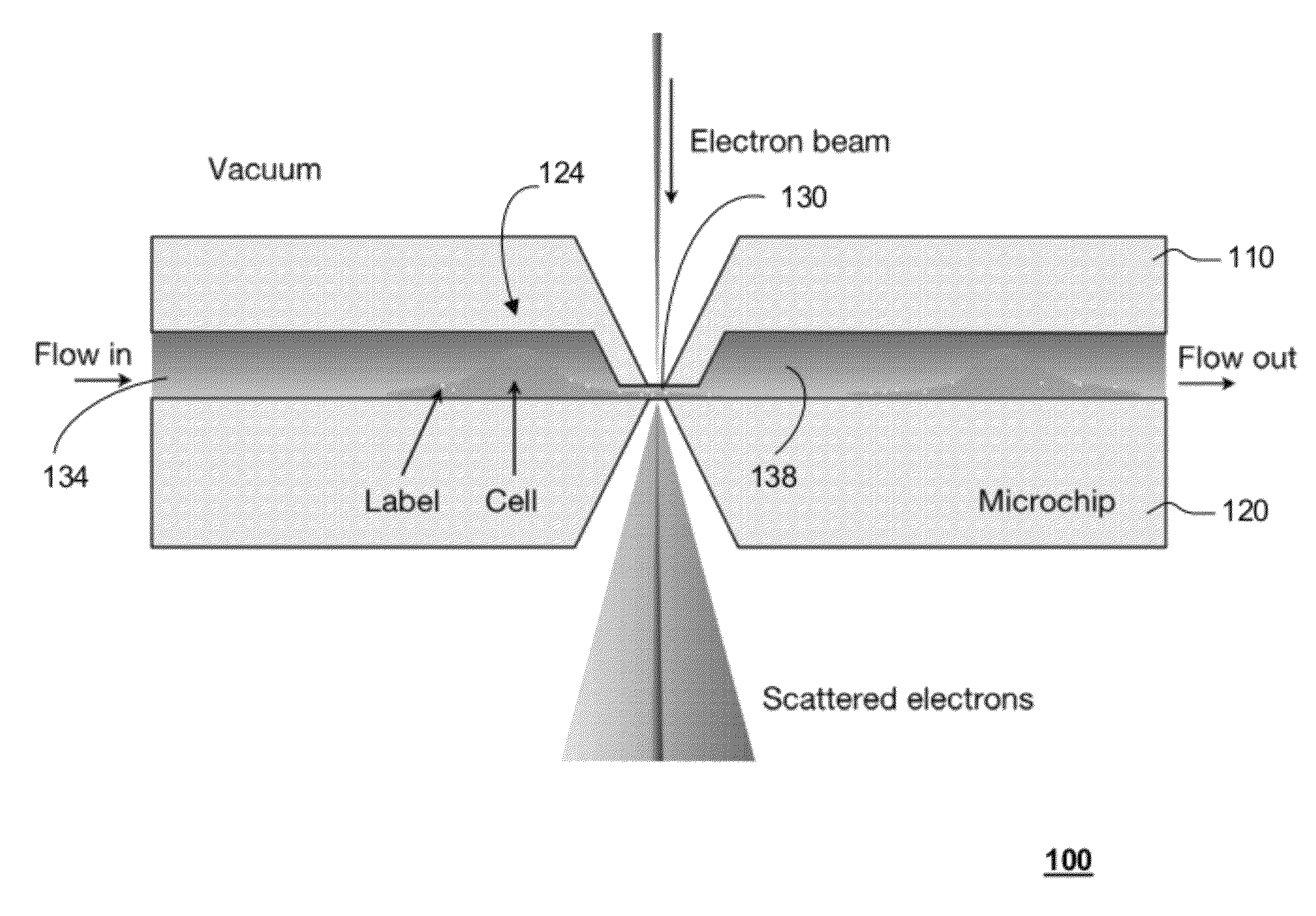
Transmission electron microscopy for imaging live cells
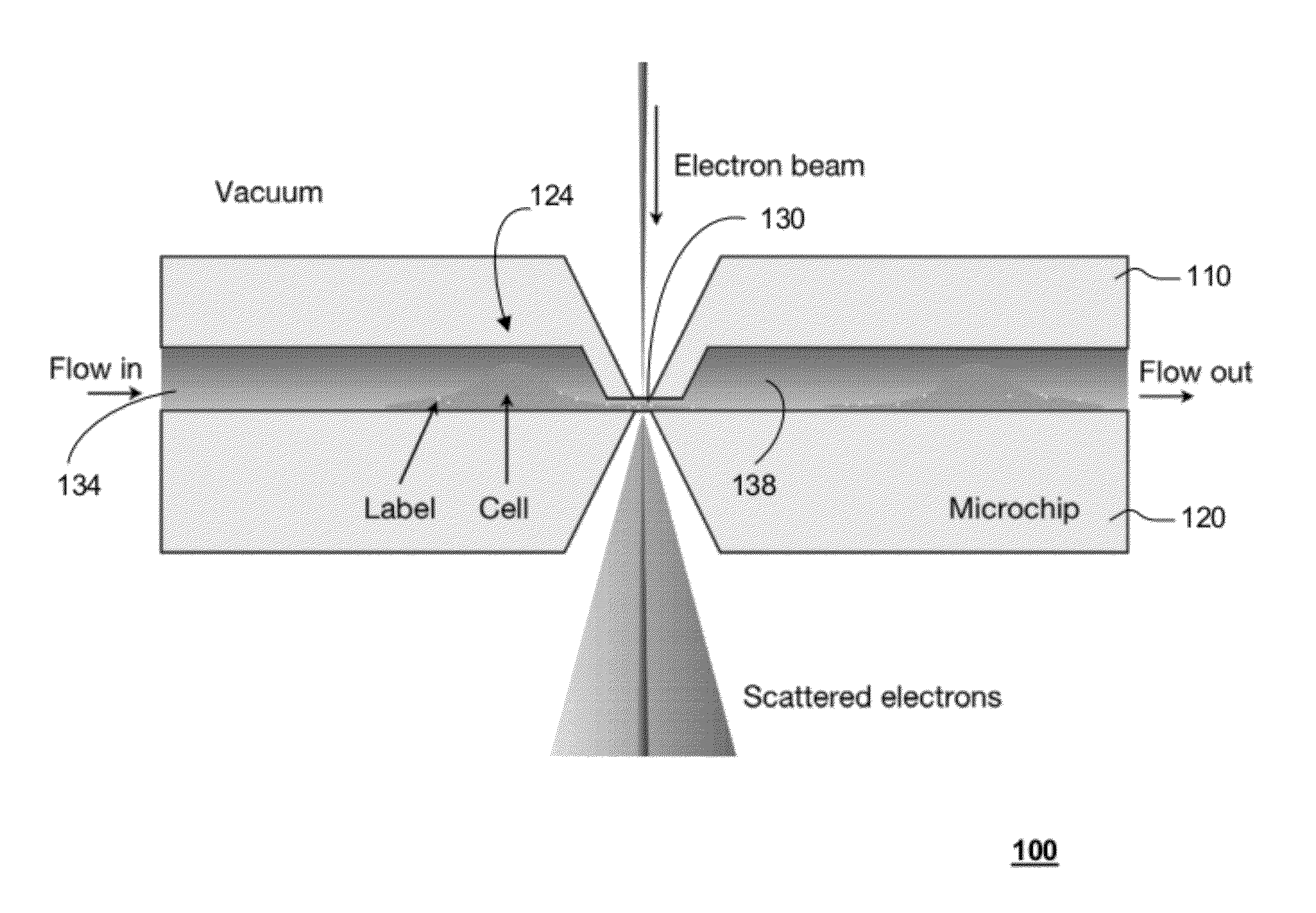
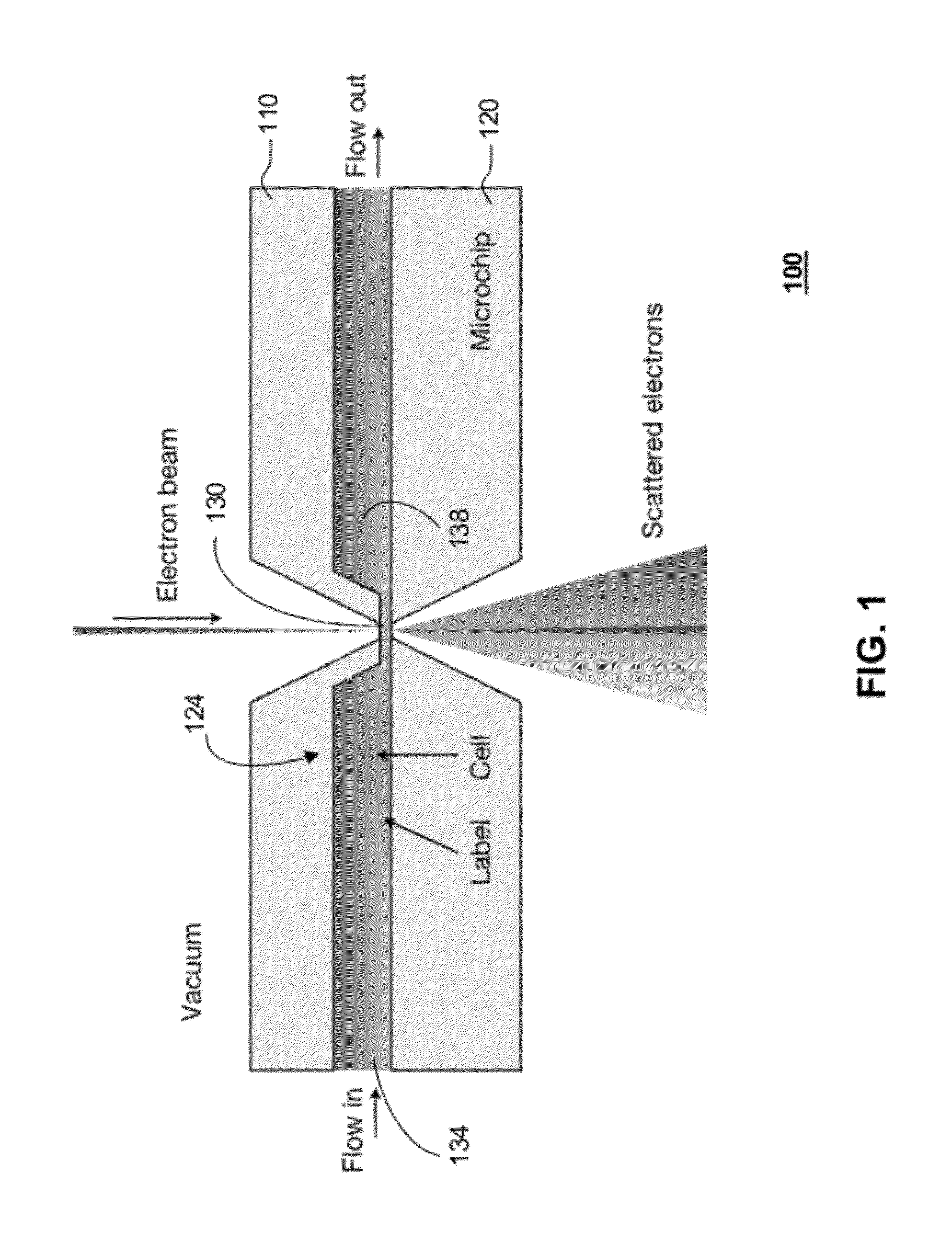
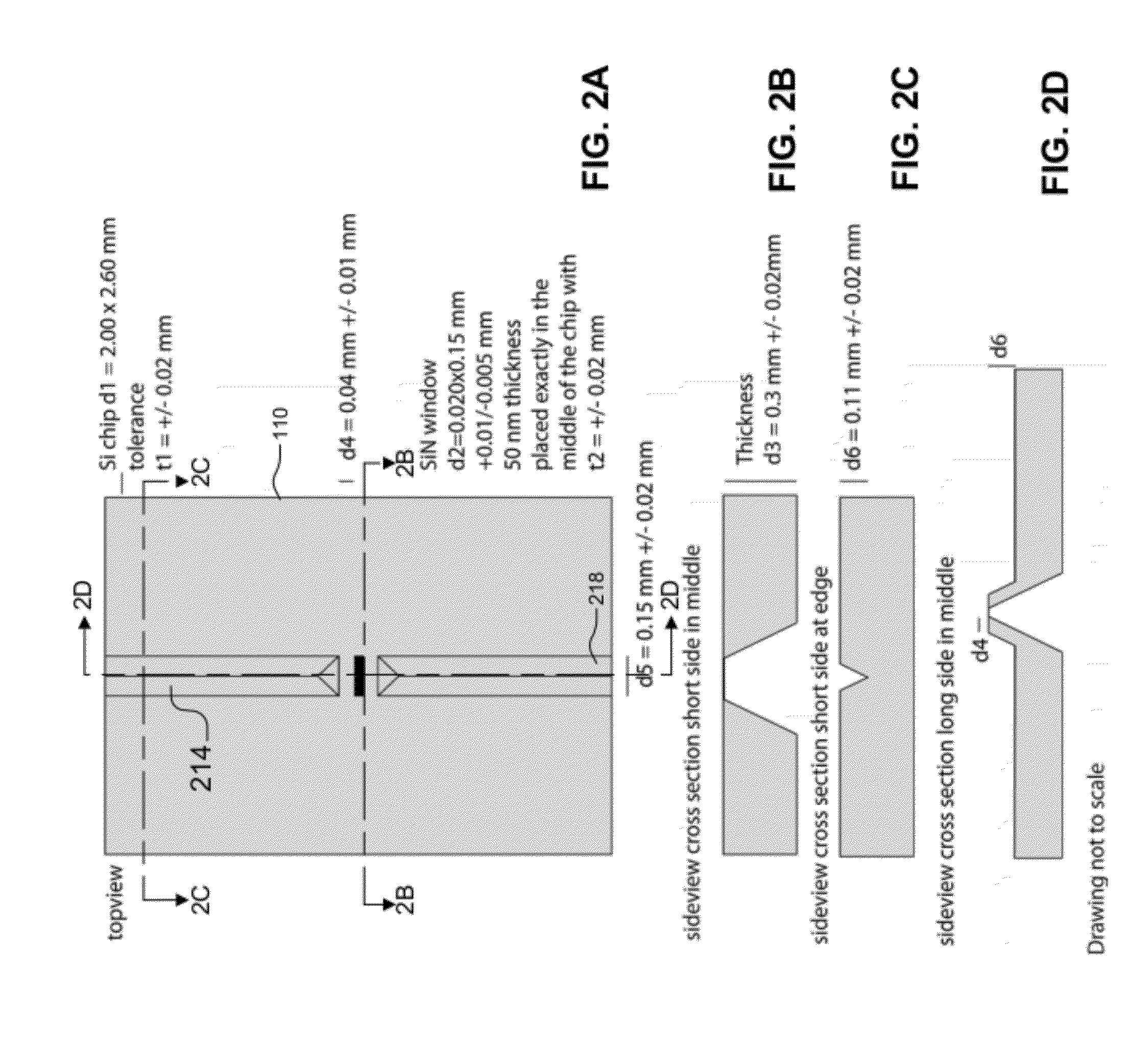
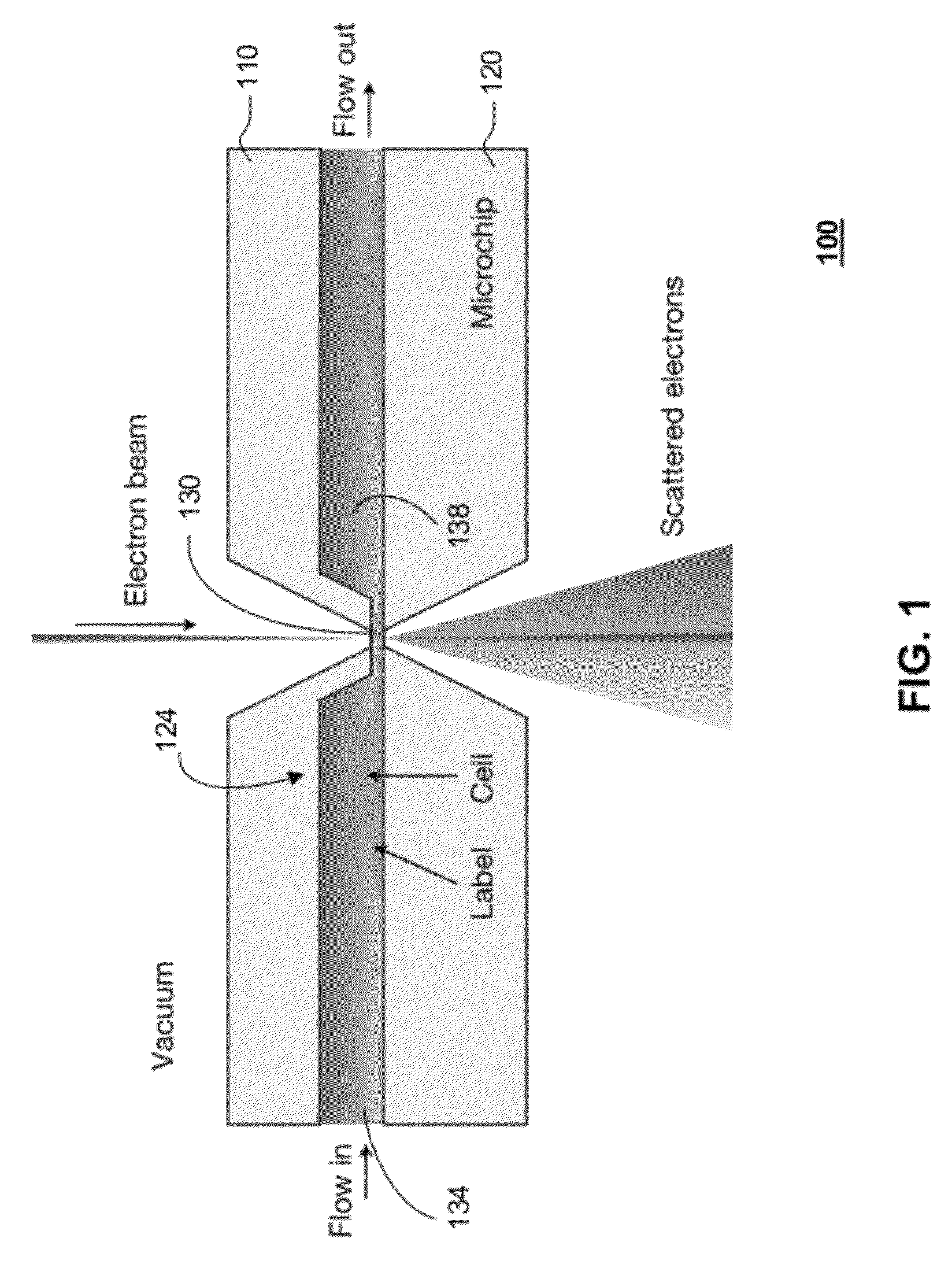
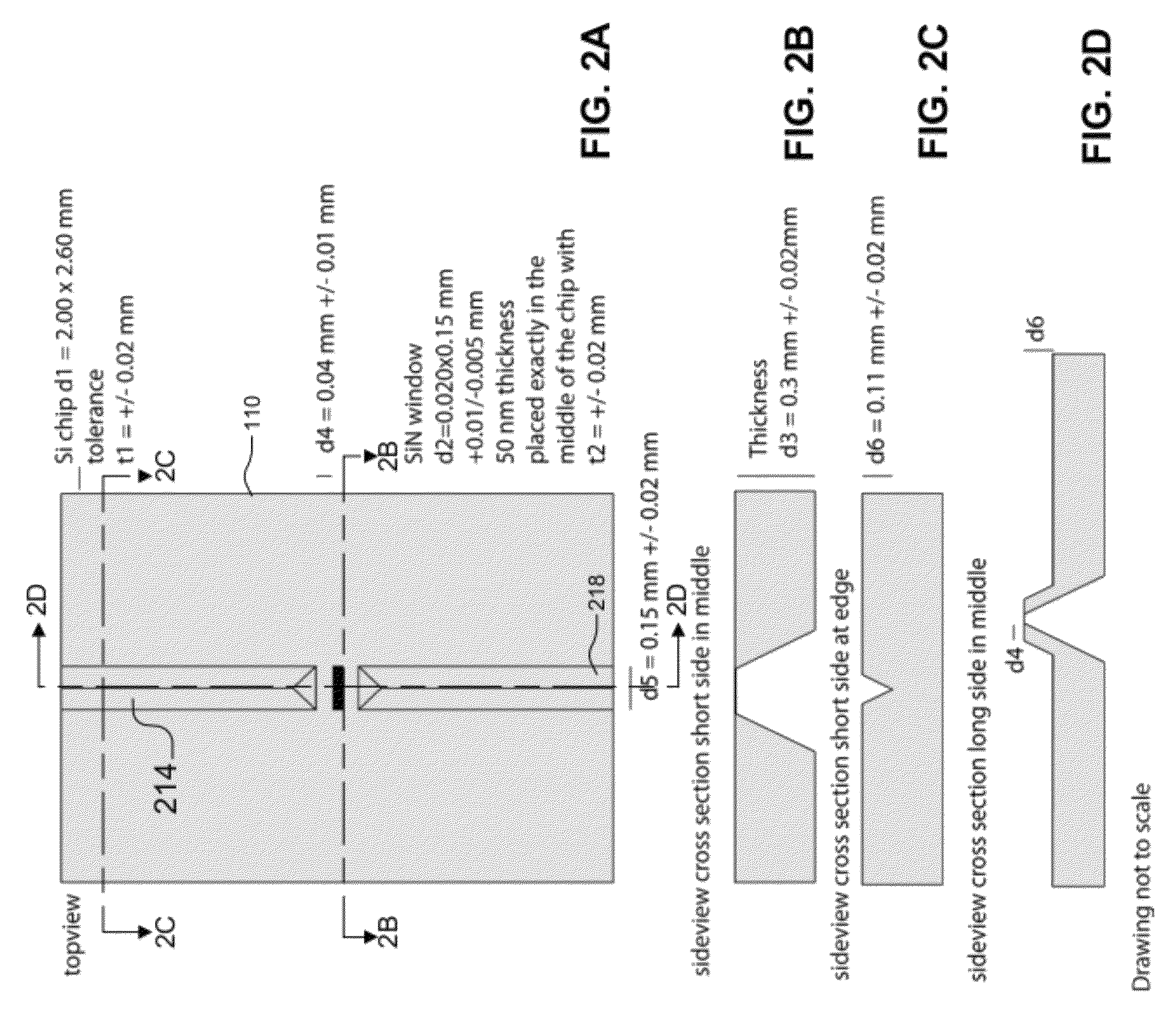
ActiveUS20120120226A1Not to damageReduce intensityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesMedicineLive cell imaging
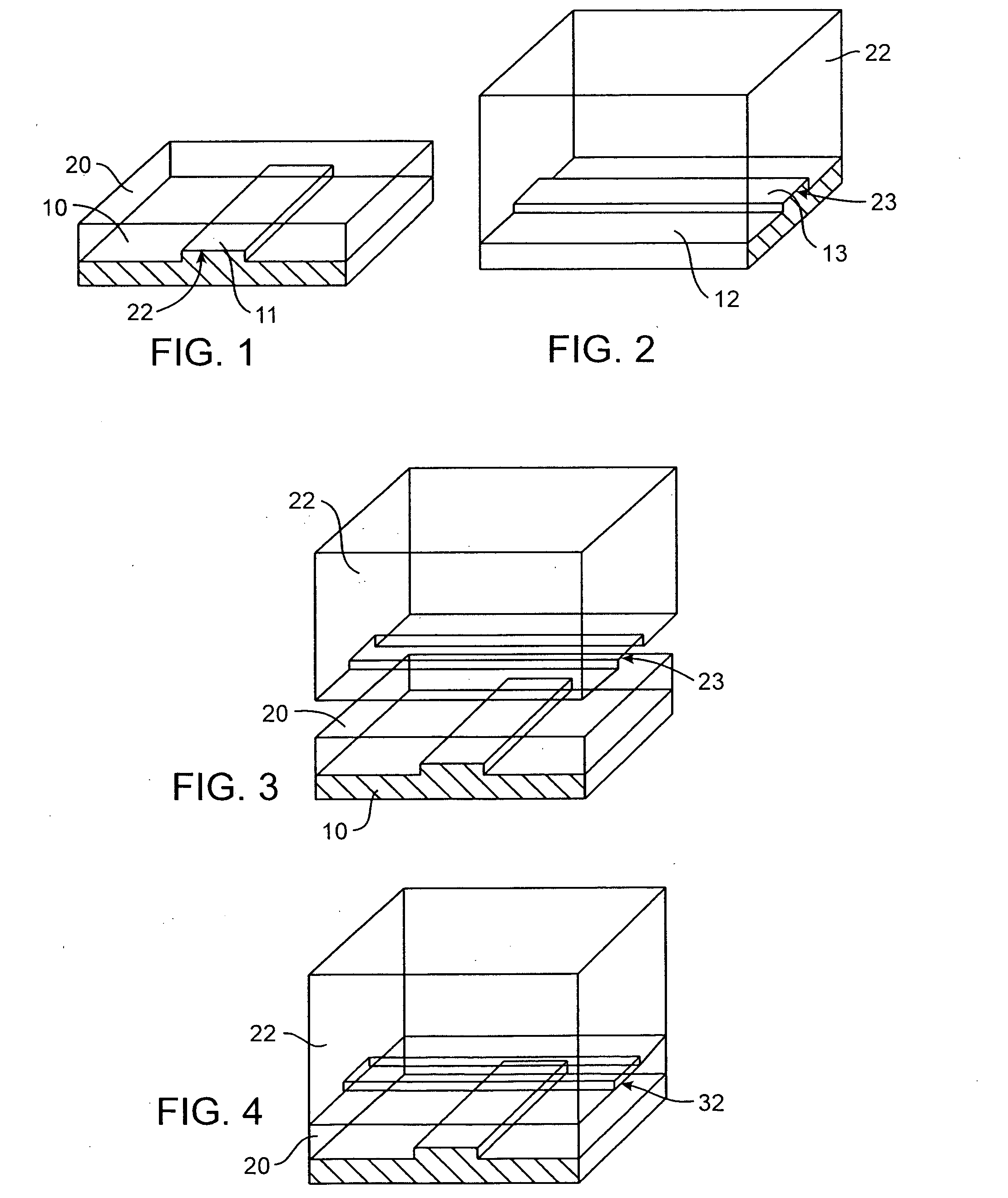
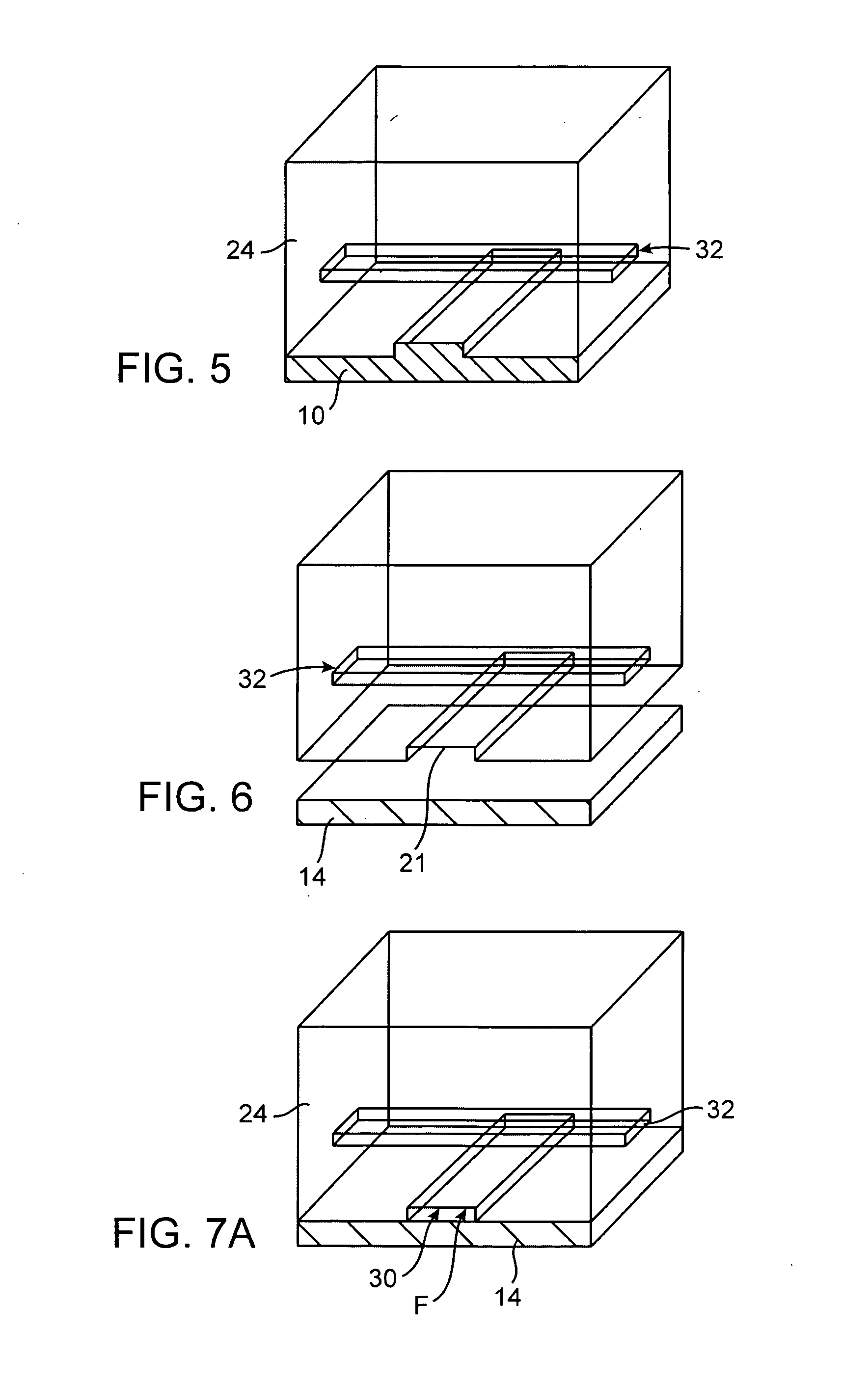
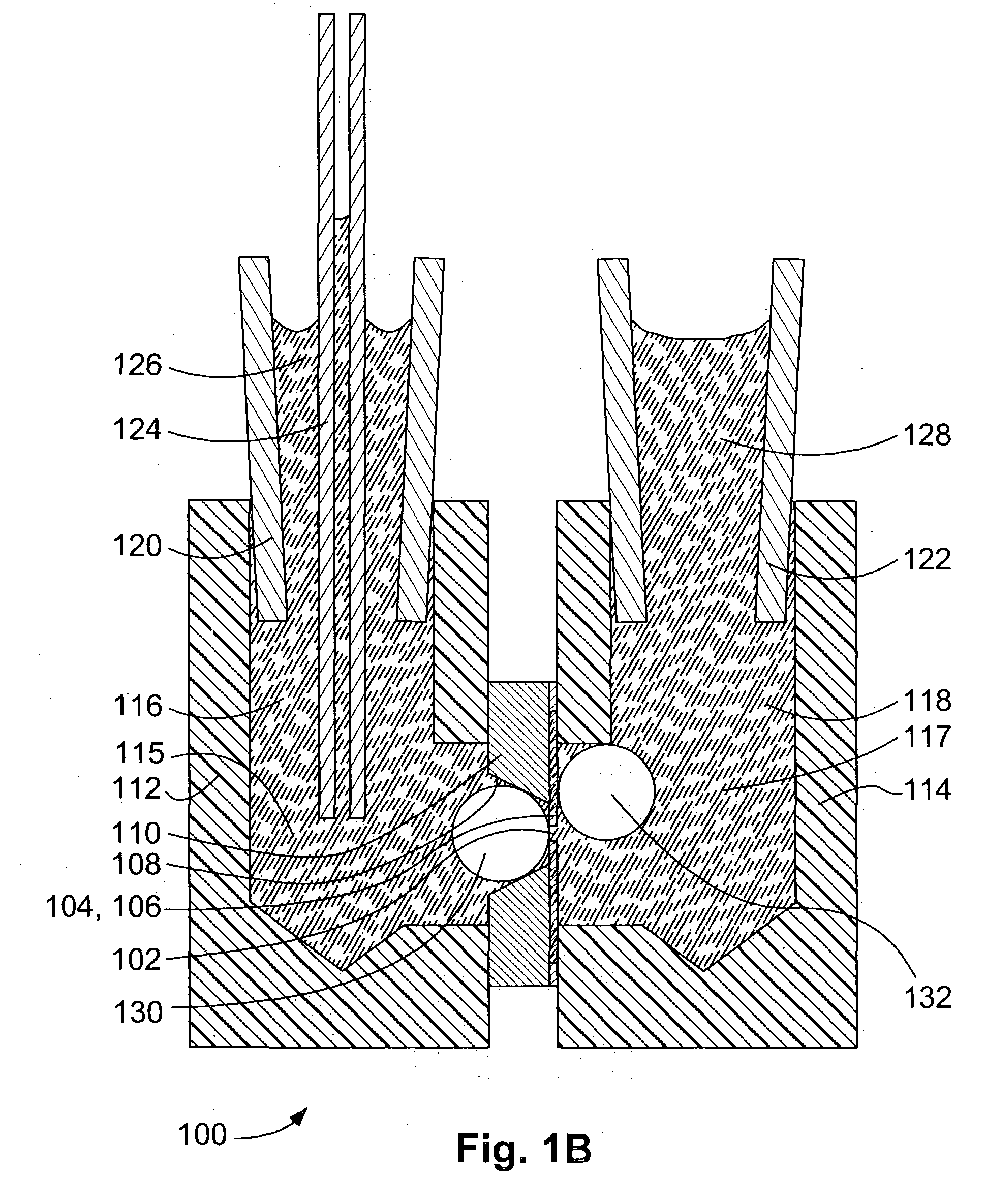
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a microfluidic chamber. In one embodiment, the microfluidic chamber has a first sub-chamber and at least one second sub-chamber. The first sub-chamber has a first window and a second window. Both the first window and the second window are transparent to electrons of certain energies. The second window is positioned substantially parallel and opposite to the first window defining a first volume therebetween. The first window and the second window are separated by a distance that is sufficiently small such that an electron beam that enters from the first window can propagate through the first sub-chamber and exit from the second window. The at least one second sub-chamber is in fluid communication with the first sub-chamber and has a second volume that is greater than the first volume of the first sub-chamber.
Owner:DE JONGE VILIJA +2
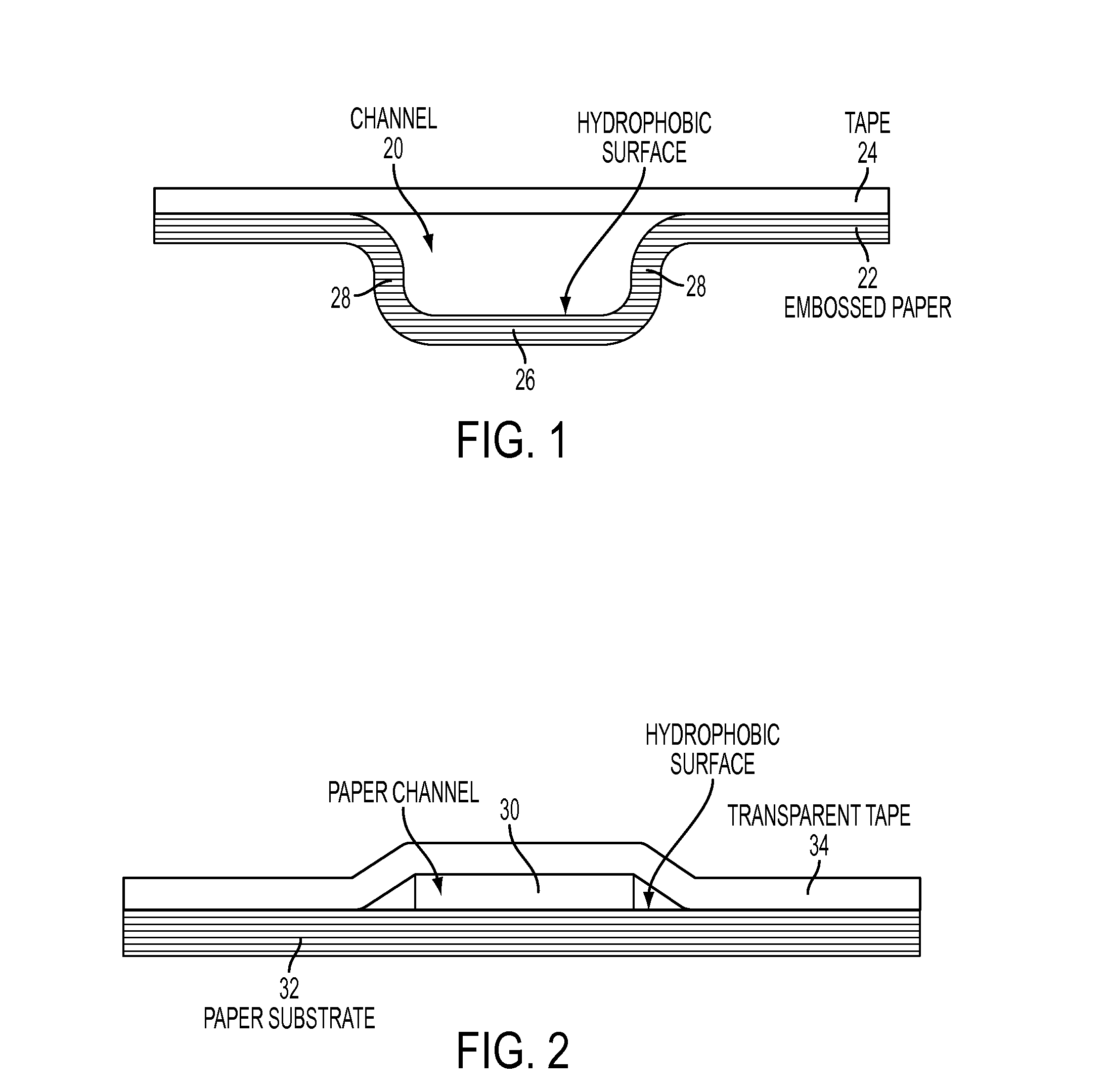
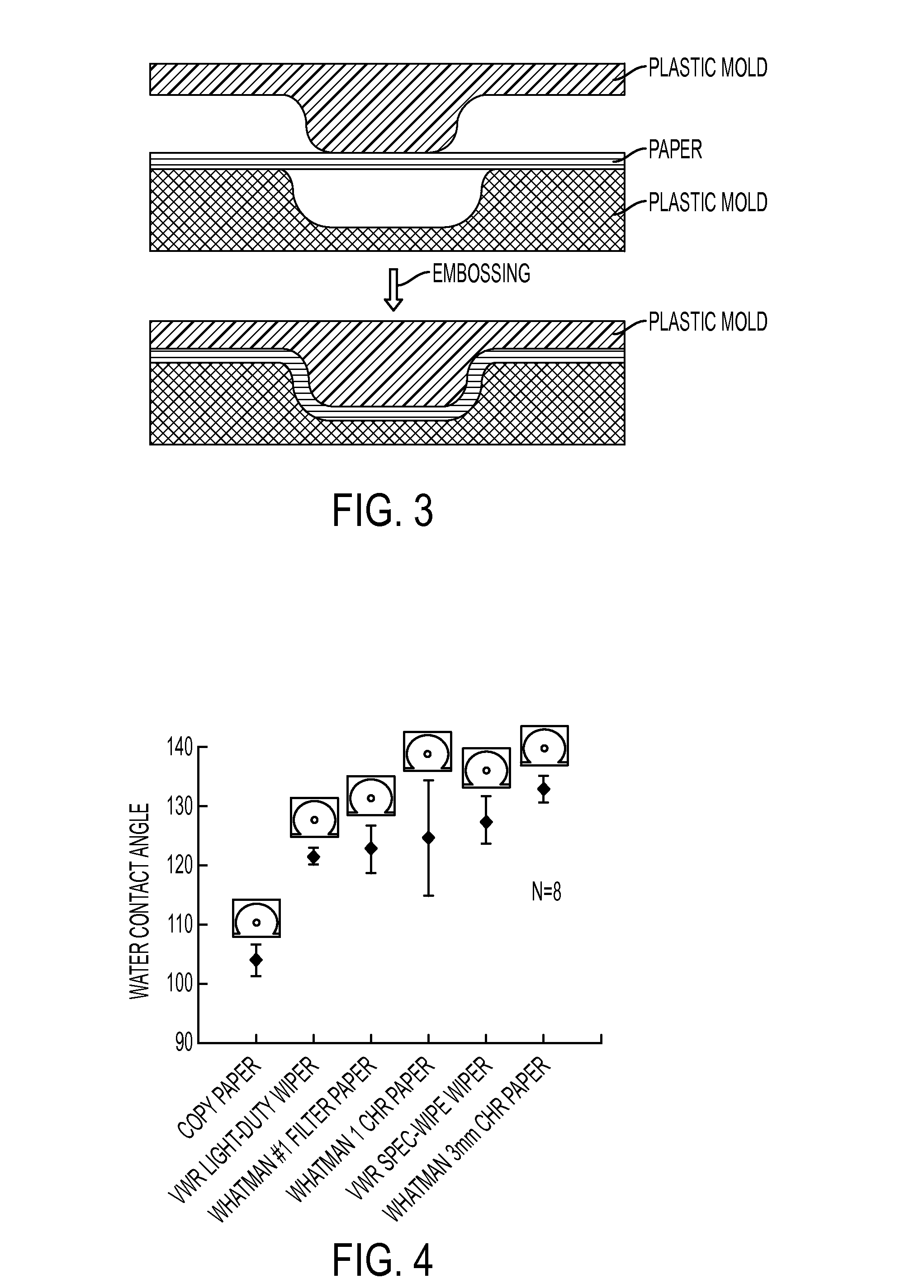
Microfluidic Devices Formed From Hydrophobic Paper
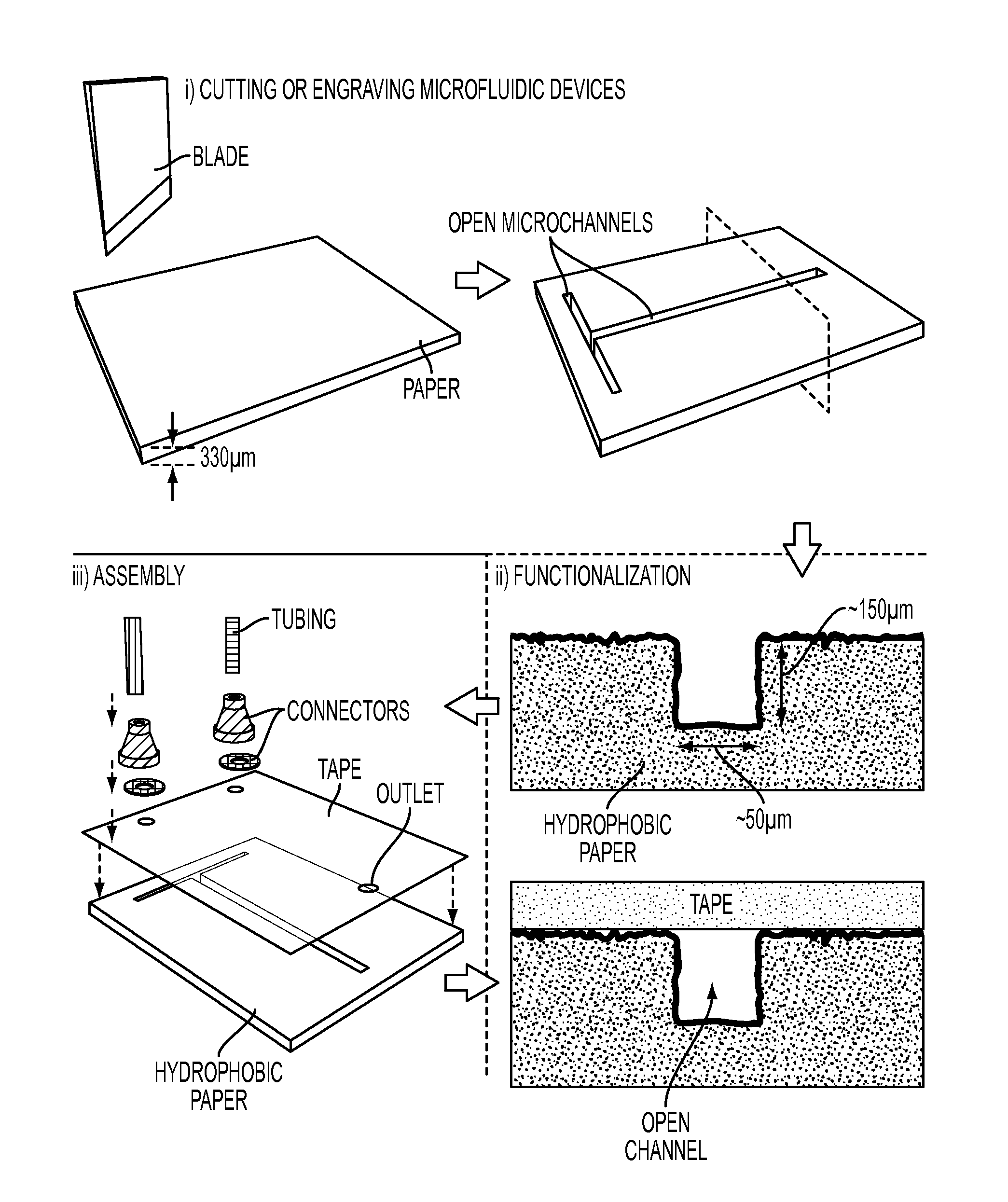
InactiveUS20150132742A1Improve hydrophobicityEasy and inexpensive to fabricateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDevice formEngineering
Microfluidic devices fabricated from paper that has been covalently modified to increase its hydrophobicity, as well as methods of making and using thereof are provided herein. The devices are typically small, portable, flexible, and both easy and inexpensive to fabricate. Microfluidic devices contain a network of microfluidic components, including microfluidic channels, microfluidic chambers, microwells, or combinations thereof, designed to carry, store, mix, react, and / or analyze liquid samples. The microfluidic channels may be open channels, closed channels, or combinations thereof. The microfluidic devices may be used to detect and / or quantify an analyte, such as a small molecules, proteins, lipids polysaccharides, nucleic acids, prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells, particles, viruses, metal ions, and combinations thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Integrated nucleic acid analysis
ActiveUS20090059222A1High resolutionIncrease contentRadiation pyrometryHeating or cooling apparatusFluorescenceDNA fragmentation
The present disclosure provides fully integrated microfluidic systems to perform nucleic acid analysis. These processes include sample collection, nucleic acid extraction and purification, amplification, sequencing, and separation and detection. The present disclosure also provides optical detection systems and methods for separation and detection of biological molecules. In particular, the various aspects of the invention enable the simultaneous separation and detection of a plurality of biological molecules, typically fluorescent dye-labeled nucleic acids, within one or a plurality of microfluidic chambers or channels. The nucleic acids can be labeled with at least 6 dyes, each having a unique peak emission wavelength. The present systems and methods are particularly useful for DNA fragment sizing applications such as human identification by genetic fingerprinting and DNA sequencing applications such as clinical diagnostics.
Owner:ANDE CORP
Methods and apparatus for introducing liquids into microfluidic chambers
InactiveUS6843281B1High energyPotential energyLiquid degasificationCircuit elementsHigh energyEngineering
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
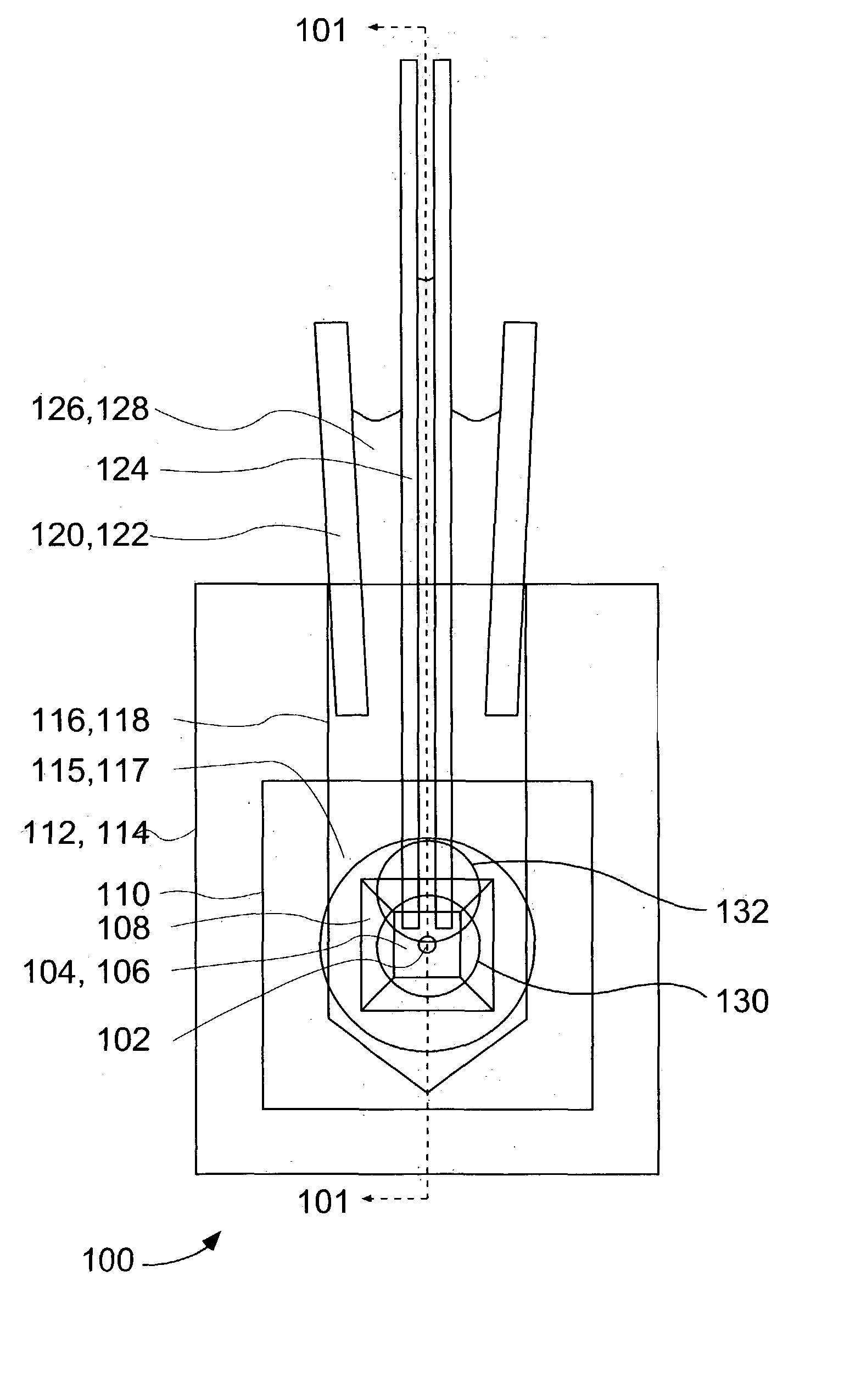
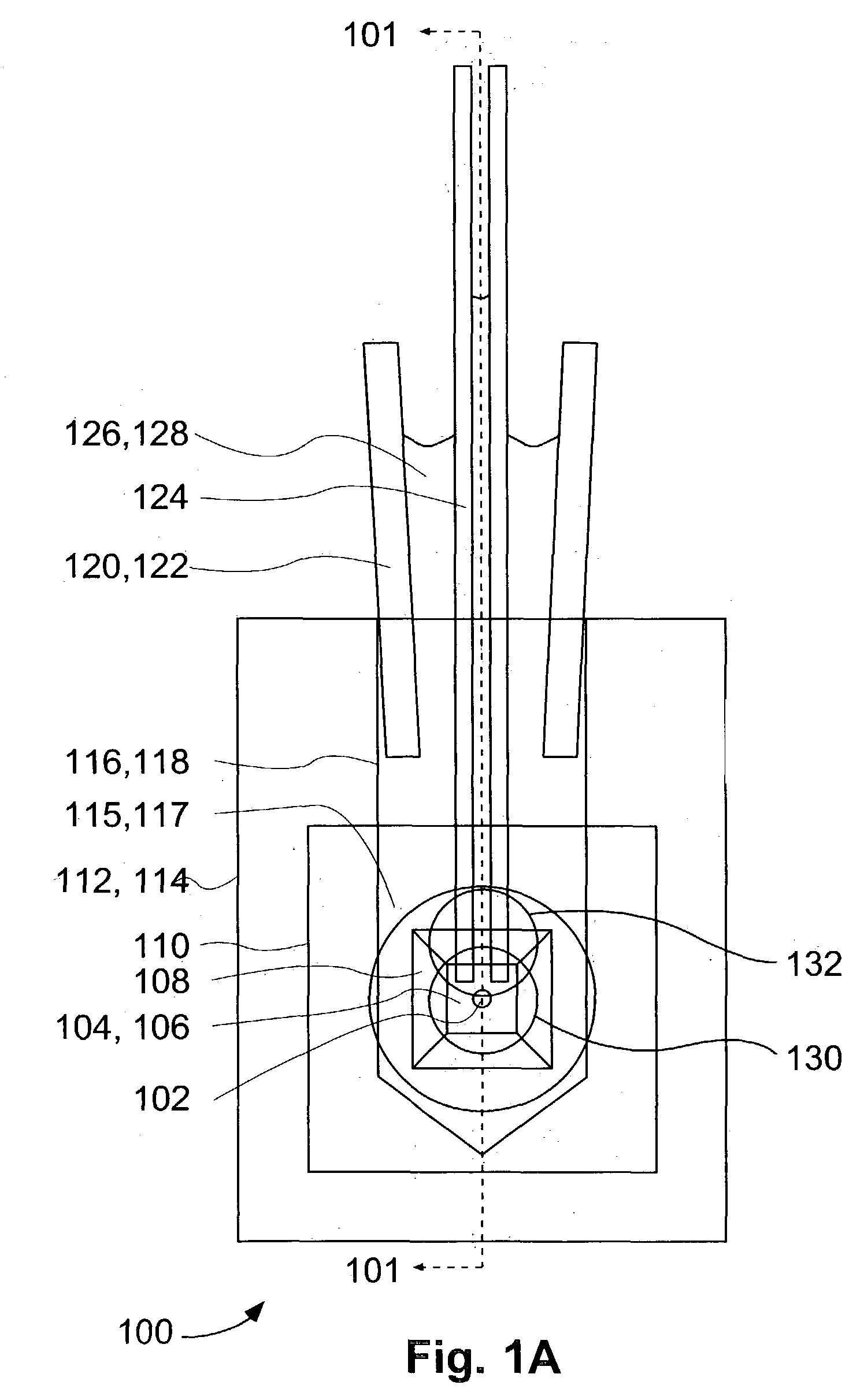
Microfluidic device
InactiveUS20100216126A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove operationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTelevision system detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A microfluidic device comprising; i) an inlet; ii) a first layer comprising at least first and second current carrying structures, wherein the at least first and second current carrying structures each comprise a plurality of teeth, and wherein the teeth of the first and second current carrying structures are optionally offset such that the teeth of the first current carrying structure are positioned between the teeth of the second current carrying structure; iii) a second layer comprising a first microfluidic chamber in fluid communication with the inlet positioned above the at least first and second current carrying structures of the first layer; and iv) a third layer comprising at least third and fourth current carrying structures wherein the at least third and fourth current carrying structures each comprise a plurality of teeth, and wherein the teeth of the third and fourth current carrying structures are optionally offset such that the teeth of the third current carrying structure are positioned between the teeth of the fourth current carrying structure; and wherein the at least third and fourth current carrying structures are positioned in the third layer so as to be above the first microfluidic chamber and such that the teeth of the third current carrying structure are positioned substantially vertically above or offset from the teeth of the first current carrying structure and the teeth of the fourth current carrying structure are positioned substantially vertically above or offset from the teeth of the second current carrying structure; wherein the teeth have a stem having substantially elliptical tip.
Owner:BRUNEL UNIVERSITY
Method of transporting magnetic particles
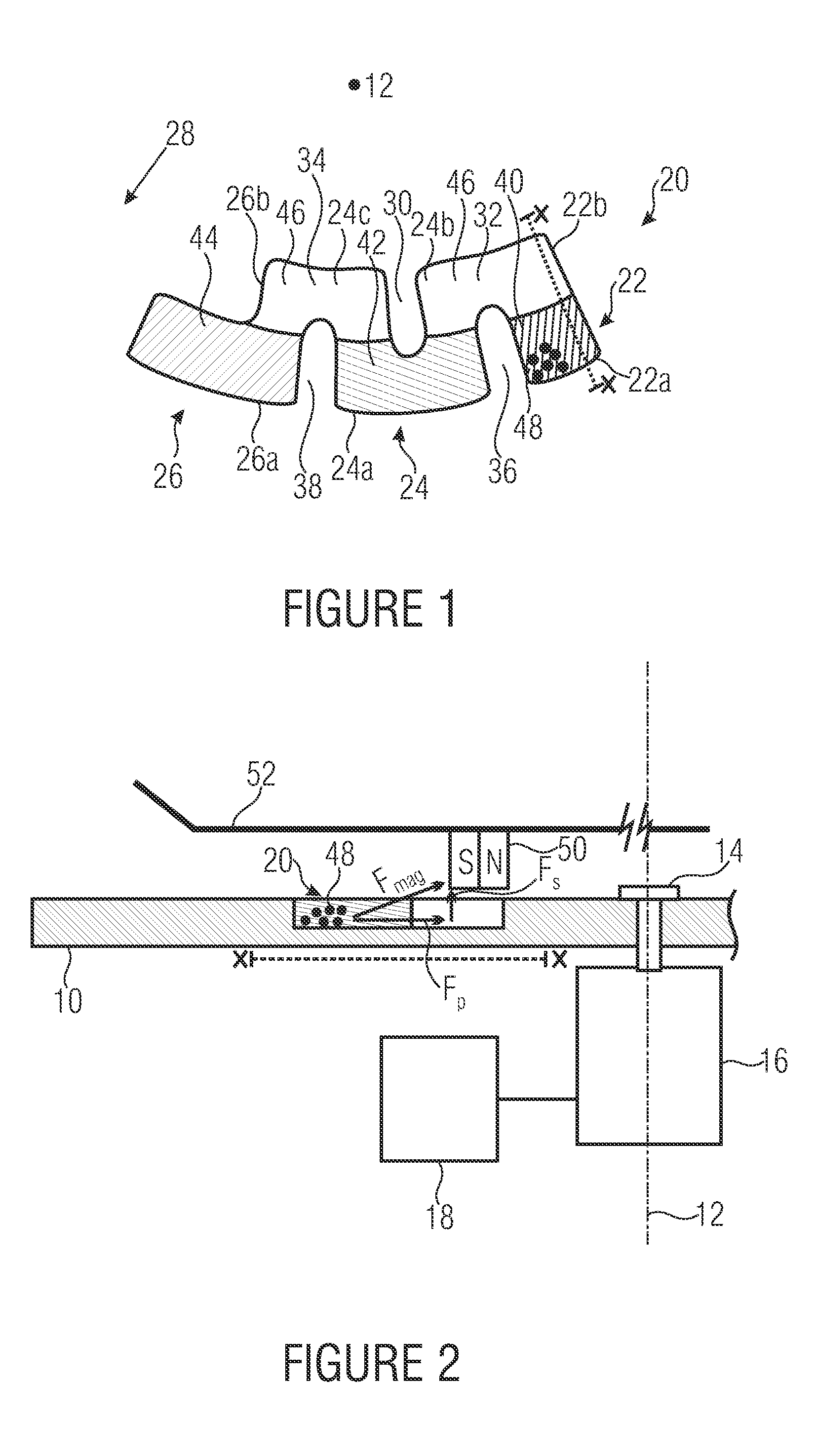
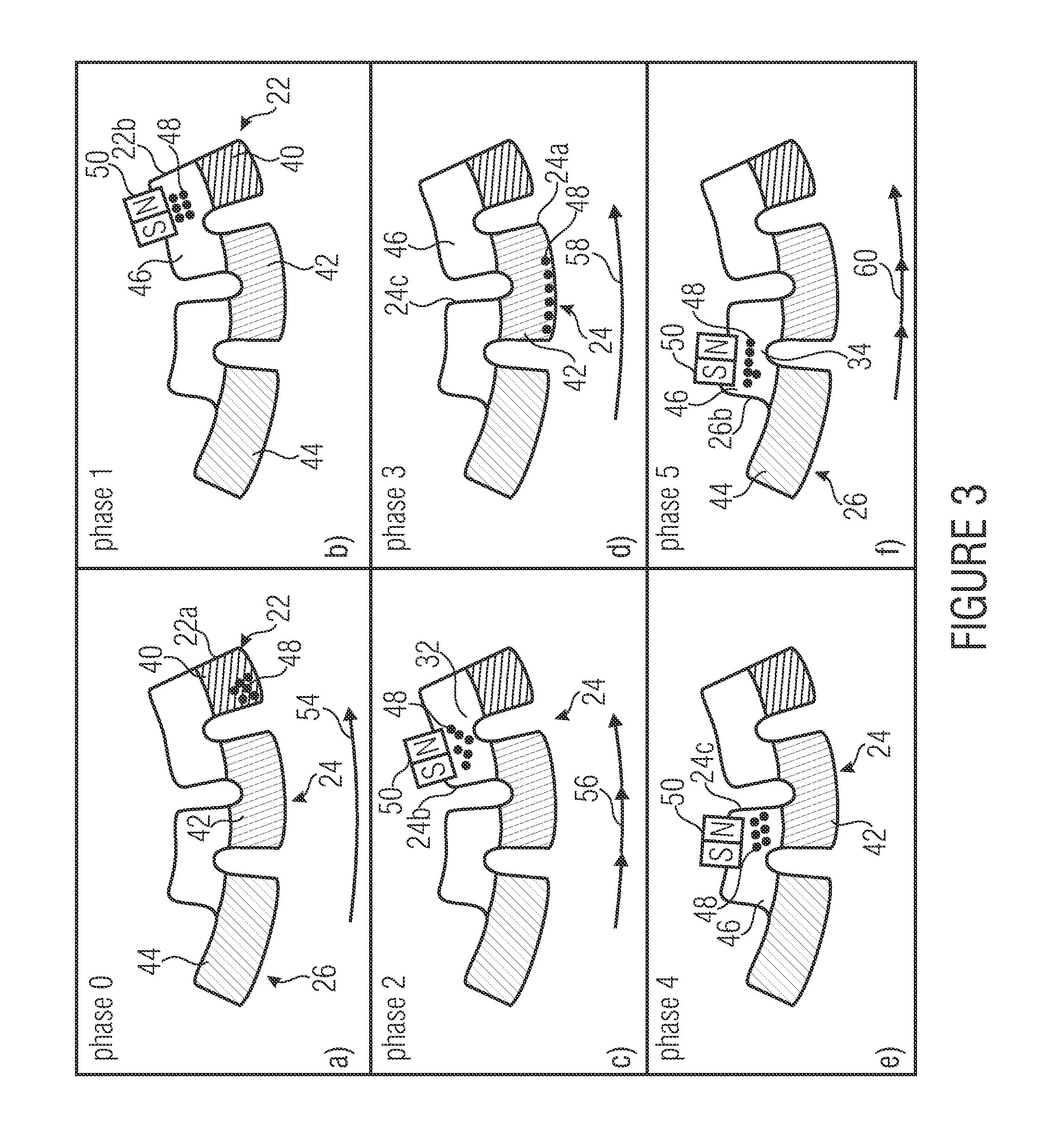
ActiveUS20130206701A1Low costIncrease spaceSemi-permeable membranesFixed microstructural devicesMagnetic tension forceEngineering
Owner:HAHN SCHICKARD GESELLSCHAFT FUER ANGEWANDTE FORSCHUNG EV
Microfluidic chamber device and fabrication
A microfluidic flow cell subassembly, which may be assembled into a flow cell having fluidic connections outside of the main substrate, is described for encapsulating a sample to allow for subsequent controlled delivery of reagents to the sample, such as multiplexed in situ biomarker staining and analysis. Methods for fabricating the subassembly and assembled flow cell are also provided. The method includes the steps of adhering a gasket layer to a substrate layer, wherein the gasket layer may contain enclosed features and adhering an adherent layer to the gasket layer. The subassembly may be sealed against a solid support to form a flow cell.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Method of transporting magnetic particles
ActiveUS8951417B2Low costIncrease spaceFixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringCentrifugal force
Owner:HAHN SCHICKARD GESELLSCHAFT FUER ANGEWANDTE FORSCHUNG EV
Microfluidic platform for discrete cell assay
ActiveUS20130130301A1Prevent escapeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsValve arrangementsSecreted substancePerfusion
A microfluidic chamber for use in individual cell assays. The microfluidic chamber includes a cell microchamber having an interior region and front and rear valves, each of which are separately controllable so that they can be selectively opened and closed to thereby permit the transference of an individual cell into and out of the interior region. Cell secretion and contact interaction studies can be carried out using the microchambers, with the valves permitting either complete isolation or perfusion media flow through the microchambers. An internal perfusion wall can be included to partition the microchamber for non-contact perfusion studies of secretion interactions between cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Microfluidic Chamber Assembly for Mastitis Assay
ActiveUS20140315242A1Easy to doSmall volumeSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseWhite blood cell
The present invention relates to a device and method for the detection of mastitis or other disease from a body fluid of a mammal for example from cow's milk. The device and method relates to a wedge microfluidic chamber for using a minimal amount of fluid and being able to use the device to observe leukocytes in a mono-layer for the purpose of disease detection, cell counts or the like.
Owner:ADVANCED ANIMAL DIAGNOSTICS
Microfluidic device
A microfluidic device comprising; i) an inlet; ii) a first layer comprising at least first and second current carrying structures, wherein the at least first and second current carrying structures each comprise a plurality of teeth, and wherein the teeth of the first and second current carrying structures are optionally offset such that the teeth of the first current carrying structure are positioned between the teeth of the second current carrying structure; iii) a second layer comprising a first microfluidic chamber in fluid communication with the inlet positioned above the at least first and second current carrying structures of the first layer; and iv) a third layer comprising at least third and fourth current carrying structures wherein the at least third and fourth current carrying structures each comprise a plurality of teeth, and wherein the teeth of the third and fourth current carrying structures are optionally offset such that the teeth of the third current carrying structure are positioned between the teeth of the fourth current carrying structure; and wherein the at least third and fourth current carrying structures are positioned in the third layer so as to be above the first microfluidic chamber and such that the teeth of the third current carrying structure are positioned substantially vertically above or offset from the teeth of the first current carrying structure and the teeth of the fourth current carrying structure are positioned substantially vertically above or offset from the teeth of the second current carrying structure; wherein the teeth have a stem having substantially elliptical tip.
Owner:BRUNEL UNIVERSITY
Hexagonal surface wave acoustic tweezer chip for cell arrangement and assembly
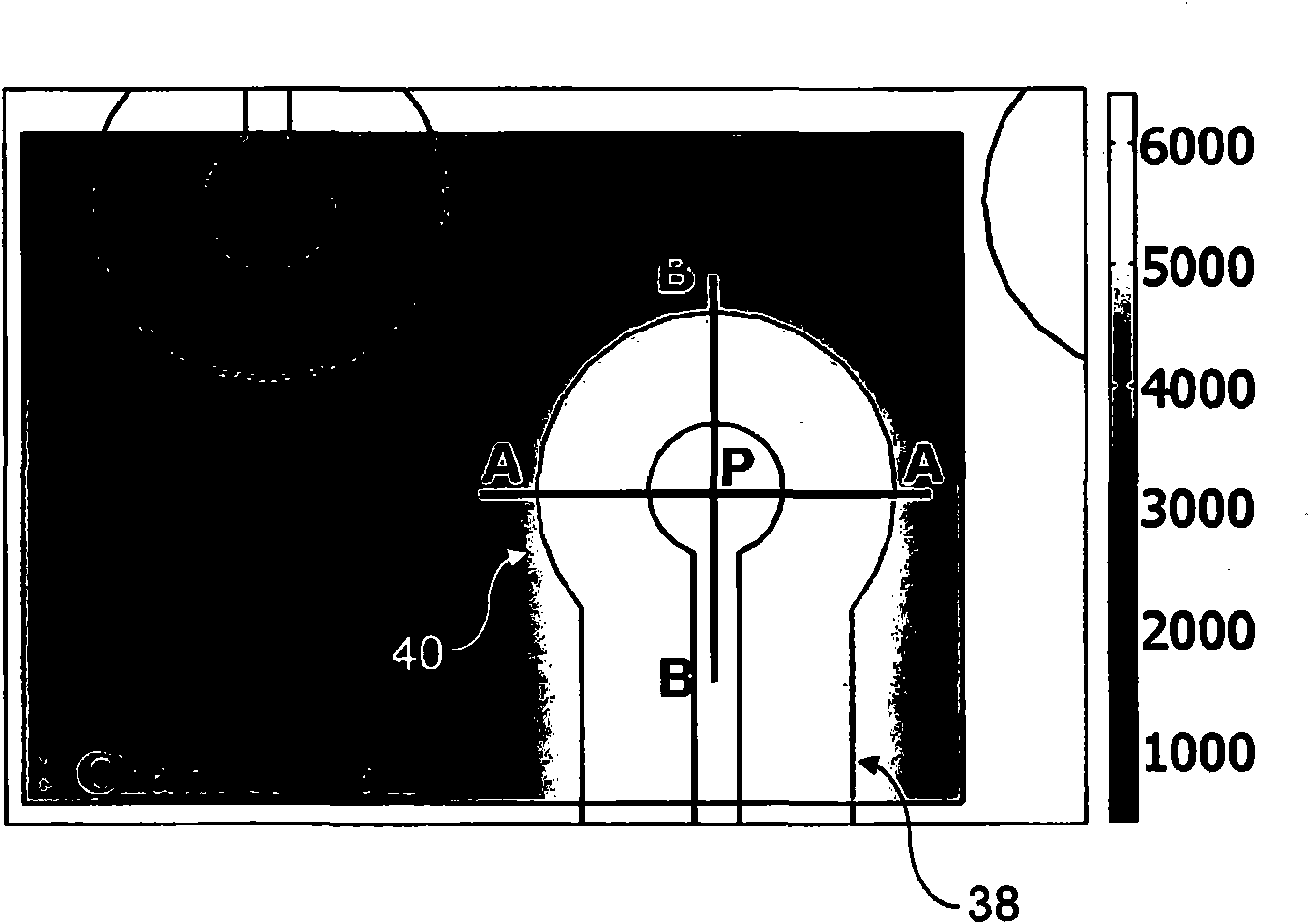
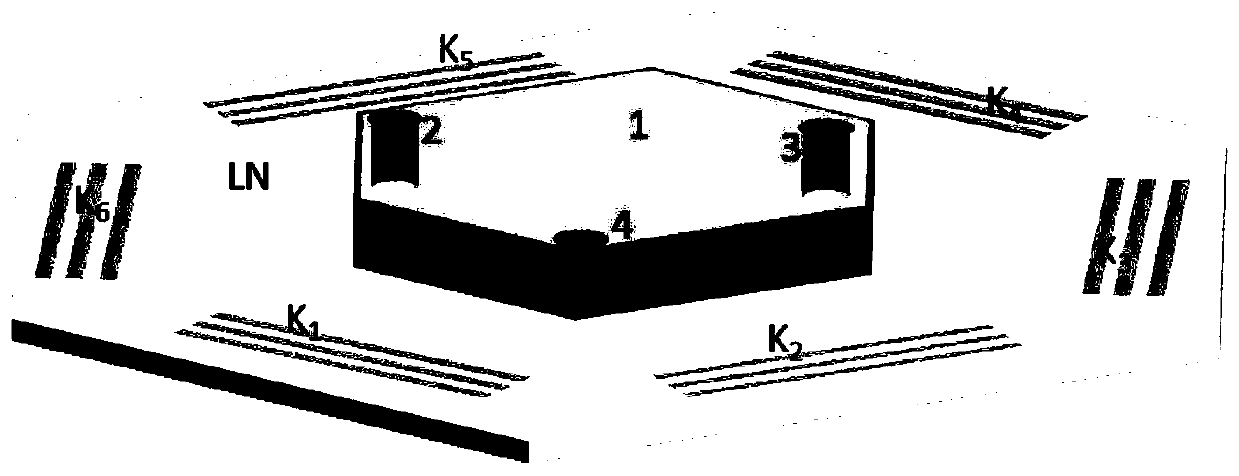
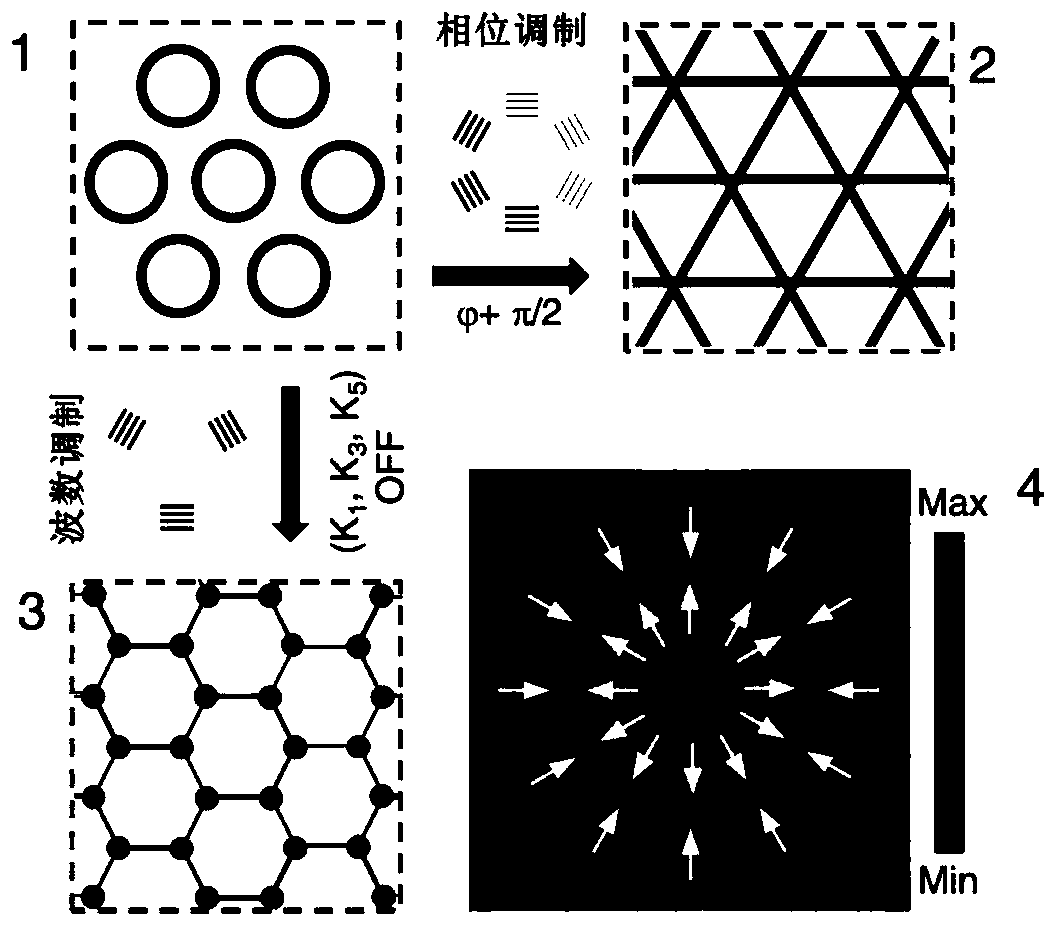
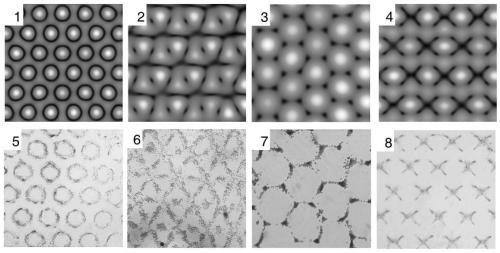
ActiveCN111254076ASuitable for control needsFlexible Surface Wave Acoustic PatternsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringLithium niobate
The invention discloses a hexagonal surface wave acoustic tweezer chip for cell arrangement and assembly. The hexagonal surface wave acoustic tweezer chip includes a hexagonal acoustic tweezer and a microfluidic cavity, a Z-cut lithium niobate piezoelectric substrate is used, six interdigital transducers are made on the substrate, through the combination of different beams and individual phase modulation of the beams, sound field patterns far more than traditional acoustic tweezers can be produced, a sound field structure is also more flexible and adjustable, and when the chip is used for cellmanipulation and assembly, a more diverse assembly structure and more powerful control ability are provided. Through the individual modulation and combination application of the transducers, multi-wave interference can be carried out in the way, a variety of sound field structures and flexible regulation are realized. The hexagonal surface wave acoustic tweezer chip can be more suitable for various application scenarios that require cell manipulation and assembly without damage and contact, a more flexible surface wave sound field pattern is realized, the hexagonal surface wave acoustic tweezer chip is more suitable for various cell manipulation needs of biological research and tissue engineering, and the application prospects are huge.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Sample processing device with detachable slide
ActiveUS20150005190A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringHigh pressure
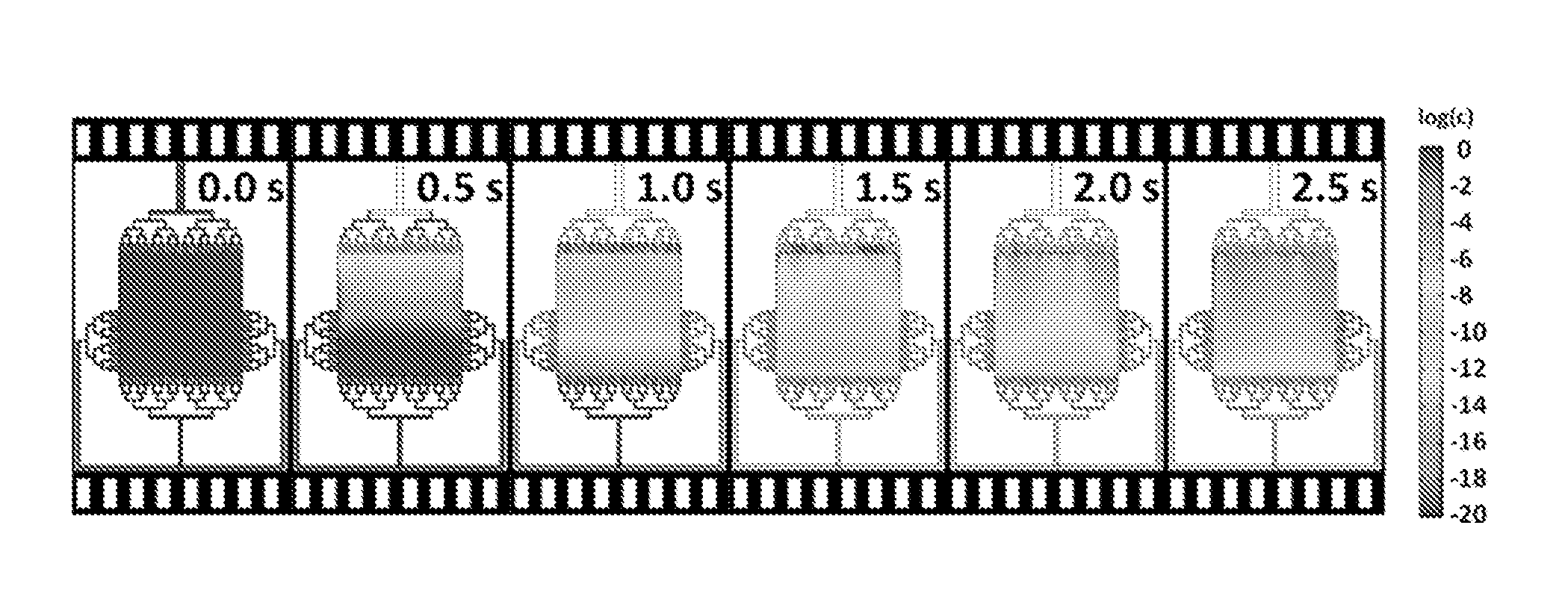
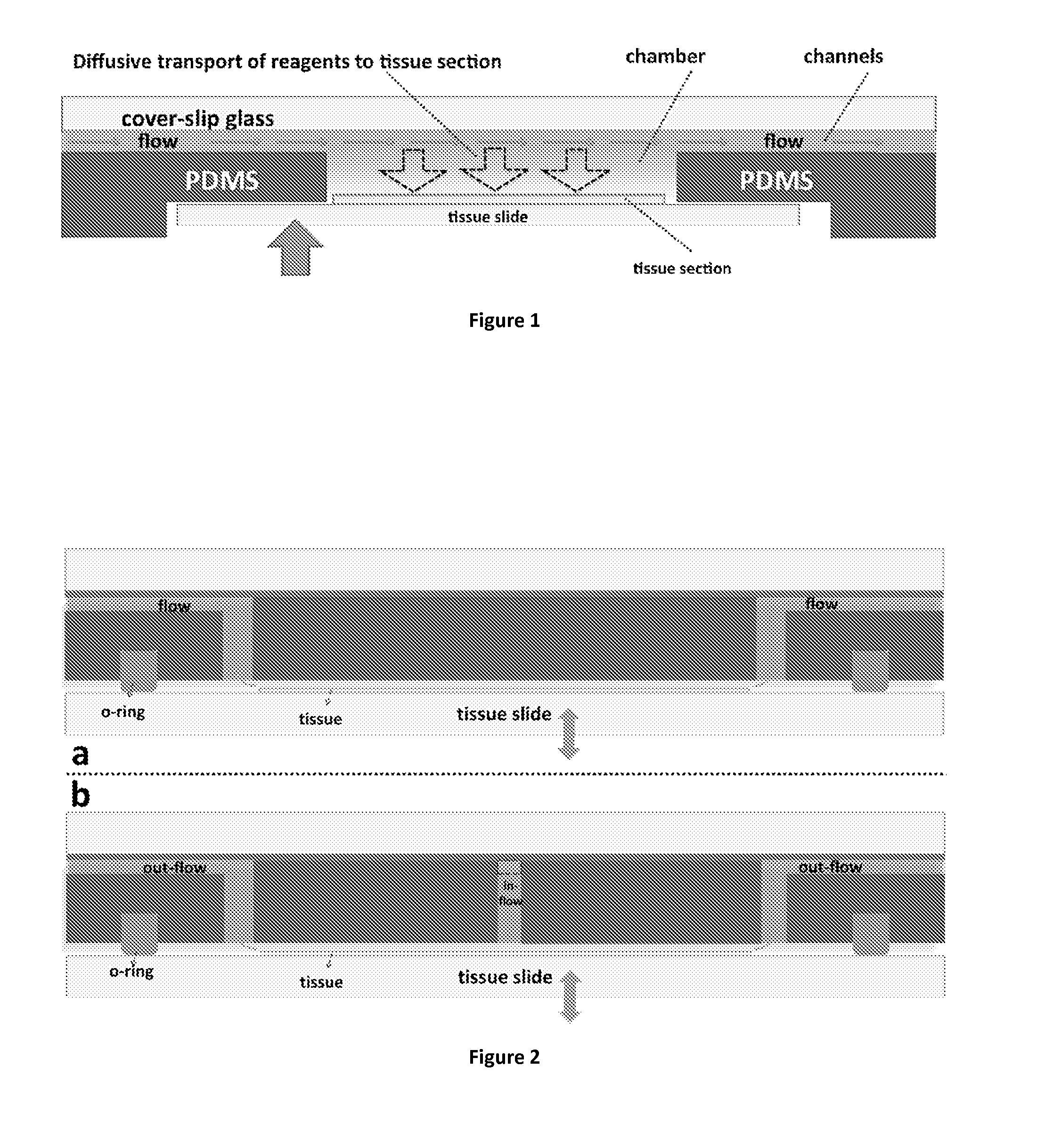
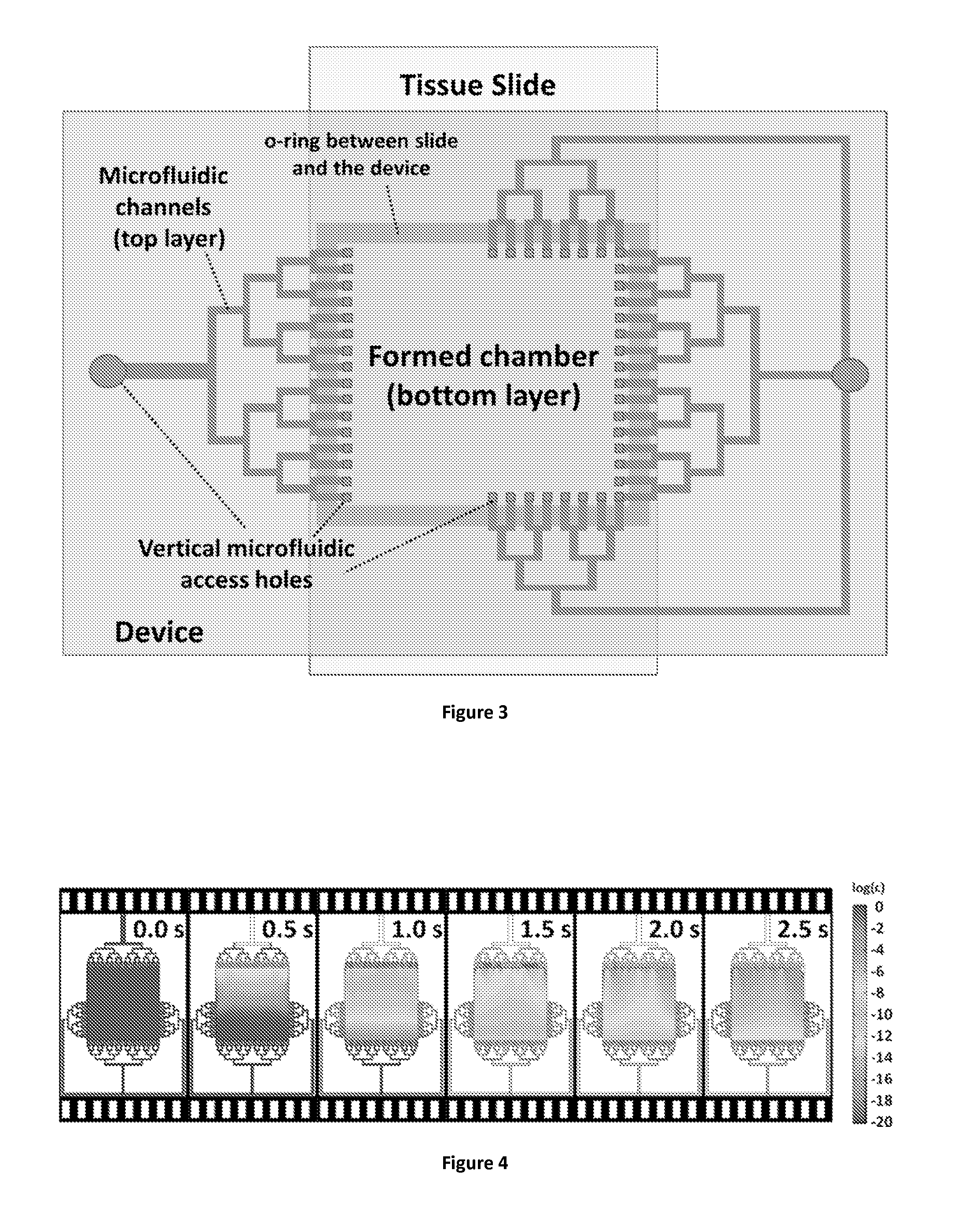
A biological and chemical sample processing device that b. comprises a high pressure-resistant, shallow and wide area microfluidic chamber having at least one wall formed by a detachable slide containing samples such as immobilized entities, biological samples or molecules, c. comprises an arrangement of microfluidic access holes for injecting to and collecting fluid form said chamber, d. is interfaced with inlet ports and microfluidic channels which are formed external to the chamber, e. is configured so that the slide may be brought into contact with the device to form the said chamber, f. is adapted to deliver and to transport fluidic substances and reagents inside said chamber in a fast manner, preferably within less than 15 seconds, and in a regular or uniform way owing to said arrangement of microfluidic access holes.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Porous membrane apparatus, method, and applications
ActiveUS20150174573A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical physicsPhysical chemistry
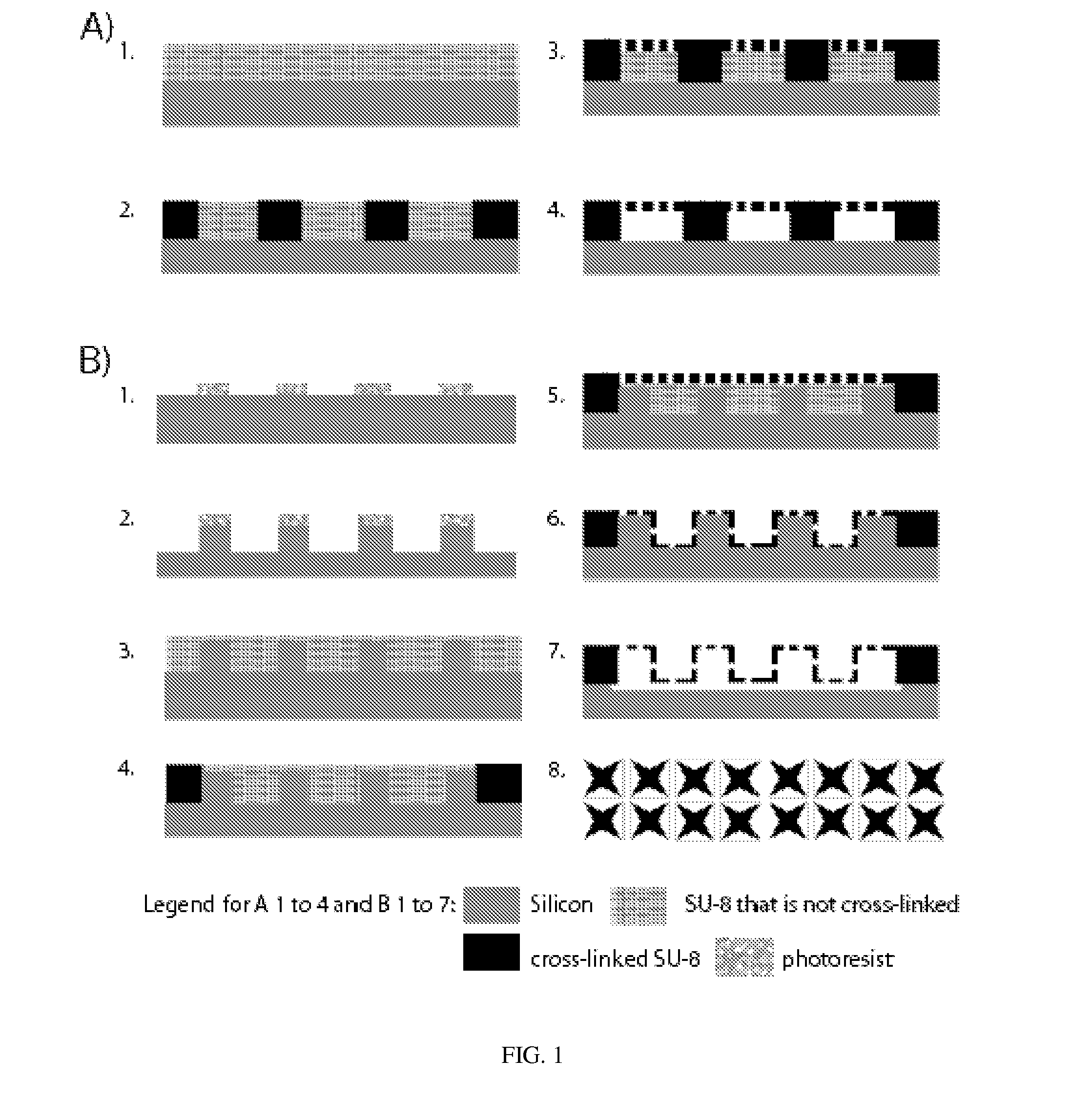
Microporous membranes formed in a microfluidic device, and methods of manufacture. A method comprises the steps of etching a plurality of pillars in a microfluidic chamber, applying a first polymer material layer, applying a photoresist layer, exposing the photoresist layer to radiation to cross-link it to the microfluidic chamber, masking the photoresist layer with a porous mask, exposing the top layer of the masked photoresist layer to radiation to form a porous membrane layer of cross-linked photoresist material, removing the non-exposed photoresist material from under the porous membrane layer, drying the porous membrane layer, and removing the first polymer material from under the porous membrane layer.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Method and device for generating diffusive gradients in a microfluidic chamber
ActiveUS8216526B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismEngineering
A microfluidic device is described, capable of generating multiple spatial chemical gradients simultaneously inside a microfluidic chamber. The chemical gradients are generated by diffusion, without convection, and can either be maintained constant over long time periods, or modified dynamically. A representative device is described with a circular chamber in which diffusion occurs, with three access ports for the delivery and removal of solutes. A gradient typically forms in minutes, and can be maintained constant indefinitely. Gradients overlapping with different spatial location, and a controlled rotation of a gradient formed by diffusion are demonstrated. The device can also be used to evaluate chemotactic responses of bacteria or other microorganisms in the absence of convective flow.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE COMMERCE
Microfluidic chamber device and fabrication
A microfluidic flow cell subassembly, which may be assembled into a flow cell having fluidic connections outside of the main substrate, is described for encapsulating a sample to allow for subsequent controlled delivery of reagents to the sample, such as multiplexed in situ biomarker staining and analysis. Methods for fabricating the subassembly and assembled flow cell are also provided. The method includes the steps of adhering a gasket layer to a substrate layer, wherein the gasket layer may contain enclosed features and adhering an adherent layer to the gasket layer. The subassembly may be sealed against a solid support to form a flow cell.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Microfluidic nucleic acid analysis
ActiveUS8871446B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCells isolationCDNA library
Nucleic acid from cells and viruses sampled from a variety of environments may purified and expressed utilizing microfluidic techniques. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, individual or small groups of cells or viruses may be isolated in microfluidic chambers by dilution, sorting, and / or segmentation. The isolated cells or viruses may be lysed directly in the microfluidic chamber, and the resulting nucleic acid purified by exposure to affinity beads. Subsequent elution of the purified nucleic acid may be followed by ligation and cell transformation, all within the same microfluidic chip. In one specific application, cell isolation, lysis, and nucleic acid purification may be performed utilizing a highly parallelized microfluidic architecture to construct gDNA and cDNA libraries.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Transmission electron microscopy for imaging live cells
ActiveUS9207196B2Not to damageReduce intensityElectric discharge tubesLaboratory glasswaresEnergy filtered transmission electron microscopyLiving cell
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a microfluidic chamber. In one embodiment, the microfluidic chamber has a first sub-chamber and at least one second sub-chamber. The first sub-chamber has a first window and a second window. Both the first window and the second window are transparent to electrons of certain energies. The second window is positioned substantially parallel and opposite to the first window defining a first volume therebetween. The first window and the second window are separated by a distance that is sufficiently small such that an electron beam that enters from the first window can propagate through the first sub-chamber and exit from the second window. The at least one second sub-chamber is in fluid communication with the first sub-chamber and has a second volume that is greater than the first volume of the first sub-chamber.
Owner:DE JONGE VILIJA +2
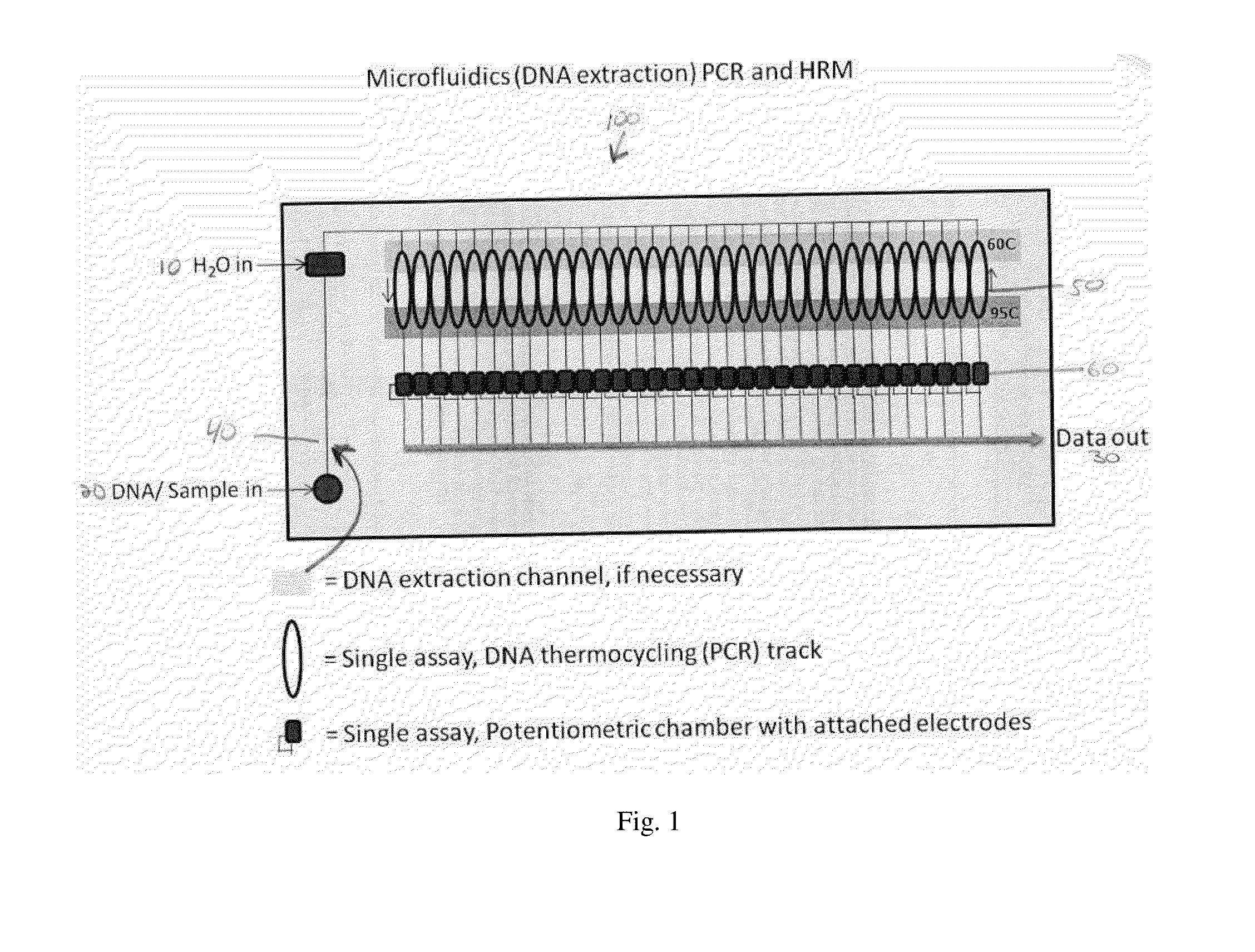
Microfluidics Polymerase Chain Reaction and High Resolution Melt Detection
ActiveUS20140287420A1Rugged designBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyHigh resolution
The present invention relates to a method and system for Polymerase Chain Reaction (“PCR”), High Resolution Melt (“HRM”) analysis and microfluidics, and, more specifically, to a method and system for implementing the processes of PCR and HRM on a microscale in a microfluidics chamber for certain purposes including for purposes of DNA detection and / or extraction.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
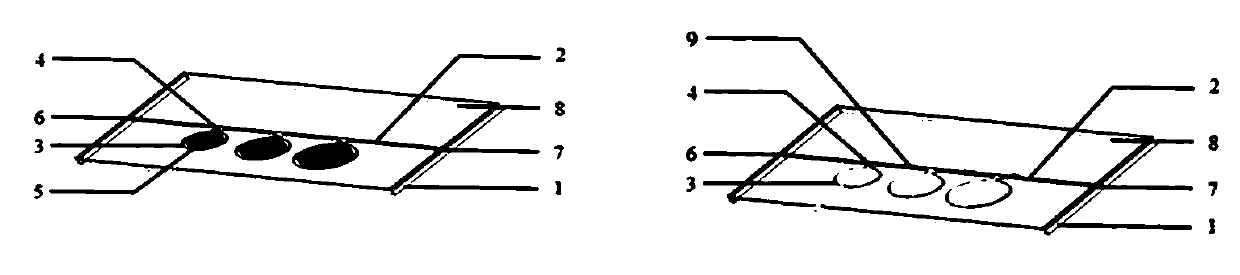
Stereo micro-fluidic chip and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105396631AReduce deformationHigh success rate of preparationLaboratory glasswaresPolymer sciencePolymer
The invention discloses a stereo micro-fluidic chip, comprising a first substrate, a second substrate, ..., and an N substrate, wherein the first to N substrates are provided with micro-fluidic channels or micro-fluidic chambers and successively and mutually connected via polymer layers, which enables the micro-fluidic channels or micro-fluidic chambers of the first to N substrates to be communicated, so a stereo micro-fluidic structure is formed. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the micro-fluidic chip. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly coating the substrates with a prefabricated polymer and carrying out drying so as to obtain the polymer layers with sizes of 1 [mu]m to 100 [mu]m; and separately bonding the first substrate and the second substrate with one of the polymer layers and carrying out repeated lamination so as to obtain the micro-fluidic chip. Thus, bonding of the micro-fluidic chip is realized without application of pressure; and the method is simple and can be extensively used for preparation of the micro-fluidic chip.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
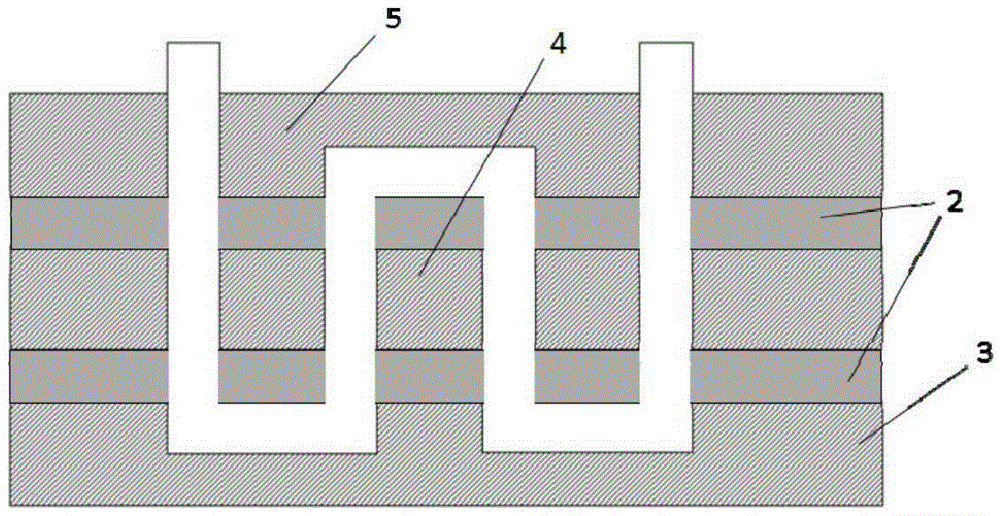
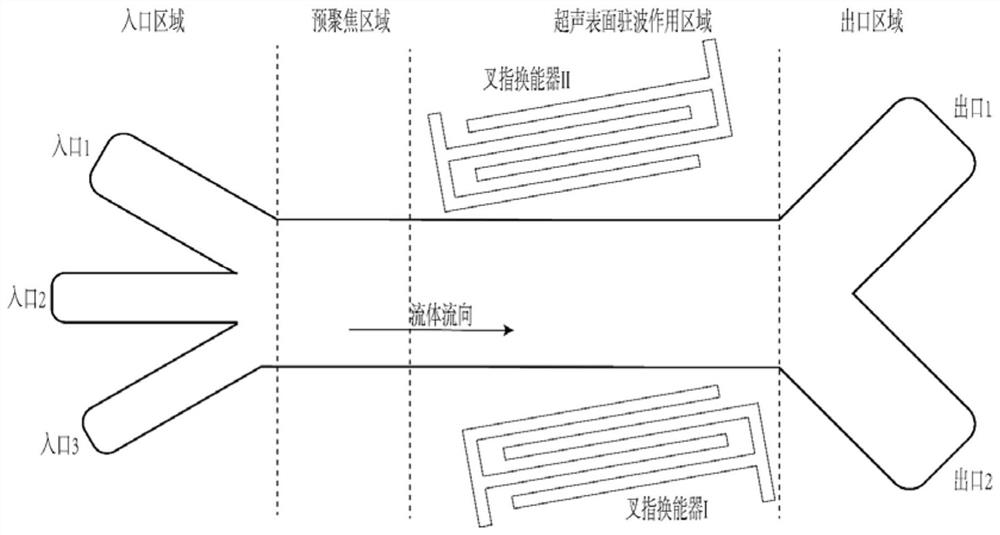
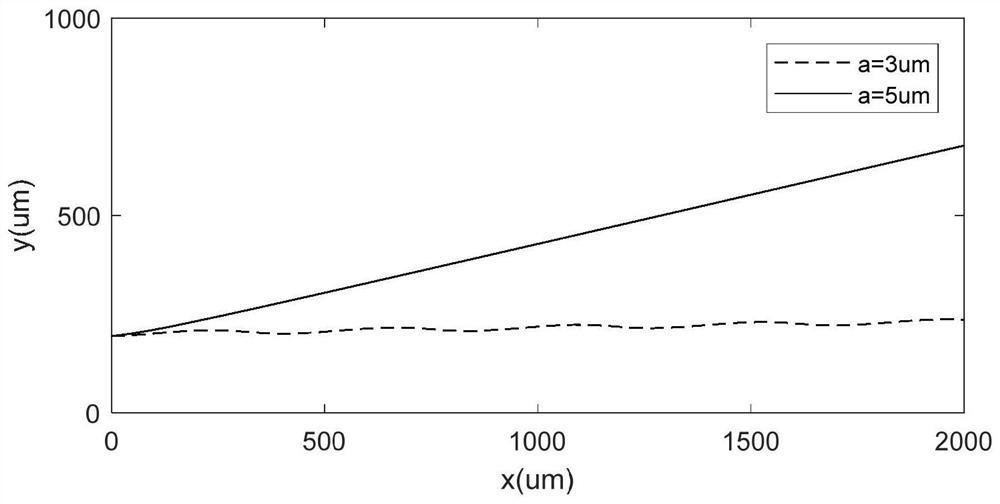
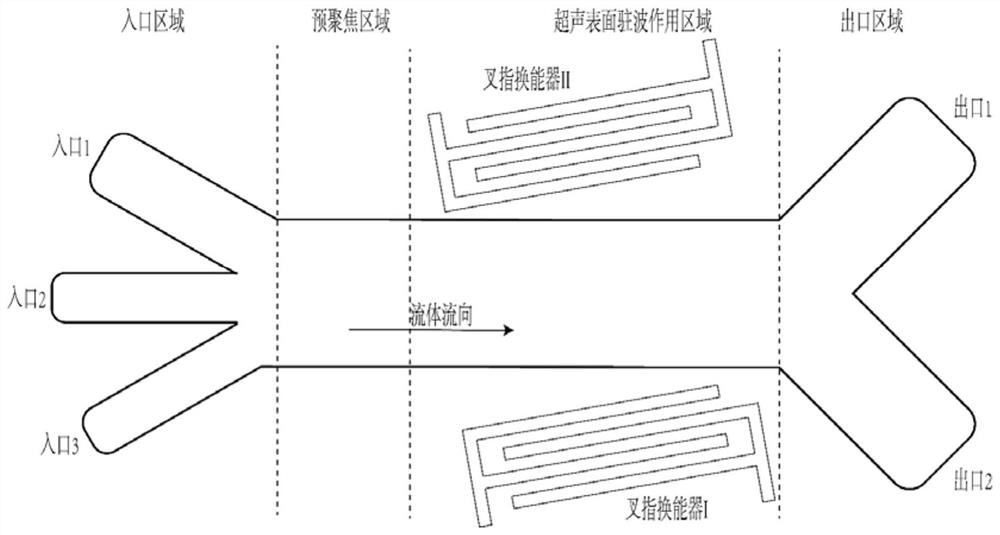
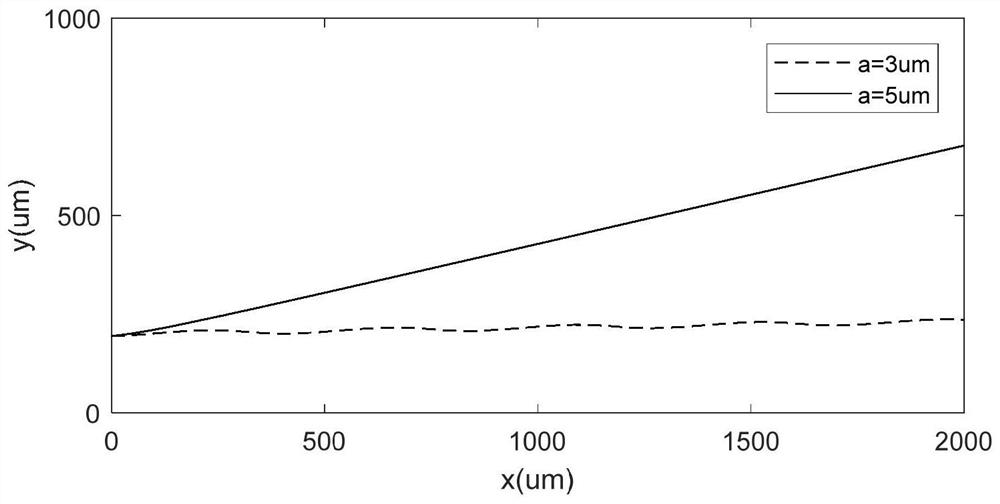
Ultrasonic surface standing wave microfluidic chip for micro-particle separation and application
ActiveCN111659478AReduce difficultyImprove separation efficiencyLaboratory glasswaresFluid controllersUltrasonic standing waveMechanical engineering
The invention discloses an ultrasonic surface standing wave microfluidic chip for micro-particle separation and application, belongs to the technical field of microfluidic analysis, and aims at the problems in the prior art that when a microfluidic chip is used for separating micro-particles, parameter design of the ultrasonic surface standing wave action area is judged only according to experience, particle separation efficiency is low and a large amount of time and cost are wasted. The invention provides a method for separating micro-particles based on an ultrasonic surface standing wave microfluidic chip. The method comprises the steps: determining the size of the sectional area of an internal channel of a microfluidic cavity of the microfluidic chip, the length of an ultrasonic standing wave action area, the inclination angle of the interdigital transducer, the phase change rate of the interdigital transducer, the aperture size of the interdigital transducer, the liquid flow rate during working and the input voltage, and carrying out particle separation. During micro-particle separation, chip design mainly relates to an ultrasonic surface standing wave action area, other areasand focusing methods are not limited, particle separation operation steps and device preparation difficulty are reduced, and particle separation efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Microfluidic device for automatic quantitative distribution, collection and detection and using method of microfluidic device
InactiveCN109806920ASimplify complexityImprove detection accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLaboratory glasswaresPorous mediumEngineering
The invention discloses a microfluidic device for automatic quantitative distribution, collection and detection and a using method of the microfluidic device. The device realizes automatic quantitative distribution, collection and detection by changing local hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity. The first method comprises the step that hydrophilic materials such as porous media are added into microfluidic cavities, and valves corresponding to the hydrophilic materials are additionally arranged in the microfluidic cavities; and the second method comprises the step that hydrophobic treatment is conducted at the specific location of a microfluidic channel. The microfluidic device comprises a base, a cover plate, a fluid inlet, a fluid outlet, the microfluidic channel, side microfluidic cavities anda valve, sample liquid in the microfluidic device enters the side microfluidic cavities quantitatively, according to the characteristic of selective flowing of the liquid in a hydrophobic area and a hydrophilic area, the liquid in each cavity does not interfere with each other, whether detecting reagents are added into the side microfluidic cavities or not is decided according to the needs, and thus prepared sample liquid is automatically and quantitatively distributed, collected and detected. The microfluidic device for automatic quantitative distribution, collection and detection and the using method of the microfluidic device can be applied to a micro-biochemical reactor and a device laboratory.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Design method of ultrasonic surface standing wave micro-fluidic chip for micro-particle separation
ActiveCN111659479AImprove separation efficiencyHigh separation purityLaboratory glasswaresFluid controllersEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a design method of an ultrasonic surface standing wave micro-fluidic chip for micro-particle separation, belongs to the technical field of micro-fluidic analysis, and aims at the problems in the prior art that when a microfluidic chip is used for separating micro-particles, parameter design of the ultrasonic surface standing wave action area is judged only according to experience, particle separation efficiency is low and a large amount of time and cost are wasted. The invention provides a design method of a micro-fluidic chip for micro-particle separation. The method is based on the theory of stress and movement of micro-particles in an ultrasonic surface standing wave micro-fluidic chip. The method comprises the following steps: separating parameters of micro-particles and structure composition of a chip, determining the working frequency and the liquid flow parameters of the chip, further determining the design parameters of the interdigital transducer and the micro-fluidic cavity, finally determining the cavity design and the working parameters of the chip are determined, and based on the particle separation technology of the ultrasonic surface standingwave micro-fluidic chip, the device preparation difficulty is reduced, and the particle separation efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
A micro-nanofluidic device for cell migration research
InactiveCN103992948BEasy to operateCompact structureTissue/virus culture apparatusMicro nanoFluidics
The invention relates to a micronanofluidic device for researching cell migration. The micronanofluidic device comprises a glass substrate at the bottommost layer, a PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) layer which is arranged at the middle layer and provided with microfluidic channels at the bottom and two glass cylinder fluid reservoir at the uppermost layer. The PDMS-molded microfluidic chamber is divided by two hydrogel-molded nano-porous partition grids into three independent regions, namely fluid channels at the two sides and a cell culture region at the center. The solutions with different concentrations are added at the inlets of the fluid channels at the two sides and a stable concentration gradient can be formed in the cell culture region at the center by diffusion. Two slender and flexible channels and a balance region are also designed in the device to balance the pressures in the fluid channels at the two sides to ensure the repeatability and stability of the concentration gradient of the cell culture region. The structure of the device is simple, the reconfiguration can be easily realized and the control over the concentration gradient and other parameters influencing the cell migration can be realized by adjusting the thickness of the hydrogel partition grids, so as to meet the requirements of different studies.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
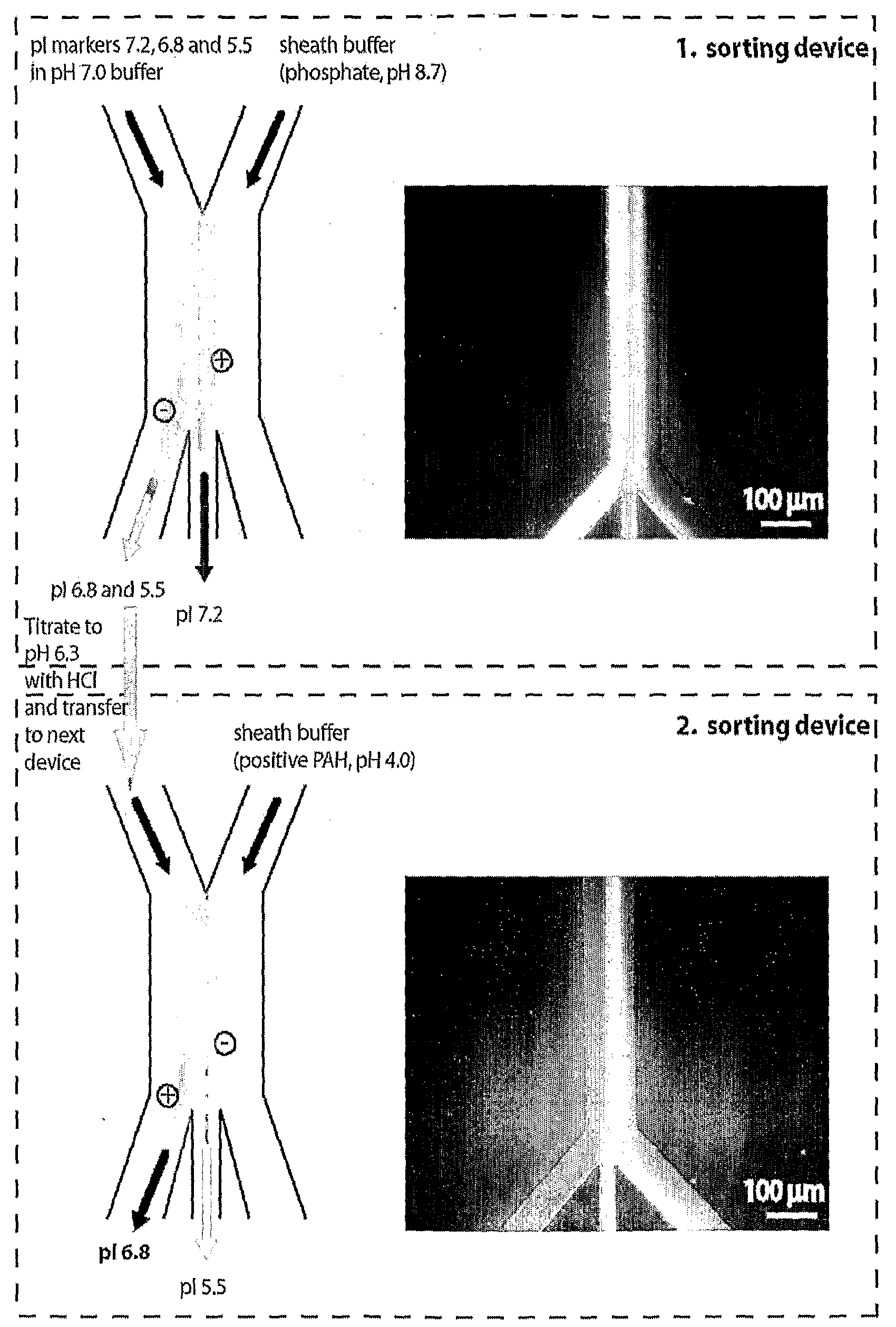
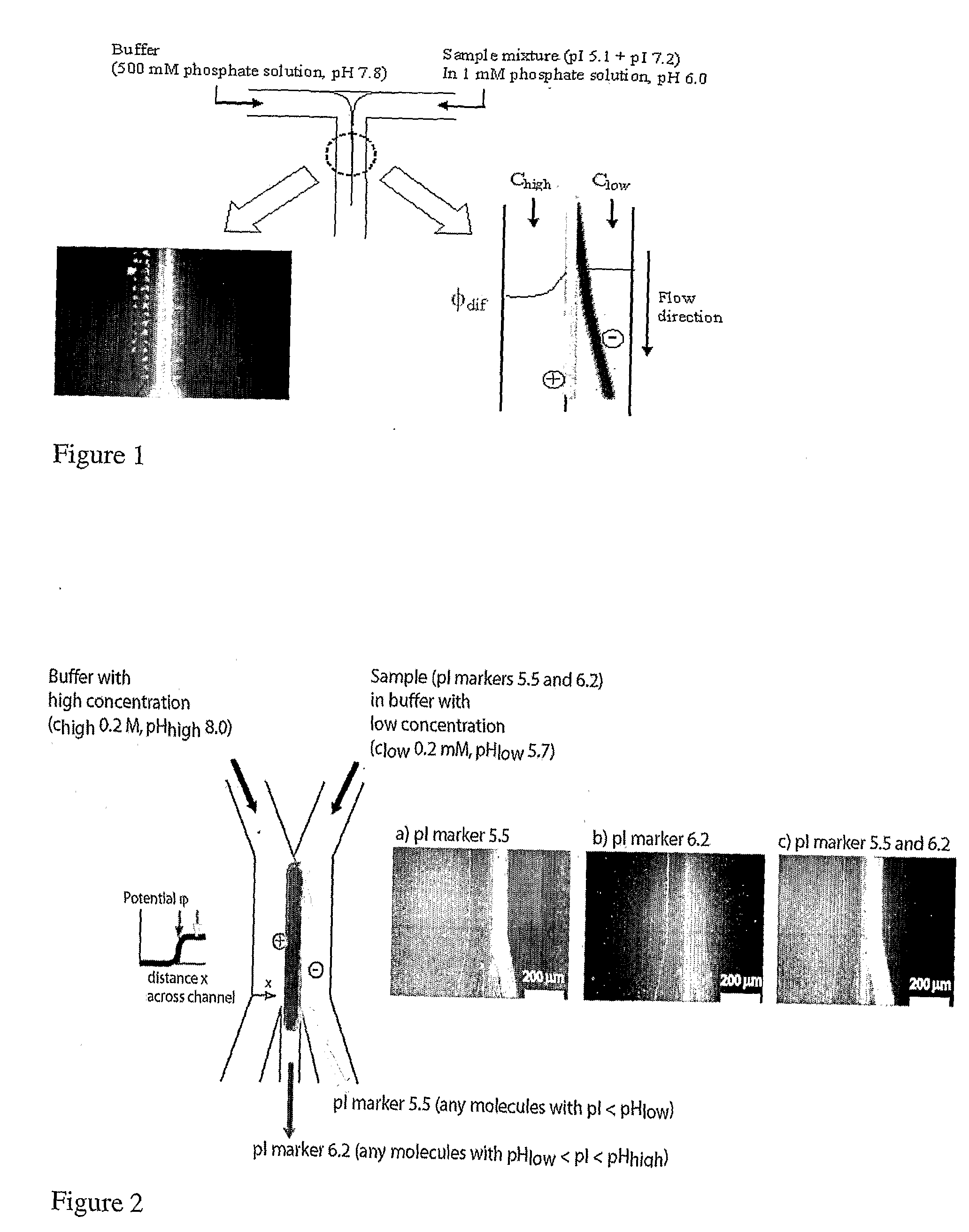
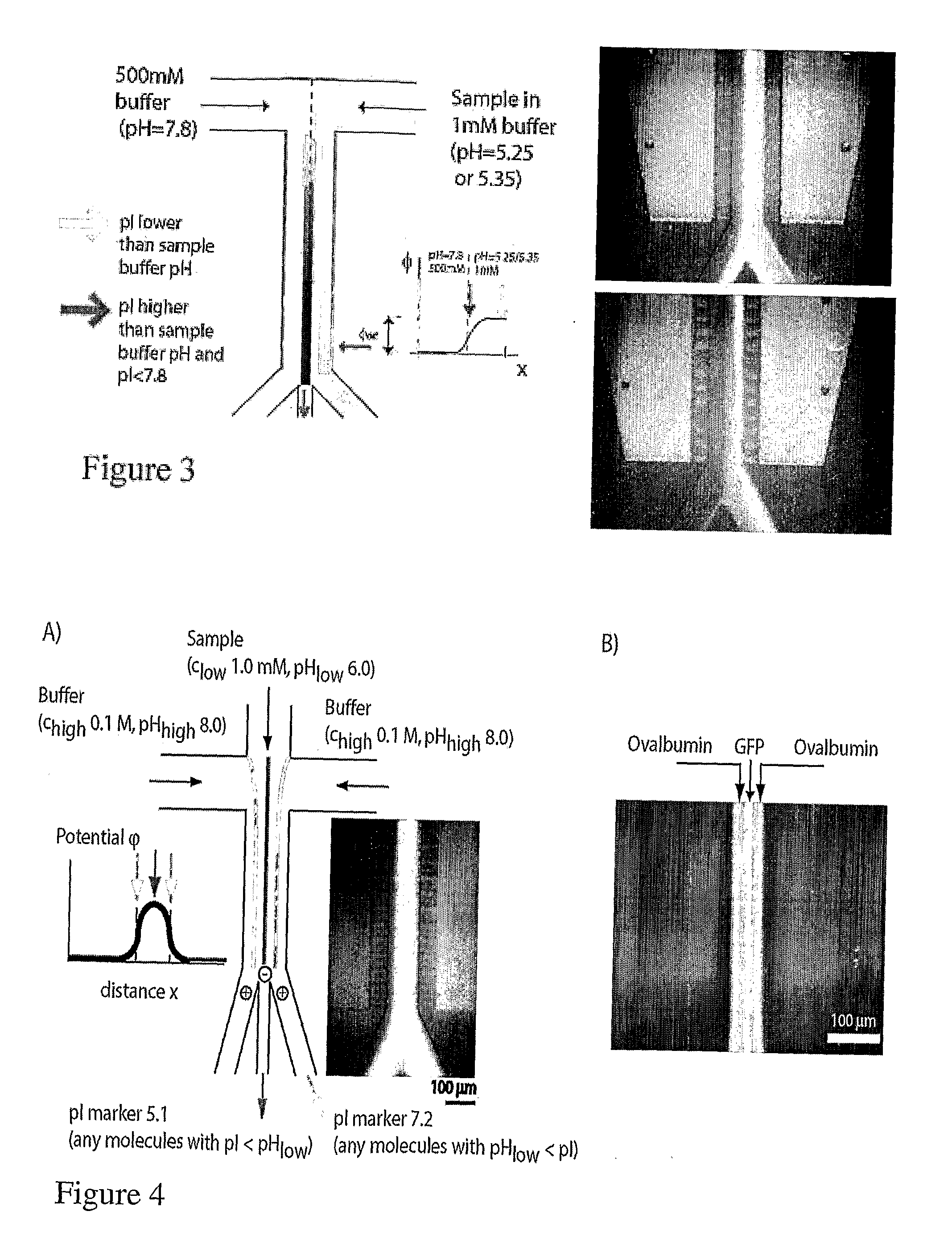
Microfluidic pl-based molecular sorting
This invention is directed to methods and devices for separating molecules in a sample, based on differences in their isoelectric point (pI). The methods and devices make use of a diffusion potential created in a microfluidic chamber when a buffered solution comprising molecules, which differ in terms of their isoelectric point (pI) values and a second buffer, which differs from the buffered solution in terms of its pH or salt concentration are introduced in the chamber. The diffusion potential, in turn, enables charge-based separation of the molecules. Applications and permutations of the methods and devices are described.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
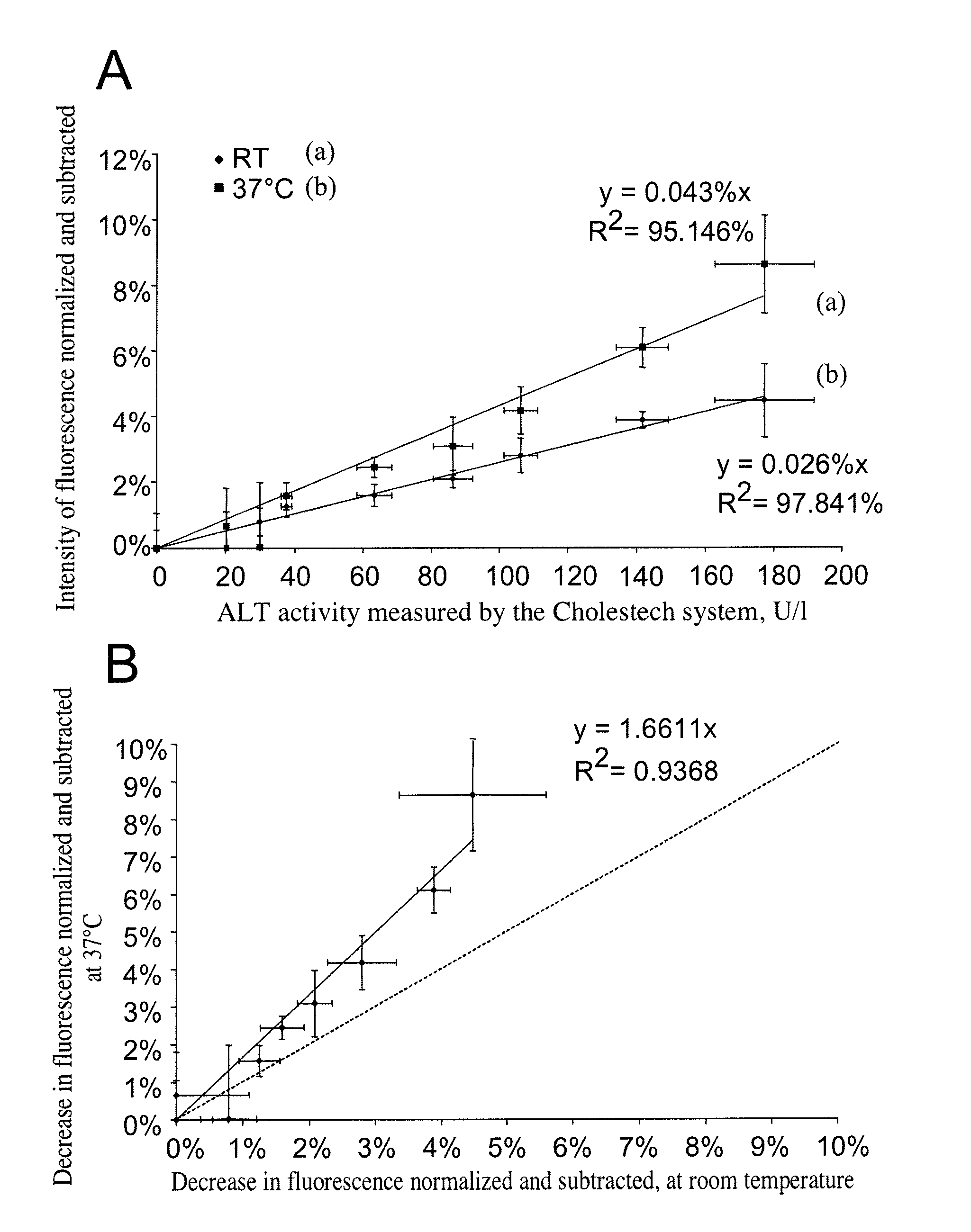
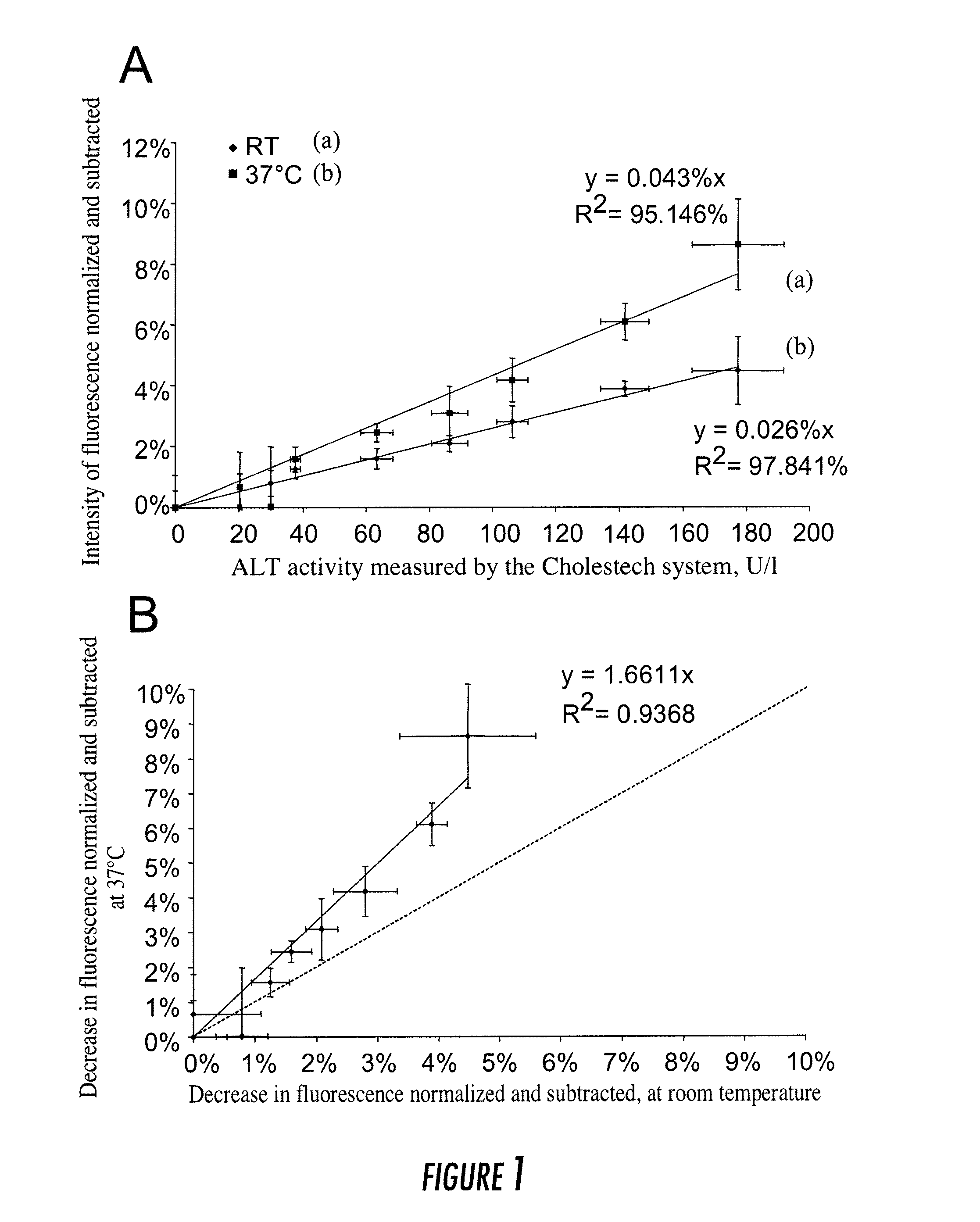
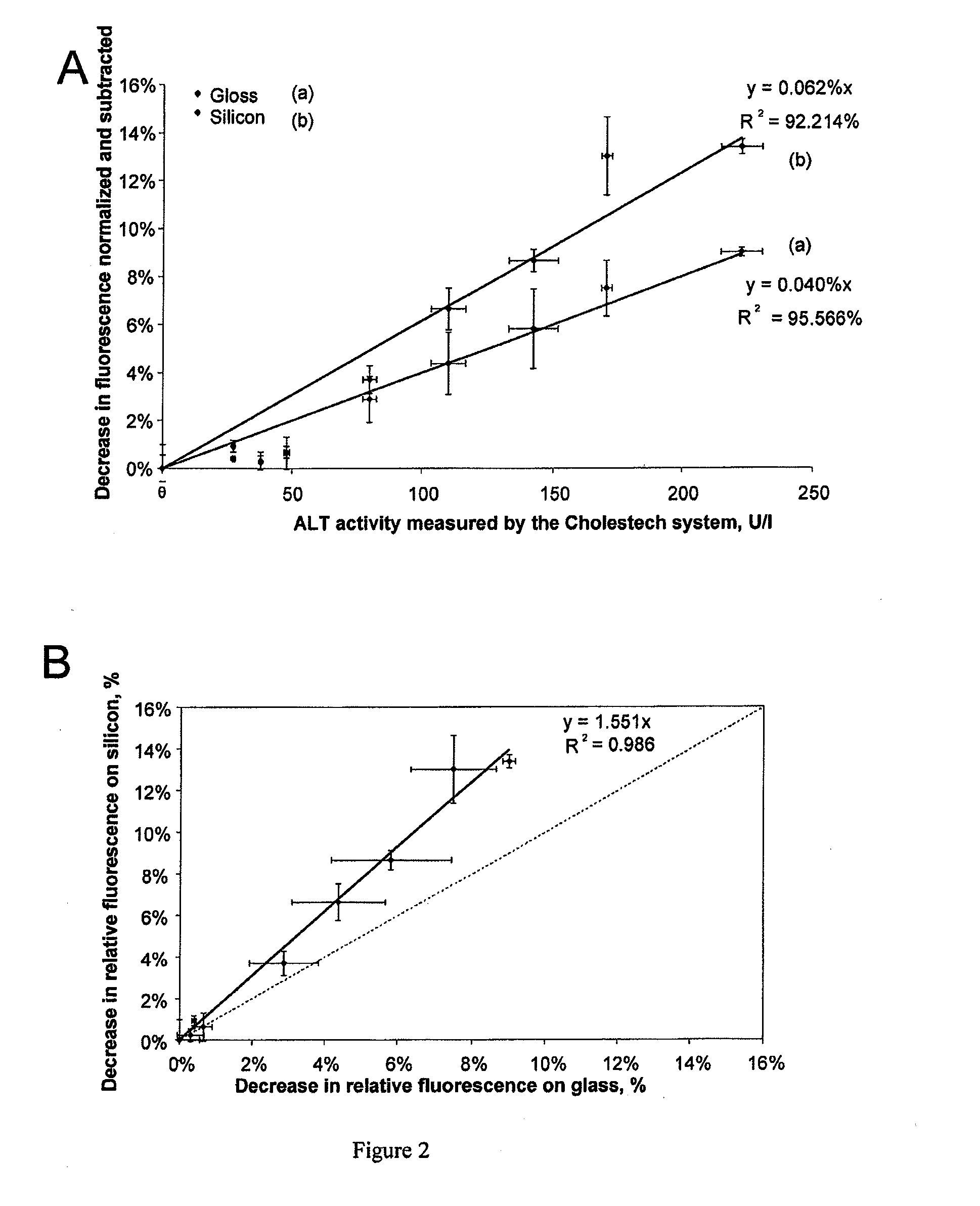
Method for Assaying Plasma Enzymes in Whole Blood
ActiveUS20110104712A1Reduce fluorescenceIncrease valueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPlasma enzymeBlood plasma
The present invention relates to a method for assaying catalytic plasma enzymes, such as transaminases and NADH-dependent enzymes, in a sample of whole blood, by measuring, in a microfluidic chamber, the decrease in the fluorescence of NADH consumed during the enzymatic reactions catalyzed by the NADH-dependent enzymes.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com