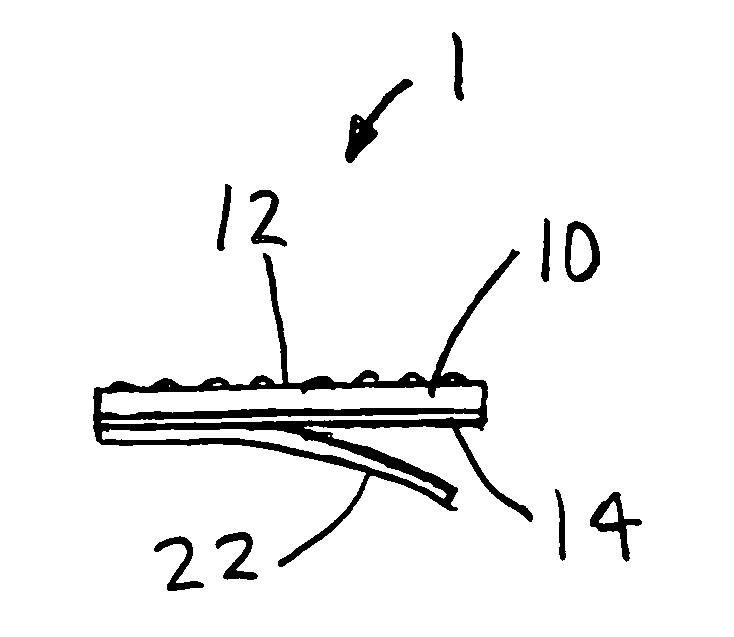
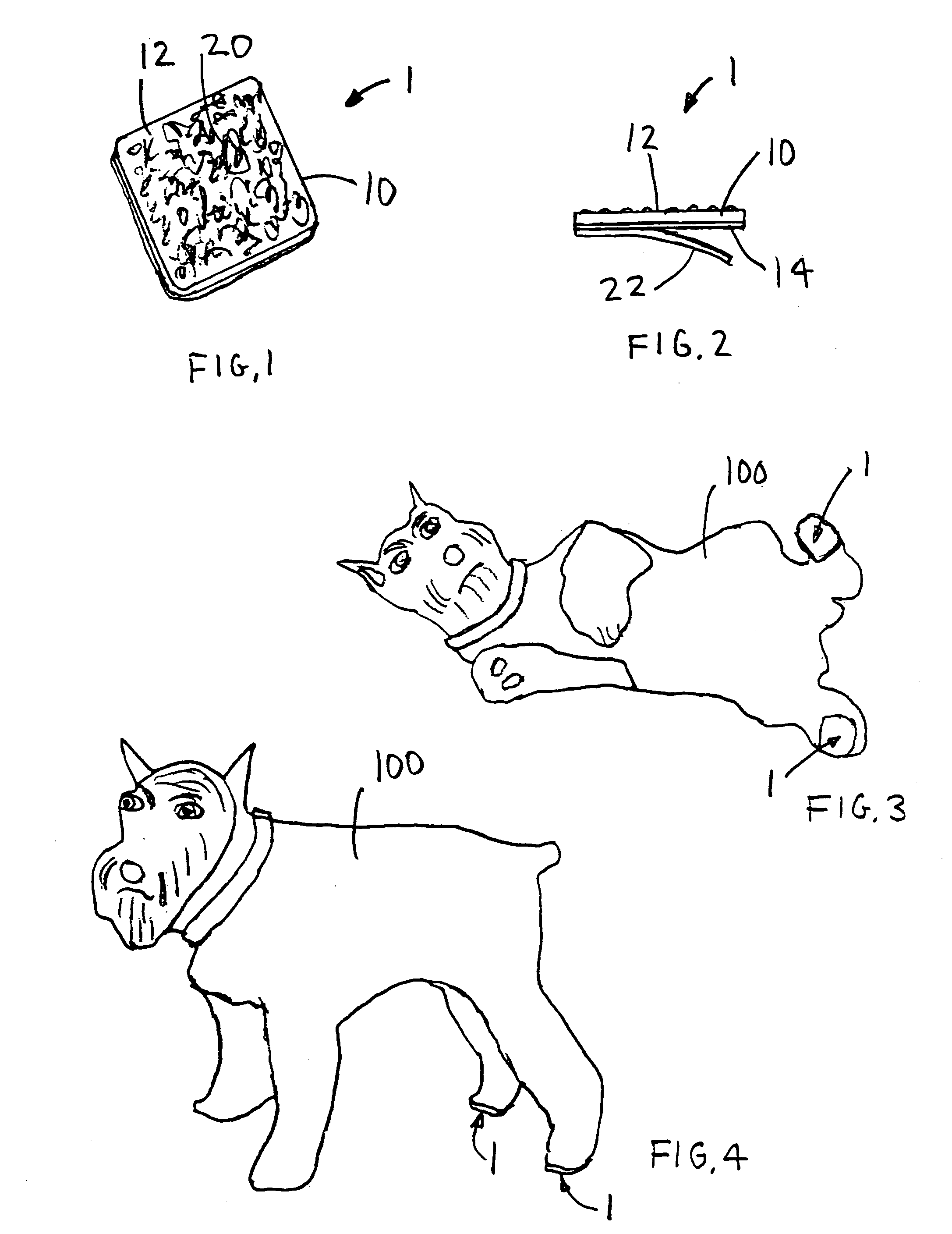
Patents
Literature
257results about "Veterinary bandages" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
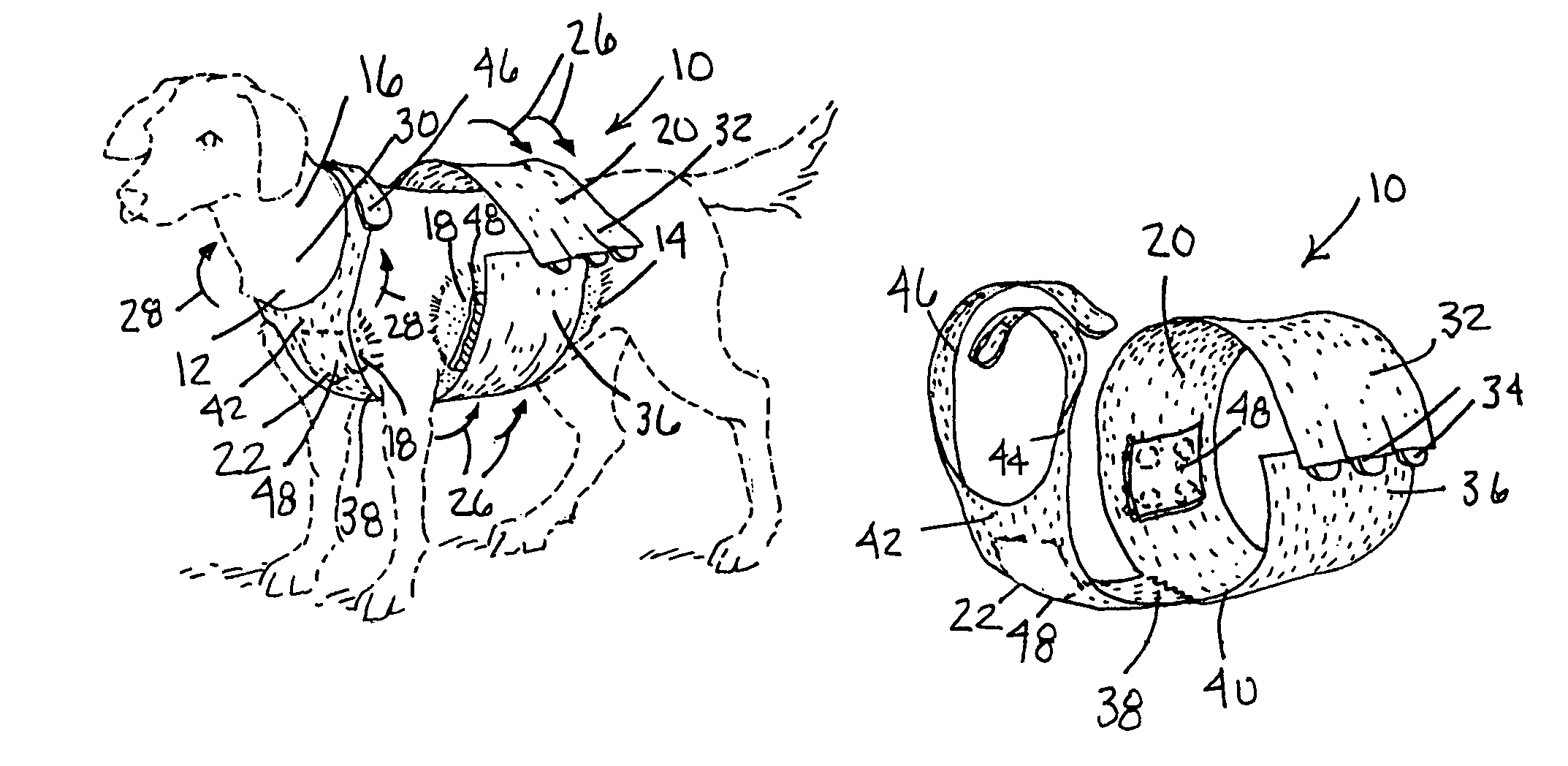
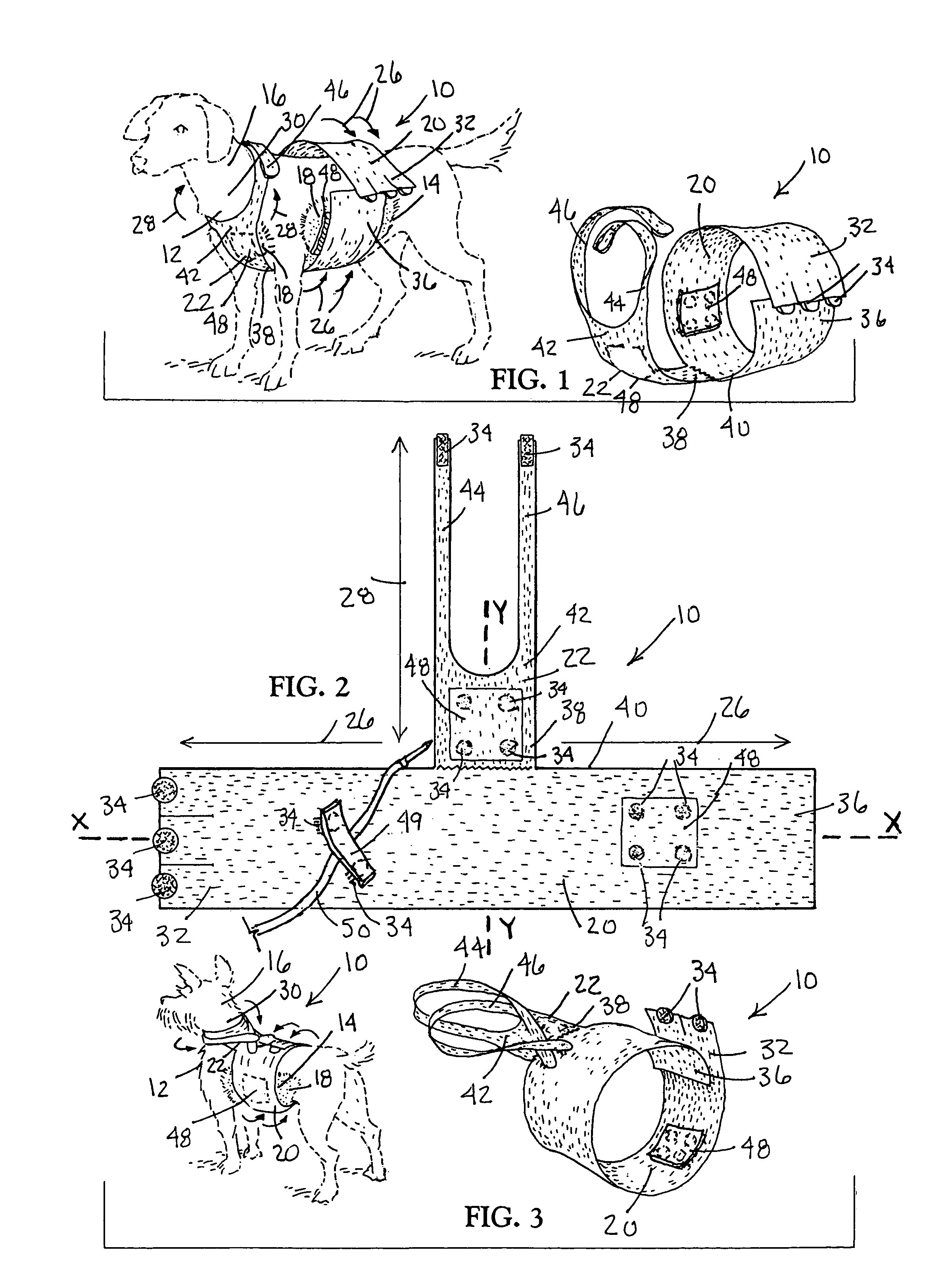
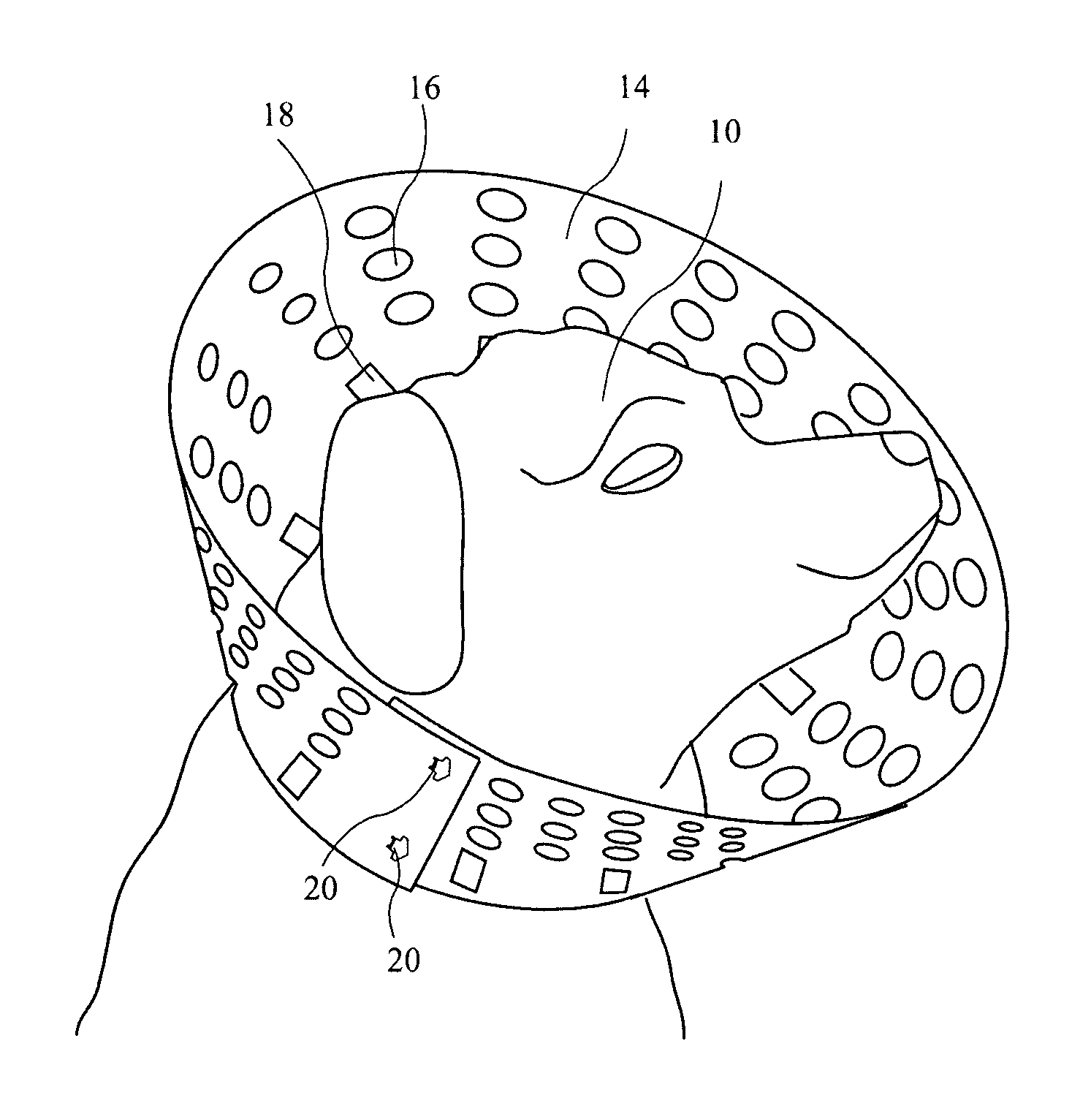
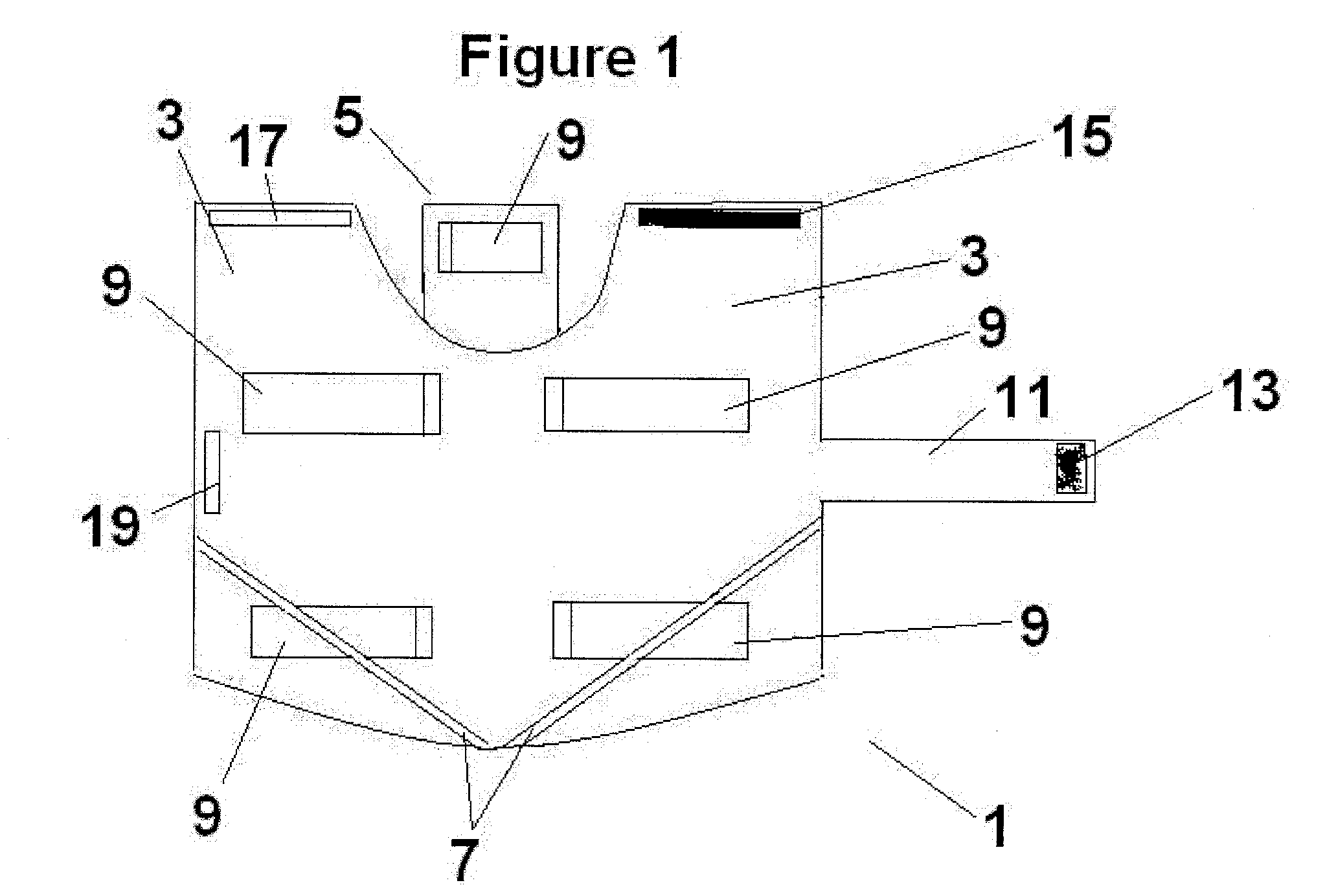
Pet animal collar for health & vital signs monitoring, alert and diagnosis
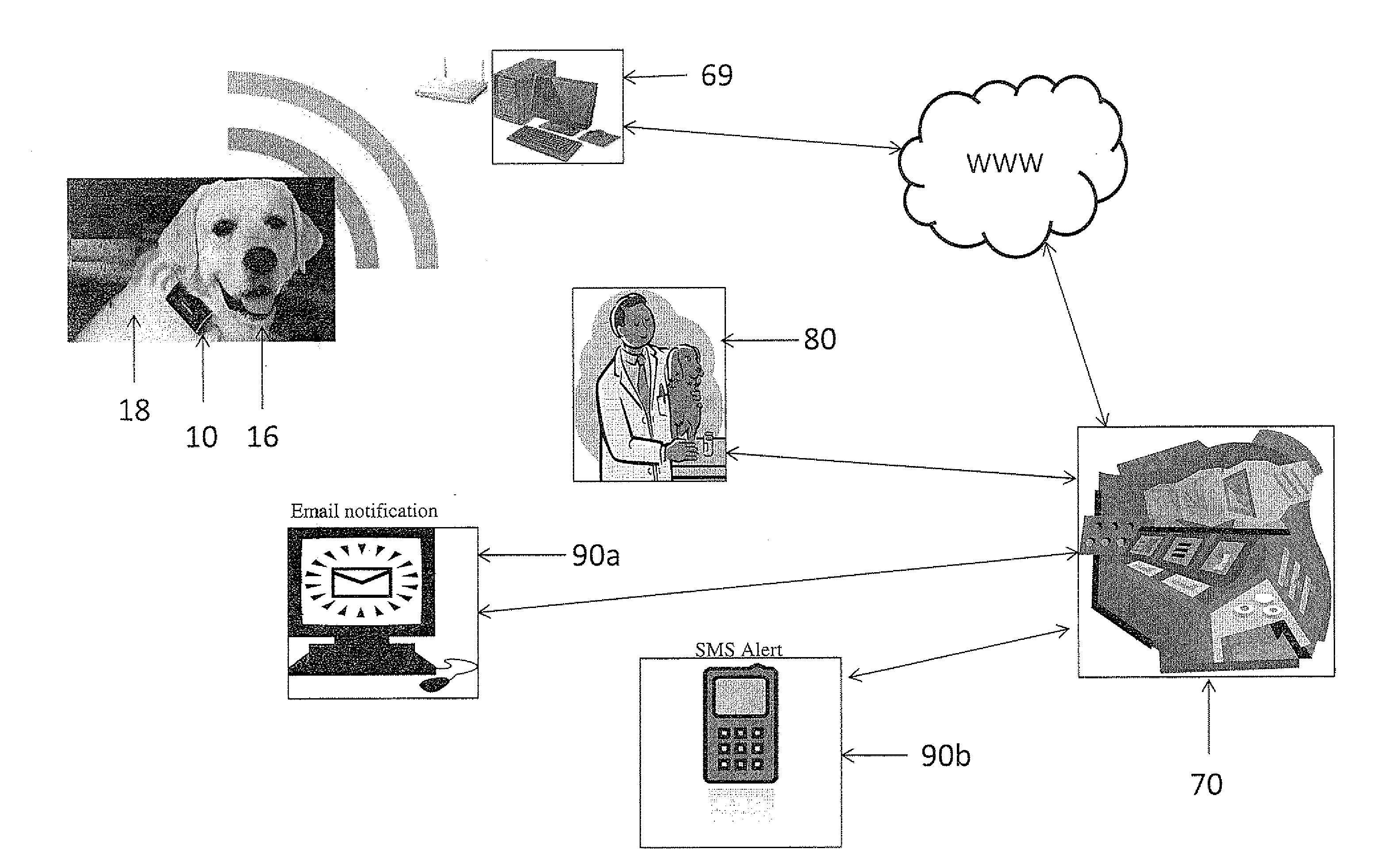
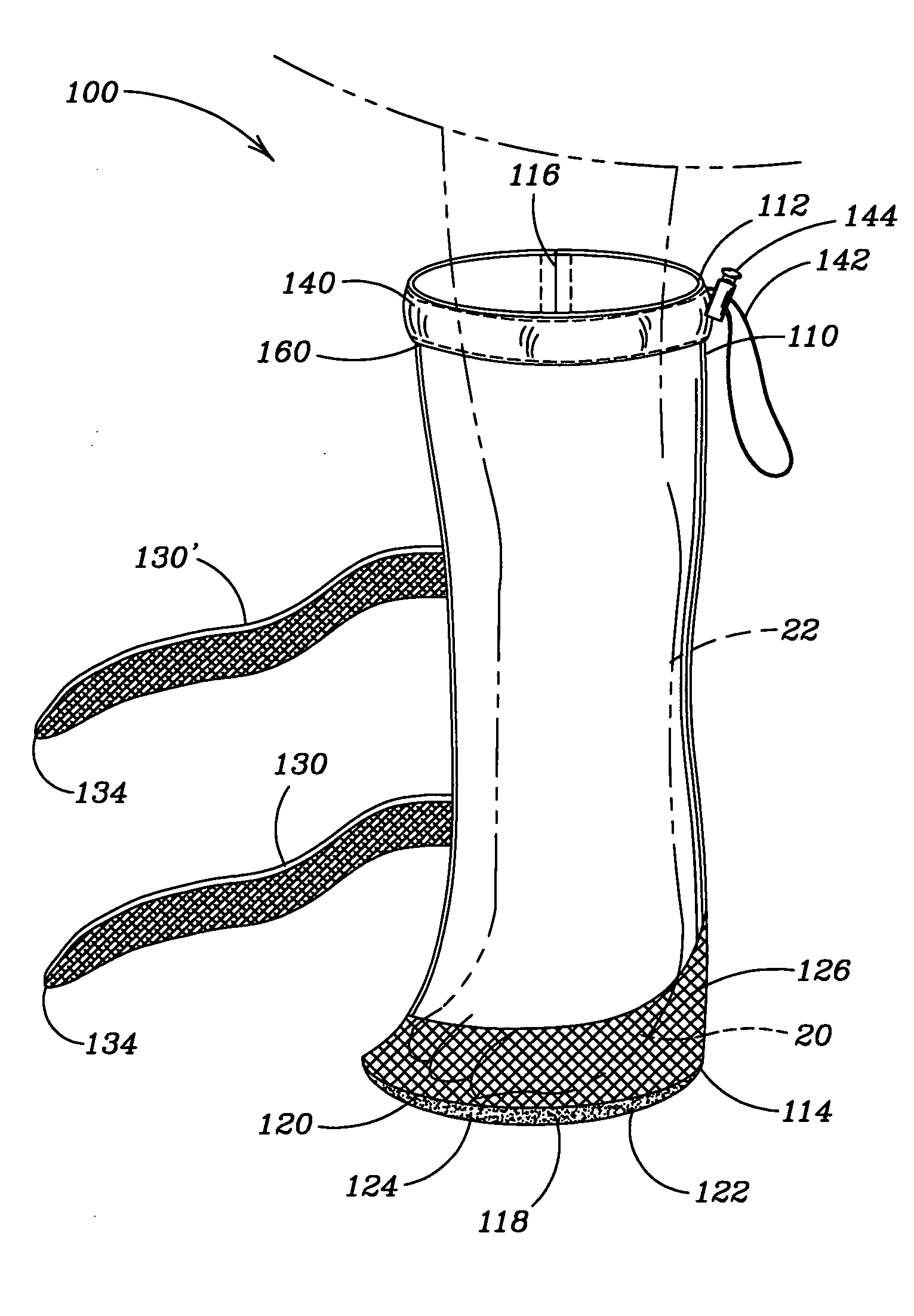
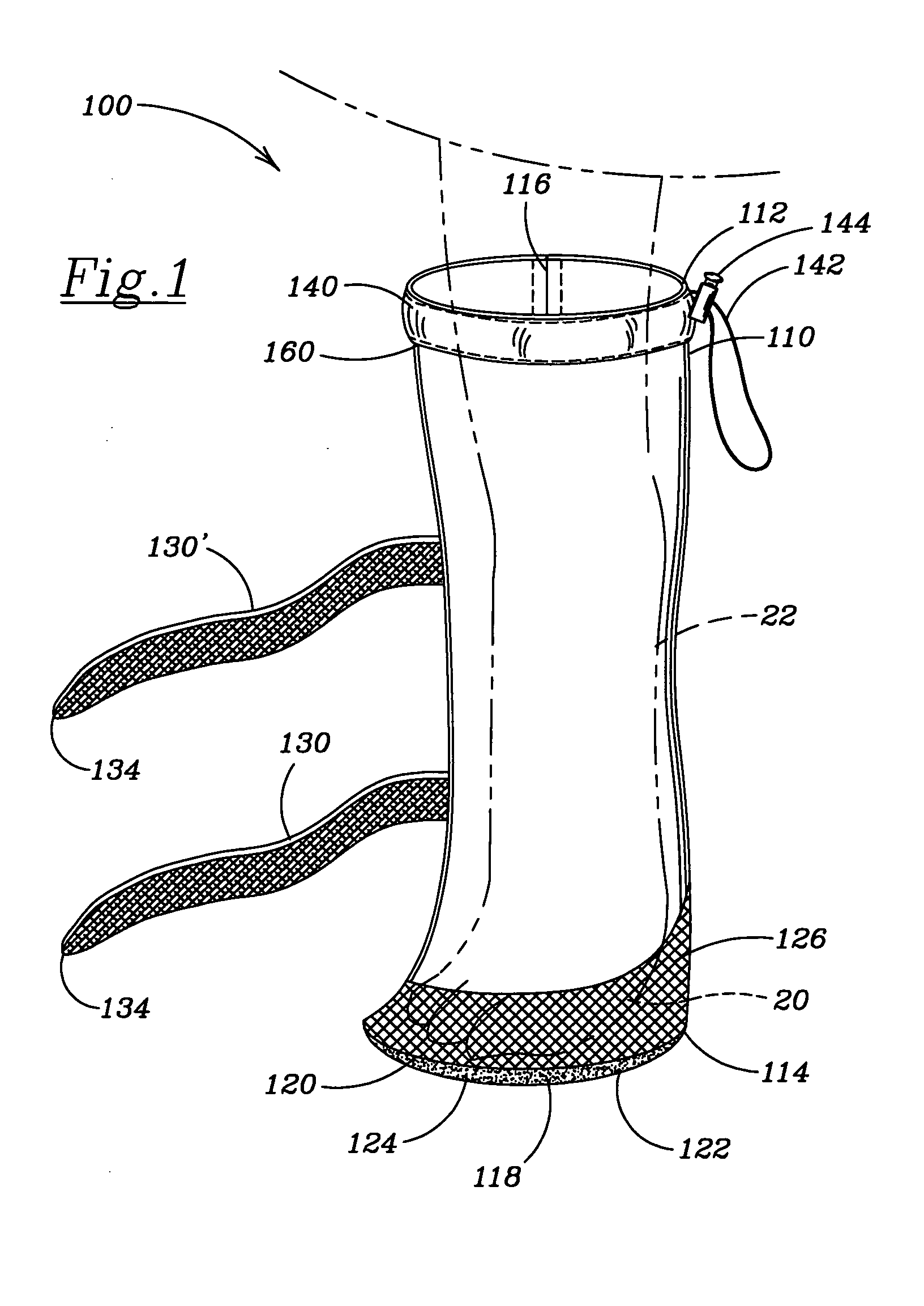
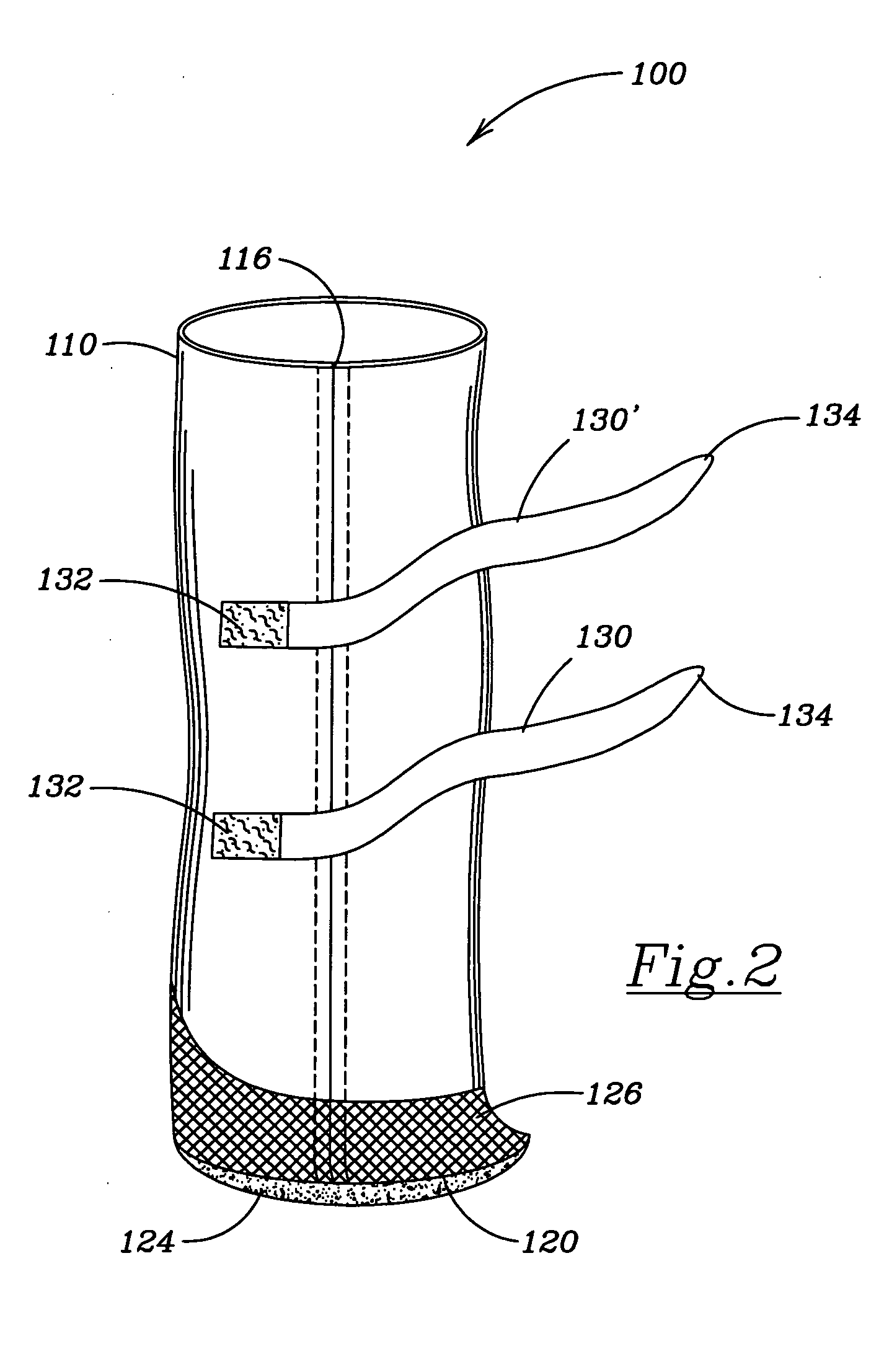
A collar for pet animals may have sensor elements remotely actuatable to measure vital signs of the animal (such as respiration, pulse, temperature and movement) and a processor that can interpret the results of multiple vital sign readings. A two way communication device alerts the pet owner, veterinarian or authorities. A veterinarian can remotely take a particular vital sign measurement when alerted. The sensor elements embedded in the collar's band has at least one elastic pin extending toward the animal's neck to gather data processed on the collar or remotely. To improve STN ratio, an elastic layer may absorb noise from friction due to movement of the animal's head. The collar may adjust the tightness of the band for taking vital sign readings. For example pump may injects air through a tubular compertment running along the circumference of the band. A safety mechanism may release the collar.
Owner:PETPACE
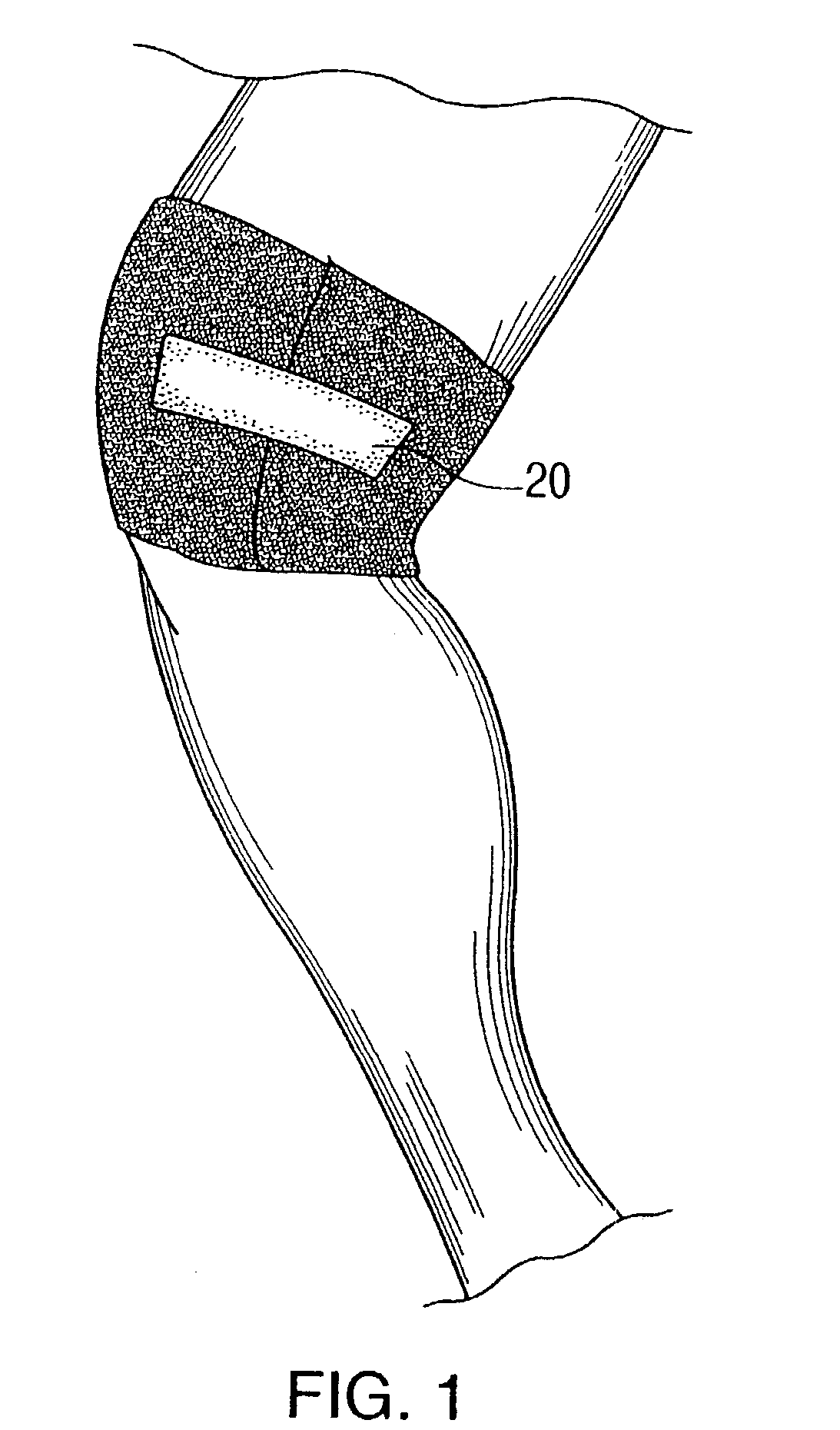
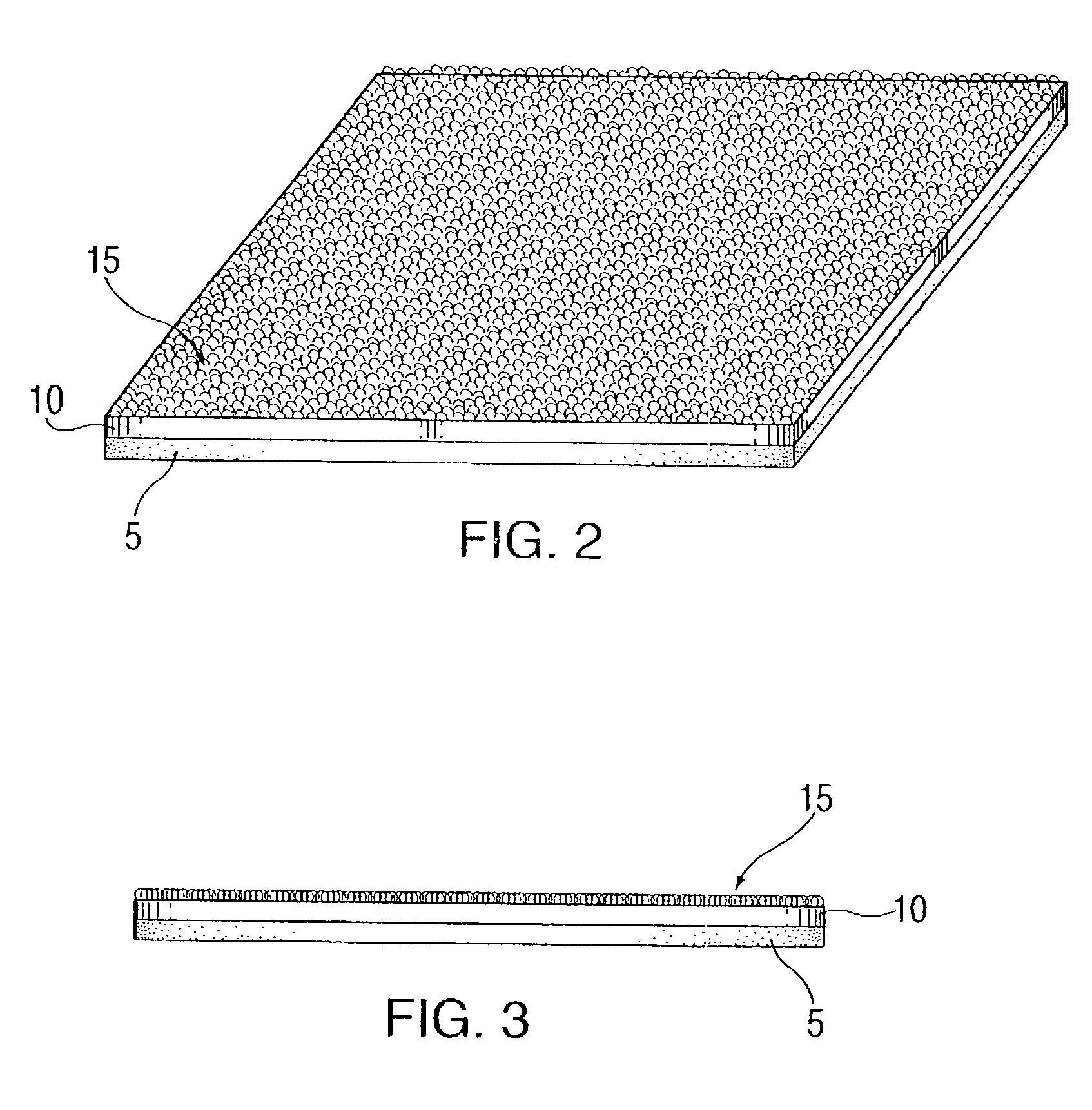
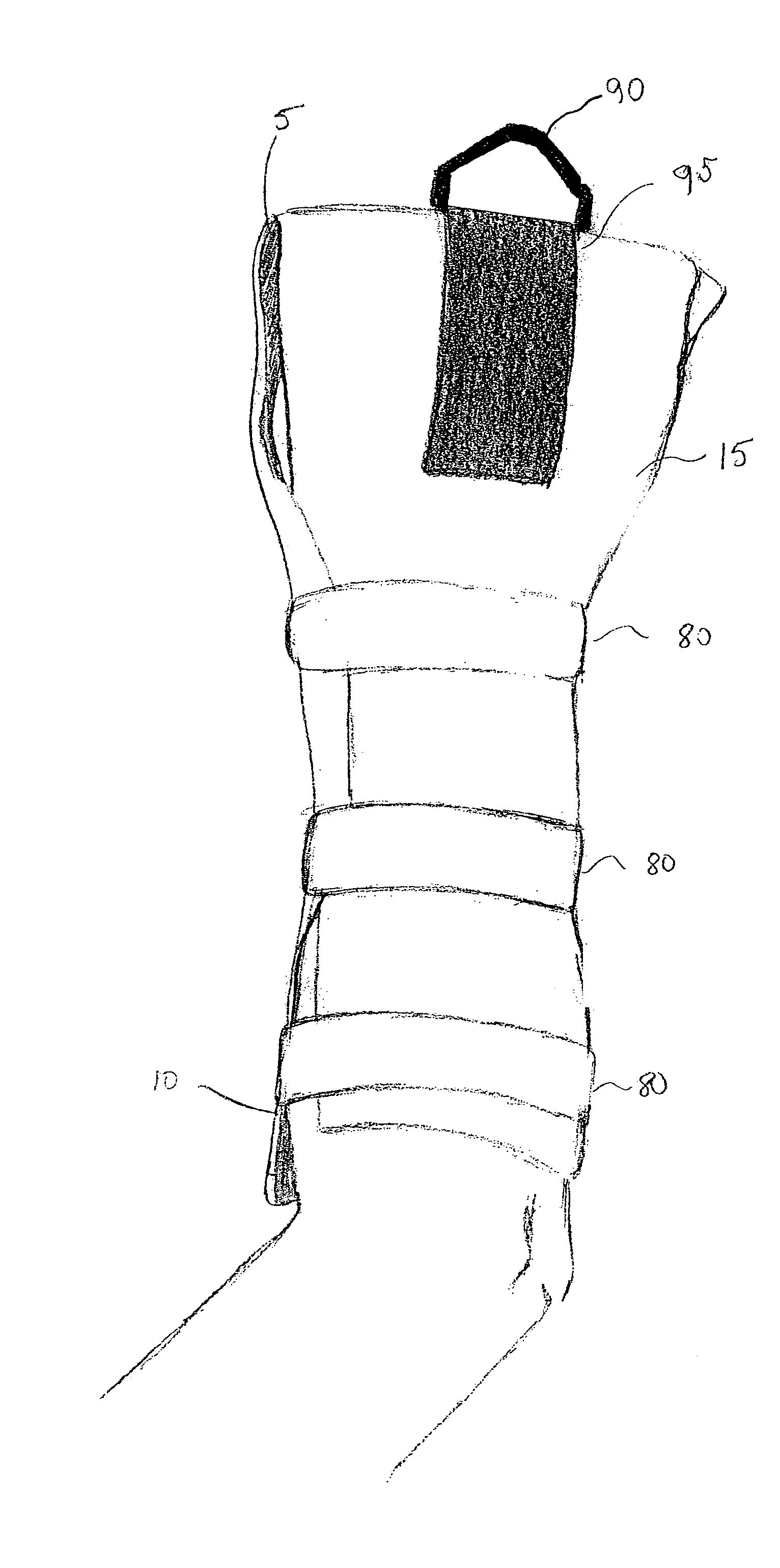
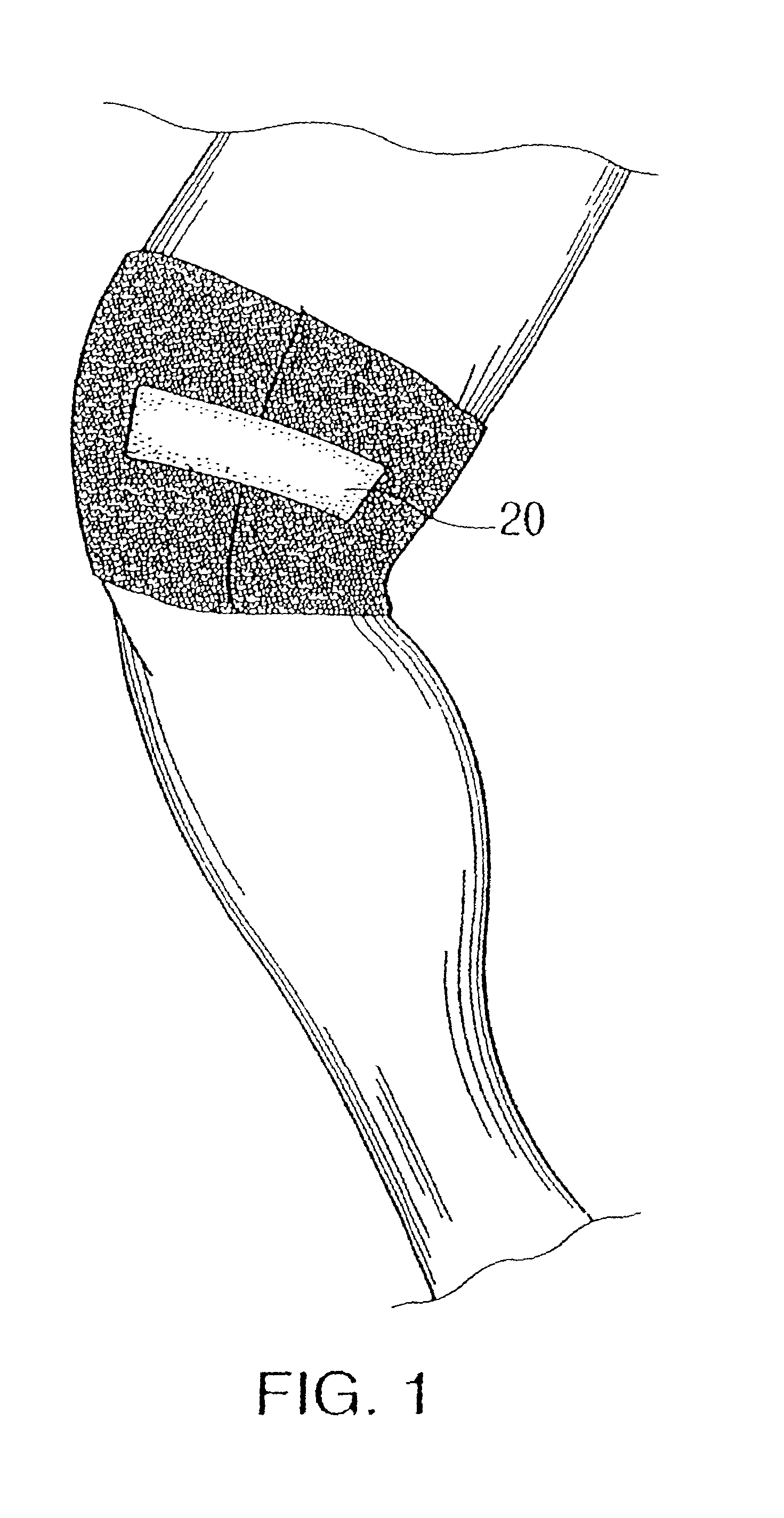
Gel wrap providing musculo-skeletal support
InactiveUS7303539B2Improve comfortGreat comfort and durabilityNon-adhesive dressingsVeterinary bandagesMoistureBiomedical engineering
Owner:GELZONE
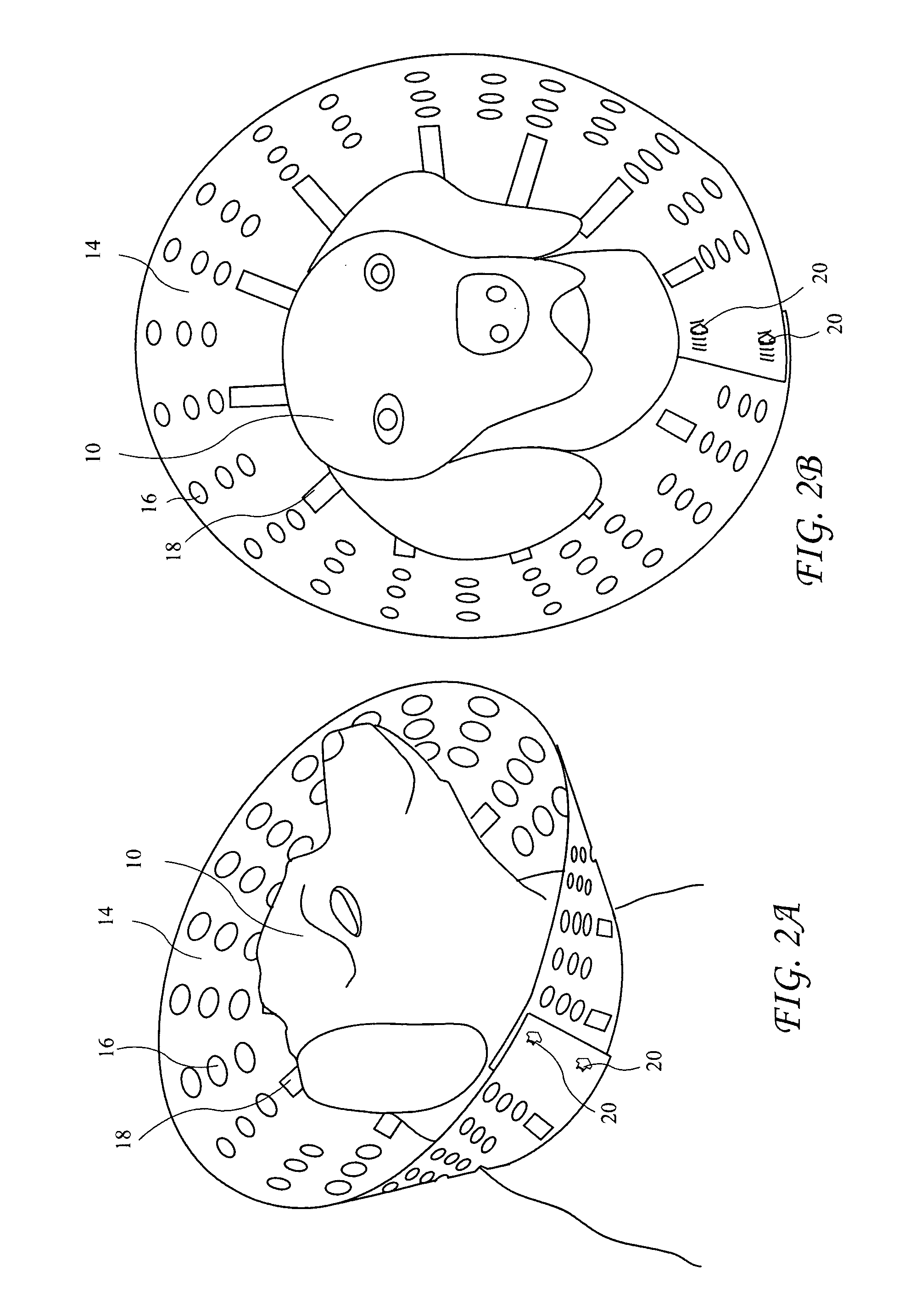
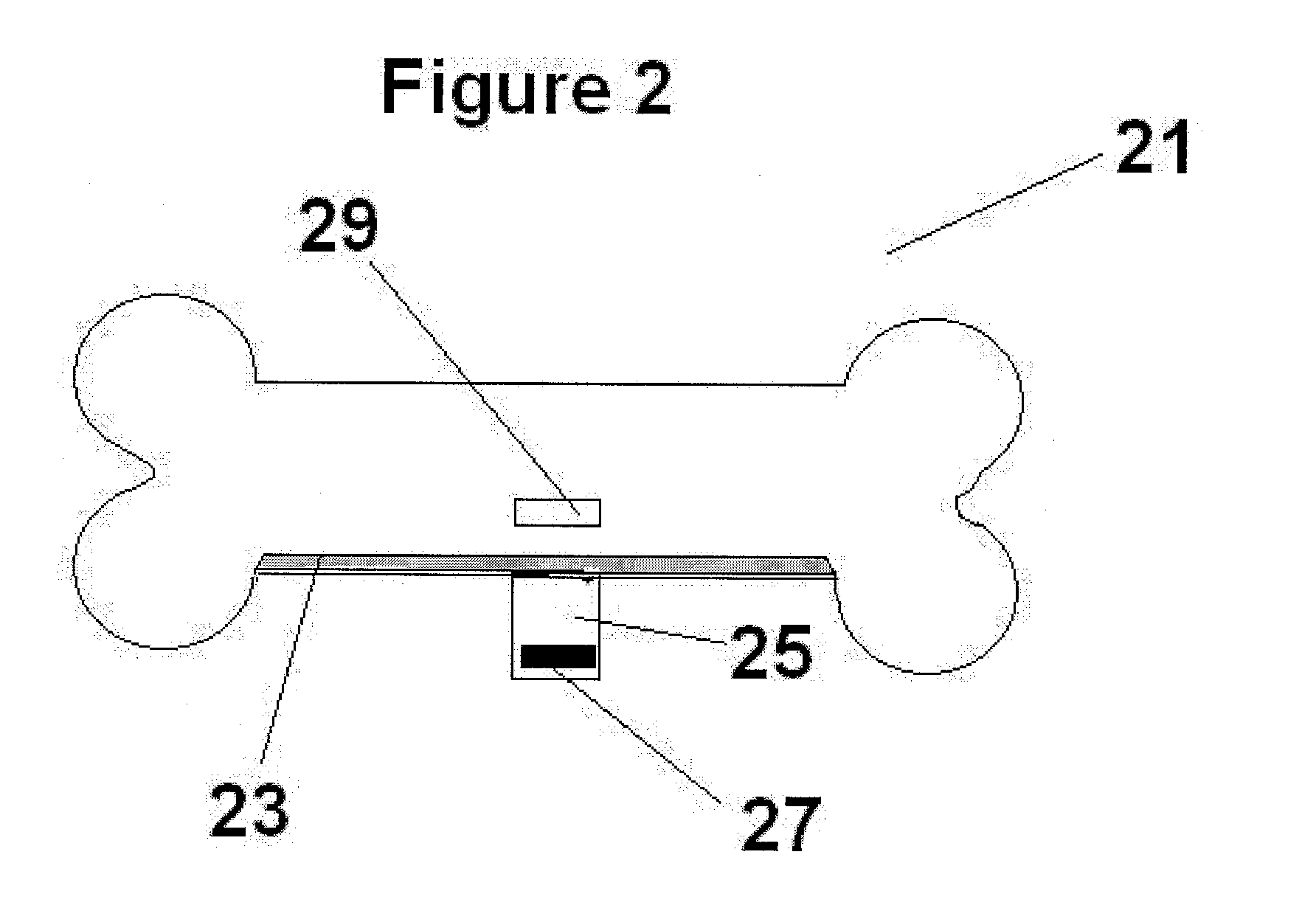
Pet Animal Collar for Health & Vital Signs Monitoring, Alert and Diagnosis
A system for monitoring vital signs of a pet animal comprises an annular band, an accelerometer configured to measure at least one of resting patterns, activity patterns, movement patterns, position patterns relating to, for example the pet animal relieving itself, lameness and scratching, and a non-accelerometer sensor configured to measure at least one of the following non-accelerometer-measured bioparameters of the pet animal: temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate. One or more processors are configured to receive sensor output data and reference data concerning the measured bioparameters of the pet animal or of a population of the pet animal, and determine a suspicion of a specific medical condition by: (i) scoring at least two bioparameters and comparing a cumulative score to a threshold cumulative score or to a threshold cumulative range; or (ii) identifying an abnormal pattern. The processor(s) may send an alert if at least one specific medical condition is suspected.
Owner:PETPACE
Arm suspension sleeve
InactiveUS7297128B2Easy to storeEasy to handleFinger bandagesVeterinary bandagesSecondary layerFastener
A multi-layer wrap, for providing more comfortable gel treatment to skin while providing orthopedic support having a first layer of gel for contacting the skin and a second layer of an elastic and supportive loop portion of a hook and loop fastener, the wrap allowing for migration of moisture away from the skin. The wrap can be used as part of a suspension sleeve for use during arm surgery or post-operative recovery. The product is economically manufactured in the form of long rolls or as a sheet and is easily cut to any desired shape.
Owner:GELZONE
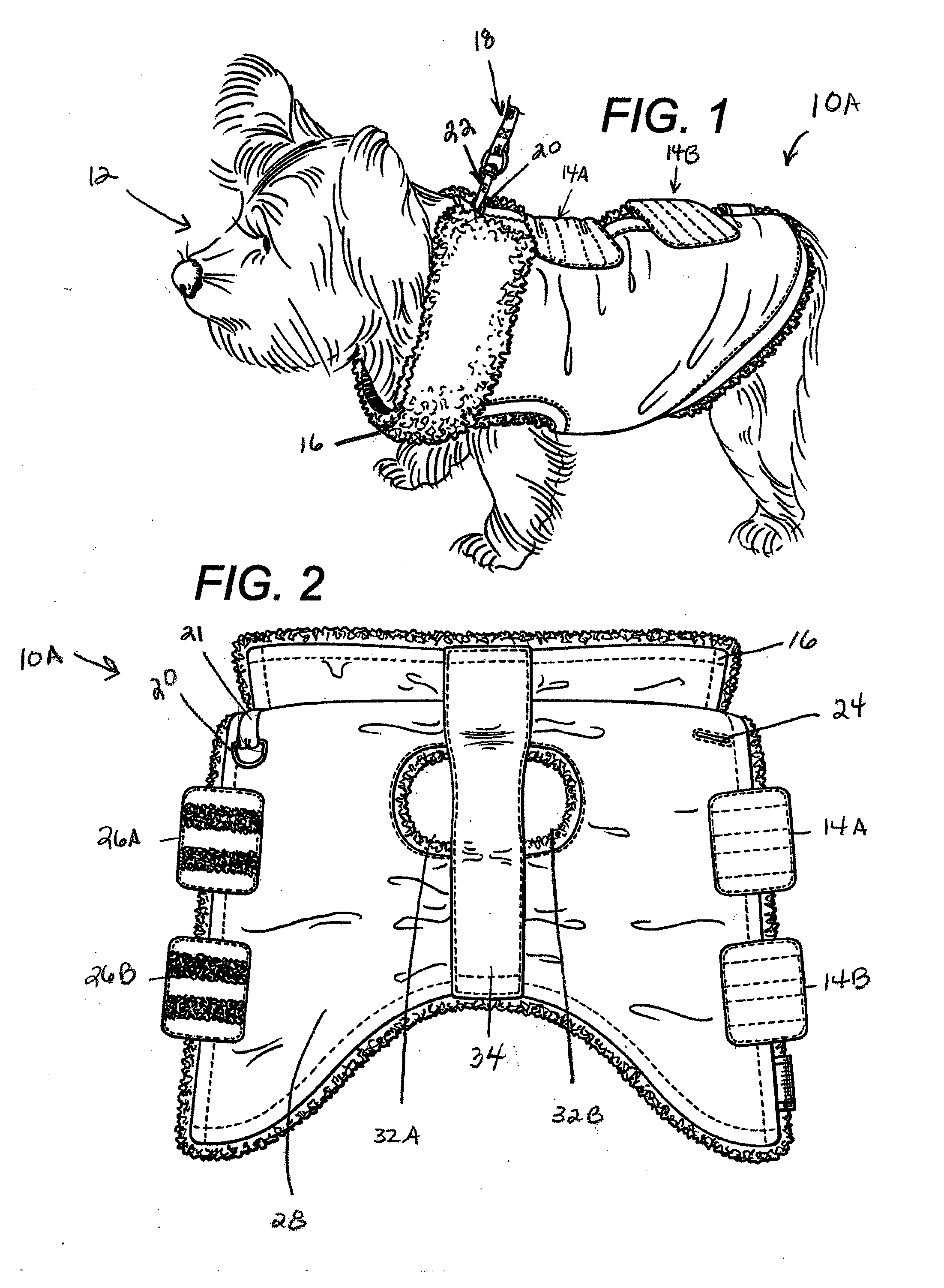
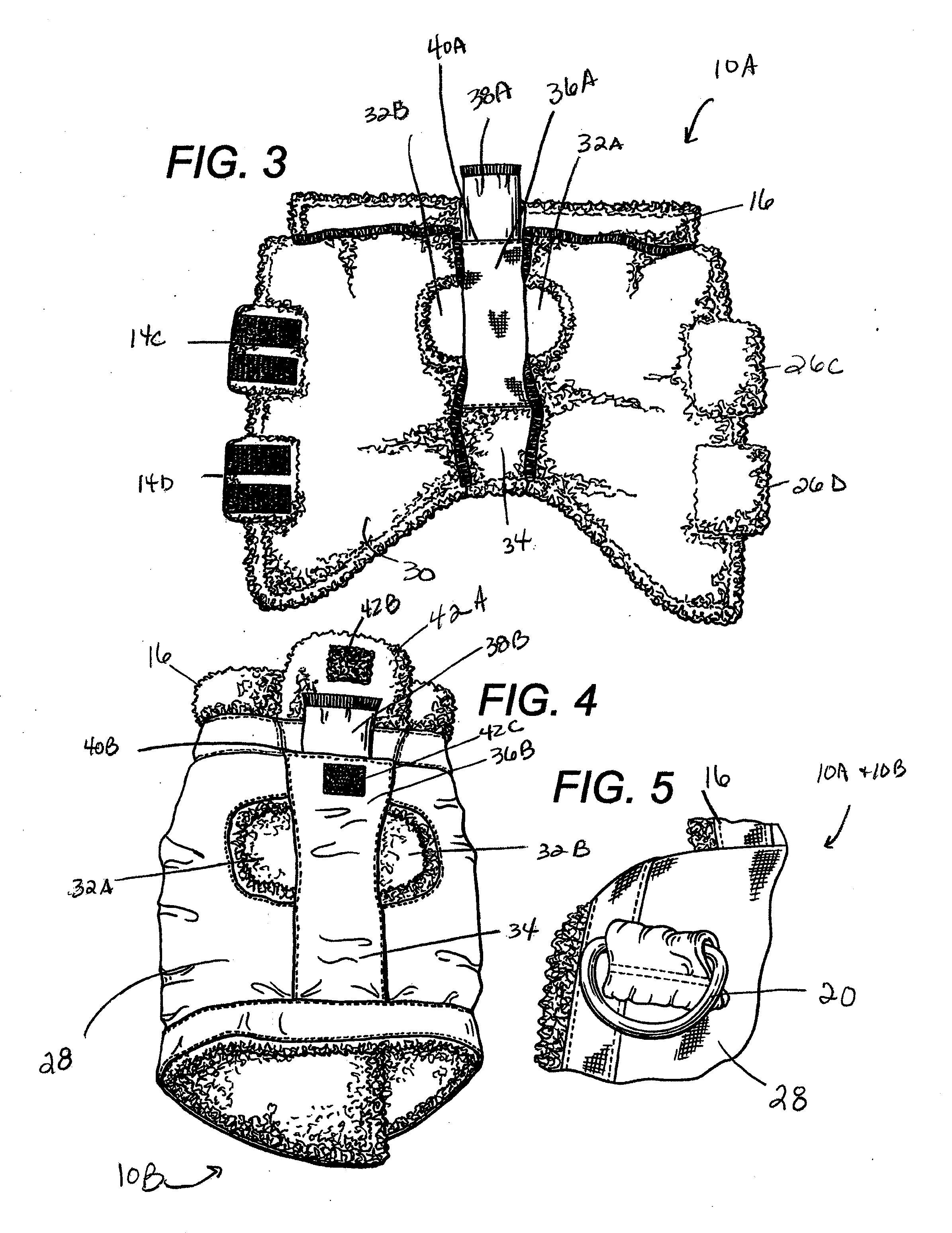
Animal wound wrap for holding a primary wound dressing on an animal wound
InactiveUS7004922B1Easy to adaptRapid and painless accessVeterinary bandagesTaming and training devicesWound dressingAbdomen
An animal wound wrap used for holding a primary wound dressing, an IV tube and / or drain tube in place on an animal's body. The animal wound wrap includes an elongated abdomen wrap portion and an elongated extension wrap portion. The two wrap portions are made of stretchable loop-like loose weave material along their length. The abdomen wrap portion can be stretched along a first axis while the extension wrap portion can be stretched along a second axis at an angle to the first axis. The abdomen wrap portion includes a first end portion with hook fasteners and a second end portion for releasably engaging the hook fasteners. The extension wrap portion includes a first end portion attached to a side of the abdomen wrap portion and at an angle thereto. The extension wrap also includes a “U” shaped second end portion. The “U” shaped second end portion includes a first strap and a second strap. The straps are adapted for receipt around the animal's neck, tail, leg or other parts of the animal's body. The hook fasteners are used for securing the straps thereon.
Owner:SHESOL BARRY F +1
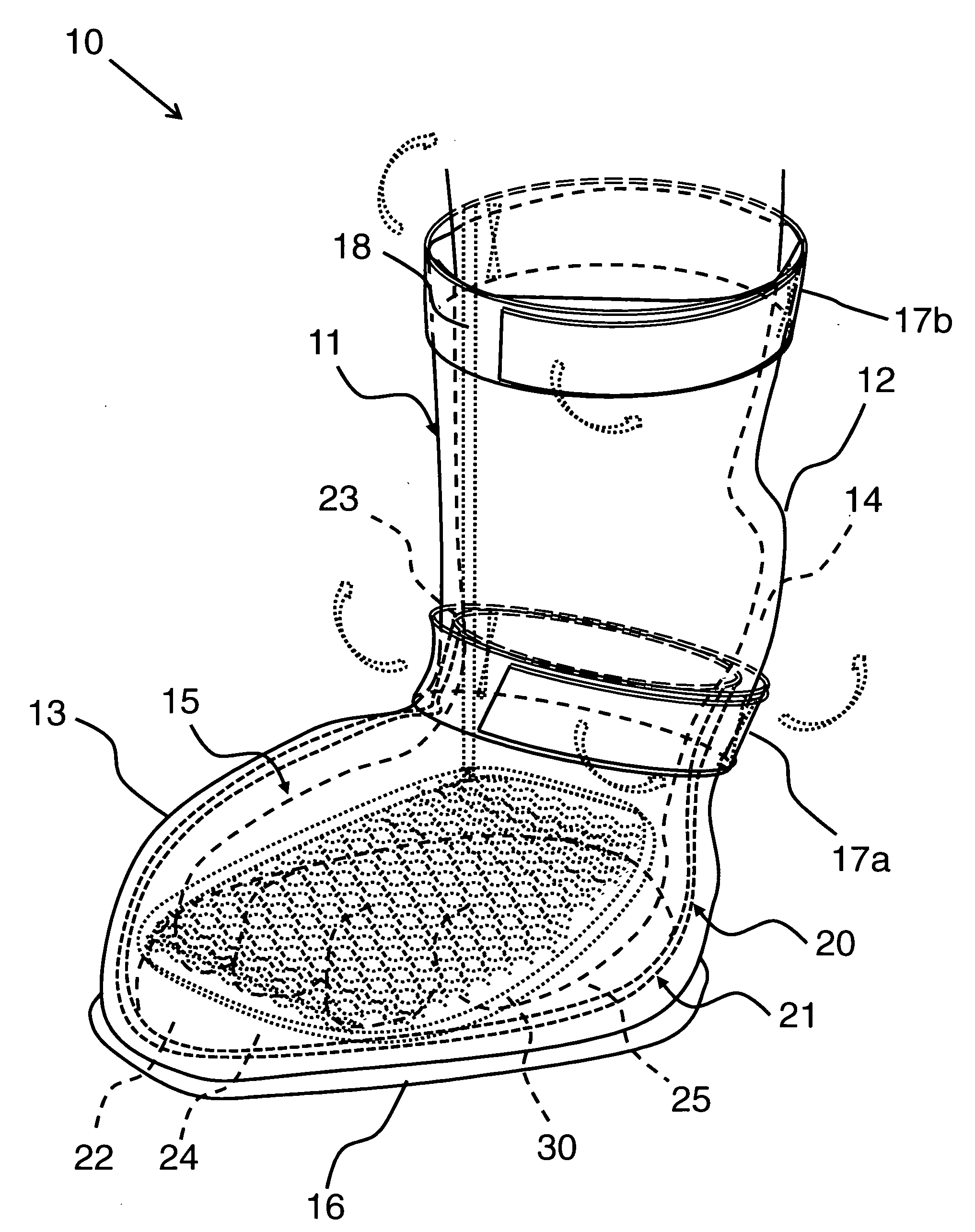
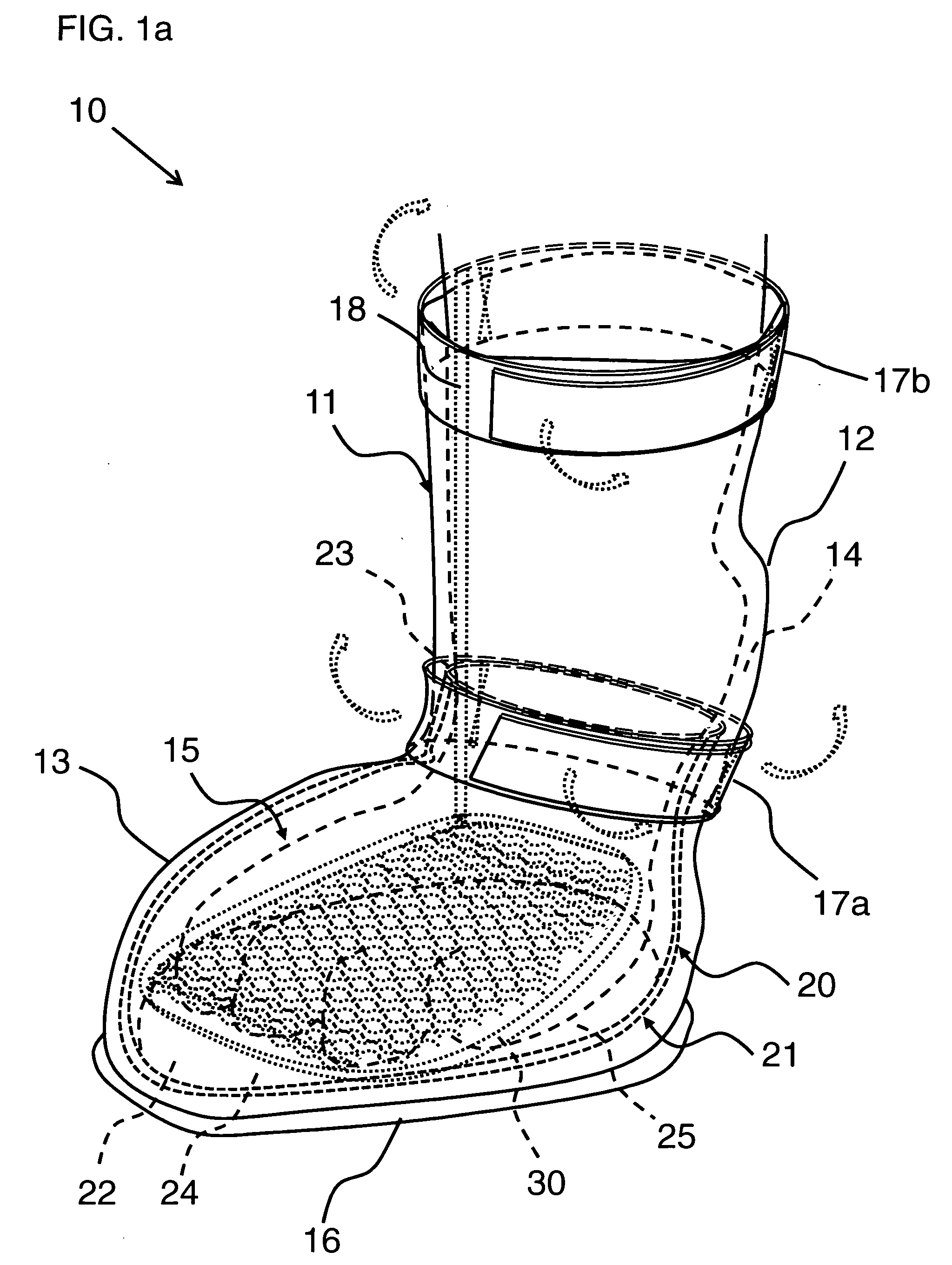
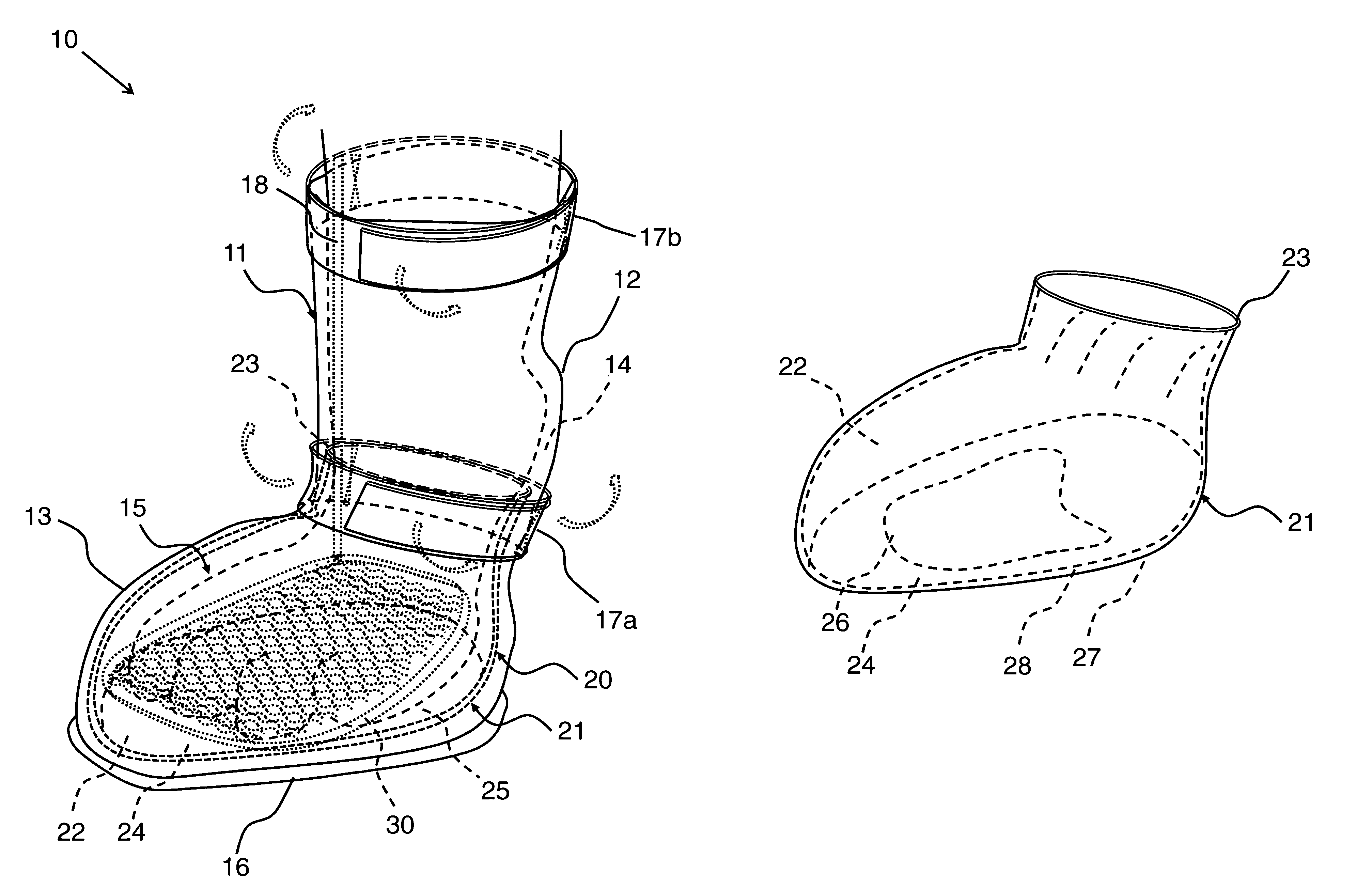
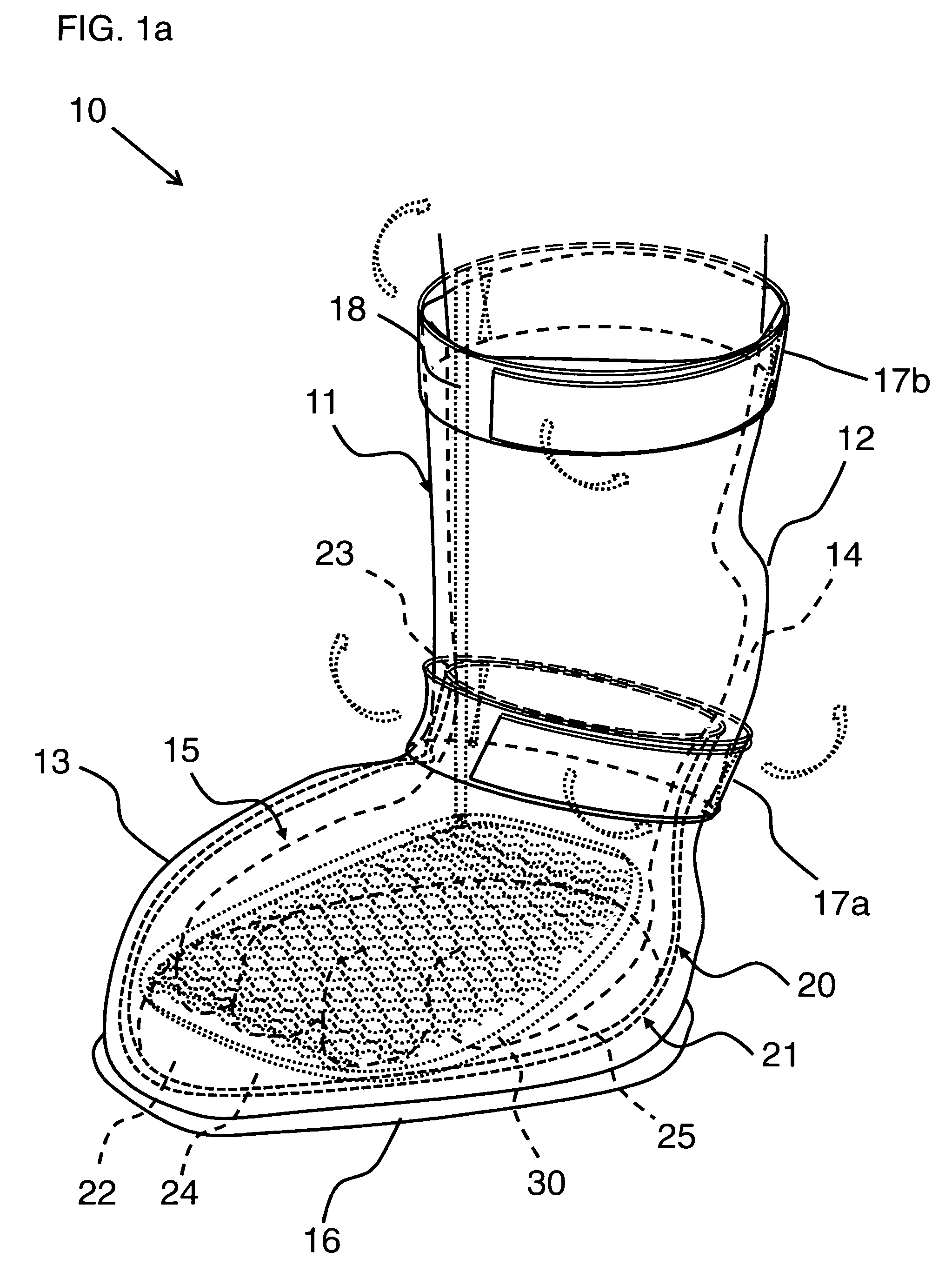
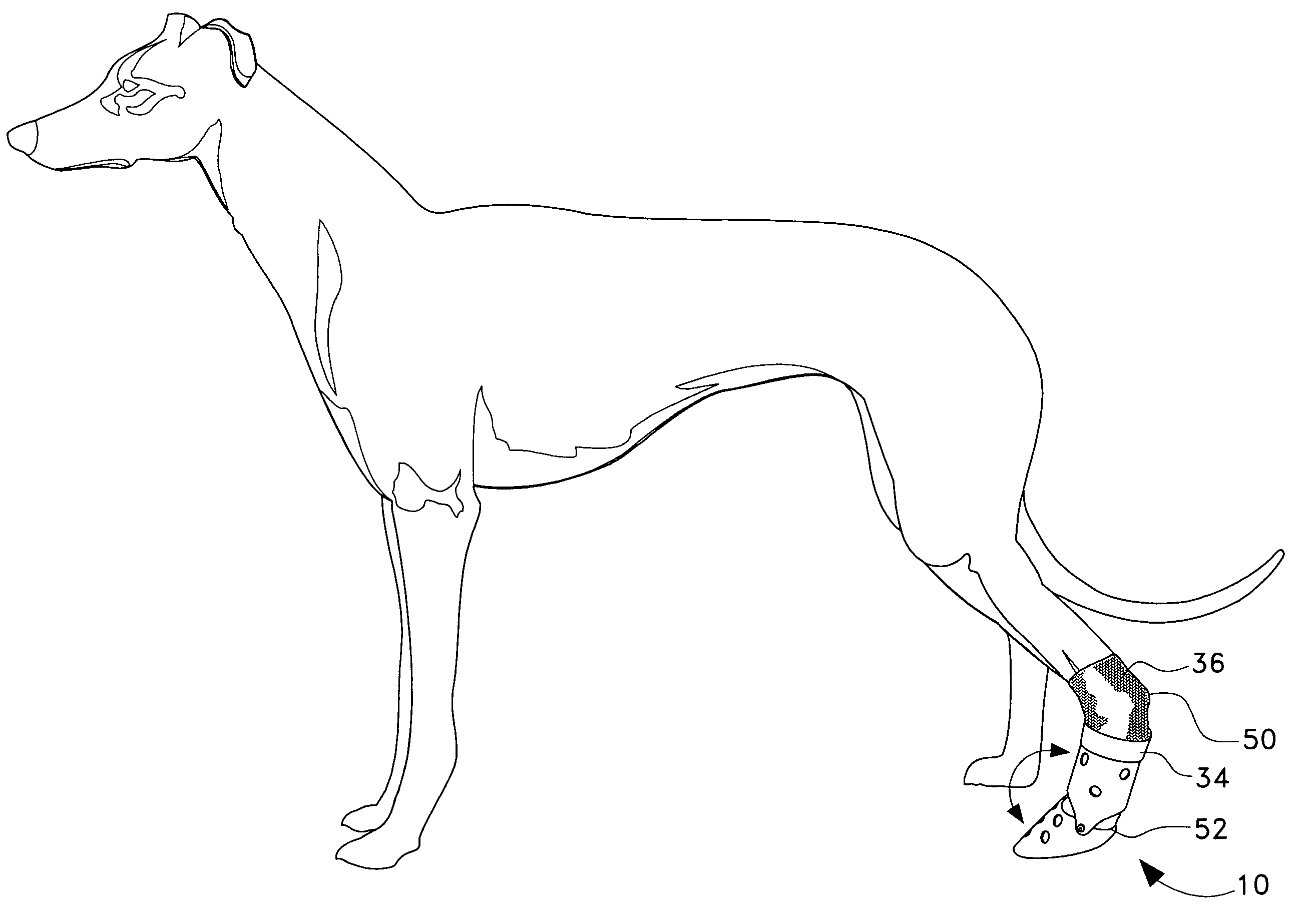
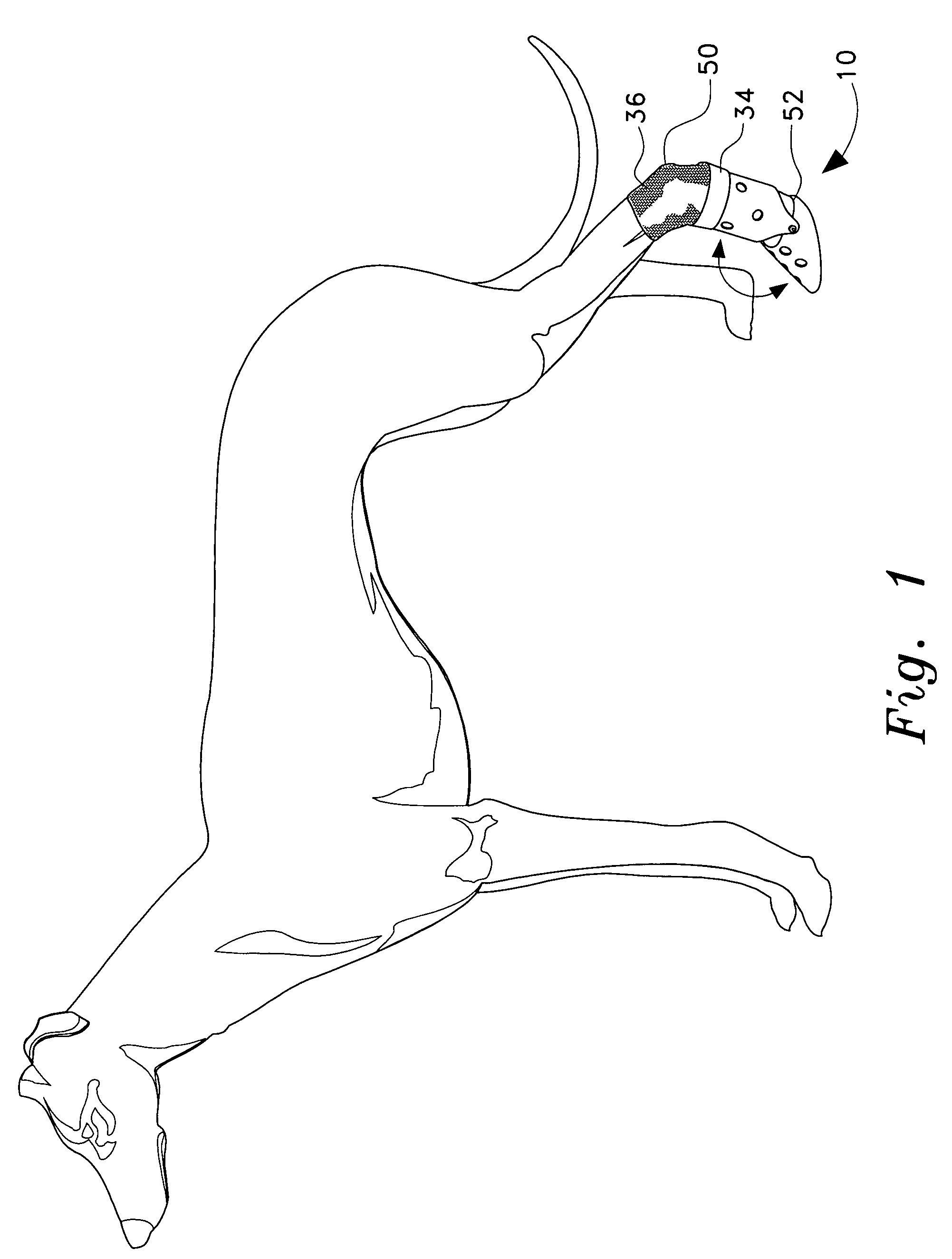
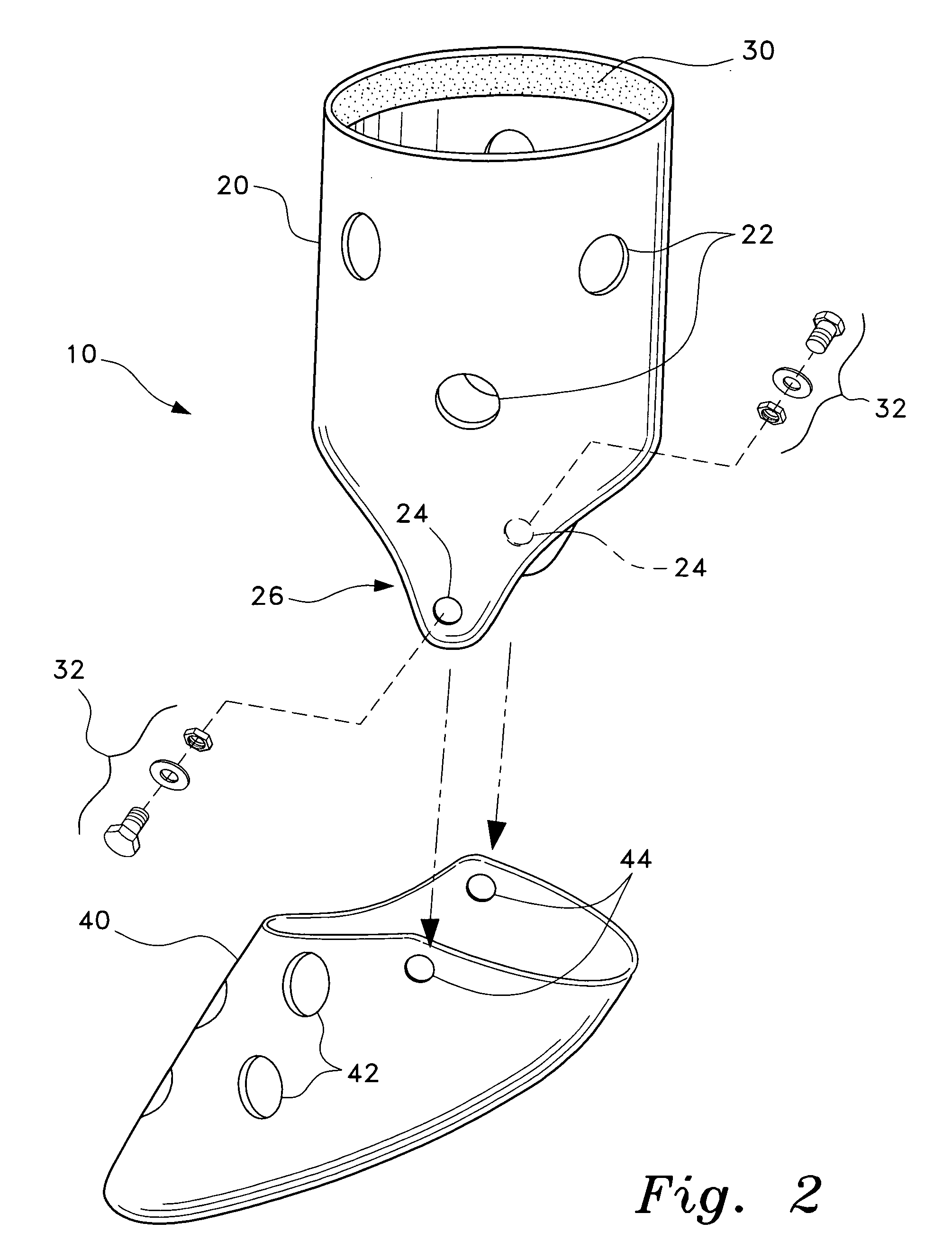
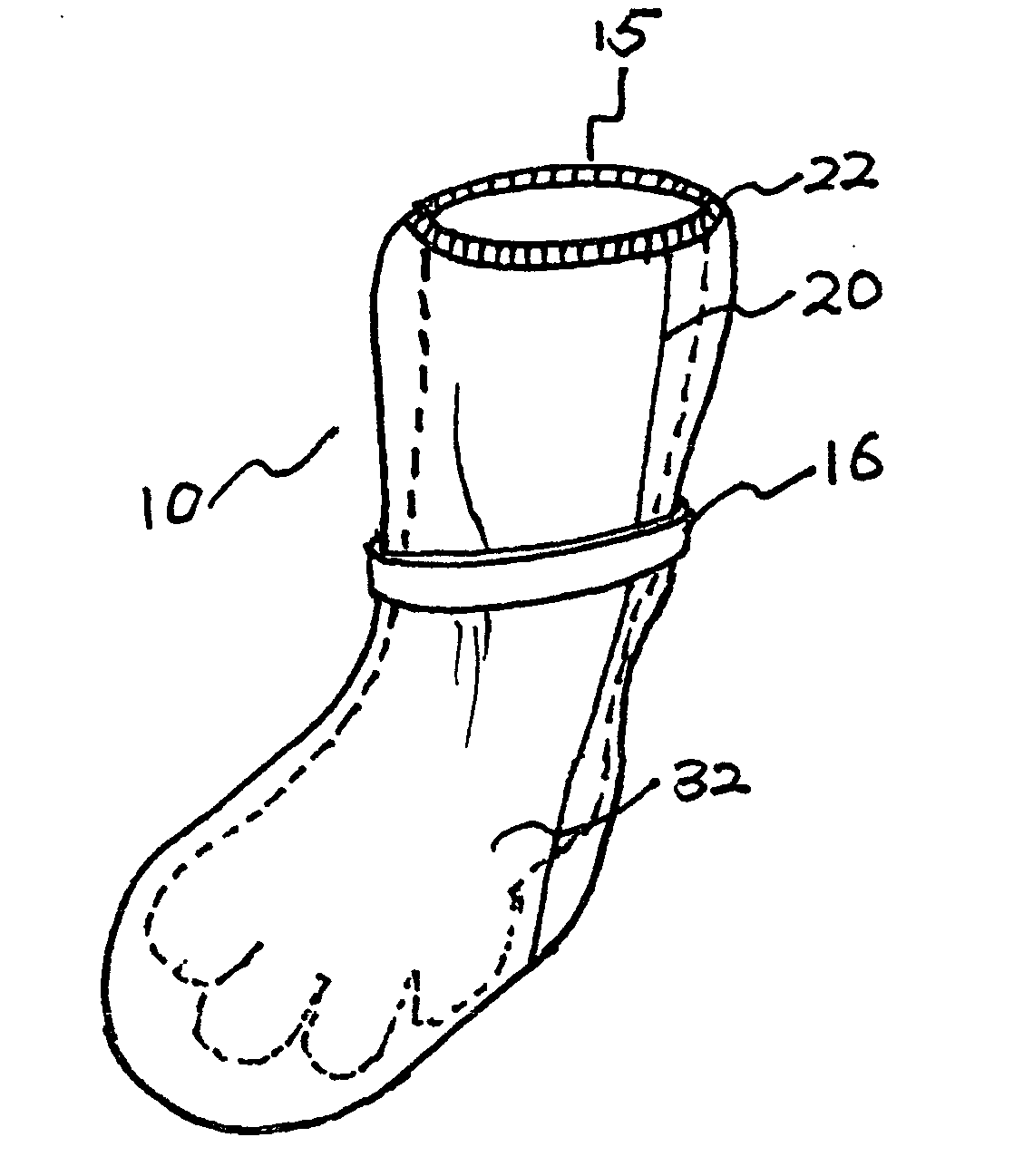
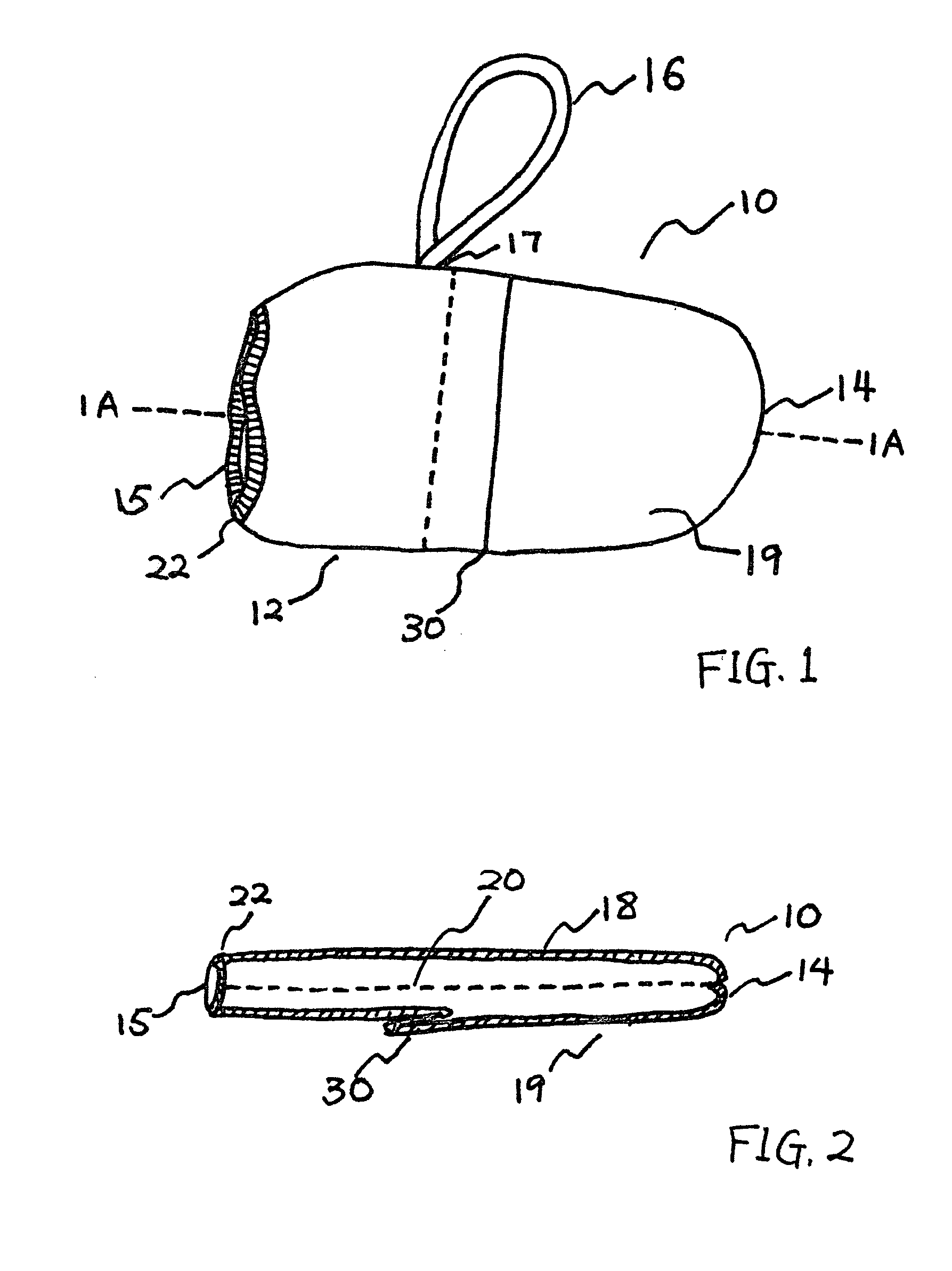
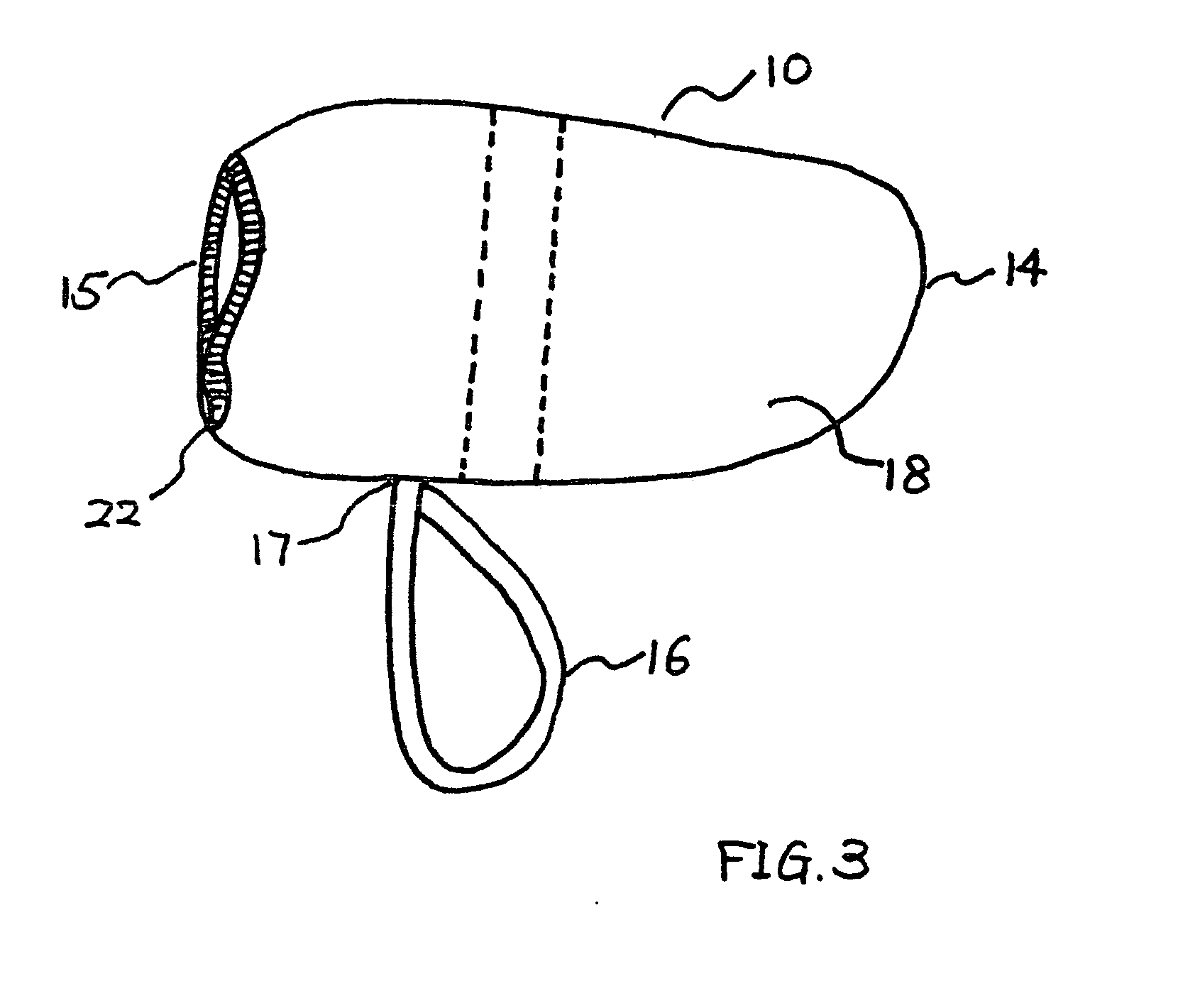
Therapeutic pet boot
InactiveUS20110041779A1Promote healingHealing of the paw is facilitatedSolesVeterinary bandagesCushioningCold treatment
A pet boot having therapeutic properties is worn on a pet's injured or sensitive paw to facilitate healing and or provide protection. The therapeutic pet boot includes an external boot member having a shaft and a paw portion constructed to form a cavity integrated therein appointed to receive an injured paw of a pet. The therapeutic pet boot further includes an internal therapeutic member appointed to be received within the cavity of the external boot member and is appointed to intimately contact the injured paw. The therapeutic pet boot is appointed to be worn on the injured paw of the pet to facilitate healing. The internal therapeutic member may comprise a gel bootee having a massaging gel sole or may comprise a gel inner layer or gel insole. Advantageously, the internal therapeutic member may directly deliver medicament to the paw and / or provide cold treatment or hot treatment therapies to the paw, while providing cushioning, shock absorption and protection from dirt and debris.
Owner:I DID IT
Pivotable strap-buckle assembly
This invention is directed towards an apparatus for securing and adjusting a strap. More particularly, the present invention is directed towards a buckle assembly having a pivotable member pivotably attached to opposed regions of the buckle frame. In one embodiment, a sport-goggle assembly has a pivotable buckle assembly attached to one end of a strap. In another embodiment, a sport-goggle assembly has a pivotable buckle assembly attached to each of the two straps. In other embodiments, the pivotable buckle assembly can be used in association with a strap-lengthening member.
Owner:SMITH OPTICS
Non-slip pads for animal paws
Non-slip pads for animal paws include a pad with a non-slip surface on one side and a pressure sensitive adhesive on the other side. The pad is fabricated from a material with superior grip characteristics, such as neoprene. The non-slip surface is also preferably textured to increase grip. The pressure sensitive adhesive is preferably a medical adhesive suitable for contact with an animal. A peel-off label is attached to the adhesive to prevent the adhesive from prematurely bonding to another surface. In use, the animal's paw is first cleaned and dried. The peel-off label is removed from the pad and the adhesive side is applied to the cleaned and dried paw.
Owner:FLEMING MARLENE M
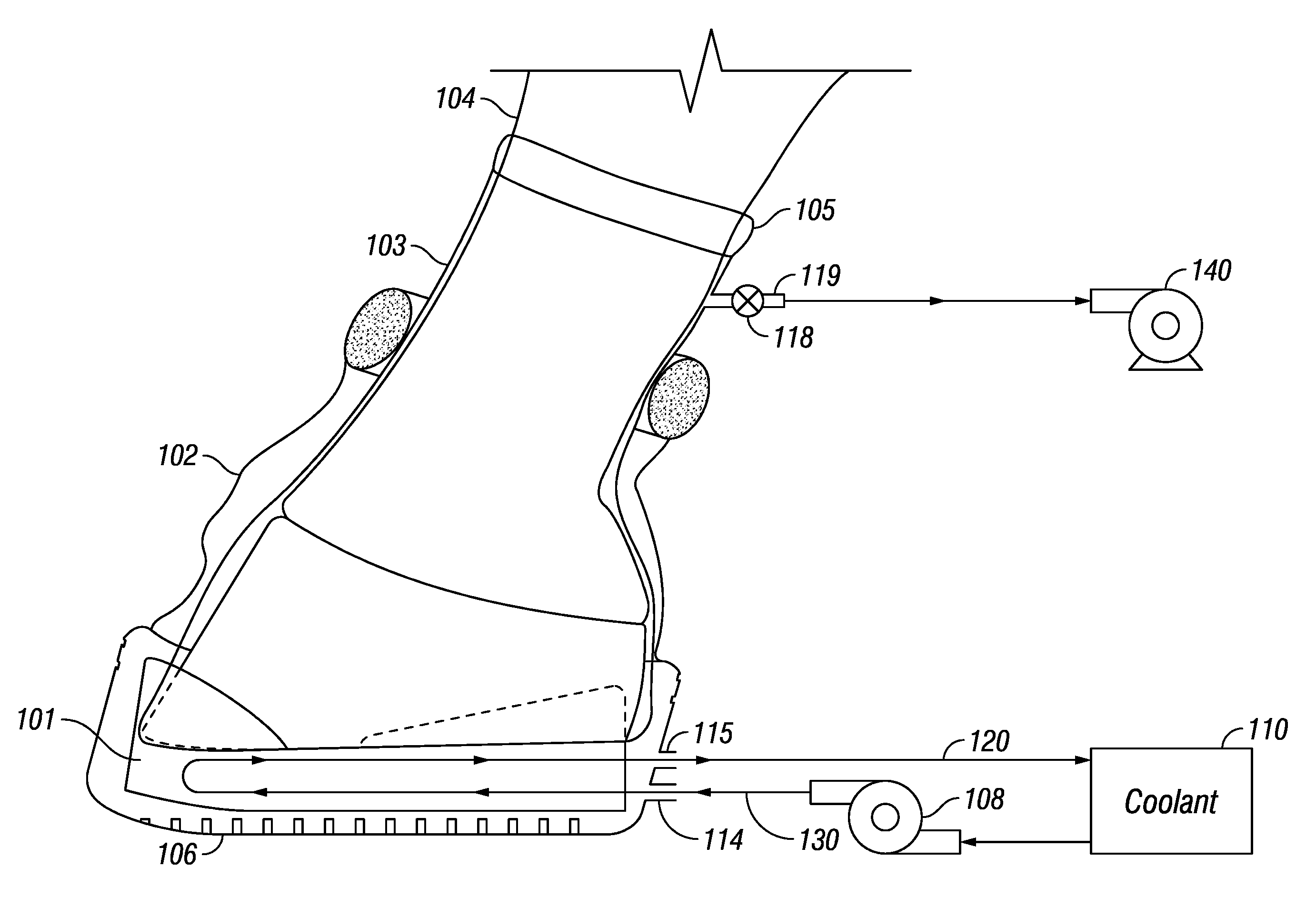
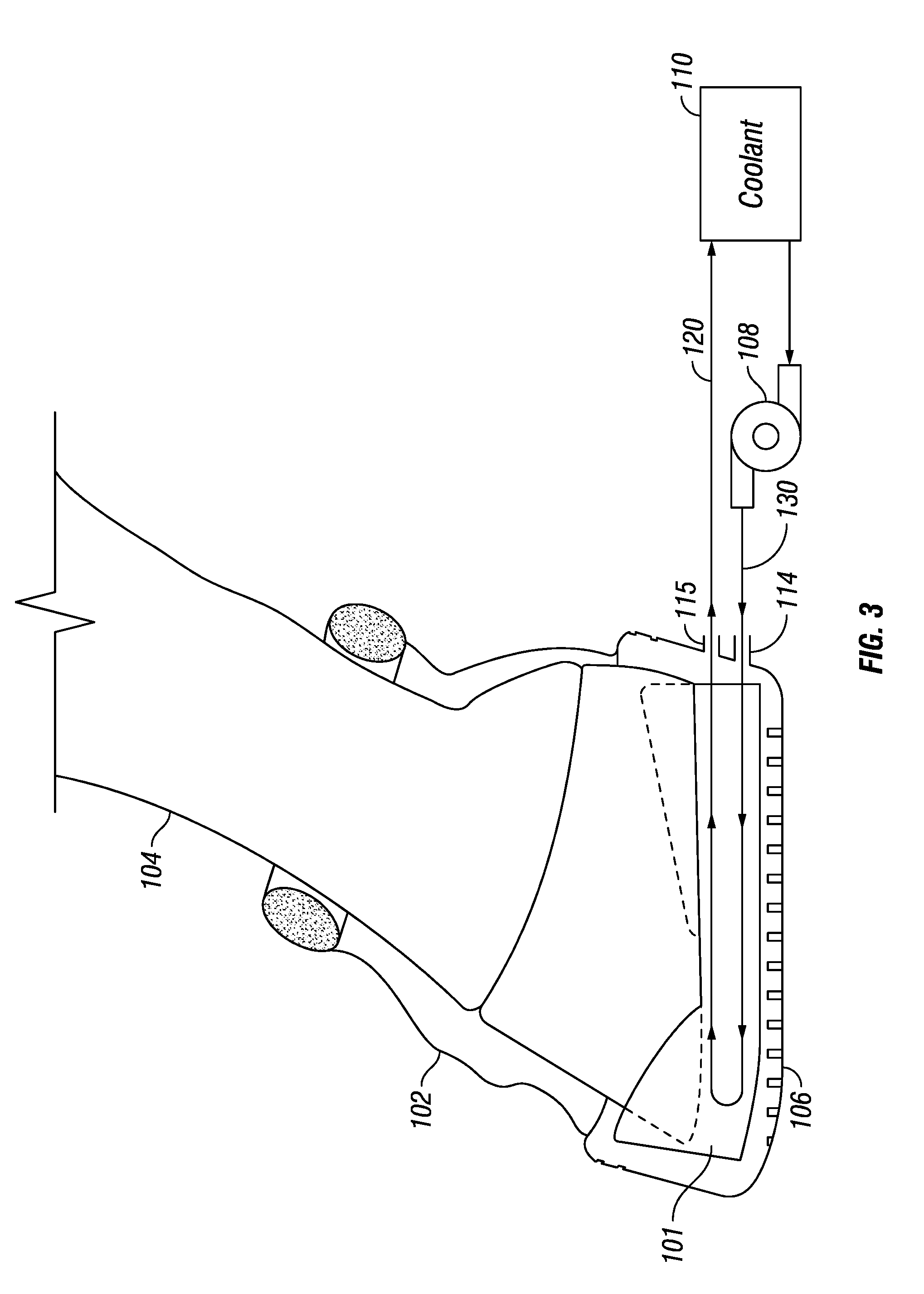
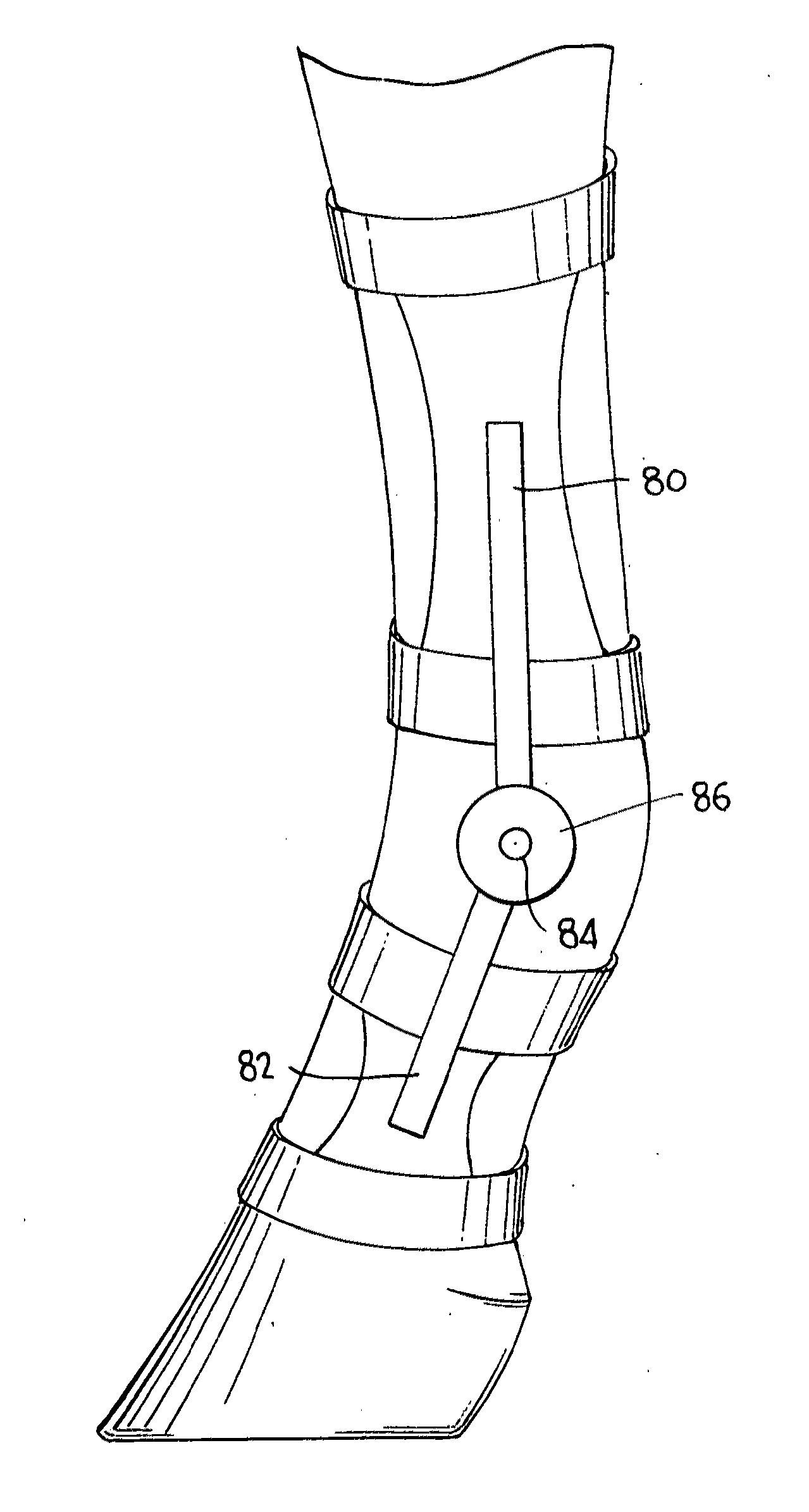
Equine Cold Therapy Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20100095641A1Heating fastImprove performanceProtection coversVeterinary bandagesEquine SpeciesEngineering
Apparatus for and methods of core cooling the blood of an equine animal. The apparatus is a flexible boot having disposed in it an orthotic pad that has means for circulating coolant so the bottom hoof area of an equine can be cooled. Optionally the pad is designed to allow cooling under vacuum. In some aspects the apparatus also provides means for cooling the lower leg of the equine in a way designed to allow coolant circulated through the boot pad to also be circulated through the leg cooling means while maintaining a controlled temperature against the leg surface. The invention is also a method of core cooling an animal utilizing the apparatus described.
Owner:RUETENIK MONTY L
Vision cone collar
InactiveUS20090241855A1Increase air circulationRelieve stressVeterinary bandagesTaming and training devicesAir cycleEngineering
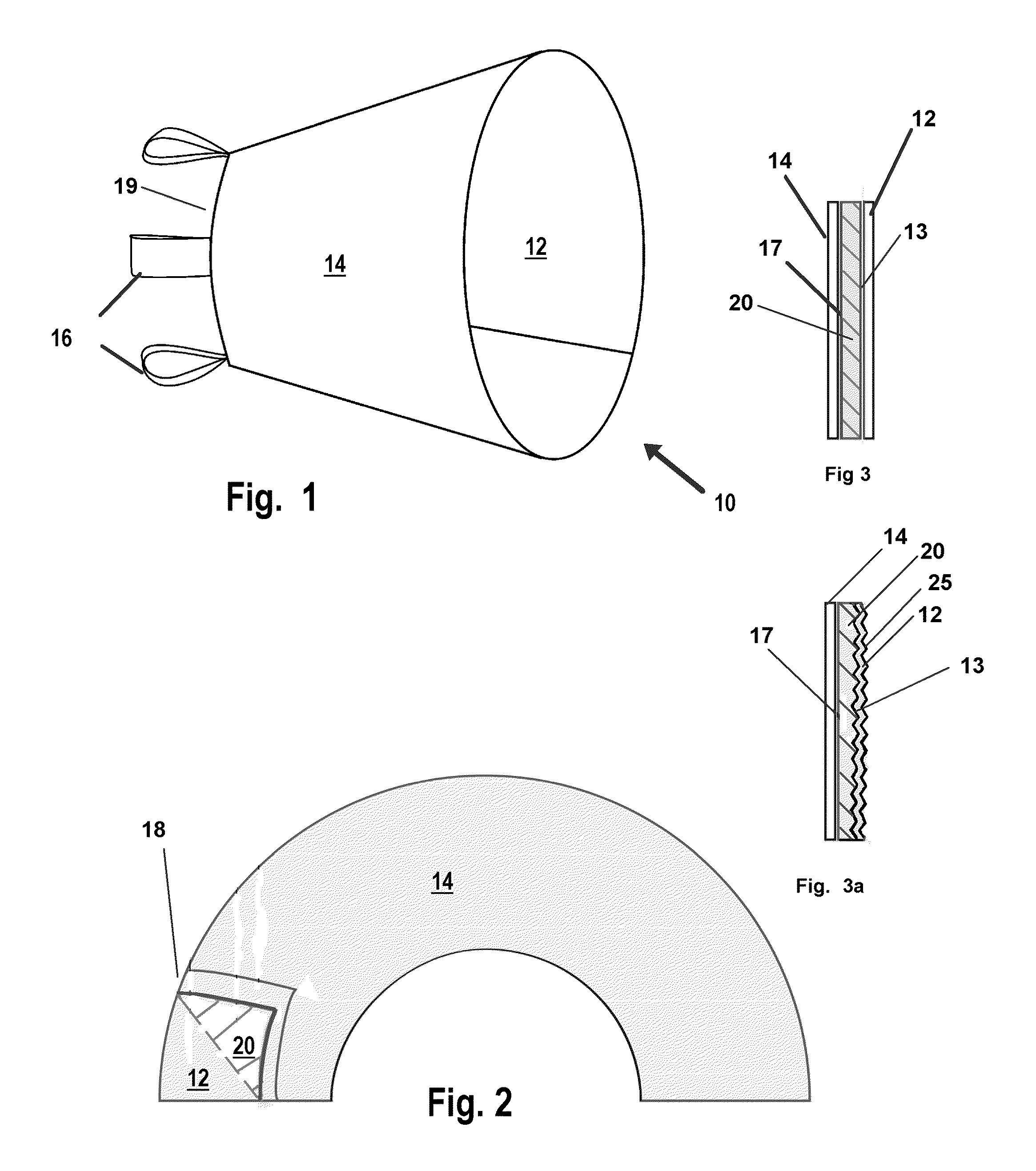
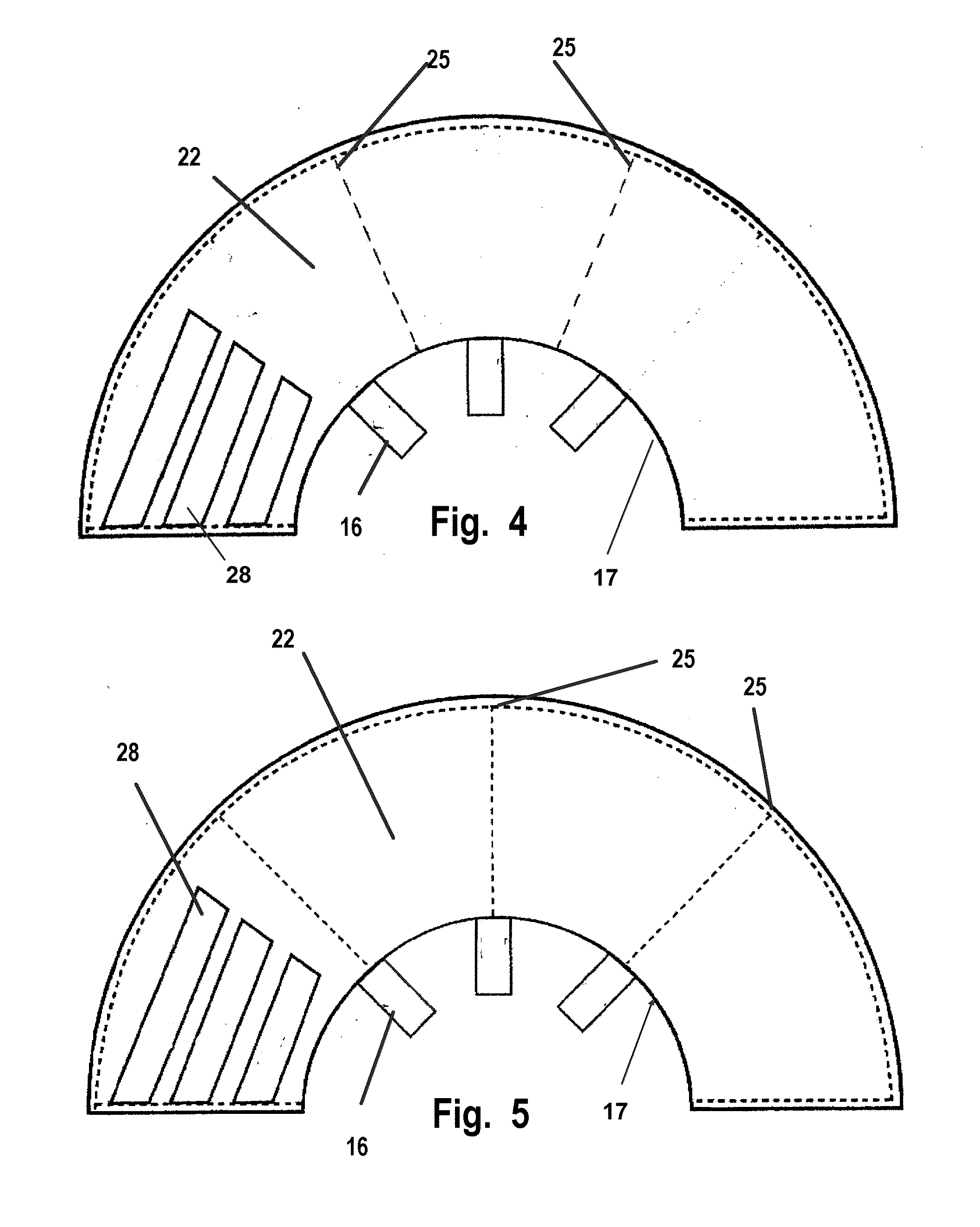
An improved animal medical collar includes openings allowing pets, domestic, and captive wild animals wearing the medical collar to freely see and smell their surroundings while preventing access to a wound or surgical area. The openings are sized and spaced to allow the animal to view and smell it's surroundings and provides increased air circulation around the animal's head. Providing such viewing and perception of odors and scents relieves the stress and anxiety the animal would otherwise experience.
Owner:STOCKI MICHAEL L +1
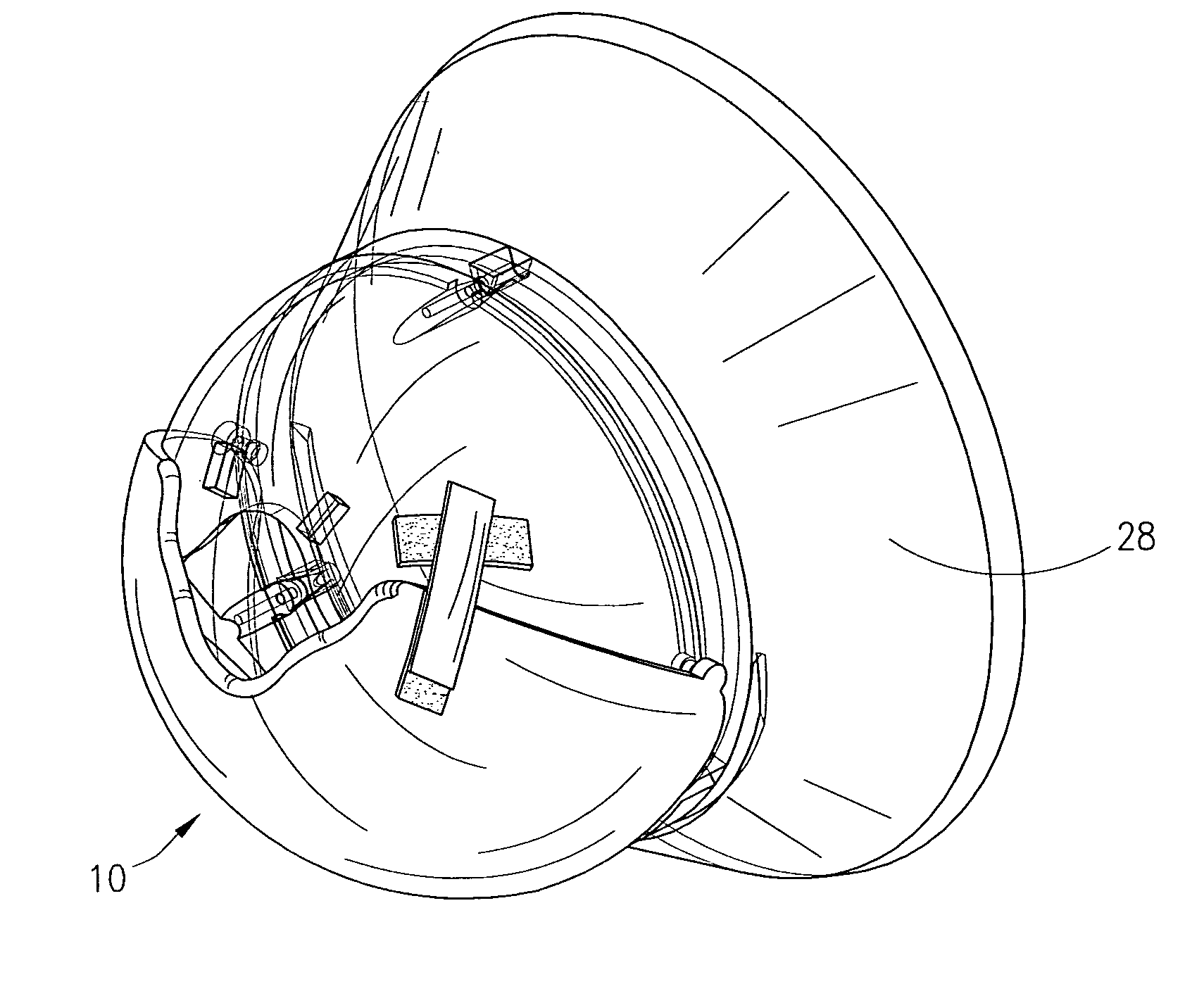
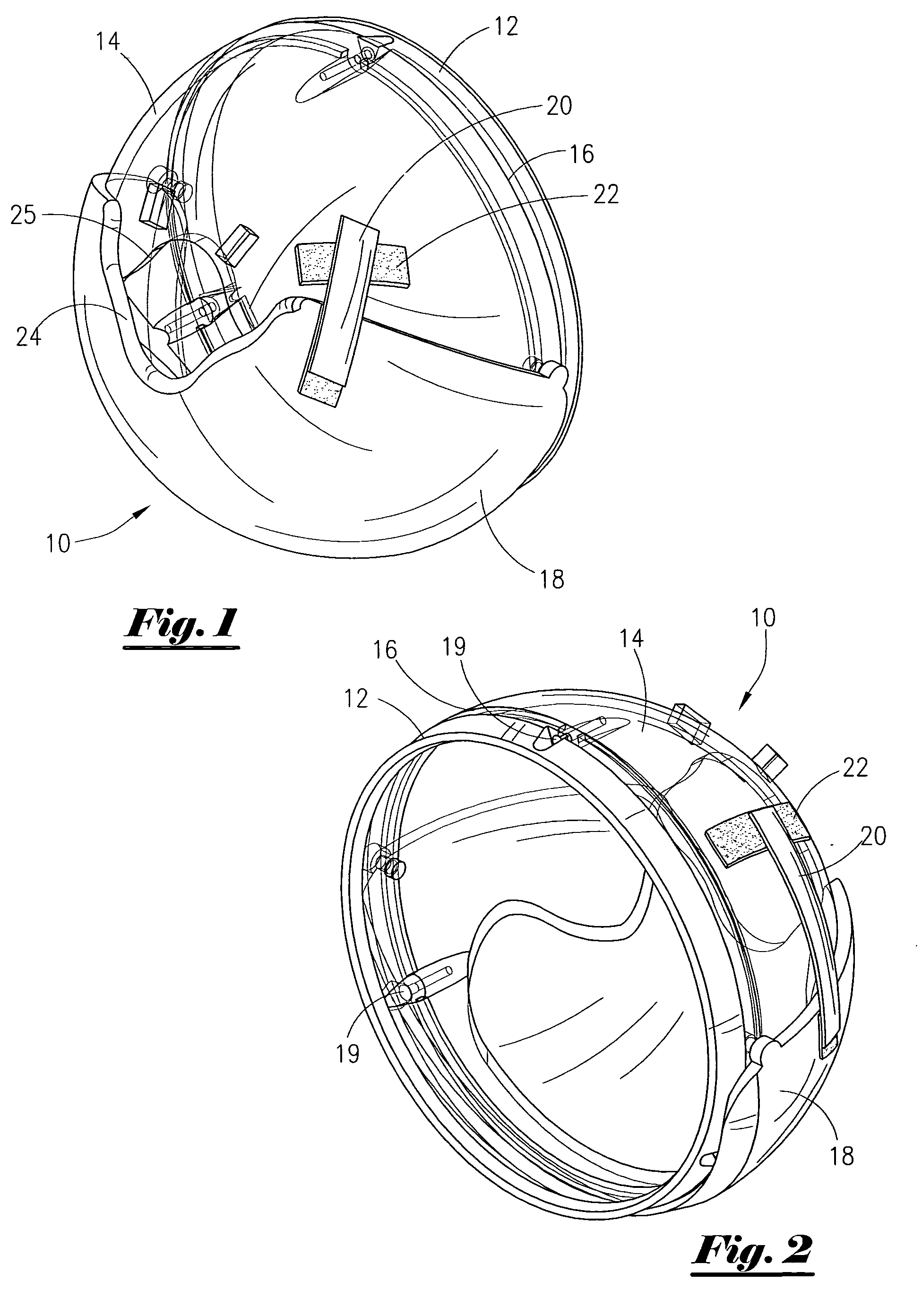
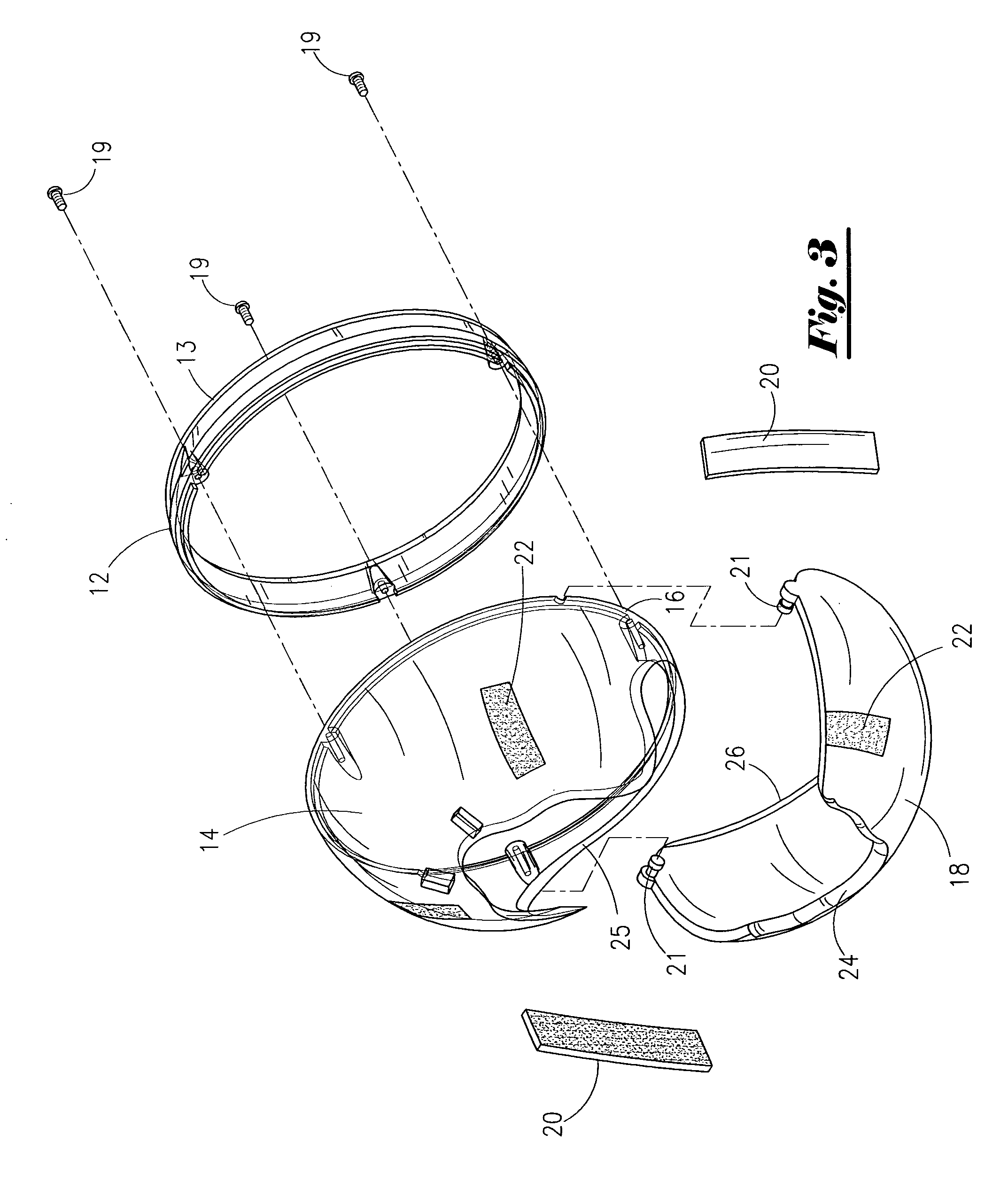
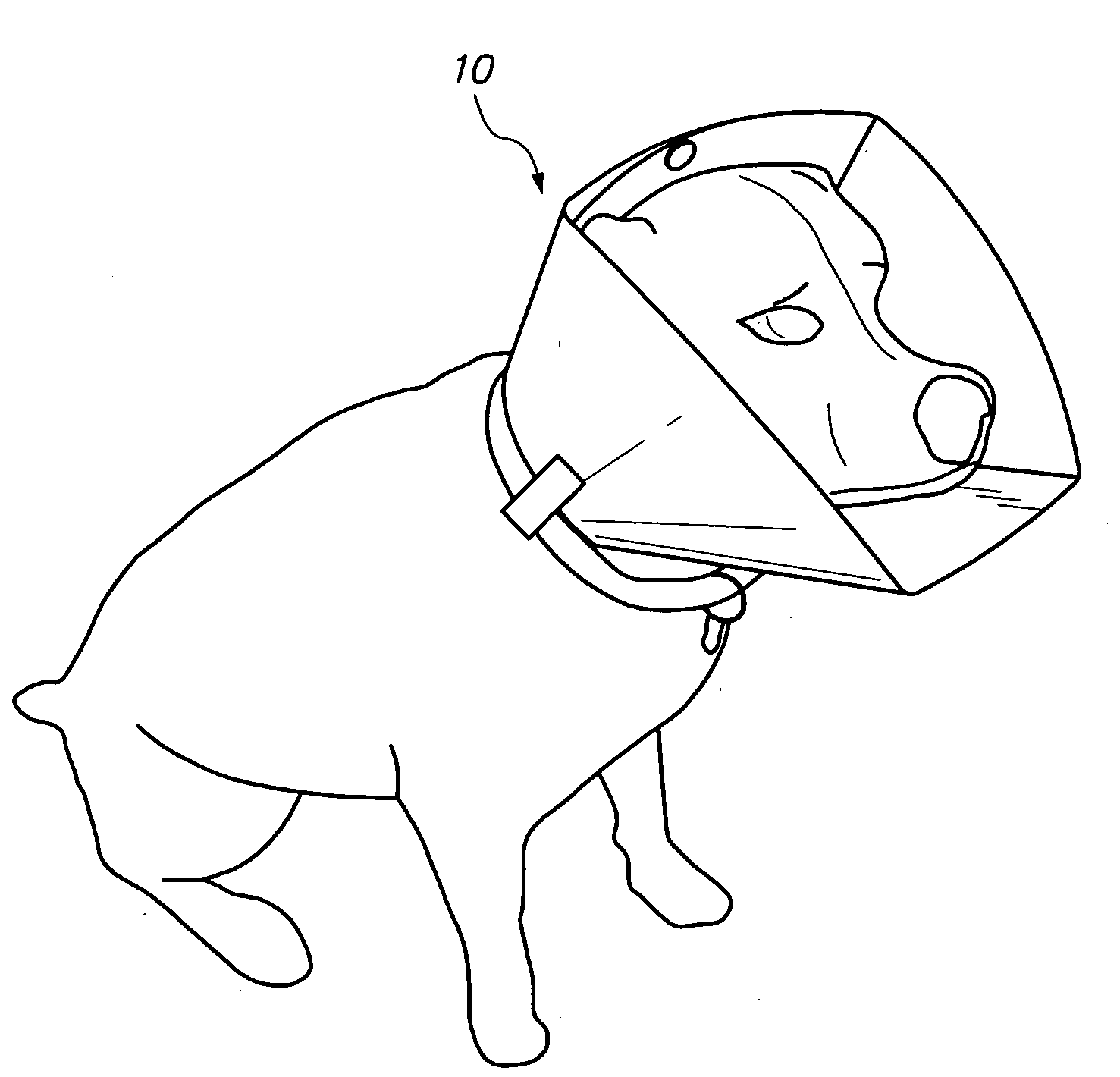
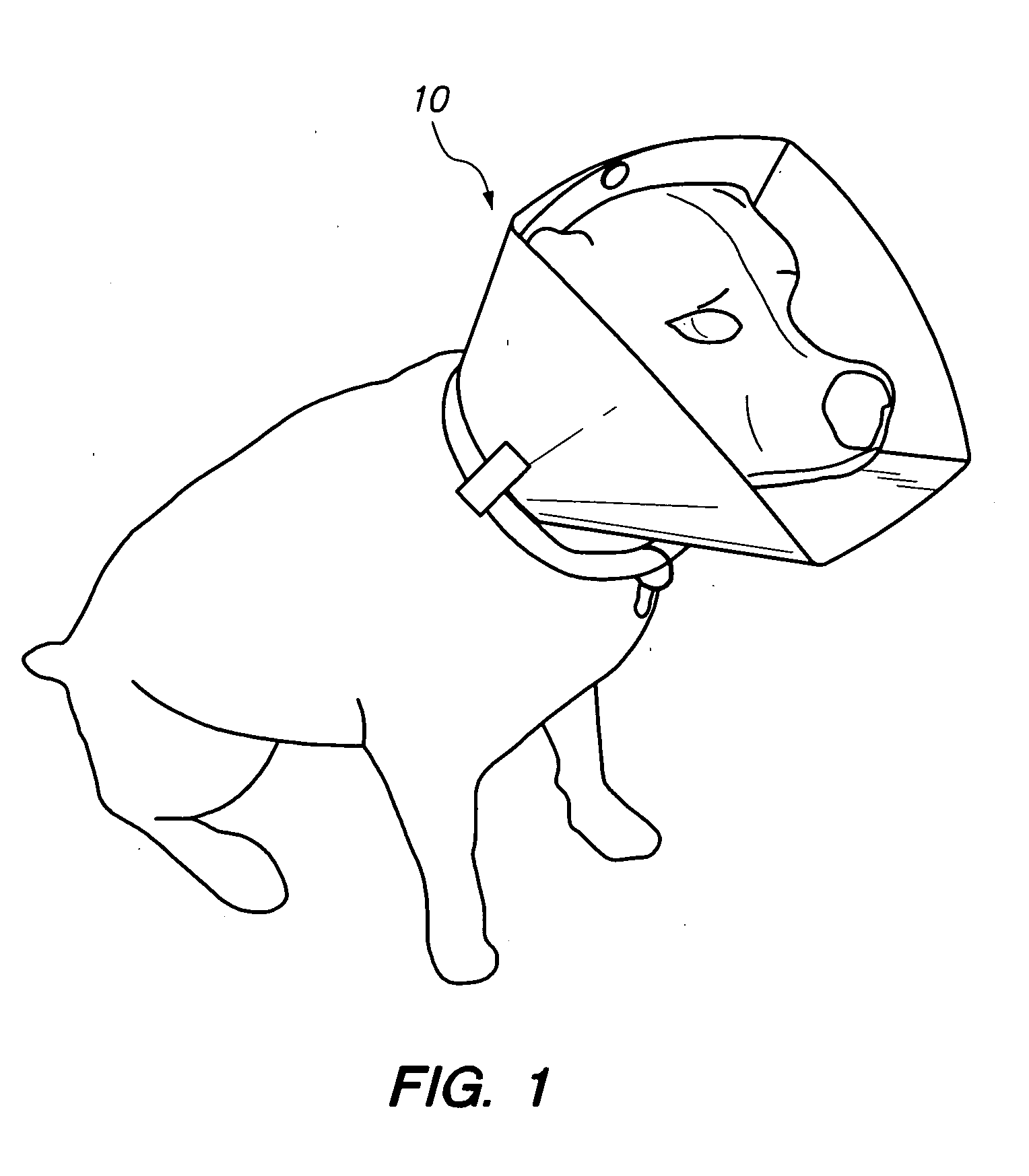
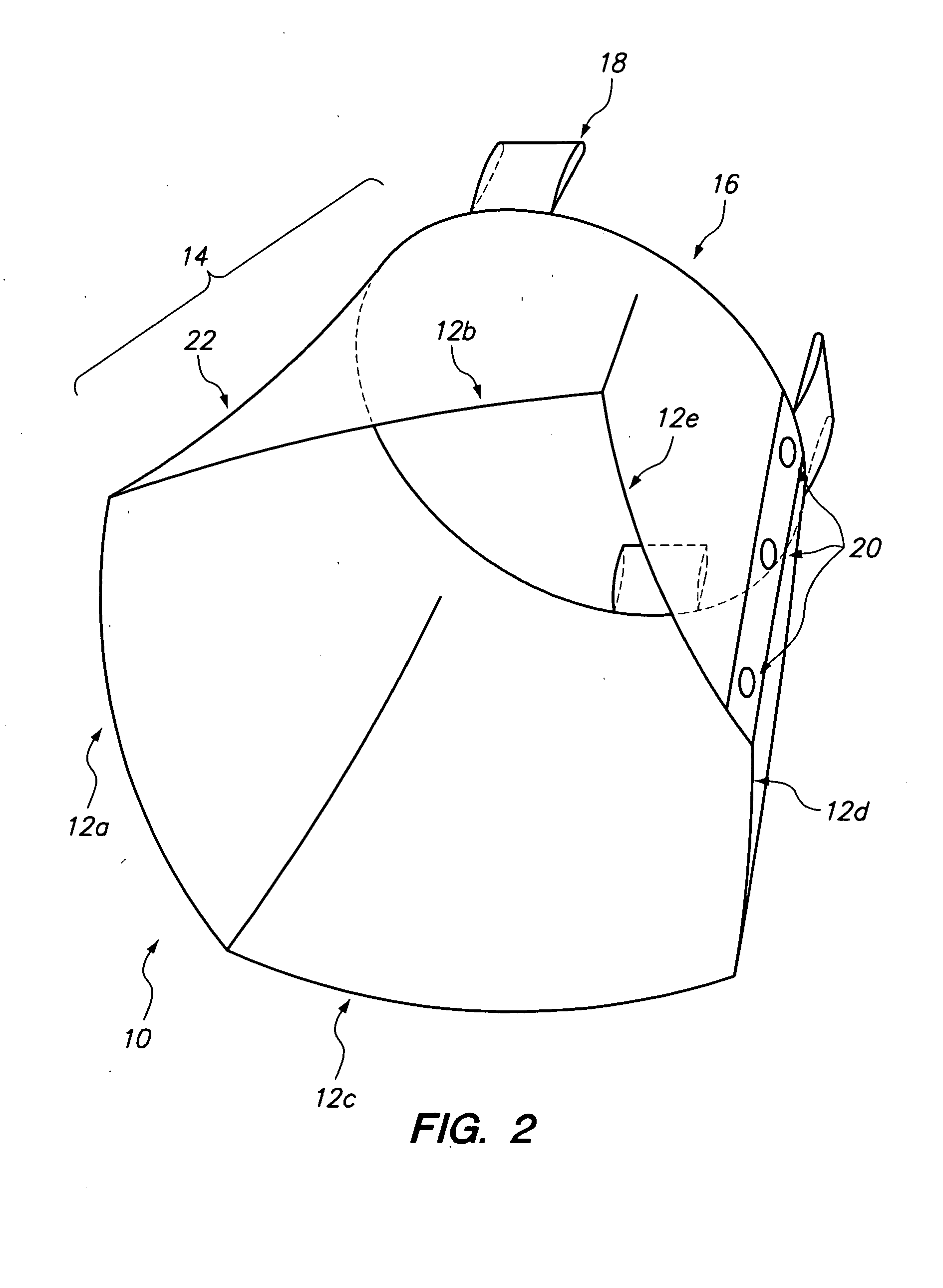
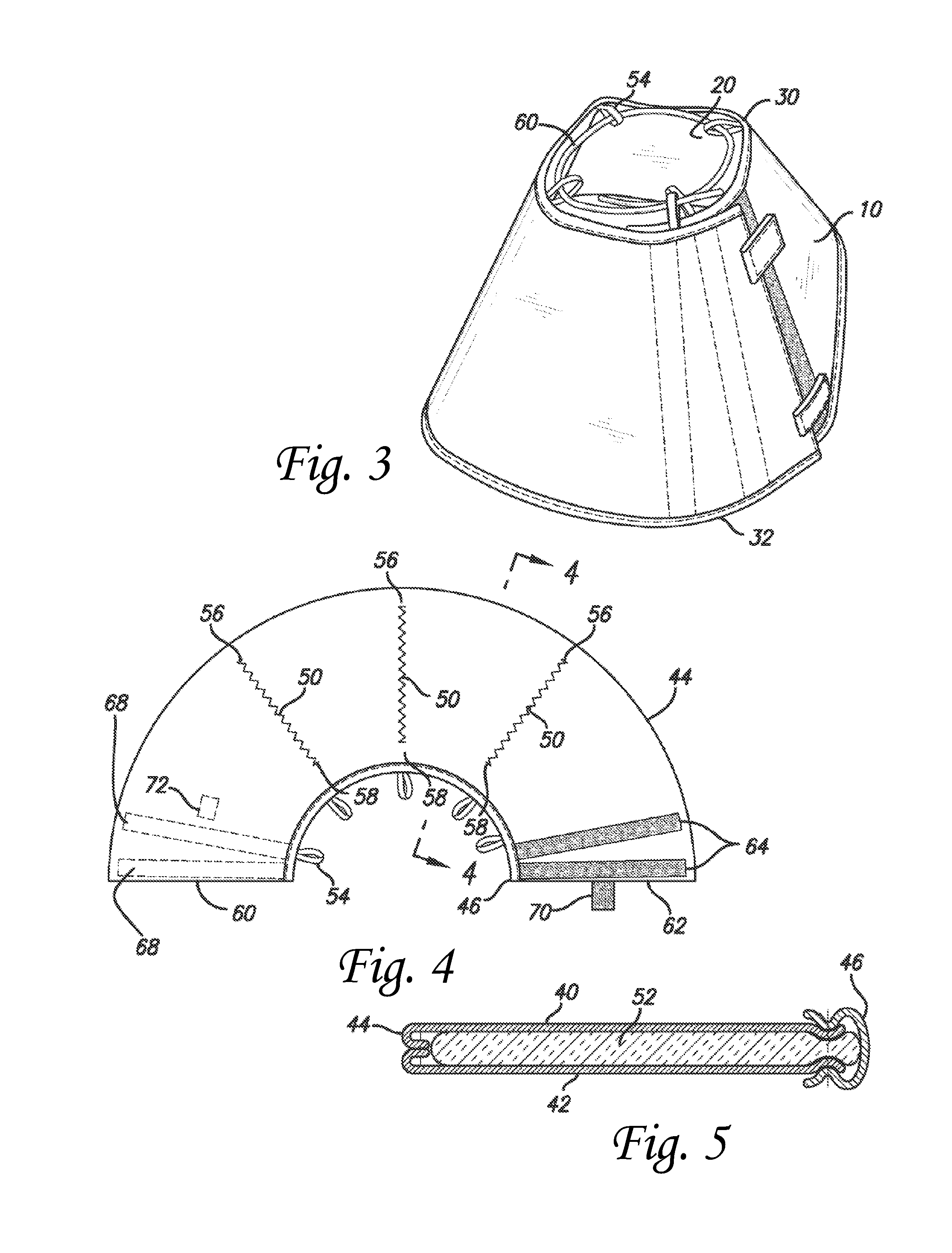
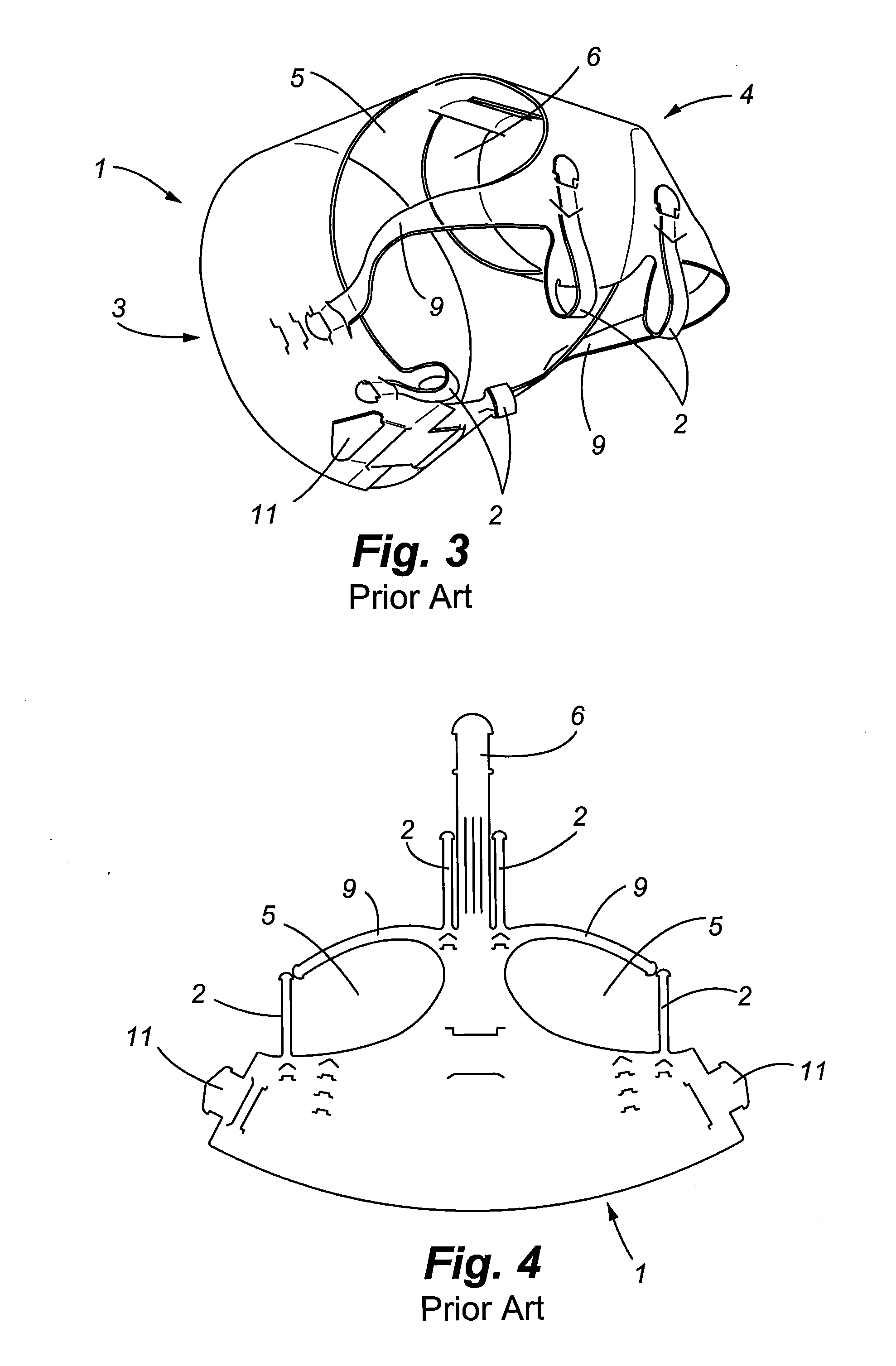
Apparatus and method for partially encapsulating an animal's head
A hemispherical shaped animal protective head shield with detachable optional rings and a pivotal visor member. The hemispherical shield is a transparent shell with an irregular aperture therein covered by a visor having a parabolic notch forming parabolic opening between the visor and shell for inserting an animals head and closing around the animal's neck. Optional elements may be attached to the hemispherical shape, thus forming a cylindrical or conical portion. Hook and latch elements are added for securing the visor in position relative to the hemispherical shell thereby providing infinite adjustment for capturing and partially encapsulating an animal's head.
Owner:WEXLER TOBY
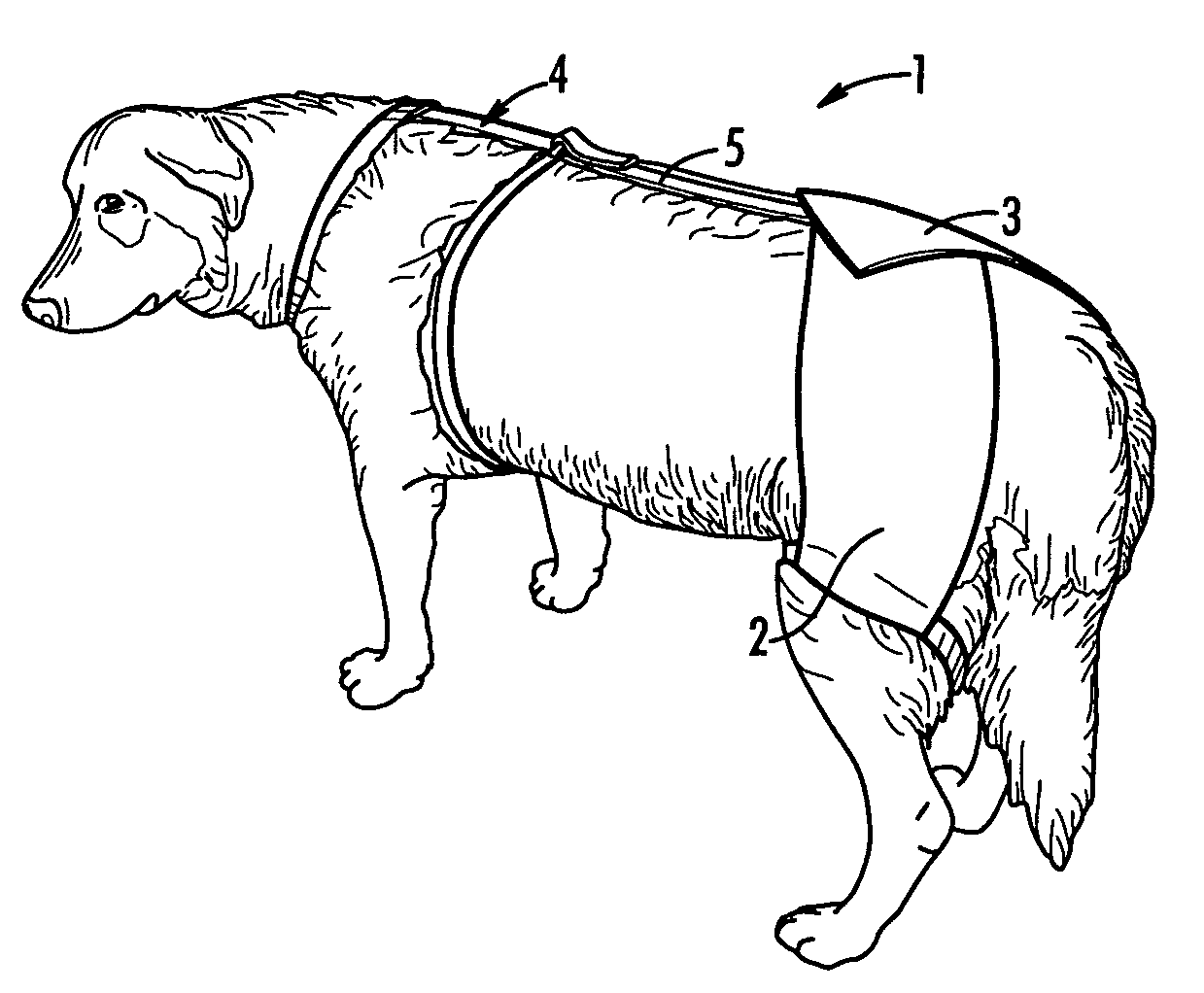
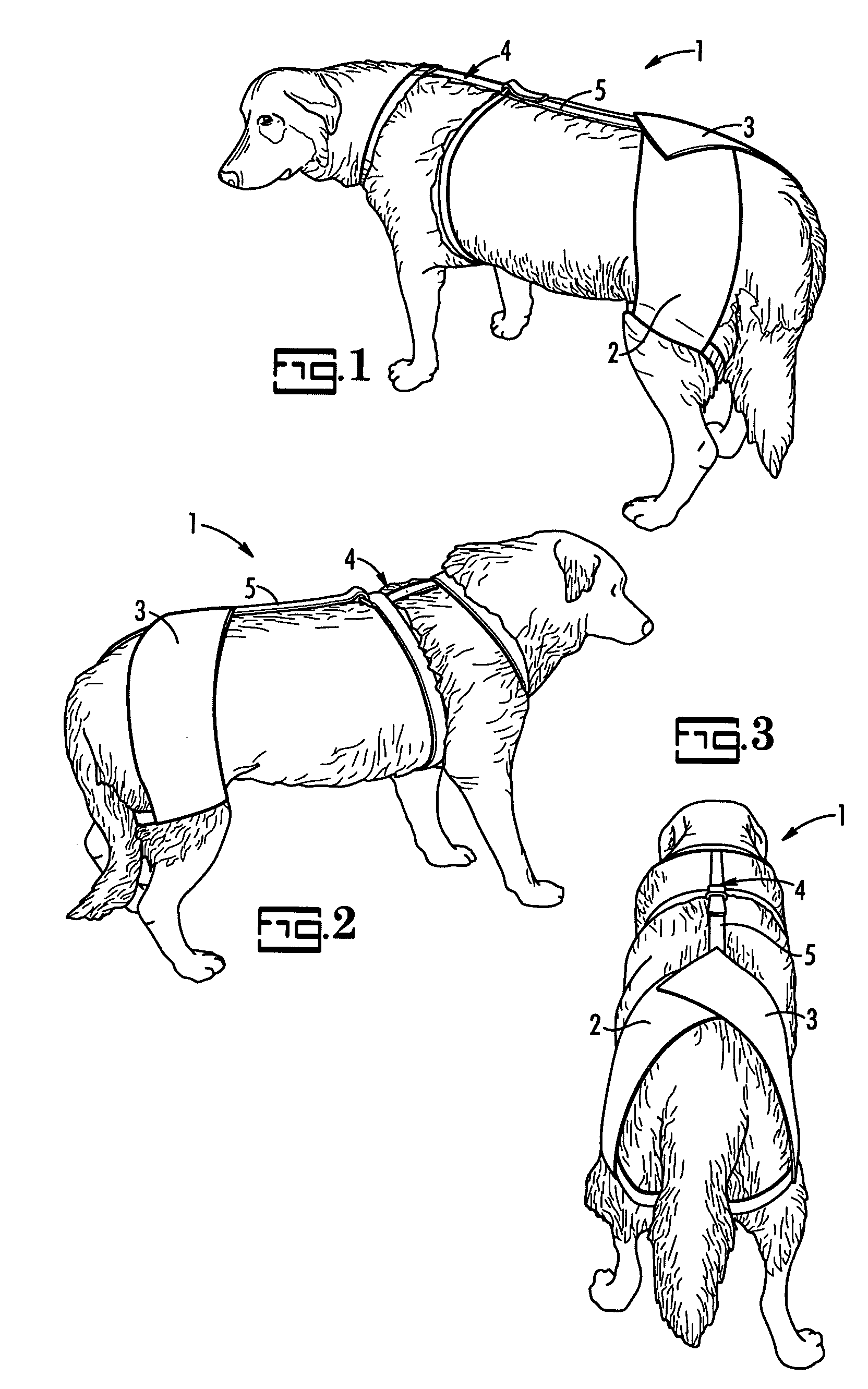
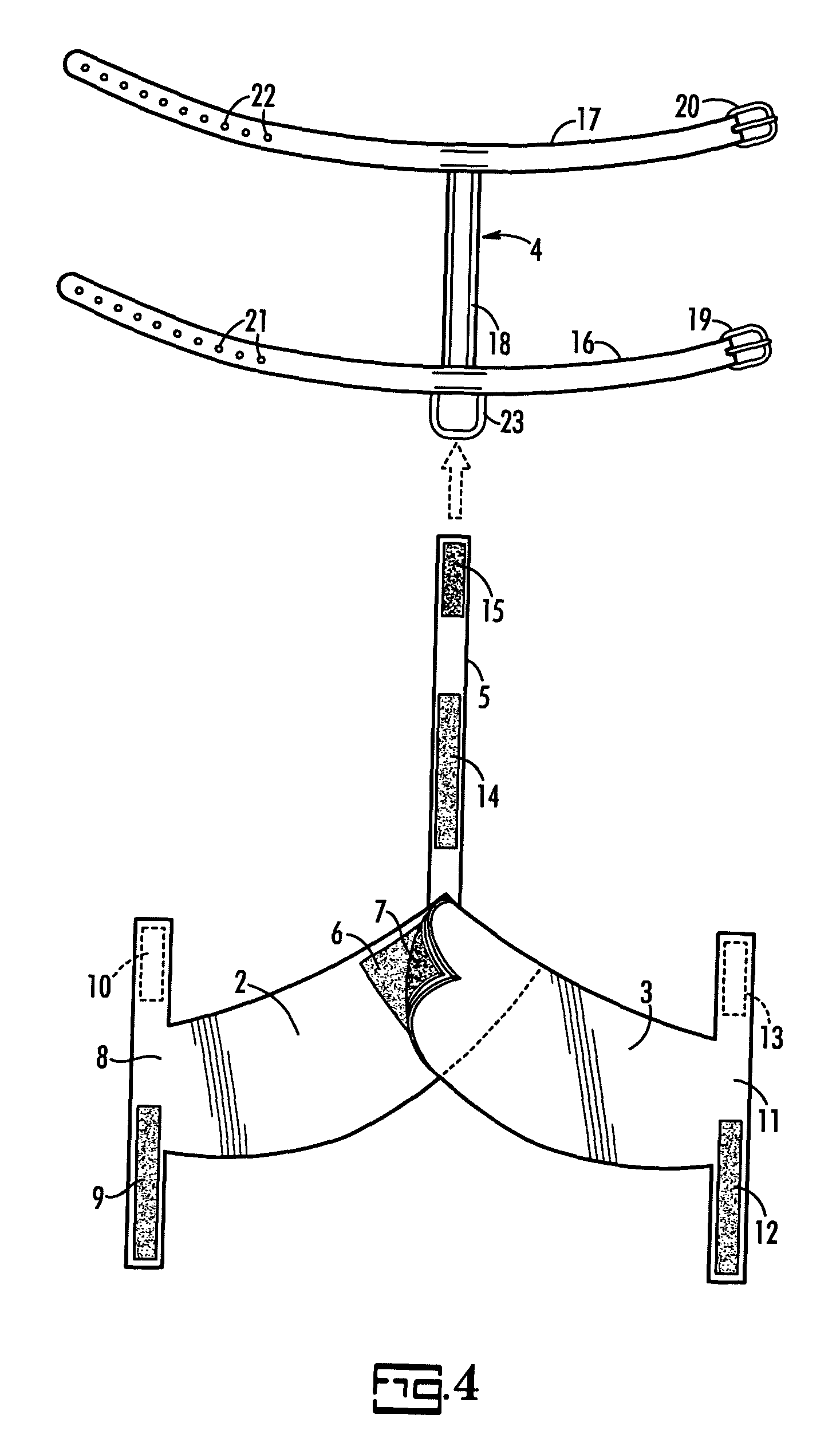
Support for treatment of canine hip dysplasia and lumbosacral disorders
InactiveUS6880489B2Relieve symptomsReduce joint painVeterinary bandagesTaming and training devicesDiseaseMuscles of the hip
A prosthetic device suitable for treating canine hip dysplasia and lumbosacral disorders and method of use. The prosthetic device comprises a harness attachable to the canine. Complementary rear braces are provided comprising a right brace and a left brace wherein the right brace comprises a right leg strap for encircling the right leg of the canine, and the left brace comprises a left leg strap for encircling the left leg of the canine. The right brace and left brace are engageable to apply force to persuade the hip towards a natural position. A tether between the harness and the complementary rear braces draws the right brace and left brace forward.
Owner:HARTMANN KAREN C +1
Therapeutic pet boot
InactiveUS8176880B2Healing of the paw is facilitatedProvide supportSolesVeterinary bandagesCushioningCold treatment
A pet boot having therapeutic properties is worn on a pet's injured or sensitive paw to facilitate healing and or provide protection. The therapeutic pet boot includes an external boot member having a shaft and a paw portion constructed to form a cavity integrated therein appointed to receive an injured paw of a pet. The therapeutic pet boot further includes an internal therapeutic member appointed to be received within the cavity of the external boot member and is appointed to intimately contact the injured paw. The therapeutic pet boot is appointed to be worn on the injured paw of the pet to facilitate healing. The internal therapeutic member may comprise a gel bootee having a massaging gel sole or may comprise a gel inner layer or gel insole. Advantageously, the internal therapeutic member may directly deliver medicament to the paw and / or provide cold treatment or hot treatment therapies to the paw, while providing cushioning, shock absorption and protection from dirt and debris.
Owner:I DID IT
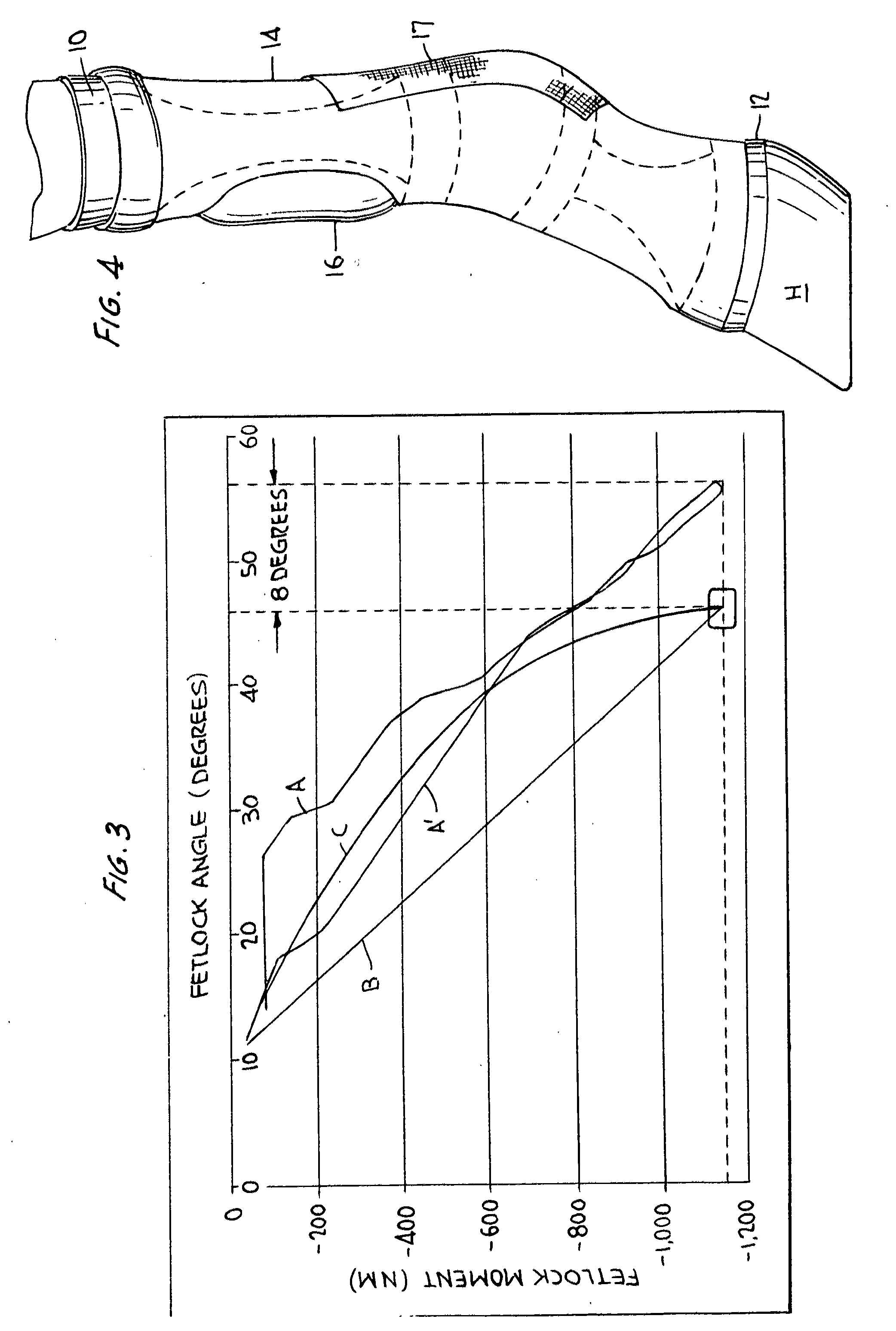
Orthopedic boot for animals
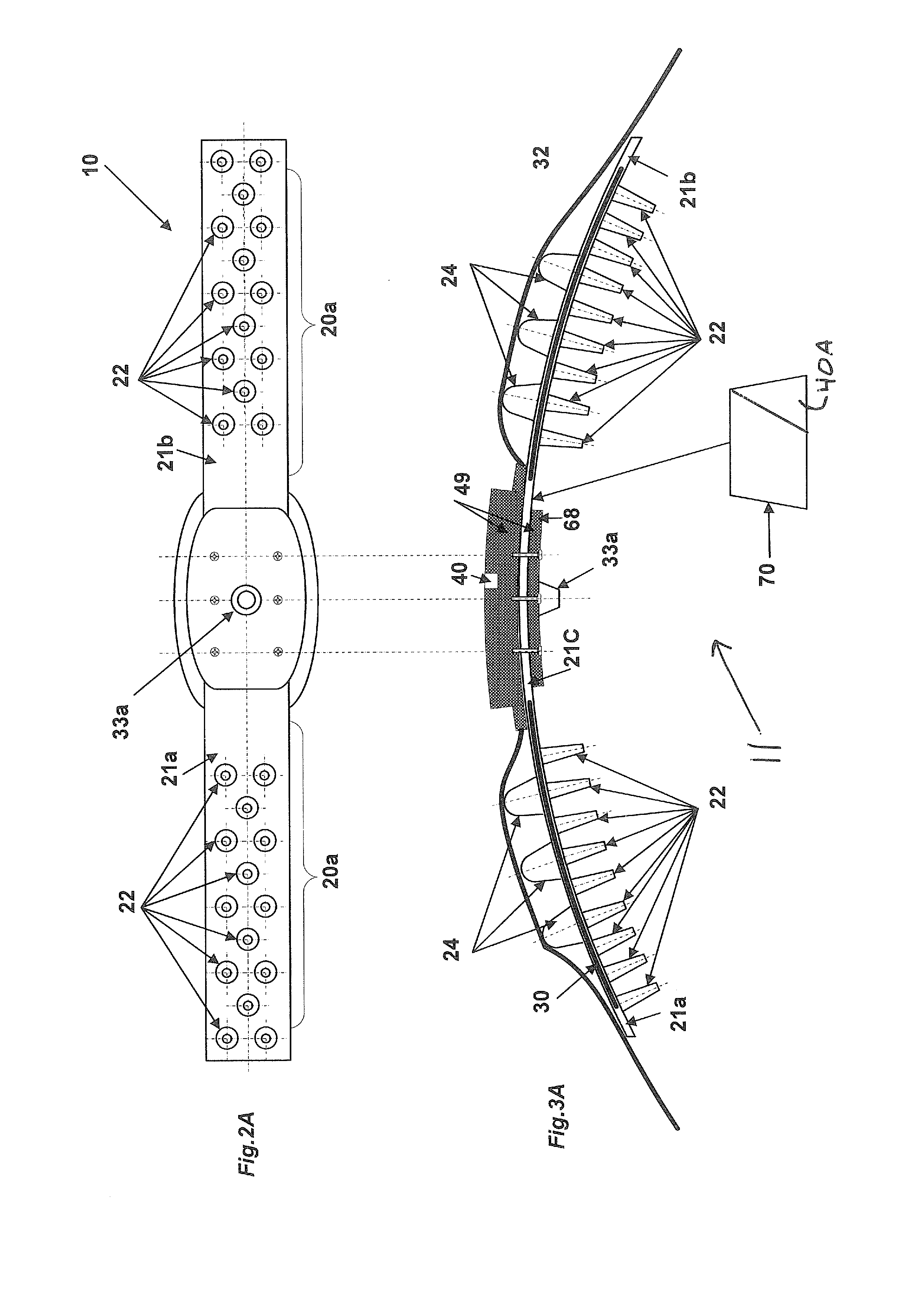
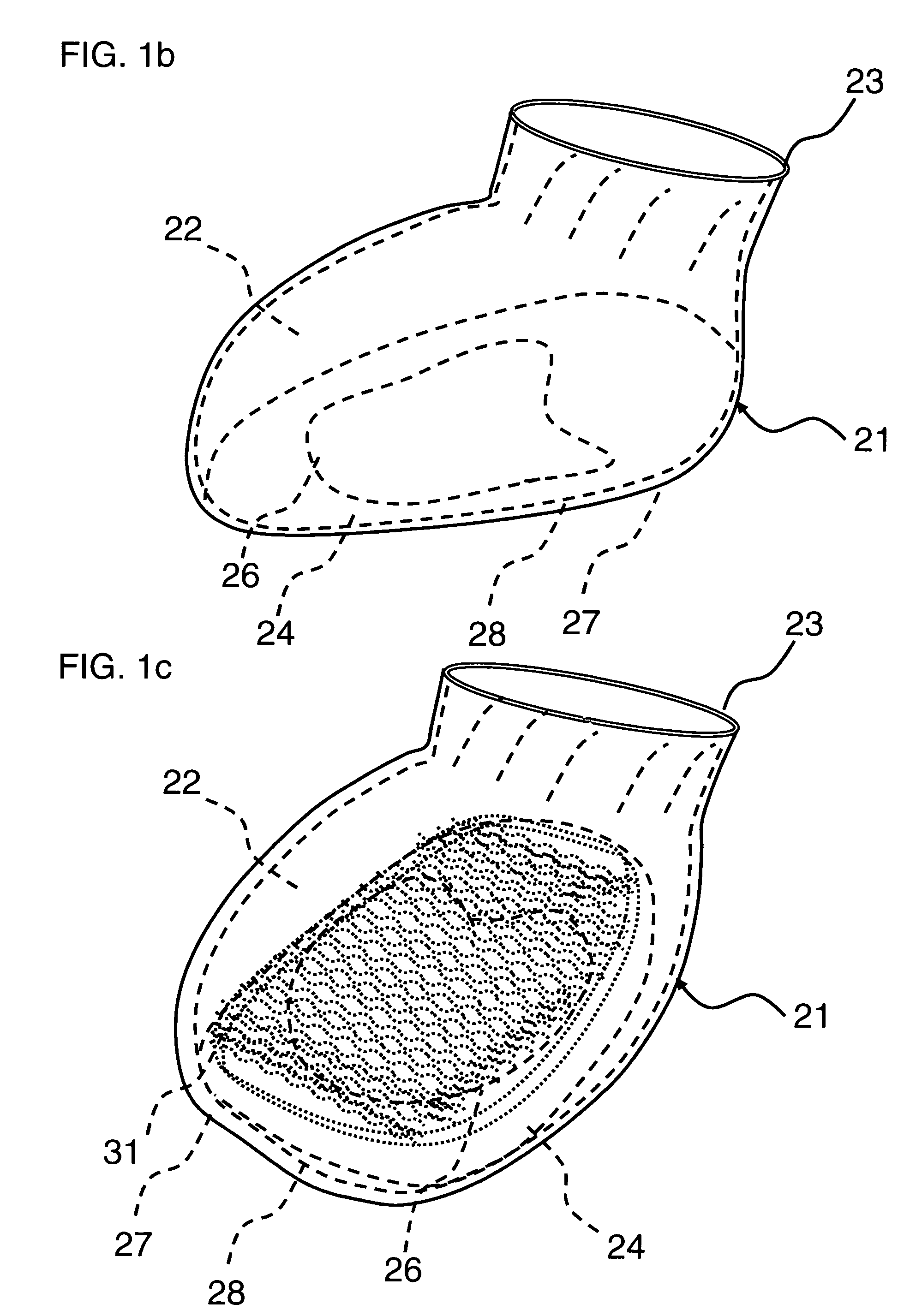
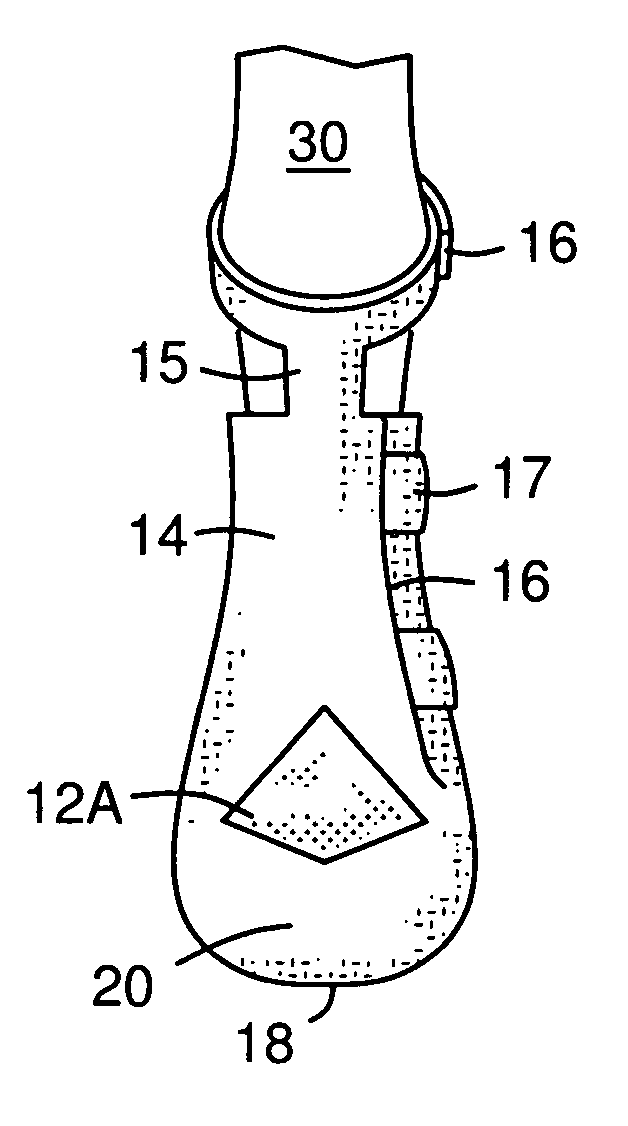
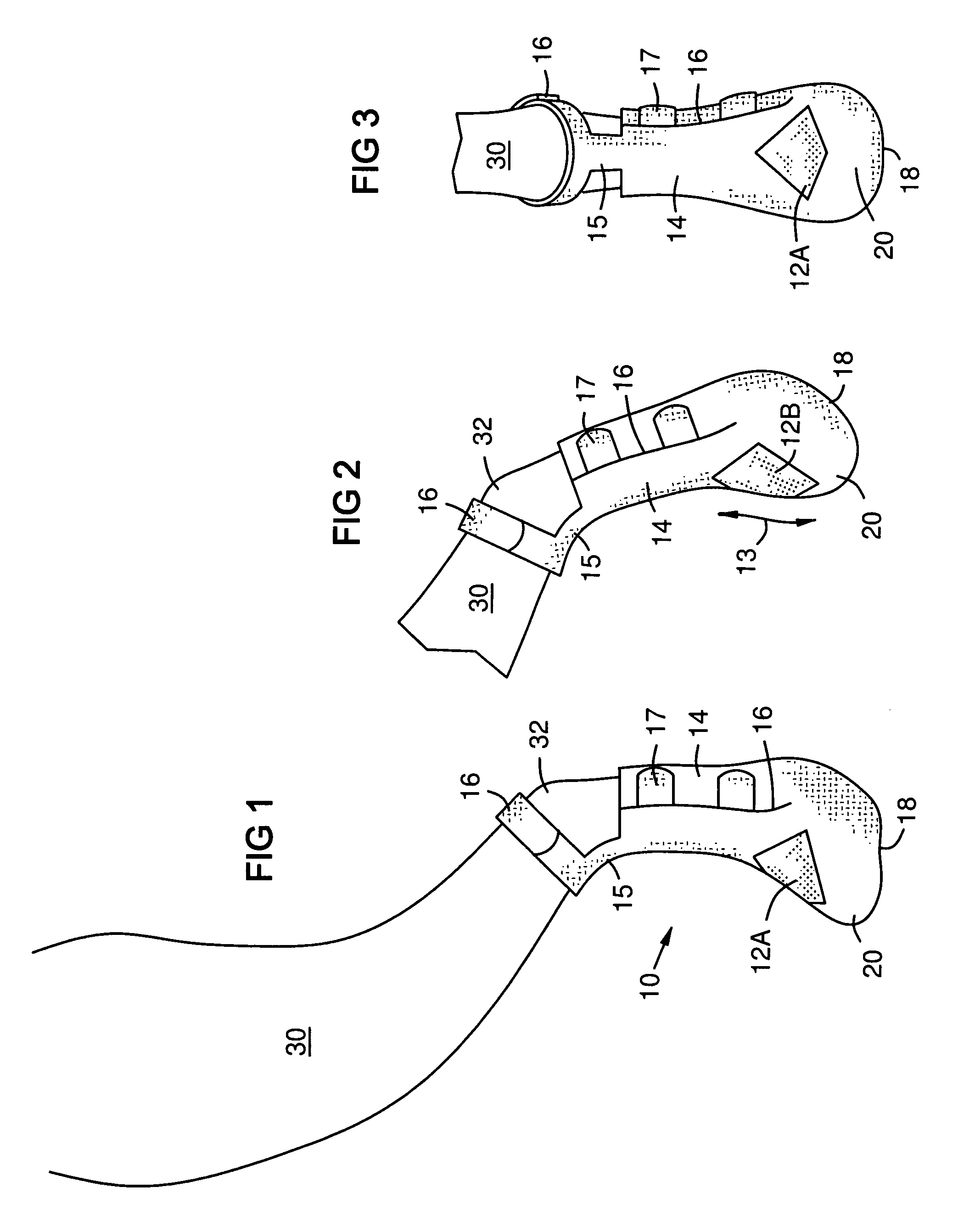
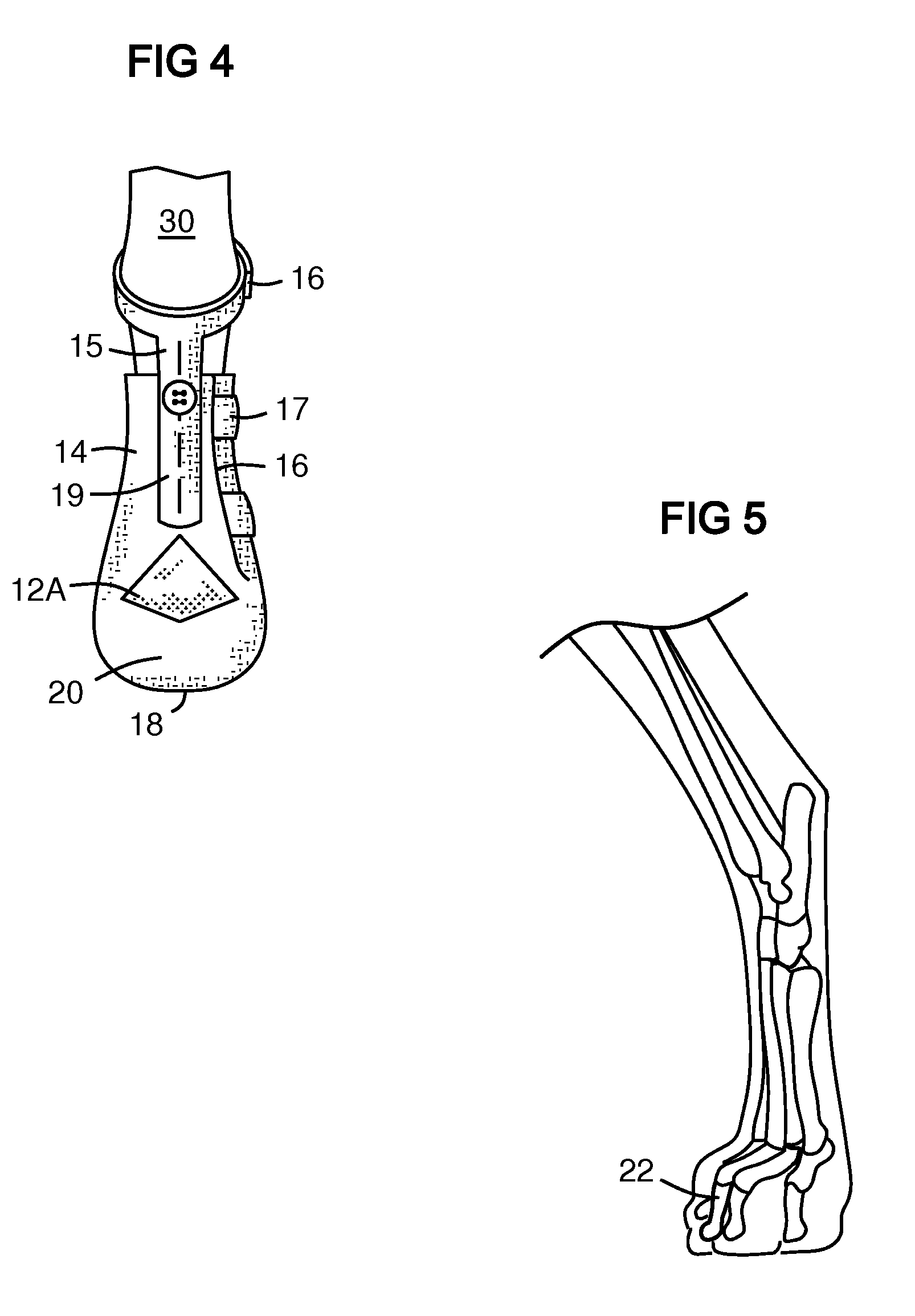
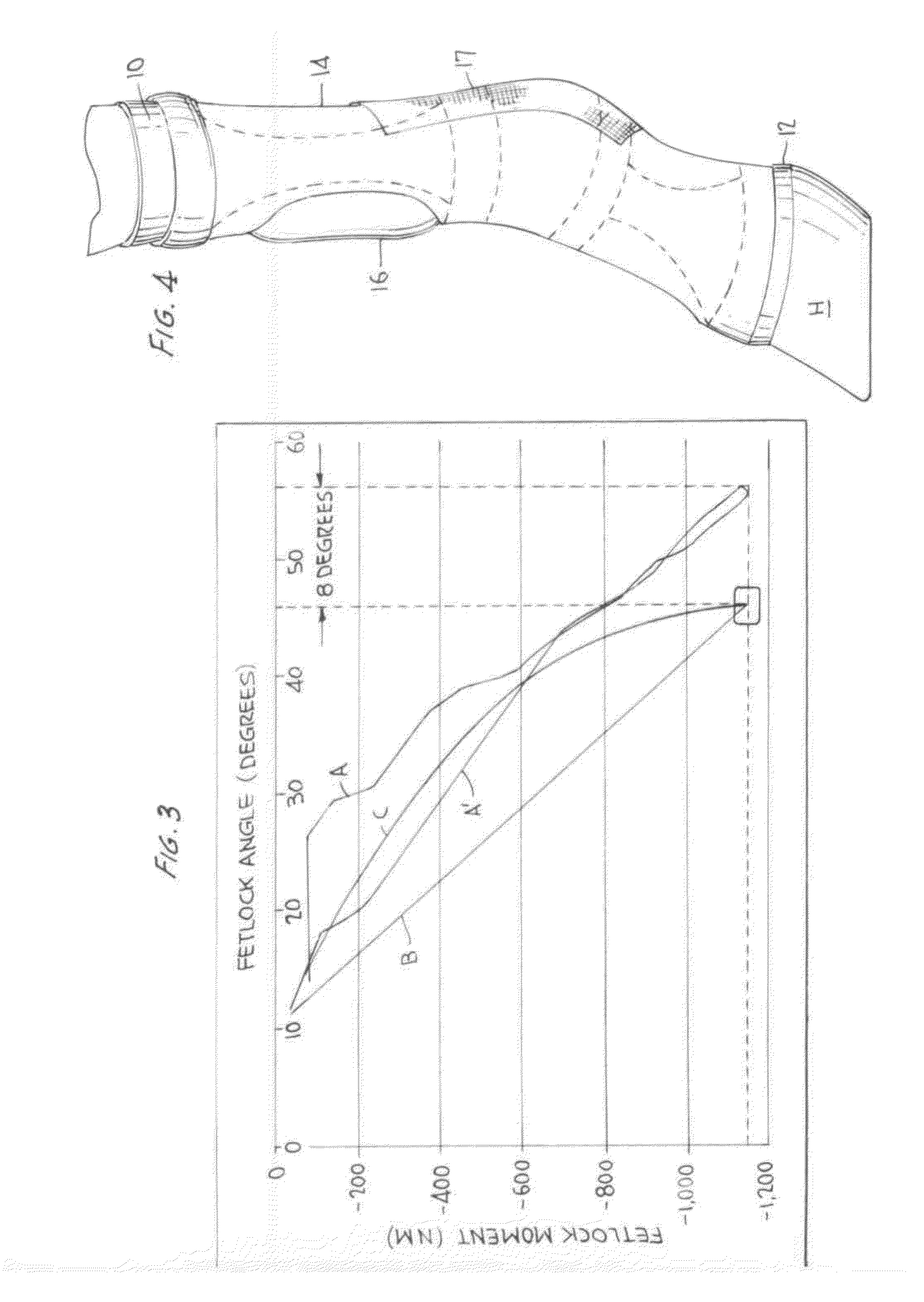
ActiveUS7677206B1Flexible controlAvoid curlVeterinary bandagesGrooming devicesEngineeringTarsal Joint
A boot (10) for enclosing a foot of a quadruped up to, but not including, a carpal or tarsal joint (32), made generally of a first flexible material (14) with a slit (16) forming an opening for inserting the foot. A lower portion of the first flexible material forms a toe box (20). An upper portion of the toe box is formed of a second flexible material (12A, 12B) that is more elastic than the first flexible material, such as an elastic fabric. The elastic fabric allows the toes to flex downward at the end of each step, then pulls them upward to prevent them from curling under the foot on the next step. An upper retainer (16) may be provided on an upward extension strap (15). The upper retainer loops around the leg above the carpal or tarsal joint (32) to provide vertical retention of the boot.
Owner:SOUTHWORTH WILLIAM W
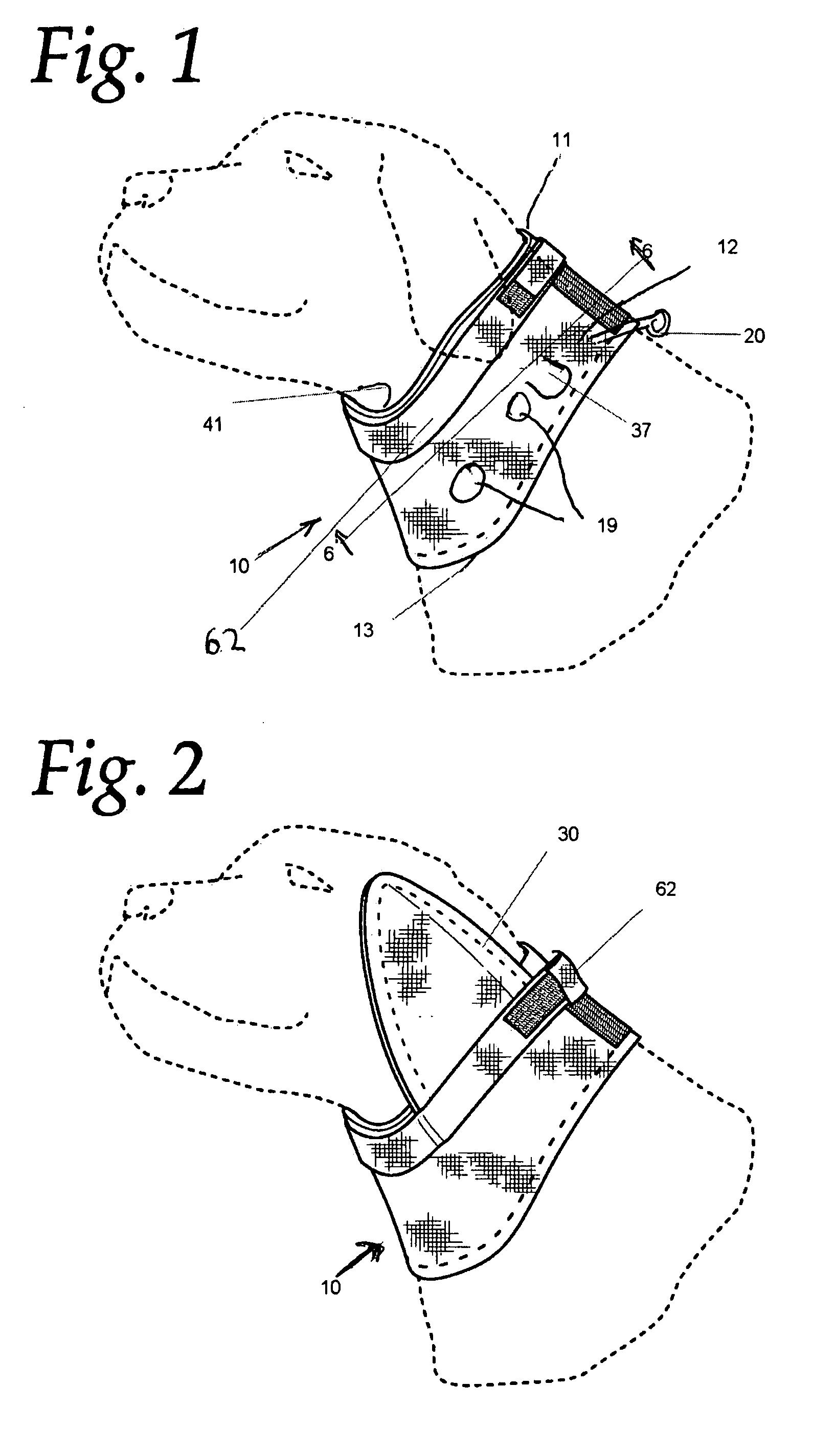
Protective pet device
InactiveUS20100024745A1Avoid injuryPrecise positioningVeterinary bandagesOther apparatusPlastic materialsEngineering
According to certain preferred embodiments of the present invention, protective devices configured to be located around the neck region of a pet are provided, which are capable of preventing the pet from biting, licking, or otherwise irritating a wound located on the body of the pet. According to certain embodiments, device has five contiguously connected sides, a first open end and a second open end. The first open end is located around the pet's head and exhibits a pentagon-shaped peripheral edge, whereas the second open end is located around the pet's neck and comprises a circular (or oval) shaped peripheral edge. Preferably, the device will be comprised of a clear, or substantially clear, plastic material, such that the pet's peripheral vision is not impeded during use of the device.
Owner:HARLOW JOHN
Pet garment with treatment element
InactiveUS20110174237A1Maximum comfortAvoid the needSafety beltsVeterinary bandagesCompanion animalBiomedical engineering
Owner:GJM
Pet Protective Collar With Stays
ActiveUS20120325163A1Preventing unwanted escapeVeterinary bandagesTaming and training devicesEngineeringCompanion animal
Owner:IMAGINE THAT INT
Pet collar with ear guards
InactiveUS20070199521A1Protect earsMinimize chafingVeterinary bandagesTaming and training devicesHead movementsEngineering
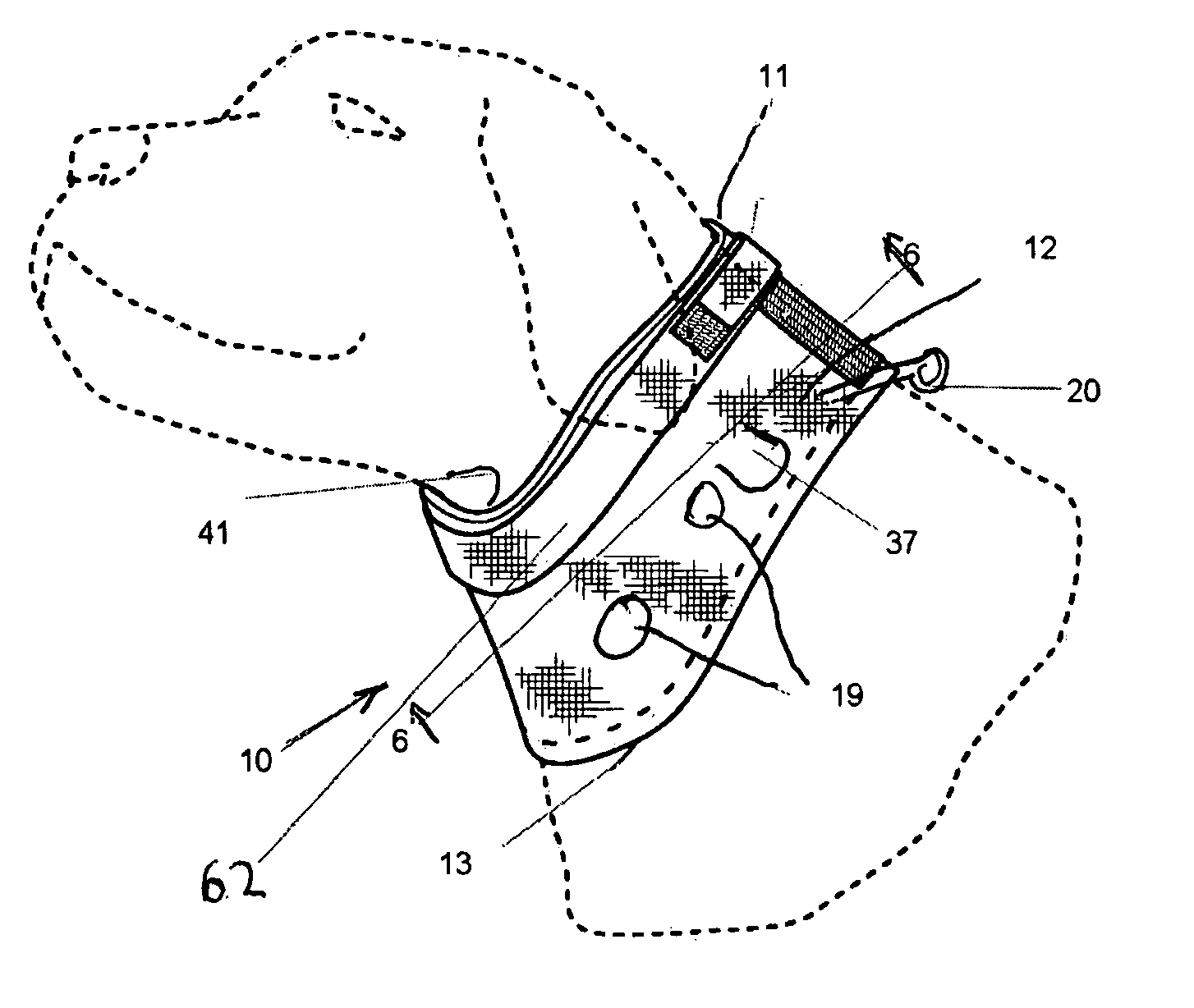
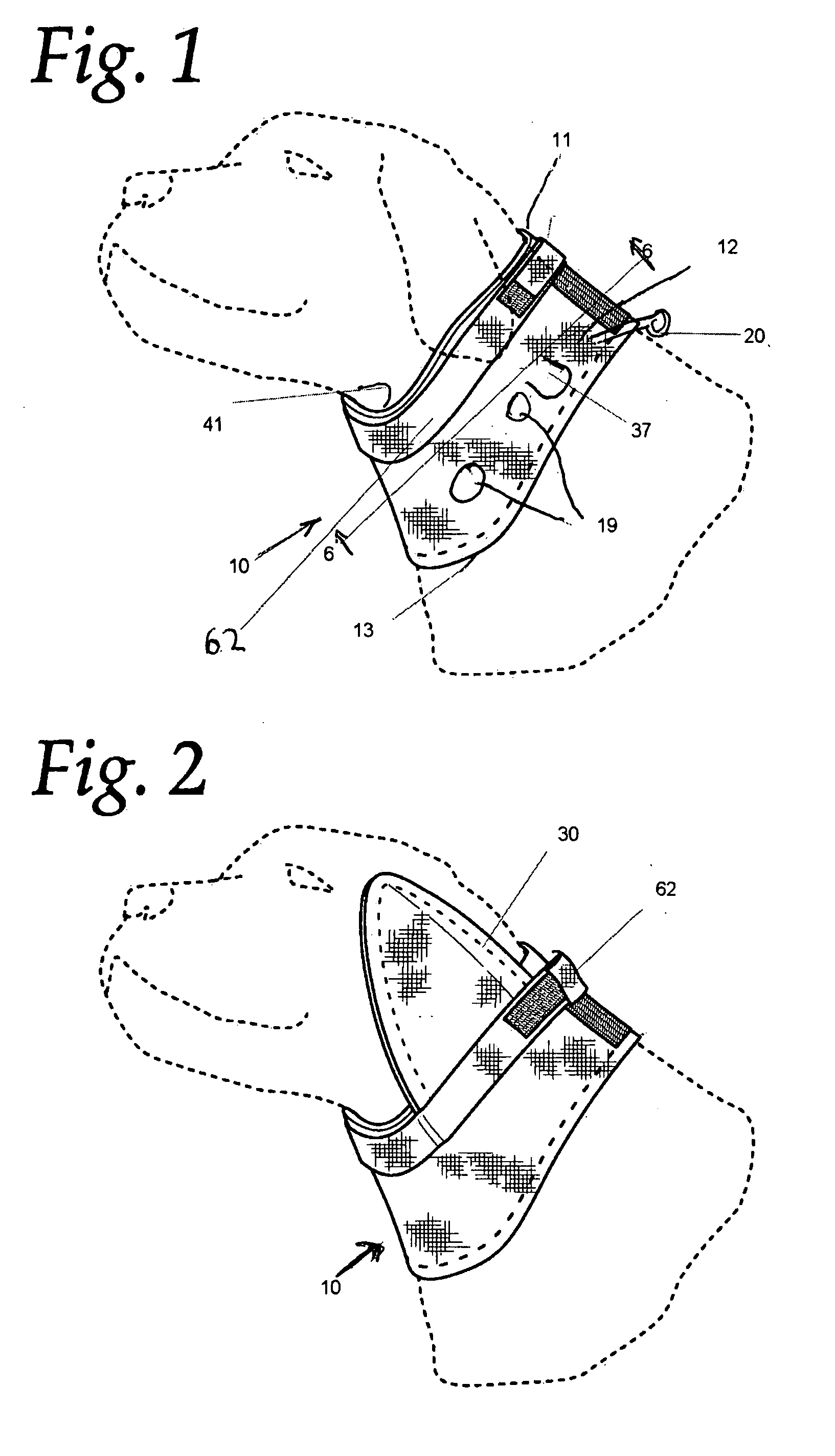
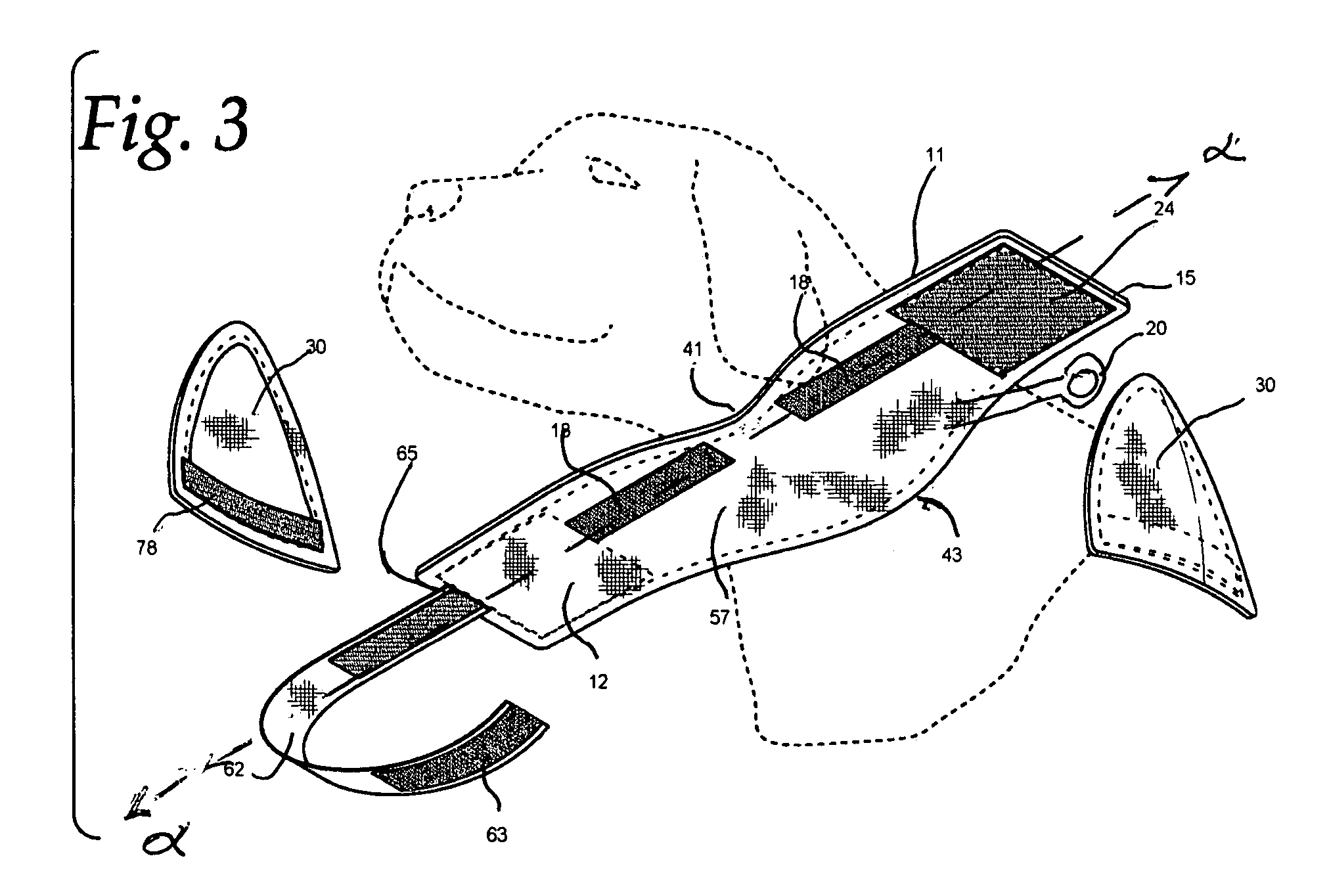
This invention relates to a collar device that limits the head movement for a canine or feline pet while the pet is recuperating from surgery or injury. The collar may be fitted with removable ear guards. The collar is capable of being coupled to a leash so the animal can be taken on a walk with the protective collar in an operative position.
Owner:WINESTOCK NANCY
Animal wound shield
The animal wound shield is a protective casing having a shank portion and an appendage cover that can be disposed around a limb and an attached appendage of the animal. The appendage cover is articulated to a lower end of the shank. Thus, the appendage cover is pivotally connected to the shank and moves with the movement of the appendage. The shank may have more than one section, or an upper and lower portion, to extend further up on the limb, and yet still accommodate for joints. The shield is designed for use around an injured limb to cover a bandaged area and prevent further damage to the wounded site. Vent openings are defined in the shank and the appendage cover to permit air circulation. Fasteners may be used at a top end of the shank to hold the shank on the limb.
Owner:FAULK KEVIN
Therapeutic pet jacket and bed
A pet jacket and bed which possesses pockets therein for receiving removably insertable gel packs or grain (oatmeal) packs, which packs can be heated up or cooled as necessary so as to provide hot and cold therapies for convalescent arthritic pets, pets with injuries or which can simply alter temperature and comfort for the pet.
Owner:A TOUCH OF LOVE
Pet collar with ear guards
InactiveUS7743736B2High tensile strengthIncrease flexibilityVeterinary bandagesTaming and training devicesHead movementsEngineering
This invention relates to a collar device that limits the head movement for a canine or feline pet while the pet is recuperating from surgery or injury. The collar may be fitted with removable ear guards. The collar is capable of being coupled to a leash so the animal can be taken on a walk with the protective collar in an operative position.
Owner:WINESTOCK NANCY
Horse orthotic
Embodiments of this invention include orthotic devices for treating hoof ailments, including laminitis and founder, and methods of treating the hoof ailments using an orthotic. In one embodiment, the hoof orthotic includes a platform having a heel end, a toe end, an inside and an outside edge, the heel end comprising a center section of the platform. The toe end includes a first tip and a second tip having a space therebetween such that the toe end is not enclosed. The platform includes an upper hoof contact surface and a lower surface, the upper surface being elevated at the heel end of the platform and sloping such that the heel end has a greater vertical height than the toe end. The orthotic also includes attachment means that extend vertically from the platform for attaching the orthotic to the animal hoof. The orthotic can be made from a resilient and / or elastomeric material that may also provide cushioning and fitting advantages.
Owner:OSBORNE ROBERT CLARK
Animal limb protective boot
ActiveUS20090094864A1Reduce the overall diameterAvoid insufficient lengthVeterinary bandagesGrooming devicesEngineering
A protective boot for an animal including a generally cylindrical leg portion having a top end and a bottom end and a top closure affixed to and circumscribing the top end of the leg portion that is drawn inward against the leg of the animal to protect against the infiltration of extraneous material into and against the self-removal of the protective boot by the animal. The base portion of the protective boot is sealed to the bottom end of the leg portion and is enhanced with a non-slip material to provide substitute traction for the animal. At least one strap is fixedly connected to the leg portion and is operable to reduce the diameter of the leg portion in the vicinity of the strap. The protective boot is sealed at each seam or point of attachment between elements so that the boot is waterproof.
Owner:MEDIVET PROD INC
Protective Collar Adapted for Engagement to Animal Neck
InactiveUS20110277701A1Muffled soundDampen incoming soundVeterinary bandagesTaming and training devicesEngineering
Owner:KING MARGIE
Animal protective device and method
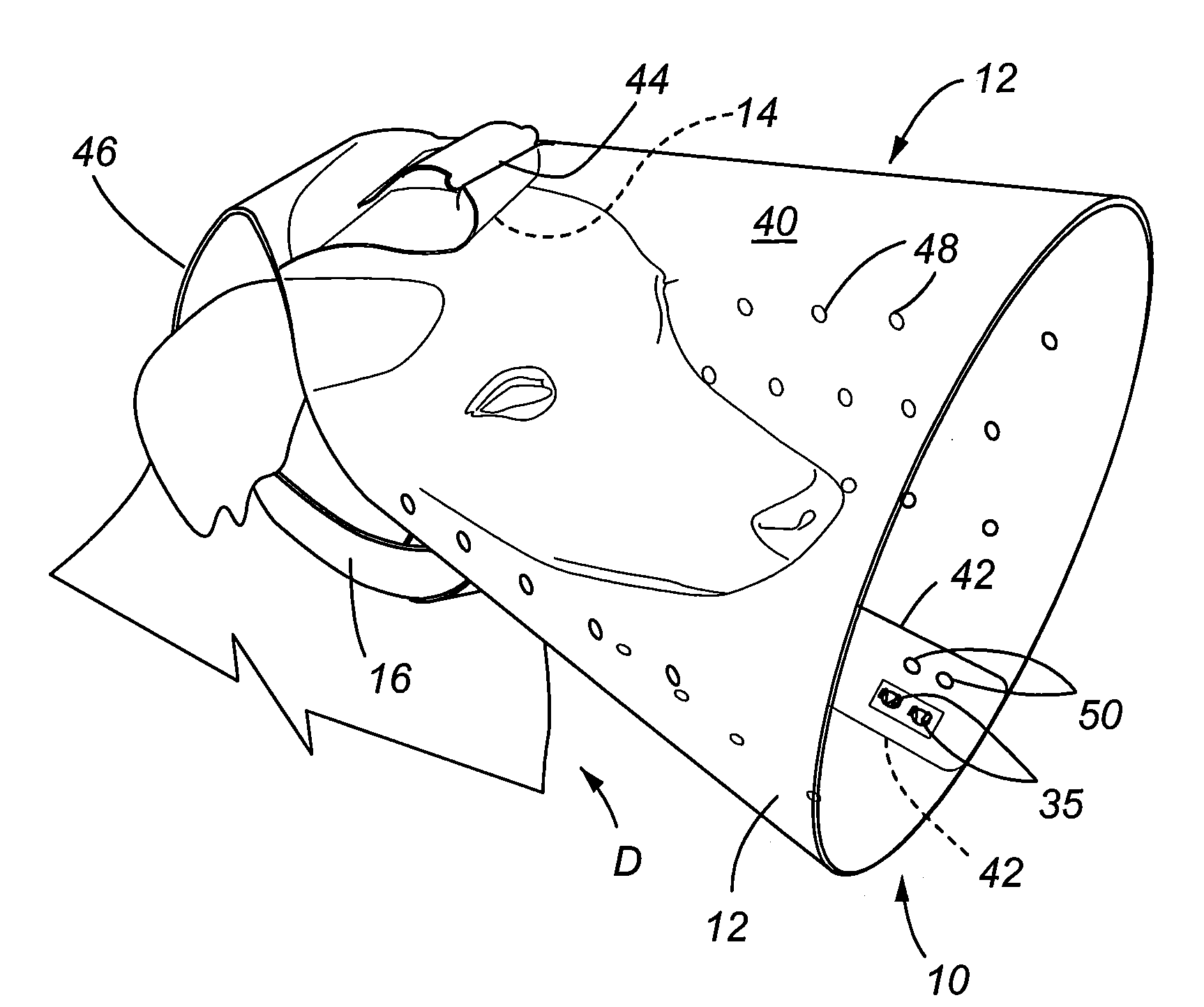
InactiveUS20090090307A1Avoid bad contactImprove cooling effectVeterinary bandagesTaming and training devicesNoseEngineering
An animal protective device and method are provided for preventing contact of the animal's head with other parts of the animal. The device includes a body formed in a truncated cone shape. A pressure strap maintains contact with the upper portion and back portion of the animal's head in order to keep the device aligned with the nose and mouth area of the animal. An integral attachment strap is provided that is routed around the neck of the animal to further stabilize the device on the animal. The device may be adjusted at the attachment strap as well as the body to ensure that the device is correctly fitted to the animal. The device is of one-piece construction and does not require use of a separate collar, such as the identification collar of the animal.
Owner:KVP INT INC
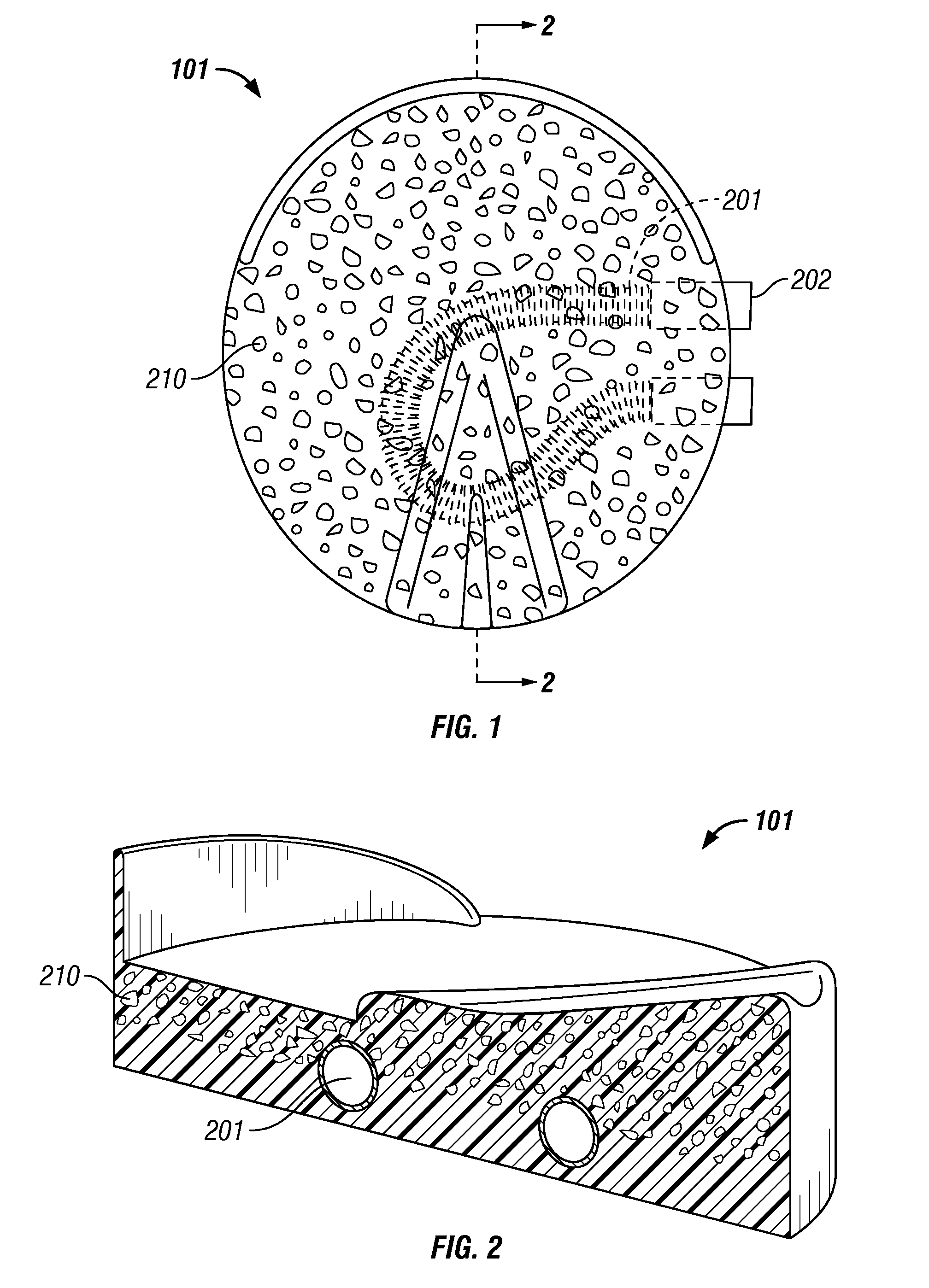
Reduced Weight Equine Orthotic Pad and Method
ActiveUS20120279184A1Reduction in in thermal insulationReduce weightProtection coversVeterinary bandagesElastomerDraft animals
There is disclosed an improved shock absorbing, light-weight, thermally insulative orthotic pad designed for use in a pad and boot assembly for hoofed livestock. The pad is comprised of a mixture of flexible spheroids and elastomeric materials. In a preferred embodiment, elastomeric material generally is more concentrated at the top portion of the pad, and spheroids dispersed in a matrix of elastomeric material concentrated at the bottom section of the pad. The spheroids have a lower density than the elastomeric materials and possess better thermally insulative properties, and in a particularly preferred embodiment, at least some of the spheroids are comprised of closed-cell polypropylene foam. A method of making the light weight pad is also disclosed
Owner:RUETENIK MONTY L
Disposable bootie for pets
InactiveUS20070175409A1The process is convenient and fastFaster and easier to engage about the legVeterinary bandagesGrooming devicesCompanion animalMechanical engineering
Owner:ROTANO INT
Limb protection device
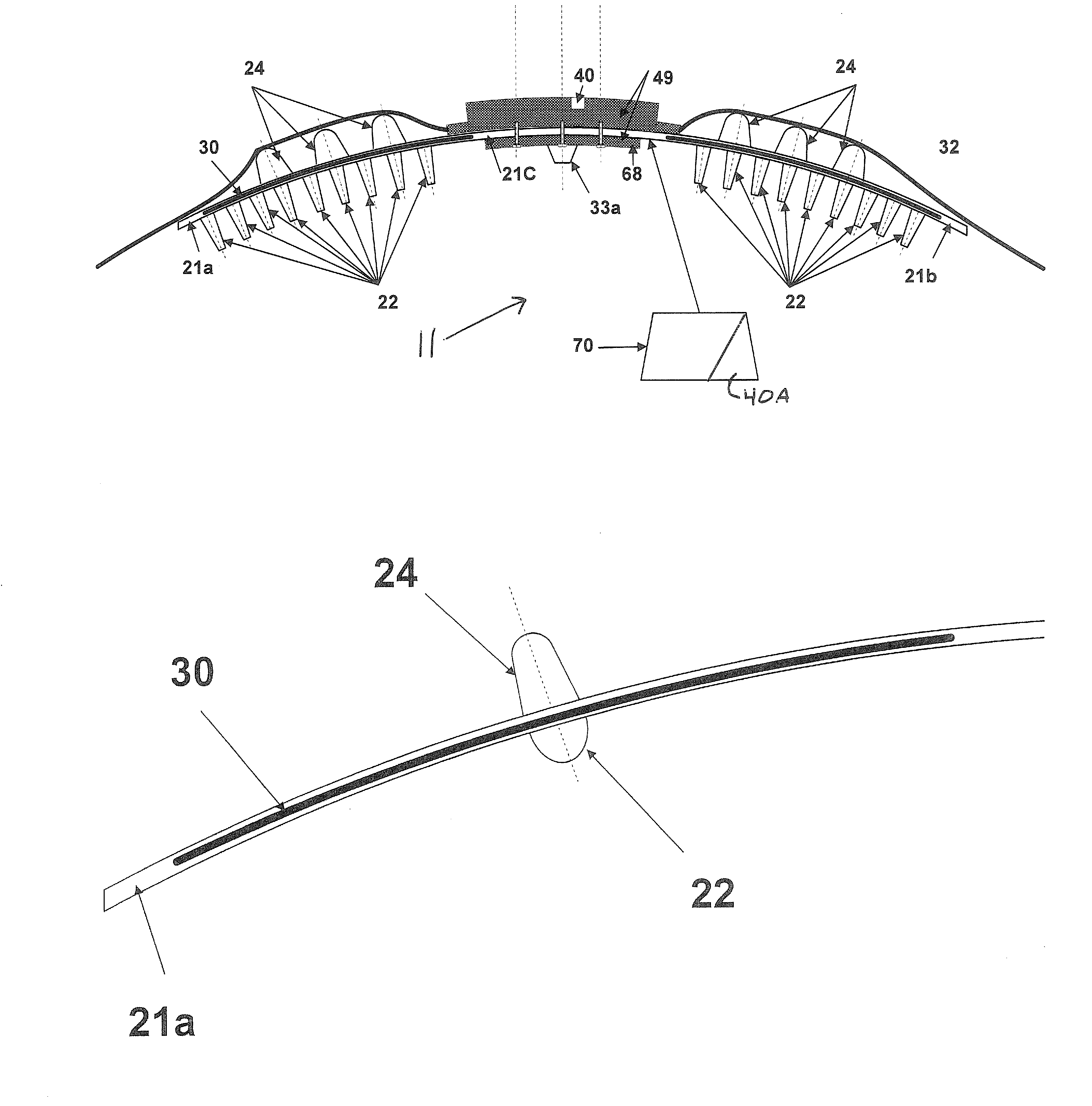
ActiveUS20120089065A1Significant elastic propertyEffective protectionVeterinary bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesYarnMedicine
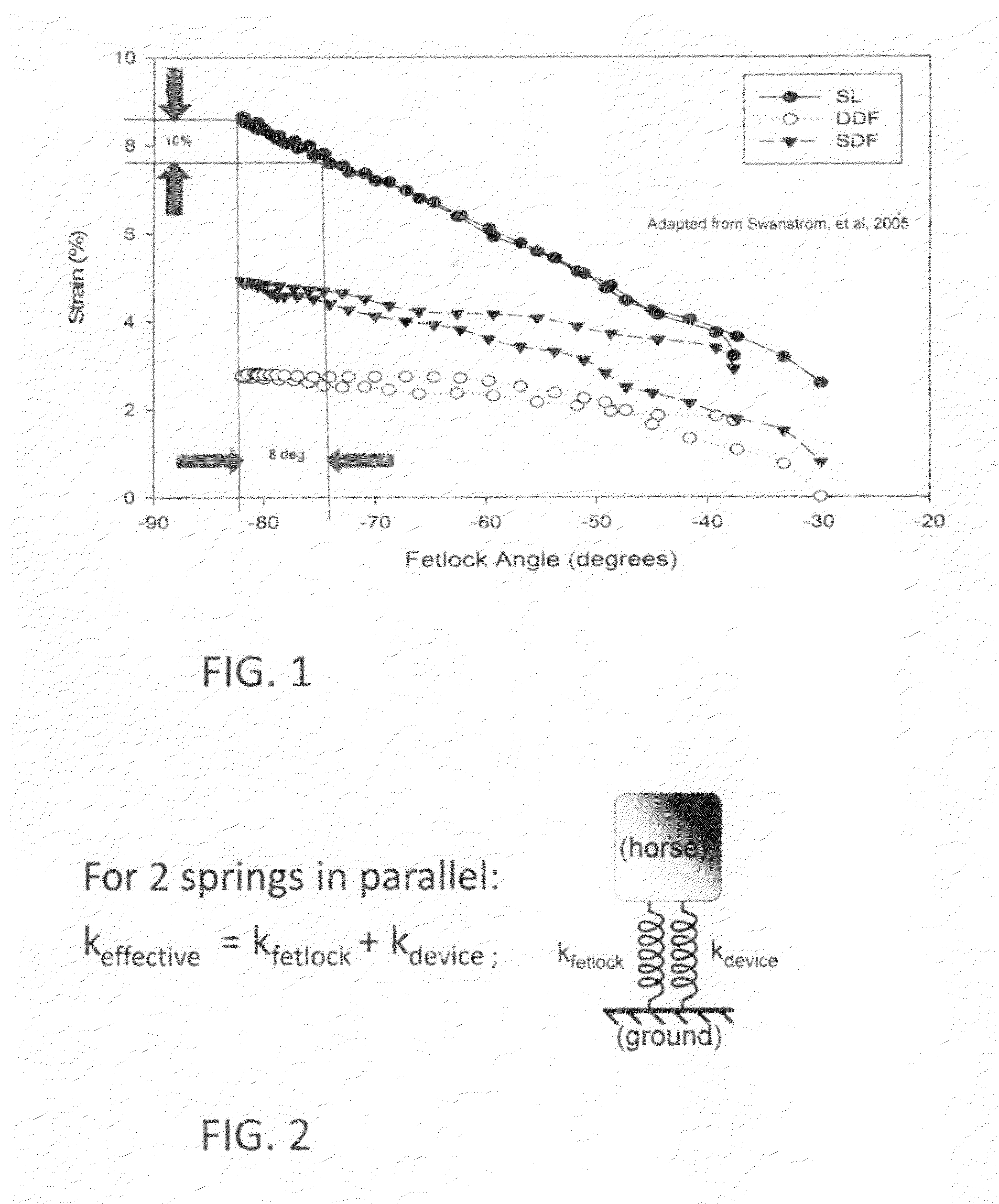
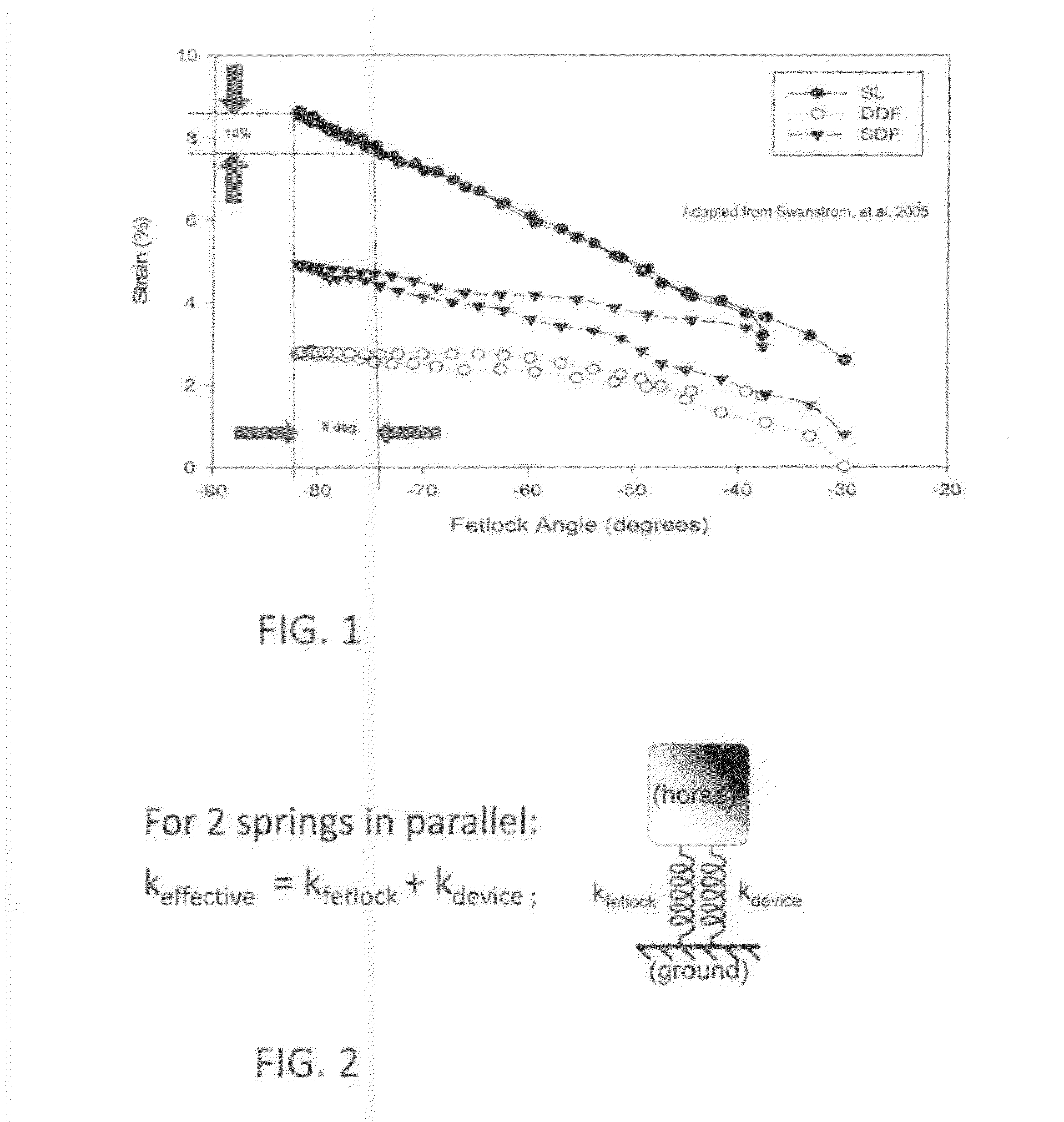
A joint-supporting device comprises tensile members extending from above the joint to below it, supplementing the tensile characteristics of the joint's tendons, ligaments, and other structure. The tension members extend between a proximal cuff above the joint to a distal cuff below it, and pass over a pad at the apex of the joint, redirecting the tension members. In order that the cuffs are supported in position so that the tension members can effectively support the joint, they are spaced away from the joint by compression members bearing on proximal and distal bolsters, in turn located positively by the boney structure of the joint.In order that the structure of the invention not interfere overly with the normal function of the joint, the device employs dilatant materials having the property of varying their hardness upon motion. The dilatant material is disposed so as to limit the relative angular velocity of the members of the joint. The dilatant material can be disposed in pad form, arranged to be compressed by the tensile members as the joint is extended, and / or as the core of a composite tensile member, sheathed in a cover woven of high tensile strength filaments or yarns.
Owner:HORSEPOWER TECHNOLOGIES INC
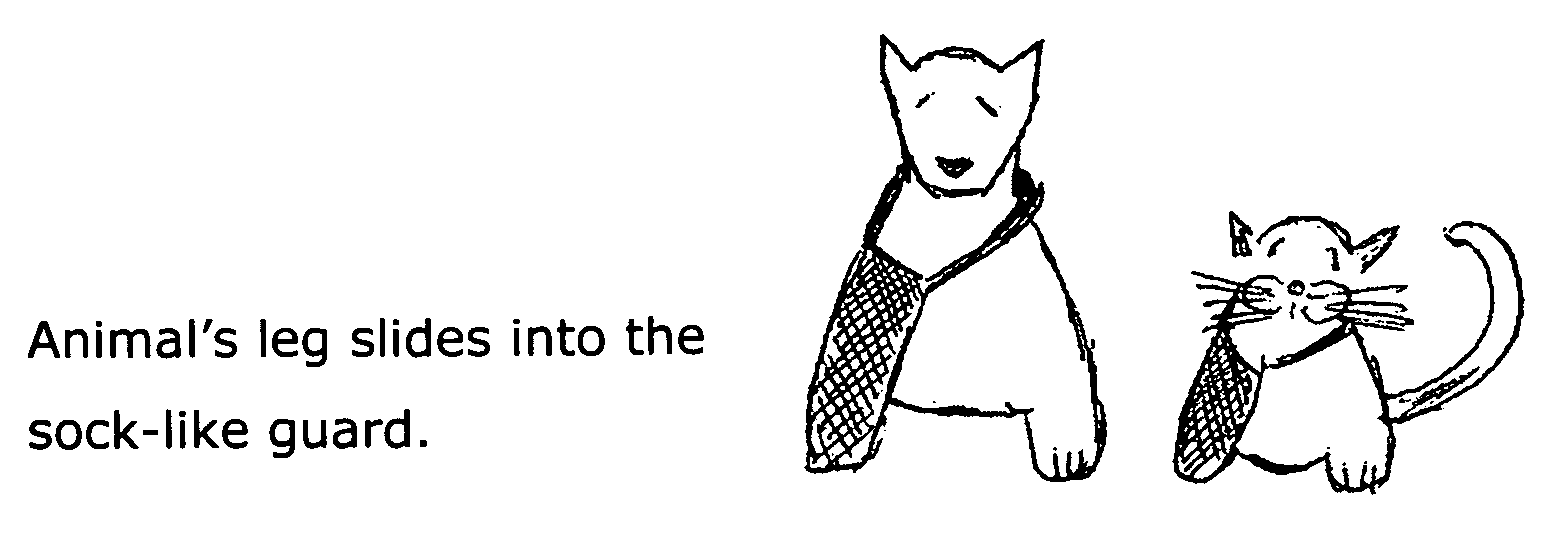
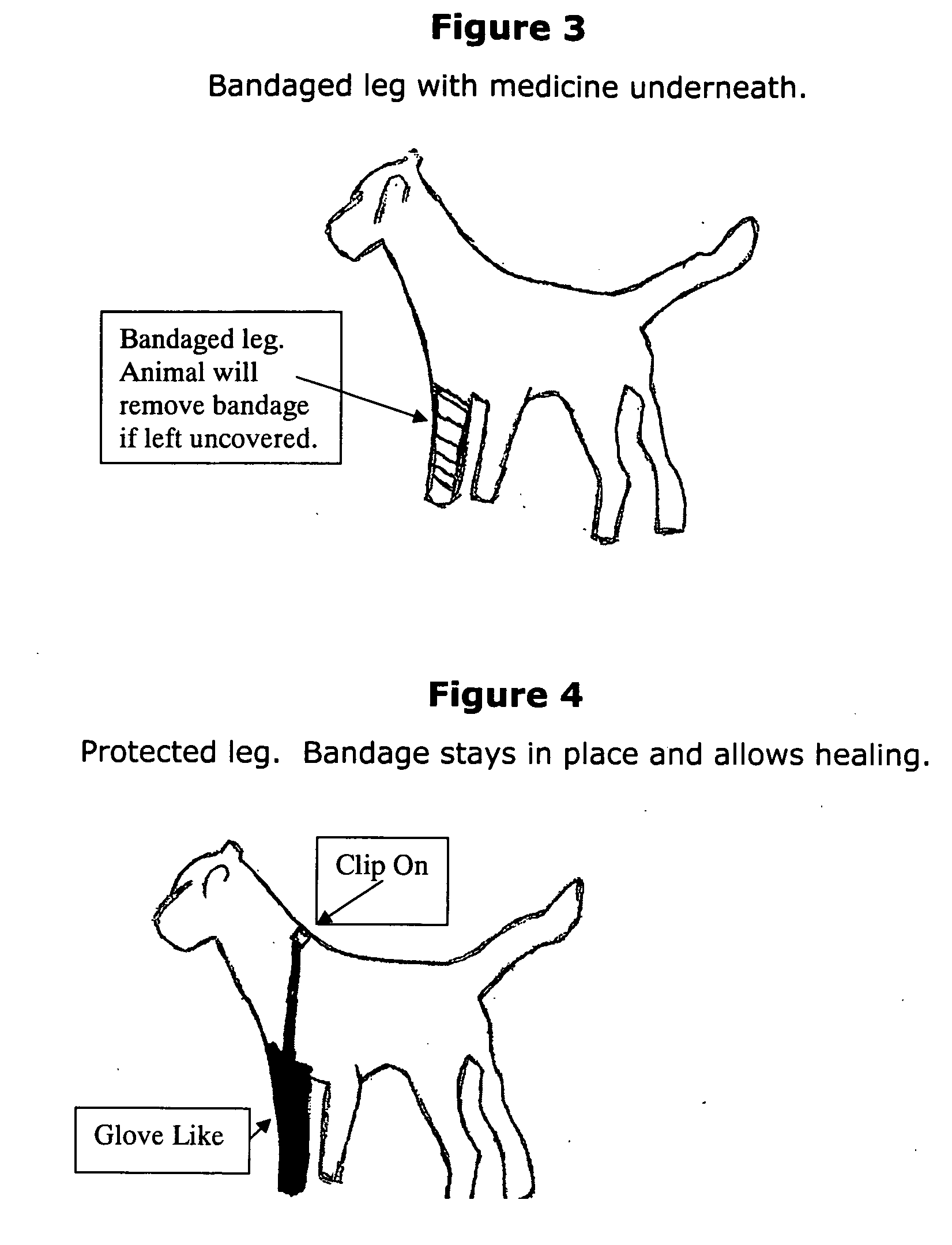
Protective foot and leg cover guard for wounds and allergies
The Protective Foot and Leg Cover Guard is a sock-like, one-piece garment that the animal's front or rear leg can slide into. There are no wraps or clasps. The leg simply slides into it. It has an adjustable clasp that joins in back of the neck far from the animal's potential reach. Therefore, it is impossible for the animal to remove it or break the clasp. It is for dogs and cats and other four legged animals. Mainly to be used to cover a bandaged leg and / or foot and prevents the animal from licking, biting, scratching or removing bandages. It allows a cut or injury to heal undisturbed. The fabric is the same fabric used on muzzles—durable nylon. No need to put the animal in a brace or apparatus of any kind. It is bendable, but not easily ripped and washable.
Owner:FRANCO EUNICE
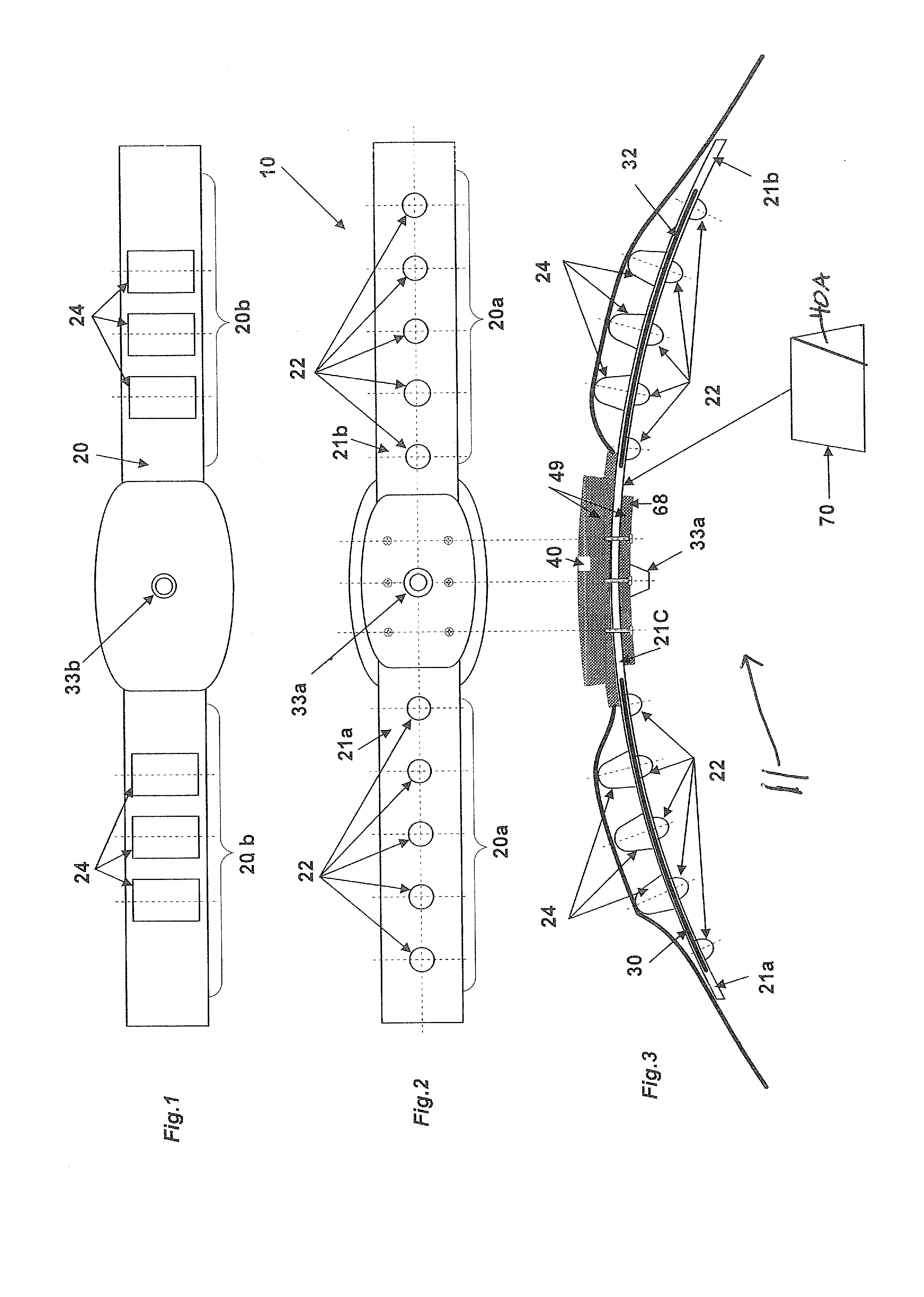
Limb Protection Device
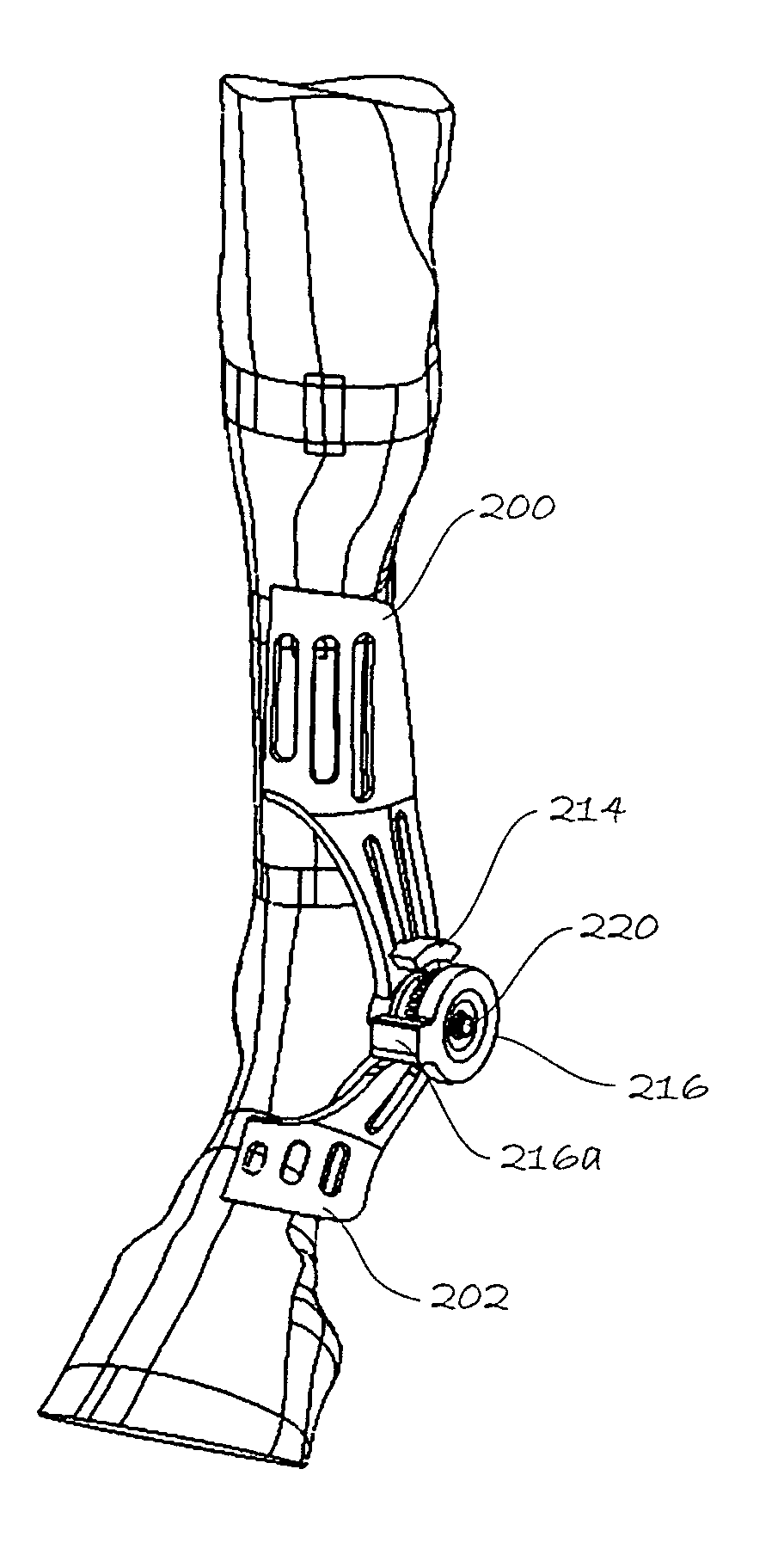
ActiveUS20140148746A1Limiting overheatingEffective supportVeterinary bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesRange of motionAngular velocity
A joint-supporting device comprises tensile members extending from a proximal cuff secured to the limb above the joint to a distal cuff secured to the limb below the joint, supplementing the tensile characteristics of the joint's tendons, ligaments, and other structure. The device may also comprise structure for limiting the range of motion and angular velocity of the joint.
Owner:HORSEPOWER TECHNOLOGIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com