Patents
Literature
116 results about "Hindlimb" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A hindlimb is a posterior limb on an animal, especially the quadrupeds. When referring to quadrupeds, the term hind leg is often instead used.
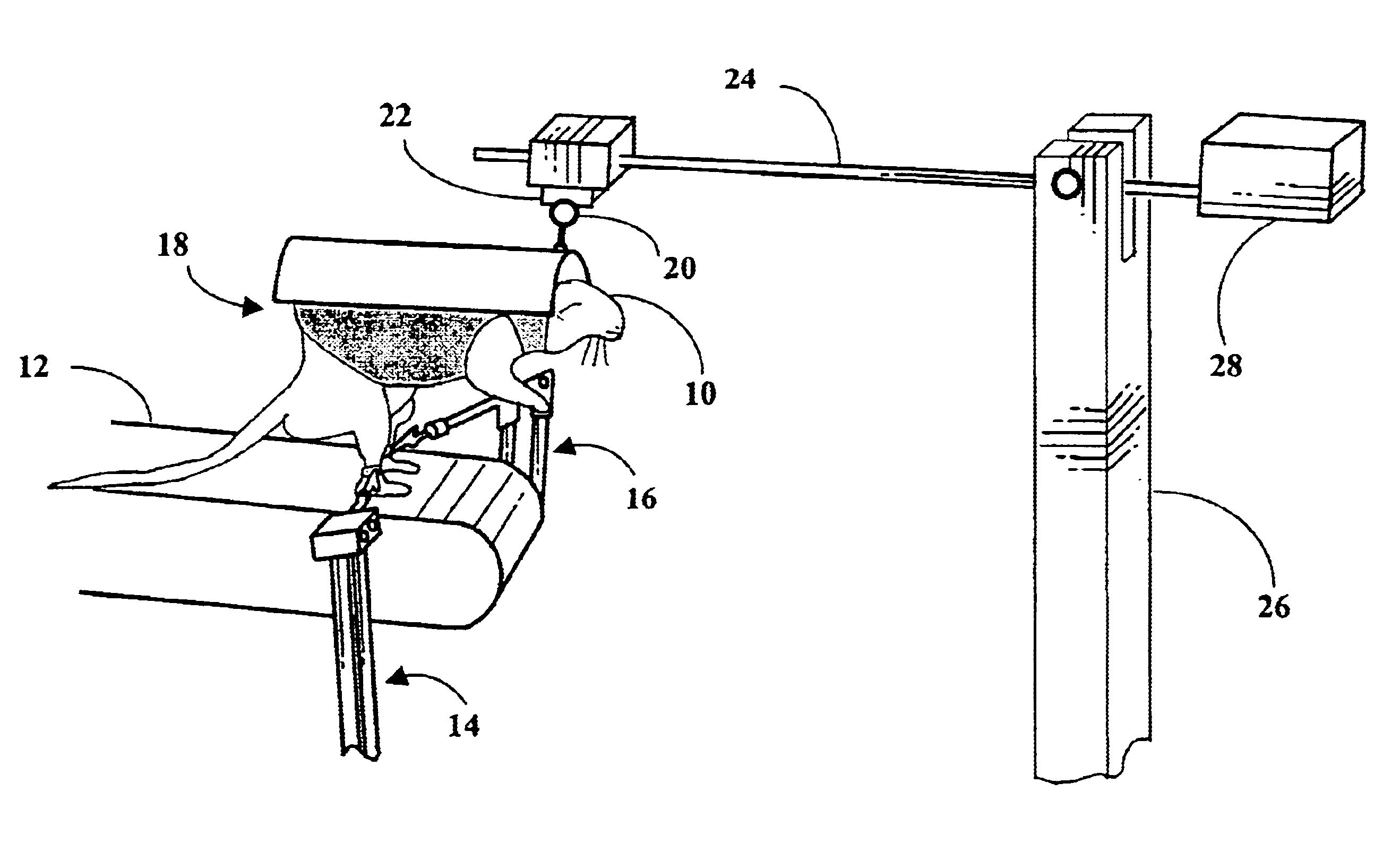
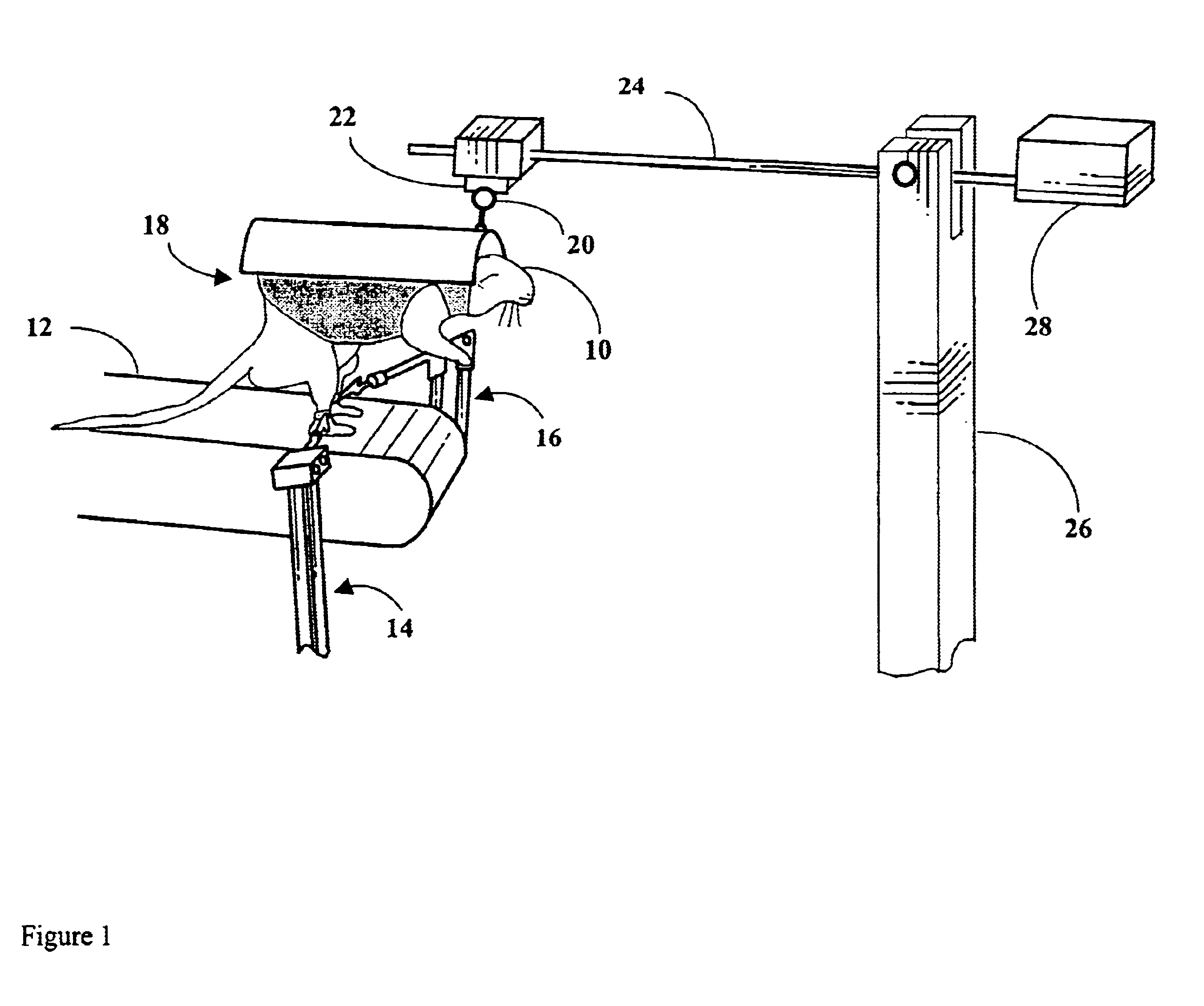
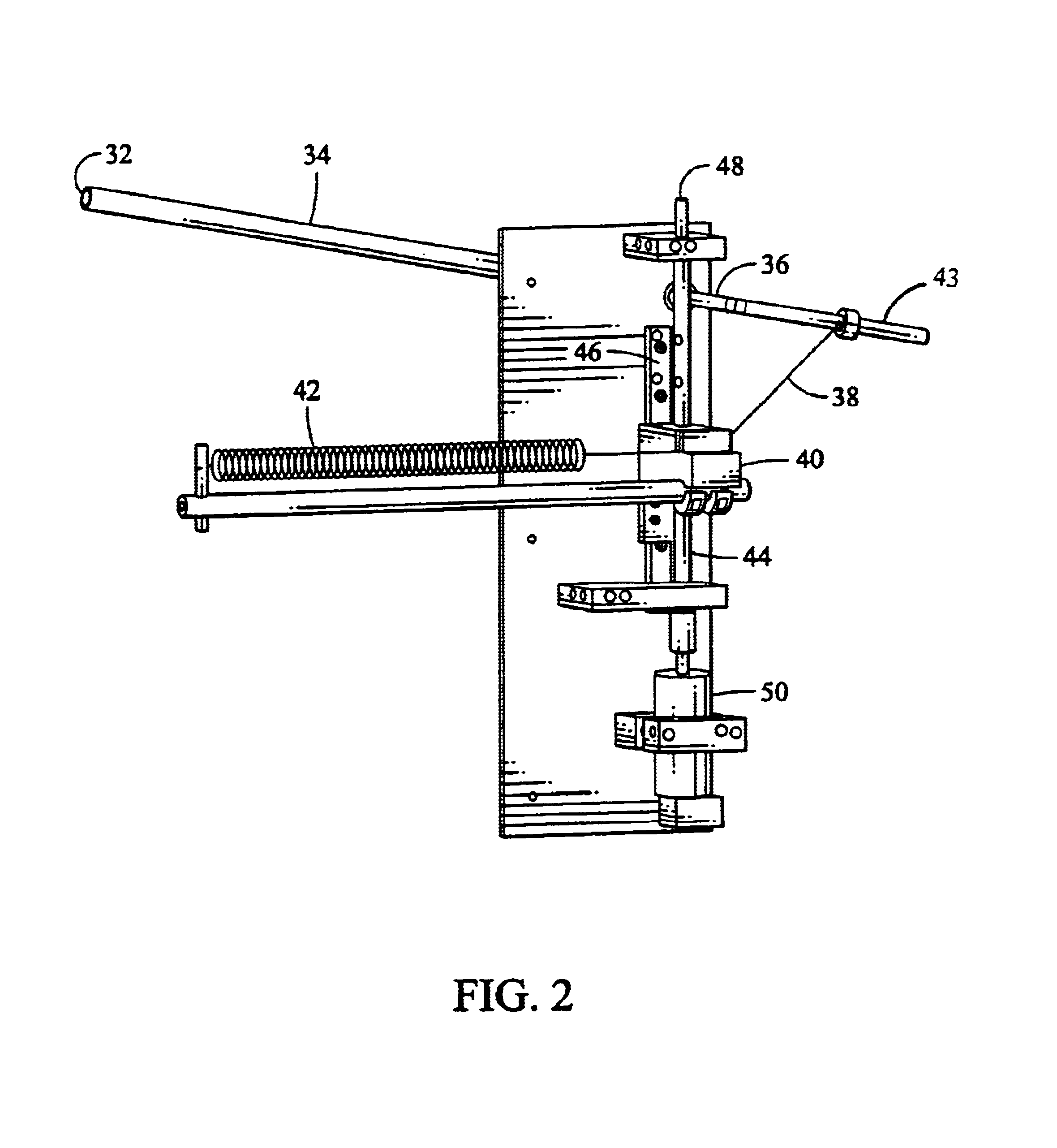
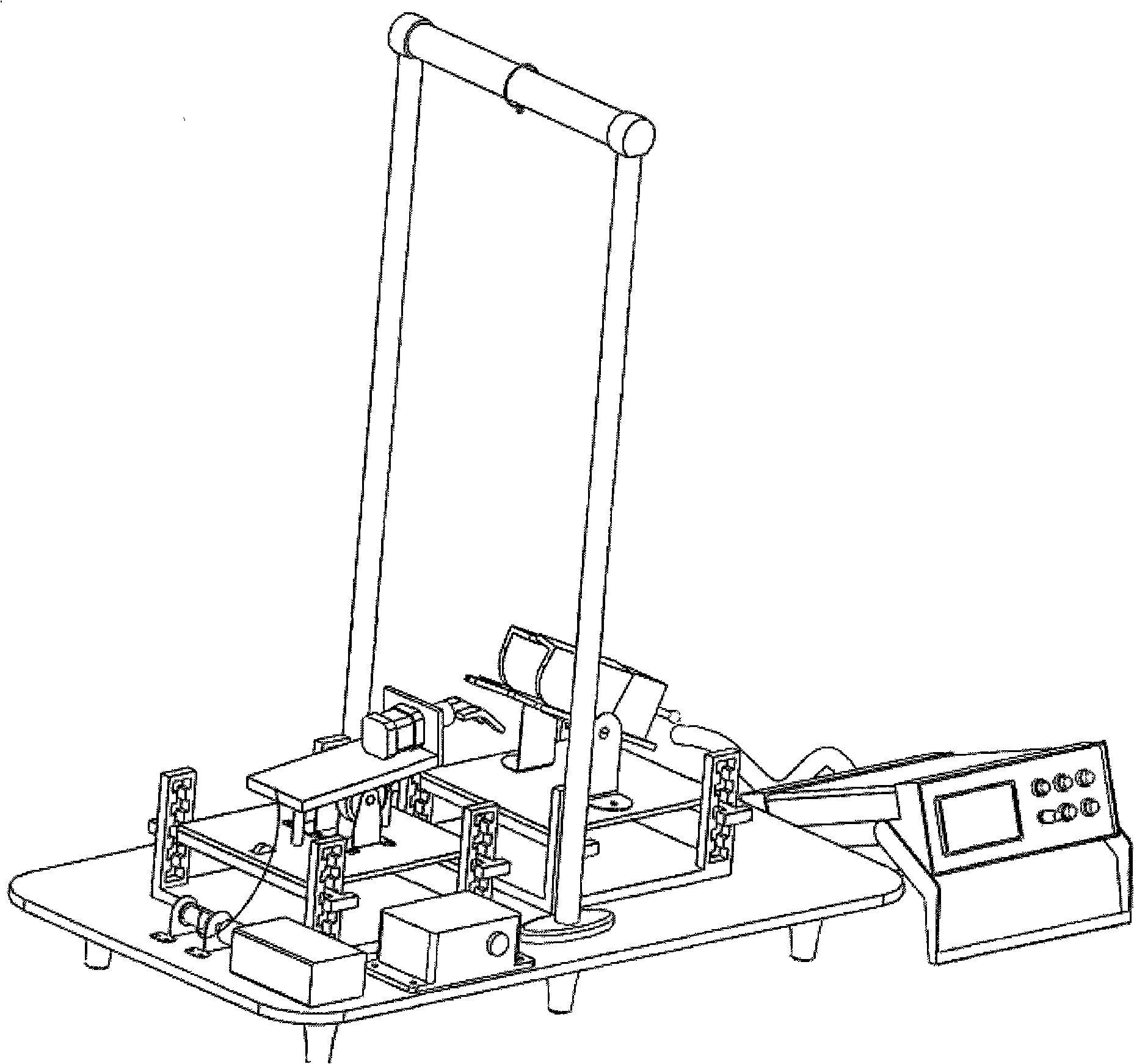
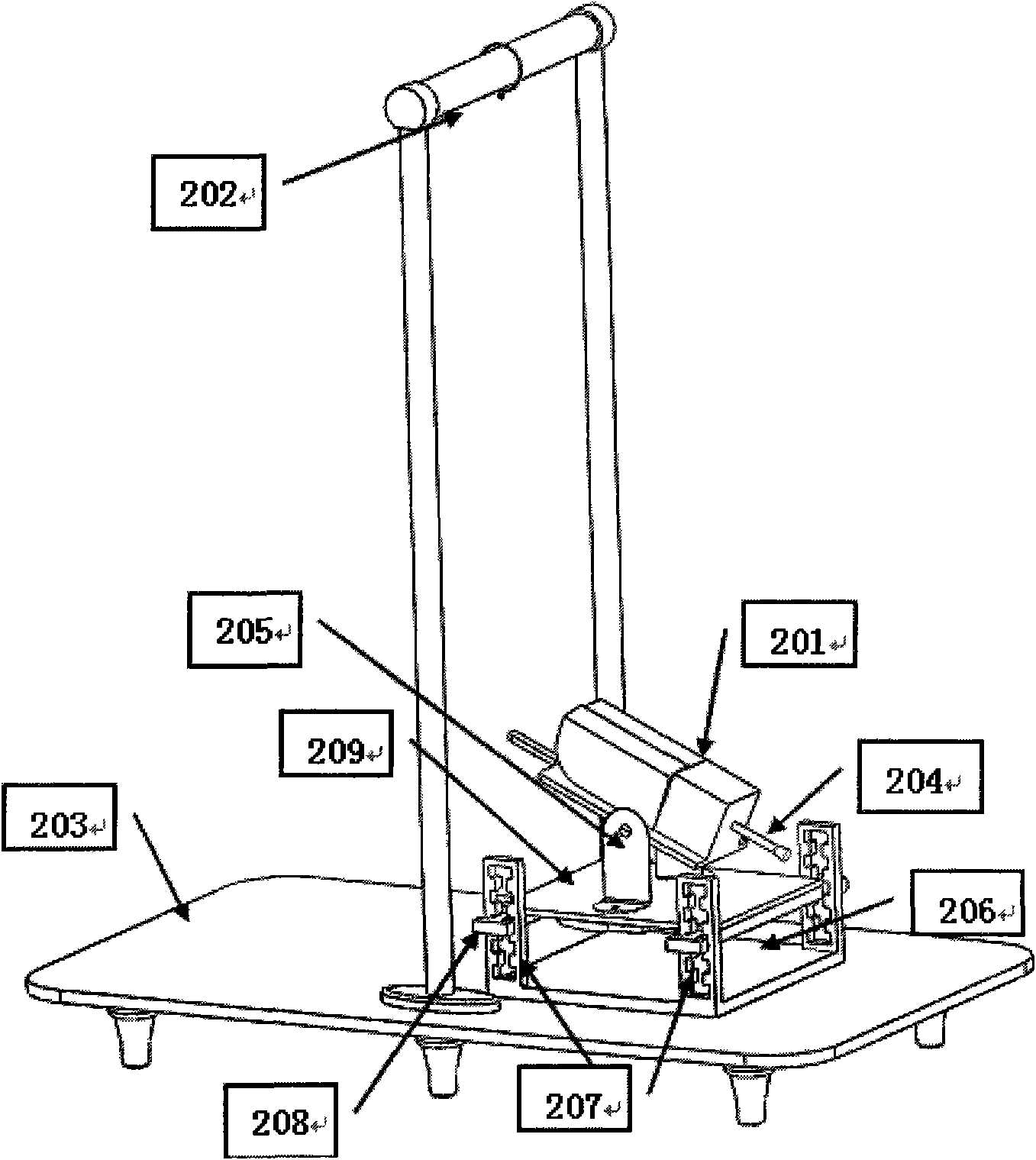
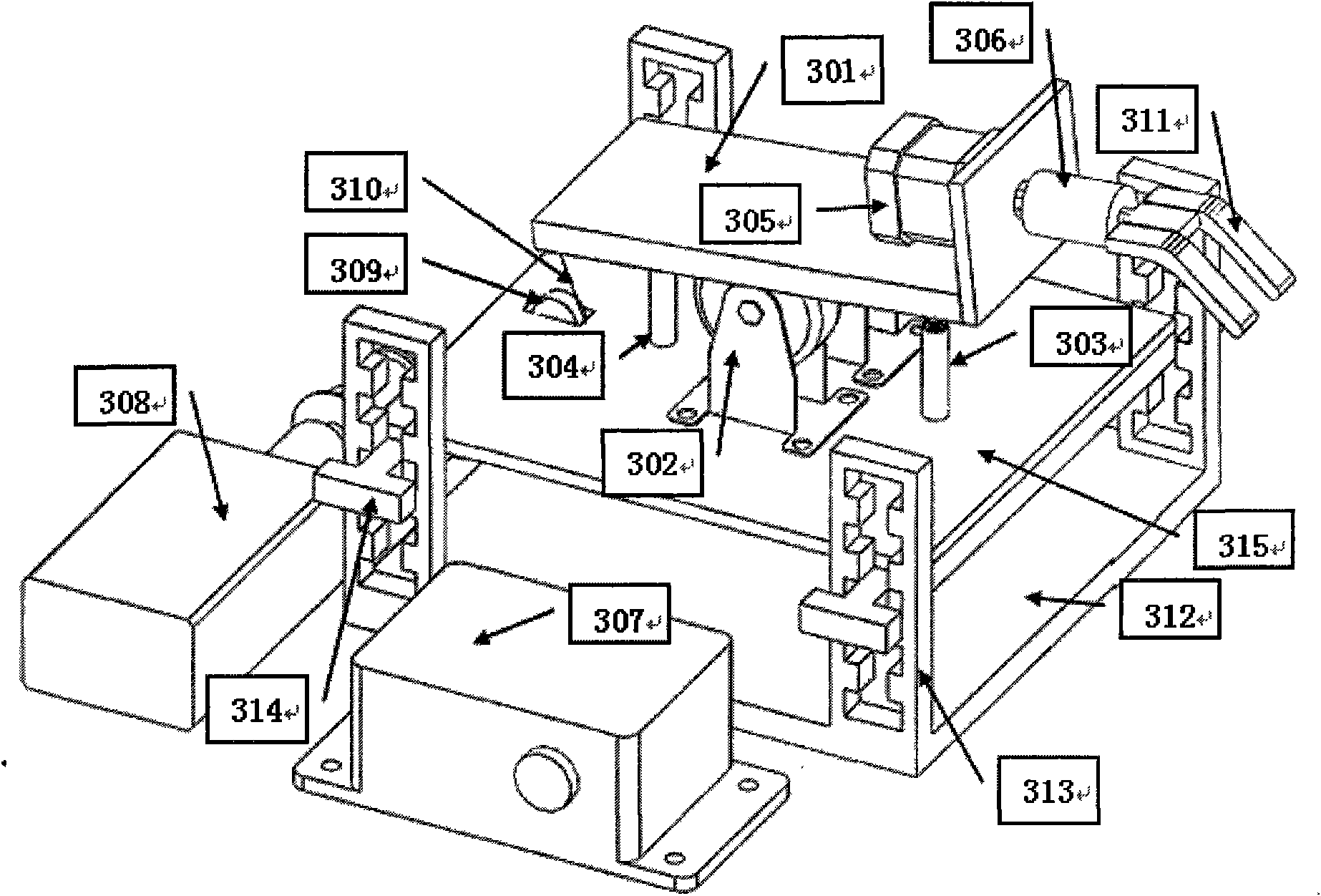
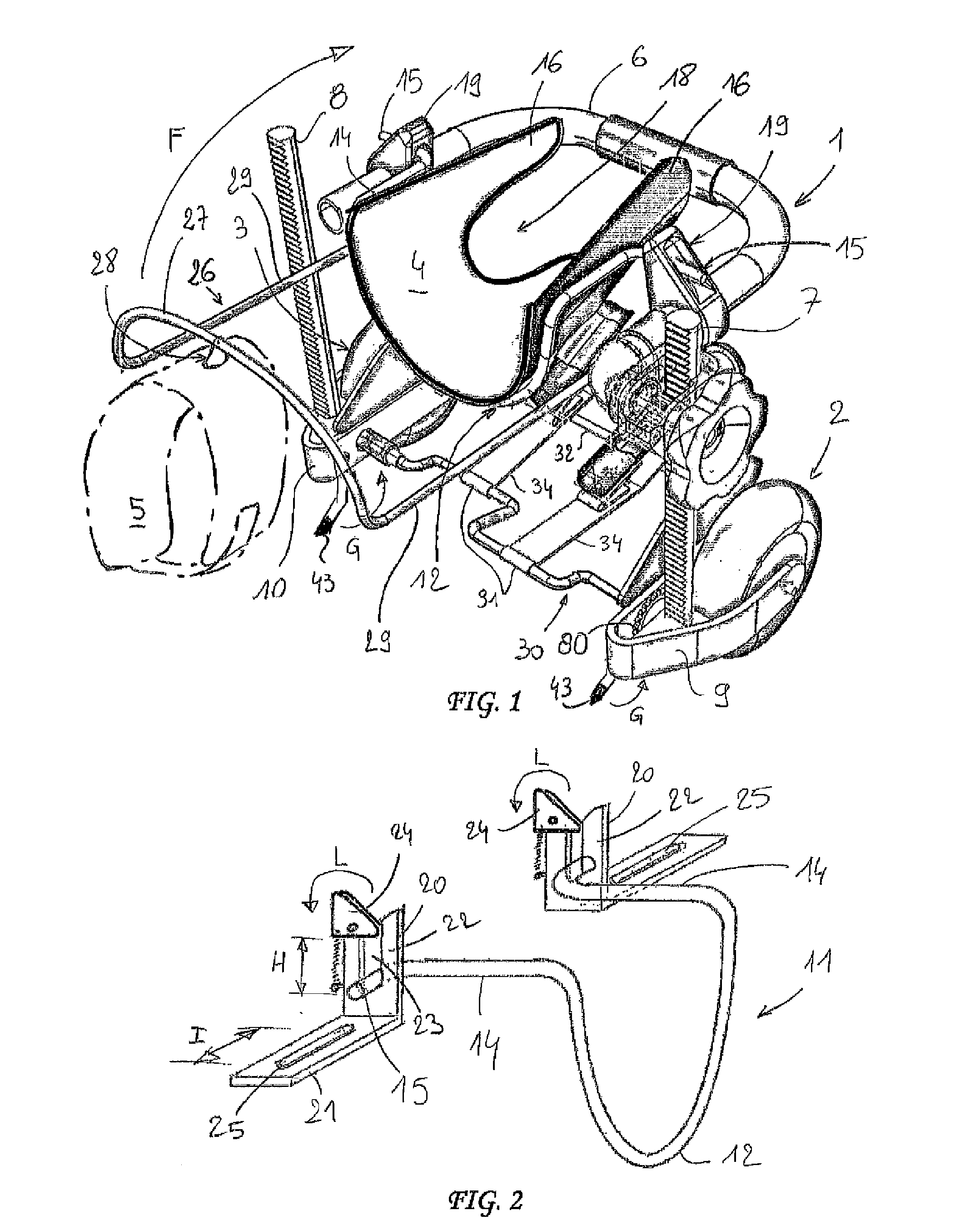
Robotic device for locomotor training
InactiveUS6880487B2Easy to testAssessing the efficacy of potential therapeutic interventionsChiropractic devicesWalking aidsRobotic systemsRobotic arm
A robotic system and method for locomotion assessment and training of a mammal, exemplified by a rodent. A neurologically impaired animal is suspended over a moving surface in a harness, and the animal's hindlimbs are connected to robotic arms that apply force to the hindlimbs or measure limb movement characteristics. The moving surface can be a physical or virtual surface. A single robotic mechanism comprising two robotic arms can simultaneously apply force, measure limb movement, and provide a virtual surface. Manual or automatic adjustment of load support allows the mammal to step at varying body weight loads.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
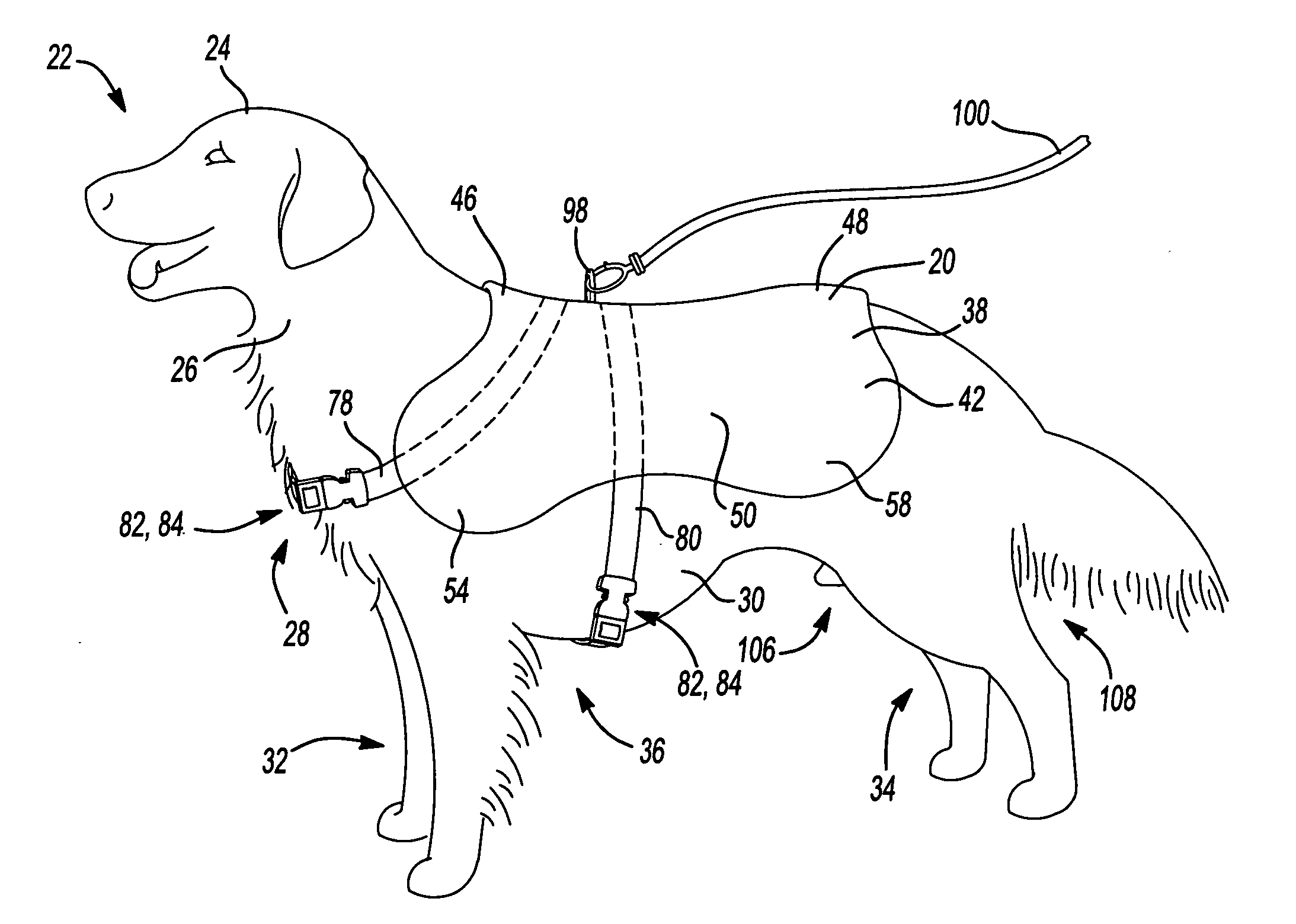
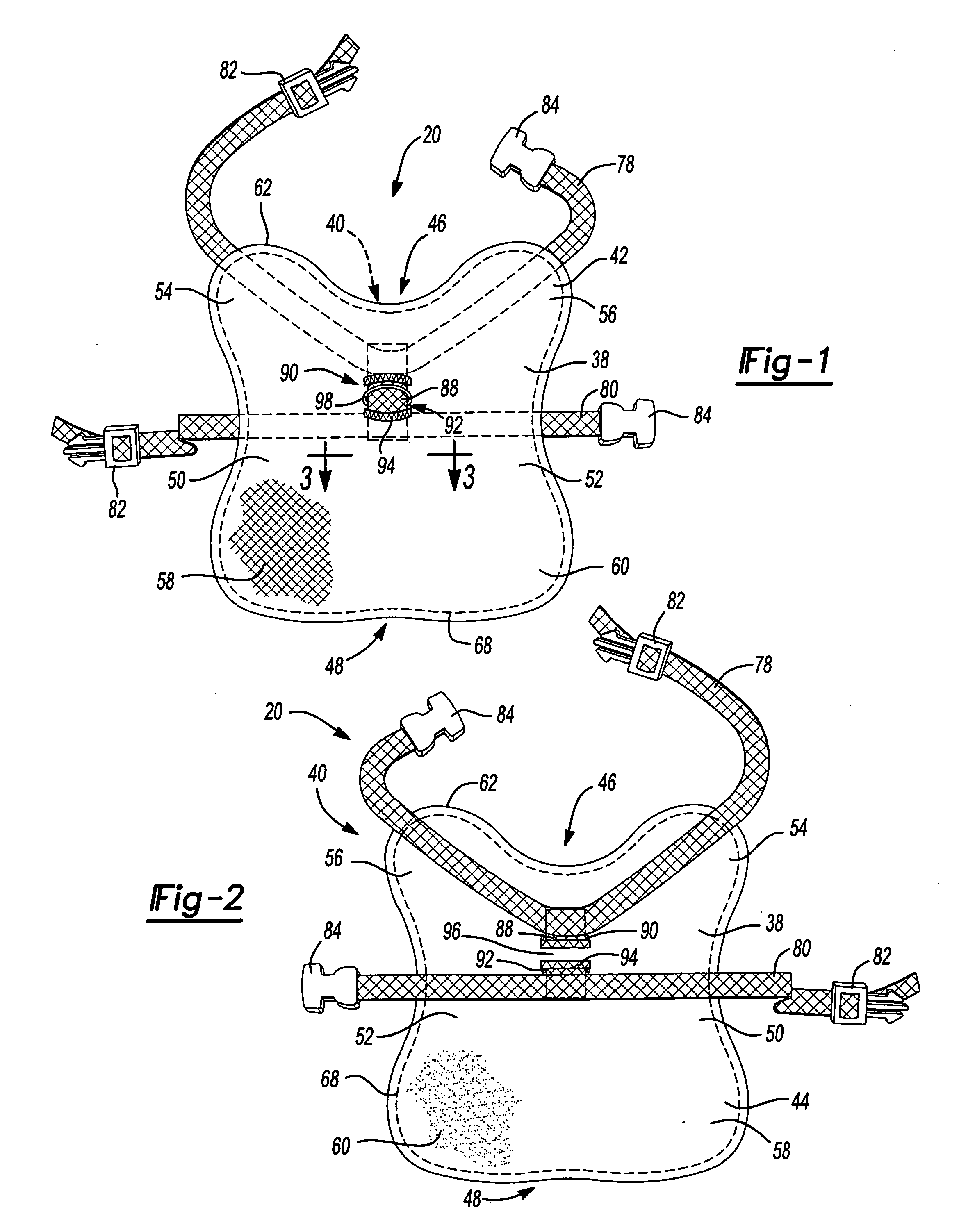
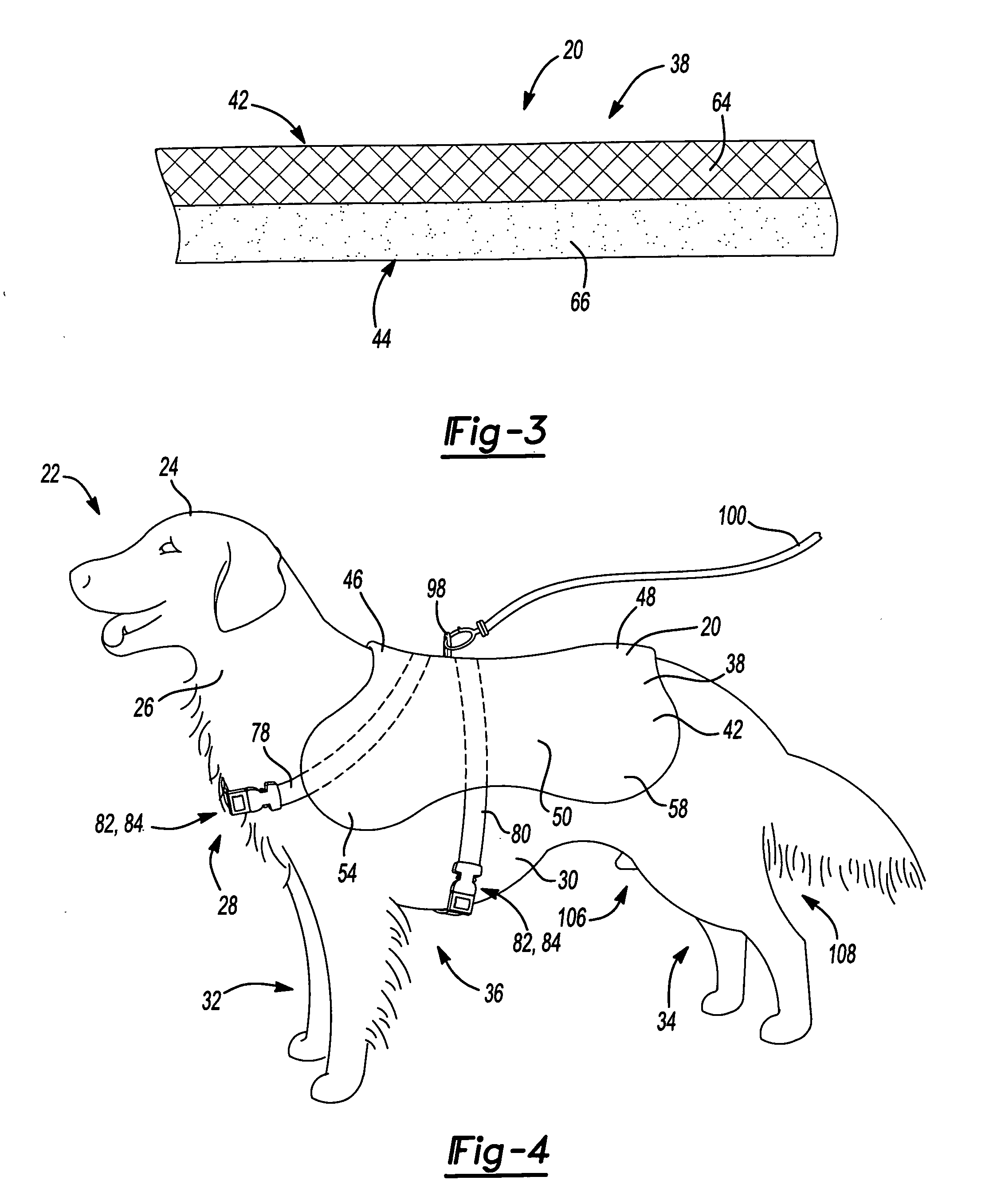
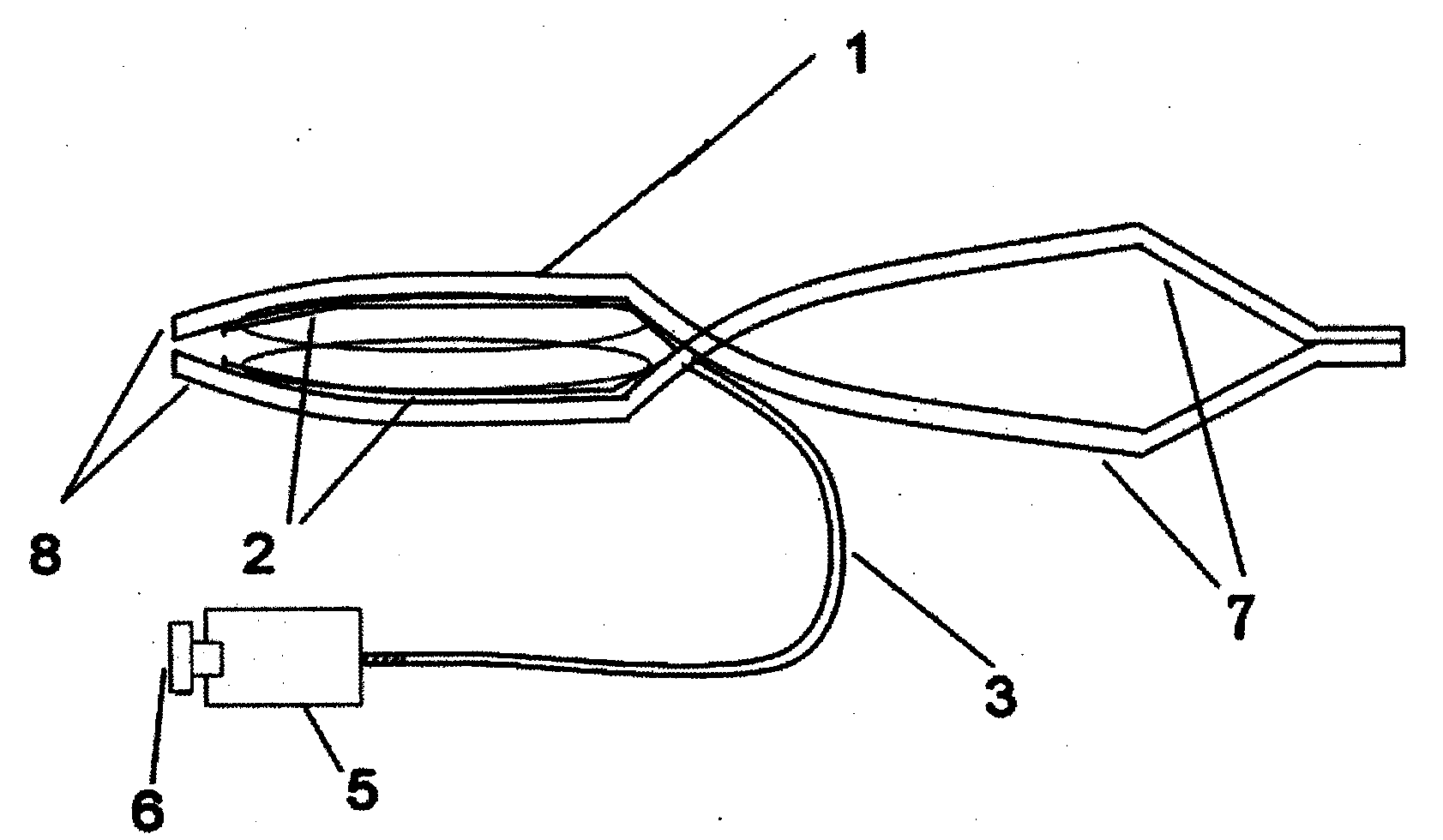
Animal coat harness
InactiveUS20060090711A1Add featureImprove functionalityAnimal housingTaming and training devicesAnimal CoatEngineering
Owner:RICHARDS RUTH E
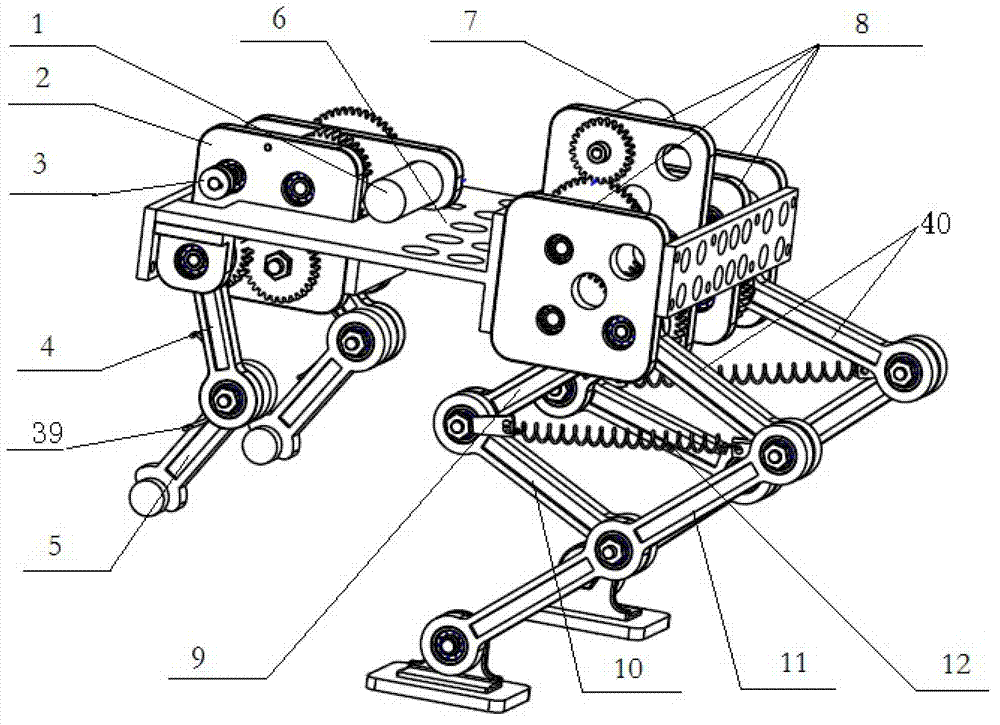
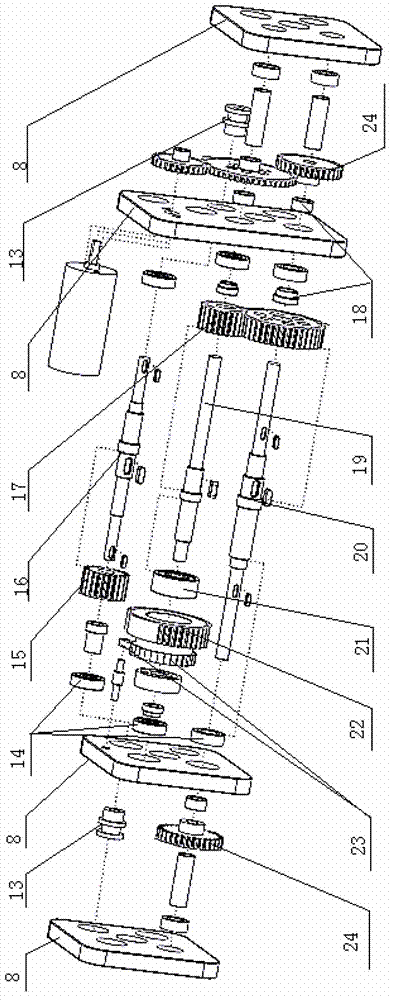
Frog-inspired biomimetic jumping robot
InactiveCN102806951AIncrease the level of releaseEnhance jumping abilityVehiclesHindlimbConductor Coil
The invention provides a frog-inspired biomimetic jumping robot. Forelimb and hindlimb driving mechanisms are mounted on a body mounting plate and connected with forelimb and hindlimb actuating mechanisms respectively, each of the forelimb driving mechanism and the hindlimb driving mechanism comprises an input shaft, a second gear, a one-way bearing, an incomplete gear and a ratchet pawl are mounted on each input shaft, each second gear is in gear transmission with a second output shaft, each incomplete gear is in gear transmission with a first output shaft, ropes are wound on second winding drums which are mounted at two ends of each first output shaft respectively, and output gears are mounted at two ends of each second output shaft respectively. By means of reasonable arrangement of the forelimb and hindlimb driving mechanisms and the forelimb and hindlimb actuating mechanisms, utilization rate of driving elements of the robot is increased, mechanical structures of legs are optimized, biomimetic degree of the robot is increased, jumping capability of the robot is enhanced, flexibility of mechanical mechanisms of the robot is improved, and posture stability during jumping is improved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
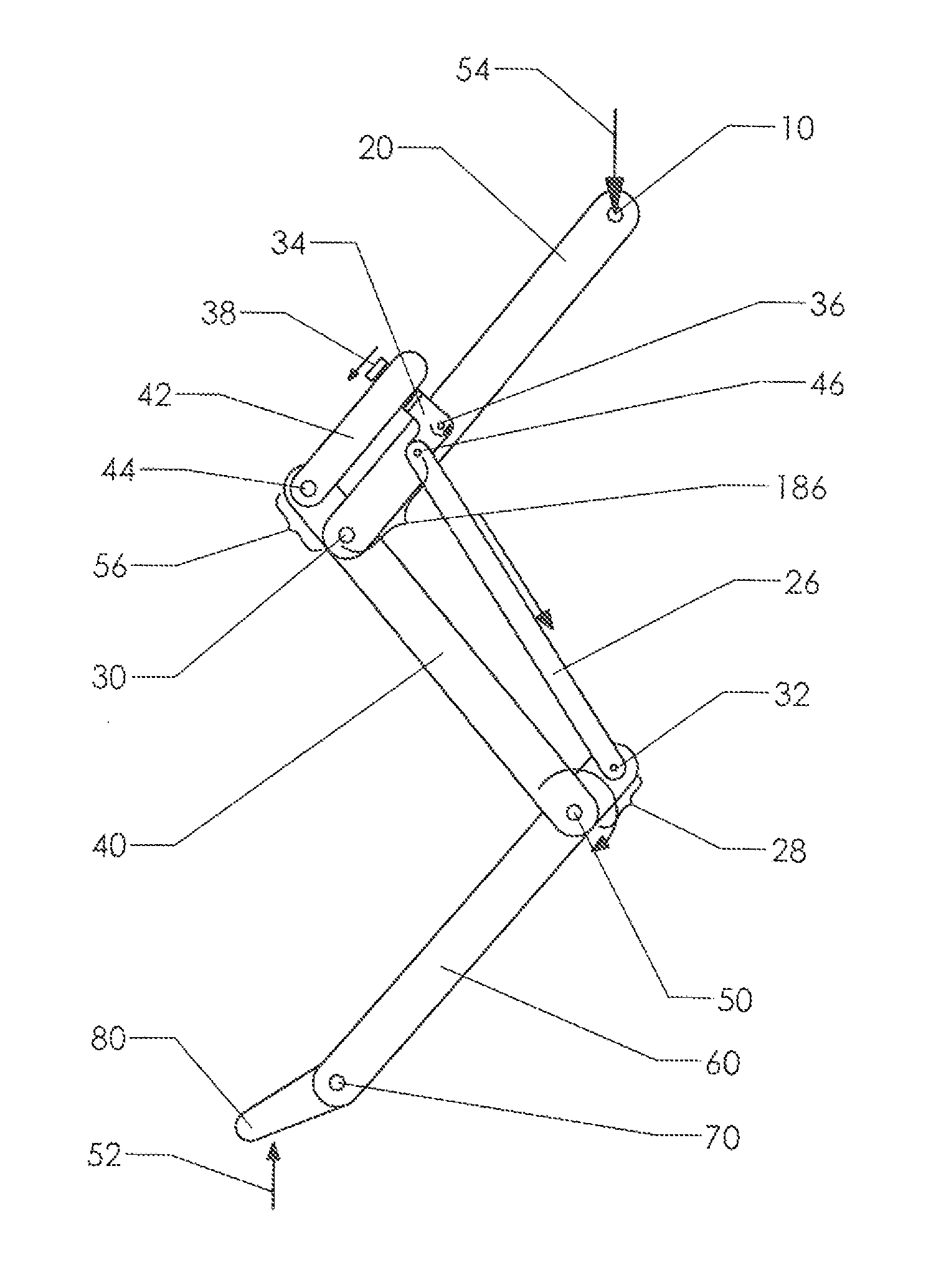
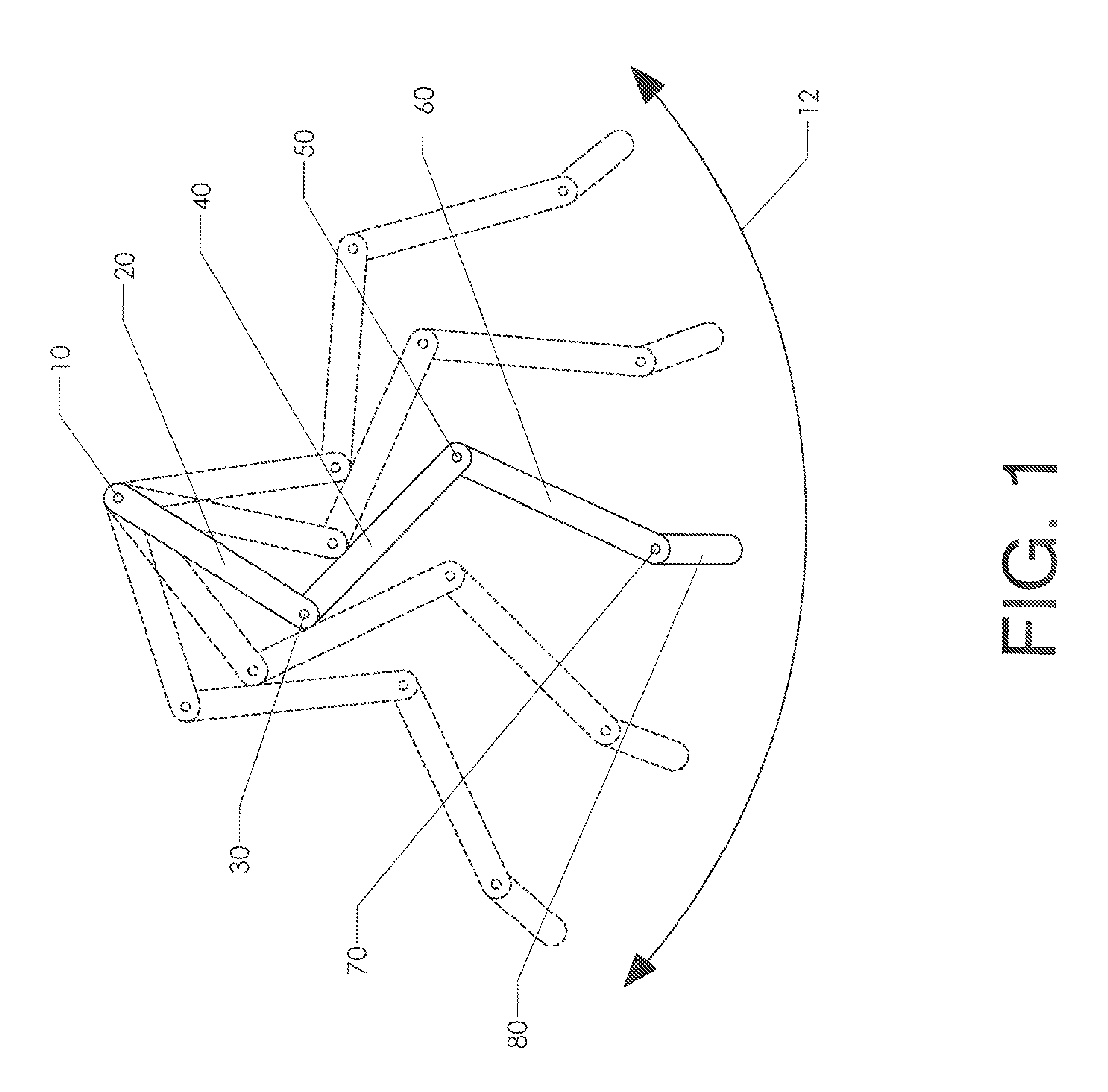
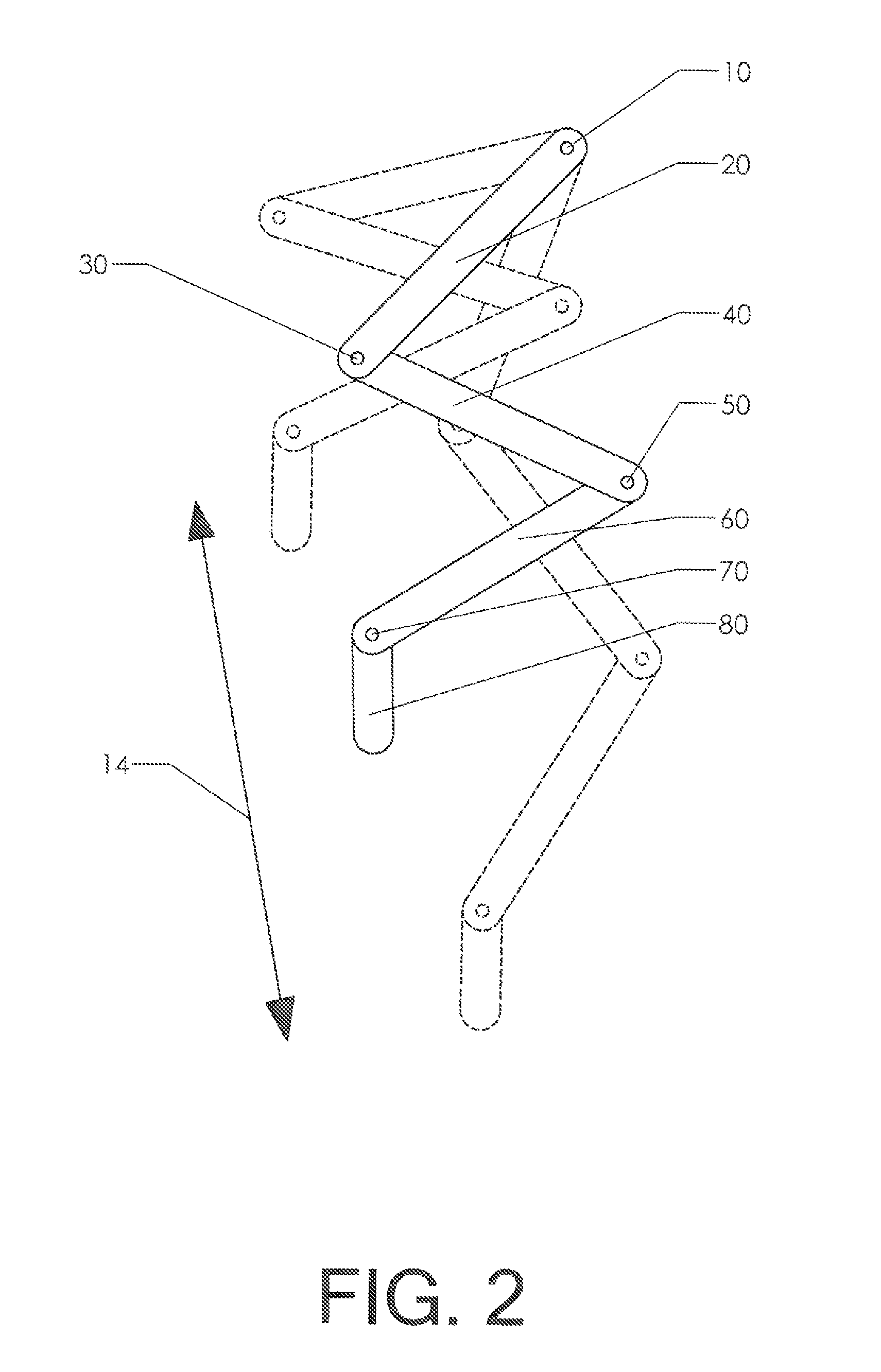
Fast Runner Limb Articulation System
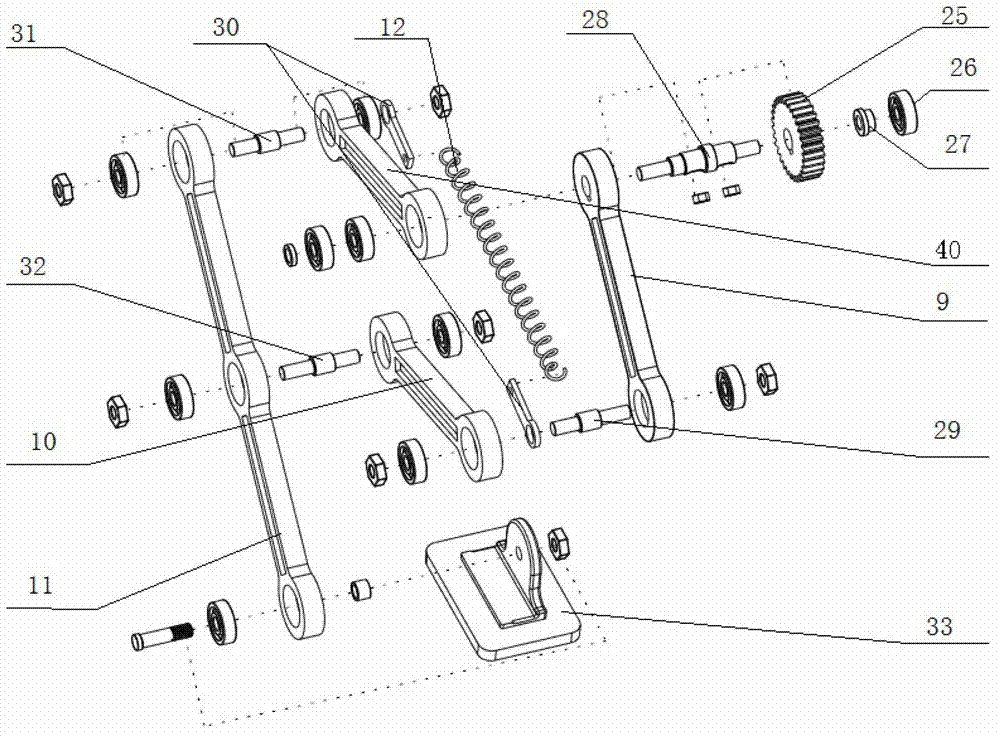
ActiveUS20130192406A1High speedMinimize energy usageProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusThighMuscles of the hip
A robotic limb structure which is capable of achieving high speeds. In the context of a biped, the structure is used for a pair of hind limbs. The limb structure includes a primary driven link—such as a thigh pivoting about a hip joint in the case of a hind limb. Secondary links are pivotally connected to the primary driving link. Auxiliary links are provided to constrain the motion between the links. Elastic trim elements are also provided to define a “relaxed” state for the limb and to influence the resonance characteristics of the structure. The control system takes advantage of the resonant characteristics of the structure as a whole.
Owner:FLORIDA INST FOR HUMAN & MACHINE COGNITION
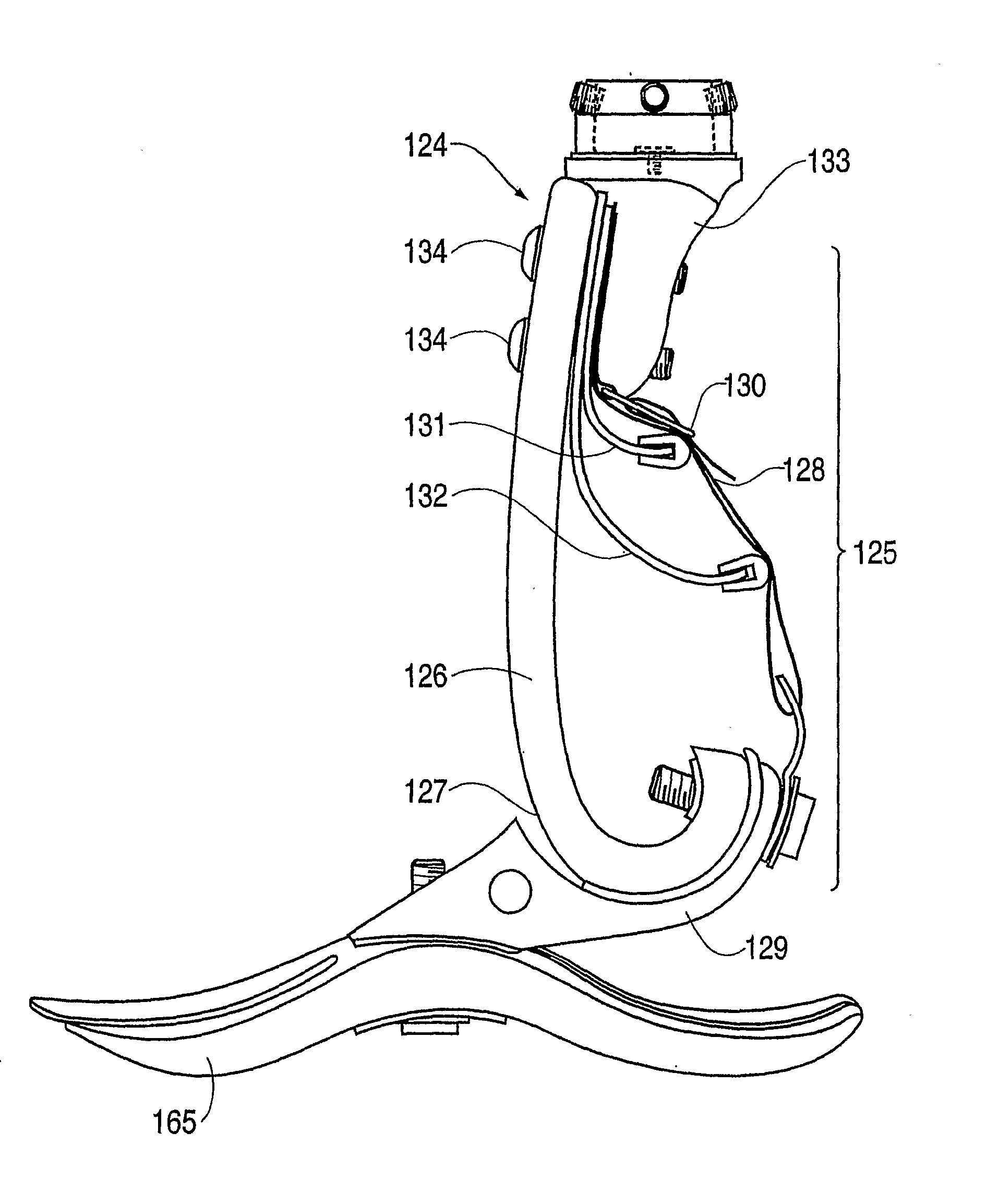
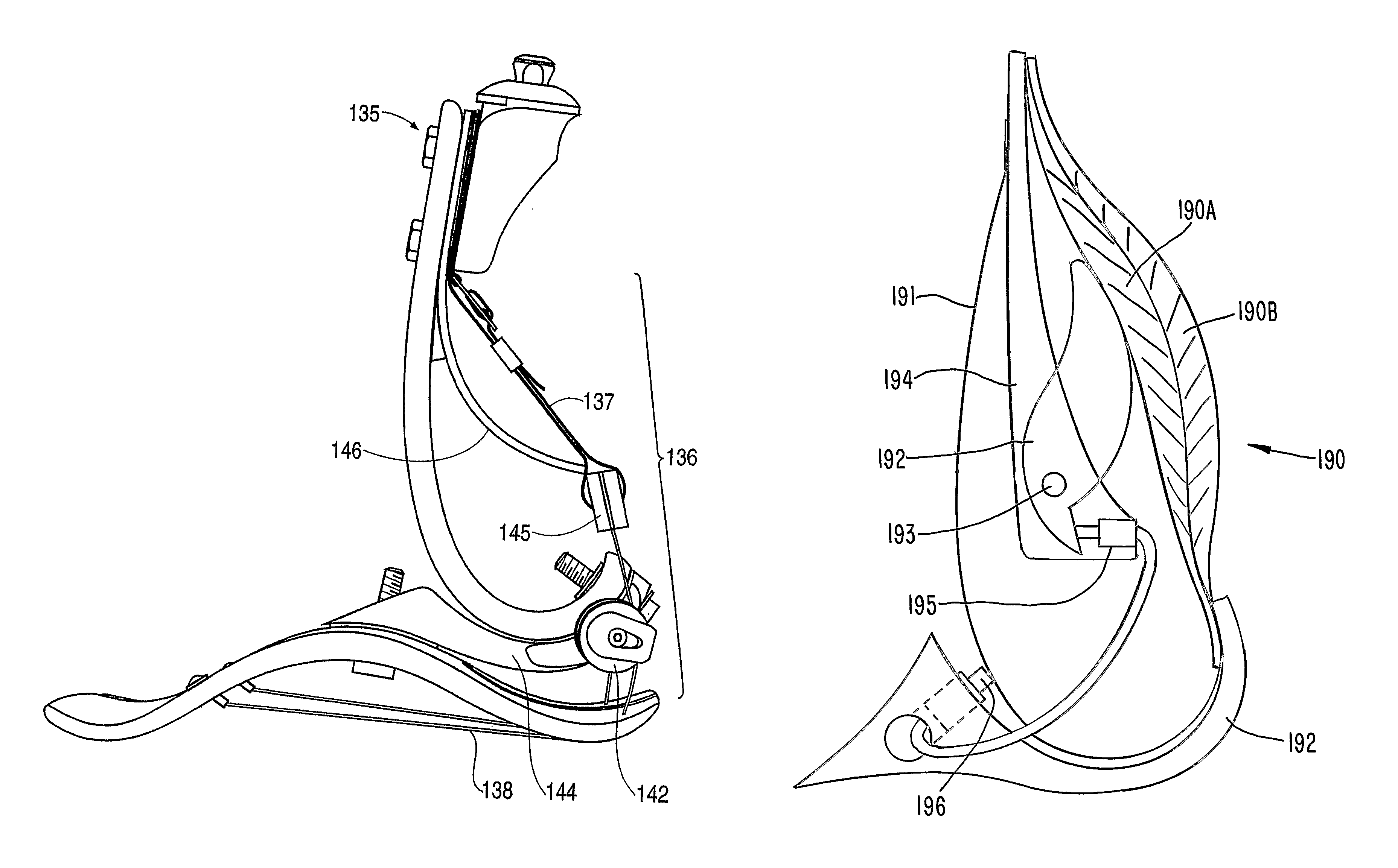
Prosthetic Foot with Tunable Performance
InactiveUS20070213840A1Improve performanceImproved applied mechanicLigamentsMusclesStored energyHindlimb
A resilient lower extremity prosthesis comprising a foot, an ankle and a shank above the ankle is provided with an artificial muscle (190) on the shank (191) of the prosthesis for storing energy during force loading of the prosthesis in the active propulsion phase of a person's gait and in the later stages of stance-phase of gait releasing the stored energy to aid propulsion of the person's trailing limb and body.
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
Multi-function animal weight-losing running table and control system thereof
InactiveCN101822223ATaming and training devicesProgramme total factory controlSpinal cordEngineering
The invention discloses a multi-function animal weight-losing running table and a control system thereof. The running table comprises a running machine, a weight-losing support device and a recovery robot. Running training or combination training of running training and electric stimulus is performed on the experimental animal by arranging organic glass and a stimulating electrode on the running machine; and the weight-losing running table training combining running table training and weight-losing support is performed on the experimental animal by arranging the weight-losing support device on the running machine. In the process of weight-losing running table training, the recovery robot can assist hind legs of the experimental animal in doing exercise training, so that a correct or preset training task is provided for a passive training model, the movement locus of the hind legs in the positive training model is recorded and the record is used for quantitatively evaluating the exercising function. The invention also provides a medicinal animal experiment device which is mainly used for walking function recovery of the experimental animal with hurt spinal cord and providing the animal running table training needed by sports medicine.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Mechanical leg imitating ostrich hind limb
The invention discloses a bionic mechanical leg imitating the motion function characteristic of an ostrich hind limb. The mechanical leg comprises a body, a hip joint motion mechanism, a knee joint motion mechanism and an ankle joint motion mechanism. The hip joint motion mechanism is composed of a motor and a crank-rocker mechanism, wherein the crank-rocker mechanism comprises a crank, a femur and a connecting rod. The knee joint motion mechanism comprises the femur, a first spring, a tibia, a metatarsus, a brake cable, a lower fibula, a second spring, an air cylinder and an upper fibula. The ankle joint motion mechanism comprises the metatarsus, a first apotelus bone, a second apotelus bone, a third apotelus bone, a third torsional spring, a second torsional spring and a first torsional spring. The ostrich hind limb capable of efficiently moving serves as the bionic prototype, through combination of testing on hind limb motion parameters during running of an ostrich and biological anatomic analysis, the mechanical leg imitating the ostrich hind limb is obtained through optimization design according to the tendon-bone and muscle-tendon interaction mechanism of the ostrich, and the mechanical leg is simple in structure, safe, reliable, low in vibration, and capable of efficiently saving energy.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Application of lnc (long non-coding) RNA lnc-DIF
InactiveCN106676177AInhibition of differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseBone tissue
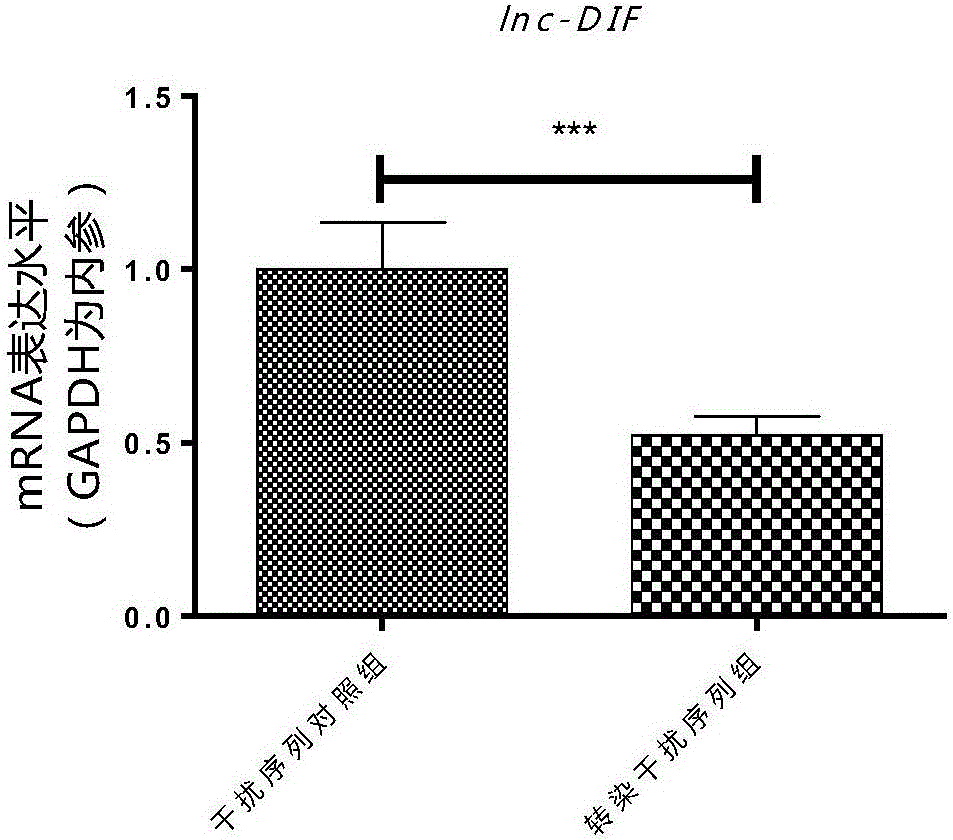
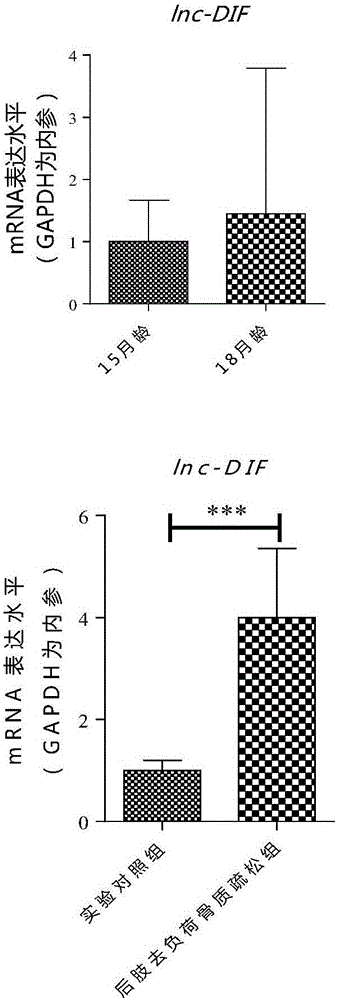
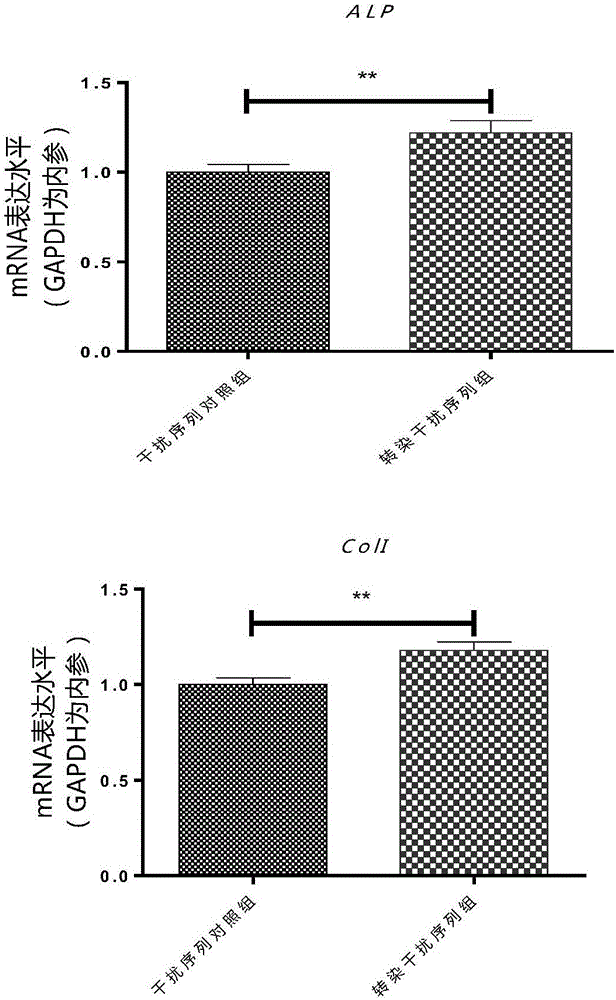
The invention discloses an application of lnc (long non-coding) RNA lnc-DIF. The technical scheme is that a femur sample of an old osteoporotic mouse model and a femur sample of a hindlimb-unloaded osteoporotic mouse model are detected firstly, and high expression of the lnc RNA lnc-DIF in bone tissue of the old and hindlimb-unloaded osteoporotic mouse models is discovered. An RNA interference sequence of the lnc RNA lnc-DIF is further designed and prepared, osteogenic differentiation function experiments discover that the lnc RNA lnc-DIF inhibits osteogenic cell differentiation and can be specifically bound to osteogenesis related miR-489-3p. Accordingly, the lnc RNA lnc-DIF can be used for preparing drugs for treating osteoporosis caused by various factors as well as other diseases of a skeletal system.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Vibration/motion training device for simulating weightless tail suspended rats
InactiveCN101558991AEasy to placeEasy to fixDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMotor speedSimulated weightlessness
The invention discloses a tail-suspended rat fixing device, which comprises a rat fixing box, a tail suspension device and an angle adjusting device. The invention also provides a tail-suspended rat vibration / motion training device, which comprises a motion track limit device, a vibration training device, an active motion training device, a passive motion training device, a rat hind limb fixing device and a height adjusting device. The invention also provides a vibration / motion control device, which comprises a display screen, a key, a direct-current motor speed adjusting knob, a power supply adapter, a switch, a USB interface and an internal circuit, wherein the direct-current motor speed adjusting knob is used for adjusting the rotating speed of a direct-current motor during passive motion training; the power supply adapter and the switch are used for supplying power for the whole device; the USB interface is used for carrying out function expansion later; and the internal circuit is used for controlling and quantifying rat vibration / motion training and supplying power. The device can keep the same tail-suspended height, can carry out equal-length and equal-tension motion by combining vibration and motion training, and simultaneously achieves training quantification and control.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Prosthetic foot with tunable performance
InactiveUS8070829B2Improve performanceImproved applied mechanicLigamentsMusclesHindlimbArtificial muscle
Owner:BIOQUEST PROSTHETICS
Energy-saving walking leg mechanism simulating ostrich hindlimb movement function characteristic
The invention discloses an energy-saving walking leg mechanism simulating ostrich hindlimb movement function characteristic. The energy-saving walking leg mechanism comprises a rack, a crank connection rod mechanism, a rebounding mechanism and a toe, wherein the crank connection rod mechanism comprises a crank, a thigh and a rocking rod; the rebounding mechanism comprises a fixed sliding block, a crus, a movable sliding block, a connection rod, a spring, a baffle plate, a ratchet mechanism, a brake cable, an angle limiter and metatarsal bones. The energy-saving walking leg mechanism is designed on the basis of the size parameters of the ostrich hindlimb and the rebounding characteristics of joints between ostrich tarsal bones; an energy-saving and efficient walking leg is designed by simulating the ostrich hindlimb movement; the metatarsal bones automatically stretch by using the rebounding force generated by compressing the spring, so that the energy loss is reduced; the energy-saving and efficient walking leg simulating ostrich hindlimb movement function characteristic can achieve the energy-saving and efficient purpose.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
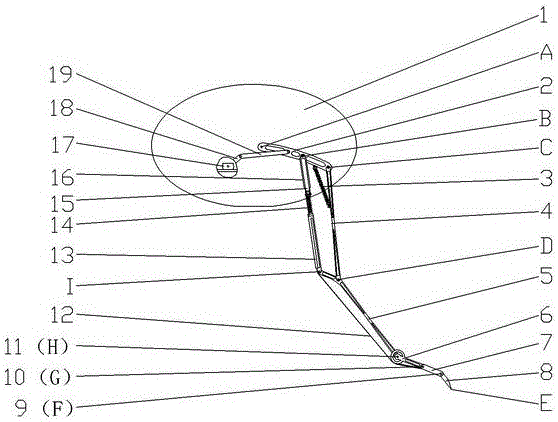
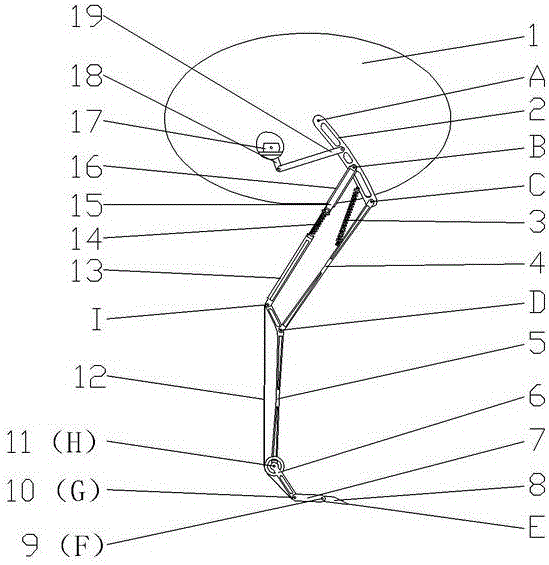
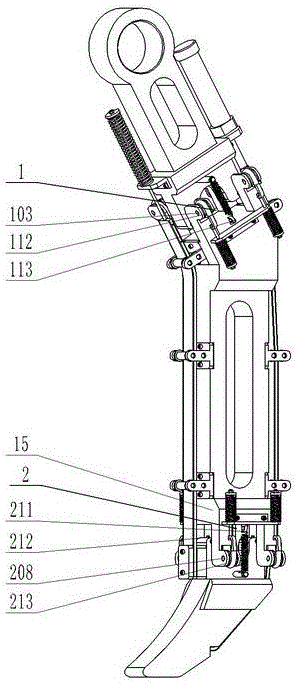
Pneumatic-muscles-based robot hind limb simulating cheetah
The invention provides a pneumatic-muscles-based robot hind limb simulating a cheetah. The structure of the robot hind limb comprises a hip unit 1, a thigh unit 2, a shin unit 3 and a foot unit 4, wherein the hip unit 1, the thigh unit and the shin unit respectively comprise a diaphysis and joint parts. The overall robot hind limb adopts a structural form that the diaphysis is placed inside and pneumatic muscles are placed outside to package the periphery of the diaphysis, the structural form is similar to the real body structure of an organism and approaches to a force-exerting form of the cheetah hind limb. The joint of the robot hind limb passes through a connector of upper and lower diaphyses by a connecting shaft and is supported by a rolling bearing; and one end of the connecting shaft extends out of the bearing to be connected with an angle sensor so as to obtain joint angle-rotating information and provide data for motion control. The joint ensures that linear force of the muscles is converted to rotating torque of the joint in a form of pulling (in opposite directions) of pneumatic muscles, and the rigidity is adjustable.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Fast runner limb articulation system
ActiveUS9283673B2Use minimizedProgramme-controlled manipulatorMechanical apparatusThighMuscles of the hip
A robotic limb structure which is capable of achieving high speeds. In the context of a biped, the structure is used for a pair of hind limbs. The limb structure includes a primary driven link—such as a thigh pivoting about a hip joint in the case of a hind limb. Secondary links are pivotally connected to the primary driving link. Auxiliary links are provided to constrain the motion between the links. Elastic trim elements are also provided to define a “relaxed” state for the limb and to influence the resonance characteristics of the structure. The control system takes advantage of the resonant characteristics of the structure as a whole.
Owner:FLORIDA INST FOR HUMAN & MACHINE COGNITION
Bionic four-foot robot hind limb with tensegrity structure
ActiveCN106672105AAvoid concentrated distribution of shear stressFree from shear damageVehiclesShear stressBionics
The invention discloses a bionic four-foot robot hind limb with a tensegrity structure. The hind limb comprises a knee joint, an ankle joint, a first leg component, a second leg component, a third leg component and the like. A first inhaul cable, a second inhaul cable, a first torsion spring, a second torsion spring, a third inhaul cable and a fourth inhaul cable form a tensioned part of the tensegrity structure of the robot hind limb together, and the tension part and stressed parts including the first leg component, the second leg component, the third leg component and the like complete movement of the robot hind limb together. The third inhaul cable and the fourth inhaul cable are matched with the first inhaul cable, the second inhaul cable, the first torsion spring and the second torsion spring to achieve movement of the knee joint and the ankle joint, and abrasion and impact between the first leg component and the second leg component and between the second leg component and the third leg component are avoided. Meanwhile, shearing stress concentrated distribution of the leg components of the robot hind limb in the earth contacting impact process is effectively avoided due to the third inhaul cable and the fourth inhaul cable, and accordingly the leg components of the robot hind limb are protected against shear failure.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
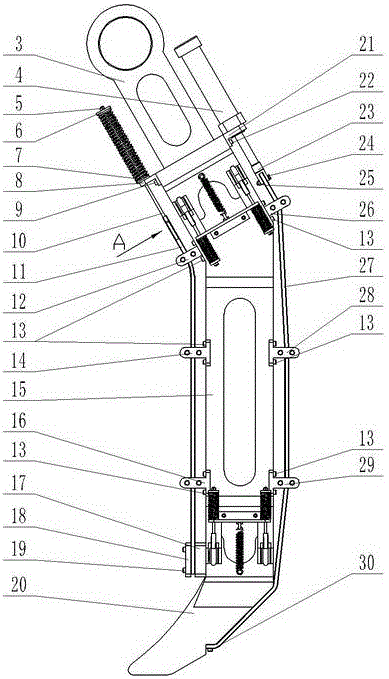
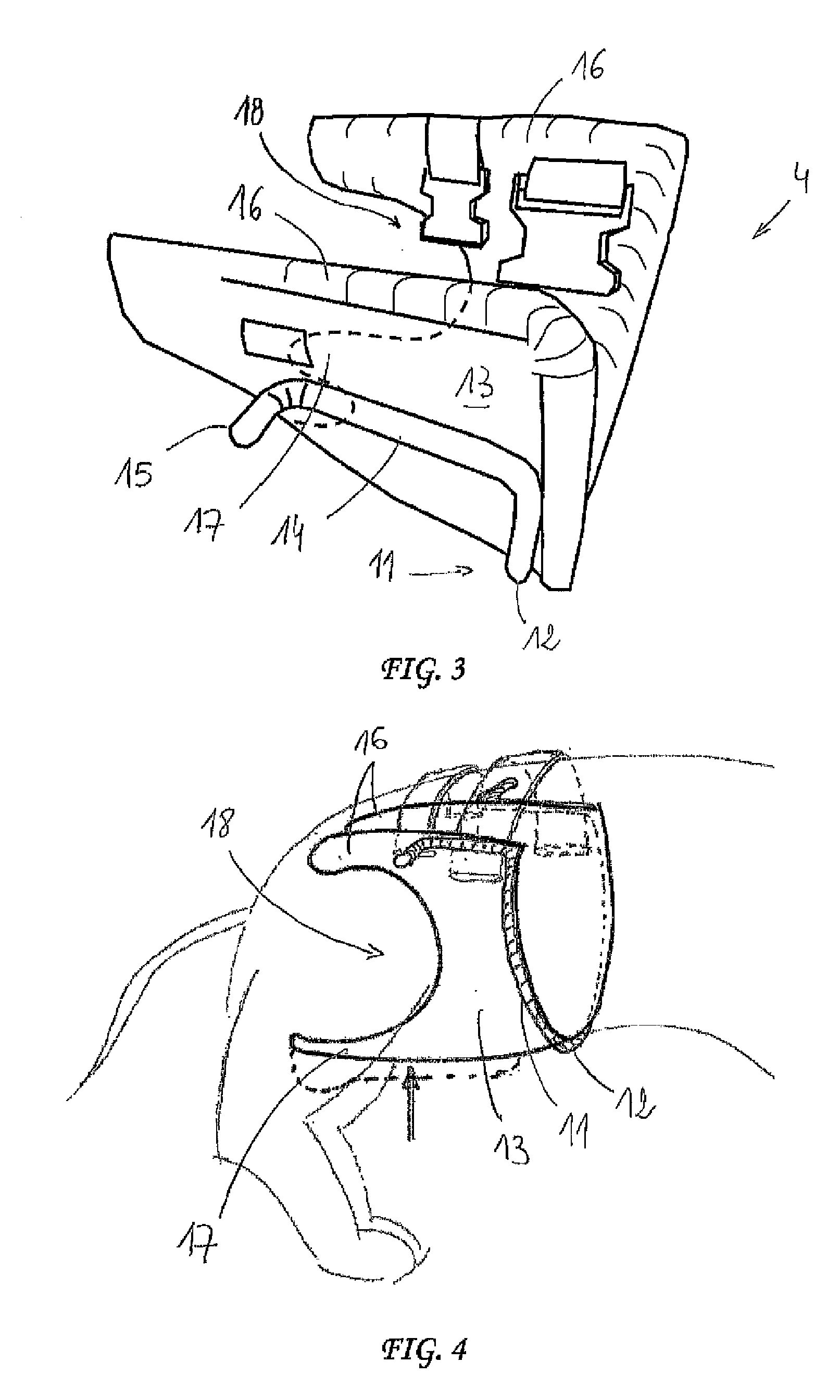
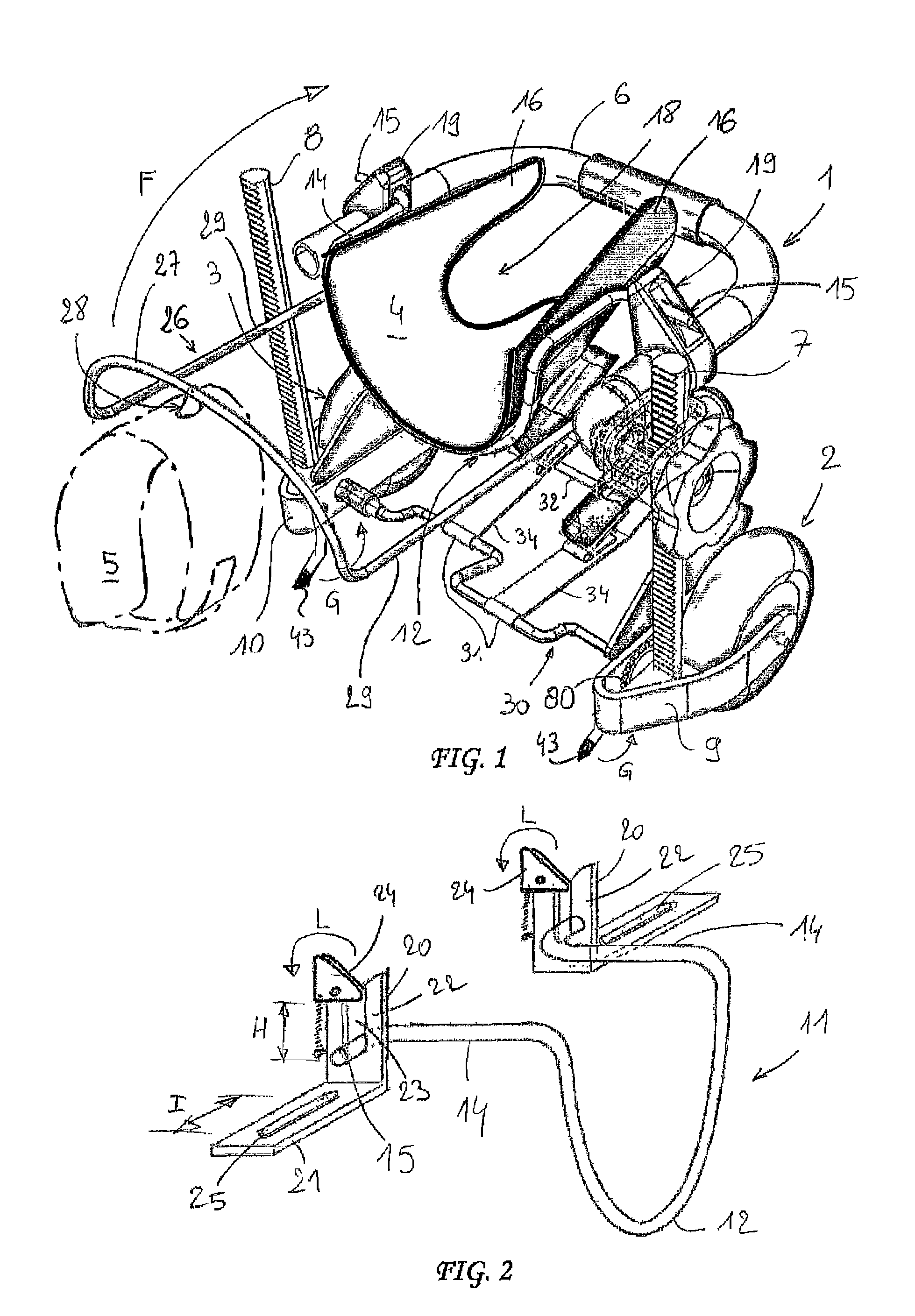
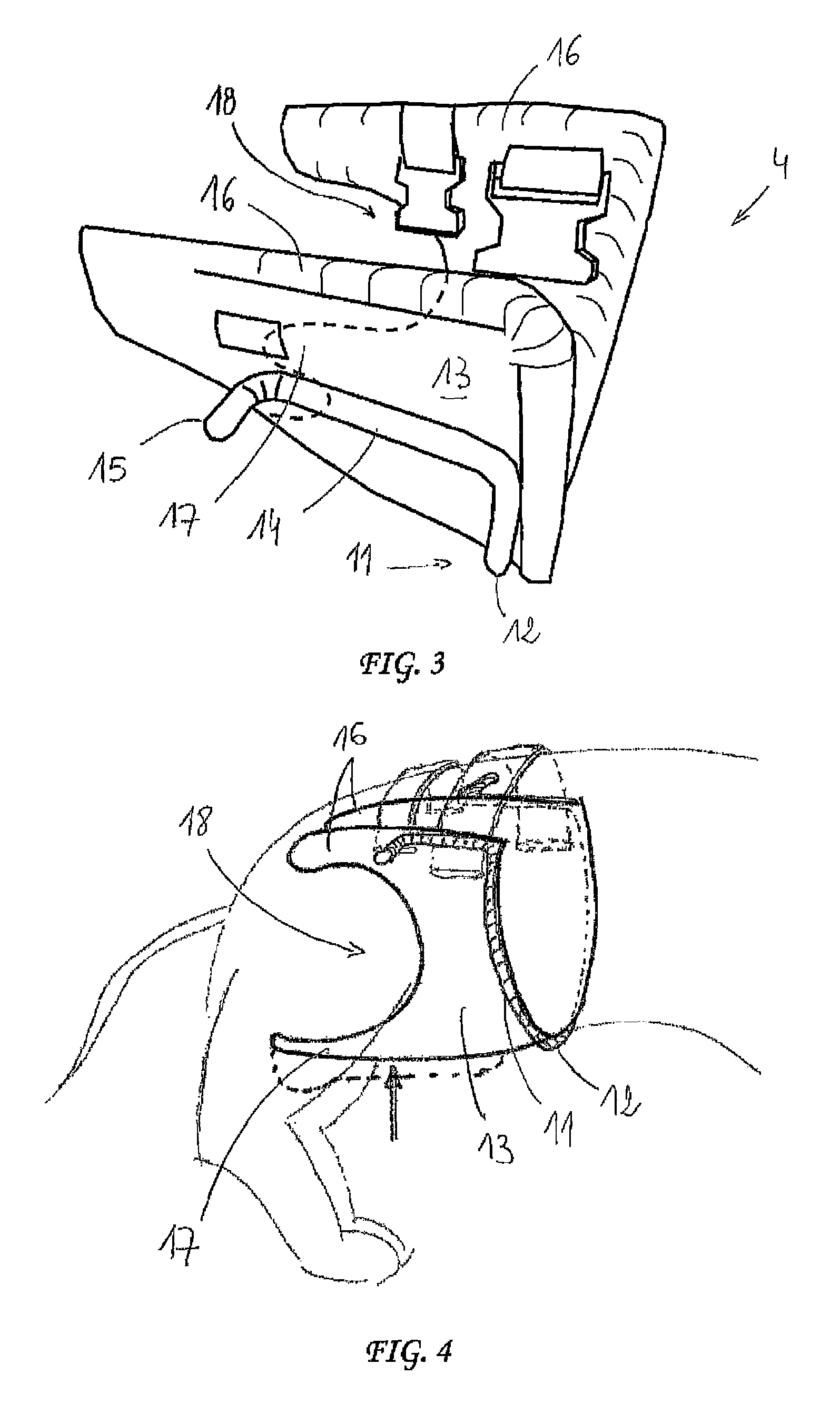
Rehabilitation or mobility assistance device for a quadruped animal
ActiveUS20120160185A1Easy to adaptProtect the legsVeterinary bandagesWalking aidsThumb oppositionDrive shaft
A device allowing a quadruped animal that is disabled in the hindquarters thereof to move about, while automatically moving the hind legs of the animal. The device includes: a chassis, on which two side wheels are mounted; a rear harness for receiving and supporting the hindquarters of the animal, which harness can be supported by the chassis; a crankshaft-type driveshaft having two crankpins to which are attached means for moving the hind legs of the animal, said driveshaft being shaped so as to move each of the two hind legs of the animal synchronously in phase opposition like the movement of a chainset; and a transmission for controlling the rotation of the driveshaft from at least one wheel.
Owner:SOPHIADOG
Rehabilitation or mobility assistance device for a quadruped animal
ActiveUS8919291B2Easy to adaptProtect the legsVeterinary bandagesAnimal fetteringThumb oppositionDrive shaft
A device allowing a quadruped animal that is disabled in the hindquarters thereof to move about, while automatically moving the hind legs of the animal. The device includes: a chassis, on which two side wheels are mounted; a rear harness for receiving and supporting the hindquarters of the animal, which harness can be supported by the chassis; and a crankshaft-type driveshaft having two crankpins to which are attached cradles for moving the hind legs of the animal where the driveshaft is shaped so as to move each of the two hind legs of the animal synchronously in phase opposition. A transmission device is configured to control the rotation of the driveshaft from at least one wheel.
Owner:SOPHIADOG
Mole-imitating excavation robot
InactiveCN102975195ASmall turning radiusFlexible trajectoryProgramme-controlled manipulatorTunnelsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationVertical plane
The invention provides a mole-imitating excavation robot which comprises a body, a left fore limb and a right fore limb which are arranged in front of the body, a left posterior limb and a right posterior limb which are arranged in rear of the body, wherein fore limb claw toes are arranged on the left fore limb and the right fore limb, and posterior limb buckets are arranged on the left posterior limb and the right posterior limb. Four limbs are two-degrees-of-freedom mechanisms, independently move, circulate according to a desired trajectory and are changeable in trajectory radiuses. The left fore limb and the right fore limb mainly complete an excavation movement, and the left posterior limb and the right posterior limb mainly complete a dumping movement. Through a coordination movement of the four limbs, an advancing movement and a turning movement in a horizontal plane can be realized. The body is divided into a front part and a rear part which are connected through a torsion shaft and can relatively rotate by a certain angle, and therefore, the excavation trajectory of the robot turns in a vertical plane. The fore limb claw toes and the posterior limb buckets are fixed on the tail ends of the limbs through auxiliary slide blocks, and can rotate with the rotation of the limbs and retract with the retraction of the limbs, and therefore the functions of earth cutting and earth dumping are realized.
Owner:三亚哈尔滨工程大学南海创新发展基地
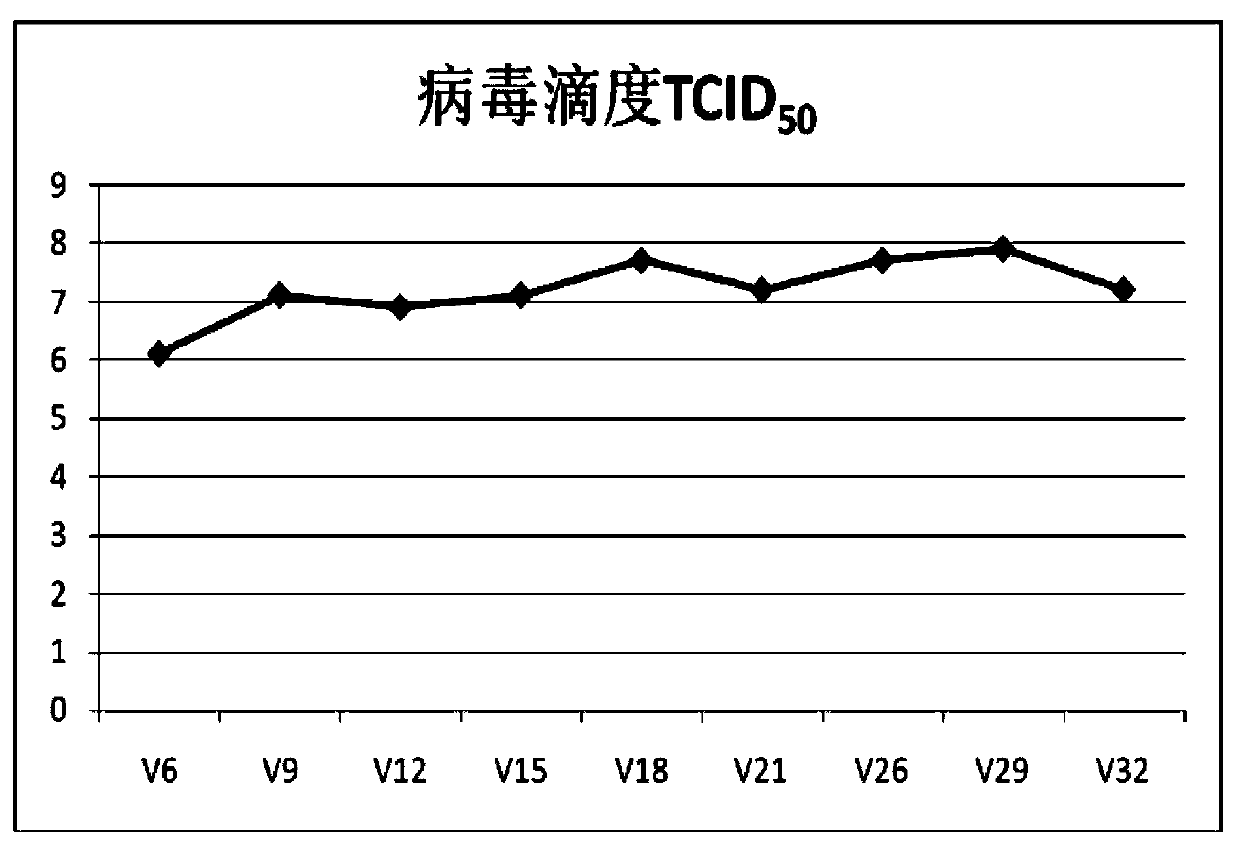
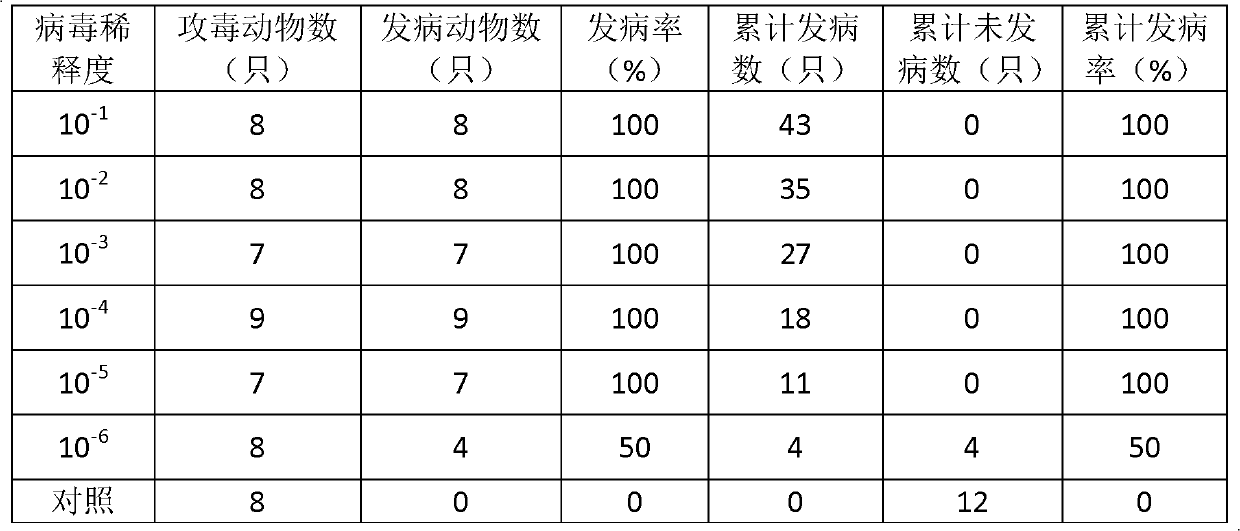
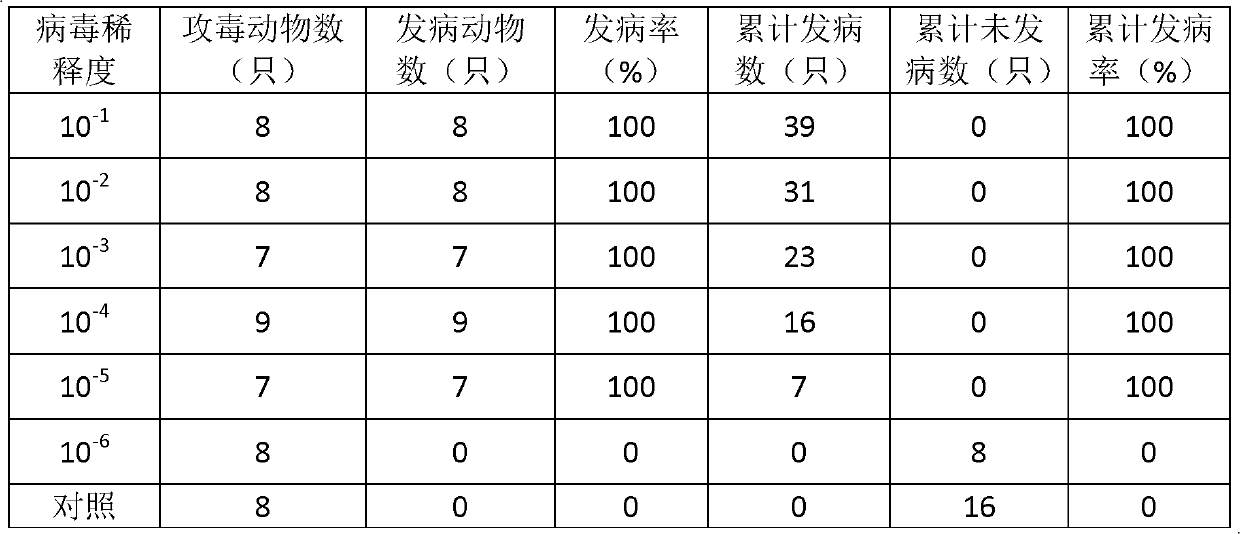
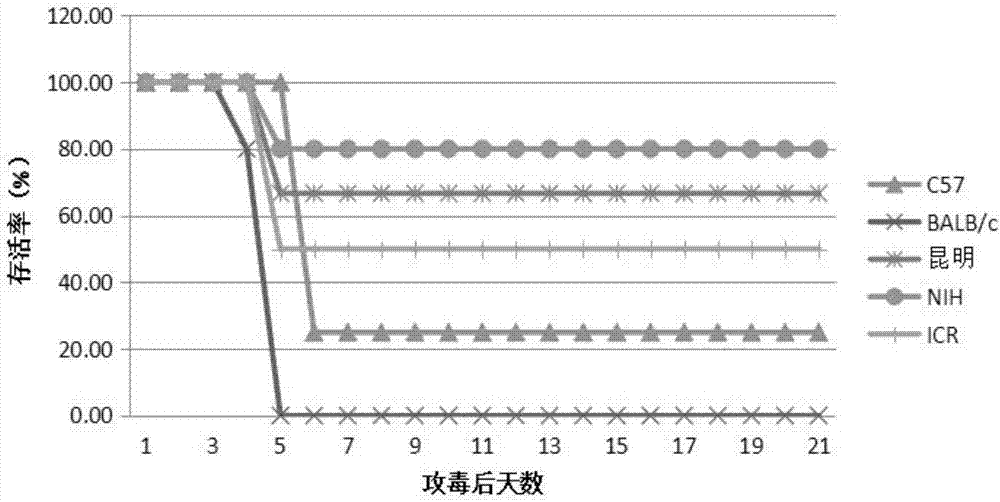
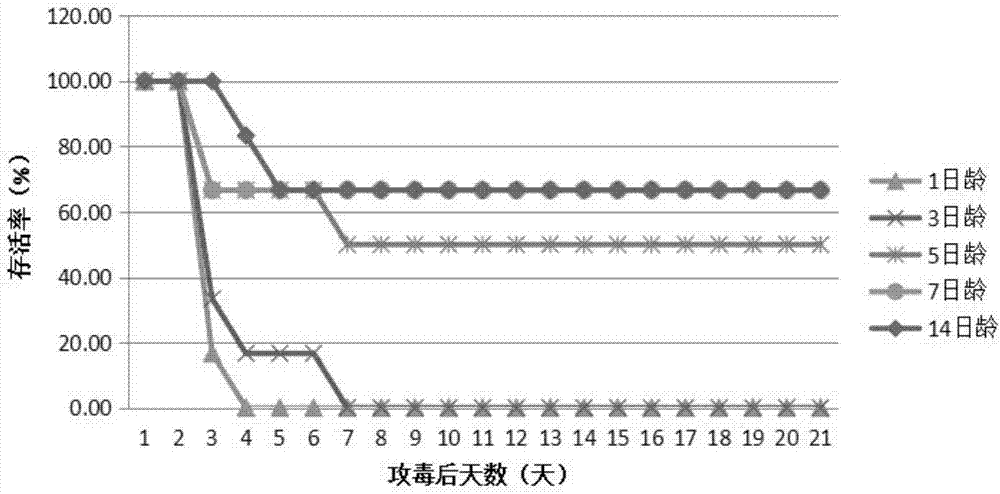
Novel EV71 virus strain and application thereof
ActiveCN103374549AEasy to set upDeepen understandingViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsMicroorganism based processesBALB/cIntraperitoneal route
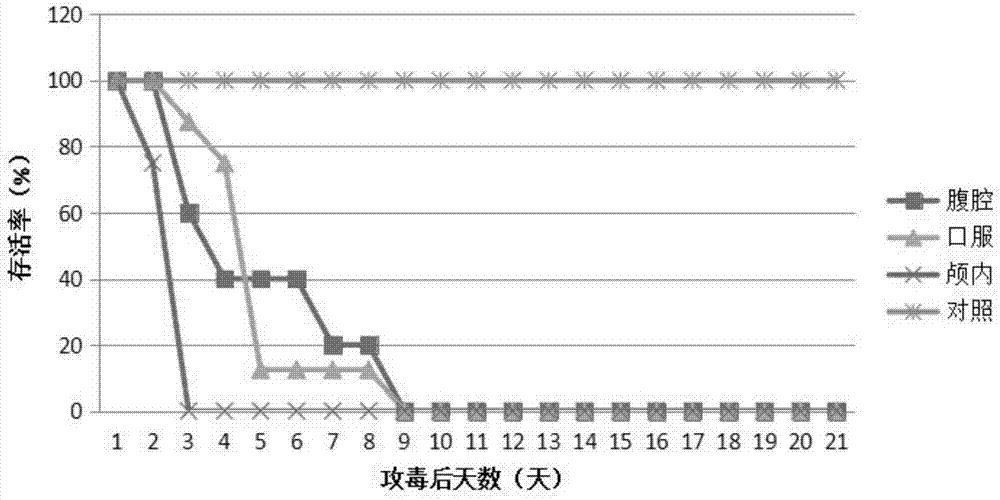
The invention discloses a novel EV71 virus strain of which the whole-genome length is 7405bp and the sequence is shown in SEQID NO:1. The virus strain can infect ICR, KM, BALB / c and NIH mice; the virus dosage of larger than 1*10<2>-1*10<7> TCID50 can cause the disease attack or death of 1-17 days mice; the administration route can be intraperitoneal injection, encephalocoele injection and intragastric administration; the symptoms are typical symptoms of EV71 virus infection and are divided into the following five levels according to stages of the disease: Level 0: not attacked; L1: motion incoordination and weakness of limbs; L2: hypokinesia and paralysis of fore or posterior limbs; L3: quadriplegia and dying; and L4: death. Various animal evaluation models such as an immunogenicity animal evaluation model of hand-foot-and-mouth disease vaccine and an animal evaluation model of EV71 therapeutic drug and therapeutic vaccine, can be built conveniently.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNITED VACCINE INST
Coxsackievirus B5 CV-B5 and application thereof in preparing infectious animal models and kits
PendingCN107236713AEffective infectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsCoxsackieviruses BNeural cell
The invention relates to Coxsackievirus B5 CV-B5 CVB5 / JS417 capable of being stably copied and abdicated. The preservation number of the virus is CGMCC (China general microbiological culture collection center) No. 13851. The invention further relates to an application of Coxsackievirus B5 CV-B5 the CVB5 / JS417 in preparing a Coxsackievirus B5 CV-B5 infected mouse. The experimental results show that obvious eosinophilic necrosis and vacuolar degeneration necrosis in spots of the brain, spinal cord, cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle of hind limbs of the Coxsackievirus B5 CV-B5 infected mouse can be seen, and meanwhile, immunohistochemistry shows that positive or strong positive reaction appears in brain and spinal neural cells and cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle cells of the hind limbs, which verifies that the CVB5 / JS417 can cause obvious lesions and necrosis to the brain, spinal nerves, cardiac muscle and skeletal muscle of the hind limbs of the infected mouse.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Method for detecting special growth and development law of muscles of Jingning chicken
The invention provides a method for detecting a special growth and development law of muscles of Jingning chicken. The Jingning chicken are unique and peculiar local chicken of the Gansu province, are fresh and tender in texture and unique in flavor, and have good public praise, however, the Jingning chicken are endangered, and the prospect is grim. In the method for detecting the special growth and development law of the muscles of the Jingning chicken, chick embryos of the Jingning chicken are researched, and special meat quality trait controlling genes such as growth and development gap-associated proteins: CECR2 (cat eye syndrome chromosome region) and IGF-1 (insulinlike growth factor-1), fatty acid metabolism gap-associated proteins: Ex-FABP (fatty acid-binding protein) and LPL (lipoprotein lipase) and protein degradation gap-associated proteins: CAST and CAPN1 are selected. Protein expression distribution and change of expression level of proteins in posterior limb buds and body segments in a chick embryo development HH19-31 period are detected by using methods of immunohistochemistry and Western blotting and the like, and the Jingning chicken are compared to white feather broilers, yellow feather broilers and hyline brown chicken. By the method for detecting the special growth and development law of the muscles of the Jingning chicken, the relation of growth and development regulatory functional genes, growth performance and meat quality is discussed, and data are provided for establishing target genes of transgenic chicken. Moreover, the resource superiority can be widely developed and used, and new vitality is injected to development of local economy.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
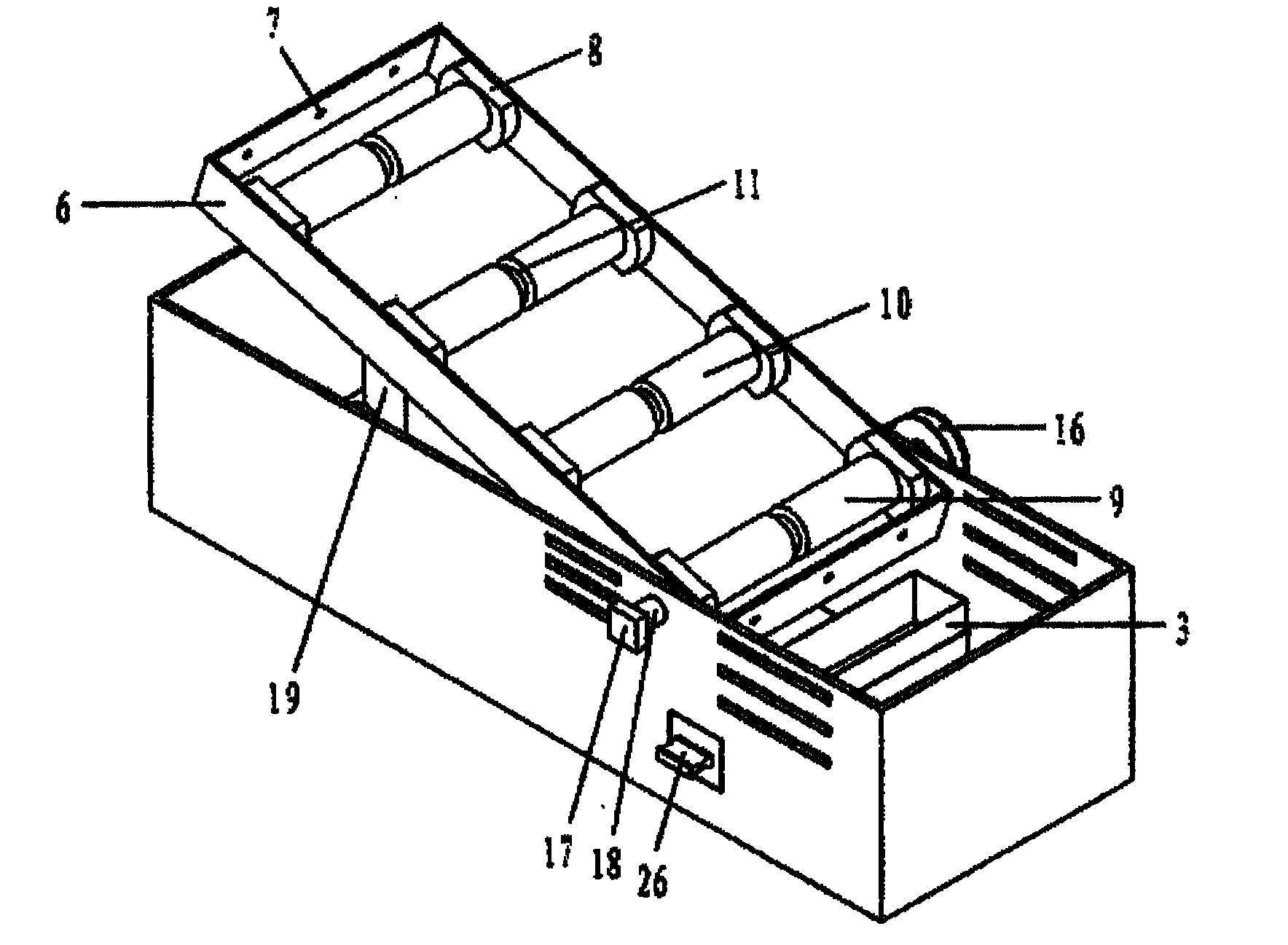
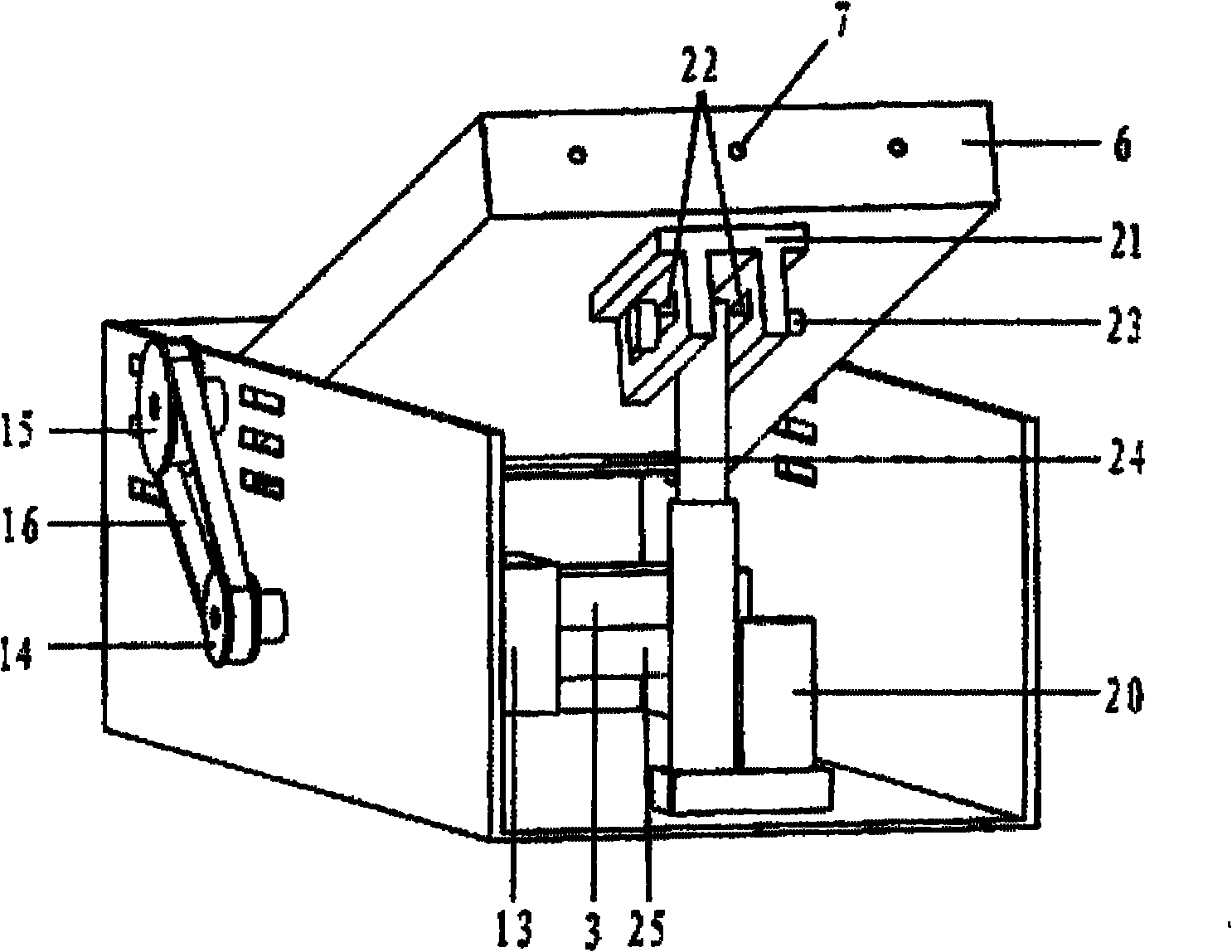
Body-weight support treadmill training device for rats with spinal cord injury
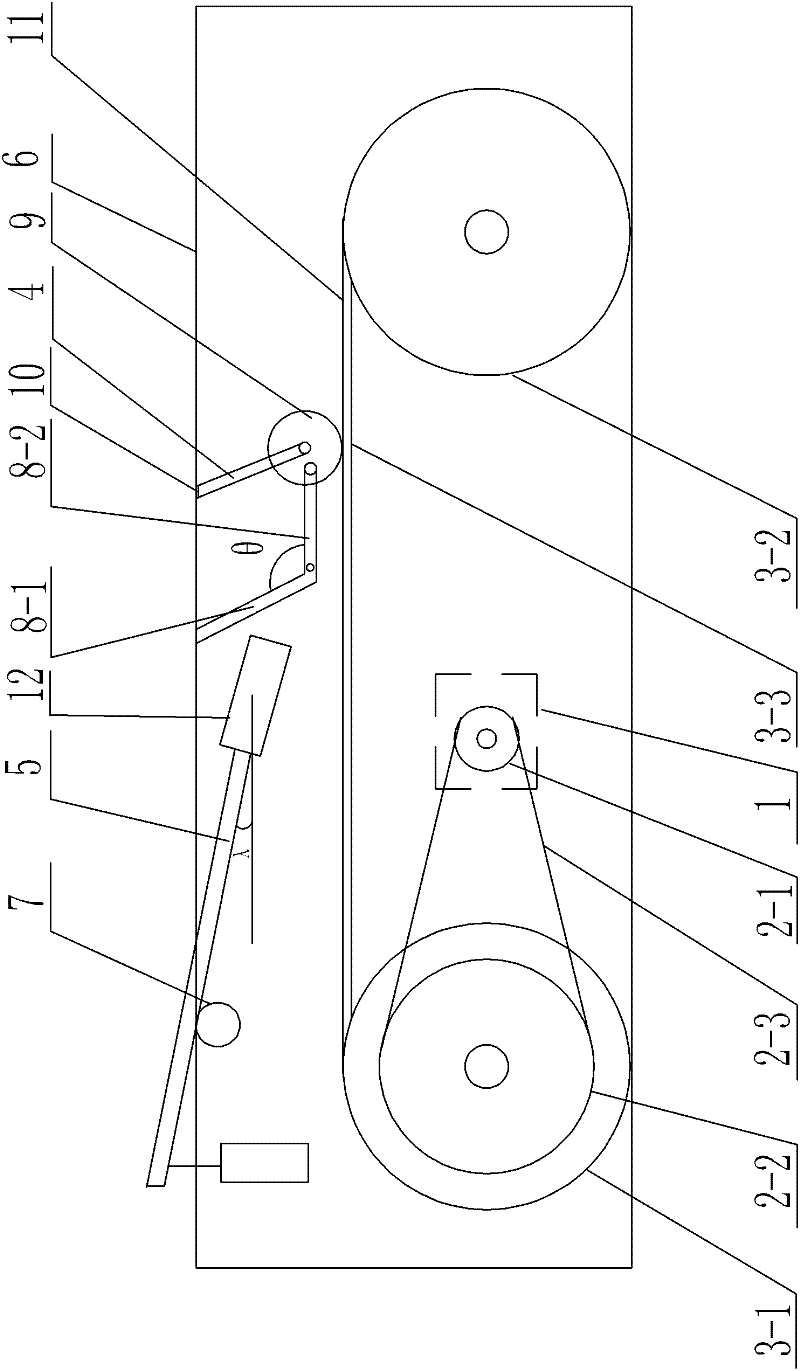
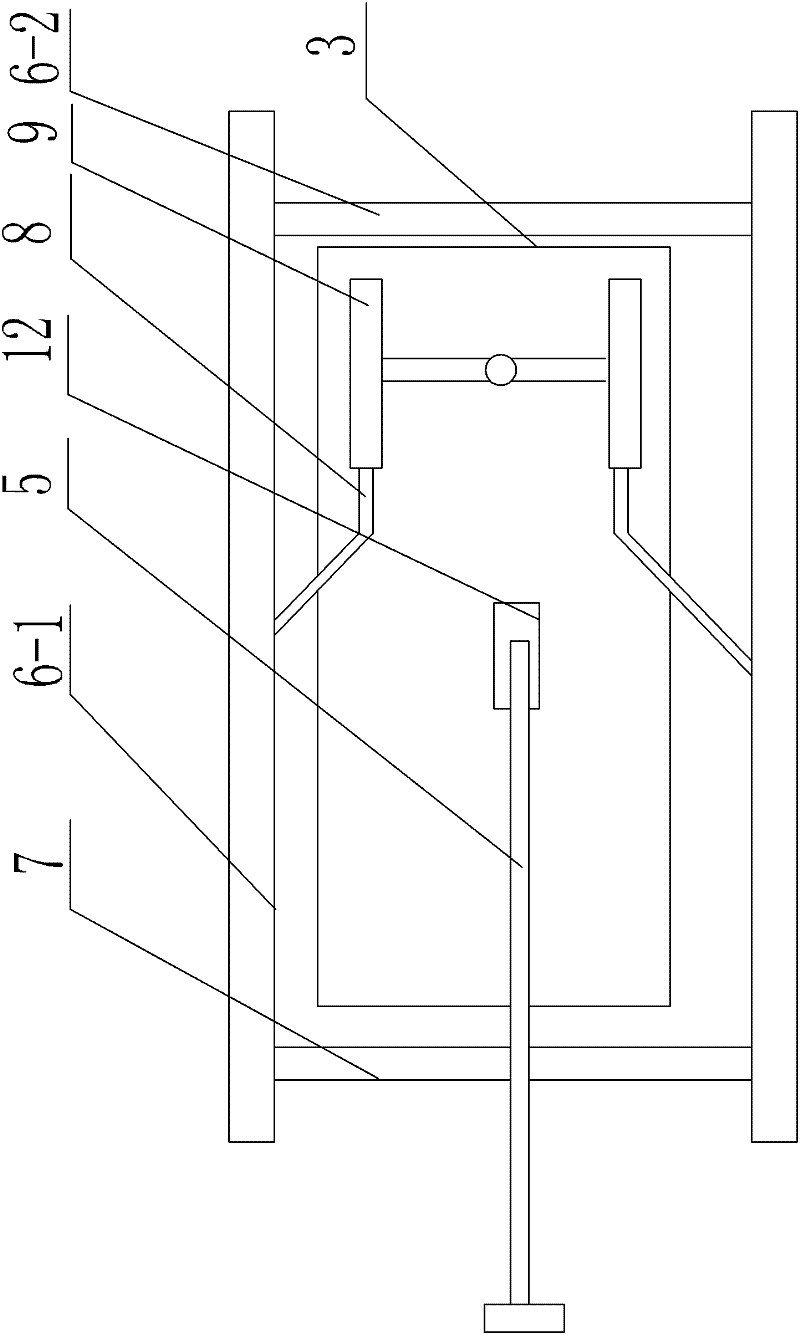
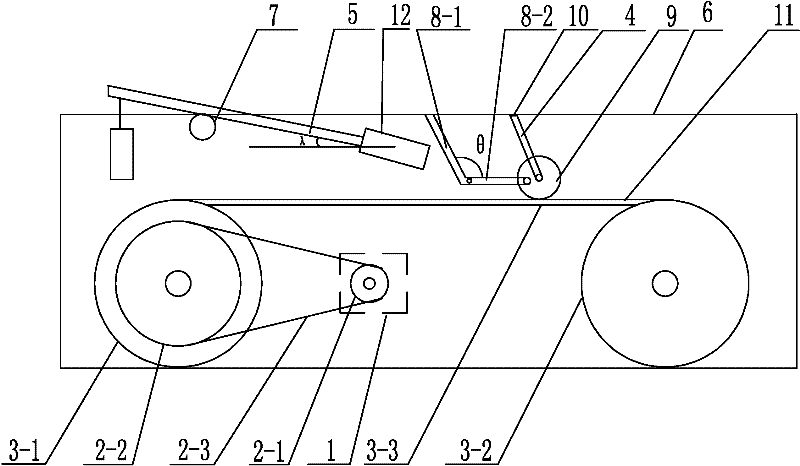
A walking training device for rats with spinal cord injury of which blended leg motion is synchronized with a belt running speed relates to a walking training device for the rats and solves the problems that the prior device for training a hind limb blended leg motion of the rats with the spinal cord injury can not ensure the running speed synchronism of the blended leg motion and the movement slab. Two friction wheels are arranged on the upper end surface of a belt, and the two friction wheel are fixedly installed on a connection plate through a support rod. The connection plate is fixedly installed on a fixing frame. The outer lateral wall of each friction wheel is fixedly connected with one end of a corresponding linkage rod, and the other end of each linkage rod is fixedly connected with the fixing frame. Each linkage rod comprises a first rod and a second rod; one end of the first rod is hinged with one end of the second rod 8-2, and the angle between the first rod and the second rod is 60 degrees to 120 degrees; and the first linkage rod is fixedly connected with the fixing frame. One end of a weight reduction rod passes through the first connection rod to be arranged at the upper side of the belt and fixedly connected with a cylinder, and the other end of the weight reduction rod is provided with a weight; and the angle between the weight reduction rod and the horizontal line is 45 degrees to 60 degrees. The invention is suitable for training the hind limbs of the rats with the spinal cord injury.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Method for building small pig model for research on lower limb deep venous thrombus formation and pulmonary embolism
InactiveCN102940537AAccelerates blood clotting processImprove toughnessIn-vivo testing preparationsSurgical veterinaryDiseaseSurgical operation
The invention belongs to the field of animal medical models and particularly relates to a method for building a small pig model for researches on lower limb deep venous thrombus formation and pulmonary embolism. The method is characterized in that the method comprises the steps of firstly forming small pig posterior limb deep venous thrombus, cutting a small pig anterior limb cephalic vein open for intubation, injecting the in-vitro prepared thrombus into a superior vena cava and delivering the thrombus to a pulmonary artery through cardiac circulation to cause pulmonary artery embolism to build the small pig model for researches on lower limb deep venous thrombus formation and pulmonary embolism, wherein aminomethylbenzoic acid injection in appropriate proportion being 1: (15-20) is added during the preparation of the in-vitro thrombus. By building the small pig model for researches on lower limb deep venous thrombus formation and pulmonary embolism, a good animal model can be provided for pathophysiologic researches on diseases, clinical drug researches and surgical practices. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple anesthesia operation, clear effect, simple and rapid surgical operation, high pulmonary embolism formation success rate, low fatality rate, convenient inspection means and the like.
Owner:JINHUA MUNICIPAL CENT HOSPITAL
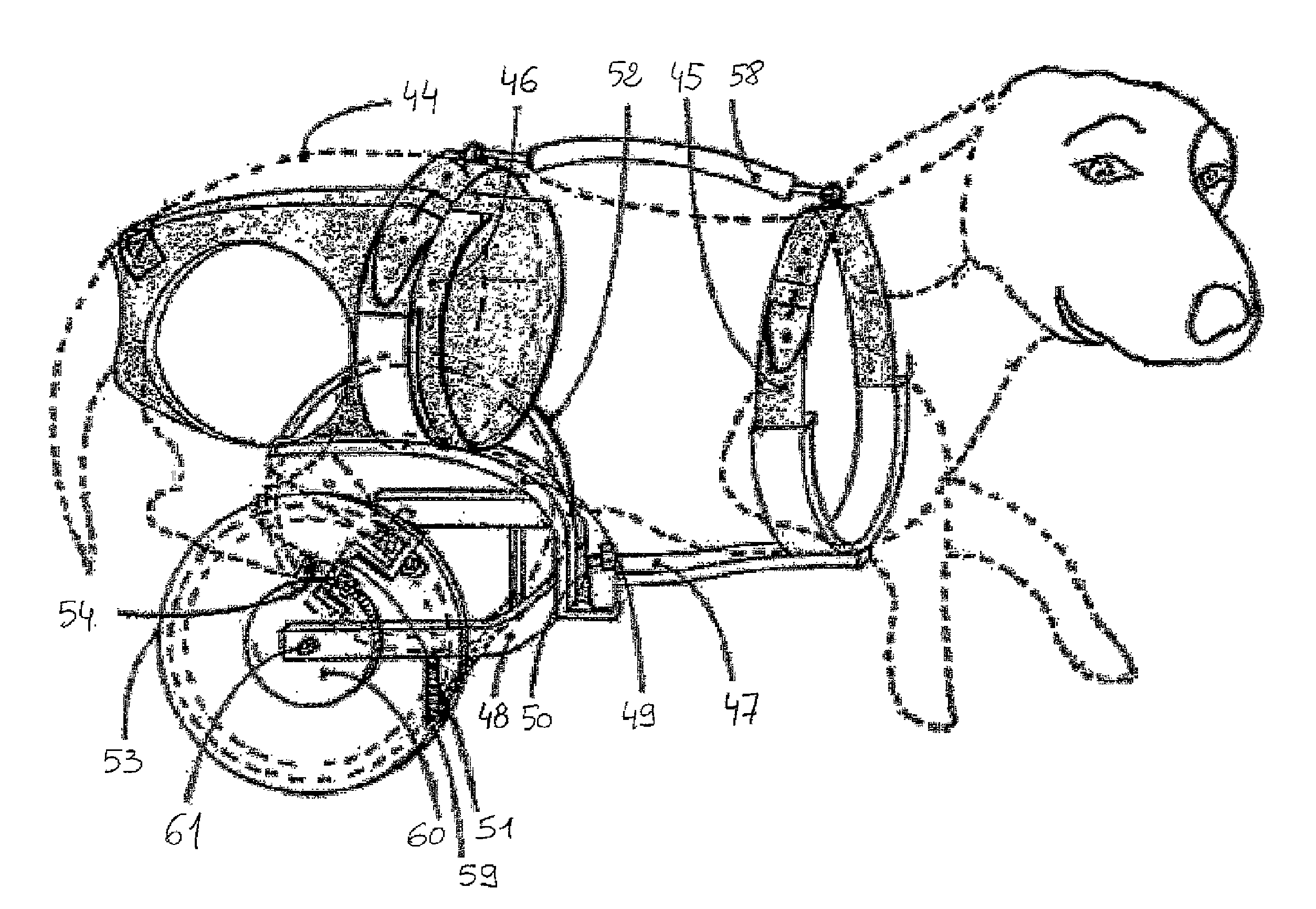
A foot-and-leg bionic robot mouse
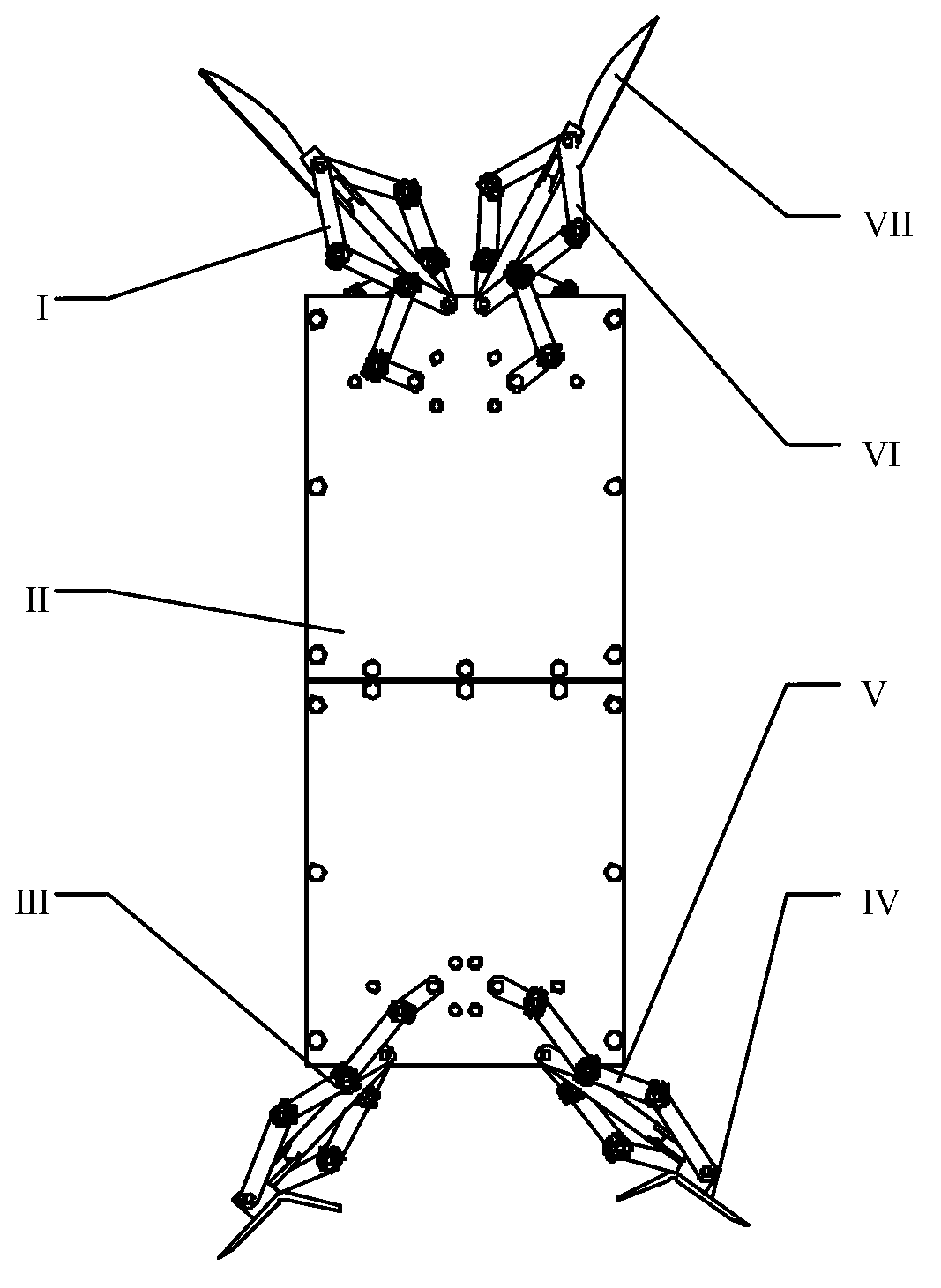
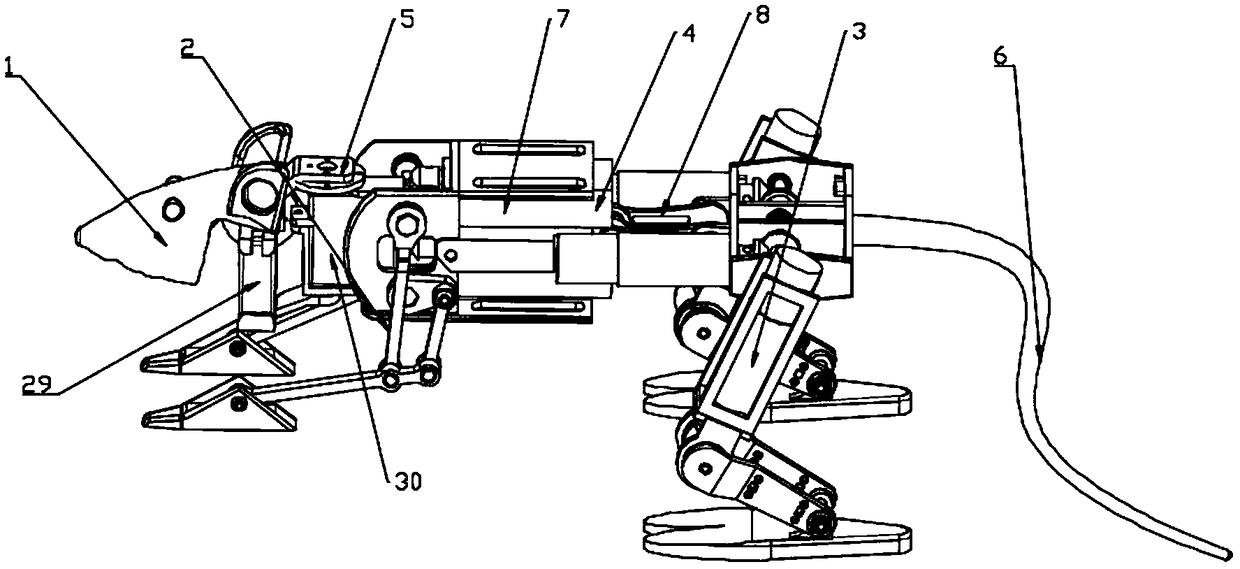
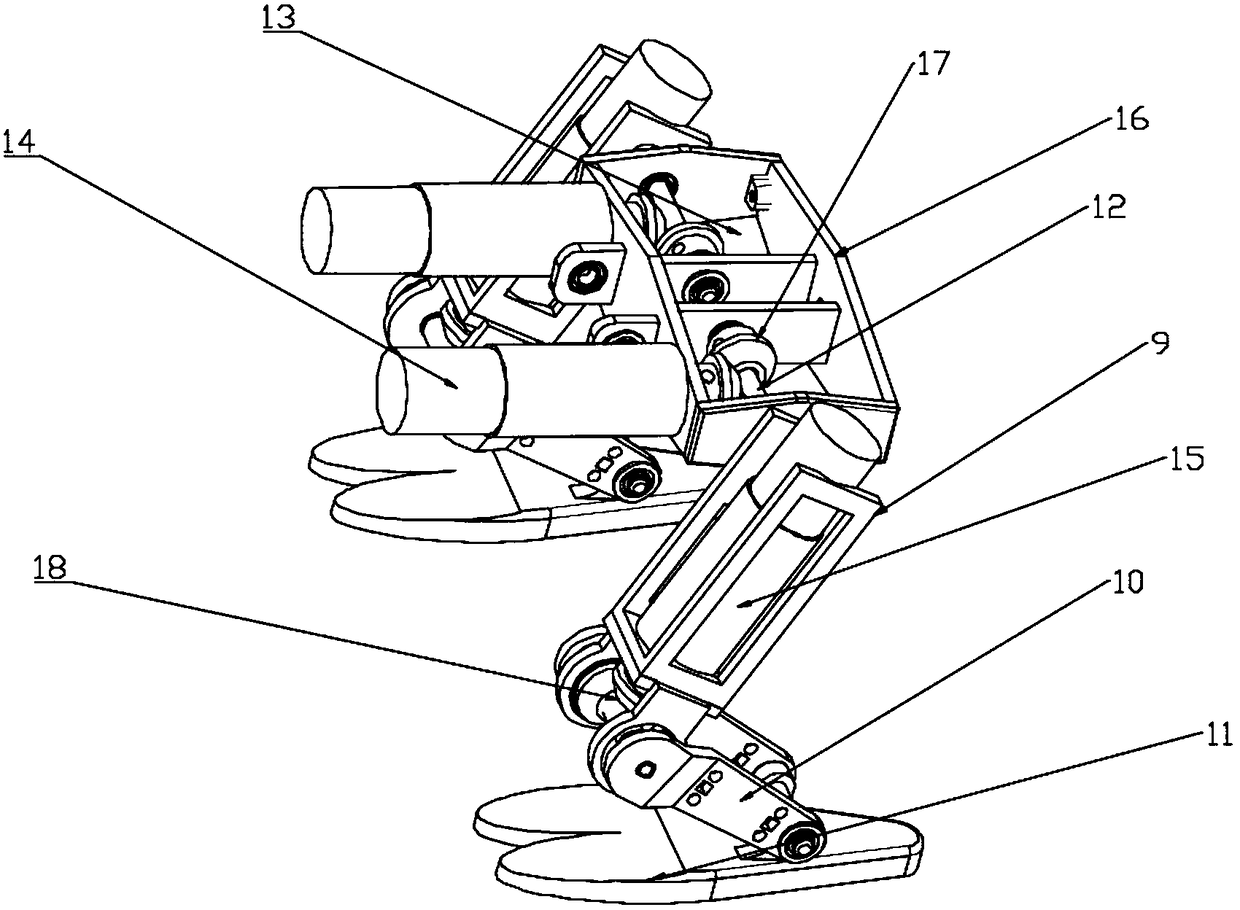
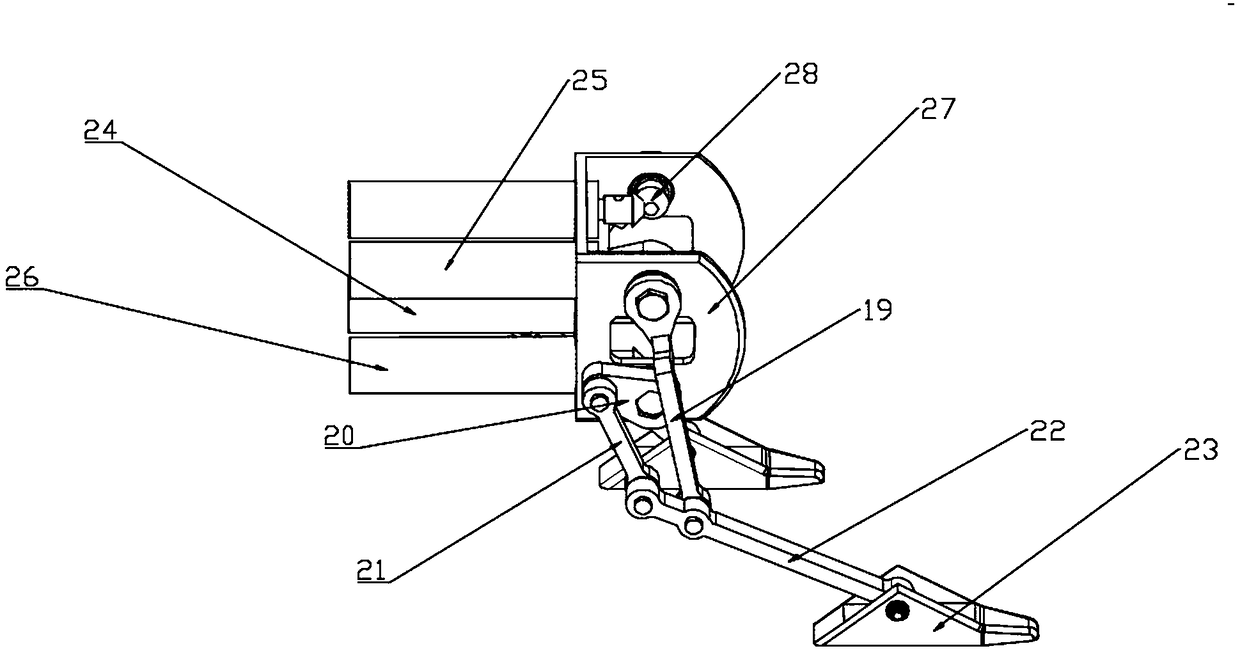
InactiveCN109018064AMorphological approximationImprove environmental adaptabilityVehiclesBionicsHindlimb
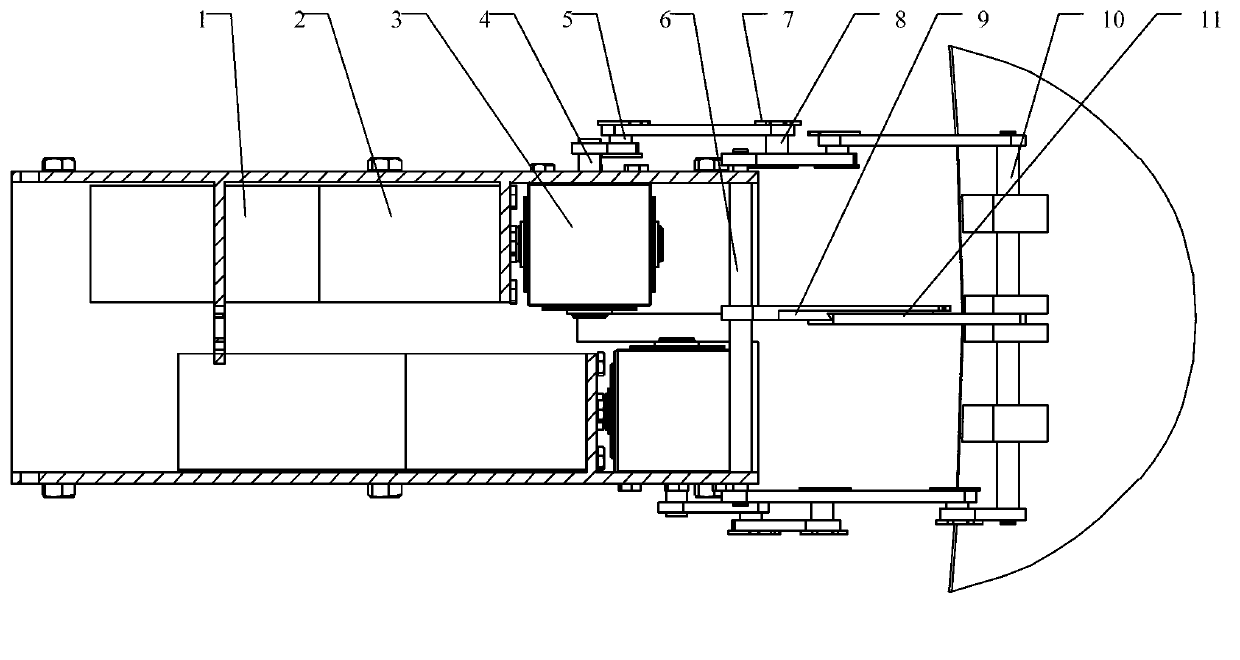
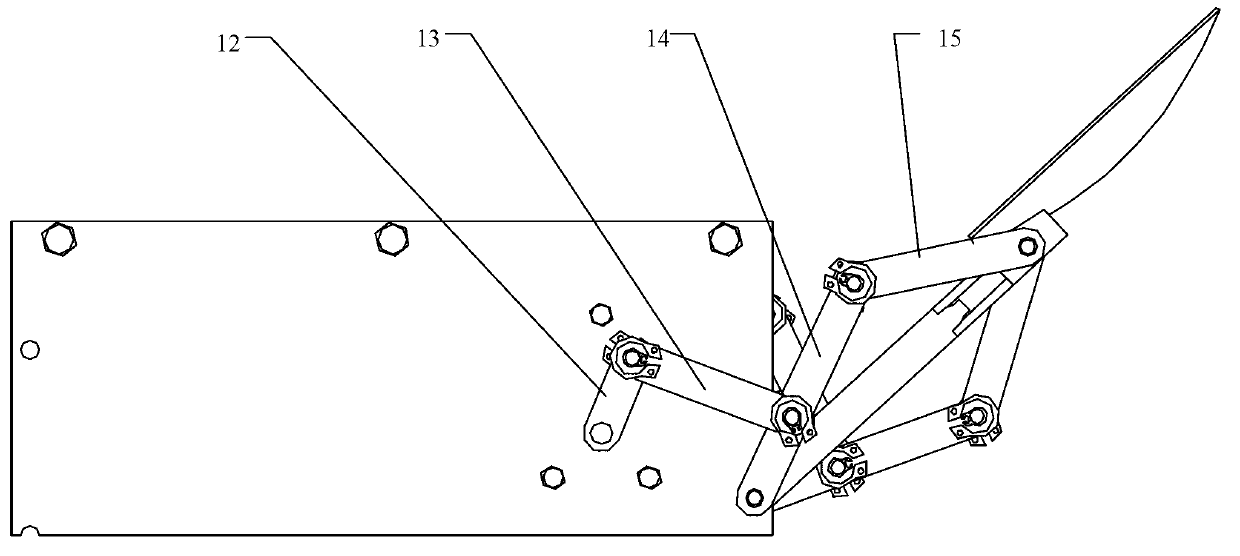
The invention discloses a leg-foot type bionic robot mouse. The biomimetic robot mouse comprises a mouse head assembly (1), a forelimb assembly (2), a hind limb assembly (3), a waist assembly (4), anda neck. A forelimb attachment assembly (5), and a tail (6); The rear limb assembly (3) comprises a rear limb motor bracket (16) and a rear limb driving device (13) for directly driving the movement of the rear limb of a biomimetic robotic mouse (10). The forelimb assembly (2) comprising a forelimb motor bracket (27), forelimb driving means (24) for directly driving the forelimb movement of a mouse of a biomimetic robot, the mouse head assembly (1) comprising a mouse head, a steering gear I (29) and a steering gear II (30) for directly driving the mouse head of the biomimetic robot to pitch, yaw, neck, respectively. The forelimb driving means (24) comprises: The forelimb connecting assembly (5) is connected with the mouse head assembly (1) and the forelimb assembly (2), and the lumbar assembly (4) is connected with the forelimb assembly (2) and the hindlimb assembly (3). Thus, the bionic robot mouse of the present invention can solve the problems of low degree of bionics and low flexibility.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Primate Restraining Device
ActiveCN102480928ARestricted movementSafe and easy to injectAnimal housingAnimal fetteringPrimateHindlimb
A primate restraining device capable of restraining the movement of a monkey and, particularly, capable of facilitating injection or blood drawing. A primate restraining device comprising: a containing body having both side surfaces, a top surface, and a bottom surface; a door provided to the rear surface side of the containing body and capable of opening and closing the rear surface side of the containing body by sliding up and down; and a partition wall which is formed so as to close the inside of the containing body from the front surface side and to be movable forward and backward within the containing body and which is configured to be able to be affixed at a desired position within the containing body. The partition wall has provided therein hind-limb protrusion openings from which the hind limbs of the contained primate are caused to protrude to the outside.
Owner:SHIN NIPPON BIOMEDICAL LAB
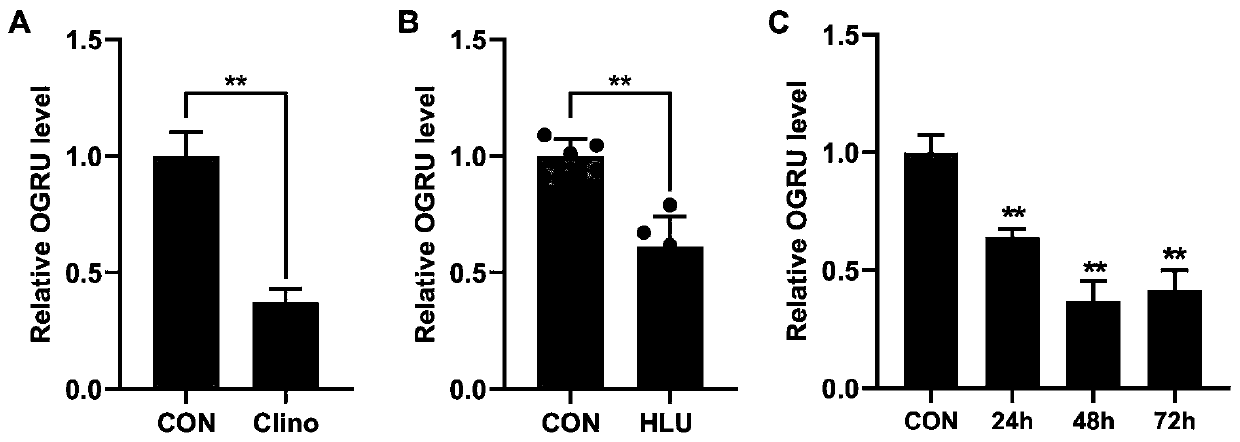
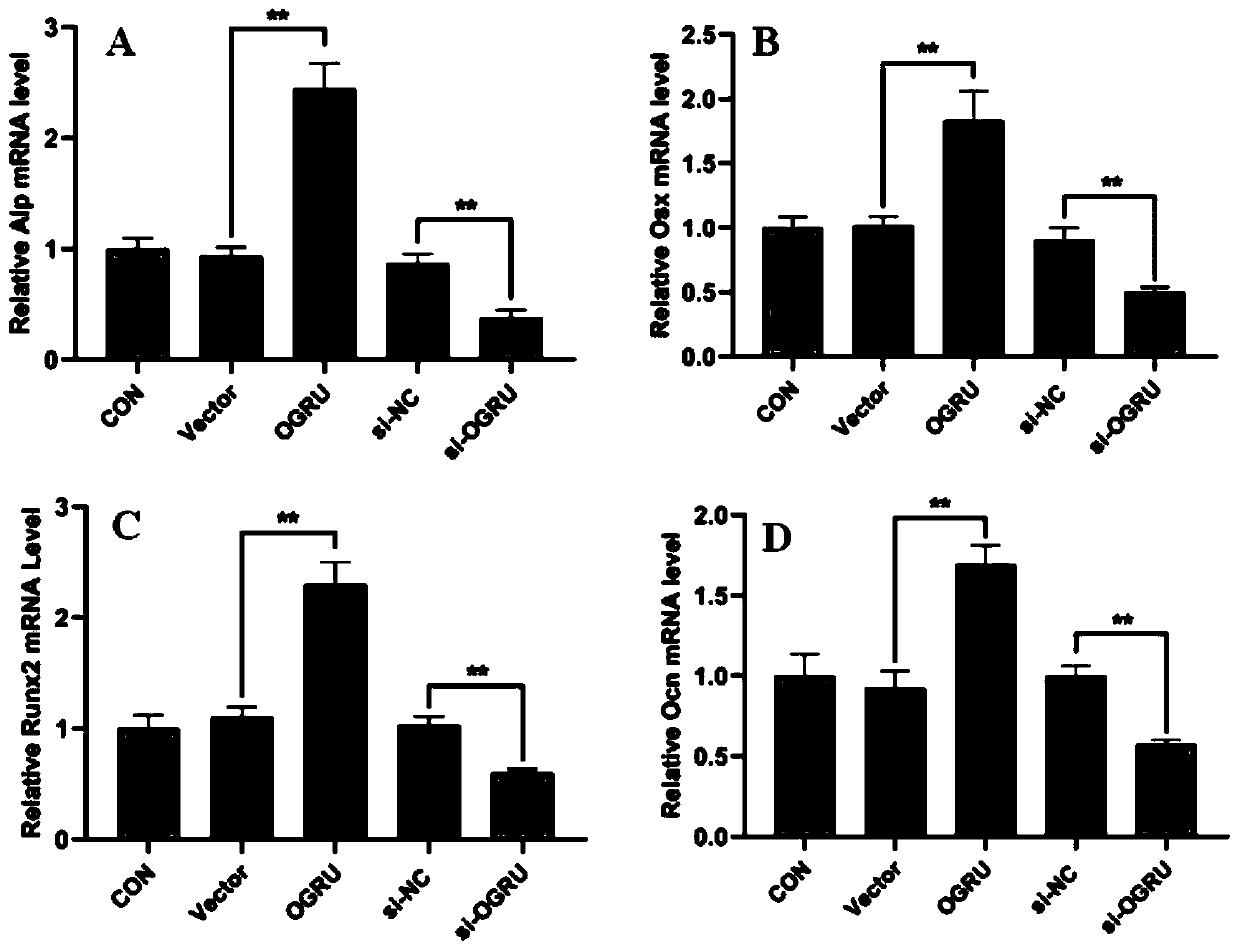
lncRNA OGRU and drug use of lncRNA OGRU overexpression vector
ActiveCN110438129APromote differentiationGood mineralization effectOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementLoad modelHindlimb
The invention discloses lncRNA OGRU and drug use of an lncRNA OGRU overexpression vector. The expression of the lncRNA OGRU in a 2D rotation MC3T3-E1 cell de-load model and a mouse hind limb unweighted (HLU) de-load model is significantly reduced, the OGRU overexpression vector pcDNA3.1(+)-OGRU promotes cell differentiation of mouse preosteoblast MC3T3-E1 in the 2D rotation MC3T3-E1 cell de-load model, and pcDNA3.1(+)-OGRU is delivered to a mouse osteogenesis area by a bone targeted delivery system (DSS) 6-liposome to effectively relieve osteoporosis caused by HLU; and OGRU has potential to become a new target for disuse osteoporosis diagnosis biomarkers and treatment, and the OGRU overexpression vector is used in drugs for treating the disuse osteoporosis.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Spinal cord closed-loop electrical stimulation system
ActiveCN110404164ARecovery of hindlimb motor functionSpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringClosed loopHindlimb
The invention relates to a spinal cord closed-loop electrical stimulation system, which comprises a spinal epidural electrical stimulation electrode, a leg electrical stimulation electrode, a closed-loop electrical stimulator and a controller, the spinal epidural electrical stimulation electrode and the leg electrical stimulation electrode are respectively connected with the closed-loop electricalstimulator, the controller is electrically connected with the closed-loop electrical stimulator, the spinal epidural electrical stimulation electrode is used to implant the spinal epidural of a subject and to apply a first electrical stimulus to the spinal epidural, the leg electrical stimulation electrode is used to implant the subject's leg and apply to the leg with second electrical stimulus,the first electrical stimulus has a voltage of 400 to 600 mV and a frequency of 10 to 20 Hz, and the second electrical stimulus has the voltage of 1 V to 1.5 V and the frequency of 10 to 20 Hz. The spinal cord closed-loop electrical stimulation system of the present invention can issue an electrophysiological signal similar to a spinal cord sensory-motor neural circuit to the subject after spinalcord injury, the neural circuit can be activated and reshaped after closed-loop electrical stimulation, and the recovery of the motor function of the hind limb of the subject can be promoted.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
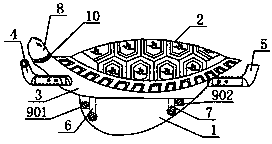
Bionic fitness equipment
ActiveCN103785134AAvoid negative effectsSmall footprintMovement coordination devicesCardiovascular exercising devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationBionics
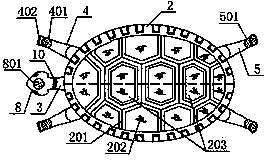
The invention relates to fitness equipment bionic in modeling and action. The appearance of the equipment is a result of turtle-crane fusion, the bionic fitness equipment comprises a crane-belly-shaped base (1), a turtle-shell-shaped cover plate (2), a turtle-body-shaped case (3), fore limbs (4), hind limbs (5), a front support (6), a rear support (7), a turtle head (8), an inner driving mechanism (9) and a circular control panel (10). The fore limbs and the hind limbs can perform a positive symmetry action, an inverse symmetry action and a cross type arc action under the driving of speed changes and direction changes of an inner motor so as to drive a body builder who lies on the turtle shell to imitate crawling of a turtle, flying of a crane, diving of the turtle, waist arching of civet, crawling of a snake, fishtailing of a tiger, leg warping of a migratory locust and other bionic actions, and massage of acupuncture points in the hands, the feet and the belly can be achieved. Compared with an existing machine, the fitness equipment has more interestingness and action diversity, integrates aesthetics, medical science and bionics, and has huge market attractiveness.
Owner:蒋日磊
Remote control bulldog clamp used in laparoscopic surgery
The invention relates to a remote control bulldog clamp used in a laparoscopic surgery. The remote control bulldog clamp is characterized by comprising a clamp body, wherein one end of the clamp body is two front limbs closed in a normal state, and the other end of the clamp body is a back limb for operating the two front limbs to open; an oval space is defined when the two front limbs are closed, and the short diameter of the oval space is matched with the diameter of the renal artery; the inner surface of each front limb is provided with a water bag, the sum of the diameters of the two water bags filled with liquid is larger than the diameter of the renal artery, and the water bags filled with the liquid can push the two front limbs to open towards the two sides; the water bags are connected with a puncture needle through a thin plastic guiding pipe in the process of puncturing, and are connected with a water pump provided with an adjusting knob in the process of water injection; the diameter of each water bag filled with the liquid is controlled by operating the adjusting knob. Compared with the prior art, the remote control bulldog clamp has the advantages that the artery is blocked and opened while a doctor does not stop cutting, and warm ischemia time of the organs is shortened to the maximum extent.
Owner:NANTONG YIKAI MEDICAL DEVICES CO LTD
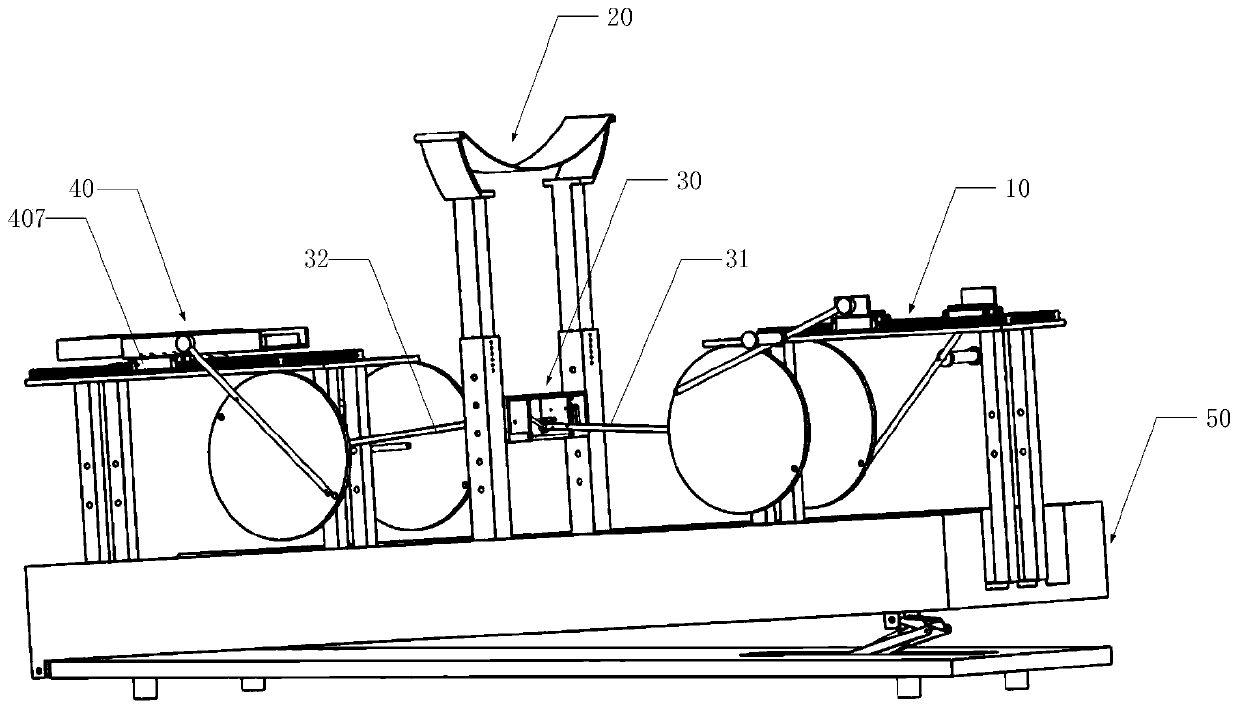
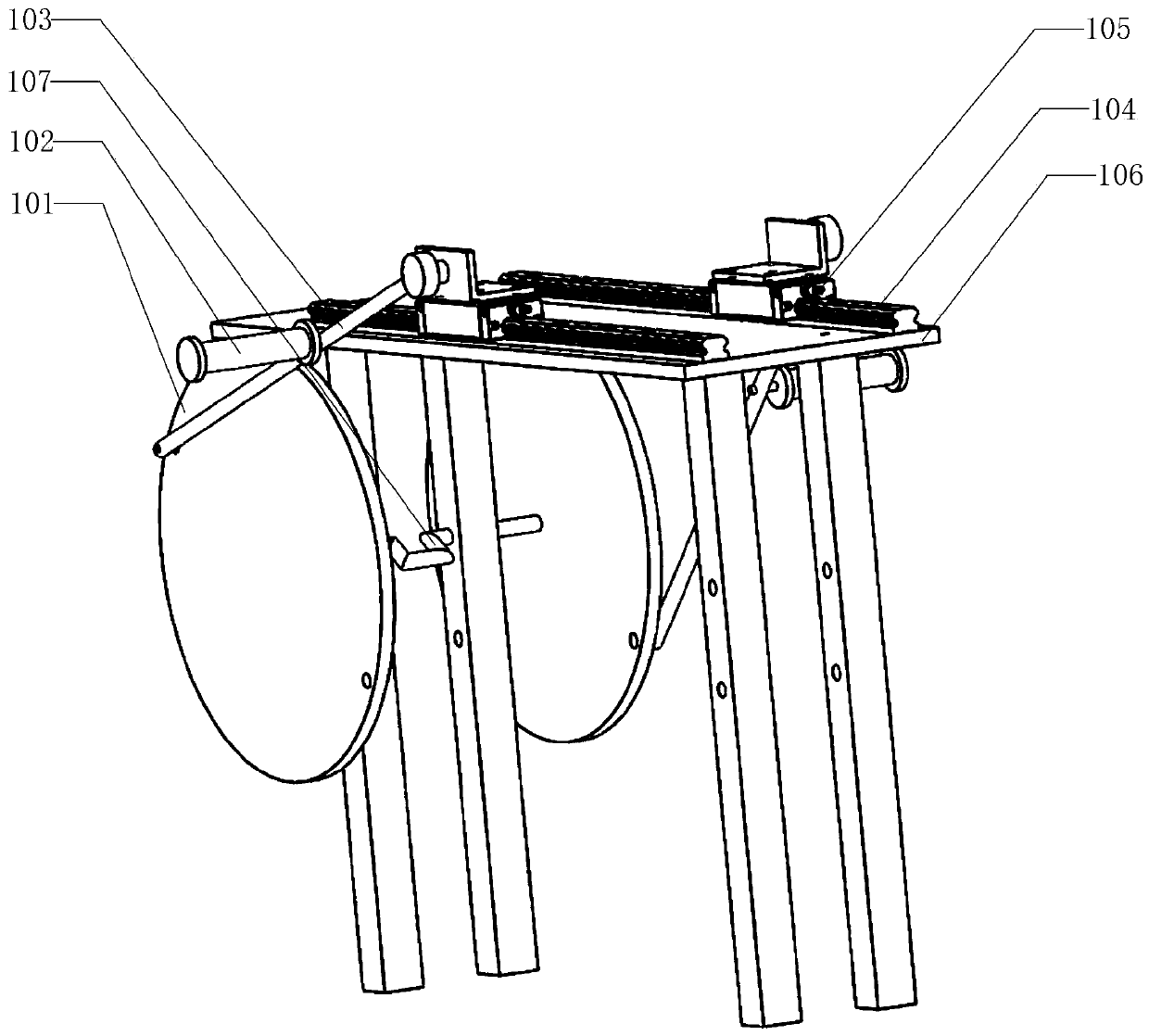
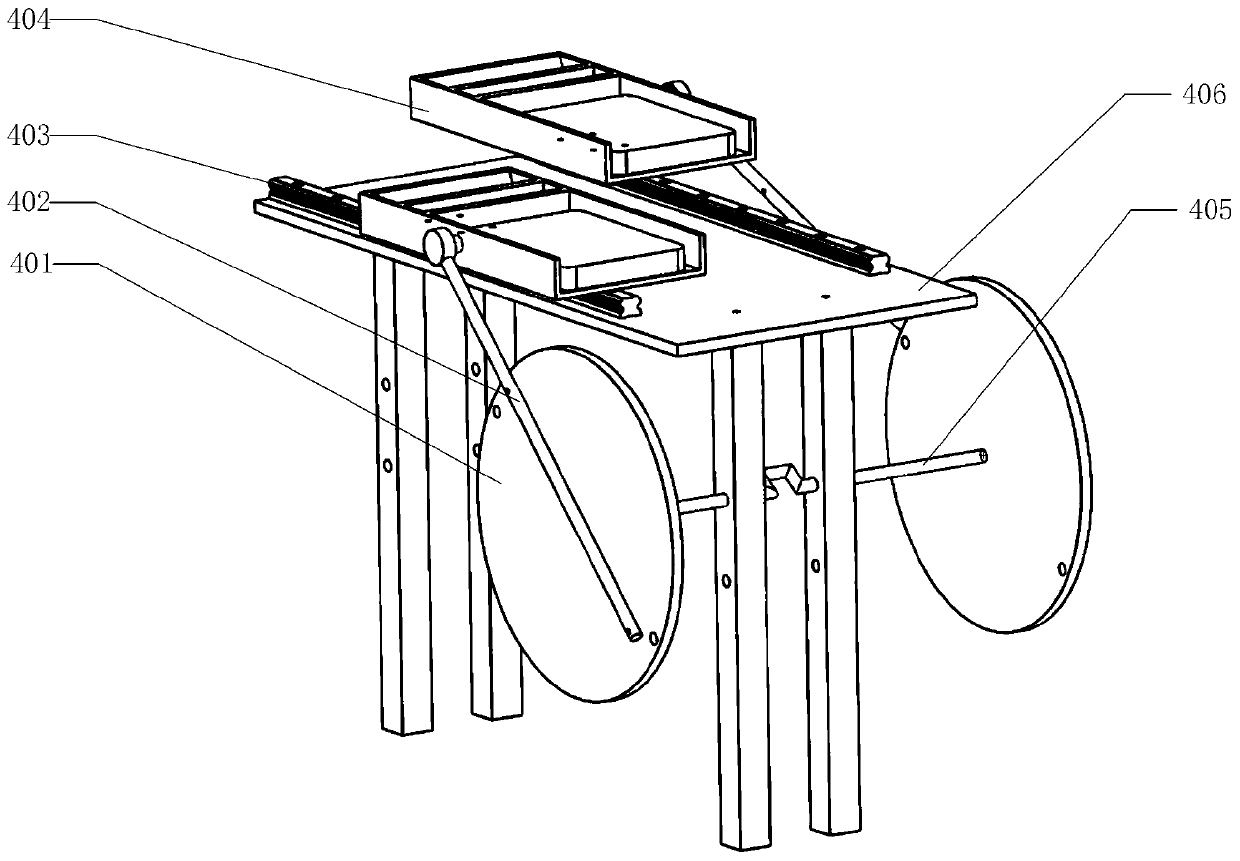
Training device and training method
PendingCN111068251AImprove comfortImprove corrective crawling postureChiropractic devicesMuscle exercising devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationHindlimb
The invention discloses a training device and a training method. The training device comprises a forelimb movement mechanism, a posterior limb movement mechanism, a linkage mechanism, a middle supporting mechanism and an inclination mechanism. The forelimb movement mechanism is installed on the tilting mechanism, the posterior limb movement mechanism is installed on the tilting mechanism, the linkage mechanism is connected with the forelimb movement mechanism and the posterior limb movement mechanism, the middle supporting mechanism is installed on the tilting mechanism, and the linkage mechanism is installed on the middle supporting mechanism. According to the training device, the comfort degree of a patient during crawling is greatly improved, and the crawling posture is corrected.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
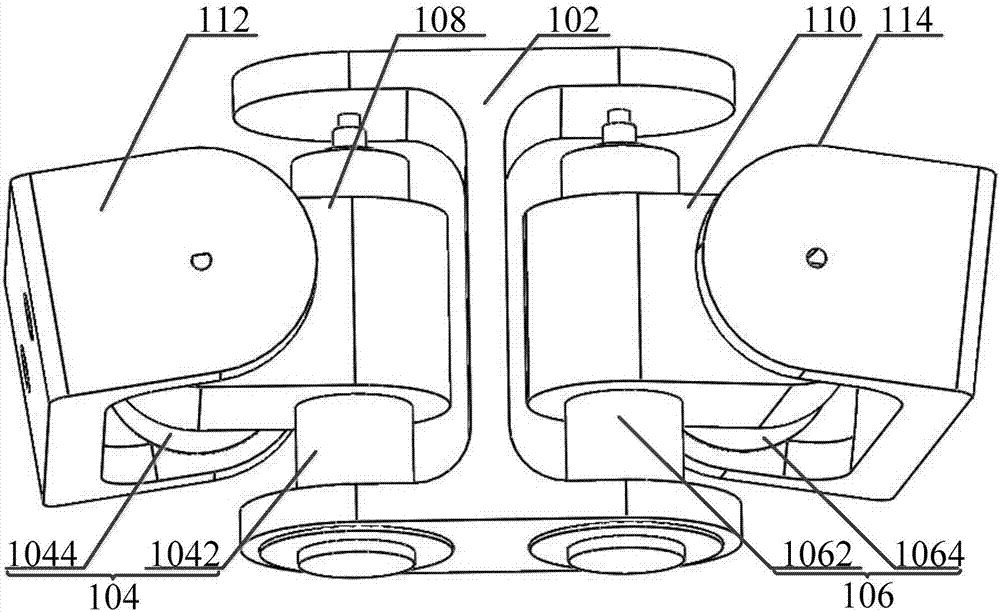
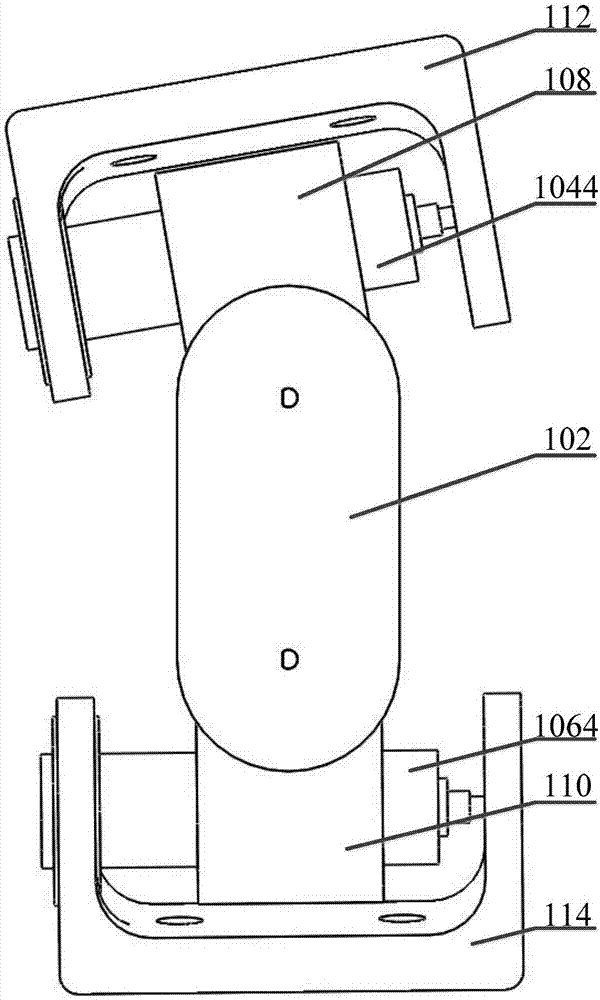
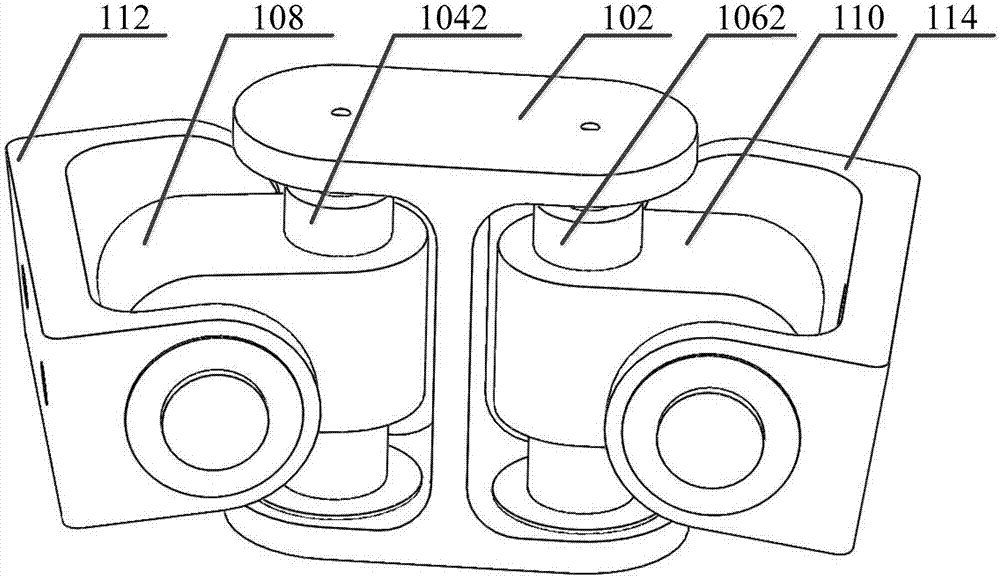
Waist motion bionic structure and bionic machine rat including waist motion bionic structure
The invention relates to the technical field of bionic structures, in particular to a waist motion bionic structure and a bionic machine rat including the waist motion bionic structure. The waist motion bionic structure aims at solving the problem that in the prior art, motion flexibility and structural compactness of a waist motion bionic structure in the prior art are poor. In order to achieve the aim, the waist motion bionic structure comprises a rack, a front drive device and a rear drive device, wherein the front drive device is connected to the front end of the rack in a pivot manner, and is used for driving a front limb at the front end of the rack to swing left and right and up and down; the rear drive device is connected to the rear end of the rack in a pivot manner and is used for driving a rear limb at the rear end of the rack to swing left and right and up and down. Through the technical scheme, motion flexibility and structure compactness of the waist motion bionic structure are improved, consistency of the waist motion bionic structure and an animal waist structure is improved, research of biologists, neuroscientists and brain researchers for the waist structure is facilitated, and the effective control over the behavior of the waist structure is achieved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com