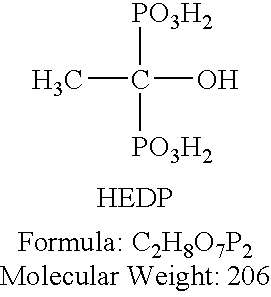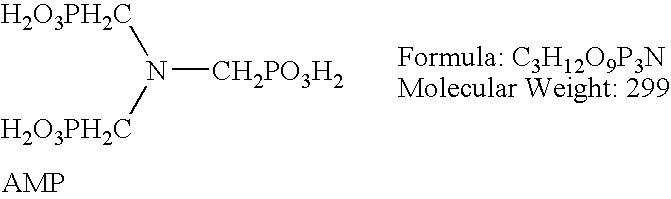Corrosion inhibitor
a corrosion inhibitor and corrosion technology, applied in the field of corrosion inhibitors, can solve the problems of low inhibitor cost, sludge formation, foam formation, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing or reducing the formation of precipitates and preventing the occurrence of under-deposit corrosion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0015] Tests were run on carbon steel coupons using a variety of phosphate compounds combined with molybdate. Table 1 summarizes the results of the first of these tests. An uninhibited 65 weight % aqueous solution of UAN was utilized (32% elemental Nitrogen). UAN solution was added to a 1 liter volumetric flask, and the volumes of required inhibitor compounds required to equal the proper dosage, as set forth in Table 1, were calculated. Each of the individual specific gravities of each solution was determined at 60 degrees F. using a 10 ml precision picometer. The individual test solutions were prepared by withdrawing aliquots of each corrosion inhibitor using a one CC precision syringe and injecting the resulting volume into the one liter volumetric flask containing the UAN solution. A water bath maintained at 89 degrees F. was utilized. Beakers containing the test solutions and metal test coupons were placed into the water bath. The ppm dosages of each inhibitor is expressed in re...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com