Patents
Literature
63results about How to "Potential energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
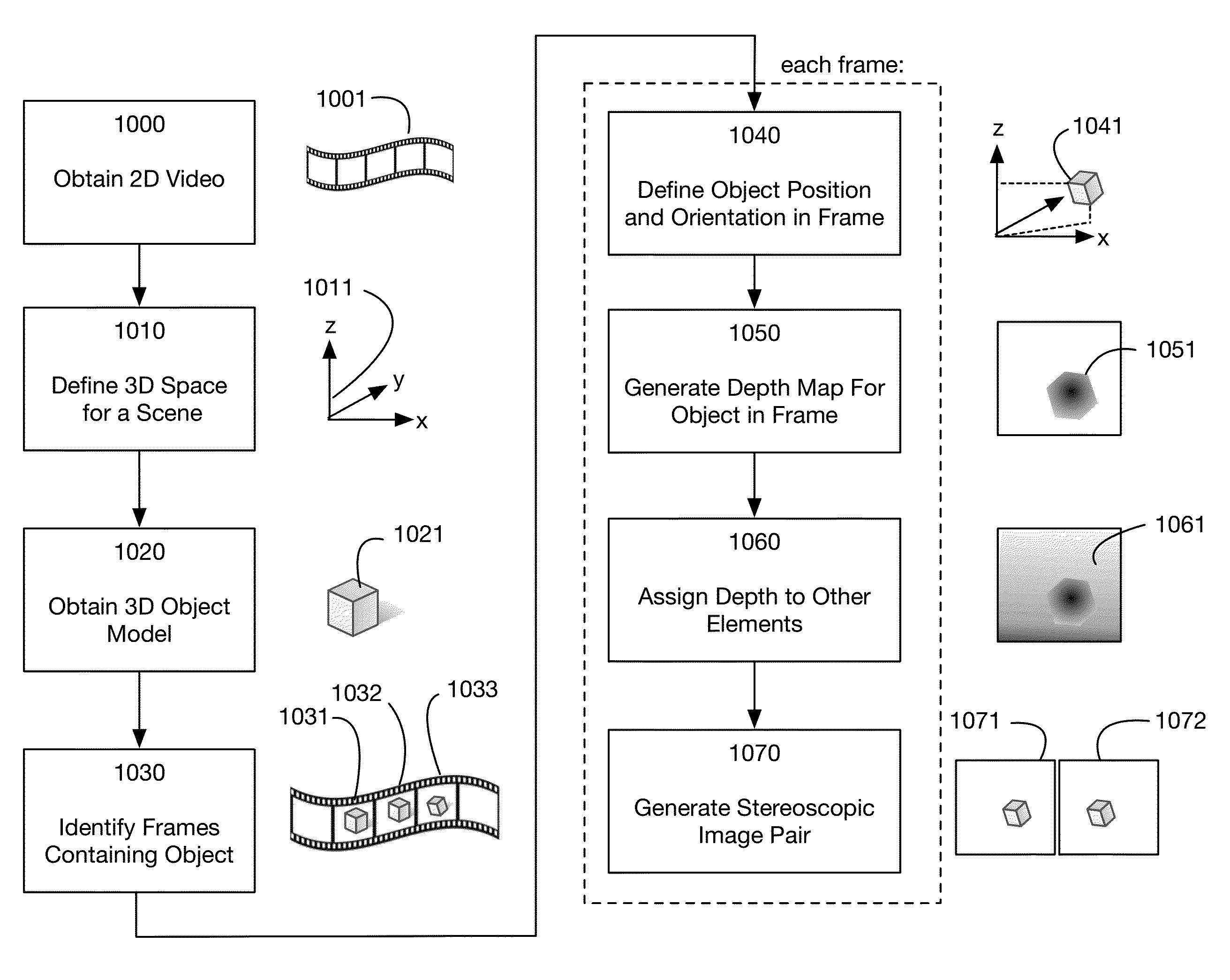
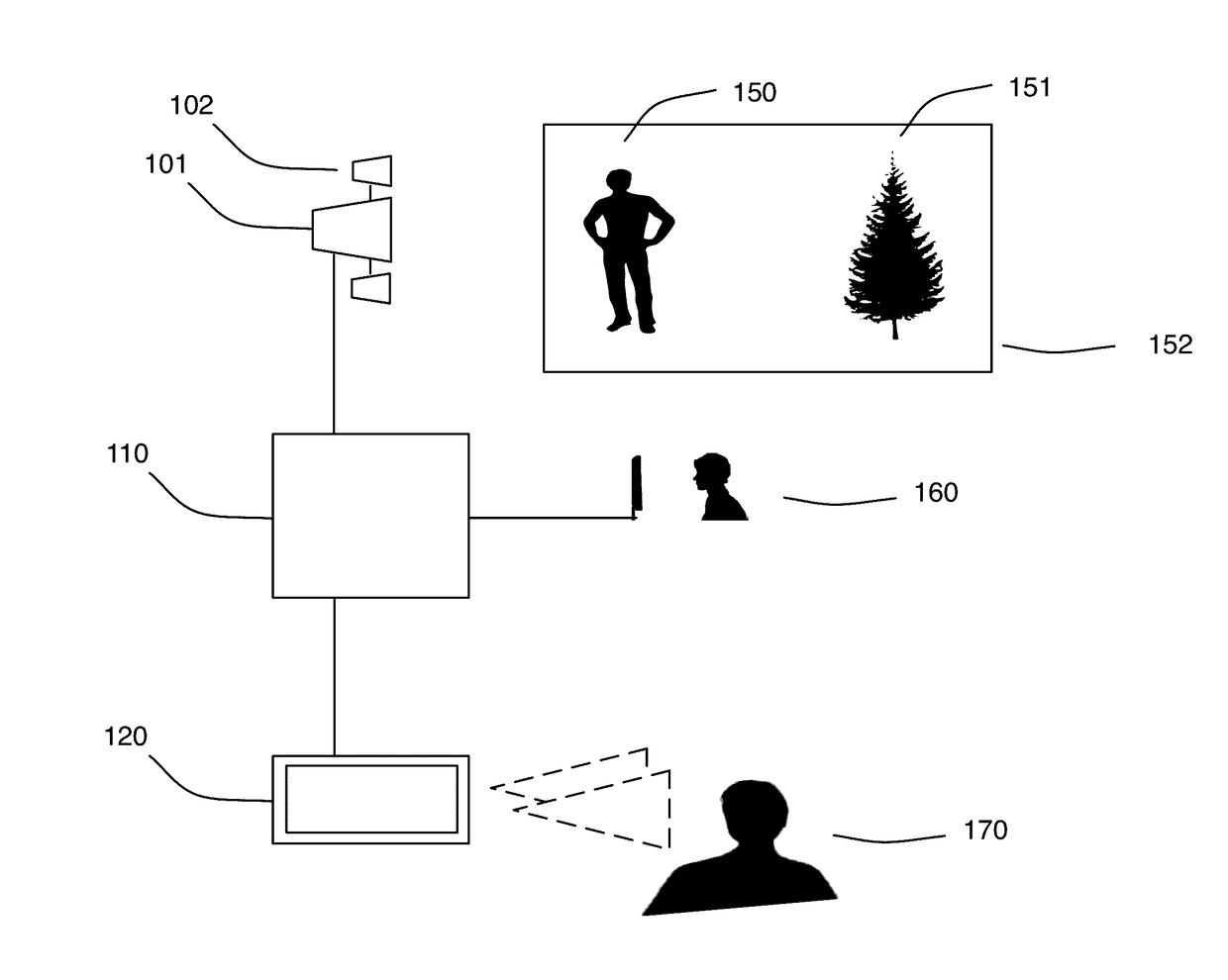
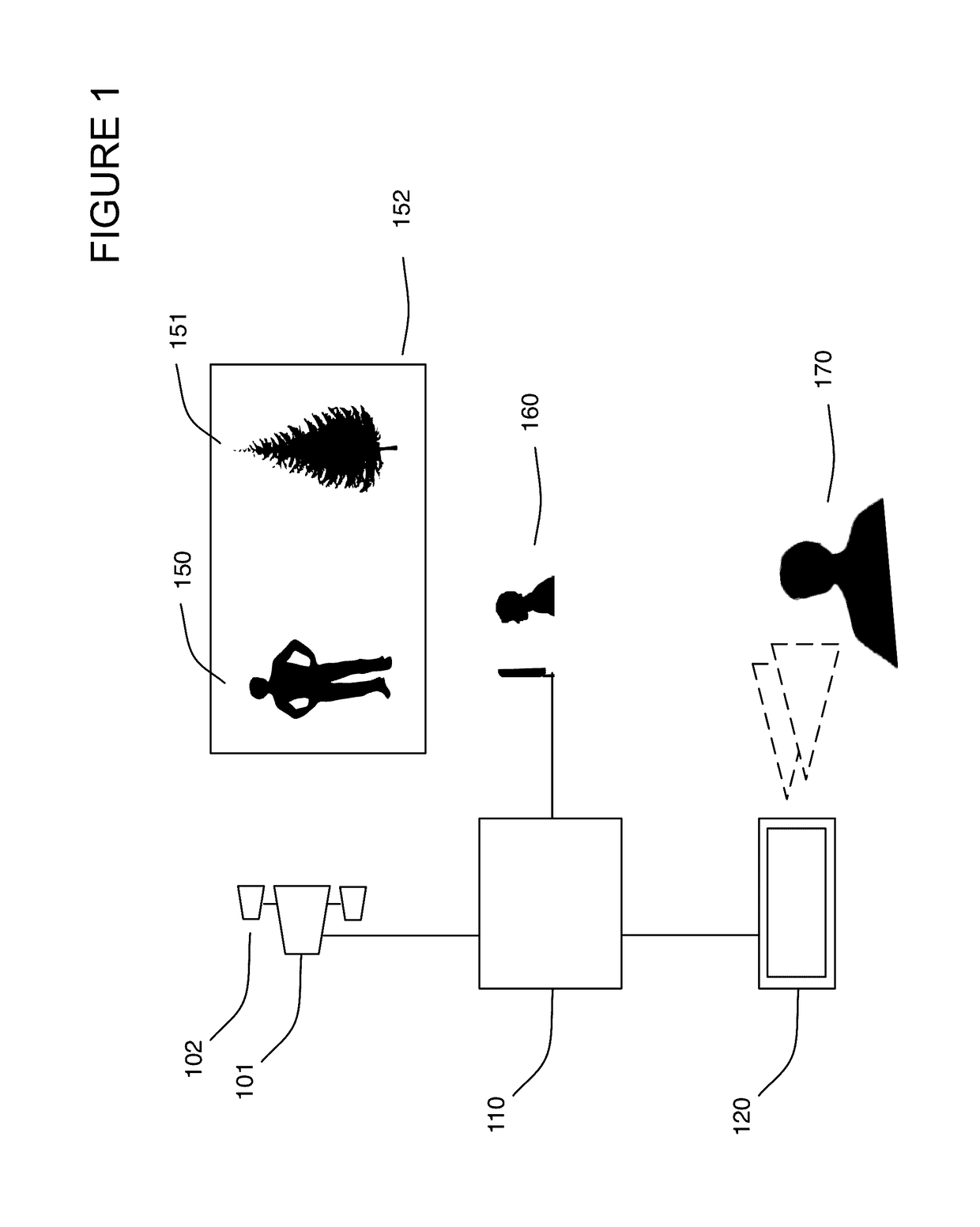
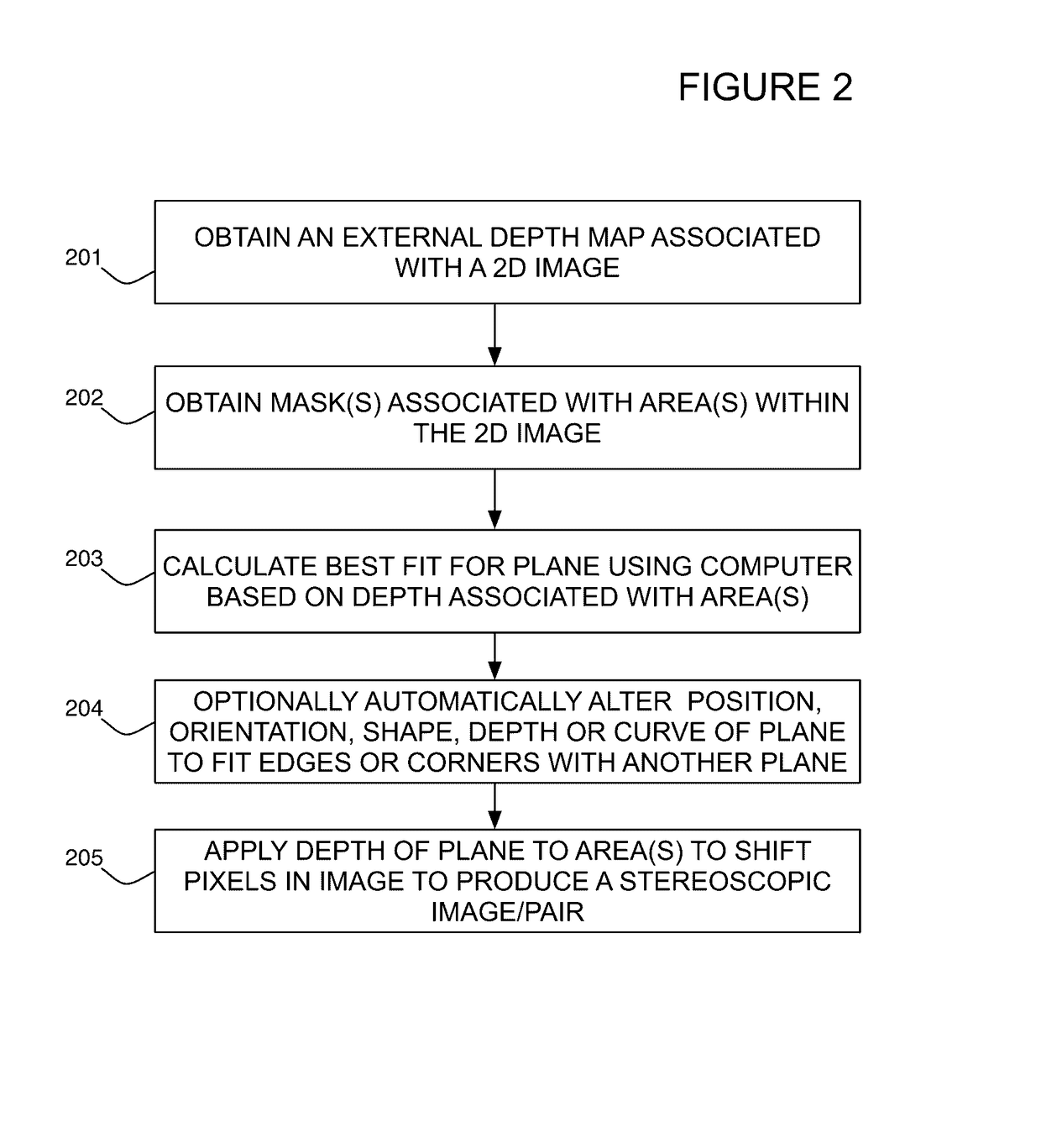
Method of converting 2D video to 3D video using 3D object models
InactiveUS9438878B2Quick conversionIncrease flexibilityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature trackingDegrees of freedom
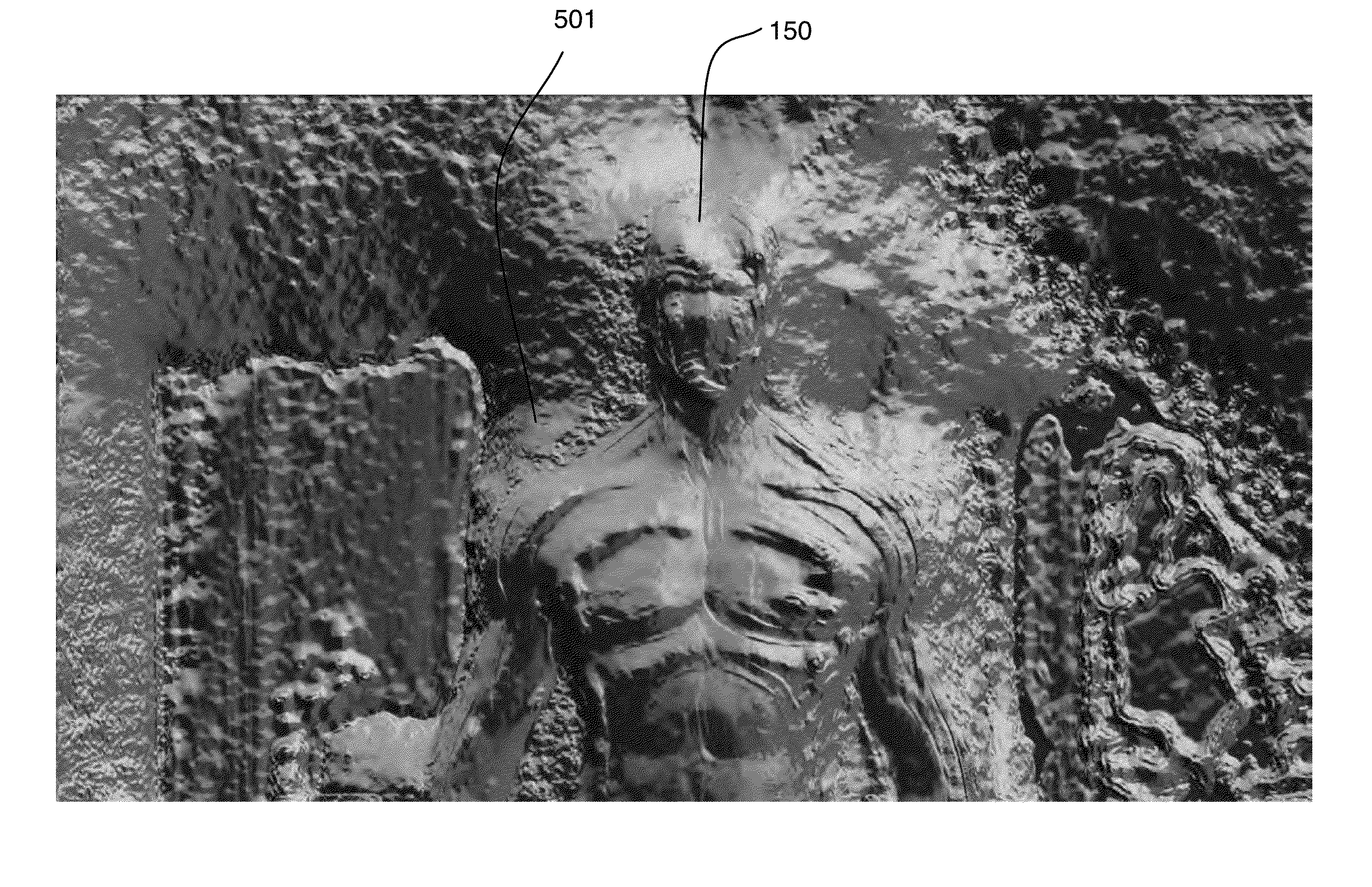
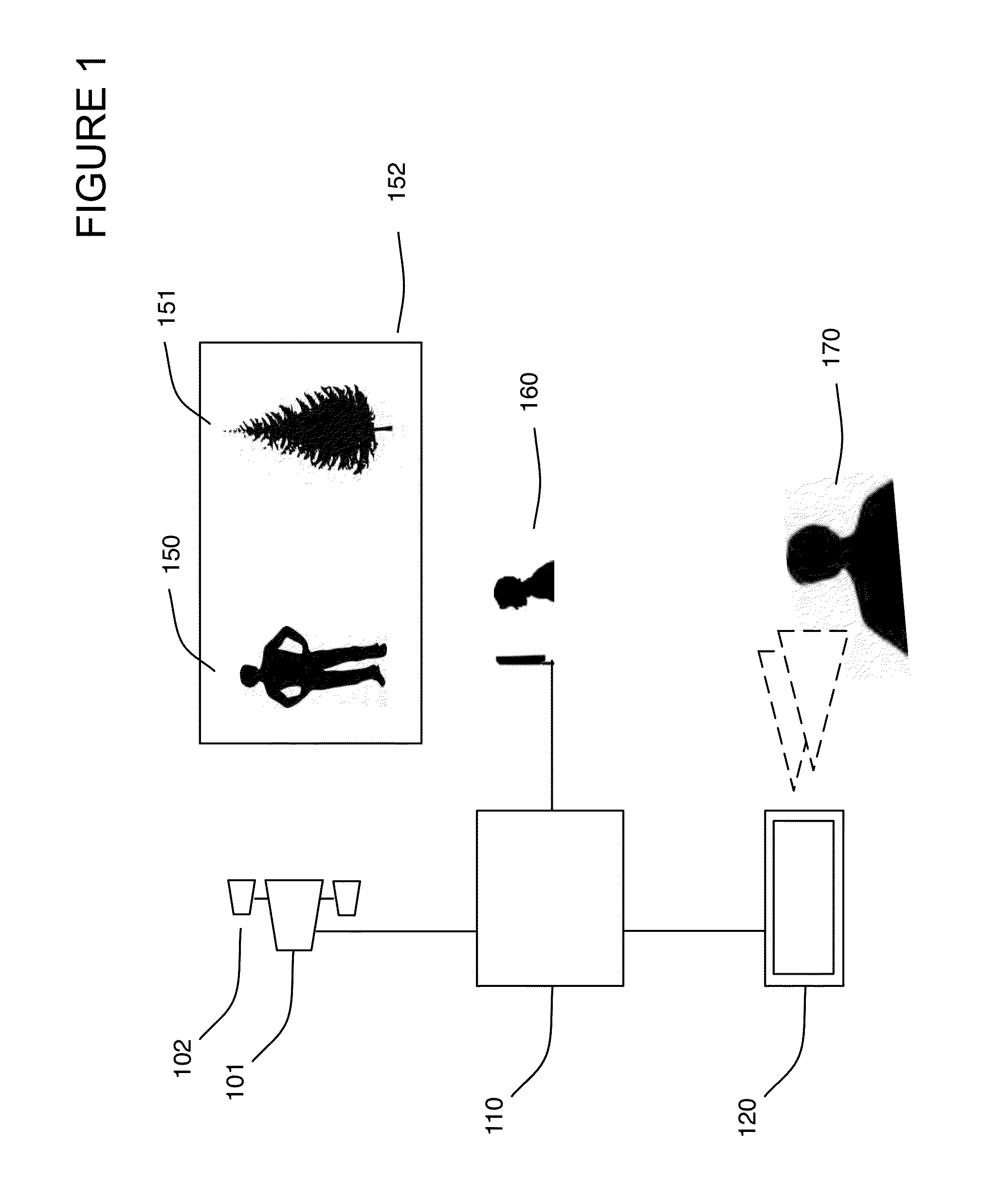
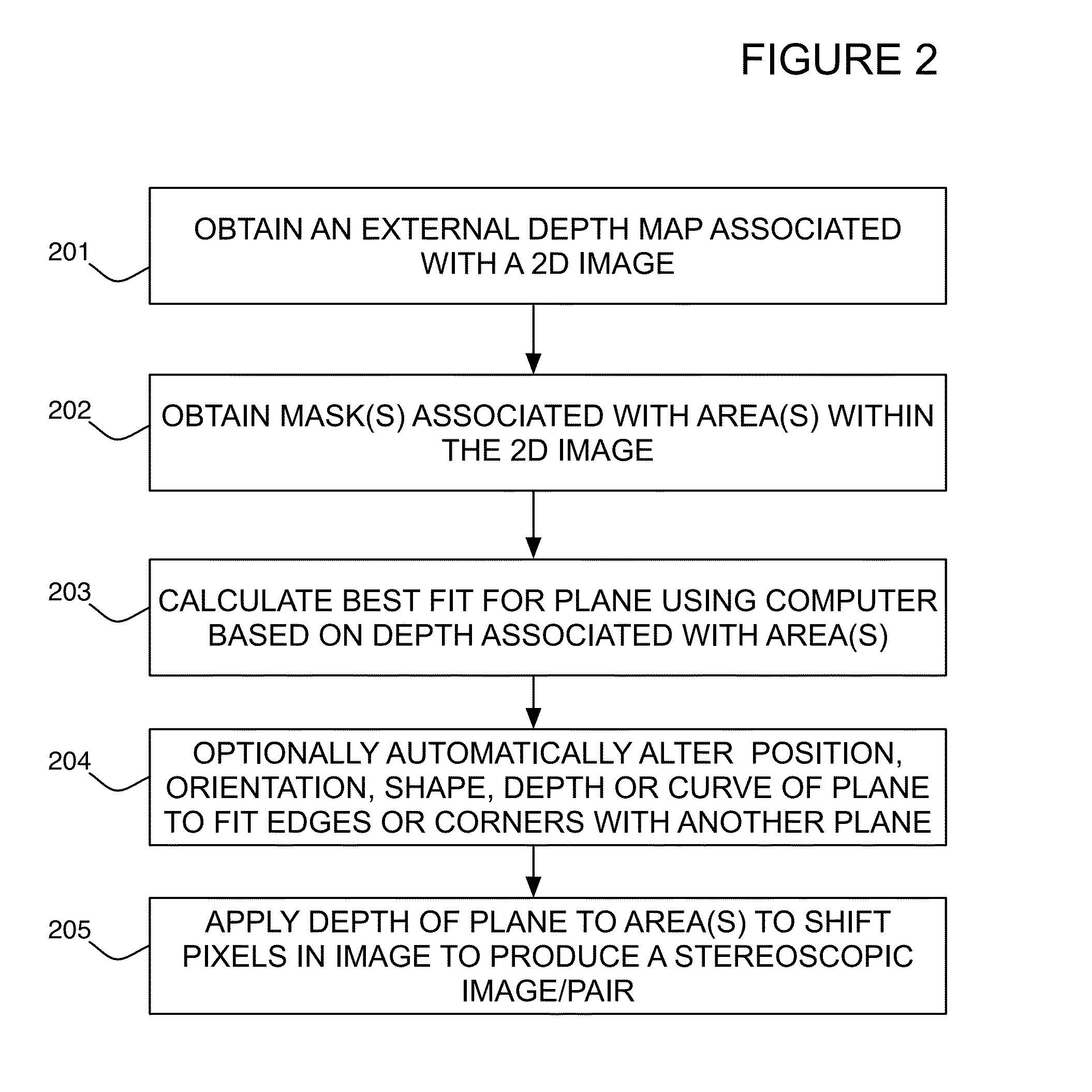
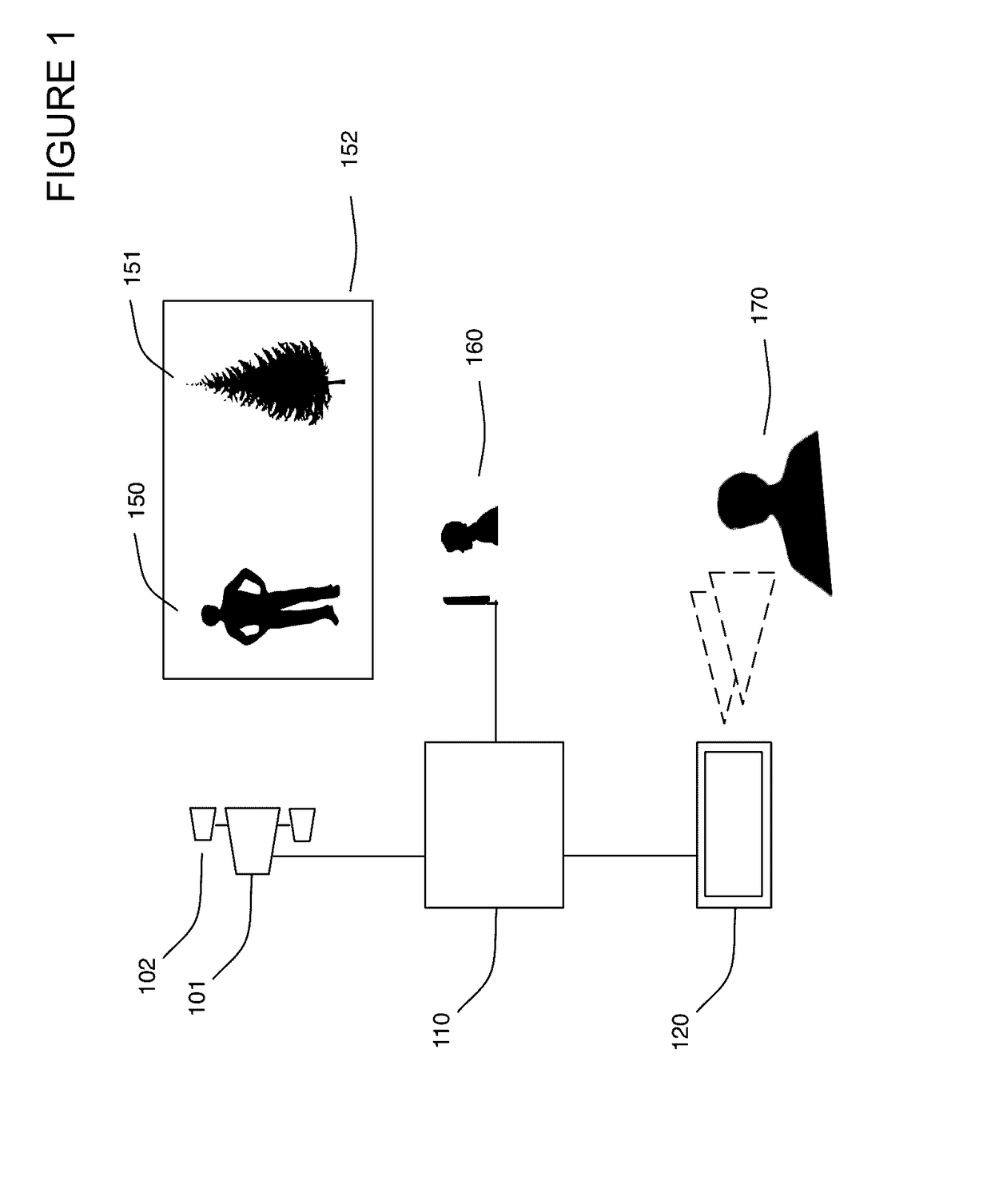
Method for converting 2D video to 3D video using 3D object models. Embodiments of the invention obtain a 3D object model for one or more objects in a 2D video scene, such as a character. Object models may for example be derived from 3D scanner data; planes, polygons, or surfaces may be fit to this data to generate a 3D model. In each frame in which a modeled object appears, the location and orientation of the 3D model may be determined in the frame, and a depth map for the object may be generated from the model. 3D video may be generated using the depth map. Embodiments may use feature tracking to automatically determine object location and orientation. Embodiments may use rigged 3D models with degrees of freedom to model objects with parts that move relative to one another.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
Methods and apparatus for introducing liquids into microfluidic chambers
InactiveUS20050022895A1High energyPotential energyLiquid degasificationCircuit elementsHigh energyEngineering
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
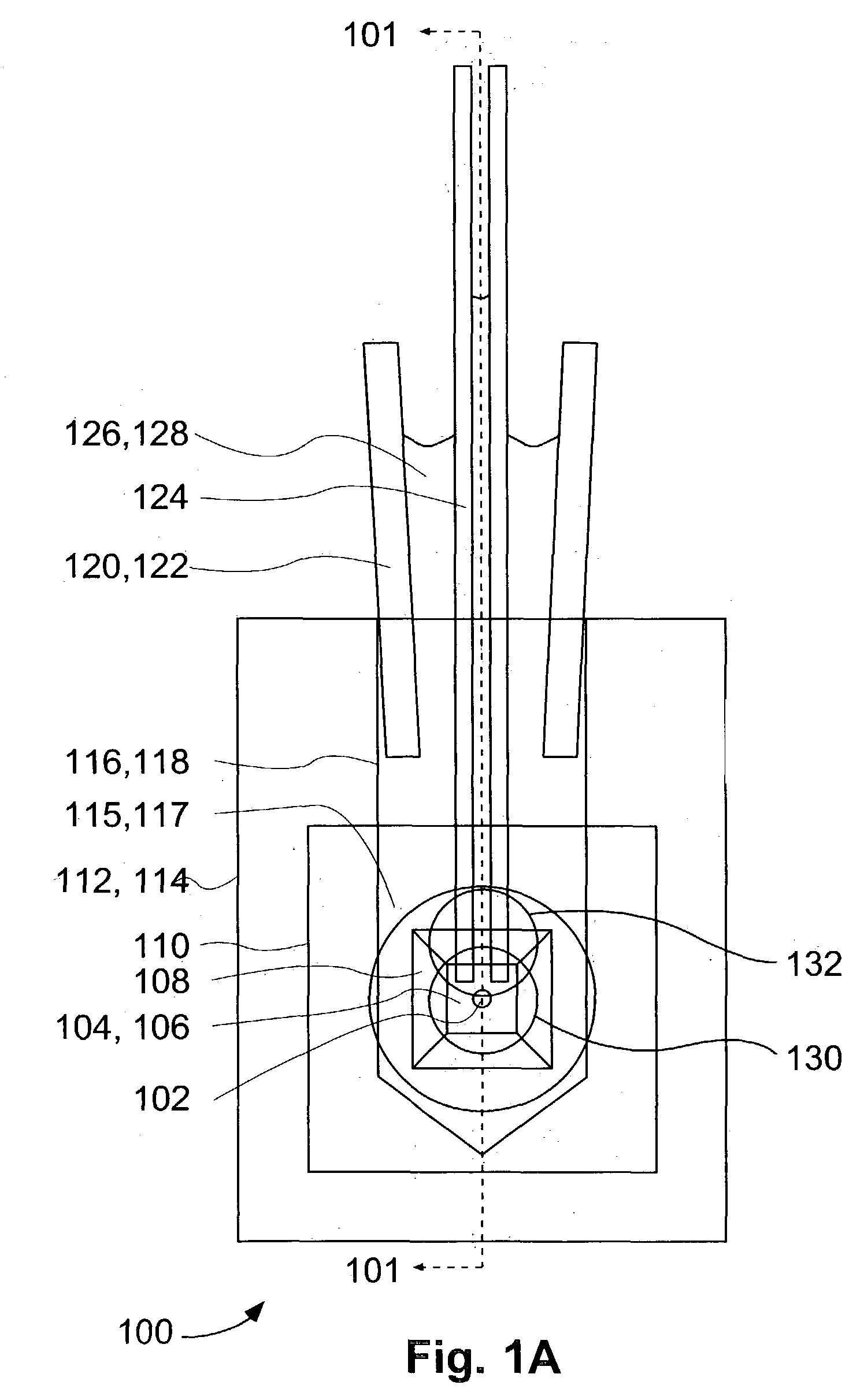
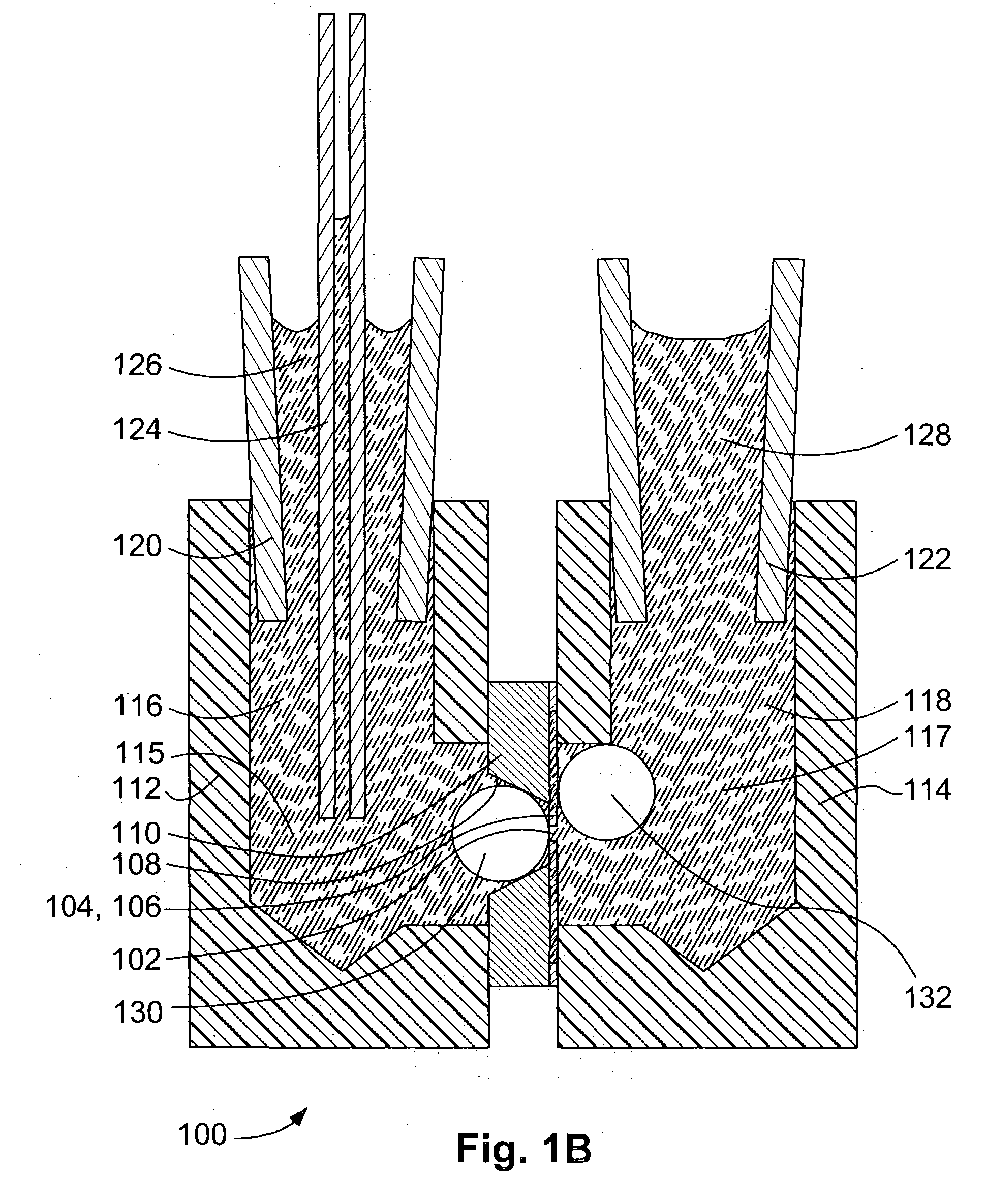
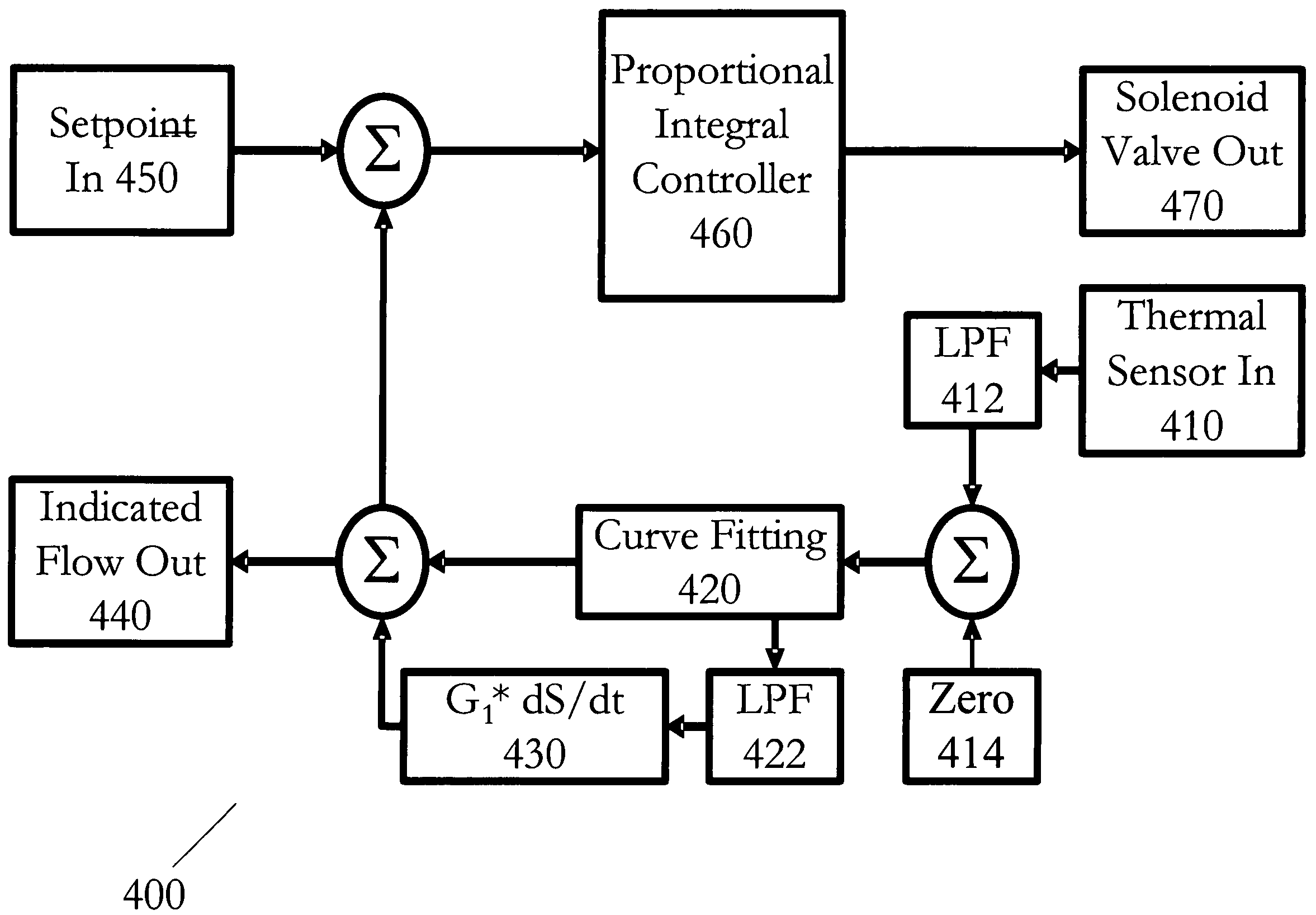
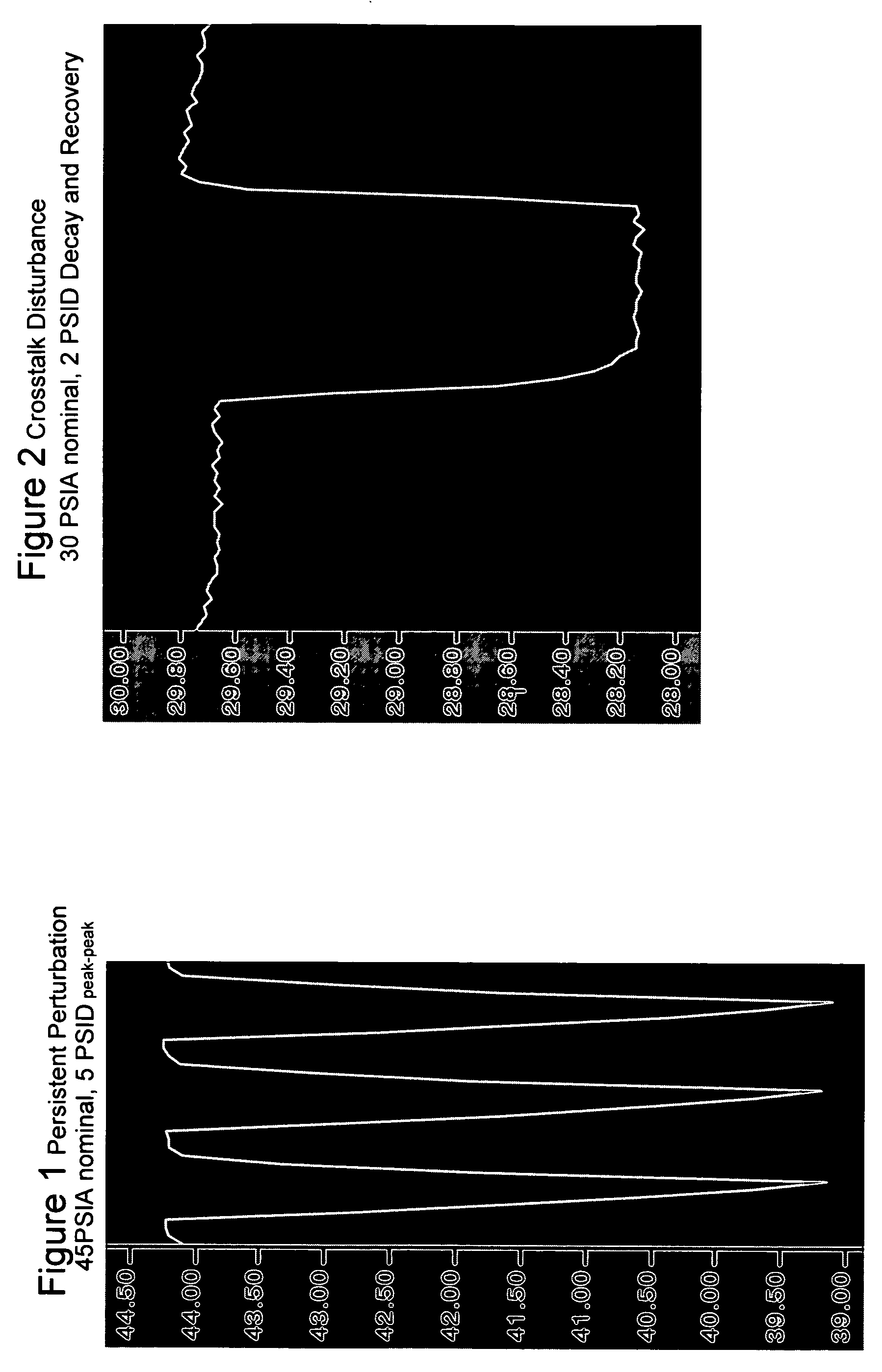
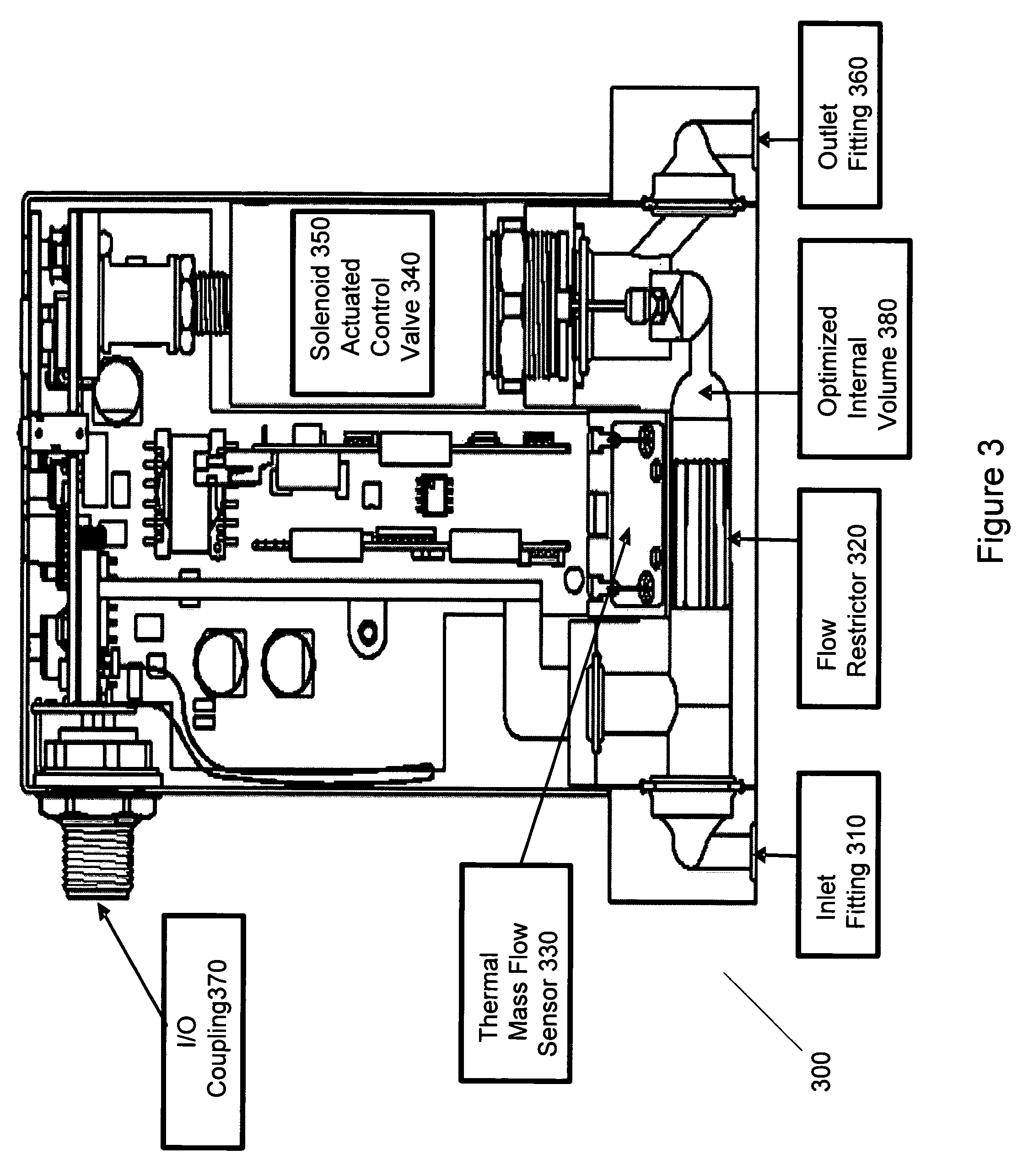
Method and system for a mass flow controller with reduced pressure sensitivity
InactiveUS7216019B2Reduce sensitivityReduce in quantityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesVolume/mass flow measurementIsolation valveTransducer
Systems and methods for mass flow controllers which minimize false flow conditions and display a reduced sensitivity to pressure transients are disclosed. Pressure gradients that exist within the volume of a mass flow controller fluid path are minimized in order to limit the potential energy contained in compressed or pressurized process gas. Additionally, process gas pressure may be monitored using a pressure sensor. This pressure signal is utilized in conjunction with a control algorithm to cancel the detrimental effect of certain flow components. These mass flow controllers may be used as drop in replacements for legacy mass flow controllers and reduce the cost of gas sticks due to elimination of discrete components such as pressure regulators, gas filters, pressure transducers, local pressure displays, isolation valves, seals, etc.
Owner:BROOKS INSTRUMENT +1
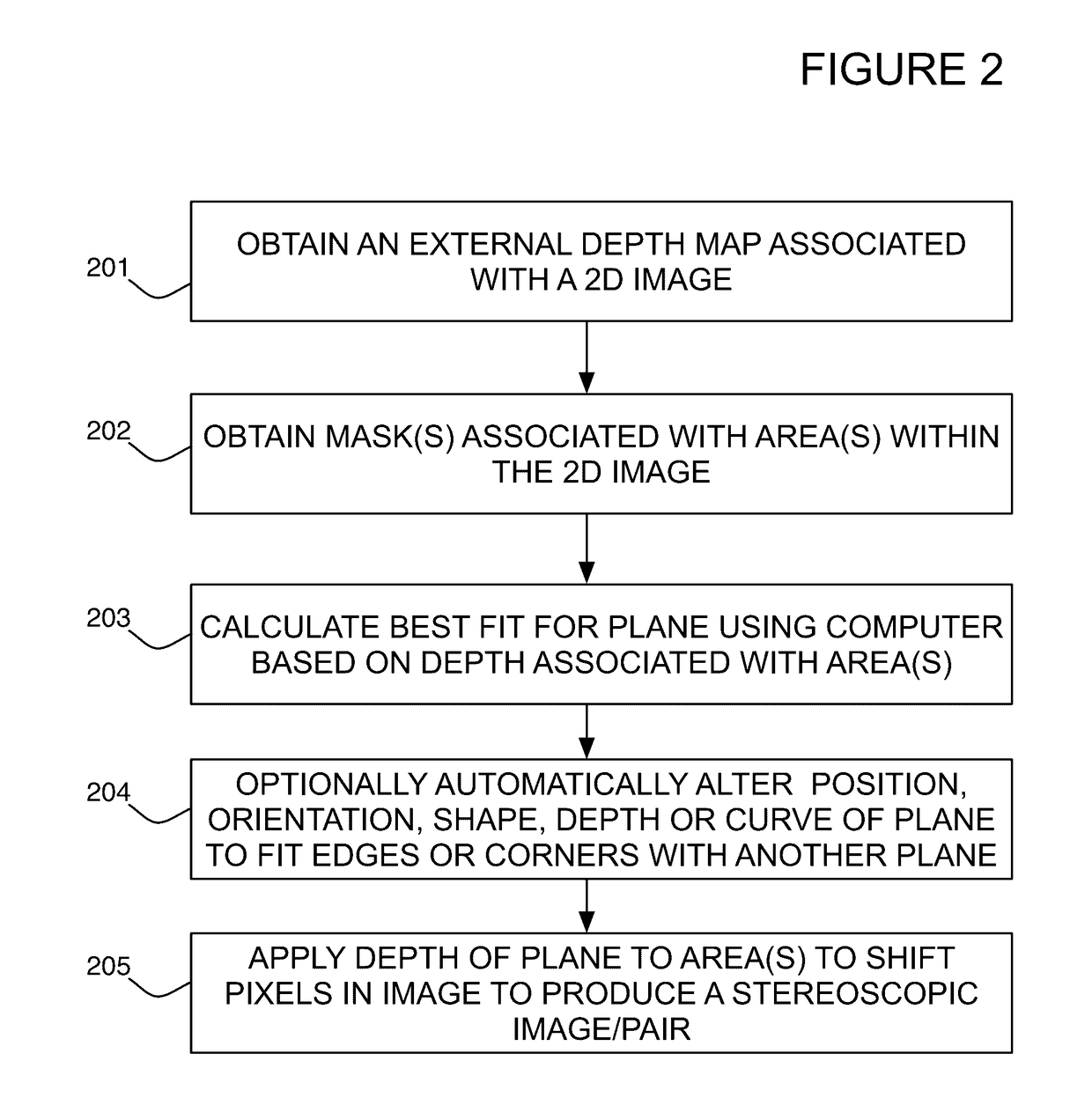
Method of converting 2d video to 3D video using machine learning
ActiveUS20170085863A1Increased artisticIncreased technical flexibilityImage enhancementImage analysis2D to 3D conversionObject label
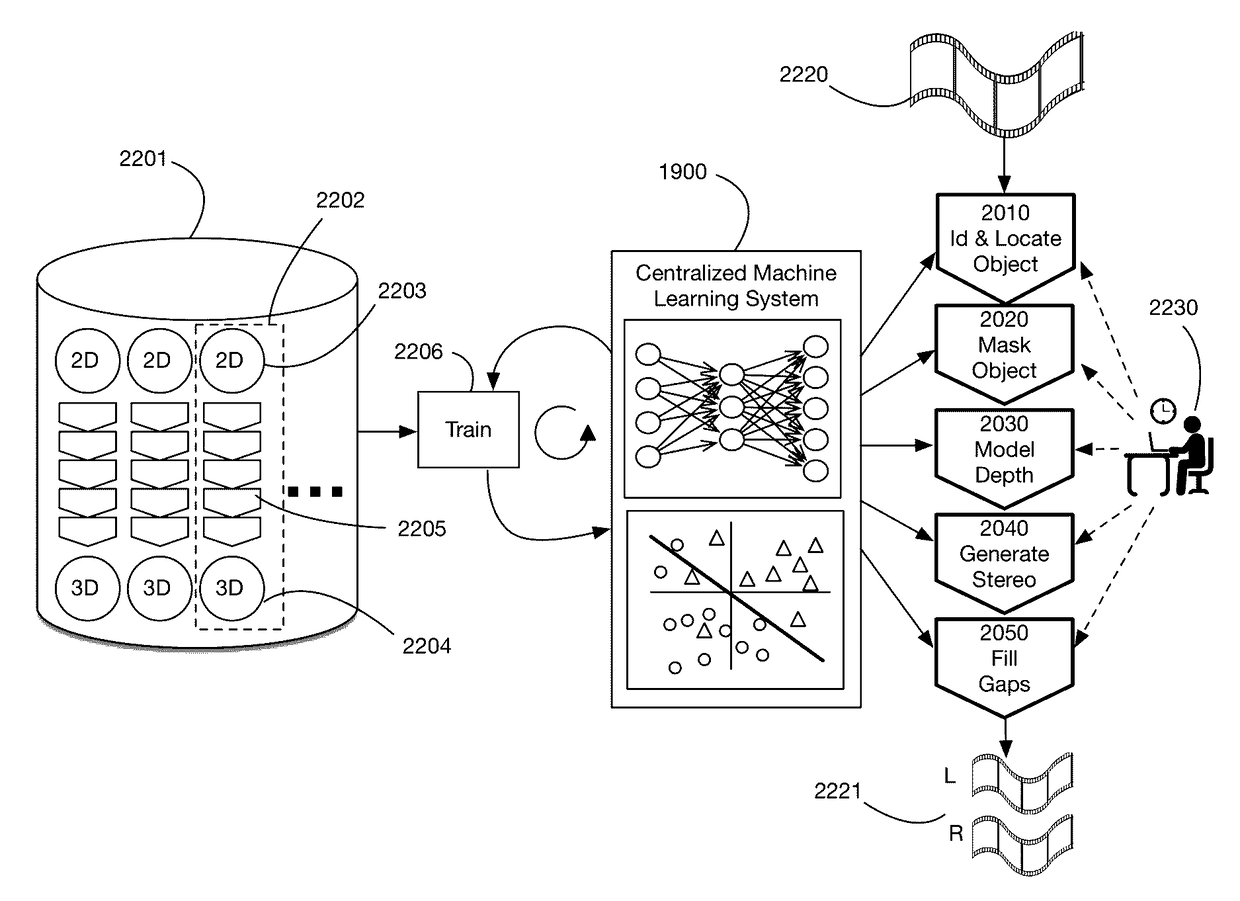
Machine learning method that learns to convert 2D video to 3D video from a set of training examples. Uses machine learning to perform any or all of the 2D to 3D conversion steps of identifying and locating objects, masking objects, modeling object depth, generating stereoscopic image pairs, and filling gaps created by pixel displacement for depth effects. Training examples comprise inputs and outputs for the conversion steps. The machine learning system generates transformation functions that generate the outputs from the inputs; these functions may then be used on new 2D videos to automate or semi-automate the conversion process. Operator input may be used to augment the results of the machine learning system. Illustrative representations for conversion data in the training examples include object tags to identify objects and locate their features, Bézier curves to mask object regions, and point clouds or geometric shapes to model object depth.
Owner:USFT PATENTS INC
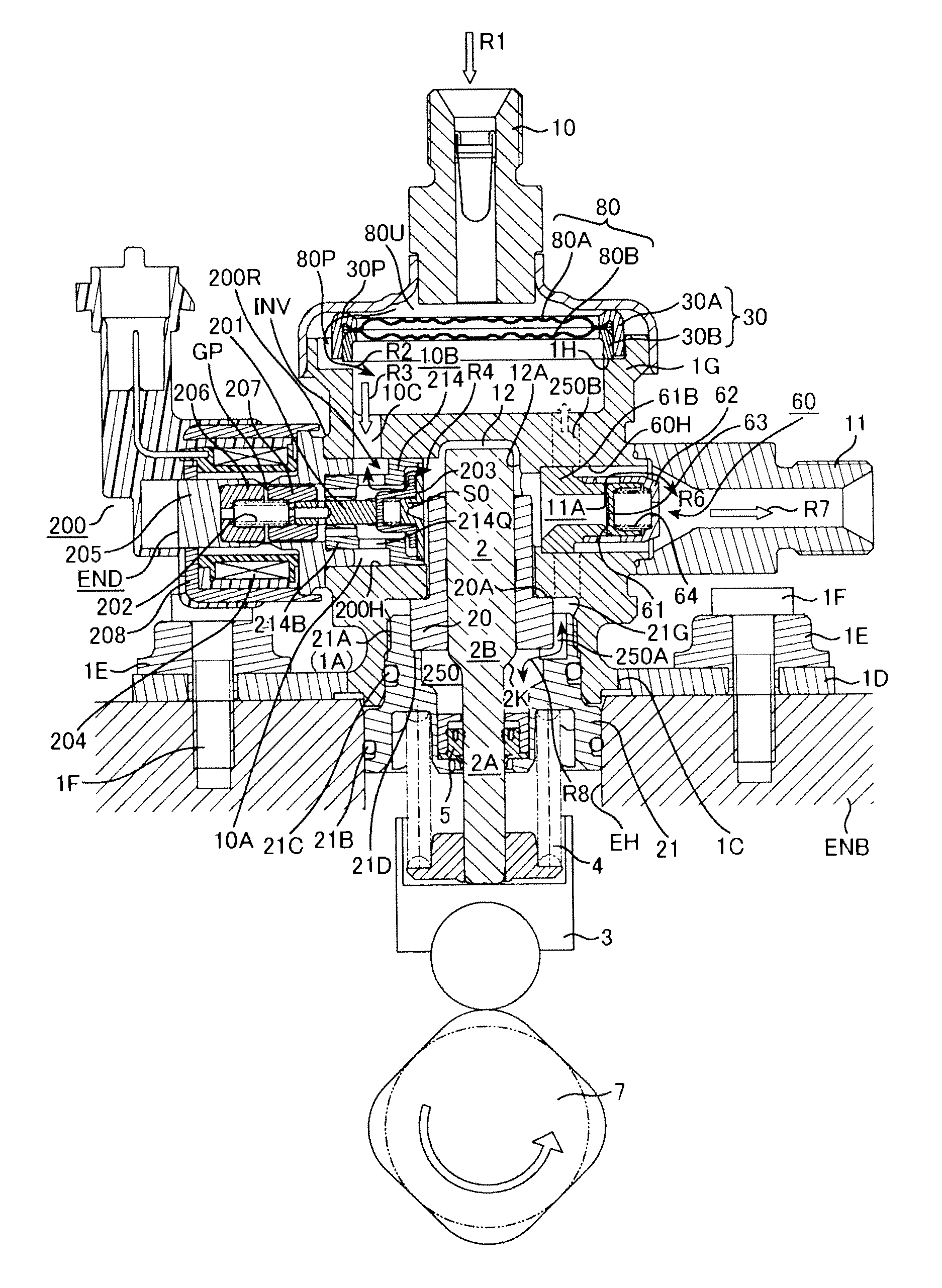
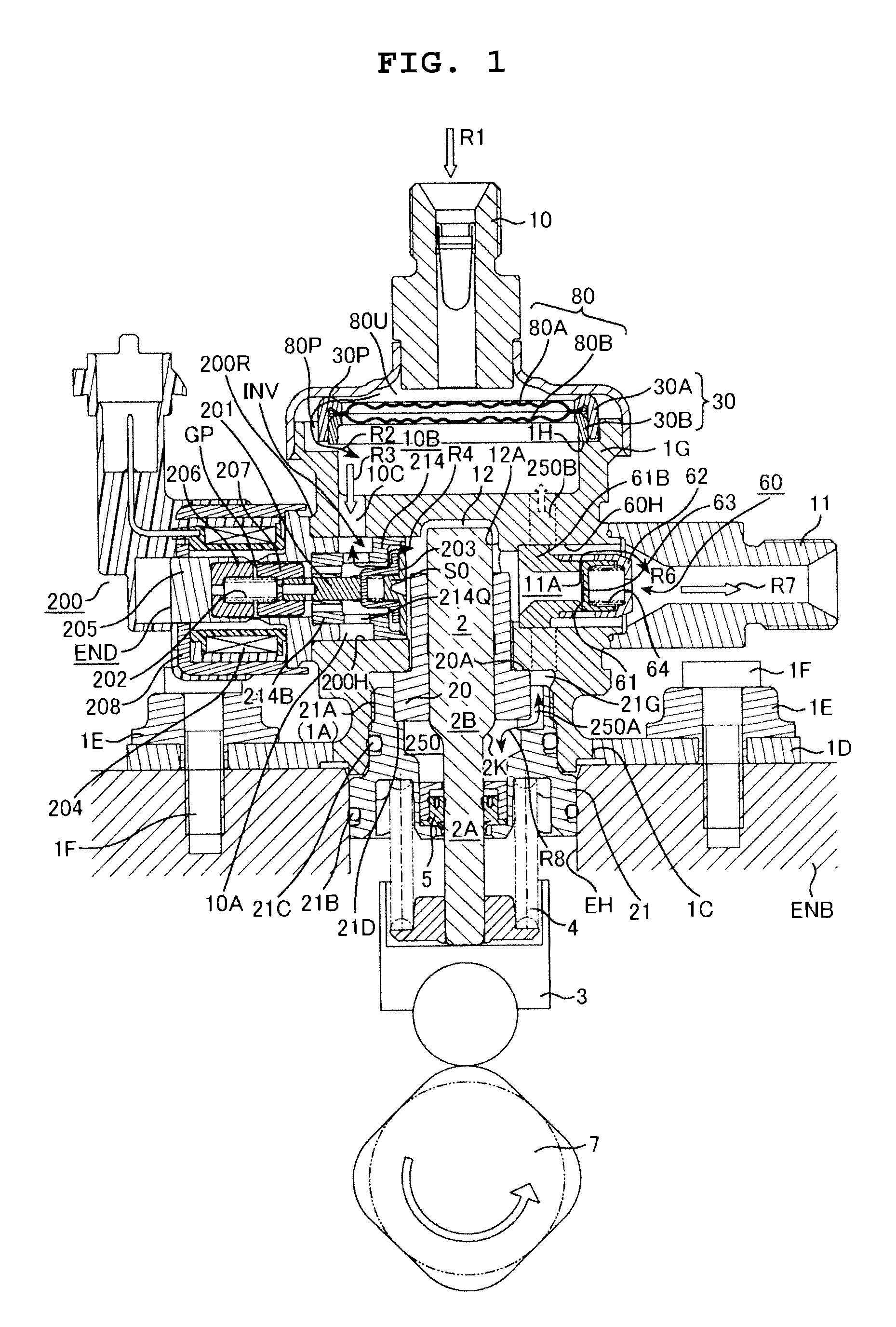
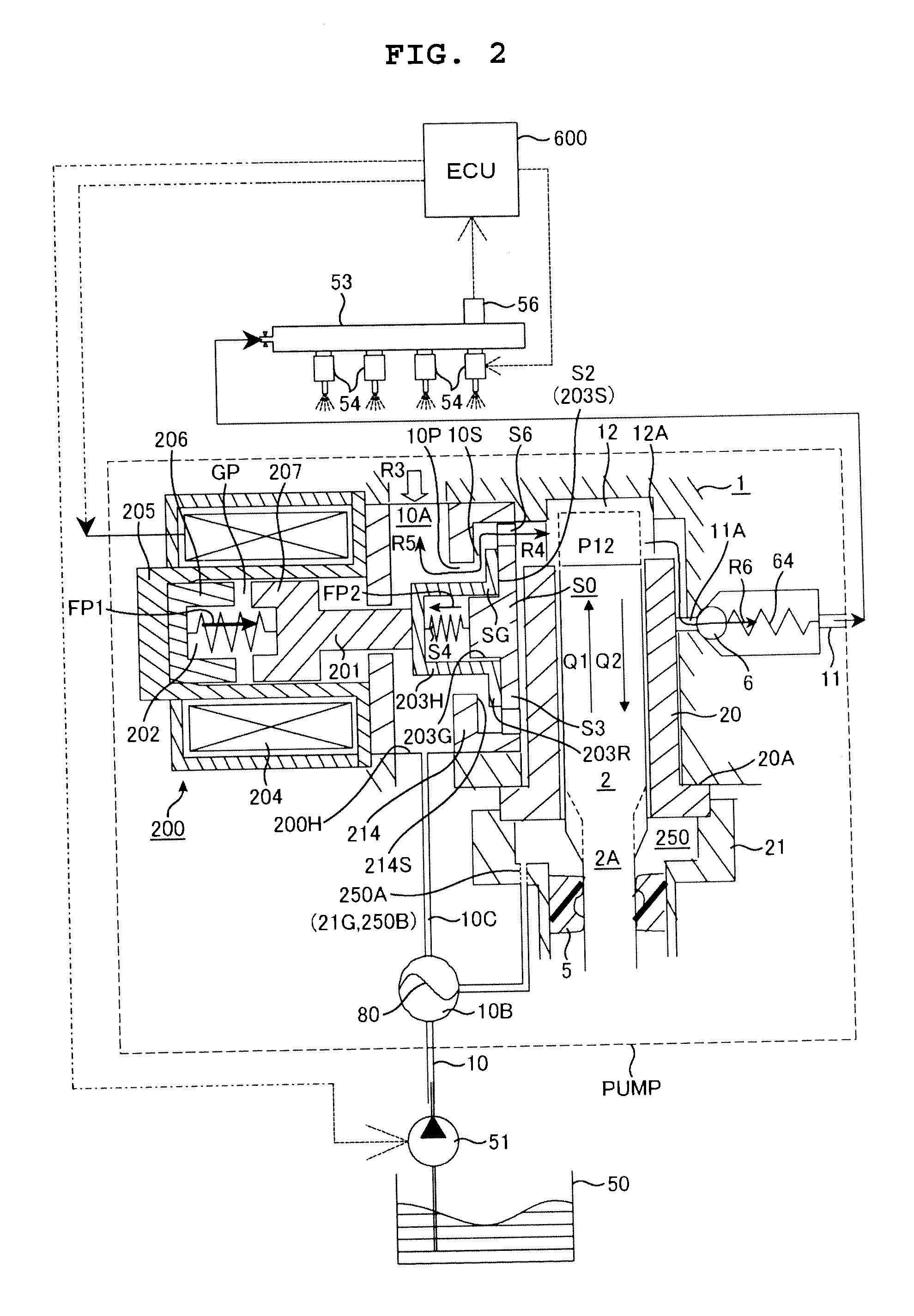
Control method of magnetic solenoid valve, control method of electromagnetically controlled inlet valve of high pressure fuel pump, and control device for electromagnetic actuator of electromagnetically controlled inlet valve
ActiveUS20130032212A1Current consumptionReduce noiseOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrical controlTop dead centerSolenoid valve
In an electromagnetically controlled inlet valve actuator provided to a high pressure fuel pump, an impinging sound which is generated at the time of operating the mechanism is reduced. In a high pressure fuel pump provided with an electromagnetically controlled inlet valve (operated by way of a plunger rod), a current supply period includes a 1st current supply period for performing an operation of attracting the plunger rod in a valve closing direction, a 2nd current supply period for alleviating a speed at which the plunger rod moves in a valve opening direction, and a limited current supply period disposed between the 1st current supply period and the 2nd current supply period in the form of spanning a pump top dead center.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
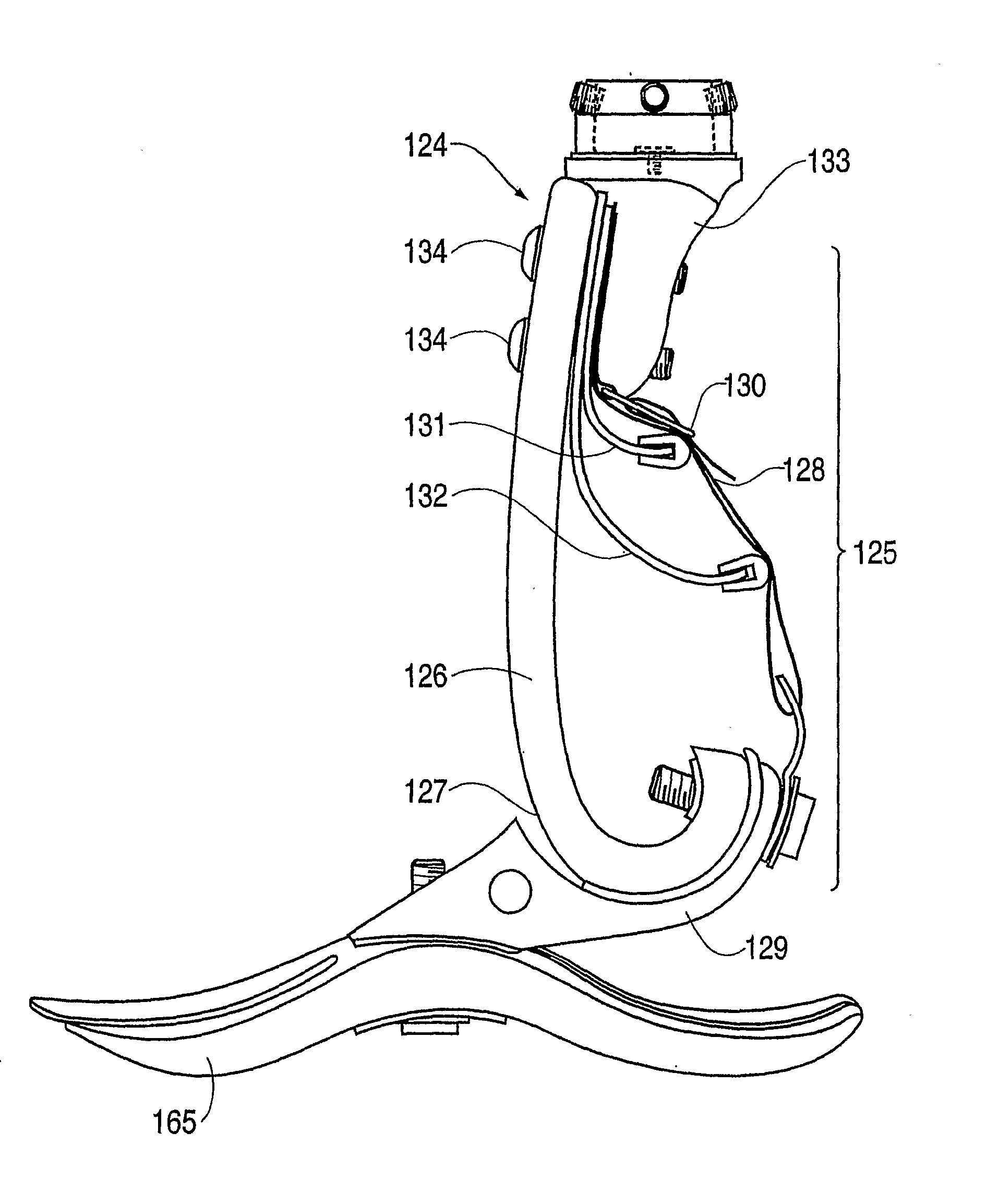
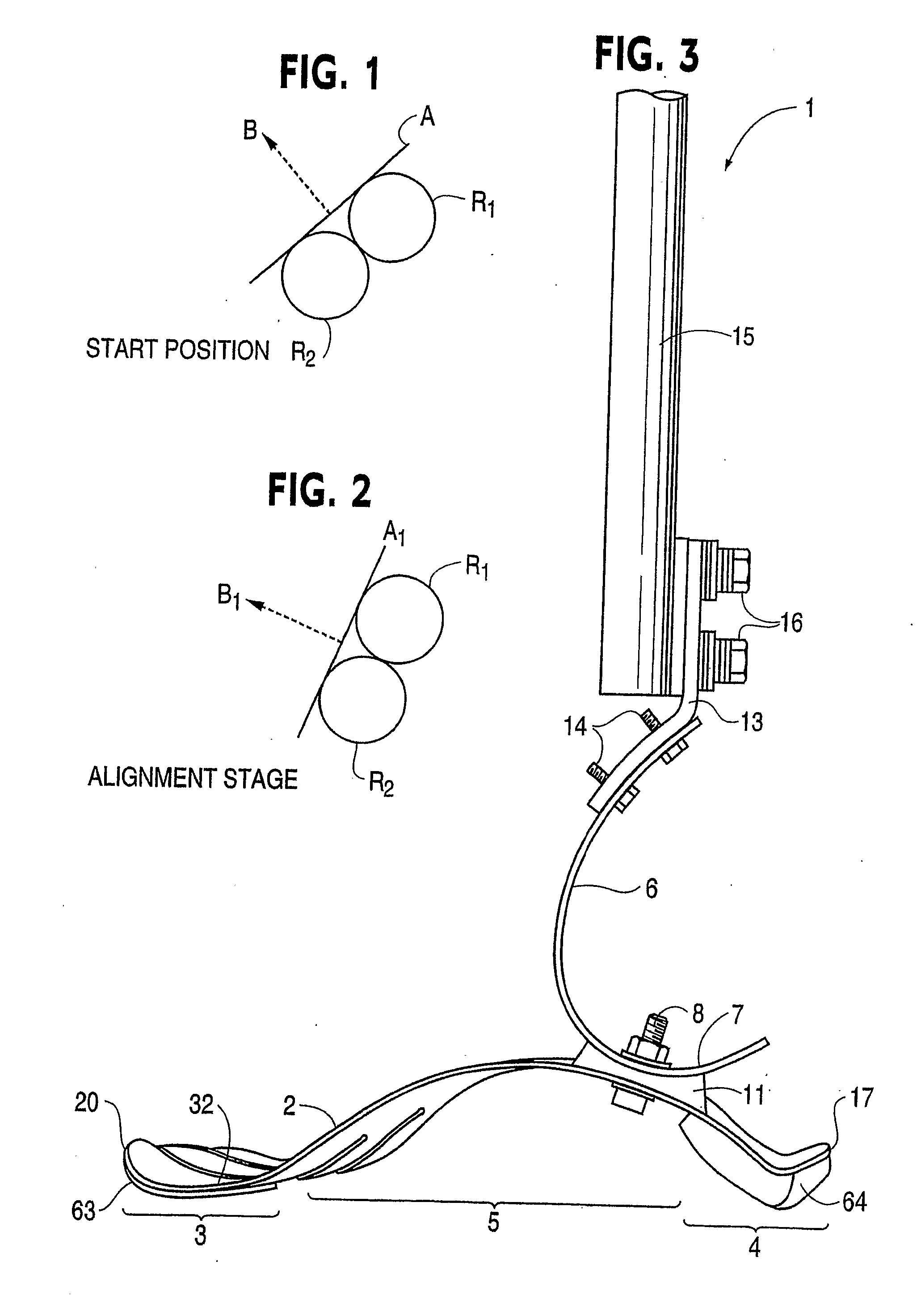
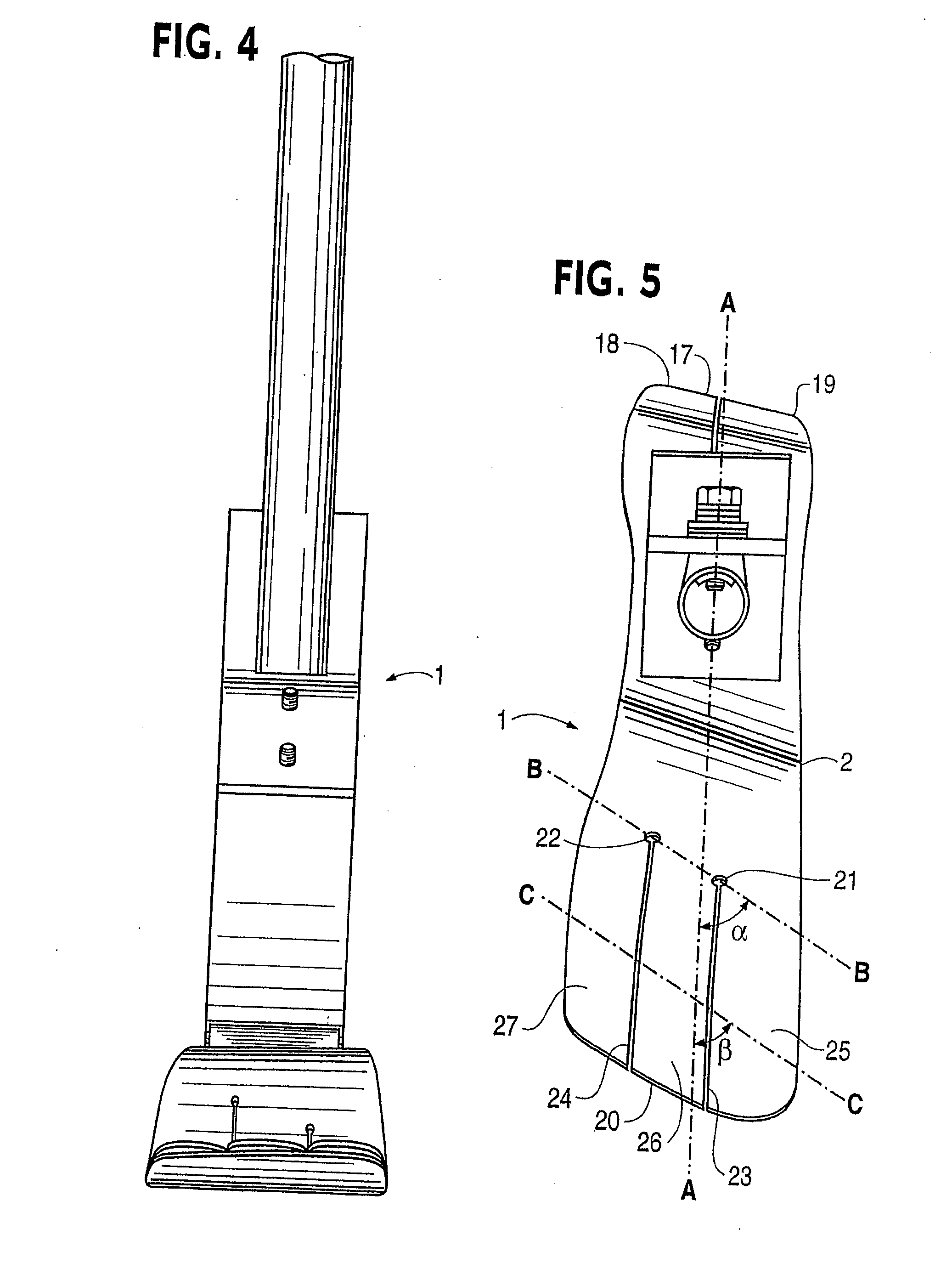
Prosthetic Foot with Tunable Performance
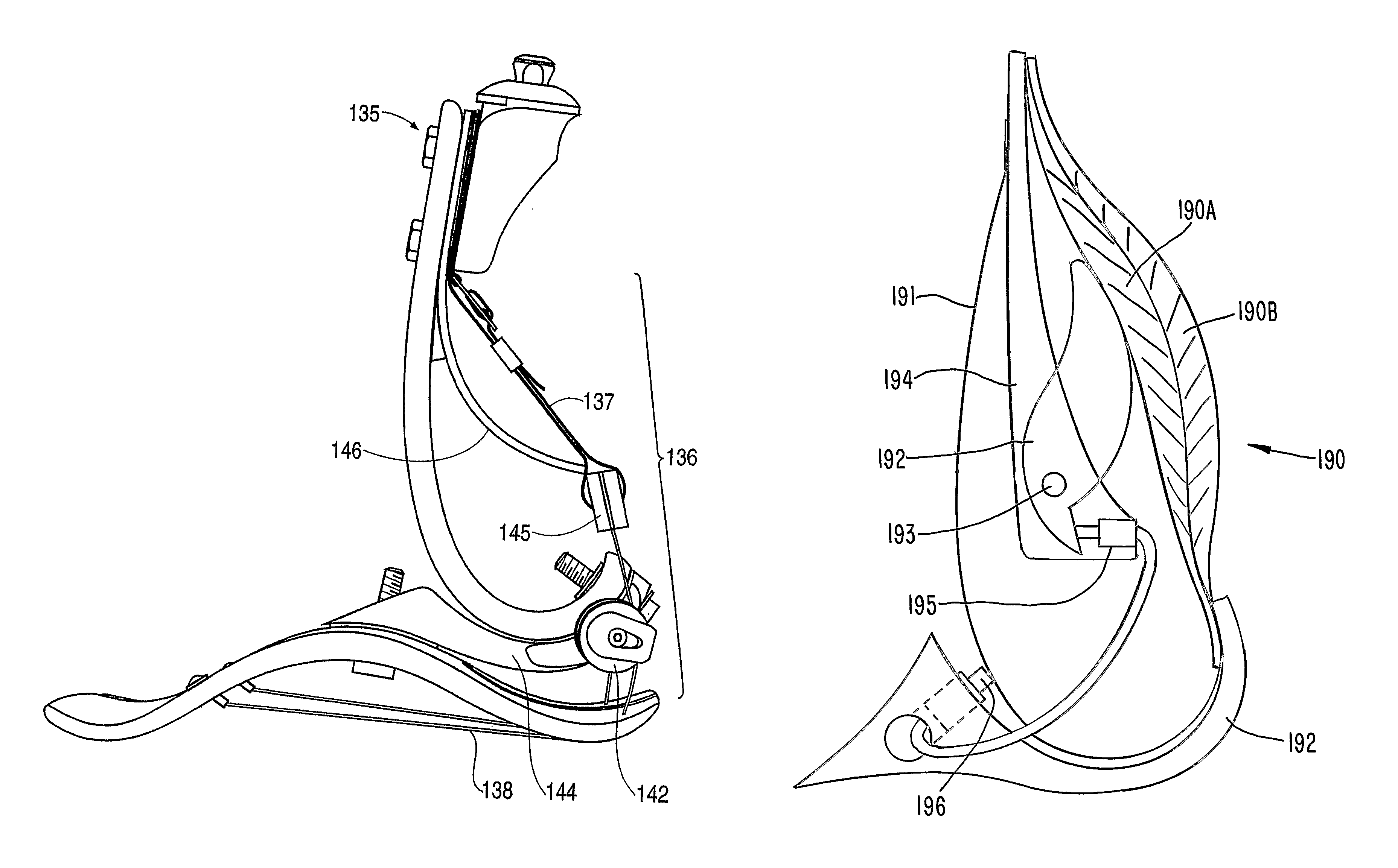
InactiveUS20070213840A1Improve performanceImproved applied mechanicLigamentsMusclesStored energyHindlimb
A resilient lower extremity prosthesis comprising a foot, an ankle and a shank above the ankle is provided with an artificial muscle (190) on the shank (191) of the prosthesis for storing energy during force loading of the prosthesis in the active propulsion phase of a person's gait and in the later stages of stance-phase of gait releasing the stored energy to aid propulsion of the person's trailing limb and body.
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
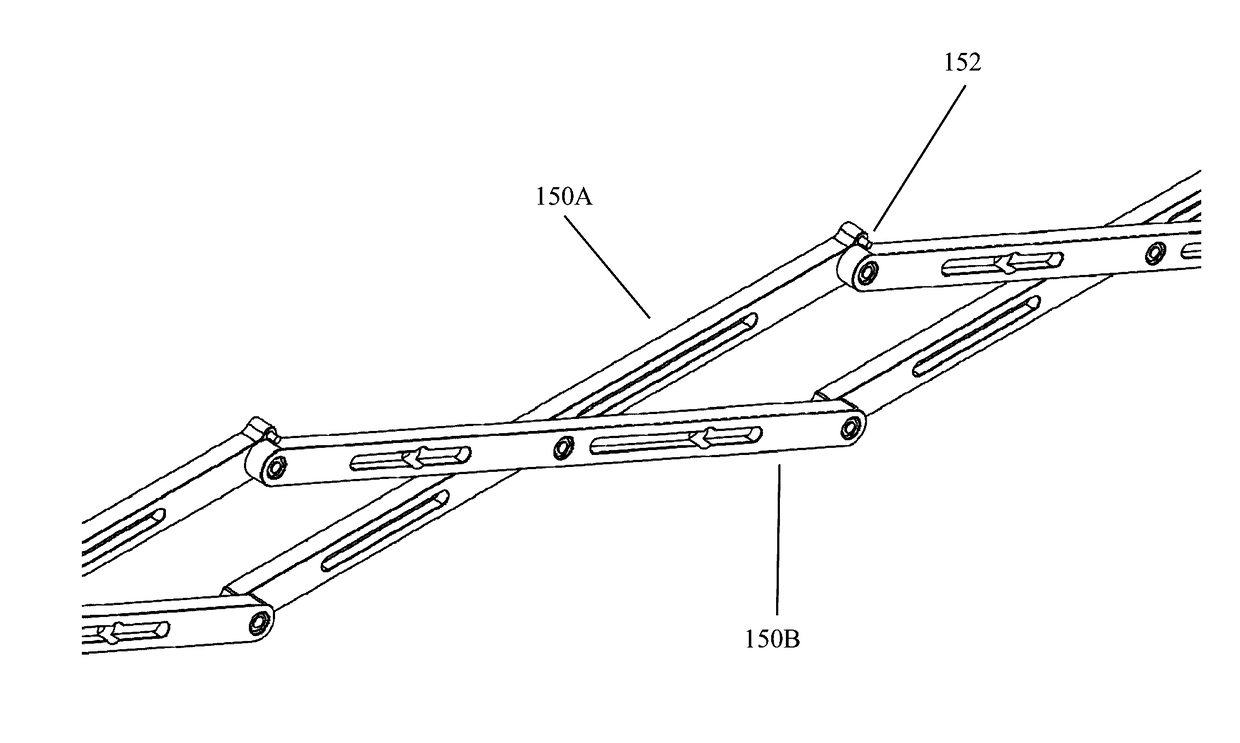
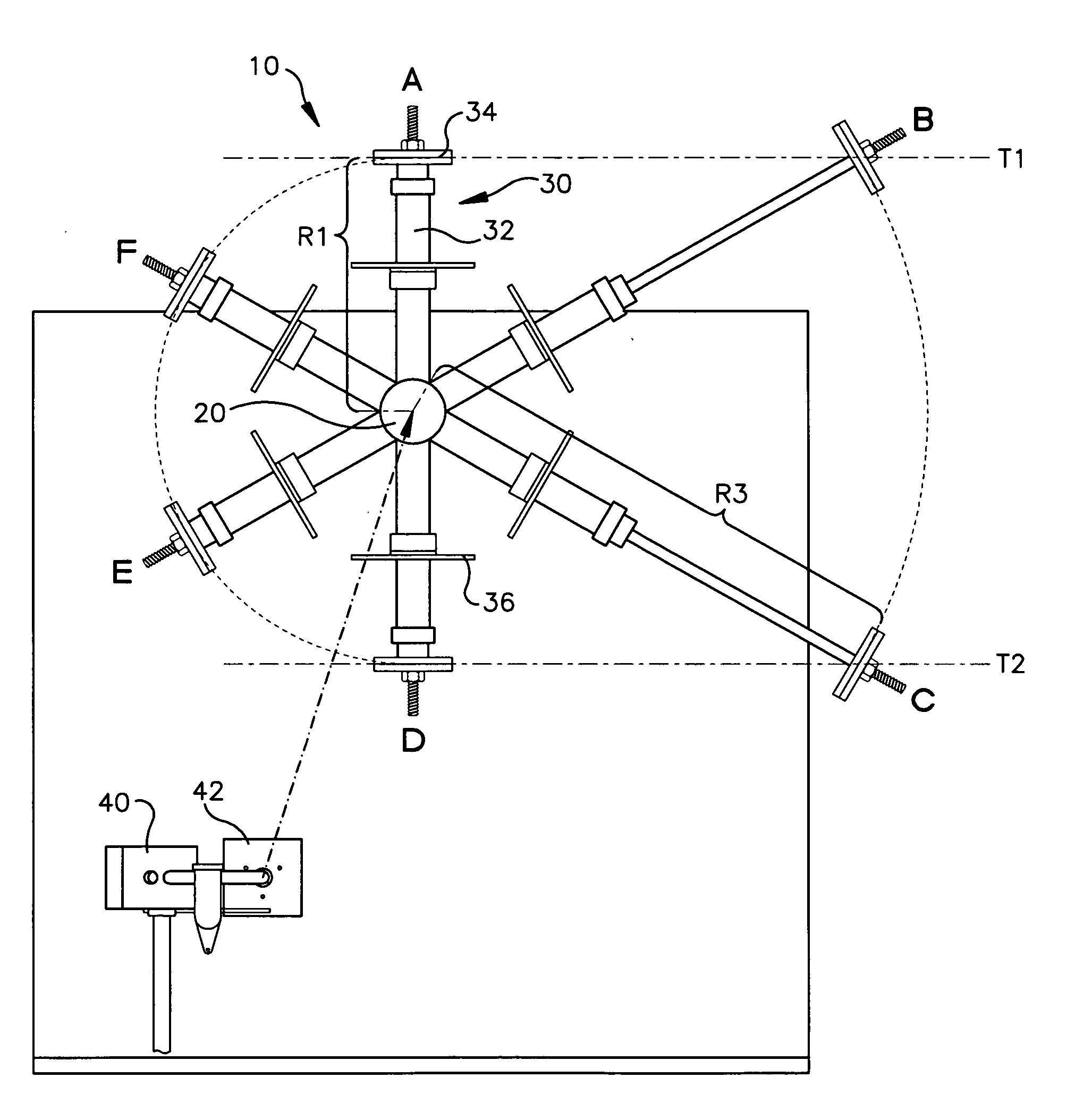
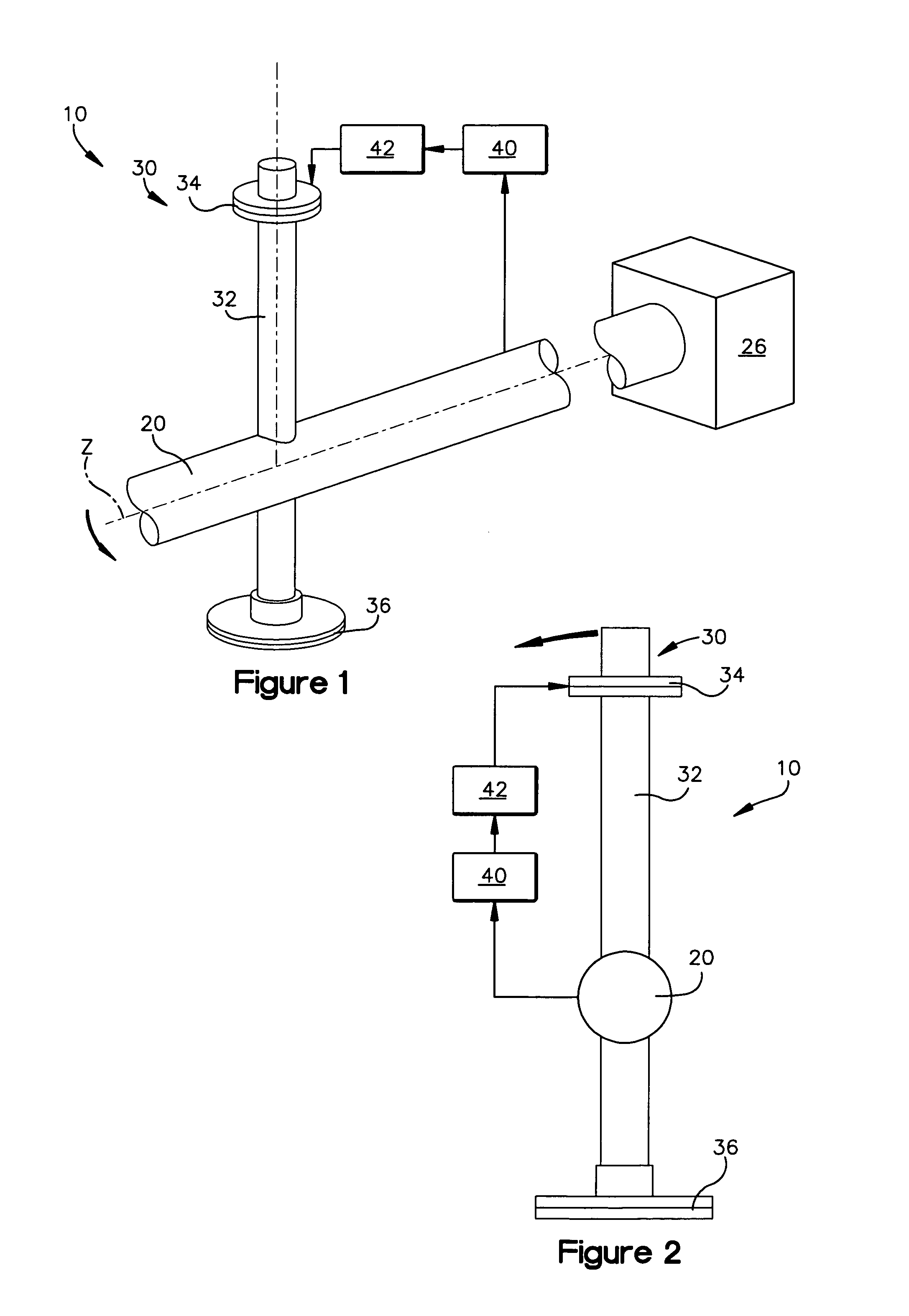
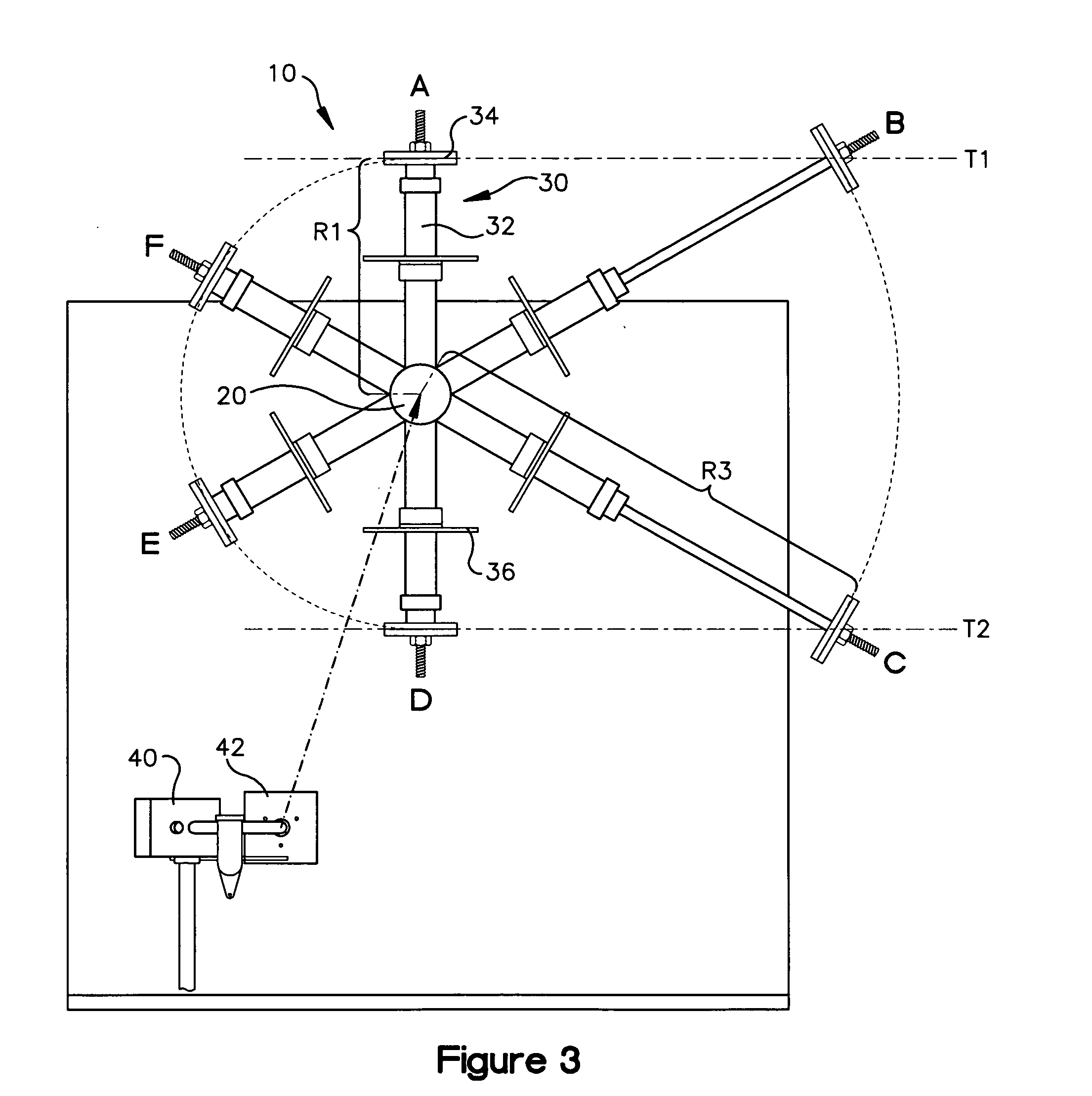
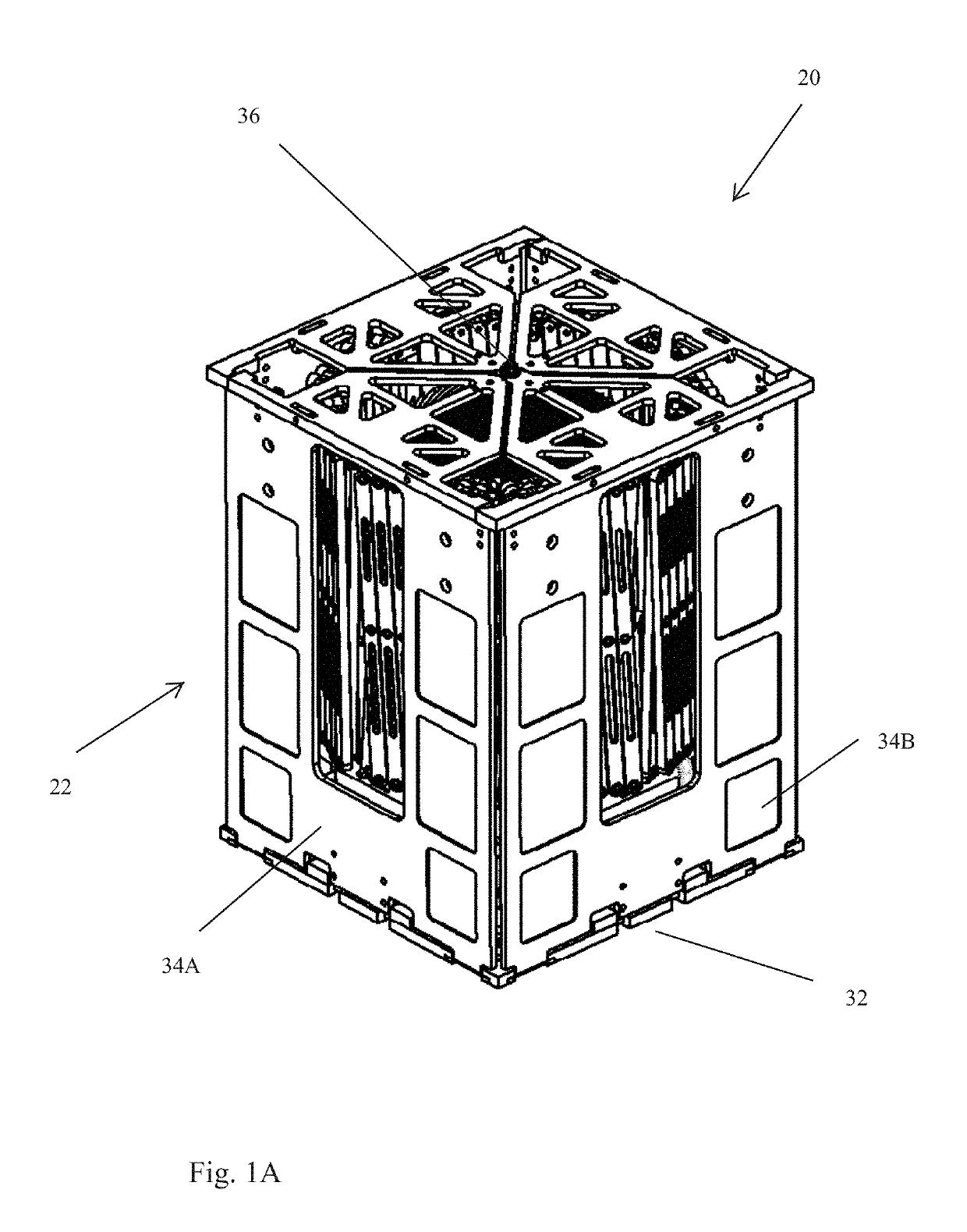
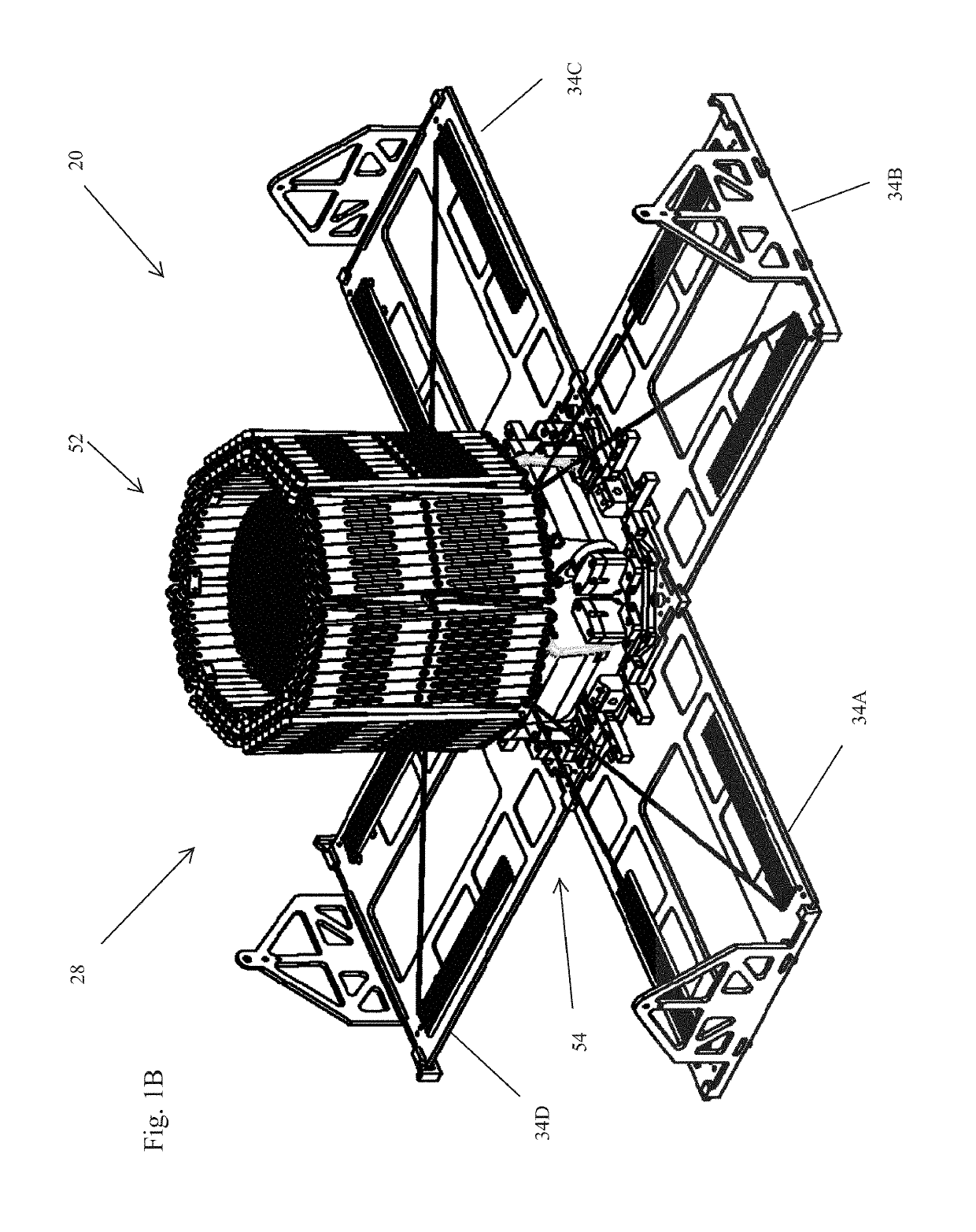
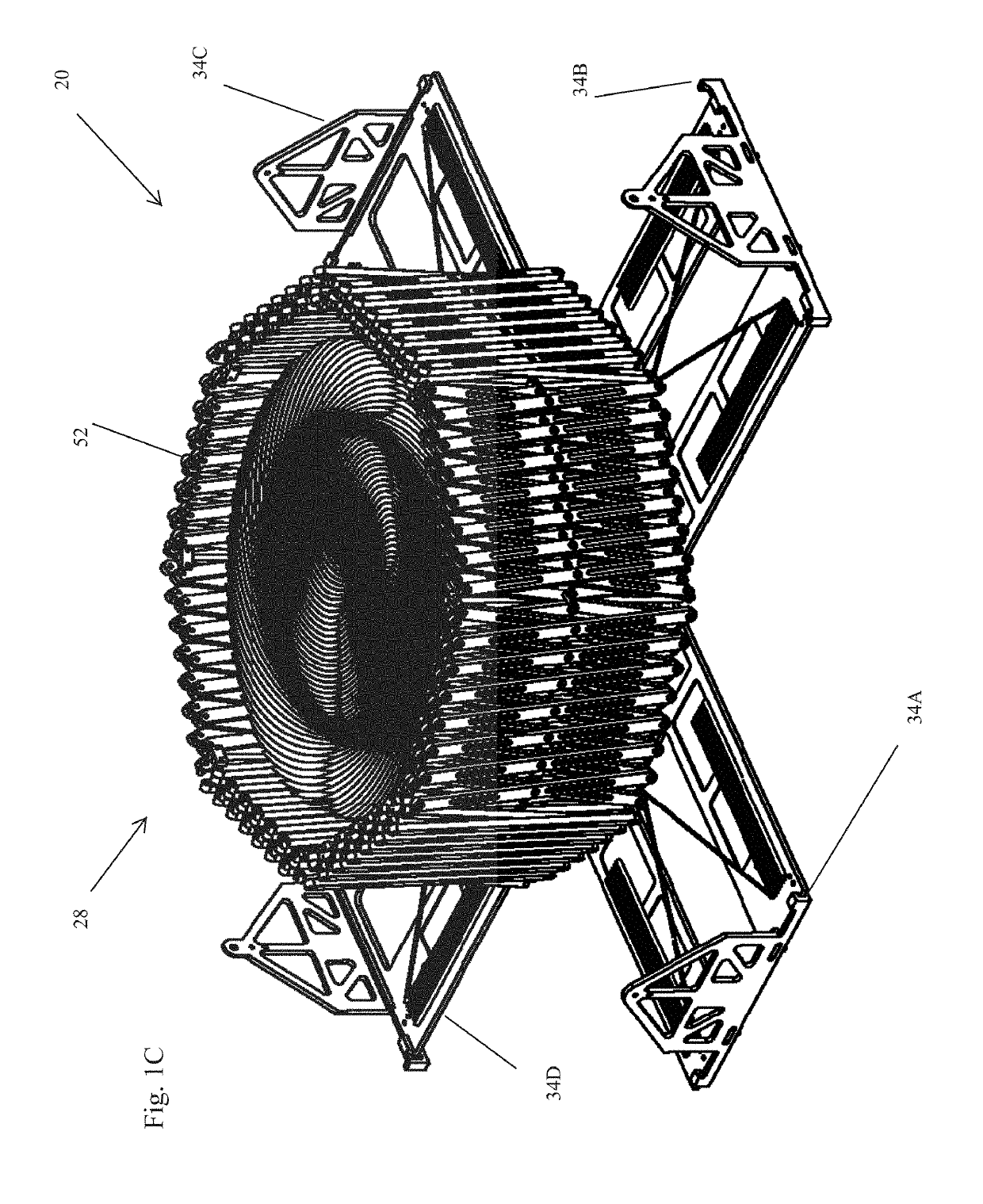
Deployable Structure for Use in Establishing a Reflectarray Antenna
ActiveUS20170093046A1Help positioningEasy to deployCollapsable antennas meansCosmonautic vehiclesPantographWaste management
A deployable structure for use in establishing a reflectarray antenna is provided that includes a flexible reflectarray and a deployment structure that includes an endless pantograph for deploying the flexible reflectarray from a folded, undeployed state towards a deployed state in which the flexible reflectarray is substantially planar. In a particular embodiment, the deployment structure includes a plurality of tapes that engage the endless pantograph and are used to establish a positional relationship between the deployed reflectarray and another component of the reflectarray antenna.
Owner:M M A DESIGN
Machine for preparing coffee
InactiveUS20120017767A1No power consumptionDrawback can be solvedBeverage vesselsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A Machine for preparing coffee comprising a infusion chamber to house at least a coffee dose, and means for feeding pressurized water to said infusion chamber, said means comprising a cylinder and plunger assembly, said plunger defining inside the cylinder a chamber to house a preset quantity of water, and said plunger being able to accumulate, in an active position, potential energy capable of being transmitted as a pressure to the water of said chamber, when said plunger contacts, in said active position, with the water of said chamber. It is characterized in that said infusion chamber is placed adjacent below the water chamber of said cylinder, both chambers including at least one hole through which, once opened, passes the pressurized water to said infusion chamber, said plunger moving back to the rest position inside said chamber as pressurized water is fed through said hole.
Owner:MINIMMA ESPRESSO
Method of converting 2d video to 3D video using 3D object models
InactiveUS20160005228A1Increased artisticIncreased technical flexibilityImage analysisSteroscopic systemsFeature trackingDegrees of freedom
Method for converting 2D video to 3D video using 3D object models. Embodiments of the invention obtain a 3D object model for one or more objects in a 2D video scene, such as a character. Object models may for example be derived from 3D scanner data; planes, polygons, or surfaces may be fit to this data to generate a 3D model. In each frame in which a modeled object appears, the location and orientation of the 3D model may be determined in the frame, and a depth map for the object may be generated from the model. 3D video may be generated using the depth map. Embodiments may use feature tracking to automatically determine object location and orientation. Embodiments may use rigged 3D models with degrees of freedom to model objects with parts that move relative to one another.
Owner:LEGEND FILMS INC
Method of converting 2D video to 3D video using machine learning
ActiveUS9609307B1Quick conversionIncrease flexibilityImage enhancementImage analysisLearning machinePoint cloud
Machine learning method that learns to convert 2D video to 3D video from a set of training examples. Uses machine learning to perform any or all of the 2D to 3D conversion steps of identifying and locating objects, masking objects, modeling object depth, generating stereoscopic image pairs, and filling gaps created by pixel displacement for depth effects. Training examples comprise inputs and outputs for the conversion steps. The machine learning system generates transformation functions that generate the outputs from the inputs; these functions may then be used on new 2D videos to automate or semi-automate the conversion process. Operator input may be used to augment the results of the machine learning system. Illustrative representations for conversion data in the training examples include object tags to identify objects and locate their features, Bézier curves to mask object regions, and point clouds or geometric shapes to model object depth.
Owner:USFT PATENTS INC
Hard hat sun shade
A sun shade for a hard hat includes a piece of flexible material removably and adjustably attached to a hard hat that is stretched to a substantially consistent shape by a piece of springing material. The flexible material may be attached to the hard hat using an elastic band, drawstring, or similar means for attaching. When not in use, the springing material may be removed from the flexible material and stored as a straight piece of material or rolled and stored as a coil. Additionally, the flexible material, such as fabric or soft plastic, may be folded and stored. The flexible material may also include a flap that drapes over the sides and back of the user's neck to provide enhanced protection from direct radiant energy.
Owner:ROSAS GILBERT M
Machine and method for converting a linear input to a rotational output
The invention is a device that converts a linear input to a rotational output. The invention includes a system of one or more extendable and retractable members that actively change the radius of rotation of weights on the members. The members are connected to a rotatable member for rotation about a non-vertical axis. By actively changing the radius of rotation of a weight, a non-circular path is established for each weight to follow. This path is biased so that, while the weight has the greatest radius of rotation, it also is undergoing a downward stroke. While the weight is undergoing an upward stroke, the radius of rotation is at its minimum. The system thereby utilizes the force of gravity during transitions between maximum and minimum radii to produce a rotational output.
Owner:KUNNAS RICHARD
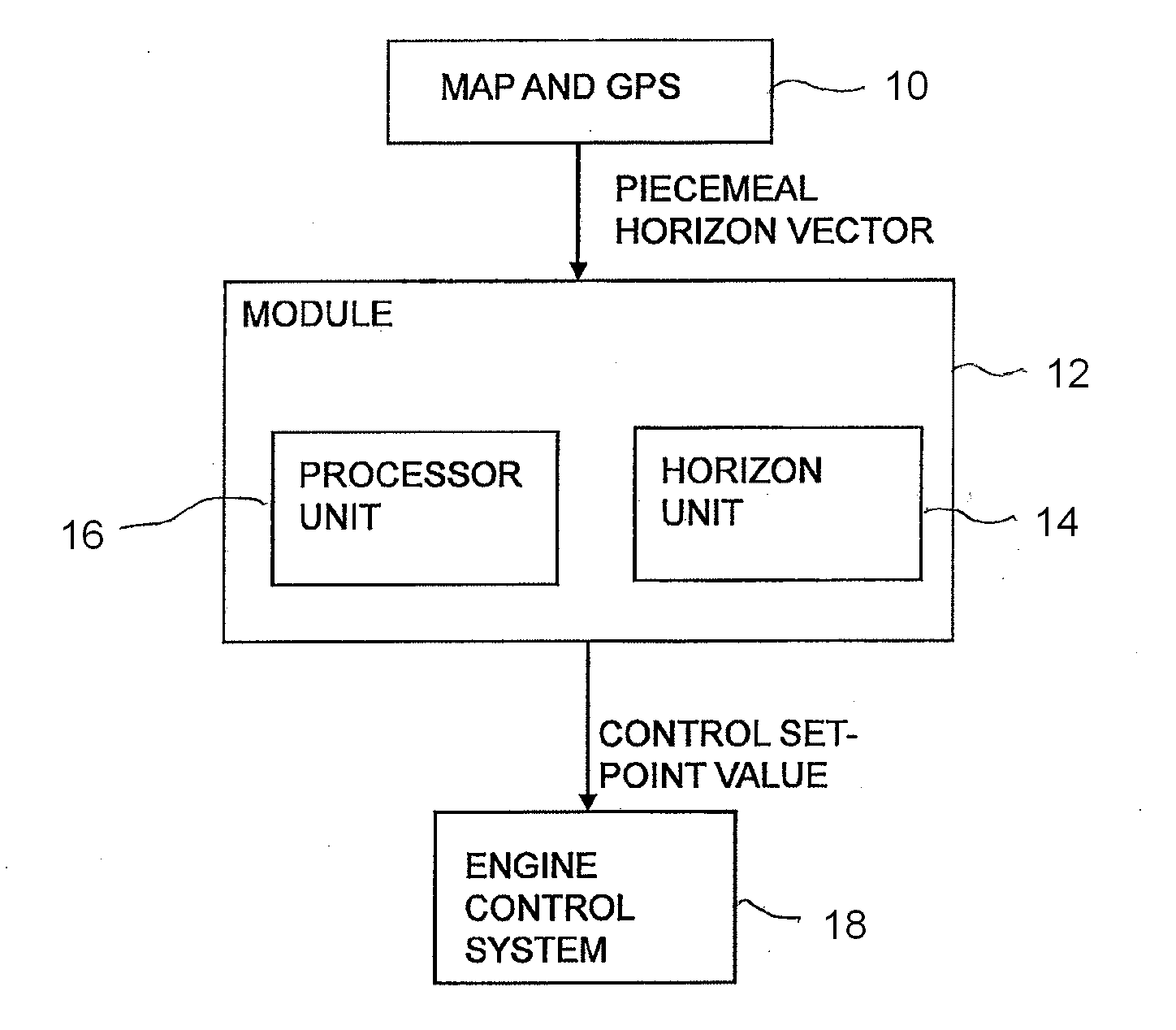
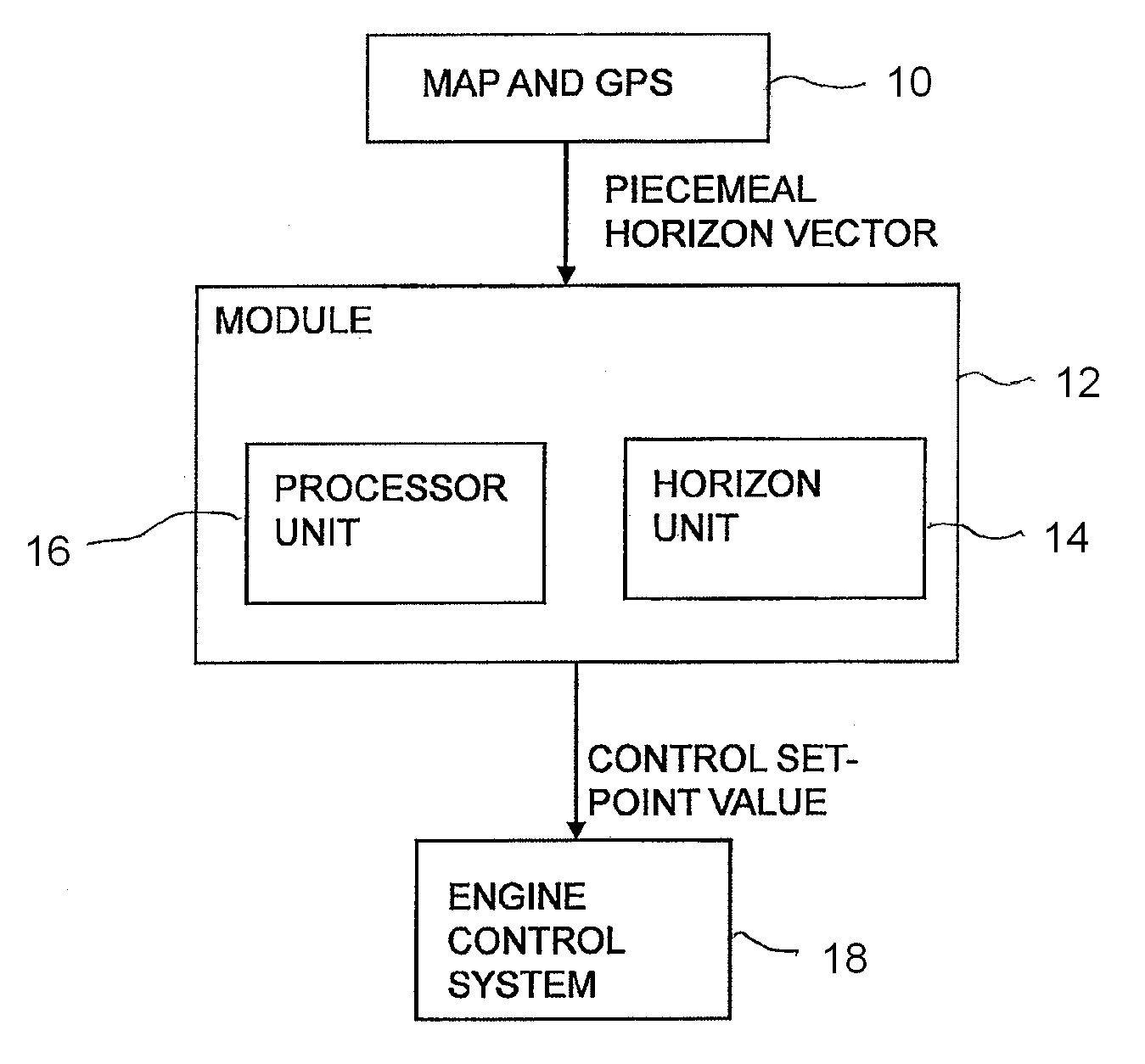
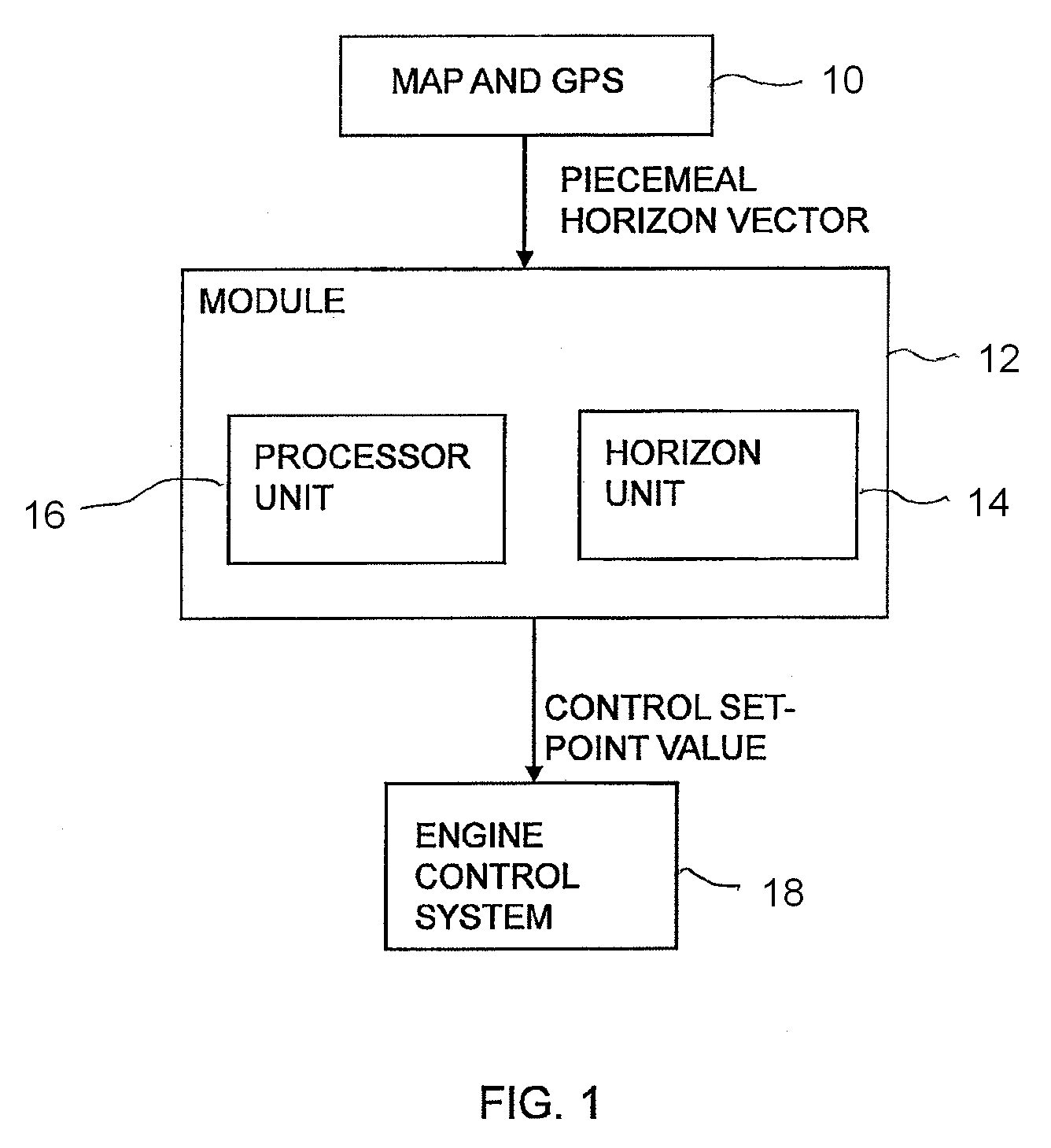
Method and module for controlling a velocity of a vehicle
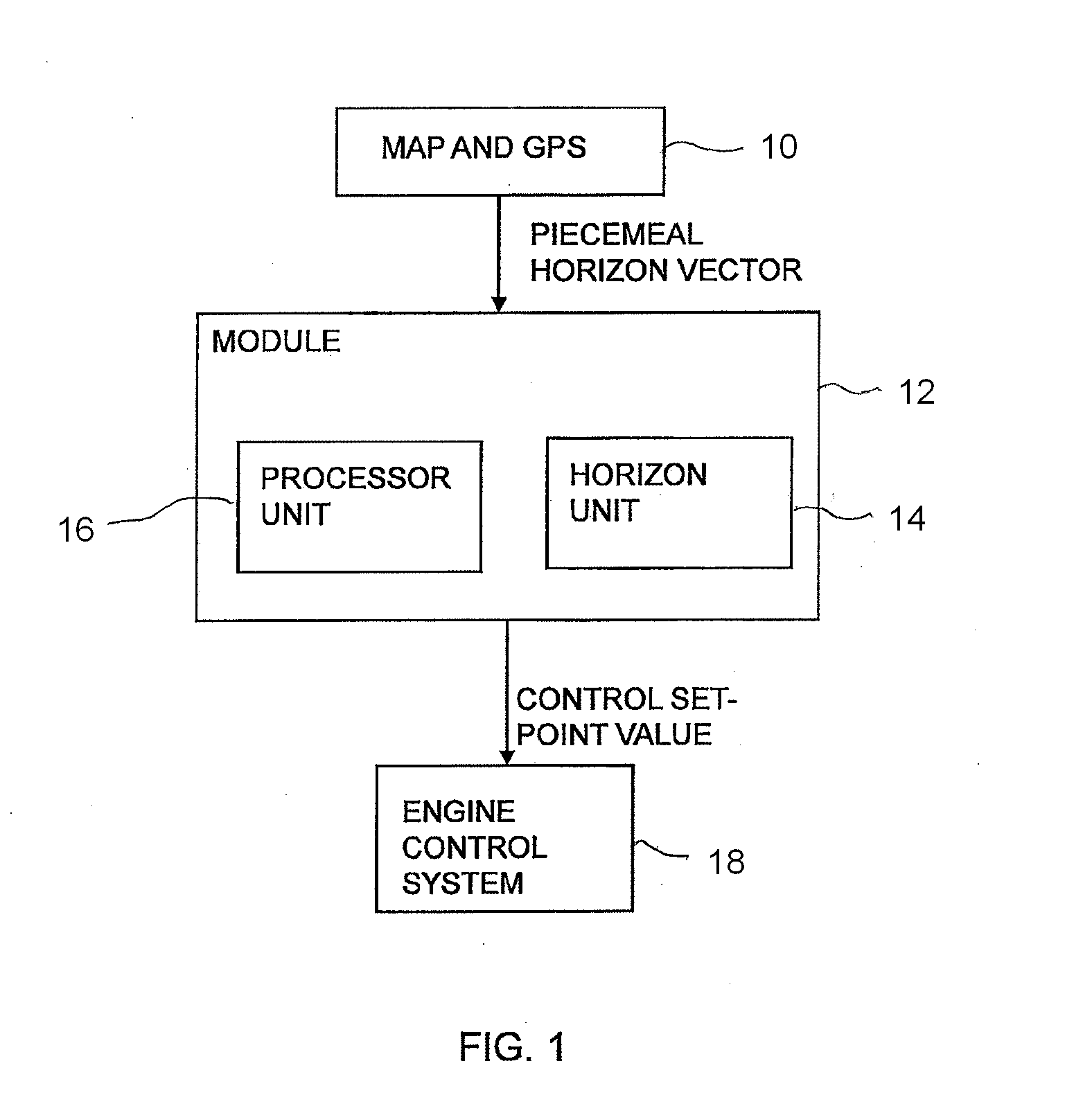
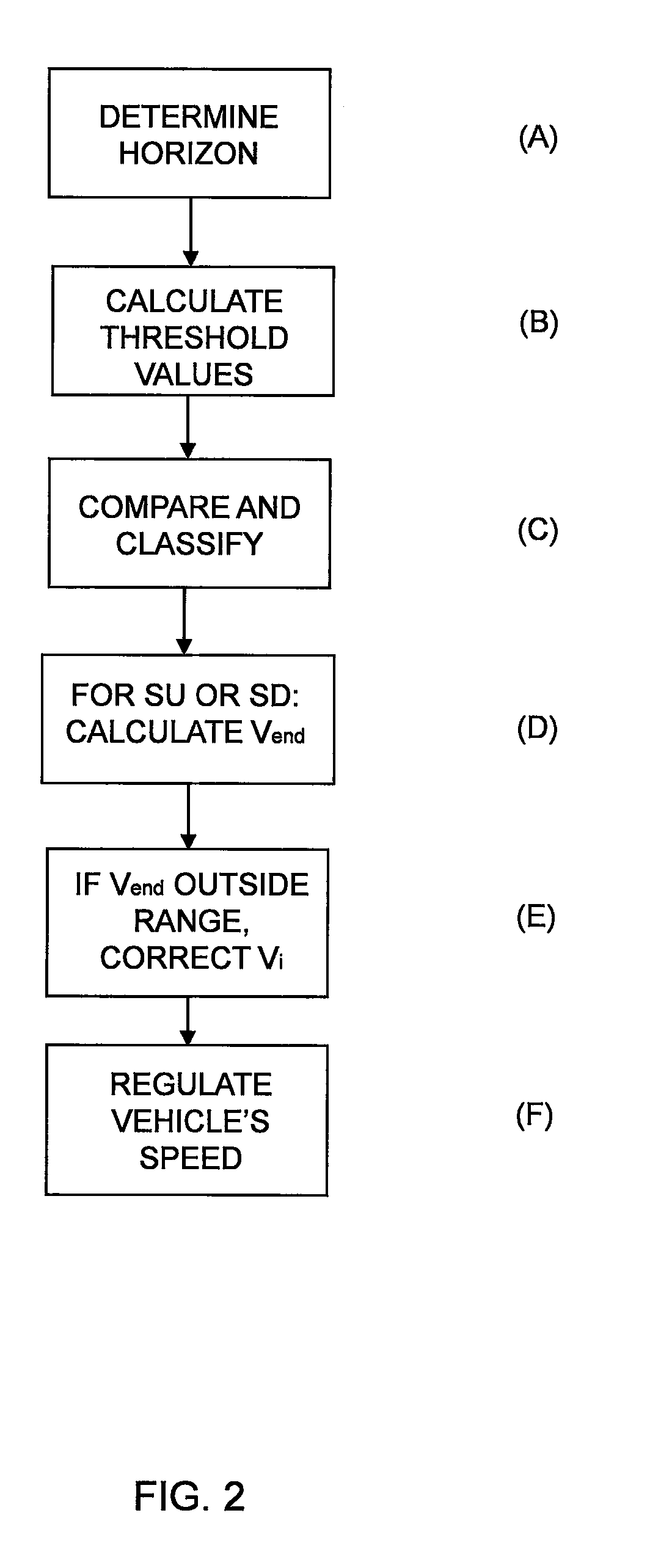
ActiveUS20120083985A1Robust and computationally effective algorithmQuickly and reliably generatesInstruments for road network navigationVehicle fittingsHorizonSimulation
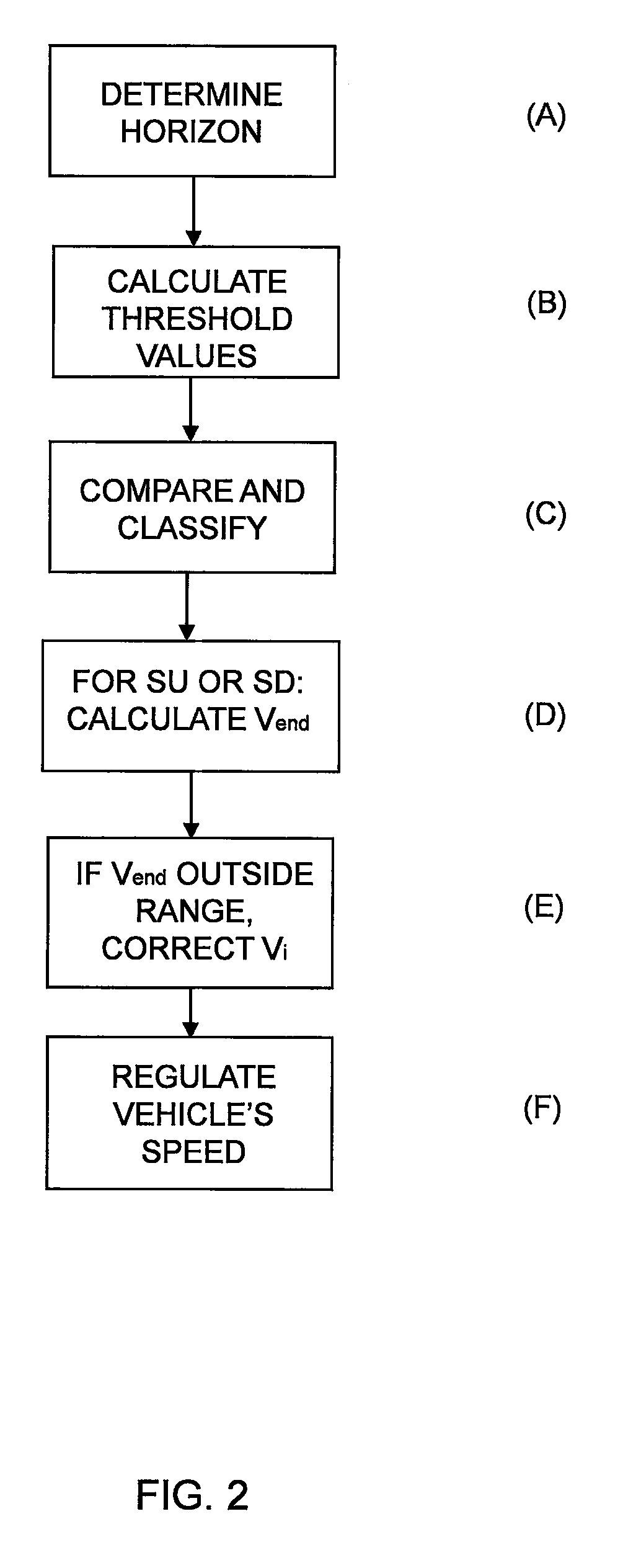
A method for regulating a vehicle's speed including the steps of: determining a horizon by means of position data and map data of an itinerary made up of route segments with length and gradient characteristics for each segment; calculating threshold values for the gradient of segments according to one or more vehicle-specific values, which threshold values serve as boundaries for assigning segments to various categories; comparing the gradient of each segment with the threshold values and placing each segment within the horizon in a category according to the results of the comparisons; and, for each segment within the horizon which is in a category indicating a steep upgrade or a steep downgrade, calculating the vehicle's final speed vend after the end of the segment, based inter alia on the entry speed vi to the segment; and determining the entry speed vi for said segment based on the calculated final speed vend for the segment, which determination is defined by rules for said segment's category, so that the vehicle's final speed Vend is within the range defined by vmax and vmin for the vehicle's current reference speed vset, on the supposition that vi is determined within the same range; and regulating the vehicle's speed according to speed set-point values vref based on the entry speeds vi to each segment.
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
Prosthetic foot with tunable performance
InactiveUS8070829B2Improve performanceImproved applied mechanicLigamentsMusclesHindlimbArtificial muscle
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
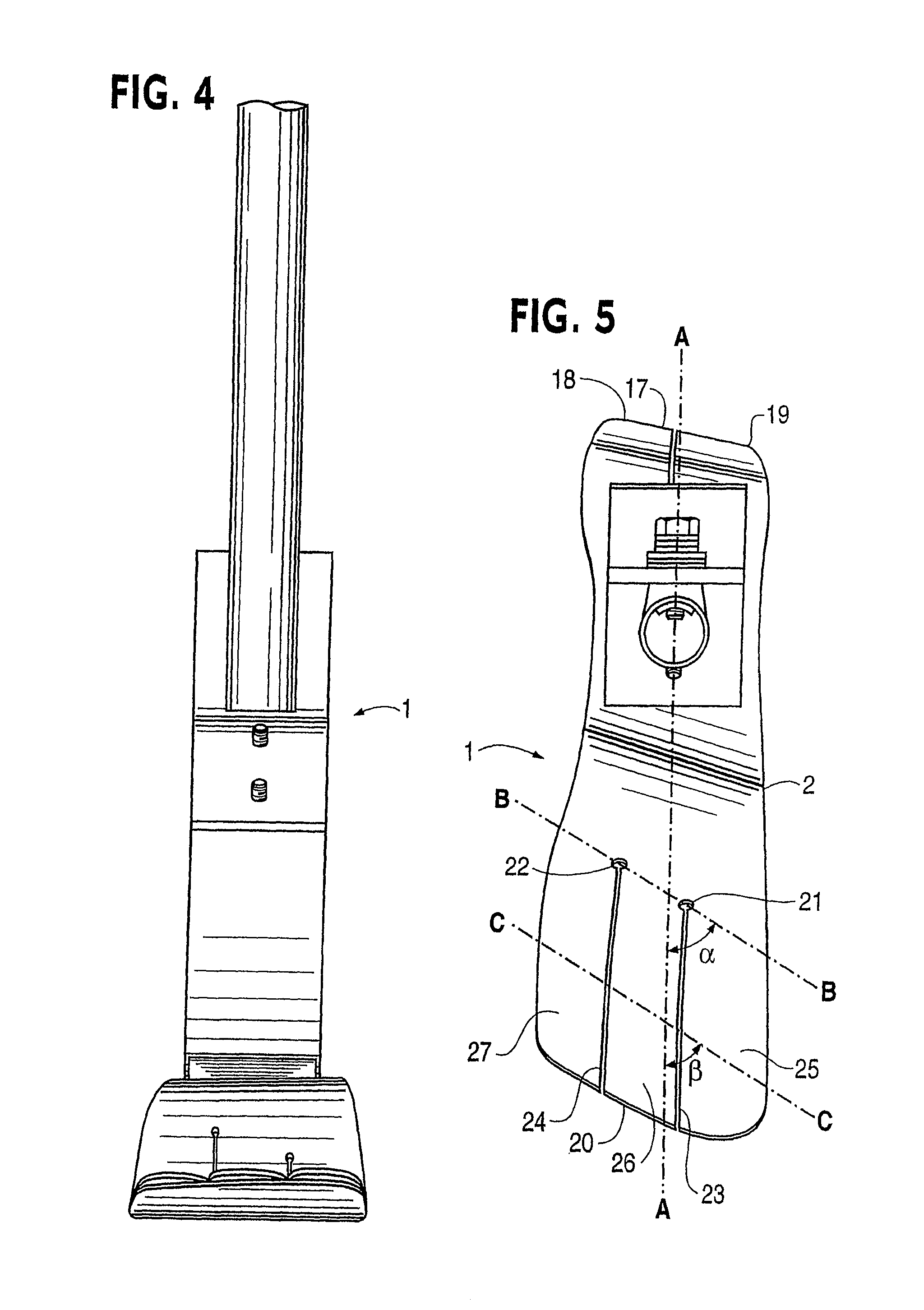
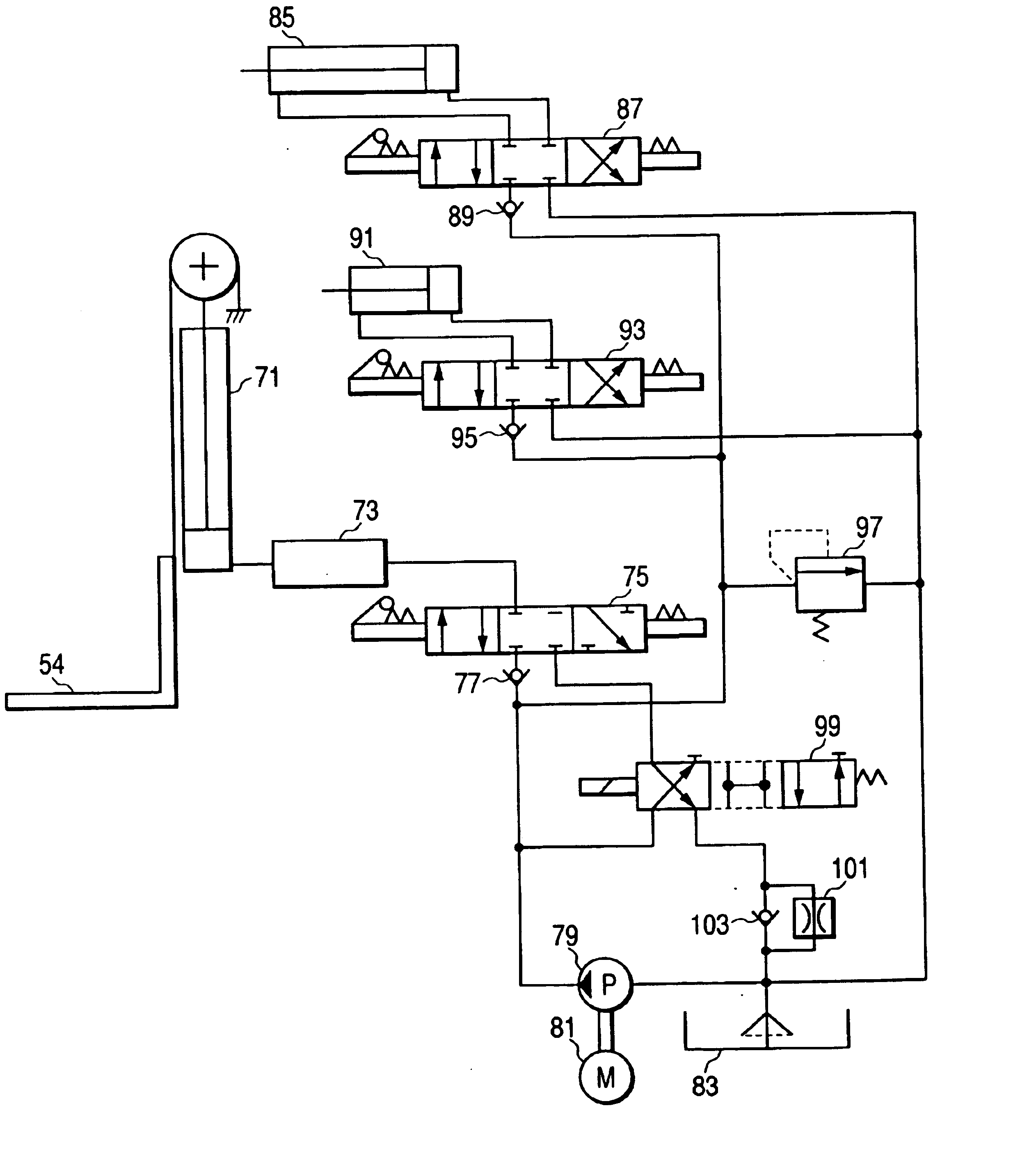
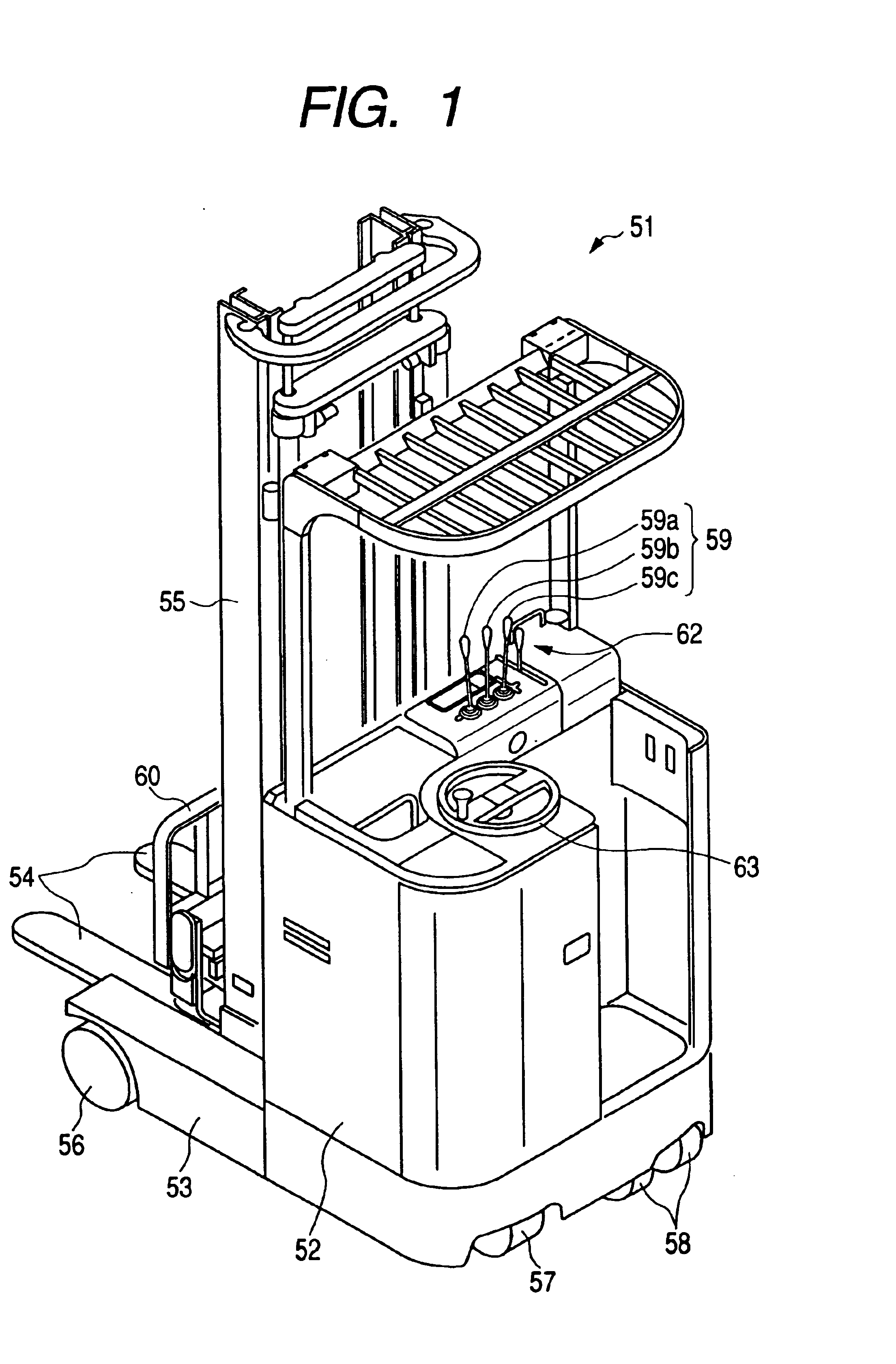
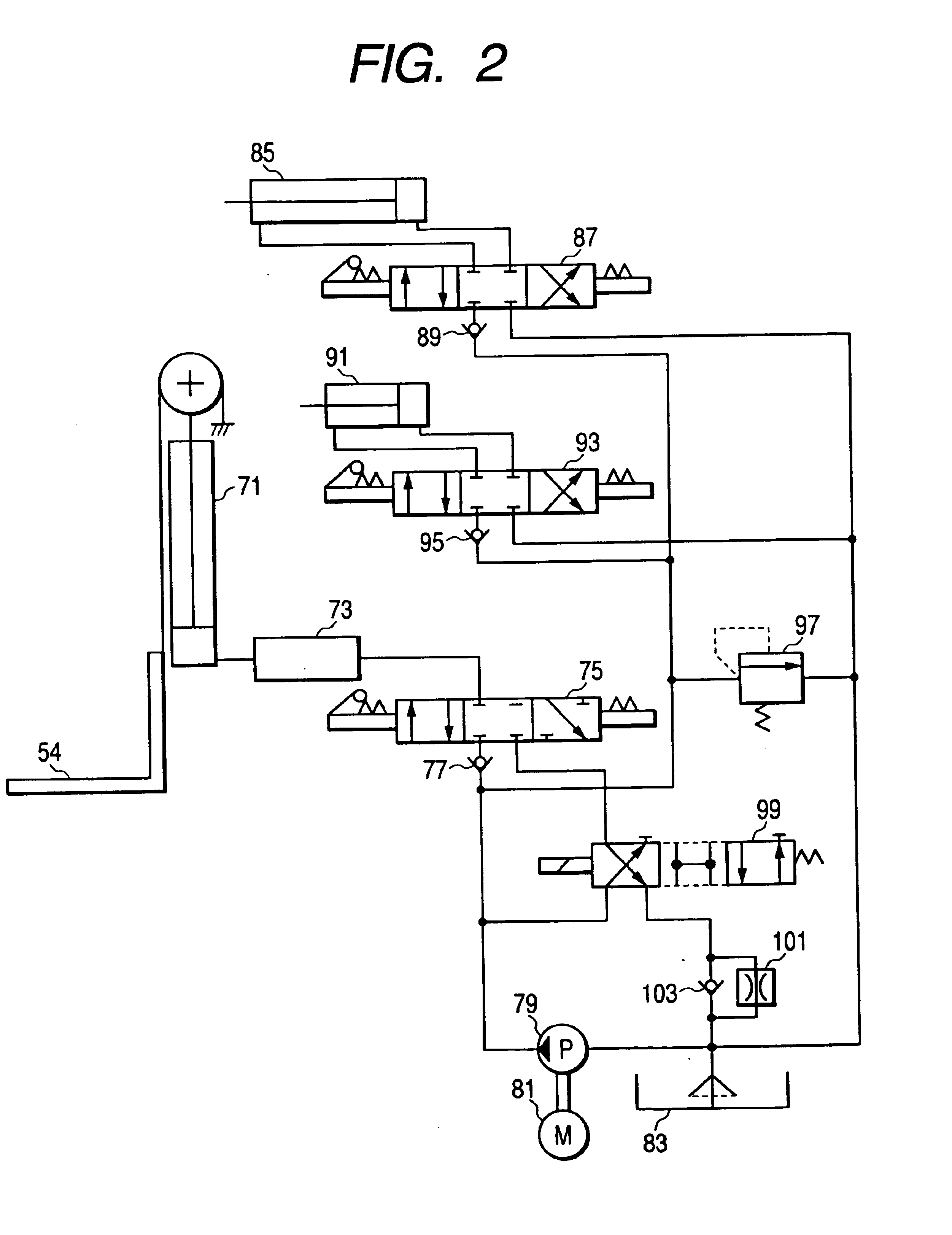
Control apparatus and control method for a forklift and forklift
InactiveUS6850828B2Useful energyControl the lift-down speed of the forksAnalogue computers for trafficServomotorsFlux controlForklift truck
A control apparatus includes a target acceleration obtaining device for obtaining a target acceleration of a hydraulic motor based on an operation amount of a lift lever; a torque command value obtaining device for obtaining a torque command value of a hydraulic motor based on the target acceleration; a determining device for determining as a non-regeneration state or as a regeneration state based the torque command value; and a change-over control device for changing over a change-over member so as to couple a lift cylinder to a flow rate control valve when determined as the non-regeneration state, and for changing over the change-over member so as to couple the lift cylinder to a hydraulic pump and making an inverter controller control the hydraulic motor in accordance with the torque command value when determined as the regeneration state.
Owner:NIPPON YUSOKI
Short circuit-resistant polyethylene microporous film
InactiveUS6054498AHigh short resistanceIncreasing temperature of resinCell component detailsLow-density polyethylenePolymer science
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 03783 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 24, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 24, 1998 PCT Filed Dec. 25, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 23554 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 3, 1997A microporous film comprising a high-density polyethylene and a linear copolymer polyethylene and having a terminal vinyl group concentration of 2 or more per 10,000 carbon atoms in the polyethylene, as measured by an infrared spectroscopic method.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
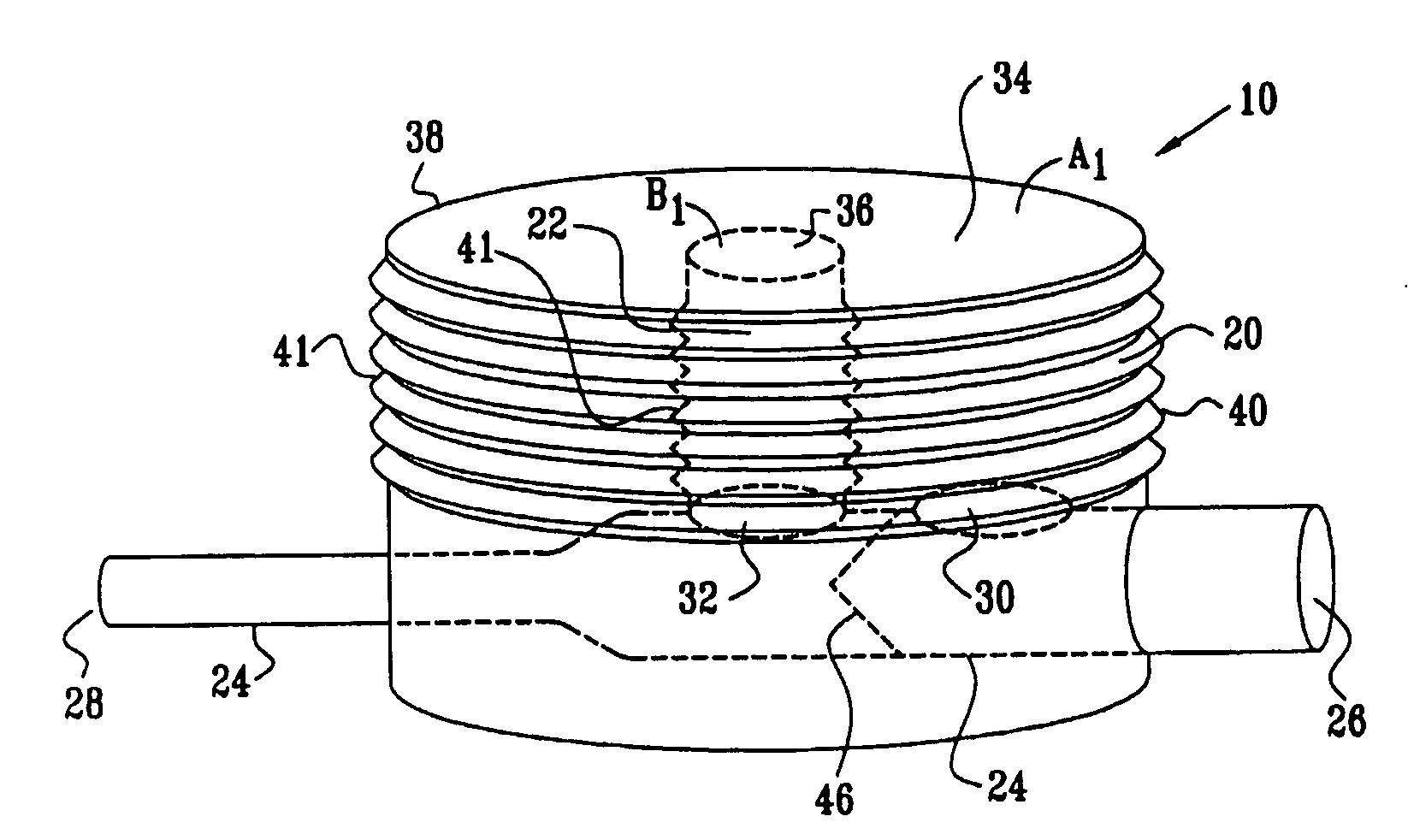
Apparatus and method for releaseably joining elements
InactiveUS7367738B2Gentle releaseLess risk of damageYielding couplingCosmonautic vehiclesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The apparatus and method for releasably joining first and second elements according to the present invention include a retaining member mounted to one of the elements and a reshapeable tube near the retaining member. The reshapeable tube has at least two states, an at least partially collapsed state and an at least partially expanded state. As such, the retaining member joins the elements while the reshapeable tube is in the at least partially collapsed state. Furthermore, the retaining member releases the other element while the reshapeable tube is in the at least partially expanded state, which deflects the retaining member. Thus, because components of the apparatus are not broken during the release of the elements, the amount of constrained or potential energy that is released when the retaining member releases the elements is substantially reduced or eliminated, which protects the elements from being damaged during the release.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
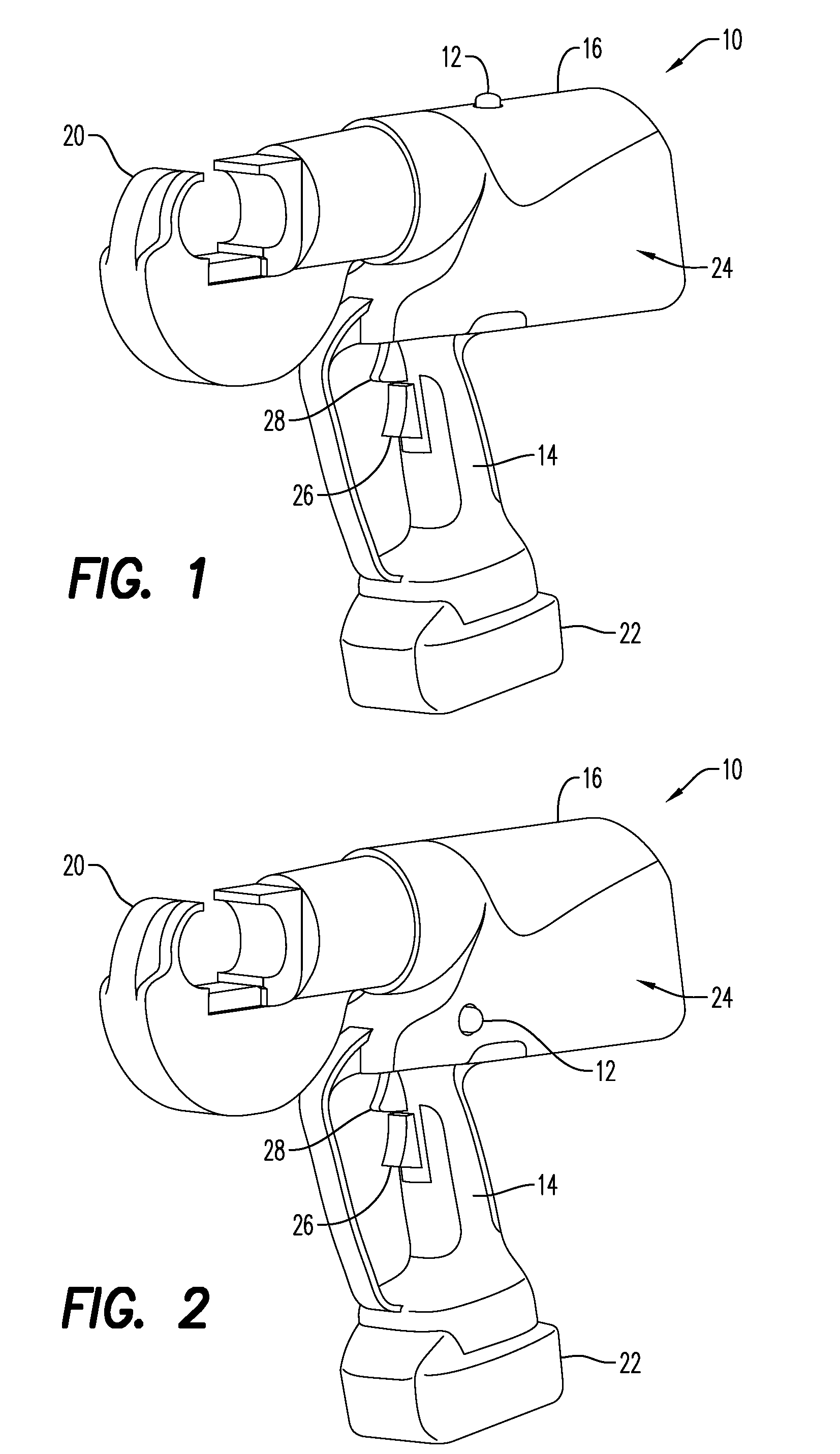
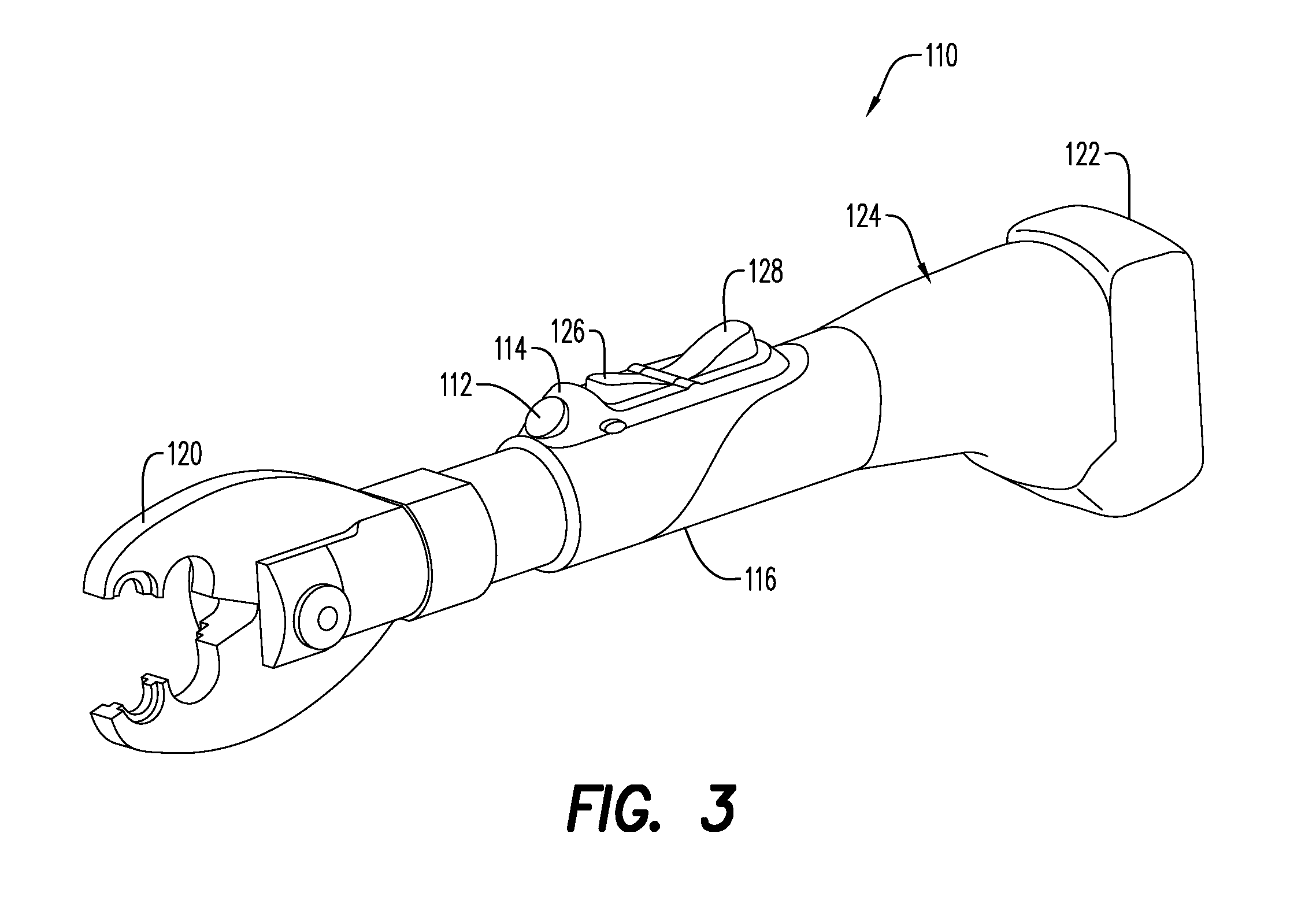
Trigger activated tools having activation lockouts
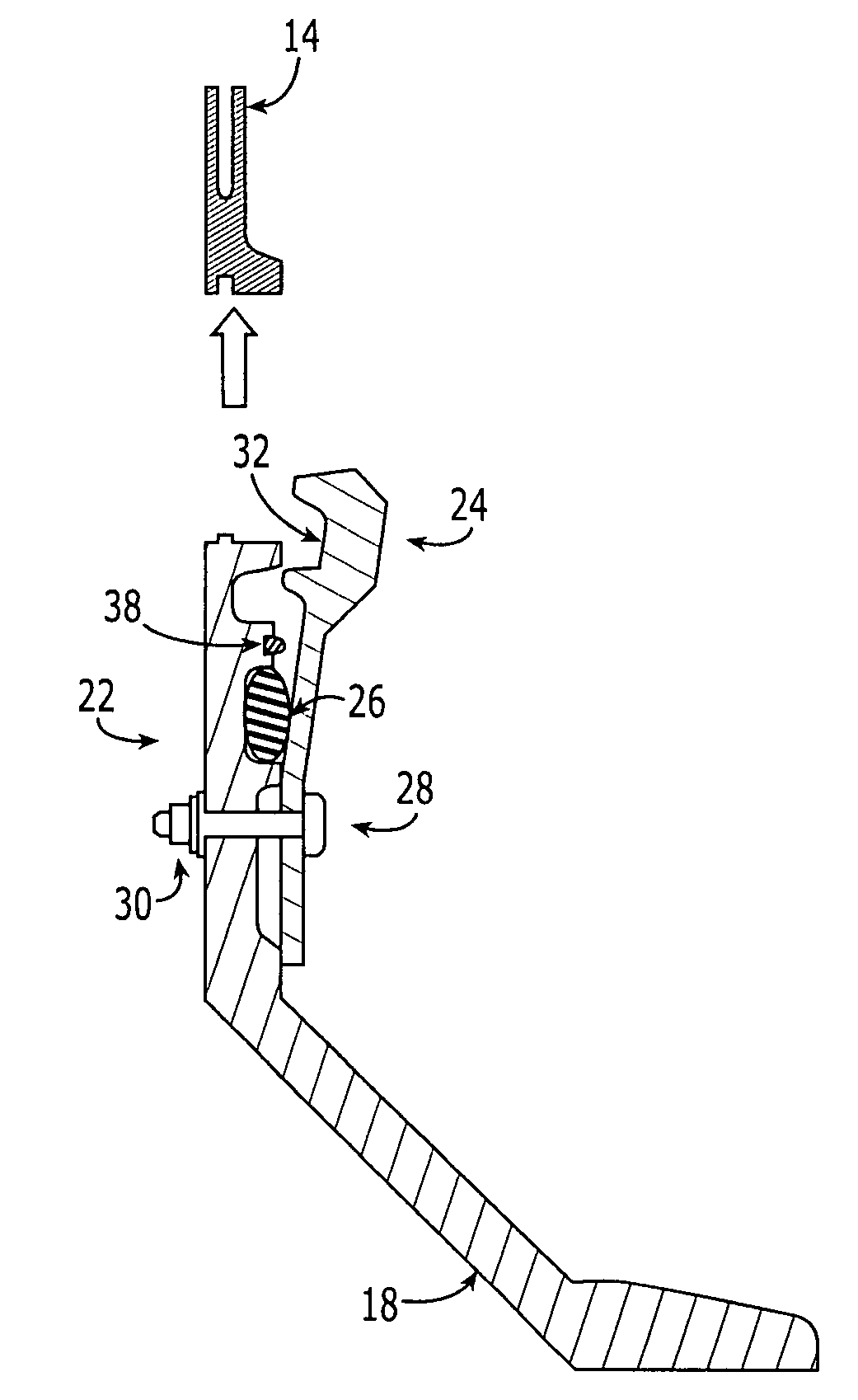
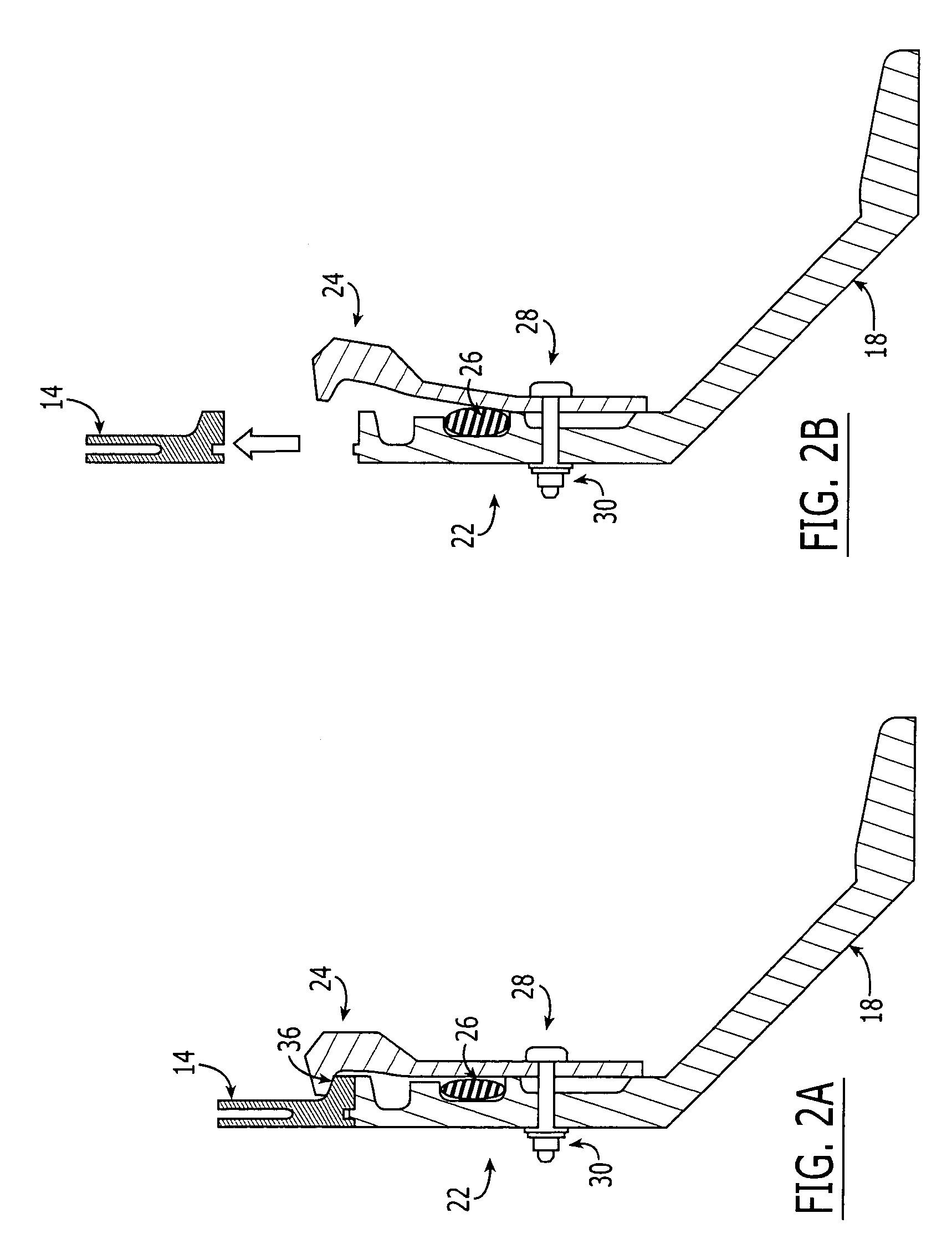
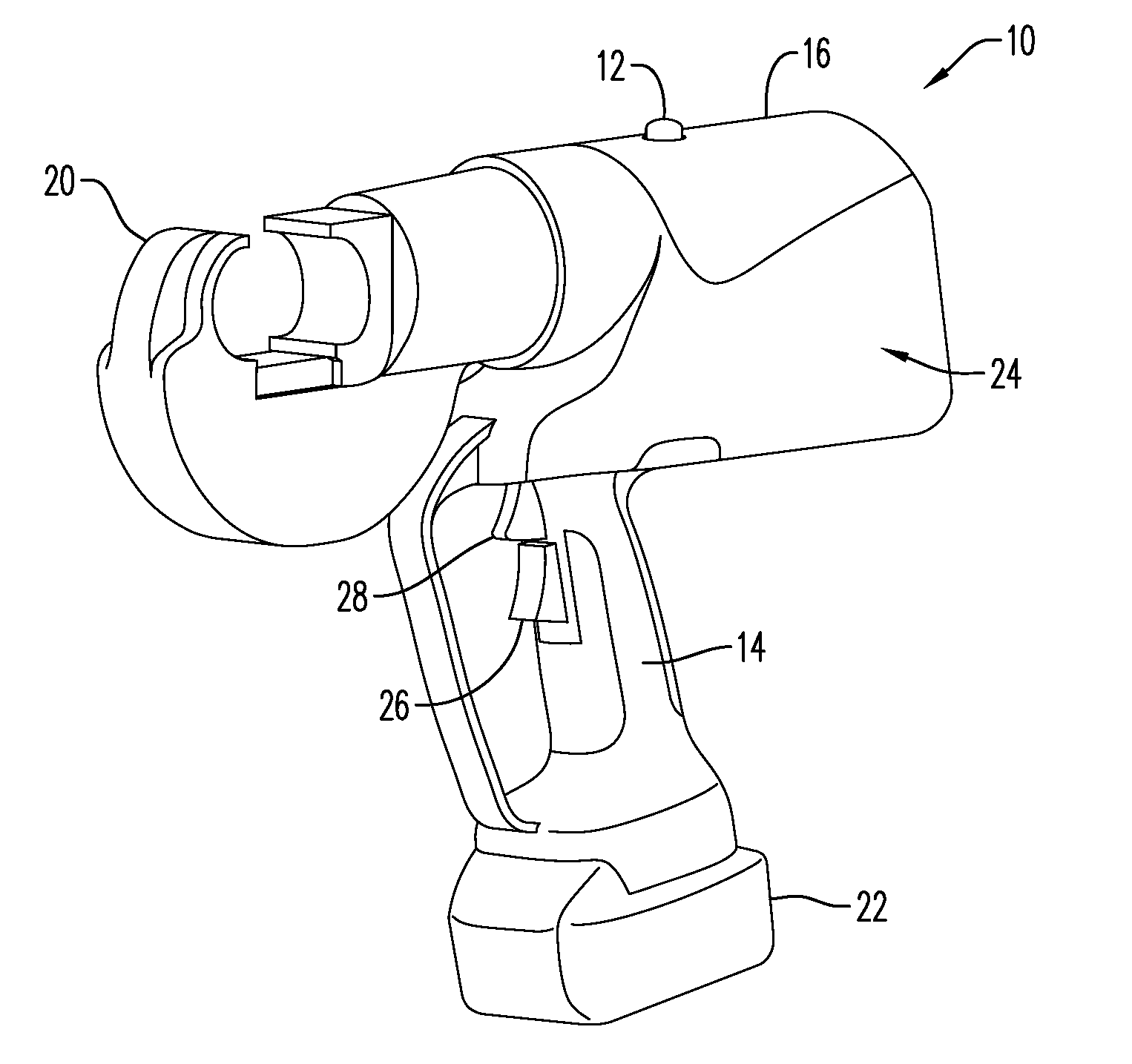
ActiveUS20160268068A1Prevent inadvertent activationInhibition of activationContact operating partsPortable power-driven toolsBiological activationBiomedical engineering
Owner:HUBBELL INC
Method and module for controlling a velocity of a vehicle
ActiveUS8620558B2Quickly and reliably generatesRobust and computationally effective algorithmInstruments for road network navigationVehicle fittingsHorizonSimulation
A method for regulating a vehicle's speed including the steps of: determining a horizon by means of position data and map data of an itinerary made up of route segments with length and gradient characteristics for each segment; calculating threshold values for the gradient of segments according to one or more vehicle-specific values, which threshold values serve as boundaries for assigning segments to various categories; comparing the gradient of each segment with the threshold values and placing each segment within the horizon in a category according to the results of the comparisons; and, for each segment within the horizon which is in a category indicating a steep upgrade or a steep downgrade, calculating the vehicle's final speed vend after the end of the segment, based inter alia on the entry speed vi to the segment; and determining the entry speed vi for said segment based on the calculated final speed vend for the segment, which determination is defined by rules for said segment's category, so that the vehicle's final speed vend is within the range defined by vmax and vmin for the vehicle's current reference speed vset, on the supposition that vi is determined within the same range; and regulating the vehicle's speed according to speed set-point values vref based on the entry speeds vi to each segment.
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
Hydraulic motor using buoyant and gravitational forces to generate kinetic energy
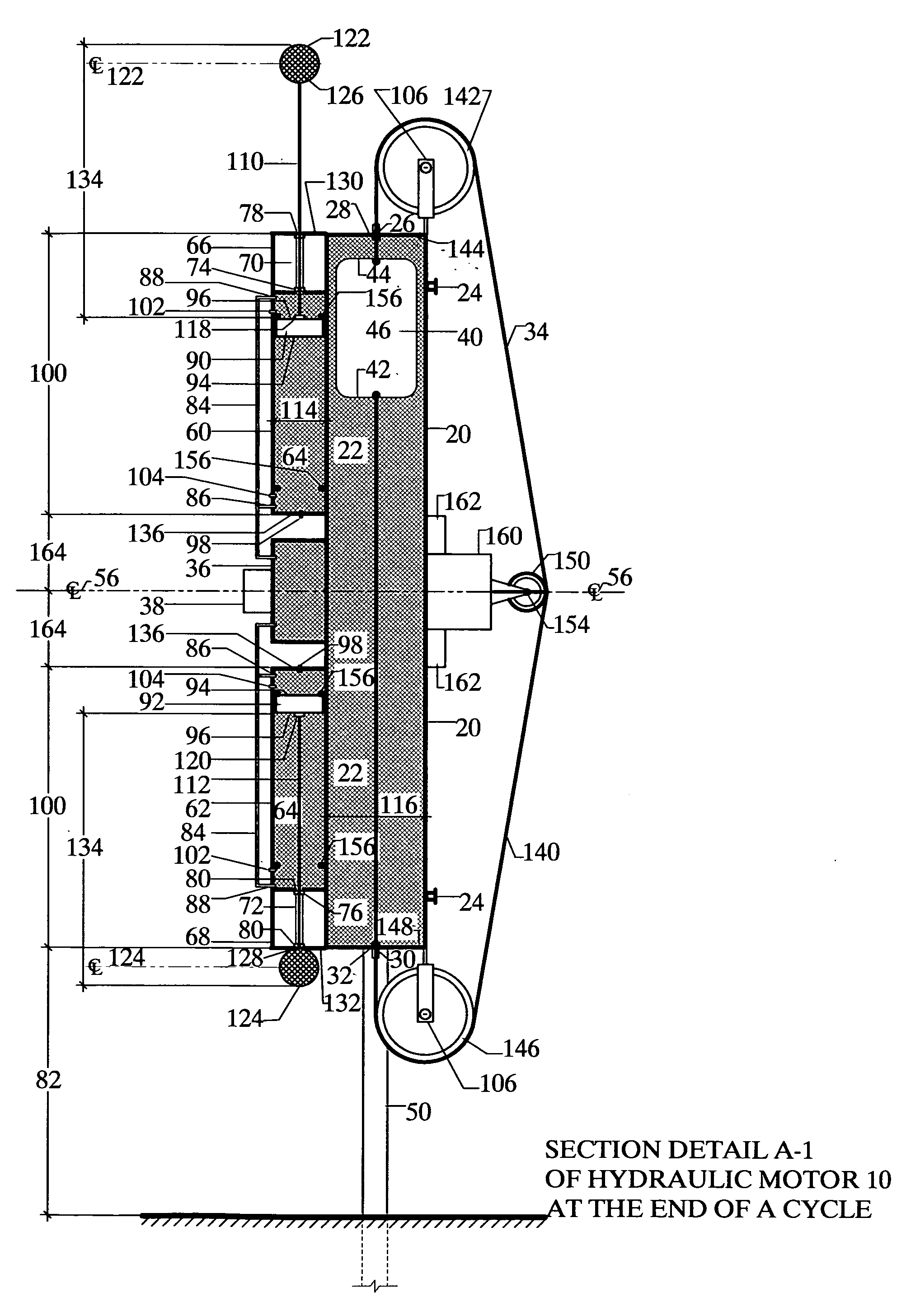
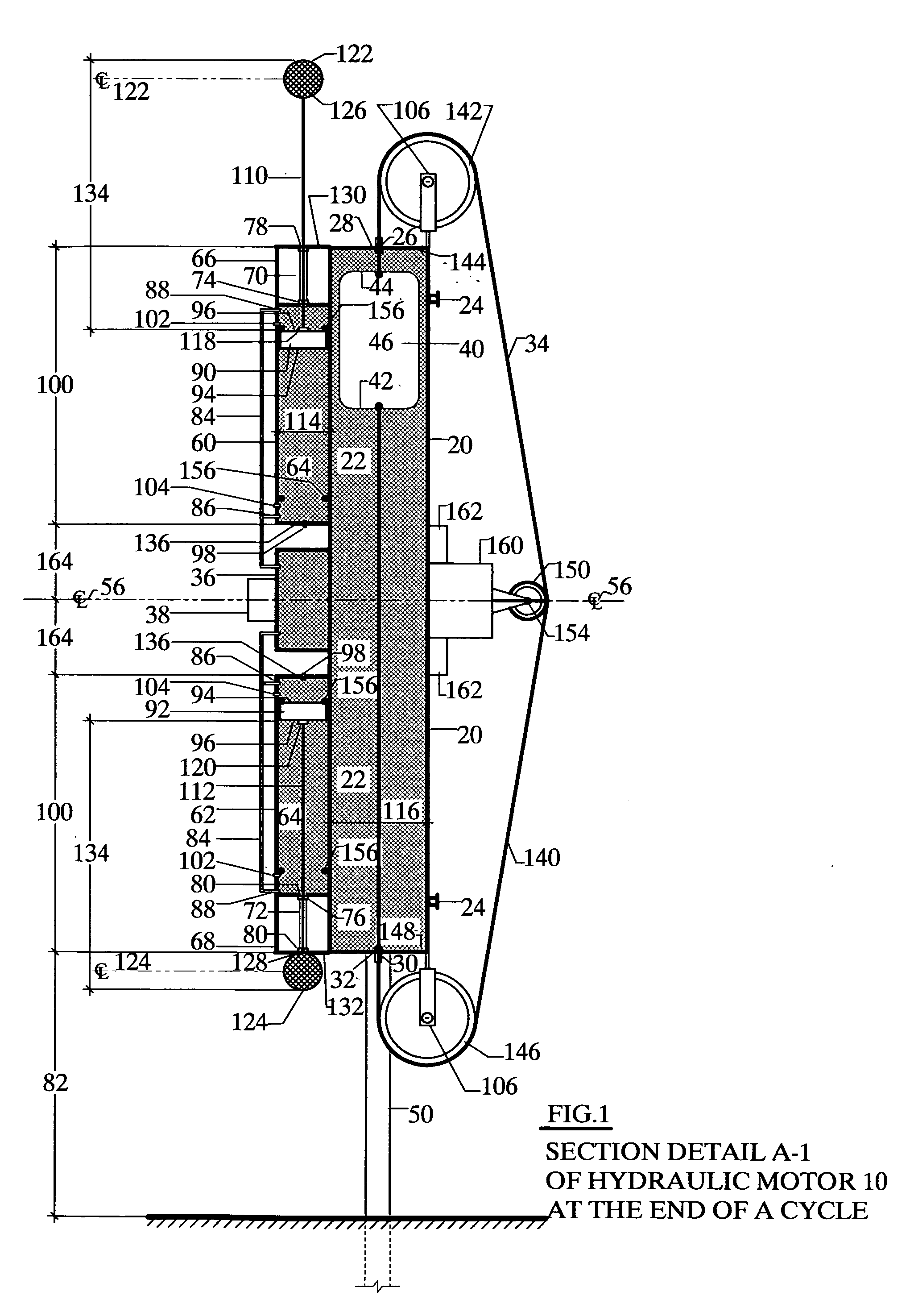
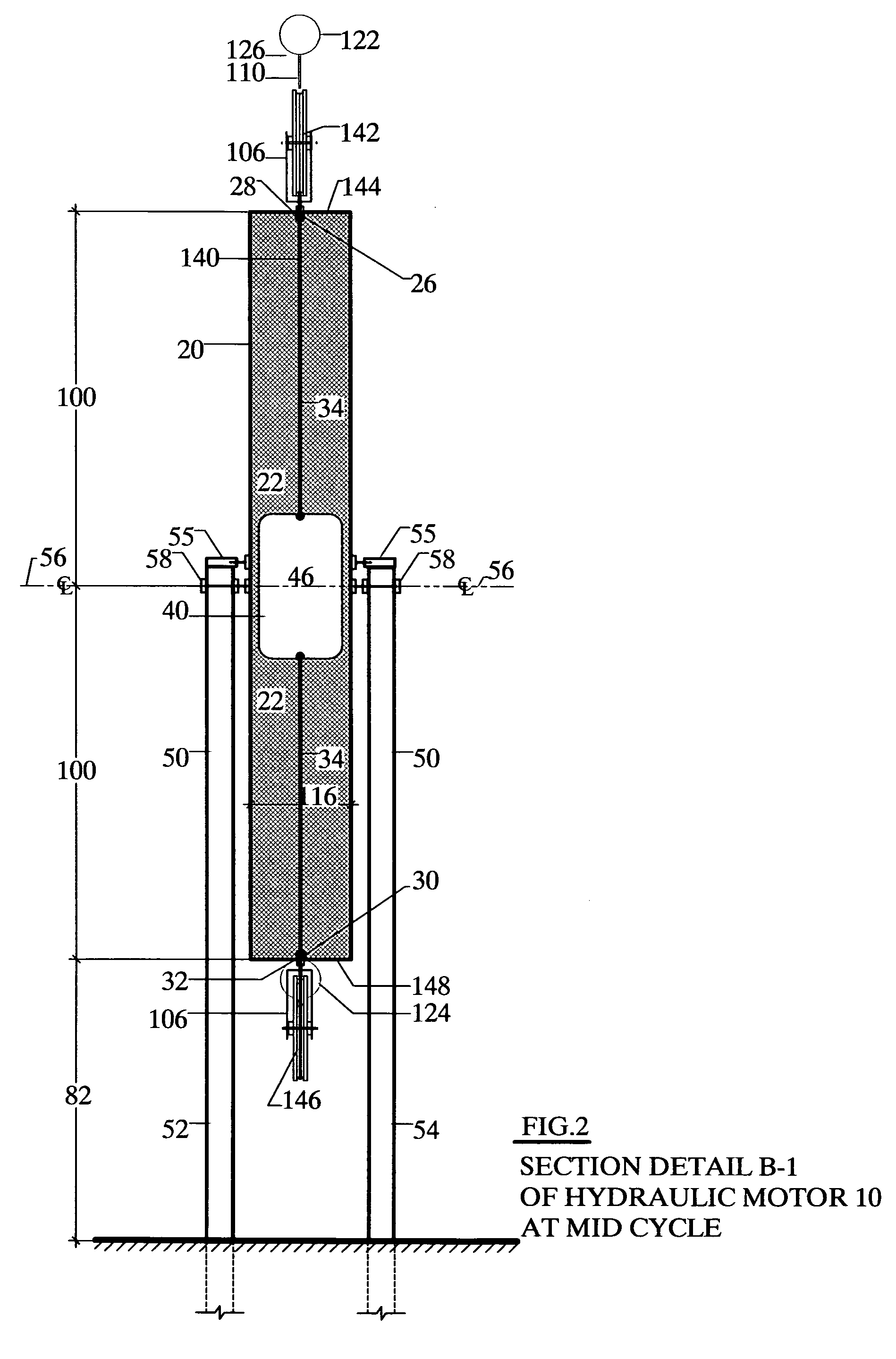
A motor mounted on a structural support with a pivot at its center line which comprises a cylindrical vessel for holding a fluid in a closed system and in which a buoyant cylinder containing a lighter fluid is allowed to free float so that a cable attached to either end of the buoyant cylinder may be used to transfer energy to a energy storage unit, a crank or a generator. Two moment arms having a weight attached at the exterior end and inside attachably connected to the surface of two drive pistons that operate in pressure tanks which force a compressed gas against the pistons through pre-sequenced automatic activated valves to extend or retract the moment arms at the end of a cycle. The motor then becomes top heavy and rotates 180 degrees by gravity and relocks in place to repeat the cycle.
Owner:DAVIS STEPHEN E
Method and device for generating waves in an aquarium
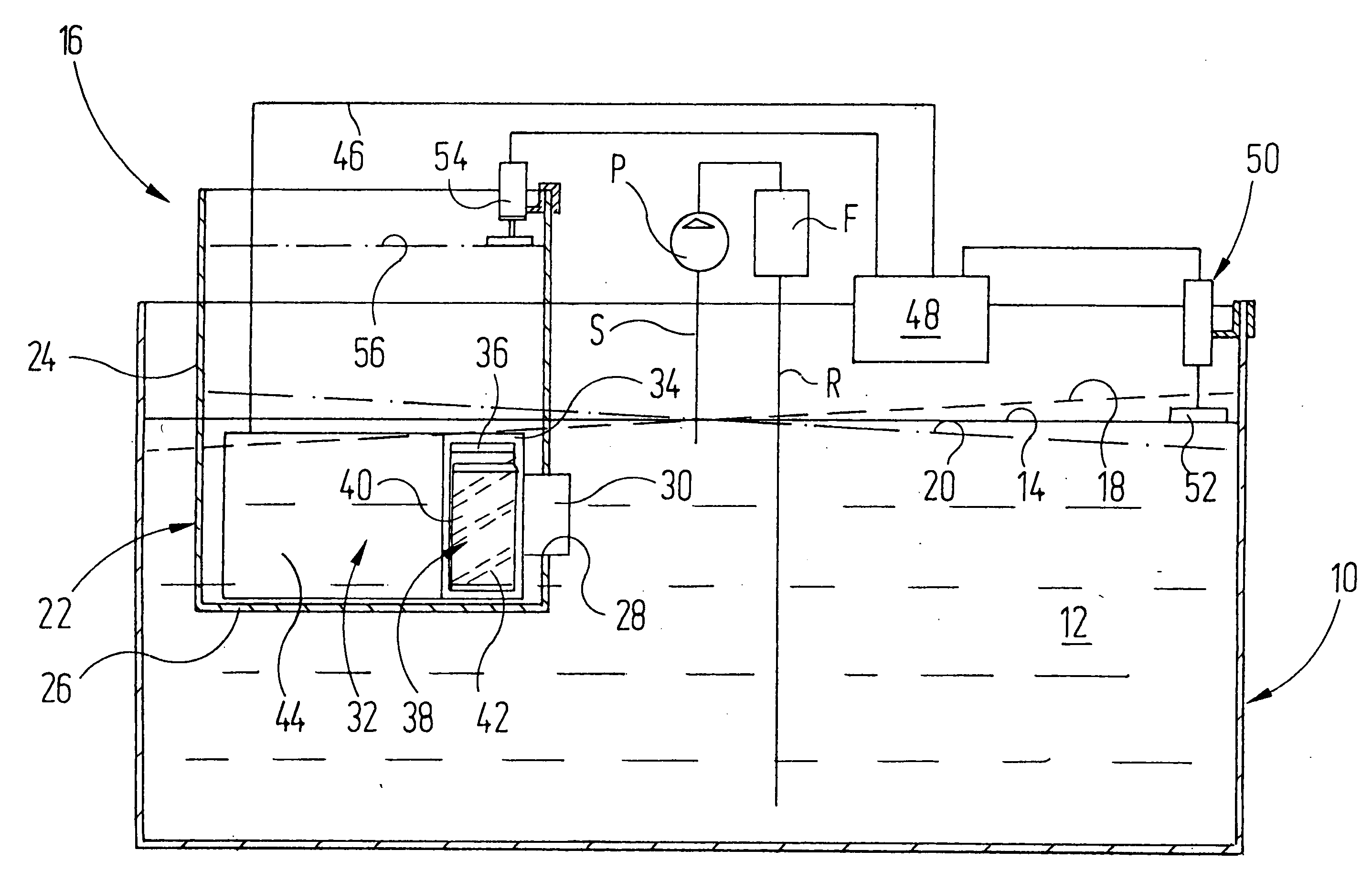
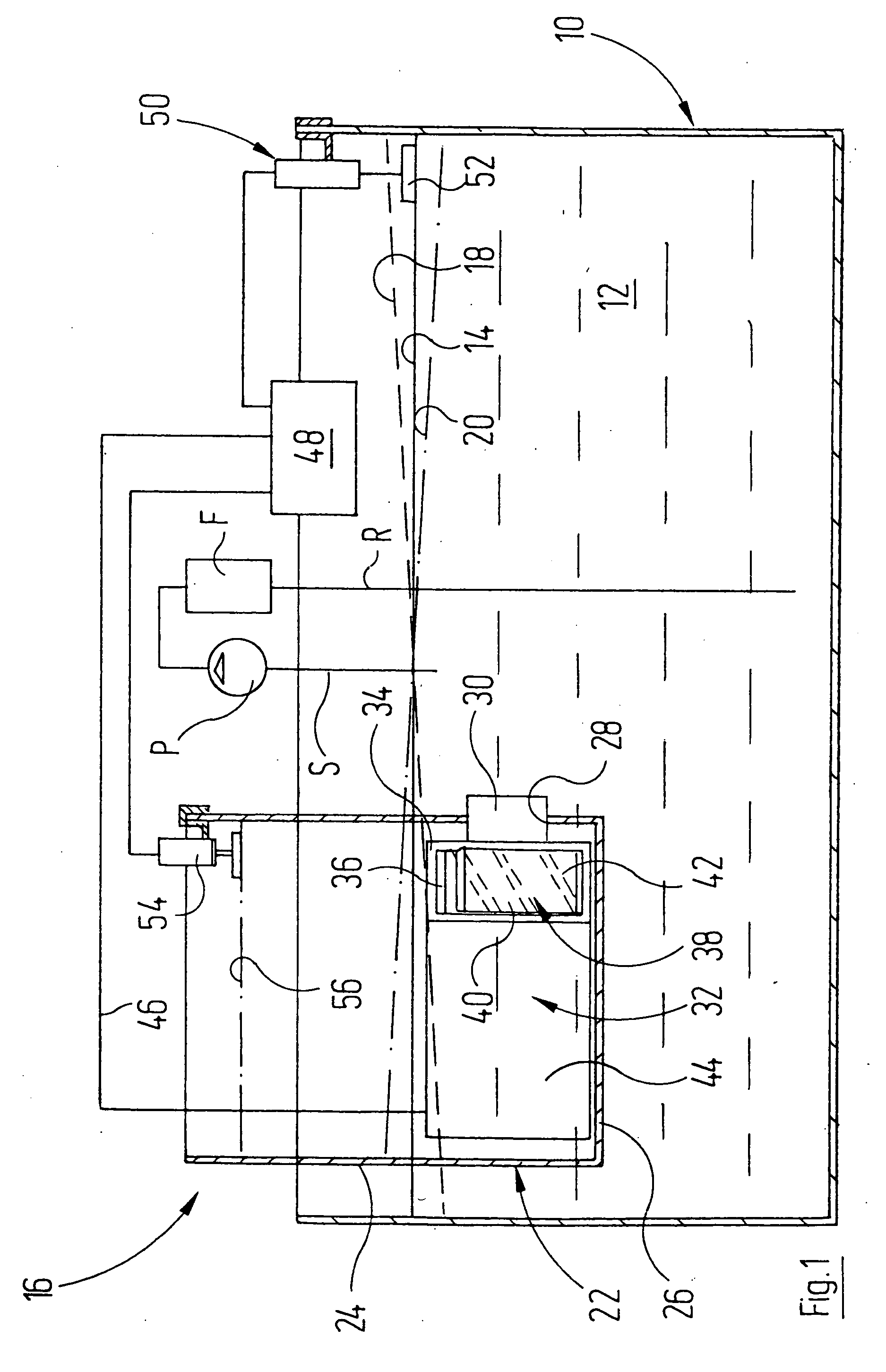
InactiveUS20050263090A1Reduce internal frictionPotential energyBathsDouchesEnvironmental engineeringMechanical load
In order to generate waves in a volume of water (12) of an aquarium, it is proposed that a storage container (22) which extends beyond the surface of the volume of water (12) should be provided in the aquarium (10). Using a pump (32), water is periodically pumped from the water container (10) into the storage container (22) and returned from the storage container (23) into the aquarium (10). The energy delivered to the water during this leads to fluctuations in the position of the free surface (14) of the volume of water (12) and in-phase operation of the pump (32) provides stronger surface displacements in the aquarium (10), which are comparable with a wave in open water and which expose the plants and living beings in the aquarium to an alternating mechanical load.
Owner:TUNZE AQUARIENTECHN
Methods and systems for generating high energy photons or quantum energy
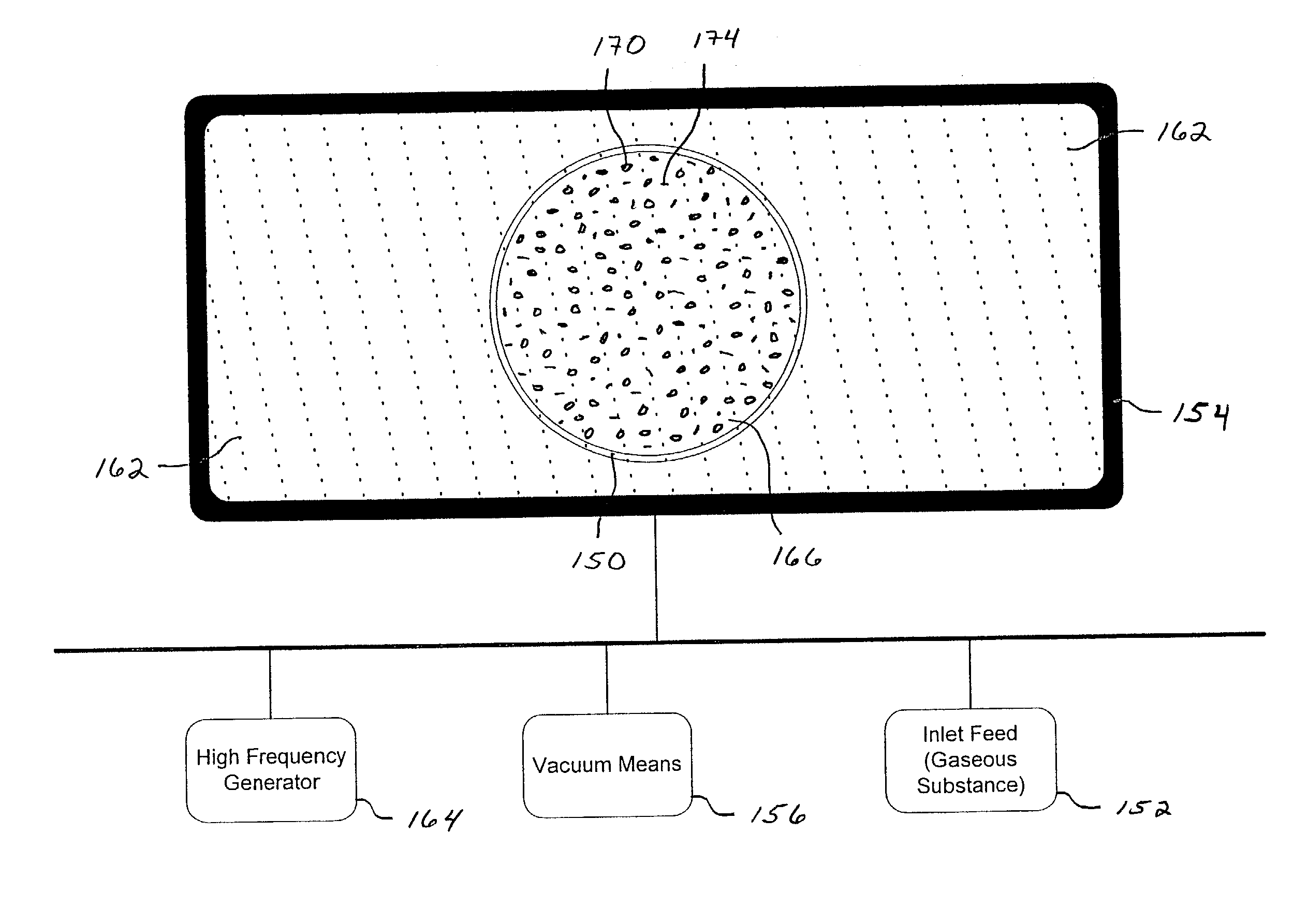
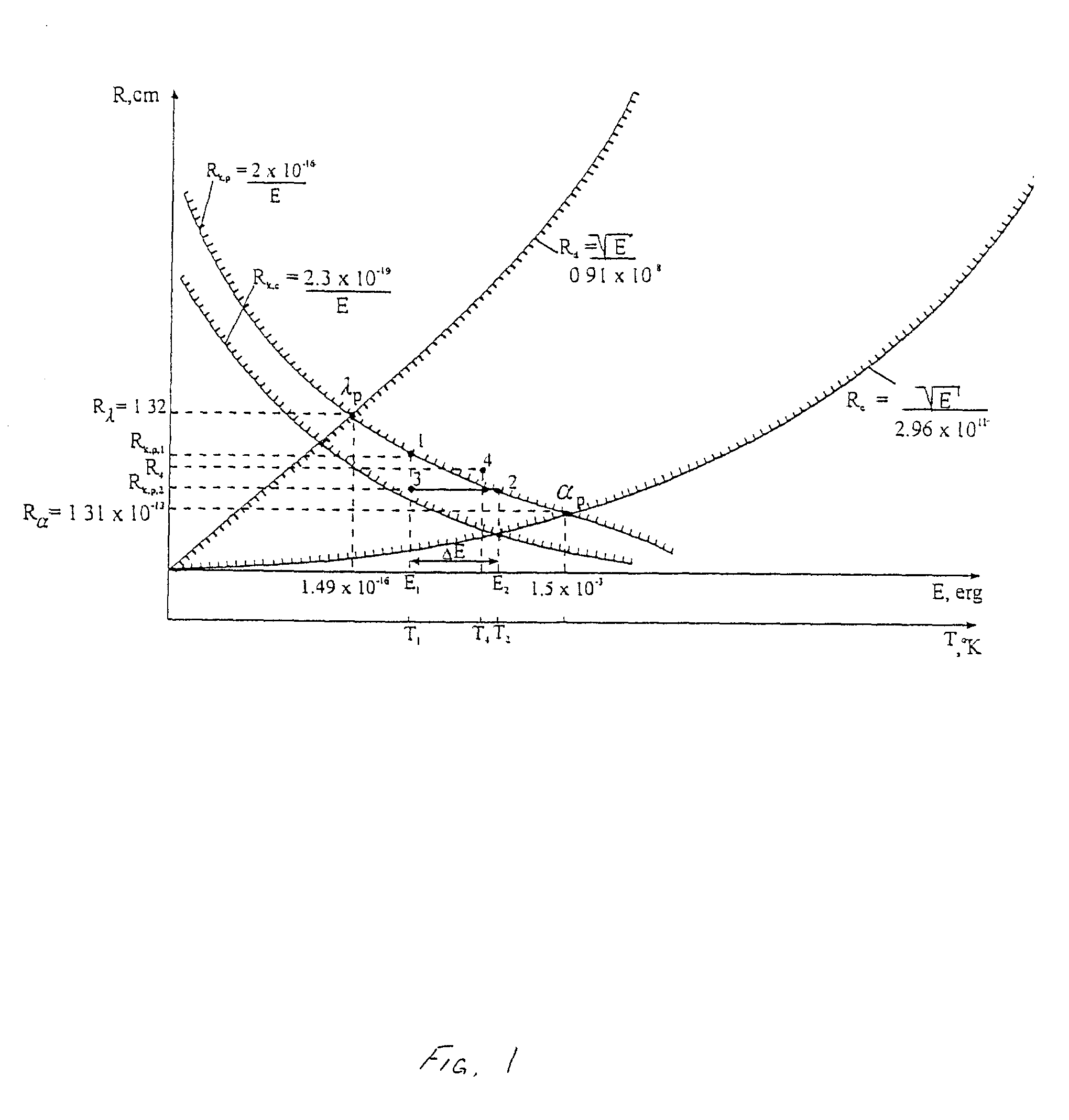
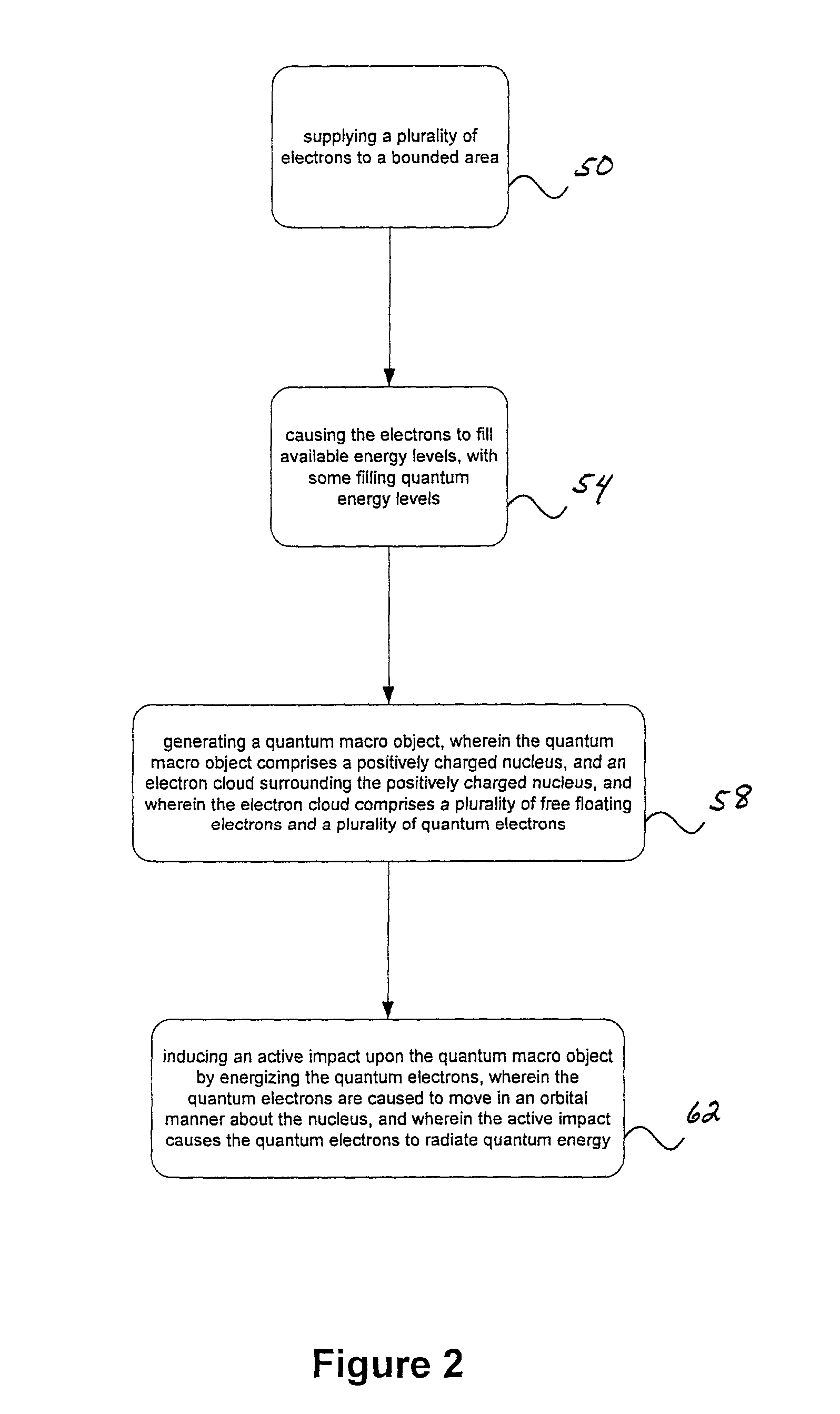
InactiveUS20030094911A1Potential energyIncrease gas pressureRadiation/particle handlingNuclear energy generationDielectricEnergy particle
Methods and systems are described for generating high-energy particles, or quantum energy, from a quantum macro object. Specifically, the method of generating high-energy photons, or quantum energy, comprises in general: (a) isolating a gaseous substance within a bounded area, wherein the gaseous substance and the bounded area contain a plurality of composition particles; (b) energizing the gaseous substance, and particularly the particles within the gaseous substance and the bounded area, thus causing the gaseous substance to transition into a glow discharge plasma state, wherein the particles are separated into their component atomic nuclei and electron parts; (c) increasing the gas pressure within the bounded area to transition the glow discharge plasma to a quantum macro object, wherein the quantum macro object comprises a positively charged nucleus and an electron cloud surrounding the positively charged nucleus, the electron cloud comprising a plurality of quantum electrons and a plurality of free-floating electrons, the quantum electrons comprising large amounts of potential quantum energy; (d) energizing the quantum electrons by inducing an active impact upon the quantum macro object, wherein the quantum electrons are caused to orbit the nucleus of the quantum macro object such that the potential energy existing within the quantum electrons is converted and released in the form of quantum energy in a continuous and inexhaustible manner. The bounded area is typically created by a dielectric of various sorts, such as within a dielectric container or properly charged air.
Owner:CHUKANOV QUANTUM ENERGY
Mass spectrometers comprising accelerator devices
ActiveUS9318309B2High ion energySolve the low detection efficiencyTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsPotential differenceMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A method of mass spectrometry is disclosed comprising providing a flight region for ions to travel through and a detector or fragmentation device. A potential profile is maintained along the flight region such that ions travel towards the detector or fragmentation device. The potential at which a first length of the flight region is maintained is then changed from a first potential to a second potential while at least some ions are travelling within the first length of flight region. The changed potential provides a first potential difference at an exit of the length of flight region, through which the ions are accelerated as they leave the length of flight region. This increases the kinetic energy of the ions prior to them reaching the detector or fragmentation cell.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
Method and system of automatic arrangement of composing elements
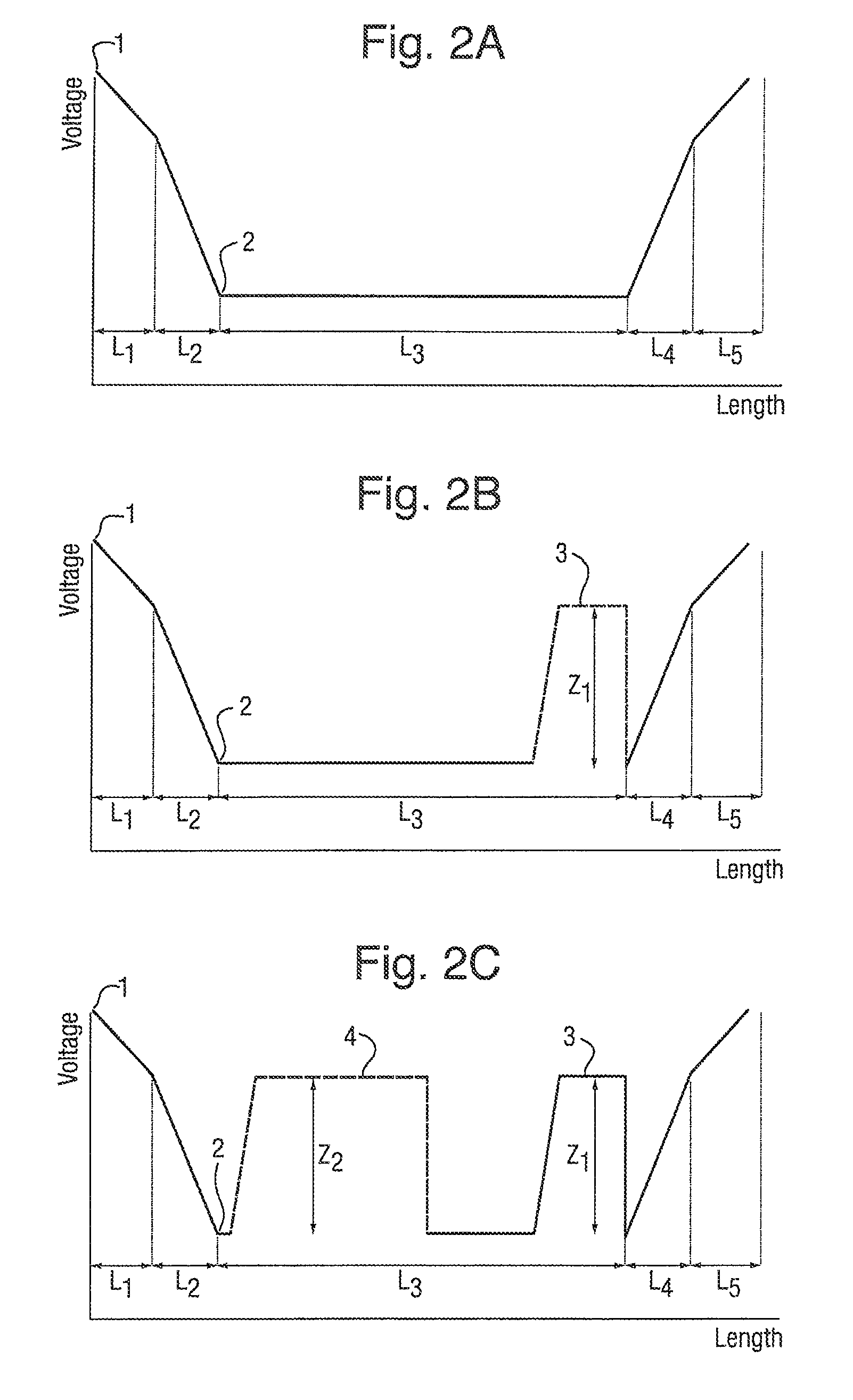
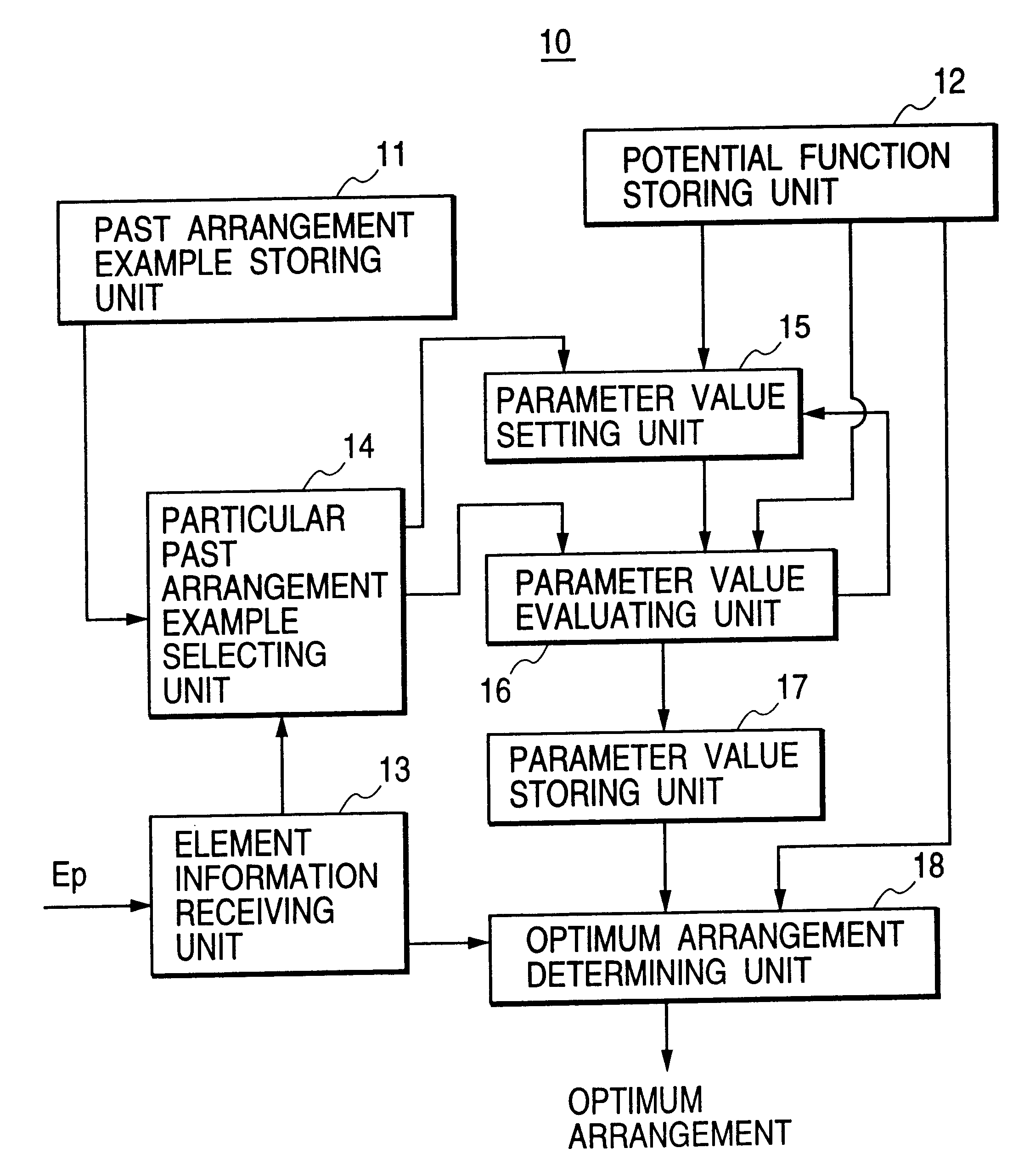
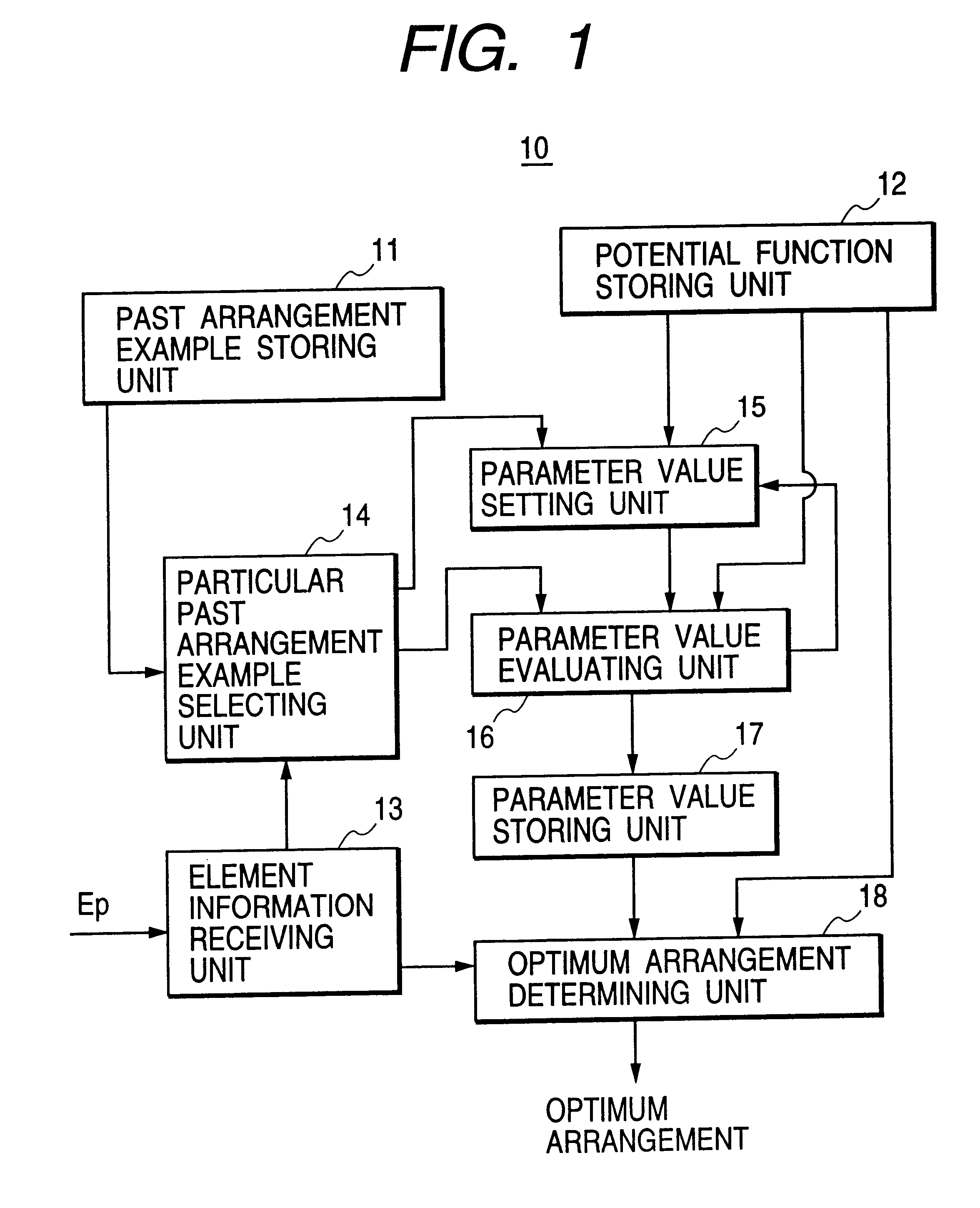
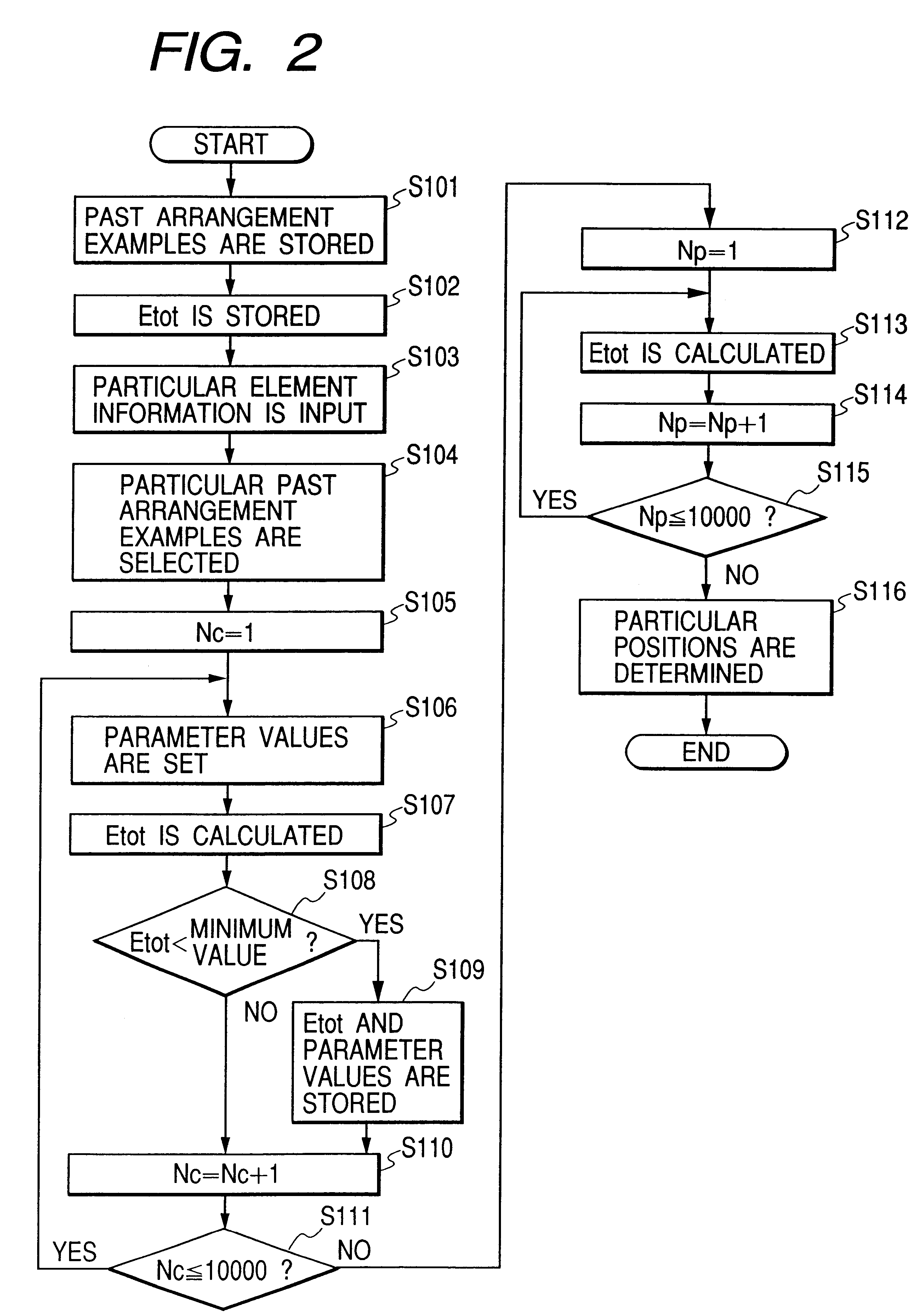
InactiveUS6336107B1Potential energyGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsEngineeringPotential energy
past positions of a plurality of composing elements indicated by various past arrangement examples are given to each potential function corresponding to one composing element, and parameter values of the potential functions corresponding to the composing elements are automatically set on condition that a past total potential energy obtained by solving the potential functions is minimized. Thereafter, the parameter values are given to the potential functions in which a position of any composing element is not determined, and particular positions of the composing elements are determined on condition that a total potential energy obtained by solving the potential functions is minimized. Because each potential function corresponding to one composing element has an attraction term indicating the attraction between the composing element and the other composing elements and an attraction-repulsion term indicating the setting of the composing element at a position spaced at moderate distances from the other composing elements, the particular positions of the composing elements are set in an optimum arrangement. Accordingly, the optimum arrangement of the composing elements can be automatically obtained without extracting any arrangement knowledge from a skilled person.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Mass Spectrometers Comprising Accelerator Devices
ActiveUS20140284471A1Increase ion energyIncrease energyTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsKinetic energySpectrometer
A method of mass spectrometry is disclosed comprising providing a flight region for ions to travel through and a detector or fragmentation device. A potential profile is maintained along the flight region such that ions travel towards the detector or fragmentation device. The potential at which a first length of the flight region is maintained is then changed from a first potential to a second potential whilst at least some ions are travelling within the first length of flight region. The changed potential provides a first potential difference at an exit of the length of flight region, through which the ions are accelerated as they leave the length of flight region. This increases the kinetic energy of the ions prior to them reaching the detector or fragmentation cell.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD
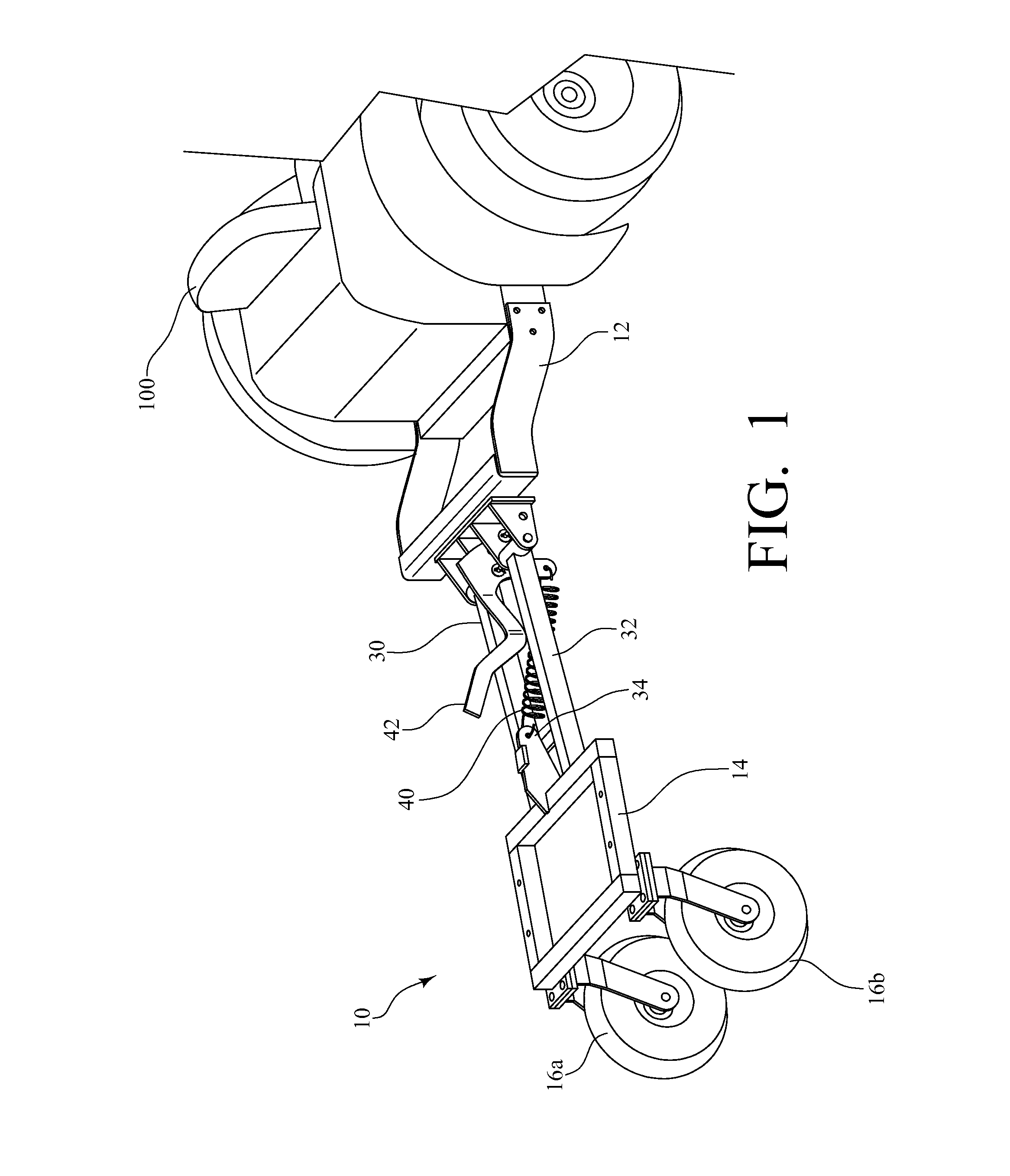
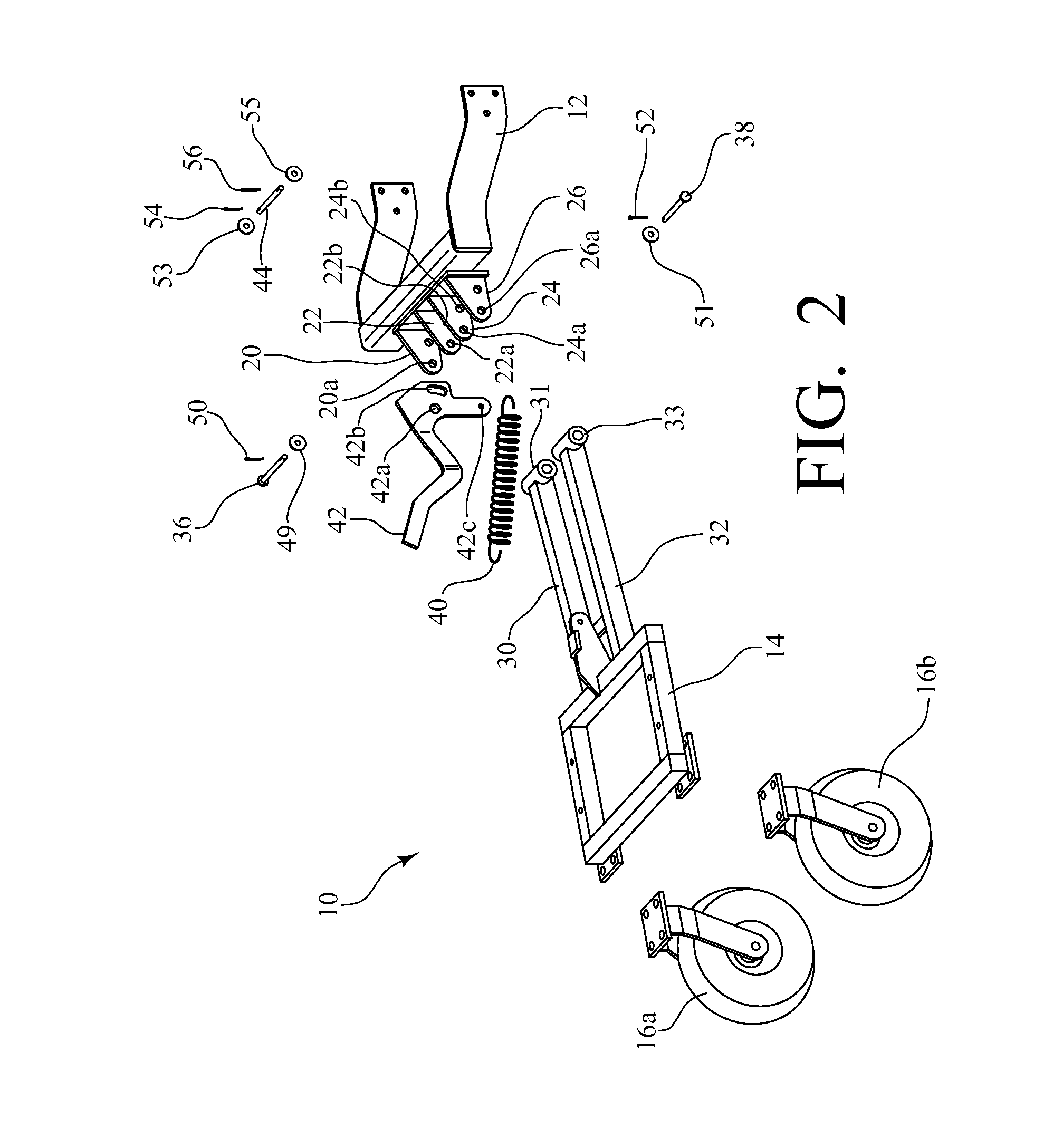
Platform assembly for a towed implement
A platform assembly for a towed implement comprises a bracket for securing the platform assembly to a vehicle; a frame connected to the bracket for supporting the towed implement; one or more wheels connected to the frame for contacting the underlying ground surface; and a biasing means for providing an upward force that counteracts a downward force applied to the rear of the vehicle by the platform assembly and the towed implement.
Owner:BRINLY-HARDY COMPANY
Control method of magnetic solenoid valve, control method of electromagnetically controlled inlet valve of high pressure fuel pump, and control device for electromagnetic actuator of electromagnetically controlled inlet valve
ActiveUS9726104B2Suppress generationReduce impact noiseElectrical controlPump controlTop dead centerSolenoid valve
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
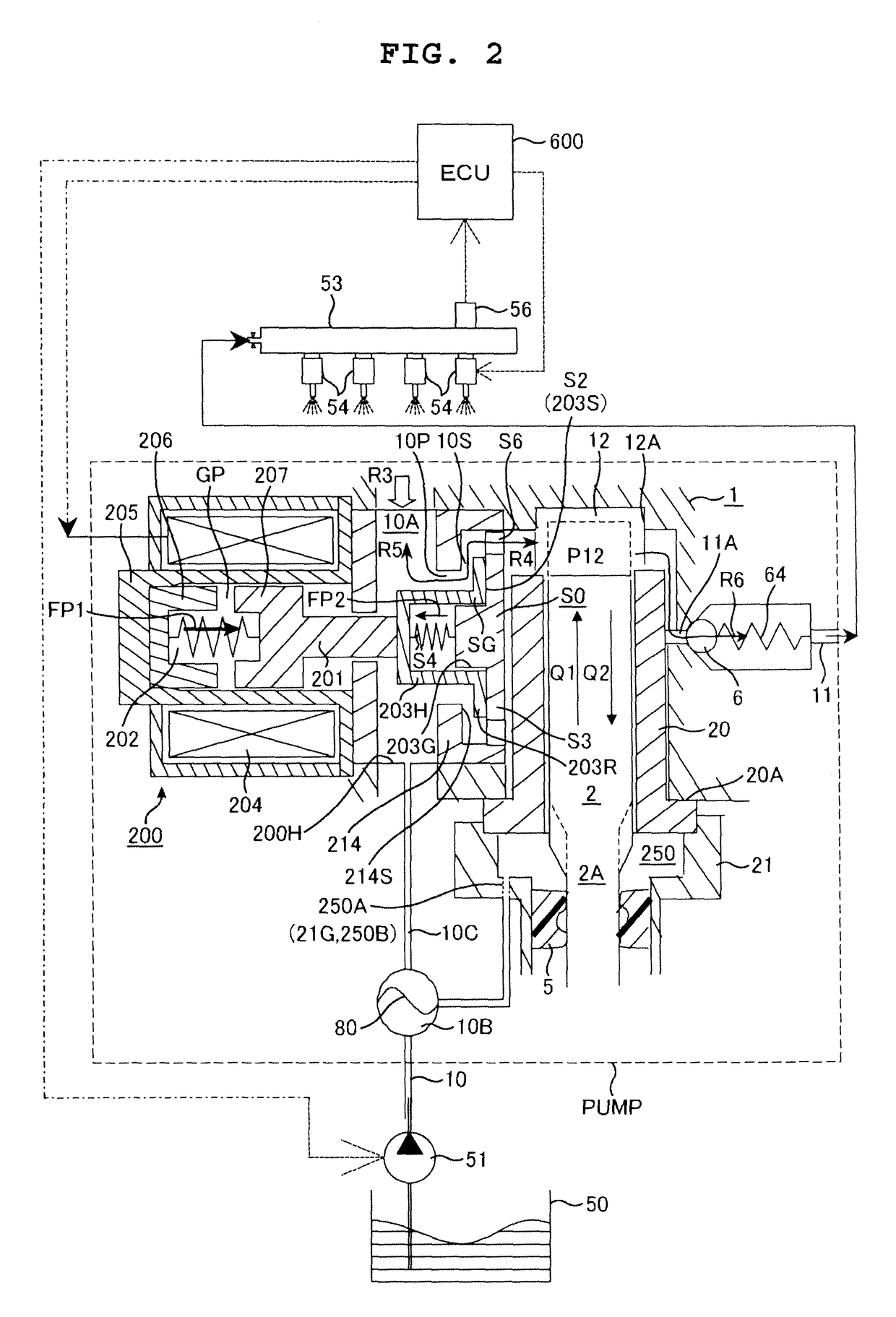
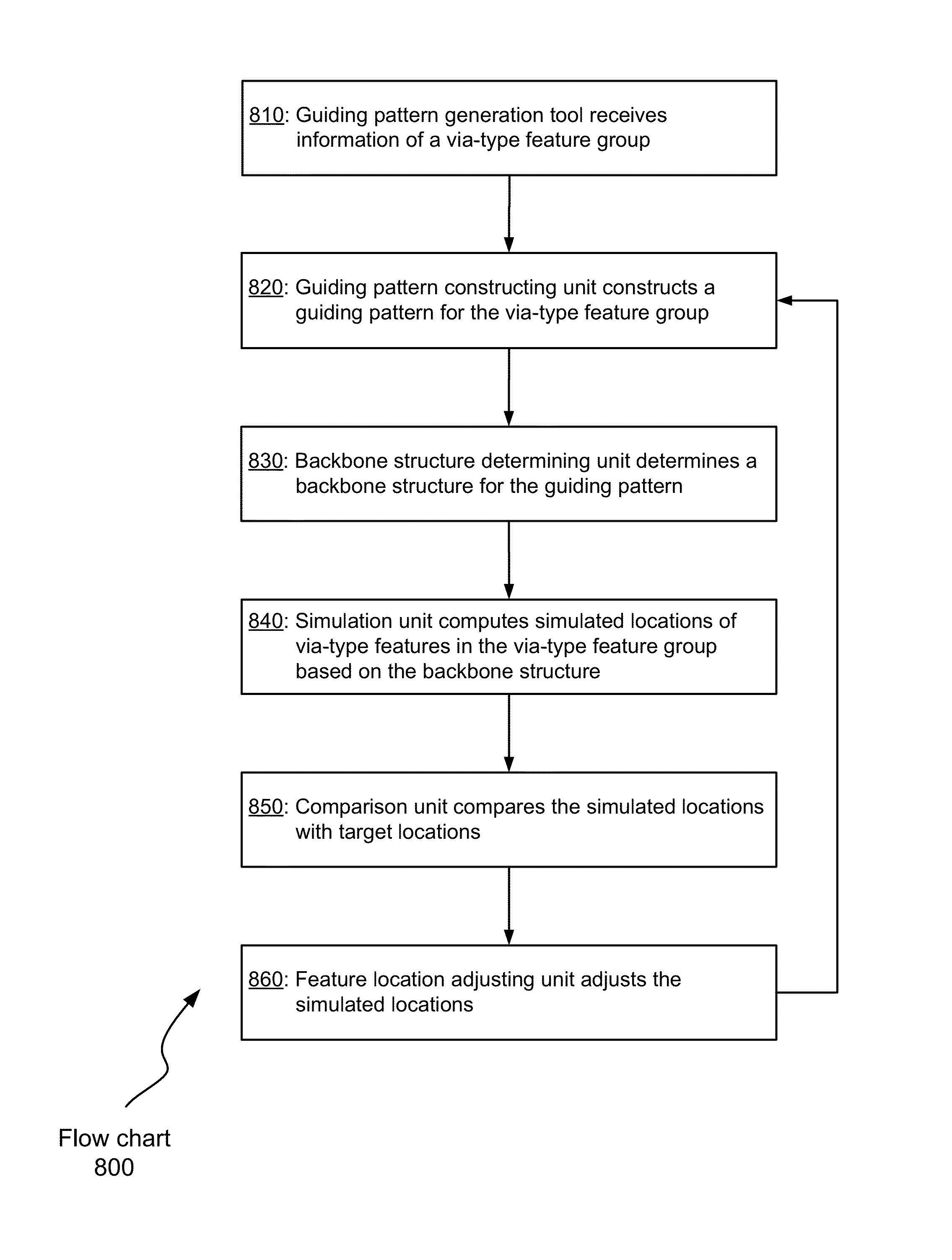
Generating guiding patterns for directed self-assembly
ActiveUS9032357B1Potential energyDetecting faulty computer hardwarePhotomechanical apparatusSimulationSelf-assembly
Aspects of the invention relate to techniques of generating guiding patterns for via-type feature groups. A guiding pattern may be constructed for a via-type feature group that comprises two or more via-type features in a layout design. A backbone structure may then be determined for the guiding pattern. Based on the backbone structure and a self-assembly model, simulated locations of the two or more via-type features are computed. The simulated locations are compared with targeted locations. If the simulated locations do not match the targeted locations based on a predetermined criterion, the simulated locations adjusted to derive modified locations. Using the modified locations, the above operations may be repeated until the simulated locations match the targeted location based on a predetermined criterion or for a predetermined number of times.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Deployable structure for use in establishing a reflectarray antenna
ActiveUS10283835B2Increase stiffnessReduce bowingCollapsable antennas meansCosmonautic vehiclesPantographWaste management
A deployable structure for use in establishing a reflectarray antenna is provided that includes a flexible reflectarray and a deployment structure that includes an endless pantograph for deploying the flexible reflectarray from a folded, undeployed state towards a deployed state in which the flexible reflectarray is substantially planar. In a particular embodiment, the deployment structure includes a plurality of tapes that engage the endless pantograph and are used to establish a positional relationship between the deployed reflectarray and another component of the reflectarray antenna.
Owner:M M A DESIGN
Extracardiac Blood Flow Amplification Device
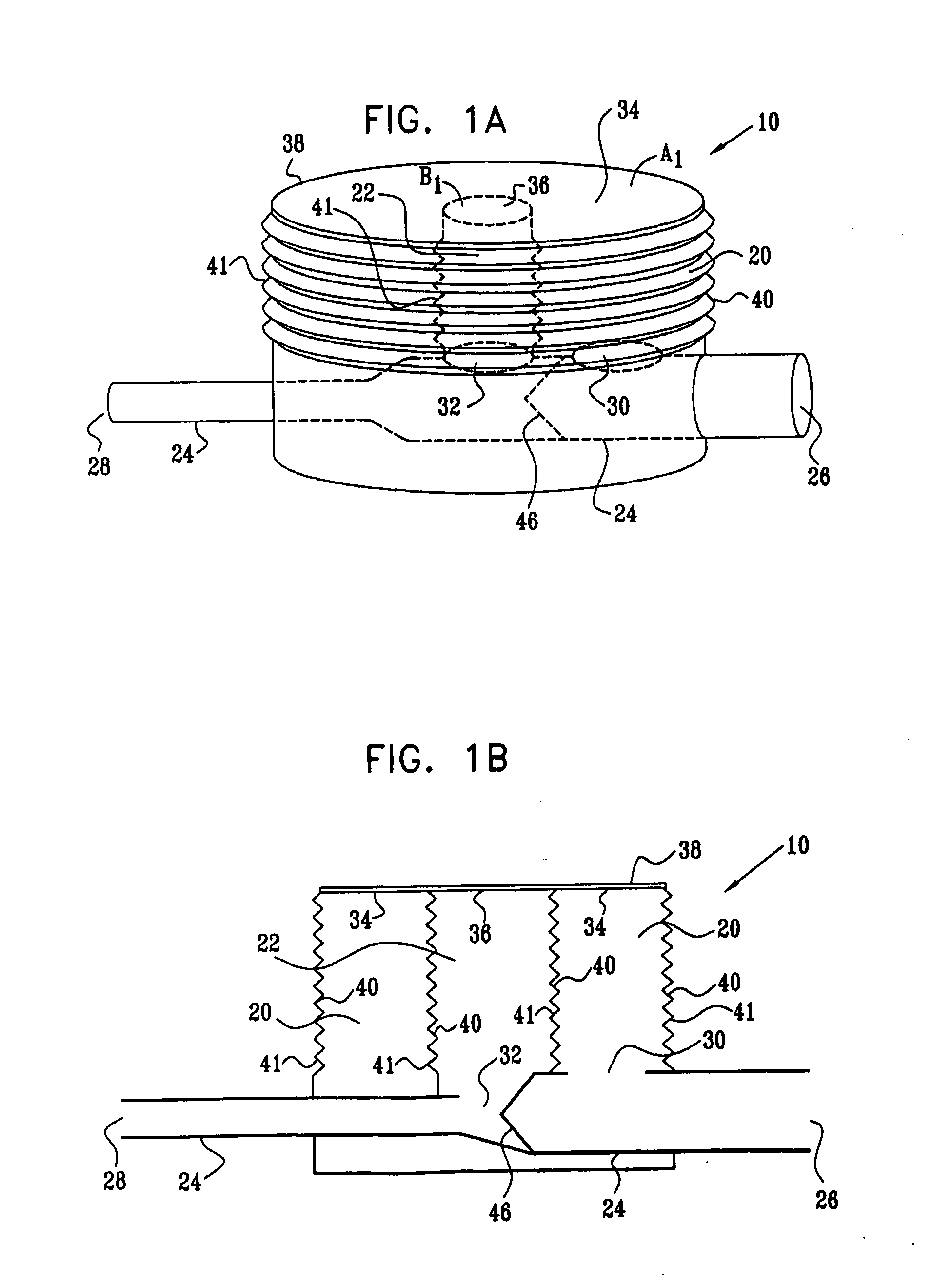
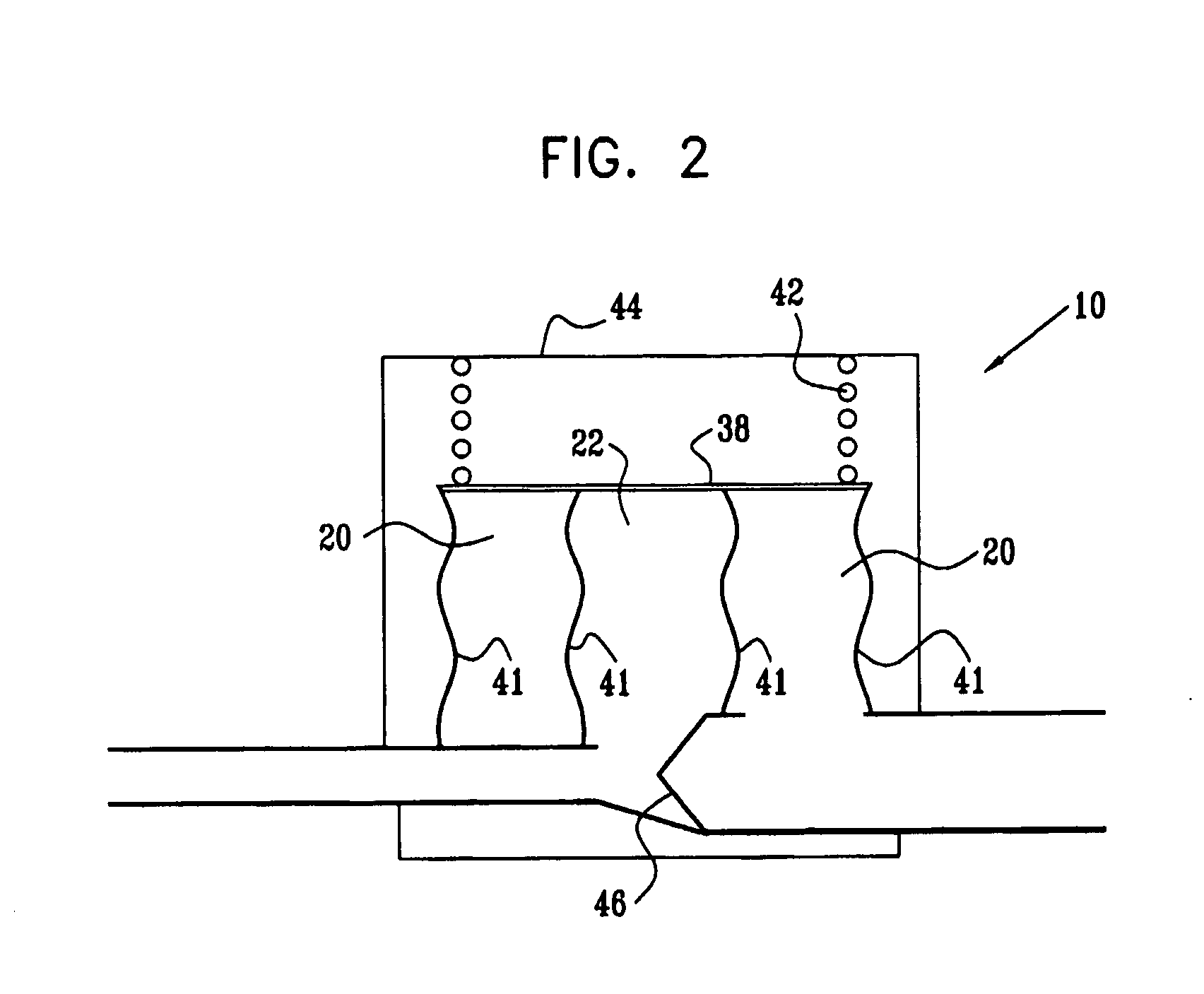
InactiveUS20080234537A1Reduce stressIncrease blood flowIntravenous devicesBlood pumpCardiac cycleMedicine
Apparatus (10) is provided including a first chamber (20) and a second chamber (22), adapted to be in fluid communication with a first volume and a second volume of oxygenated blood of a subject, respectively, the first chamber (20) and the second chamber (22) having a first surface (34) and a second surface (36), respectively. The apparatus (10) further includes a third surface (38) adapted to apply an elastically-derived force, at least a first portion of the third surface (38) in mechanical communication with the first surface (34), and at least a second portion of the third surface (38) in mechanical communication with the second surface (36) during at least a portion of a cardiac cycle. A pressure-sensitive valve (46) is coupled between the first chamber (20) and the second chamber (22), the valve (46) adapted: (a) to be in an open position during at least a portion of systole, such that the first chamber (20) is in fluid communication with the second chamber (22) and the first volume is in fluid communication with the second volume; and (b) to be in a substantially closed position during diastole, such that the first chamber (20) is substantially not in fluid communication with the second chamber (22) and the first volume is substantially not in fluid communication with the second volume. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:RAINBOW MEDICAL LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com