Locust microsporidia, suspension culture method and applications thereof
A locust microsporidia, locust technology, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve heavy and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
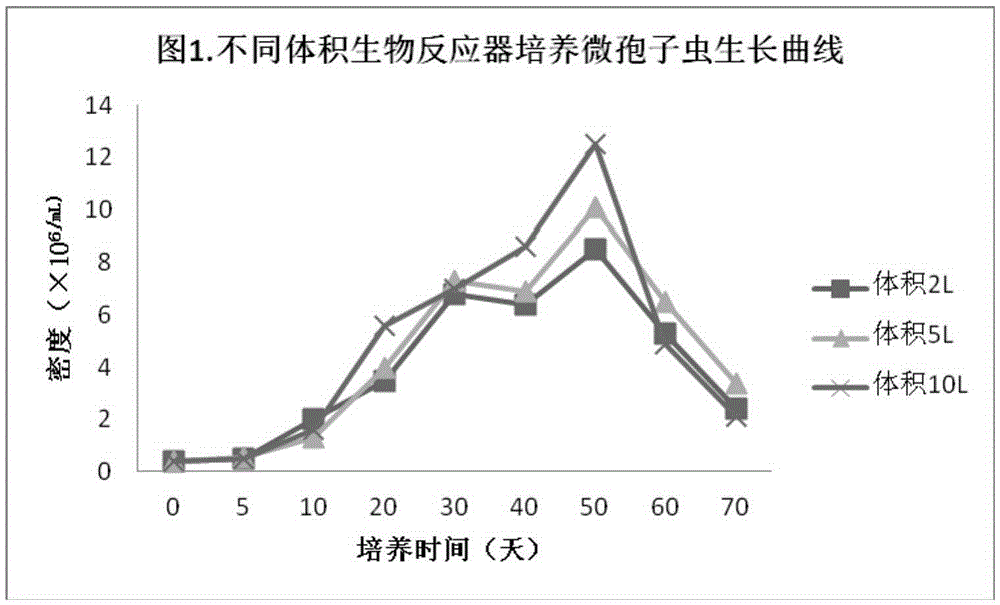
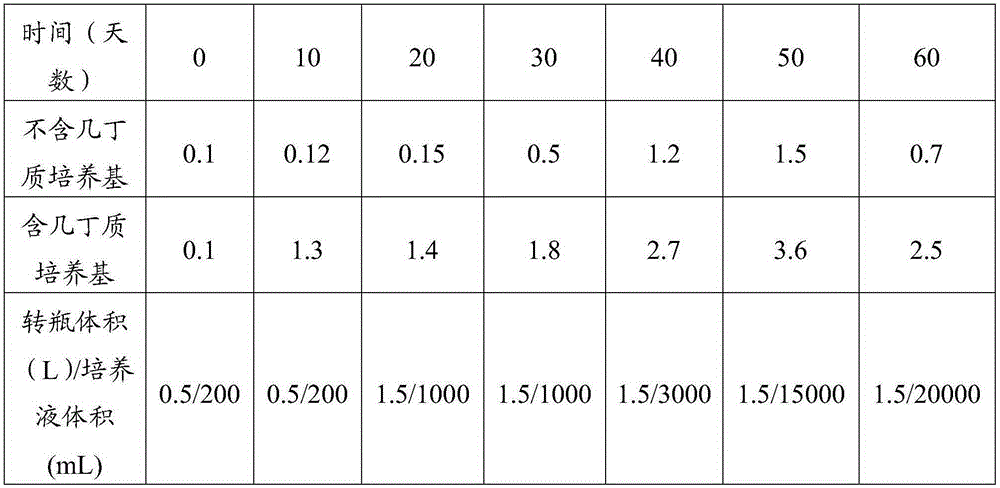
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0080] Example 1 Locust Microsporidia Isolation and Preliminary Identification
[0081] 1 Materials and methods
[0082] 1.1 Isolation and purification of microsporidia
[0083] Microsporidia migratiosa in the wild was isolated from Burqin County, Altay Prefecture, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Three-day-old locust gnats (n=50) were raised in the laboratory at a room temperature of 30±1°C, fed with corn leaves mixed with a small amount of wheat bran. Homogenate the isolated microsporidia-infected tissue to make spore suspension, count the microsporidia in suspension with a hemocytometer, and feed 10 5 or 10 7 The spores are applied on the corn leaves and fed to 4-5 instar locust gnats after drying. After 24 hours of feeding, replace fresh corn leaves. Diseases and insects were kept in an inoculation room equipped with 4-watt fluorescent lamps, day and night light, and a temperature of 30±1°C. After the locust gnats have grown to old age or adult stage, collect the cor...
Embodiment 2
[0133] Embodiment 2. In vivo reproduction of isolated locust microsporidia
[0134] 1. Materials and Methods
[0135] 1.1 Materials: Nosemasp-XJ-10, multiplied by migratory locust. The locusts were collected from locust eggs in the Altay area of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, and were reared indoors as test insects.
[0136] 1.2 Test method
[0137] 1.2.1 Massive proliferation of locust micropaedia
[0138] 1) The relationship between host lethal time and pathogen developmental stage
[0139] Dilute the microsporidia spore solution to 1×10 8 Spores / mL, take 10 microliters and drop it on the leaves of wheat seedlings with a diameter of 10mm. After drying, feed them to the 4th instar locust gnats subcultured in this room, one piece per head, about 10 in total. After 24 hours, the locust gnats that had eaten up all the leaves of the wheat seedlings were used as test insects, and they were raised in a large plastic tube at 30 ± 1, humidity 70%, light day and night, and f...
Embodiment 3
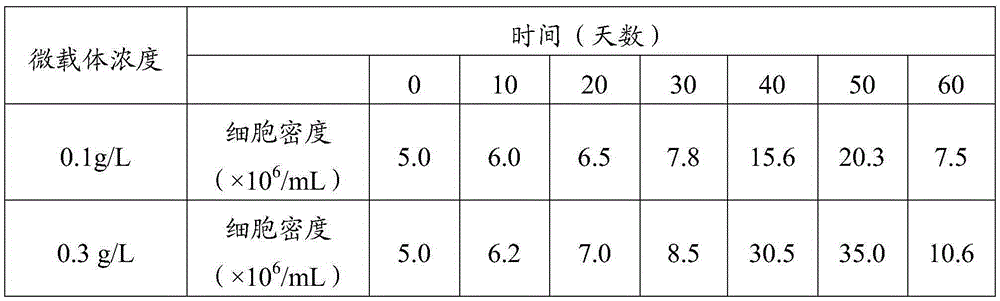
[0160] Example 3. Preparation of Microsporidia locust in vitro culture medium, extracellular matrix and adaptation in vitro of No. locust locust
[0161] 3.1 Self-made locust microsporidia medium MX, volume 1L, add the following substances into pure water.
[0162] Inorganic salt mixture: NaH 2 PO 4 2H 2 O507mg / L; NaHCO 3 300mg / L; KCl1720mg / L; CaCl 2 2H 2 O750mg / L; CuCl 2 ·H 2 O0.1mg / L; CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O0.03mg / L; FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.28mg / L; MgCl 2 4H 2 O1140mg / L; MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O3269mg / L; MnCl 2 4H 2 O0.01mg / L; NaCl1425mg / L; NaH 2 PO 4 4H 2 O580mg / L; (NH 4 ) 6 (Mo 7 o 24 )·4H2O0.02mg / L and ZnCl20.02mg / L.
[0163] Sugar mixture: D-glucose 2917mg / L; fructose 20.9mg / L; sucrose 11865mg / L; malic acid 306mg / L; alpha-ketoglutaric acid 169mg / L; succinic acid 27.4mg / L; fumaric acid 25.2mg / L; Maltose 500mg / L.
[0164] Amino acid mixture: L-alpha-alanine 131.5mg / L; beta-alanine 234mg / L; L-arginine hydrochloride 692mg / L; L-asparagine 797mg / L; L-aspartic acid 797mg / L; L-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com