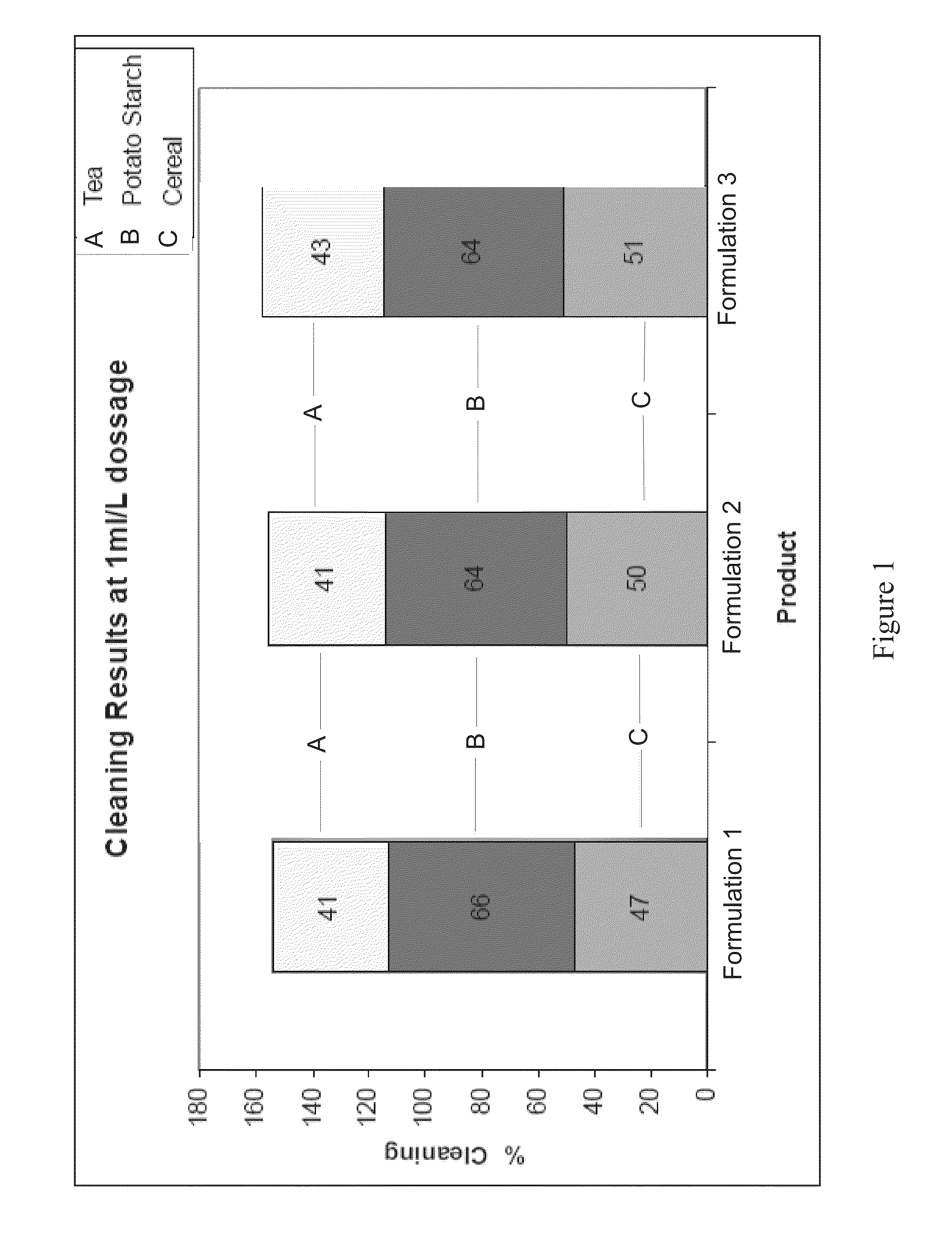
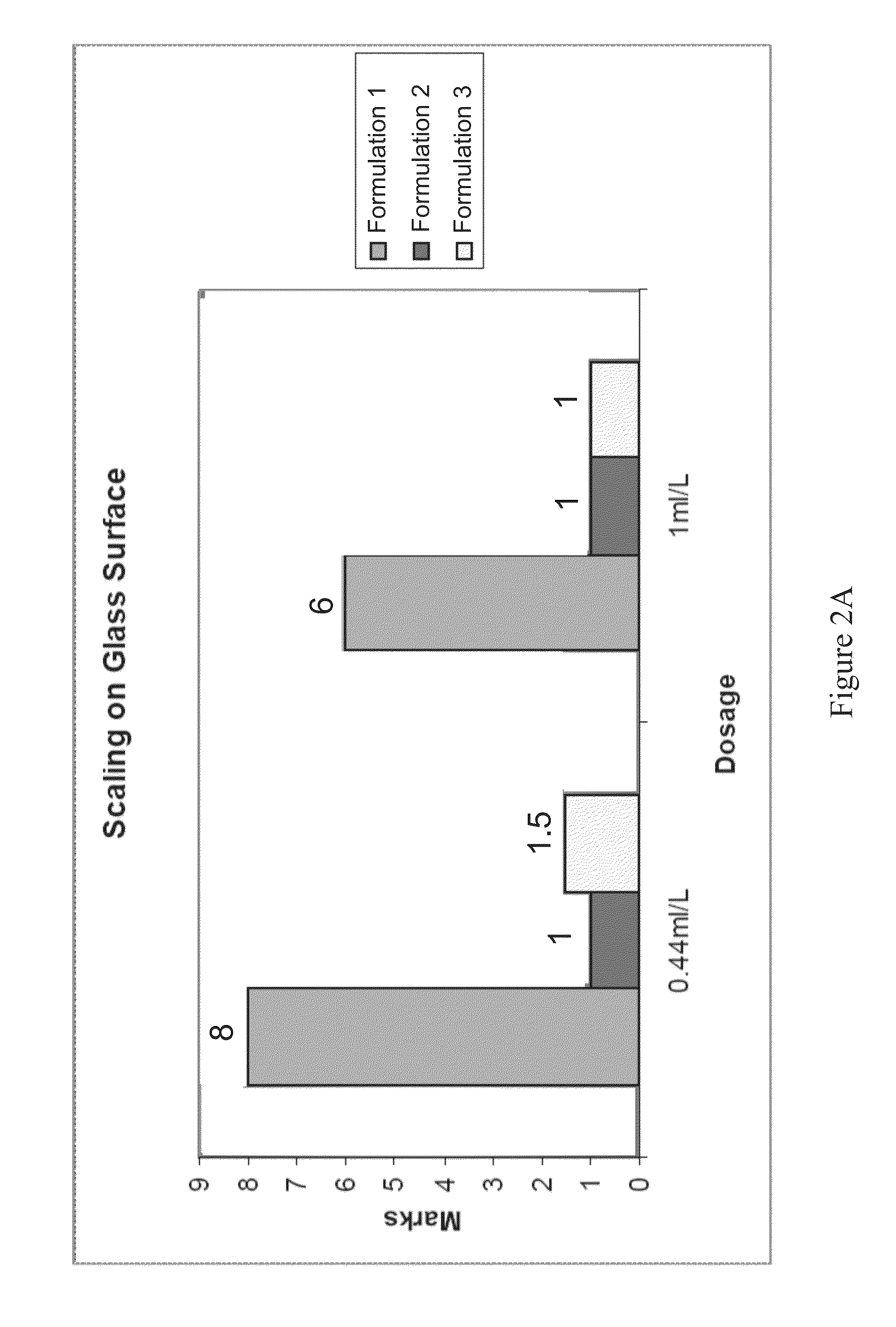
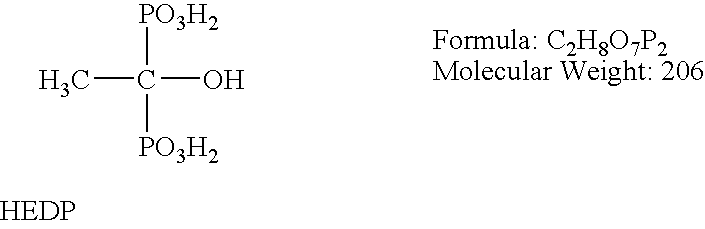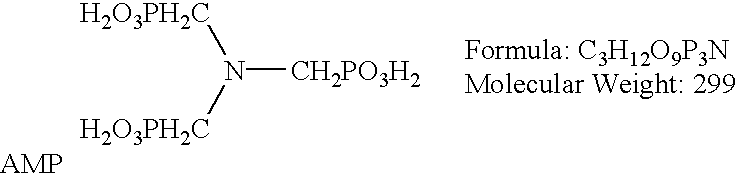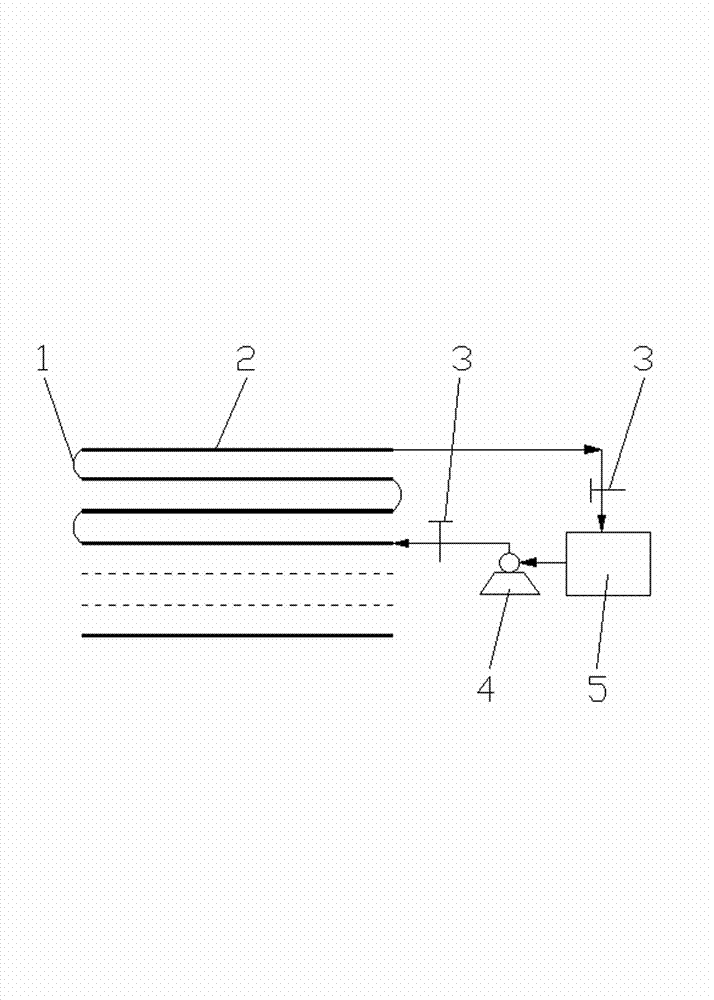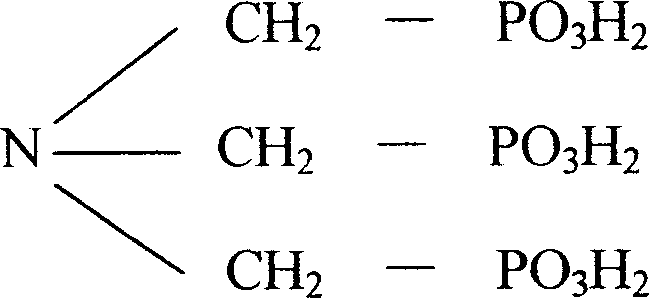Patents
Literature
87 results about "ATMP" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
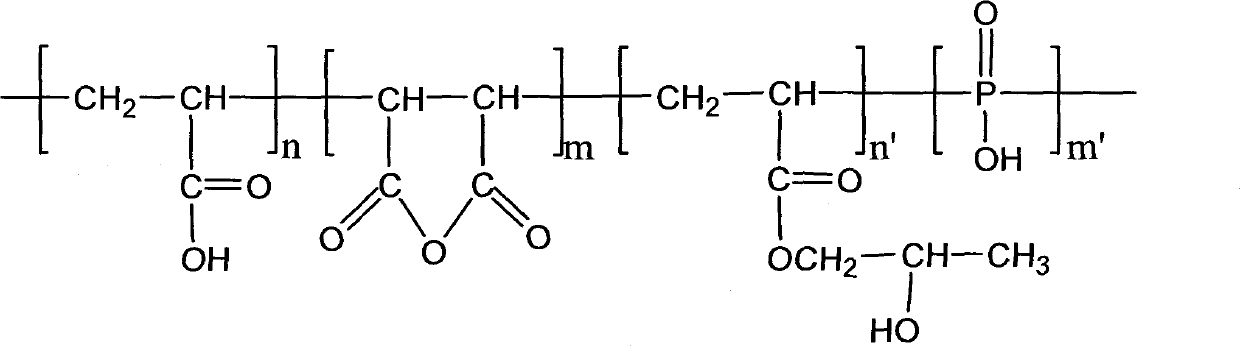
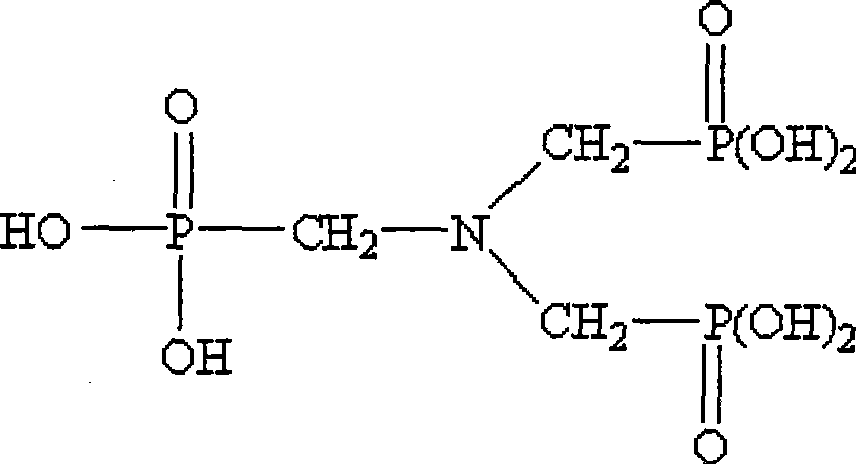
ATMP or aminotris(methylenephosphonic acid) is a phosphonic acid with chemical formula N(CH₂PO₃H₂)₃. It has chelating properties. It can be synthesized from the Mannich-type reaction of ammonia, formaldehyde, and phosphorous acid, in a manner similar to the Kabachnik–Fields reaction.
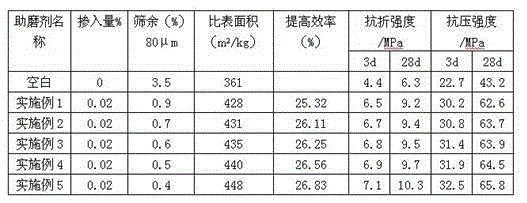
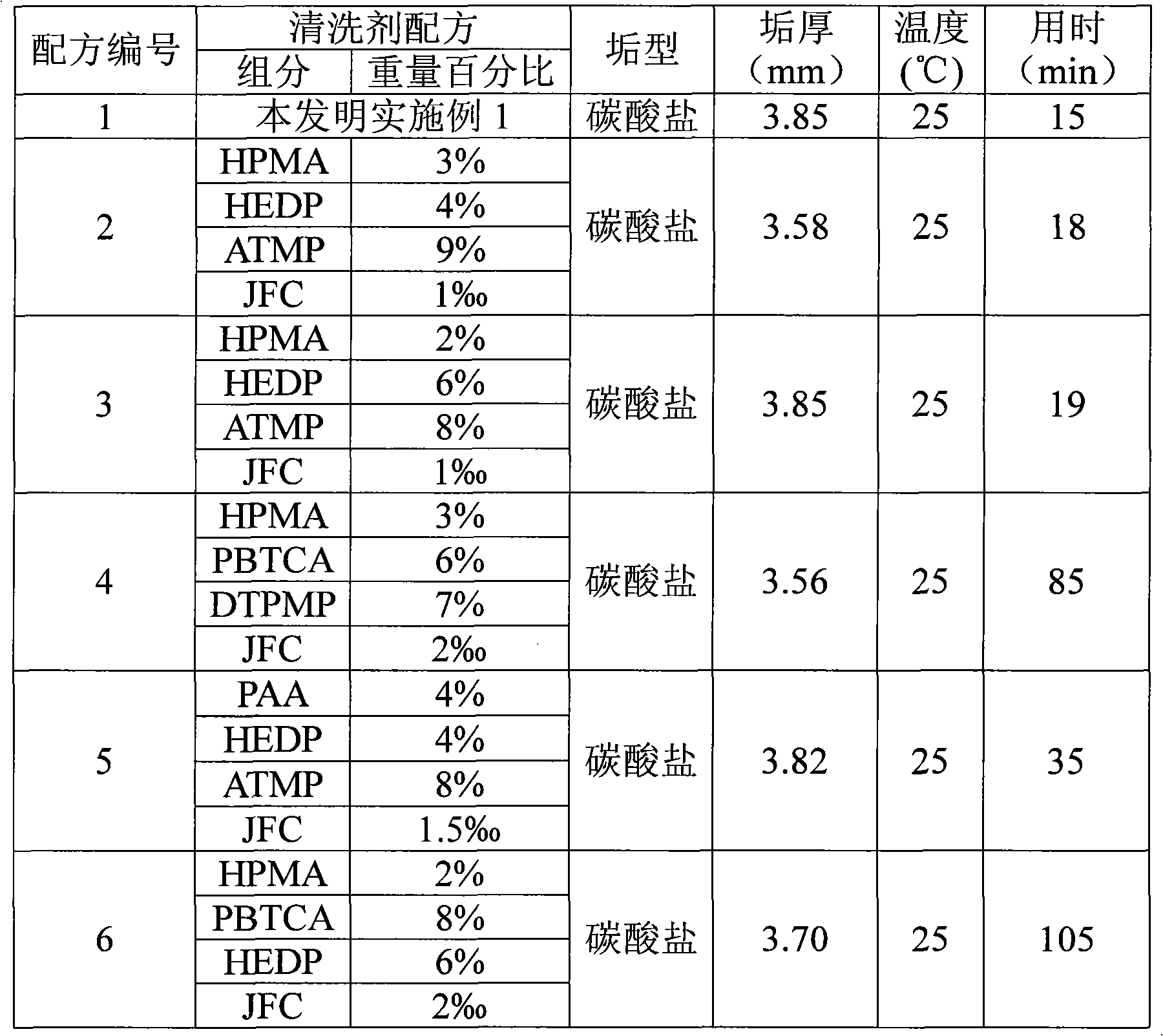
Silicate cement grinding aid and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a silicate cement grinding aid and a preparation method thereof. The silicate cement grinding aid is prepared from the following main raw materials by weight: 3-6 parts of sodium hexametaphosphate, 2-5 parts of aluminum sulfate, 5-8 parts of tetra sodium salt of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP.Na4), 4-6 parts of ethylene diamine tetra (methylene phosphonic acid) sodium, 38-45 parts of polymeric alkylol amine, 34-42 parts of triisopropanolamine, 8-12 parts of waste engine oil, 2-5 parts of sodium alpha-olefin sulfonate, 10-16 parts of sorbitol, 15-20 parts of diethylene glycol, 8-13 parts of polypropylene wax, 6-10 parts of oxidized polyethlene wax, 4-8 parts of lignite wax, 20-30 parts of odium thiosulfate, 12-18 parts of sodium thiosulfate and 15-20 parts of quicklime powder. The prepared silicate cement grinding aid has the advantages that the quality is stable, the effect is remarkable, the adding amount is small, the use is simple, and the adding is more convenient and reliable to control.
Owner:王金奎
Oil field compound type anti-scale corrosion inhibitor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102911651AGood synergyGood scale and corrosion inhibitionBorehole/well accessoriesSodium phosphatesSimple component
The invention relates to an oil field compound type anti-scale corrosion inhibitor and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of corrosion inhibitor. The oil field compound type anti-scale corrosion inhibitor is characterized by comprising the components by mass percent: 5-10% of sodium molybdate, 10-20% of sodium phosphate, 0.5-1% of acrylic acid-2-acrylamido-2-methyl propane sulfonic acid (AA-AMPS) copolymer, 1-2% of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid and 1-2% of hydroxyl ethylidene diphosphonic acid (HEDP). The preparation method comprises the steps of: firstly, completely dissolving sodium molybdate and sodium phosphate by using water; then, adding the AA-AMPS copolymer under the condition of stirring until the copolymer is completely dissolved; subsequently, adding ATMP and the HEDP, and further stirring for dissolving; and finally, adding water until the concentration of the mixed solution is in accordance with the requirement, so as to obtain the oil field compound type anti-scale corrosion inhibitor. The inhibitor disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple components, available raw materials, simple technology, high efficiency, low cost, low dosage, good scale inhibition, descaling and corrosion inhibition effects and the like, and is convenient to prepare, rapid.
Owner:E TECH ENERGY TECH DEV CORP
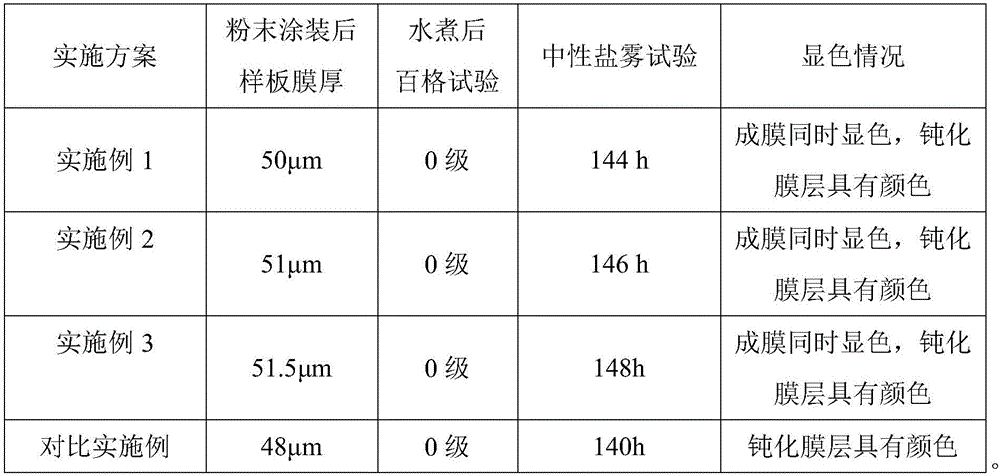
Chromate-free passivation agent for aluminum alloy
InactiveCN105779984AIncreasing the thicknessImprove compactnessMetallic material coating processesEpoxySilanes
The invention discloses a chromate-free passivation agent for an aluminum alloy. Per liter of chromate-free passivation agent is composed of, by mass, 10 mg to 300 mg of amino silane or / and epoxy silane, 1 mg-100 mg of dispersible nano particles, 10 mg-500 mg of a zirconium compound or / and a titanium compound, 1 mg-150 mg of metal ions, 10 mg-150 mg of fluoride, 1 mg-20 mg of a complexing agent, 75 mg-100 mg of organic phosphoric acid and the balance water; and the organic phosphoric acid is at least two of HEDP, HPMA, EDTMP, DTPMP, ATMP and PBTCA. According to the passivation agent, multiple kinds of organic phosphoric acid, multiple kinds of metal ions and multiple kinds of nano particles are chelated to the different degrees; on one aspect, the thickness and the compactness of a passivation film layer can be strengthened; and meanwhile, the passivation film layer (inorganic film layer) formed after chelation can show a color to a certain degree on the surface of the aluminum alloy.
Owner:NANJING KERUN LUBRICANTS
Scale and corrosion inhibitor for circulating cooling water
ActiveCN102198982AImprove stabilityImprove protectionScale removal and water softeningTricarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
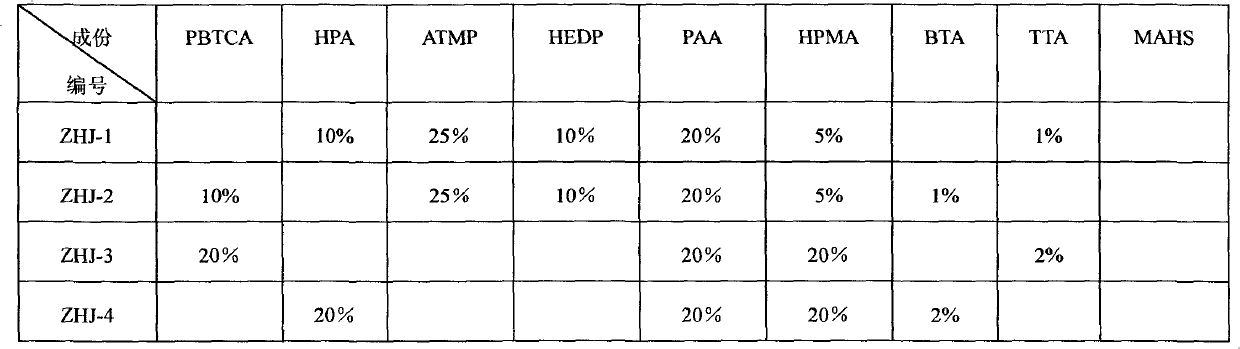
The invention relates to a scale and corrosion inhibitor for circulating cooling water. The inhibitor comprises components of, by weight: 15% to 30% of 2-phosphonobutane-1,2,4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTCA) and / or 5% to 20% of 2-hydroxyl-phosphino acetic acid (HPAA); and 10% to 30% of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP) and / or 5% to 10% of 1-hydroxy ethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP) and / or 10% to 20% of polyacrylic acid (PAA) and / or 5% to 20% of polymaleic anhydride (PMA); and 1% to 2% of benzotriazole (BTA) or 1% to 2% of methylbenzotriazole (TTA); and / or 10% to 20% of phosphono-carboxylic acid copolymer (MAHS) and rest amount of deionized water. The CaCO3 inhibiting performance and corrosion inhibiting performance of the present inhibitor surpass that of the IDA-II scale and corrosion inhibitor. The Zn<2+> stabilizing capacity of the present inhibitor also surpasses that of IDA-II inhibitor. When the present inhibitor is added with a dosage of 50mg / L to 100mg / L, the phosphorcontent in the cooling water is only 0.210mg / L (calculated according to PO4<3-> content), thus the phosphor content is below the limited phosphor discharging quantity (which is below or equal to 0.5m / L) within the primary standard.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
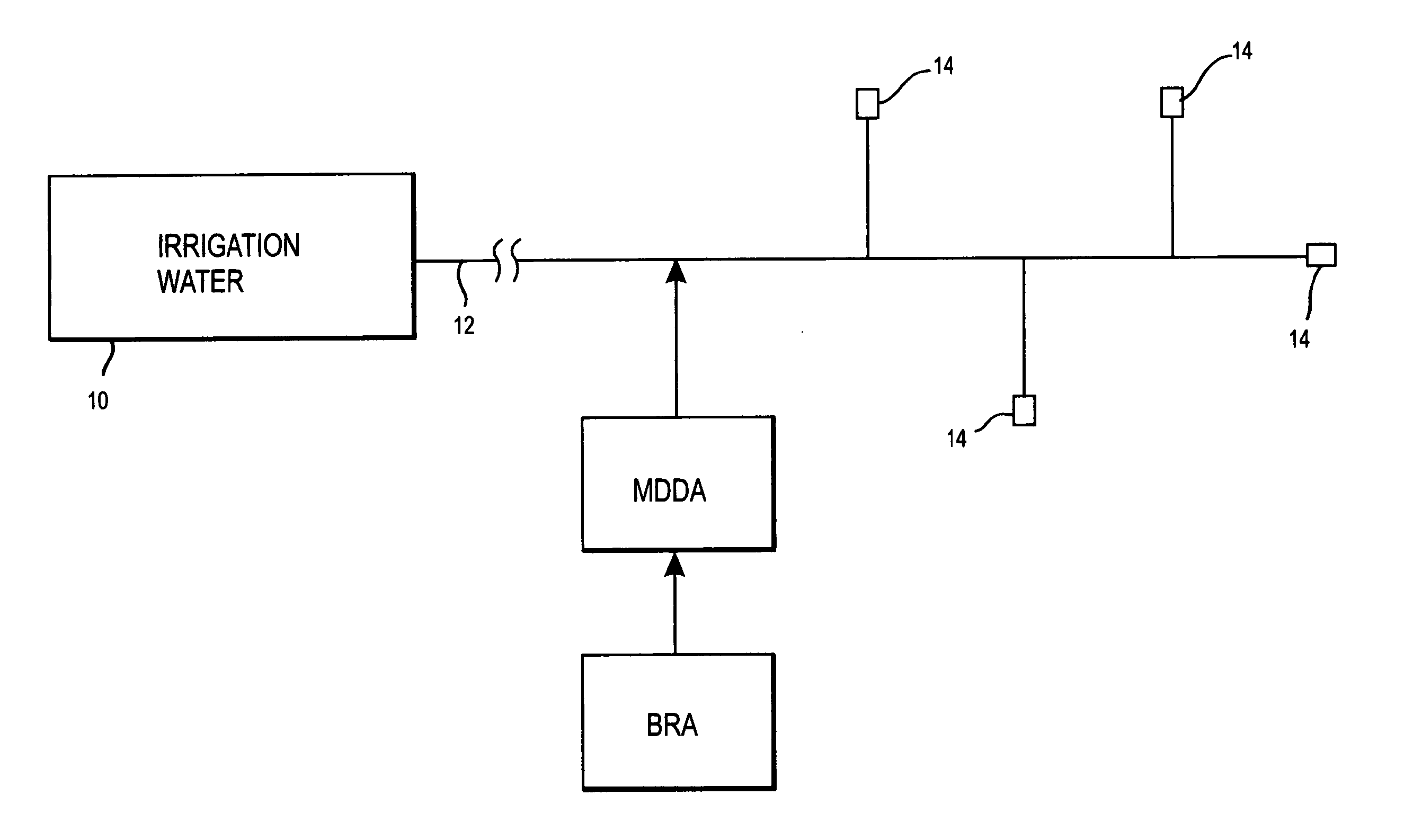
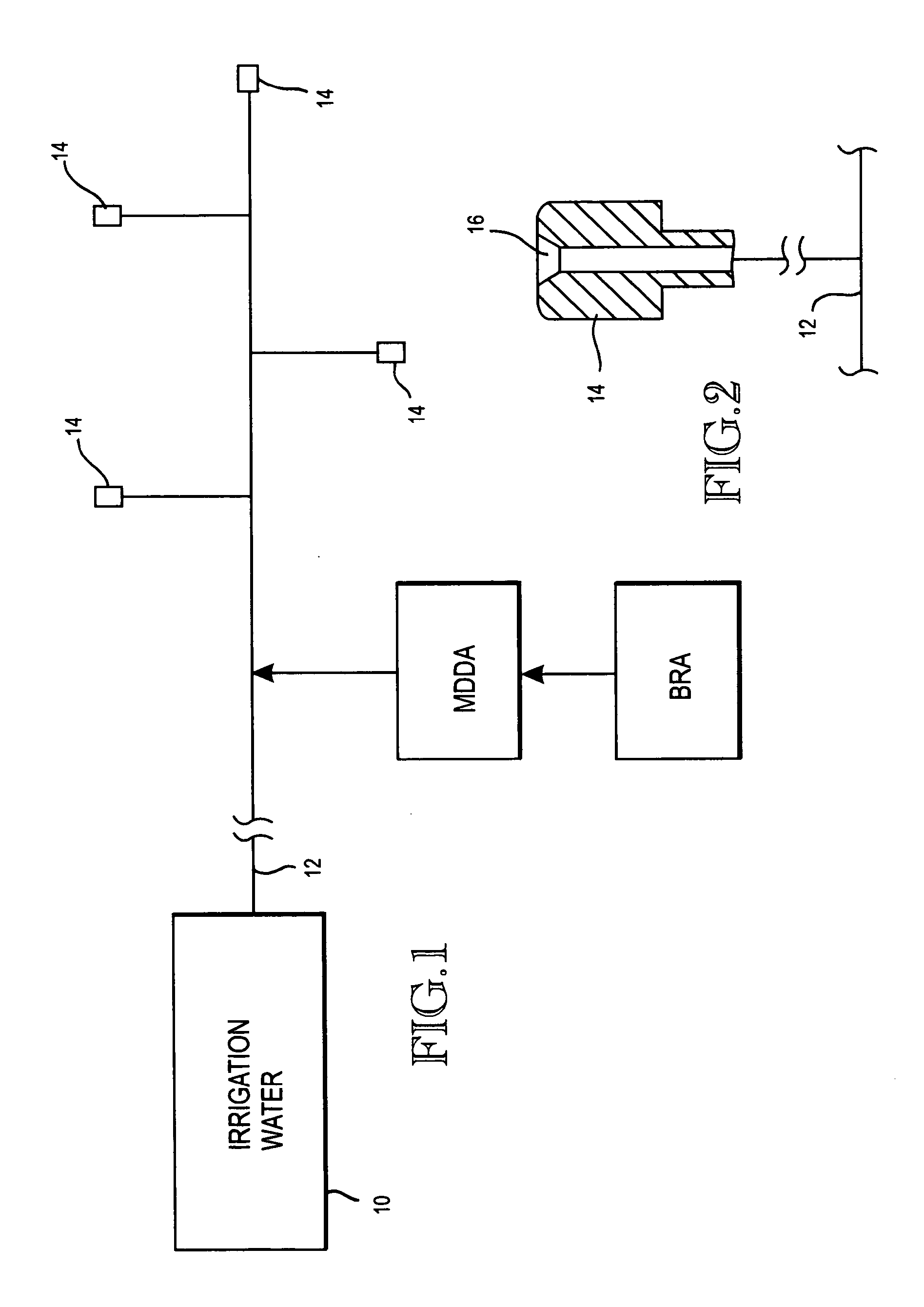
Method of promoting unrestricted flow of irrigation water through irrigation networks
ActiveUS7601266B2Preserving unrestricted flowEliminates biofilm formationSpecific water treatment objectivesWatering devicesChlorine dioxideHypochlorite
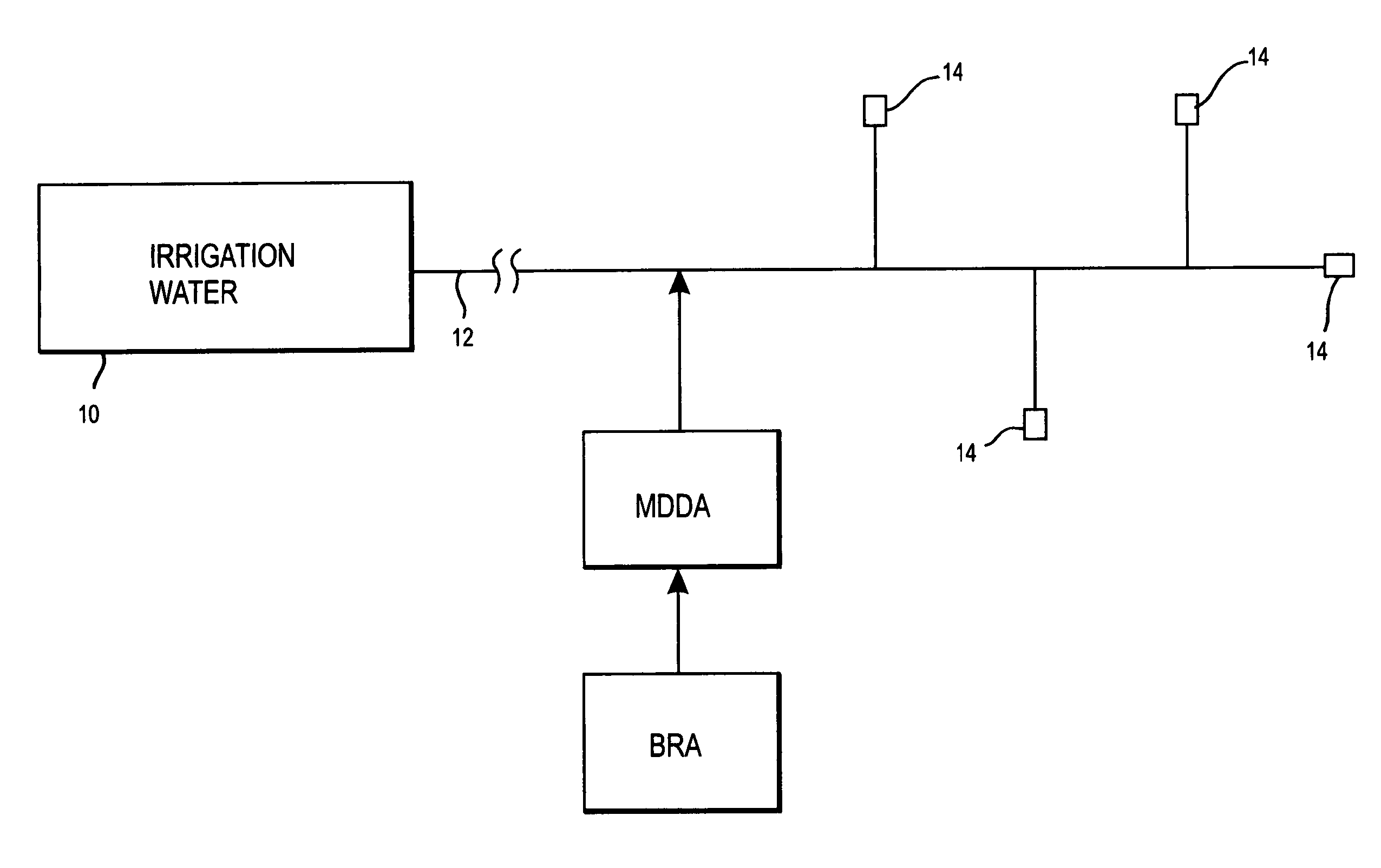
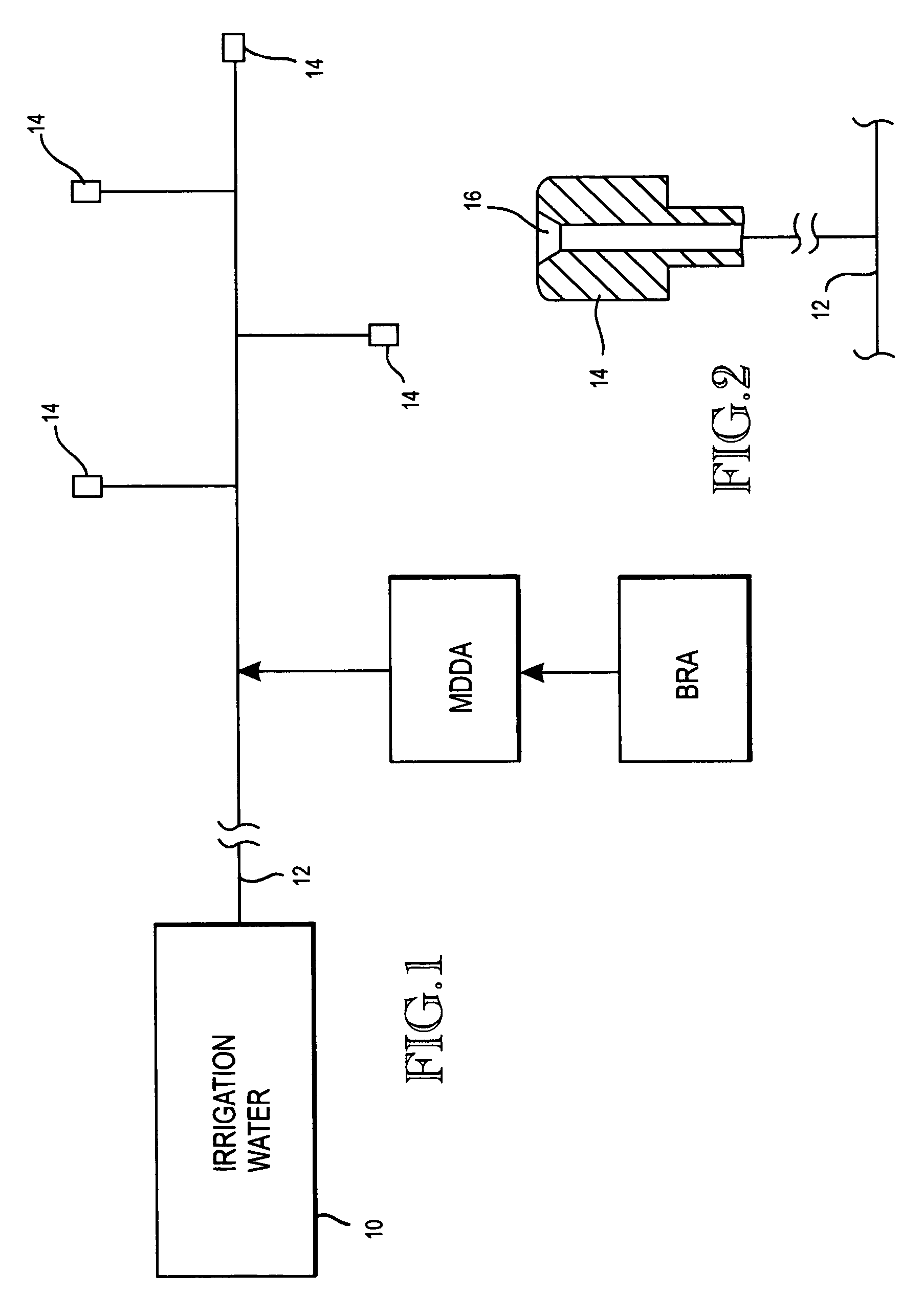
A biofilm reducing agent (BRA) and a mineral deposit distorting agent (MDDA) are admixed to irrigation water in amounts sufficient to substantially eliminate biofilm formation in the emitters (14) of an irrigation system (10) and produce amorphous mineral deposits in the emitters that are easily washed away by the irrigation water as it flows through the emitters (14). The BRA may be an oxidizer selected from the group consisting of chlorine, ozone, chlorine dioxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxy peracitic acid, iodine, bromine, hydrogen dioxide, chlorate salts, chlorite salts and hypochlorite compounds and mixtures thereof. The MDDA is a phosphonate selected from the group comprising AMP, ATMP, HEDP, EDTMPA, HMDTMPA, DETPMPA, BHMPTMPA, PBTC, HPA, PCA, NTMP, and DTPMP.
Owner:CH20
Organic descaling composition, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101565660AStrong chelationGood dispersionHollow article cleaningOrganic non-surface-active detergent compositionsReaction speedCleansing Agents
The invention provides an organic descaling composition, which includes an organic cleaning agent and a corrosion inhibitor CM-911, and the weight ratio of the organic cleaning agent and the corrosion inhibitor is 100:0.1-0.3. The organic cleaning agent includes the follow components by weight: 1%-15% of maleic acid-crylic acid copolymer (MA-AA), 1%-25% of 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP), 2%-30% of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP), 0.03%-0.5% of penetrating agent JFC and balance of water. The organic descaling agent provided by the present invention has advantages of fast reaction speed, small corrosivity for material and high descaling efficiency.
Owner:河南伯淼水处理有限公司
Composite antisludging agent of reverse osmosis/nanofiltration system
ActiveCN103007768AImprove work efficiencyExtended cleaning cycleSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisColloidal silicaUltrafiltration
The invention provides a composite antisludging agent of a reverse osmosis / nanofiltration system. The composite antisludging agent comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 2%-10% of cyclodextrin solution, namely a component I, 80%-90% of at least one or a mixture of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP), a copolymer of maleic anhydride-acrylic acid (MA-AA), 2-phosphonic acid butane-1, 2,4-tricarboxylic acid (PBTCA), and hydroxyl ethylidene diphosphonic acid (HEDP), namely a component II, and 1%-10% of 2,2-dibromo-2-cyano-acetamid (DBNPA), namely a component III. The composite antisludging agent is prepared by mixing the component II and the component III, and then fusing the obtained mixture with the component I. When being applied to the reverse osmosis / nanofiltration / ultrafiltration system, the composite antisludging agent can be used for effectively relieving the pollution to the reverse osmosis / nanofiltration / ultrafiltration system caused by polcard, calcium sulphate salt, barium sulfate, strontium sulfate, calcium fluoride, colloidal iron and colloidal silica, relieving biological contamination simultaneously, improving the working efficiency of the system, prolonging the cleaning period and the service life of the reverse osmosis / nanofiltration / ultrafiltration system, and reducing the cost of reverse osmosis.
Owner:辽宁莱特莱德环境工程有限公司
Method of promoting unrestricted flow of irrigation water through irrigation networks
ActiveUS20070257127A1Preserving unrestricted flowEliminates biofilm formationWatering devicesDifferential sedimentationHypochloriteChlorine dioxide
A biofilm reducing agent (BRA) and a mineral deposit distorting agent (MDDA) are admixed to irrigation water in amounts sufficient to substantially eliminate biofilm formation in the emitters (14) of an irrigation system (10) and produce amorphous mineral deposits in the emitters that are easily washed away by the irrigation water as it flows through the emitters (14). The BRA may be an oxidizer selected from the group consisting of chlorine, ozone, chlorine dioxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxy peracitic acid, iodine, bromine, hydrogen dioxide, chlorate salts, chlorite salts and hypochlorite compounds and mixtures thereof. The MDDA is a phosphonate selected from the group comprising AMP, ATMP, HEDP, EDTMPA, HMDTMPA, DETPMPA, BHMPTMPA, PBTC, HPA, PCA, NTMP, and DTPMP.
Owner:CH20
Method for restoring lead polluted soil with amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP)
InactiveCN103639190APromote degradationEasy to operateContaminated soil reclamationEnvironmental engineeringPb contamination
The invention discloses a method for restoring lead polluted soil with amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP), which has the advantages of higher biodegradability and higher rinsing efficiency. The method comprises the following steps: accurately weighing 1.00g of lead polluted soil sample, adding a 10-70% ATMP solution in a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:25, oscillating at room temperature, standing, centrifugating and filtering to complete the rinsing process, wherein the oscillation time is 12 hours, the standing time is 12 hours, the centrifugating speed is 4000 r / min, and the centrifugating time is 20 minutes. The lead concentration of the polluted soil is 1000-4020 mg.kg<-1>. By using the ATMP for reinforced restoration of the lead polluted soil, the method has the characteristics of high restoration efficiency, high operability, low environmental risk and the like.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Compound scale inhibitor for treating recirculated cooling water and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101519244AReduce contentReduce spawn rateTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsEutrophicationHeating temperature
The invention discloses a compound scale inhibitor for treating recirculated cooling water and a preparation method thereof. The scale inhibitor consists of polyaspartic acid and three or more HEDP, ATMP, SHMP, PESA, and PAPE, wherein the PASP is between 10 and 25 mg / L, the HEDP is between 1 and 10 mg / L, the ATMP is between 1 and 5 mg / L, the PESA is between 1 and 10 mg / L, the SHMP is between 1 and 5 mg / L, and the PAPE is between 1 and 5 mg / L. During the preparation of the compound scale inhibitor, the polyaspartic acid is added first, and then other materials are added into the polyaspartic acid; the heating temperature is between 60 and 80 DEG C, the stirring speed is 300 r / m, and the pH value is between 8.1 and 10.2; and the obtained product is kept stand for 1 to 6 hours. The compound scale inhibitor has excellent scale-inhibiting property and belongs to a low phosphorous formula, the formation rate of calcium phosphate scale is extremely low during the use, wastewater discharged by the formula cannot cause eutrophication pollution to the environment, and the compound scale inhibitor belongs to an environment-friendly product and is particularly suitable for the treatment of recirculated water with high calcium hardness and high alkali hardness.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
Corrosion inhibitor
InactiveUS6953537B2Reduce and prevent formationAvoid it happening againOther chemical processesAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAcetodiphosphonic acidTricarboxylic acid
A corrosion inhibitor for use with Urea Ammonium Nitrate solutions is disclosed, comprising a blend of molybdate and one or more of the inorganic phosphates (including phosphates, polyphosphates, and pyrophosphates) and organic phosphates or phosphonates. Inorganic phosphates include, but are not limited to, SHMP (Sodium Hexametaphosphate) and TKPP (Tetra-Potassium Pyrophosphate). There are numerous other inorganic phosphates that will also serve as suitable secondary inhibitors. Organic phosphates or phosphonates include, but are not limited to, HEDP (1-Hydroxyethylidine-1,1-diphosphonic acid; also known as ethanol diphosphonate, acetodiphosphonic acid, or etidronic acid), ATMP or AMP (aminotri(methylenephosphonic acid)), PBTC (Phosphonobutane tricarboxylic acid), DETPMP (Diethylenetriaminepenta(methylene phosphonic acid)), and HPA (hydroxyphosphono acetic acid). There are numerous other organic phosphates and phosphonates that will also serve as suitable secondary inhibitors. The amount of molybdate can range from 1 ppm to 500 ppm by weight of fertilizer solution, with the preferred range from 10 ppm to 200 ppm. Amounts of inorganic or organic phosphate can also range from levels as low as 1 ppm up to 500 ppm, with the preferred range being from 5 ppm to 50 ppm.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Antisludging agent of reverse osmosis water treatment system
ActiveCN101172721AImprove performanceExtended service lifeScale removal and water softeningWater treatment systemSludge
The invention provides anti-sludge inhibitor with relatively higher comprehensive performance. The anti-sludge inhibitor comprises 25 to 55 percent (weight percentage) of organic phosphonic acid. The organic phosphonic acid is selected three or more than three kinds from hydroxide radical ethylidene group bis phosphoric acid, ATMP, quadrol tetramethylene bis phosphoric acid, DTPA and multi-amino multi-ether methene phosphonic acid. The organic phosphonic acid comprises the components with the following weight percentage: 10 to 25 percent of hydroxide radical ethylidene group bis phosphoric acid, 10 to 30 percent of DTPA, and 5 to 20 percent of multi-amino multi-ether methene phosphonic acid.
Owner:OCHEMATE MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Scale inhibitor for circulating water
ActiveCN101412568AGood anti-scaling effectAdaptableScale removal and water softeningPolyaspartic acidALLYL SUCROSE
The invention relates to a circulating water scale inhibitor, which comprises the following components by weight portion: 2. 5 to 2.8 portions of PASP (polyaspartic acid), 1 to 1.2 portions of ATMP (amino trimethylene phosphonic acid), 2.4 to 2.6 portions of HPMA (hydrolyzed polymaleic anhydride), 1.2 to 1.4 portions of AA / AMPS (acrylic acid and 2-acrylamide-2-methyl propane sulfonic acid copolymer), 1.1 to 1.3 portions of PAA (polyacrylic acid), and 0.7 to 1.8 portions of water. The scale inhibitor prepared by the formulation is environment-friendly, has the characteristics of safety and reliability, easy preparation, convenient use and the like, and is suitable to be used as medicaments for preventing scale on circulating water systems in the fields of electric power, chemical engineering, medicine, petroleum, and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID HEBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Chrome-free passivant for hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104911576AAccelerated corrosionImprove oxidation resistanceMetallic material coating processesThioureaAcrylic resin
The invention discloses a chrome-free passivant for a hot-dip galvanized steel sheet and a preparation method thereof. The passivant comprises acrylic resin, phytic acid, sodium silicate, ATMP, thiourea, titanium trichloride hydrochloric acid solution, tannin, succinic acid, 1-octanesulfonic acid sodium salt, benzothiazole, silica sol, triethoxyphenylsilane, HEDP, vanadyl acetylacetonate, polyethyleneimine and deionized water. The preparation method of the chrome-free passivant comprises the steps of firstly adding the acrylic resin, the phytic acid, the sodium silicate, the ATMP and the thiourea into the deionized water, heating and stirring, cooling down the mixture, then adding the titanium trichloride hydrochloric acid solution, the tannin, the succinic acid, the 1-octanesulfonic acid sodium salt and the benzothiazole, preserving the heat and stirring, cooling down the mixture and then adding the silica sol, the triethoxyphenylsilane and the HEDP, preserving the heat and stirring, cooling down the mixture, then adding the vanadyl acetylacetonate and the polyethyleneimine, stirring and obtaining the passivant. The passivant disclosed by the invention does not contain chrome and is environmentally friendly, and the galvanized steel sheet passivated by the passivant has higher corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance.
Owner:CHANGSHU FENGFAN POWER EQUIP
Treatment Fluids Comprising Vitrified Shale and Methods of Using Such Fluids in Subterranean Formations
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
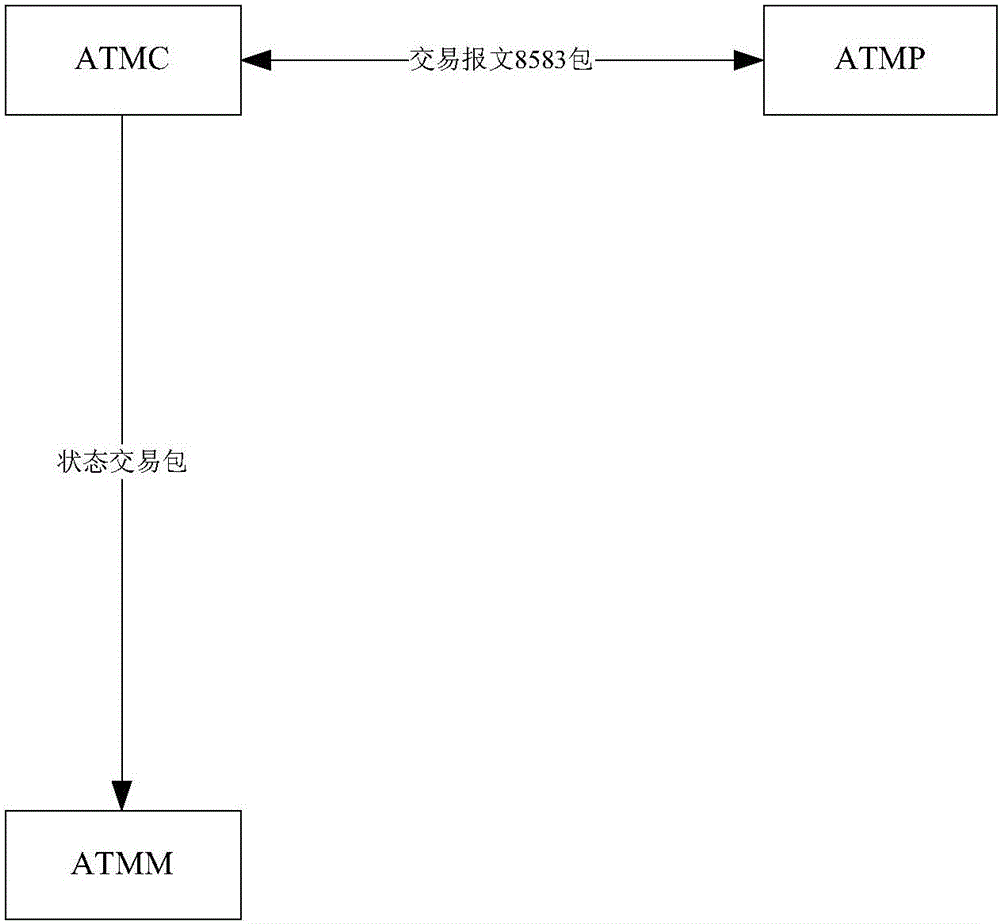
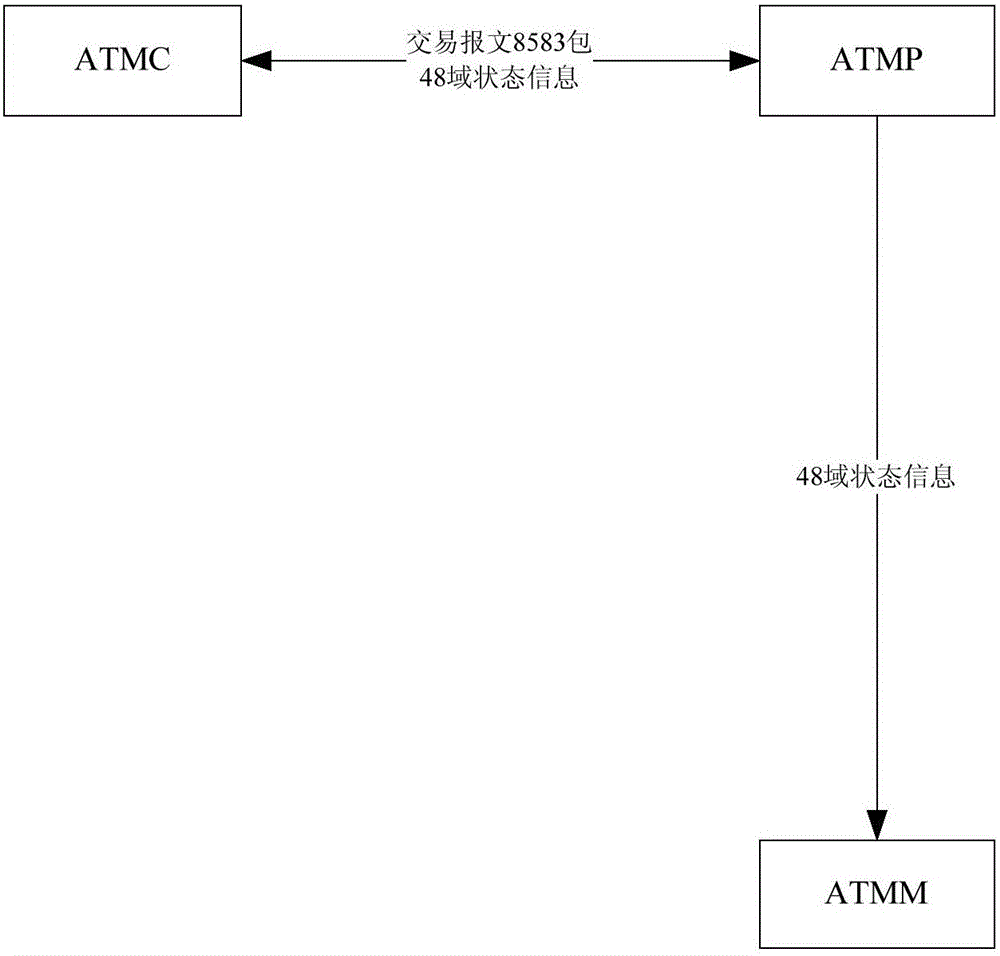
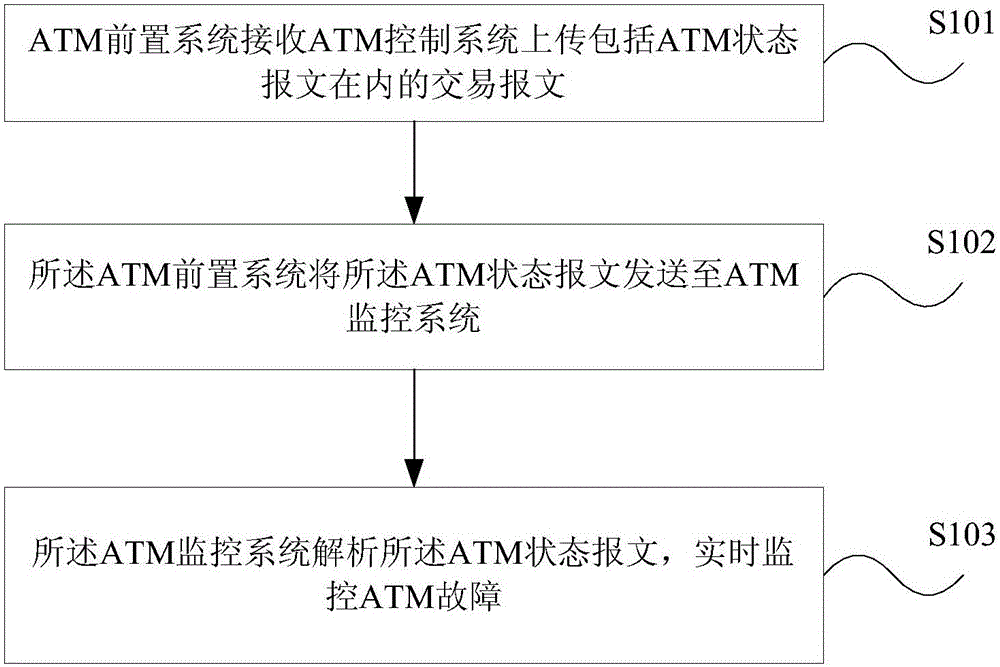
ATM fault monitoring method and device
The embodiments of the invention provide an ATM fault monitoring method and device. The method comprises the steps that: an ATM preposed system receives a transaction message which is uploaded by an ATM control system and includes an ATM state message; the ATM preposed system sends the ATM state message to an ATM monitoring system; and the ATM monitoring system analyzes the ATM state message and monitors ATM faults in real time. According to the embodiments of the invention, the stage message of an ATM machine and the transaction message are respectively uploaded to the ATMP, then the ATMP forwards the state message to the ATMM, and the consistent route is ensured, so that the accuracy and timeliness of ATM machine fault monitoring are ensured.
Owner:BANK OF CHINA
Corrosion inhibitor
InactiveUS20060043341A1Reduce and prevent formationAvoid it happening againOther chemical processesAmmonium nitrate fertilisersAcetodiphosphonic acidO-Phosphoric Acid
A corrosion inhibitor for use with Urea Ammonium Nitrate solutions is disclosed, comprising a blend of molybdate and one or more of the inorganic phosphates (including phosphates, polyphosphates, and pyrophosphates) and organic phosphates or phosphonates. Inorganic phosphates include, but are not limited to, SHMP (Sodium Hexametaphosphate) and TKPP (Tetra-Potassium Pyrophosphate). Phosphoric acid may also be utilized to provide phosphate ions, by itself or in combination with other phosphorous containing compounds as a secondary inhibitor. There are numerous other inorganic phosphates that will also serve as suitable secondary inhibitors. Organic phosphates or phosphonates include, but are not limited to, HEDP (1-Hydroxyethylidine-1,1-diphosphonic acid; also known as ethanol diphosphonate, acetodiphosphonic acid, or etidronic acid), ATMP (aminotri(methylenephosphonic acid)), PBTC (Phosphonobutane tricarboxylic acid), DETPMP (Diethylenetriaminepenta(methylene phosphonic acid)), and HPA (hydroxyphosphono acetic acid). There are numerous other organic phosphates and phosphonates that will also serve as suitable secondary inhibitors. The amount of molybdate can range from 1 ppm to 500 ppm by weight of fertilizer solution, with the preferred range from 10 ppm to 200 ppm. Amounts of inorganic or organic phosphate can also range from levels as low as 1 ppm up to 500 ppm, with the preferred range being from 5 ppm to 50 ppm.
Owner:TRAHAN SCOTT DAVID +1
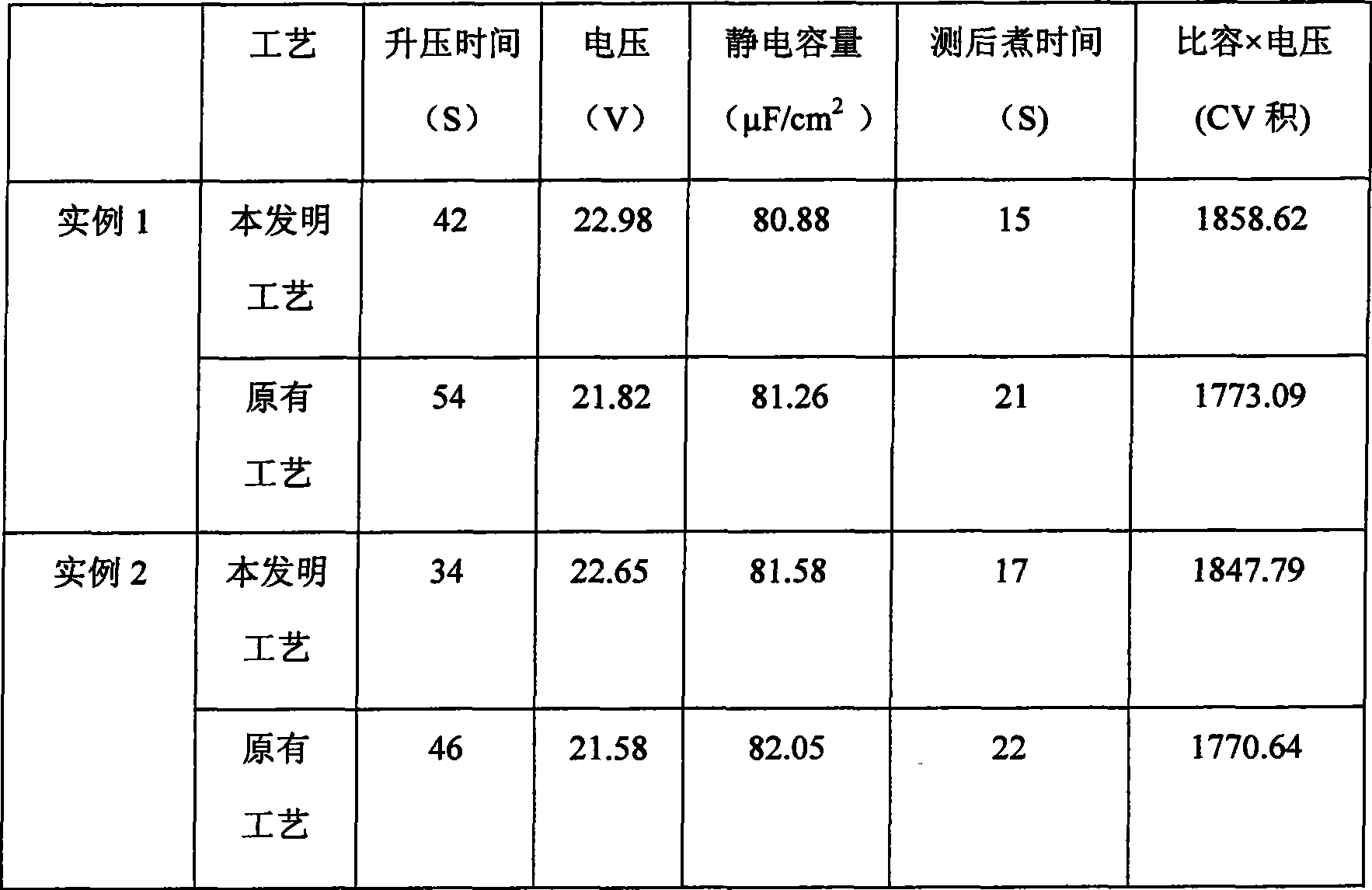
Low voltage aluminum electrolysis capacitor formed foil production method
ActiveCN101425384AReduce solubilityHigh capacitanceElectrolytic capacitorsMetallic material coating processesChemical treatmentSolubility
The invention relates to a preparation method of a formed foil used for low-voltage aluminum electrolytic capacitors. The aluminum foil is respectively added with two new treating agents during formation, i.e. phosphite and amino trimethylene phosphonic acid ( ATMP); the aluminum foil which generates a filam is put in a phosphate dilute solution to be chemically treated, and a layer of aluminum phosphide film is generated on the surface of the aluminum foil to improve the hydration resistance of the foil; the aluminum foil is formed in an ATMP solution, which ensures that not only a hydration resistant phosphating film can be generated, but also the formed aluminum foil has high efficiency and more complete covering; the solubility of oxide film is much lower, thereby a very good water resistant film is obtained and the aluminum foil obtains higher electrostatic capacity simultaneously.
Owner:YIDU DONGYANGGUANG FORMED FOIL
Electrochemical corrosive process of anode aluminum foil
InactiveCN101029412AHigh mechanical strengthObservation uniformCapacitor electrodesAluminum IonPhosphate
An electrochemical corrosion technology for anode aluminum foils consists of two DC electrochemical corrosion processes. The first electrochemical corrosion process is carried out in mixed solution sulfuric acid, chlorine ion and aluminum ion; the second electrochemical corrosion process is carried out by adding into organic phosphonic acid or phosphate, ATMP, HEDP and EDTMP. It has homogenous appearance, large capacity ration, excellent mechanical strength and water-proof performance.
Owner:DONGGUAN HEC CONDENSER CO LTD
Preparation process for a solid aminotrimethylenephosphonic acid (ATMP) or 1-hydoxy ethyidene-1.1-diphosphonic acid
InactiveCN101597305AReduce packaging costsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMethylphosphinic acidMethylphosphonic acid
The invention relates to a preparation process for a solid aminotrimethylenephosphonic acid (ATMP) or 1-hydoxy ethyidene-1.1-diphosphonic acid, in particular to a high purity preparation process for the solid aminotrimethylenephosphonic acid (ATMP) or the 1-hydoxy ethyidene-1.1-diphosphonic acid, comprising the following steps: a, crystallization: controlling the temperature of the aminotrimethylenephosphonic acid (ATMP) or 1-hydoxy ethyidene-1.1-diphosphonic acid with 68-85% of the content of effective substance at 30-90 DEG C, adding ice crystal particles, and then precipitating the crystal; b, solid-liquid separation: carrying out centrifugal dewatering on the materials after crystal precipitation, and obtaining the sold aminotrimethylenephosphonic acid (ATMP) or the 1-hydoxy ethyidene-1.1-diphosphonic acid; c, product post-treatment: drying the solid aminotrimethylenephosphonic acid (ATMP) or the 1-hydoxy ethyidene-1.1-diphosphonic acid, removing crystal water under the temperature of 60-120 DEG C, then solid packing. The preparation process in the invention solves the problem of introducing impurity crystal nucleus in the solid preparation process of the aminotrimethylenephosphonic acid (ATMP) or the 1-hydoxy ethyidene-1.1-diphosphonic acid.
Owner:CHANGZHOU YAOS TONGDE CHEM
Reverse osmosis membrane scale inhibitor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103768957AExcellent anti-scaling performanceFree from breedingSemi-permeable membranesReverse osmosisHard water
The invention provides a reverse osmosis membrane scale inhibitor and a preparation method thereof. The scale inhibitor comprises the following components in parts by weight: 25-36 parts of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP), 8-15 parts of acrylate, 6-12 parts of benzylethylene sulfonated acid, 3-10 parts of poly-L-aspartic acid, 35-48 parts of hydrolyzed polymaleic anhydride, 2-5 parts of polyepoxysuccinic acid, and 8-10 parts of polylactic acid; the preparation method of the reverse osmosis membrane scale inhibitor comprises the steps of firstly, adding all the components into a reaction kettle, starting a stirring motor, stirring for 60-90 minutes and standing for 5-10 minutes, and then filtering the mixed solution, thus obtaining the reverse osmosis membrane scale inhibitor. The reverse osmosis membrane scale inhibitor is high in scale inhibition property and applicable to high hard water, contains sterile component to ensure that bacteria and algae cannot breed on the membranes, and has multiple properties of bacteria inhibition, corrosion inhibition and scale inhibition.
Owner:NANTONG SUTONG SEPARATION ENG & TECH
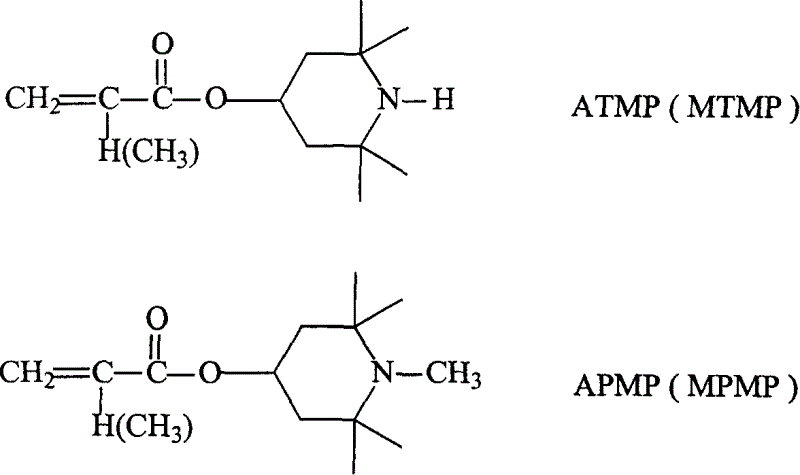
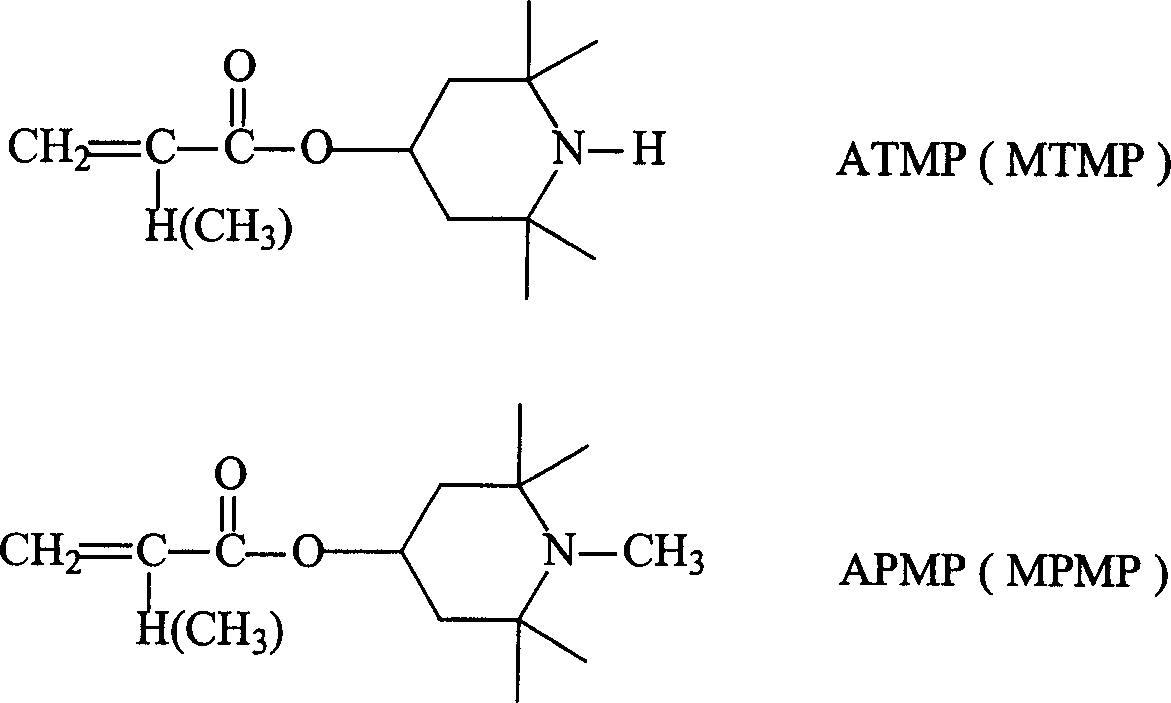
Use of reaction type hindered amine, coating formula and method for in-situ photostabilization of coating layer
ActiveCN1640956APretreated surfacesPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsOligomerHindered amine light stabilizers
The present invention relates to the application of reactive hindered amine (gamma-HALS), light cured paint recipe and coating in-situ light stabilizing method. Gamma-HALS (ATMP, MTMP, APMP and MPMP) is used as the light stabilizer of ultraviolet light cured polymer paint system, and the polymer paint has recipe comprising gamma-HALS, oily oligomer, diluent, light initirator and other assistant. The in-situ light stabilizing method of ultraviolet light cured polymer paint system includes the steps of: homogenizing prepolymer, coating, vacuum stoving, ultraviolet light curing, etc. Experiment shows that the ultraviolet light cured polymer coating the paint of the present invention forms has excellent light protection performance.
Owner:FOSHAN 3Q ELECTRONICS MATERIALS
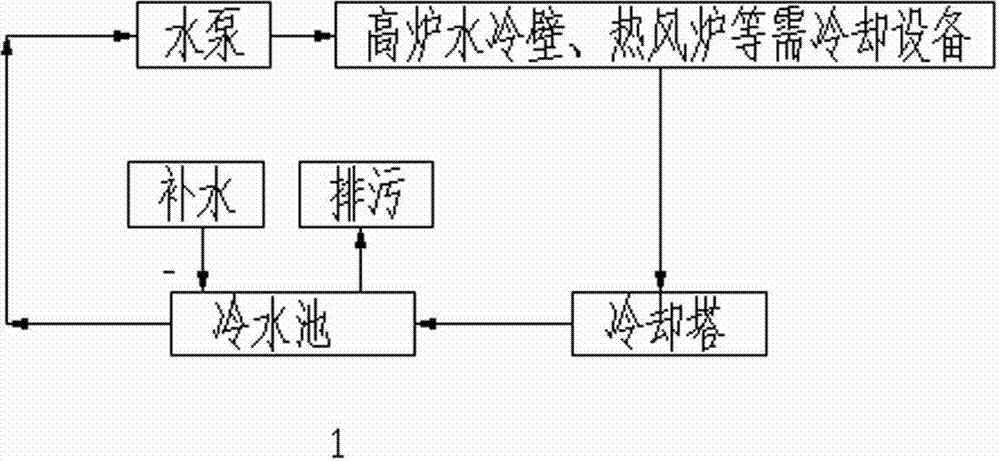
Cleaning agent for locally cleaning ironmaking blast furnace water-cooling wall in on-line loading manner and application thereof
InactiveCN103194761ARecovery of heat transfer efficiencySave energyCooling devicesCleansing AgentsHydroxyethylidene Diphosphonic Acid
The invention relates to a cleaning agent for locally cleaning an ironmaking blast furnace water-cooling wall in an on-line loading manner and an application thereof. The cleaning agent consists of the following components by weight percent: 15-30% of hydrochloric acid (by the HCl), 10-20% of sulfamic acid, 10-20% of citric acid, 5-15% of 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic (HEDP), 5-15% of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP), 0.2-1.0% of a corrosion inhibitor and 30-40% of water. Layering segmented cleaning is selectively carried out on the blast furnace water-cooling wall according to the scaling conditions of the blast furnace water-cooling wall, the blast furnace water-cooling wall is completely cleaned according to practical requirements, and equipment which does not need to be cleaned is not connected in a local cleaning process; the heat exchange efficiency of the blast furnace water-cooling wall is recovered, and energy sources are saved; the service life of the equipment can be prolonged; and the production efficiency is increased, and potential safety hazards are eliminated.
Owner:韶关市雅鲁环保实业有限公司
Scale-inhibition compositions and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS9139799B1Organic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsHexamethylenediamineDiethylenetriamine
Provided are scale-inhibition compositions comprising (a) a first acrylic acid polymer having an average molecular weight of about 3000 to about 6000; (b) a second acrylic acid polymer having an average molecular weight of about 6000 to about 10000; (c) an aminocarboxylic acid selected from methylglycine diacetic acid (MGDA), glutamic acid diacetic acid (GLDA), diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA), hydroxyethyl ethylene diamine triacetic acid (HEDTA), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and a combination thereof; and (d) a phosphonic acid selected from 1-hydroxyethane 1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP), amino tris(methylenephosphonic acid) (ATMP), ethylenediamine tetra(methylene phosphonic acid) (EDTMP), tetramethylenediamine tetra(methylene phosphonic acid) (TDTMP), hexamethylenediamine tetra(methylene phosphonic acid) (HDTMP), diethylenetriamine penta(methylene phosphonic acid) (DTPMP), and a combination thereof. The scale-inhibition compositions may be useful in machine ware washing detergents and formulations.
Owner:JOHNSONDIVERSEY INC
Amino trimethylene phosphonic acid with content of greater than or equal to 90 percent and process for making same
InactiveCN1699380AIncrease contentEasy to packGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSodium acetateAlcohol
The invention discloses an amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP) with content of greater than or equal to 90 percent and process for preparation, wherein the product comprises (by weight percentage) amino trimethylene phosphonic acid 90-98%, unavoidable impurity substance 1-2%, and balancing water. The production process comprises the steps of stock preparation, charging sodium acetate as crystal nucleon, agitating, charging anhydrous alcohol as crystallizing aid agent, dewatering, and drying.
Owner:CHANGZHOU JIAYOU CHEM CO LTD
Scale-inhibition compositions and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20160010031A1Organic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsHexamethylenediamineDiethylenetriamine
Provided are scale-inhibition compositions comprising (a) a first acrylic acid polymer having an average molecular weight of about 3000 to about 6000; (b) a second acrylic acid polymer having an average molecular weight of about 6000 to about 10000; (c) an aminocarboxylic acid selected from methylglycine diacetic acid (MGDA), glutamic acid diacetic acid (GLDA), diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid (DTPA), hydroxyethyl ethylene diamine triacetic acid (HEDTA), ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and a combination thereof; and (d) a phosphonic acid selected from from 1-hydroxyethane 1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP), amino tris(methylenephosphonic acid) (ATMP), ethylenediamine tetra(methylene phosphonic acid) (EDTMP), tetramethylenediamine tetra(methylene phosphonic acid) (TDTMP), hexamethylenediamine tetra(methylene phosphonic acid) (HDTMP), diethylenetriamine penta(methylene phosphonic acid) (DTPMP), and a combination thereof. The scale-inhibition compositions may be useful in machine ware washing detergents and formulations.
Owner:JOHNSONDIVERSEY INC
Scale inhibitor for circulating water
ActiveCN101412568BGood anti-scaling effectAdaptableScale removal and water softeningPolyaspartic acidMethylphosphinic acid
The invention relates to a circulating water scale inhibitor, which comprises the following components by weight portion: 2. 5 to 2.8 portions of PASP (polyaspartic acid), 1 to 1.2 portions of ATMP (amino trimethylene phosphonic acid), 2.4 to 2.6 portions of HPMA (hydrolyzed polymaleic anhydride), 1.2 to 1.4 portions of AA / AMPS (acrylic acid and 2-acrylamide-2-methyl propane sulfonic acid copolymer), 1.1 to 1.3 portions of PAA (polyacrylic acid), and 0.7 to 1.8 portions of water. The scale inhibitor prepared by the formulation is environment-friendly, has the characteristics of safety and reliability, easy preparation, convenient use and the like, and is suitable to be used as medicaments for preventing scale on circulating water systems in the fields of electric power, chemical engineering, medicine, petroleum, and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID HEBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Reverse osmosis membrane special-purpose scale inhibitor and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN102423639ARestoring and Extending LifeEfficient and stable water production statusSemi-permeable membranesWater productionReverse osmosis
The invention relates to a reverse osmosis membrane special-purpose scale inhibitor and its manufacturing method. The scale inhibitor contains the following components of: by weight, 5-10 parts of hydroxyethylidene diphosphonic acid and sodium salt, 15-30 parts of amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP), 10-20 parts of ethylenediamine tetra methylenephosphonic acid and sodium salt, 5-10 parts of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt, 15-30 parts of 2-phosphonic acid-1,2,4-tricarboxyl butane, 15-30 parts of polyacrylic acid and sodium salt, 20-35 parts of an acrylic acid multipolymer, 15-30 parts of an acrylic acid sulfonic acid copolymer, 5-20 parts of hydrolyzed polymaleic anhydride and 30-40 parts of desalted water. The scale inhibitor provided by the invention can be used to effectively control sediments such as CaCO3, Ca3(PO4)2, CaSO4, BaSO4, SrSO4, SiO2 and the like, effectively stabilize Ca<2+> and Mg<2+> ions in process water, prevent the formation of insoluble fouling substances which precipitate to obstruct membrane pores, prevent coalescence of various scale and insoluble salt solids on the surface of the high-molecular reverse osmosis membrane, maintain good water molecule permeability of the reverse osmosis membrane, maintain normal water production capability and stabilize the quality of pure water.
Owner:上海久安水质稳定剂厂
Method for manufacturing foil by composite oxidation film at low pressure
InactiveCN101423964AHigh passivation treatment efficiencyReduce solubilityAnodisationElectrolytic capacitorsLow voltageAluminum silicate
The invention relates to the technical field of formed foils, in particular to a method for manufacturing a composite oxide film low-voltage formed foil. The method is as follows: firstly, a formed foil is treated by sodium silicate, and an aluminum silicate film is generated on the surface of the formed foil, is a good hydration resistant film and can improve the hydration resistance of the formed foil; and secondly, the formed foil is formed in a mixture of ATMP and ammonium adipate, and a hydrous aluminum phosphate film with good water resistance is generated. The aluminum silicate film and the hydrous aluminum phosphate film can effectively prevent reaction of an alumina film and water, improve the hydration resistance of the composite oxide film low-voltage formed foil, and prolong the service life of a capacitor.
Owner:DONGGUAN HEC CONDENSER CO LTD
Concrete super-retarding agent
The invention discloses a concrete super-retarding agent. The concrete super-retarding agent comprises components in parts by weight as follows: 15-20 parts of EDTMPA (ethylenediamine tetramethylenephosphonic acid), 10-15 parts of ATMP (amino trimethylene phosphonic acid), 15-20 parts of HPMC (hydroxyl propyl methyl cellulose), 10-15 parts of white sugar and 30-50 parts of water. The concrete super-retarding agent has the advantages that the mixing amount is only 0.3%-0.5% of the mass of a cementing material, but the retarding time can be prolonged to 80-100 h, the 28 d setting time is not shortened, but the later strength of concrete still reaches the standard, and compared with an ordinary retarding agent, the concrete super-retarding agent is low in product cost and realizes both economic and technical indicators.
Owner:JIANGSU MINGHE GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com