Patents
Literature
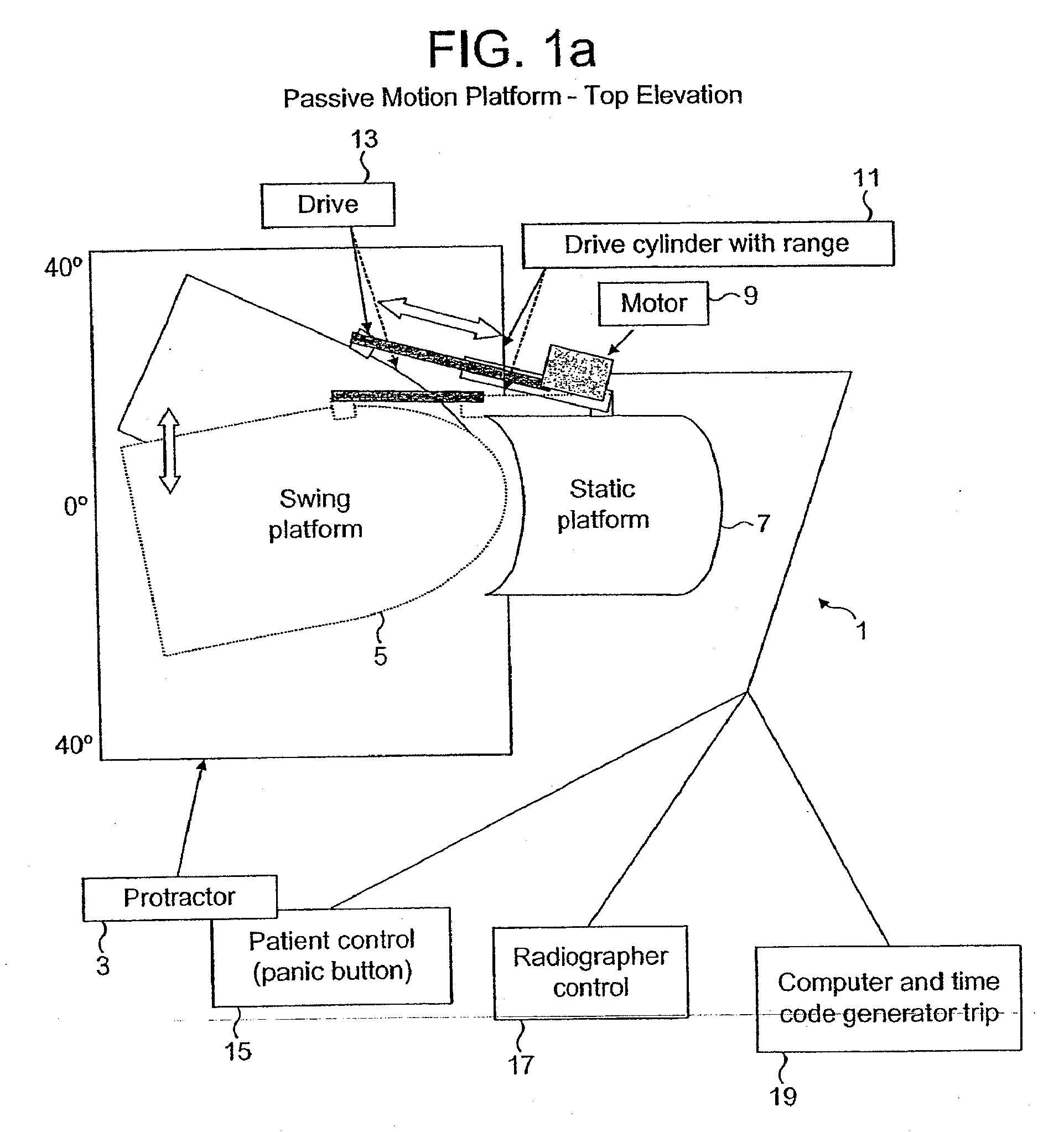
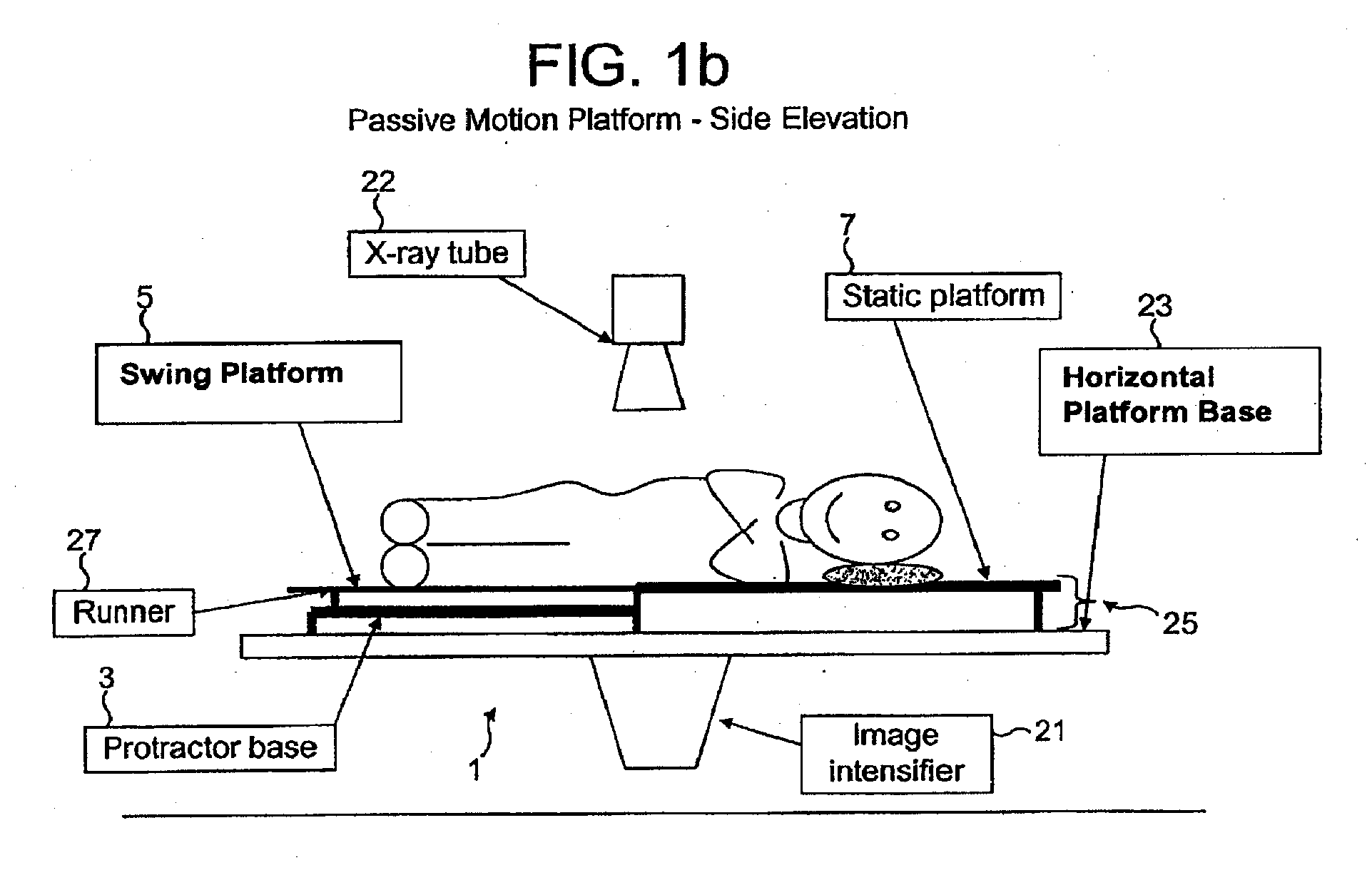
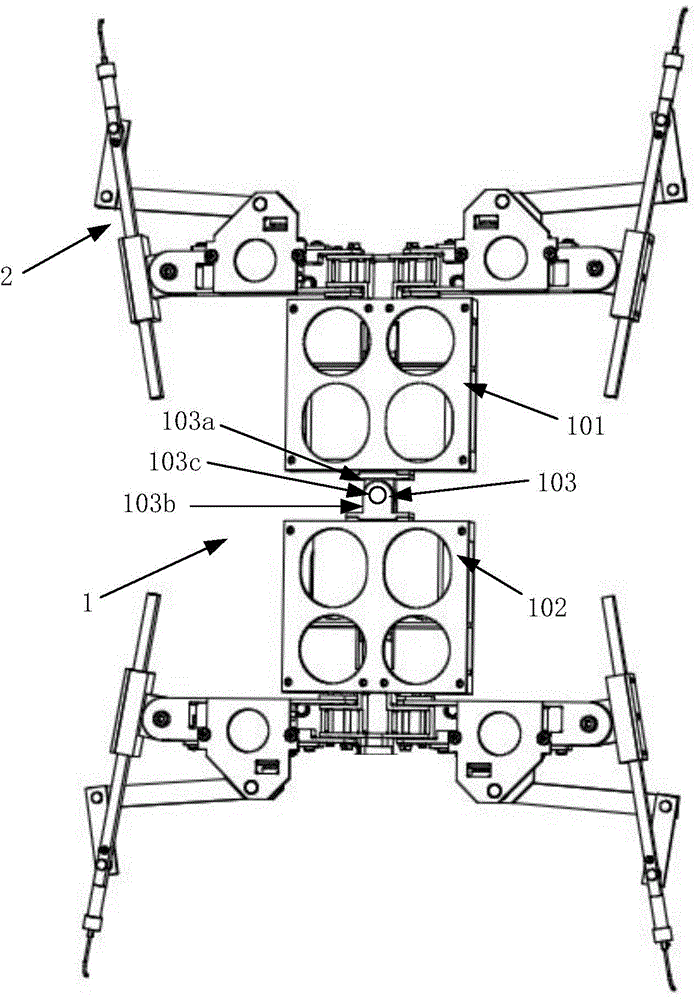
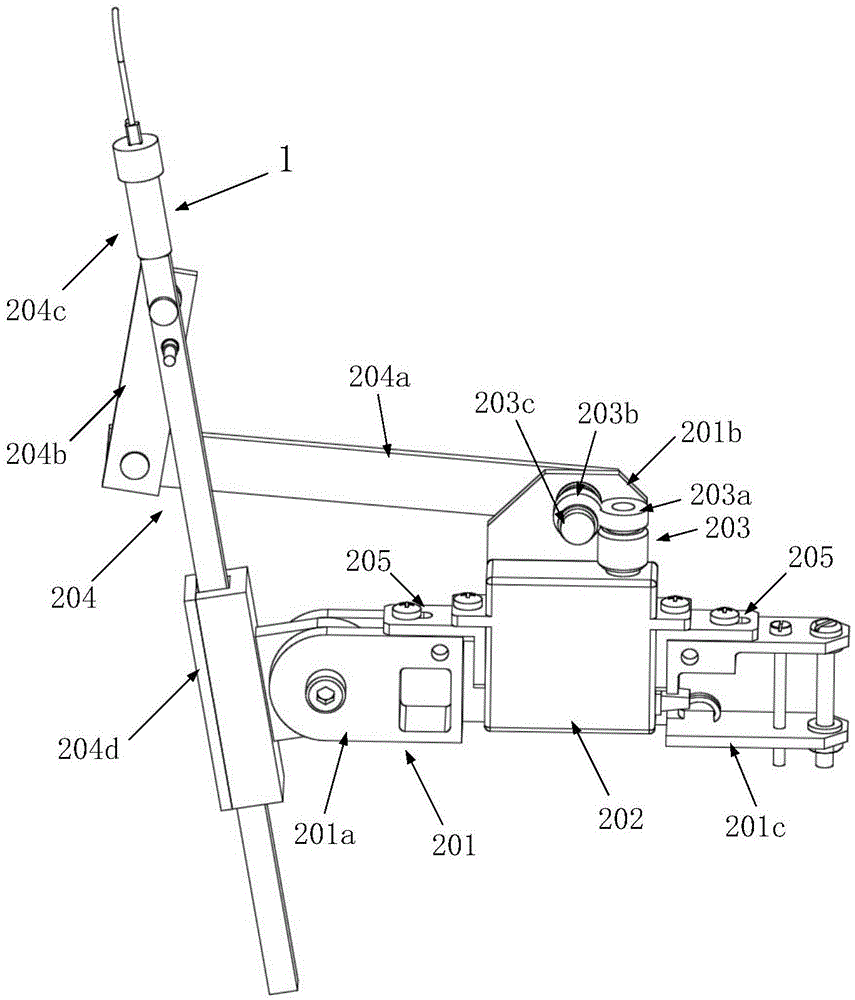
89 results about "Passive motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
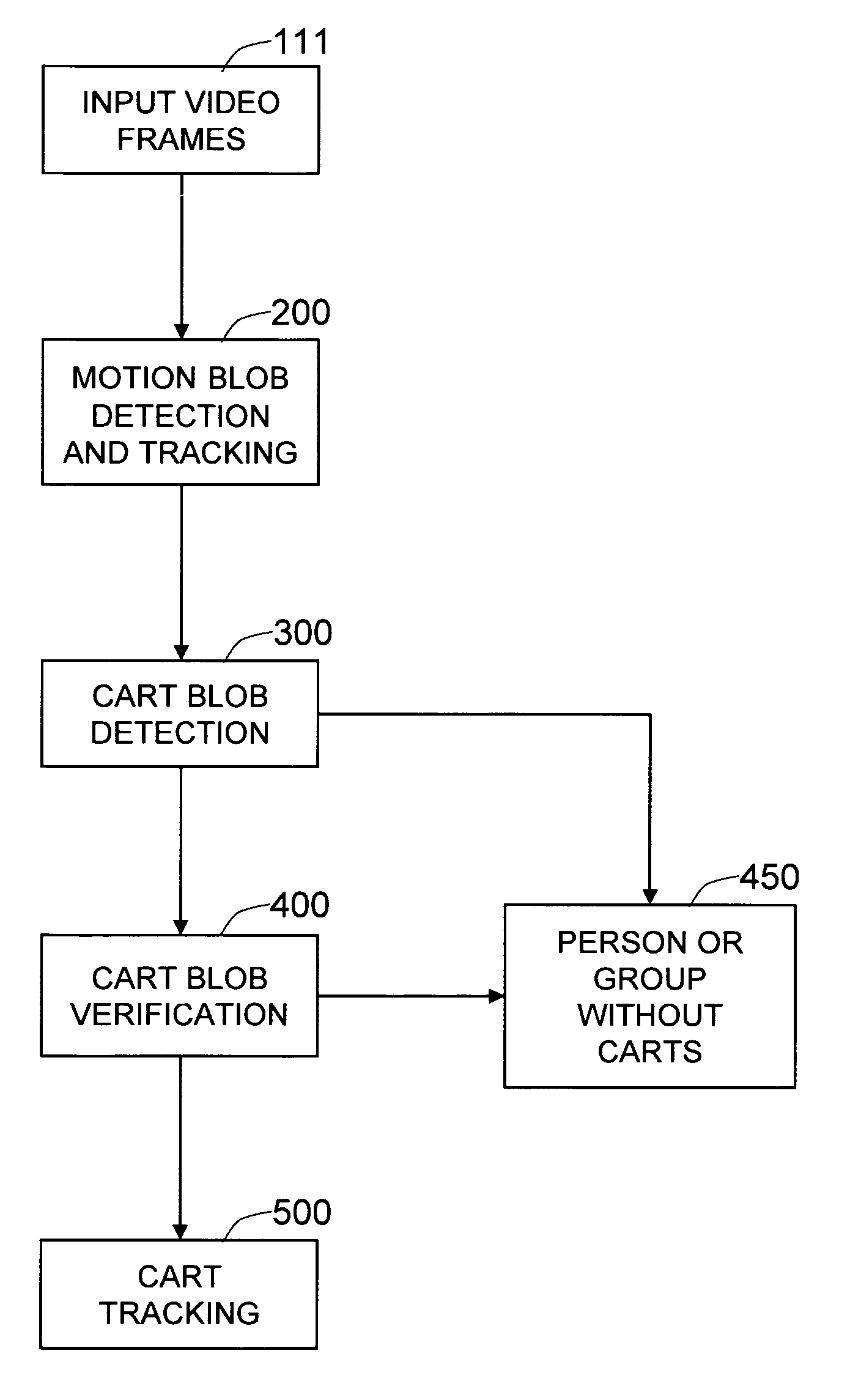
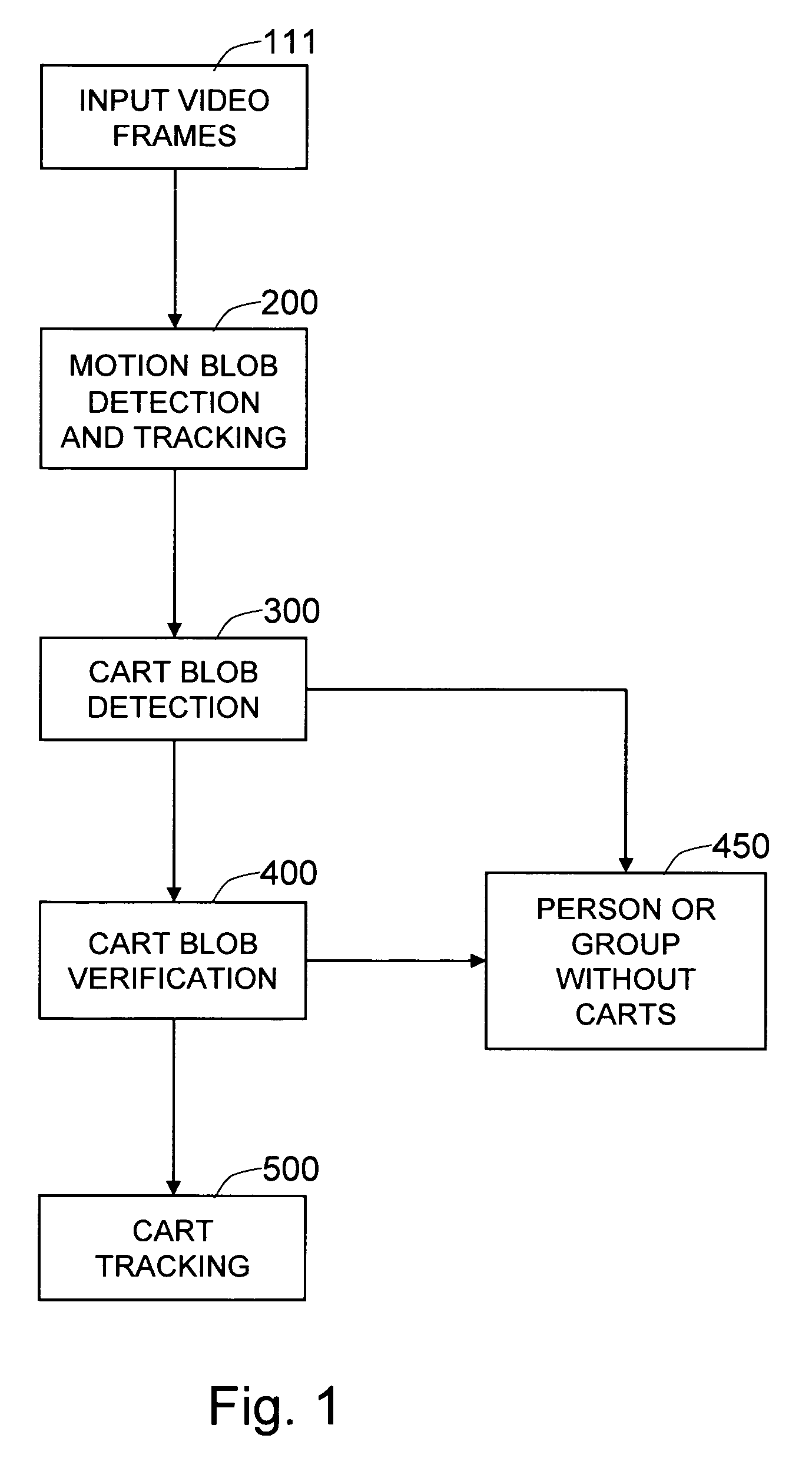
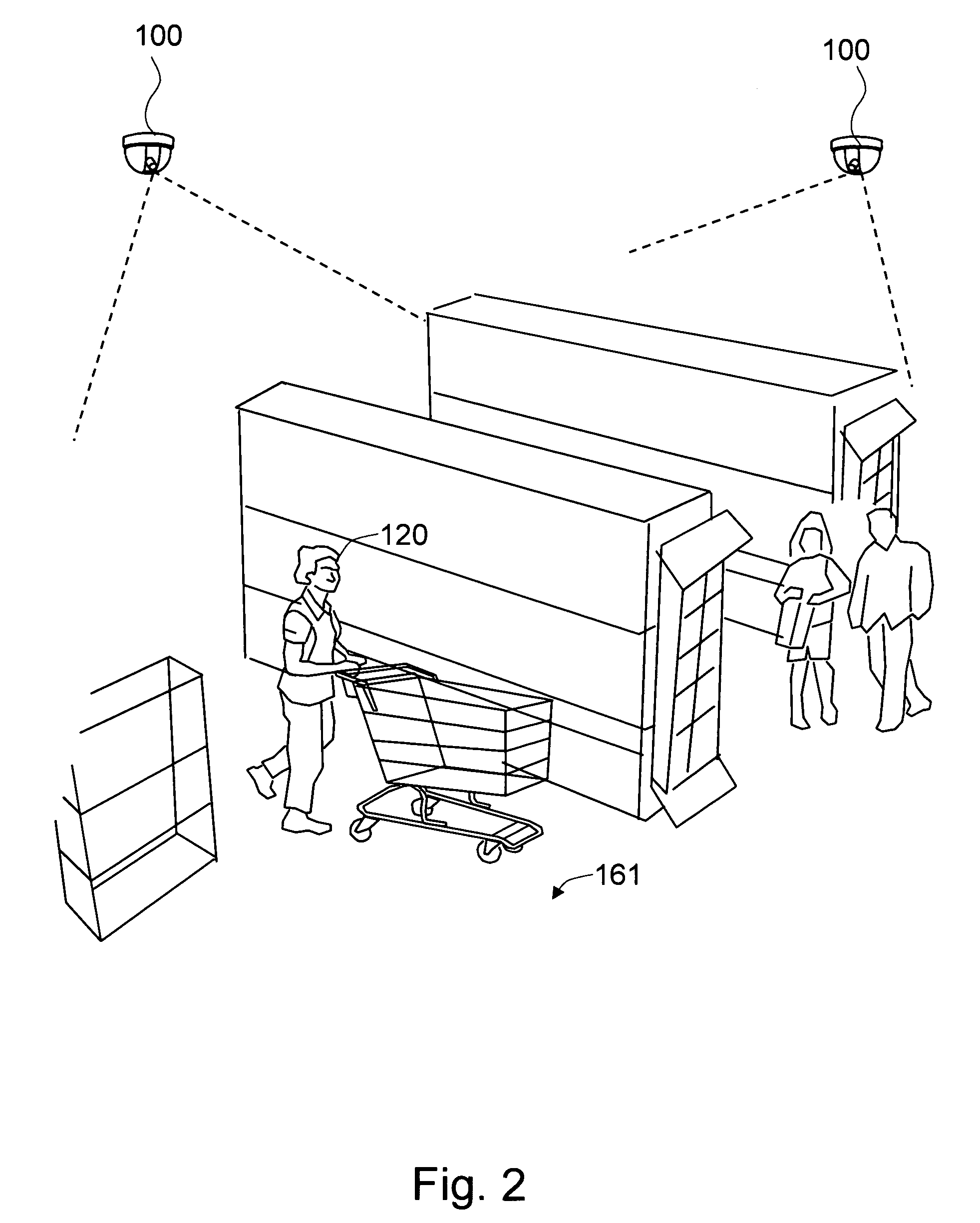
Method and system for detecting and tracking shopping carts from videos
ActiveUS8325982B1Efficient detectionTelevision system detailsImage analysisPattern recognitionObject motion
The present invention is a method and system for detecting and tracking shopping carts from video images in a retail environment. First, motion blobs are detected and tracked from the video frames. Then these motion blobs are examined to determine whether or not some of them contain carts, based on the presence or absence of linear edge motion. Linear edges are detected within consecutive video frames, and their estimated motions vote for the presence of a cart. The motion blobs receiving enough votes are classified as cart candidate blobs. A more elaborate model of passive motions within blobs containing a cart is constructed. The detected cart candidate blob is then analyzed based on the constructed passive object motion model to verify whether or not the blob indeed shows the characteristic passive motion of a person pushing a cart. Then the finally-detected carts are corresponded across the video frames to generate cart tracks.
Owner:VIDEOMINING CORP
Orthopedic seat with inflatable cells
A passive-motion having a support surface provided by a plurality of bellows-like or bladder-like cells which are sequentially or independently inflatable and deflatable to alter the configuration of the support surface continuously to cause a person seated on the support surface to continuously and instinctively adjust the additude of his spinal column and associated muscles.
Owner:SAND THERAPEUTIC +1
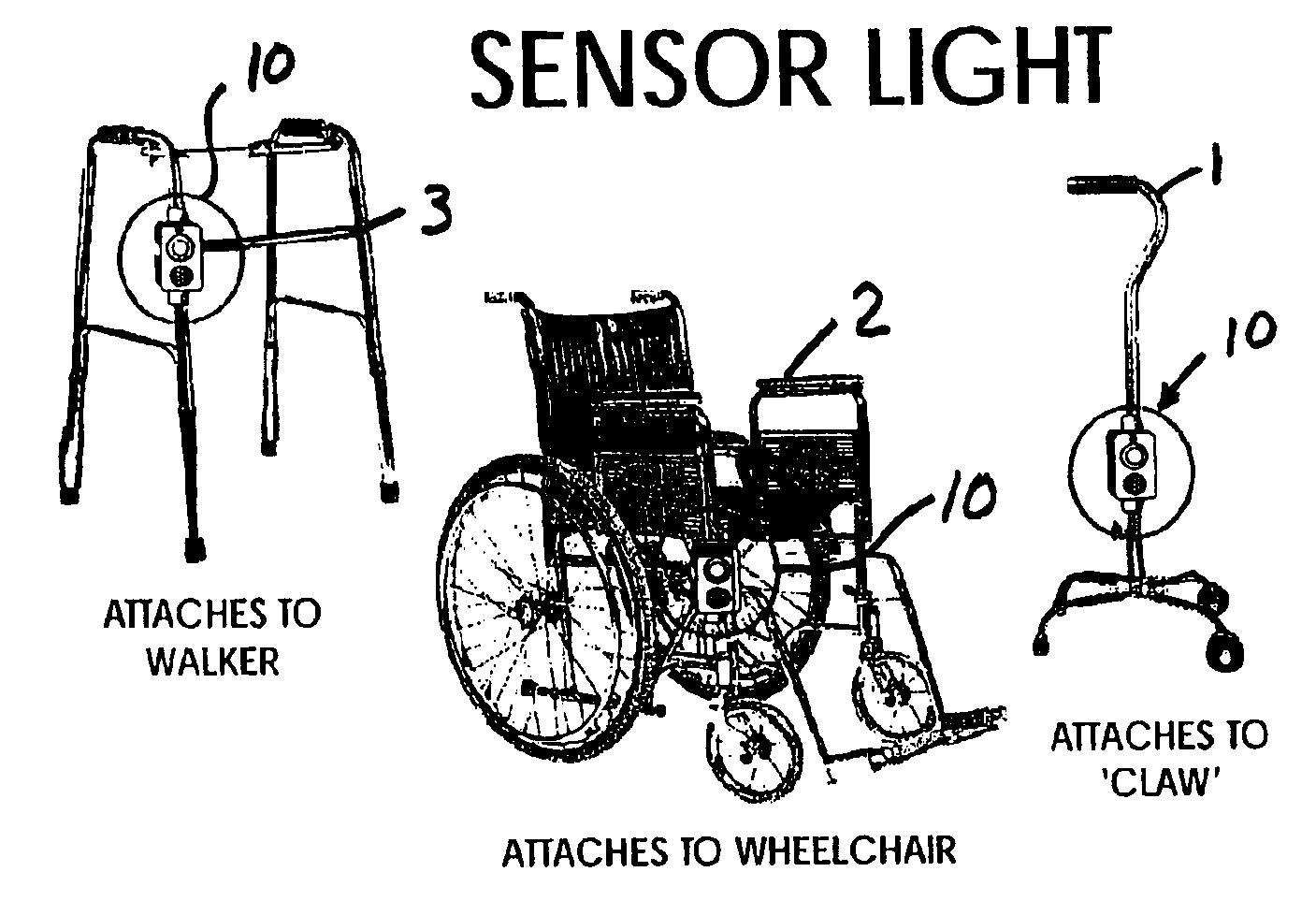
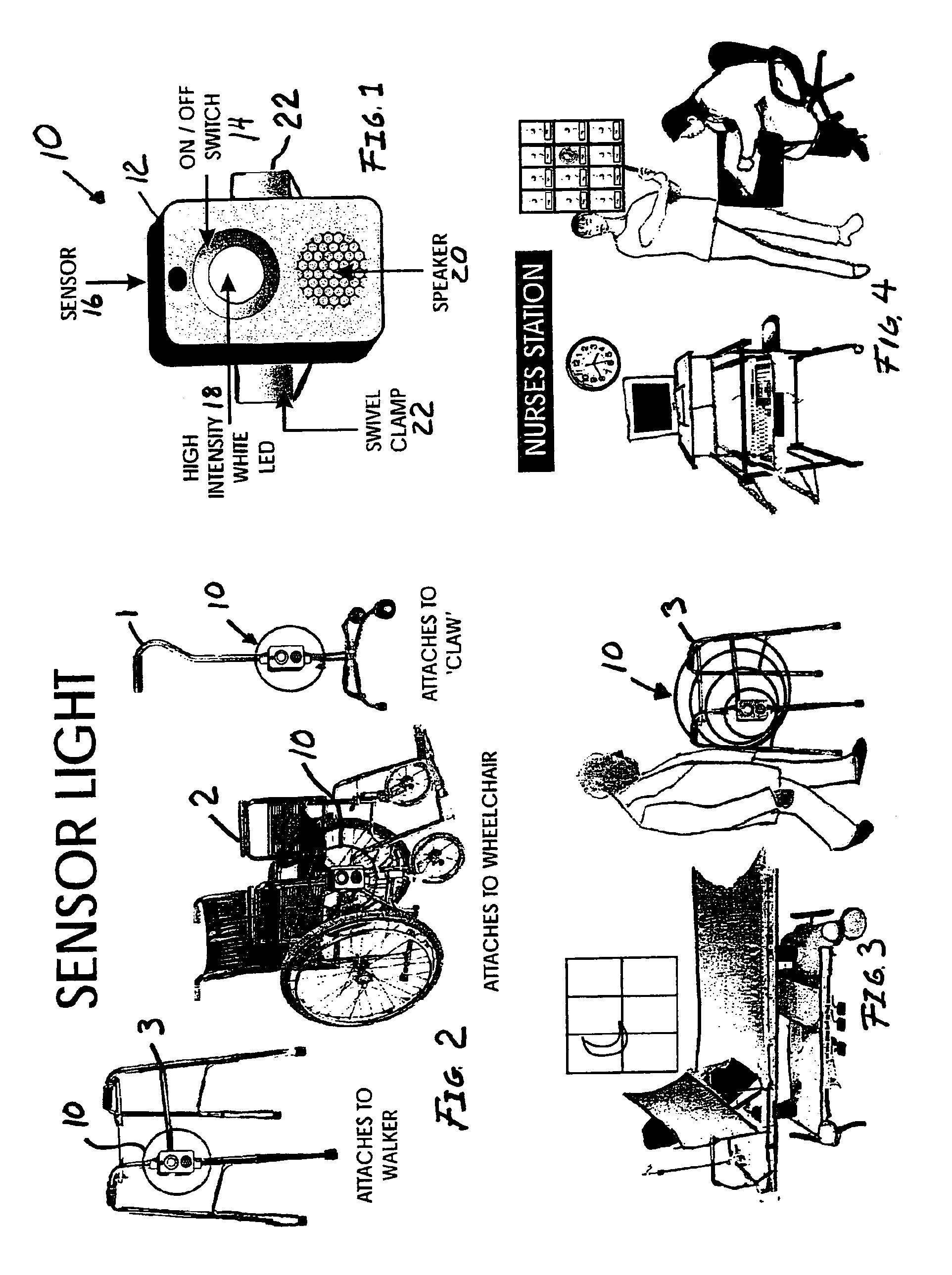
Sensor light device
An automatic functioning light and warning system with remote signaling for use with mobility assistance devices, such as wheelchairs and walkers, having a housing, at least one detachable clamp connected to the housing, a battery-powered light incorporated into the housing, an internal audio alarm incorporated into the housing, an active or passive motion detection sensor and associated signal processing circuitry incorporated within the housing. The invention may use replaceable or rechargeable batteries as the power source. The remote receiver may be a stand alone device or interfaced into a monitoring system. A time delay circuit may be incorporated into the invention to automatically turn the light or alarm off at a predetermined time after activation and a sensor that prevents actuation of the light source when ambient light is above a predetermined threshold.
Owner:JACKSON IVETTE
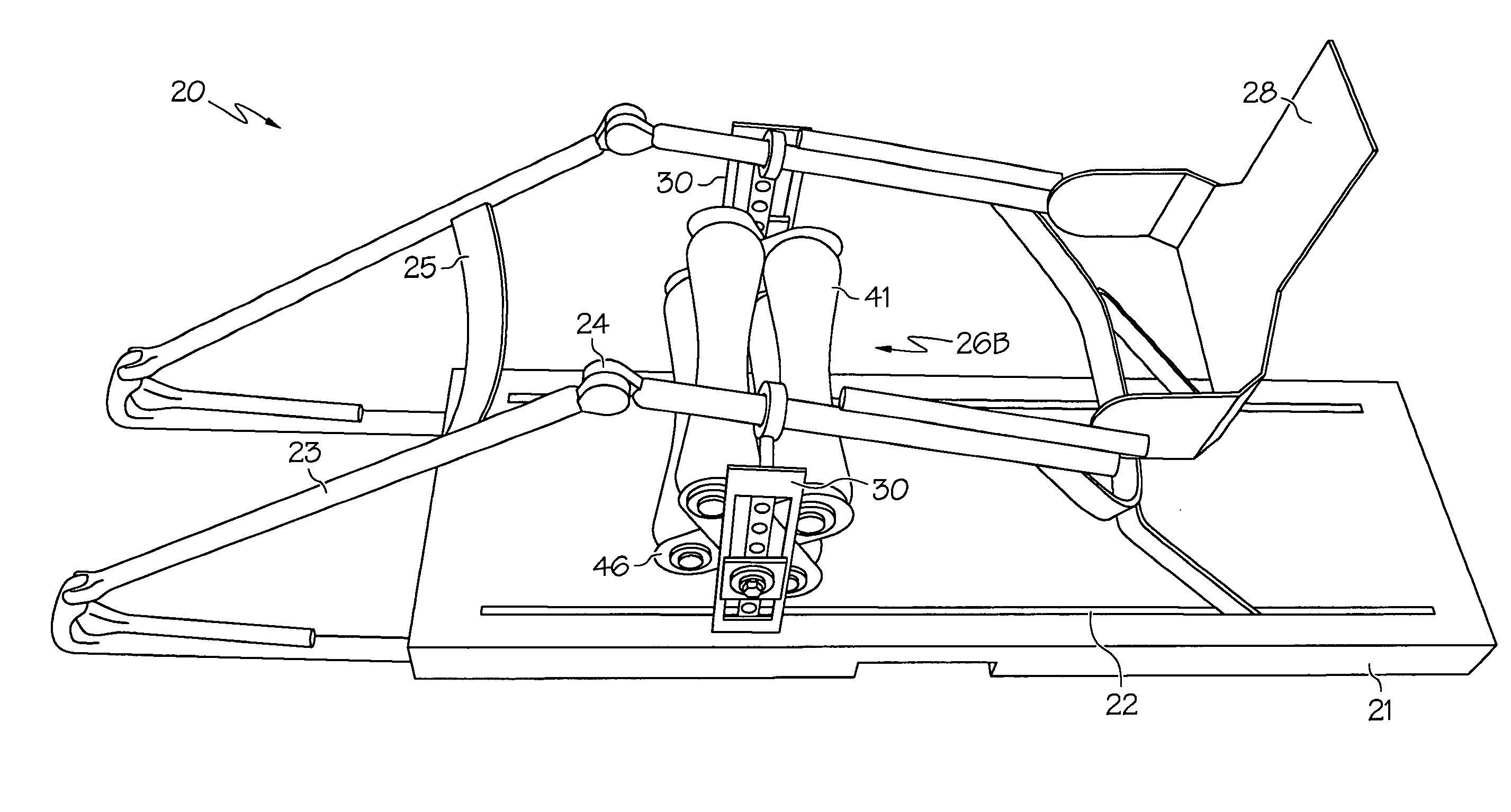
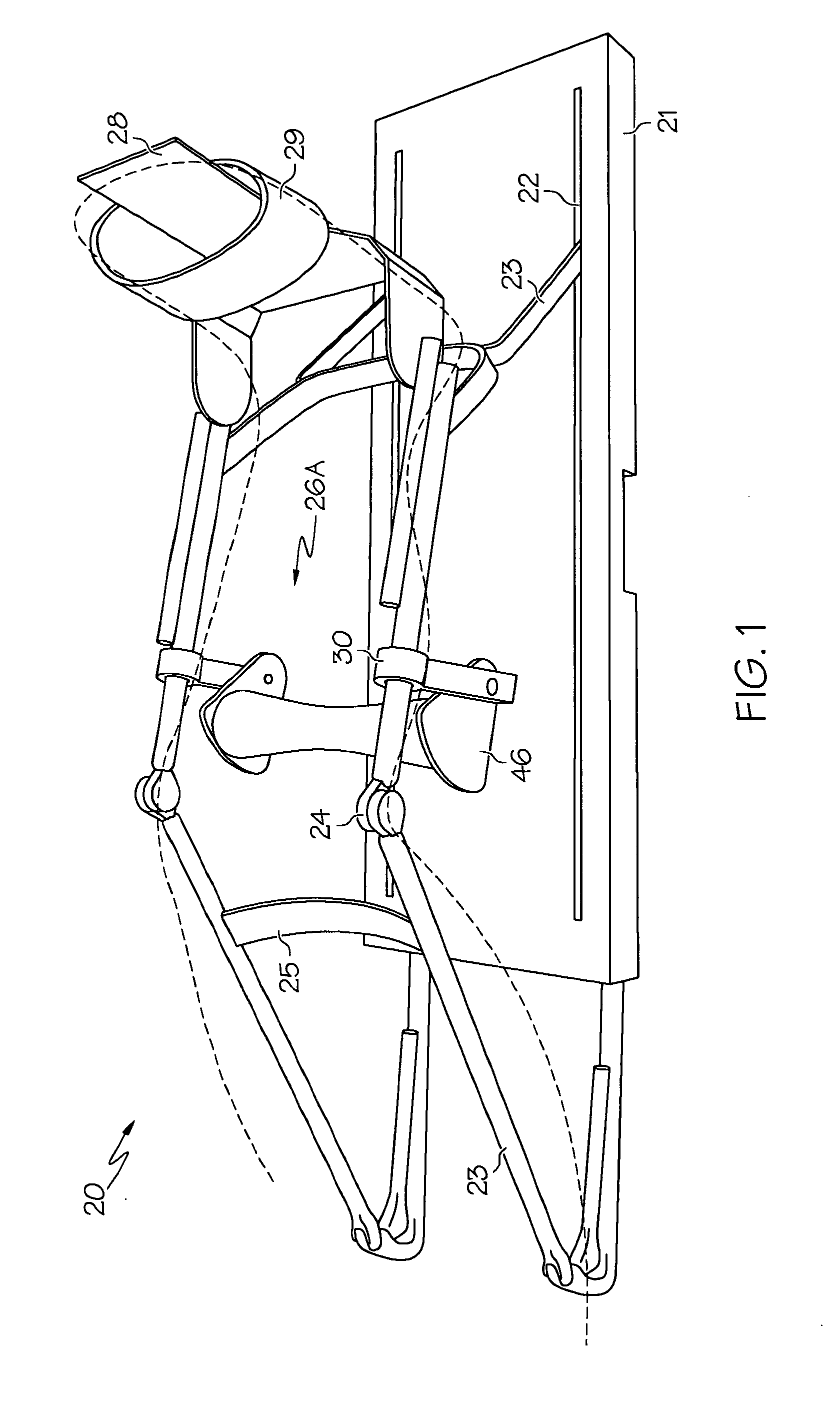
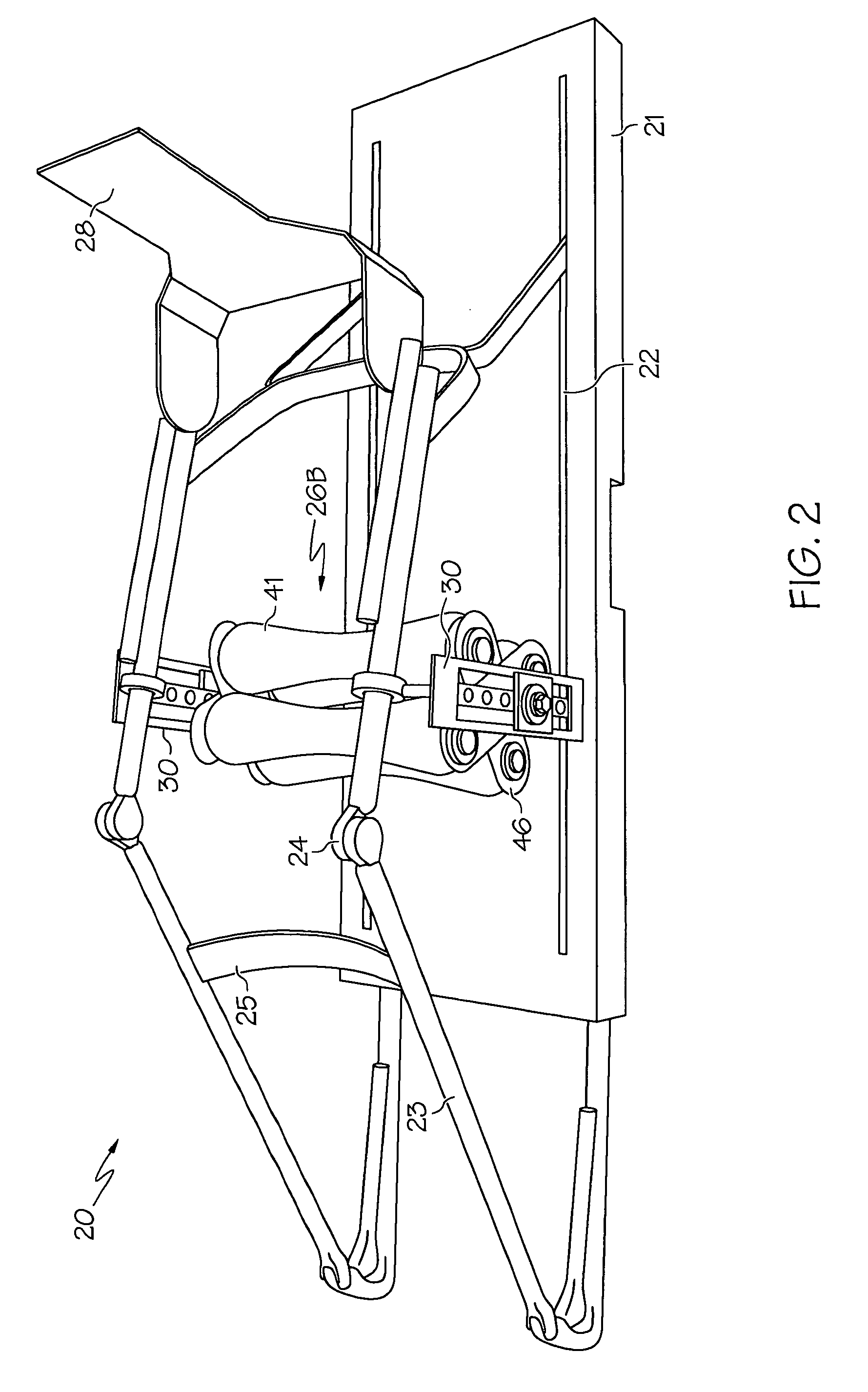
Passive motion machine with integrated mechanical DVT prophylactic therapy
There is provided a continuous passive motion (CPM) machine with integrated mechanical deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis for providing simultaneous CPM therapy and DVT prophylactic therapy to a human patient. The passive motion machine may include a base, at least one motor, one or more hinged frame rails, one or more support or suspension structures and a roller assembly. The hinged frame rails are driven to impart CPM to a patient's limb. The roller assembly can be a single roller, a multiple roller unit, or a belt and roller apparatus. A motor and connecting drive rotates the roller assembly. The roller assembly engages the patient's limb and the one or more rollers apply a mechanical DVT prophylaxis therapy to the limb, reducing the risk of blood clotting.
Owner:LYMAN JEFFREY R M D
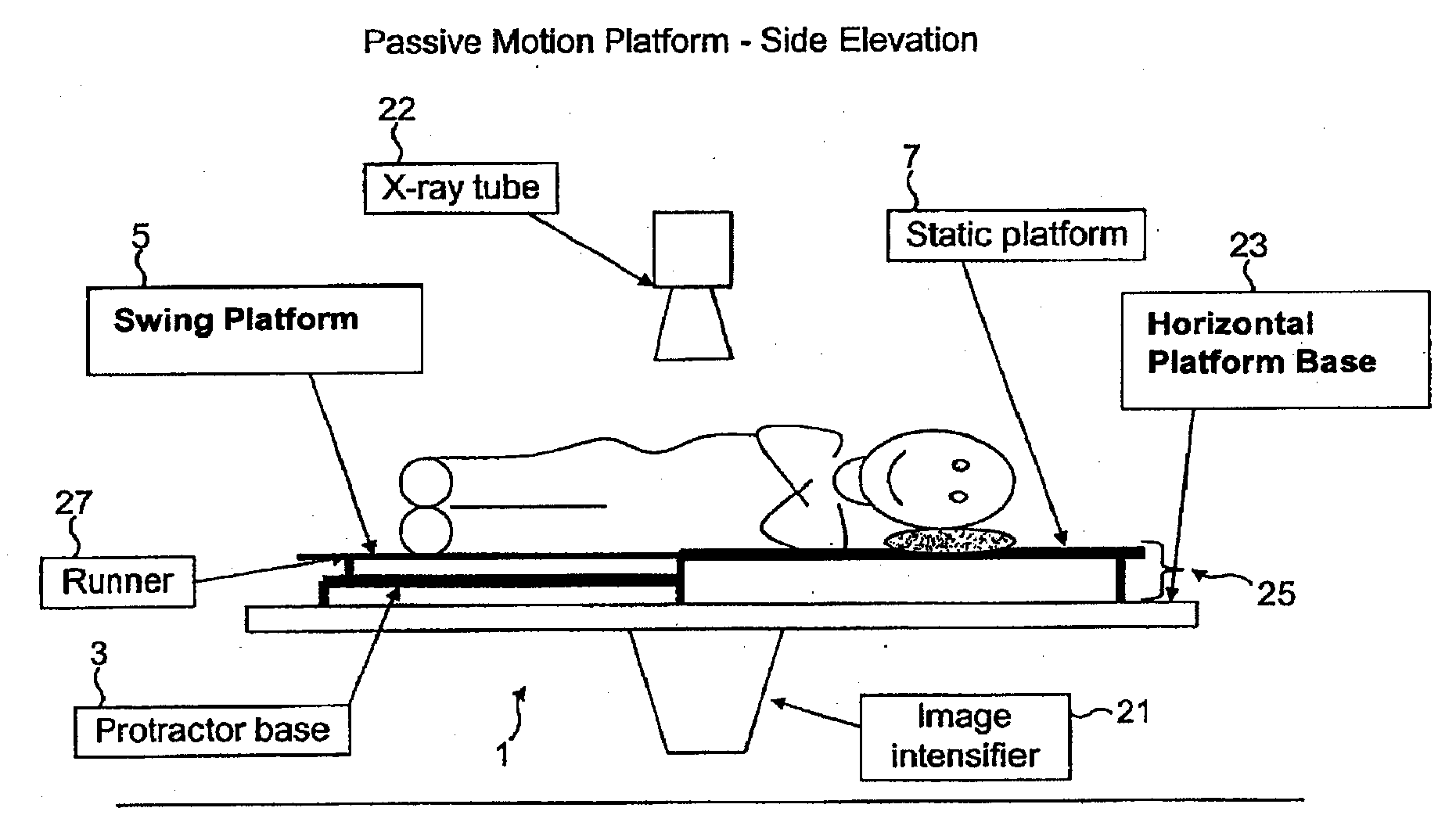
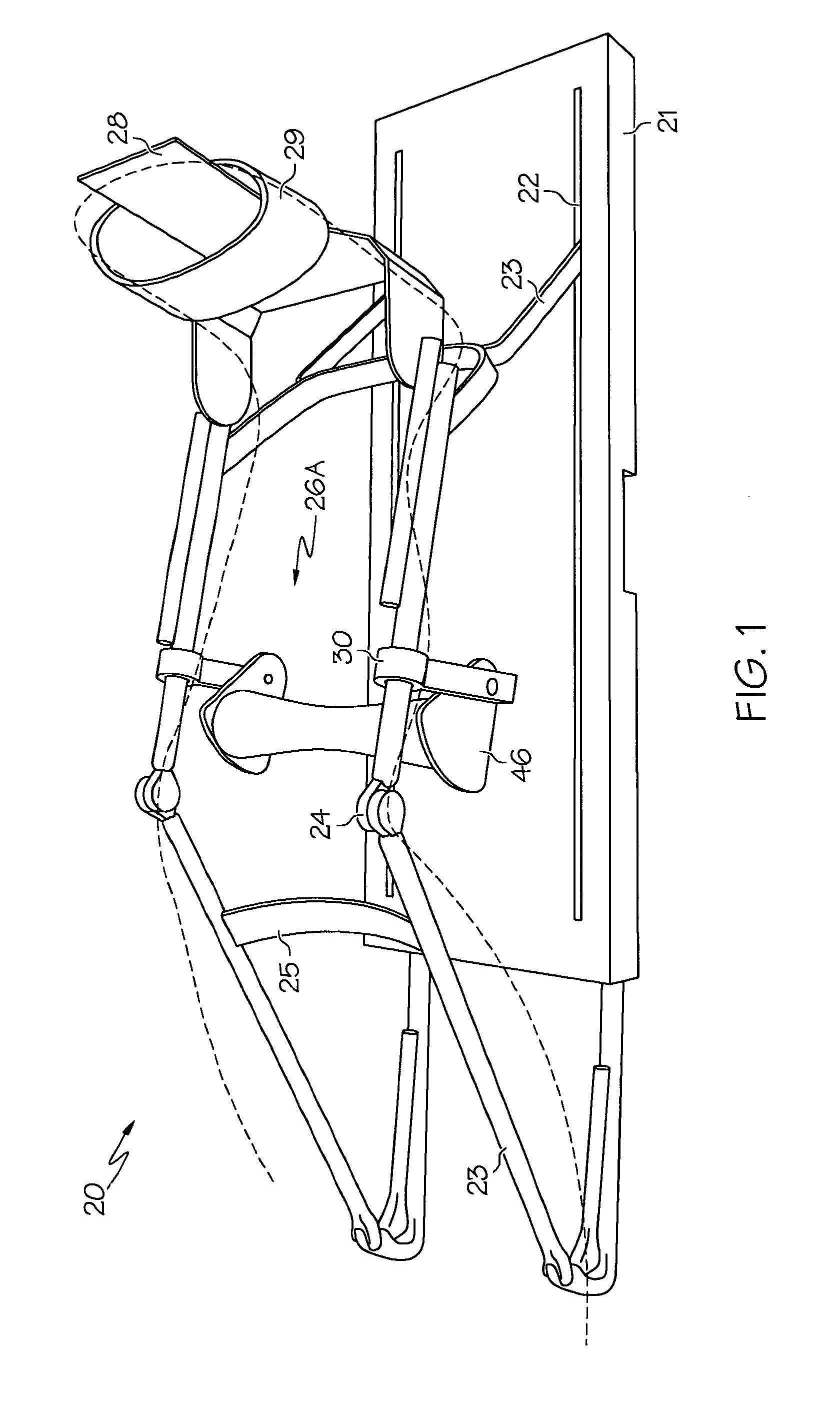
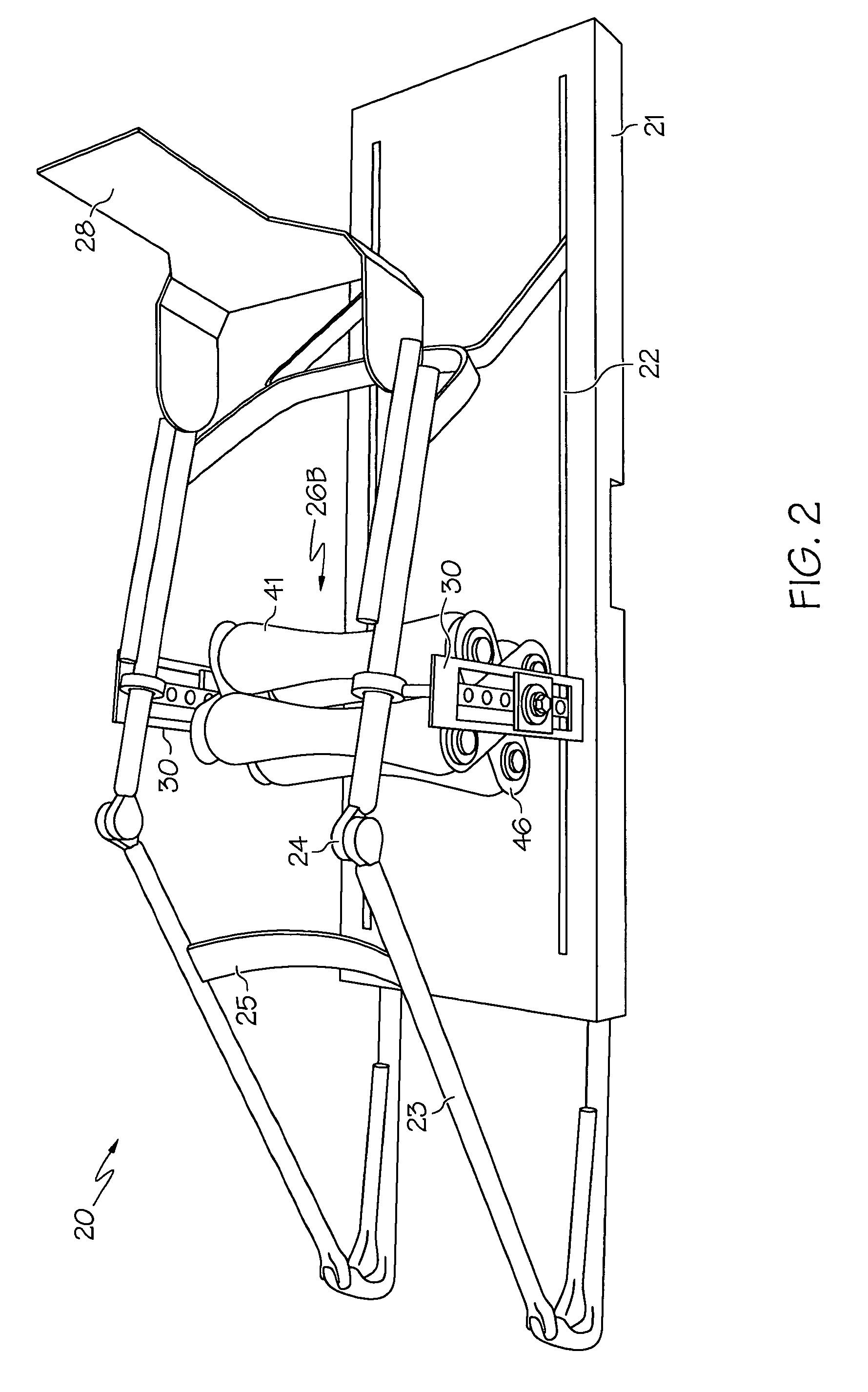
Apparatus and Method for Imaging the Relative Motion of Skeletal Segments
InactiveUS20080125678A1Minimal invasivenessAvoid necessityImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsCorrelation function
Apparatus provided for the measurement of skeletal joint motion in a subject which comprises a passive motion device, an imaging device and a processing system incorporating a means for real time digital sampling of images of moving joints, means for recognising templates attributed to individual bones and tracking these automatically using cross-correlation functions and means for geometric transformation of the positional data to graphically display their relative motion over time. Also provided is a method for the automated measurement of the relative motion of skeletal structures in vivo using such apparatus and a method for the diagnosis of a pseudoarthrosis in a subject which comprises the use of such apparatus.
Owner:AECC ENTERPRISES
Four-foot-swing wall-climbing robot with driven waist joint
The invention discloses a four-foot-swing wall-climbing robot with a driven waist joint. The wall-climbing robot comprises four telescopic foot modules, an upper body part, a lower body part and a tail module; the telescopic foot modules are active motion modules and each composed of a steering engine and a transmission mechanism, each transmission mechanism is formed by bevel gears and a crank slide bar mechanism to transmit power of the corresponding steering engine, and then four telescopic legs can do linearly telescopic motion. The four telescopic foot modules are connected with the left side and the right side of the upper body part and the left side and the right side of the lower body part respectively. The upper body part and the lower body part are internally provided with cavities used for installing a control panel and a battery and are connected through the waist joint. The waist joint does passive motion, and the robot can climb a wall or walk through active motion of telescopic feet of skew symmetry. The wall-climbing robot has the advantages that the overall structure is compact and flat and high in stability; the ratio of the upper body to the lower body can be adjusted according to optimization needs; changes of mass center motion tracks and foot end force of climbing animals can be fitted, and the motion speed of the four-foot-swing wall-climbing robot with the driven waist joint is effectively increased.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Vibration/motion training device for simulating weightless tail suspended rats
InactiveCN101558991AEasy to placeEasy to fixDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMotor speedSimulated weightlessness
The invention discloses a tail-suspended rat fixing device, which comprises a rat fixing box, a tail suspension device and an angle adjusting device. The invention also provides a tail-suspended rat vibration / motion training device, which comprises a motion track limit device, a vibration training device, an active motion training device, a passive motion training device, a rat hind limb fixing device and a height adjusting device. The invention also provides a vibration / motion control device, which comprises a display screen, a key, a direct-current motor speed adjusting knob, a power supply adapter, a switch, a USB interface and an internal circuit, wherein the direct-current motor speed adjusting knob is used for adjusting the rotating speed of a direct-current motor during passive motion training; the power supply adapter and the switch are used for supplying power for the whole device; the USB interface is used for carrying out function expansion later; and the internal circuit is used for controlling and quantifying rat vibration / motion training and supplying power. The device can keep the same tail-suspended height, can carry out equal-length and equal-tension motion by combining vibration and motion training, and simultaneously achieves training quantification and control.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
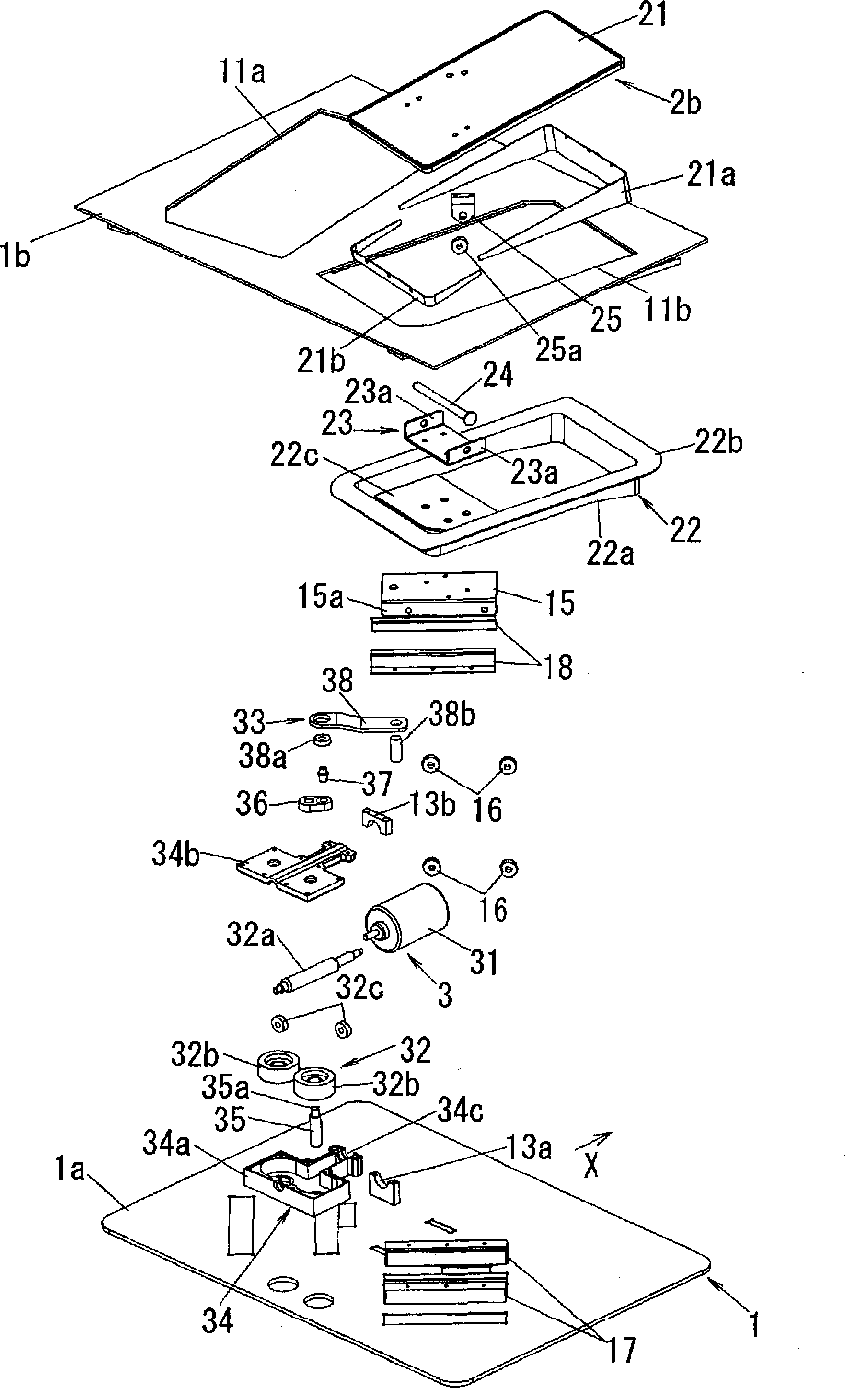
Jaw exerciser
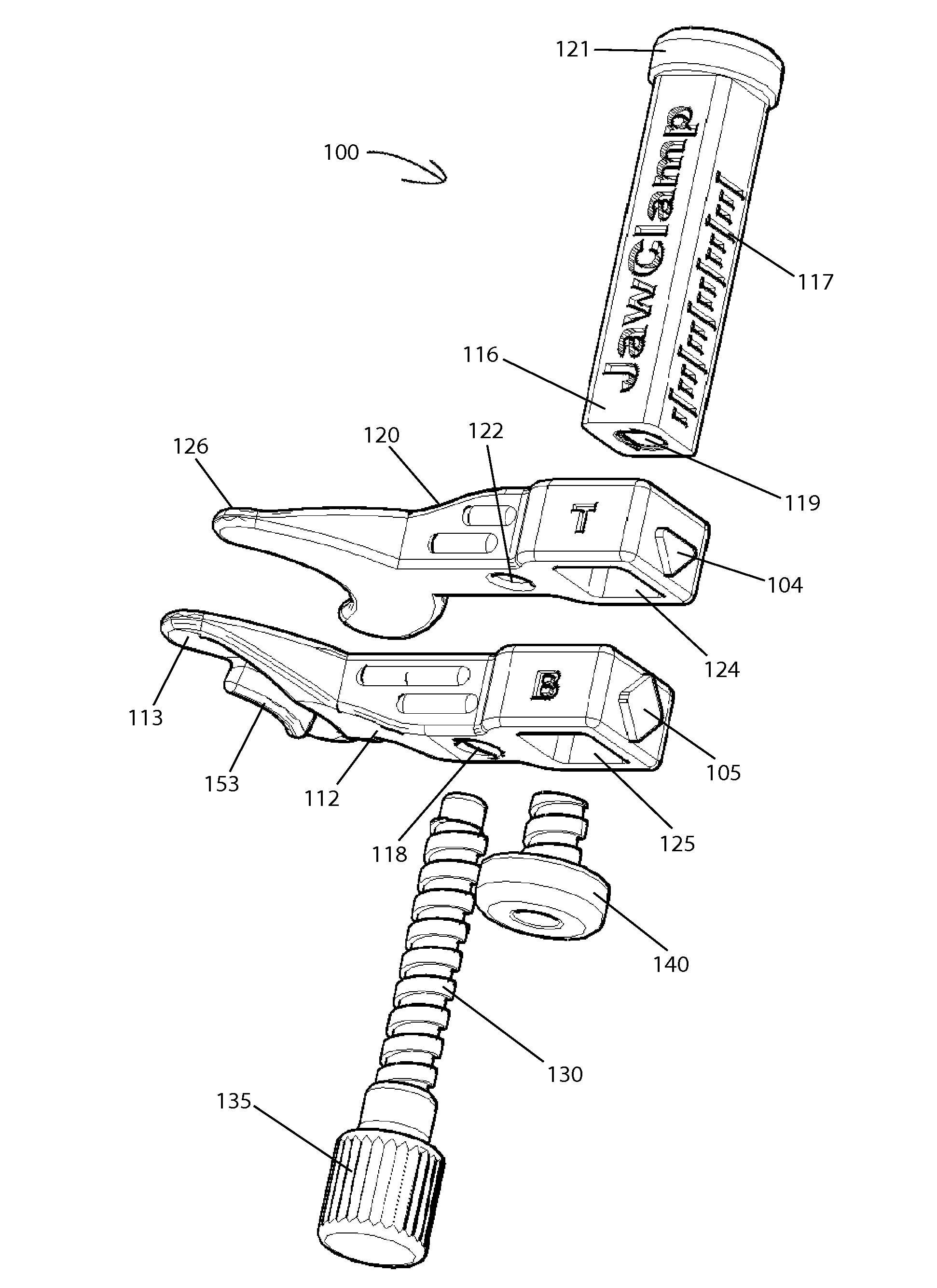
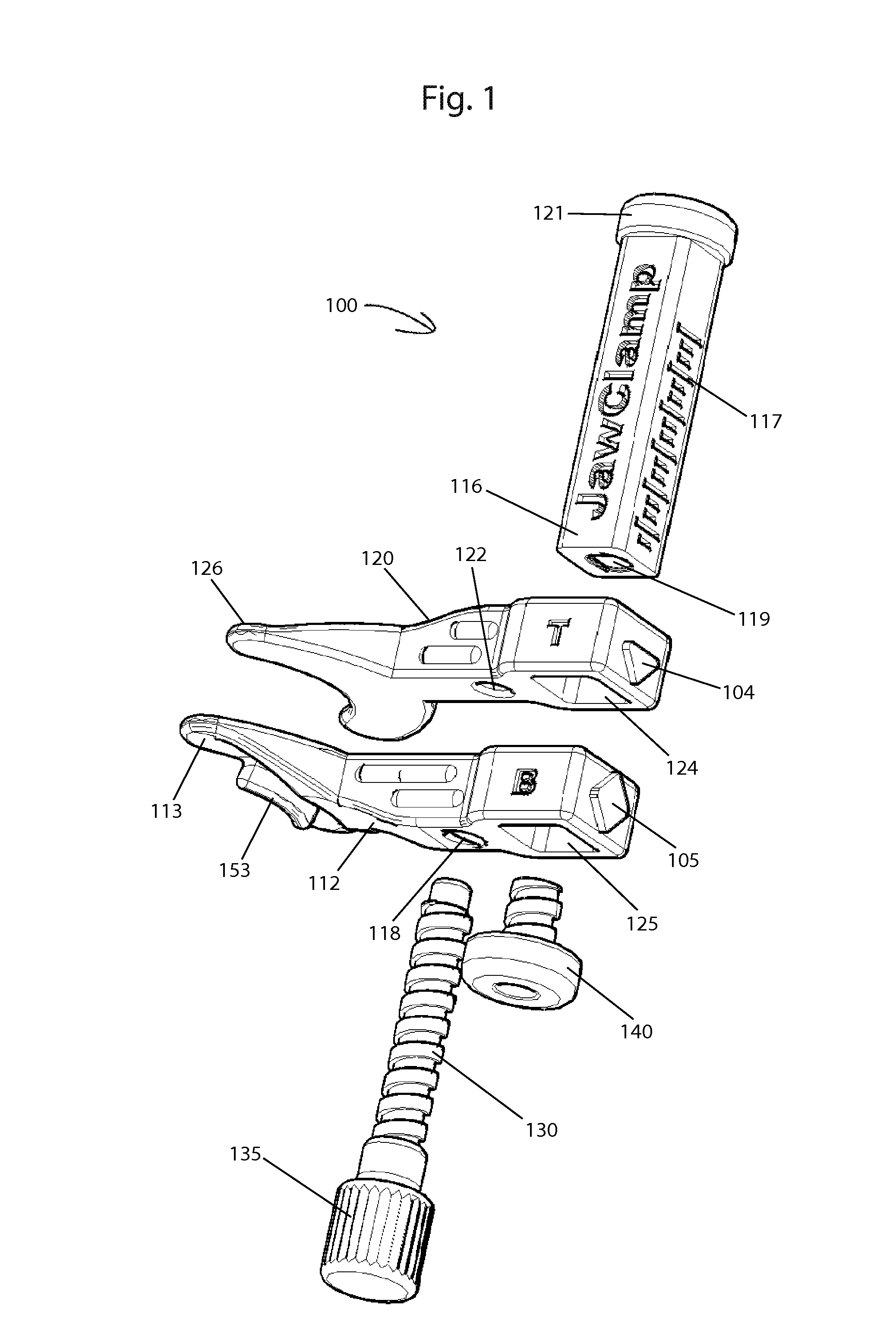
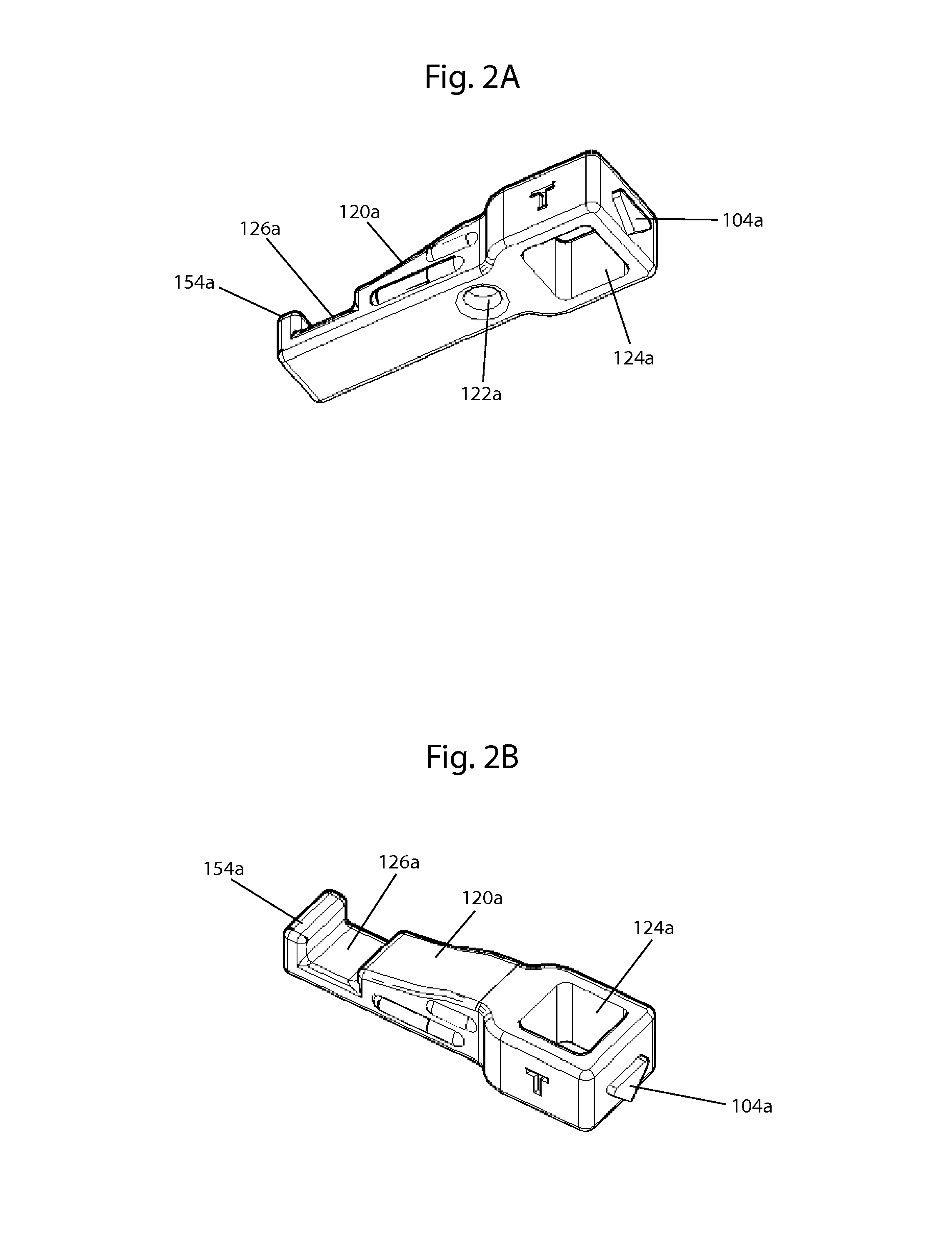
ActiveUS20160101315A1Easy to carryQuick assemblyGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesIliac screwPassive motion
A jaw exerciser for providing passive motion therapy such as that used to treat trismus is provided. The jaw exerciser has a user-adjustable distance between the upper jaw support and the lower jaw support. The jaw exerciser includes a shaft, a first or upper jaw support frame including a first jaw support, a second or lower jaw support frame including a second jaw support, a distance adjuster which may be in the form of a jack screw for manually adjusting the distance between the first jaw support and the second jaw support, and a retaining screw. The jack screw may be received by the second or lower jaw support frame and engage the first or upper jaw support frame. Removable bite pads may optionally be provided for installing on the first jaw support and the second jaw support.
Owner:GARAY ARAUZ ALEXIS
Intelligent limb rehabilitation training device and training method
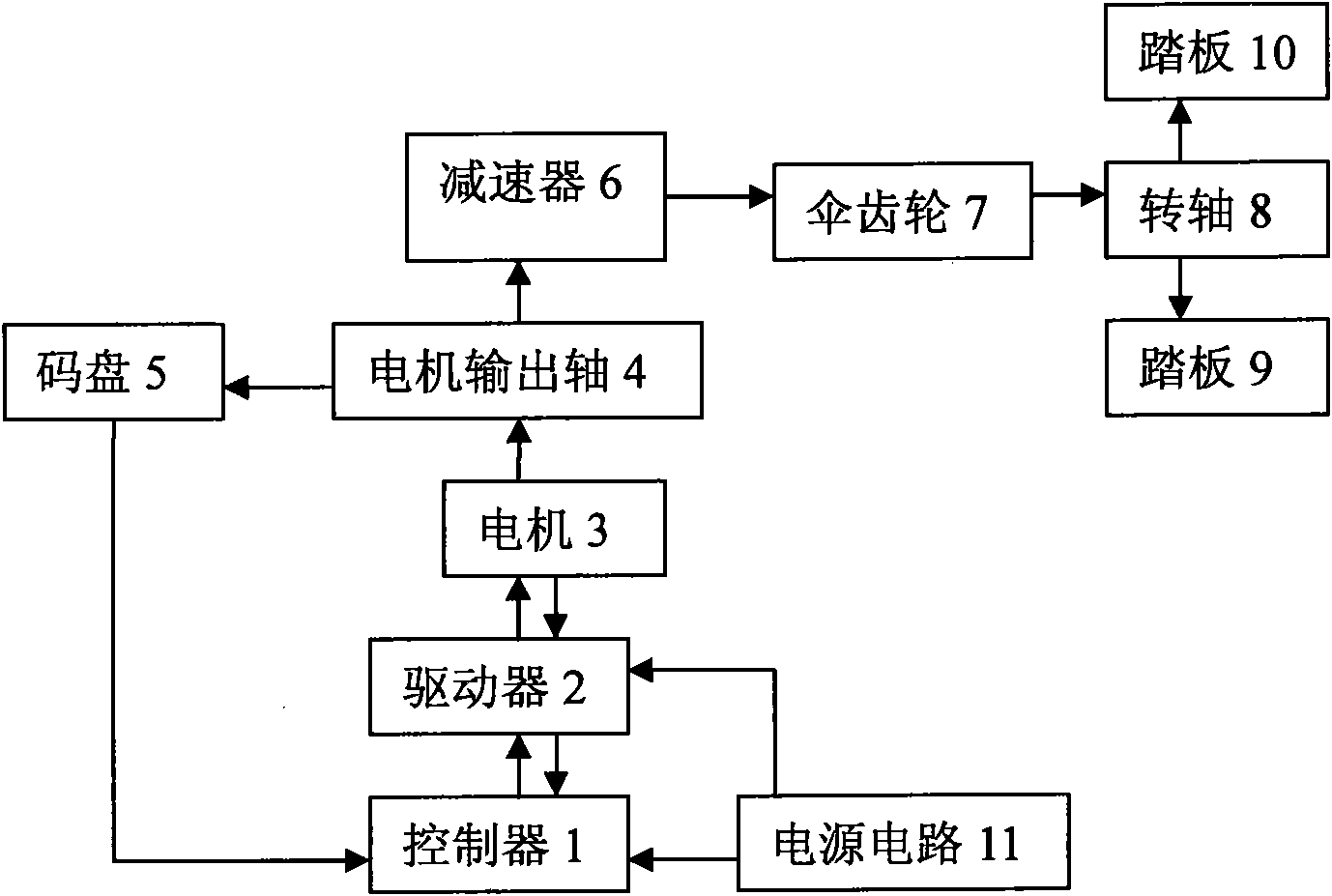
ActiveCN101816609ARehabilitation is goodScientific and effective rehabilitation trainingChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesMotion parameterEngineering
The invention discloses an intelligent limb rehabilitation training device capable of performing rehabilitation training on limbs automatically and a training method. In the intelligent limb rehabilitation training device, the output end of a controller is connected with the input end of the a driver through a serial port; the output end of the driver is connected with a power supply of a motor; the other end of a motor output shaft is connected with a code disc; the output of the code disc is connected with the controller; and the output of a power circuit is connected with the controller and the driver respectively. Three training modes of active motion, passive motion and spasmodic muscle remission can be automatically performed under set programs; and the motion parameters can be adjusted according to the actual condition of a patient so as to help the patient to perform the best scientific and effective training and make the motor function of the patient recover better.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Exercise stand and active/passive pedalling device
InactiveUS20080221492A1Simple processPromote circulationChiropractic devicesEye exercisersTherapeutic exerciseWheelchair user
An active and passive motion device for therapeutic exercise of upper and lower extremities, in the form of a pedaling device for therapy of leg and associated articulations. The device comprises a combination exercise stand and active / passive pedaling device that enables users with and / or without motor skills to remain generally stationary and seated in a chair or wheel chair and use their legs to actively pedal the device or have their legs moved by the pedaling device. Disclosed in an aspect thereof is an improved ankle strap sandal for use in such therapy. A lift enables the pedaling device to be vertically positioned relative to the wheelchair user when atop the support stand.
Owner:ELCHONEN AVRAHM
Touch pad, led motion detector head
InactiveUS6472997B2Controlled heatingControl to motionElectric/electromagnetic visible signallingIdentification meansMotion detectorMembrane switch
Owner:COLEMAN CABLE INC
Method for man hand, upper limb and lower limb passive exercising
The invention provides a method for the passive motion of human hand, upper limb and lower limb. The hand passive motion is to put air bag below palm and make hand on it open and contract passively by aerating and degassing the air bad. The extension of upper limb and lower limb is to select proper extension points on upper and lower limbs, and realizes passive exercises around shoulder joint or hip joint through extension rope's motion. The invention can increase exercise amount for hand, upper limb and lower limb, especially suitable for patients with cerebral thrombus. It can help them to recovery and prevent further limb atrophy.
Owner:朱铁成
Mobile support device for computer or display device
InactiveCN101382230AReduce health risksDigital data processing detailsStands/trestlesDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:耿乐
Mouse path exercising model and intelligent action inspecting system
InactiveCN1817327AInconsistent dwell timeOvercoming the presence of rats that must be transported from the isolation area to the training area via a conveyor beltEducational modelsVeterinary instrumentsData acquisitionClosed loop
A mouse's path training model and its intelligent behavior detection system are disclosed. A circular dark box type labyrinth is used as the behavior data acquiring unit. The mouse to be tested passes through a tubular channel with adjustable one-way gates along a pointed path and closed loop for performing the cyclic training. The signals about the active movement and passive movement caused by electric shock are acquired and processed by the data processing control unit. Said signals are transmitted via PCI bus to the Access database in control system, and then processed by the statistical software package, so controlling and monitoring the behavior of mouse at any time.
Owner:SHENYANG MEDICAL COLLEGE
Positive/passive exercise training device for simulating weightless tail suspended rats
InactiveCN101283675AEasy to controlConsistent trajectoryTaming and training devicesPassive exercisesSimulated weightlessness
The invention provides a tail-suspended rat fixing device which comprises a tail suspension device, a rat fixing box for storing the head and body of a rat, a body fixing device for fixing the body of a rat, an angle control device for controlling the included angle between the rat fixing box and a pedestal of the tail-suspended rat fixing device. The invention also provides a tail-suspended rat active / passive motion training device which comprises a rat hind limb motion device for training active / passive motion of the hind limb of a rat and further comprises a motion orbit control device for limiting the motion range of the hind limb of a rat, an active motion training device for training the active motion of the hind limb of a rat, and a passive motion training device for training the passive motion of the hind limb of a rat. The invention realizes the motion training and simultaneously keeps the tail suspension angle unchanged, that is, keeps the rat in a simulated weightlessness state.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Passive motion body articulating apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060161203A1Increase patternEase of controlChiropractic devicesEye exercisersEngineeringActuator
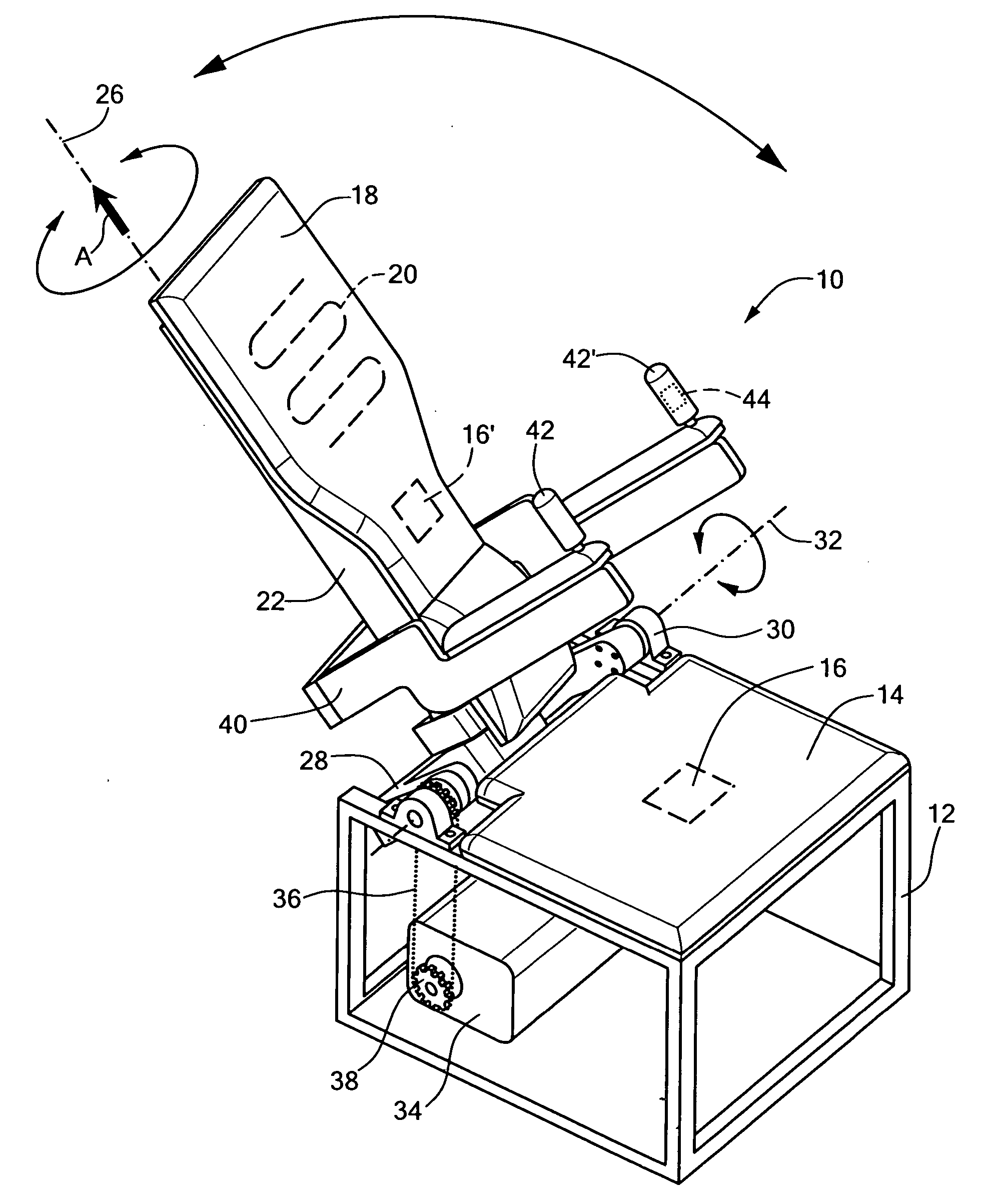
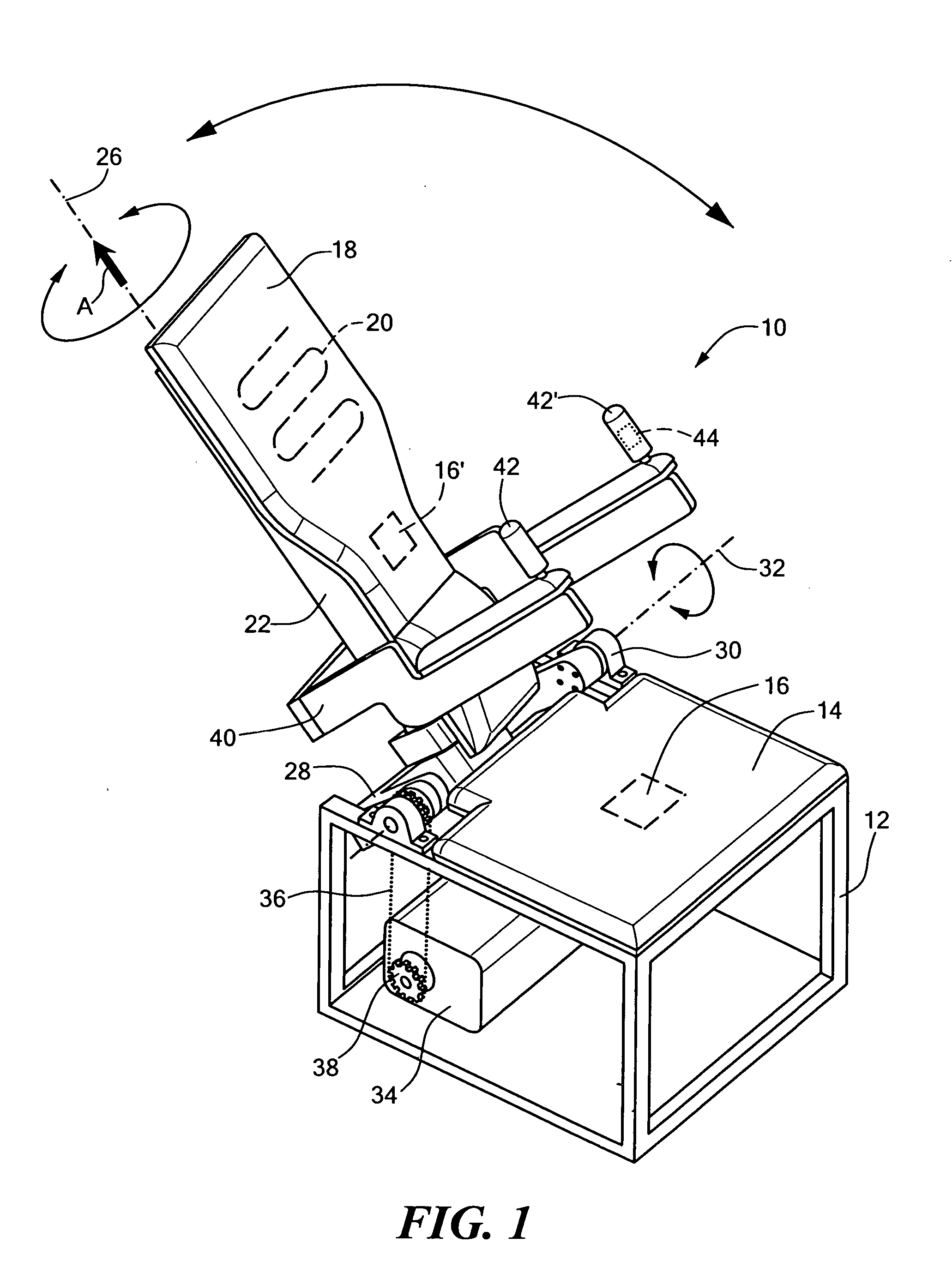
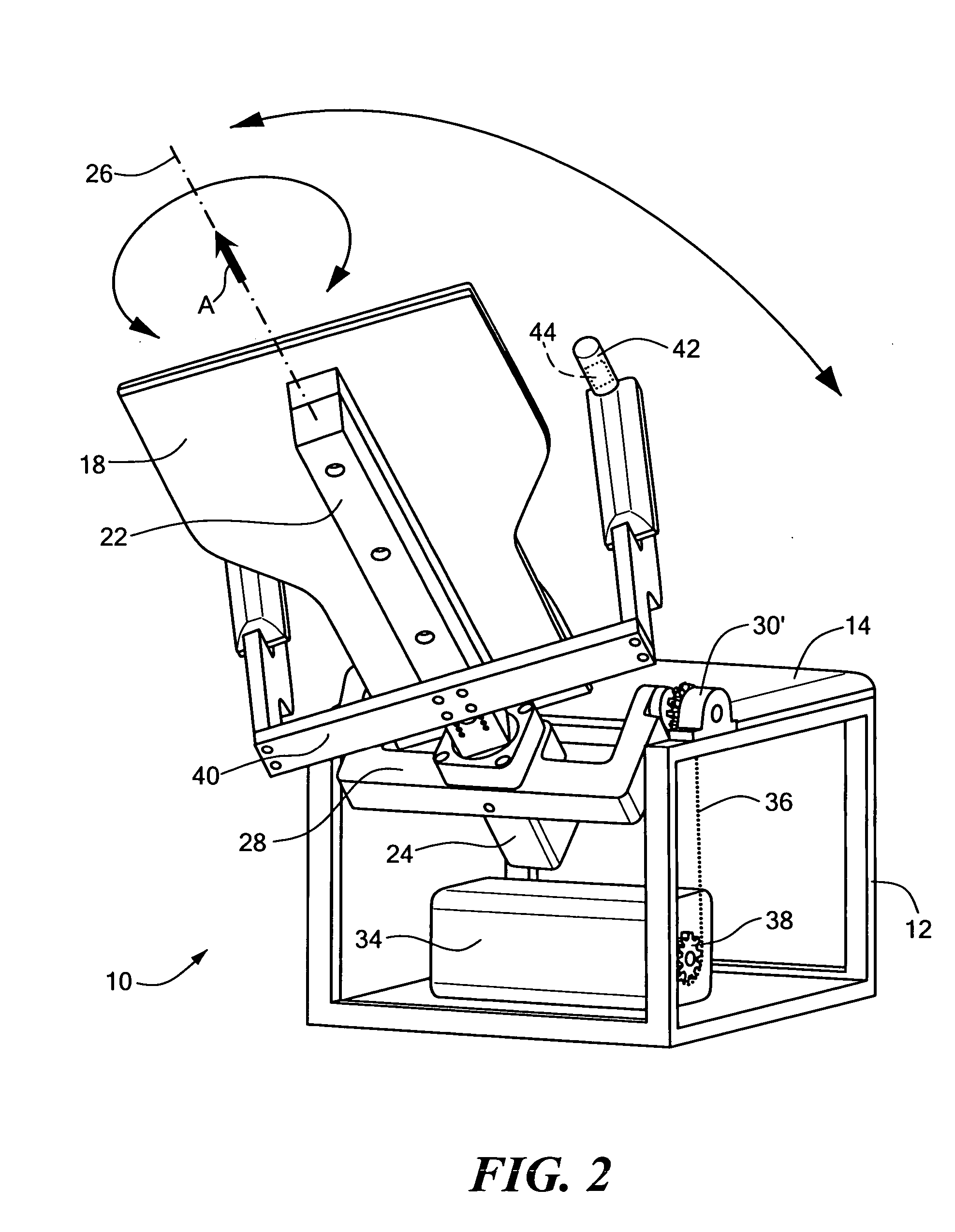
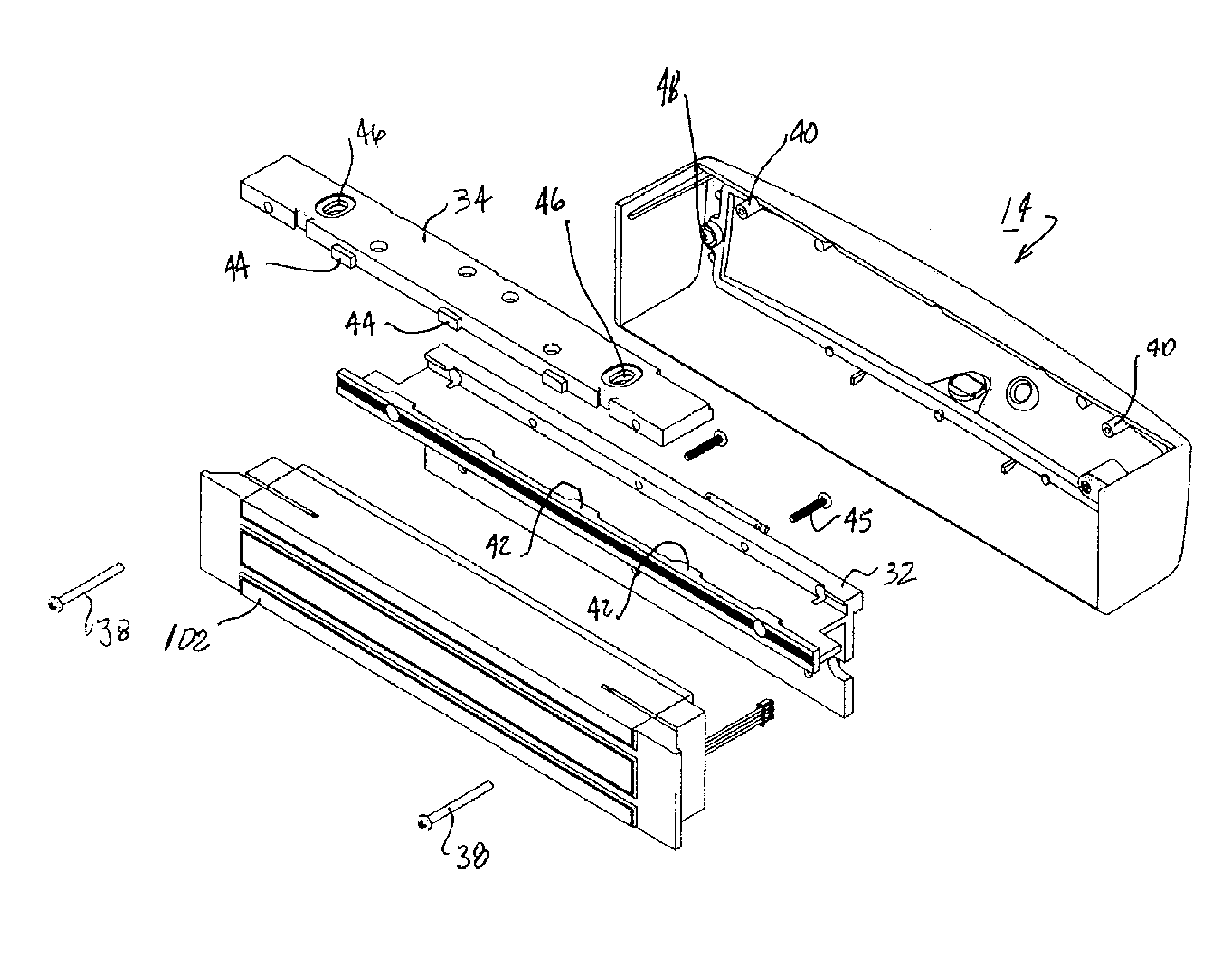
A physical therapy chair having a first support element defining a seating surface, a second support element defining a backrest, wherein the second support element is pivotable with respect to the first support element and rotatable with respect to the first support element. The chair further including an arm support element coupled to the second support element, as well as a first motion actuator coupled to the second support element to rotate the second support element with respect to the first support element, and a second motion actuator coupled to the second support to pivot the second support element with respect to the first support element. The chair also includes a first controller that allows a user to modify an operational characteristic of the first motion actuator and a second controller that allows a user to modify an operational characteristic of the second motion actuator.
Owner:TOTAL MOTION DEV
Access Control Devices of the Electromagnetic Lock Module Type
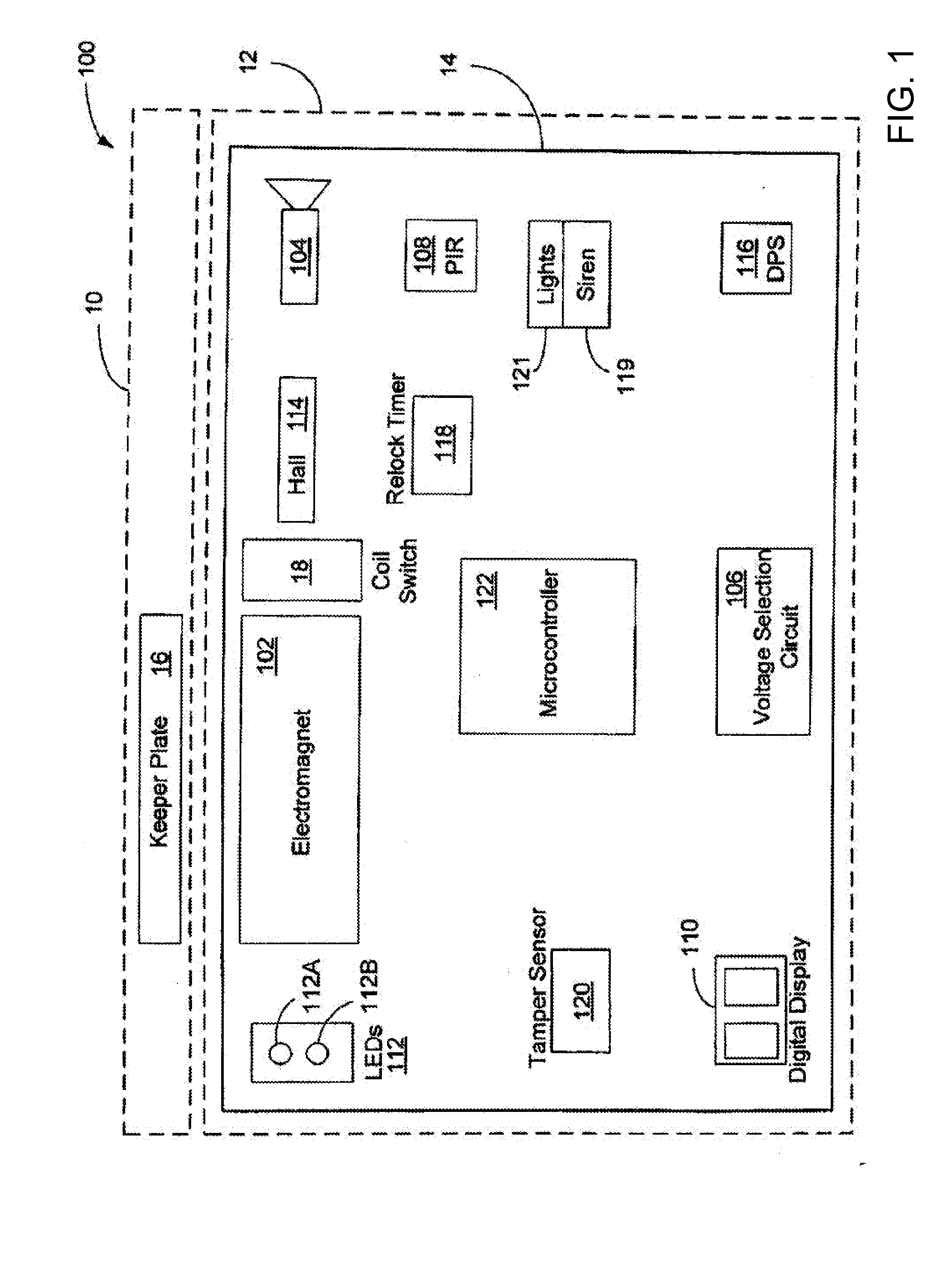
ActiveUS20130127260A1Minimize voltage dropReduce clamping forceDc network circuit arrangementsBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsCCTV - Closed circuit televisionElectromagnetic lock
An access control device including an electromagnetic lock module for selectively locking and unlocking a door in a door frame is provided. The access control device provides a lower profiled electromagnetic lock module to improve the aesthetics and functionality of the module, supports and integrates modern accessories such as CCTV, CCD cameras, passive motion detection with automatic background correction, digital notification display, automatic source voltage selection, door and lock status indicators, and ease of installation. The present invention further provides components and circuitry to enable connection of the electromagnetic control module to 12 or 24 volts DC or to an unfiltered rectified AC power supply.
Owner:HANCHETT ENTRY SYST
Passive motion-type exercise assistance device
InactiveCN101516315APromote sugar intakeSymptoms improvedGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesFoot supportsEngineering
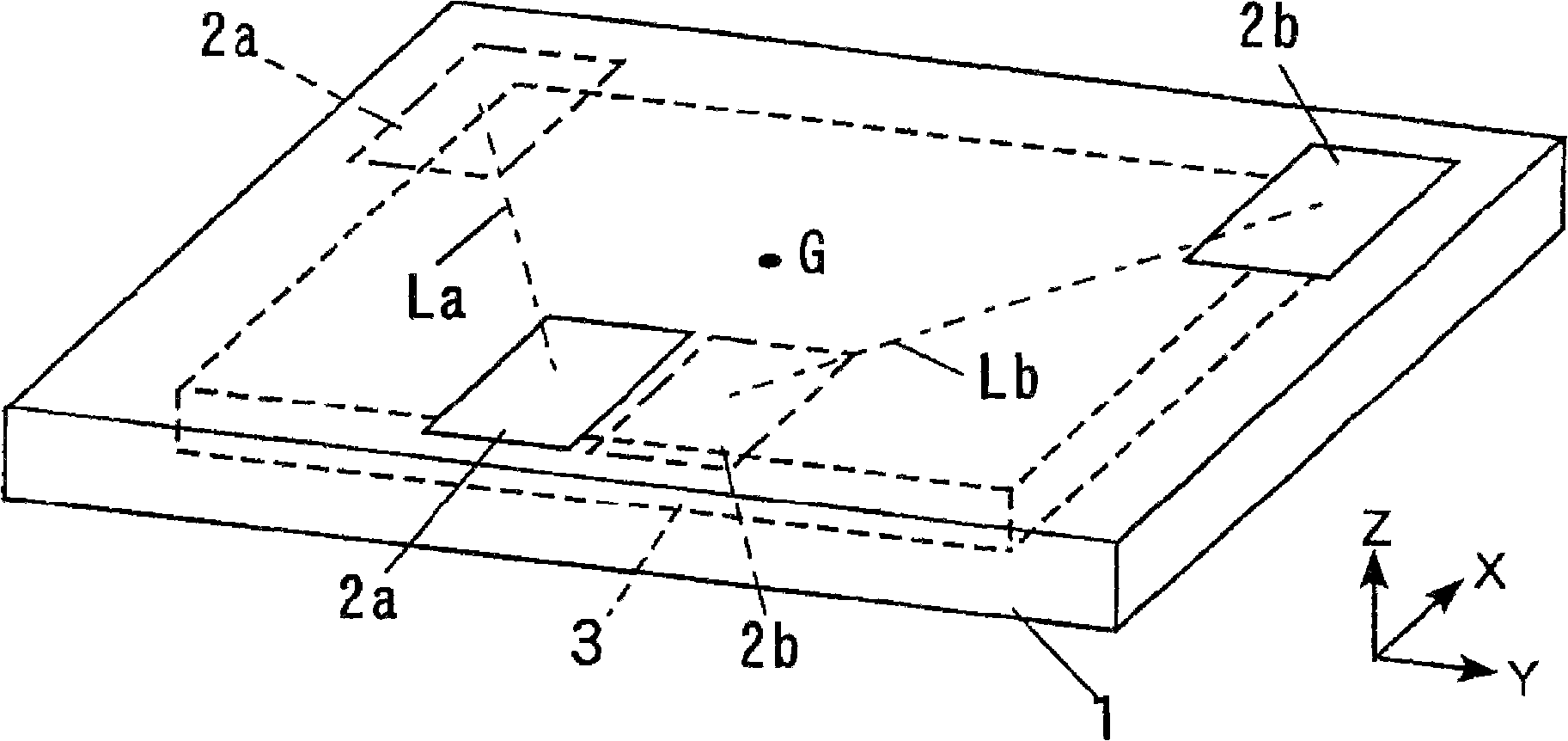
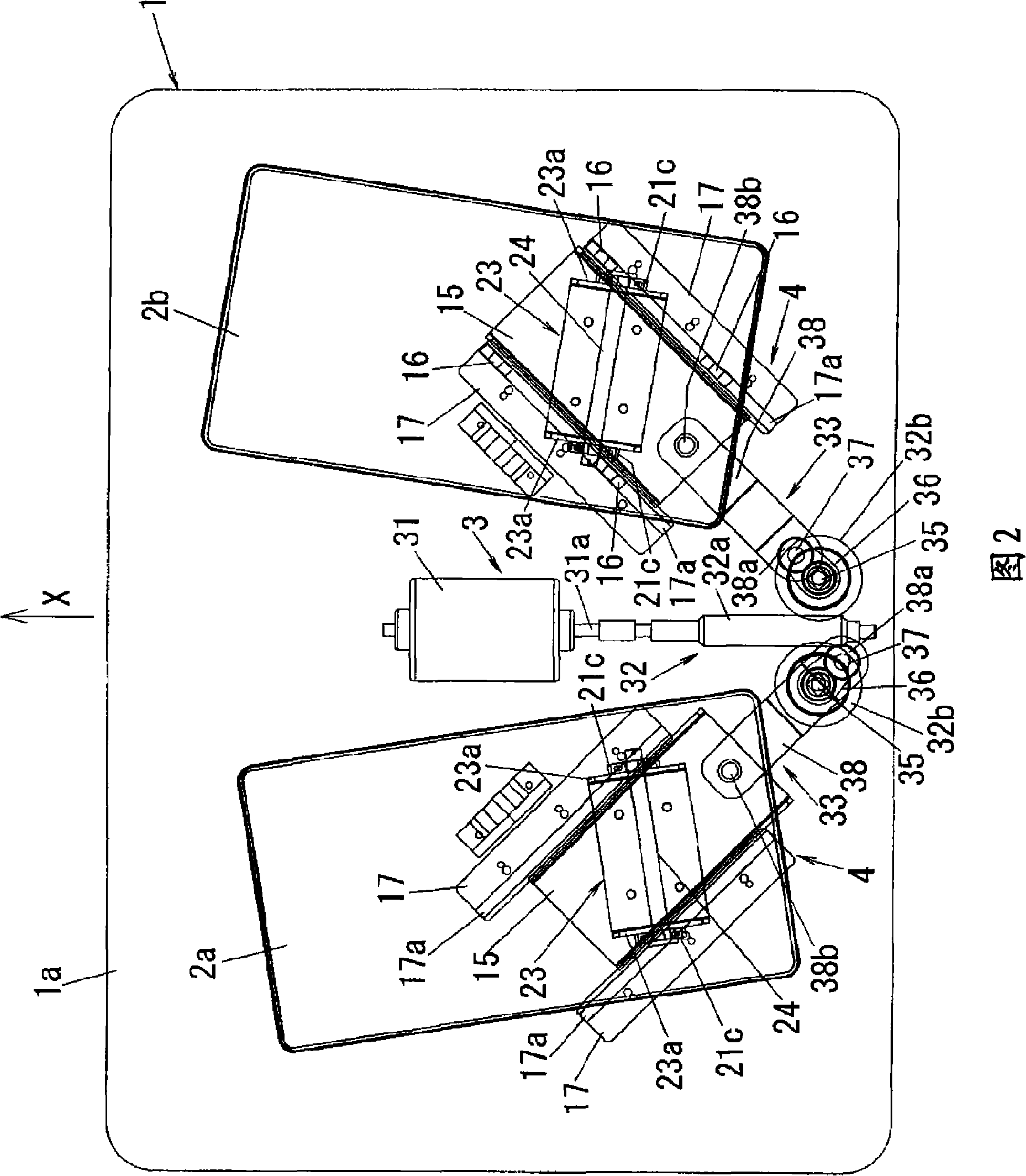
A passive motion-type exercise assistance device in which a left foot support table (2a) and right foot support table (2b), on which left and right feet of the user are respectively placed, are provided on the upper surface of a housing (1) installed on a floor. The left and right foot support tables (2a, 2b) are associated with each other by a drive device (3) and positionally moved. As the drive device (3) changes the positions in the front-rear direction of the left and right foot support tables (2a, 2b), it reciprocates the support tables (2a, 2b) so that their positions in the left-right direction are changed and, also, it moves the support tables (2a, 2b) so that the distance between them in the left-right direction at the front end positions in the movement loci (La, Lb) of representative points of the support tables (2a, 2b) is greater than the distance in the left-right direction of the points at their rear end positions.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
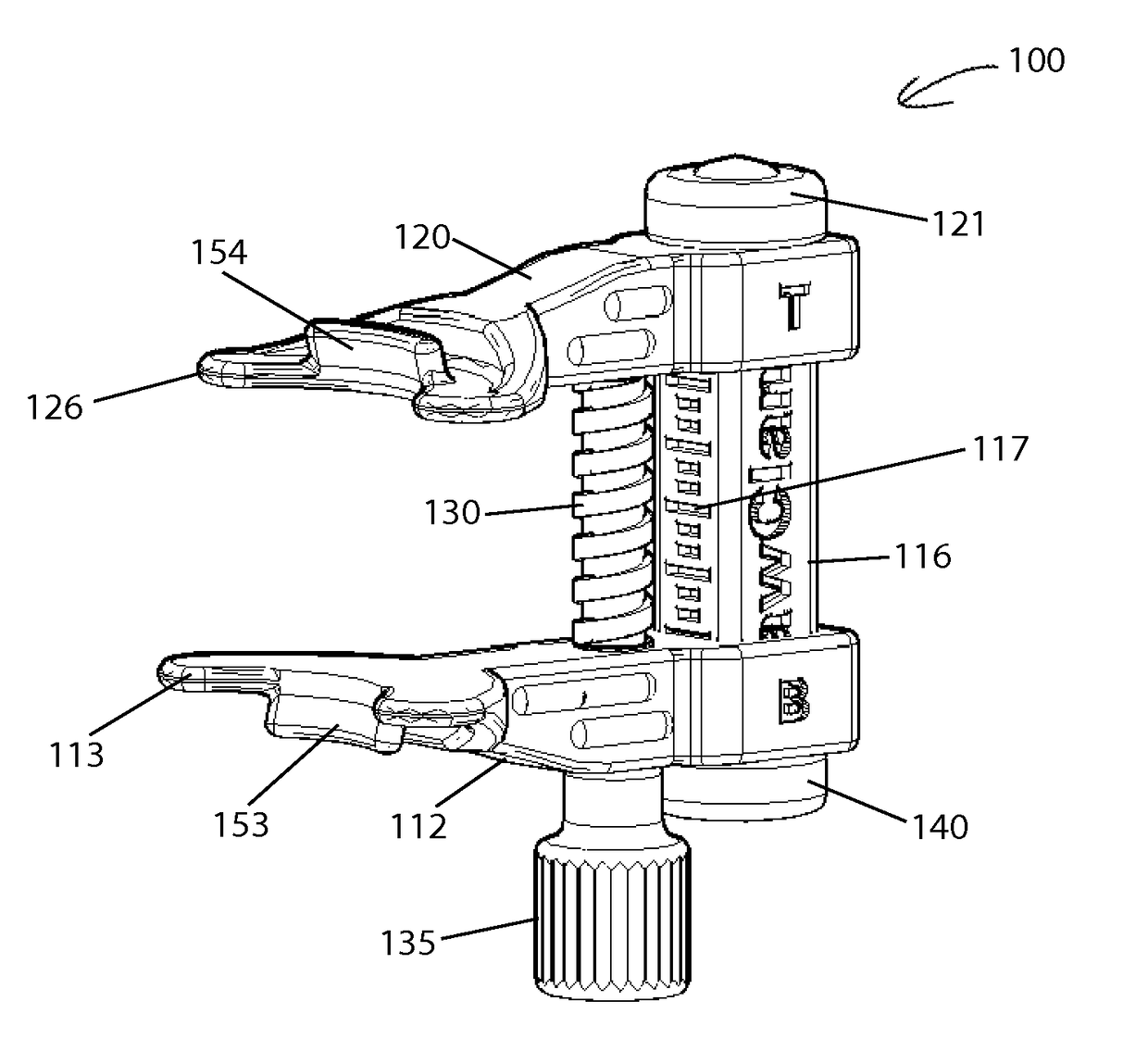
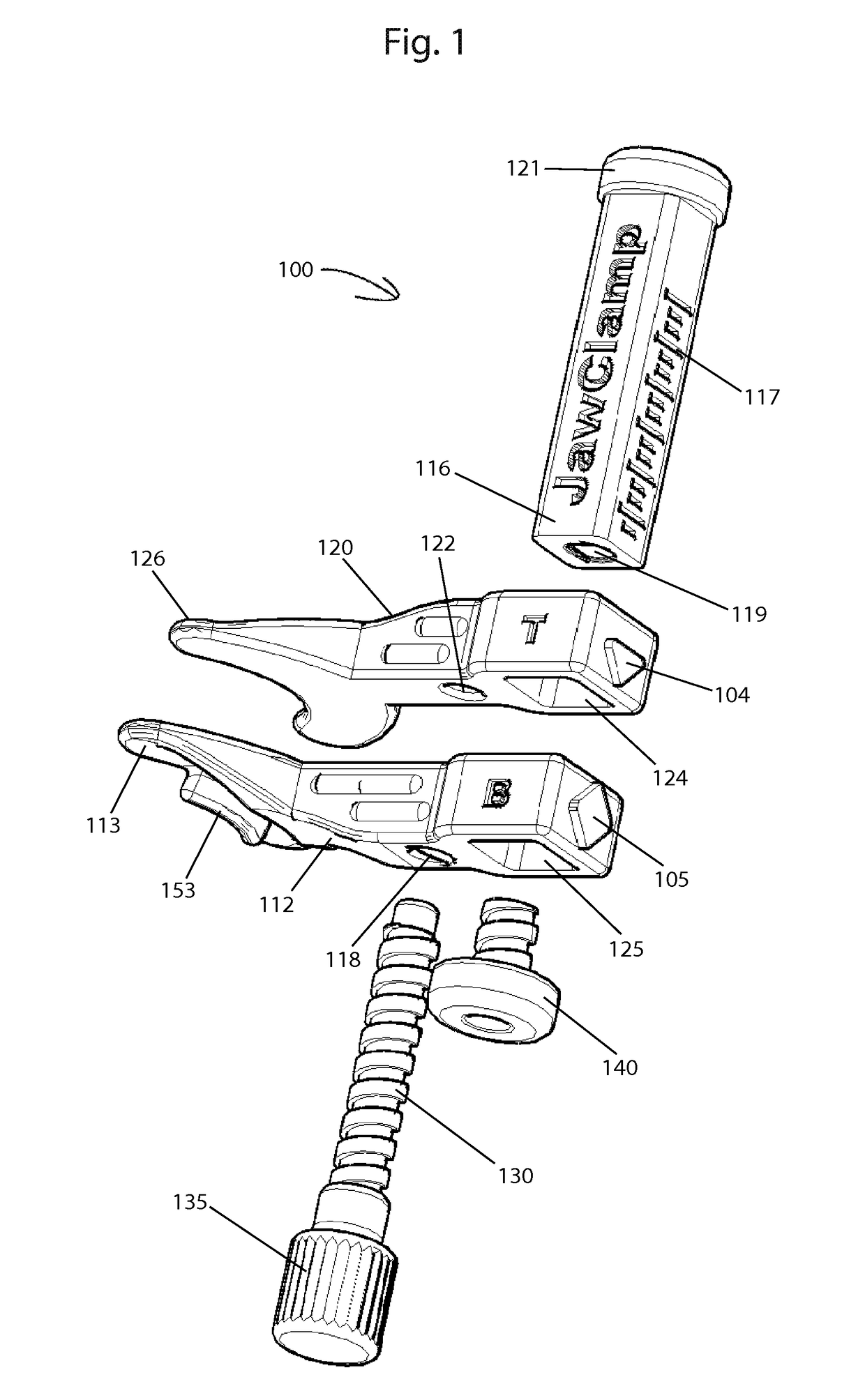
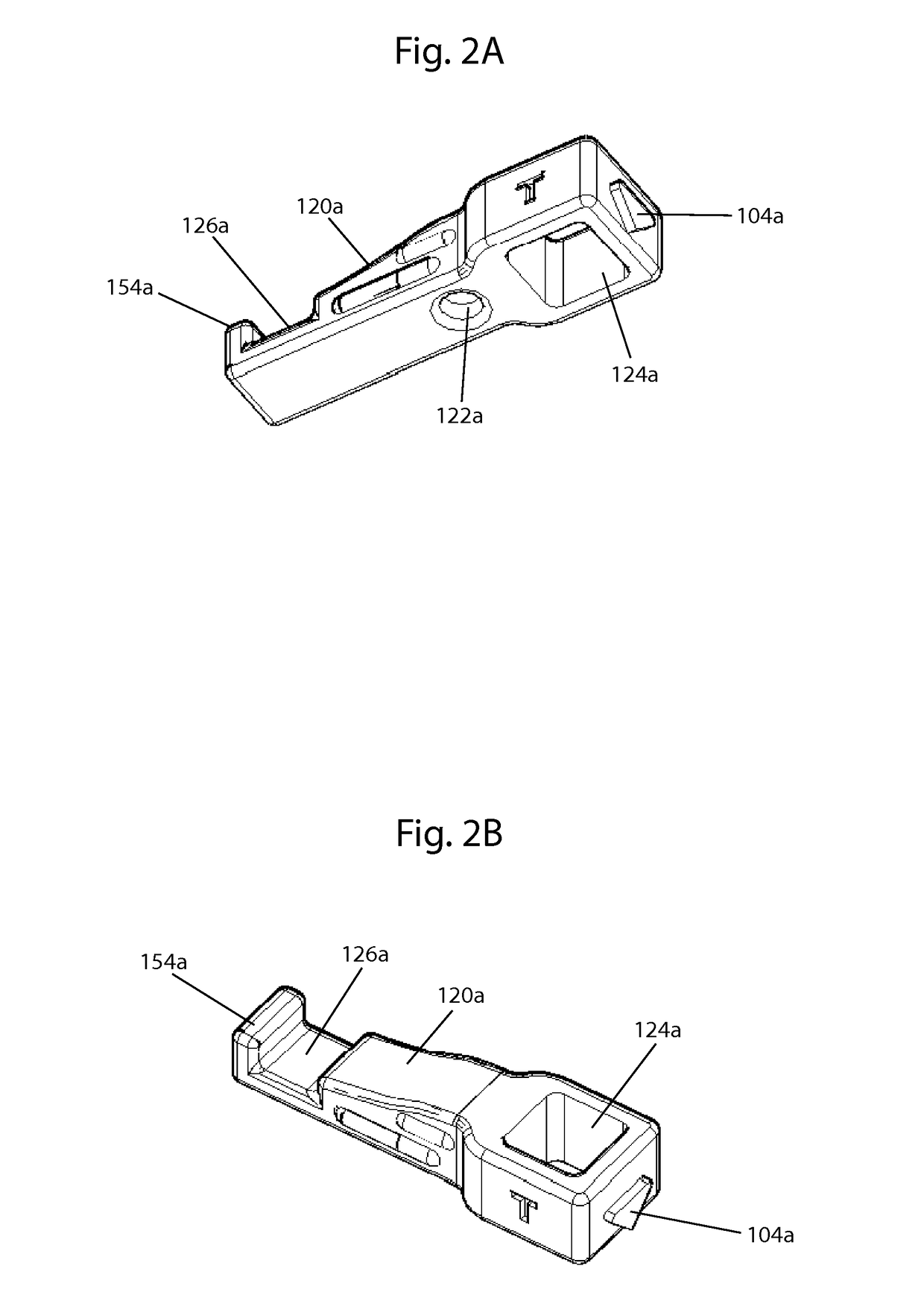
Jaw exerciser
ActiveUS9867753B2Easy to carryQuick assemblyGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesJackscrewPassive motion
A jaw exerciser for providing passive motion therapy such as that used to treat trismus is provided. The jaw exerciser has a user-adjustable distance between the upper jaw support and the lower jaw support. The jaw exerciser includes a shaft, a first or upper jaw support frame including a first jaw support, a second or lower jaw support frame including a second jaw support, a distance adjuster which may be in the form of a jack screw for manually adjusting the distance between the first jaw support and the second jaw support, and a retaining screw. The jack screw may be received by the second or lower jaw support frame and engage the first or upper jaw support frame. Removable bite pads may optionally be provided for installing on the first jaw support and the second jaw support.
Owner:GARAY ARAUZ ALEXIS
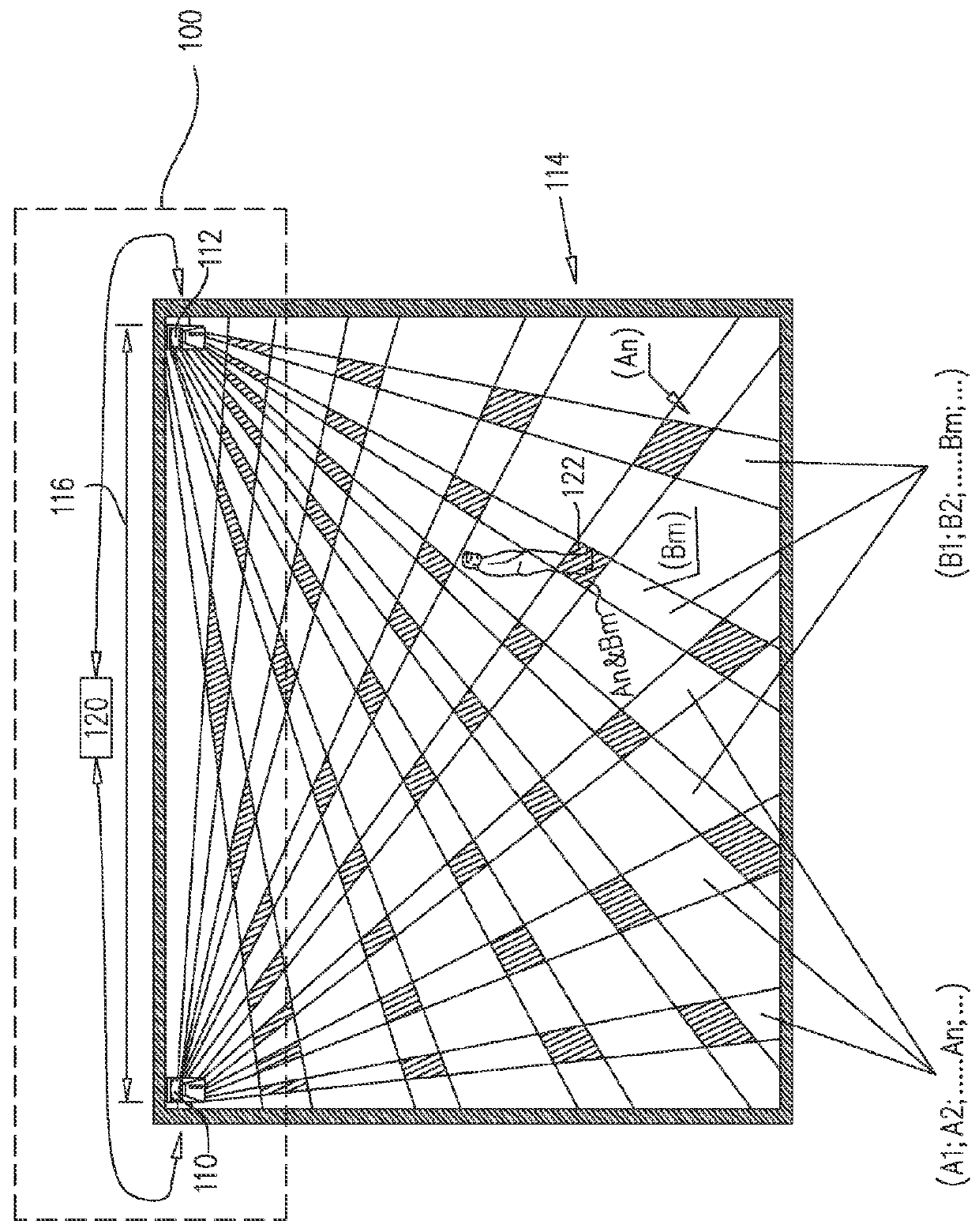
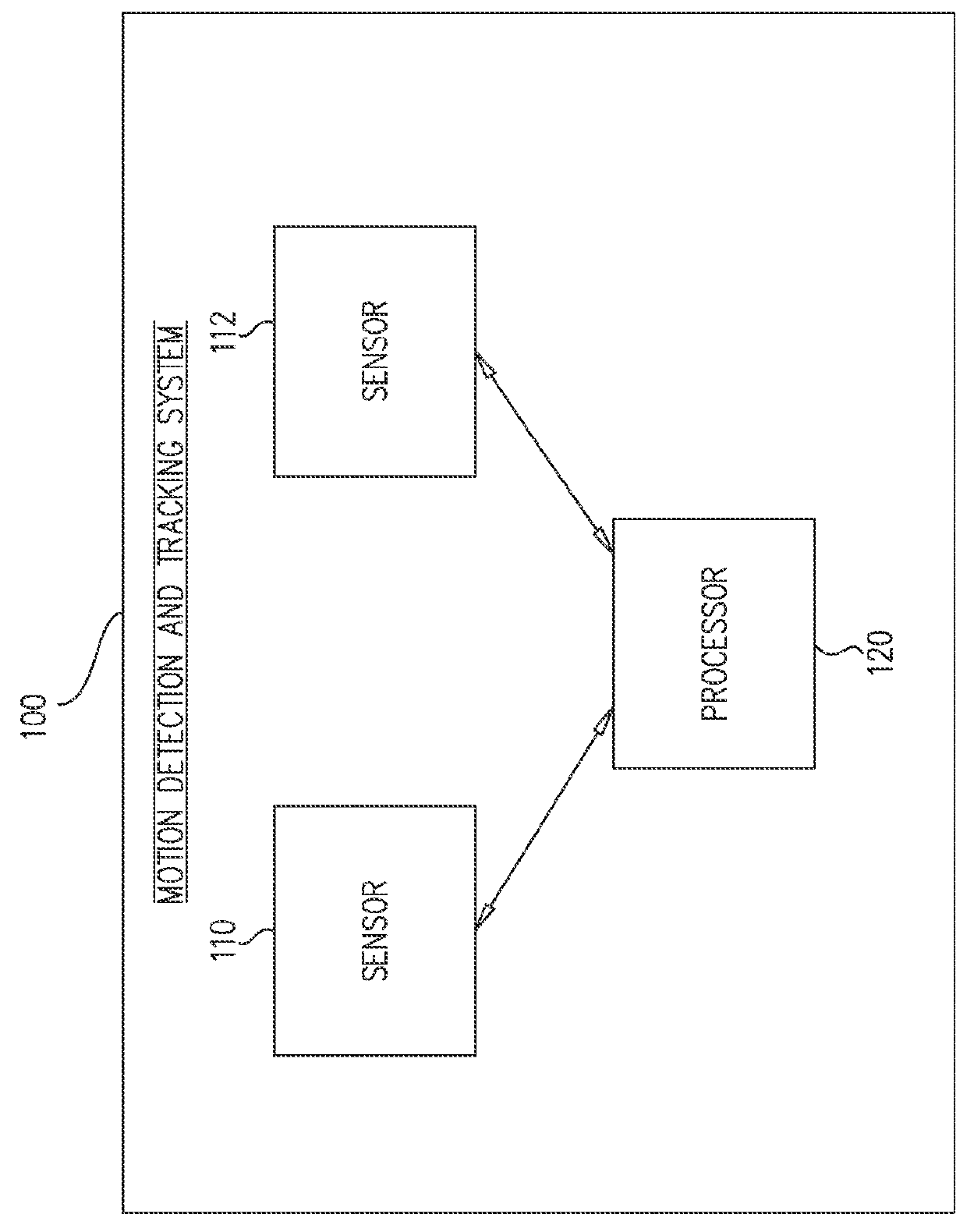
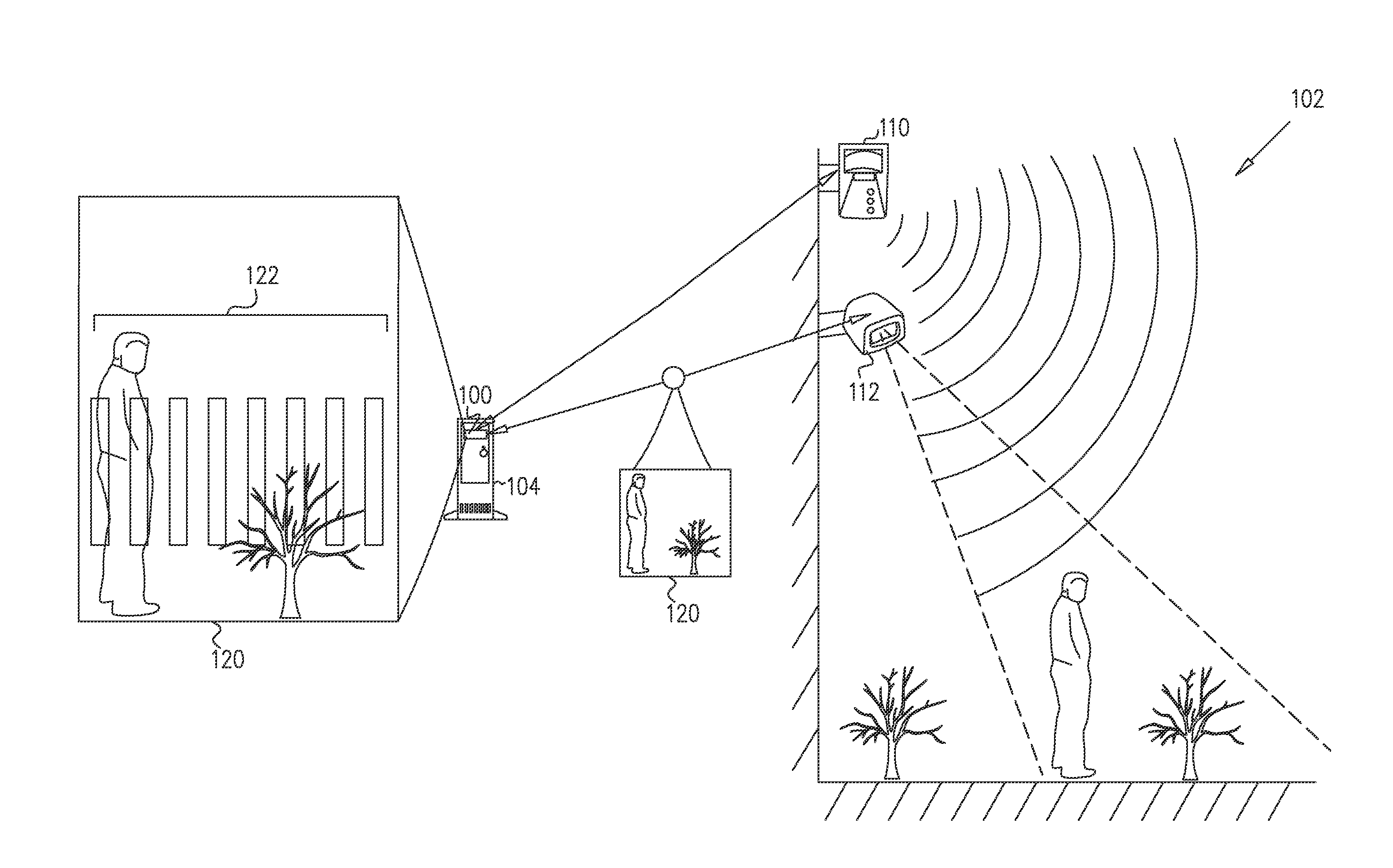
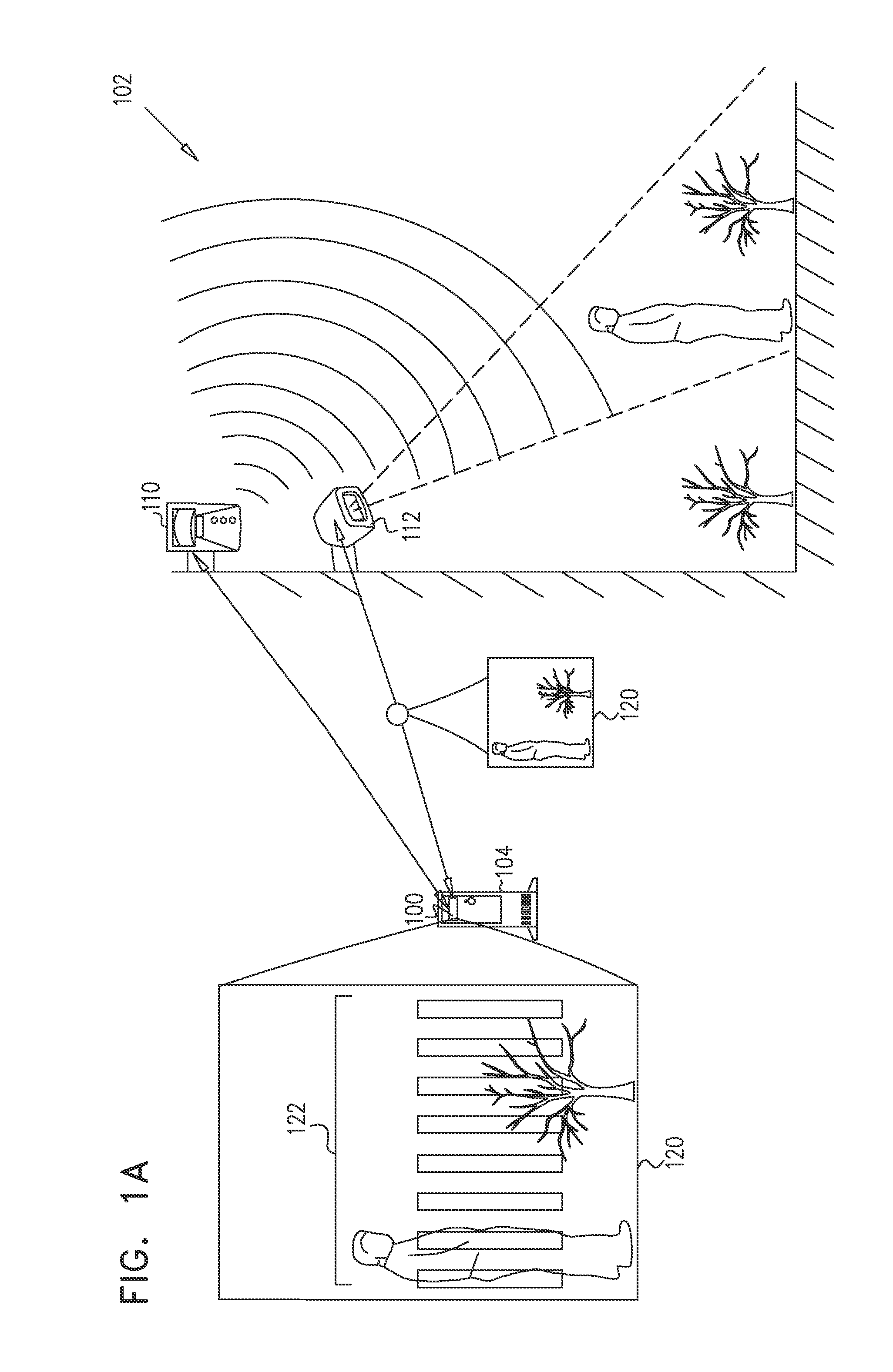
Method and system for passive tracking of moving objects
A system for detecting and tracking motion in a given area, including a first passive motion detection sensor operable for passively detecting motion in any of a first multiplicity of detection zones and, responsive thereto, for providing a first detection output signal including an indication of a first detection zone in which the motion was detected, a second passive motion detection sensor operable for passively detecting motion in any of a second multiplicity of detection zones, each of the second multiplicity of detection zones at least partially overlapping each of the first multiplicity of detection zones, and, responsive thereto, for providing a second detection output signal including an indication of a second detection zone in which the motion was detected, and a processor operable for receiving the first and second detection output signals and, responsive thereto, for providing an indication of a location of the motion.
Owner:TYCO FIRE & SECURITY GMBH
Ultra-large bearing omnidirectional carrying posture adjusting platform and ground self-adaptive omnidirectional moving unit
ActiveCN110469758AHigh movement precisionHigh precision of attitude adjustmentStands/trestlesWheelsTransfer modeDegrees of freedom
The invention relates to an ultra-large bearing omnidirectional carrying posture adjusting platform. The platform comprises an omnidirectional moving posture adjusting unit, an X-direction driving electric bar, a vehicle body frame, a storage battery and a control unit, wherein the omnidirectional moving posture adjusting unit comprises a moving frame, a left-hand Mecanum wheel set, a right-hand Mecanum wheel set, a driving unit and a moving structure; and the movements of the omnidirectional moving posture adjusting unit include the movements in the X and Y directions and rotation of Z-axis based on Mecanum wheels and the movements in the X, Y and Z directions and rotation of the X and Y axes based on a guide rail and a screw rod, and have eight degrees of freedom, wherein the omnidirectional movement and rotation based on the Mecanum wheels, and the movements of the X, Y and Z axes are driving movements, and the rotation of the X and Y axes is a driven movement. According to the platform, large-bearing omnidirectional motions and posture adjustment are integrated, the switching among a transfer mode, a large-range low-precision posture adjustment mode and a small-range high-precision posture adjustment mode is achieved, and the application range of a six-degree-of-freedom posture adjustment platform is effectively expanded.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Compensator
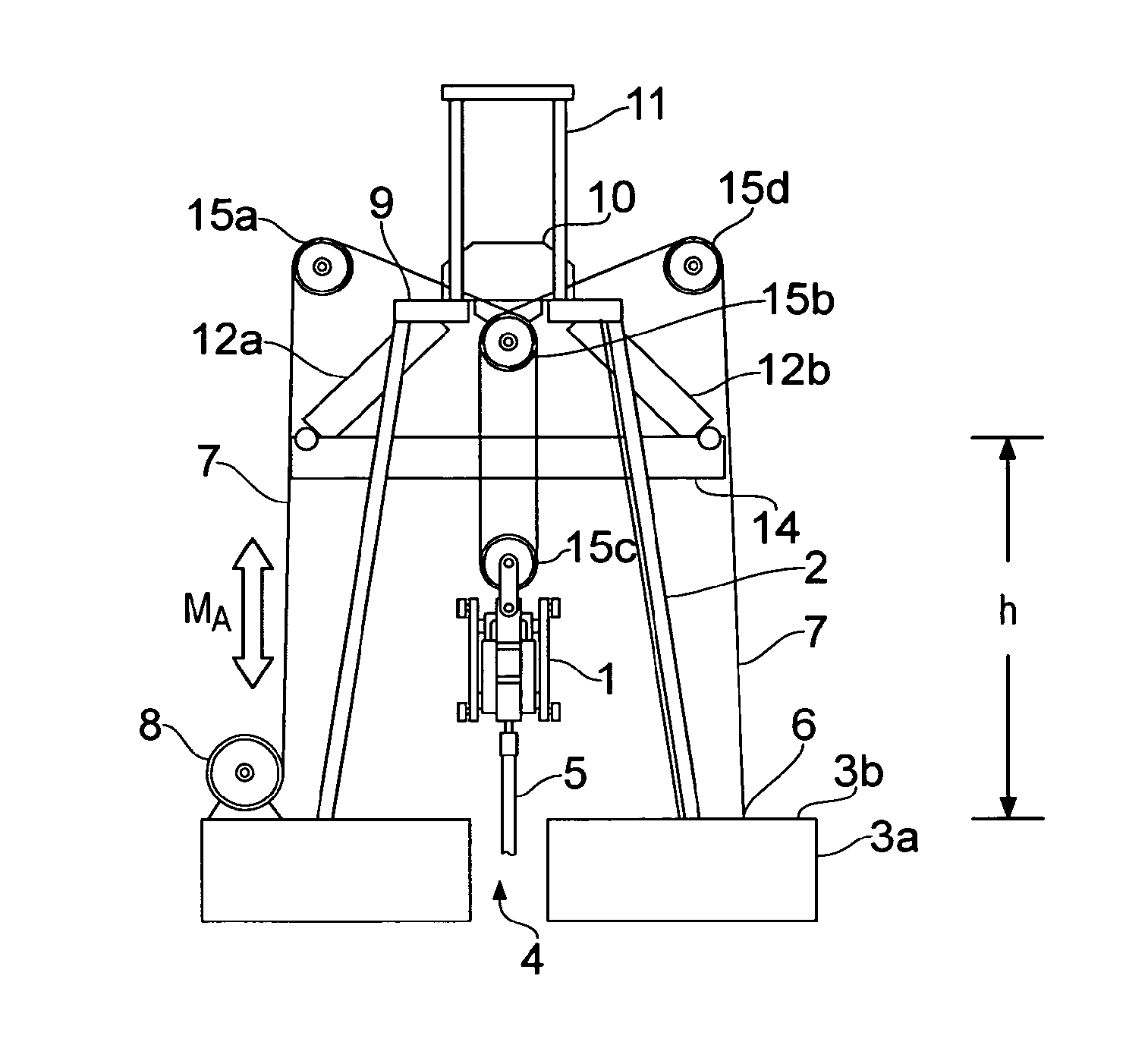
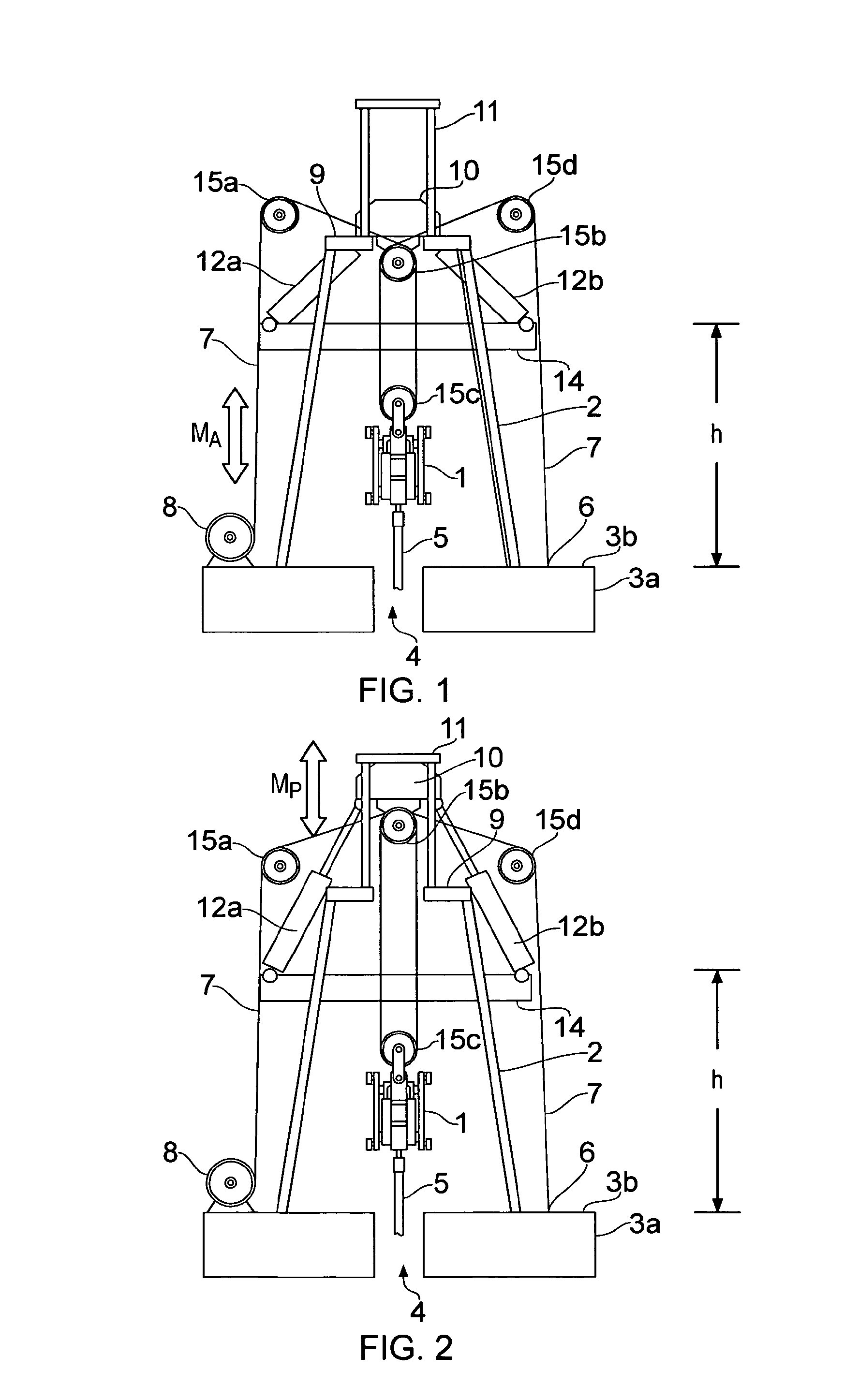
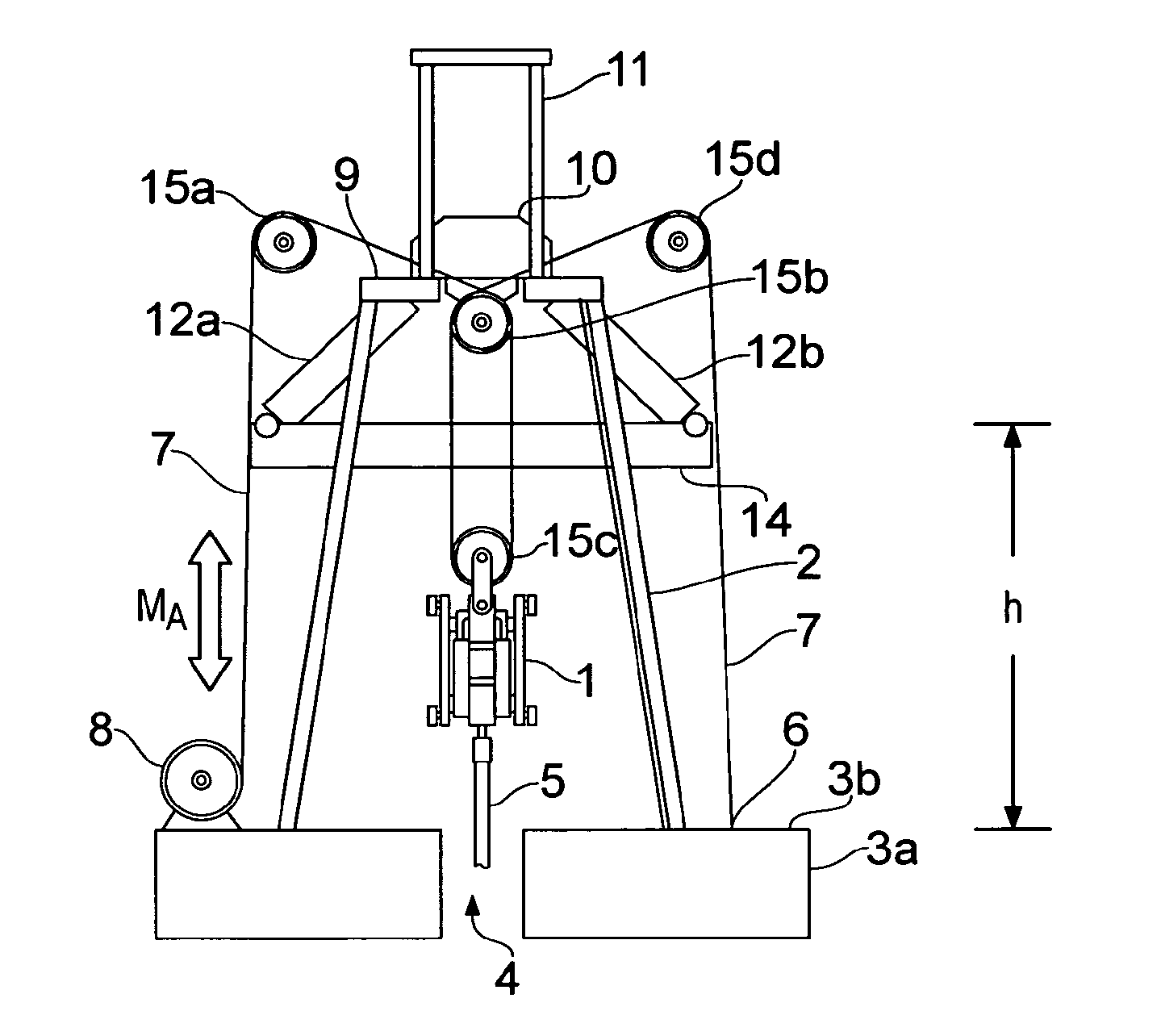
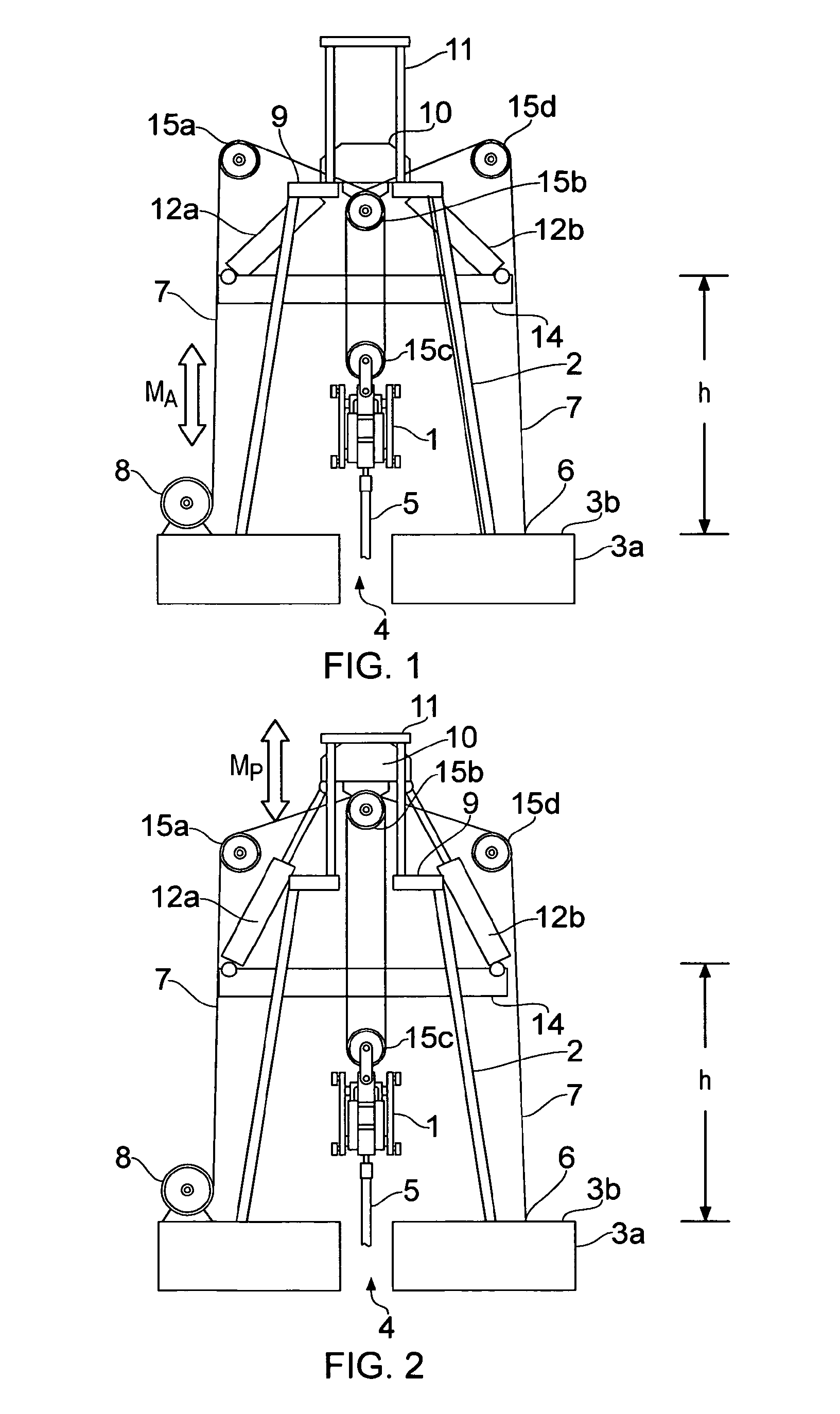
ActiveUS20140246203A1Reduce capacityEliminate riskDrilling rodsFluid removalEngineeringPassive motion
A motion compensation system is provided for controlling relative movements between a floating vessel and an elongate element, where the elongate element is suspended by the vessel at a first end and extends into a body of water below the floating vessel. An active motion compensator is connected to the elongate element first end via an element arranged in an upper region of an erect support structure and a passive motion compensator is connected to the elongate element first end via the element. The motion compensators are structurally and operationally separate and independent units and are configured for separate and mutually independent operation.
Owner:MHWIRTH
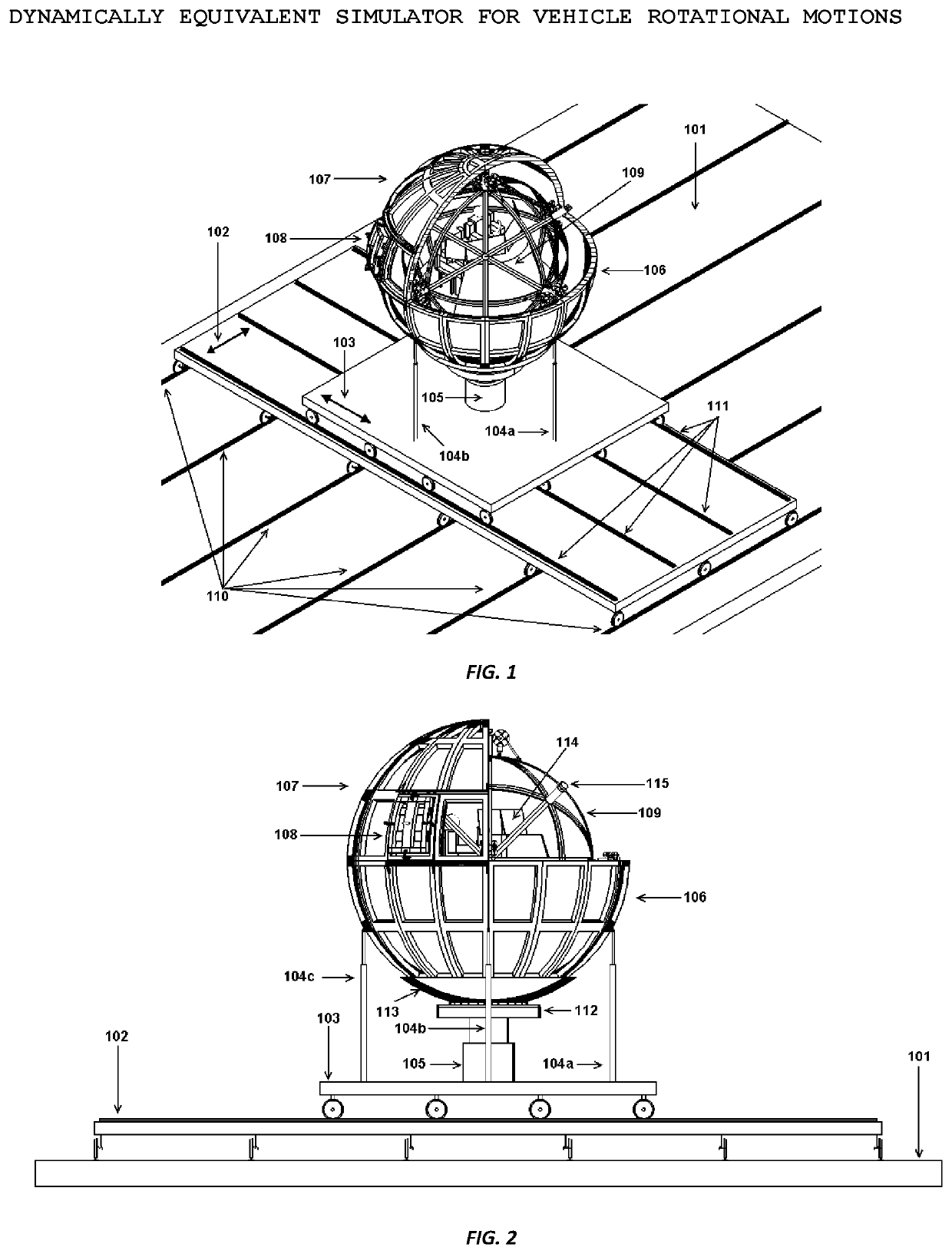
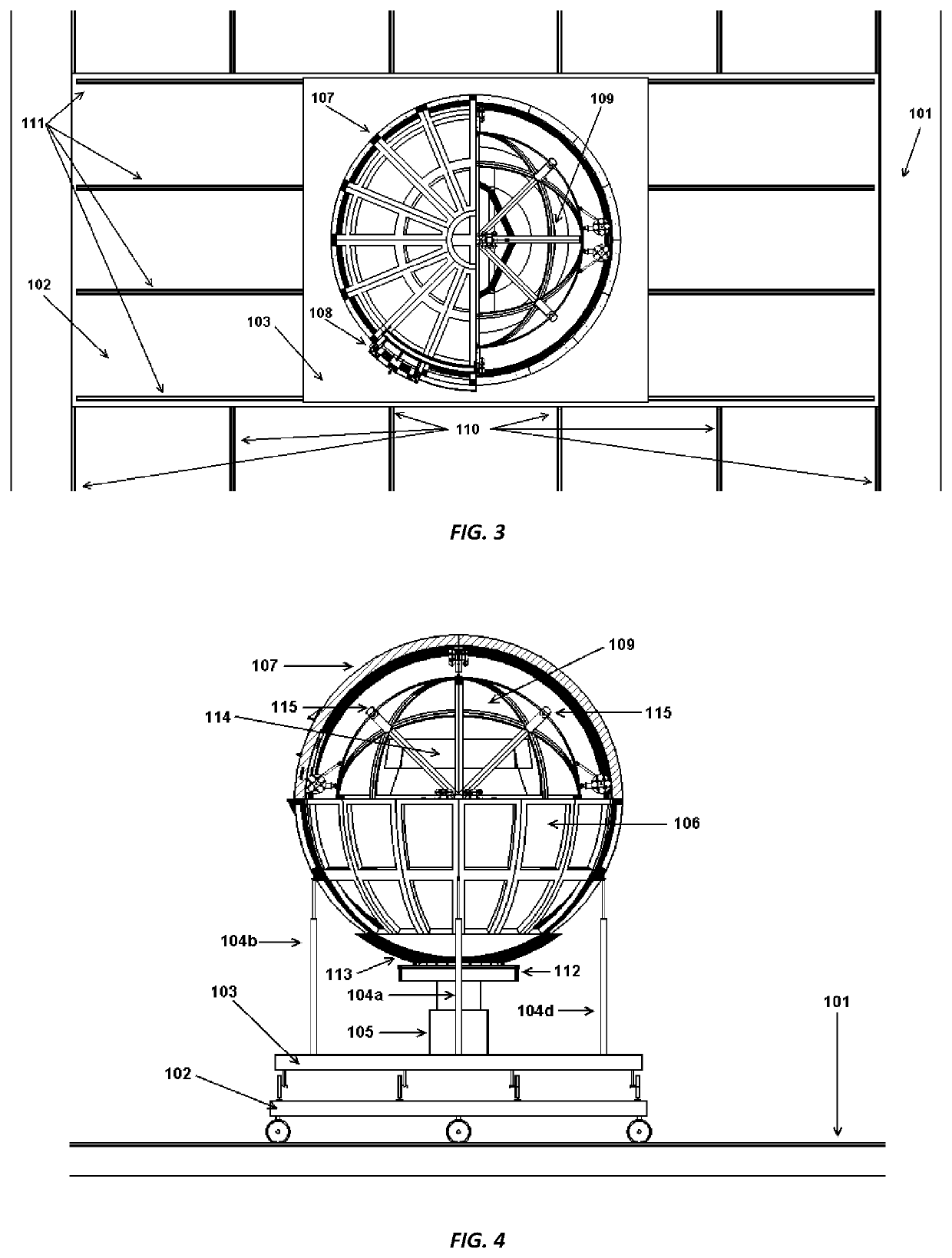
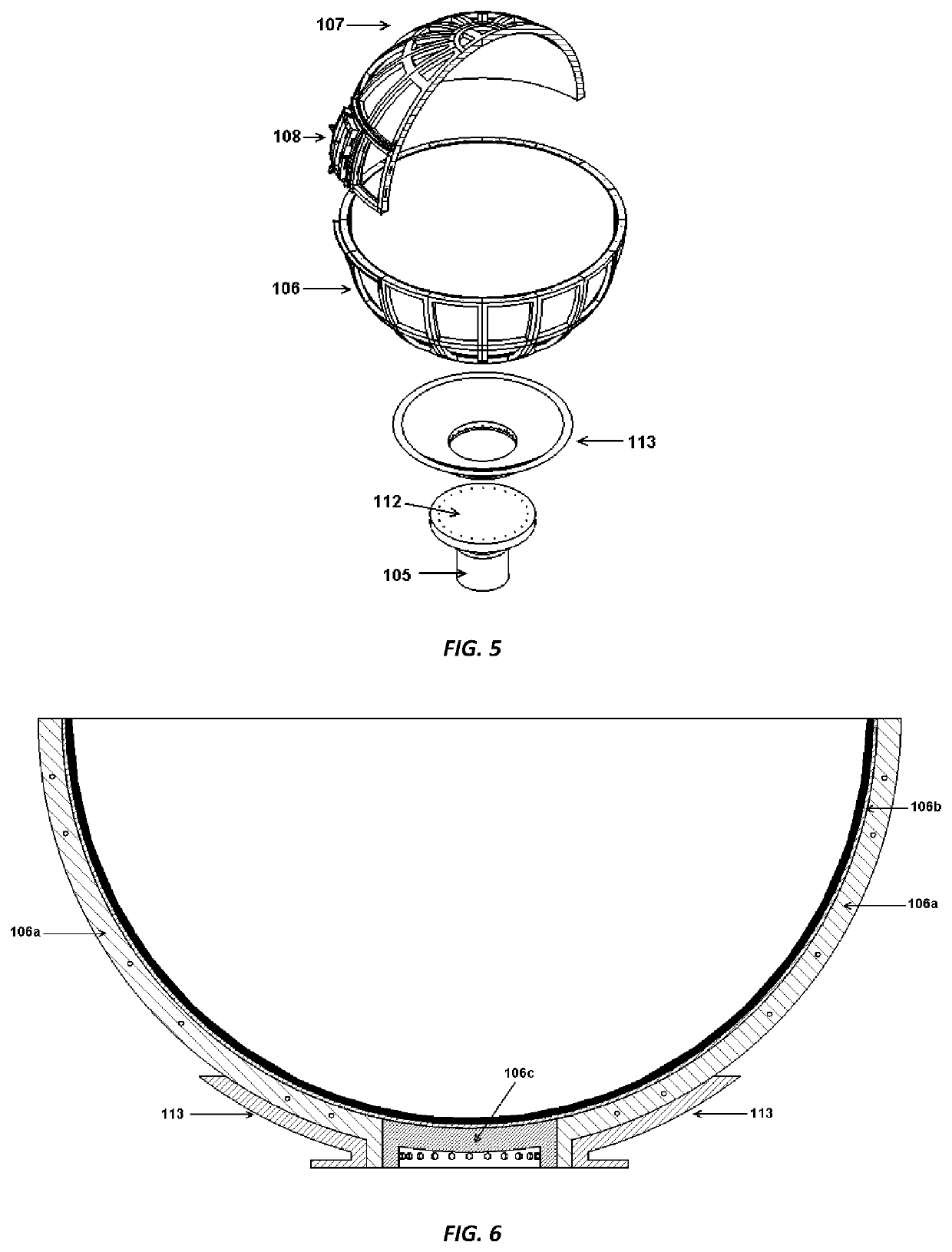
Dynamically Equivalent Simulator for Vehicle Rotational Motions
ActiveUS20200111381A1Reduce vehicle weightImprove bending strengthGeometric CADCosmonautic condition simulationsAir bearingBall bearing
A vehicle nonlinear dynamics simulation device, such as flight simulator, including a motorized spherical vehicle suspended inside another spherical shell which has smooth inner surface. The spherical vehicle is supported by a plurality of spiky legs of either air-bearing assemblies or omni-directional ball bearing assemblies. The outer spherical shell is supported by three controllable translational motion platforms. Simulating equipment for a pilot cabin is mounted inside the spherical vehicle. The spherical vehicle has driving, restoring, and damping capabilities in roll, pitch, and yaw directions and is capable to rotate 360° in any directions. Therefore it provides a dynamically equivalent model to simulate a vehicle rotational dynamics. The driving and restoring means include Omni wheel assemblies mounted outside of the spherical vehicle and operable to contact the inner surface of the shell to drive the spherical vehicle in roll, pitch, and yaw directions. The driving means include electrical motors. The restoring and damping mechanisms are provided by rotational springs and rotational dampers, respectively. The rotational movements of the spherical vehicle are active and controlled by the driving system and also by the nonlinear dynamics of the spherical vehicle itself, in contrast to the passive movements of the simulation platforms currently used in industries.
Owner:TANG SHAOJIE
Passive motion machine with integrated mechanical DVT prophylactic therapy
There is provided a continuous passive motion (CPM) machine with integrated mechanical deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis for providing simultaneous CPM therapy and DVT prophylactic therapy to a human patient. The passive motion machine may include a base, at least one motor, one or more hinged frame rails, one or more support or suspension structures and a roller assembly. The hinged frame rails are driven to impart CPM to a patient's limb. The roller assembly can be a single roller, a multiple roller unit, or a belt and roller apparatus. A motor and connecting drive rotates the roller assembly. The roller assembly engages the patient's limb and the one or more rollers apply a mechanical DVT prophylaxis therapy to the limb, reducing the risk of blood clotting.
Owner:LYMAN JEFFREY R M D
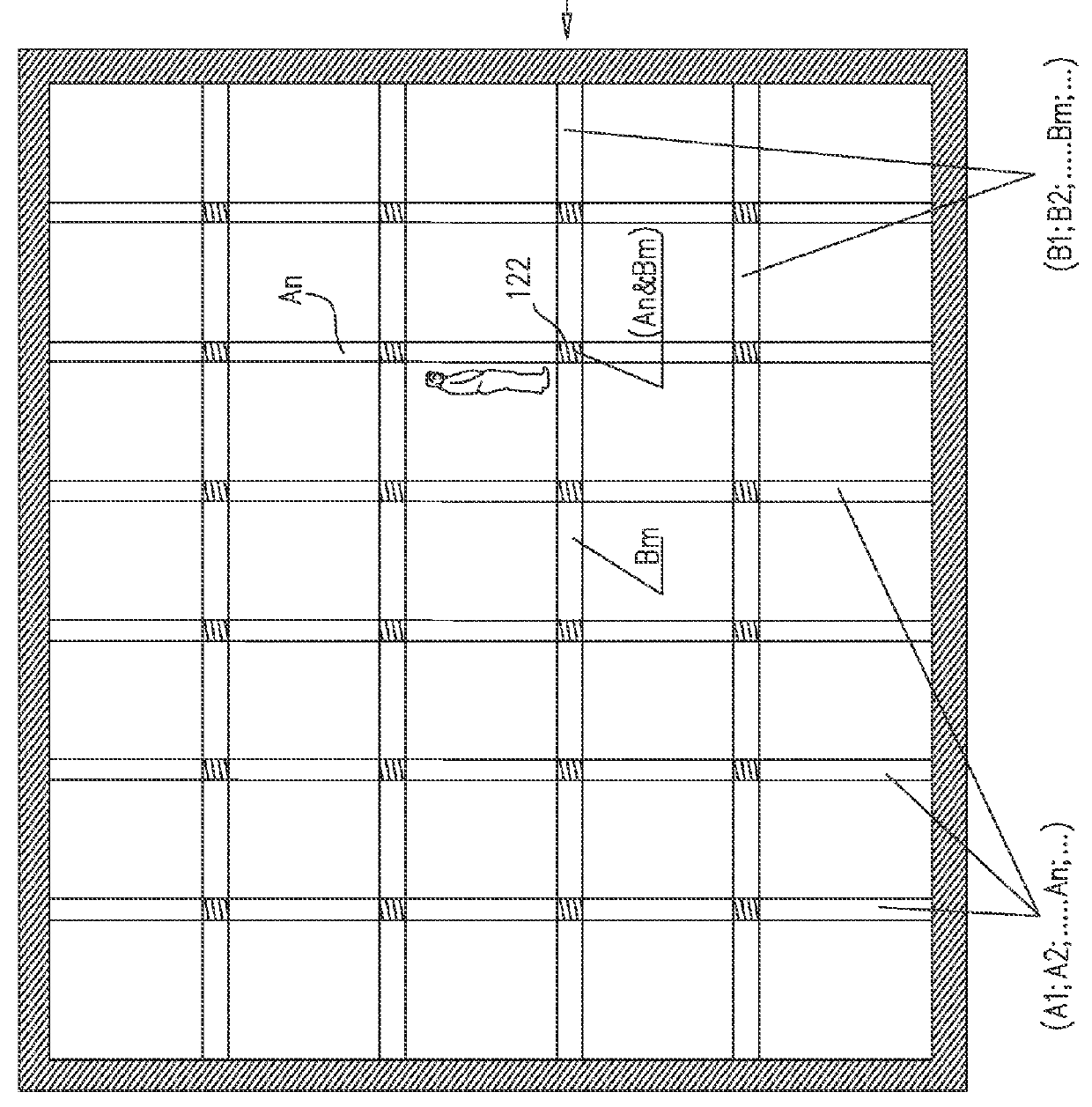
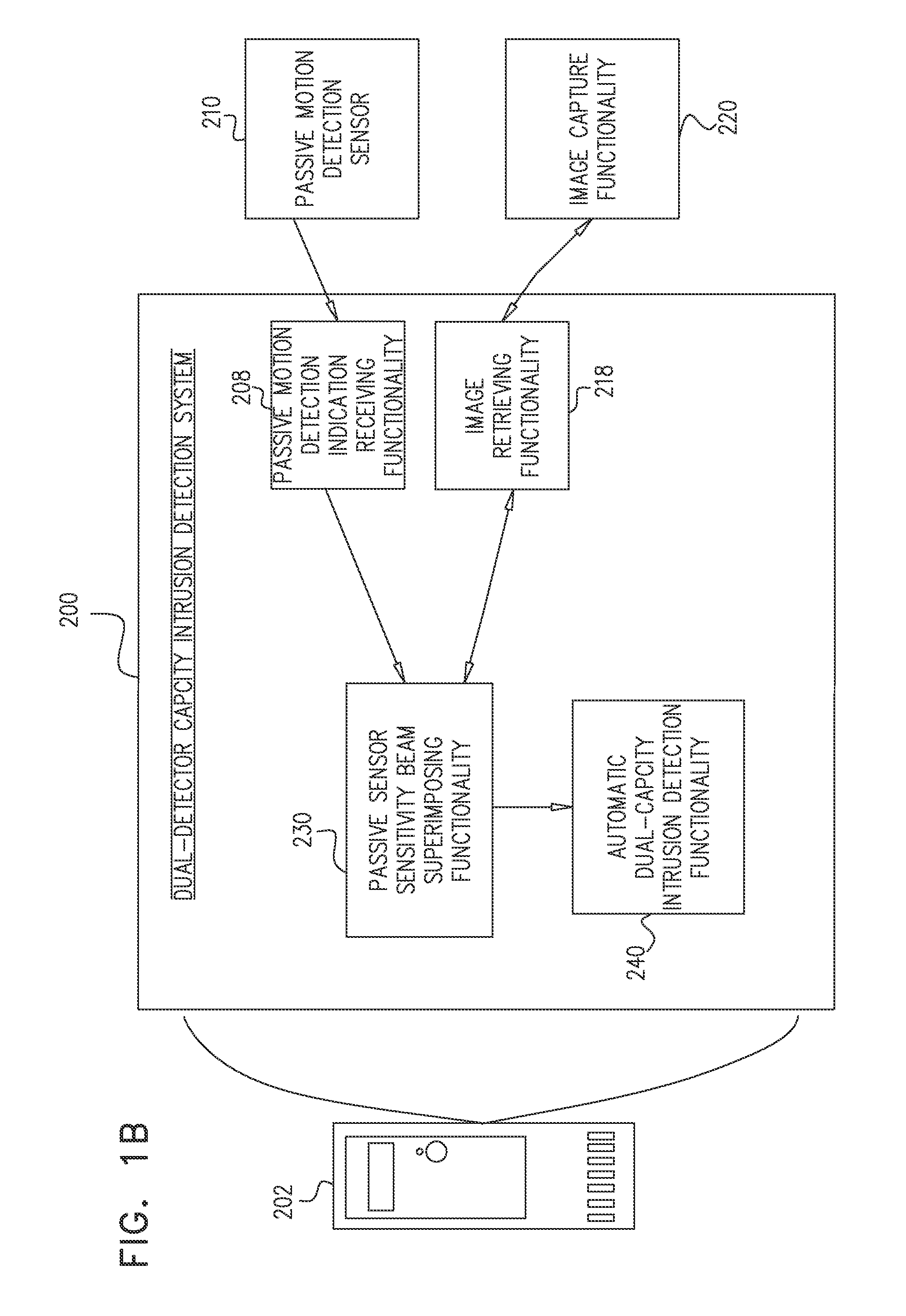
Dual-detector capacity intrusion detection systems and methods and systems and methods for configuration thereof
ActiveUS20150325092A1Easy remote controlClosed circuit television systemsBurglar alarm electric actuationLight beamComputer vision
A method for automatically orienting passive motion detection sensors in a given area, the method including capturing an image of at least a first portion of the given area, and responsive to capturing of an image of the first portion of the given area, superimposing, onto the image, a multiplicity of virtual passive sensor sensitivity beams virtually originating from at least one passive motion detection sensor, the at least one passive motion detection sensor being operable for passively detecting motion in at least a second portion of the given area, the sensitivity beams demarcating the second portion of the given area, thereby enabling ascertaining a measure of overlap between the first and second portions of the given area.
Owner:TYCO FIRE & SECURITY GMBH
Orthopedic arm and shoulder brace
InactiveUS8142379B2Easy to useImprove abilitiesChiropractic devicesEye exercisersEngineeringPlastic surgery
The present invention relates to a portable device for providing continuous passive motion of a limb comprising a brace for supporting said limb. A programmable motor, mechanically connected to the brace, provides continuous passive motion of a limb. The movement of the limb is controlled in two control points of movement at the lower arm. Flexible positioning means are provided with a fastening means positioning the brace and the programmable motor on the body of a person carrying said device in a stable position. The programmable motor is partially housed within the positioning means. The invention is particularly suitable for use in paramedical and orthopedic applications. It allows adduction and abduction, rotation and exo / endo rotation of a limb.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Touch pad, led motion detector head
InactiveUS20020030593A1Electric/electromagnetic visible signallingIdentification meansMotion detectorMembrane switch
An improved motion detector that includes a passive motion sensor with "test," "sensitivity" and "timer" adjustable functions, mounted inside an outer housing with two water-resistant touch-operated membrane switches used to control these settings. Also mounted on the sides of the outer housing and connected to the motion sensor are at least two bright LED lights designed to illuminate in one of three possible colors to visually indicate the current "test", "sensitivity" or "timer" setting of the motion detector.
Owner:COLEMAN CABLE INC
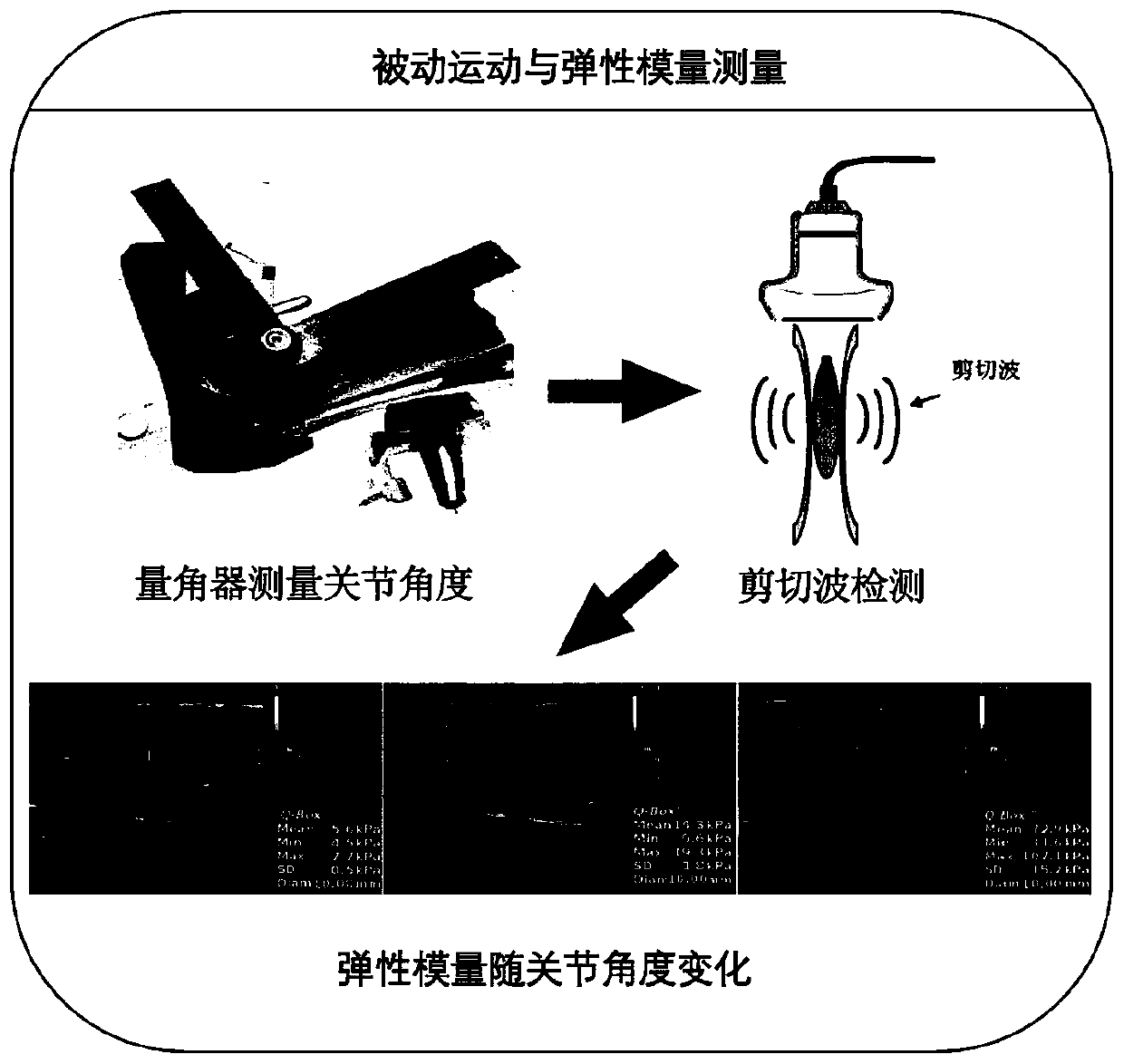
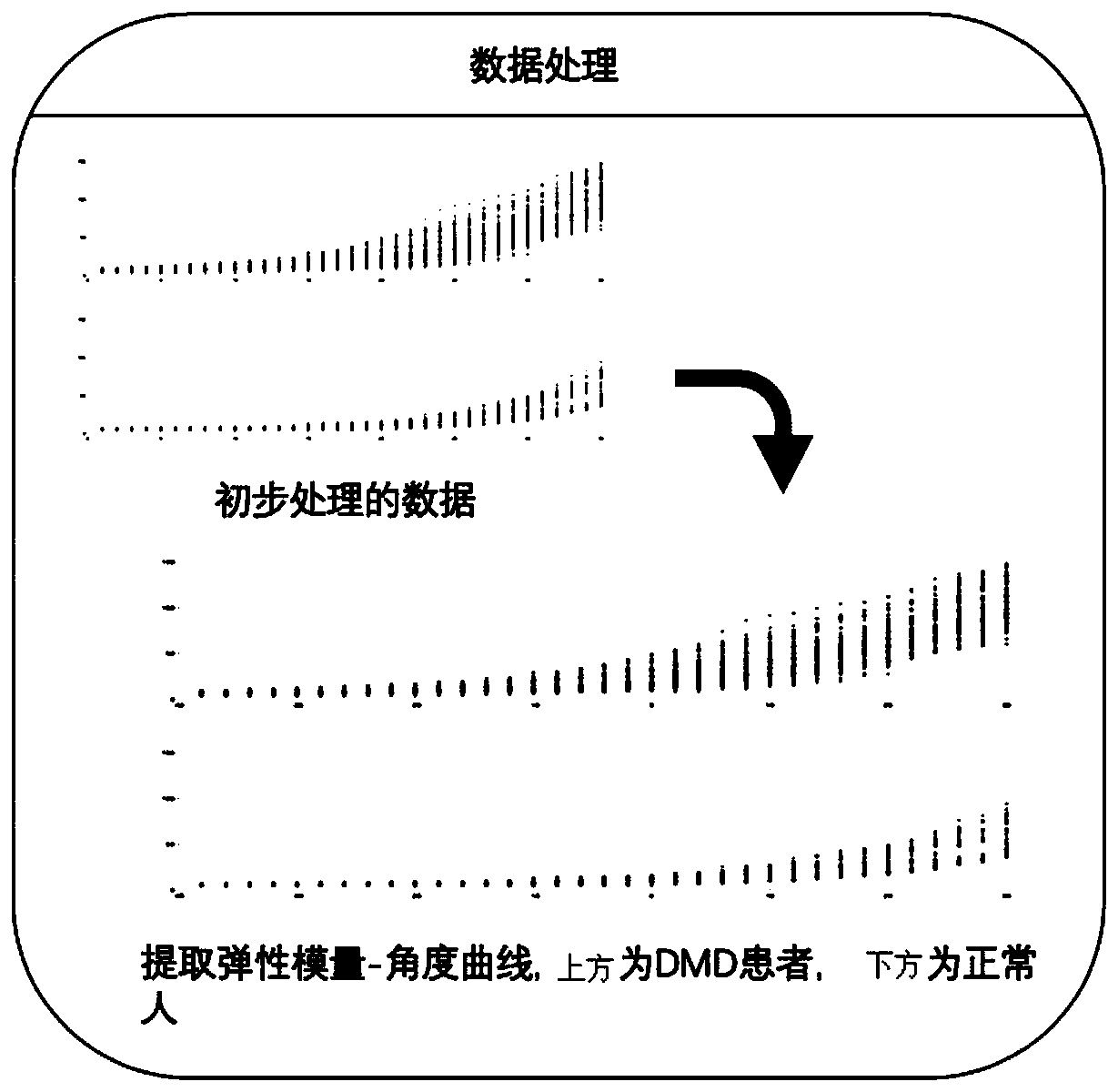
Muscle disease assessment method and system and electronic device
InactiveCN110693526AEasy to operateFast imagingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsData setPassive motion
The invention relates to a muscle disease assessment method and system and an electronic device. The muscle disease assessment method includes the steps: a driving passive motion of a subject by external driving, and acquiring a motion angle of the subject; b acquiring dynamic change of detected skeletal muscle without the motion angle by the aid of an ultrasonic shear wave elasticity imaging technique, and extracting elasticity measurement data of the dynamic change; c extracting a corresponding relationship between elasticity modulus of the detected skeletal muscle and a joint angle from theelasticity measurement data, and taking the corresponding relationship between the elasticity modulus and the joint angle as characteristics to make a data set; d building a probabilistic neural network model, inputting the data set into a probabilistic neural network to perform training, and outputting a muscle disease of the subject and categories of the muscle disease by the probabilistic neural network. According to the method, by the aid of the artificial intelligence neural network, classification results are more reliable, generalization ability is better, and a new method is providedfor assessment of muscle diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Passive motion device applied to human body tissue
PendingCN106943272AImprove immunityImprove experienceChiropractic devicesHuman bodyClassical mechanics
A passive motion device applied to human body tissues belongs to the health care body-building apparatus field, and comprises a bed base plate, a bed panel supported by telescopic support rods on the bed base plate, a telescopic mechanism arranged on the top end face of the bed base plate and used for pushing human body tissues to move, and a coupled control circuit; the motion device also comprises support elastic members arranged on two sides in middle of the bed base plate, and a horizontal position adjusting mechanism arranged between the telescopic mechanism bottom and the bed base plate; the telescopic mechanism comprises a telescopic housing arranged on the bed base plate, a piston rod arranged in the telescopic housing, a support arranged on the piston top, a connecting hole arranged on the telescopic housing, and an adjustable amplitude output mechanism connected with the connecting hole through a pipeline. A human body arms and legs motion mechanism can be improved so as to remove working noises, thus improving user experience effects.
Owner:王继文
Compensator
ActiveUS9140079B2Reduce capacityEliminate riskDrilling rodsDrilling casingsEngineeringPassive motion
A motion compensation system is provided for controlling relative movements between a floating vessel and an elongate element, where the elongate element is suspended by the vessel at a first end and extends into a body of water below the floating vessel. An active motion compensator is connected to the elongate element first end via an element arranged in an upper region of an erect support structure and a passive motion compensator is connected to the elongate element first end via the element. The motion compensators are structurally and operationally separate and independent units and are configured for separate and mutually independent operation.
Owner:MHWIRTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com