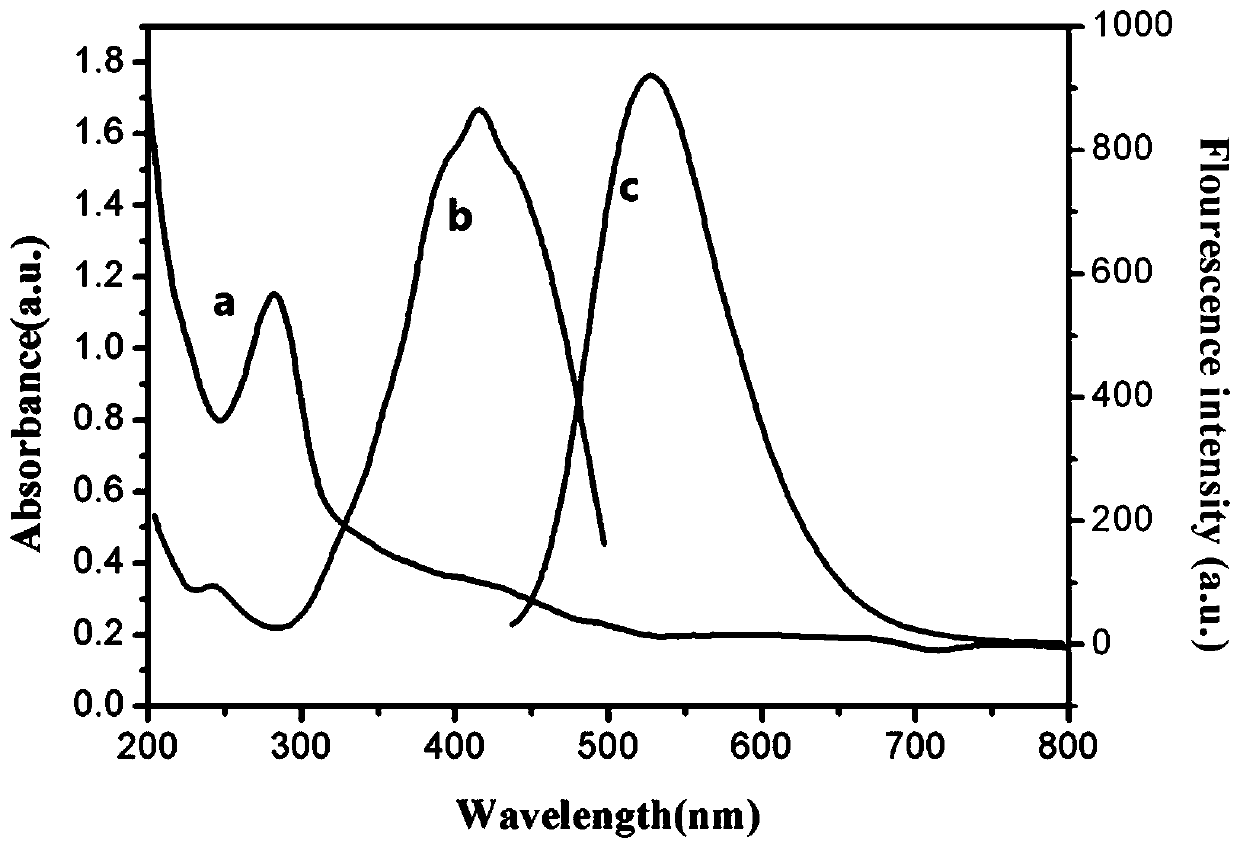
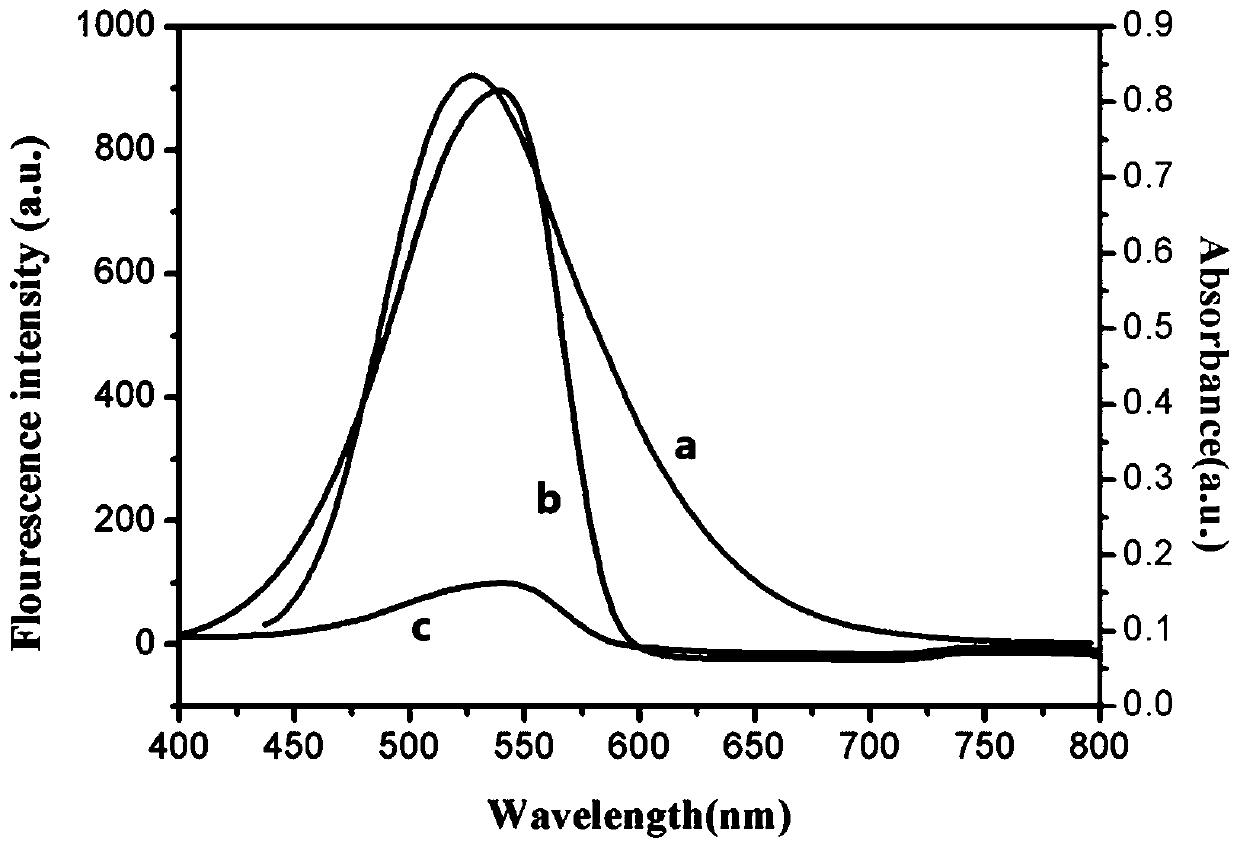
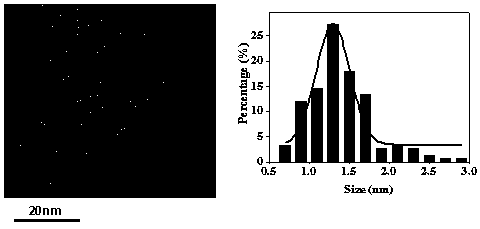
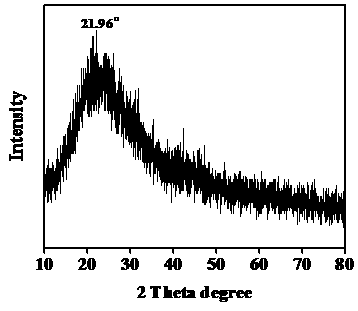
Patents
Literature
118 results about "Live cell imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Live cell imaging is the study of living cells using time-lapse microscopy. It is used by scientists to obtain a better understanding of biological function through the study of cellular dynamics. Live cell imaging was pioneered in first decade of the 20th century. One of the first time-lapse microcinematographic films of cells ever made was made by Julius Ries, showing the fertilization and development of the sea urchin egg. Since then, several microscopy methods have been developed which allow researchers to study living cells in greater detail with less effort. A newer type of imaging utilizing quantum dots have been used as they are shown to be more stable. The development of holotomographic microscopy has disregarded phototoxicity and other staining-derived disadvantages by implementing digital staining based on cells’ refractive index.
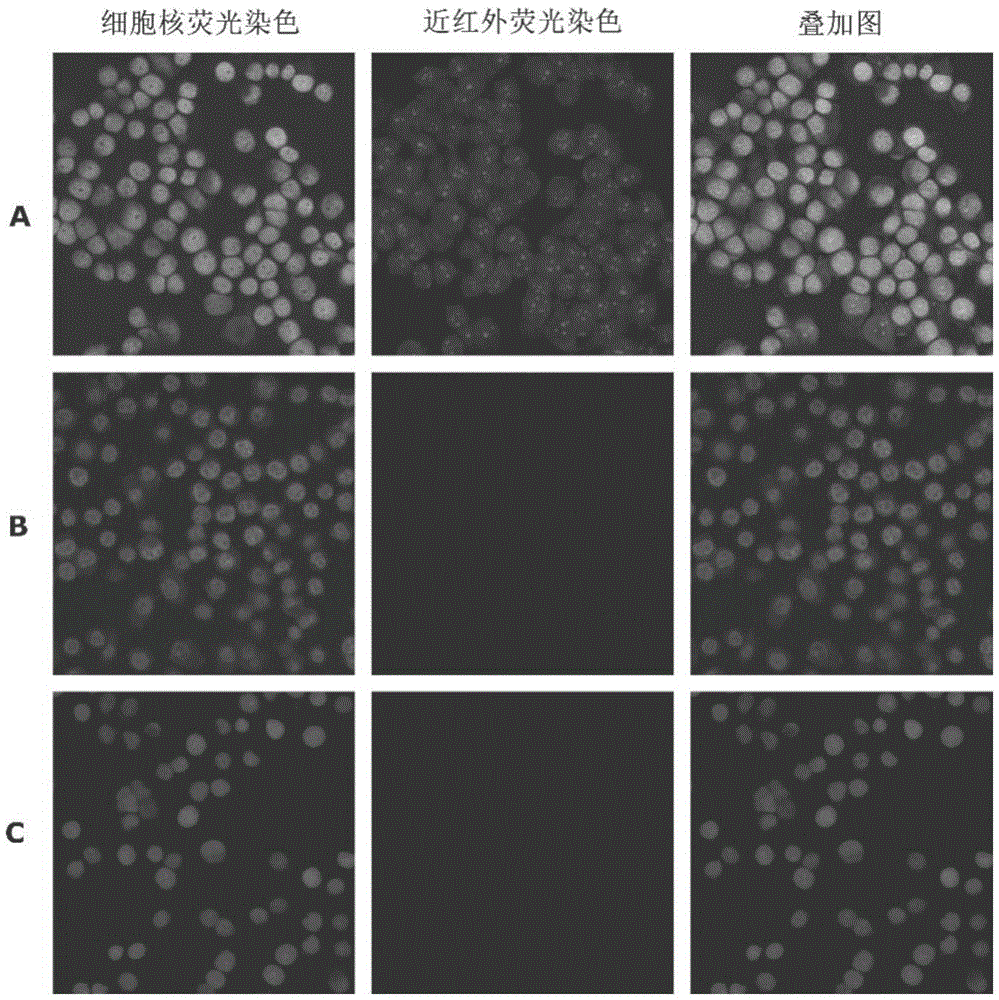
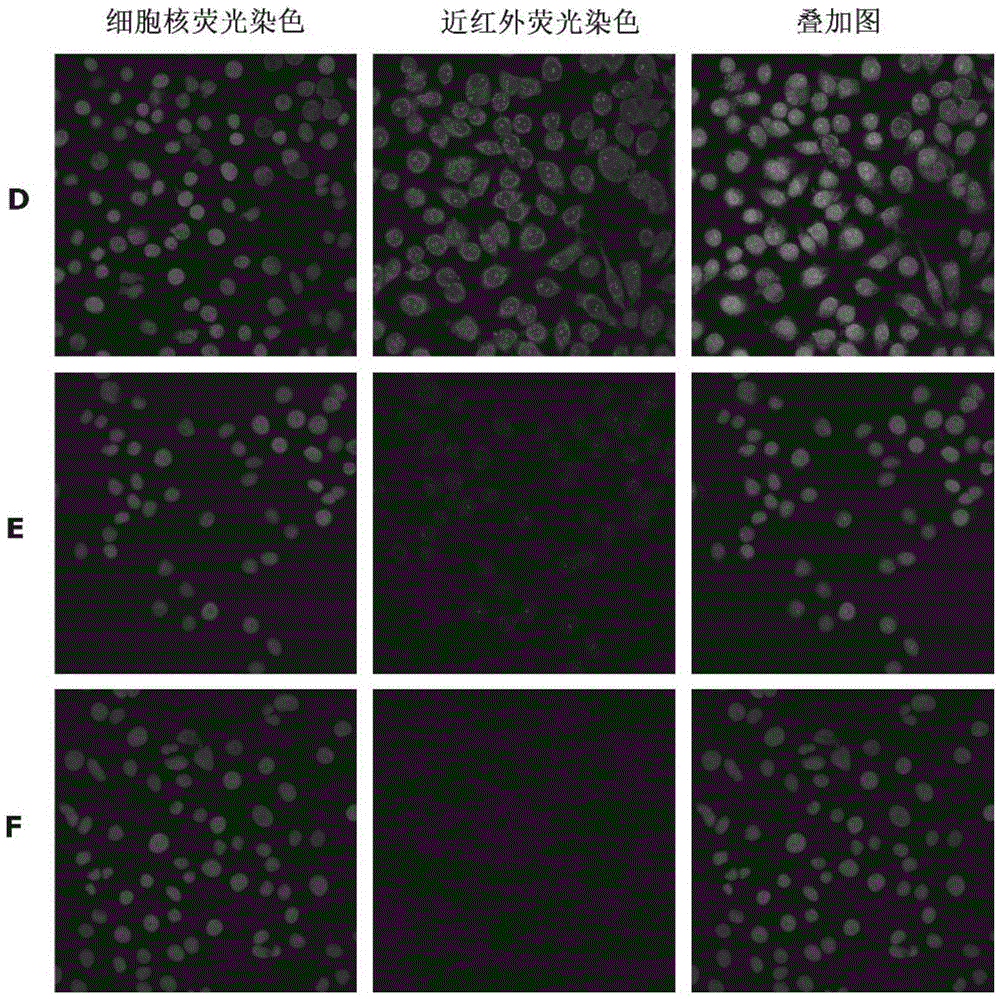
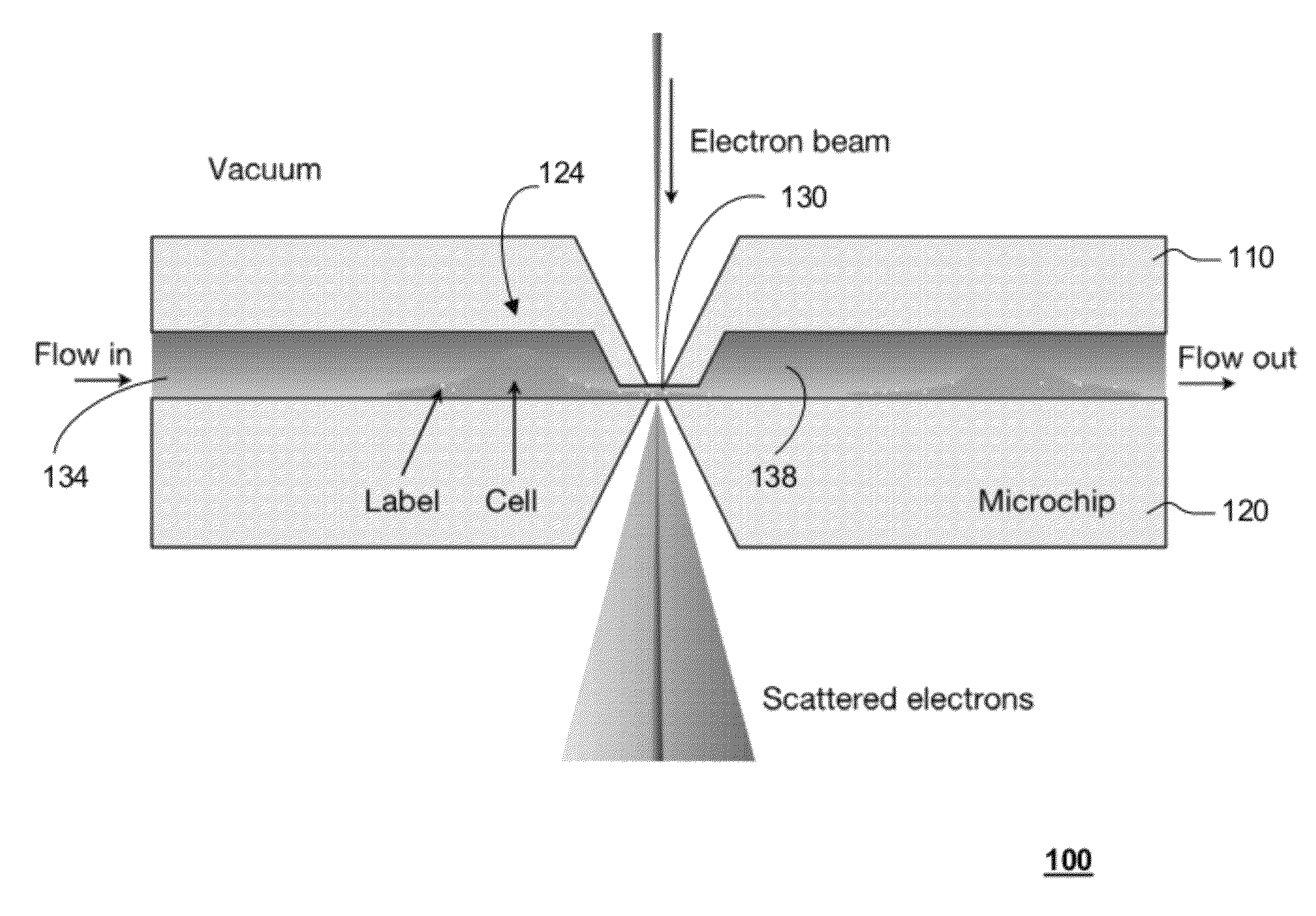
Transmission electron microscopy for imaging live cells
ActiveUS20120120226A1Not to damageReduce intensityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesMedicineLive cell imaging
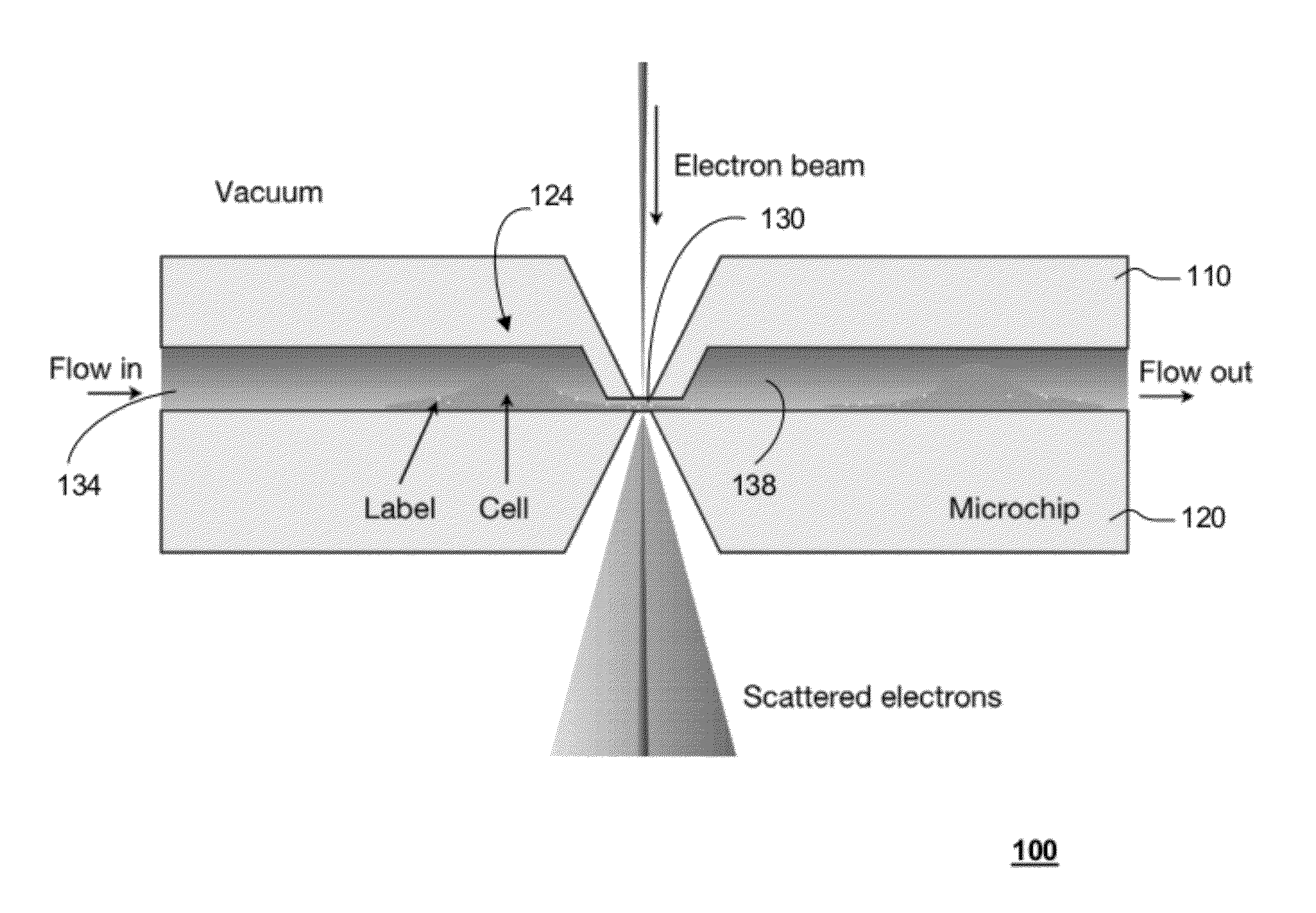
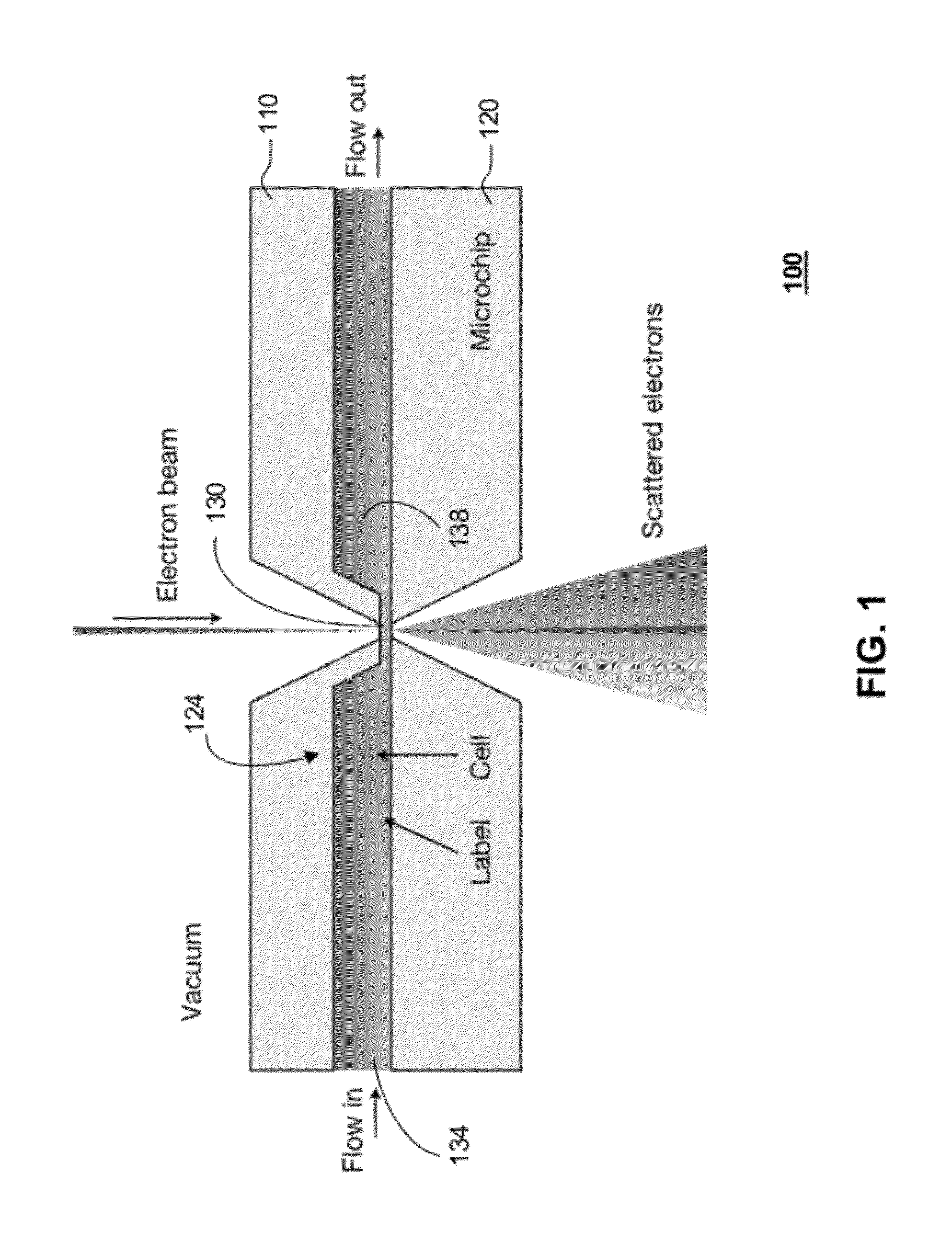
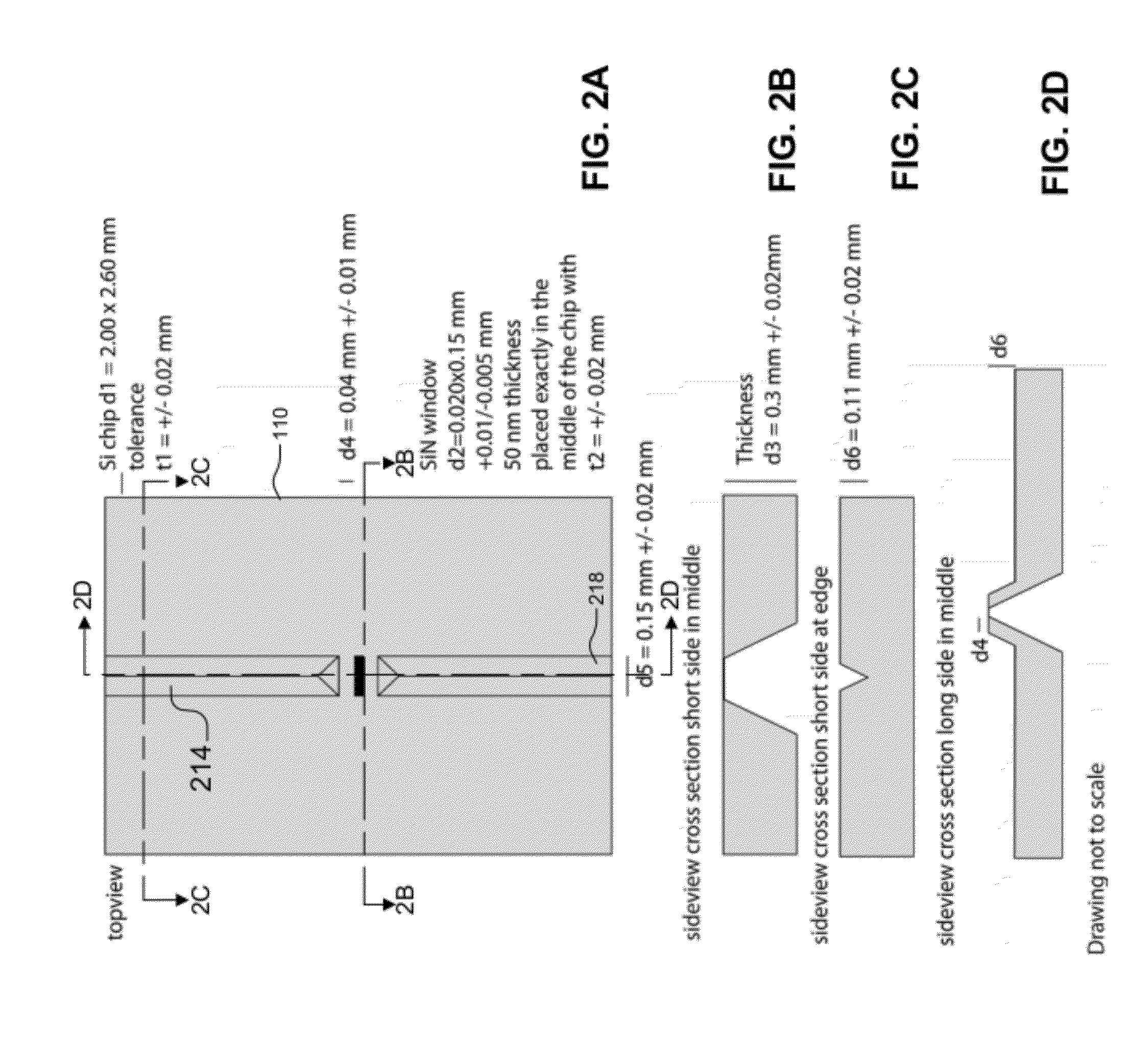
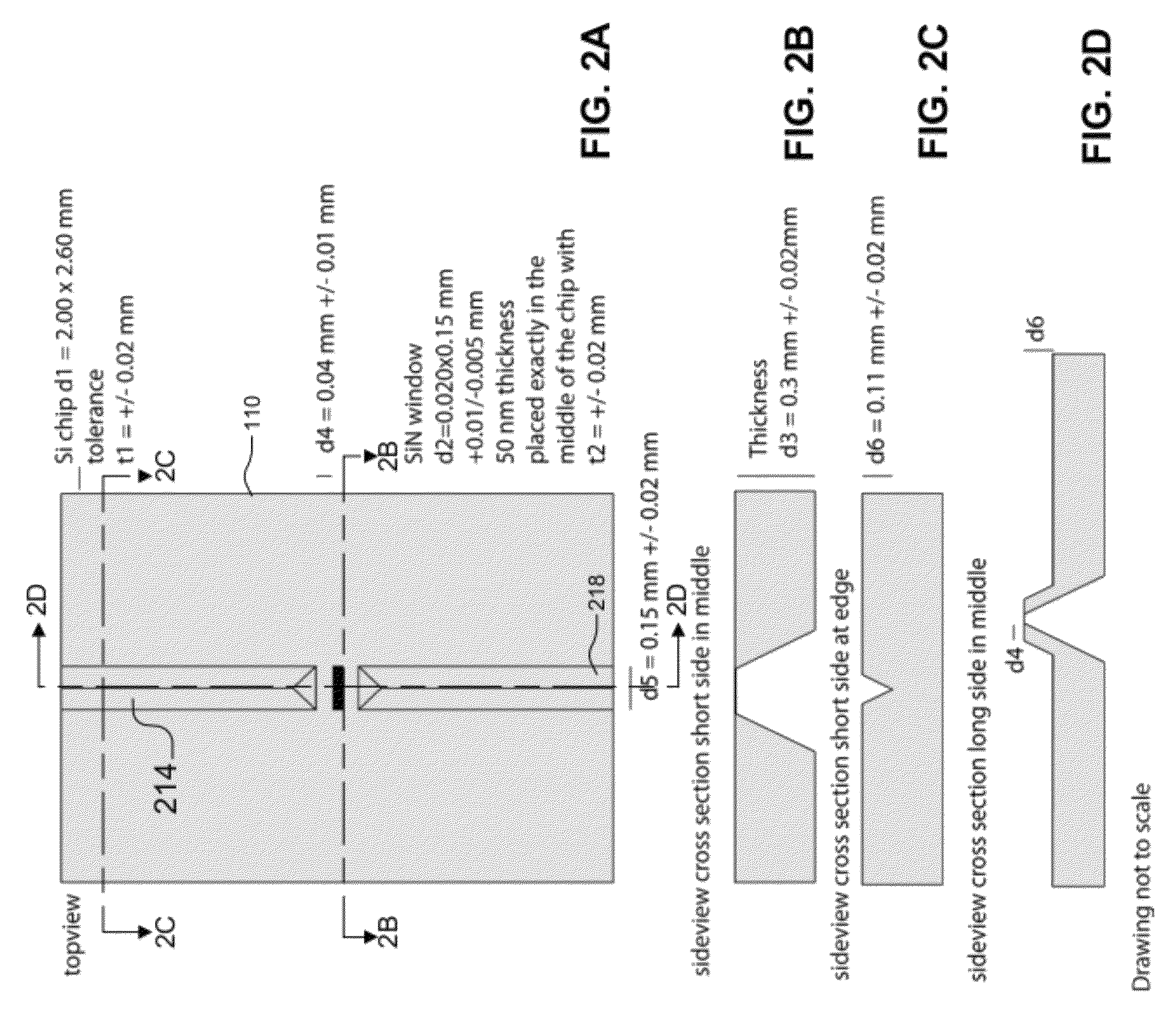
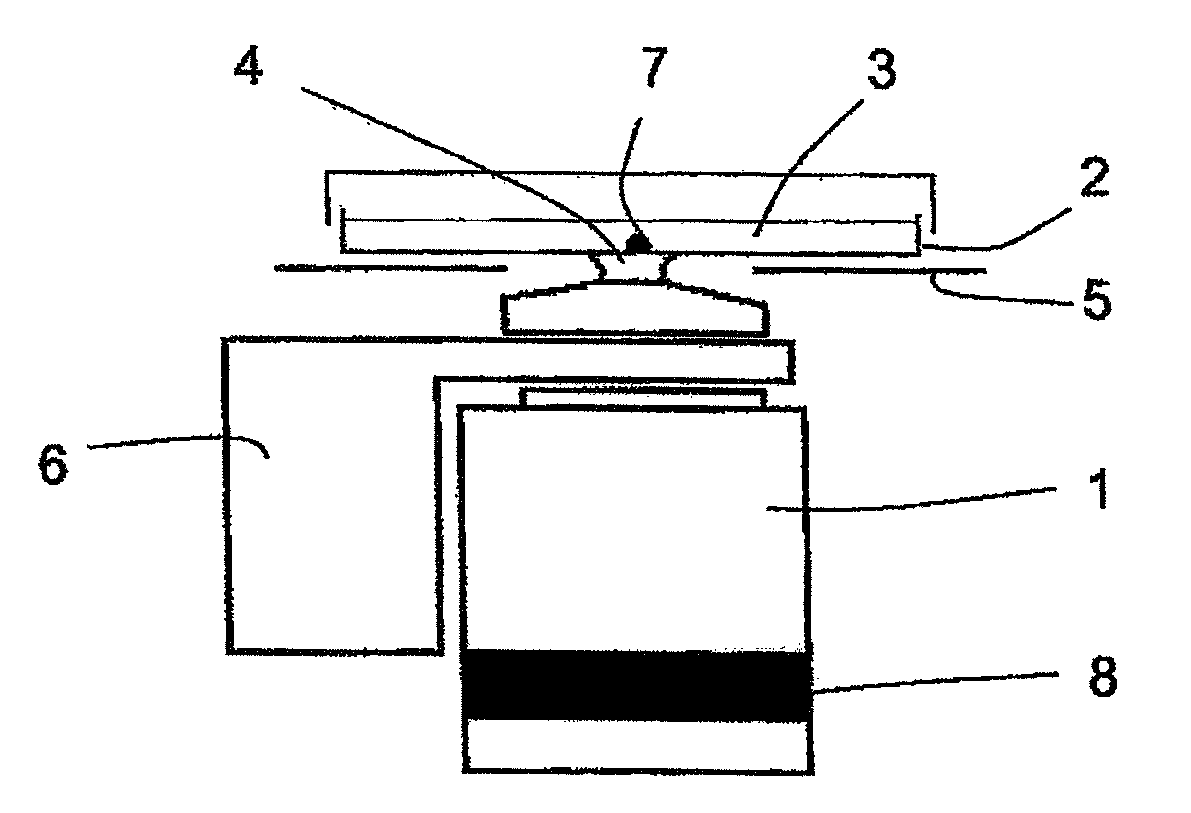
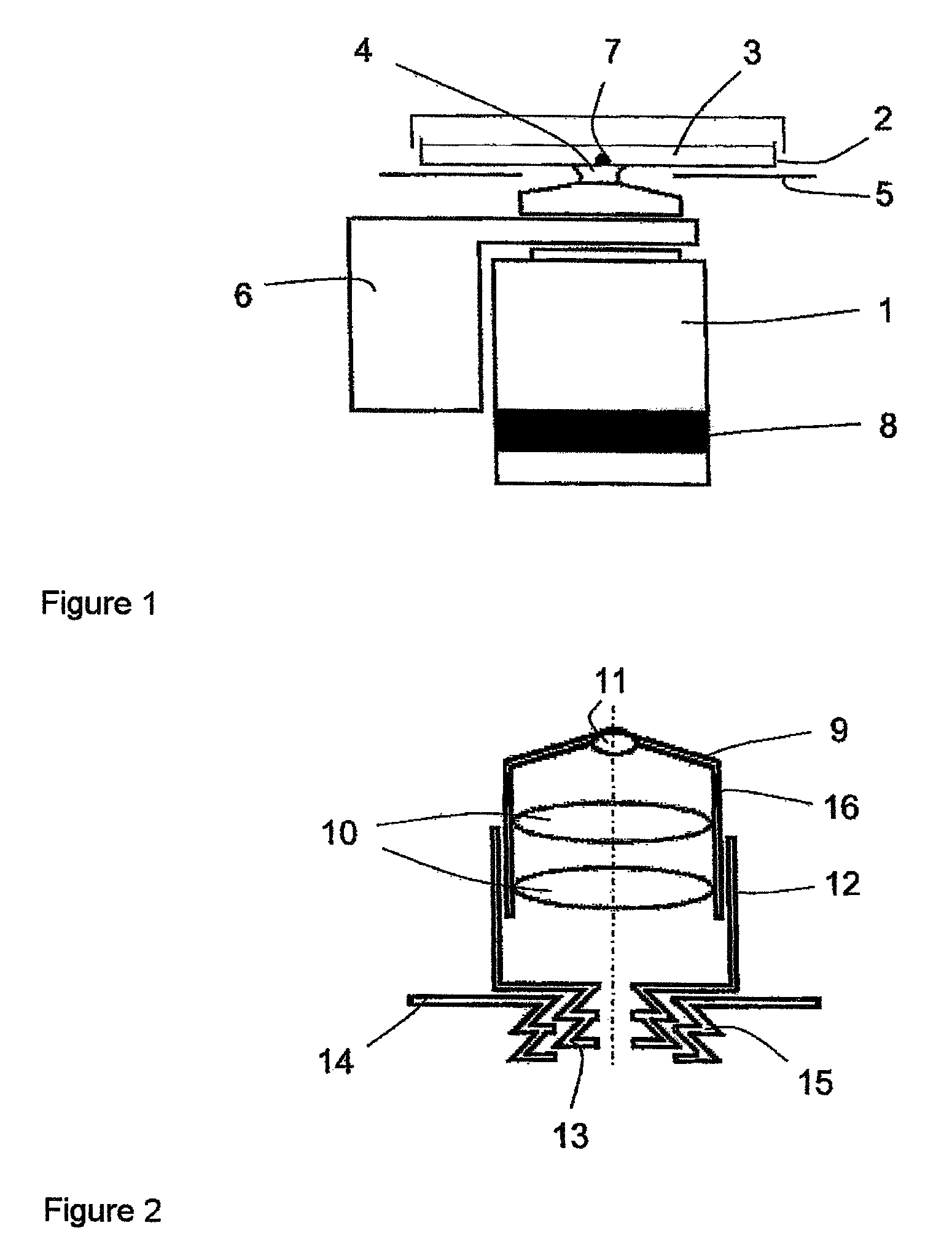
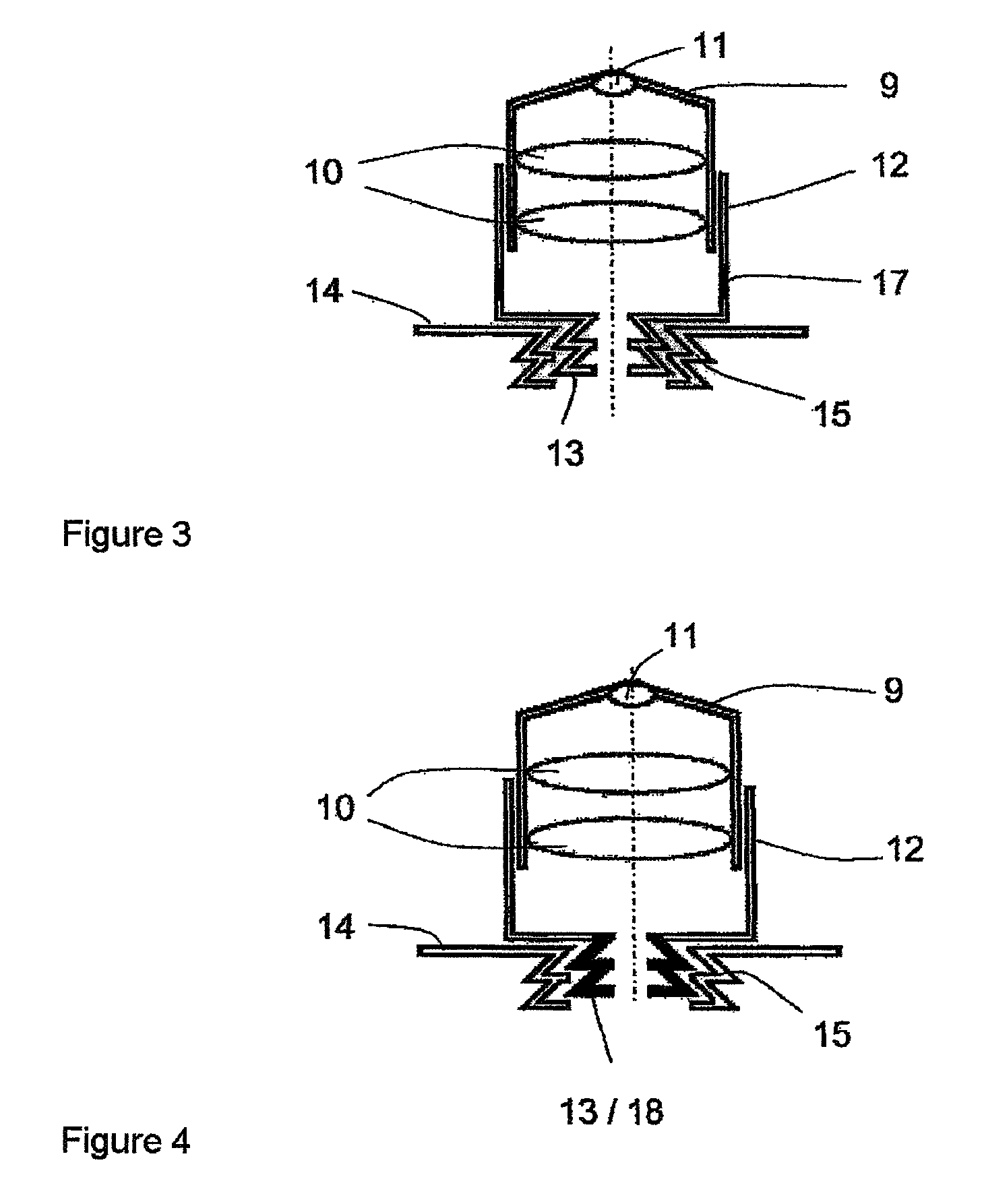
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a microfluidic chamber. In one embodiment, the microfluidic chamber has a first sub-chamber and at least one second sub-chamber. The first sub-chamber has a first window and a second window. Both the first window and the second window are transparent to electrons of certain energies. The second window is positioned substantially parallel and opposite to the first window defining a first volume therebetween. The first window and the second window are separated by a distance that is sufficiently small such that an electron beam that enters from the first window can propagate through the first sub-chamber and exit from the second window. The at least one second sub-chamber is in fluid communication with the first sub-chamber and has a second volume that is greater than the first volume of the first sub-chamber.
Owner:DE JONGE VILIJA +2
Preparation method of carbon quantum dots with adjustable fluorescence colors
InactiveCN103663412AHigh yieldImprove quantum efficiencyNano-carbonFluorescence/phosphorescenceUltraviolet lightsTumor cells
The present invention relates to a preparation method of carbon quantum dots with adjustable fluorescence colors, and belongs to the technical field of nanometer materials. According to method, citric acid or a citrate is adopted as a carbon source, a nitrogen-containing compound is adopted as a nitridation agent, hydrogen peroxide is adopted as an oxidant, a hydrothermal synthesis method is adopted to obtain an aqueous solution of carbon quantum dots emitting blue or green fluorescence under ultraviolet light excitation, reaction conditions are easily controlled, and the method is suitable for scale production. The prepared carbon quantum dots have advantages of adjustable fluorescence color, high yield, high quantum efficiency, good result reproducibility and the like, wherein the product can be directly used for tumor cell labeling and live cell imaging labeling. According to the present invention, only the one reactant is required, the raw materials are easily-available and non-toxic, the production process does not require special protection, the reaction condition is easily controlled, and the obtained carbon quantum dots have advantages of high yield, high quantum efficiency, good result reproducibility and the like; and the method has characteristics of high yield, simple preparation process, low cost, easy scale production and the like.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Preparation and application of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum-dot two-photon fluorescence
InactiveCN104109534AEasy to prepareNo precipitationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceTwo-photon absorptionNitrogen
The invention discloses a nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot, a preparation method thereof and application thereof as a two-photon fluorescence probe to imaging of living cells. The nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot is simple in preparation method, is good in imaging effect when applied to two-photon fluorescence imaging of living cells, and has extremely strong two-photon fluorescence in a relatively wide pH scope, and the two-photon absorption cross section can reach 48000 GM; the nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot is extremely easy to dissolve in water, free of toxicity and good in light stability; and a solution of the nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot has extremely strong stability, is capable of keeping stable within 24 months, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
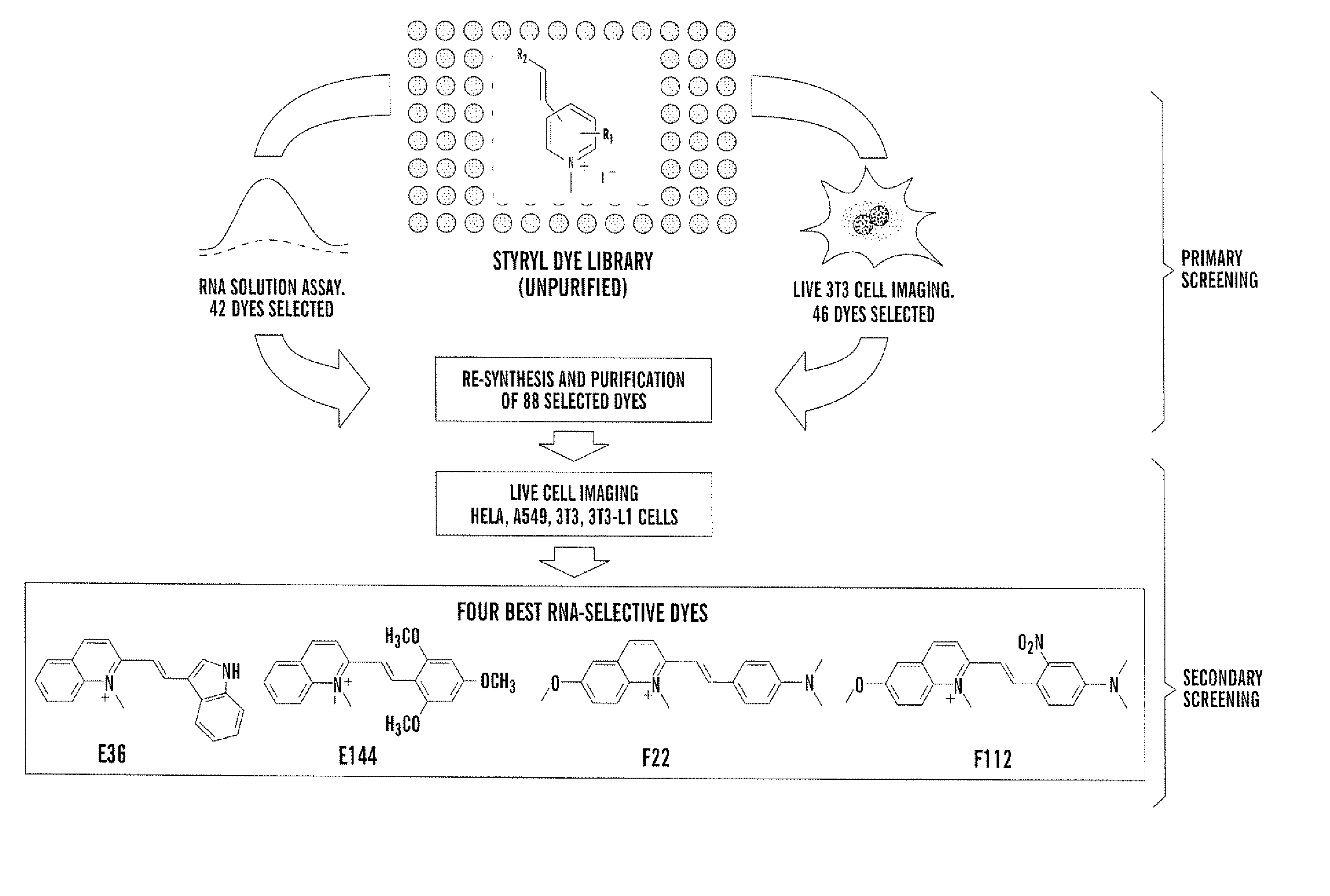
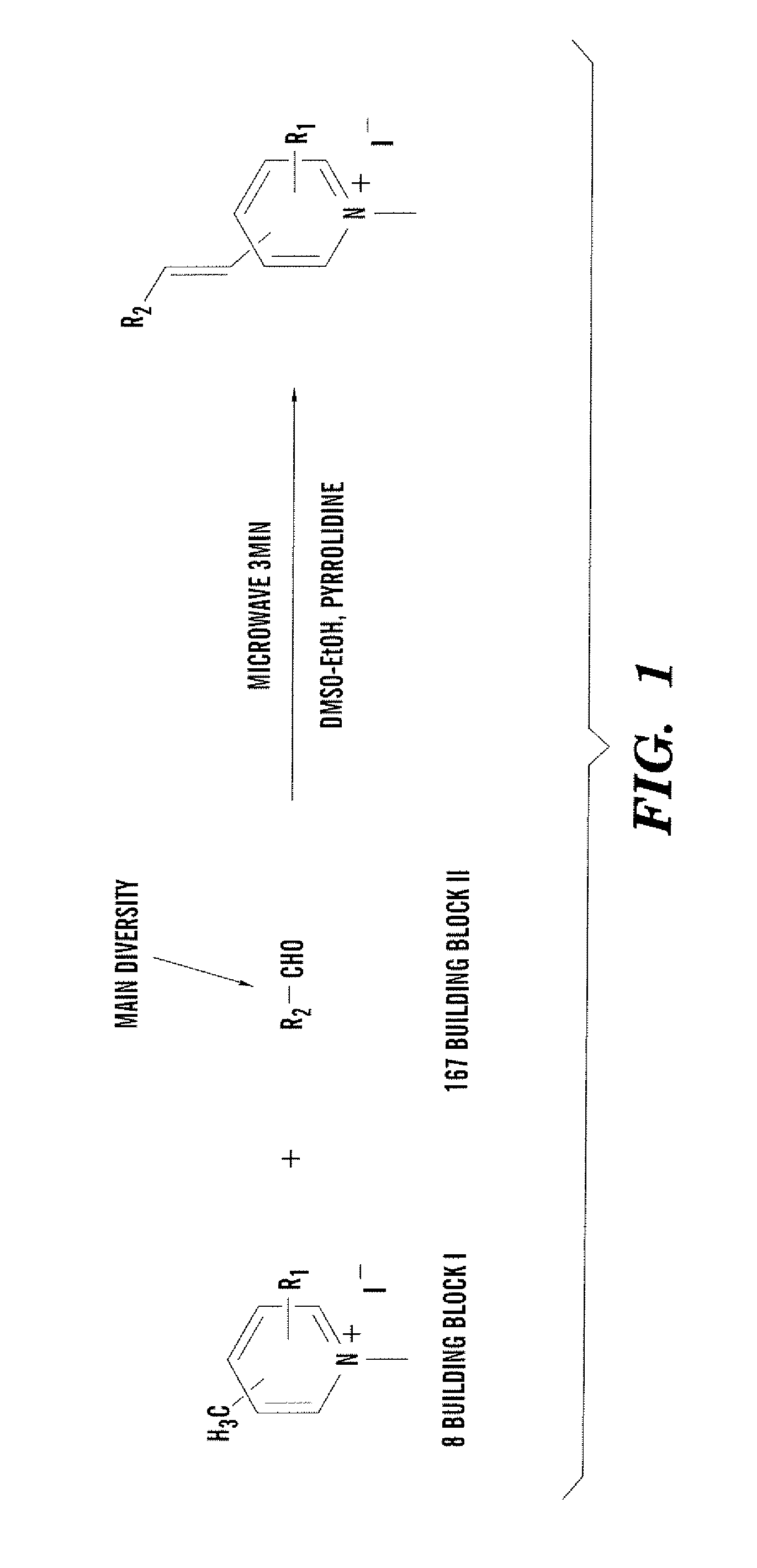
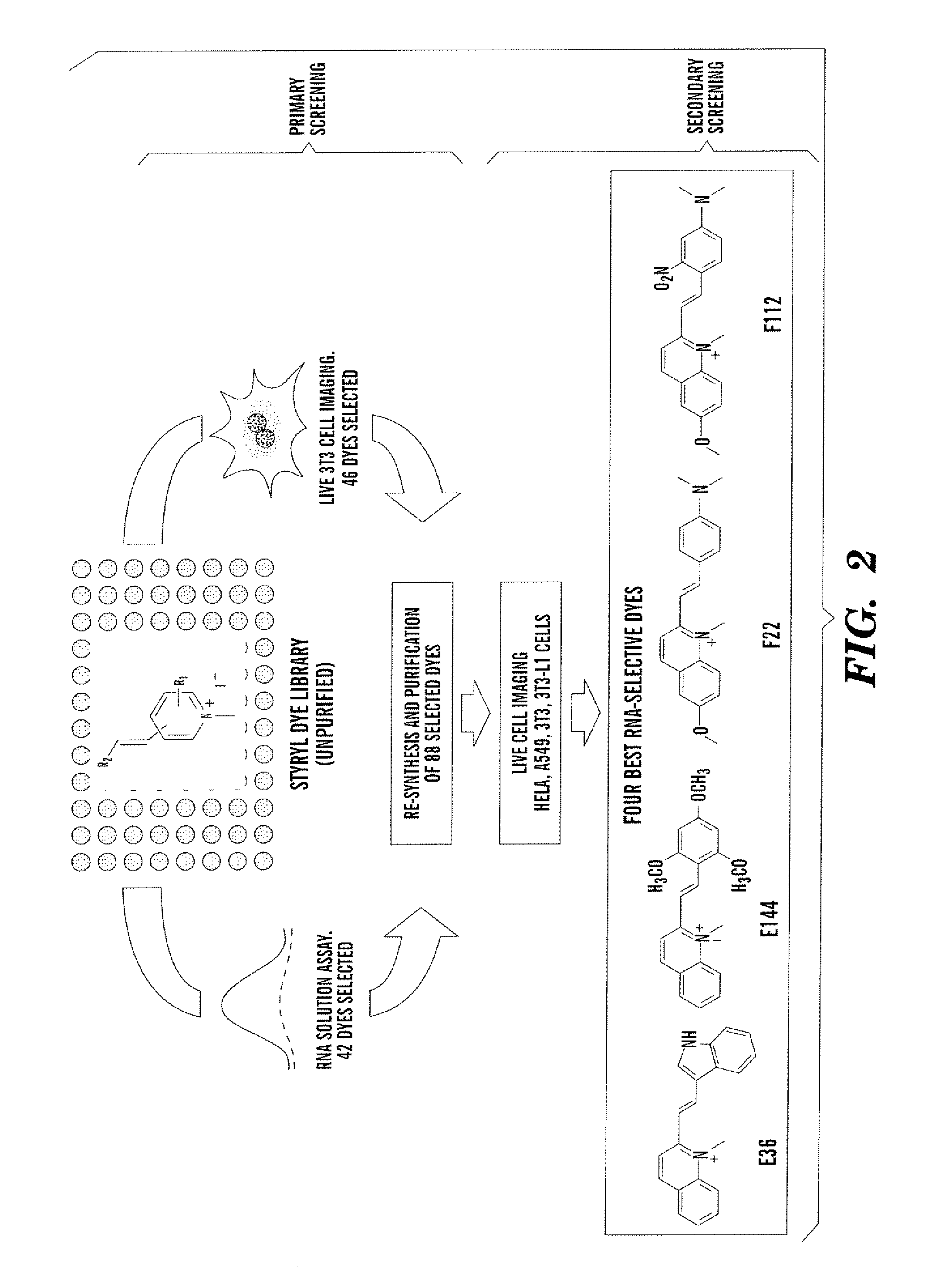
RNA-selective probes for live cell imaging of nuclear structure and function
The present invention is directed to fluorescent compounds and methods of making said compounds that selectively bind to cellular RNA. The fluorescent compounds of the present invention are useful for live cell imaging applications.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Copper ion fluorescence probe and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN103013495ALow toxicitySmall inhibition rateGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceSynthesis methodsMethyl group
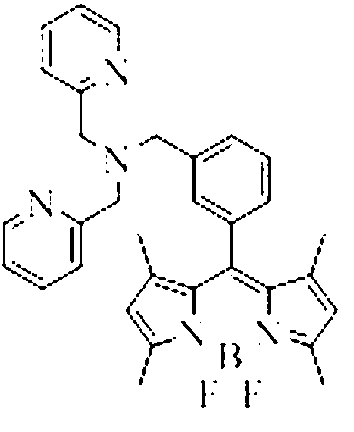
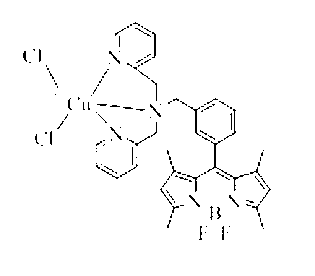
The invention belongs to the technical field of analysis chemistry and relates to a copper ion fluorescence probe and a synthetic method of the copper ion fluorescence probe. The copper ion fluorescence probe disclosed by the invention has a chemical name of 8-[di(2-picolyl)amine-3-benzyl]-4, 4-difluoro-1,3,5,7-tetramethyl-4-boron-3a, 4a-dipyrrole (called BODIPY-DPA for short). The synthetic method of the copper ion fluorescence probe comprises the steps of: mixing 2, 4-dimethylpyrrole with 3-chloromethyl benzoyl chloride, then adding CH2Cl2 into the mixture, then adding boron trifluoride for reaction, and then orderly adding di(2-picoly)amine and triethylamine for reaction, at last, obtaining the copper ion fluorescence probe. The BODIPY-DPA shows light yellow in the solution, has high fluorescence emission at 590 nm, can enter HepG-2 to show green fluorescence imaging, and has a lowest limit of detection of 2.78 muM on copper ions in water solution. The copper ion fluorescence probe prepared by the synthetic method is characterized in low toxicity and the inhibition rate of 100 muM of HepG-2 is smaller than 10%, so the copper ion fluorescence probe can be used for detection of living cell imaging and copper irons in the cell, and has a very good application prospect in environment monitoring and detection of copper irons in a biologic system.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Conjugated chain functional benzoindole hematocyanine dye and application
InactiveCN109370247AThe synthesis steps are simpleEasy to purifyMethine/polymethine dyesEnergy modified materialsFunctional activityIn vivo
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic chemistry and discloses a conjugated chain functional benzoindole hematocyanine dye and an application. The stability of the novel hematocyaninedye is obviously superior to that of an existing cyanine fluorescent probe, and the novel hematocyanine dye has the multiple functional activity such as near infrared fluorescence and tumor mitochondria targeted accumulation and photo-thermal and photo-power synergic treatment of killing tumor cells. Applied as the near infrared fluorescence probe in living cell imaging research and living body infrared optical molecular imaging, a precise and efficient photo-thermal and photo-power antitumor effect is achieved synchronously. The dye can be applied to near infrared in vivo optical imaging andphoto-sound imaging of tumors, is applied to optical assisted operation navigation, and has an efficient antitumor function. The dye not only can develop a target tissue in real time, but also kill tumor cells specifically. The preparation method of the benzoindole hematocyanine dye is mild in reaction condition, simple in step and easy to operate and low in raw material cost, and is easy to purify and relatively high in yield.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Gold-as-core silver-as-shell ''Raman silent zone'' substrate and preparation method and application thereof
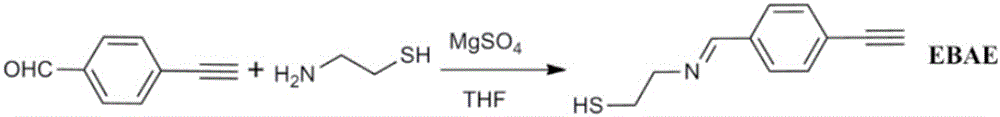
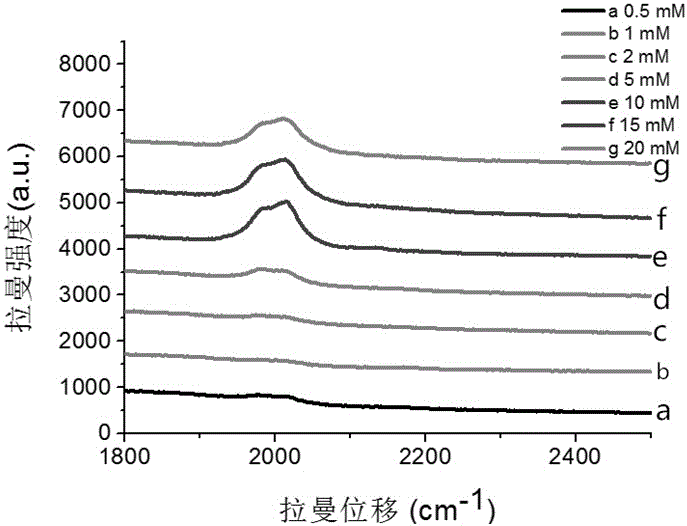
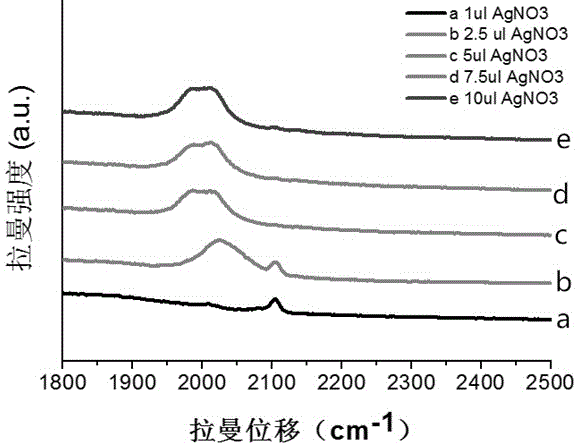
ActiveCN106248648AEnhancement effect is goodKeep aliveRaman scatteringRaman imagingBovine serum albumin
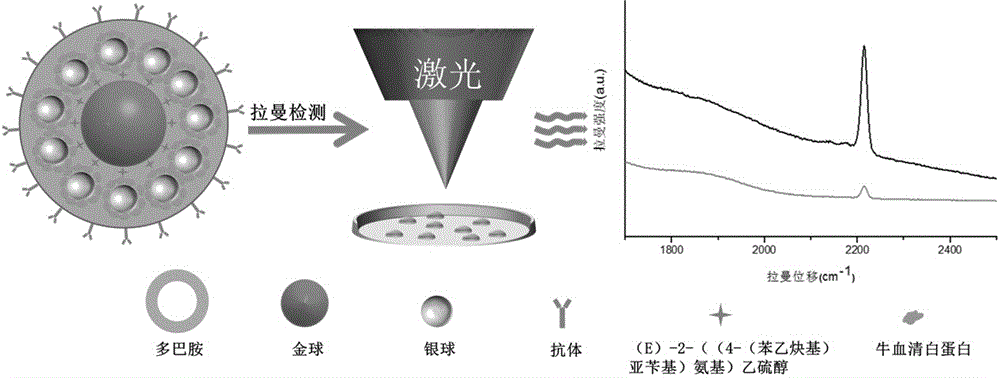
The invention belongs to the technical field of separation and analysis of biological macromolecules, and particularly relates to a gold-as-core silver-as-shell ''Raman silent zone'' surface enhancement Raman scattering substrate and a preparation method and application thereof in Raman imaging in living cells. The preparation process is as follows: gold nanoparticles containing ''Raman silent zone'' probe molecules are in situ synthesized by hydrothermal method, the gold nanoparticles are re-dissolved in a borax solution, and ''Raman silent zone'' molecules (E) 2 ((4 (phenyl ethynyl) benzylidene) amino) ethyl mercaptan are added; ascorbic acid and silver nitrate are added for in situ reduction of silver nanoparticles; bovine serum albumin is added, and finally through dopamine self polymerization, an antibody is connected to the material for preparing the ''Raman silent zone'' surface enhancement Raman scattering substrate capable of specifically recognizing tumor cells. Experiments show that the ''Raman silent zone'' surface enhancement Raman scattering substrate has a prominent enhancing effect on a probe signal, the ''Raman silent zone'' surface enhancement Raman scattering substrate material is free of template, low-cost and low-toxicity, is used in imaging in living cells, and is novel, convenient, practical and efficient.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Stimulated emission loss fluorescent lifetime super-resolution imaging device
InactiveCN109211871ABig life changeSmall lifetime changeFluorescence/phosphorescenceSynchronous controlLive cell imaging
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Optical microscopy and its use in the study of cells
InactiveUS6929934B1Minimize damageExposure of light can be limitedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIon currentLive cell imaging
The present invention pertains to an apparatus for imaging an object, comprising a probe via which an assay component may be delivered; a sensor to detect ion current; and means for controlling the position of the probe relative to the object in response to the ion current. Such apparatus can be used to image live cells, without affecting them, in solution, e.g., using light, wherein the distance between probe and cell is less than the wavelength of light.
Owner:IONSCOPE
Click chemistry-based tumor marker probe, preparation method and application
InactiveCN105419781AImprove bioavailabilityHigh monitoring sensitivityDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionPeptide preparation methodsBiological studiesMolecular imaging
The invention discloses a click chemistry-based tumor marker probe, a preparation method and application. The tumor marker probe comprising a click reaction module with a tumor-specific factor and a click reaction module with a fluorescent marker is designed using reaction characteristics of click chemistry, such as high selectivity, high efficiency and high speed, and the two click reaction modules may be combined quickly through click reaction. The tumor marker probe is efficient in quickly combining to tumor tissues or cells, the life of the probe in viable tumor tissues and its detection time are effectively prolonged, the problem that an existing probe has poor specificity is effectively solved, and a new direction is provided for the in-vivo optical molecular imaging and live cell imaging of tumors as well as further targeted diagnosis and biological study of tumors.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
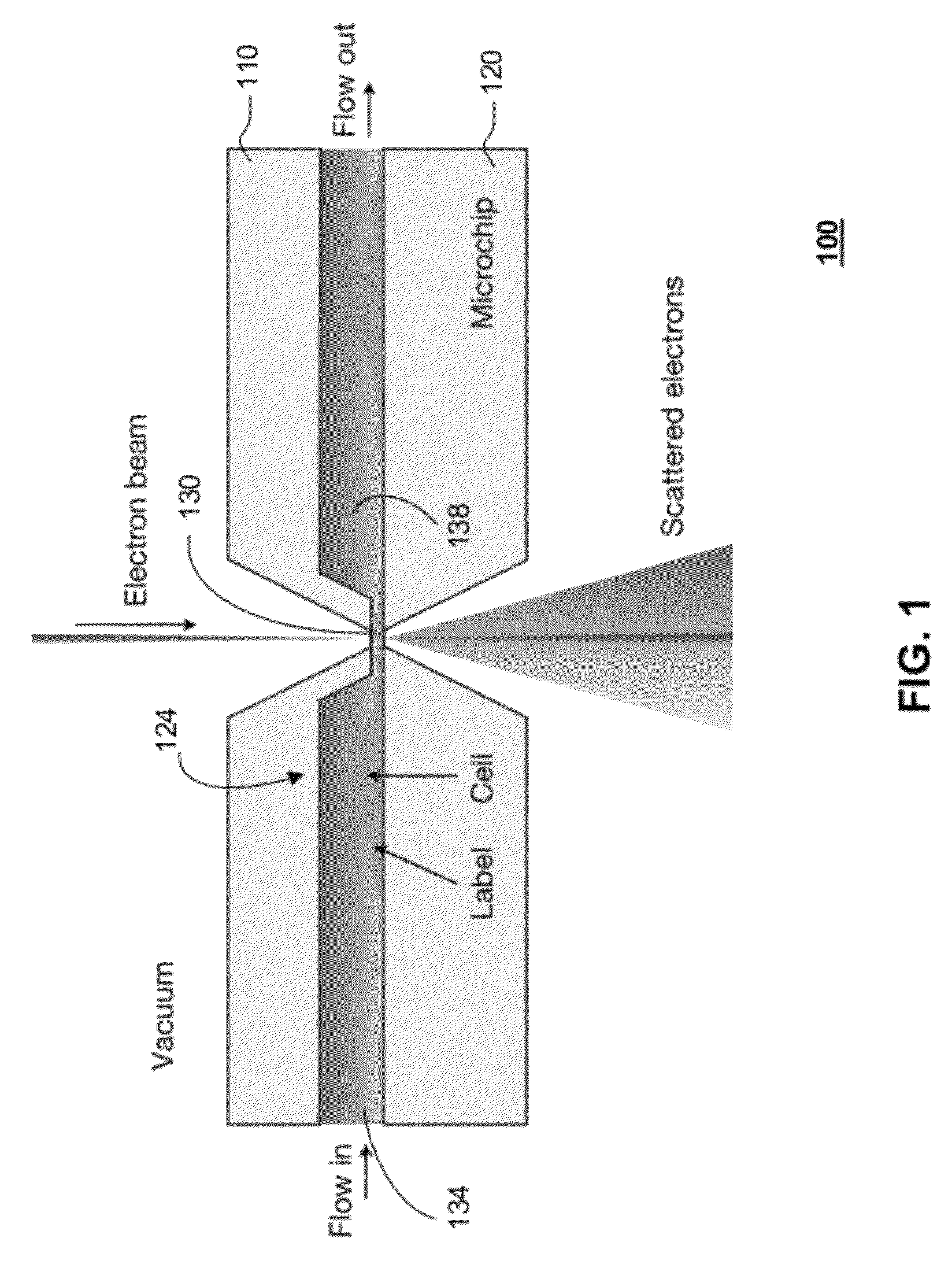
Transmission electron microscopy for imaging live cells
ActiveUS9207196B2Not to damageReduce intensityElectric discharge tubesLaboratory glasswaresEnergy filtered transmission electron microscopyLiving cell
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a microfluidic chamber. In one embodiment, the microfluidic chamber has a first sub-chamber and at least one second sub-chamber. The first sub-chamber has a first window and a second window. Both the first window and the second window are transparent to electrons of certain energies. The second window is positioned substantially parallel and opposite to the first window defining a first volume therebetween. The first window and the second window are separated by a distance that is sufficiently small such that an electron beam that enters from the first window can propagate through the first sub-chamber and exit from the second window. The at least one second sub-chamber is in fluid communication with the first sub-chamber and has a second volume that is greater than the first volume of the first sub-chamber.
Owner:DE JONGE VILIJA +2
Method for detecting content of free tryptophan in tryptophan and serum sample
ActiveCN102914527AEasy to distinguishEasy to synthesizeGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceSomatic cellCell
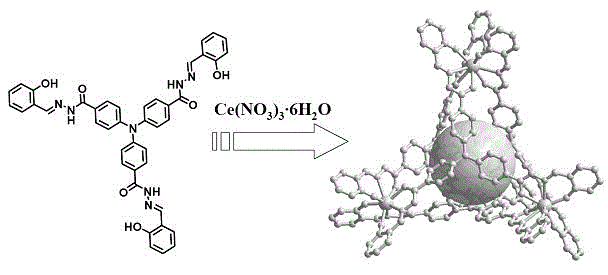
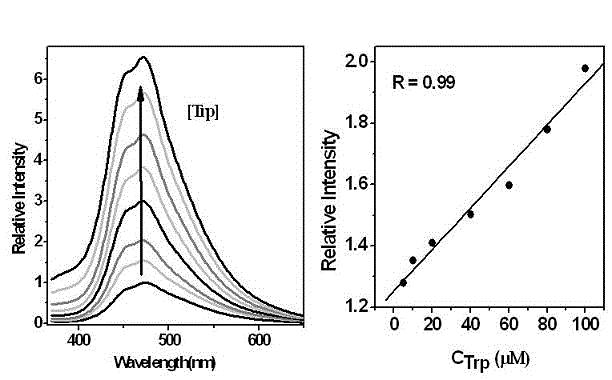
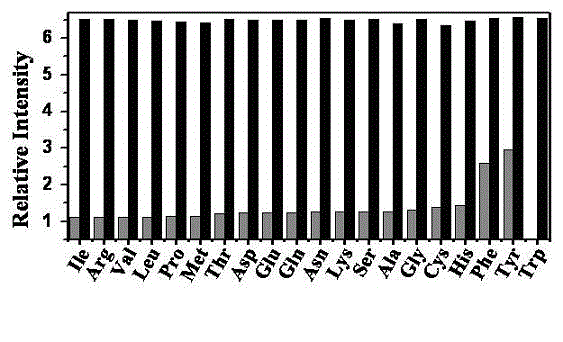
The invention provides a method for detecting content of free tryptophan in a tryptophan and serum sample, which relates to a method for detecting the content of free tryptophan. The invention provides a method for identifying and detecting free tryptophan in the natural amino acid and serum sample by using a metal organic tetrahedral compound based on fluorescence functionalization and for achieving biological cell imaging application. In the method, a tetrahedral compound, which is obtained by self-assembling a three-tooth ligand constructed by using triphenylamine as a parent body and cerous nitrate, is used as a material; the material can high-selectively identify the tryptophan in 20 types of natural amino acid, and a response range is 0-0.1 mM; in addition, the material can also effectively distinguish free and combined tryptophan, so that the content of free tryptophan in the serum sample is detected and the application on living cell imaging is also preferably achieved. Therefore, the material provides a method for testing the content of free tryptophan in the serum sample, and the method has the advantages of high sensitivity and simplicity in operation.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
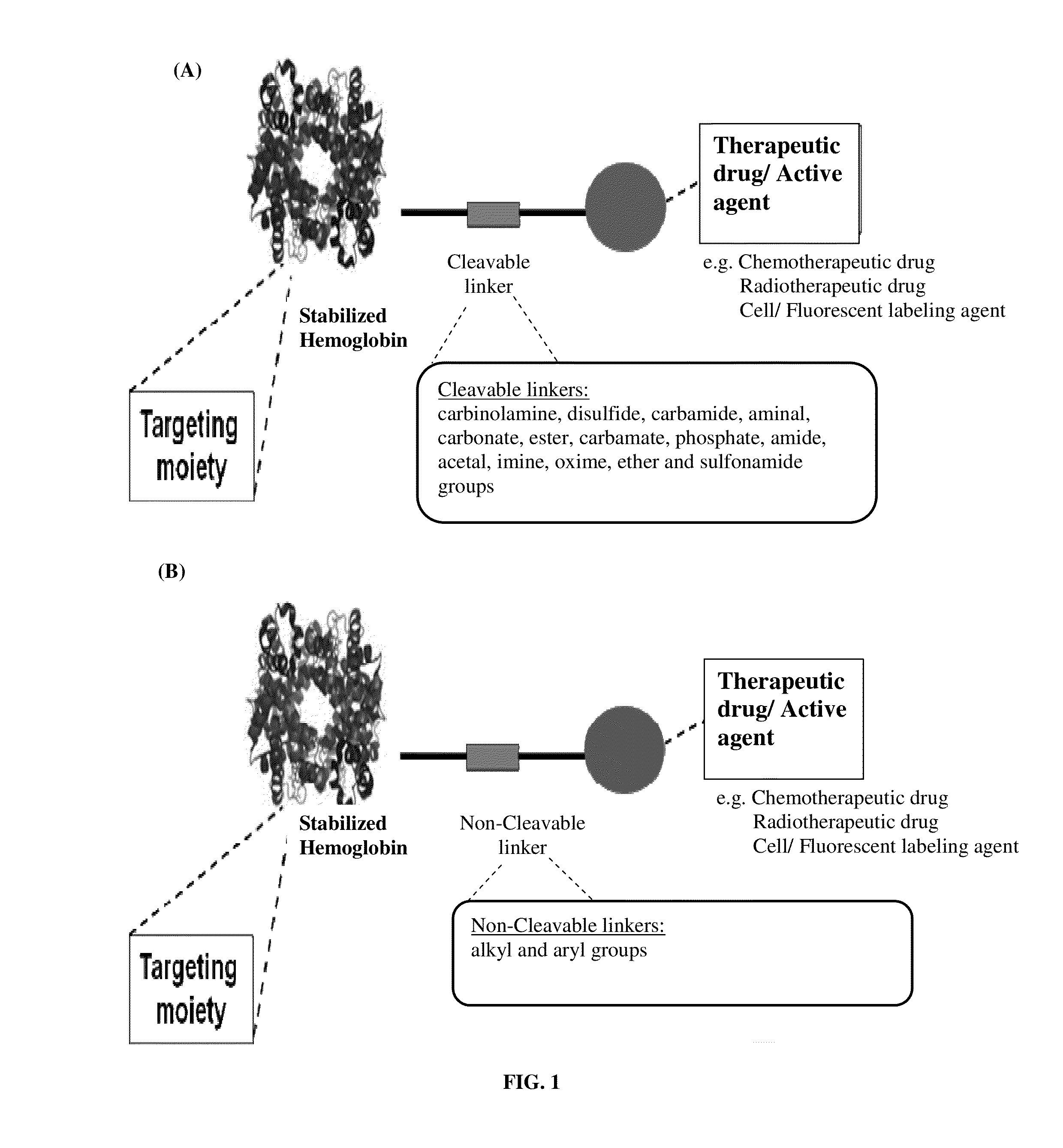
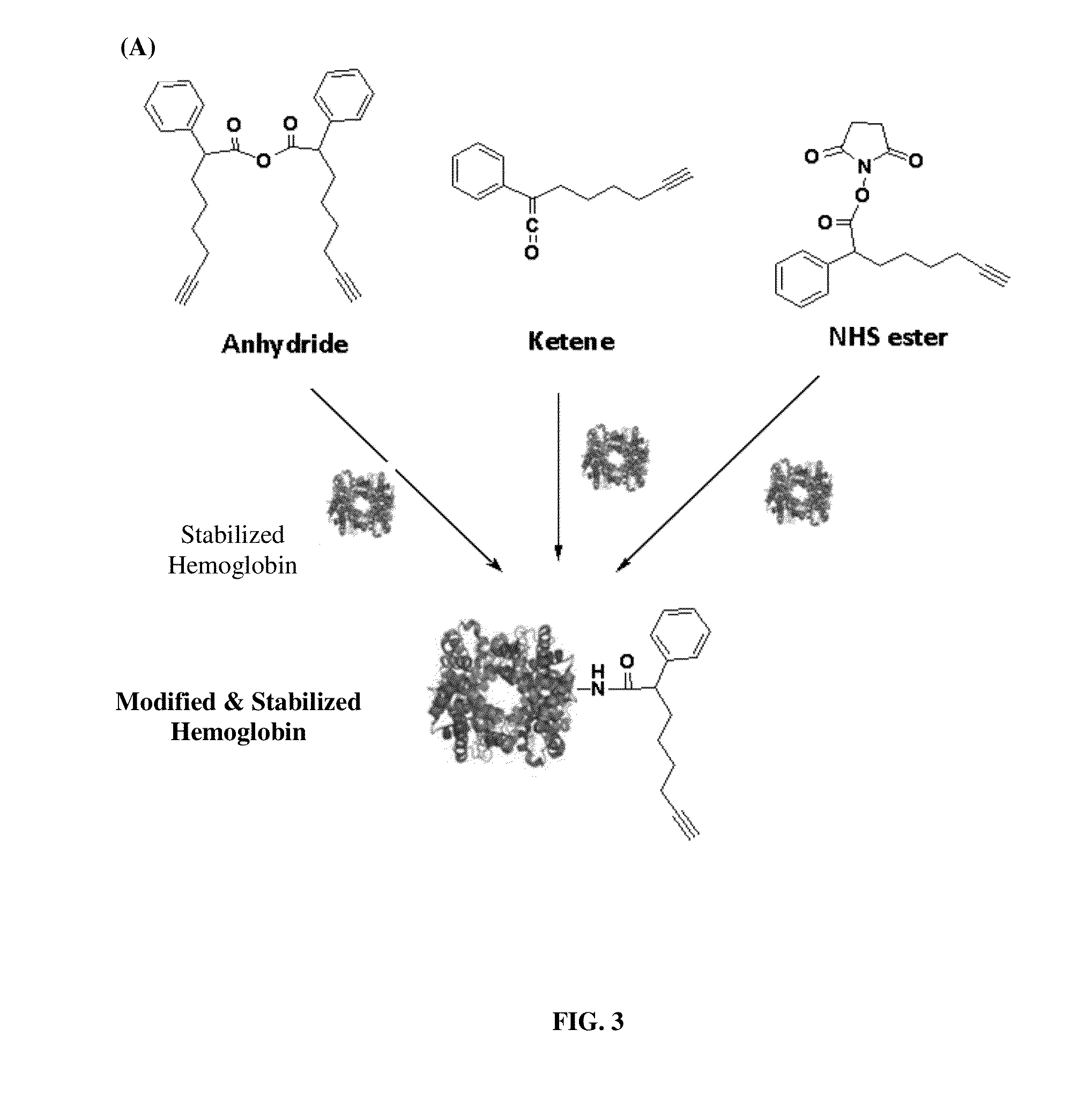
Pharmaceutical composition comprising modified hemoglobin-based therapeutic agent for cancer targeting treatment and diagnostic imaging
ActiveUS20140335018A1Synergistic effectEfficient killingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsLymphatic SpreadCancer targeting
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition containing hemoglobin-based therapeutic agent for treating cancer. The hemoglobin moiety can target cancer cells and the therapeutic moiety (i.e. active agent / therapeutic drug) can kill the cancer cells efficiently. The hemoglobin-based therapeutic agent used in the present invention can be used in the treatment of various cancers such as pancreatic cancer, leukemia, head and neck cancer, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, liver cancer, nasopharyngeal cancer, esophageal cancer, prostate cancer, stomach cancer and brain cancer. The composition can be used alone or in combination with other therapeutic agent(s) such as chemotherapeutic agent to give a synergistic effect on cancer treatment, inhibiting metastasis and / or reducing recurrence. The presently claimed hemoglobin-based 5FU-two-dye conjugate and / or hemoglobin-based 5FU-one-dye conjugate can also be used in live-cell imaging and diagnostic imaging.
Owner:VISION GLOBAL HLDG
Material for constructing temperature-responsive aggregates in cells and preparation method and application of material
ActiveCN107137724AOrganic active ingredientsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsLive cell imagingLiving cell
The invention provides a material for constructing temperature-responsive aggregates in cells and a preparation method and application of the material. The material for constructing the temperature-responsive aggregates in the cells comprises a polypeptide sequence composed of responsive polypeptide and cell-penetrating peptide, and a temperature-sensitive polymer, wherein the responsive polypeptide of the polypeptide sequence is connected to the temperature-sensitive polymer. The material for constructing the temperature-responsive aggregates in the cells enters the cells with the assistance of the cell-penetrating peptide and responds to specific stimulating signals in the cells after entering the cells, the hydrophilic polypeptide is removed, the phase transition temperature of the material is changed into the physiological temperature of 37 DEG C or below, collapse and aggregation of the material are caused finally, and the nano-aggregates are formed. With the strategy, long-time retention of the material in the cells can be achieved, and the material has good application prospects in live cell imaging or high-retention-rate drug delivery.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
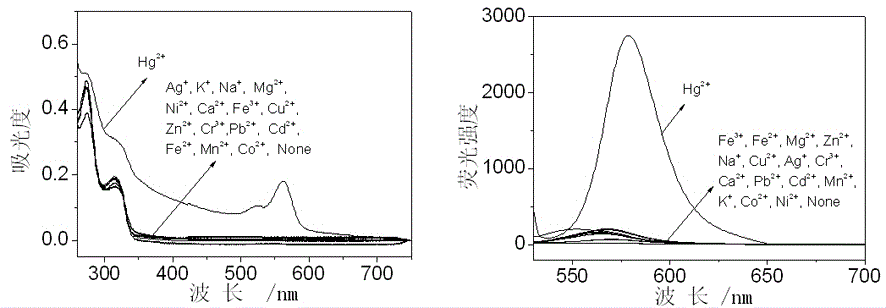
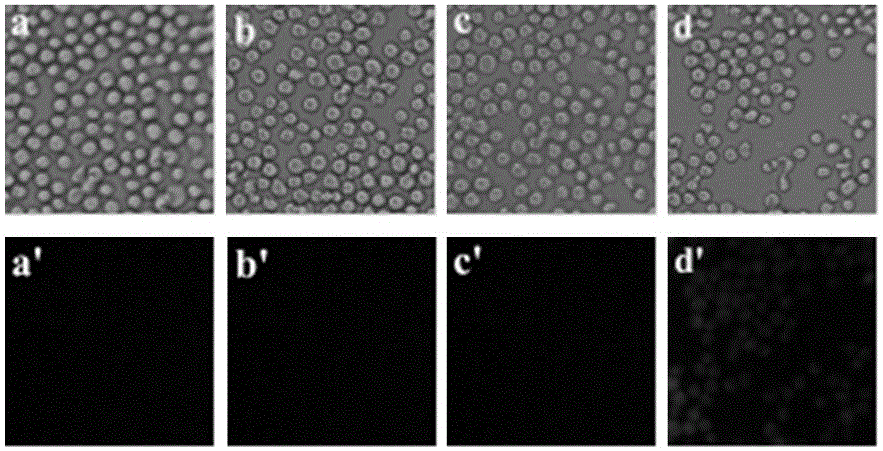
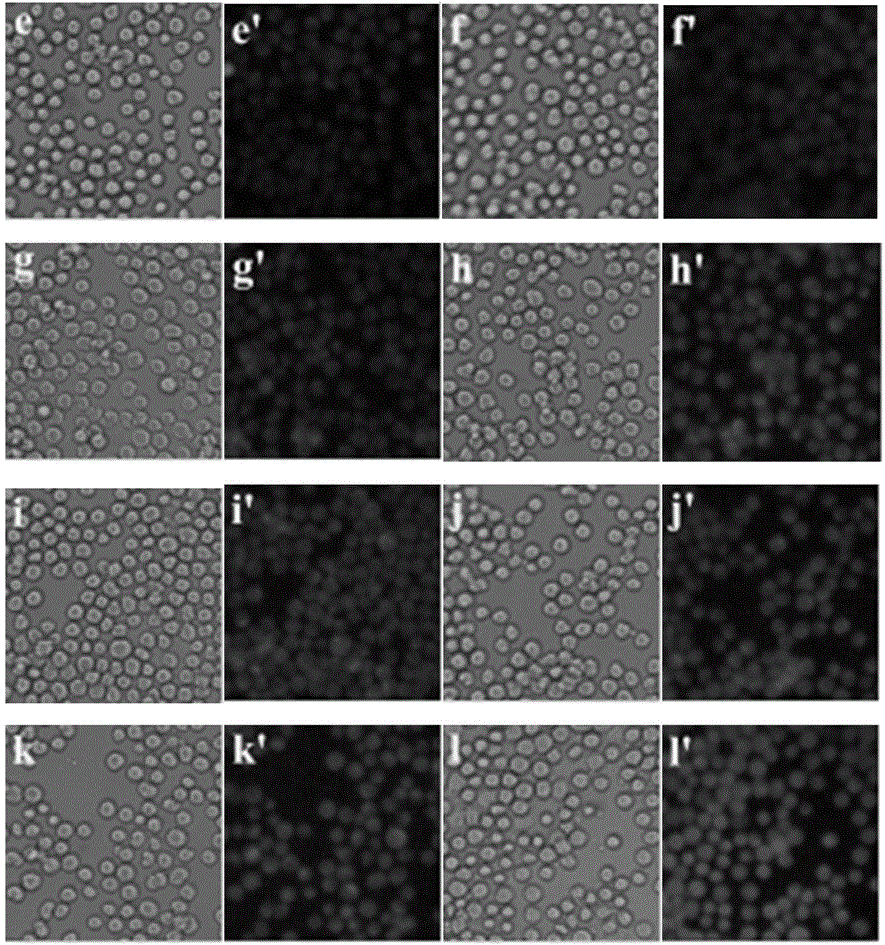
Application of compounds based on rhodamine B and thiobisethylamine in live cell imaging
ActiveCN106011217AHigh sensitivityGood choiceOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementLive cell imagingBuffer solution
The invention discloses application of compounds based on rhodamine B and thiobisethylamine in live cell imaging. Materials for the compounds are easy to obtain, and the compounds are simple to synthesize and simple in molecular structure; the compounds are good in Hg2+ selectivity and high in sensitivity; the compounds are useful for detecting Hg2+ in nearly neutral and almost pure water buffer solution; the compounds are useful for detecting Hg2+ in HgCl2; particularly, the compounds are slightly toxic to living cells and are useful for living cell imaging to detect Hg2+ concentration in living cells.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Tetrazine-containing compounds and synthetic methods thereof
InactiveUS20160223559A1Sugar derivativesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsFluorescenceLive cell imaging
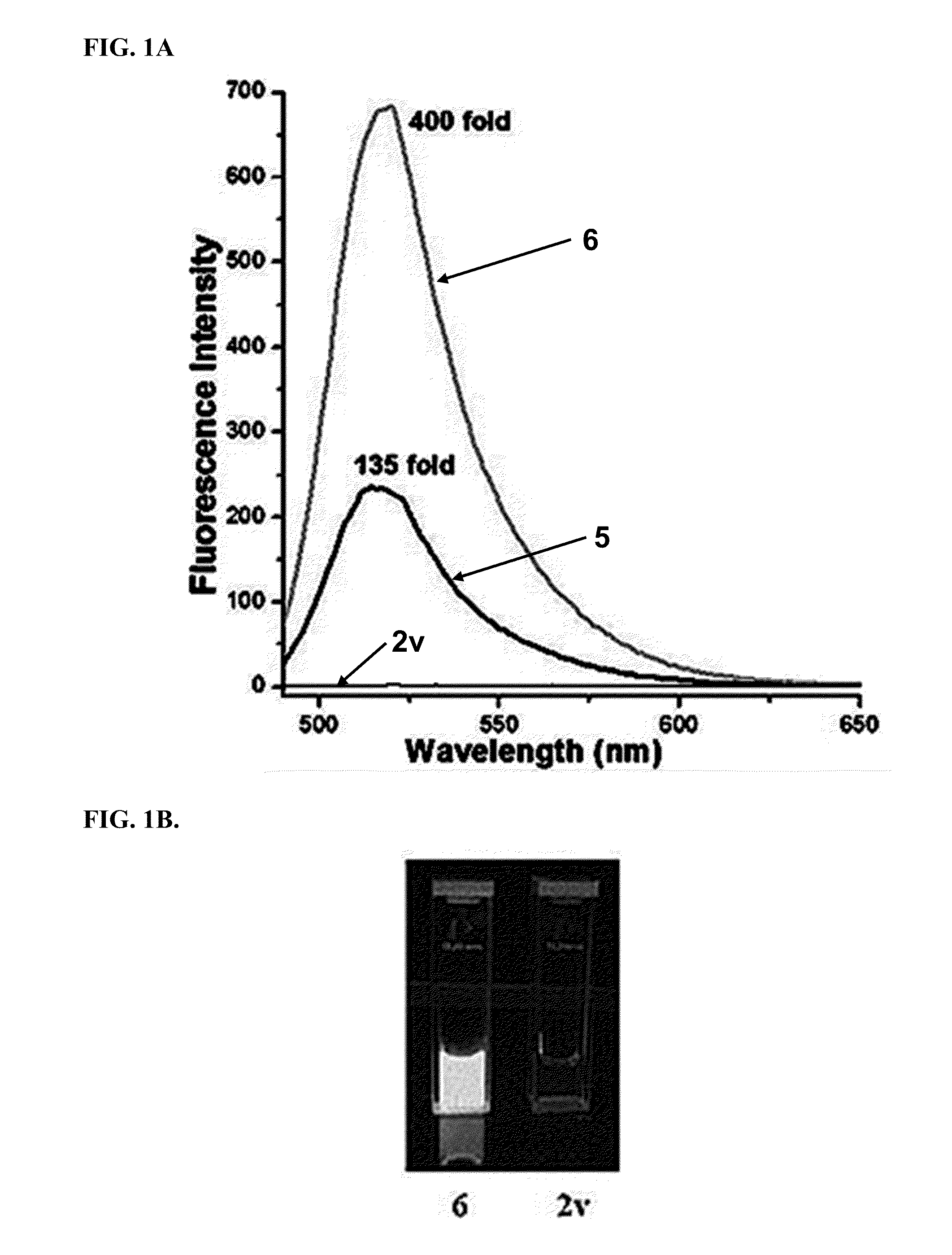
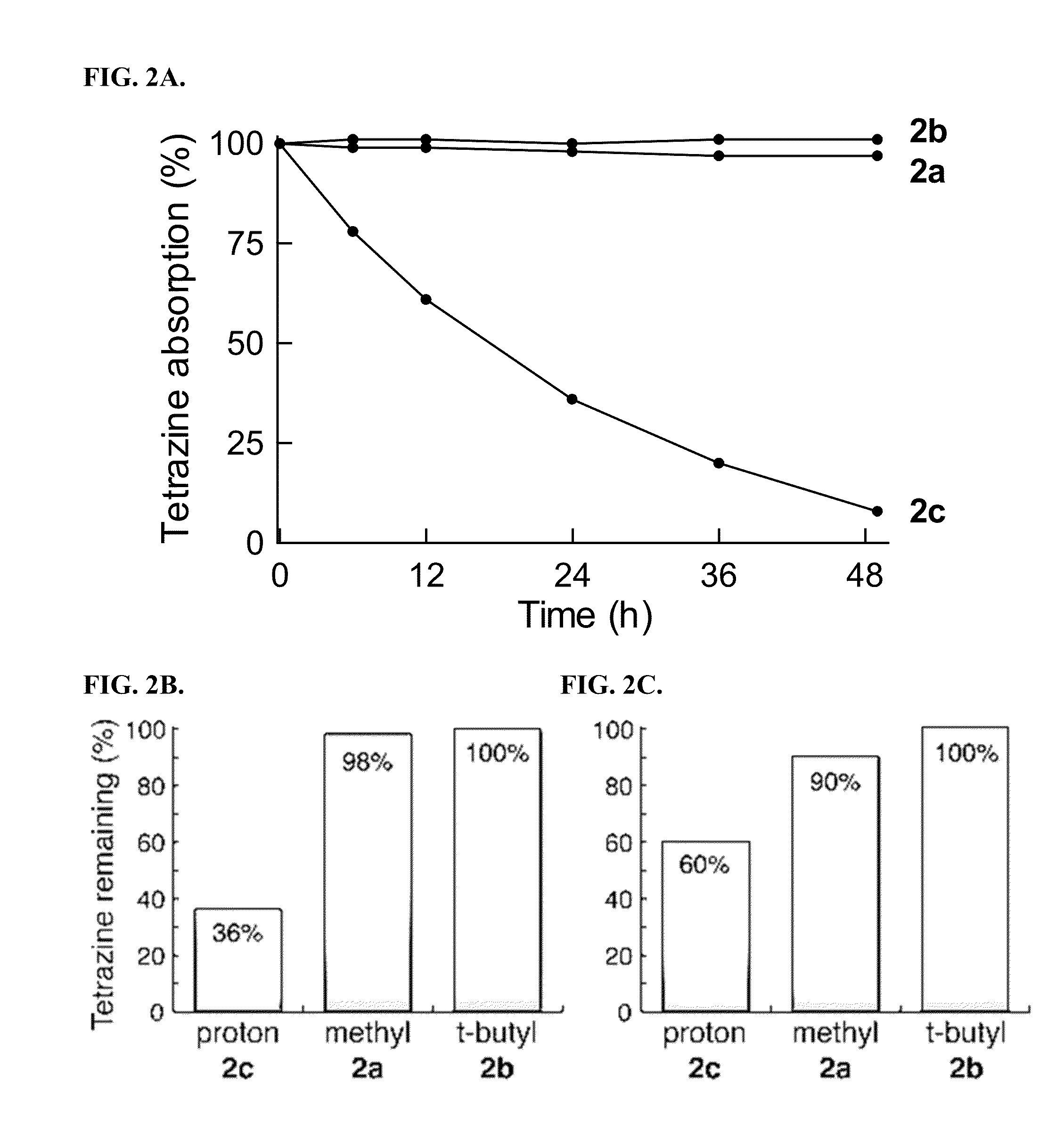
Described herein are tetrazine derivatives and efficient synthetic methods of synthesis thereof using elimination-Heck cascade reaction. Provided herein is the synthesis of conjugated tetrazines from the tetrazine derivatives. Also provided herein are methods of use of the conjugated tetrazines as fluorogenic probes for live-cell imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
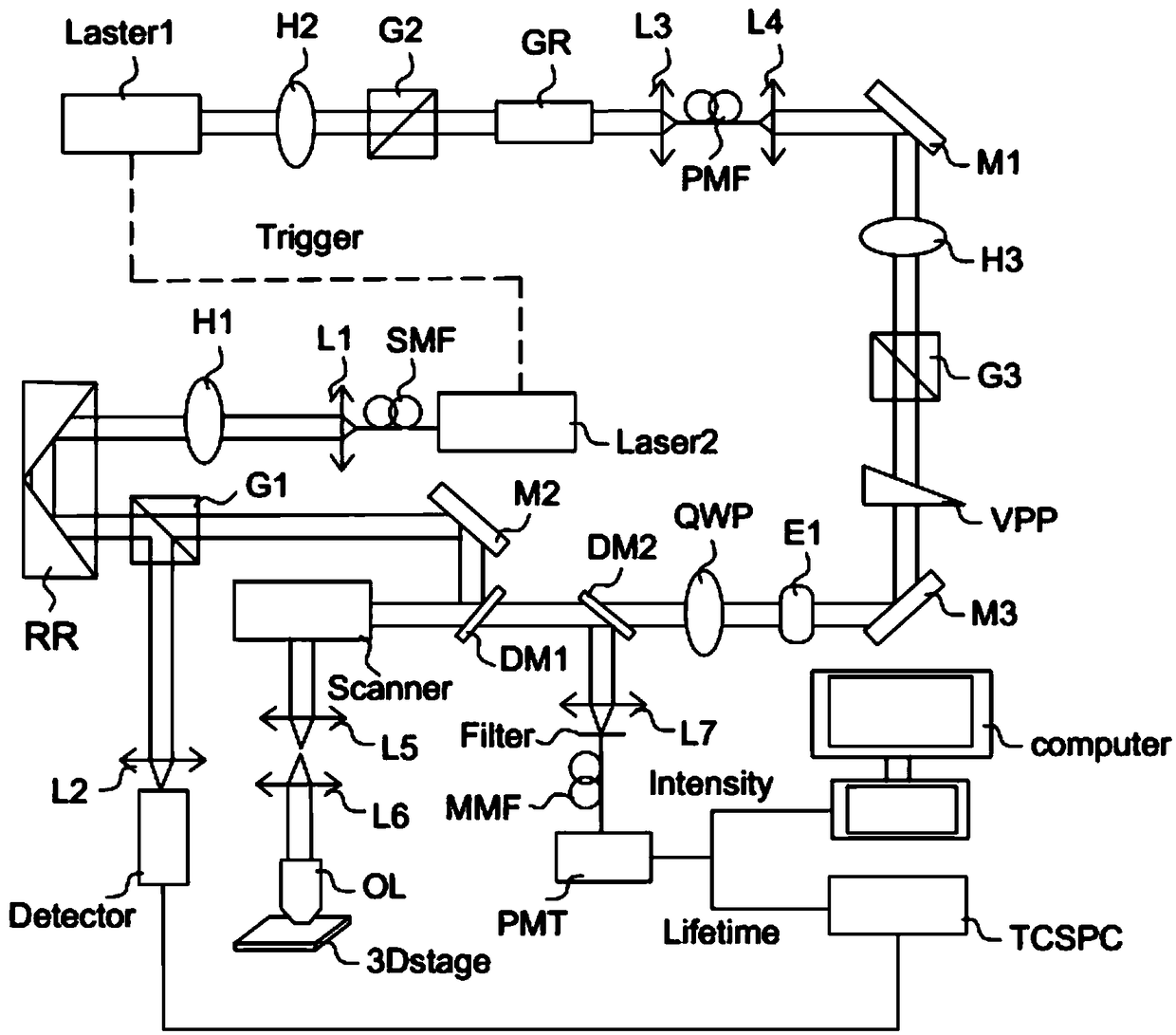
High resolution holographic microscope and method for living cell imaging
ActiveCN110455799AMake full use of limited space bandwidthLow densityPhase-affecting property measurementsMicroscopesMicron scaleCcd camera
The present invention discloses a high resolution holographic microscope and a method for living cell imaging, and belongs to the technical field of holographic microimaging. In a holographic opticalpath, when a secondary point light source passes through a living cell sample, diffracted object light interferes with undiffracted reference light to form an in-line hologram; the image is magnifiedby a high power microobjective, received by a CCD camera and stored in a computer; and a reconstructed image is obtained by computer numerical reconstruction. The invention uses a low power microobjective to convert a parallel light source into the secondary point light source combined with the object light and the reference light in the same direction during a recording process, makes full use ofa limited spatial bandwidth of the CCD camera, greatly improves the resolution of the holographic microscope system, uses a three-dimensional micron-scale displacement platform to precisely adjust the microscopic resolution and receives more interference outer ring fringes by shortening the recording distance, which includes high-frequency information of the sample playing a key role in reconstructing the image. Combined with the high power microobjective in front of the CCD camera, non-contact, non-invasive, fast, quantitative and high-resolution holographic microimaging of the living cell sample can be realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Observation chamber for studying temperature-dependent events and method thereof
Live-cell imaging chambers are used in a wide range of cell biology research. Recently, chambers capable of taking high-resolution and time-lapse images of live cells have been developed and become commercially available. However, since most of these chambers are designed to maintain a thermally stable environment for the cells under study, it is usually very difficult to use them to study temperature-dependent cellular events. The present invention provides a live-cell observation equipment for a non light-transmitting microscope to study temperature-dependent events and method thereof.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
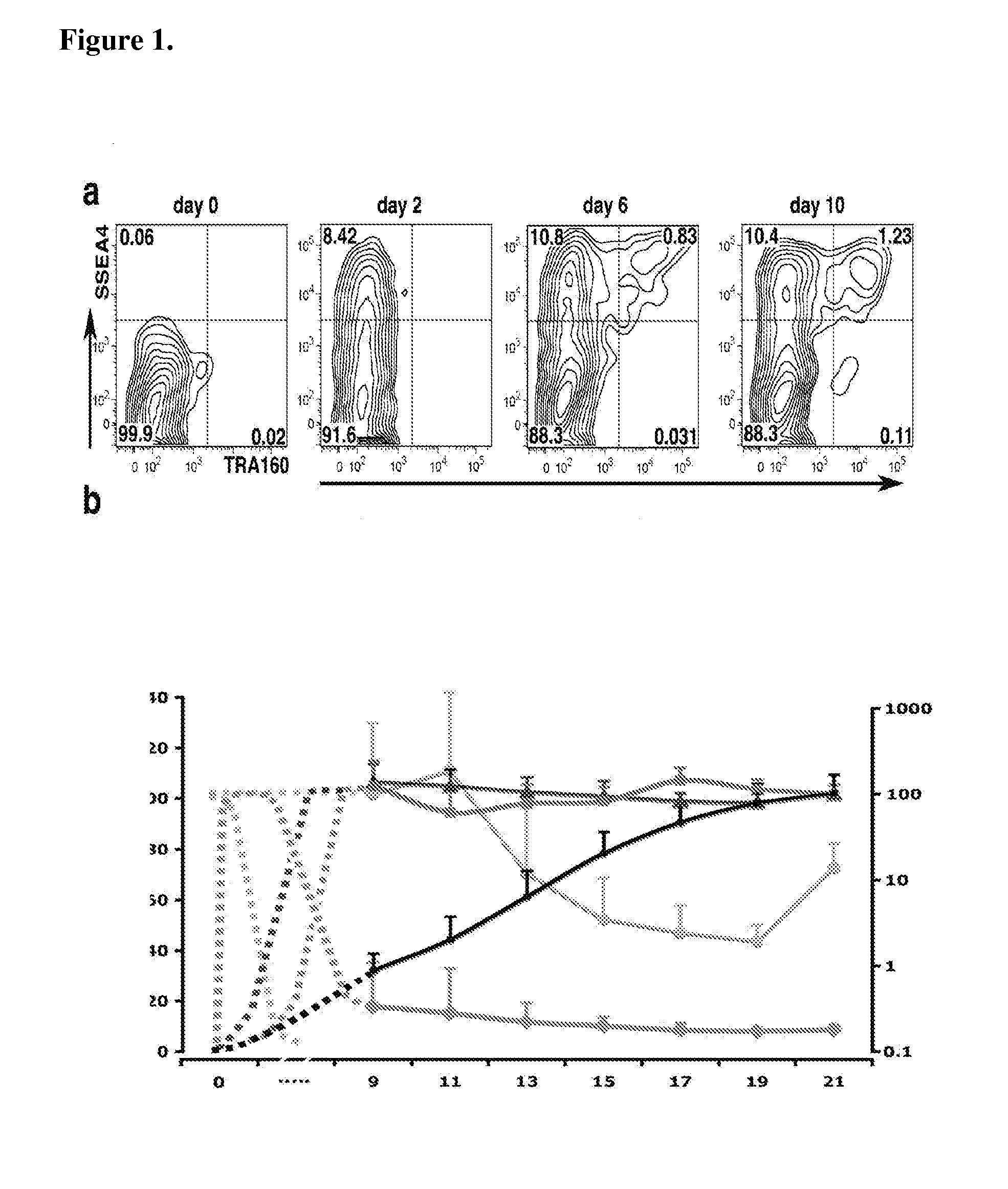
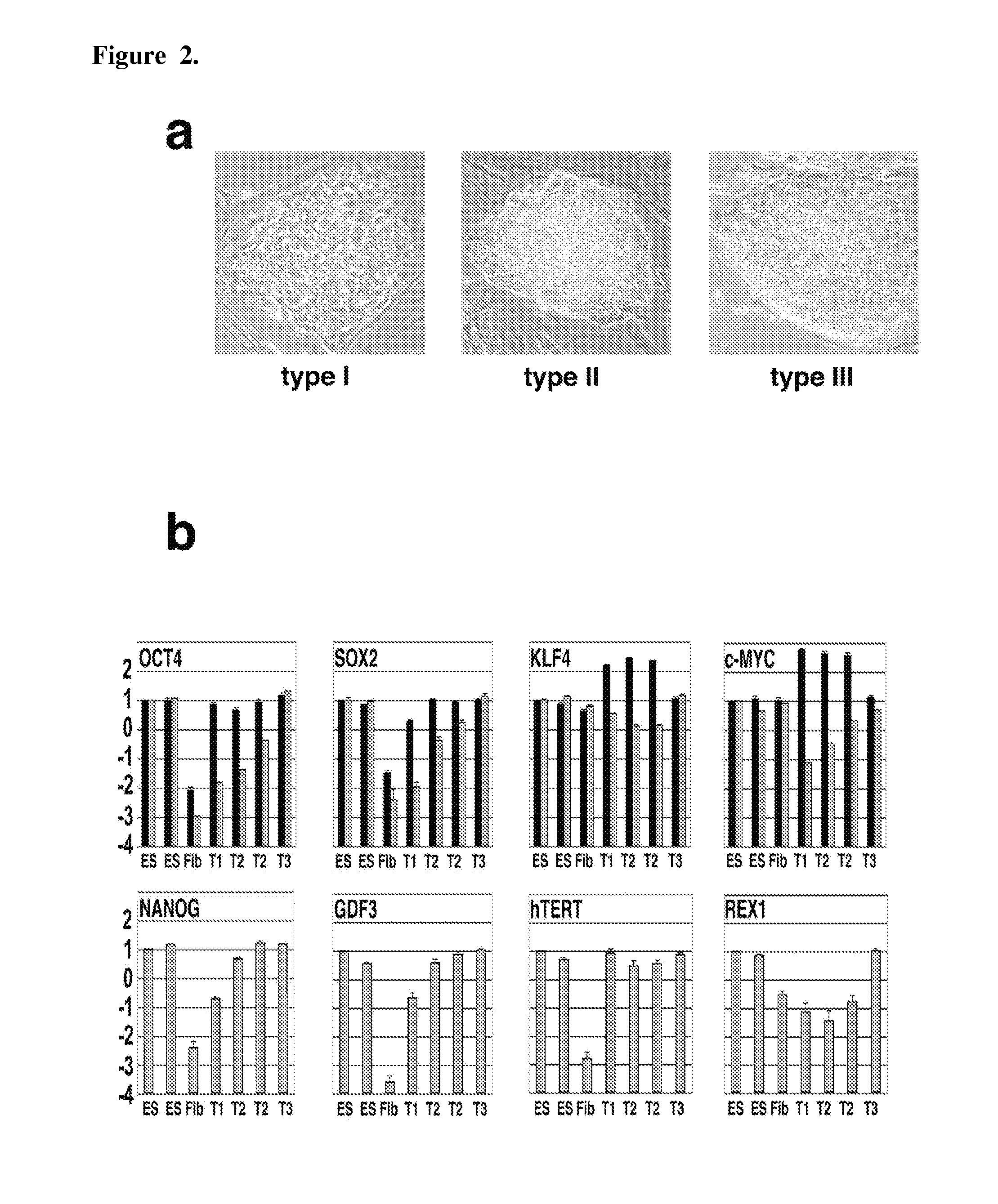
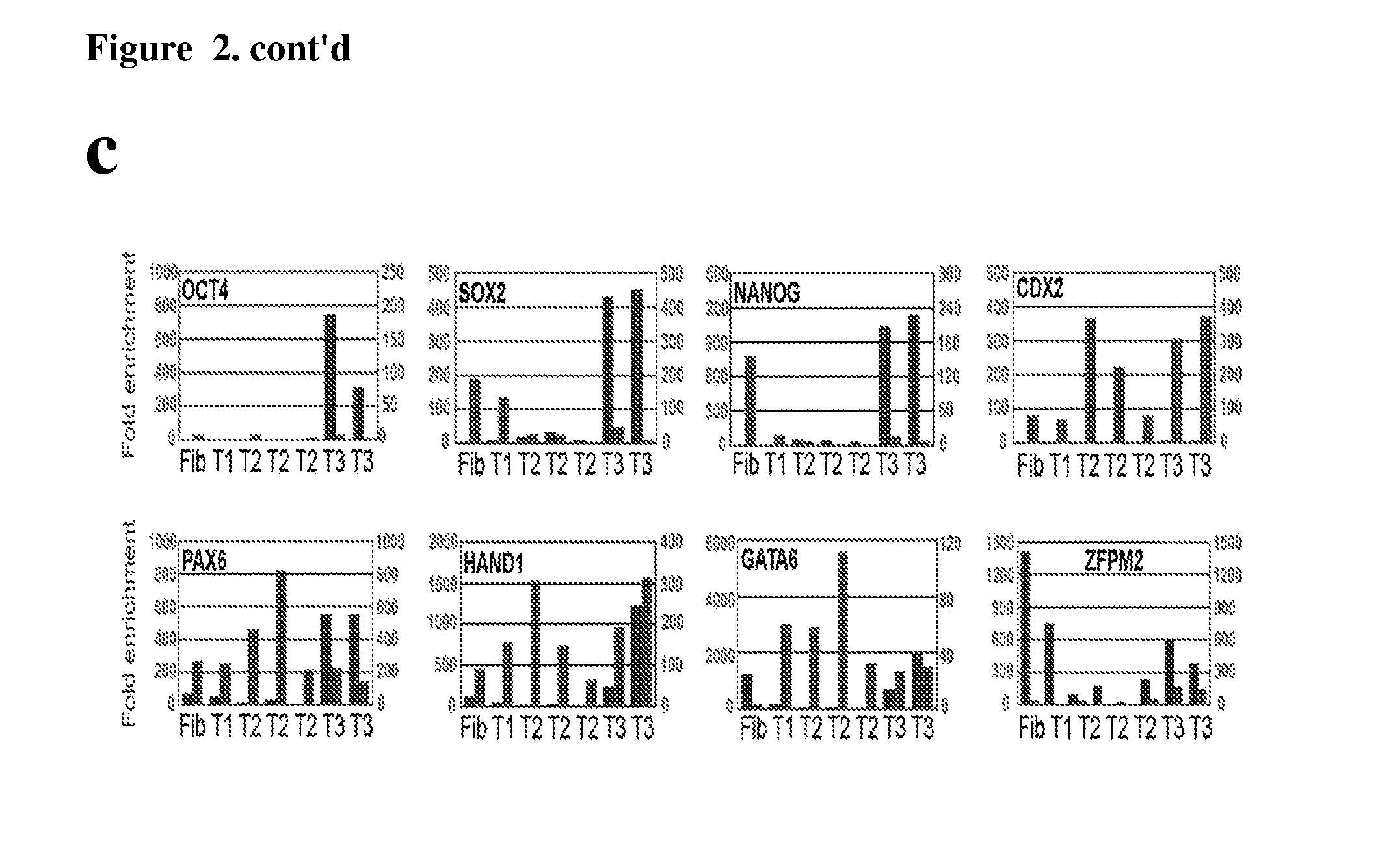
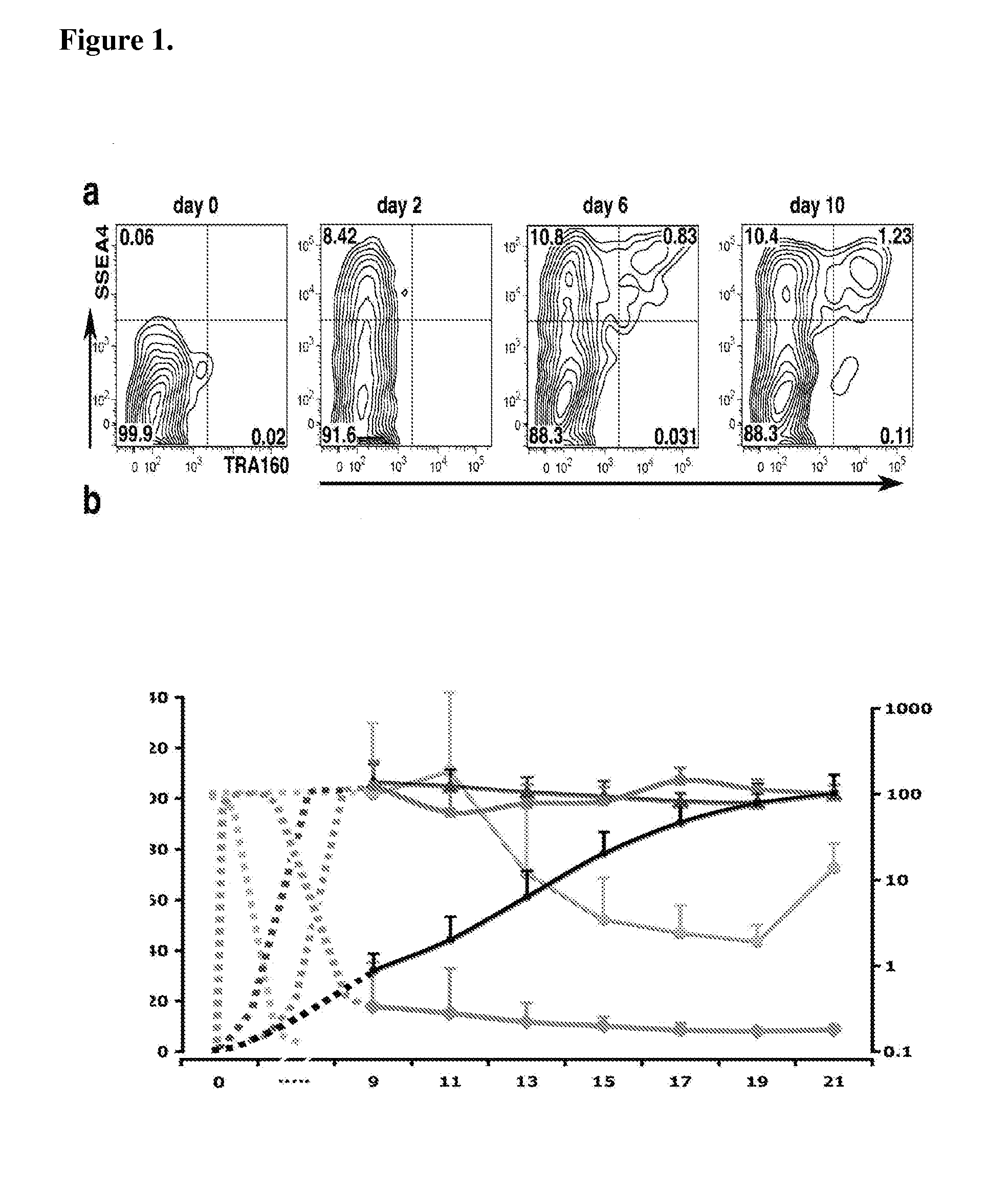
Detection of human somatic cell reprogramming
InactiveUS8703413B2Promotes reprogrammingEnhances reprogrammingCompound screeningApoptosis detectionReprogrammingLive cell imaging
The methods and kits described herein are based, in part, to the discovery phenotype representing a fully-reprogrammed iPS cell and several reprogramming intermediates. The methods and kits described herein permit identification of fully-reprogrammed iPS cells and further permits one of skill in the art to monitor the emergence of iPS cells during the reprogramming process. The methods / kits can also be performed using real time using live cell imaging. Also described herein are methods for screening candidate reprogramming agents by monitoring the emergence of fully-reprogrammed iPS cells in the presence and absence of such an agent.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
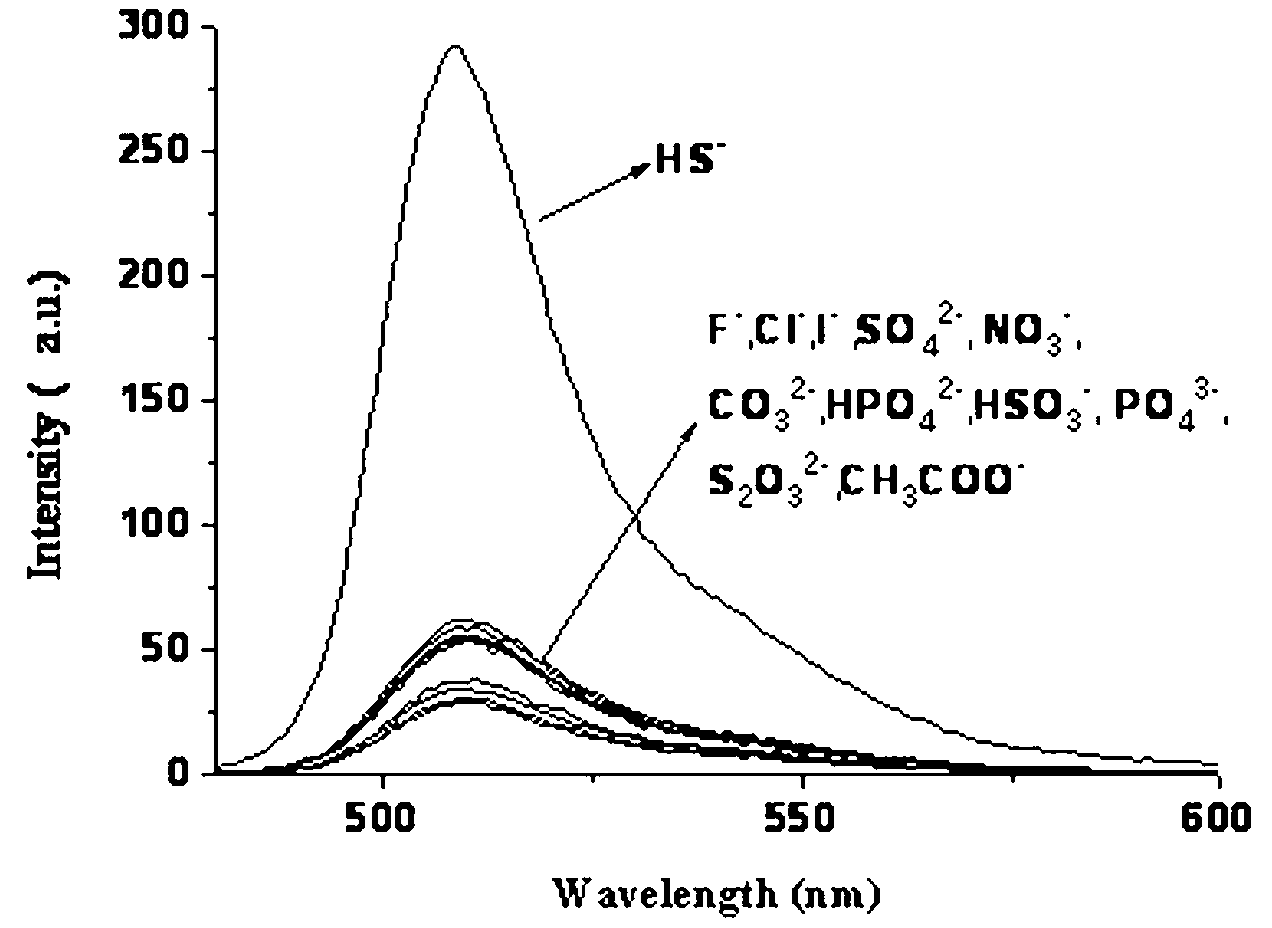
Sulfhydryl group ion fuorescence probe and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN103013496ALow toxicitySmall inhibition rateCopper organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceSynthesis methodsFluorescence
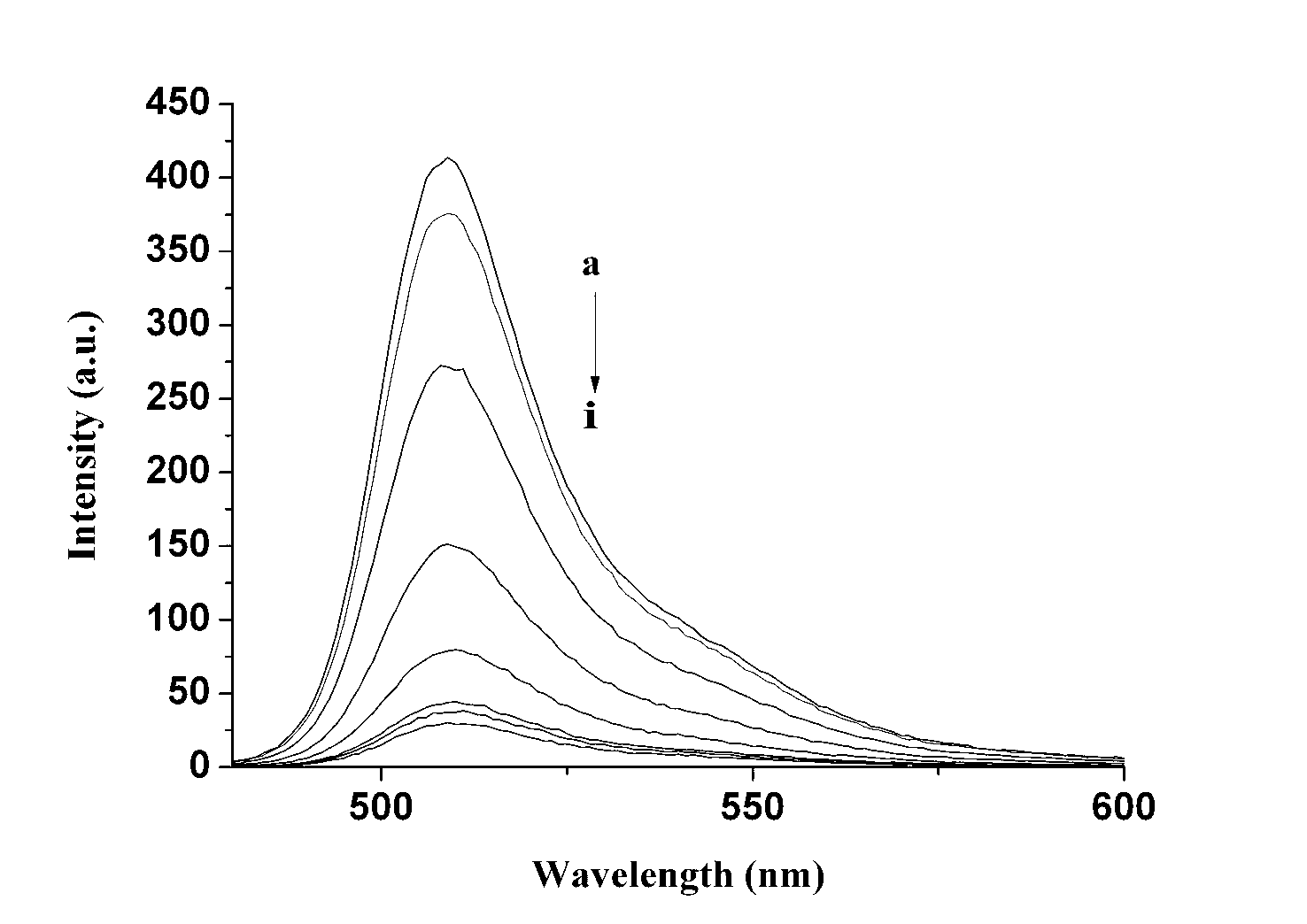
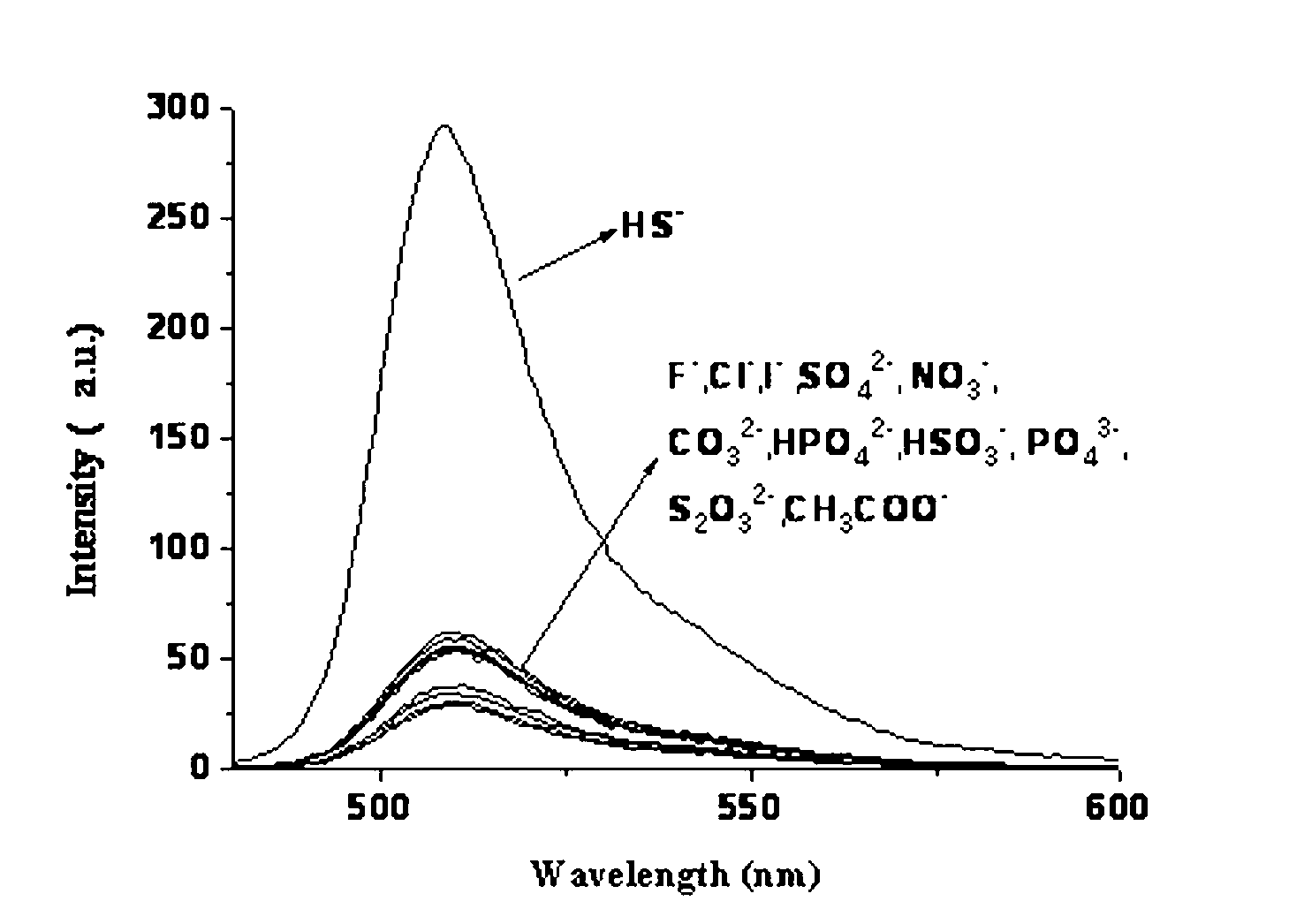
The invention belongs to the field of analytic chemistry technologies and relates to a sulfhydryl group ion fuorescence probe and a synthesis method thereof. The chemical name of the sulfhydryl group ion fuorescence probe is [8-di(2-picolyl)amine-3-benzyl-4,4-difluoro-1,3,5,7-tetramethyl-4-boron-3a,4a-dipyrrole] copperdichloride (BODIPY-DPA-Cu for short). The synthesis method of the sulfhydryl group ion fuorescence probe comprises the following steps: mixing 8-[di(2-(2-picolyl)amine-3-benzyl]-4,4-difluoro-1,3,5,7-tetramethyl-4-boron-3a,4a-dipyrrole] (BODIPY-DPA for short) with CuCl2 (copper chloride) to be dissolved in methanol; and reacting for 5-60 minutes at room temperature, thereby obtaining the sulfhydryl group ion fuorescence probe. The sulfhydryl group ion fuorescence probe can respond HS- in a buffering solution and living cell with a phenomenon of green fluorescence recovery, and has the characteristic of low toxicity; the inhibition ratio of 100 mu M HepG-2 is less than 10%; a living cell imaging experiment shows that the BODIPY-DPA-Cu system can detect the HS- in the HepG-2 cell, the detection limit reaches 1.12 mu M, so the sulfhydryl group ion fuorescence probe is an extremely sensitive detection system and can be used for the detection of the HS- in a living body and environmental protection.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
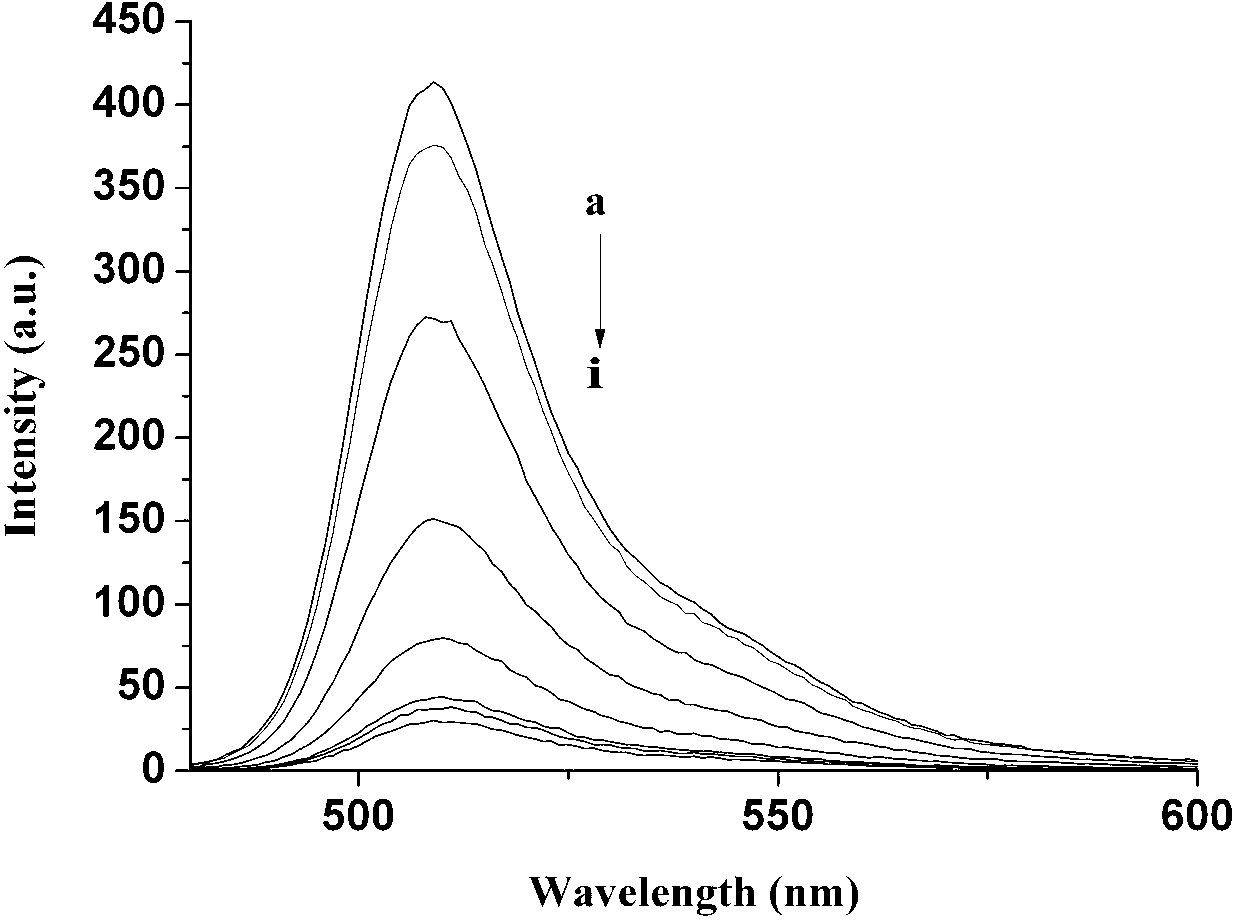
Fluorescent carbon dot nano-probe for detecting hydrogen sulfide and imaging hydrogen sulfide in living cells based on inner filter effect, and using method thereof
ActiveCN110358535ALow costHigh selectivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceLive cell imaging
The invention proposes a fluorescent carbon dot nano-probe for detecting hydrogen sulfide and imaging hydrogen sulfide in living cells based on the inner filter effect, and a using method thereof. A simple green method for fluorescence detection of hydrogen sulfide and tracing of hydrogen sulfide in living cells is established. Fluorescent carbon dots are prepared from tomatoes, the carbon dots (CDs) have strong green fluorescence at 520 nm under the irradiation of 410 nm ultraviolet light, red shift of the fluorescence emission peak gradually occurs with the increase of the wavelength of theexcitation light, the relative fluorescence quantum yield is 53%, the carbon dots acting as a fluorescence donor and an organic small-molecular receptor (DMI) form the probe based on the inner filtereffect, and the probe is used for detecting exogenous and endogenous hydrogen sulfide. A sensing system is successfully applied to hydrogen sulfide detection and live cell imaging analysis as the fluorescent probe, and a sensing method has broad application prospects in the fields of environmental analysis, biochemical analysis and cell imaging analysis.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of carbon nano-particles from mature vinegar
InactiveCN107603610ASmall sizeGood fluorescence propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of carbon nano-particles from mature vinegar, in which carbon nano-particles are separated and purified and then collected through a macroporous resin adsorption method with the mature vinegar as a main raw material. The carbon nano-particles can be subjected to fluorescence resonance energy transfer with dopamine, wherein optical features of the carbonnano-particles are changed; under ultraviolet irradiation at 365 nm, blue fluorescence is gradually turned into green fluorescence. The color-adjustable carbon nano-particles can be directly appliedto living cell fluorescent imaging. The preparation method is simple and is low in cost. The carbon nano-particles are low in toxicity and have good biocompatibility. After reaction with the dopamine,water solubility of fluorescent carbon nano-particles is excellent, so that the carbon nano-particles can be used for living cell imaging as a fluorescent dye, and can be applied to the fields of fluorescence labeling and biology.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
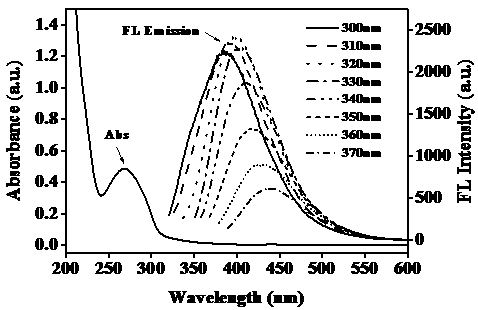
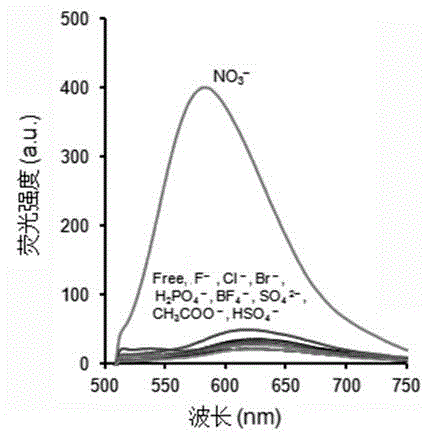
NO<3><-> ion detection reagent and application thereof
ActiveCN104962279ALow detection limitStrong scientific researchOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesStaining
The invention relates to an NO<3><-> ion detection reagent and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of analysis chemistry. A tiny amount of NO<3><-> in a neutral aqueous solution is detected through a fluorescence method by using a 9,10-dipyridylvinyl anthracene cation derivative as a fluorescence probe a. When NO<3><-> in the aqueous solution is determined, the fluorescence intensity at 575nm is determined by using 470nm as fluorescence excitation wavelength, the detection concentration linear range is 1.5*10<-7>-2.1*10<-5>mol.L<-1>, and the lowest detection limit is 10<-8>mol.L<-1>. After the probe a and NO<3><-> are intracellularly stained in a living cell imaging, a fluorescence inverted microscope detection result shows that clear yellow fluorescence cell distribution exists, a cell image is shot to obtain a clear cell contour image, and staining has specific area selective aggregation capability.
Owner:北京传奇优声文化传媒有限公司
Raman silence region substrate with gold as core and dopamine as shell and preparation method and application of substrate
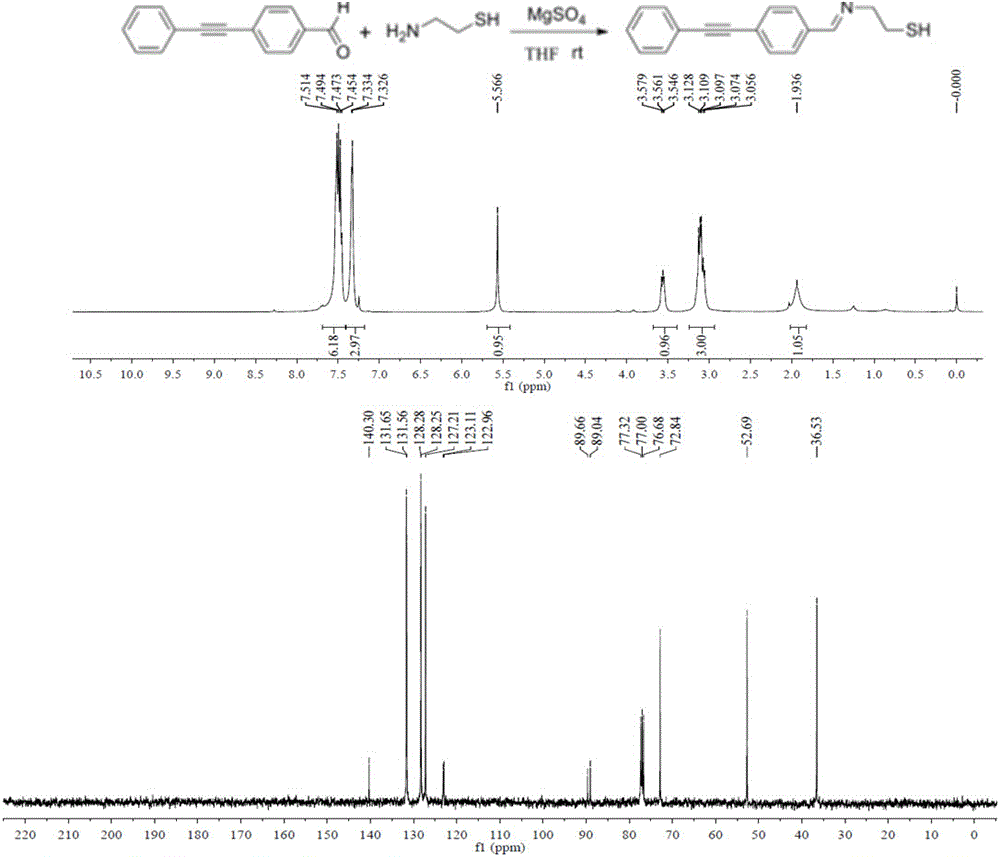
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomacromolecule separation and analysis, and particularly relates to a Raman silence region substrate with gold as a core and dopamine as a shell and a preparation method and application of the substrate. The preparation method includes the steps that gold nanoparticles are directly reduced through the hydrothermal method and then dissolved in a borax solution after being centrifuged, and Raman silence region molecules (E)-2-((4-(acetenyl)benzal)amino)ethanethio prepared through the hydrothermal method are added; then a trace amount of silver nitrate is added, then dopamine is added, and accordingly silver nanoparticles are reduced in situ; by means of auto-polymerization of dopamine, the stable Raman substrate of the Raman silence region is generated. Experiments represent that novel Rama probe molecules achieve an excellent Raman imaging effect on the insides of cells under the enhancement function of enhancement surfaces of the gold nanoparticles. The substrate is free of template and low in cost and toxicity, is applied to live cell imaging, and is easy to operate, novel, convenient to use, practical and efficient.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Arrangement for regulating the temperature of the sample space of a microscope
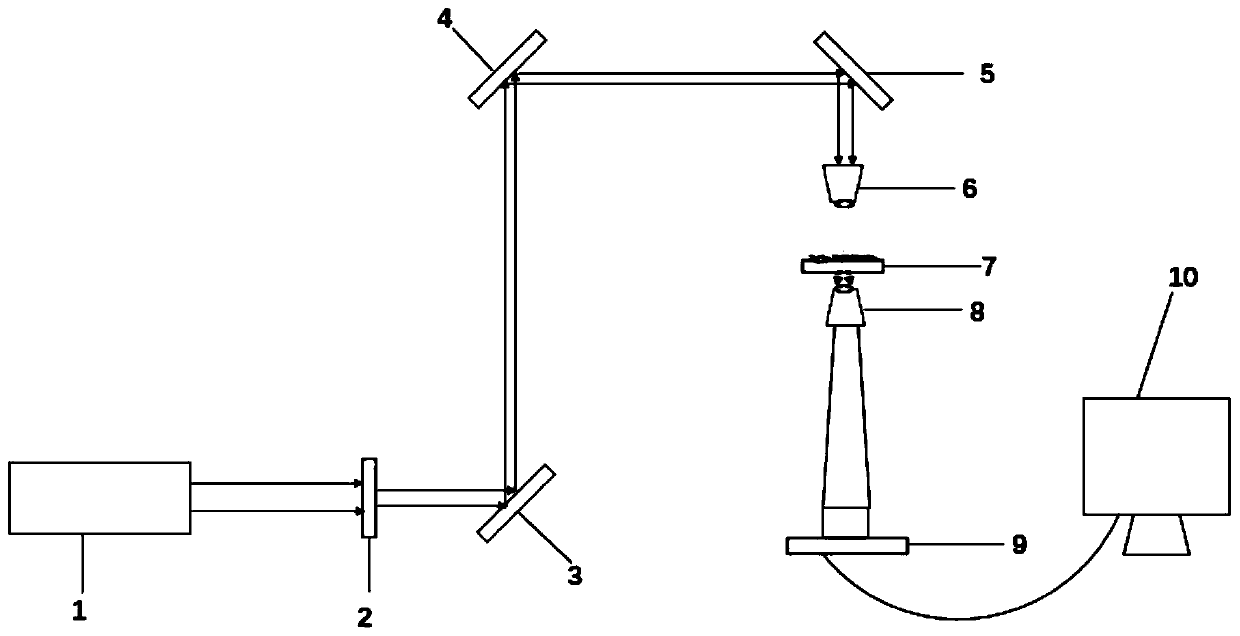
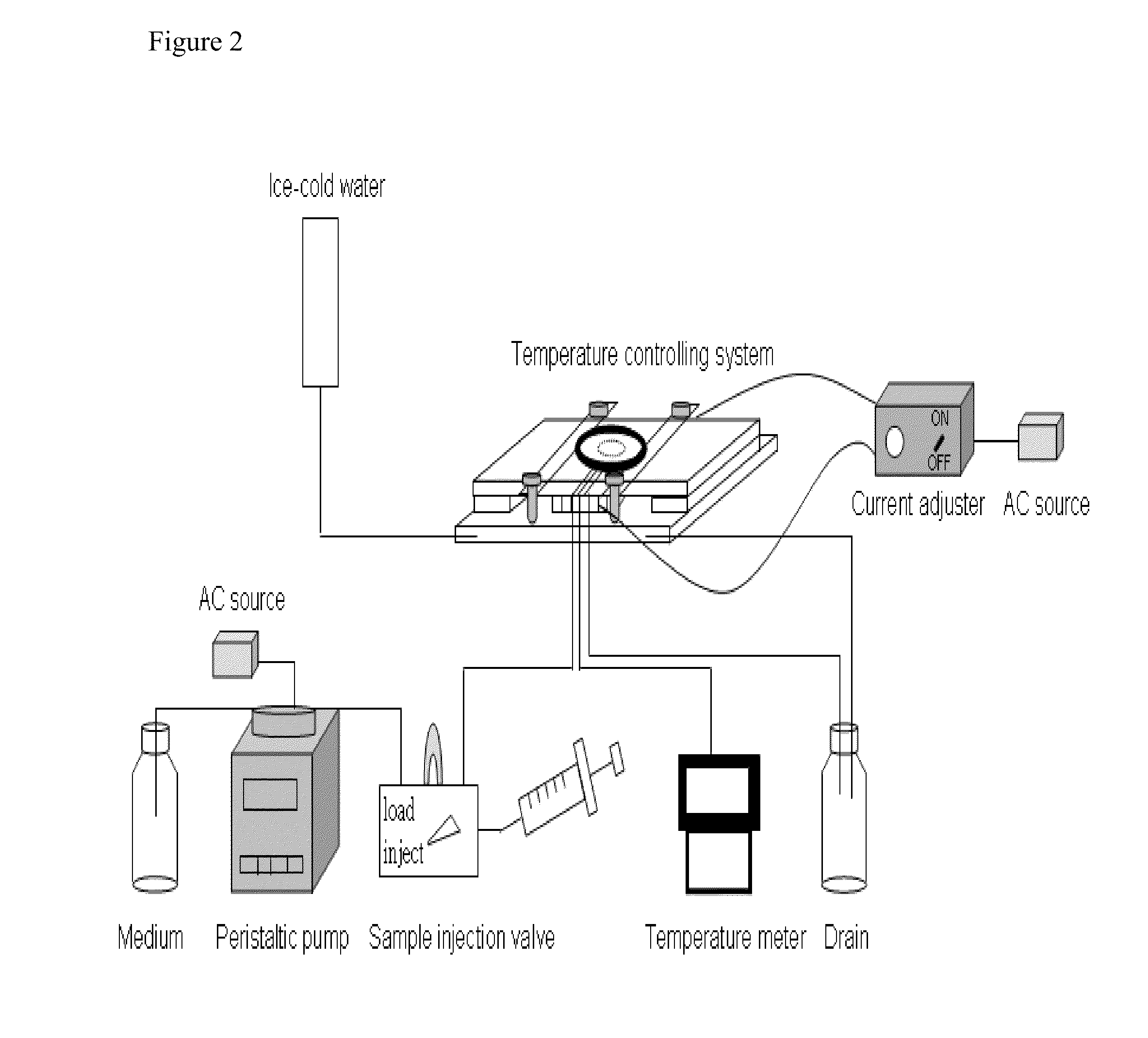
The invention is directed to an arrangement for regulating the temperature of the sample space of a microscope, preferably for observing cells (live cell imaging) with an objective turret carrying objectives, a sample holder serving to receive a sample, a heating or cooling insert with an incubator hood for managing the temperature of the sample holder, and an objective heating element or objective cooling element. According to the invention, at least one structural component part which blocks the heating flow or cooling flow is provided between the objective heating element or objective cooling element and the objective turret.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Method of using glycine modified quantum dot probes to mark living cell
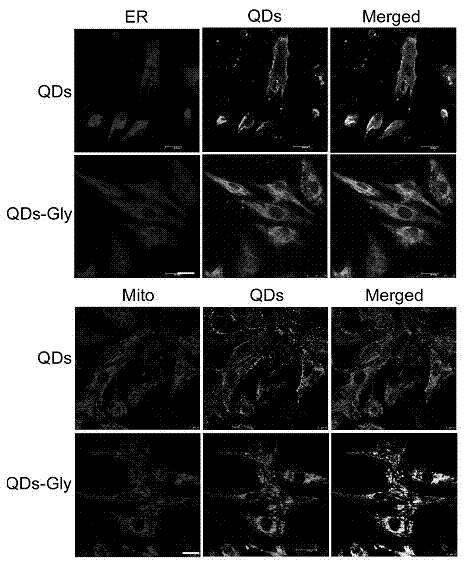
InactiveCN103048298AShort reaction timeLow requirements for experimental conditionsFluorescence/phosphorescenceGlycineCoupling
The invention discloses a method of using glycine modified quantum dot probes to mark a living cell, which comprises the following steps: coupling glycine and quantum dots to prepare the probes, marking of living cell using the glycine modified quantum dot probes, imaging of living cell and tracing, and the like. According to the invention, the quantum dots can hardly penetrate cell membranes, the probes used for the imaging of living cell are coupled with other molecules so as to enter the cell, and comparatively available coupling molecules are cell-penetrating peptide. The water-soluble quantum dots and the glycine are coupled to improve the cell-penetrating ability of the quantum dots, so as to allow the quantum dots in the cell to play the role of marking and tracing the cells. The glycine modified quantum dots are uniformly distributed in cytoplasm and are uniform and dispersed in shining, and the non-modified quantum dots are mainly attached on the cell membranes, and are comparatively large in particle and not uniform compared with the cell-penetrating peptide modified quantum dots. Besides, the glycine modified quantum dot probe has the advantages of low cost, quickness in manufacturing, stable quality, convenience in use, uniform cell-in distribution and the like.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Fluorescent probe for detecting human serum albumin as well as synthetic method and application of fluorescent probe
ActiveCN110183376ARealize quantitative detectionReduce usageOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceOrganic synthesisFluorescence
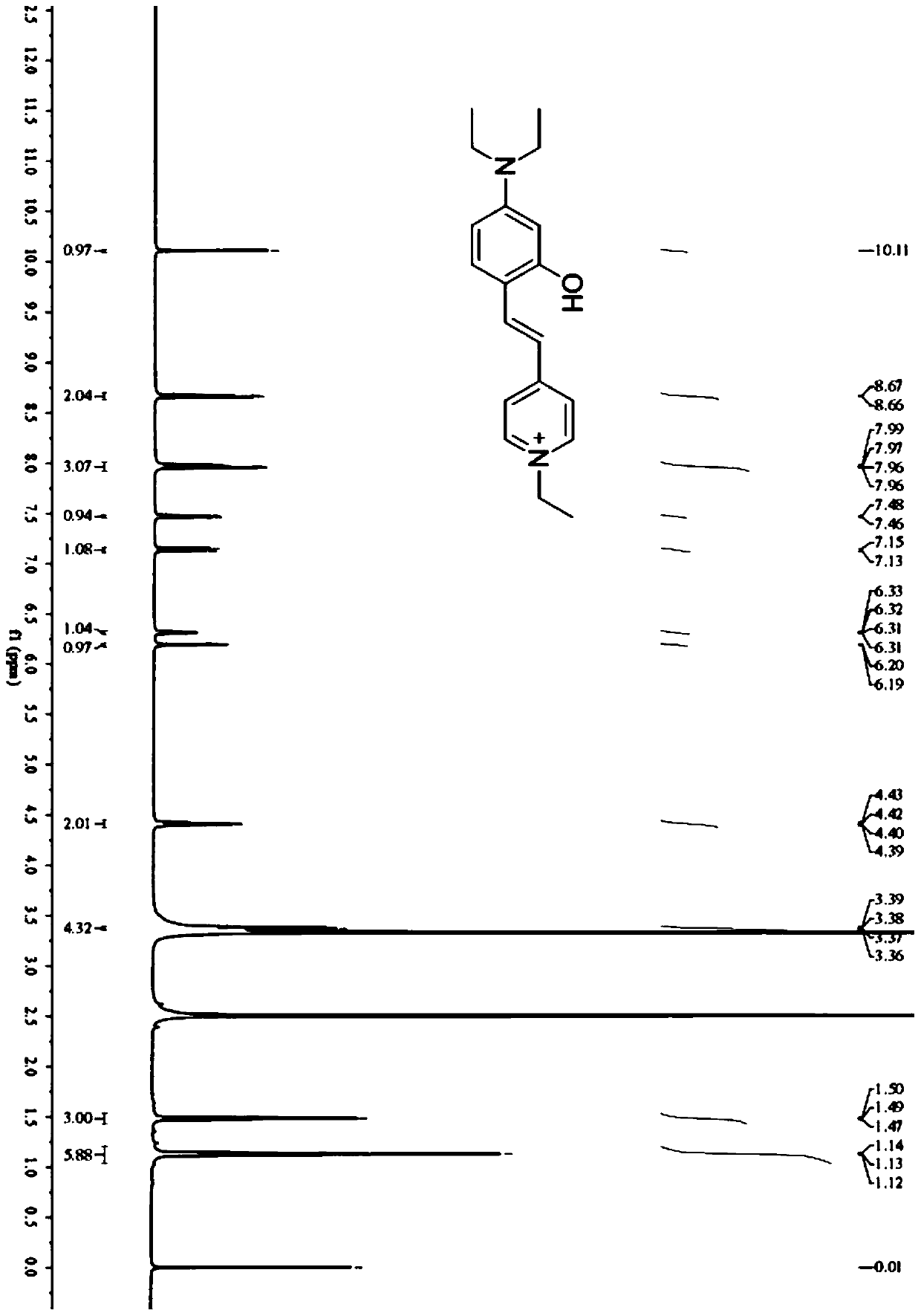
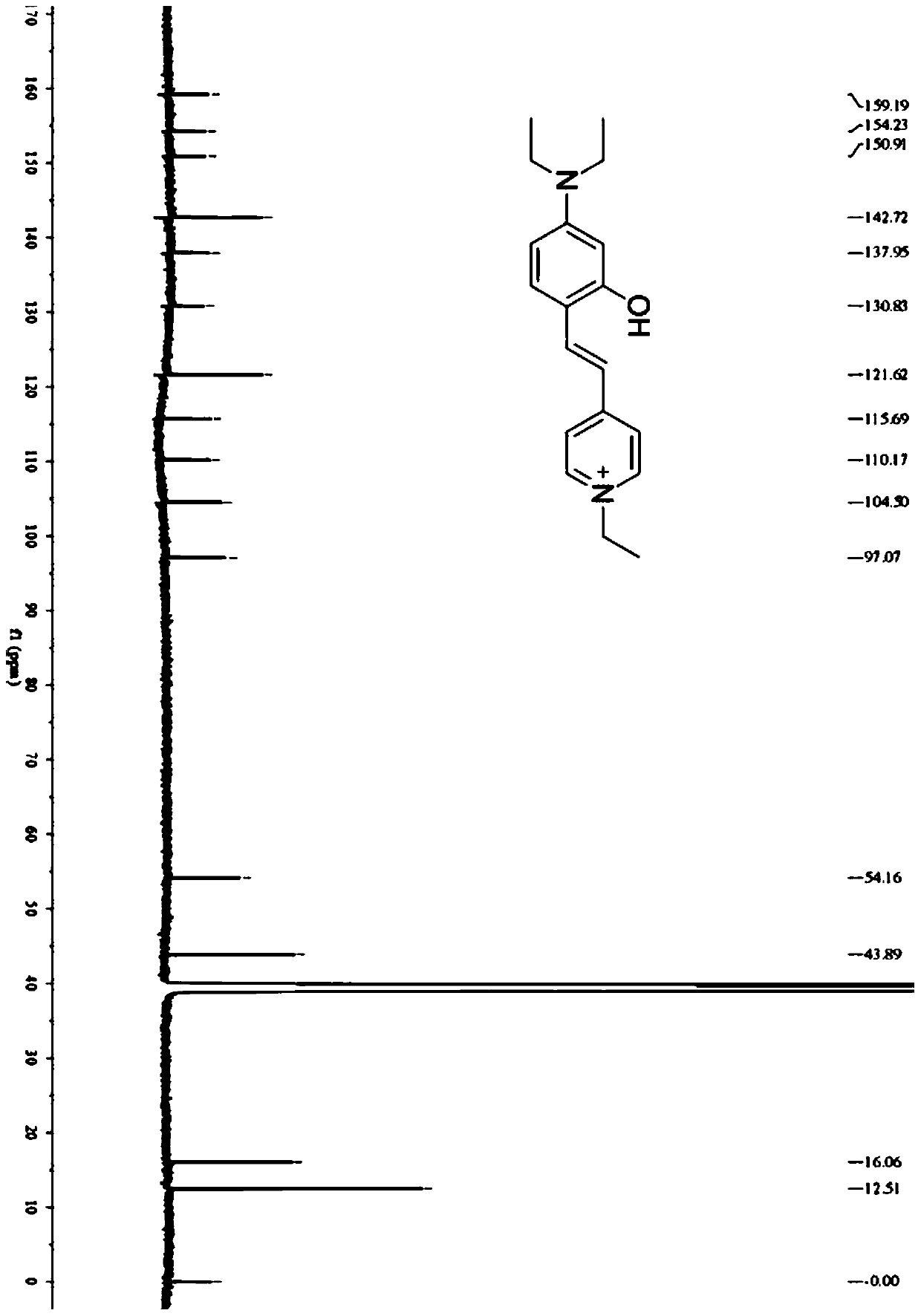
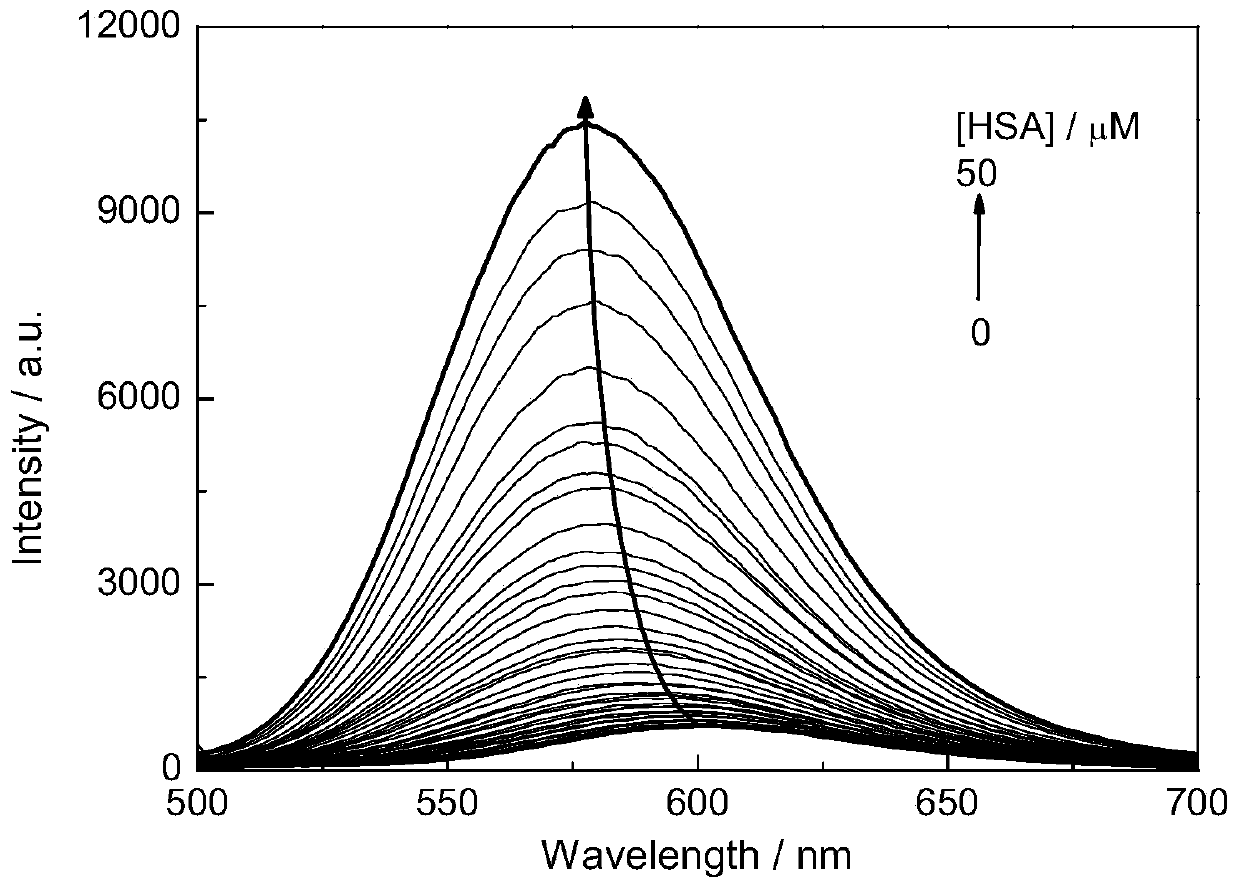
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe for detecting human serum albumin (HAS) as well as a synthetic method and application of the fluorescent probe. Piperidine is added as a catalyst to promotea condensation reaction of 2-hydroxy-4-diethylaminobenzaldehyde and 1-ethyl-4-methylpyridine iodide to form a hydroxyl-containing chromophore DMHP as an indicator of detection of the HSA. According to the method provided by the invention, the fluorescent probe DMHP synthesized by a one-step reaction can specifically recognize the HSA, realizes quantitative detection of the HSA in an aqueous phase, and avoids cumbersome organic synthesis and use of organic solvents; and in addition, experimental studies in actual serum and live cell imaging show that the probe (E)-4-(4-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxystyryl)-1-ethylpyridin-1-iodide (DMHP) has good stability in sensitivity, anti-interference ability and imaging, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:JIERUI BIOENG SHANGHAI
Detection of human somatic cell reprogramming
InactiveUS20110256526A1Promotes reprogrammingEnhances reprogrammingCompound screeningApoptosis detectionReprogrammingLive cell imaging
The methods and kits described herein are based, in part, to the discovery phenotype representing a fully-reprogrammed iPS cell and several reprogramming intermediates. The methods and kits described herein permit identification of fully-reprogrammed iPS cells and further permits one of skill in the art to monitor the emergence of iPS cells during the reprogramming process. The methods / kits can also be performed using real time using live cell imaging. Also described herein are methods for screening candidate reprogramming agents by monitoring the emergence of fully-reprogrammed iPS cells in the presence and absence of such an agent.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Preparation and application of fluorescent carbon dot nanoprobe for detecting methylene blue and living cell imaging
The invention relates to preparation and application of a fluorescent carbon dot nanoprobe for detecting methylene blue and living cell imaging. Under the excitation wavelength of 320nm, the maximum emission wavelength of carbon dots (CDs) appears at 440nm and strong blue fluorescence is emitted. Methylene blue can be used for quenching the fluorescence of the carbon dots, and in a cell culture dish, a living cell incubates for 24 hours with the methylene blue, and the cell is observed by using a laser confocal microscopy system and continuously emits blue fluorescence. According to the preparation and the application, the carbon dots carbonized by semen litchi can be used for detecting the methylene blue by quenching a fluorescent signal. As an effective means for detecting the methylene blue, the method shows a remarkable advantage. The detection limit is as low as 0.05micro mol / L and the linear response range is 0.8-10micro mol / L [R<2>=0.9930]. As being a fluorescent probe, a sensing system has the optical characteristics of simplicity, low cost, greenness, high selectivity, rapidness and sensitivity and is successfully applied to methylene blue detecting and living cell imaging analysis. The sensing method has a broad application prospect in the field of environmental analysis and the cell imaging analysis.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
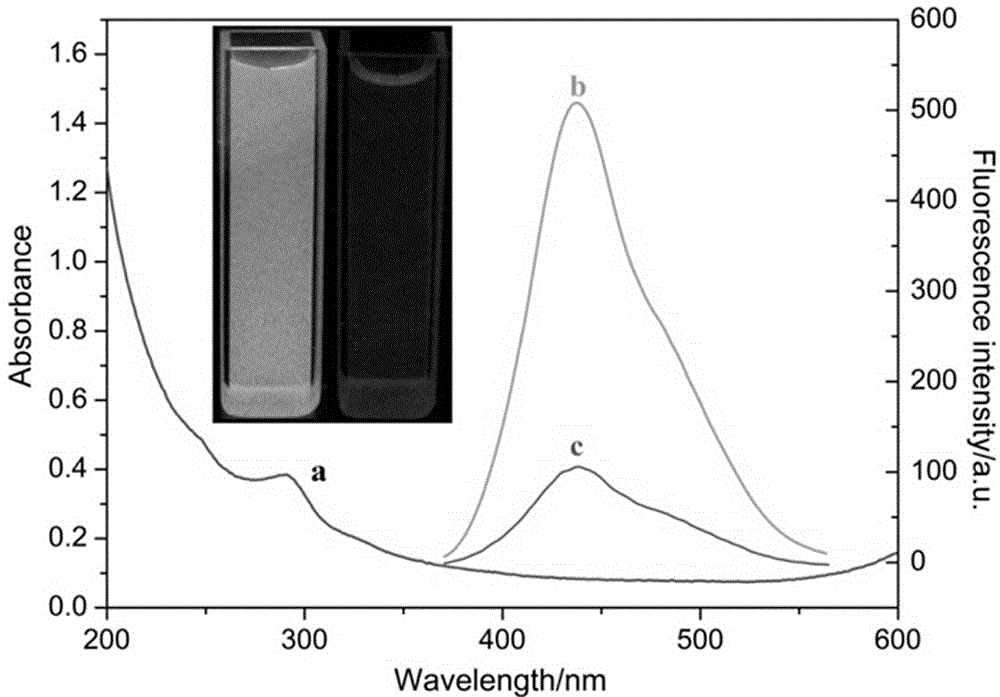
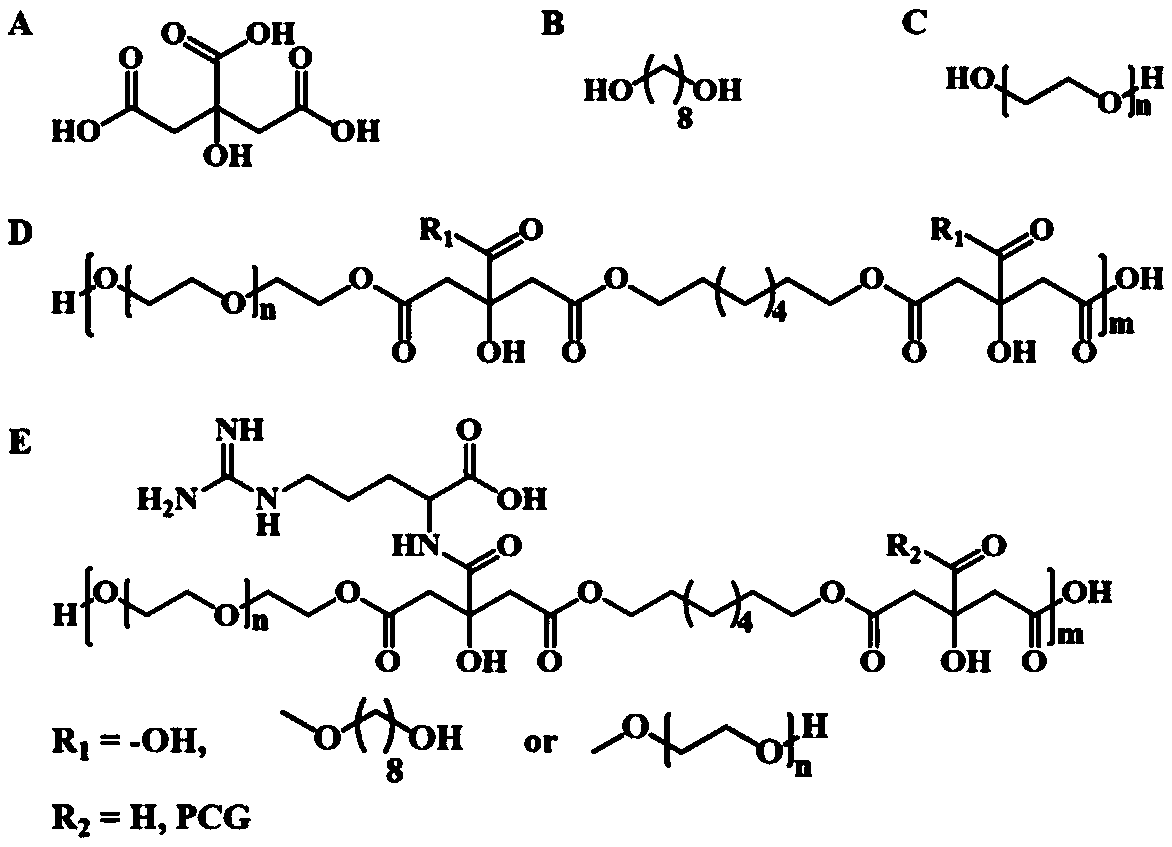
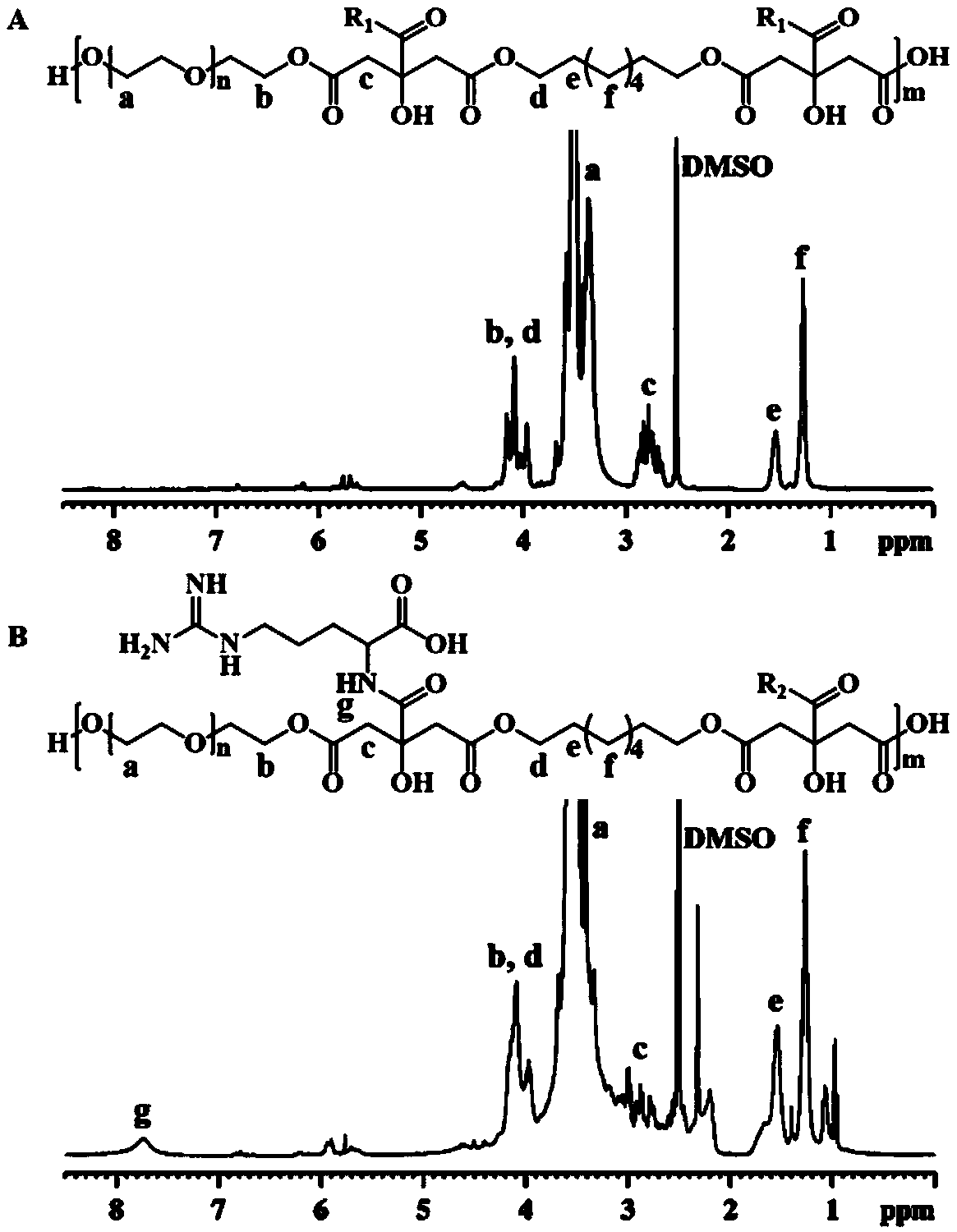
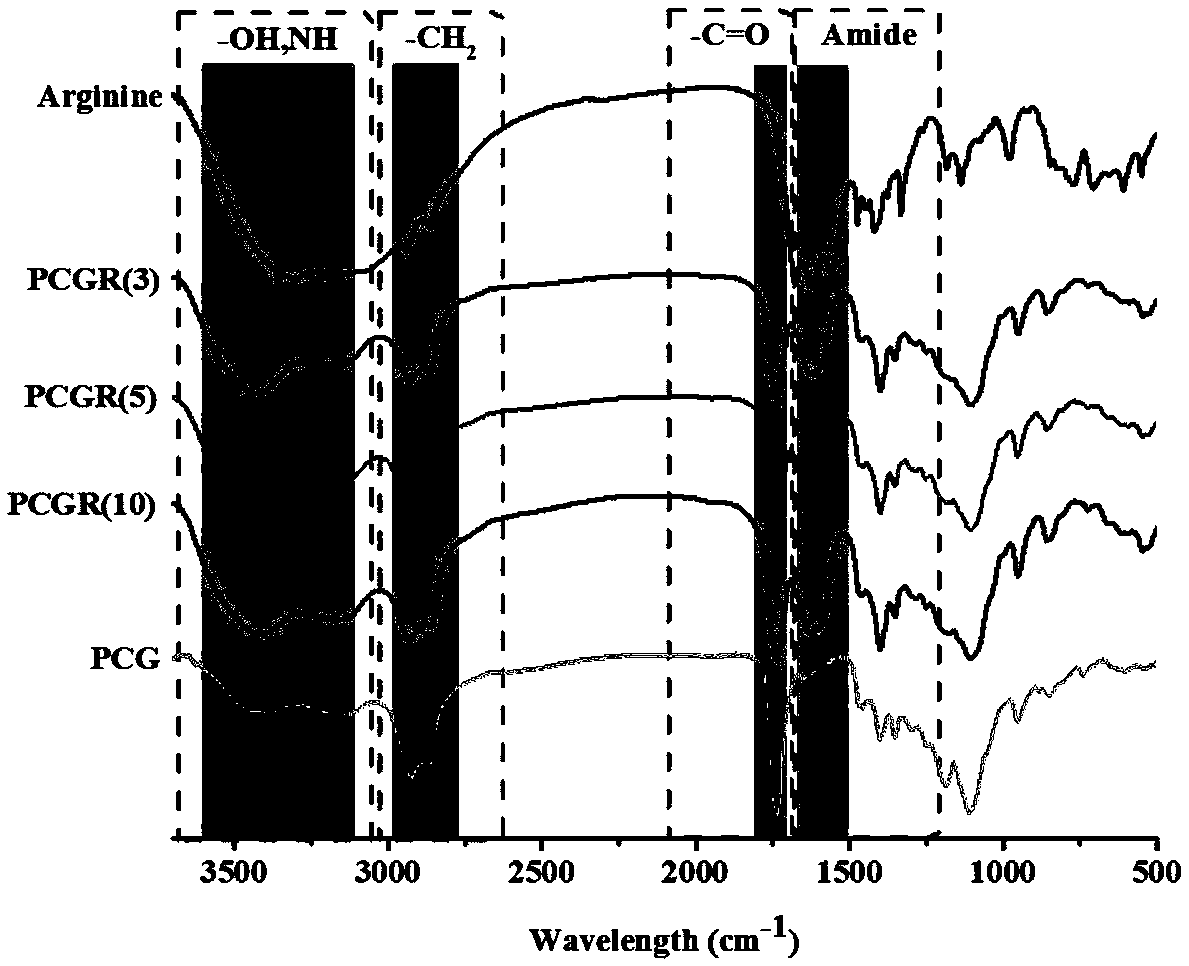
Water-soluble degradable live cell fluorescent imaging material of non-conjugated structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN108912327AGood biocompatibilityImprove hydrophilicityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsSynthesis methodsSilanes
The invention discloses a water-soluble degradable live cell fluorescent imaging material of a non-conjugated structure as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the steps that citric acid, 1,8-octanediol and polyethylene glycol are subjected to thermal polymerization so as to obtain a PCG prepolymer; and then certain amino acids or silane derivatives are grafted to the PCG prepolymer for synthesis so as to obtain a polymer. The preparation method has the advantages of being simple and environmentally friendly, the synthetic raw materials are low in cost andnon-toxic, the prepared polymer has good blood compatibility and cytocompatibility, meanwhile, the material also shows good fluorescence characteristics and optical stability, and therefore the method has a good application prospect in live cell imaging.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com