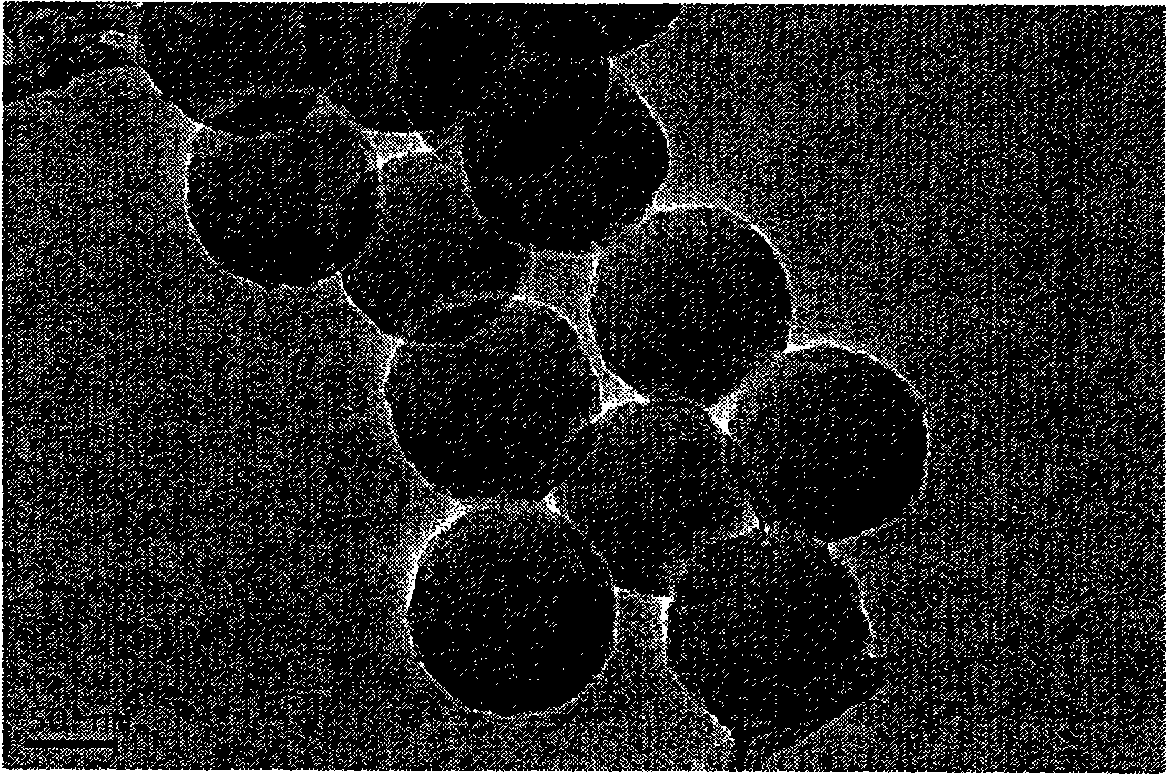
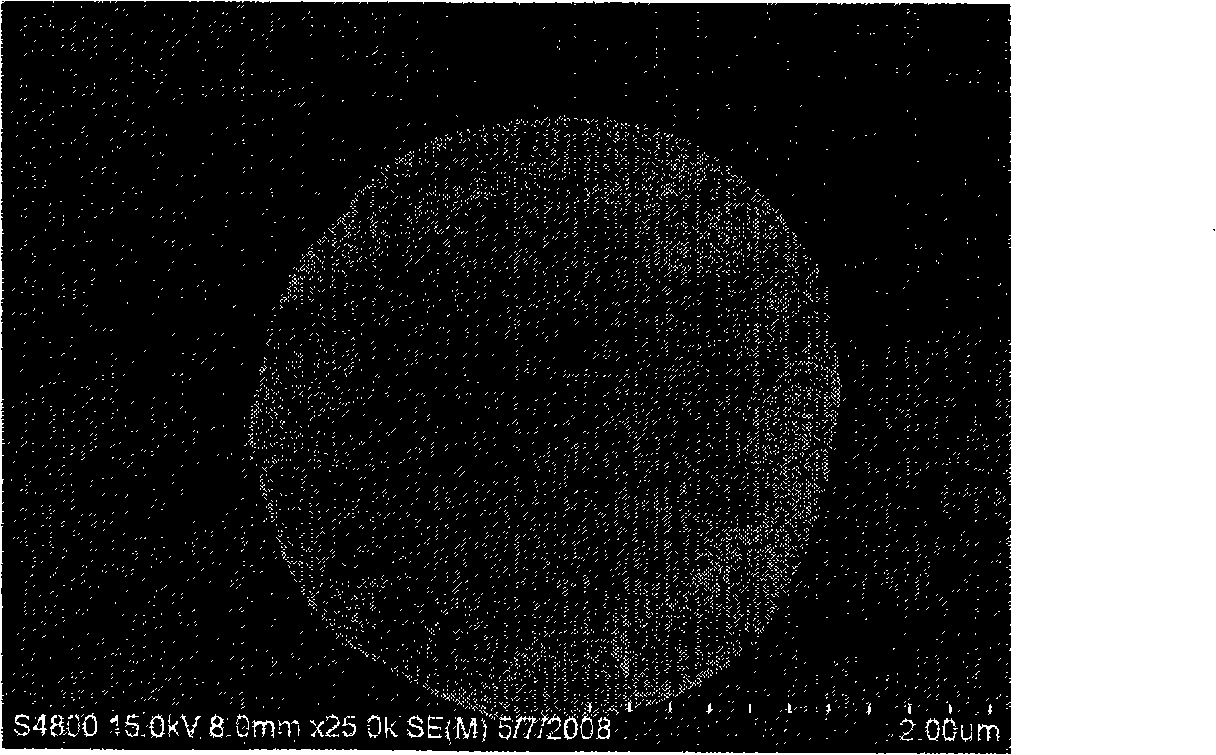
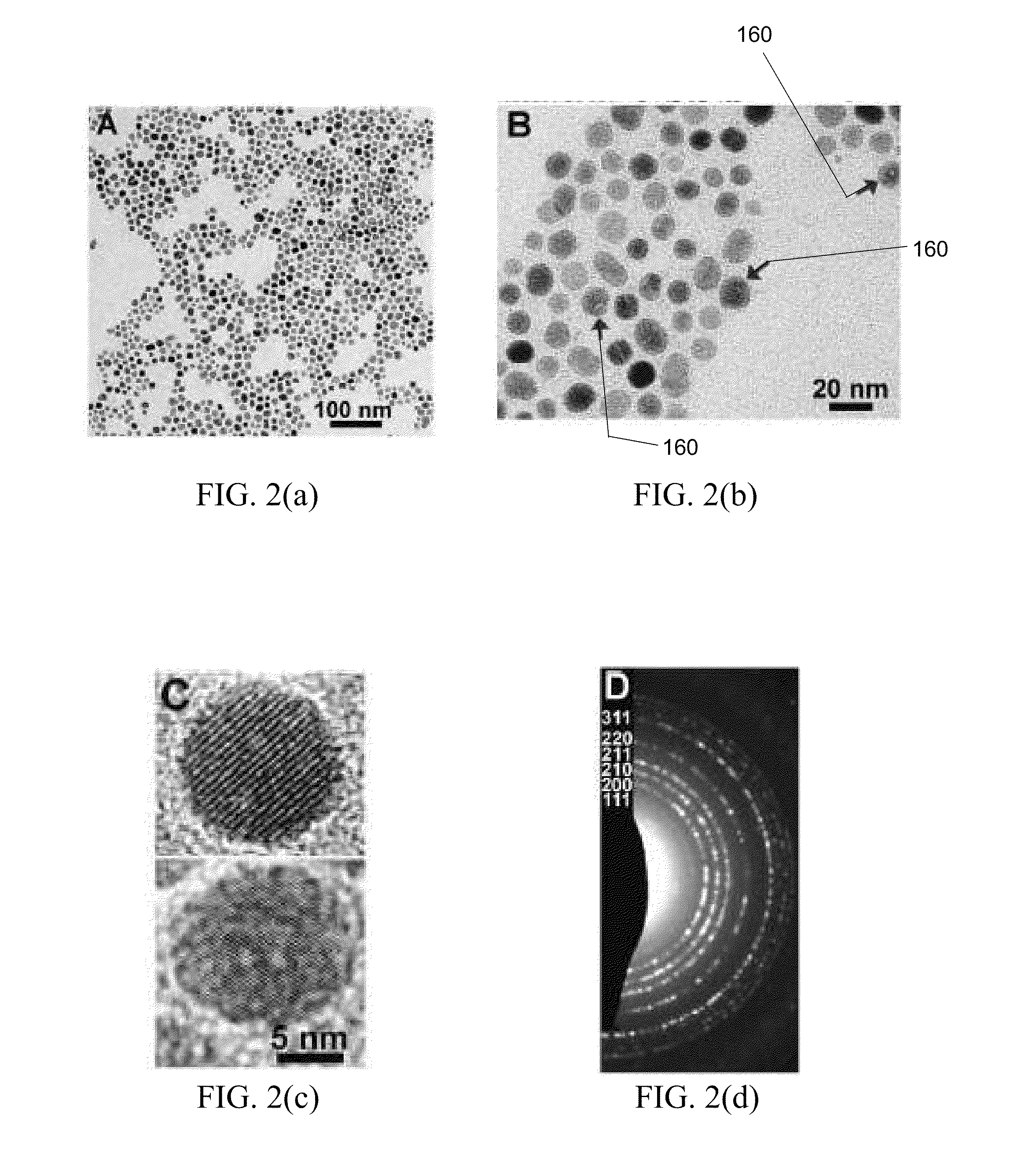
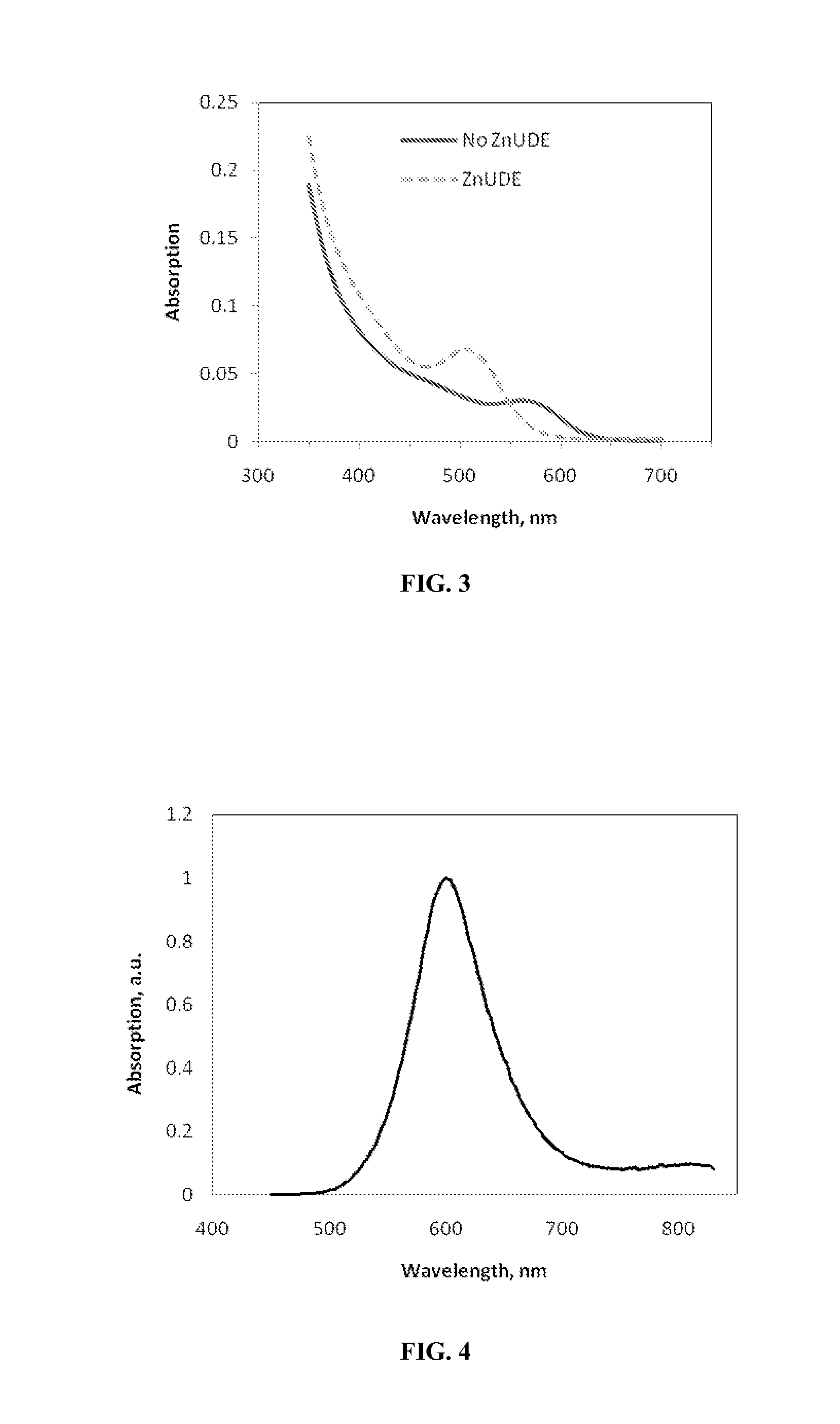
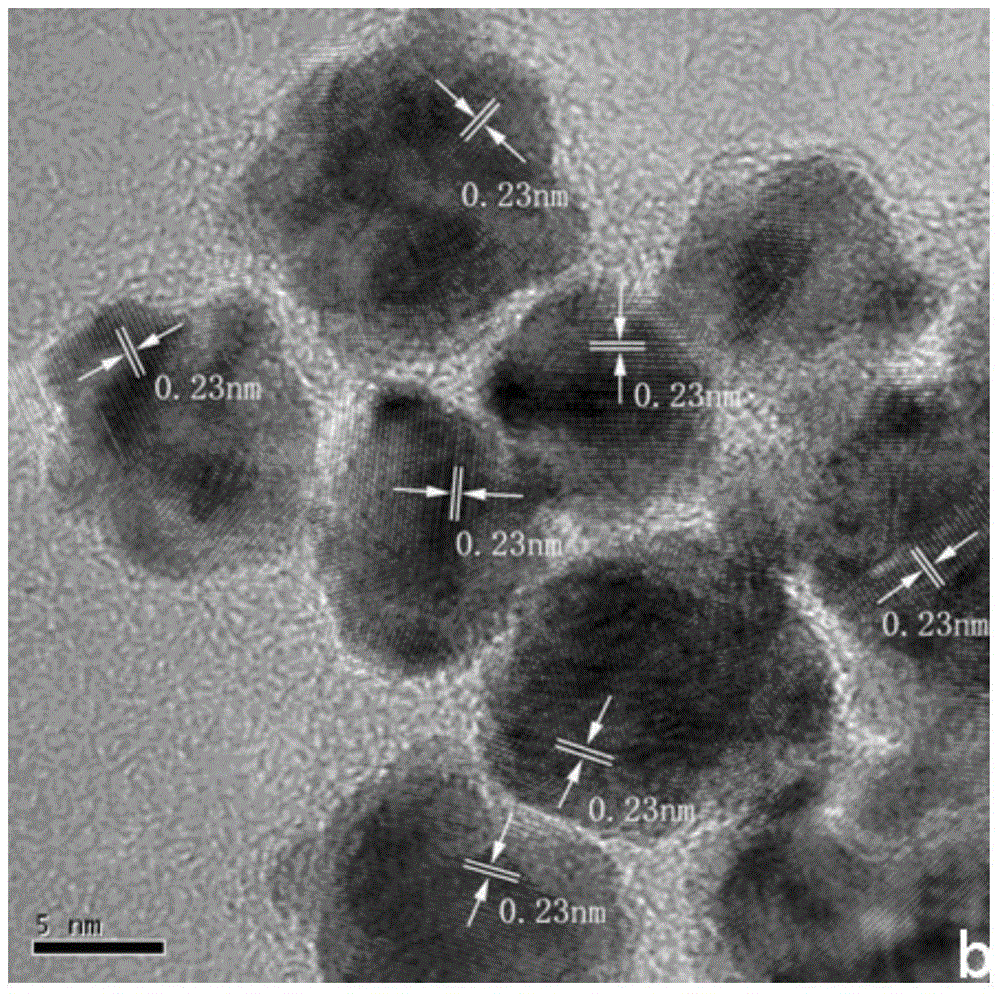
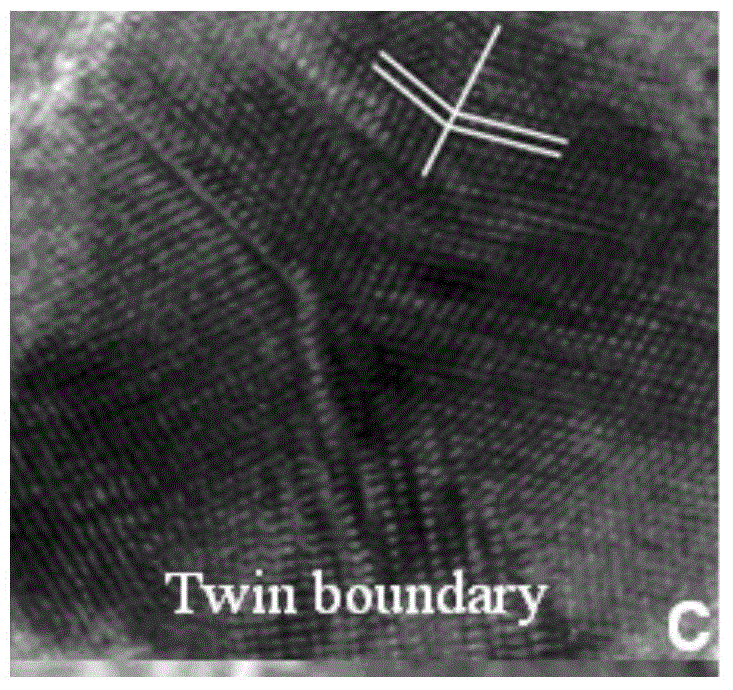
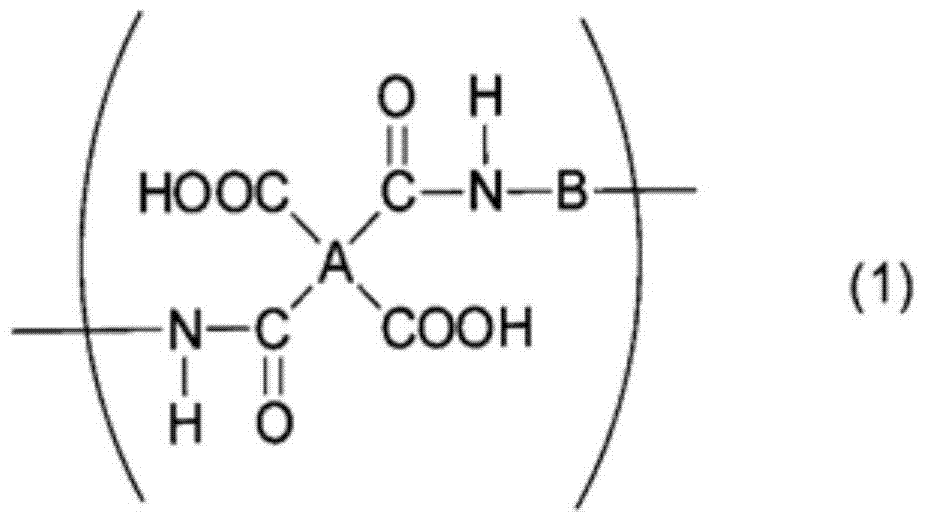
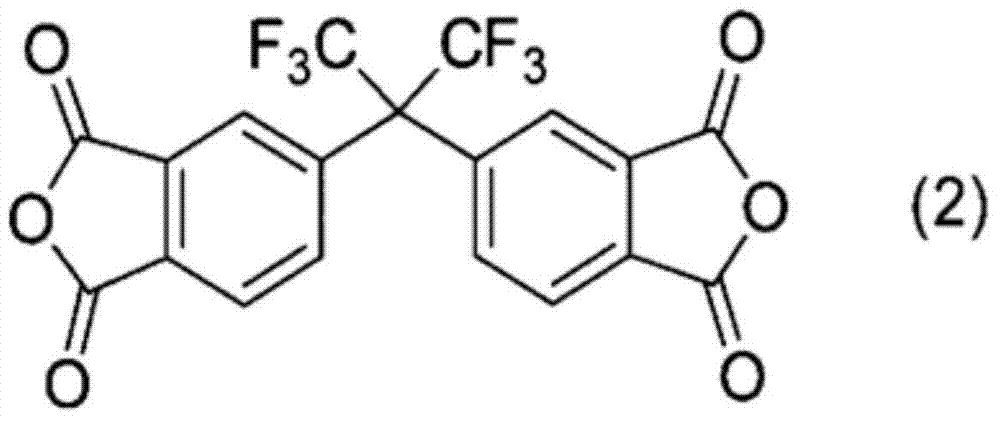
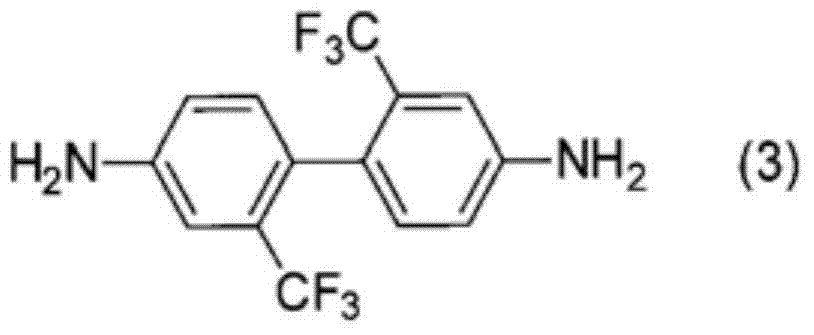
Patents
Literature
124 results about "Colloidal iron" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Colloidal iron is an organic form of iron that can combine with other naturally occurring organic materials such as humic acids (tannins). Colloidal iron and will require strong oxidation, usually by injection of chlorine, ozone or hydrogen peroxide followed by filtration (The Iron Max) to remove the oxidized iron.
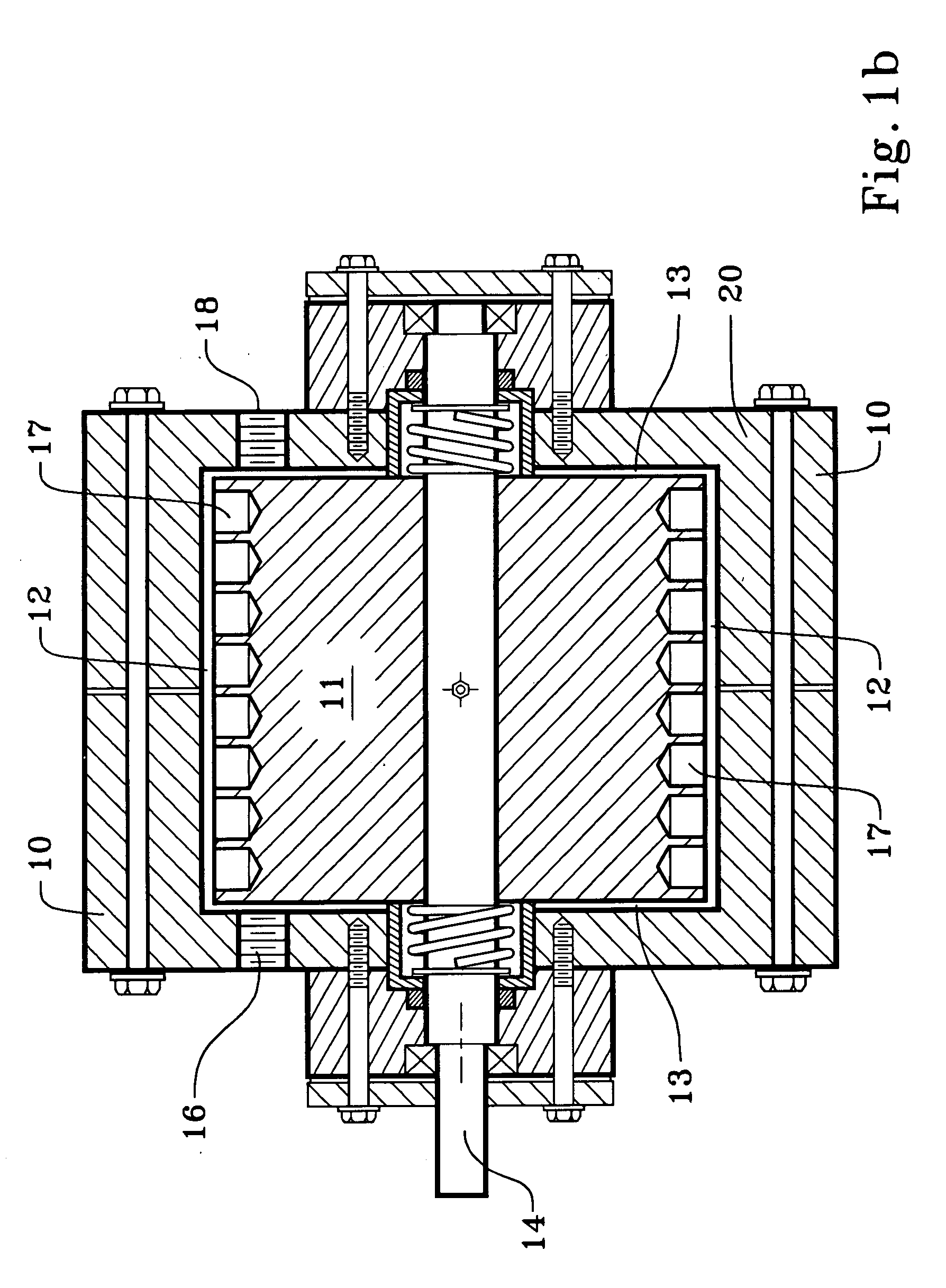
Method for preparing loading type nano Pd/C catalyst from colloidal solution
InactiveCN1966144AAvoid organic pollutionReduce manufacturing costCatalyst carriersNanostructure manufacturePalladium catalystChemical reduction
The invention relates to a method for using colloid solution to prepare carrier nanometer Pd / C catalyst, wherein said method comprises that using chemical reduction to process palladium salt to prepare the nanometer palladium colloid solution with stable surface activity, then using some carrier to absorb it to obtain the palladium colloid, to obtain the nanometer palladium catalyst with different loaded amounts. The inventive catalyst can be used in hydrogenation.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method To Synthesize Colloidal Iron Pyrite (FeS2) Nanocrystals And Fabricate Iron Pyrite Thin Film Solar Cells
InactiveUS20110240108A1Excellent manufacturing scalabilityLow costMaterial nanotechnologySulfur compoundsHeterojunctionMetal foil
Systems and methods are provided for the fabrication and manufacture of efficient, low-cost p-n heterojunction pyrite solar cells. The p-n heterojunction pyrite solar cells can include a pyrite thin cell component, a window layer component, and a top surface contact component. The pyrite thin cell component can be fabricated from nanocrystal paint deposited onto metal foils or microcrystalline pyrite deposited onto foil by chemical vapor deposition. A method of synthesizing colloidal pyrite nanocrystals is provided. Methods of manufacturing the efficient, low-cost p-n heterojunction pyrite solar cells are also provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Indium phosphide colloidal nanocrystals
InactiveUS20120205586A1High crystallinityNarrow size distributionPolycrystalline material growthLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor nanocrystalsSolvent
A method of making a colloidal solution of indium phosphide semiconductor nanocrystals, includes forming a first solution by combining solvents and ligands; and heating the first solution to a temperature equal to or higher than 290° C. and, while heating, adding to the first solution, a second solution containing trialkylindium, a phosphorus precursor and solvents and ligands so that a reaction takes place that forms a colloidal solution of indium phosphide semiconductor nanocrystals. The method further includes forming core shell indium phosphide semiconductor nanocrystals by forming semiconducting shells on the nanocrystals.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Nano compound oxide preparation method
ActiveCN1865151ALarge particle sizeHigh yieldCatalyst carriersCatalyst activation/preparationMolten saltNanometre
This invention discloses a method for producing nanometer composite oxides. The procedures comprise: solubilise the molten substance in the mixture of hydrocarbon component and surfactantto form the molten salt-in-oil super solubilising colloidal group, which limits the hydroxide generated by the reaction of molten substance and precipitant in the colloidal group, so as to avoid the increase of particle size, and then obtain the nanometer composite oxides by burning.This invention is characterized of low cost of surfactant and hydrocarbon component, single distributed colloidal groups, narrow particle size distribution range and high yield. Besides, the process is simple and is adapted for industrial mass production. The nanometer composite oxide produced by this invention has large specific surface area and pore size, which makes it suitable for being used as catalyst carrier.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Ultra-dispersed nanocarbon and method for preparing the same
Ultradispersed ones of primary particles of nanometer-sized carbon are obtained by applying a wet-type milling method and / or a wet dispersion method to an aggregate structure of the primary particles to overcome van der Waals forces, by which forces the primary particles are held together to form the aggregate structure, whereby the ultradispersed primary particles are obtained in a colloidal dispersion on a large-scale basis at low cost without using any additive. In a method of manufacturing the ultradispersed primary particles, the wet-type milling method is carried out in a ball mill, preferably in combination with a high-energy ultrasonic-wave process carried out in a dispersing medium such as pure water, whereby a colloidal solution or slurry with a low-concentration of the primary particles ultradispersed in the dispersing medium is obtained.
Owner:FUTABA CORPORATION +2
Preparation method of biomass-based colloidal carbon
The invention discloses a preparation method of biomass-based colloidal carbon and in particular relates to a colloidal carbon ball using xylose or glucose as a precursor. The colloidal carbon ball is prepared by hydrolyzing biomass by using dilute acid or concentrated acid respectively to obtain saccharic acid solution of xylose and glucose and performing in-situ polycondensation and carbonization on the saccharic acid solution. The preparation method particular comprises the following steps of: hydrolyzing the biomass by using dilute acid at a certain concentration; filtering to obtain xylosic acid solution and filter residues; adjusting the concentration of the saccharic acid solution and performing polycondensation and carbonization to prepare the colloidal carbon ball with grain size of 160 to 1,800 nm; performing alkali boiling on the residues to remove lignin; performing hydrolysis reaction on the residues and the concentrated sulfuric acid; filtering to obtain acid solution of the glucose; and performing in-situ polycondensation and carbonization to prepare the colloidal carbon ball with grain size of 180 to 2,000 nm. The method for preparing the colloidal carbon from the biomass is a green production route of sustainable development.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparation method for one-size nano-particle fluorescence microsphere
InactiveCN101342472AAvoid adsorptionImprove uniformityMicroballoon preparationLuminescent compositionsSolubilityOil phase
The present invention provides a preparation method of an uniform-size nanoparticle fluorescent microsphere. The density of fluorescent nanoparticle colloidal aqueous solution of the microsphere is adjusted to the micro-mol level so as to obtain the colloidal solution evenly scattered in the aqueous solution; the evenly scattered colloidal solution in the aqueous solution is injected into oil-phase solvent through capillary at the speed of 0.5 to 1.25 percent Vs / min so as to form droplets and Vs is the volume of the oil-phase solvent; the oil-phase solvent adopts bi- or multi-mixture with the solubility between 2 to 10 percent and the density equal to the density of water; containers and reflux pipes adopt the hydrophobic material; the water in droplets is absorbed by the oil phase and the nanoparticles form a dense sphere; an absorbent continuously absorbs the water dissolved in the oil phase, so that the water content in the oil phase is far lower than the saturation; the nanoparticle polymer with the size from dozens of nano to hundreds of nano, the spherical height higher than 5 percent and the size error less than 10 percent is obtained through regulating the density of the quantum pot colloidal solution and the velocity of the reflux pipe.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method of removing dissolved iron in aqueous systems
InactiveUS20090184056A1Rapidly decompose peroxideIncrease oxidation rateTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersActivated carbonCavitation
Oilfield completion, drilling, produced, flowback, and workover fluids containing iron are treated to remove the iron by passing them through a cavitation device together with an oxidizing agent and with the addition of lime. The cavitation device intimately mixes the oxidizing agent with the fluid while increasing the temperature of the fluid, thus promoting the oxidation reaction. Lime contributes to an increase in pH while promoting the formation of floc. Ferric hydrate and other solids or colloidal iron are removed in a filter capable of removing particles as small as 0.5 micron. The system may be enhanced by the addition of a bed of activated carbon capable of catalyzing the oxidation reaction.
Owner:TOTAL SEPARATION SOLUTIONS
Immuno-chromatography kit for quickly and quantitatively detecting calprotectin in excrement
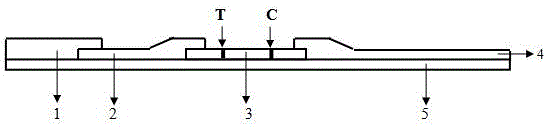
The invention provides an immuno-chromatography kit for quickly and quantitatively detecting calprotectin in excrement and belongs to the technical field of clinical in-vitro diagnosis reagents. The kit includes: a test strip, which includes a substrate, and a sample pad, a marker combination pad, a nitrocellulose membrane and a water absorption pad which are all arranged on the substrate. The marker combination pad is coated with a calprotectin monoclonal antibody A marked by colloidal gold particles, colloidal silver particles, colloidal iron particles, magnetic particles, fuel particles, latex particles or fluorescent particles. The nitrocellulose membrane contains a detection line T and a quality control line C, wherein the detection line T is formed by a calprotectin monoclonal antibody B, and the quality control line C is formed by goat-anti-mouse IgG. The calprotectin monoclonal antibody A and the calprotectin monoclonal antibody B respectively recognize different epitopes of the calprotectin. The kit is convenient and quick, is simple in operation, has accurate result and is suitable for clinical quick detection.
Owner:江苏奥的特生物技术有限公司
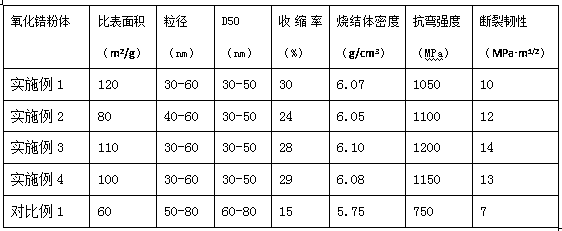
Preparation method of nanometer yttrium stabilized zirconia powder
ActiveCN107628643AHigh sintering shrinkageHigh sintered body densityNanotechnologyZirconium oxidesEthylenediamineMass ratio
The invention discloses a preparation method of nanometer yttrium stabilized zirconia powder. The preparation method comprises mixing zirconium oxychloride, yttrium oxide and deionized water accordingto a mass ratio of (50-60): (0.8-1): (10-12), heating the mixture to 90-110 DEG C, carrying out heat preservation for 1-3h, adding plant gum into the mixture, then adding at least one of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid or citric acid into the mixture, carrying out stirring for 3-5h to obtain a colloidal solution, adding an ammonia solution into the colloidal solution along with stirring for 8-10huntil pH of 10.0-11.0 so that white precipitates are produced, standing the white precipitates for aging for 24-48h, washing and filtering the precipitates, carrying out spray drying and fluid energymilling to obtain precursor powder, and calcining the precursor powder at 450-600 DEG C for 5-7h to obtain the nanometer yttrium stabilized zirconia powder. The zirconia powder has a high sintering shrinkage rate, high sintering density, good strength, good performances, small particle size and narrow distribution.
Owner:汉中市恒宝锆业科技有限责任公司
Medical device for short time use with quickly releasable antibacterial agent
InactiveUS20110152843A1Easy to controlReduce decreaseGlovesSurgeryHydrophilic polymersAntibacterial activity
A method is disclosed for providing a medical device with antibacterial activity, comprising the steps of providing a substrate material coated with a hydrophilic polymer, said hydrophilic polymer exhibiting a low friction when wetted; providing a colloidal solution comprising chemically reduced particles of an oligodynamic metal and a hydrophilic polymer, said hydrophilic polymer being the same as in the coating of the substrate material; and dipping said substrate material in the solution. A medical device prepared accordingly is also disclosed.By means of this method, very advantageous properties of the antibacterial coating are obtained. In particular, a relatively low release rate is obtained in the wetting fluid, and a relatively high release rate is obtained in the intended use situation, e.g. when inserted into the urethra.
Owner:ASTRA TECH SE
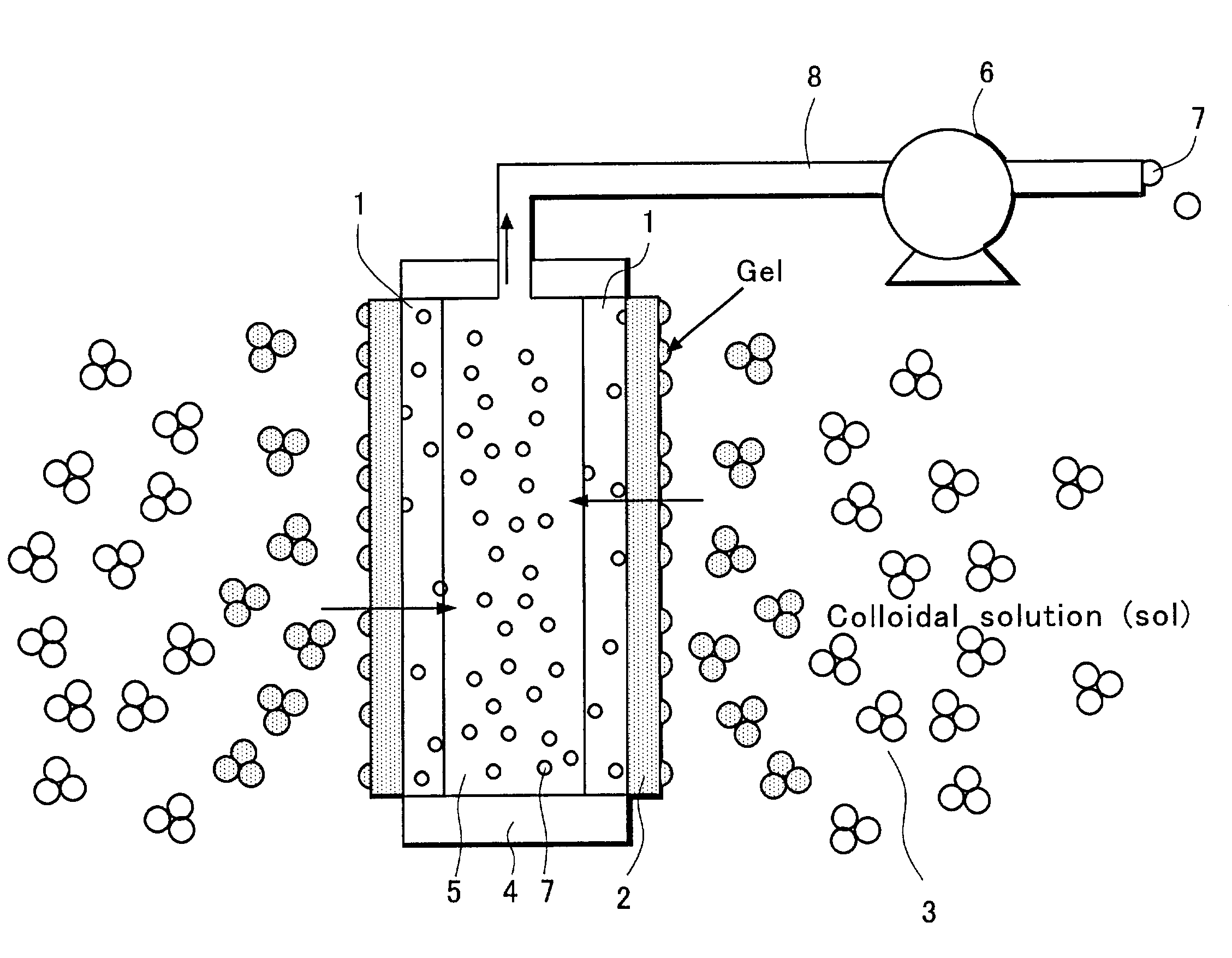
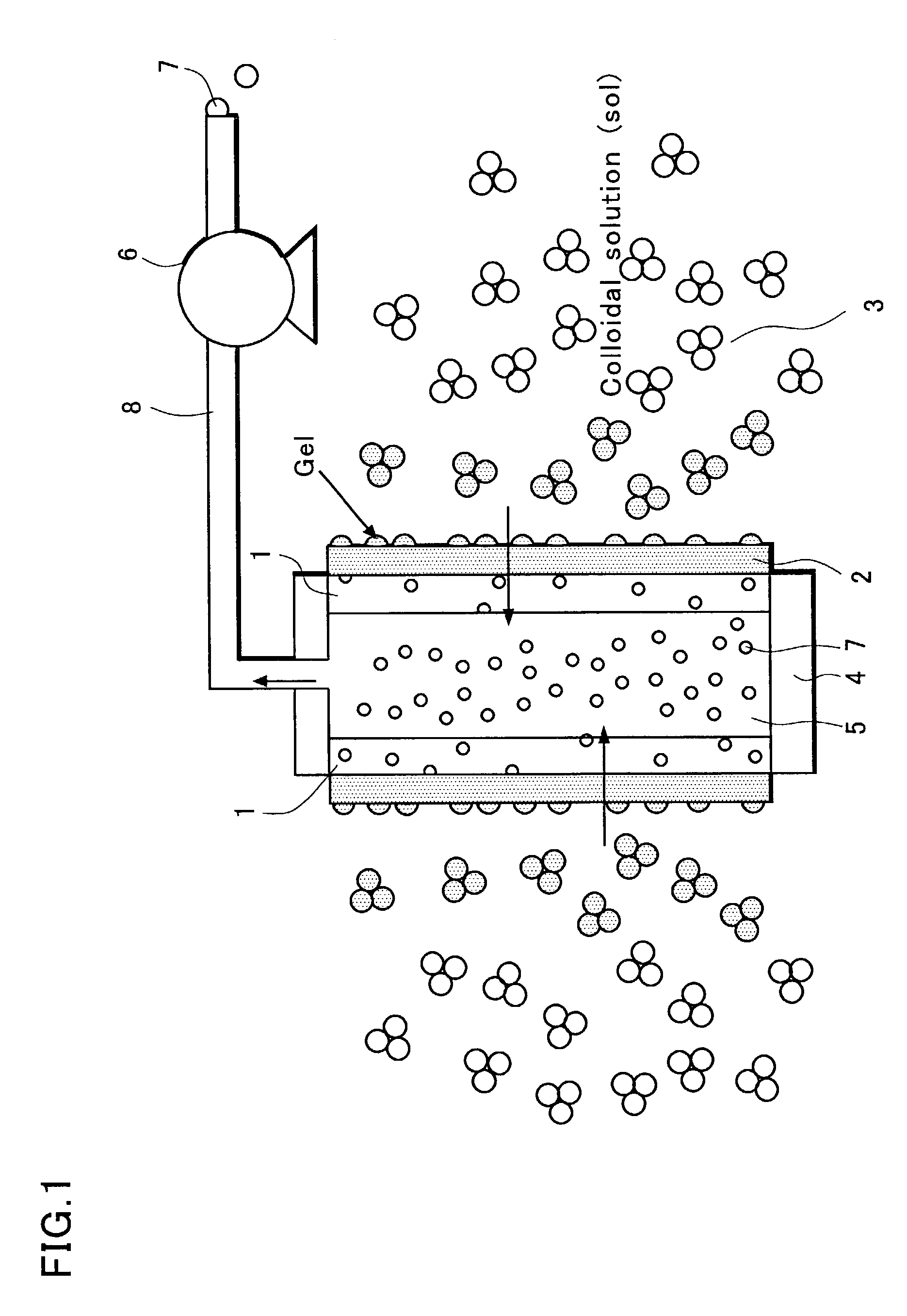
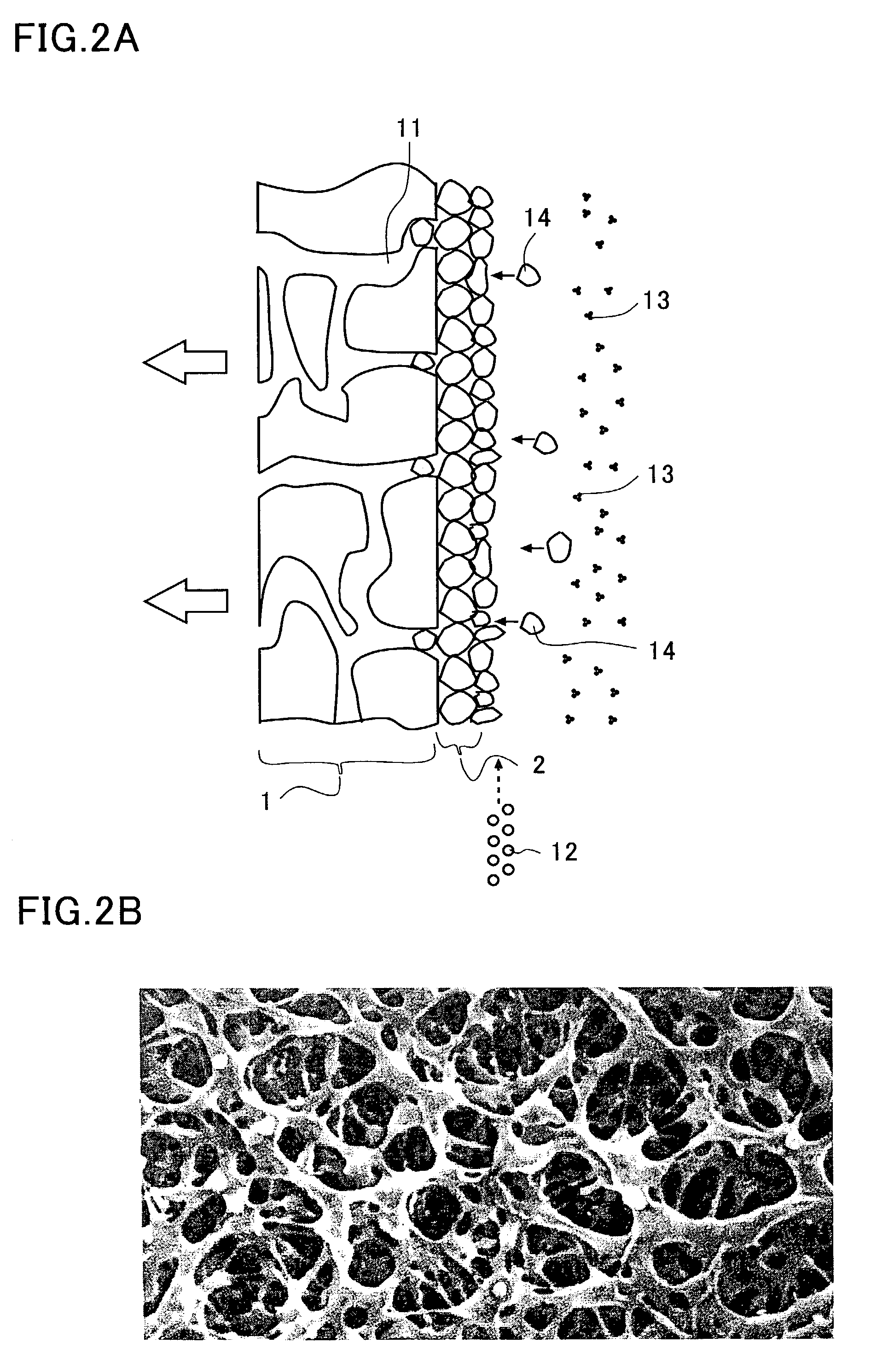
Filtering method of a colloidal solution
InactiveUS7014770B2Fast loadingDifficult to processUltrafiltrationSolid sorbent liquid separationWastewaterFilter methods
A filtering method is directed to a wastewater of CMP process, which includes sub-micrometer particles suspended as colloid. The wastewater is filtered by a gel membrane formed on a surface of plastic filter. A coagulant or a pH adjuster is added to the wastewater so that the sub-micrometer particles are coagulated to form the gel membrane.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for coloring ceramics via colloidal dispersion
ActiveUS9365459B2Maintain colloidal stabilityFacilitate homogenous solutionImpression capsDentistry preparationsOrganic solventSlurry
Coloring in a slip casting process by which a ceramic slurry is cast into green state bodies. It is during this slip casting that a coloring solution consisting of metallic salts is introduced to the slurry and subsequently slip-cast. A coloring solution may comprise for example a metallic salt, a solvent, an organic solvent such as derivatives of propylene oxides, and an acid can be introduced to the slip casting process. Such a coloring solution can be added to the slip casting process. The solution is thoroughly mixed with the ceramic slurry, after which the ceramic body is cast, dried and finally subjected to a sintering process. After final sinter, the resulting ceramic body possesses an innate color that is homogenous throughout its composition. The method is especially useful for coloring zirconia dental restorations.
Owner:JAMES R GLIDEWELL DENTAL CERAMICS
Method for manufacturing coloring ceramics via colloidal dispersion followed by conventional pressing techniques
ActiveUS9512317B2Maintain colloidal stabilityFacilitate homogenous solutionPigmenting treatmentImpression capsOrganic solventSlurry
A colored ceramic powder is produced from a mixture of coloring solutions consisting of metallic salts that are introduced to a ceramic slurry and subsequently dried. The coloring solution may comprise for example of chosen metallic salts, a solvent, an organic solvent such as derivatives of propylene oxides, an acid and a possible binder. Once all the constituents are thoroughly mixed to a homogeneous state, the slip is dried to a powder form, which spray drying equipment can be used. The dried powder can then be subjected to an isostatic or biaxial press manufacturing process to create a green state ceramic body. Once pressed, the ceramic body can be subjected to a sintering process. After final sinter, the resulting ceramic body possesses an innate color that is homogenous throughout its composition. The method is especially useful for coloring zirconia dental restorations.
Owner:JAMES R GLIDEWELL DENTAL CERAMICS
Preparation method of coppor cerium catalyst coated on FeCrAl carrior
InactiveCN1830566AStrong adhesionNot easy to fall offCatalyst carriersCatalyst activation/preparationCerium nitrateMixed oxide
A process for preparing the CuCe / FeCrAl catalyst includes such steps as washing FeCrAl carrier with acetone, oxidizing, immersing it in gamma-Al2O3 sol, drying, calcining, quickly putting it in the colloidal solution prepared from copper nitrate, cerium nitrate and citric acid, and calcining.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Composite antisludging agent of reverse osmosis/nanofiltration system
ActiveCN103007768AImprove work efficiencyExtended cleaning cycleSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisColloidal silicaUltrafiltration
The invention provides a composite antisludging agent of a reverse osmosis / nanofiltration system. The composite antisludging agent comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 2%-10% of cyclodextrin solution, namely a component I, 80%-90% of at least one or a mixture of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP), a copolymer of maleic anhydride-acrylic acid (MA-AA), 2-phosphonic acid butane-1, 2,4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTCA), and hydroxyl ethylidene diphosphonic acid (HEDP), namely a component II, and 1%-10% of 2,2-dibromo-2-cyano-acetamid (DBNPA), namely a component III. The composite antisludging agent is prepared by mixing the component II and the component III, and then fusing the obtained mixture with the component I. When being applied to the reverse osmosis / nanofiltration / ultrafiltration system, the composite antisludging agent can be used for effectively relieving the pollution to the reverse osmosis / nanofiltration / ultrafiltration system caused by polcard, calcium sulphate salt, barium sulfate, strontium sulfate, calcium fluoride, colloidal iron and colloidal silica, relieving biological contamination simultaneously, improving the working efficiency of the system, prolonging the cleaning period and the service life of the reverse osmosis / nanofiltration / ultrafiltration system, and reducing the cost of reverse osmosis.
Owner:辽宁莱特莱德环境工程有限公司
Method of removing dissolved iron in aqueous systems
InactiveUS20090183922A1Rapidly decompose peroxideIncrease oxidation rateWaste water treatment from quariesWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsActivated carbonCavitation
Oilfield completion, drilling and workover fluids containing iron are treated to remove the iron by passing them through a cavitation device together with an oxidizing agent. The cavitation device intimately mixes the oxidizing agent with the fluid while increasing the temperature of the fluid, thus promoting the oxidation reaction. Ferric hydrate and other solids or colloidal iron are removed in a filter capable of removing particles as small as 0.5 micron. The system may be enhanced by the addition of a bed of activated carbon capable of catalyzing the oxidation reaction.
Owner:TOTAL SEPARATION SOLUTIONS
Preparation process for nano zirconia powder
InactiveCN103588246AEasy to operateReduction procedureMaterial nanotechnologyZirconium oxidesAqueous solutionAzeotropic distillation
The invention relates to a preparation process for nano zirconia powder. The preparation process comprises the steps of adding an alkaline precipitating agent in a zircon salt-containing aqueous solution to obtain a hydroxide precipitate; and then filtering, washing, dehydrating, drying and sintering to obtain zirconia powder. A colloidal solution obtained by dehydration with an azeotropic distillation method is dried in a distillation apparatus; and the colloidal solution is continuously stirred during dehydration and drying. The preparation process has the advantages of short reaction time, few procedures, large production capacity and high security, is suitable for large-scale production and can greatly reduce production cost.
Owner:NANNING DINGFA POWDER METALLURGY
Nano transitional metallic oxide preparation method
This invention discloses a method for producing nanometer transition metal oxide. The procedures comprise: solubilise the melting transition metal salt in the mixture of hydrocarbon component and surfactantto form the molten salt-in-oil super solubilising colloidal group, which limits the transition metal hydroxide generated by the reaction of molten salt and precipitant in the colloidal group, so as to avoid the increase of particle size and narrow the particle size distribution range. and then obtain the nanometer transition metal oxide by cleaning, drying and burning. This invention is characterized of high yield and purity,with low cost of surfactant and hydrocarbon component. Besides, the process is simple and is adapted for industrial mass production.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
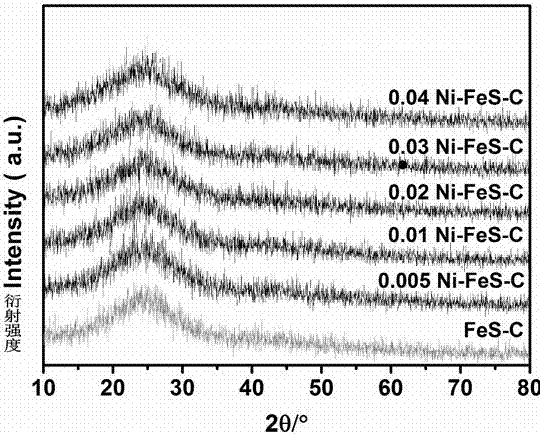
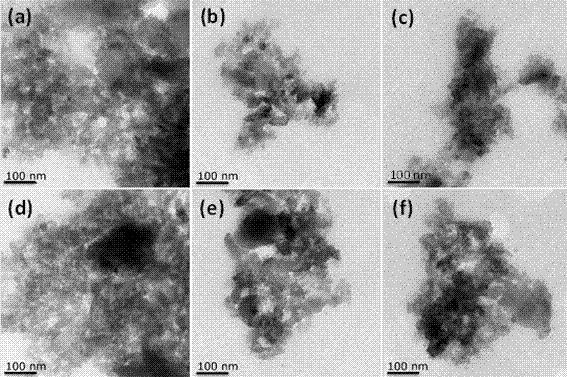
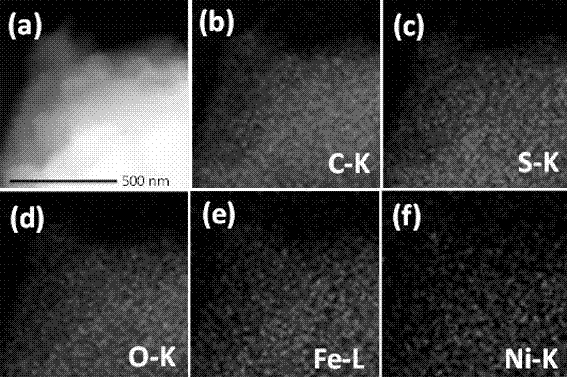
Preparation method of coating type nickel-doped ferrous sulfide/carbon composite electrode
ActiveCN107460496AImprove electrochemical performanceImprove stabilityPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesCarbon compositesDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrochemistry and relates to a preparation method of a coating type ferrous sulfide / carbon composite, in particular to a preparation method of a coating type nickel-doped ferrous sulfide / carbon composite electrode. The preparation method comprises the steps that firstly, a tannic acid aqueous solution and a ferric nitrate aqueous solution are respectively prepared, and the ferric nitrate aqueous solution is dropwise added to the tannic acid aqueous solution under the condition of stirring at the normal temperature, so that a colloidal solution is formed; secondly, hydrazine hydrate is added to a nickel chloride hexahydrate aqueous solution, and the obtained mixed solution is dropwise added to the colloidal solution and evenly mixed with the colloidal solution; a substrate material is soaked in the mixed system to obtain a precursor, after being taken out, the precursor together with sulfur powder is calcinated in the inert gas shielding atmosphere for 0.5-2 h, and the coating type nickel-doped ferrous sulfide / carbon composite electrode is obtained after cooling. By the adoption of the preparation method of the coating type nickel-doped ferrous sulfide / carbon composite electrode, operation is simple and easy to conduct, multiple kinds of substrates can be coated, the reaction time is short, and industrialization is easy; the prepared composite electrode has good electrochemical performance and stability, raw materials are at a low price, easy to obtain and free of toxicity, the prepared composite electrode can be directly used as the electrode for an electro-catalytic water decomposition oxygen evolution reaction; and when the current density is 10 mA.cm<-2>, the overpotential reaches 320 mV, and the Tafel slope is 43 mV.dec<-1>.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
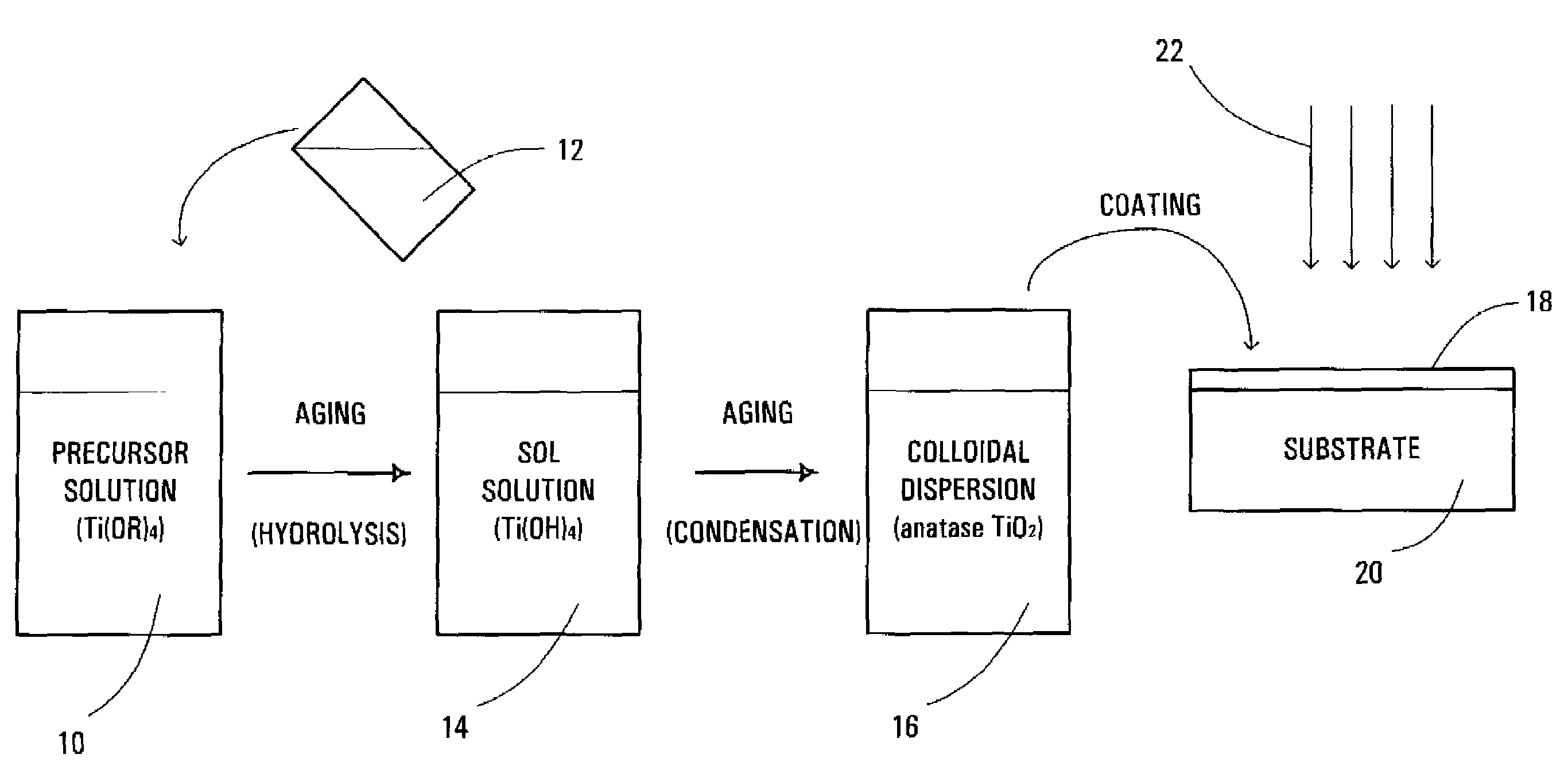
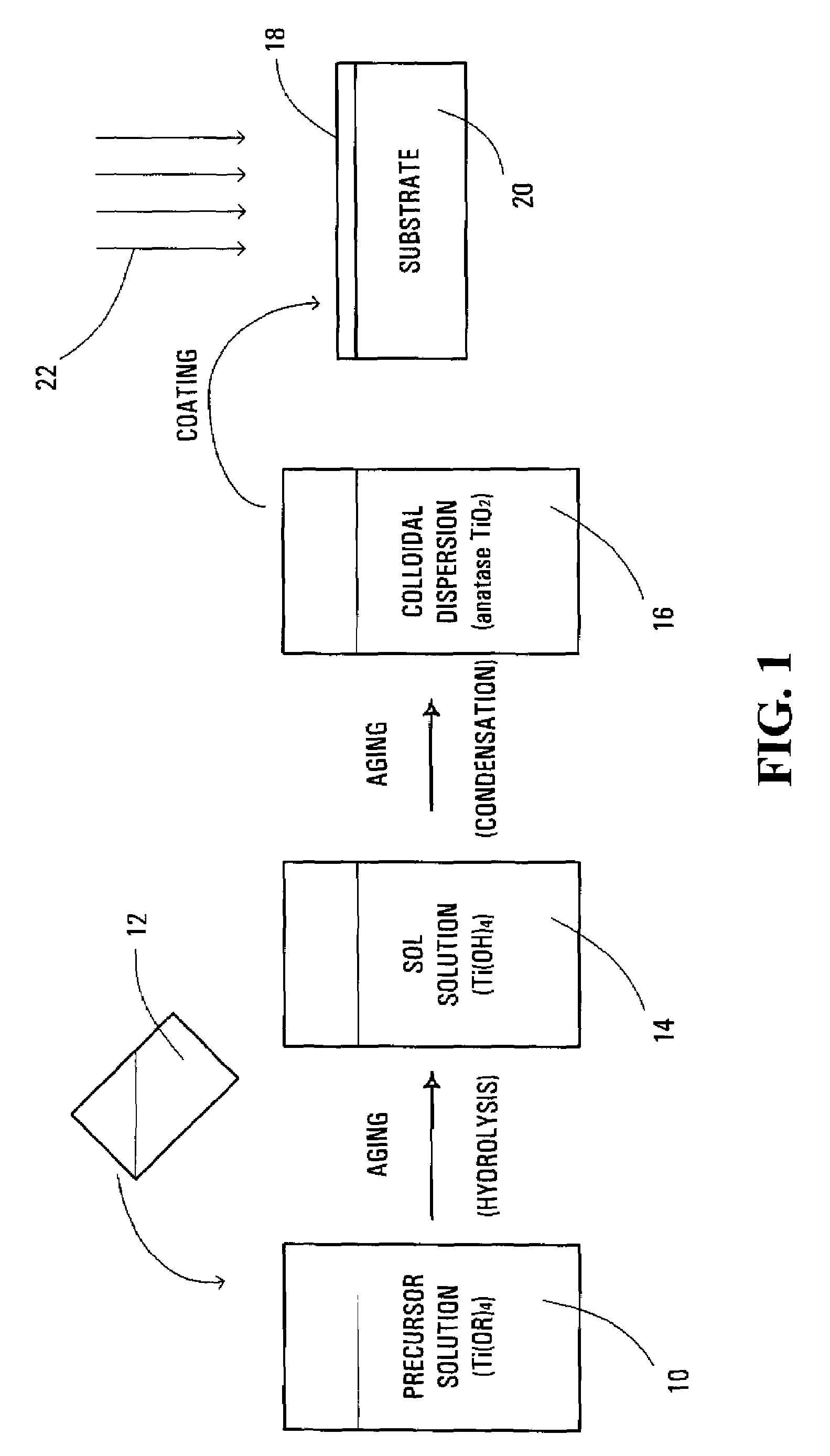
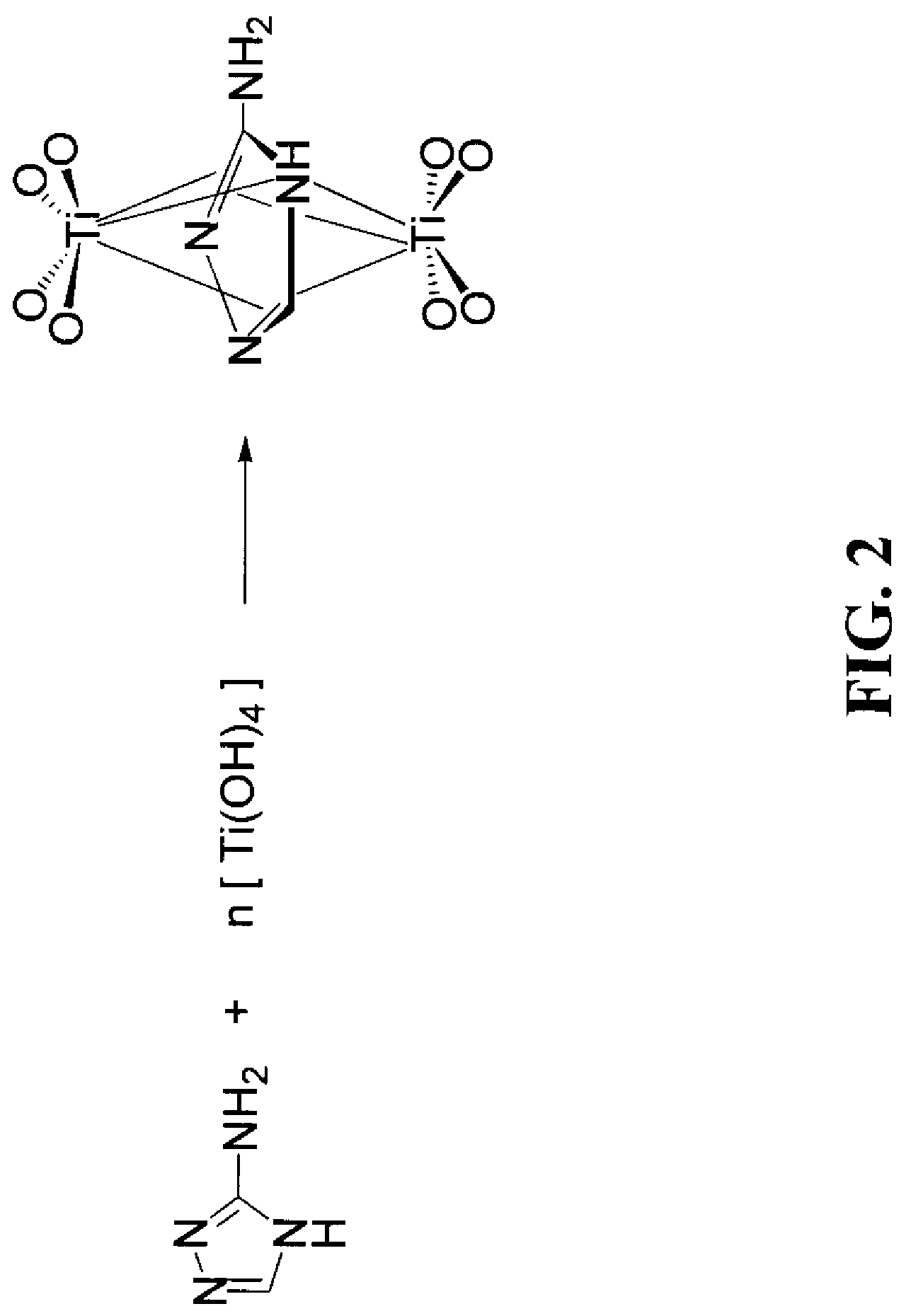
Method and solution for forming anatase titanium dioxide, and titanium dioxide particles, colloidal dispersion and film
InactiveUS7534293B2Improved propertyAccelerated agingOther chemical processesWater-repelling agents additionOrganic acidTitanium chloride
A sol solution containing poly(titanic acid) and a planar heterocyclic ligand is provided. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) particles are formed by aging the sol solution at a temperature below about 140° C. The particles have multi-coordinated Ti-complexes comprising the heterocyclic ligand and can be substantially in the anatase phase. The heterocyclic ligands can be triazole, tetrazole, or thiadiazole. The sol solution may be prepared by aging a precursor solution. The precursor solution may contain the heterocyclic ligands and a precursor for poly(titanic acid). The precursor may be titanium alkoxide or titanium chloride. The sol solution may also contain at least one of an organic acid, a base, and a surfactant. The aged sol solution may form a colloidal dispersion of the TiO2 particles. A photo-catalytic and transparent film may be formed from the TiO2 particles by depositing a layer of the colloidal dispersion on a support.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
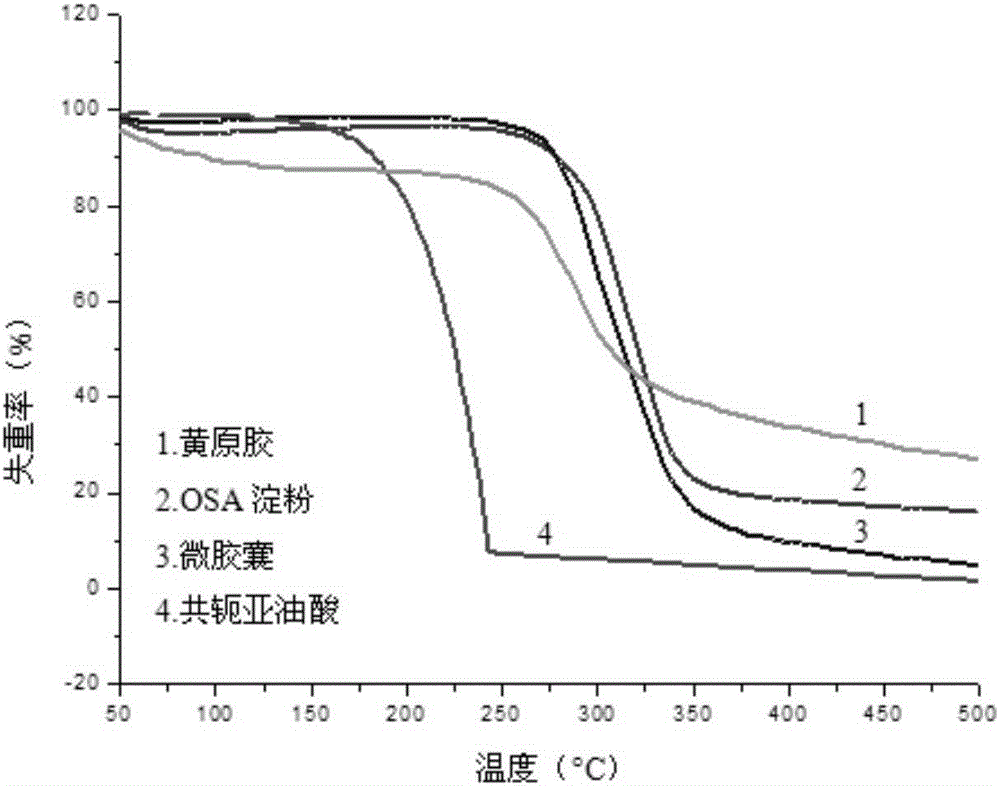
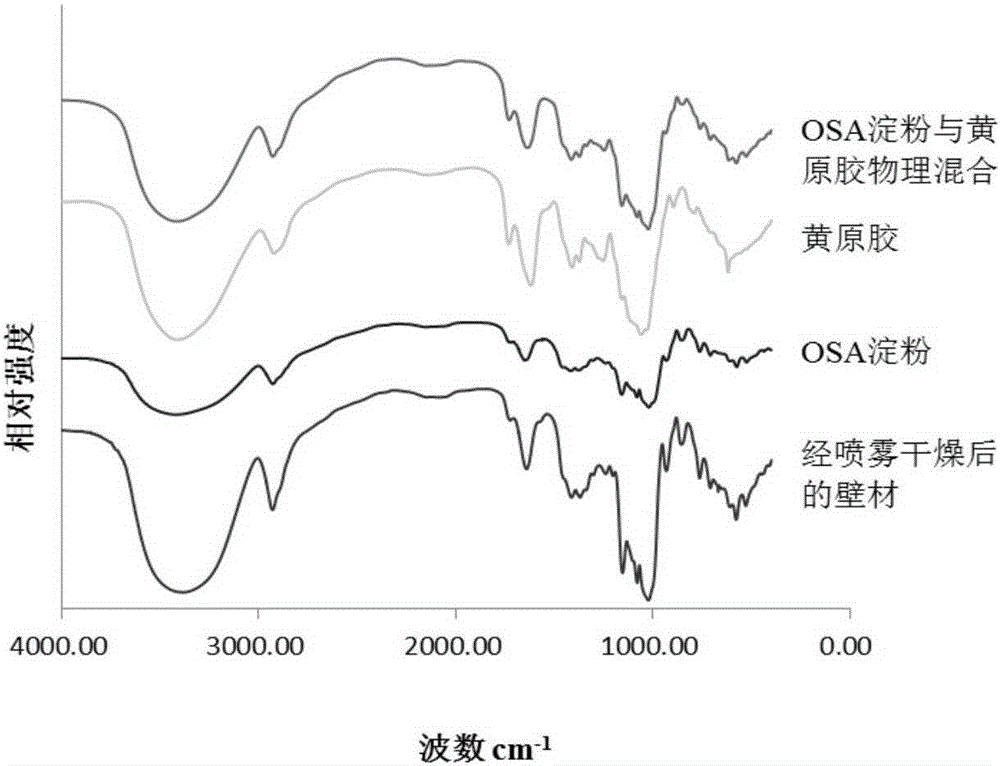
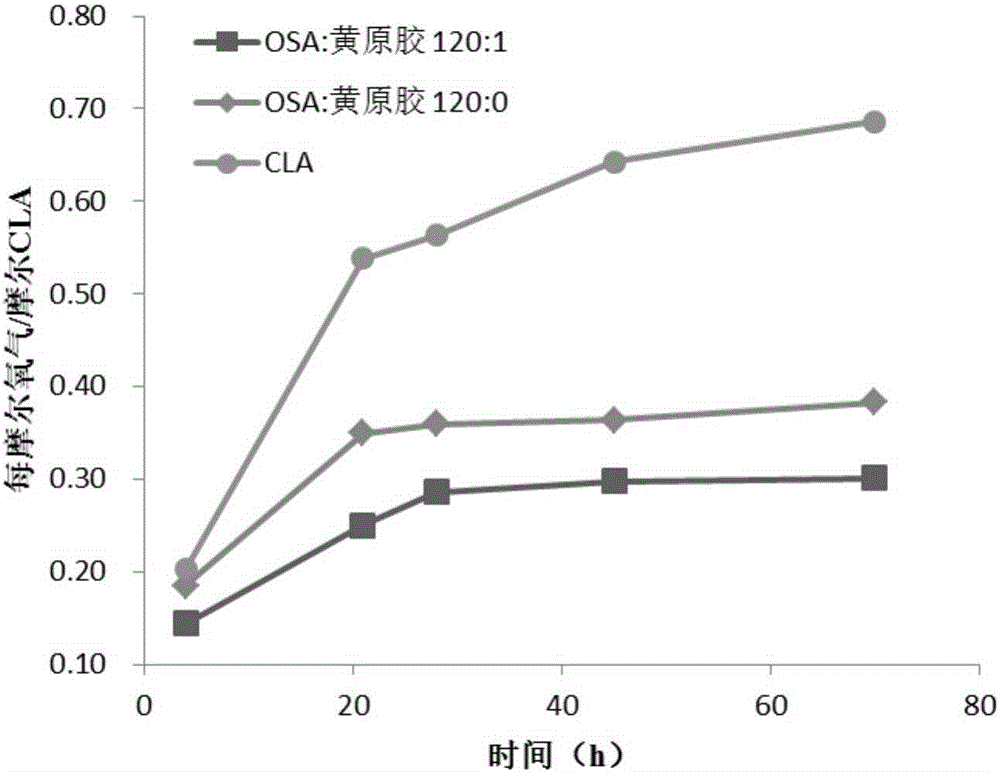
Conjugated linoleic acid embedded microcapsule preparation method
InactiveCN105166885APromote digestionImprove emulsion stabilityFood ingredient functionsFood preparationEmulsionOCTENYLSUCCINIC ACID
The present invention discloses a conjugated linoleic acid embedded microcapsule preparation method which uses octenyl succinic anhydride starch esters and hydrophilic colloids as main raw materials and comprises the following specific steps: firstly, the hydrophilic colloids are uniformly dispersed in water to be prepared into a colloidal solution; then the octenyl succinic anhydride starch esters are added into the colloidal solution to prepare a compound solution of the octenyl succinic anhydride starch esters and the hydrophilic colloids; then conjugated linoleic acids are added into the compound solution to prepare an emulsion; and finally the emulsion is subjected to spray drying to prepare the embedded conjugated linoleic acid microcapsules. The method provides a novel embedding wall material, which improves the oxidative stability of the conjugated linoleic acids, and has a slow-release function, and thus solves the problems that the conjugated linoleic acids are easy for auto-oxidation and low in physiological activity before entering into human body small intestines, and the microcapsule can be used as a nutritional fortifier to be added into functionally and nutritionally fortified food and staple food.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Structured liquid compositions comprising colloidal dispersions of poly alpha-1,3-glucan
Polysaccharides can be used to provide a liquid composition with desirable rheological properties while being compatible with other ingredients, such as enzymes, that may be used in formulating the liquid composition. The polysaccharides can be i) a colloidal dispersion of poly alpha-1,3-glucan, ii) poly alpha-1,3-glucan fibrids, iii) soy polysaccharide; or iv) a combination thereof.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 4 INC +1
Preparation method of graphene quantum dots
The invention relates to a preparation method of graphene quantum dots. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking zinc oxide adopting a hexagonal crystal structure and having the grain diameter of 5 nm to 30 nm as a seed crystal nucleus; adding single-layer graphene oxide into solvent to prepare graphene oxide dispersion liquid, adding zinc oxide adopting a hexagonal crystal structure, then adding a stabilizer, and uniformly dispersing to obtain a colloidal solution; performing hydrothermal reaction on the colloidal solution for 0.5 h to 2 h at 160 DEG C to 300 DEG C to obtain turbid liquid containing graphene quantum dots; adding acid to the turbid liquid containing graphene quantum dots to clarify the turbid liquid containing graphene quantum dots, filtering, regulating the pH value of the filter liquor to be 7 to 8, stirring and filtering to obtain a solution containing graphene quantum dots; extracting the solution containing graphene quantum dots, and evaporating to remove an extractant so as to obtain graphene quantum dots. The method is relatively simple in technology and can be used for preparing graphene quantum dots which are narrower in size distribution.
Owner:湖北高地石墨烯科技有限公司
Au@AuPt alloy nanoparticles and preparation method of colloidal dispersion system
InactiveCN103600090ASimple preparation processReaction is easy to controlNanotechnologyReducing agentMaterials science
The invention discloses Au@AuPt alloy nanoparticles and a preparation method of a colloidal dispersion system, and particularly provides nanoparticles having a preparation method and a controllable reaction process and a preparation method of a colloidal dispersion system. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a system A: the system A contains a dispersion reagent, a gold precursor, a platinum precursor and a protective agent, wherein the protective agent is sodium di-n-octyl sulfosuccinate, the gold precursor is HAuCl4, NaAuCl4 or AuCl3, and the platinum precursor is H2PtCl6 or Na2PtCl6; at room temperature, adding a reducer A into the system A while stirring to reduce part of the gold precursor, adding a reducer B, and continuing stirring at room temperature until the reaction is complete, thereby obtaining the core-shell-structure Au@AuPt alloy nanoparticles, wherein the reducer A is ascorbic acid, and the reducer B is a hydrazine hydrate water solution; and adding ethanol or methanol into the reaction system, carrying out centrifugal settling, taking the precipitate, and washing the precipitate to obtain the core-shell-structure Au@AuPt alloy nanoparticle powder. The method has the advantages of simple preparation technique and low energy consumption.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
Polyamic acid solution composition and polyimide
ActiveCN104245845ASmall coefficient of linear expansionLow linear expansion coefficient controlExtraction purification/separationCoatingsColloidal silicaOrganic solvent
The present invention relates to a polyamic acid solution composition, which is obtained by reacting a tetracarboxylic acid component comprising at least 50 mol% of a fluorine atom-containing tetracarboxylic dianhydride and a diamine component comprising at least 50 mol% of a fluorine atom-containing diamine in a solvent and adding to the resulting polyamic acid solution a colloidal solution of colloidal silica dispersed in an organic solvent such that the amount of the silica is 1 to 100 parts by mass per a total of 100 parts by mass of the tetracarboxylic acid component and the diamine component.
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Catalyst application solution, electroless plating method using same, and direct plating method
ActiveUS20120171363A1Simple treatmentReducing treatmentPretreated surfacesAnti-corrosive paintsAntioxidantDisplacement reactions
Disclosed is a catalyst application solution for plating an insulating portion of an object to be plated that comprises the insulating portion. The catalyst application solution is characterized by containing a water-soluble palladium compound, a reducer, a dispersant, catechol, a copper antioxidant and a buffering agent, and by having a pH of not less than 4. When the catalyst application solution is compared with a Pd—Sn colloidal solution, the catalyst application solution has the following advantages: since the catalyst application solution is a colloidal solution of Pd only that does not contain Sn, a pre-dip process and an Sn removal process are unnecessary and thus the catalyst application process can be simplified; since the catalyst application solution has a pH of not less than 4, haloing does not occur; and since the catalyst application solution is in a reducing atmosphere due to the reducer contained therein, a copper surface is not oxidized and no copper dissolution occurs, thereby causing no palladium displacement reaction.
Owner:C UYEMURA & CO LTD
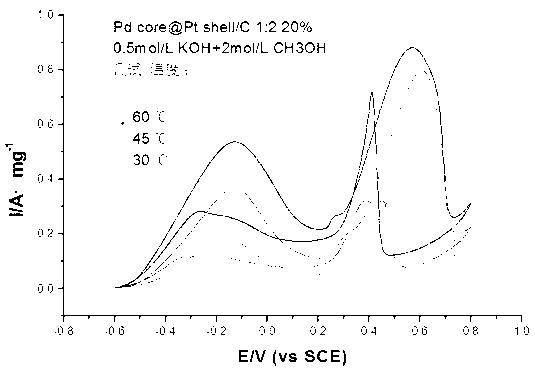
Photochemical preparation method for Pd core @Pt shell nanometer catalyst
InactiveCN102836707AThe size is easy to controlSimple preparation processCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNano catalystAqueous acetone
The invention provides a photochemical preparation method for a Pd core @Pt shell nanometer catalyst and relates to a preparation method for a catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking and mixing PdCl2 aqueous solution, polyethylene glycol and acetone aqueous solution, thereby obtaining a mixed solution a; taking and mixing H2PtCl6 aqueous solution, polyethylene glycol and acetone aqueous solution, thereby obtaining a mixed solution b; irradiating the mixed solution a by adopting ultraviolet rays, thereby obtaining a nanometer Pd colloidal solution c; mixing the solution c with the mixed solution b, thereby obtaining a mixed solution d; irradiating the mixed solution d by adopting the ultraviolet rays, thereby obtaining a Pd core @Pt shell nanometer colloidal solution e; and under the condition of the colloidal solution e obtained through stirring, immersing a carbon carrier for 2-24h, leaching and washing with de-ionized water till no chlorine exists, thereby obtaining the Pd core @Pt shell nanometer catalyst. The catalyst nanometer grain obtained according to the technology has a core-shell compound structure; the size of the grain is easily controlled and the monodispersity is excellent; and the preparation method is widely applied to the field of low-temperature fuel cells.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF ENG
Preparation process of lithium iron phosphate material
InactiveCN101575093AImprove mixing uniformityGood repeatabilityElectrode manufacturing processesPhosphorus compoundsLithium iron phosphateNitrogen
The invention discloses a preparation process of a lithium iron phosphate material. The process includes the following steps of: step 1: formulating lithium salt solution containing dispersant polyoxyethylene; step 2: putting ferric orthophosphate into the formulated lithium salt solution step by step, continuously stirring the mixed solution to fully react, mix and form colloidal solution in which the total mol rate of lithium to iron is 1.05-1.0; step 3: adding carbon source to the prepared colloidal solution with the adding amount being 20-40g / mol (Li), and drying after uniform mixing; and step 4: sintering the dried material of step 3 under the protection of nitrogen and preparing the finished product of lithium iron phosphate. After being ground and sieved, the lithium iron phosphate material produced by using the preparation process has the carbon content of 3.8-5.2%, compact density of 1.0-1.3g / mL and testing volume up to 150-160mA / h (0.2C). The volume is improved by over 15% compared with that of a solid ball milling method.
Owner:郑州瑞普生物工程有限公司
Colloidal dispersions comprising precious metal particles and acidic ionomer components and methods of their manufacture and use
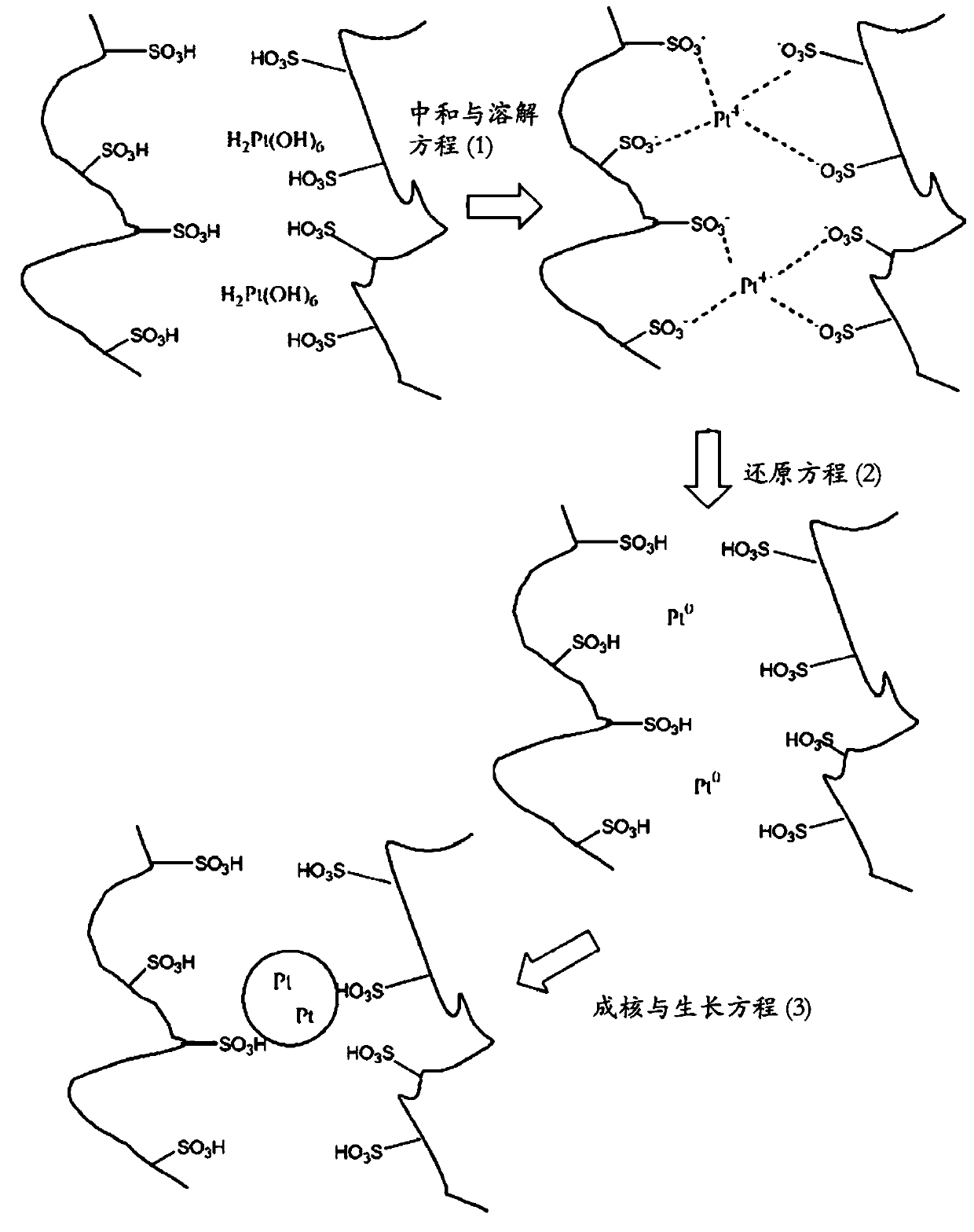
The invention relates to colloidal dispersions comprising nano-sized precious metal particles (e.g. platinum or platinum alloy particles) and at least one ionomer component having acidic groups. The method for its manufacturing is based on a neutralization and dissolving process of a suitable precious metal precursor compound with a liquid acidic ionomer component, followed by a reduction step. Suitable precious metal precursors consist of precious metal atoms, hydrogen atoms, oxygen atoms and optionally carbon atoms. Examples for precursors are H 2 Pt(OH) 6 , Pd(OH) 2 or Ir(OH) 4 , preferred reducing agents are aliphatic alcohols or hydrogen. The invention further relates to pre-products for the manufacture of such colloidal dispersions, namely to compositions which contain precious metal precursors and at least one acidic ionomer compound. The colloidal precious metal dispersions are essentially free of contaminants such as salts or surfactants and may further contain electrically conductive or non-conductive support materials. The colloidal precious metal dispersions can be used for the preparation of catalyst inks, ionomer layers, catalyst layers, electrodes or composite catalyst materials and find broad application in fuel cell technology (e.g. PEMFC, DMFC or water electrolysers).
Owner:格林纳瑞缇有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com