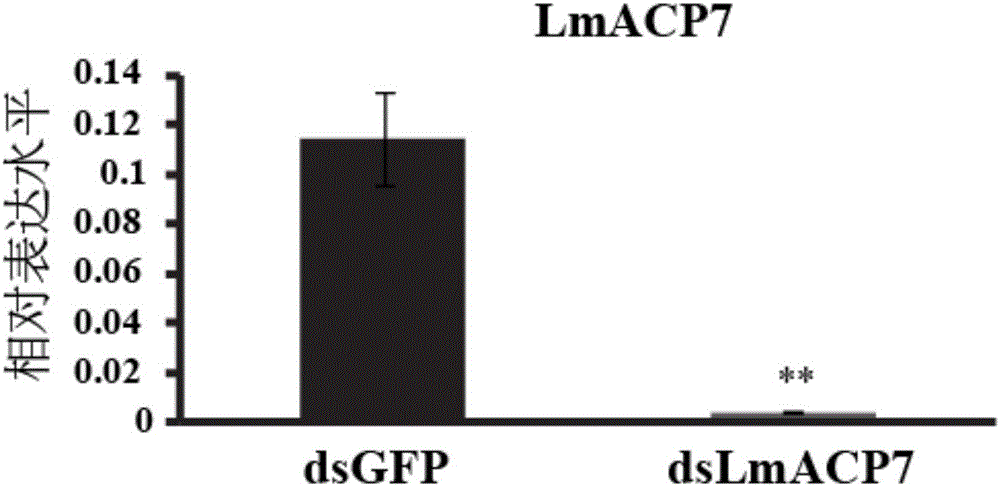
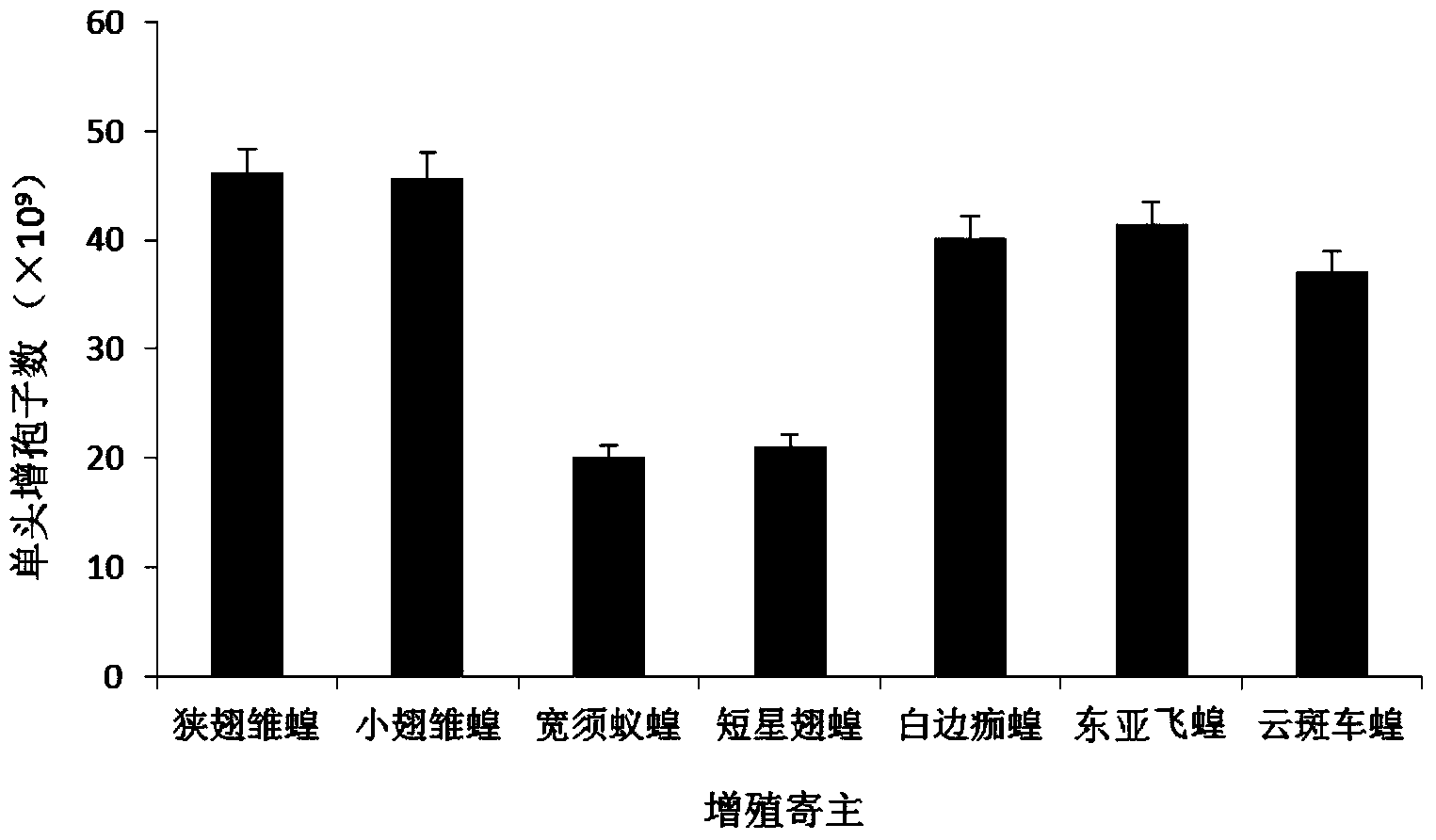
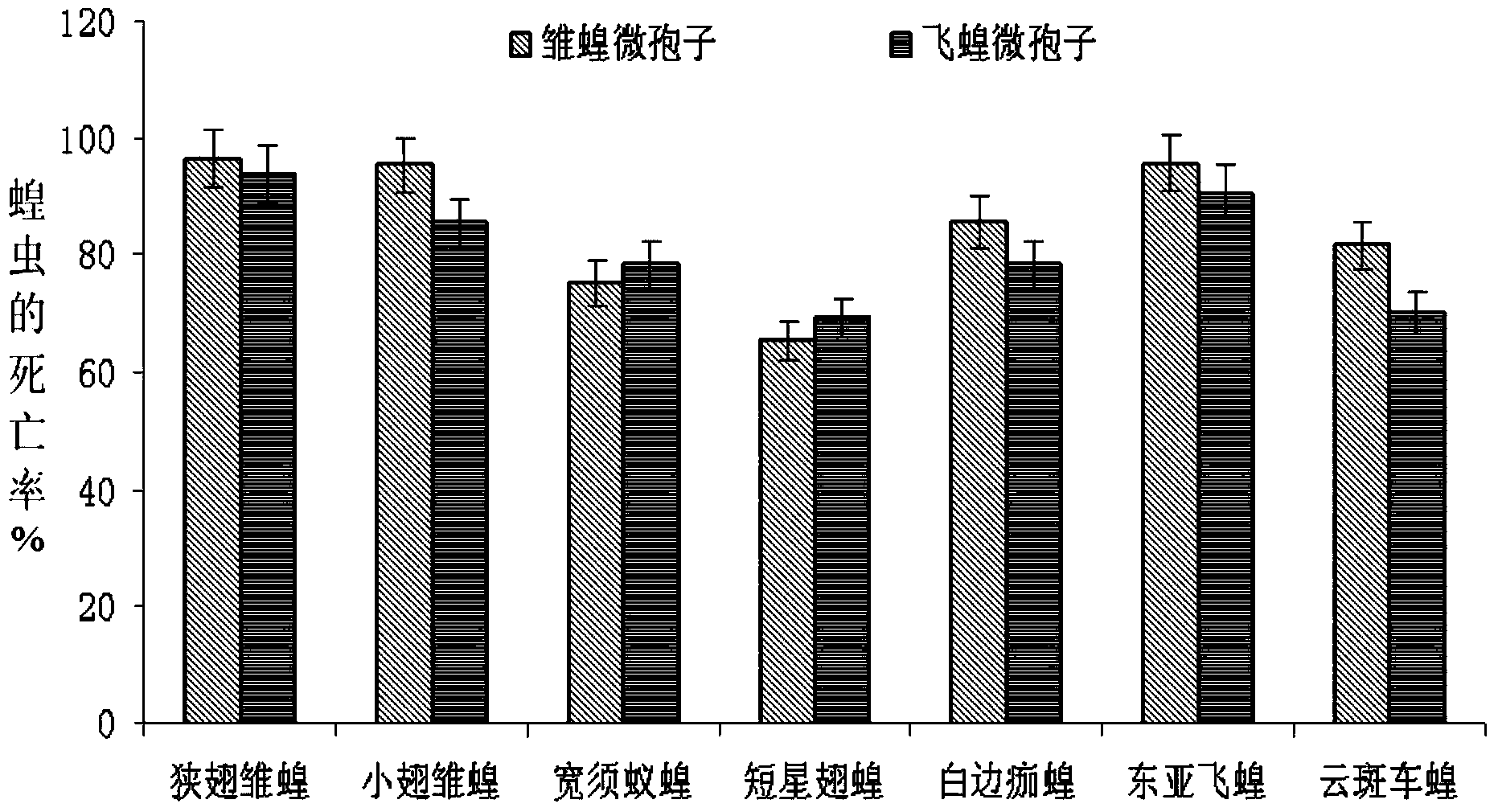
Patents
Literature
124 results about "Migratory locust" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The migratory locust (Locusta migratoria) is the most widespread locust species, and the only species in the genus Locusta. It occurs throughout Africa, Asia, Australia and New Zealand. It used to be common in Europe but has now become rare there. Because of the vast geographic area it occupies, which comprises many different ecological zones, numerous subspecies have been described. However, not all experts agree on the validity of some of these subspecies.
Chitinase genes of insects and application of dsRNA thereof
The invention provides chitinase gene sequences and application of dsRNA thereof, which can silence specific chitinase genes and make insects die of retarded development. By cloning, sequencing and analyzing expression of the chitinase genes of a plurality of locusta migratoria manilensis, the chitinase genes with a sequence of SEQ IDNO:1 are obtained; and the chitinase genes with sequences of SEQ ID NO:2 and SEQ ID NO:3 are selected and used for synthesizing the dsRNA. After the dsRNA is injected into a coelom of an insect, the insect shows difficult molting in the development process and dies. The chitinase gene sequences provide a basis for the effective prevention and control of the insects based on RNA interference, and provide a new approach for the development of a safe and pollution-free method for preventing and controlling the insects.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Metarhizium anisopliae and application thereof
ActiveCN102776130AHigh insecticidal activityStrong pathogenicityBiocideFungiMicrobiological cultureMetarhizium anisopliae
The invention discloses Metarhizium anisopliae and application of Metarhizium anisopliae. The Metarhizium anisopliae provided by the invention is Metarhizium anisopliae JF-6213 with CGMCC No. 5952 registered in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The strain (Metarhizium anisopliae) has good production traits and strong spore production capacity, strong insecticidal activity to sugarcane moth borer, good secondary infection to sugarcane moth borer, has 7.44 days LT50 (lethal time of 50%) to 3-4 years sugarcane moth borer; the strain is used for preparing insect killing fungus preparation which can effectively control population quantity of sugarcane moth borer; moreover, Metarhizium anisopliae JF-6213 has strong pathogenicity to brontispa longissima, asiatic migratory locust, leechee stinkbug and Dysmicoccus neobrevipes Beardsley, strong secondary infection capability and high stability and is quite applicable to tropical and subtropical areas.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Migratory locust wing specific cuticle protein gene and application of dsRNA thereof
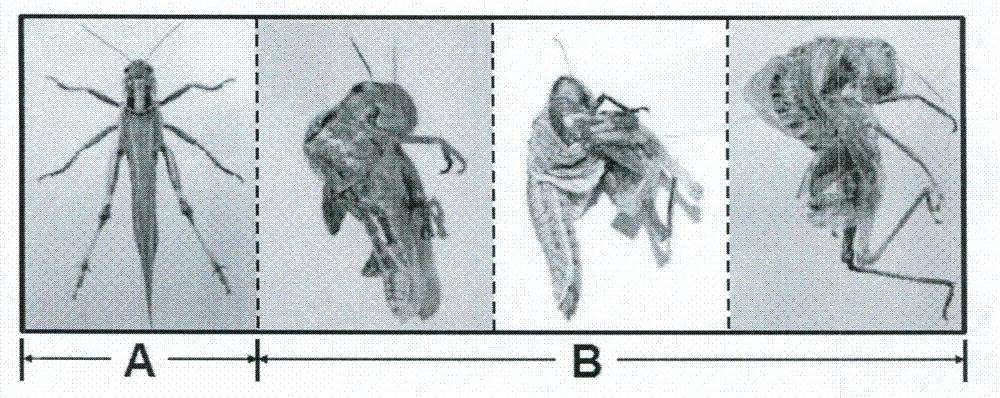
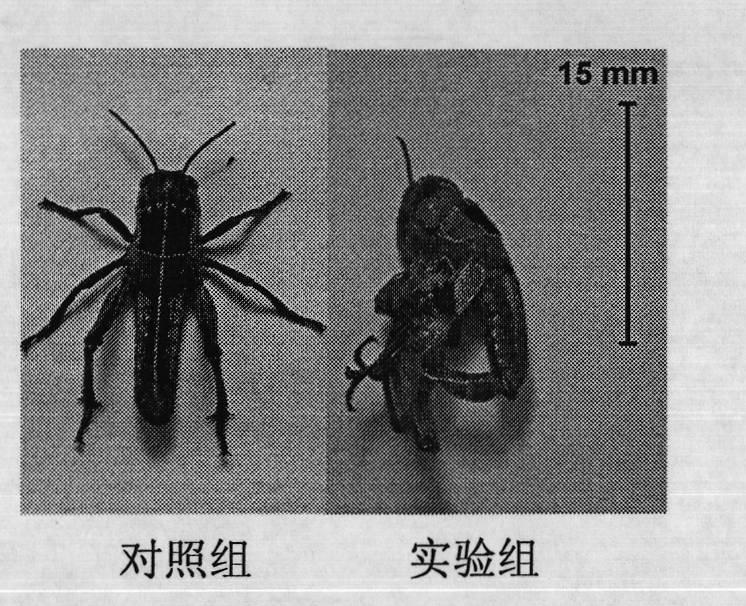
The invention provides a migratory locust wing specific cuticle protein gene and application of dsRNA thereof. DsRNA of the gene can silence the specific cuticle protein gene, so that migratory locust wings grow abnormally and migratory locust finally die.Concretely, through cloning and sequencing migratory locust cuticle protein gene, the wing cuticle protein gene with the sequence being SEQ ID NO:1 is obtained, and RT-PCR and western blot results show specific existence of the wing cuticle protein gene in migratory locust wing tissue; then a gene segment with the sequence being SEQ ID NO:2 is selected and used for double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) synthesis. After the gene dsRNA is injected into body cavities of migratory locust nymphs, wings of adult nymphs grow abnormally after molting, are manifested to grow with malformation and shrinkage and finally the migratory locusts die.A new target is provided for insect prevention and treatment based on RNA interference.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
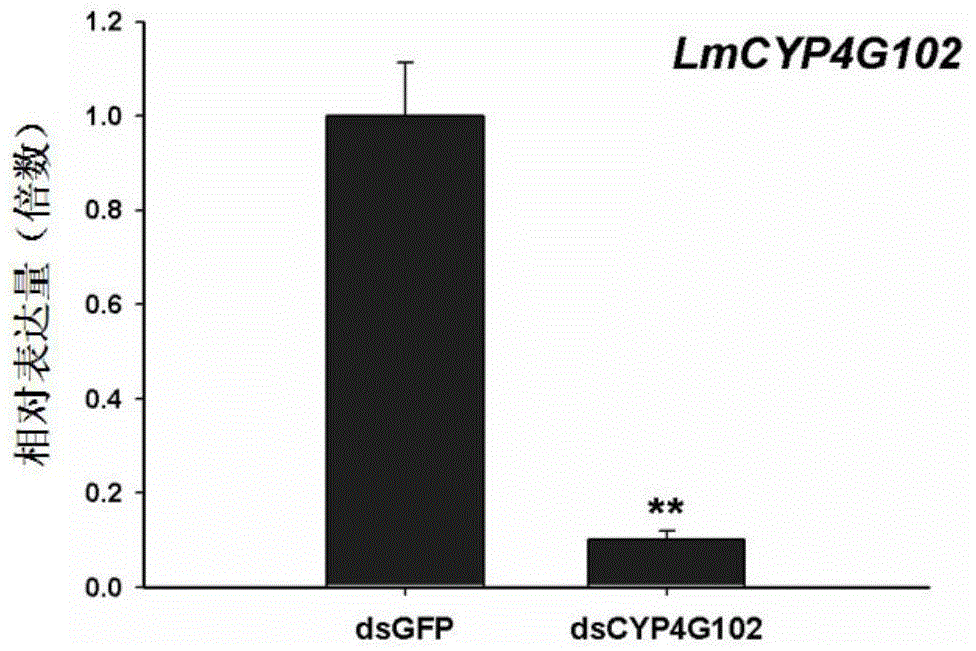
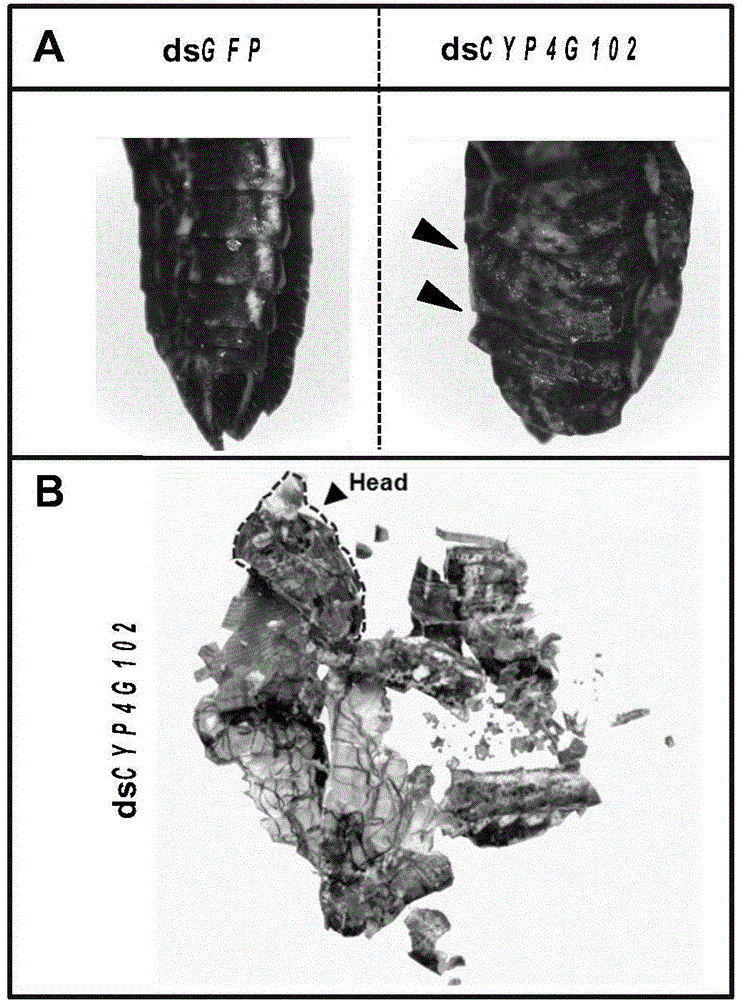
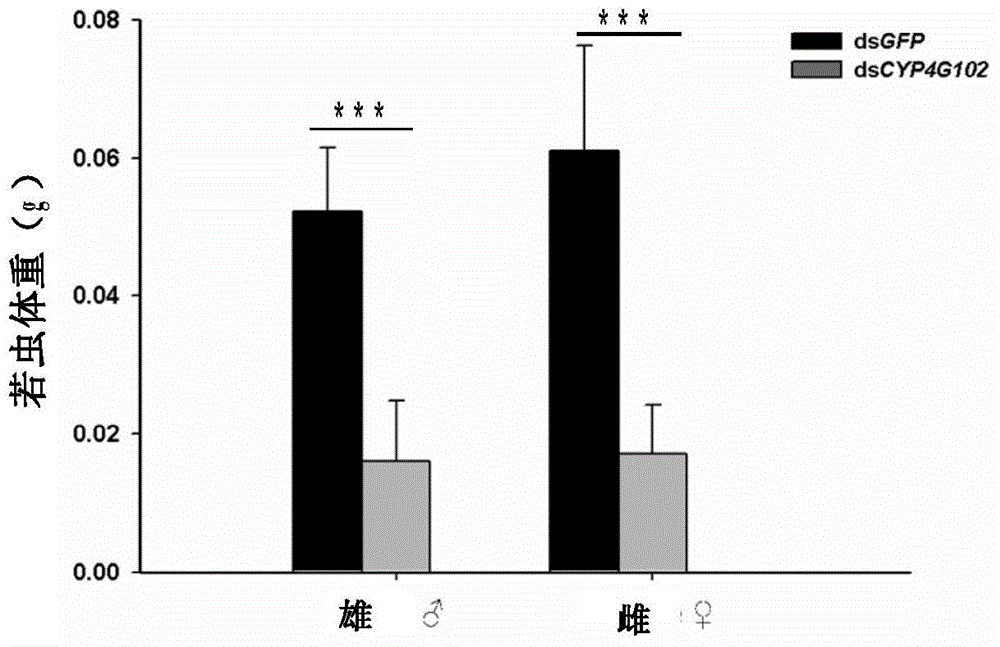
Insect cytochrome P450 gene and application thereof
The invention provides an insect cytochrome P450 gene and the application thereof, and particularly relates to the insect cytochrome P450 gene, gene fragments, dsRNA and the application of the dsRNA to killing pests. Firstly, the cytochrome P450 gene of a migratory locust is cloned and sequenced to obtain a CYP4G102 gene, an overall nucleotide sequence of the CYP4G102 gene is SEQ ID NO:1, and an amino acid sequence of the CYP4G102 gene is SEQ ID NO:2; secondly, the gene fragments of which the sequence is SEQ ID NO:3 are obtained and used for synthesizing the dsRNA. After the synthesized dsRNA is injected into the body cavity of the migratory locust, the insect dies due to excessive in-vivo water loss caused by the fact that the water retention capacity of the body wall is reduced after ecdysis, and the death rate reaches 100 percent. The insect cytochrome P450 gene provides a molecular target or pest control based on RNA interference and can be used for the pest control.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Application of Knickkopf gene dsRNA in pest control
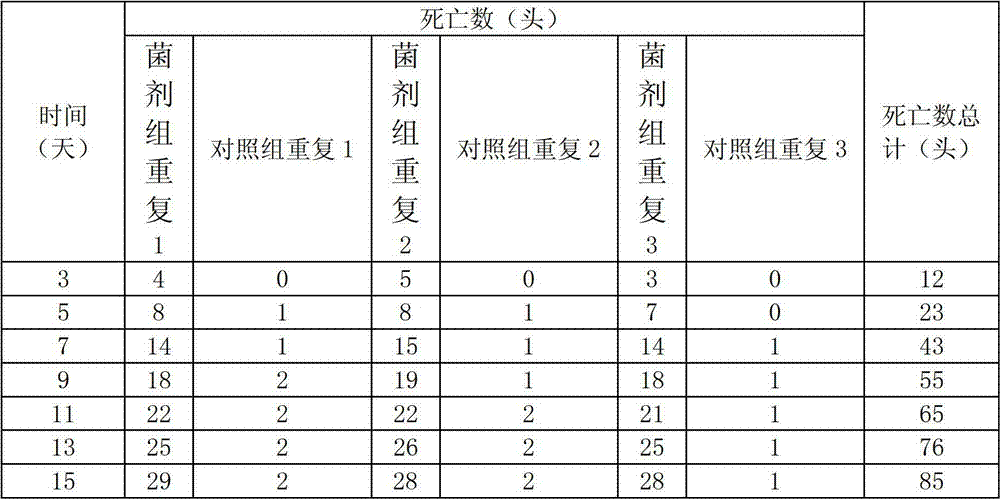
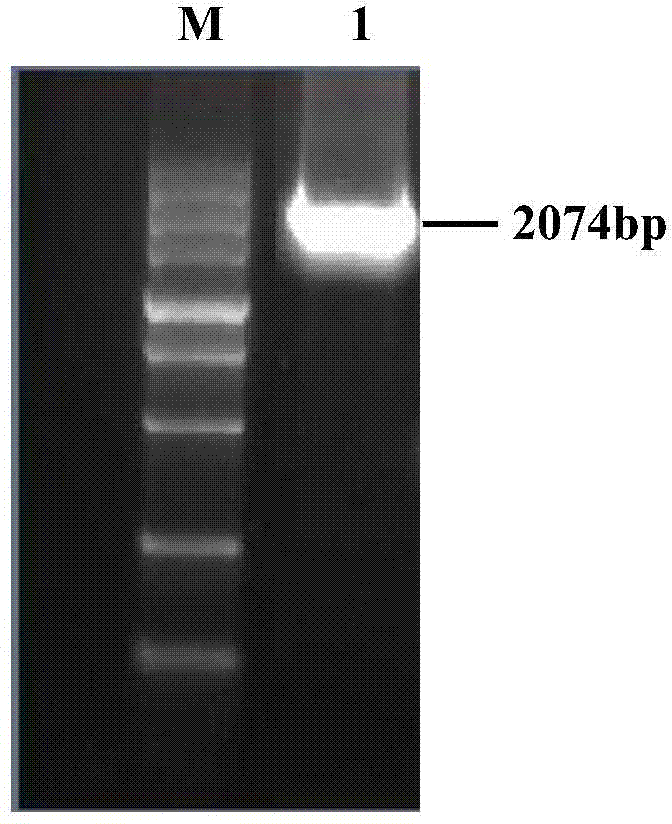
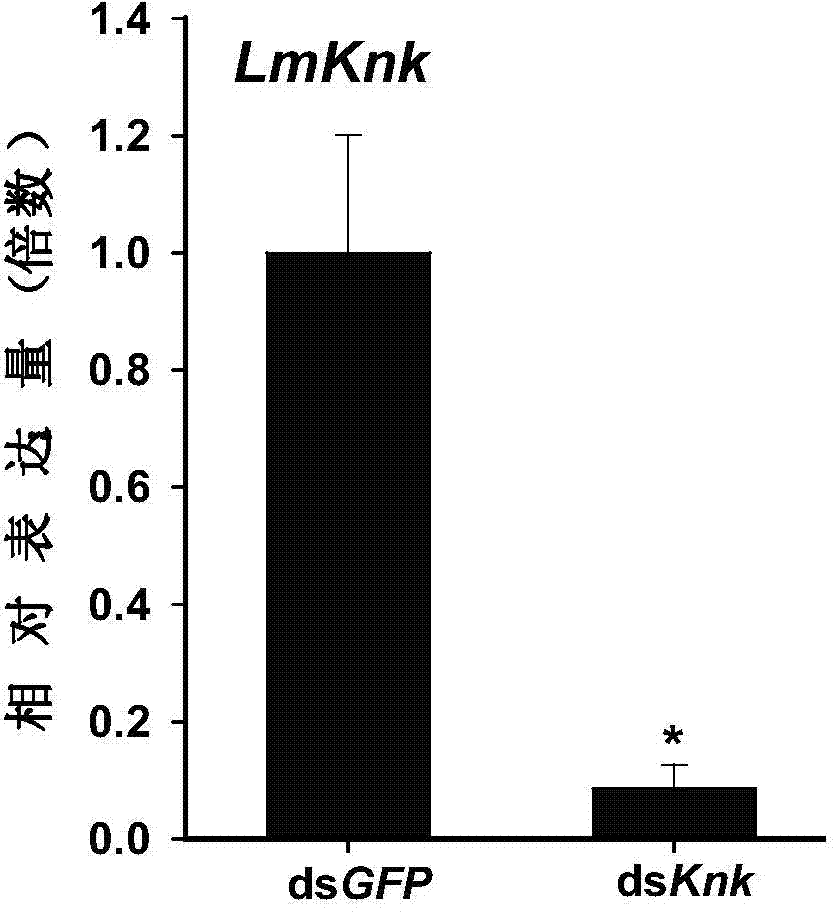
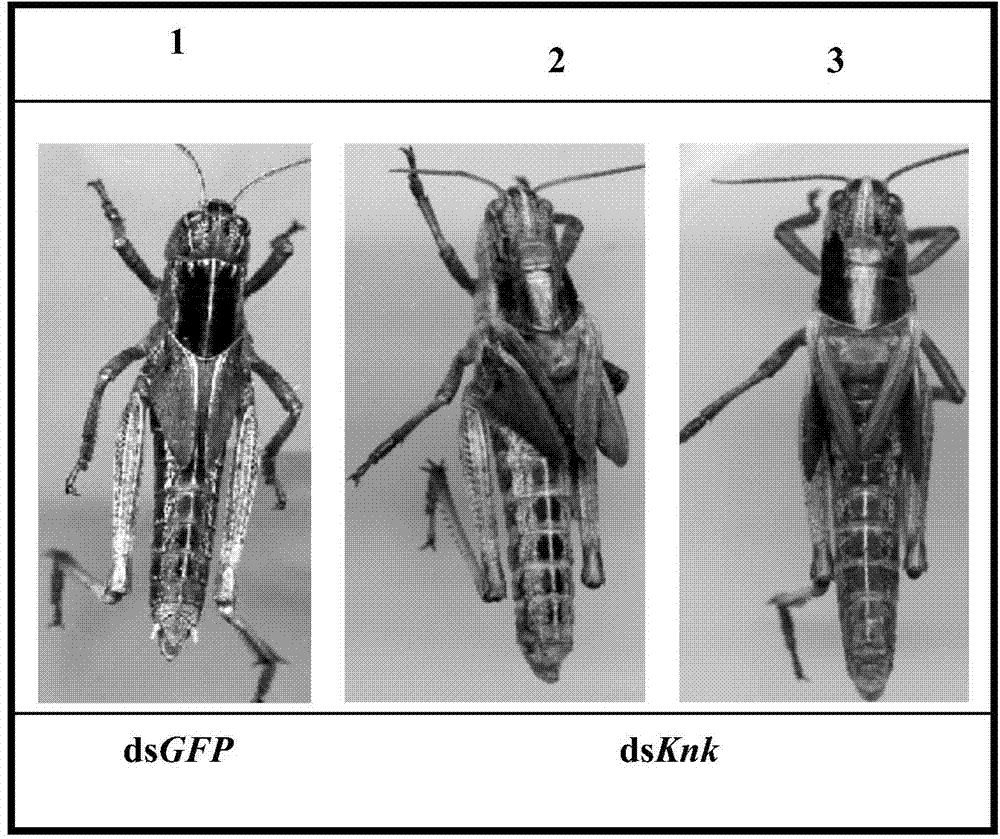
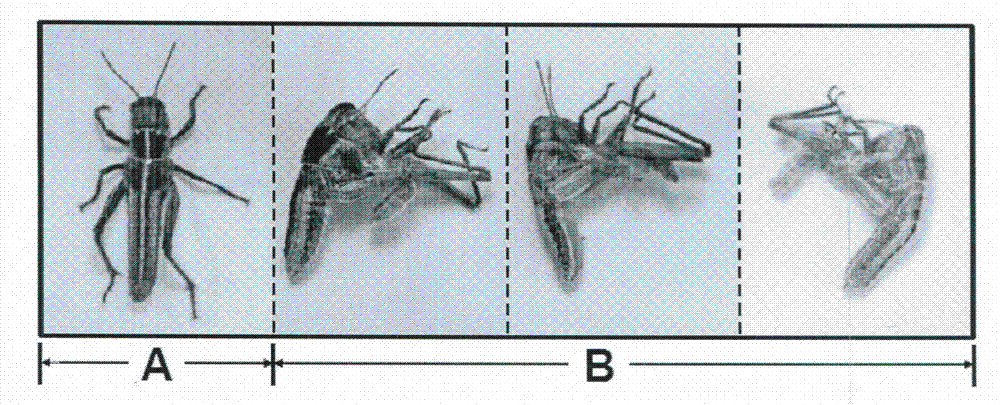
The invention provides an application of Knickkopf gene dsRNA in pest control, and in particularly relates to a migratory locust Knickkopf gene. A nucleotide sequence of the migratory locust Knickkopf gene is SEQ ID NO: 1; and based on SEQ ID NO: 1, gene segments and corresponding dsRNA are designed and synthesized. After the designed and synthesized dsRNA is injected into bodies of migratory locust, difficult molting of migratory locust can be caused to result in death of migratory locust; and the death rate can reach 76%. The Knickkopf gene obtained by screening, provided by the invention, can be taken as a molecular target for pest control, and can be used for providing a new path for effective control of pests.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase genes of insects and application thereof
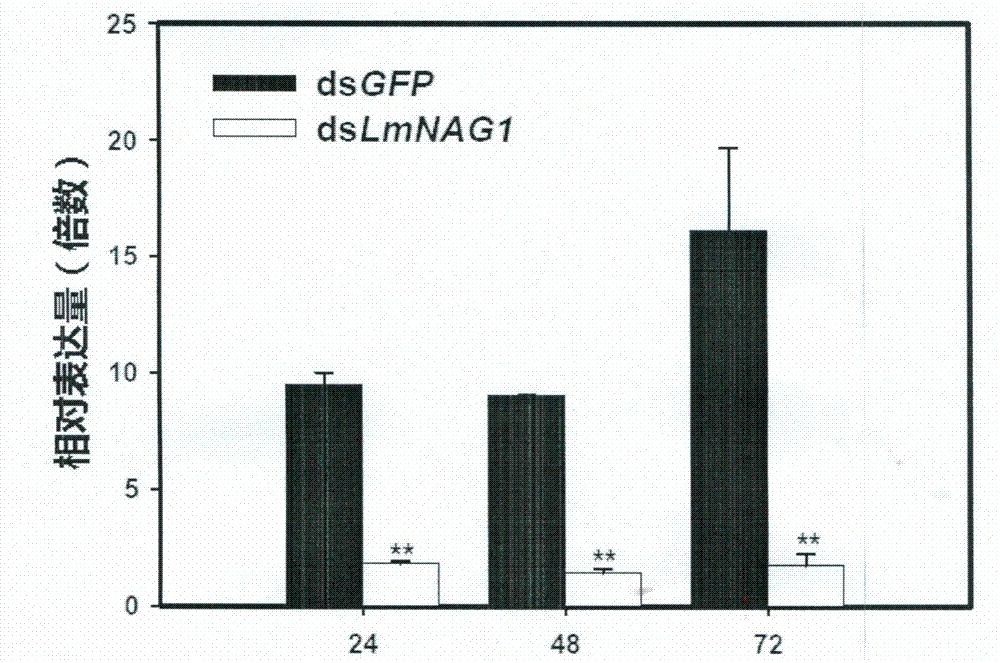
The invention provides a sequence of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase genes (NAG) of insects and an application method for double-strand ribonucleic acid (dsRNA) of the beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase genes. By the dsRNA, the specific beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase genes can be silenced, so that pests are dead. After the beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase genes of migratory locusts are cloned and sequenced, the beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase genes of which the sequence is SEQ ID NO: 1 are obtained; and fragments of the genes of which the sequence is SEQ ID NO: 2 are selected to be used for synthesizing the dsRNA. After the dsRNA of the genes is injected into body cavities of the insects, the development of the insects in the growth process is slow, and the insects cannot enter the next stadium due to incapability of smooth ecdysis, so that the insects are dead. By the beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase genes and the dsRNA, a new target is provided for RNA interference-based pest control.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Insect chitin synthase 1A gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof
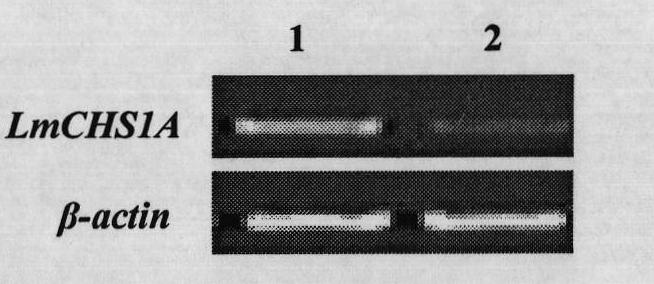
The invention provides an insect chitin synthase 1A gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof. The dsRNA is synthesized by the chitin synthase 1A gene segment with the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 which is obtained by the gene sequence of the chitin synthase 1A of Locusta migratoria manilensis with the accession number of GU067730 in an NCBI database. After the dsRNA is injected in body cavities of insects, the insects die because of difficult moulting. A new way for developing a safe and pollution-free method for preventing and controlling insect is provided.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
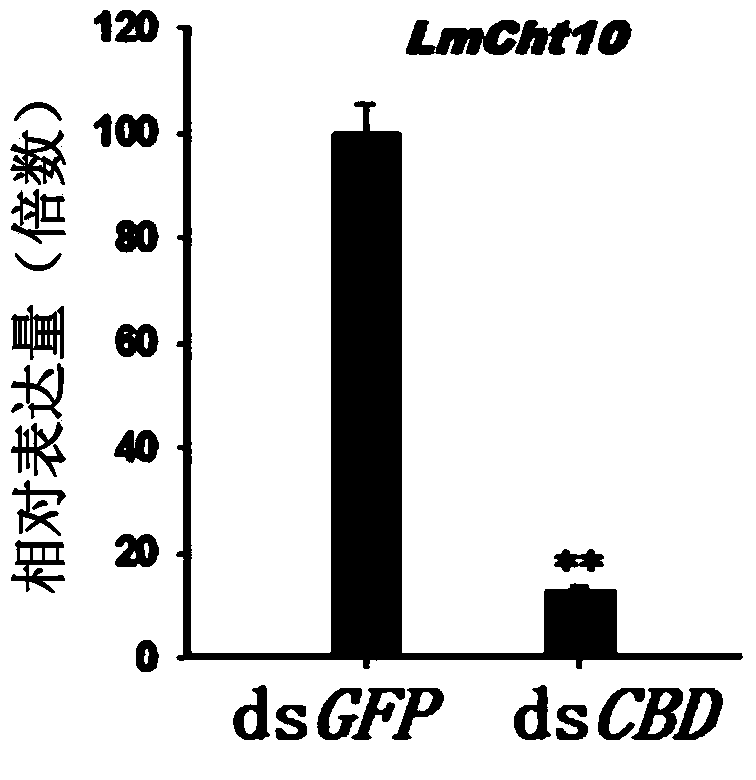
Application of type II chitinase gene specificity dsRNA (double strand ribonucleic acid) of insect
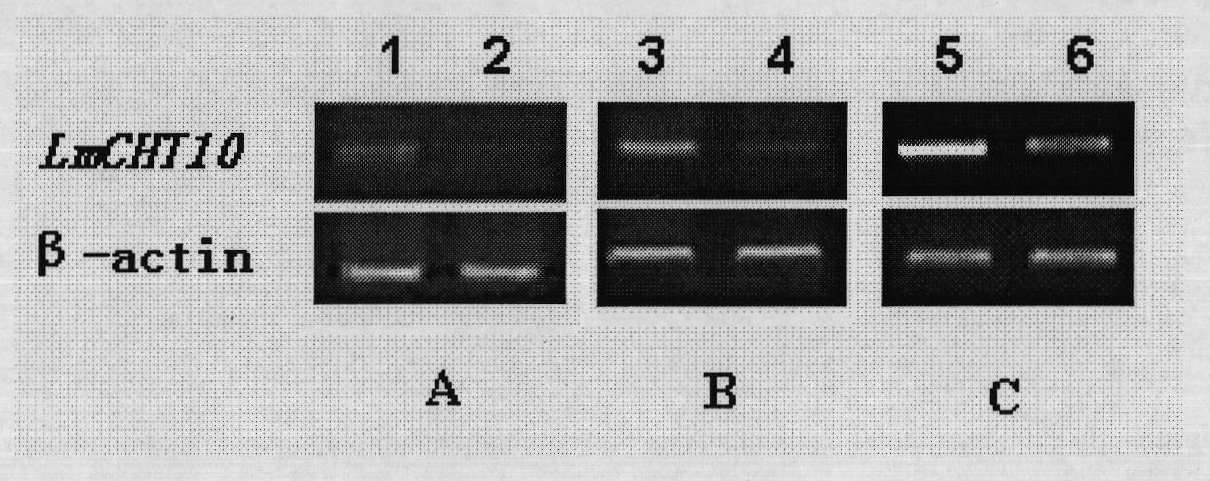
The invention provides application of a type II chitinase gene (Cht10) specificity dsRNA (double strand ribonucleic acid) of an insect. The type II chitinase gene specificity dsRNA can silence the type II chitinase gene so as to allow a migratory locust to die without affecting other insects. The type II chitinase gene of the migratory locust is cloned and sequenced, then the functional domain is analyzed, unique chitin binding domains are selected, the gene segment with the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 is designed for synthesis of specificity dsRNA. After the dsRNA is injected into the body cavity of the migratory locust, the migratory locust cannot exuviate smoothly to step into next instar and dies at the rate of 100%, but other insects injected with the dsRNA do not die. The invention provides a target for specific pest control based on RNA interference, and the type II chitinase gene specificity dsRNA can be used for preventing and controlling specific insect-migratory locust.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Antonospora locustae strain and application thereof in prevention and control of locust
ActiveCN102250772AImprove the level of prevention and control technologyNon-toxicBiocideProtozoaMicroorganismGrassland
The invention discloses an Antonospora locustae strain and application thereof in prevention and control of locust. The Antonospora locustae disclosed by the invention is named as AL2008L-04 strain, is obtained by isolating and screening from the field diseased Asiatic migrotory locust, and was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Centre (CGMCC) in No. 3 of Beichen West Road No. 1 Court, Chaoyang District, Beijing on May 23, 2011 with the culture collection number of CGMCC No. 4901. Antonospora locustae AL2008L-04 strain CGMCC No. 4901 is abbreviated as AL2008L-04 strain. The locust prevention and control agent disclosed by the invention can be used for preventing and controlling grassland locust, migratory locust and other locusts. The product belongs to a biological pesticide, has no toxic or harmful effects on environment, human, livestock and poultry, is safe for natural enemy, and has broad application prospects. The Antonospora locustae strain provided by the invention has significance in improving the level of a prevention and control technique on locust in China.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
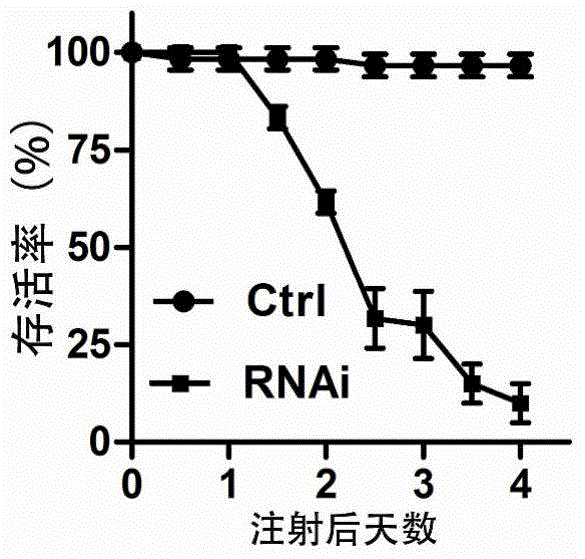
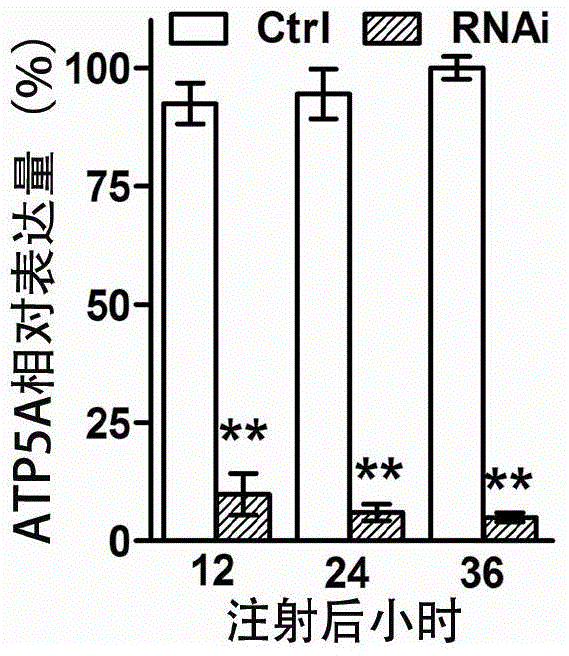
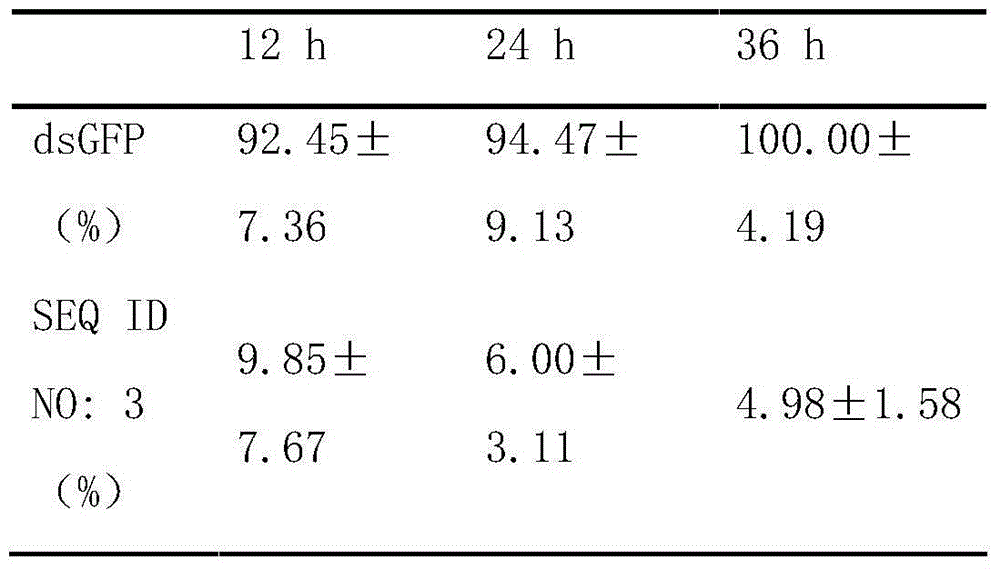
Oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene and application of dsRNA of oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene in pest control
ActiveCN104450755AWill not interfere with the impactCause interferenceBiocideAnimal repellantsConserved sequenceMigratory locust
The invention relates to an oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene and application of dsRNA of the oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene in pest control. The oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene disclosed by the invention provides the conserved sequence of ATP synthetase alpha subunit cDNA of a locust, can be used for constructing the constructs, namely RNA, DNA and the like, and obviously inhibits the expression of the ATP synthetase alpha subunit inside a locust body by silencing the ATP synthetase alpha subunit inside the locust body by utilizing an RNAi technology to cause the lethal effect on the locust, thus being applied to the RNAi technology to prevent and control oriental migratory locust pests.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Microspore preparation and its production technique
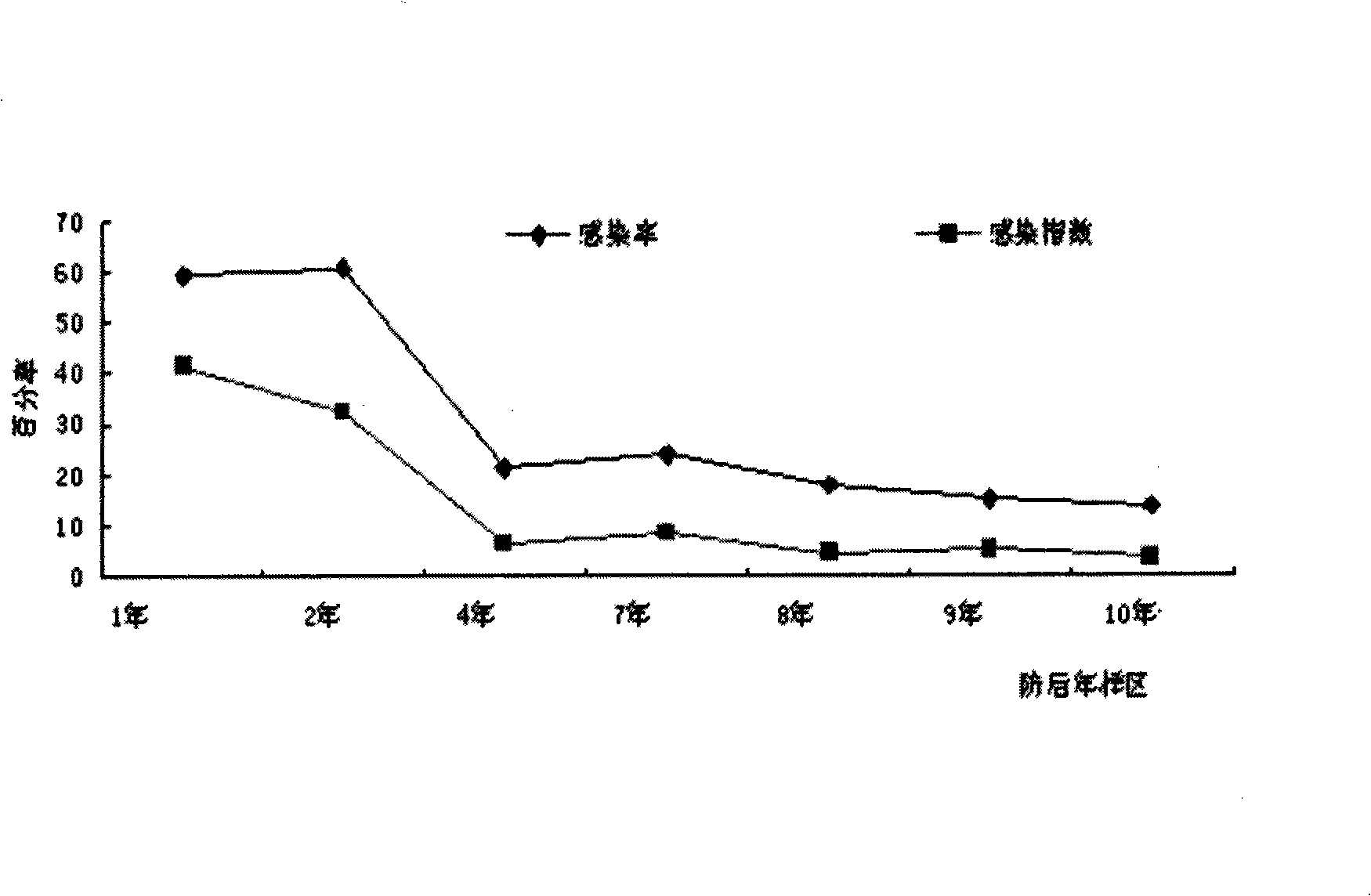
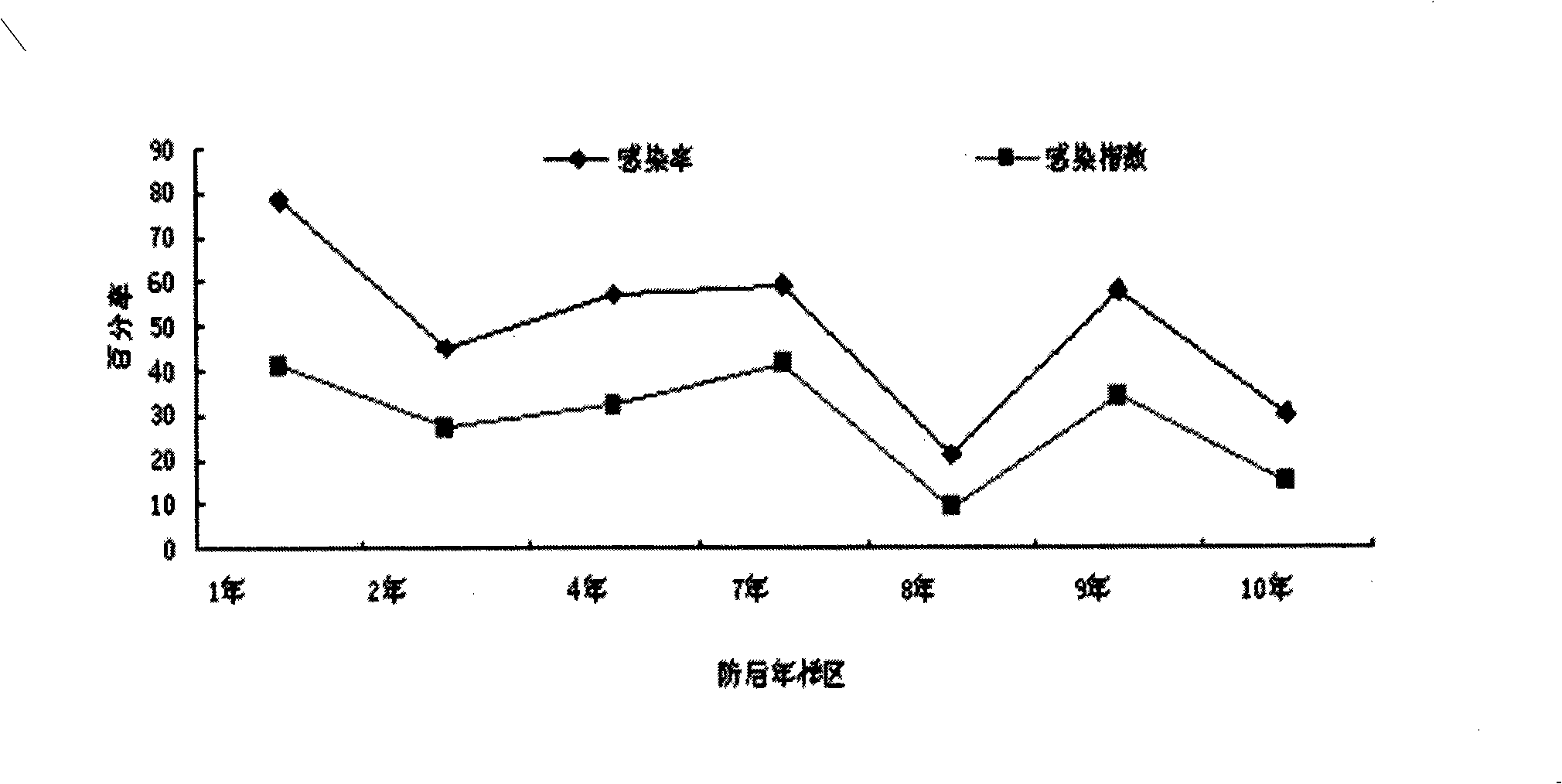
The invention provides a preparation containing 8-year-old microspores (P8) and 9-year-old microspores (P9) separated from Oedaleus asiaticus, and the preparation method thereof. The microspore preparation can be used for preventing and treating dozens of locusts such as farmland migratory locusts, grassland migratory locusts, Oedaleus asiaticus, bamboo locusts, rice locusts, etc, and can remarkably improve the locust control effect and ensure the stable prevention effect.
Owner:BEIJING MAMMOTH SEED
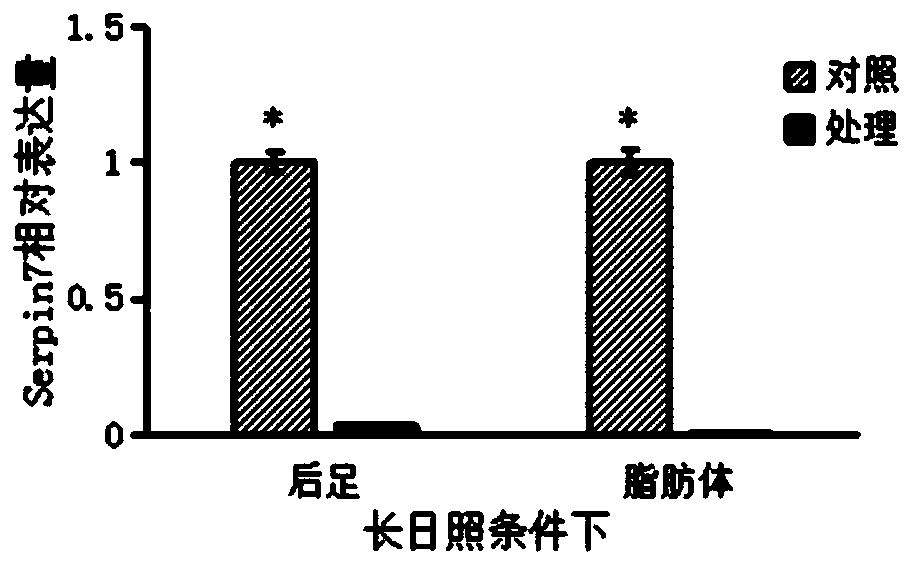
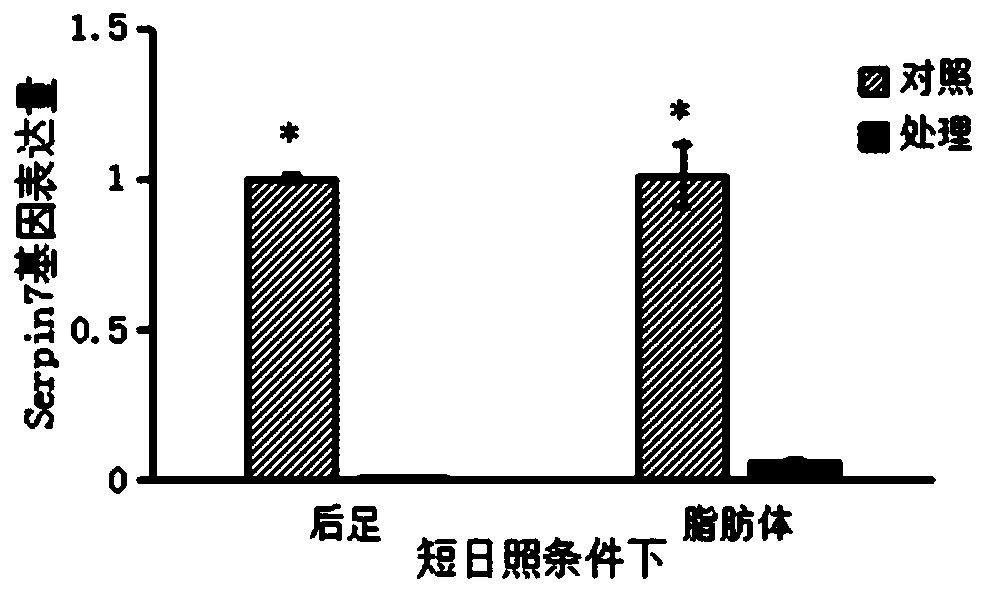
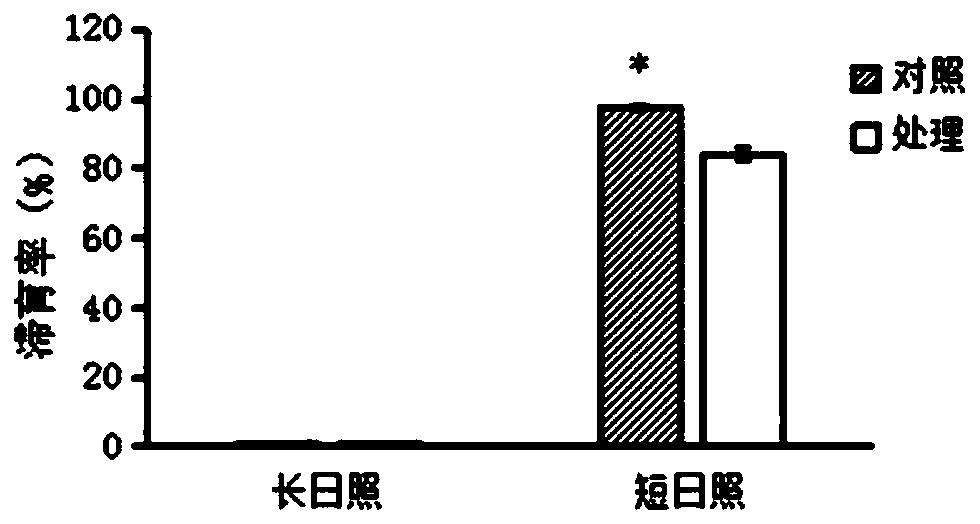
Migratory locust serine protease inhibitor 7 and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN109734798ARegulation of diapauseIn-depth understanding of diapause mechanismBiocideProtease inhibitorsSerine Protease InhibitorsDiapause
The invention discloses a migratory locust serine protease inhibitor 7 and a coding gene and application thereof. By means of a gene cloning technology, a migratory locust LmSerpin7 gene is cloned from migratory locusts, dsRNA used for interfering a migratory locust LmSerpin7 gene is synthesized, and dsRNA is guided into the migratory locusts through an injection method to conduct RNAi on the migratory locust LmSerpin7 gene. The result shows that the gene can regulate migratory locust egg diapause, and a theoretical basis is provided for further deeply understanding the migratory locust diapause mechanism and providing new biological pesticide target sites.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
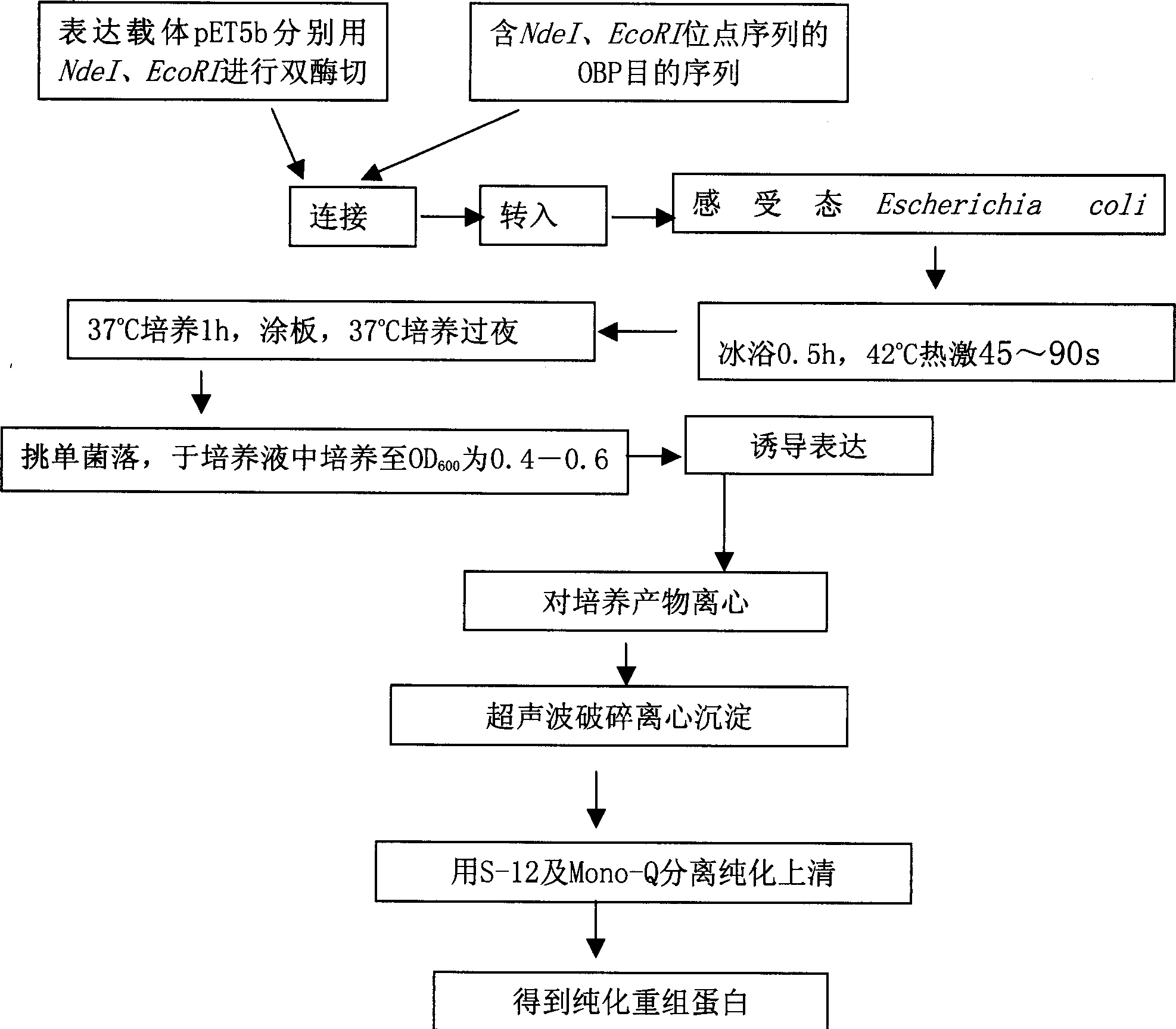
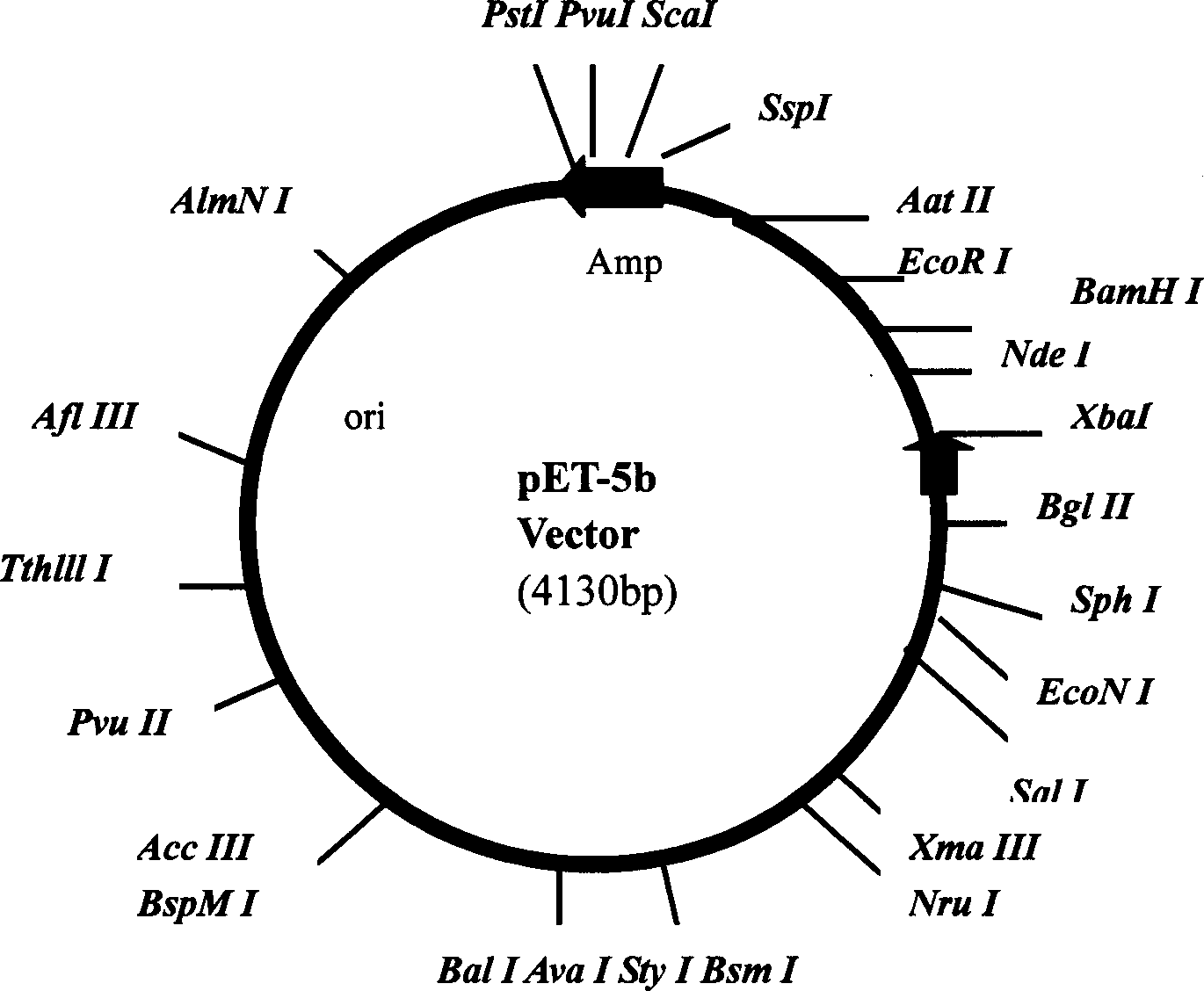
High efficiency expression of smell molecule combined protein of migratory locust in pronucleus system
InactiveCN1782073AHigh expressionSimple procedureFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMigratory locustPronucleus
The present invention discloses a method of expressing recombinant odorant binding protein (OBP) of insect in prokaryotic cell, and vector containing target nucleic acid sequence is transformed to competent prokaryotic cell. The present invention also discloses new OBP-coding nucleic acid sequence obtained from Locusta migratoria antenna.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
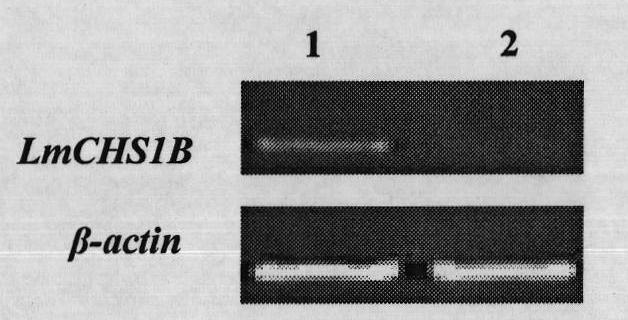
Insect chitin synthase 1B gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof
The invention provides an insect chitin synthase 1B gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof. The dsRNA is synthesized by the chitin synthase 1B gene segment with the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 which is obtained by the nucleotide sequence of the chitin synthase 1B of Locusta migratoria manilensis with the accession number of GU067731 in an NCBI database. After the dsRNA is injected in body cavities of insects, the insects die because of difficult moulting. A new way for developing a safe and pollution-free method for preventing and controlling insect is provided.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
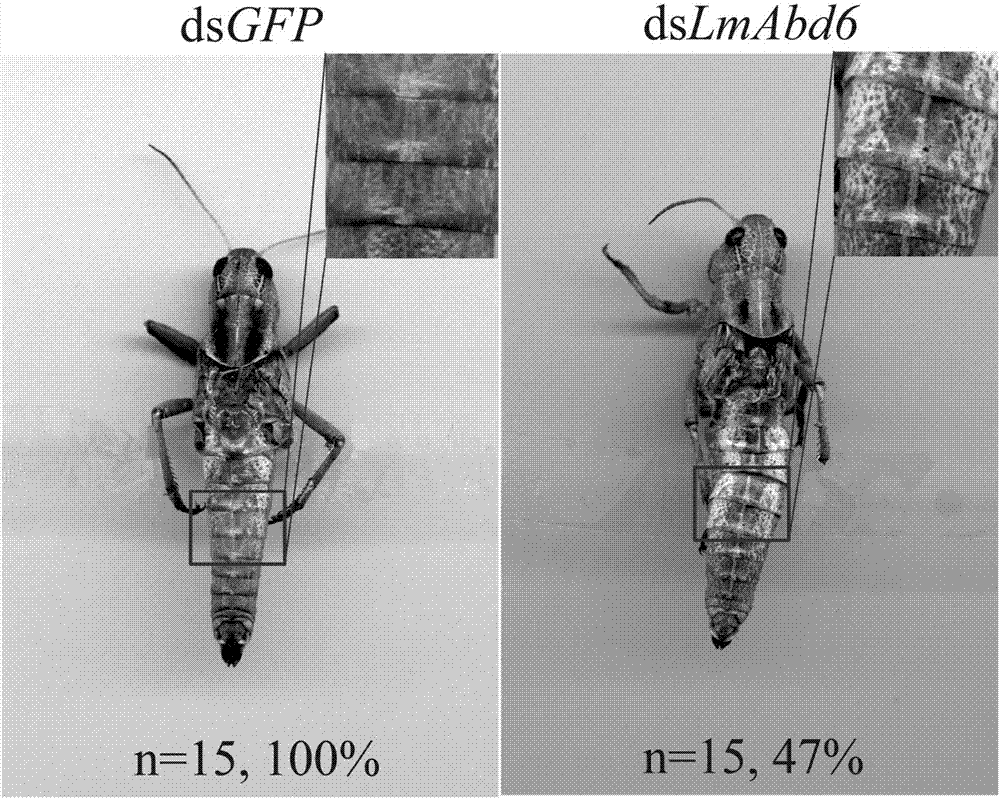
Migratory locust mesenchymal epidermal protein gene 6 and application thereof in locust control
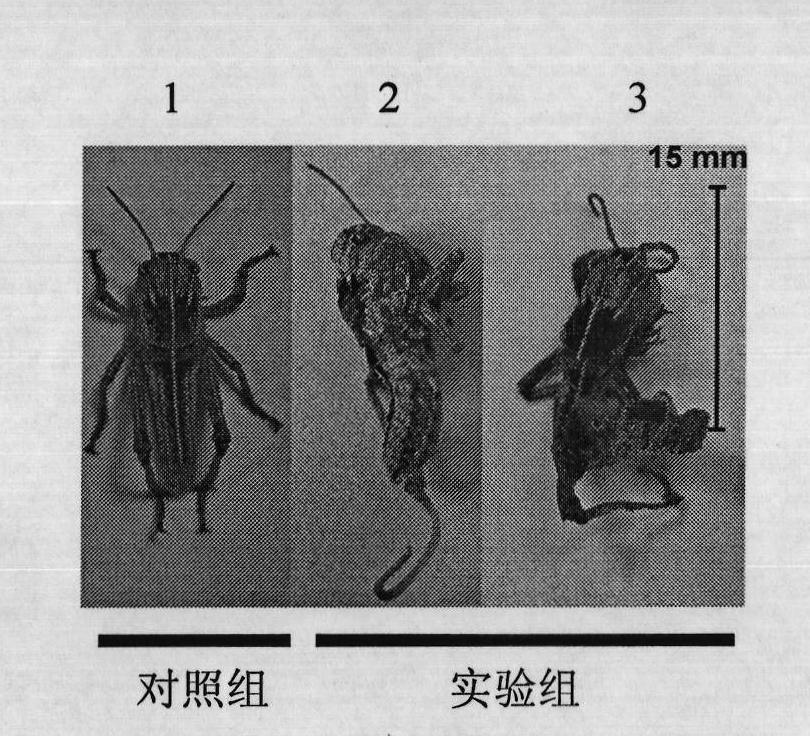
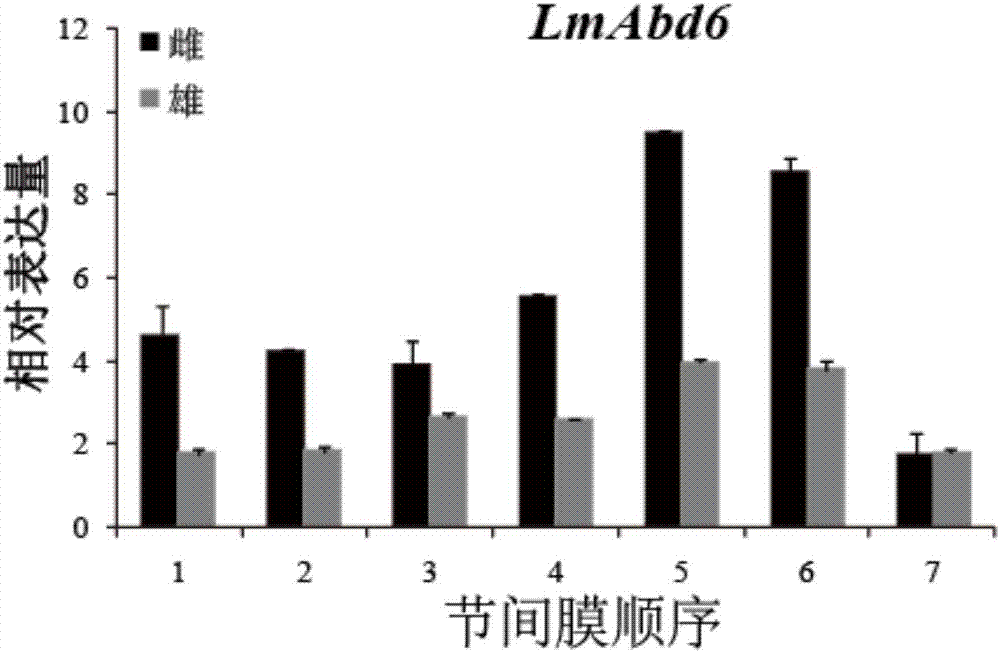
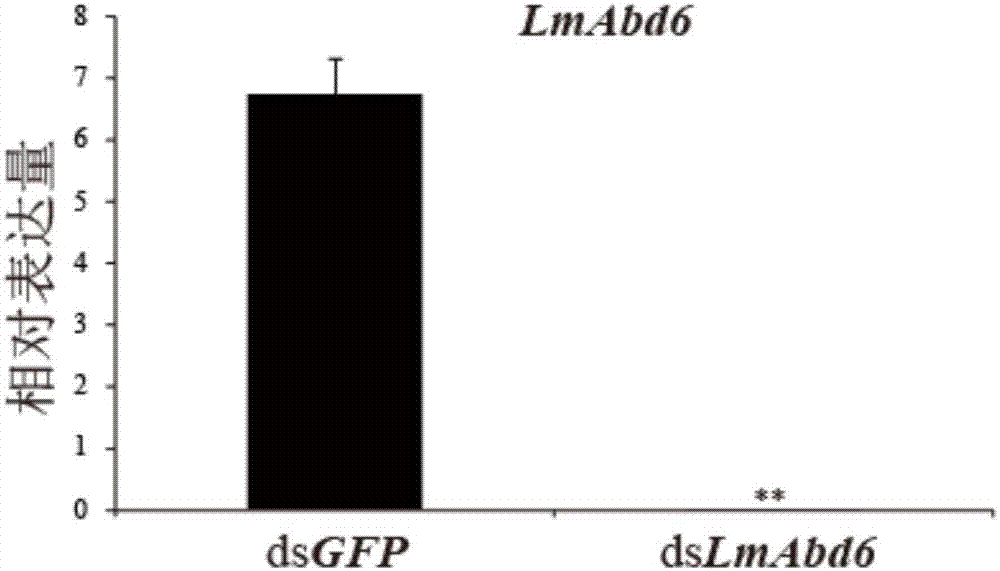
The invention provides a migratory locust mesenchymal epidermal protein gene 6 and application thereof in locust control. The method specifically comprises the following steps: acquiring a migratory locust mesenchymal epidermal protein gene from a migratory locust transcriptome by virtue of a bioinformatics method, and further obtaining full-length genes having a sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 by virtueof a migratory locust genomic sequence. dsRNA of the gene is designed and synthesized according to the SEQ ID NO:1, the dsRNA is injected into a body cavity of the migratory locust, so that target genes can be specifically silenced, ecdysis of the body is difficult, the intersegmental membrane cannot be closed, and finally abdomens of injurious insects cannot deep into soil to lay eggs so as to greatly decrease the oocyst number and ovum number. Multiple experiments show that injection of the dsRNA causes reduction of the ovum number of offspring of the migratory locust by 70% or higher. Due to specificity and high efficiency of the gene disclosed by the invention, the gene has an obvious effect of reducing the number of laid eggs of the injurious insects and the offspring population quantity, and a novel pathway can be provided for pest control.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
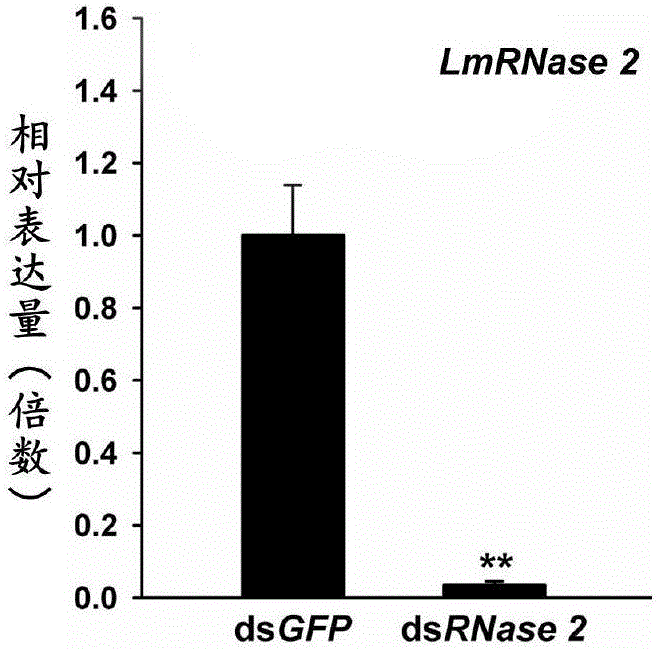
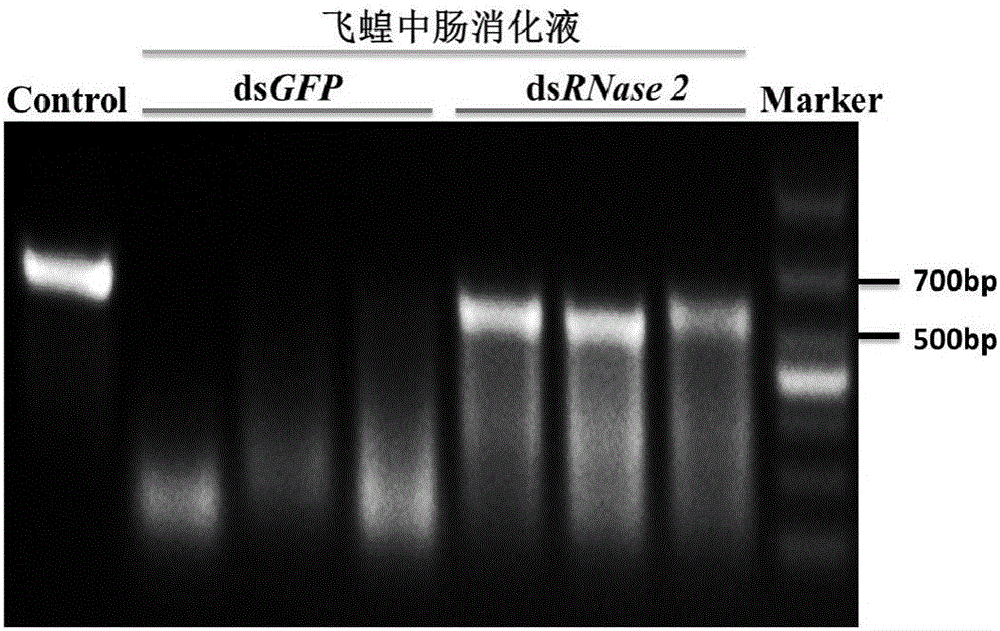
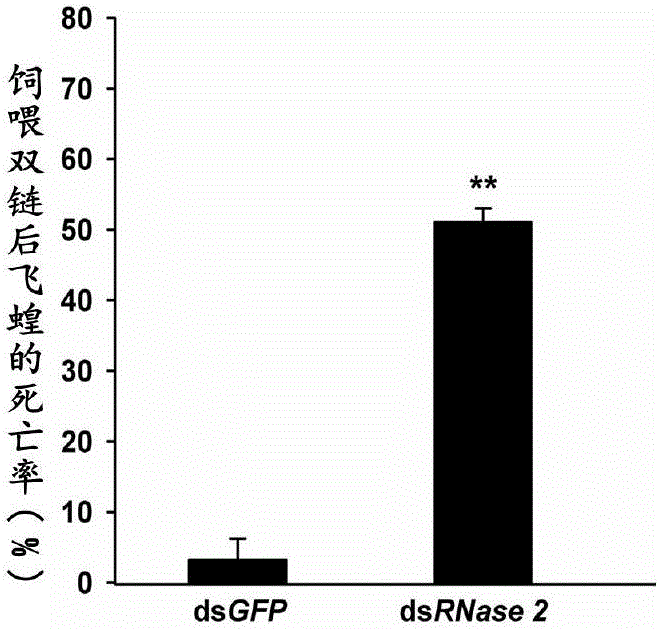
Application of migratory locust intestinal tract RNase gene 2 to pest prevention and control
The invention provides application of a migratory locust intestinal tract RNase gene 2 to agricultural pest prevention and control. Particularly, by a bioinformatic method, RNase 2 fragments are obtained from a migratory locust transcriptome; the cDNA full length sequence is obtained through PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification verification. The double-chain RNA (dsRNA) of RNase 2 is synthesized according to the design primer; after the injection into the migratory locust body cavity, the specific silencing RNase 2 can be performed; then, after the migratory locust is fed with insect-resistant gene DsRNA, the migratory locust death rate can reach 50 percent or higher; through the application of the RNase 2, the pest prevention and control through dsRNA feeding becomes possible; important practical significance can be realized on the pest prevention and control.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
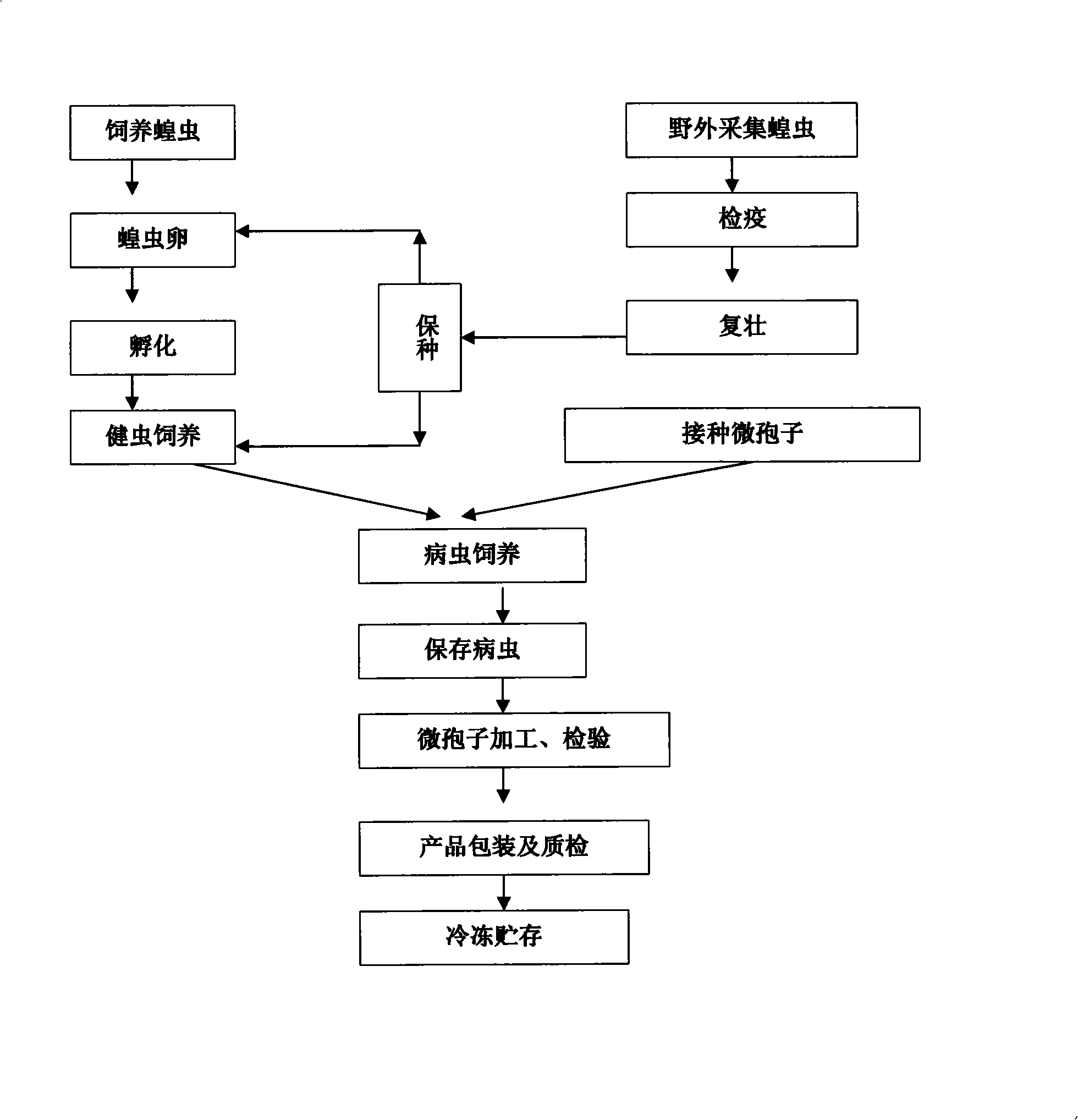
Locust microsporidia, suspension culture method and applications thereof
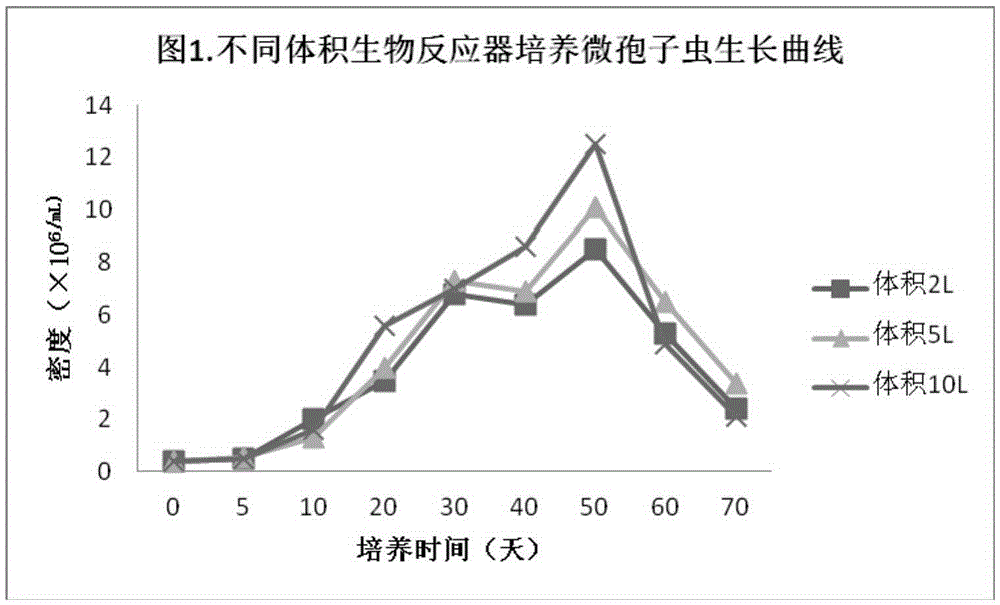
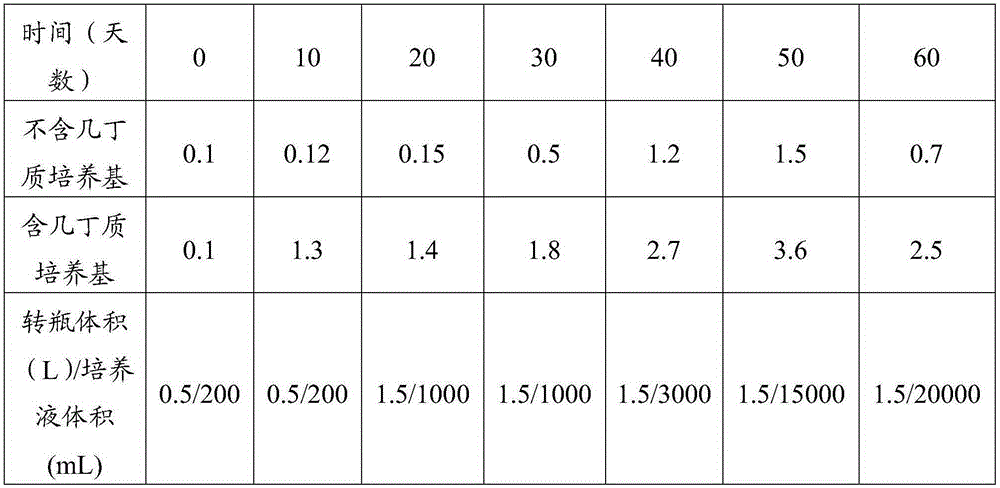
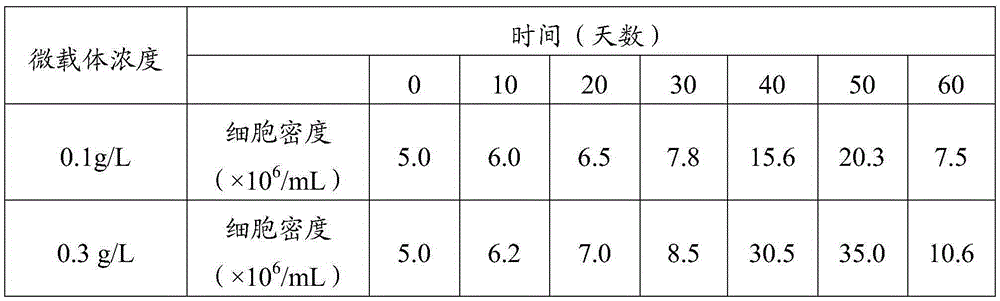
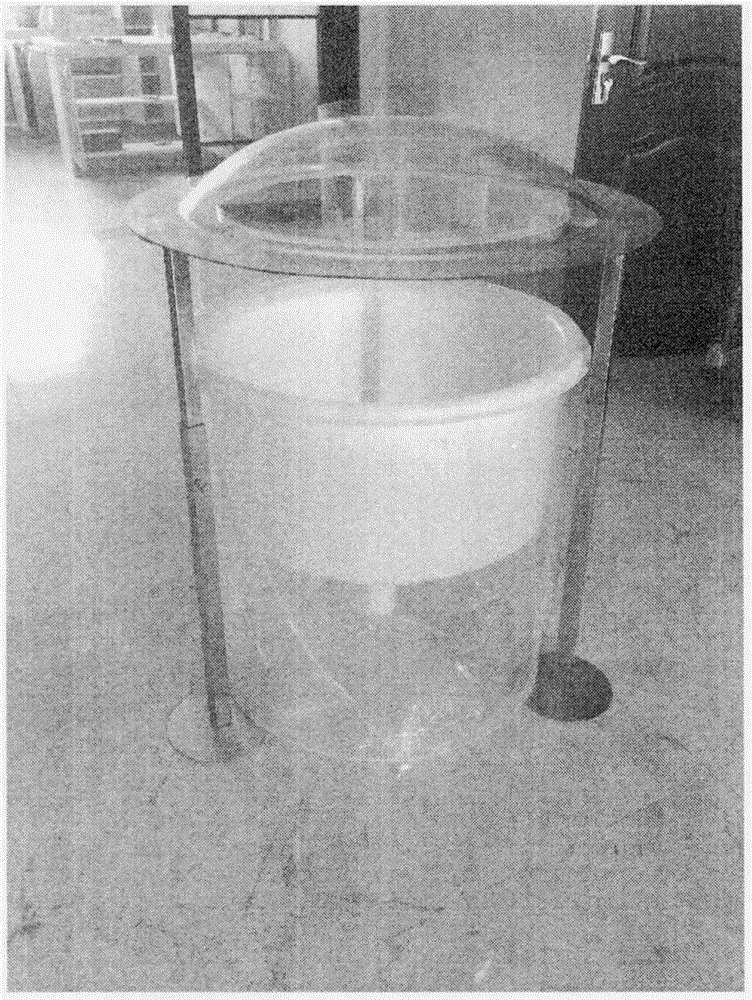
The invention discloses a locust microsporidia, a suspension culture method and applications thereof. The locust microsporidia strain is separated from Locusta migratoria L. and is prepared through 10 generations in locust body and 10 generation in-vitro culture. The preservation number is CGMCC No.11170. Moreover, the invention also provides a culture medium for in-vitro culture of locust microsporidia and a suspension culture method. In the culture medium, insect-origin, water-soluble, and de-acetylated chitin is taken as the extracellular matrix, polyvinylpyrrolidone is taken as the viscosity enhancer, and at the same time, a protein extract is added into the culture medium. The disclosed culture medium and bioreactor are used to carry out micro-carrier suspension multiplication culture, and after culture, the number of microsporidia is increased by 60 times. The invention provides a method capable of culturing a large amount of locust microsporidia and provides technical support for the massive application of locust microsporidia as a biological insecticide.
Owner:NANJING HUADEFU BIOTECH CO LTD
Automatic monitoring system for migratory-locust-nymphae occurrence density and manufacturing technology thereof
InactiveCN106614452ARealize automatic countingApparent specific attractionInsect catchers and killersInfraredManufacturing technology
The invention provides a system capable of automatically monitoring the migratory-locust-nymphae occurrence density and remotely transmitting data. An Internet-of-Things system can be composed of the system and computer software. The system can be used for automatically monitoring the occurrence density of outdoor migratory locust nymphae, the occurrence density of the outdoor migratory locust nymphae is subjected to data recording and systemic analysis through the computer software, and locust-invasion key information is provided. According to the system, a specific reaction spectrum, a specific attractant and a special trapping device for the migratory locust nymphae are adopted in cooperation with the electrooptical technology, the computer technology, the remote transmission technology and the special infrared optoelectronic switch installing mode, all electronic component compositions and the connecting modes are designed, and the migratory-locust occurrence density is automatically counted and remotely transmitted to the computer software for data analysis. The system has the advantages of being efficient, simple, convenient, automatic and high in specificity, accuracy and stability and the like, and a larger amount of cost of manpower and material resources can be saved.
Owner:张昕然 +1
Insecticidal toxicity evaluation method of green muscadine fungus and chlorantraniliprole combined utilization
The invention discloses an insecticidal toxicity evaluation method of green muscadine fungus and chlorantraniliprole combined utilization, and provides a method for identifying insecticidal efficacy of chemical agent and fungicide combined utilization. The method for identifying the insecticidal efficacy of the chemical agent and the fungicide combined utilization includes the following steps: 1) respectively detecting LC50 values of the chemical agent, the fungicide, and mixture composed of the chemical agent and the fungicide; 2) converting a bacteria agent concentration unit into a chemical agent concentration unit; 3) calculating a co-toxicity coefficient of the chemical agent and fungicide combined utilization, wherein if the co-toxicity coefficient is equal or greater than 100, the insecticidal efficacy of the chemical agent and fungicide combined utilization is equal or greater than an independent effect of the chemical agent or the fungicide, and a synergized effect is achieved, and if the co-toxicity coefficient is less than 100, the insecticidal efficacy of the chemical agent and the fungicide combined utilization is less than the independent effect, and an antagonistic effect is caused. By adopting the method for identifying the insecticidal efficacy of the chemical agent and the fungicide combined utilization, green muscadine fungus bacterial strain, the chlorantraniliprole and migratory locust are used as experimental materials, an uniform unit is used to convert the LC50 values of the green muscadine fungus and the chlorantraniliprole, and then the co-toxicity coefficient is calculated, and an evaluation criterion is set.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal protein gene and application
InactiveCN101126093ASuperior and unique insecticidal propertiesReduce manufacturing costBiocideDepsipeptidesInsecticidal crystal proteinsA-DNA
The invention discloses an insecticidal crystal protein gene of bacillus thuringiensis and the application thereof; the insecticidal protein coded by a DNA sequence of the insecticidal crystal protein gene shown in SEQ ID No.1 is an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2. The insecticidal protein coded by the gene has specific insecticidal function to orthopterous oriental migratory locust, the locust insecticide prepared by the gene has good prevention effects used for preventing and curing those locusts harmful to graminaceous crops such as grain, wheat, corn, broomcorn and pasture etc., and is safe to human and animal and plant, has low production and using cost, does not cause environmental pollution, thereby having great application value.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Chemical derivation-based detection method for hemolymph metabolin of migratory locust
InactiveCN102866220AImprove extraction efficiencyGood reproducibilityComponent separationWater bathsGas phase
The invention discloses a chemical derivation-based detection method for hemolymph metabolin of migratory locust, and relates to the field of animal ecology and analytical chemistry. The detection method specifically comprises the following steps of: taking hemolymph, deproteinizing by adding ethanol-acetonitrile mixed solvent, supersonically extracting, and centrifuging at a high speed to obtain metabolin extracting solution; drying the extracting solution by means of pressure reduction, adding methoxamine hydrochloride-pyridine solution, supersonically dissolving, blending by means of vortex, and deriving in an oximation way in a constant-temperature water bath; adding N-methyl-N-trimethylsilane-trifluoroacetamide reagent, blending by means of vortex, and deriving in an alkylation way in the constant-temperature water bath; and adding methyl oleate-normal heptane solution to compensate the volume, blending by means of vortex, and analyzing by a spare gas chromatography-mass spectra coupling technique. The detection method provided by the invention is convenient, high-efficiency, mild in reaction conditions, good in repeatability, wide in metabolin coverage, suitable for developing the multi-center and large-sample research, and capable of providing help for knowing the biological law of various migratory locust variations and the occurrence mechanism of the locust plague.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Breeding method of Asiatic migratory locusts
InactiveCN107232146APrevent intrusionImprove survival rateAnimal husbandryMigratory locustObserved Survival
The invention relates to the technical field of insect breeding, in particular to a breeding method of Asiatic migratory locusts. The method comprises the following steps of land parcel selection, foundation construction, shack construction, locust breeding and management in the growing period, and locust breeding and management in the maturation period and the reproduction period. According to the breeding method, the mode that a pit is built on flat ground and earth filling is conducted after cement ground is made is adopted, infestation of locusts by their natural enemies is effectively avoided, and the survival rate of worm eggs and imagoes is improved; the management standard is reasonable, the survival rate of bred imagoes is high, and the method is suitable for large-scale popularization.
Owner:贵州省仁怀市城旭养殖农民专业合作社
Microspore strain and use thereof
The invention provides a microspore strain extracted from gastrimargus and an application thereof. The strain has quite strong specificity and has specific action of killing grassland locusts and farmland migratory locusts, and the killing effect is relatively good. The microspore strain extracted from the gastrimargus of the invention can be used to control tens of locusts such as farmland migratory locusts, grassland locusts, gastrimargus, bamboo locusts and rice locusts, etc.
Owner:BEIJING MAMMOTH SEED
Locust microspore chorthippus strain and applications thereof
ActiveCN103451100ASimple production technologyGreat lethal effectBiocideProtozoaSpore germinationUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses a chorthippus microspore strain and applications thereof. The chorthippus microspore strain disclosed by the invention is paranosema acridophagus PA-201301 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.7757 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The paranosema acridophagus PA-201301 CGMCC No.7757 disclosed by the invention has the advantages of obvious lethal effect to chorthippus dubius, chorthippus fallax, myrmeleotettix palpalis, calliptamus abbreviatus, bryodema luctuosum, oriental migratory locust and gastrimargus marmoratus than that of an existing locust microspore, and stress resistance, in particular strong ultraviolet resistance, wherein the germination rate of spores is still more than 80% after a spore solution is irradiated by the ultraviolet light for one hour; in addition, the production technology of microspores of the chorthippus microspore strain is simple, and propagation hosts are easily obtained; after homogenating, separation is performed at the centrifugal force of about 6000g; the chorthippus microspore strain disclosed by the invention is conductive to mass production and applications.
Owner:HEBEI SHENGPU BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Multi-functional composite sound silencing gun
InactiveCN101021399AIn line with the basic policy of energy sustainable developmentIn line with the basic policy of sustainable developmentCompressed gas gunsHerdEngineering
The invention relates to a multifunctional combination muffling cannon especially used for both army and civilian including two multifunctional muffling cannons, a command car and the operation rules for launching the muffling cannon. It can be used in the agricultural herd and pest control field at usual, so it can not only perish the migratory locust in the air but perish the locust and the rats. If the war begins, it can be the new conception weapon after adjusting it to intensify the national defense construction.
Owner:陈大伟
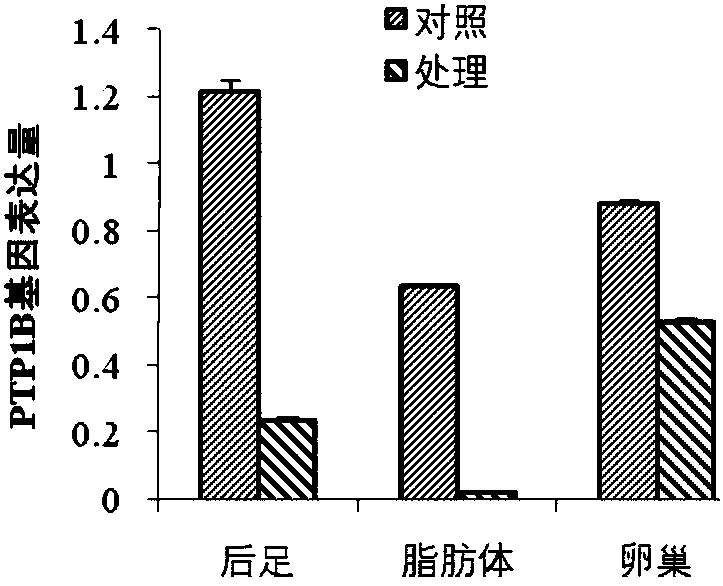
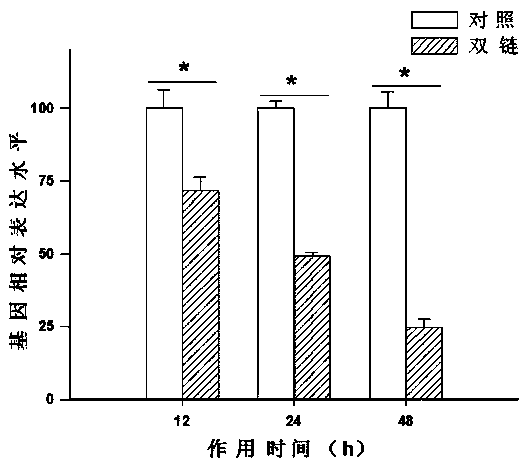
Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B of Locusta migratoria and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B of Locusta migratoria and an encoding gene and application thereof. DsRNA of protein tyrosine phosphatase gene PTP1B of protein tyrosine phosphatase is cloned from protein tyrosine phosphatase; primers are designed for the protein tyrosine phosphatase gene PTP1B of Locusta migratoria; dsRNA for interfering the protein tyrosine phosphatasegene PTP1B of Locusta migratoria is synthesized; the dsRNA can be imported into the protein tyrosine phosphatase gene PTP1B of Locusta migratoria to carry out RNAi (RNA interference). The results showthat the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B of Locusta migratoria can regulate the diapause of Locusta migratoria. Theoretical basis is provided for the deeper understanding of the diapause mechanismof Locusta migratory and the development of biopesticide preparations.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
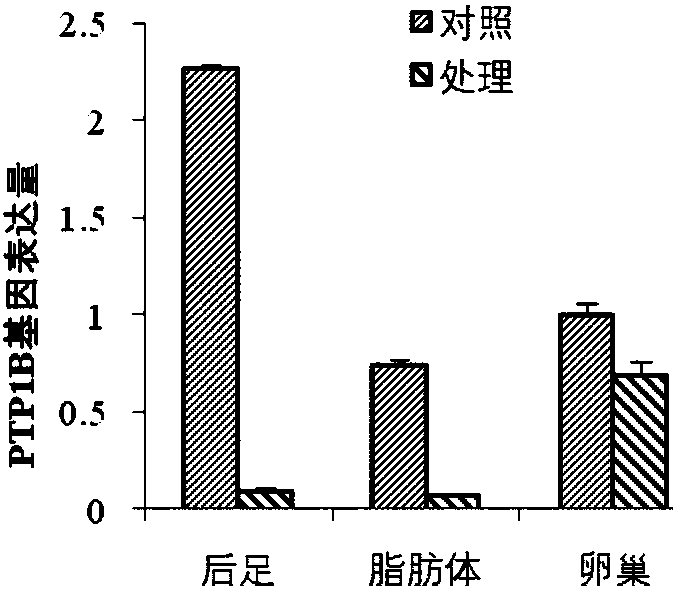
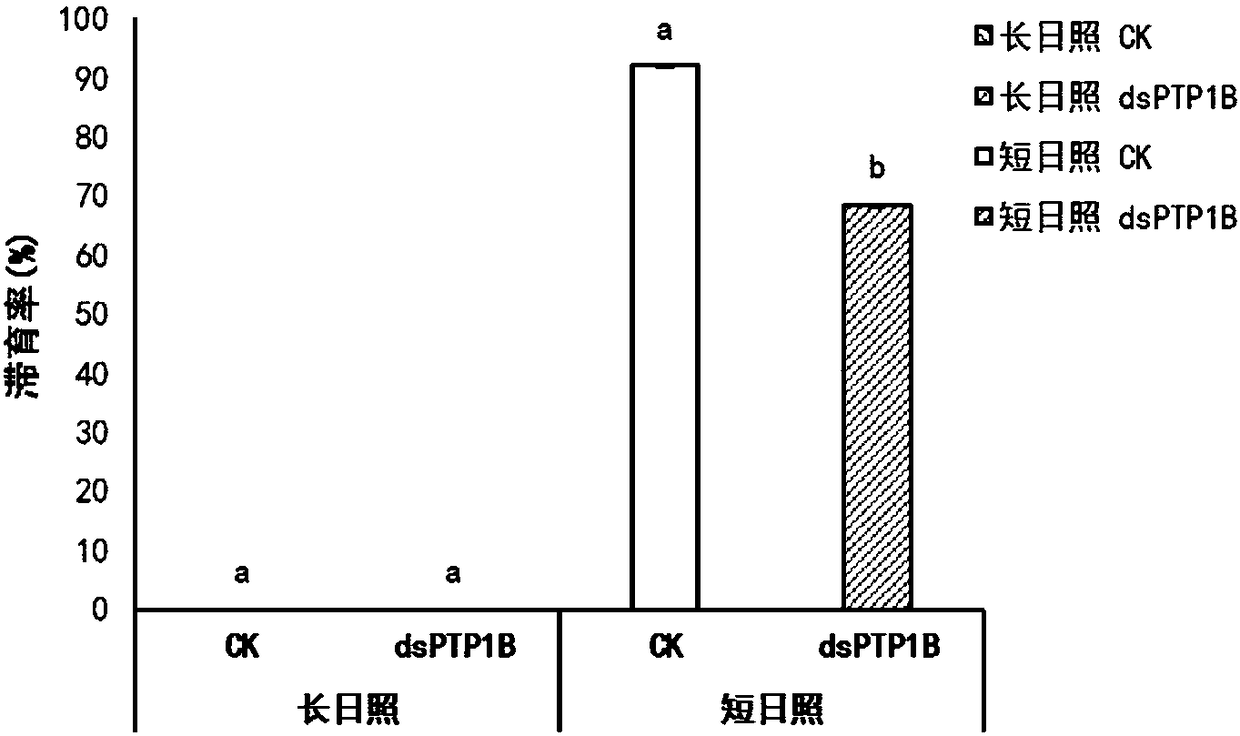
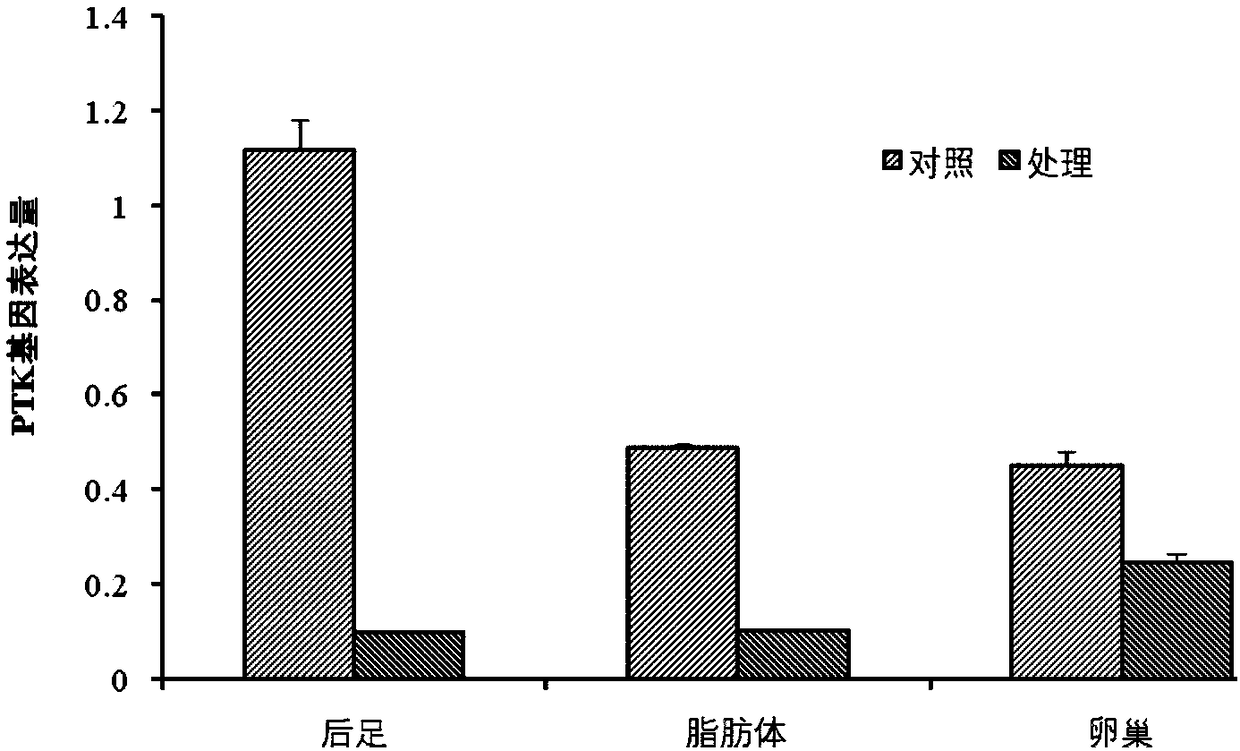
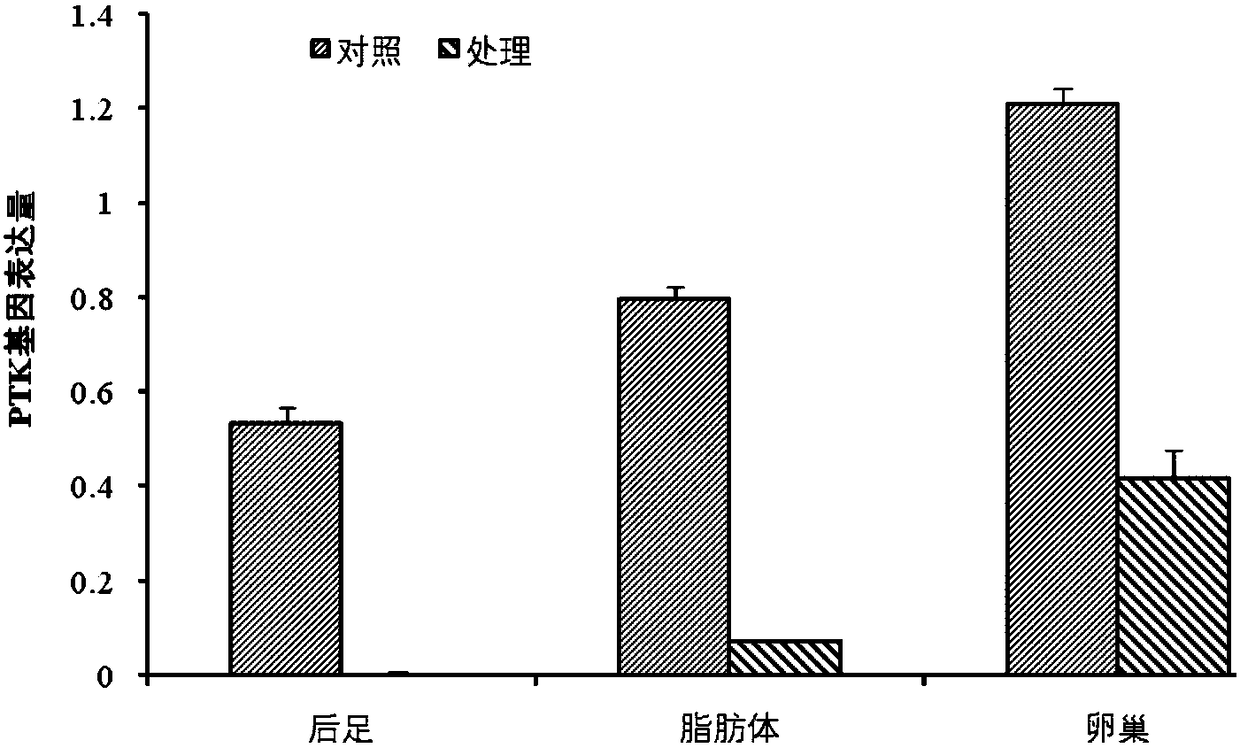
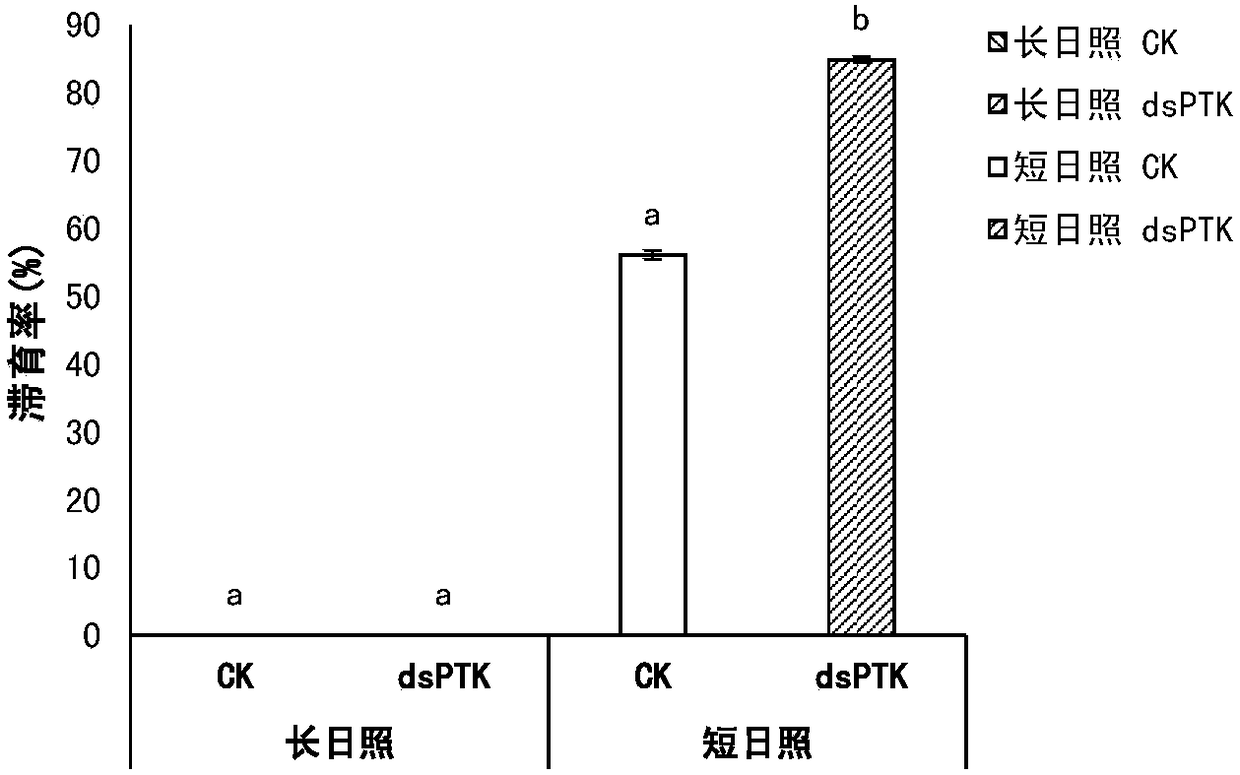
Migratory locust protein tyrosine kinase PTK and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN108060147AControllable diapause of migratory locustIn-depth understanding of the diapause mechanism of migratory locustsBiocideTransferasesDiapauseProtein-Tyrosine Kinases
The invention discloses a migratory locust protein tyrosine kinase PTK and coding gene and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: at first, cloning migratory locust protein tyrosine kinase gene PTK from the migratory locust, and designing a primer for the migratory locust protein tyrosine kinase gene PTK; synthesizing dsRNA for interfering migratory locust protein tyrosinekinase gene PTK, and then importing the dsRNA into the migratory locust to perform RNAi on the migratory locust protein tyrosine kinase gene PTK by using an injection method. The result shows that themigratory locust protein tyrosine kinase gene PTK can regulate and control the diapause of the migratory locust. The invention provides the theoretical basis for deeply understanding migratory locustdiapause mechanism and creating the new biological pesticide preparation.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
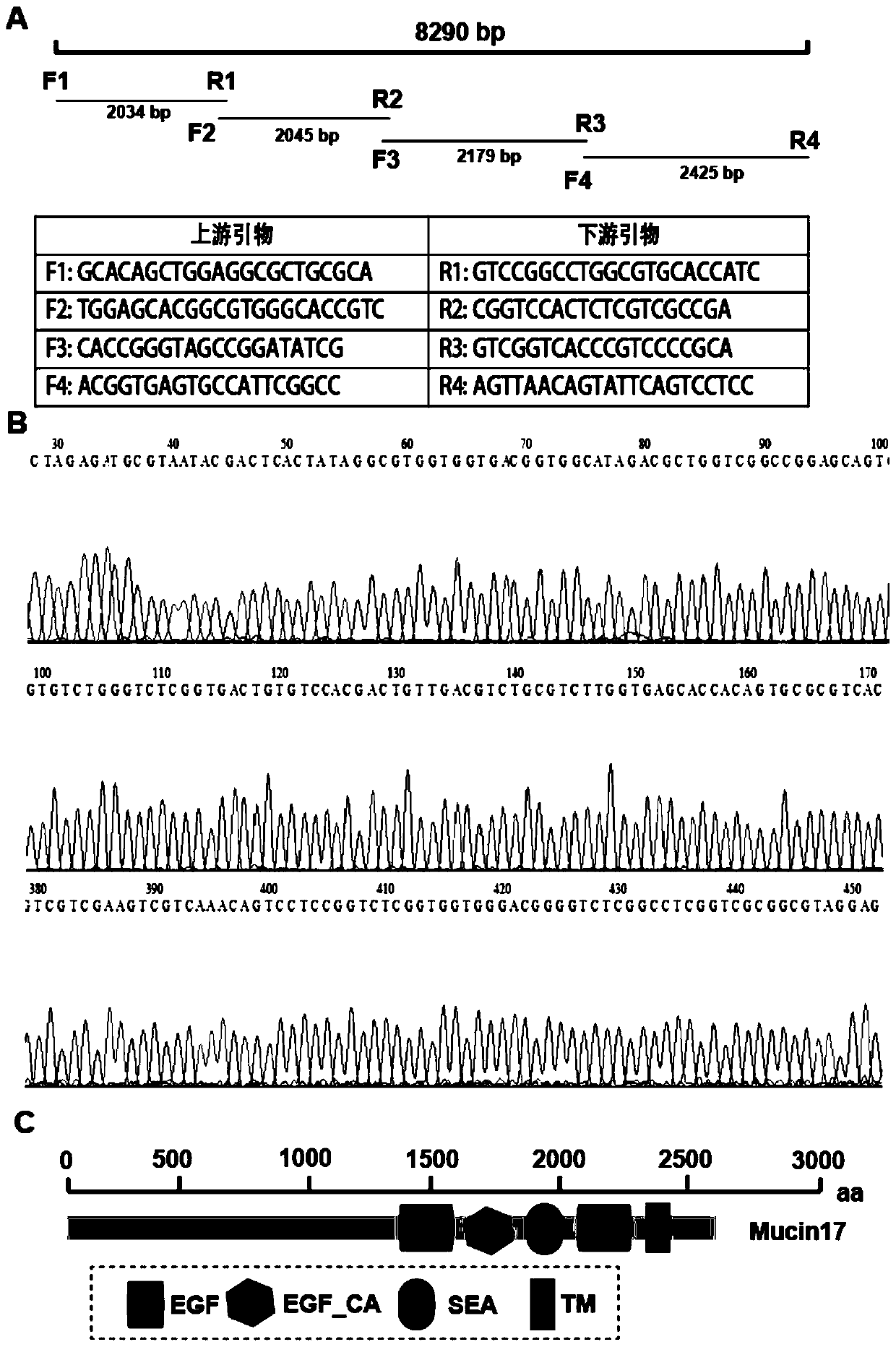
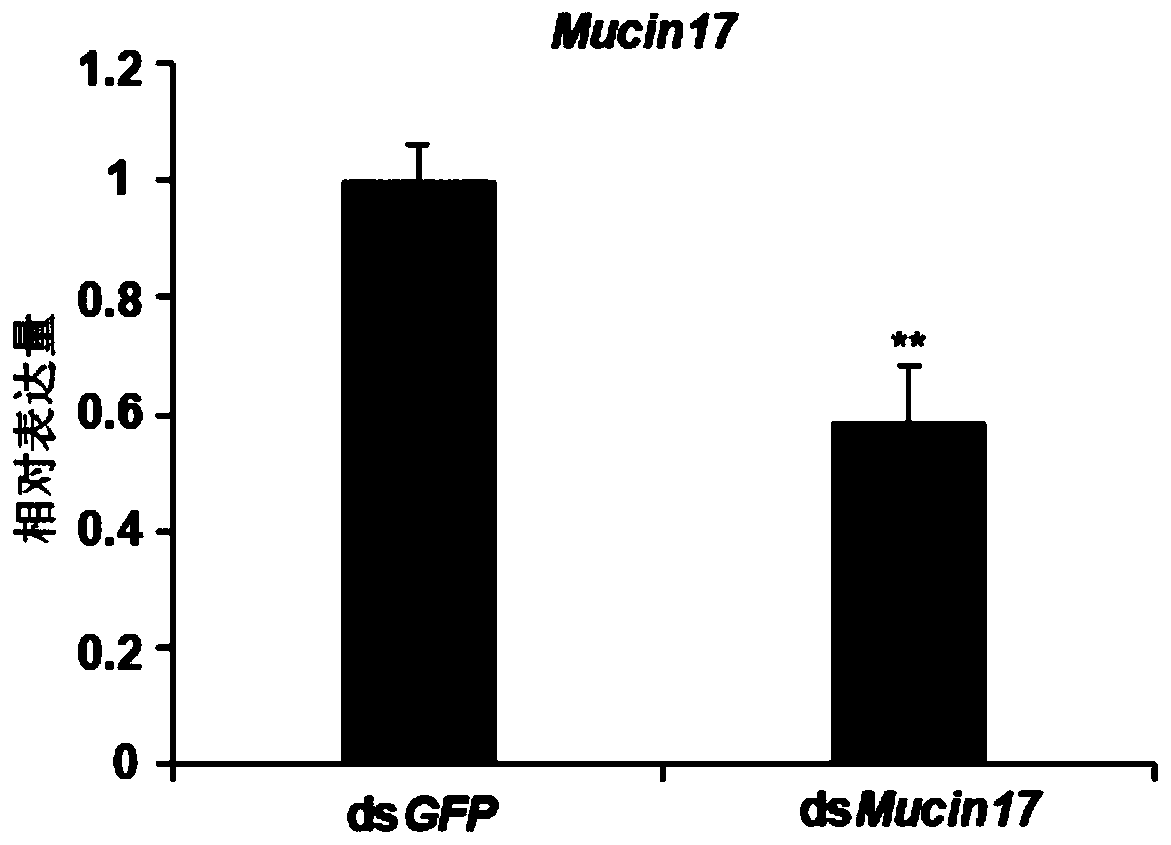
Migratory locust Mucin17 and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a migratory locust Mucin17 and a coding gene and application thereof. A migratory locust mucin gene Mucin17 is cloned from a migratory locust, and a primer is designed for themigratory locust mucin gene Mucin17, and dsRNA used for interfering the migratory locust mucin gene Mucin17 is synthesized, and the dsRNA is guided into the migratory locust through an injection method to conduct RNAi on the migratory locust mucin gene Mucin17. The result shows that after effective silencing is conducted on the migratory locust mucin gene Mucin17, death of the migratory locusts can be caused, and development of wings and hind feet of the migratory locusts is affected. Accordingly, a new target is provided for further deeply understanding the action mechanism of the mucin development of the migratory locusts, and for pest control based on RNA interference, and the migratory locust Mucin17 and the coding gene and application thereof have the theoretical significance and wideapplication prospects.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of migratory locust metallothionein I-type gene LmMt I to grasshopper control
InactiveCN109439689AReduced toleranceImprove featuresMicroinjection basedAnimal husbandryOpen reading frameMortality rate
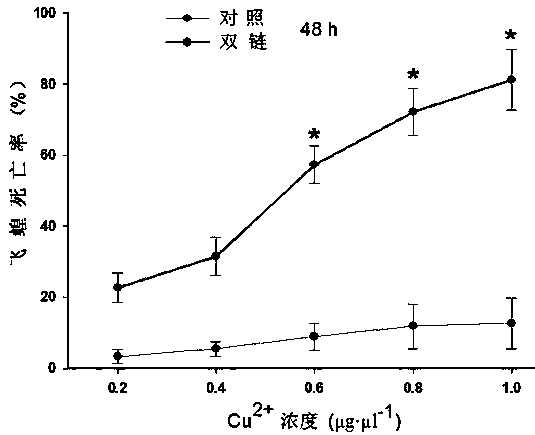
The invention discloses an application of a migratory locust metallothionein I-type gene LmMt I to grasshopper control. The high-expression metallothionein I-type gene is searched by a transcriptome sequencing and information biology method, the sequence SEQ ID NO: 1 of the gene is confirmed after clone sequencing verification, a gene segment (open reading frame) with the sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2is selected and used for synthesizing corresponding double stranded RNA (dsRNA), the double stranded RNA is injected into an abdominal cavity of a migratory locust by a micro-injector, and then a target gene LmMt I can be specifically silenced, so that the migratory locust suffers from in-vivo metal metabolic disturbance, food refusal, developmental retardation, digestive abnormity and body emaciation until death. The metal tolerance of the migratory locust injected with the double stranded RNA is greatly reduced, death rate is increased by 1.8-2.3 times after medicines of the same dose act onthe migratory locust, and the death rate of an experimental group is increased by 79.6% as compared with a control group after treatment with metal with the same concentration.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Application of migratory locust Knickkopf 3-5' gene dsRNA in pest control
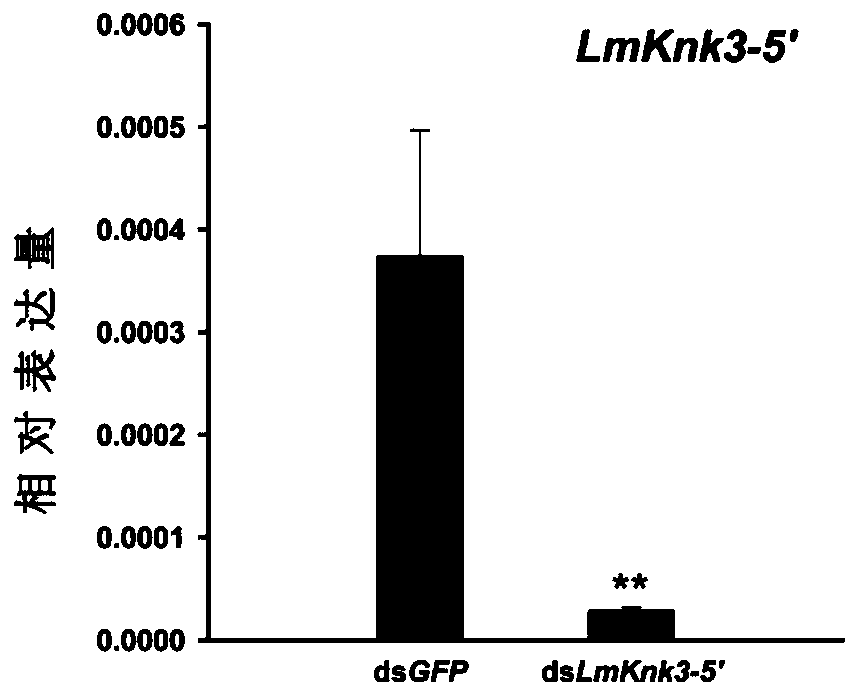
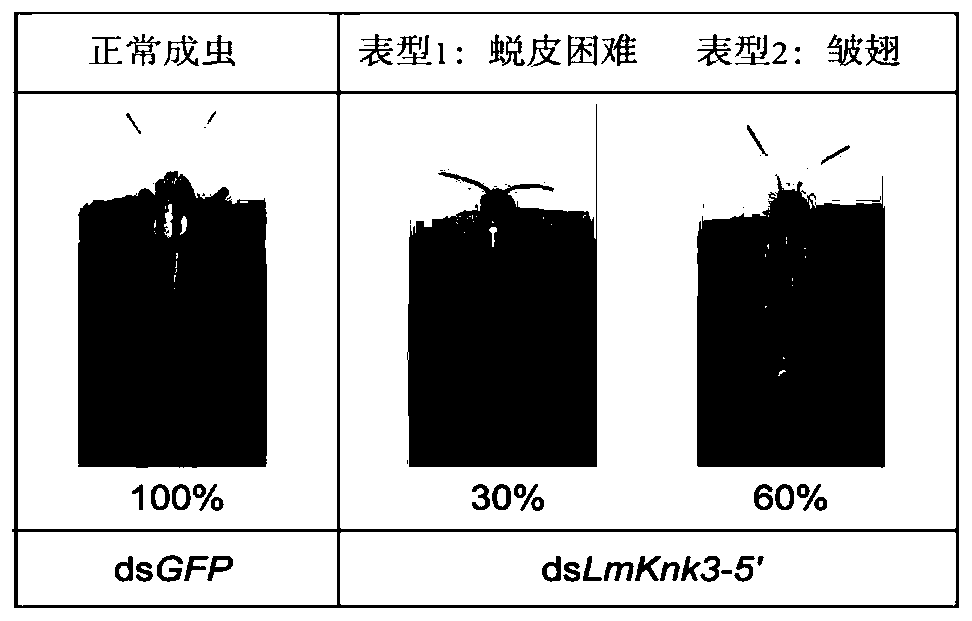
The invention provides application of a migratory locust Knickkopf 3-5' gene dsRNA in pest control, discloses a Knickkopf 3-5' gene having a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 and further discloses a migratory locust Knickkopf 3-5' gene fragment and dsRNA thereof, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene fragment is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 6. The designed and synthesized dsRNA is injectedinto a migratory locust, and the migratory locust has two phenotypes: difficult molting and death and adult wing curling, and half of the adults with curly wings die within seven days, the phenotype rate reaching 90%. The Knickkopf 3-5' gene screened and obtained by the invention can be used as an important molecular target for migratory locust control, and provides a new way for green pest control.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com