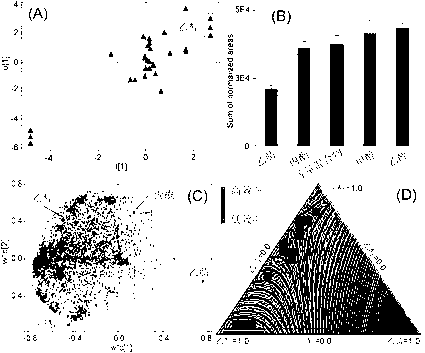
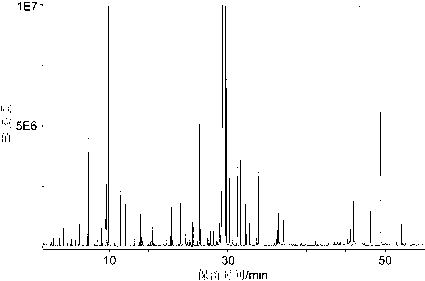
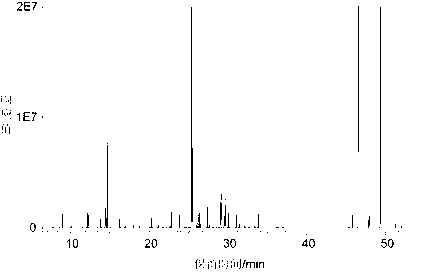
Chemical derivation-based detection method for hemolymph metabolin of migratory locust
A detection method and hemolymph technology, which are applied in the fields of animal ecology and analytical chemistry, can solve the problems such as the fingerprint detection of hemolymph metabolism of migratory locusts, high cost of construction and operation, and narrow coverage of biological information, etc., and achieve a convenient and efficient method. Low instrument requirements, complete and comprehensive effects of biological information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Take 4-year-old gregarious migratory locusts, use a micro-syringe to puncture the epidermis at the junction of the pronotum and abdomen to aspirate body fluid, centrifuge at 13,000 g for 10 min at 4°C to obtain hemolymph, and store at -80°C before analysis. After thawing at room temperature, put 50 μL of hemolymph into a 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube, add 150 μL of ethanol-acetonitrile mixed solvent (9 / 1, v / v) to precipitate protein, vortex vigorously for 1 min, ultrasonically extract for 2 min, and centrifuge at 15,000 g for 15 min at 4°C , Pipet 120 μL of the supernatant extract into another 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube, and dry under reduced pressure in a lyophilizer for 5 h. Add 50 μL of methoxyamine hydrochloride-pyridine solution (20 mg / mL) to the extract, dissolve it by ultrasonication for 1 min, vortex mix, and oximate in a constant temperature water bath at 40°C for 90 min; then, add 50 μL of N-methyl-N-trimethyl Silane-trifluoroacetamide reagent, vortex mixed, derivatized by...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Take the gregarious East Asian migratory locust with knockout carnitine-acetyltransferase, use a micro-syringe to puncture the epidermis at the junction of the pronotum and abdomen to aspirate the body fluid, centrifuge at 13000g for 10 minutes at 4°C to obtain hemolymph, and use dry ice to cool down during transportation . After thawing at room temperature, take 50 μL of hemolymph and place it in a 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube, add 150 μL of ethanol-acetonitrile mixed solvent (9 / 1, v / v) to precipitate protein, vortex vigorously for 1 min, and ultrasonically extract metabolites for 2 min, 15000 g at 4 °C Centrifuge for 15 min, pipette 120 μL supernatant extract into another 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube, and dry under reduced pressure in a lyophilizer for 5 h. Add 50 μL of methoxyamine hydrochloride-pyridine solution (20 mg / mL) to the extract residue, dissolve it by ultrasonication for 1 min, vortex and mix well, and oximate in a constant temperature water bath at 40°C for 90 min; the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com