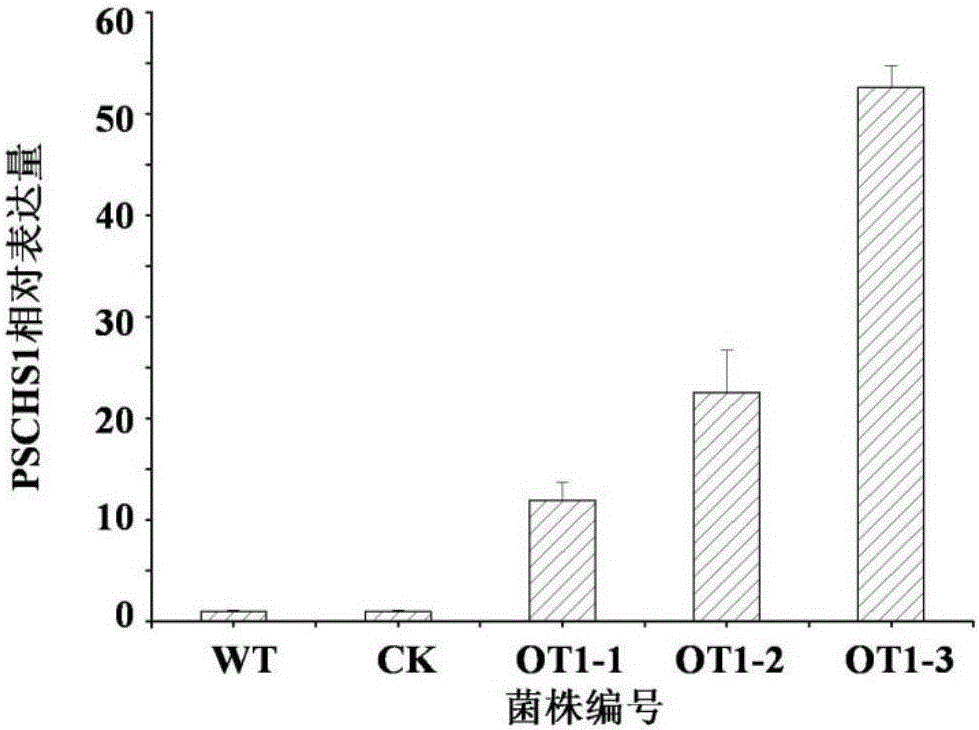
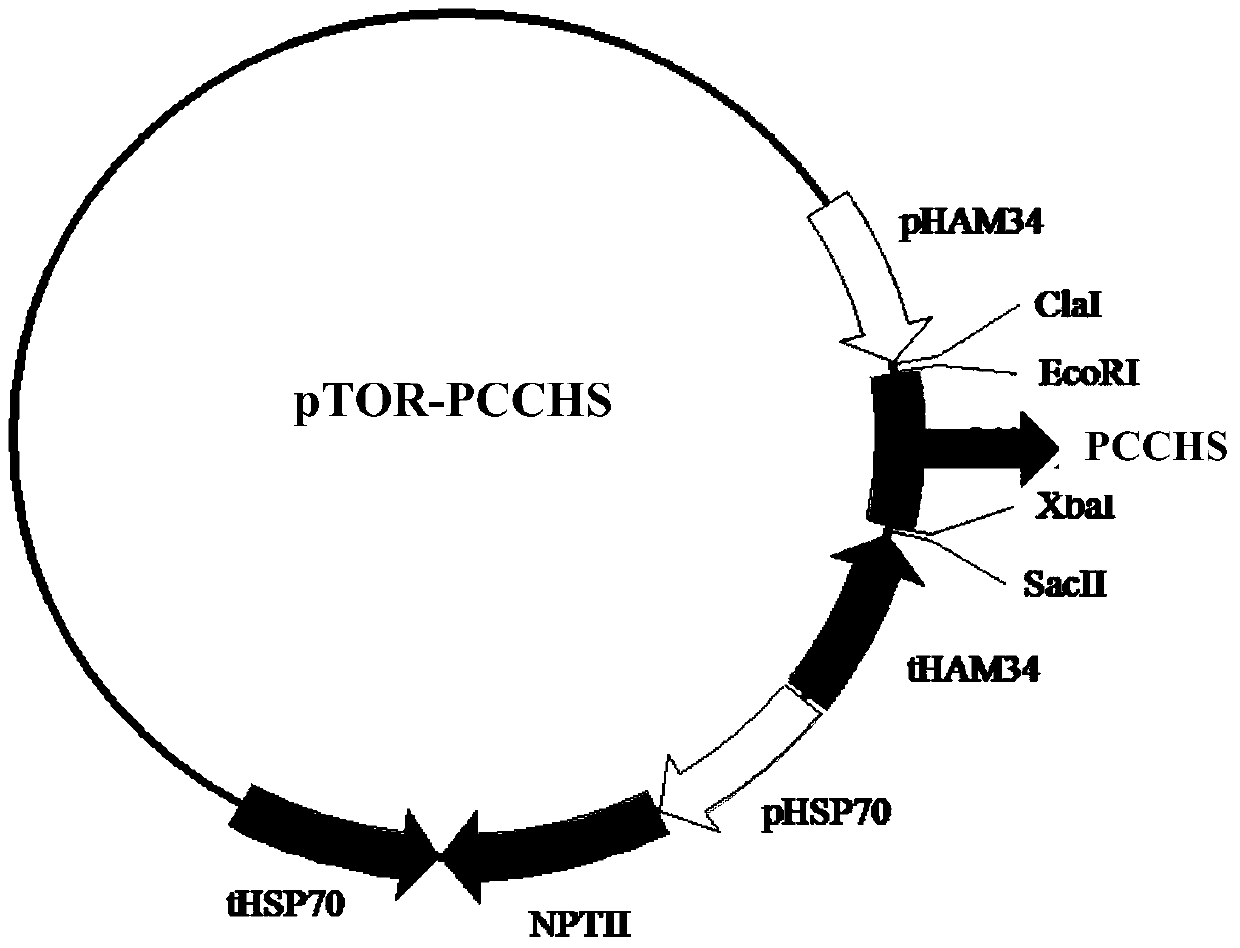
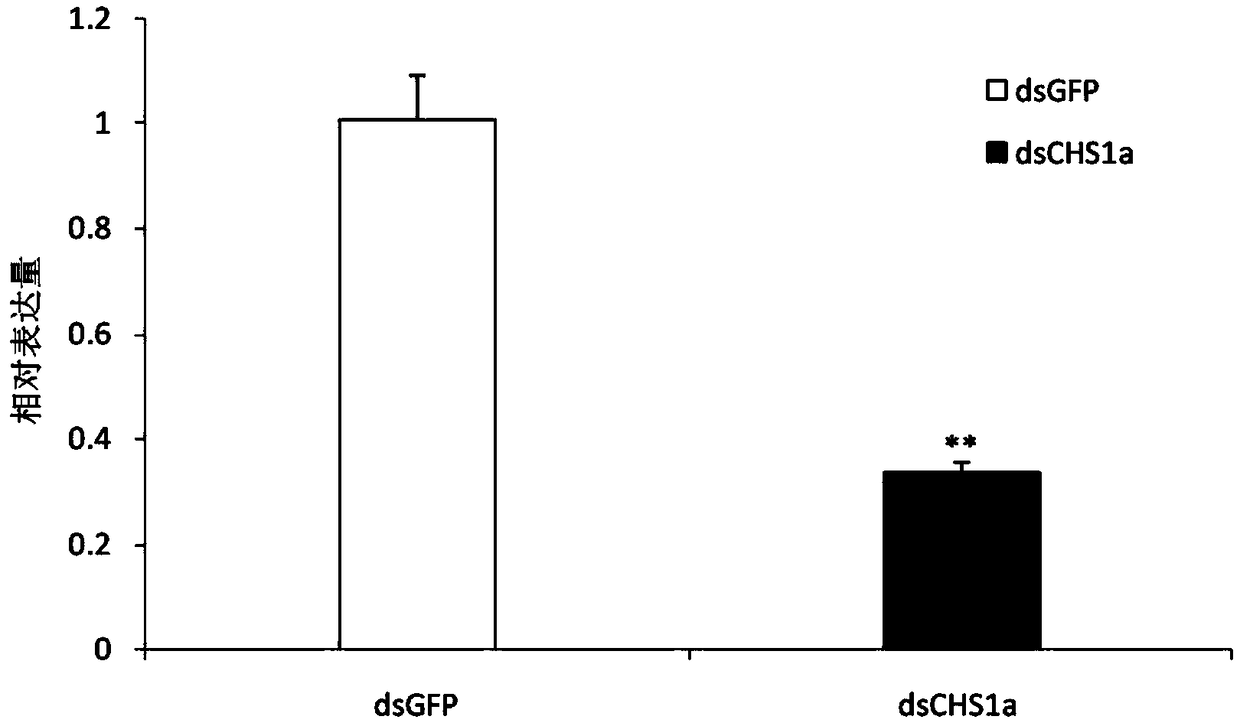
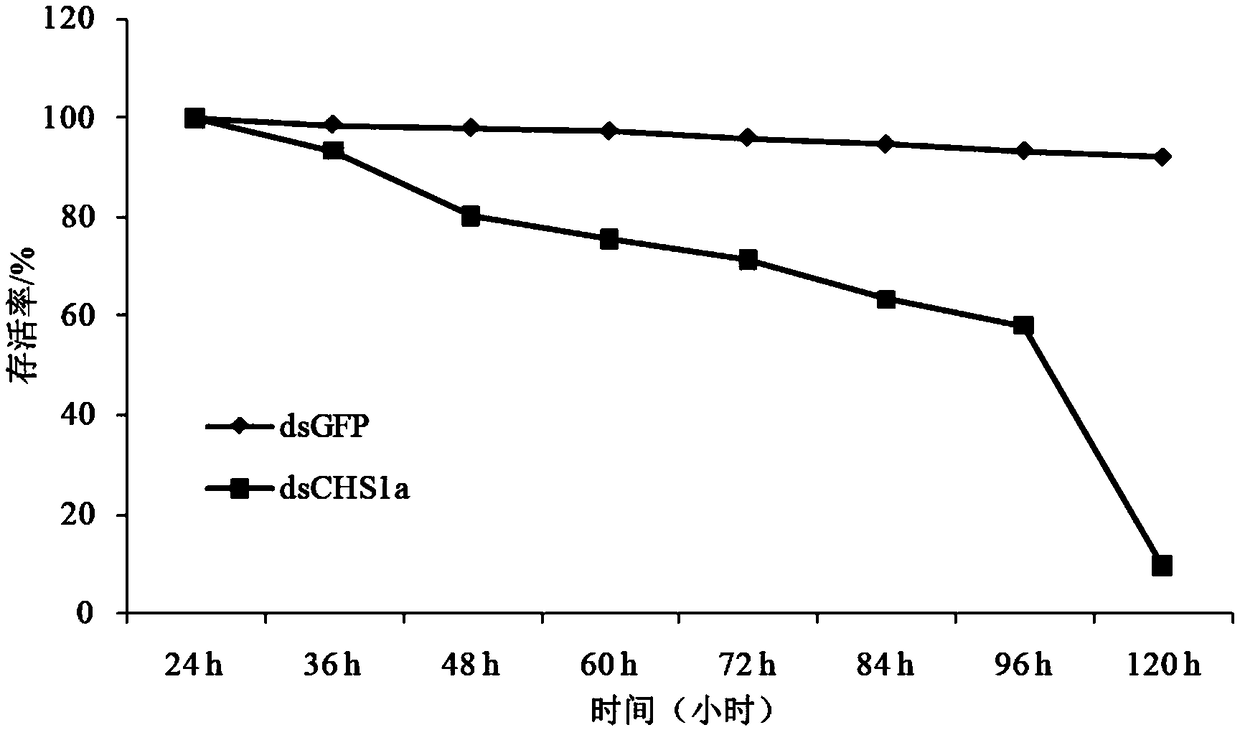
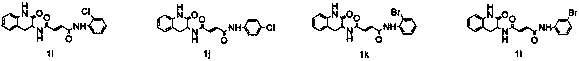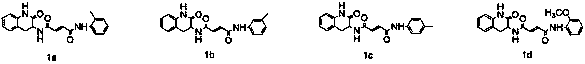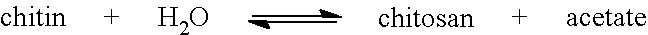Patents
Literature
35 results about "Chitin synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, a chitin synthase (EC 2.4.1.16) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + [1,4-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)]n ⇌ UDP + [1,4-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)]n⁺1 Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and [[[1,4-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)]n]], whereas its two products are UDP and [[[1,4-(N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)]n+1]].
Vaccination against Cryptococcus
ActiveUS20150328295A1Reduce and eliminate abilityReduce and eliminate expressionPowder deliverySpray deliveryVaccinationWild type
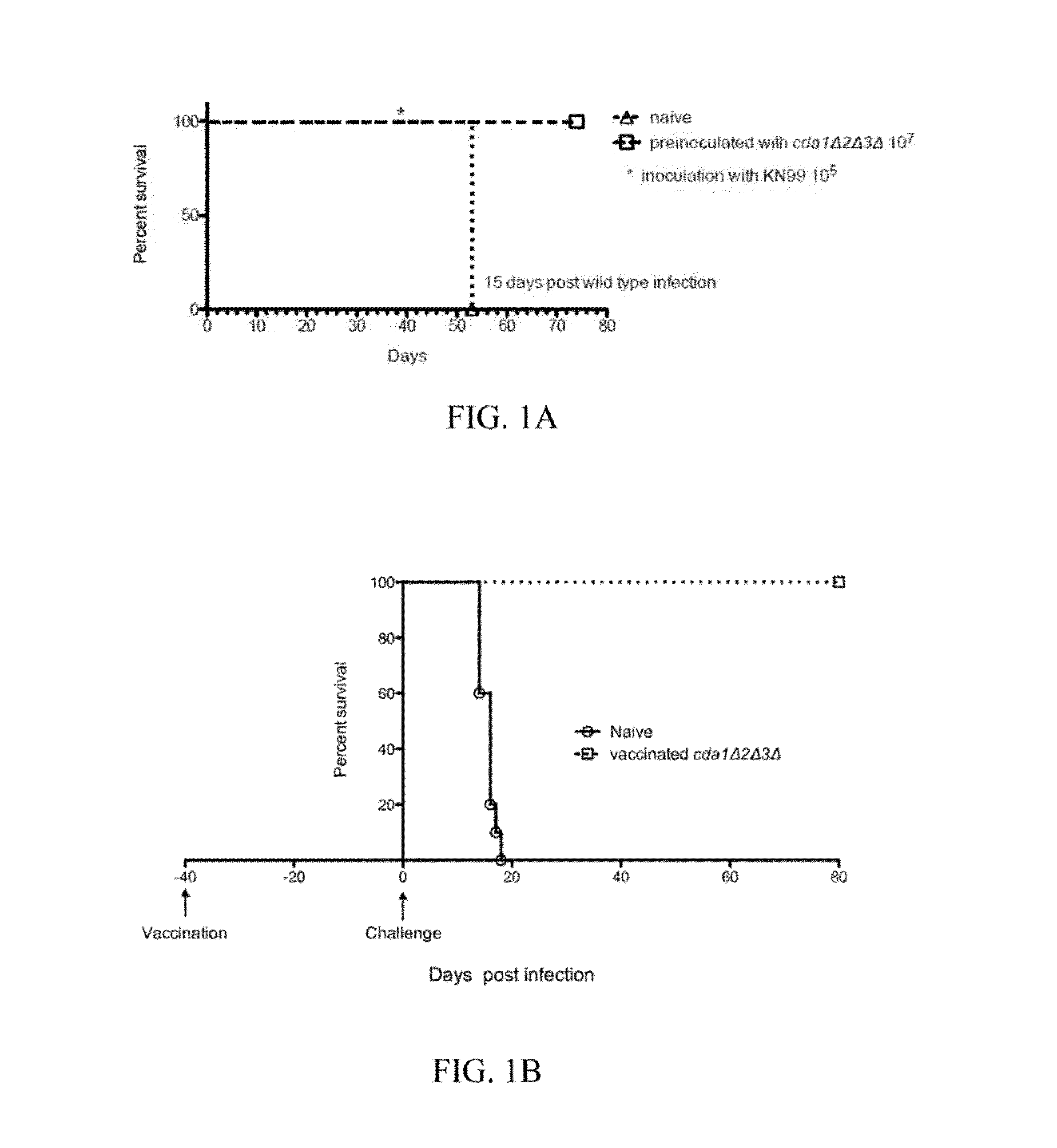
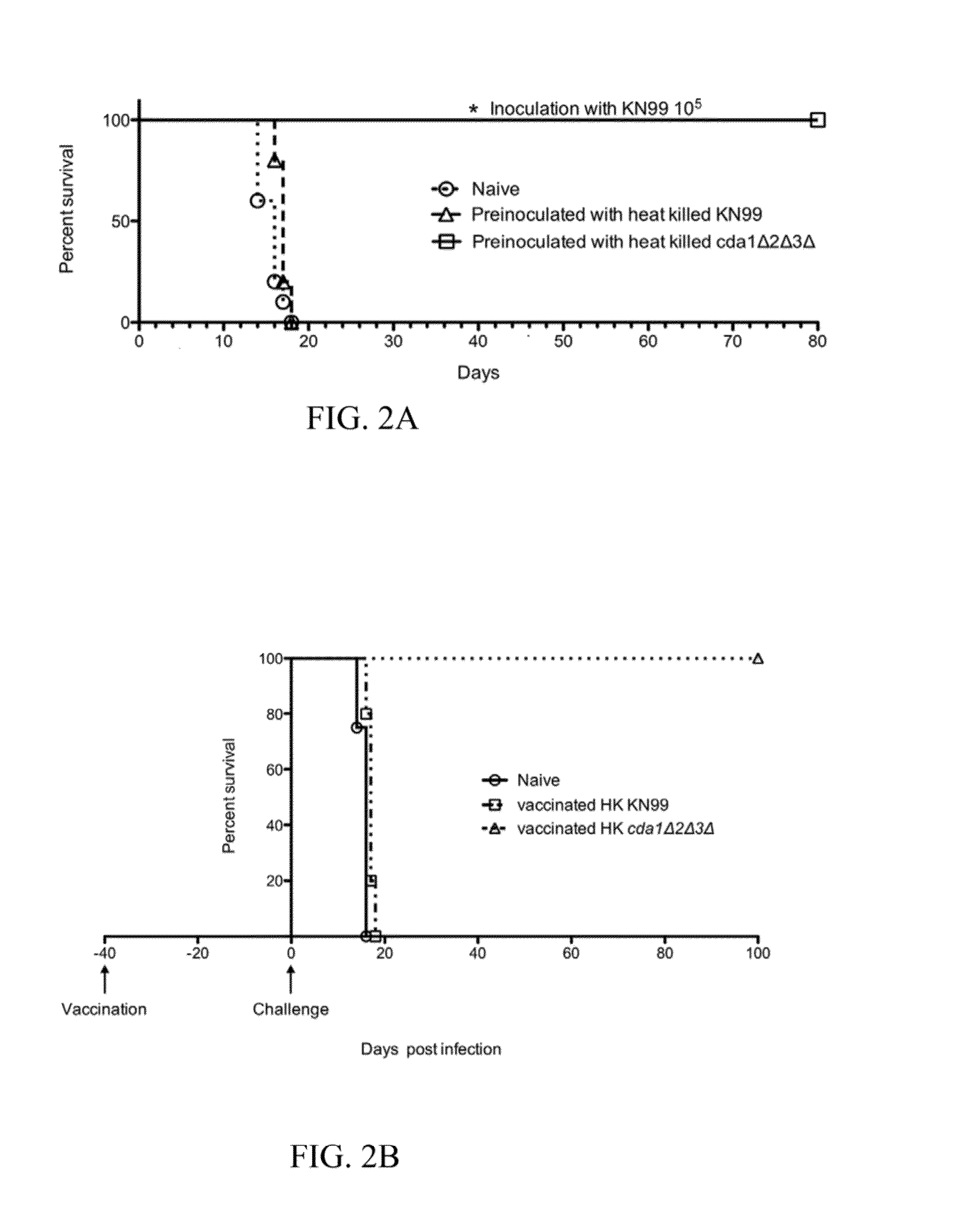
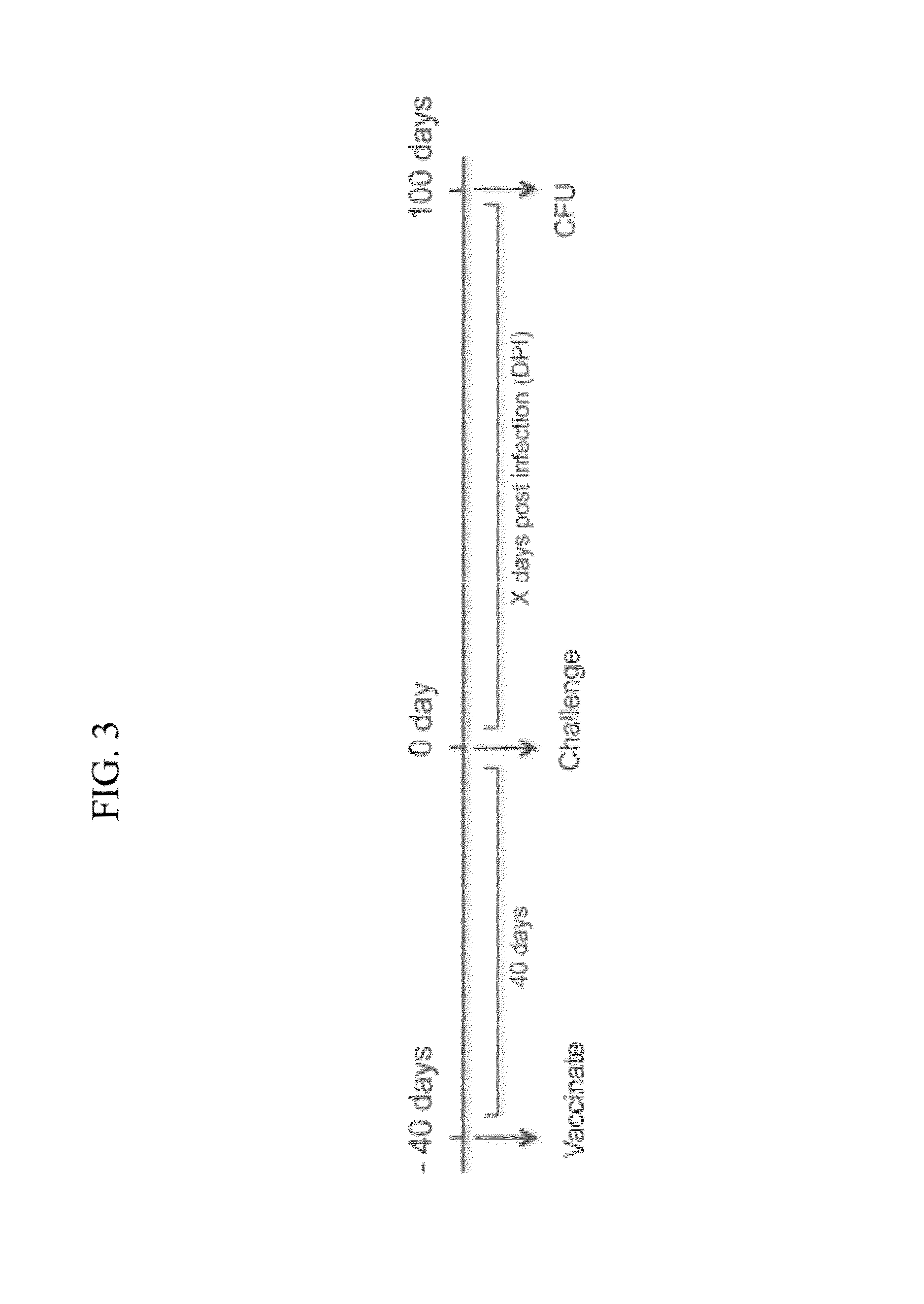
Vaccines and methods of inoculation for conferring immunity to Cryptococcus infection are disclosed. Strains of Cryptococcus fungi, including Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus gattii, can be administered to a human or animal subject via inhalation. Cryptococcus fungi that can be used to confer immunity can comprise one or more mutations in genes that contribute to chitosan production, such as genes encoding a chitin deacetylase (cda), a chitin synthase (chs) and / or a regulator of chitin synthase (csr). Inhalation administration of heat-killed Cryptococcus harboring deletions in cda1, cda2 and cda3 genes can confer immunity. In a murine model system, inhalation administration of Cryptococcus neoformans harboring deletions in cda1, cda2 and cda3 genes conferred immunity against subsequent exposure to wild type Cryptococcus neoformans in 100% of test animals. Inhalation administration of heat-killed Cryptococcus grown under conditions leading to reduced chitosan production can also confer immunity.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
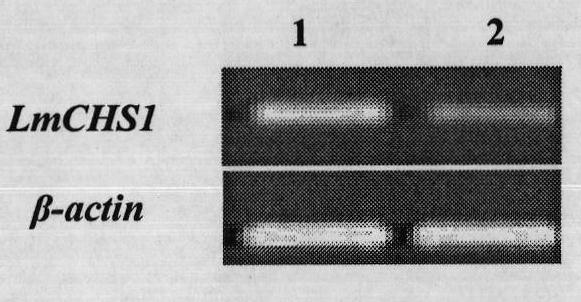
Insect chitin synthetase 1 gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof
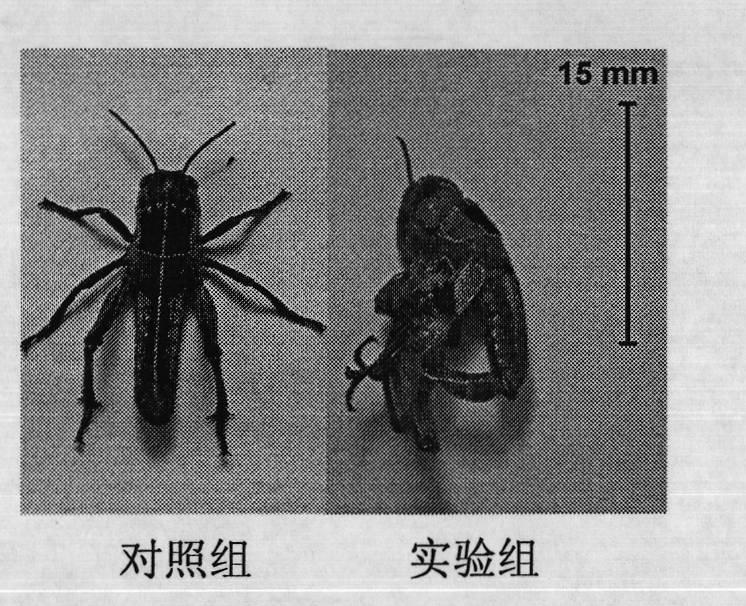
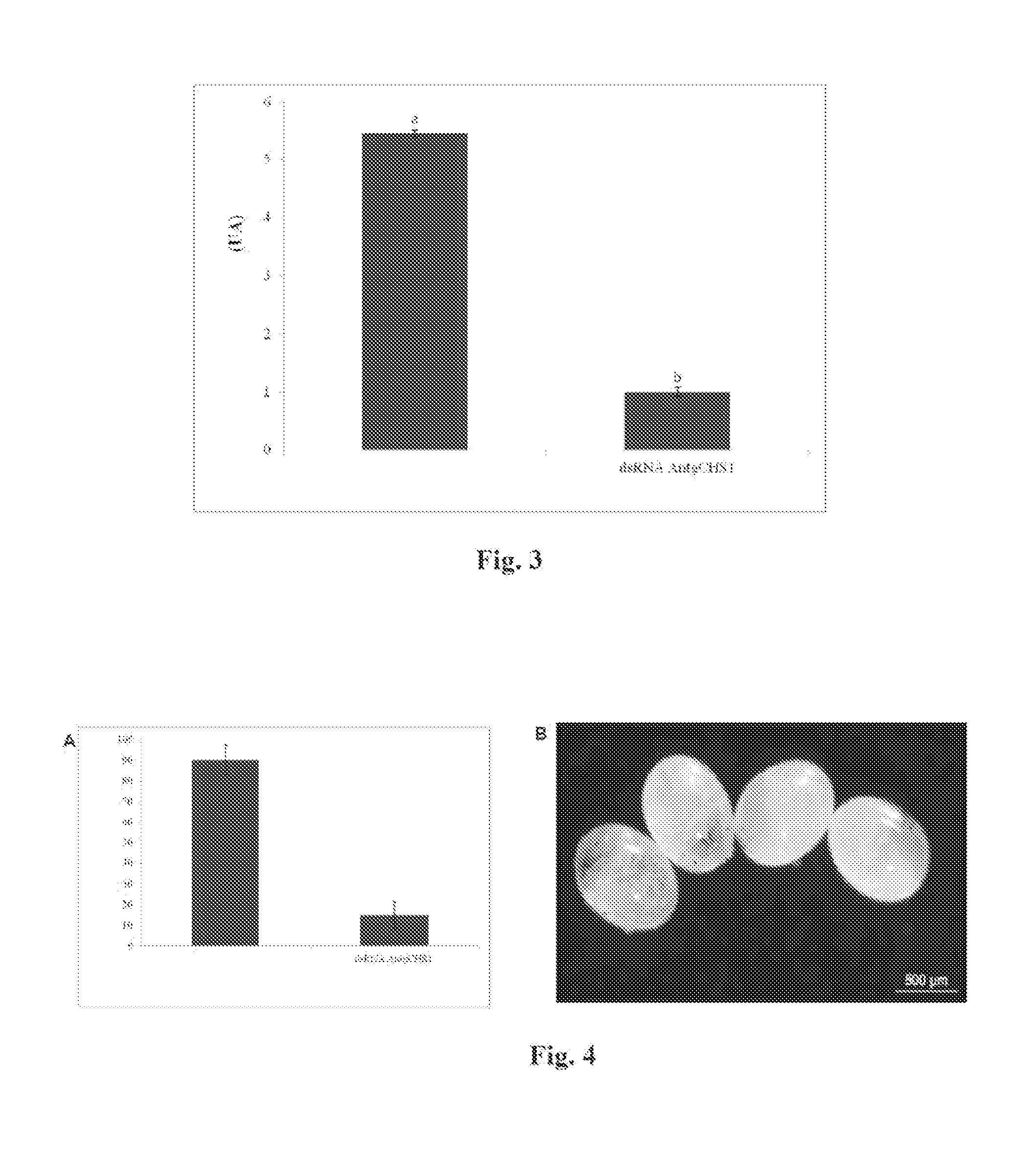
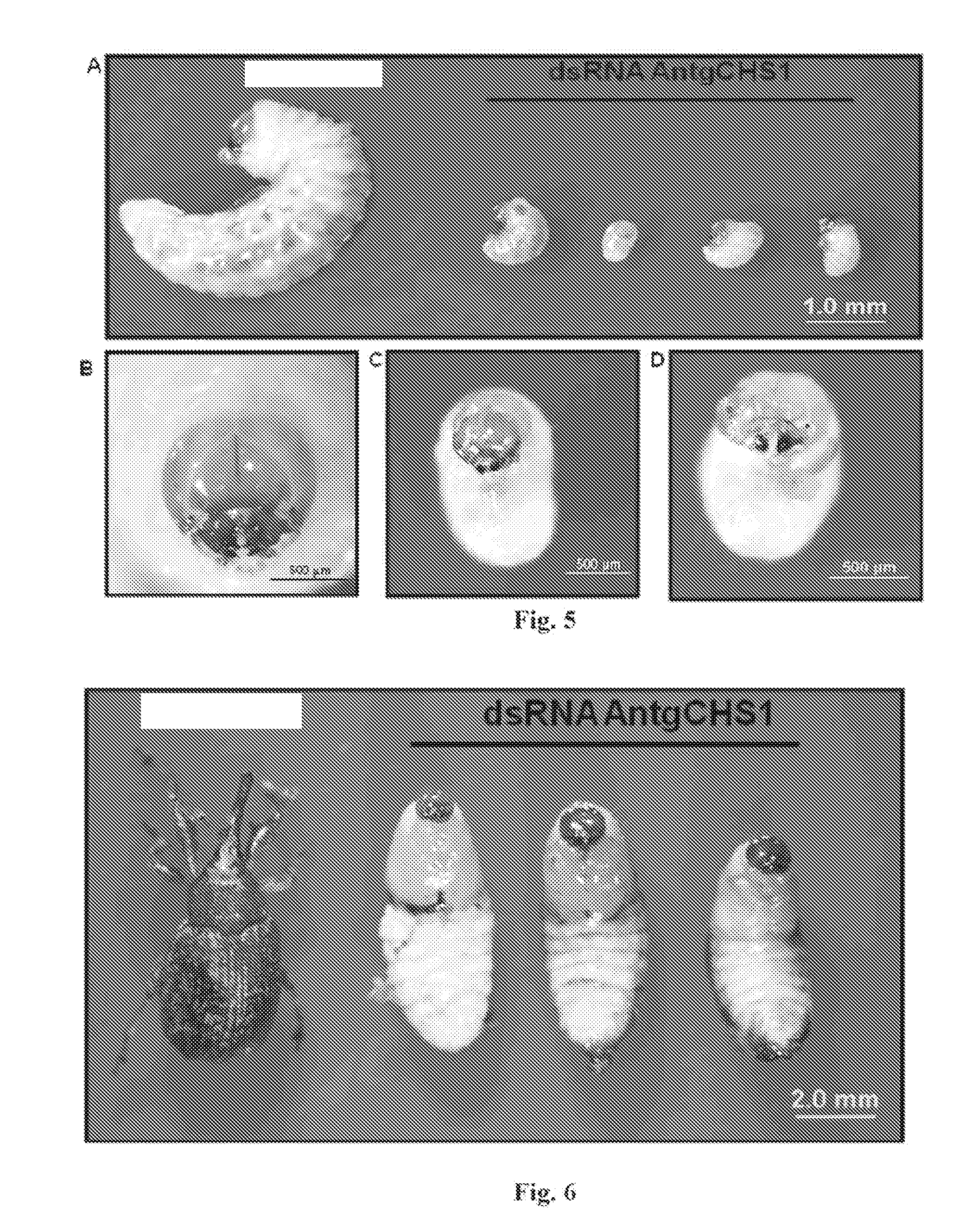
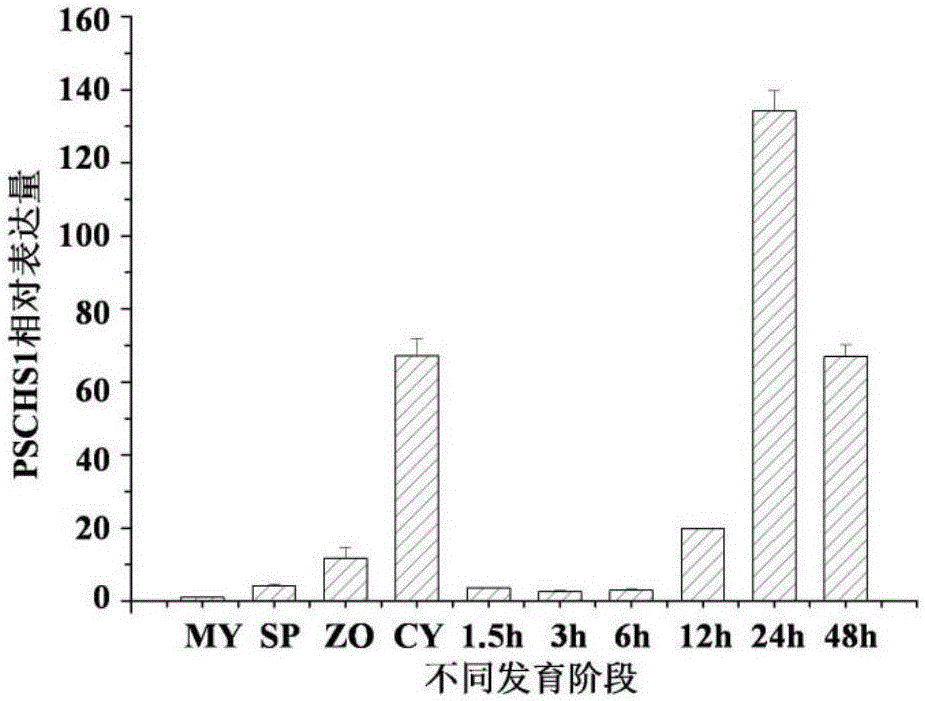
The invention provides an insect chitin synthetase 1 gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof. The chitin synthetase 1 gene segment of which the sequence is SEQ ID NO:1 is synthesized according to a common part of two chitin synthetase gene sequences with access numbers of GU067730 and GU067731 respectively in an NCBI database; and the dsRNA is synthesized by using the segment. After the synthesized dsRNA is injected into the body cavity of an insect, the insect dies from molting difficulties. Therefore, a new way is provided for the development of a safe and nuisanceless pest preventing and controlling method.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
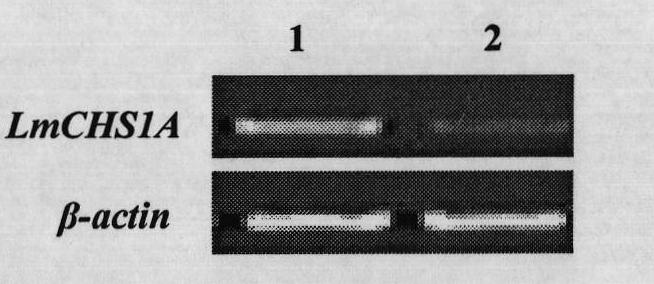
Insect chitin synthase 1A gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof
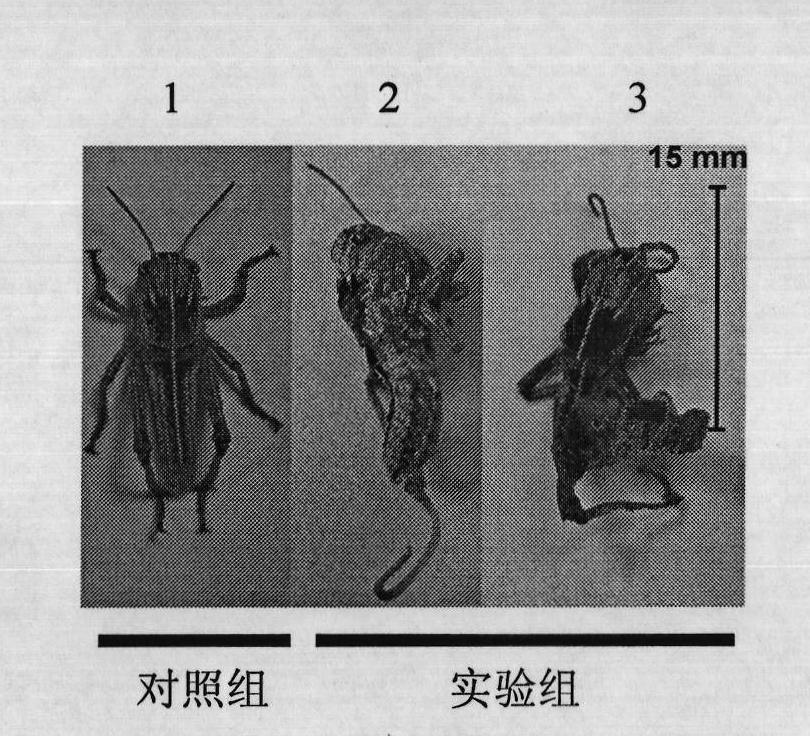
The invention provides an insect chitin synthase 1A gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof. The dsRNA is synthesized by the chitin synthase 1A gene segment with the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 which is obtained by the gene sequence of the chitin synthase 1A of Locusta migratoria manilensis with the accession number of GU067730 in an NCBI database. After the dsRNA is injected in body cavities of insects, the insects die because of difficult moulting. A new way for developing a safe and pollution-free method for preventing and controlling insect is provided.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Insect chitin synthetase 1 gene fragment and dsRNA and application thereof
The invention provides an insect chitin synthetase 1 gene fragment and an application of dsRNA thereof. By cloning and measuring the sequence of Qxya chinensis chitin synthetase 1, a chitin synthetase gene 1 of which the nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO:1 is obtained, and a chitin synthetase gene fragment of which the sequence is SEQ ID NO:2 is selected for synthesizing the dsRNA. After the dsRNA is injected into the body cavity of an insect, the insect dies because of molting difficulty. The invention provides a new approach for developing a safe and nuisance-free insect control method.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
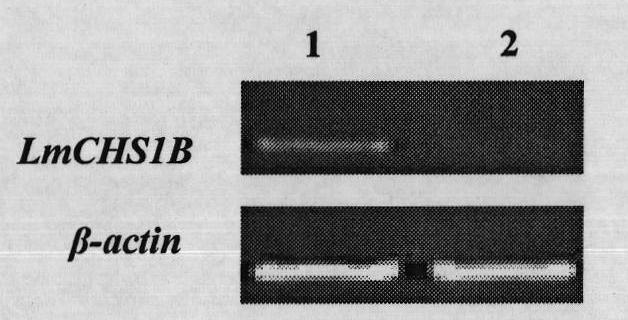
Insect chitin synthase 1B gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof
The invention provides an insect chitin synthase 1B gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof. The dsRNA is synthesized by the chitin synthase 1B gene segment with the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 which is obtained by the nucleotide sequence of the chitin synthase 1B of Locusta migratoria manilensis with the accession number of GU067731 in an NCBI database. After the dsRNA is injected in body cavities of insects, the insects die because of difficult moulting. A new way for developing a safe and pollution-free method for preventing and controlling insect is provided.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Genetic control method and compositions against insect pests in cotton plants by the silencing of genes of the laccase family
ActiveUS20150368649A1Inhibit and reduce expressionInhibit expressionBiocideBacteriaInsect pestChitin synthase
The present invention relates to the control of infestation of pests by inhibiting or reducing the expression of genes of the family of chitin synthase. The invention further provides methods and compositions for controlling pests by feeding them with one or more double-strand RNA molecules provides by the present invention. The invention further describes a method of obtaining transgenic plants that express double-strand RNA molecules. The present invention is preferably used for cotton-plants.
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE PESQUISA AGROPECUARIA EMBRAPA +1
Toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene and dsRNA thereof
InactiveCN105420255ASolving the dsRNA problemSilent efficiency is highFermentationGlycosyltransferasesBiotechnologyElectrophoresis
The invention discloses a toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene. The sequence of the toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:3. The invention further discloses dsRNA of the toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene, and the sequence of the dsRNA is shown as SEQ ID NO:6. The invention further discloses a synthesis method of the dsRNA of the toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene. The synthesis method includes the following steps that total RNA of toxoptera citricida is extracted and subjected into reverse transcription to form cDNA serving as an amplification template; PCR amplification is carried out through primers with the sequences of SEQ ID NO:4 and SEQ ID NO:5, a product is recycled after electrophoresis, and the dsRNA of the toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene is synthesized with a gel recycling product as a template. According to the dsRNA of the chitin synthase gene, gene silencing efficiency is high, toxoptera citricida has obvious phenotypic changes after gene interference, and the good application prospects are achieved in the aspect of researching and developing novel pesticide.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
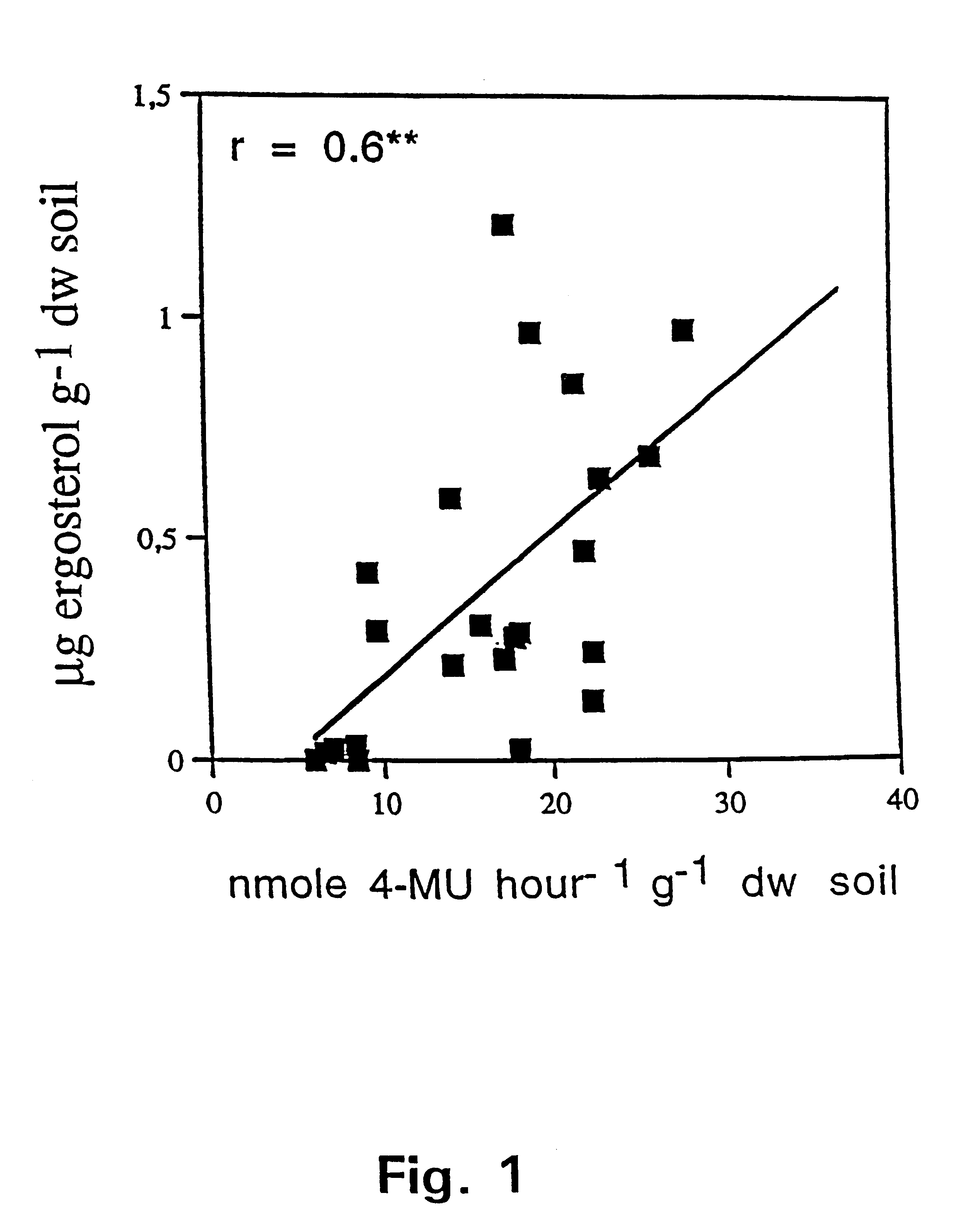
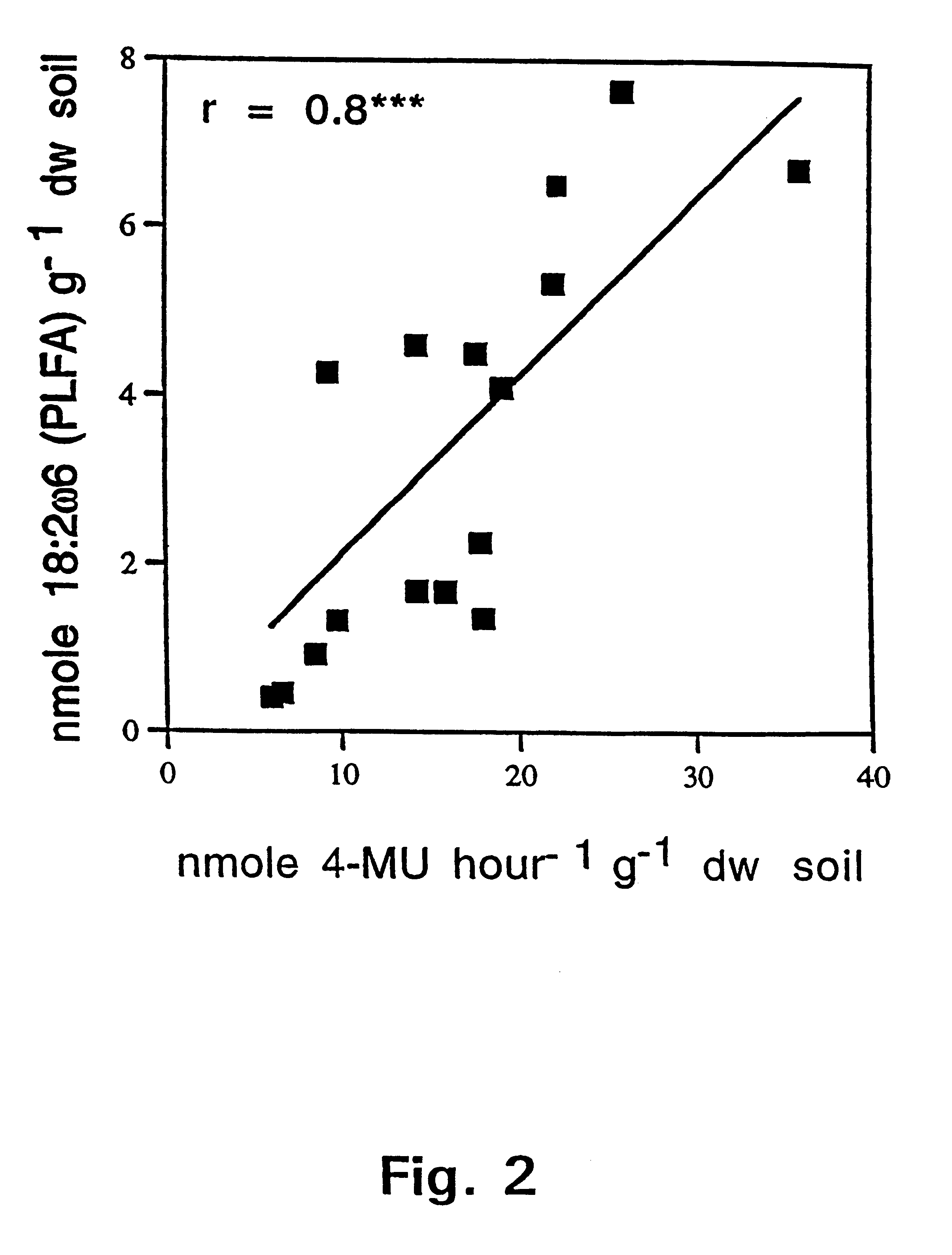
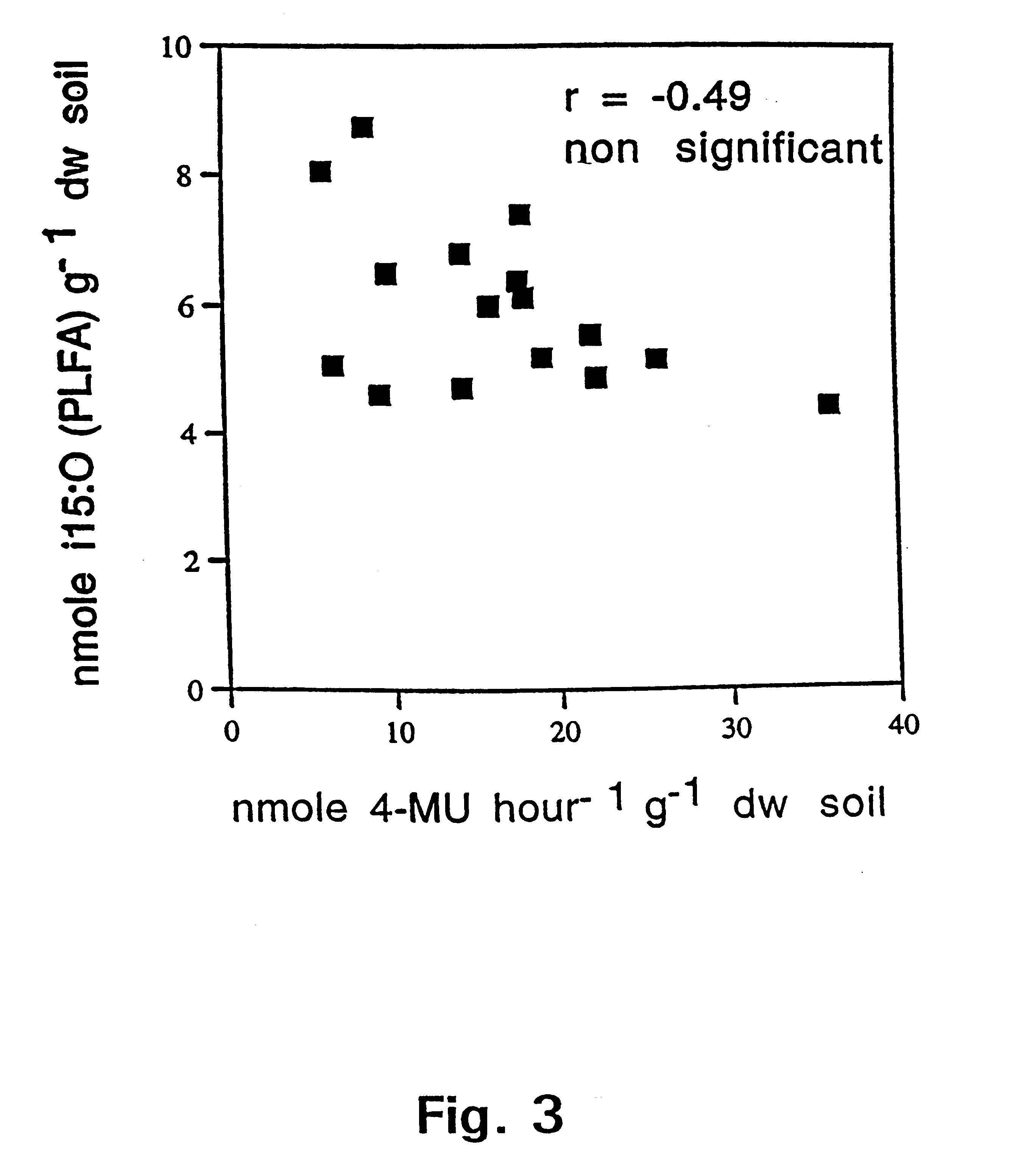
Method of selectively determining a fungal biomass
InactiveUS6372446B1High sensitivityAvoid selectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisChitinaseChitin synthase
A method for selectively determining a fungal biomass by detection of a fungal enzymatic activity that is present in substantially all fungal species, such as enzymes involved in chitin metabolism (chitinase, chitin synthase, chitosanase, N-acetyl-glucosaminidase and beta-N-acetylhexosamidase). The invention can be used for detecting a fungal biomass in environmental samples, food products, plant material, building materials, industrial fungal cultures or sample from a human being or animal including blood samples. In particular, 4-methylumbelliferyl-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminide is used as substrate for beta-N-acetylhexosamidase (EC 3.2.1.52). This enzyme activity correlates with the amount of fungal biomass present in a sample.
Owner:MYCOMETER
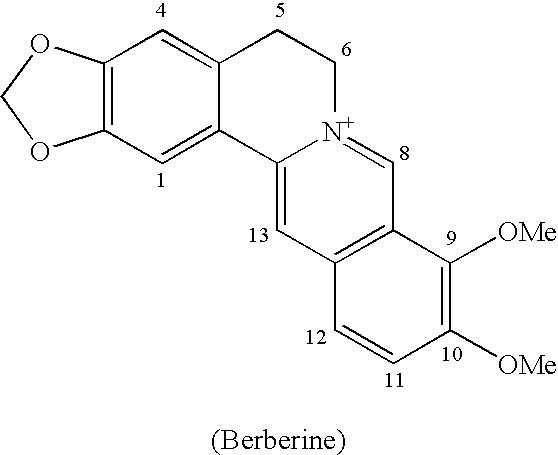
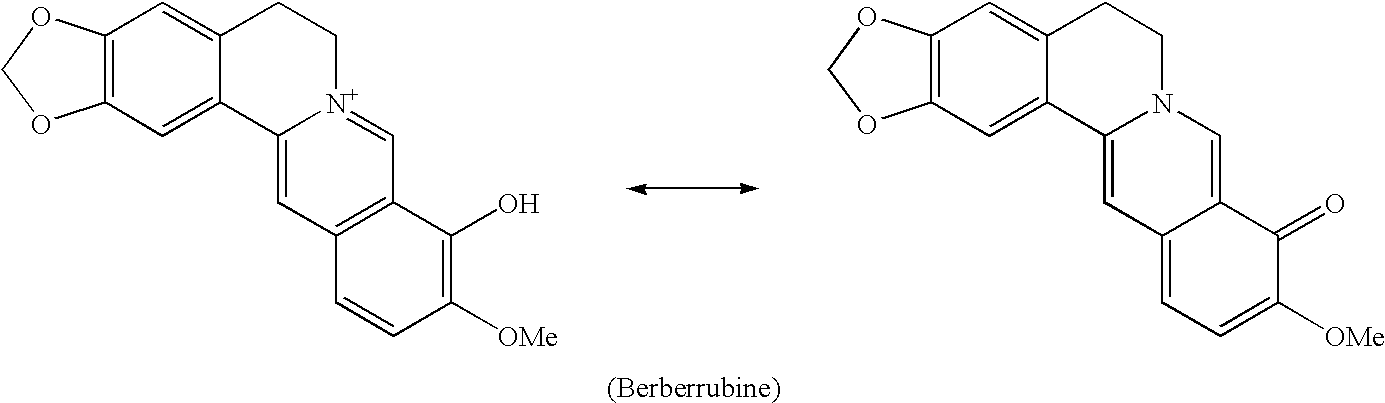
Berberrubine Derivatives Having Antifungal Activities
InactiveUS20100292476A1Selective inhibitionGood antifungal activityBiocideOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBerberineAntifungal antibiotic
The present invention relates to a berberrubine derivative having superior antifungal activity, more particularly to a berberrubine derivative having inhibitory activity against chitin synthase, which participates in the synthesis of chitin and is essential in the growth of fungi, and having a potent antifungal activity against human pathogenic fungi.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
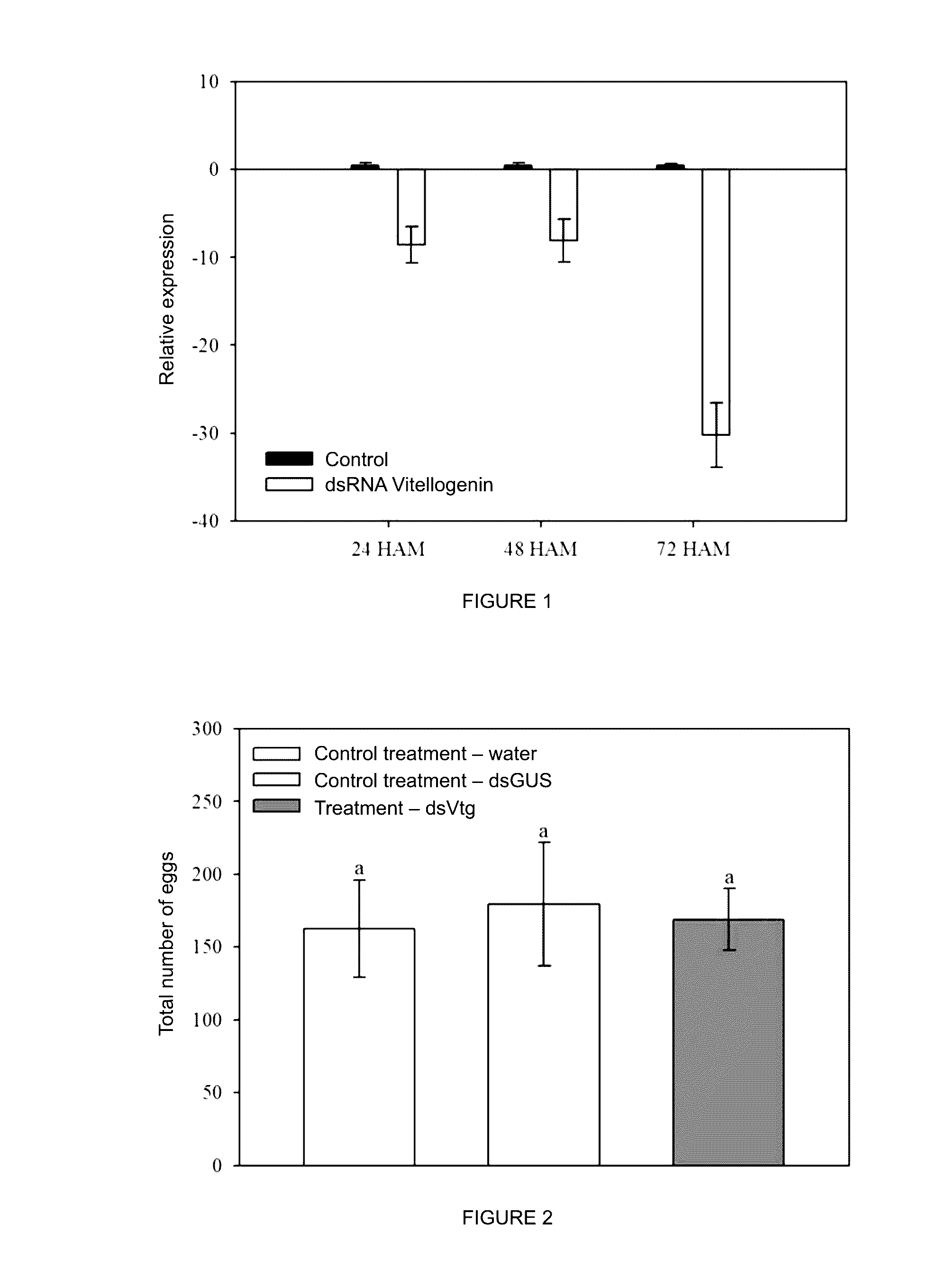
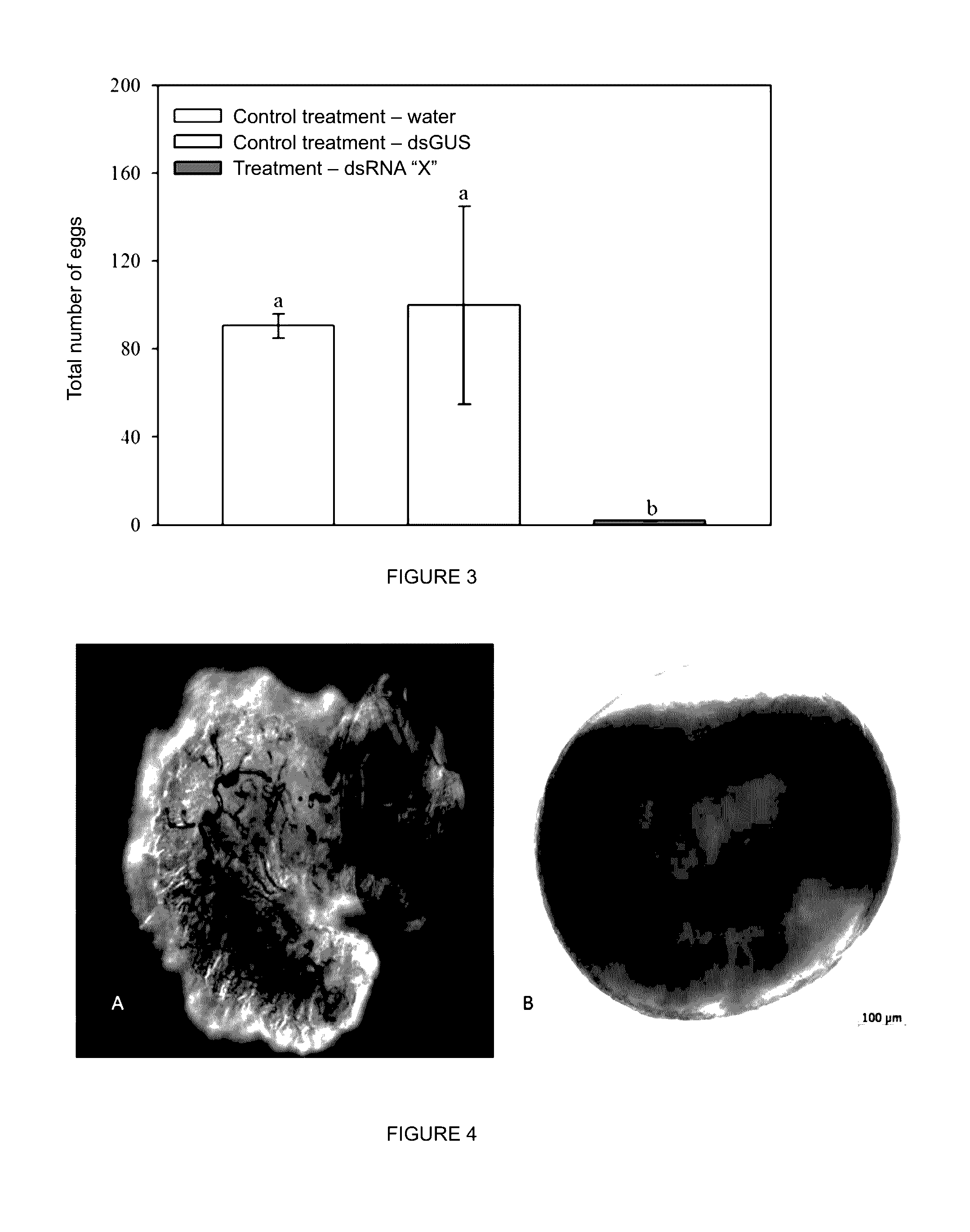
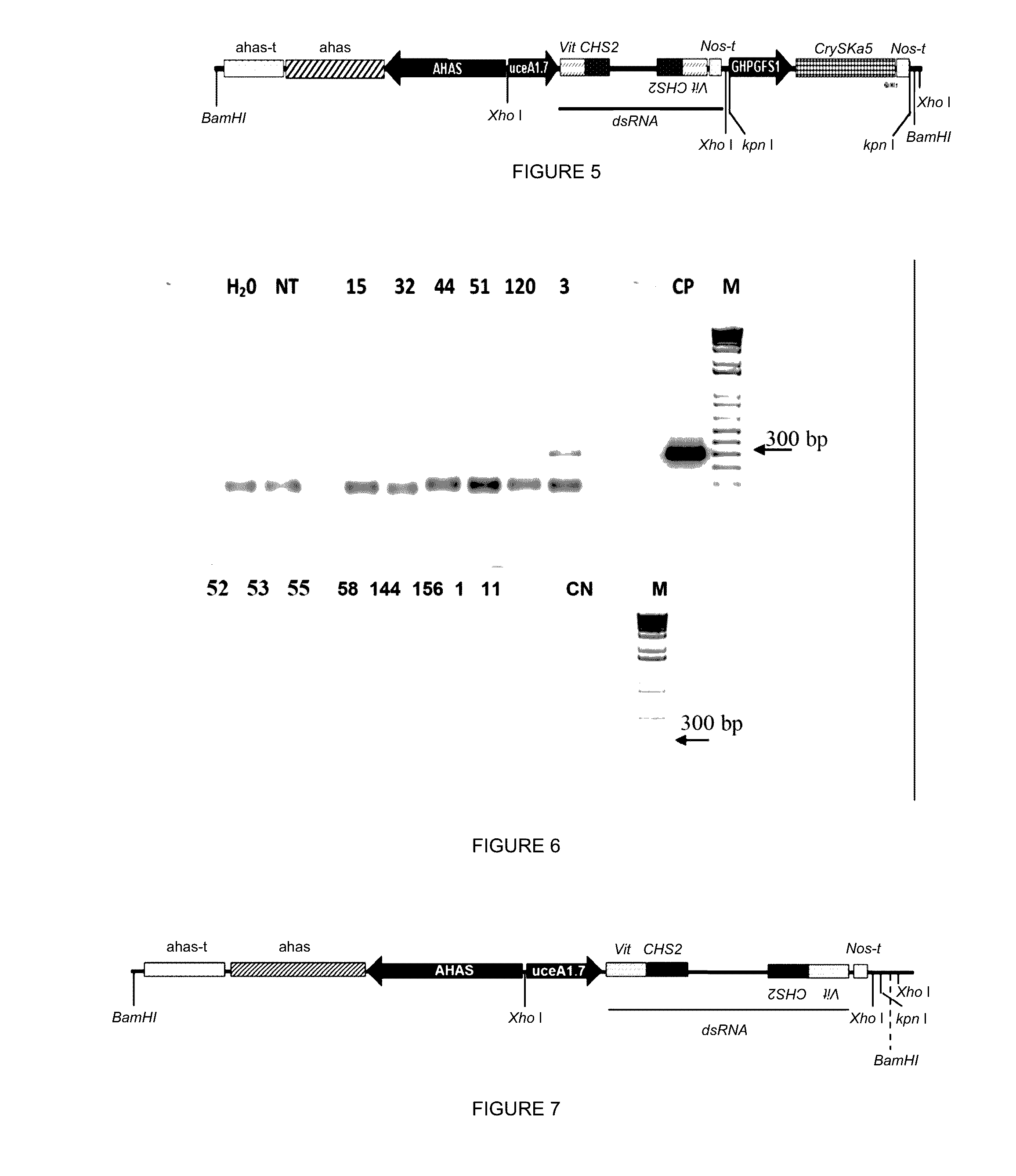
Method and compositions for controlling insect pests on plants by silencing genes of the chitin synthase and vitellogenin family, and alternatively by expression of a cry toxin gene
ActiveUS20170029843A1Climate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionVitellogeninsToxin protein
The present invention relates to the control of pest infestation by inhibiting or reducing the expression of genes of the family of chitin synthase and of vitellogenin, as well as through the expression of the toxin Cry8ka5. The invention further provides method and compositions for controlling pests, by feeding the pest with one or more double-stranded RNA molecules provided by the present invention, as well as double-stranded RNA molecule provided by the present invention, as well as through the action of the toxin Cry8ka5 on the target insect. The invention further describes a method of obtaining transgenic plants that express double-stranded RNA molecules and the toxin protein Cry8ka5. The present invention is preferably used for cotton plants.
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE PESQUISA AGROPECUARIA EMBRAPA +1
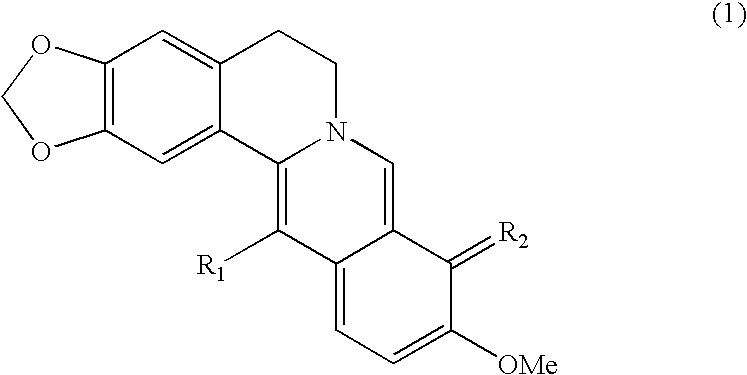
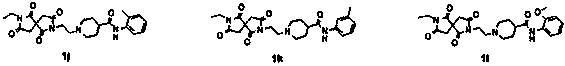
Design, synthesis and application of quinolinone fumaramide derivatives
The invention discloses design, synthesis and application of an N1-(2-oxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoline-3-yl)-N4-phenyl fumamide compound. The structure of the compound is shown as a general formula I,wherein R is hydrogen, methyl, ethyl, methoxyl and the like. Bioactivity test experiments prove that the compound has obvious inhibitory activity on chitin synthase, has good inhibitory activity on fungi such as candida albicans, aspergillus flavus, cryptococcus neoformans and aspergillus fumigatus, and can be used for preparing antifungal drugs.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method for fixed-point knockout of chitin synthase gene
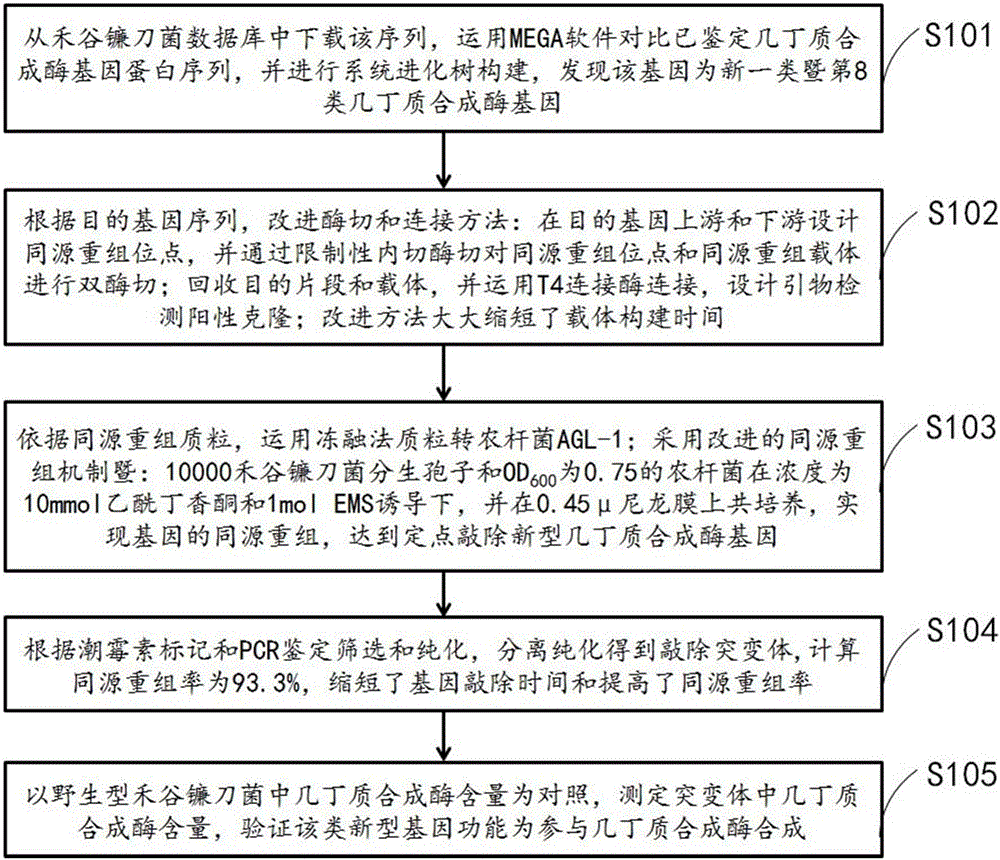
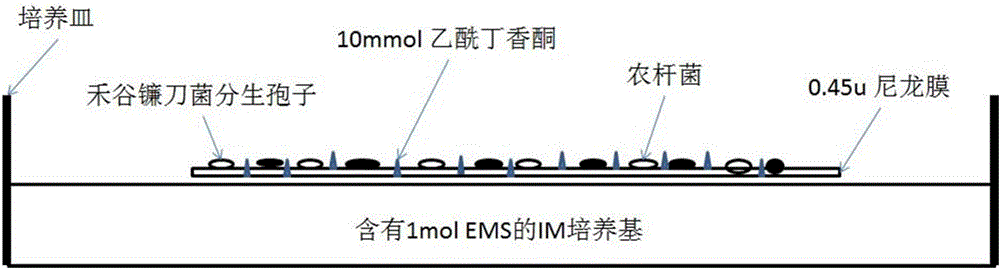
InactiveCN105936911AFull description of functionsFast and efficient targeted knockoutNucleic acid vectorFermentationBiotechnologyFreeze thawing
The invention discloses a fast and efficient method for fixed-point knockout of a novel chitin synthase gene; the novel chitin synthase gene has a DNA sequence and a cDNA sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The method adopts a freeze-thawing method for transforming a plasmid in agrobacterium AGL-1; 10000 fusarium graminearum conidiospores and agrobacterium with OD600 of 0.75 are co-cultured on a 0.45 [mu] nylon membrane; through construction of an improved homologous recombination plasmid, the construction time of a vector is shortened; the knockout method can greatly shorten the gene knockout time and increase the homologous recombination rate to 93.3%. Through determination of the content of the knockout mutant chitin synthase, the eighth chitin synthase gene is verified to have a function of regulating the synthesis of the chitin synthase. The novel eighth chitin synthase gene is found out in fusarium graminearum for the first time, a new target gene is provided for scab resistance of wheat, and the fast and efficient gene knockout method is provided for research of functional genomics.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method and compositions for the genetic control of insect pests in cotton plants by chitin synthase gene silencing
ActiveUS20160000086A1Reducing and inhibiting expression of geneBiocideBacteriaInsect pestChitin synthase
The present invention relates to the control of infestation of pests by inhibiting or reducing the expression of genes of the family of chitin synthase. The invention further provides methods and compositions for controlling pests by feeding them with one or more double-stranded RNA molecules provides by the present invention. The invention further describes a method of obtaining transgenic plants that express double-stranded RNA molecules. The present invention is preferably used for cotton-plants.
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE PESQUISA AGROPECUARIA EMBRAPA
Chitin synthase and gene thereof, and application of the chitin synthase
ActiveCN105886481AReduced amount of formationReduce outputMicrobiological testing/measurementFungicidesPathogenicityChitin synthase
The invention relates to a chitin synthase, particularly a chitin synthase in Oomycota. The amino acid sequence of the chitin synthase has more than 75% (preferably more than 80%, more preferably more than 90% and most preferably more than 95%) of similarity to the amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID No.4, and has the amino acid sequence with the same function as the amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID No.4. The activity level of the chitin synthase can regulate the yields of the active sporangia and active zoospore of oomycetes, thereby influencing the pathogenicity of the oomycetes or the disease development degree of the host.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Methods for manufacturing plant cell walls comprising chitin
Methods and means are provided for the modification of the reactivity of plant secondary cell walls, particularly in cotton cell walls found in cotton fibers. This can be conveniently achieved by expressing a chimeric gene encoding a Saprolegnia monoica chitin synthase in cotton plants.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Chitin synthase transcriptional regulation gene MedA inactivated aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a chitin synthase transcriptional regulation gene MedA inactivated aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacterium and application thereof. According to the invention, an aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacterium with chitin synthase transcriptional regulation gene MedA deletion is constructed through a gene knockout means. According to the genetically engineered bacterium, the biofilm quantity of aspergillus niger in the process of producing citric acid through immobilized fermentation is reduced, the phenomenon that the pore diameter of a carrier is blocked is effectively relieved, the oxygen and mass transfer effect between the carrier and the outside is improved, so that the advantages of immobilized fermentation are exerted, the yield of citric acid is increased, the fermentation period is shortened, and the problems of low yield and long fermentation period in citric acid production through aspergillus niger fermentation in existing industrial engineering are effectively solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +2
Chitin synthase gene and dsRNA of the brown orange aphid
InactiveCN105420255BSolving the dsRNA problemSilent efficiency is highFermentationGlycosyltransferasesBiotechnologySynthesis methods
The invention discloses a toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene. The sequence of the toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:3. The invention further discloses dsRNA of the toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene, and the sequence of the dsRNA is shown as SEQ ID NO:6. The invention further discloses a synthesis method of the dsRNA of the toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene. The synthesis method includes the following steps that total RNA of toxoptera citricida is extracted and subjected into reverse transcription to form cDNA serving as an amplification template; PCR amplification is carried out through primers with the sequences of SEQ ID NO:4 and SEQ ID NO:5, a product is recycled after electrophoresis, and the dsRNA of the toxoptera citricida chitin synthase gene is synthesized with a gel recycling product as a template. According to the dsRNA of the chitin synthase gene, gene silencing efficiency is high, toxoptera citricida has obvious phenotypic changes after gene interference, and the good application prospects are achieved in the aspect of researching and developing novel pesticide.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Chitin synthase from Phytophthora capsici and its gene and application
ActiveCN105886482BReduced amount of formationReduce outputMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSporelingCapsicum cardenasii
The invention relates to chitin synthase in phytophthora capsici. The amino acid sequence of the chitin synthase has the similarity above 90%, preferably above 95% and more preferably above 98% with an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 4 and has same functions with the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 4. By virtue of the activity level of the chitin synthase of the phytophthora capsici, the yields of active sporangia and active zoospores can be adjusted, so that the pathogenicity of the phytophthora capsici or the mobidity extent of a host is influenced.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Sogatalla furcifera chitin synthase 1a (SfCHSla) gene alternative spliceosome and application of its dsRNA in pest control
InactiveCN108753750ABlocking translationBiocideAnimal repellantsNucleotideCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention discloses a sogatalla furcifera chitin synthase 1a (SfCHSla) gene alternative spliceosome and application of its dsRNA in pest control and belongs to the technical field of insect genetic engineering. The SfCHS1a gene alternative splicesome is obtained on the basis of the nucleotide sequence of SfCHS1a of which the accession number in a GenBank database is KY350143, wherein, the nucleotide sequence is as shown as SEQ ID NO:3. Further, the dsRNA of the gene is synthesized on the basis of the sequence SEQ ID NO:3. Accordingly, The candidate gene is provided for sogatalla furciferaRNA mediated pest control strategies, and meanwhile, a theoretical basis is provided for research and development of novel insecticides.
Owner:KAILI UNIV
A cell-screening model for downregulators targeting fungal cell wall chitin synthase
ActiveCN105087630BImprove practicalityUniform screening resultsFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsMicrobiology
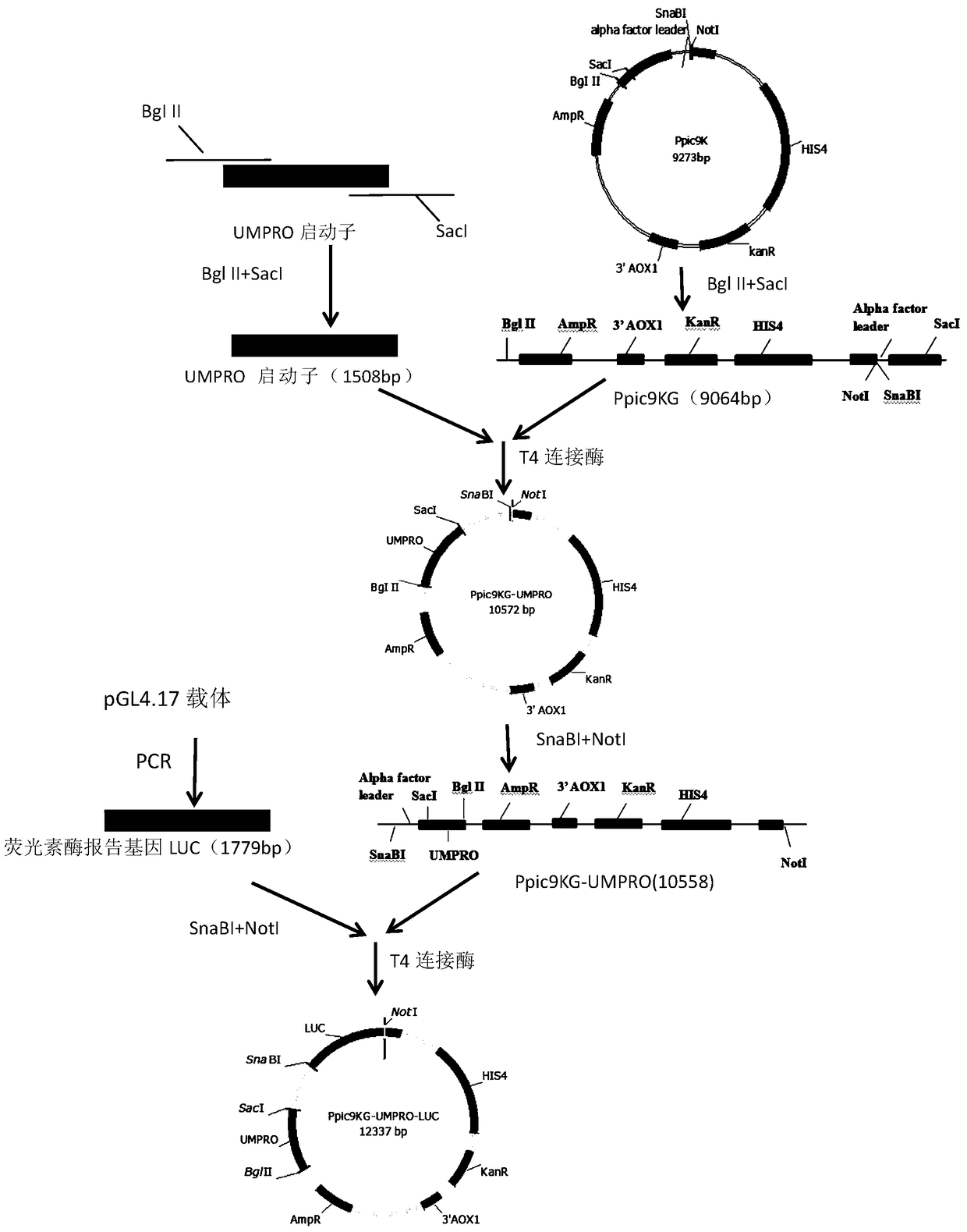
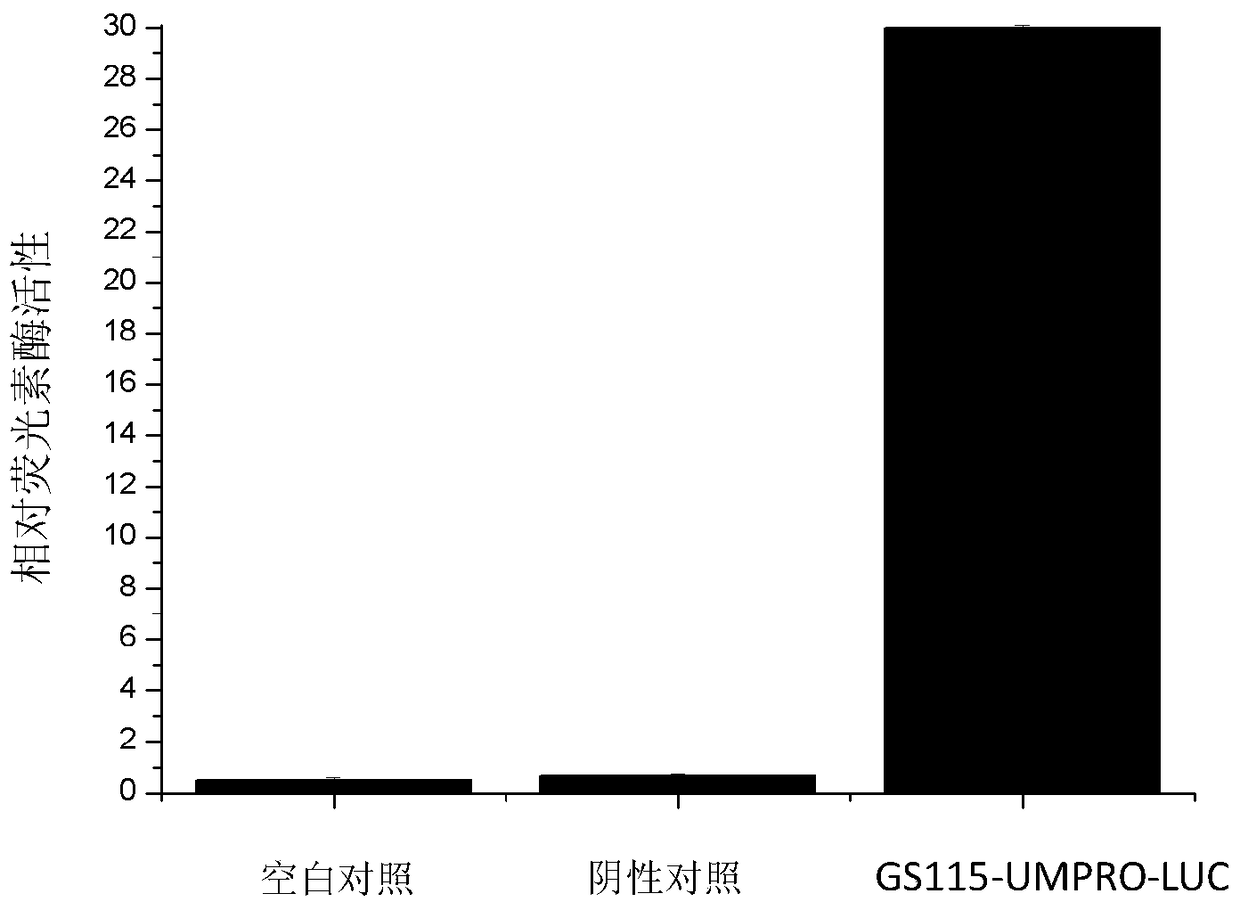
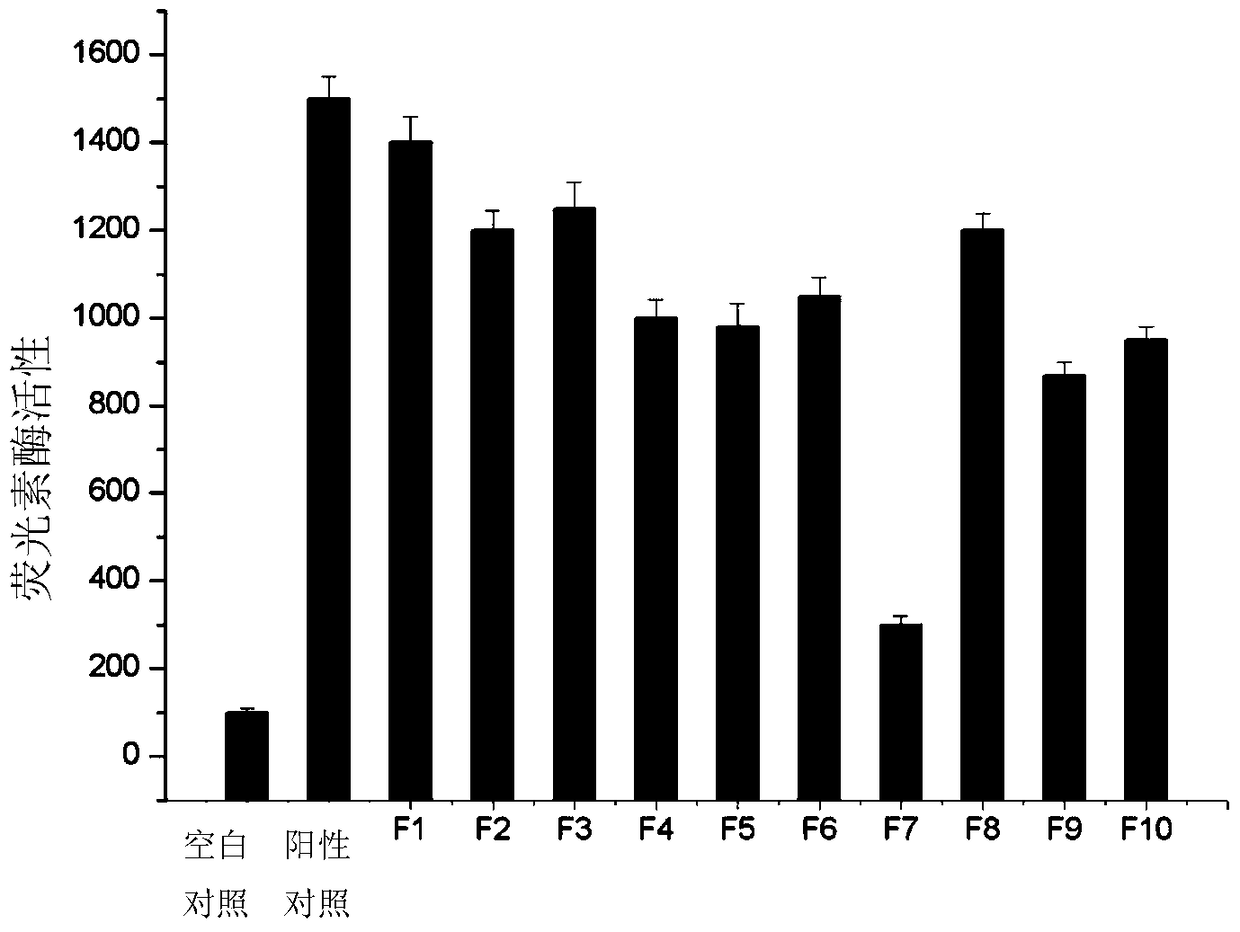
The invention relates to a target fungus cytoderm chitin synthetase decreasing agent high-throughput screening model, belonging to the field of genetic engineering, the model consists of a UMcsh5 gene promoter sequence UMPRO, a recombinant plasmid Ppic9KG-UMPRO-LUC, monoclonal cell strain GS115-UMPRO-LUC for stable expression of the UMPRO promoter, a screening reagent and a luciferase reporter gene detection system. The screening model has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, low cost, high flexibility, wide applicable range, high screening efficiency and the like and has great application potentiality.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Synthesis and application of imine spiro piperidine compounds
The invention discloses design, synthesis and application of novel imide spiro compounds. The structure of the compounds is shown as a general formula I shown in the specification, wherein R is a benzene ring or a substituted benzene ring. Bioactivity test experiments prove that most compounds show certain inhibitory activity on candida albicans, aspergillus flavus, cryptococcus neoformans and aspergillus fumigatus, and also have certain inhibitory activity on chitin synthase.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Chitin synthase of phytophthora capsici as well as gene and application of chitin synthase
ActiveCN105886482AReduced amount of formationReduce outputMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPathogenicityChitin synthase
The invention relates to chitin synthase in phytophthora capsici. The amino acid sequence of the chitin synthase has the similarity above 90%, preferably above 95% and more preferably above 98% with an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 4 and has same functions with the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID No. 4. By virtue of the activity level of the chitin synthase of the phytophthora capsici, the yields of active sporangia and active zoospores can be adjusted, so that the pathogenicity of the phytophthora capsici or the mobidity extent of a host is influenced.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
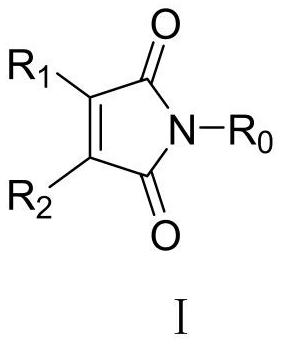
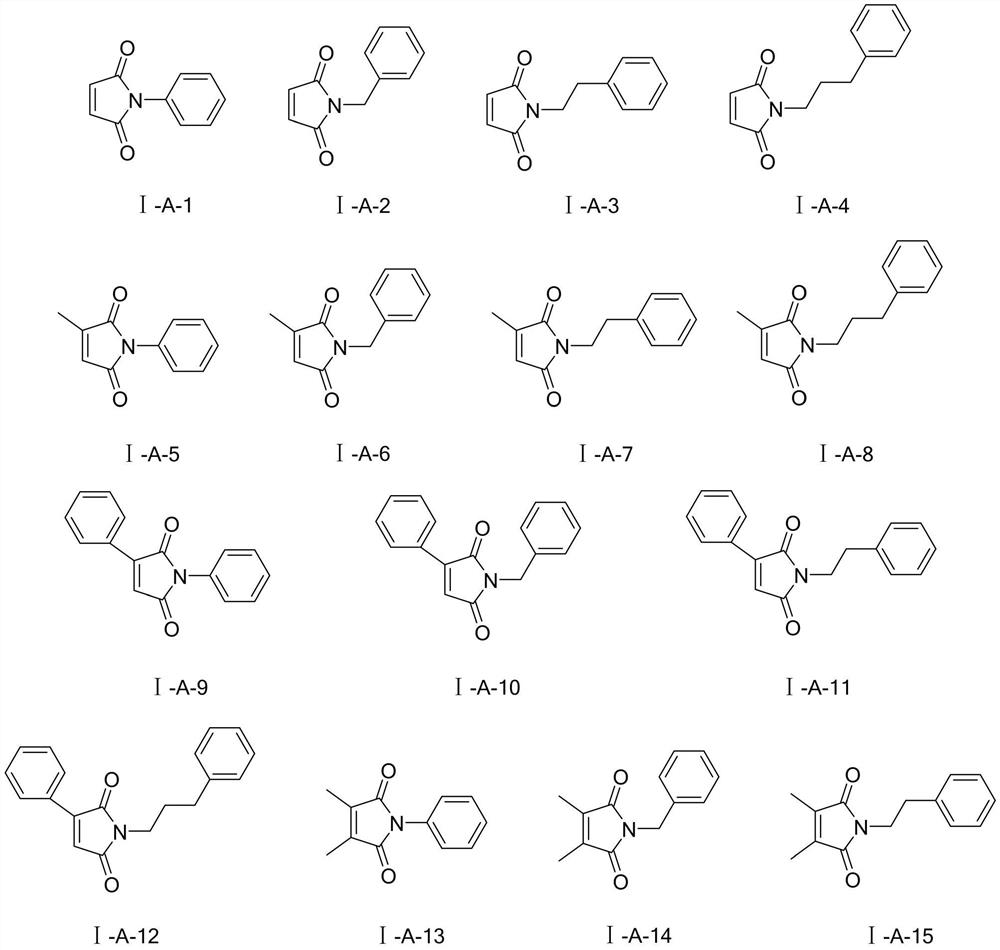
Application of maleimide compound as chitin synthase inhibitor
ActiveCN111316986AEnhanced inhibitory effectThe synthesis method is simpleBiocideOrganic active ingredientsChlorobenzeneEthyl group
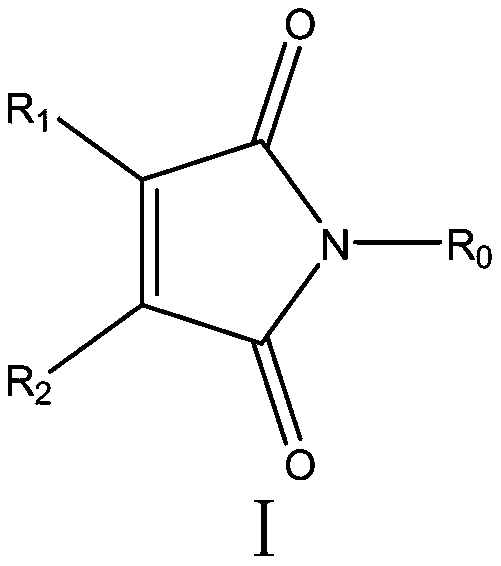
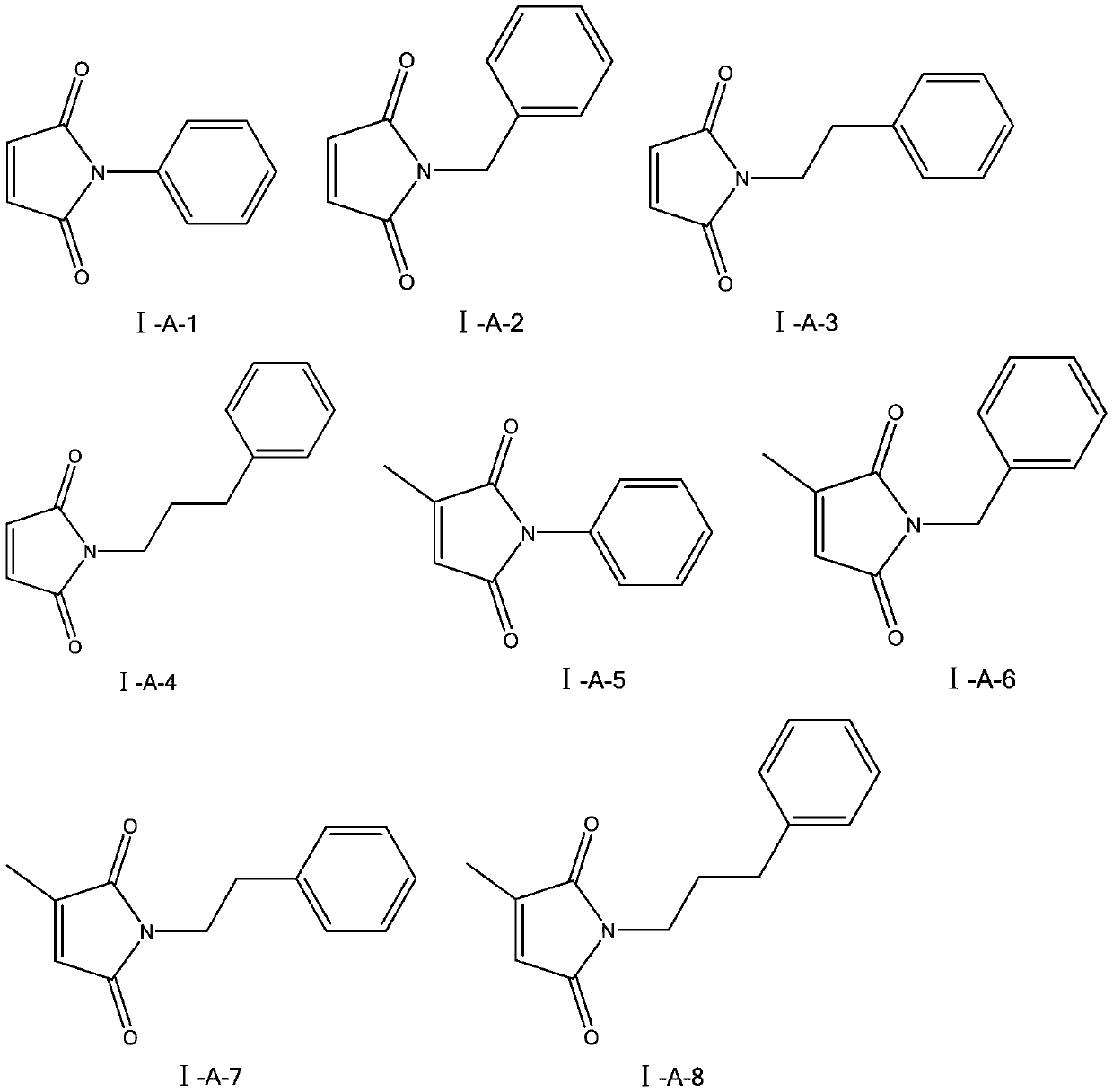
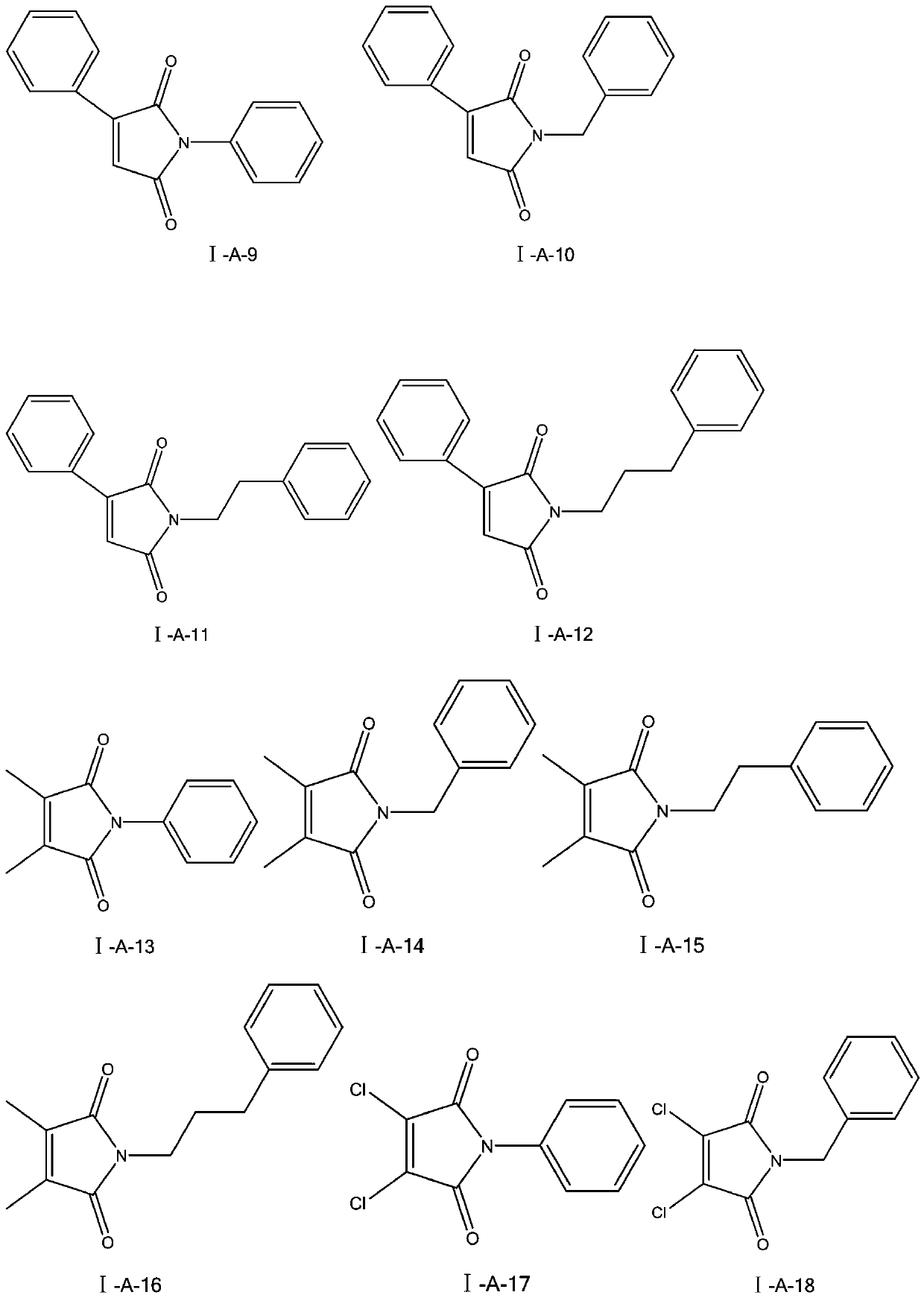
The invention discloses an application of a maleimide compound as shown in a formula I. In the formula I, R0 is phenyl, benzyl, phenethyl, phenylpropyl, p-fluorophenyl, p-chlorophenyl, p-bromophenyl,p-methoxyphenyl, p-methylphenyl or p-hydroxyphenyl, R1 is hydrogen, methyl, phenyl or chlorine; and R2 is hydrogen, methyl, phenyl or chlorine. The provided maleimide compound has a good inhibition effect on chitin synthase.
Owner:杭州佳嘉乐生物技术有限公司
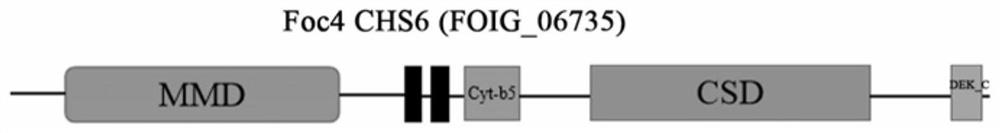
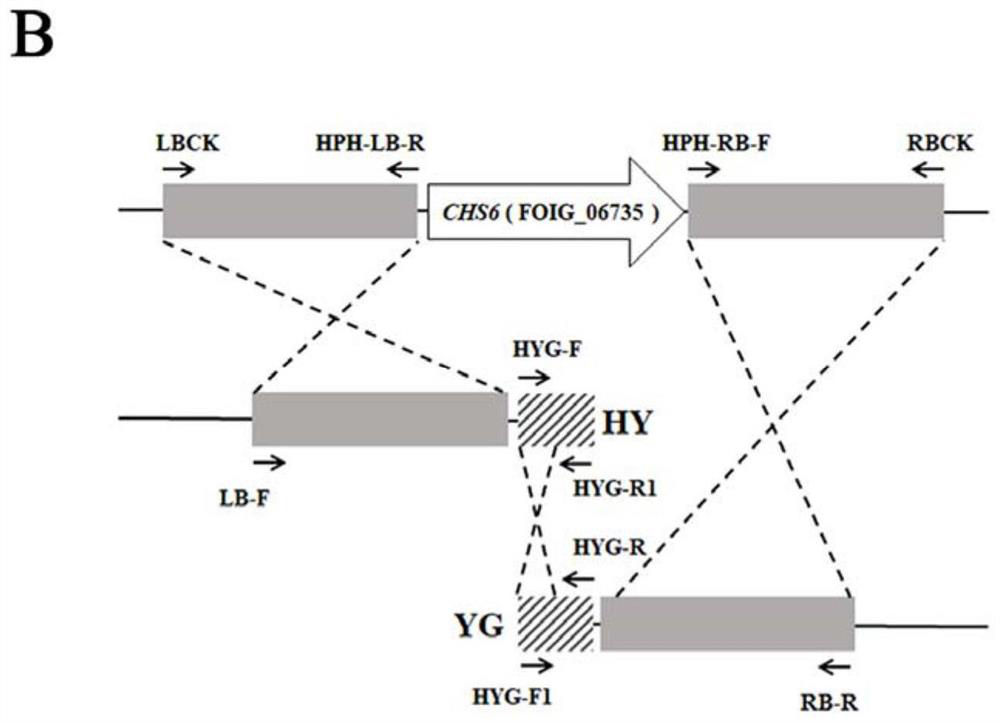
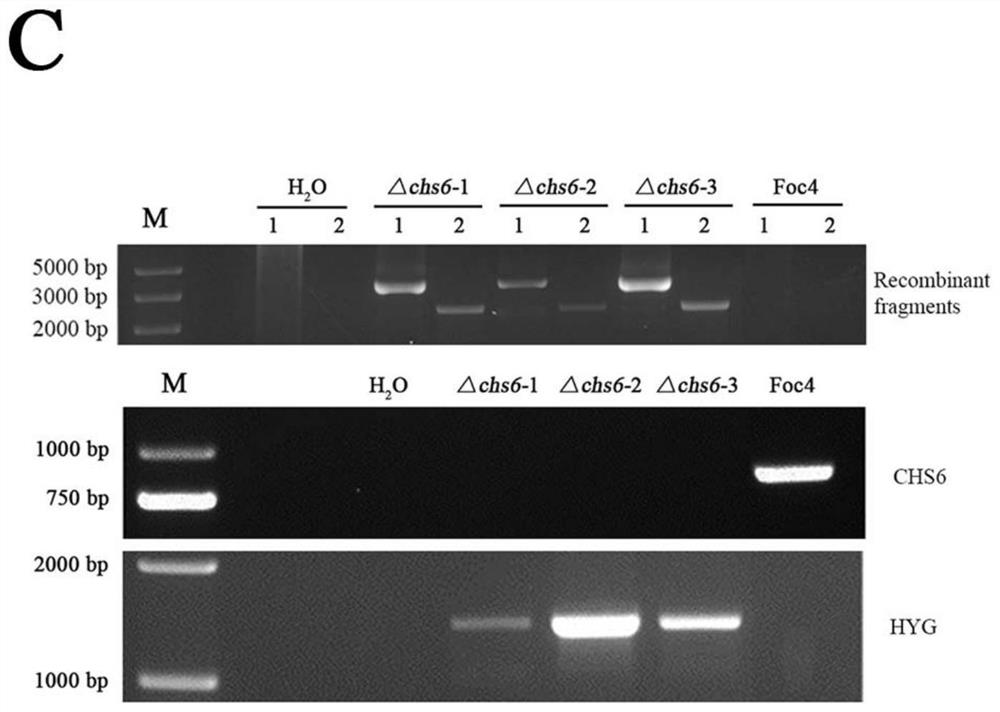
Application of banana fusarium oxysporum 4 # physiological race chitin synthase 6 gene
PendingCN114854776AIncrease pathogenicityFormation regulationFermentationHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyFungicide
The invention discloses an application of a banana fusarium oxysporum 4 # physiological race (chitin synthase 6) gene. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the banana fusarium oxysporum 4 # physiological race. Specifically, the invention provides the application of the banana wilt pathogen No.4 physiological race CHS6 gene in the pathogen resistance, pathogenicity and chlamydospore formation process. The CHS6 gene can improve pathogenicity of pathogenic bacteria and regulate and control formation of chlamydospores. The research result provided by the invention can provide a basis for the research on the drug resistance and pathogenic mechanism of the fusarium oxysporum to the phenamacril fungicides.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
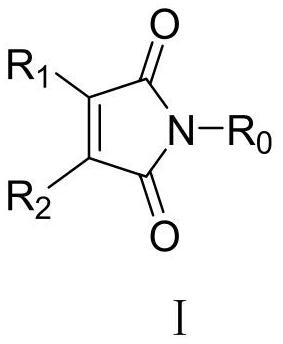
Application of Maleimide Compounds as Chitin Synthase Inhibitors
ActiveCN111316986BEnhanced inhibitory effectThe synthesis method is simpleBiocideOrganic active ingredientsChlorobenzeneEthyl group
The invention discloses the application of the maleimide compound represented by formula I as a chitin synthase inhibitor, wherein R 0 is phenyl, benzyl, phenethyl, phenylpropyl, p-fluorophenyl, p-chlorophenyl, p-bromophenyl, p-methoxyphenyl, p-methylphenyl or p-hydroxyphenyl; R 1 is hydrogen, methyl, phenyl or chlorine; R 2 is hydrogen, methyl, phenyl or chlorine. The maleimide compound provided by the invention has a good inhibitory effect on chitin synthase.
Owner:杭州佳嘉乐生物技术有限公司
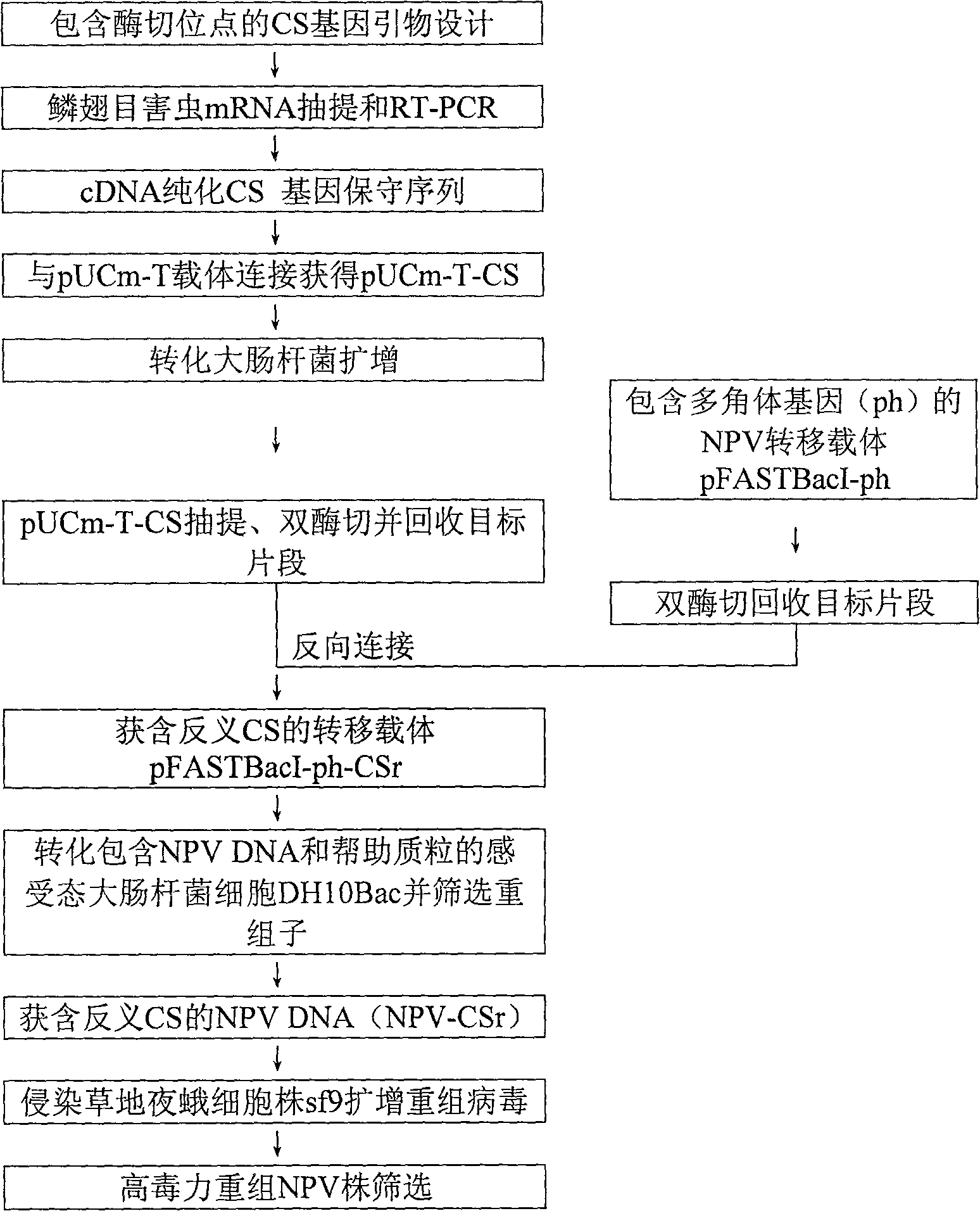
Method for reforming high-virulent nuclear polyhedrosis virus of lepidoptera pest
InactiveCN100529064CBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementConserved sequenceNuclear Polyhedrosis Virus
The method for transforming Lepidopteran pest nuclear polyhedrosis virus belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a method for transforming wild nuclear polyhedrosis virus (NPV) by using antisense gene technology and constructing a new Lepidoptera pest NPV. The invention scheme mainly includes the following steps: ① cloning of chitin synthase (CS) conserved sequence of lepidopteran pests such as inchworms; ② construction of antisense CS gene transfer vectors for lepidopteran pests; ③ recombinant NPV; ④ methods such as PCR Verify the recombinant NPV; ⑤Using the wild NPV virus as a control, evaluate and screen the insecticidal ability of the recombinant NPV to obtain a highly virulent recombinant NPV virus strain. The NPV transformed by the method of the present invention has faster diffusion and reinfection speed, and has higher toxicity to Lepidoptera pests.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
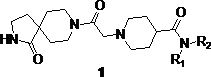
Preparation and application of diazaspirodecane piperidine carboxamides
The present invention discloses 1-oxo-2,8-diazaspiro[4.5]decane piperidine carboxylic acid amide compound and its preparation method and application. The structure of said compound is shown in general formula 1: where R 1 is hydrogen; R 2 For: various substituted aromatic amines. It has been proved by biological activity test experiments that some compounds have certain inhibitory activity against gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria and fungi, and have obvious inhibitory activity against chitin synthase, with good antibacterial effect, and can be used to prepare anti-pathogenic Microbial medicine. Moreover, the preparation raw material is simple, cheap and easy to obtain, and the application in the aspect of anti-infection is of great significance.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Insect chitin synthase 1A gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof
The invention provides an insect chitin synthase 1A gene segment, dsRNA and application thereof. The dsRNA is synthesized by the chitin synthase 1A gene segment with the sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 which is obtained by the gene sequence of the chitin synthase 1A of Locusta migratoria manilensis with the accession number of GU067730 in an NCBI database. After the dsRNA is injected in body cavities of insects, the insects die because of difficult moulting. A new way for developing a safe and pollution-free method for preventing and controlling insect is provided.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Methods for manufacturing plant cell walls comprising chitin
InactiveUS20130091602A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesFiberChitin formation
Methods and means are provided for the modification of the reactivity of plant secondary cell walls, particularly in cotton cell walls found in cotton fibers. This can be conveniently achieved by expressing a chimeric gene encoding a Saprolegnia monoica chitin synthase in cotton plants.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
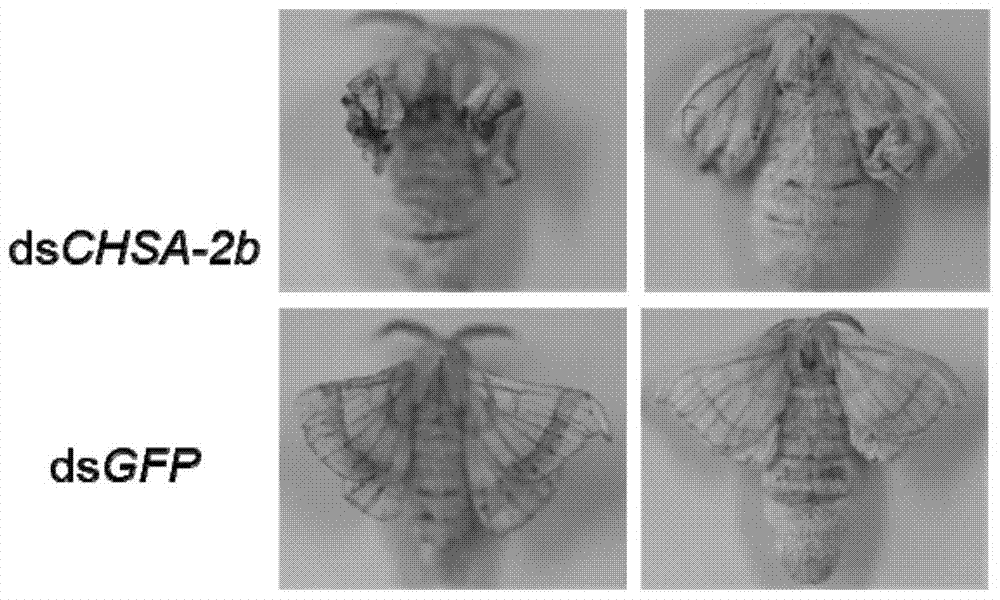
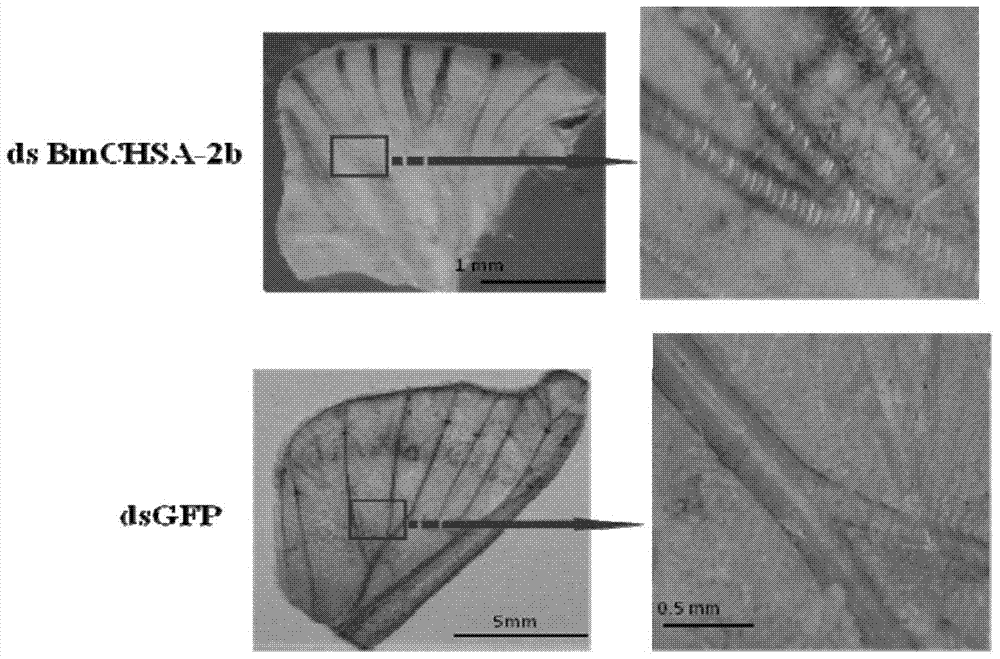
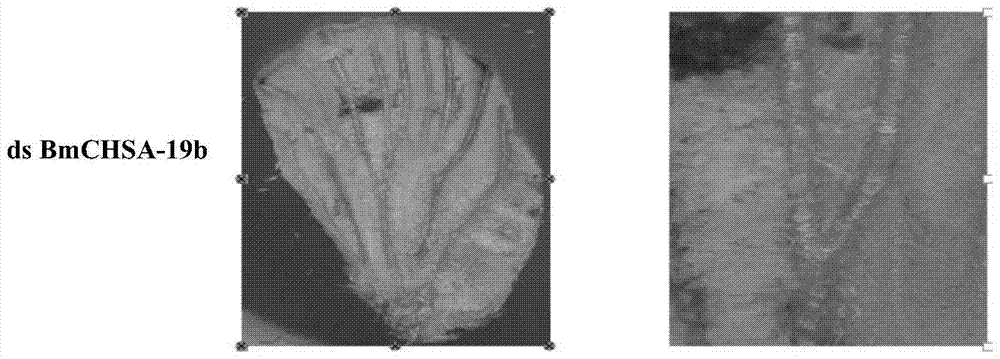
Application of chitin synthase chsa‑2b/19b from lepidopteran insects in pest control
ActiveCN105230651BAchieve the purpose of preventionBiocideAnimal repellantsOrder LepidopteraSynthetic substance
The invention discloses the application of chitin synthase CHSA‑2b / 19b of lepidopteran insects in pest control. The invention discovers malformed wing veins of insects by fully injecting dsRNA that interferes with exon 2b and 19b of lepidopteran insects. Wrinkled and thin, wings smaller, indicating that transcripts containing 2b and / or 19b affect insect wing development. Artificial substances that inhibit the expression of chitin synthase transcripts containing 2b and / or 19b in lepidopteran insects or compounds screened from plants can be used as inhibitors, such as injecting dsRNA of CHSA-2b to lepidopteran insects, The purpose of pest control can be achieved. Similarly, substances that promote the degradation of chitin synthase transcripts containing 2b and / or 19b in Lepidoptera insects, or substances that inhibit the normal function of chitin synthase transcripts containing 2b and / or 19b As a pest insecticide, it can achieve the purpose of pest control.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com